⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-21 更新
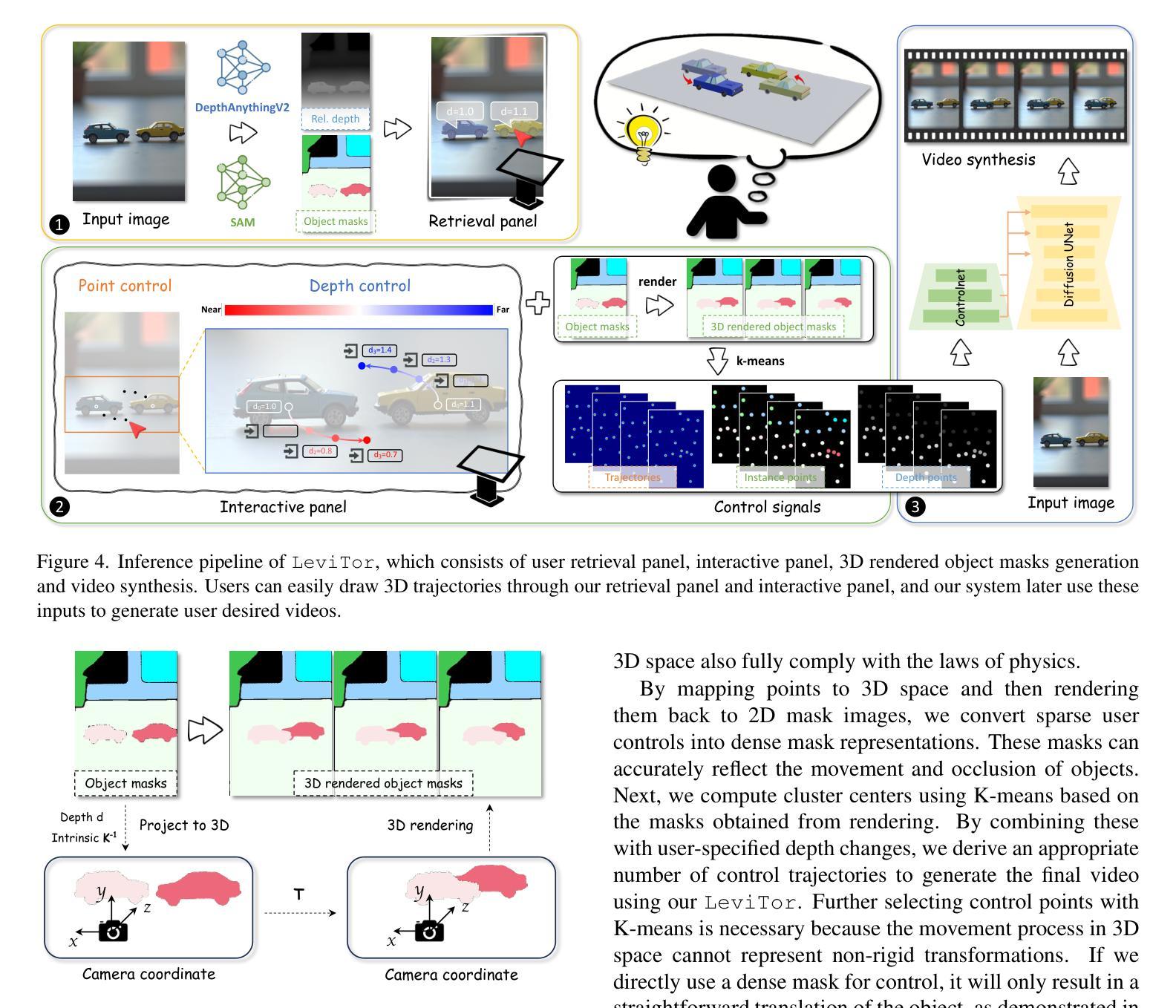
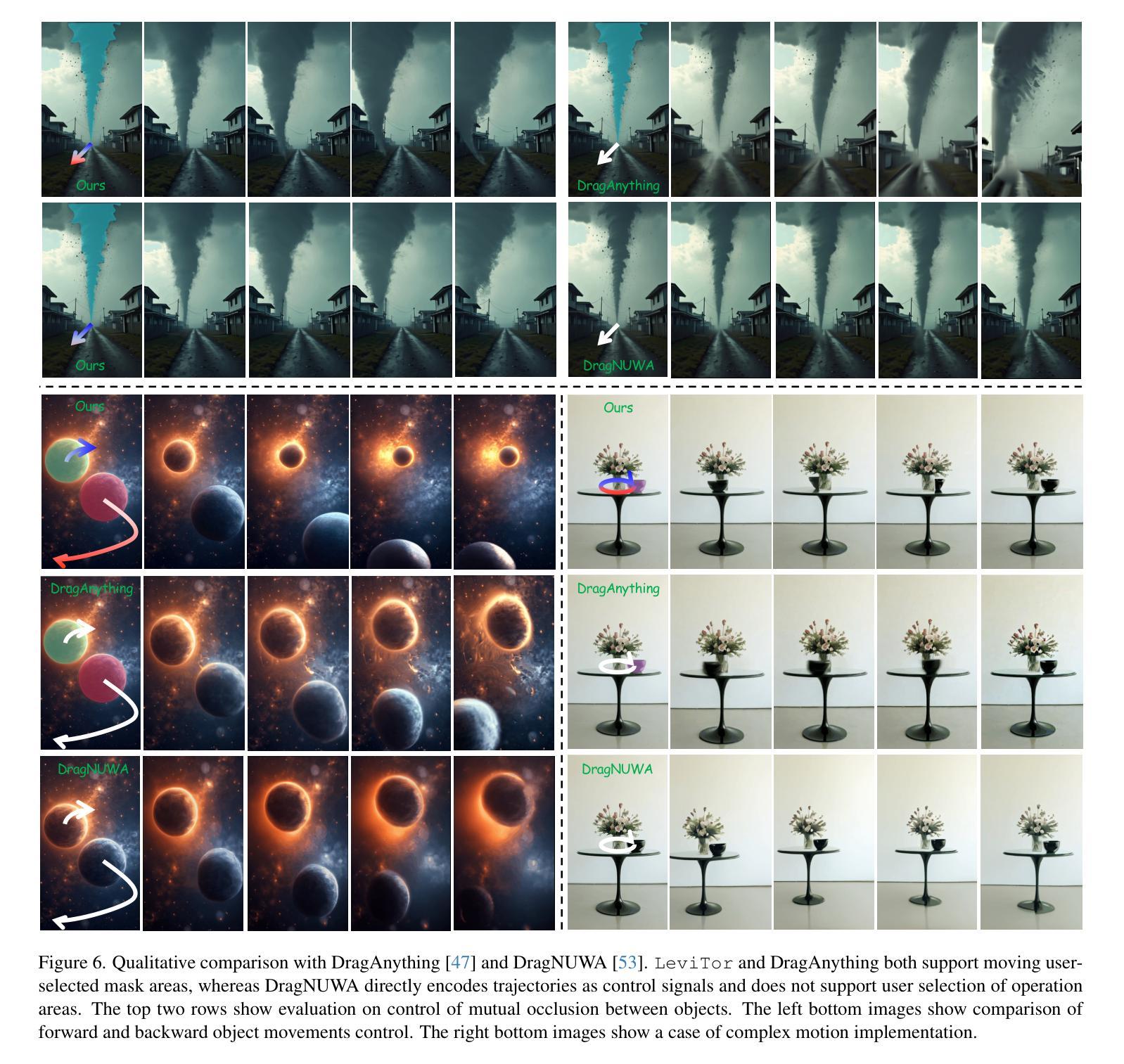
LeviTor: 3D Trajectory Oriented Image-to-Video Synthesis
Authors:Hanlin Wang, Hao Ouyang, Qiuyu Wang, Wen Wang, Ka Leong Cheng, Qifeng Chen, Yujun Shen, Limin Wang
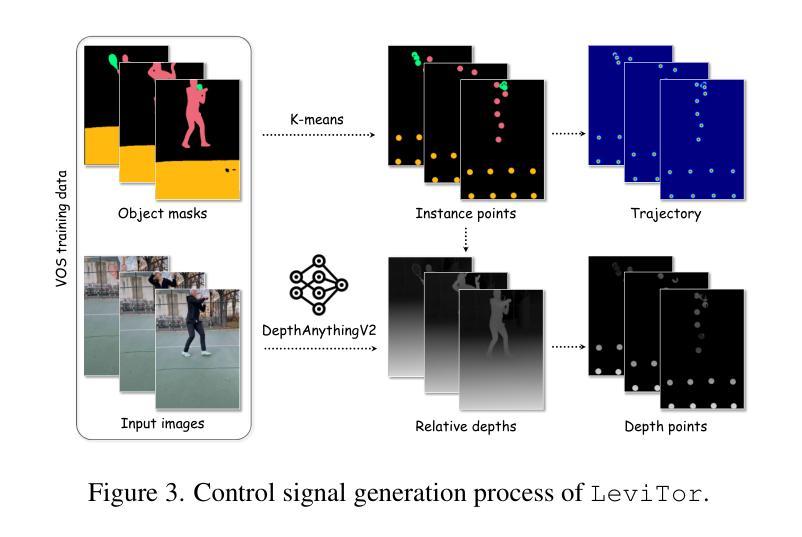
The intuitive nature of drag-based interaction has led to its growing adoption for controlling object trajectories in image-to-video synthesis. Still, existing methods that perform dragging in the 2D space usually face ambiguity when handling out-of-plane movements. In this work, we augment the interaction with a new dimension, i.e., the depth dimension, such that users are allowed to assign a relative depth for each point on the trajectory. That way, our new interaction paradigm not only inherits the convenience from 2D dragging, but facilitates trajectory control in the 3D space, broadening the scope of creativity. We propose a pioneering method for 3D trajectory control in image-to-video synthesis by abstracting object masks into a few cluster points. These points, accompanied by the depth information and the instance information, are finally fed into a video diffusion model as the control signal. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our approach, dubbed LeviTor, in precisely manipulating the object movements when producing photo-realistic videos from static images. Project page: https://ppetrichor.github.io/levitor.github.io/
基于拖动的交互方式的直观性使其在图像到视频合成中控制物体轨迹的应用越来越广泛。然而,在二维空间执行拖动操作的现有方法在应对平面外移动时通常面临模糊性。在这项工作中,我们通过引入一个新的维度来增强交互,即深度维度,使用户可以为轨迹上的每个点分配相对深度。通过这种方式,我们的新交互范式不仅继承了二维拖动的便利性,还促进了在三维空间中的轨迹控制,从而扩大了创意范围。我们提出了一种在图像到视频合成中进行三维轨迹控制的开创性方法,通过将对象蒙版抽象为几个聚类点来实现。这些点伴随深度信息和实例信息,最终作为控制信号输入到视频扩散模型中。大量实验验证了我们的方法(称为LeviTor)在生成从静态图像生成的逼真视频时精确控制物体运动的有效性。项目页面:https://ppetrichor.github.io/levitor.github.io/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page available at https://ppetrichor.github.io/levitor.github.io/
Summary
采用拖动手势交互,用户能够为图像合成视频中对象的运动轨迹指定相对深度信息,突破了原有二维拖动方法的局限性,拓宽了图像到视频合成的创造力范畴。LeviTor方法通过抽象对象掩膜为几个簇点,结合深度信息和实例信息,作为视频扩散模型的控制信号,有效精确操控对象运动,生成逼真的视频。
Key Takeaways
- 拖动手势交互在图像到视频合成中广泛应用于控制对象轨迹。
- 在处理出平面移动时,现有二维空间拖动方法面临模糊性挑战。
- 通过引入深度维度信息,用户可以为轨迹上的每个点指定相对深度。
- 新颖的交互模式继承了二维拖动的便捷性,并促进了三维空间中的轨迹控制。
- 提出了一种名为LeviTor的方法,通过抽象对象掩膜为几个簇点进行三维轨迹控制。
- 该方法结合了深度信息和实例信息,提高了精确操控对象运动的能力。
点此查看论文截图

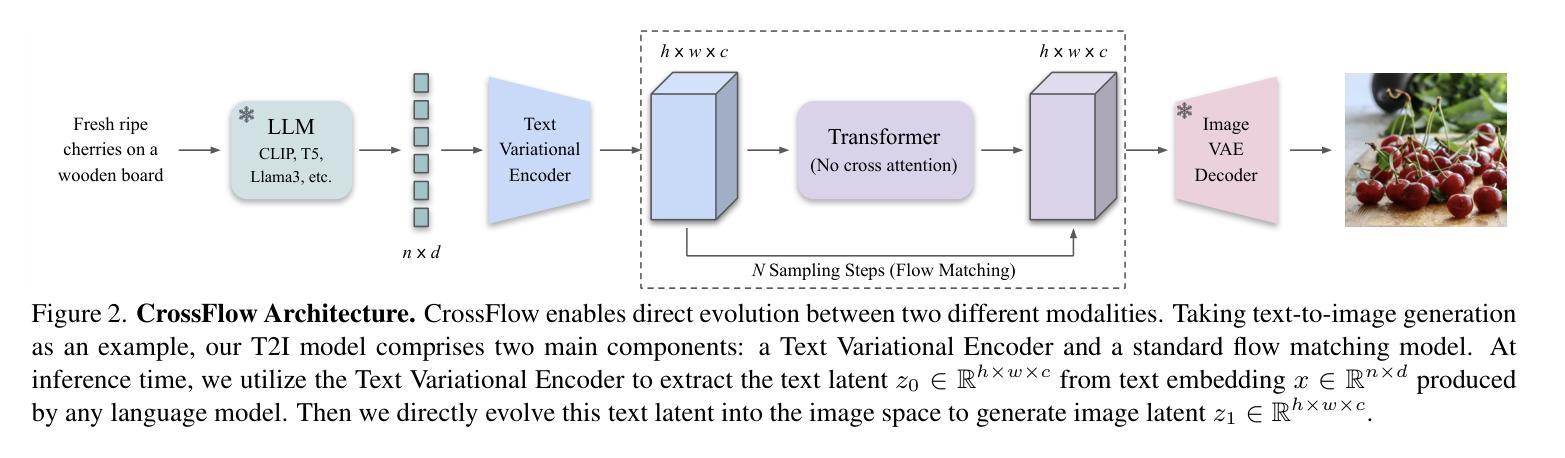
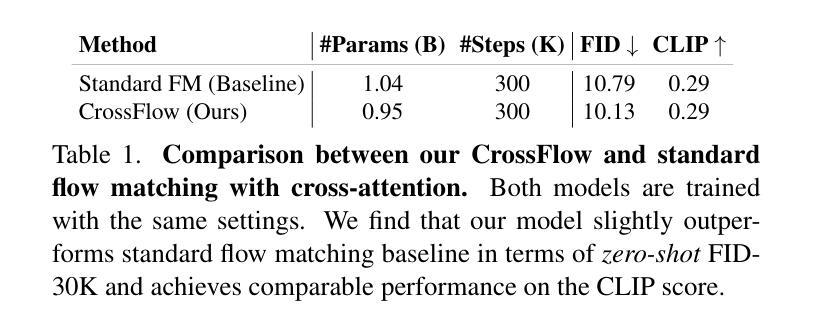
Flowing from Words to Pixels: A Framework for Cross-Modality Evolution
Authors:Qihao Liu, Xi Yin, Alan Yuille, Andrew Brown, Mannat Singh
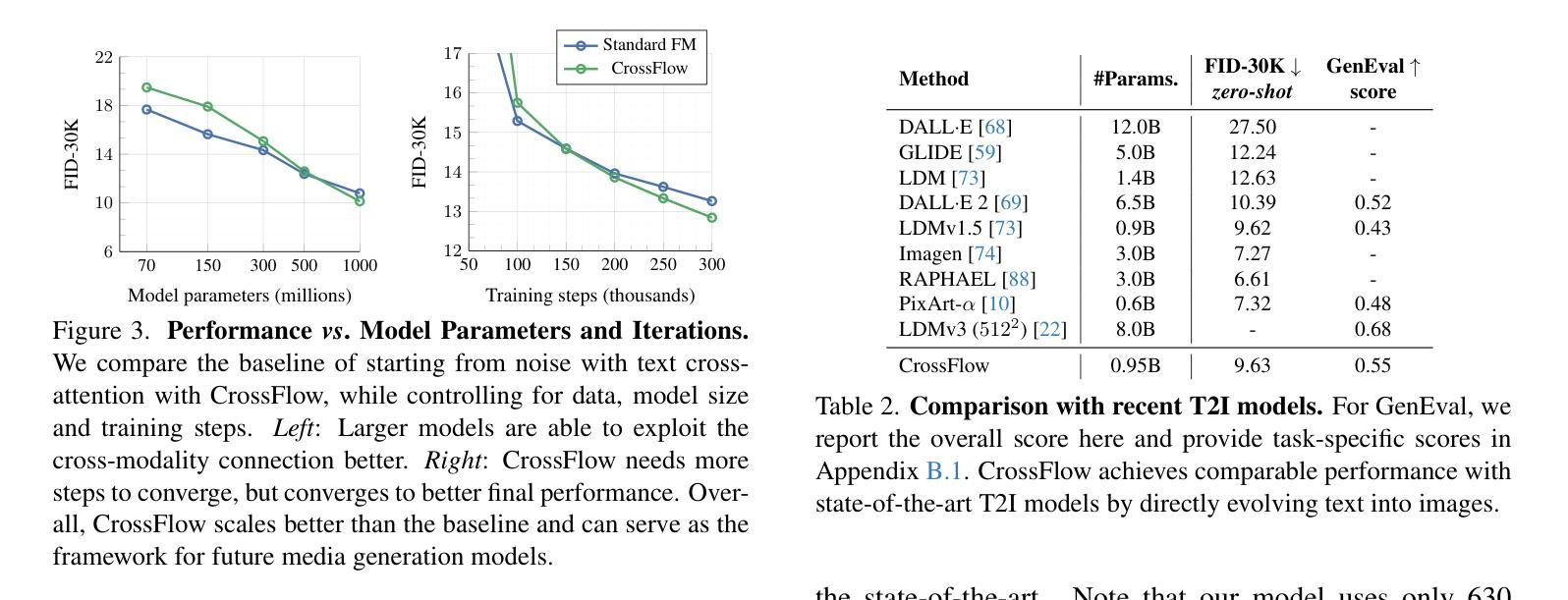
Diffusion models, and their generalization, flow matching, have had a remarkable impact on the field of media generation. Here, the conventional approach is to learn the complex mapping from a simple source distribution of Gaussian noise to the target media distribution. For cross-modal tasks such as text-to-image generation, this same mapping from noise to image is learnt whilst including a conditioning mechanism in the model. One key and thus far relatively unexplored feature of flow matching is that, unlike Diffusion models, they are not constrained for the source distribution to be noise. Hence, in this paper, we propose a paradigm shift, and ask the question of whether we can instead train flow matching models to learn a direct mapping from the distribution of one modality to the distribution of another, thus obviating the need for both the noise distribution and conditioning mechanism. We present a general and simple framework, CrossFlow, for cross-modal flow matching. We show the importance of applying Variational Encoders to the input data, and introduce a method to enable Classifier-free guidance. Surprisingly, for text-to-image, CrossFlow with a vanilla transformer without cross attention slightly outperforms standard flow matching, and we show that it scales better with training steps and model size, while also allowing for interesting latent arithmetic which results in semantically meaningful edits in the output space. To demonstrate the generalizability of our approach, we also show that CrossFlow is on par with or outperforms the state-of-the-art for various cross-modal / intra-modal mapping tasks, viz. image captioning, depth estimation, and image super-resolution. We hope this paper contributes to accelerating progress in cross-modal media generation.
扩散模型及其泛化形式——流匹配,在媒体生成领域产生了显著影响。在这里,传统的方法是学习从简单的高斯噪声源分布到目标媒体分布的复杂映射。对于跨模态任务(如文本到图像生成),在模型中引入条件机制的同时,也学习从噪声到图像的相同映射。流匹配的一个关键且迄今为止相对未被探索的特点是,与扩散模型不同,它不受源分布必须是噪声的限制。因此,在本文中,我们提出了一个范式转变,并提出了一个问题:我们是否能训练流匹配模型来学习从一种模态的分布到另一种模态的分布的直接映射,从而避免对噪声分布和条件机制的需求。我们提出了一个通用且简单的跨模态流匹配框架CrossFlow。我们强调了将变编码器应用于输入数据的重要性,并介绍了一种实现无分类器引导的方法。令人惊讶的是,对于文本到图像的任务,使用没有交叉注意力的普通变压器的CrossFlow略微优于标准流匹配,我们证明它在训练步骤和模型规模上表现更好,同时允许有趣的潜在运算,从而在输出空间产生语义上有意义的编辑。为了证明我们的方法的一般性,我们还表明CrossFlow在各种跨模态/同模态映射任务上表现与最新技术不相上下或表现更好,如图像描述、深度估计和图像超分辨率。我们希望这篇论文能促进跨模态媒体生成的进步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://cross-flow.github.io/
摘要
扩散模型及其泛化——流匹配在媒体生成领域产生了显著影响。本文突破了传统方法,不再局限于从简单的高斯噪声源分布到目标媒体分布的学习映射。针对跨模态任务如文本到图像生成,本文提出了一个新的视角,即是否可以直接训练流匹配模型从一种模态的分布学习到另一种模态的分布,而无需噪声分布和调节机制。本文提出了一个通用的简单框架CrossFlow进行跨模态流匹配,并强调了应用变分编码器于输入数据的重要性,引入了一种无分类器引导方法。令人惊讶的是,对于文本到图像任务,使用常规Transformer的CrossFlow在不使用交叉注意的情况下略微优于标准流匹配,且随着训练步骤和模型规模的扩大,表现更好。此外,它还允许有趣的潜在算术运算,在输出空间中产生语义上有意义的编辑。为证明我们方法的通用性,我们还展示了CrossFlow在各种跨模态/单模态映射任务上的表现与或优于当前最新技术,如图像描述、深度估计和图像超分辨率等。本文旨在为跨模态媒体生成的发展加速做出贡献。
关键见解
- 扩散模型和流匹配在媒体生成领域具有显著影响。
- 本文提出了一种新的方法——CrossFlow框架进行跨模态流匹配。
- CrossFlow突破了传统扩散模型的限制,可以直接学习不同模态之间的映射,无需噪声分布和调节机制。
- 变分编码器在输入数据中的应用对于提高模型性能至关重要。
- CrossFlow具有无分类器引导的能力。
- 在文本到图像任务上,CrossFlow的表现略优于标准流匹配,且具有良好的扩展性。
- CrossFlow在各种跨模态和单模态映射任务上的表现具有竞争力或优于当前技术。
点此查看论文截图

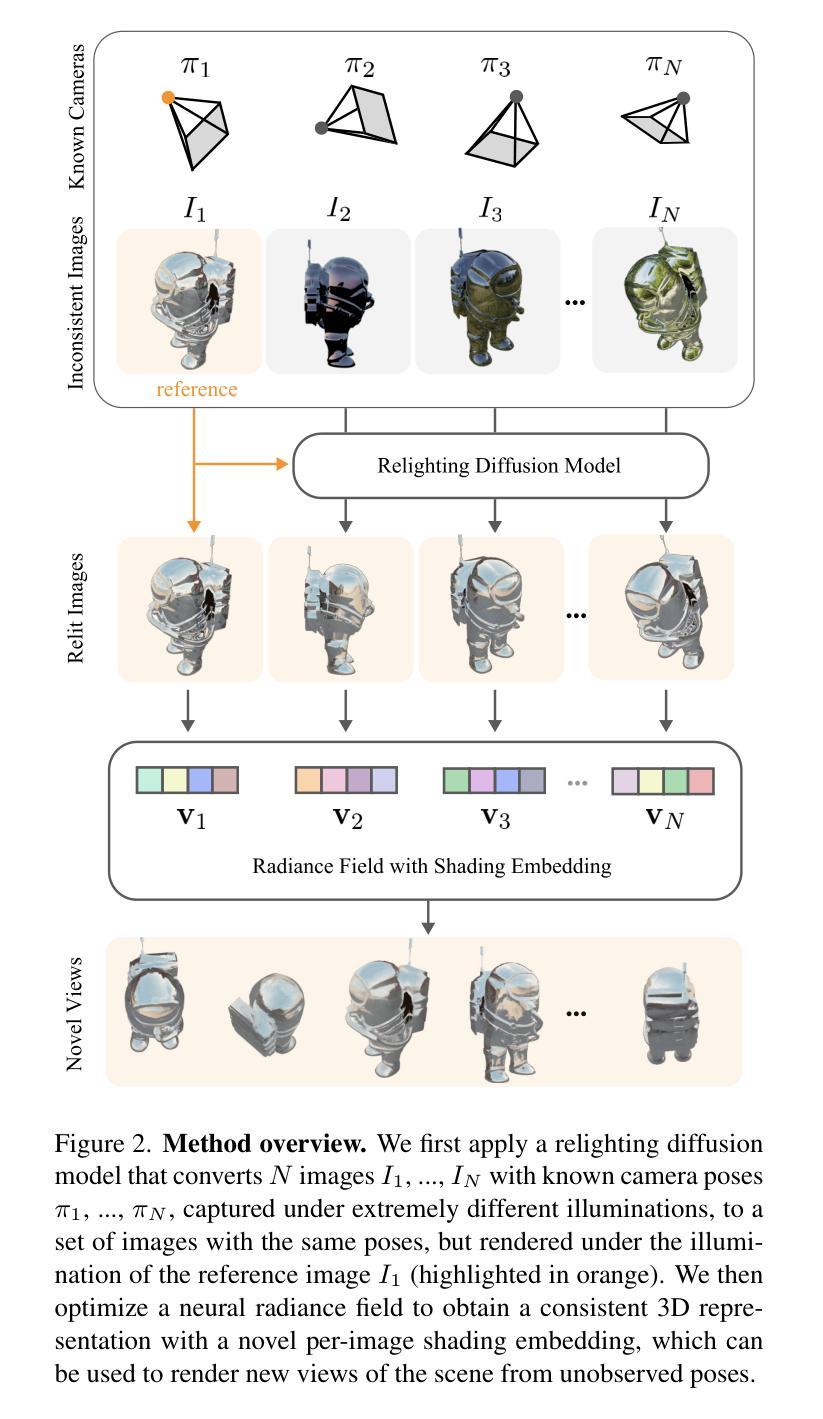
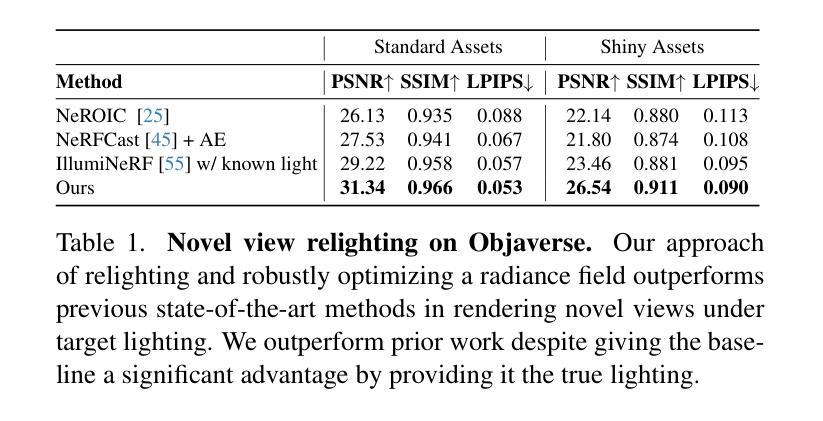
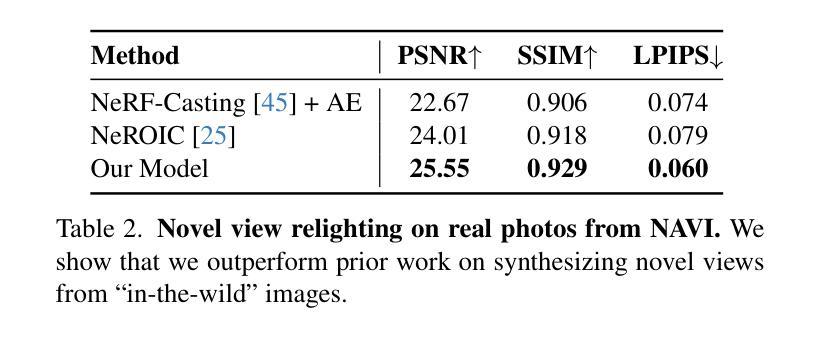
Generative Multiview Relighting for 3D Reconstruction under Extreme Illumination Variation
Authors:Hadi Alzayer, Philipp Henzler, Jonathan T. Barron, Jia-Bin Huang, Pratul P. Srinivasan, Dor Verbin
Reconstructing the geometry and appearance of objects from photographs taken in different environments is difficult as the illumination and therefore the object appearance vary across captured images. This is particularly challenging for more specular objects whose appearance strongly depends on the viewing direction. Some prior approaches model appearance variation across images using a per-image embedding vector, while others use physically-based rendering to recover the materials and per-image illumination. Such approaches fail at faithfully recovering view-dependent appearance given significant variation in input illumination and tend to produce mostly diffuse results. We present an approach that reconstructs objects from images taken under different illuminations by first relighting the images under a single reference illumination with a multiview relighting diffusion model and then reconstructing the object’s geometry and appearance with a radiance field architecture that is robust to the small remaining inconsistencies among the relit images. We validate our proposed approach on both synthetic and real datasets and demonstrate that it greatly outperforms existing techniques at reconstructing high-fidelity appearance from images taken under extreme illumination variation. Moreover, our approach is particularly effective at recovering view-dependent “shiny” appearance which cannot be reconstructed by prior methods.
从在不同环境下拍摄的照片重建物体的几何形状和外观是一项艰巨的任务,因为光照和因此物体的外观在不同捕获的图像中会有所变化。这对于具有强烈方向性外观的物体来说尤其具有挑战性。一些先前的方法使用每张图像的嵌入向量对图像中的外观变化进行建模,而其他方法则使用基于物理的渲染来恢复材料和每张图像的光照。这些方法在输入光照存在显著差异的情况下无法忠实恢复与视图相关的外观,并且往往产生大部分扩散结果。我们提出了一种方法,通过首先使用多视角重新照明扩散模型在单一参考光照下重新照明图像,然后从不同的光照条件下拍摄的照片重建物体的几何形状和外观。我们使用一种对重新照明图像之间剩余的小不一致性具有鲁棒性的辐射场架构来实现这一目标。我们在合成数据集和真实数据集上验证了我们的方法,并证明它在从极端光照变化条件下拍摄的照片重建高保真外观方面大大优于现有技术。此外,我们的方法在恢复无法由先前方法重建的与视图相关的“闪亮”外观方面特别有效。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://relight-to-reconstruct.github.io/
Summary
该文描述了一种利用多视角重光照扩散模型(multiview relighting diffusion model)从不同光照条件下拍摄的照片重建物体几何和外观的方法。通过首先在单一参考光照下重新照明图像,然后采用辐射场架构(radiance field architecture)恢复物体几何和外观,提高了在不同光照条件下拍摄物体图像的高保真重建能力,特别是对于“镜面光泽”外观的重建效果尤为显著。
Key Takeaways
- 文中提出了一种从不同光照条件下的照片重建物体几何和外观的新方法。
- 方法基于多视角重光照扩散模型进行图像重新照明。
- 通过在单一参考光照下重新照明图像,减少了光照变化对物体外观重建的影响。
- 采用辐射场架构恢复物体几何和外观,增强了重建结果的稳健性。
- 该方法对极端光照变化下的图像重建效果显著提升。
- 该方法特别适用于重建“镜面光泽”外观,这是先前方法无法实现的。
点此查看论文截图


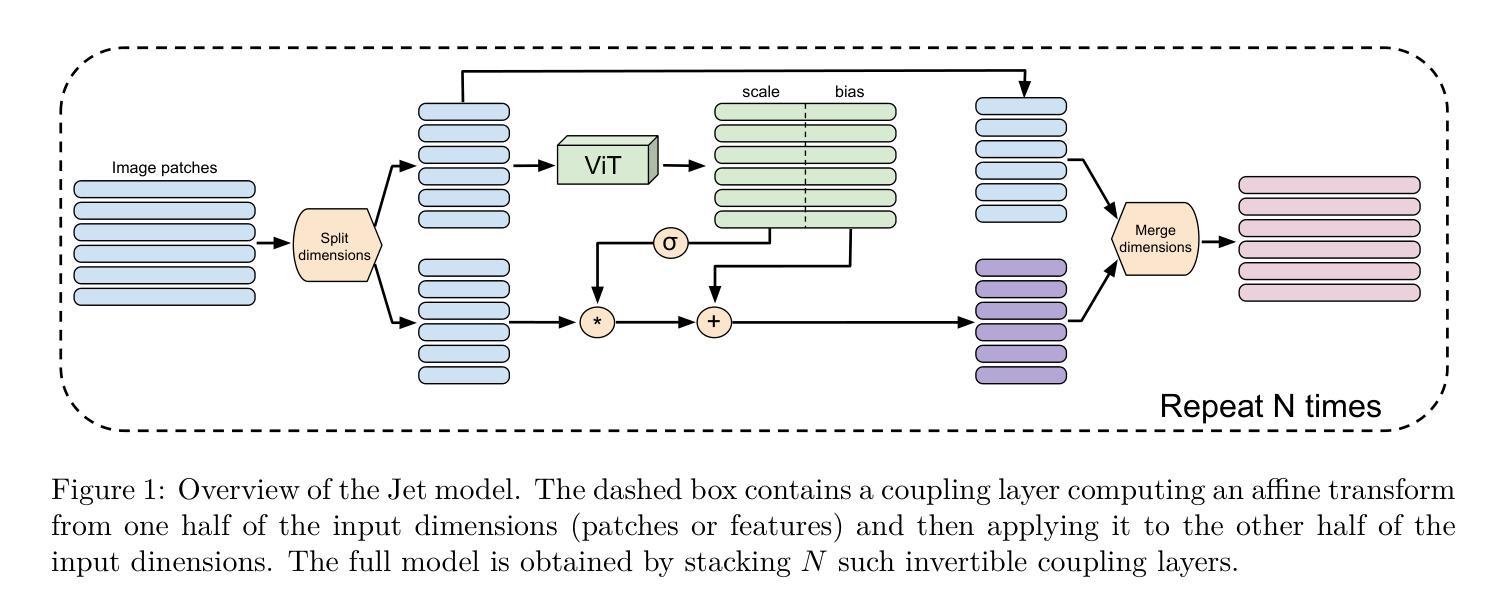
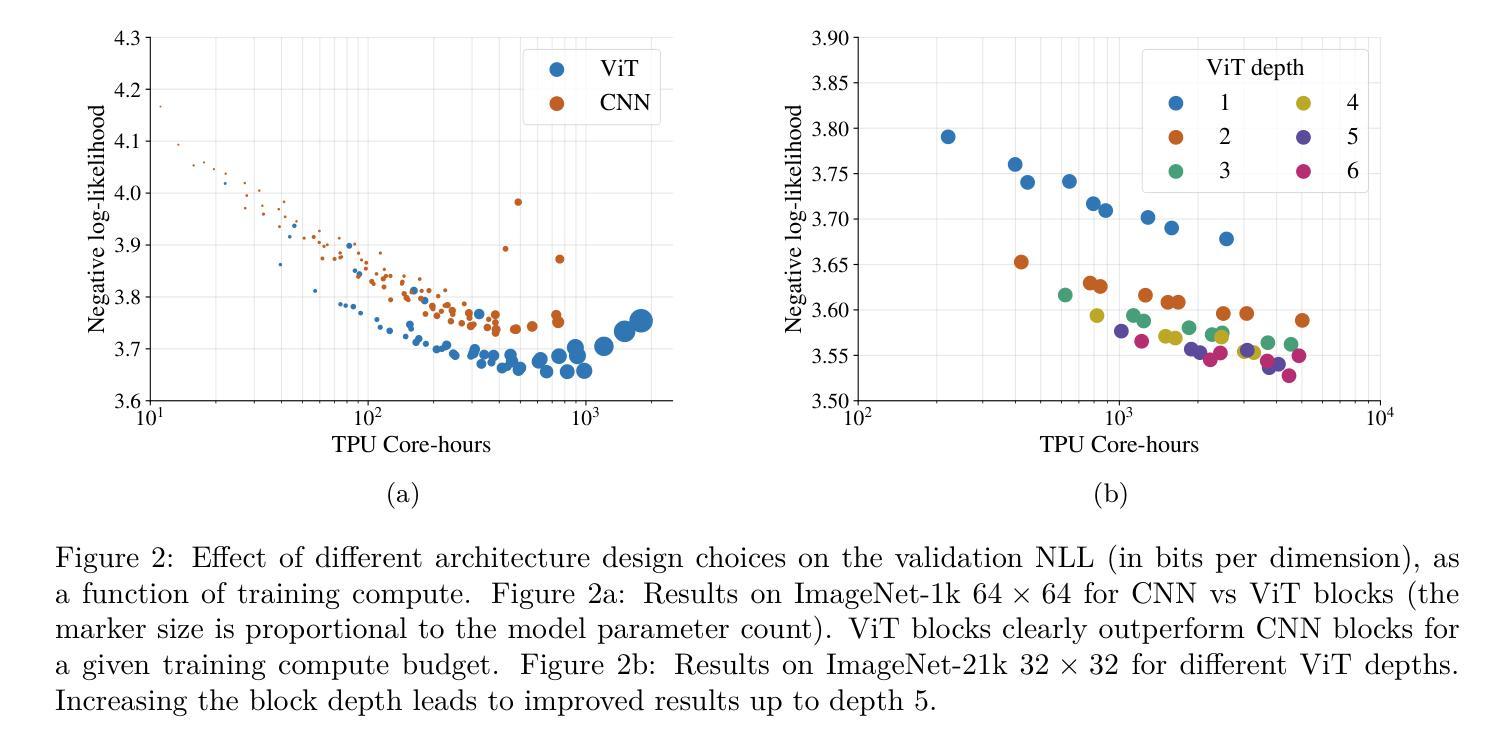
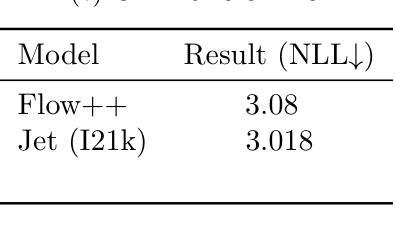
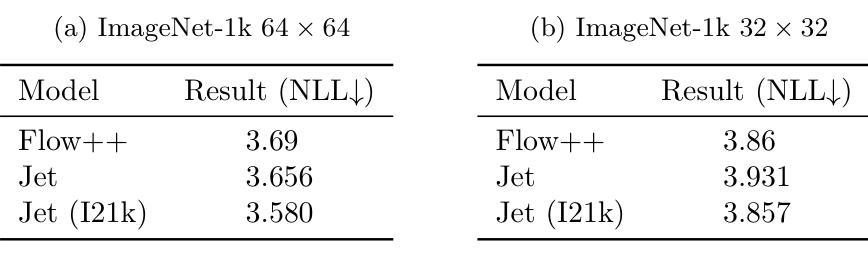
Jet: A Modern Transformer-Based Normalizing Flow
Authors:Alexander Kolesnikov, André Susano Pinto, Michael Tschannen
In the past, normalizing generative flows have emerged as a promising class of generative models for natural images. This type of model has many modeling advantages: the ability to efficiently compute log-likelihood of the input data, fast generation and simple overall structure. Normalizing flows remained a topic of active research but later fell out of favor, as visual quality of the samples was not competitive with other model classes, such as GANs, VQ-VAE-based approaches or diffusion models. In this paper we revisit the design of the coupling-based normalizing flow models by carefully ablating prior design choices and using computational blocks based on the Vision Transformer architecture, not convolutional neural networks. As a result, we achieve state-of-the-art quantitative and qualitative performance with a much simpler architecture. While the overall visual quality is still behind the current state-of-the-art models, we argue that strong normalizing flow models can help advancing research frontier by serving as building components of more powerful generative models.
过去,标准化生成流已经涌现为一类有前景的自然图像生成模型。这种模型具有许多建模优势:能够高效地计算输入数据的对数似然,生成速度快,整体结构简单。标准化流一直是活跃研究的主题,但后来因其样本的视觉质量与其他模型类别相比不具竞争力而不再受欢迎,如GAN、基于VQ-VAE的方法或扩散模型。在本文中,我们重新审视基于耦合的标准化流模型的设计,通过仔细消除先前的设计选择并使用基于视觉转换器架构的计算块(而不是卷积神经网络)。因此,我们凭借更简单的架构实现了最先进的定量和定性性能。虽然整体视觉质量仍然落后于当前最先进的模型,我们认为强大的标准化流模型可以作为更强大的生成模型的构建组件,有助于推动研究前沿。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文重新审视了基于耦合的归一化流模型的设计,通过对先前设计选择进行仔细消融,并使用基于Vision Transformer架构的计算块,而非卷积神经网络,实现了先进的质量和性能。虽然整体视觉质量仍落后于当前最先进的模型,但我们认为强大的归一化流模型可以作为更强大生成模型的构建组件,有助于推动研究前沿。
Key Takeaways
- 归一化流模型是一种具有多个建模优势的生成模型,包括计算输入数据对数似然的高效性、快速生成和简单结构。
- 之前的归一化流模型在样本的视觉质量上与其他模型类相比不具竞争力,如GANs、VQ-VAE方法和扩散模型。
- 本文通过重新审视基于耦合的归一化流模型的设计,使用Vision Transformer架构的计算块替代卷积神经网络,实现了先进的质量和性能。
- 尽管整体视觉质量仍待提高,但作者认为强大的归一化流模型可以作为构建更强大生成模型的组件,有助于推动研究前沿。
- 消融先前的设计选择是改进归一化流模型的关键步骤之一。
- 使用基于Vision Transformer的计算块在归一化流模型中产生了积极的效果。
点此查看论文截图

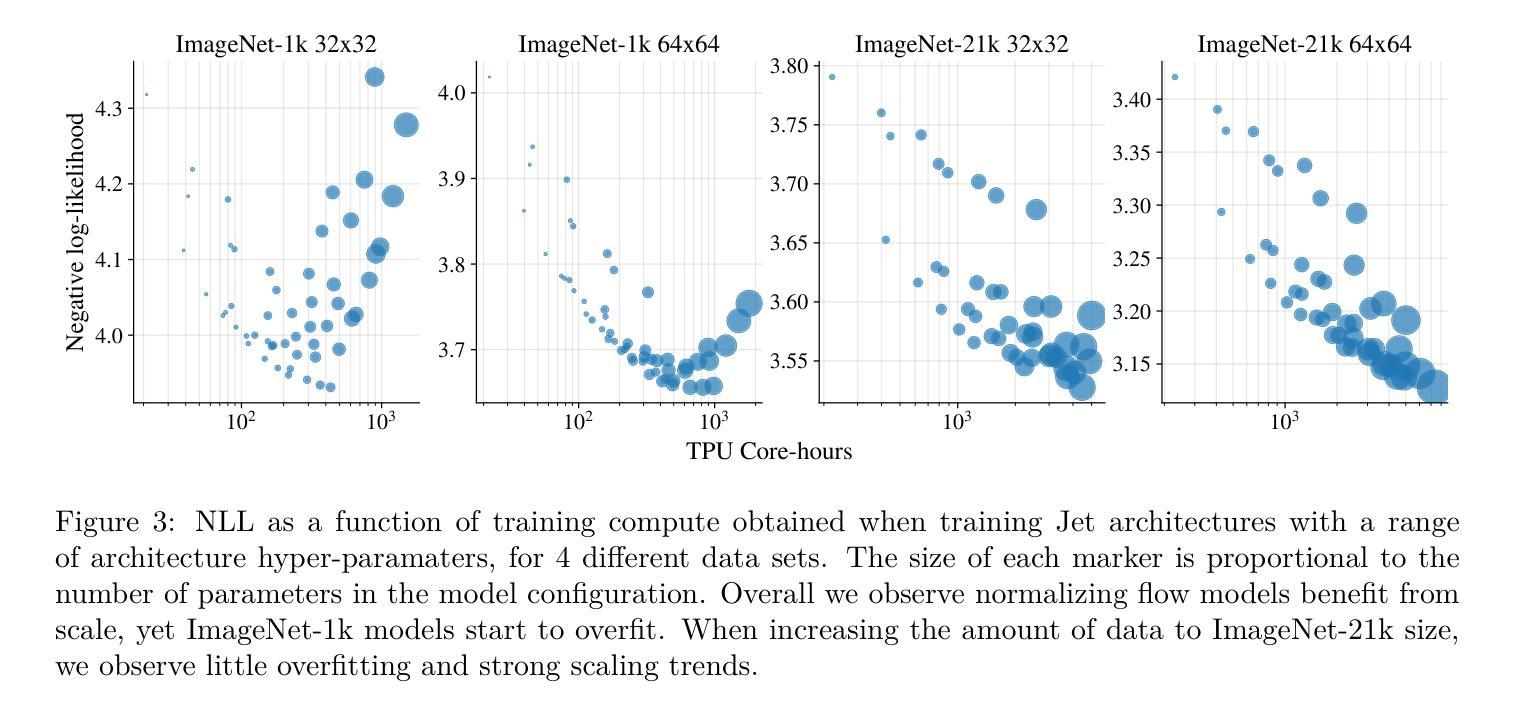
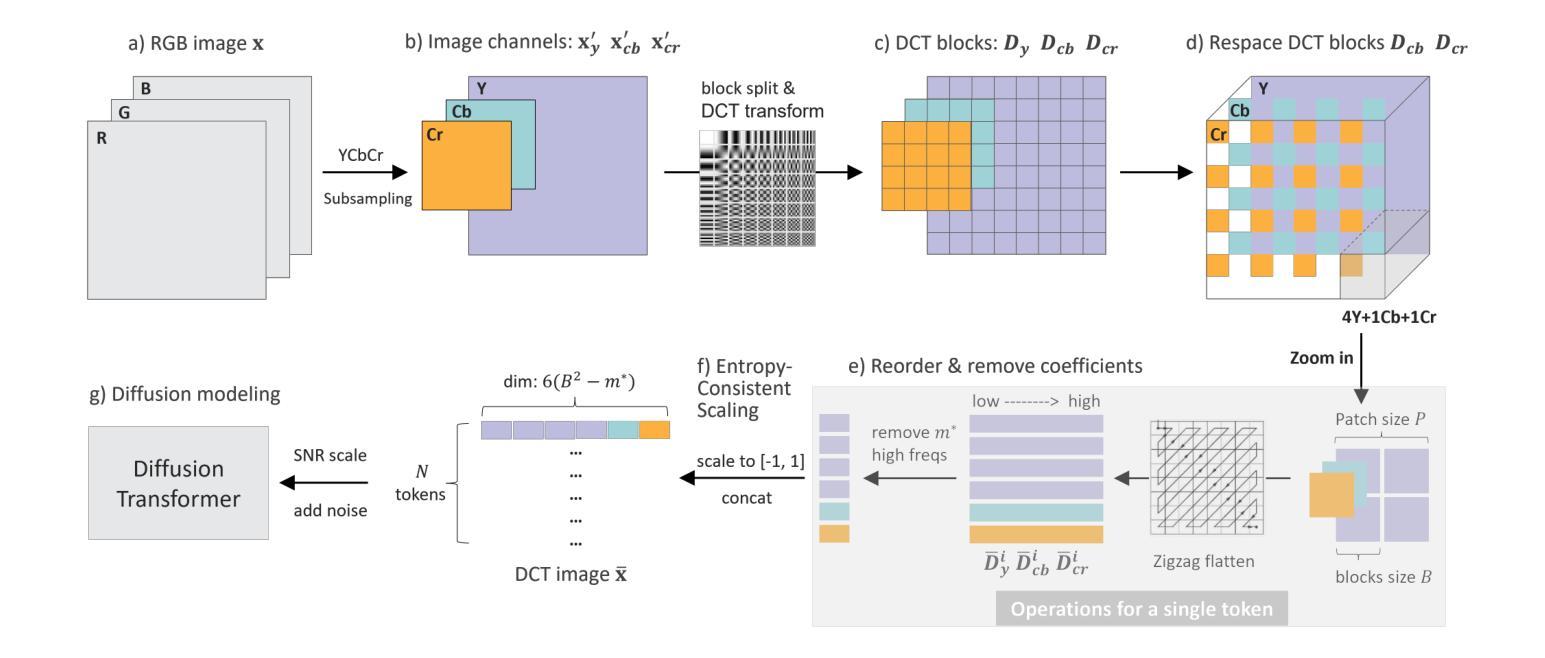
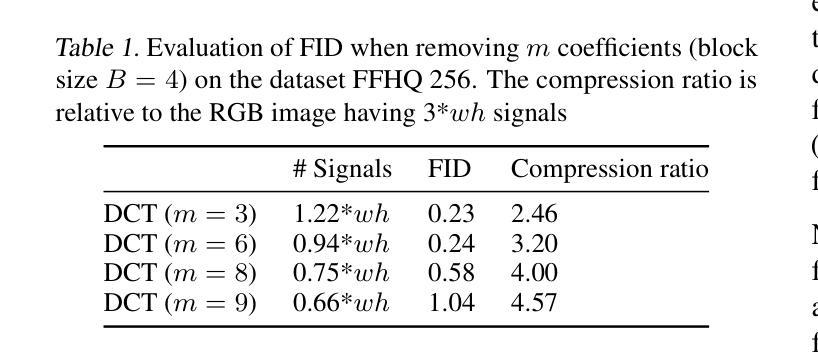
DCTdiff: Intriguing Properties of Image Generative Modeling in the DCT Space
Authors:Mang Ning, Mingxiao Li, Jianlin Su, Haozhe Jia, Lanmiao Liu, Martin Beneš, Albert Ali Salah, Itir Onal Ertugrul
This paper explores image modeling from the frequency space and introduces DCTdiff, an end-to-end diffusion generative paradigm that efficiently models images in the discrete cosine transform (DCT) space. We investigate the design space of DCTdiff and reveal the key design factors. Experiments on different frameworks (UViT, DiT), generation tasks, and various diffusion samplers demonstrate that DCTdiff outperforms pixel-based diffusion models regarding generative quality and training efficiency. Remarkably, DCTdiff can seamlessly scale up to high-resolution generation without using the latent diffusion paradigm. Finally, we illustrate several intriguing properties of DCT image modeling. For example, we provide a theoretical proof of why `image diffusion can be seen as spectral autoregression’, bridging the gap between diffusion and autoregressive models. The effectiveness of DCTdiff and the introduced properties suggest a promising direction for image modeling in the frequency space. The code is at \url{https://github.com/forever208/DCTdiff}.
本文探讨了频率空间的图像建模,并介绍了DCTdiff这一端到端的扩散生成范式,该范式在离散余弦变换(DCT)空间有效地建模图像。我们研究了DCTdiff的设计空间,揭示了关键的设计因素。在不同框架(UViT、DiT)、生成任务和多种扩散采样器上的实验表明,DCTdiff在生成质量和训练效率方面优于基于像素的扩散模型。值得注意的是,DCTdiff可以无缝地扩展到高分辨率生成,而无需使用潜在扩散范式。最后,我们说明了DCT图像建模的几个有趣特性。例如,我们提供了理论证明,解释了为什么“图像扩散可以被视为谱自回归”,从而缩小了扩散模型和自回归模型之间的差距。DCTdiff的有效性和所介绍的特性表明,频率空间的图像建模具有广阔的发展前景。代码位于\url{https://github.com/forever208/DCTdiff}。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages
Summary
本文介绍了DCTdiff,这是一种在离散余弦变换(DCT)空间中进行图像建模的端到端扩散生成范式。文章探讨了DCTdiff的设计空间,揭示了关键设计因素,并通过实验证明其在生成质量和训练效率上优于基于像素的扩散模型。DCTdiff能够无缝地扩展到高分辨率生成,而无需使用潜在扩散方法。此外,文章还阐述了DCT图像建模的几个有趣特性,如从理论上证明了“图像扩散可以被视为谱自回归”,为扩散和自回归模型之间建立了联系。
Key Takeaways
- DCTdiff是一种在离散余弦变换(DCT)空间进行图像建模的扩散生成方法。
- DCTdiff的设计空间包括关键设计因素,这些因素对于提高生成质量和训练效率至关重要。
- DCTdiff在生成质量和训练效率上优于基于像素的扩散模型。
- DCTdiff能够无缝扩展到高分辨率图像生成。
- DCTdiff不使用潜在扩散方法。
- 文章从理论上证明了“图像扩散可以被视为谱自回归”,这是扩散和自回归模型之间的一个重要联系。
点此查看论文截图
MagicNaming: Consistent Identity Generation by Finding a “Name Space” in T2I Diffusion Models
Authors:Jing Zhao, Heliang Zheng, Chaoyue Wang, Long Lan, Wanrong Hunag, Yuhua Tang
Large-scale text-to-image diffusion models, (e.g., DALL-E, SDXL) are capable of generating famous persons by simply referring to their names. Is it possible to make such models generate generic identities as simple as the famous ones, e.g., just use a name? In this paper, we explore the existence of a “Name Space”, where any point in the space corresponds to a specific identity. Fortunately, we find some clues in the feature space spanned by text embedding of celebrities’ names. Specifically, we first extract the embeddings of celebrities’ names in the Laion5B dataset with the text encoder of diffusion models. Such embeddings are used as supervision to learn an encoder that can predict the name (actually an embedding) of a given face image. We experimentally find that such name embeddings work well in promising the generated image with good identity consistency. Note that like the names of celebrities, our predicted name embeddings are disentangled from the semantics of text inputs, making the original generation capability of text-to-image models well-preserved. Moreover, by simply plugging such name embeddings, all variants (e.g., from Civitai) derived from the same base model (i.e., SDXL) readily become identity-aware text-to-image models. Project homepage: \url{https://magicfusion.github.io/MagicNaming/}.
大规模文本到图像的扩散模型(例如DALL-E、SDXL)能够通过简单地提及名字生成名人图像。是否可能使这类模型生成像名人一样简单的普通身份呢?例如,仅仅使用一个名字?在这篇论文中,我们探索了“名称空间”的存在,该空间中的每个点都对应一个特定的身份。幸运的是,我们在由名人名字的文本嵌入所构成的特征空间中找到了一些线索。具体来说,我们首先使用扩散模型的文本编码器提取Laion5B数据集的名人名字的嵌入。这些嵌入用作监督学习,以训练一个能够对给定的面部图像进行名称预测(实际上是嵌入)的编码器。我们通过实验发现,这样的名称嵌入在保持生成的图像具有良好的身份一致性方面效果很好。值得注意的是,与名人的名字一样,我们预测的名称嵌入与文本输入的语义是分开的,使得文本到图像模型的原始生成能力得到了很好的保留。此外,通过简单地插入这样的名称嵌入,基于同一基础模型(即SDXL)的所有变体(例如来自Civitai)都能轻易成为具有身份意识的文本到图像模型。项目主页:https://magicfusion.github.io/MagicNaming/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
本文探索了文本到图像的大尺度扩散模型中的“名称空间”的存在性。研究通过提取Laion5B数据集中名人名称的文本嵌入,学习了一个能够根据面部图像预测名称的编码器。实验表明,这些名称嵌入能够确保生成的图像具有良好的身份一致性。此外,该研究方法能够使同一基础模型(如SDXL)的所有变体(如Civitai)轻易成为具有身份识别功能的文本到图像模型。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像的大尺度扩散模型能够生成特定名称的图像,本研究探讨了是否也能生成普通名称的图像。
- 研究发现了“名称空间”,其中空间的每个点都对应一个特定的身份。
- 通过提取Laion5B数据集中名人名称的文本嵌入,学习了一个预测给定面部图像名称的编码器。
- 名称嵌入在保持身份一致性的同时,不改变模型的原始文本到图像的生成能力。
- 名称嵌入技术可以应用于同一基础模型的变体,使其成为具有身份识别功能的文本到图像模型。
- 实验表明,这种技术在实际应用中表现良好。
点此查看论文截图


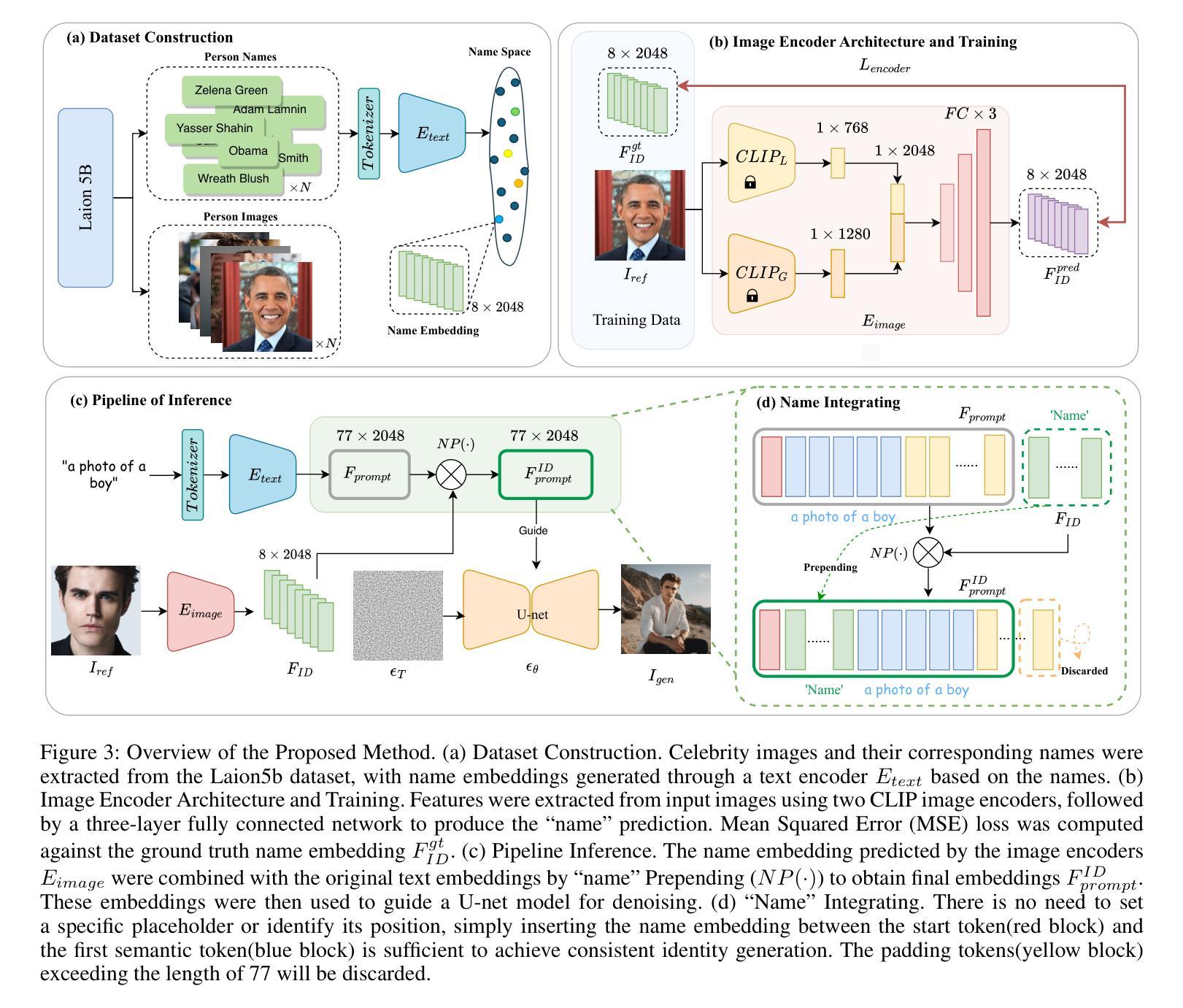

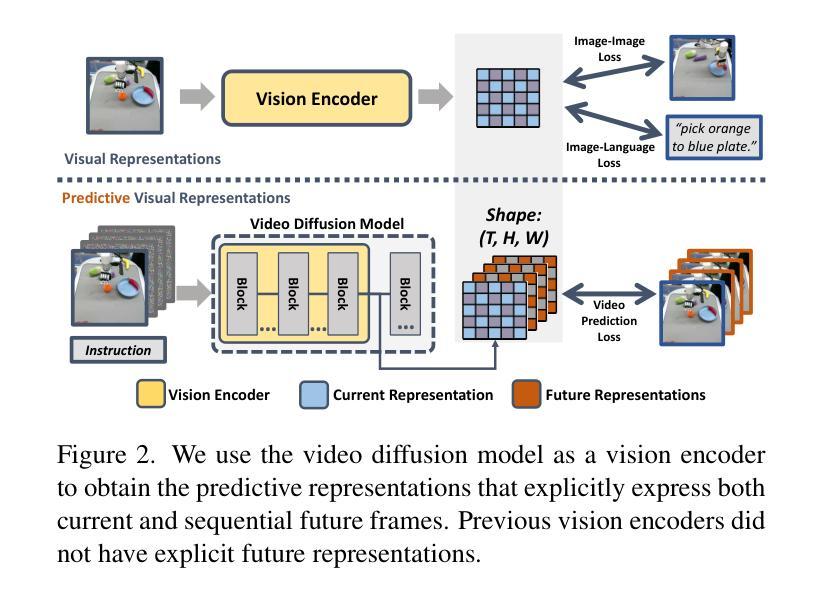
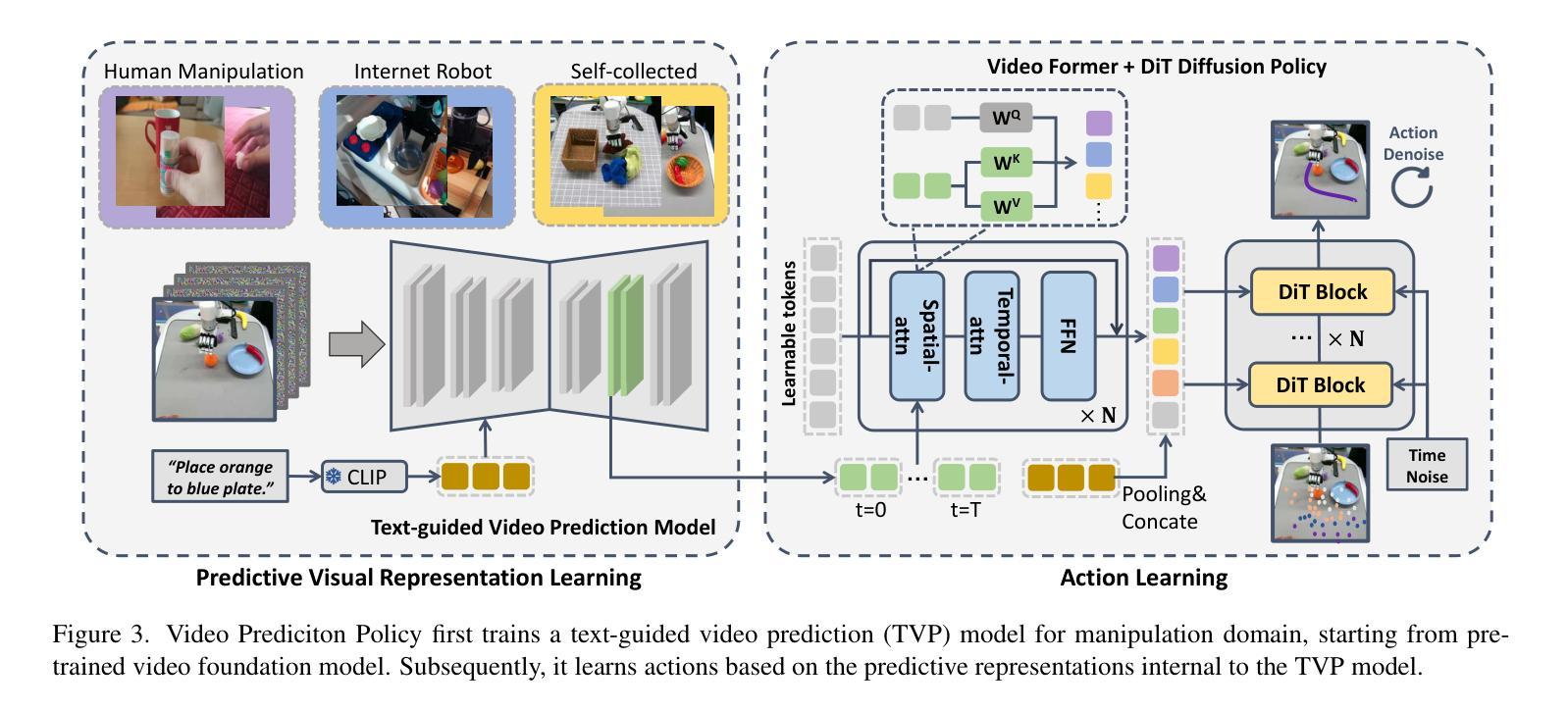
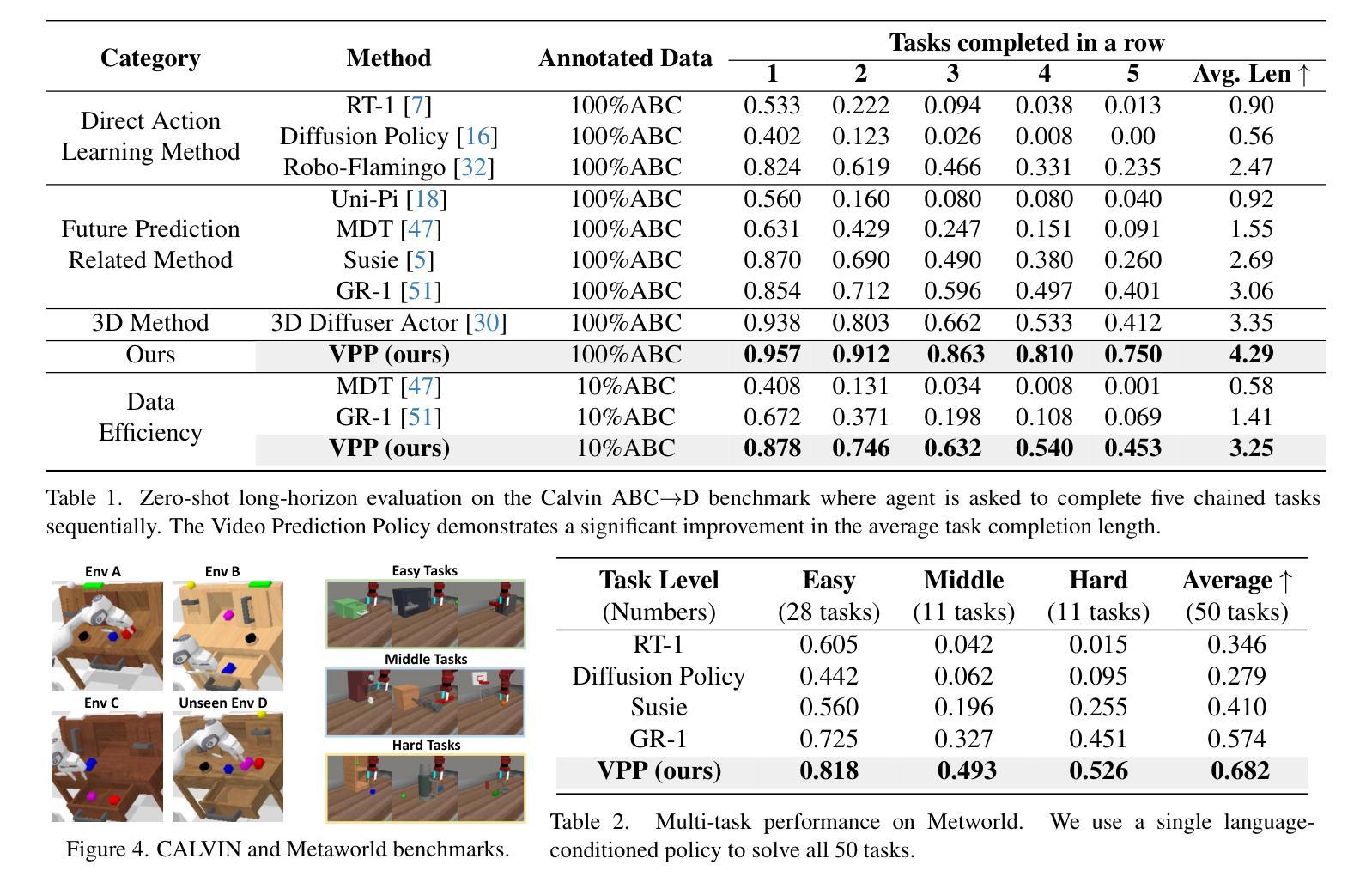
Video Prediction Policy: A Generalist Robot Policy with Predictive Visual Representations
Authors:Yucheng Hu, Yanjiang Guo, Pengchao Wang, Xiaoyu Chen, Yen-Jen Wang, Jianke Zhang, Koushil Sreenath, Chaochao Lu, Jianyu Chen
Recent advancements in robotics have focused on developing generalist policies capable of performing multiple tasks. Typically, these policies utilize pre-trained vision encoders to capture crucial information from current observations. However, previous vision encoders, which trained on two-image contrastive learning or single-image reconstruction, can not perfectly capture the sequential information essential for embodied tasks. Recently, video diffusion models (VDMs) have demonstrated the capability to accurately predict future image sequences, exhibiting a good understanding of physical dynamics. Motivated by the strong visual prediction capabilities of VDMs, we hypothesize that they inherently possess visual representations that reflect the evolution of the physical world, which we term predictive visual representations. Building on this hypothesis, we propose the Video Prediction Policy (VPP), a generalist robotic policy conditioned on the predictive visual representations from VDMs. To further enhance these representations, we incorporate diverse human or robotic manipulation datasets, employing unified video-generation training objectives. VPP consistently outperforms existing methods across two simulated and two real-world benchmarks. Notably, it achieves a 28.1% relative improvement in the Calvin ABC-D benchmark compared to the previous state-of-the-art and delivers a 28.8% increase in success rates for complex real-world dexterous manipulation tasks.
近期机器人技术的进步主要集中在开发能够执行多种任务的一般策略上。通常,这些策略会使用预训练的视觉编码器来捕获当前观察中的关键信息。然而,以前训练的视觉编码器主要依赖于两图像对比学习或单图像重建,无法完美捕获对实体任务至关重要的序列信息。最近,视频扩散模型(VDMs)已经展现出准确预测未来图像序列的能力,表现出对物理动态的良好理解。受到VDMs强大视觉预测能力的启发,我们假设它们天生就具有反映物理世界演变的视觉表征,我们称之为预测性视觉表征。基于这一假设,我们提出了视频预测策略(VPP),这是一种以VDMs的预测性视觉表征为条件的一般性机器人策略。为了进一步增强这些表征,我们融入了多样化的人类或机器人操作数据集,采用统一的视频生成训练目标。VPP在两个模拟基准测试和两个真实世界基准测试中均始终优于现有方法。值得一提的是,与之前的最新技术相比,它在Calvin ABC-D基准测试中实现了28.1%的相对改进,并在复杂的真实世界精细操作任务中成功率提高了28.8%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The first two authors contribute equally. Project Page at https://video-prediction-policy.github.io/
Summary
基于视频扩散模型(VDMs)的预测视觉表征,提出视频预测策略(VPP),结合多种数据集和目标,提升机器人执行多种任务的能力,在模拟和真实世界基准测试中表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 近期机器人技术进展集中于开发能执行多种任务的通用策略。
- 通用策略常使用预训练的视觉编码器捕捉当前观察信息。
- 以往的视觉编码器在捕捉实体任务所需的序列信息方面存在缺陷。
- 视频扩散模型(VDMs)能准确预测未来图像序列,理解物理动态。
- VDMs具有预测视觉表征,即反映物理世界演变的内在能力。
- 基于此,提出视频预测策略(VPP),结合VDMs的预测视觉表征,构建通用机器人策略。
点此查看论文截图

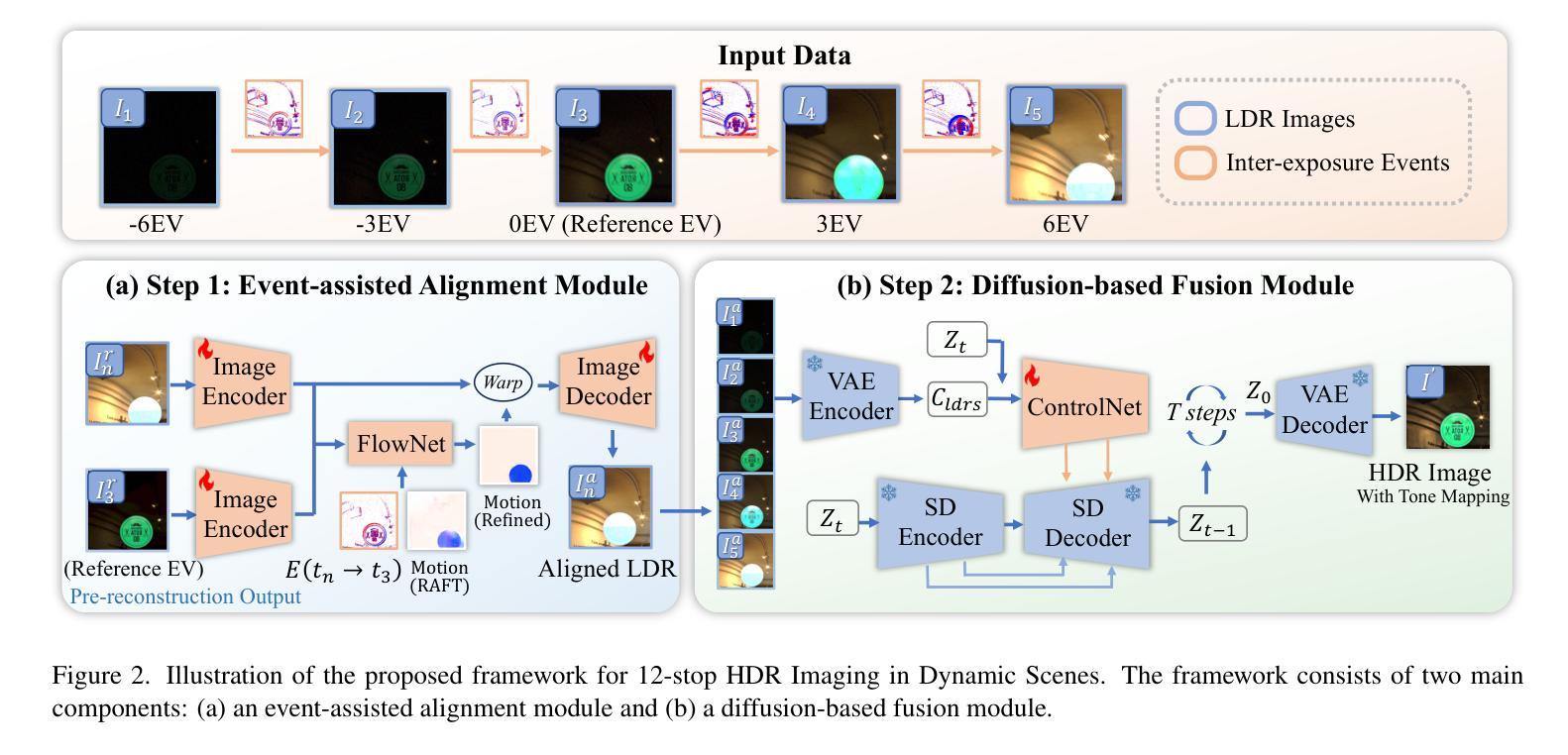
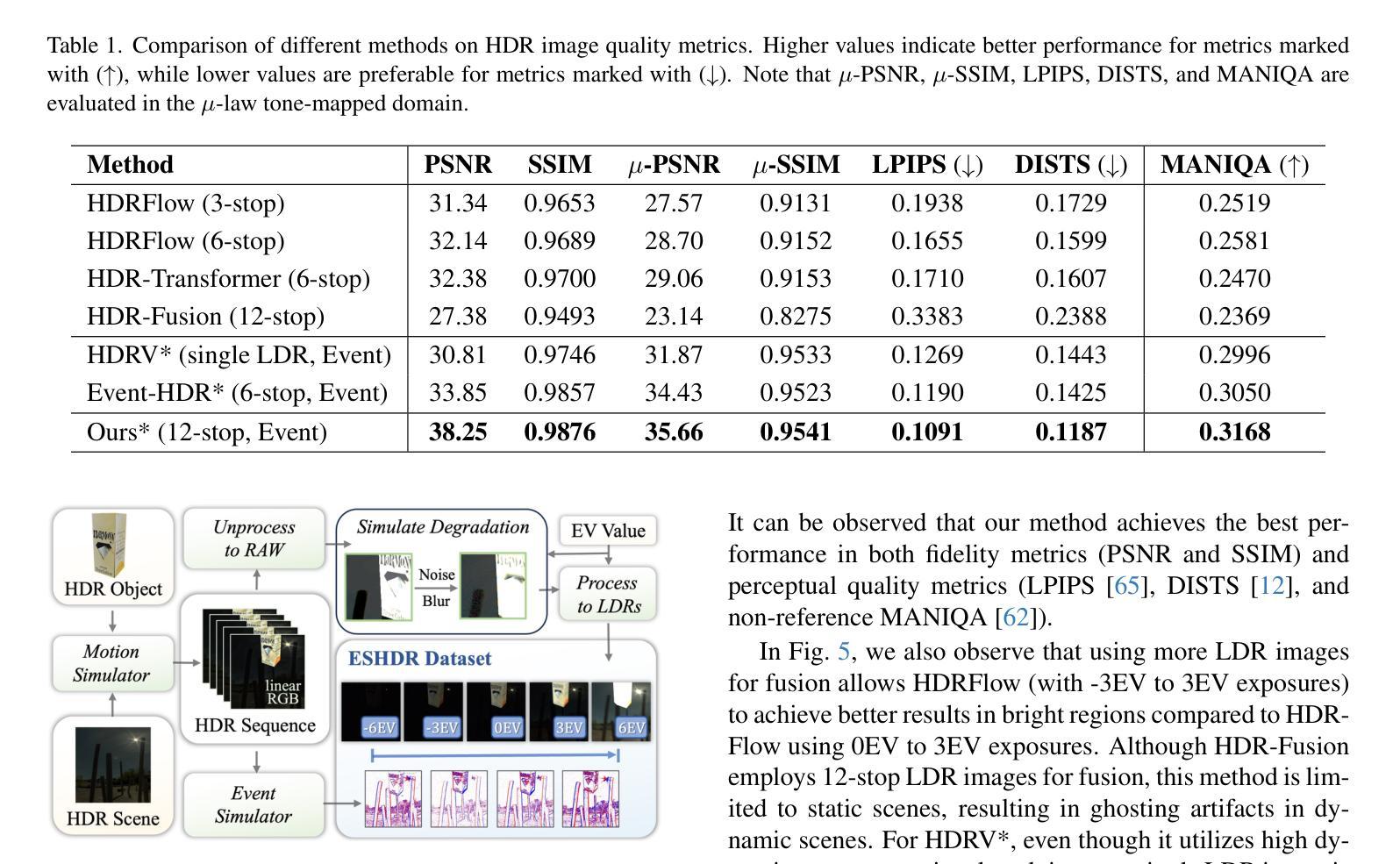
Event-assisted 12-stop HDR Imaging of Dynamic Scene
Authors:Shi Guo, Zixuan Chen, Ziran Zhang, Yutian Chen, Gangwei Xu, Tianfan Xue
High dynamic range (HDR) imaging is a crucial task in computational photography, which captures details across diverse lighting conditions. Traditional HDR fusion methods face limitations in dynamic scenes with extreme exposure differences, as aligning low dynamic range (LDR) frames becomes challenging due to motion and brightness variation. In this work, we propose a novel 12-stop HDR imaging approach for dynamic scenes, leveraging a dual-camera system with an event camera and an RGB camera. The event camera provides temporally dense, high dynamic range signals that improve alignment between LDR frames with large exposure differences, reducing ghosting artifacts caused by motion. Also, a real-world finetuning strategy is proposed to increase the generalization of alignment module on real-world events. Additionally, we introduce a diffusion-based fusion module that incorporates image priors from pre-trained diffusion models to address artifacts in high-contrast regions and minimize errors from the alignment process. To support this work, we developed the ESHDR dataset, the first dataset for 12-stop HDR imaging with synchronized event signals, and validated our approach on both simulated and real-world data. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance, successfully extending HDR imaging to 12 stops in dynamic scenes.
高动态范围(HDR)成像是计算摄影中的一项重要任务,能够在不同的光照条件下捕捉细节。传统的HDR融合方法在动态场景中存在极限,特别是在极端曝光差异的情况下,由于运动和亮度变化,对齐低动态范围(LDR)帧变得具有挑战性。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种用于动态场景的12档HDR成像新方法,利用配备事件相机和RGB相机的双相机系统进行实现。事件相机提供时间密集、高动态范围的信号,改善了具有较大曝光差异的LDR帧之间的对齐,减少了由于运动造成的鬼影伪影。此外,我们还提出了一种现实世界的微调策略,以提高对齐模块在现实事件中的通用性。另外,我们引入了一个基于扩散的融合模块,该模块结合了预训练扩散模型的图像先验信息,以解决高对比度区域的伪影问题,并最小化对齐过程中的误差。为了支持这项工作,我们开发了ESHDR数据集,这是第一个具有同步事件信号的12档HDR成像数据集,并在模拟和真实数据上验证了我们的方法。大量实验表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的性能,成功地将HDR成像扩展到动态的12档场景。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://openimaginglab.github.io/Event-Assisted-12stops-HDR/
Summary:
本文提出了一种基于双摄像头系统(事件摄像头和RGB摄像头)的12档高动态范围(HDR)成像新方法,用于动态场景的HDR成像。该方法利用事件摄像头提供的时间密集、高动态范围的信号,改进了不同曝光度之间的LDR帧对齐,减少了因运动产生的鬼影伪影。此外,引入了一个基于扩散的融合模块,利用预训练的扩散模型的图像先验信息来解决高对比度区域的伪影问题并减少对齐过程中的误差。为了支持该研究,开发了同步事件信号的ESHDR数据集,并在模拟和真实数据上验证了该方法的有效性。该方法成功将HDR成像扩展到动态场景的12档。
Key Takeaways:
- 提出了基于双摄像头系统(事件摄像头和RGB摄像头)的12档高动态范围(HDR)成像方法。
- 利用事件摄像头提供的时间密集、高动态范围的信号改进LDR帧对齐。
- 通过采用扩散融合模块解决了高对比度区域的伪影问题并减少了误差。
- 采用同步事件信号的ESHDR数据集用于验证方法的有效性。
- 方法成功将HDR成像扩展到动态场景的12档性能表现优异。
- 提出了一种现实世界的微调策略,提高了对齐模块在现实事件中的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图


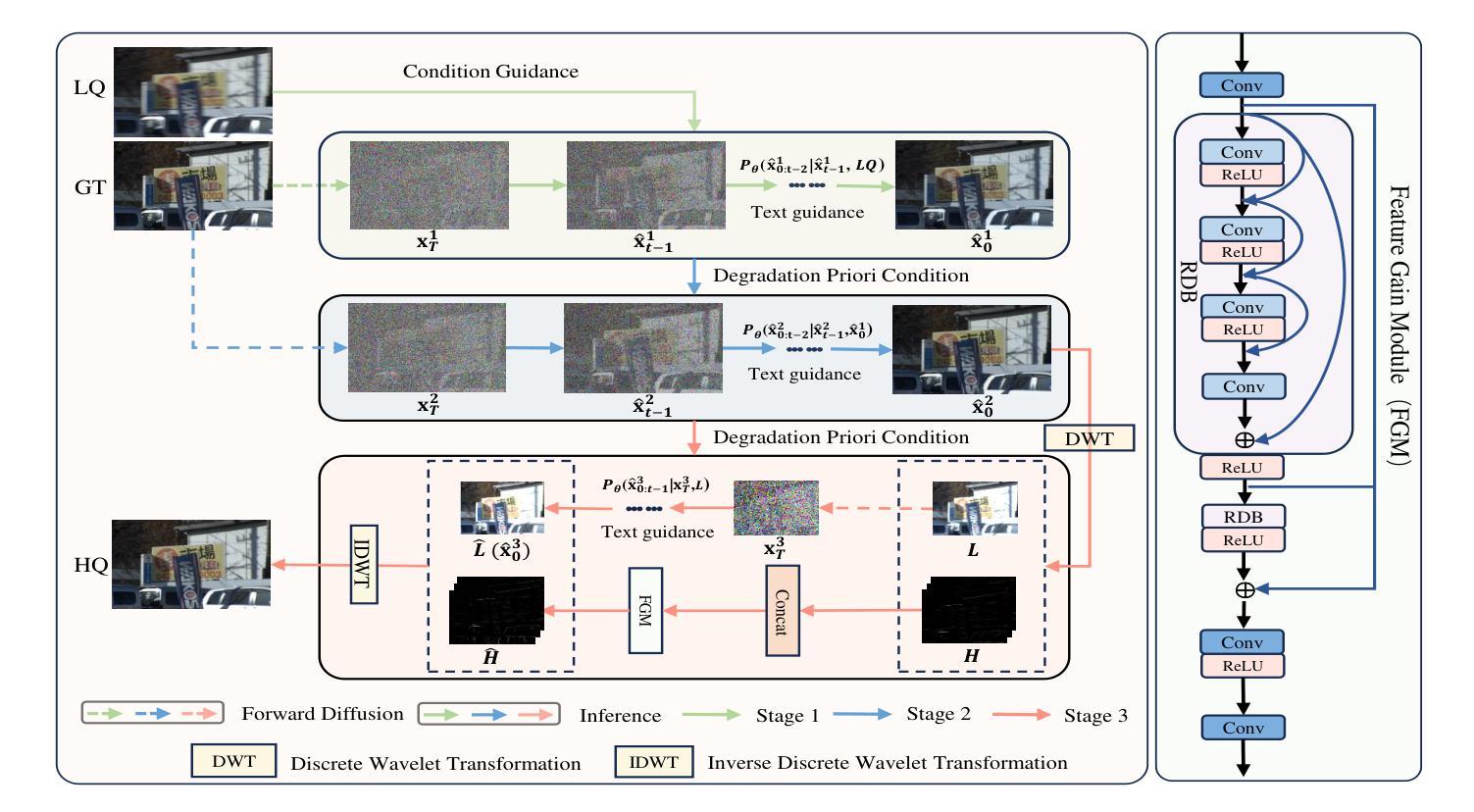
Unified Image Restoration and Enhancement: Degradation Calibrated Cycle Reconstruction Diffusion Model
Authors:Minglong Xue, Jinhong He, Shivakumara Palaiahnakote, Mingliang Zhou
Image restoration and enhancement are pivotal for numerous computer vision applications, yet unifying these tasks efficiently remains a significant challenge. Inspired by the iterative refinement capabilities of diffusion models, we propose CycleRDM, a novel framework designed to unify restoration and enhancement tasks while achieving high-quality mapping. Specifically, CycleRDM first learns the mapping relationships among the degraded domain, the rough normal domain, and the normal domain through a two-stage diffusion inference process. Subsequently, we transfer the final calibration process to the wavelet low-frequency domain using discrete wavelet transform, performing fine-grained calibration from a frequency domain perspective by leveraging task-specific frequency spaces. To improve restoration quality, we design a feature gain module for the decomposed wavelet high-frequency domain to eliminate redundant features. Additionally, we employ multimodal textual prompts and Fourier transform to drive stable denoising and reduce randomness during the inference process. After extensive validation, CycleRDM can be effectively generalized to a wide range of image restoration and enhancement tasks while requiring only a small number of training samples to be significantly superior on various benchmarks of reconstruction quality and perceptual quality. The source code will be available at https://github.com/hejh8/CycleRDM.
图像修复和增强对于许多计算机视觉应用至关重要,但是如何有效地统一这些任务仍然是一个巨大挑战。受扩散模型迭代细化能力的启发,我们提出了CycleRDM,这是一个旨在统一修复和增强任务的同时实现高质量映射的新型框架。具体来说,CycleRDM首先通过两阶段扩散推理过程学习退化域、粗略正常域和正常域之间的映射关系。随后,我们通过离散小波变换将最终的校准过程转移到小波低频域,利用任务特定的频率空间,从频率域的角度进行精细校准。为了提高恢复质量,我们为分解后的小波高频域设计了特征增益模块,以消除冗余特征。此外,我们还采用多模式文本提示和傅里叶变换来驱动稳定的去噪,减少推理过程中的随机性。经过广泛验证,CycleRDM可以有效地推广到各种图像修复和增强任务,并且只需要少量训练样本就能在重建质量和感知质量的各种基准测试中表现出卓越性能。源代码将在https://github.com/hejh8/CycleRDM上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
循环RDM框架利用扩散模型的迭代优化能力,实现了图像修复与增强的统一。它通过两阶段扩散推理学习退化域、粗略正常域和正常域之间的映射关系,并在小波低频域进行精细校准,同时消除小波高频域中的冗余特征,提高图像修复质量。此外,该框架采用多模式文本提示和傅里叶变换,以实现稳定的去噪和减少推理过程中的随机性。总体而言,CycleRDM可广泛应用于多种图像修复和增强任务,并在重建质量和感知质量方面表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- CycleRDM框架利用扩散模型的迭代优化能力,有效统一了图像修复和增强任务。
- 通过两阶段扩散推理,学习退化域、粗略正常域和正常域之间的映射关系。
- 在小波低频域进行精细校准,利用任务特定频率空间提高修复质量。
- 设计特征增益模块,消除小波高频域中的冗余特征。
- 采用多模式文本提示和傅里叶变换,实现稳定去噪,减少推理过程中的随机性。
- CycleRDM可广泛应用于多种图像修复和增强任务。
点此查看论文截图


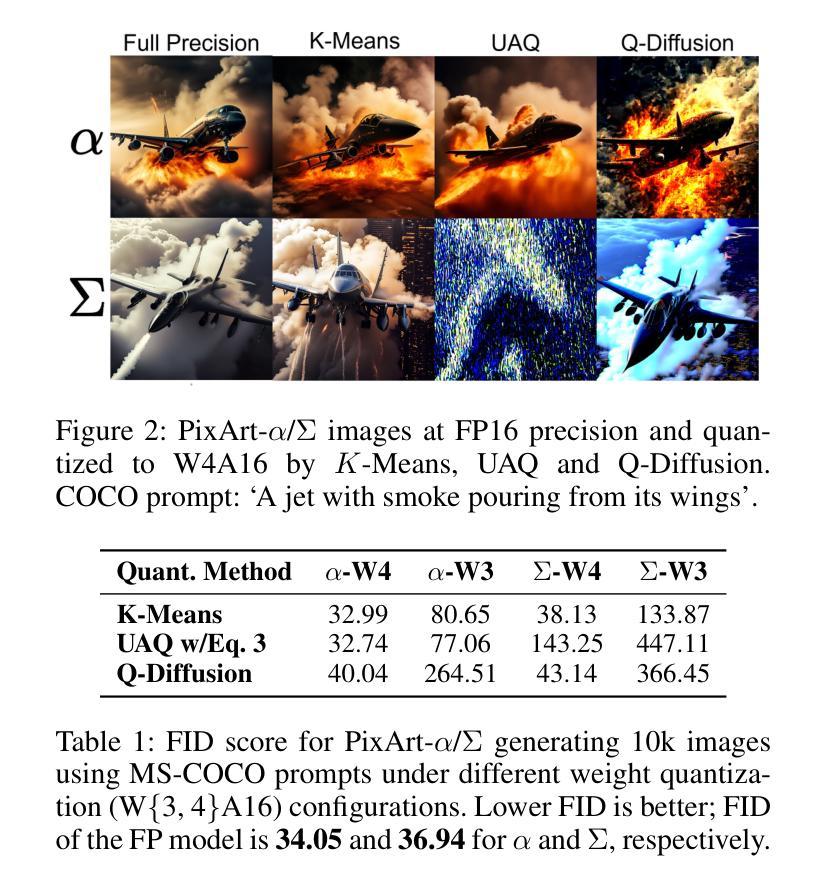
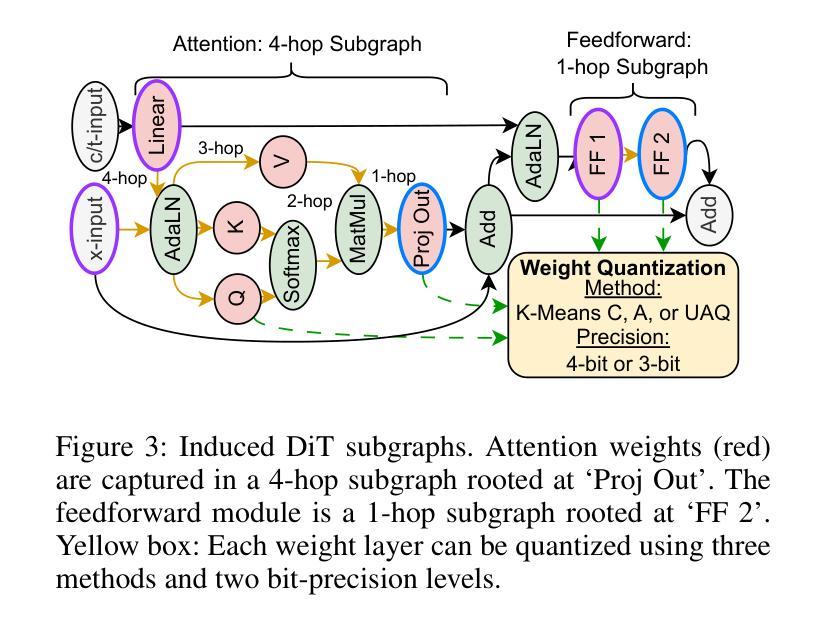
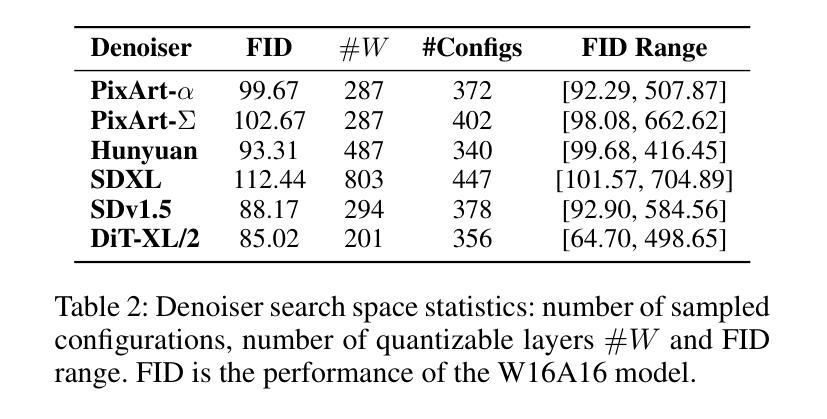
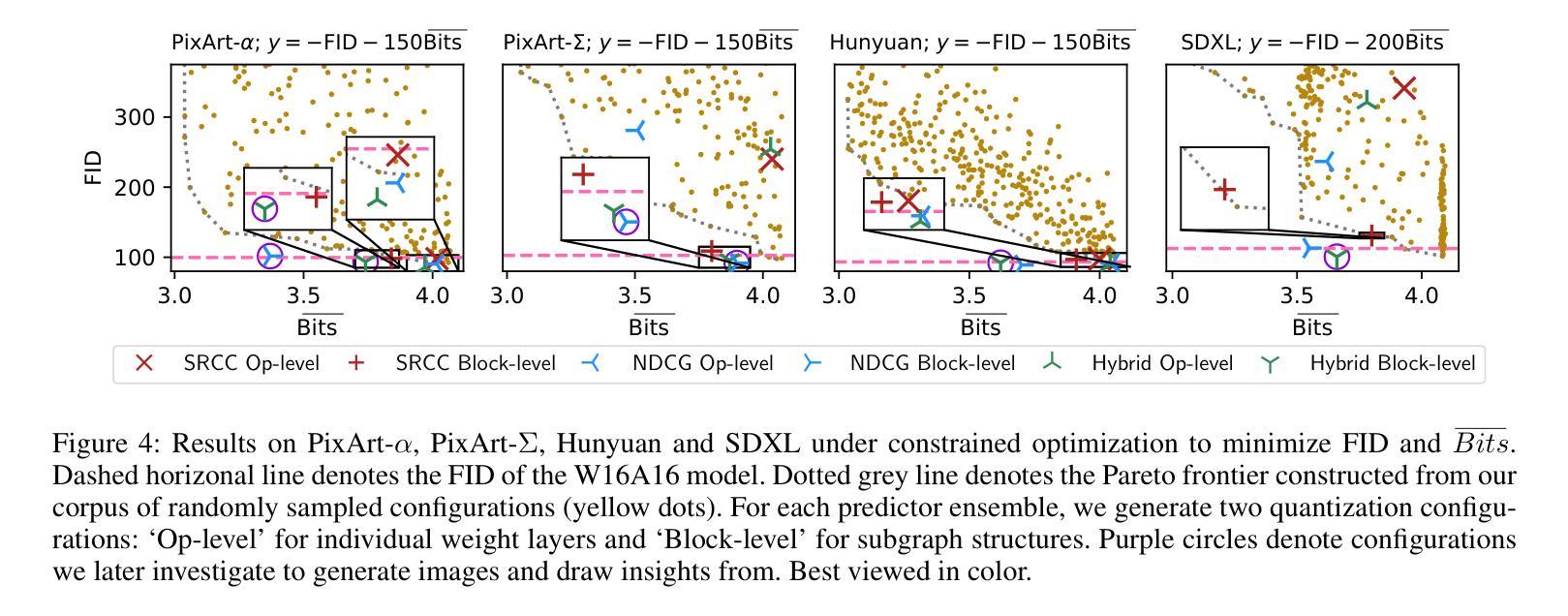
Qua$^2$SeDiMo: Quantifiable Quantization Sensitivity of Diffusion Models
Authors:Keith G. Mills, Mohammad Salameh, Ruichen Chen, Negar Hassanpour, Wei Lu, Di Niu
Diffusion Models (DM) have democratized AI image generation through an iterative denoising process. Quantization is a major technique to alleviate the inference cost and reduce the size of DM denoiser networks. However, as denoisers evolve from variants of convolutional U-Nets toward newer Transformer architectures, it is of growing importance to understand the quantization sensitivity of different weight layers, operations and architecture types to performance. In this work, we address this challenge with Qua$^2$SeDiMo, a mixed-precision Post-Training Quantization framework that generates explainable insights on the cost-effectiveness of various model weight quantization methods for different denoiser operation types and block structures. We leverage these insights to make high-quality mixed-precision quantization decisions for a myriad of diffusion models ranging from foundational U-Nets to state-of-the-art Transformers. As a result, Qua$^2$SeDiMo can construct 3.4-bit, 3.9-bit, 3.65-bit and 3.7-bit weight quantization on PixArt-${\alpha}$, PixArt-${\Sigma}$, Hunyuan-DiT and SDXL, respectively. We further pair our weight-quantization configurations with 6-bit activation quantization and outperform existing approaches in terms of quantitative metrics and generative image quality.
扩散模型(DM)通过迭代去噪过程实现了AI图像生成的普及。量化是一种主要技术,用于降低推理成本并缩小DM去噪网络的规模。然而,随着去噪器从卷积U-Net的变体向更新的Transformer架构发展,了解不同权重层、操作和架构类型对性能的量化敏感性变得越来越重要。在这项工作中,我们通过Qua$^2$SeDiMo来解决这一挑战,这是一个混合精度训练后量化框架,为各种模型权重量化方法在各种去噪器操作类型和块结构上的成本效益生成可解释的见解。我们利用这些见解来为从基础U-Net到最新Transformer的众多扩散模型做出高质量的混合精度量化决策。结果,QuasDiMo可以在PixArt-${\alpha}$、PixArt-${\Sigma}$、Hunyuan-DiT和SDXL上分别构建3.4位、3.9位、3.65位和3.7位的权重量化。我们还将我们的权重量化配置与6位激活量化相结合,并在定量指标和生成图像质量方面超越了现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI 2025; version includes supplementary material; 22 Pages, 18 Figures, 8 Tables
Summary
扩散模型(DM)通过迭代去噪过程实现了AI图像生成的普及。量化是降低推理成本并减小DM去噪网络大小的主要技术。随着去噪器从卷积U-Net变体向更新的Transformer架构发展,了解不同权重层、操作和架构类型对性能的量化敏感性变得越来越重要。在此研究中,我们借助Quamixed-precisionPost-TrainingQuantization框架解决此挑战,该框架生成有关不同模型权重量化方法的成本效益的可解释见解,适用于不同的去噪器操作类型和块结构。我们利用这些见解为从基础U-Net到最新Transformer的各种扩散模型做出高质量混合精度量化决策。结果,Quamixed可以在PixArt-α、PixArt-Σ、Hunyuan-DiT和SDXL上分别进行3.4位、3.9位、3.65位和3.7位权重量化。我们将权重量化配置与6位激活量化相结合,在定量指标和生成图像质量方面超越了现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型通过迭代去噪过程推动了AI图像生成的普及。
- 量化是降低扩散模型推理成本和减小网络大小的关键技术。
- 理解不同权重层、操作和架构类型在量化过程中的敏感性对于优化性能至关重要。
- Qua$^2$SeDiMo框架提供了对不同模型权重量化方法的成本效益的可解释见解。
- Qua$^2$SeDiMo支持从基础U-Net到高级Transformer的多种扩散模型的混合精度量化。
- 在特定的扩散模型上,Quamixed实现了低权重比特率的量化,如PixArt系列模型的3.4-3.9位权重量化。
点此查看论文截图


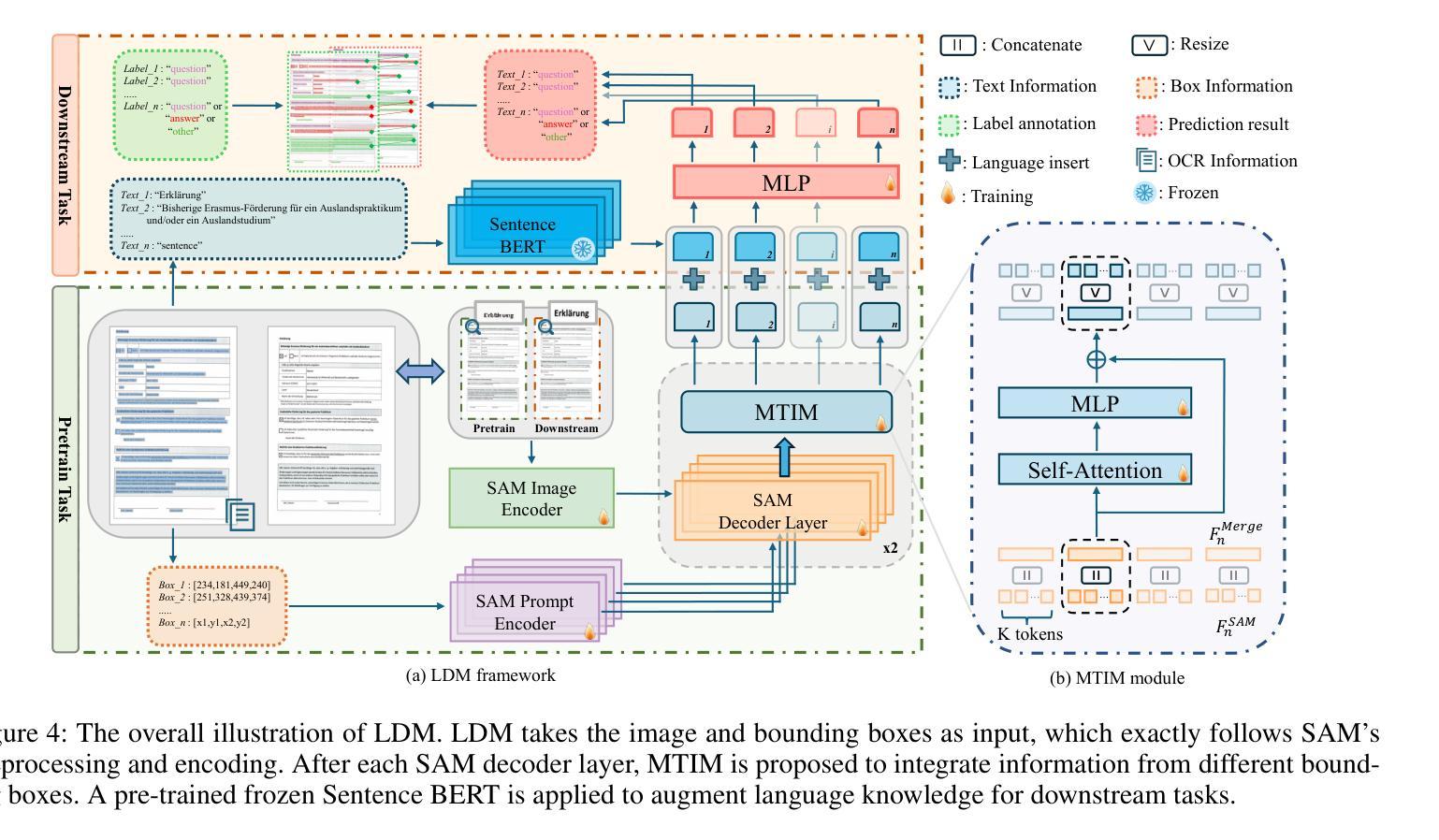
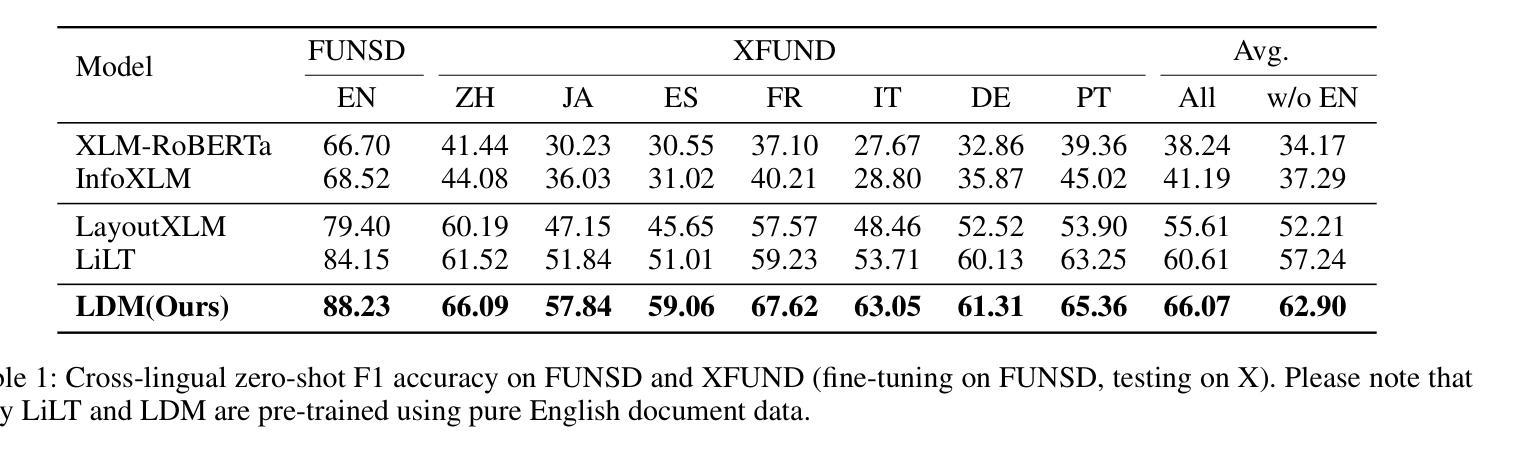
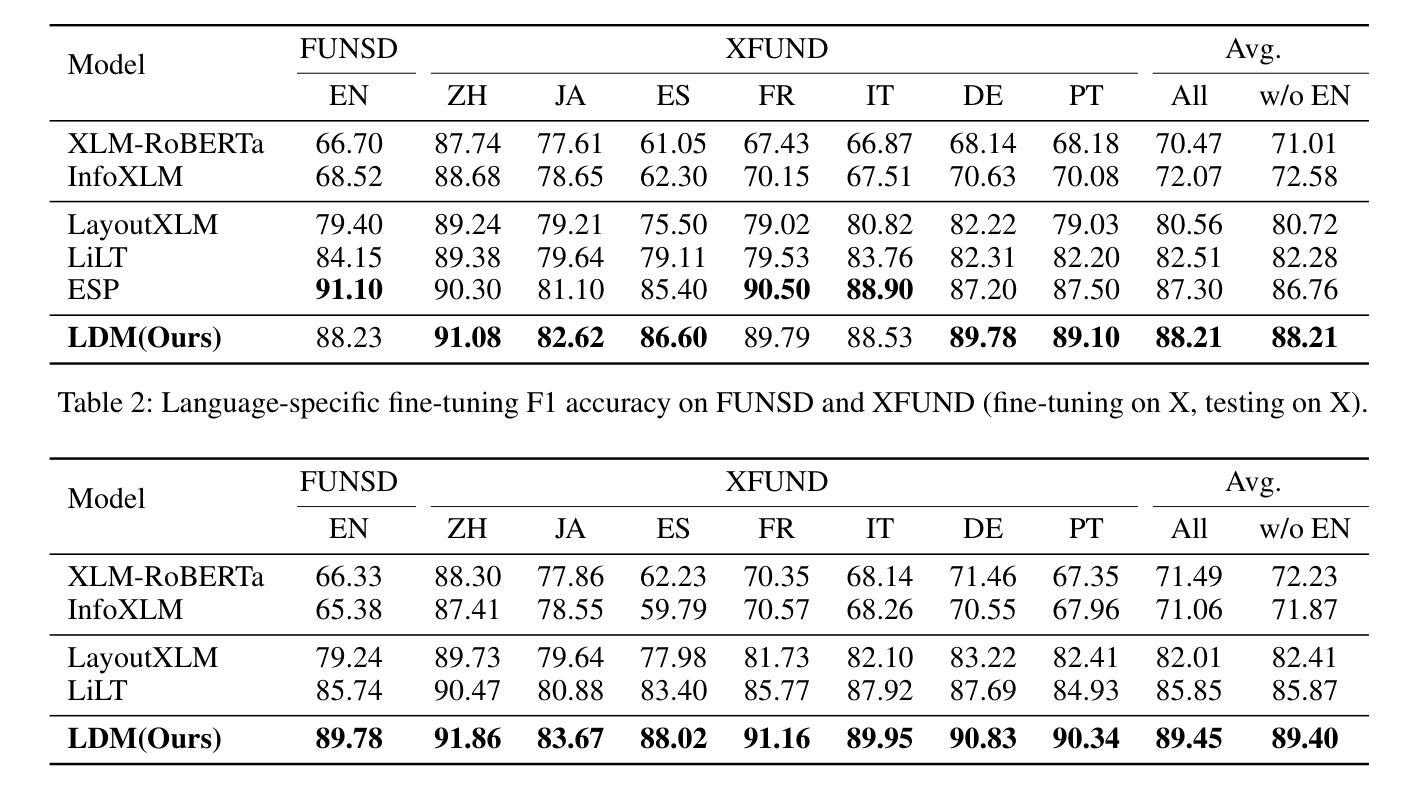
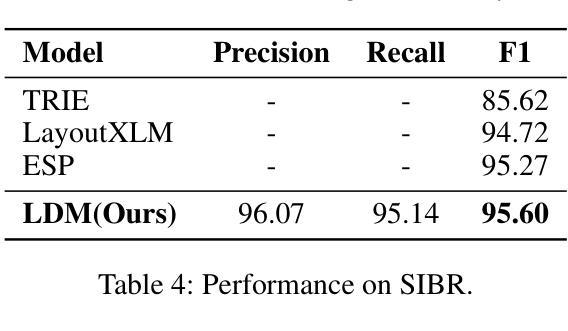
LDP: Generalizing to Multilingual Visual Information Extraction by Language Decoupled Pretraining
Authors:Huawen Shen, Gengluo Li, Jinwen Zhong, Yu Zhou
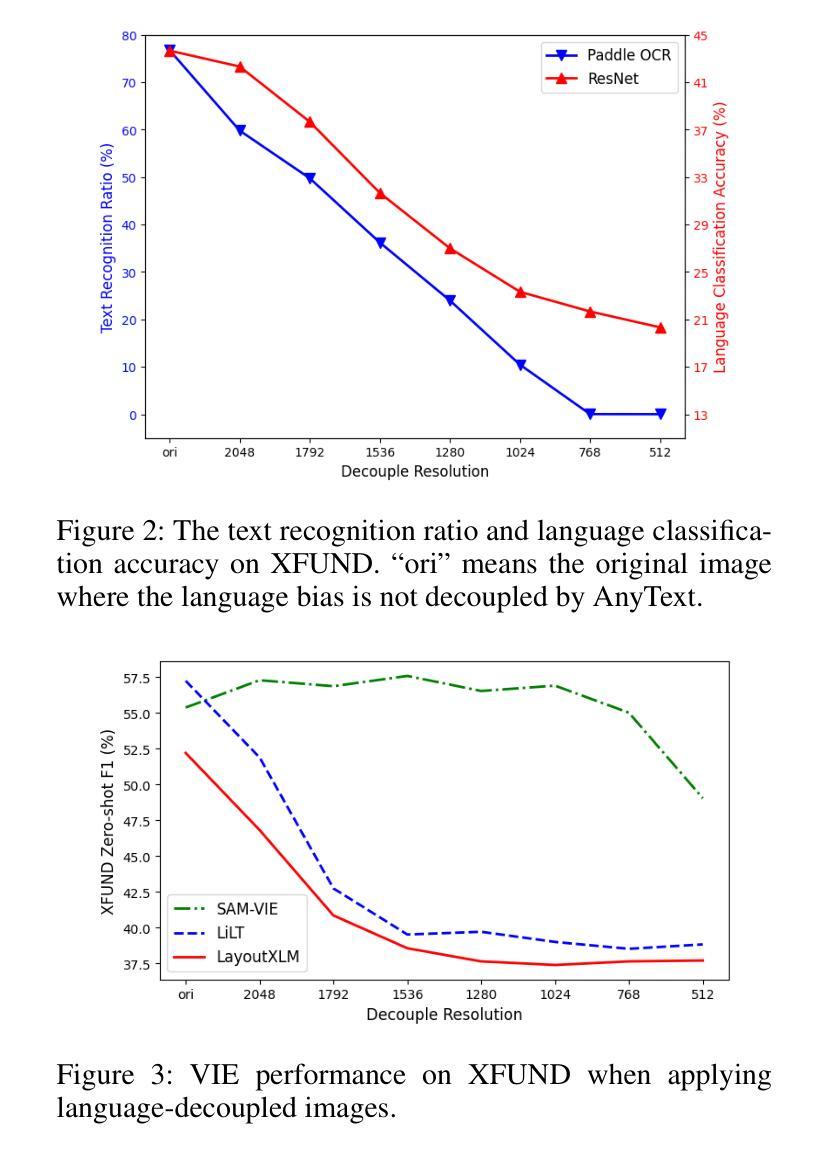
Visual Information Extraction (VIE) plays a crucial role in the comprehension of semi-structured documents, and several pre-trained models have been developed to enhance performance. However, most of these works are monolingual (usually English). Due to the extremely unbalanced quantity and quality of pre-training corpora between English and other languages, few works can extend to non-English scenarios. In this paper, we conduct systematic experiments to show that vision and layout modality hold invariance among images with different languages. If decoupling language bias from document images, a vision-layout-based model can achieve impressive cross-lingual generalization. Accordingly, we present a simple but effective multilingual training paradigm LDP (Language Decoupled Pre-training) for better utilization of monolingual pre-training data. Our proposed model LDM (Language Decoupled Model) is first pre-trained on the language-independent data, where the language knowledge is decoupled by a diffusion model, and then the LDM is fine-tuned on the downstream languages. Extensive experiments show that the LDM outperformed all SOTA multilingual pre-trained models, and also maintains competitiveness on downstream monolingual/English benchmarks.
视觉信息提取(VIE)在半结构化文档理解中起着至关重要的作用,已经开发了一些预训练模型来提高性能。然而,这些工作大多数是单语言的(通常是英语)。由于英语和其他语言之间预训练语料库的数量和质量极不平衡,很少有工作能扩展到非英语场景。在本文中,我们进行了系统的实验,结果表明,不同语言的图像在视觉和布局模式上具有不变性。如果将语言偏见从文档图像中解耦出来,基于视觉布局模型可以实现令人印象深刻的跨语言泛化能力。因此,我们提出了一种简单有效的多语言训练范式LDP(语言解耦预训练),以更好地利用单语言预训练数据。我们提出的LDM(语言解耦模型)首先是在独立于语言的数据上进行预训练的,其中语言知识通过扩散模型进行解耦,然后LDM在下游语言上进行微调。大量实验表明,LDM在所有最先进的多语言预训练模型中表现最佳,同时在下游单语言/英语基准测试中也保持竞争力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI2025
Summary
视觉信息提取(VIE)在半结构化文档理解中扮演着至关重要的角色,为提升性能,已开发多个预训练模型。然而,这些工作多数为单语言(通常为英语)。由于英语与其他语言的预训练语料库在数量和品质上存在极不均衡,少有工作能延伸至非英语场景。本文进行系统实验,证明视觉和布局模态在不同语言的图像中具有不变性。若从文档图像中解耦语言偏见,基于视觉布局模型可实现令人印象深刻的跨语言泛化。据此,本文提出一种简单有效的多语言训练范式LDP(语言解耦预训练),以更好地利用单语言预训练数据。所提出的LDM(语言解耦模型)首先在独立于语言的数据上进行预训练,其中语言知识通过扩散模型解耦,然后在下游语言上进行微调。大量实验表明,LDM在多种语言预训练模型中表现最佳,同时在下游单语言/英语基准测试中亦保持竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉信息提取(VIE)在半结构化文档理解中非常重要,并且已有多种预训练模型用于提升性能。
- 大多数相关工作为单语言(通常是英语),由于语料库的数量和质量问题,这些模型在非英语场景的应用受限。
- 实验表明视觉和布局模态在不同语言的图像中具有不变性。
- 解耦语言偏见的基于视觉布局的模型可以实现跨语言泛化。
- 提出了一种新的多语言训练范式LDP,旨在更好地利用单语言预训练数据。
- LDM模型首先在独立于语言的数据上进行预训练,然后通过扩散模型解耦语言知识,并在下游语言上进行微调。
点此查看论文截图

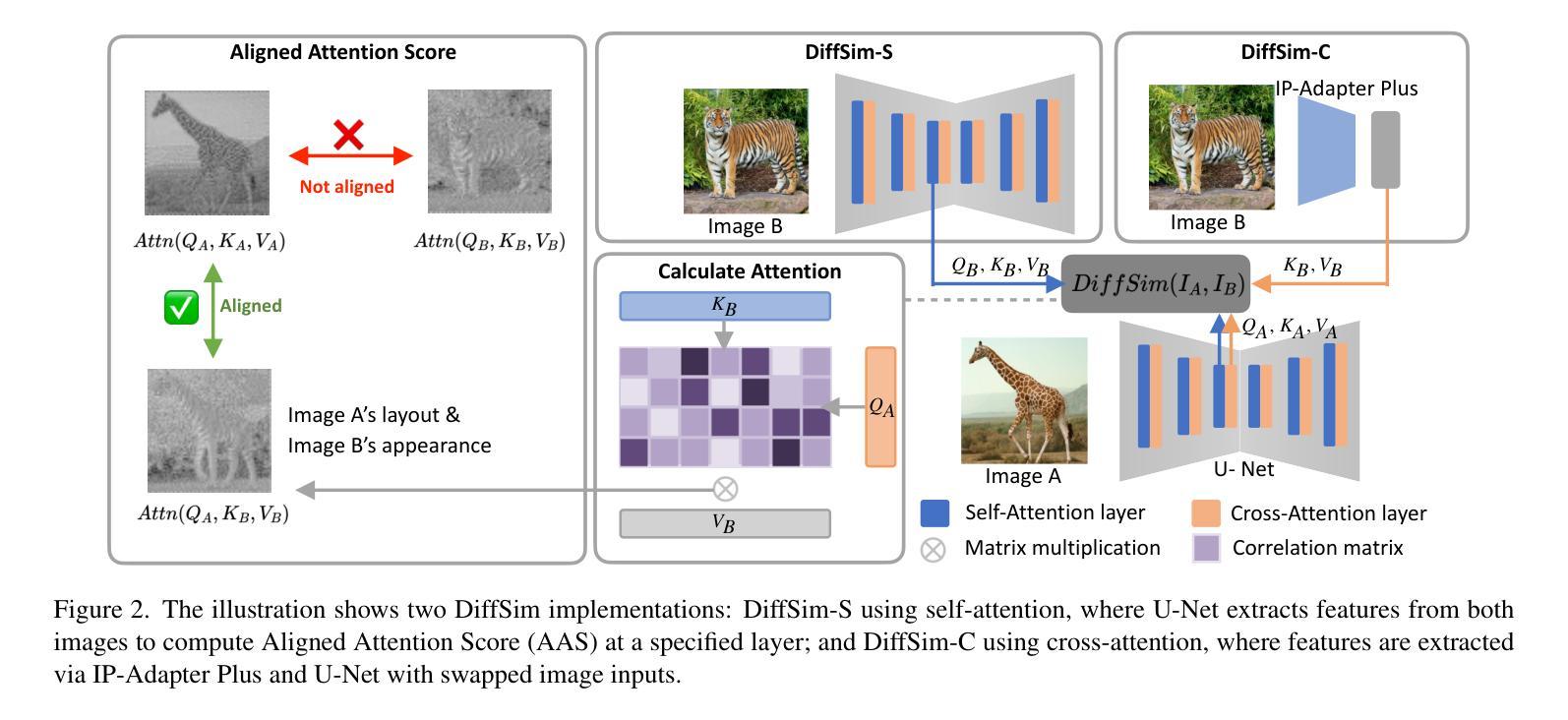
DiffSim: Taming Diffusion Models for Evaluating Visual Similarity
Authors:Yiren Song, Xiaokang Liu, Mike Zheng Shou
Diffusion models have fundamentally transformed the field of generative models, making the assessment of similarity between customized model outputs and reference inputs critically important. However, traditional perceptual similarity metrics operate primarily at the pixel and patch levels, comparing low-level colors and textures but failing to capture mid-level similarities and differences in image layout, object pose, and semantic content. Contrastive learning-based CLIP and self-supervised learning-based DINO are often used to measure semantic similarity, but they highly compress image features, inadequately assessing appearance details. This paper is the first to discover that pretrained diffusion models can be utilized for measuring visual similarity and introduces the DiffSim method, addressing the limitations of traditional metrics in capturing perceptual consistency in custom generation tasks. By aligning features in the attention layers of the denoising U-Net, DiffSim evaluates both appearance and style similarity, showing superior alignment with human visual preferences. Additionally, we introduce the Sref and IP benchmarks to evaluate visual similarity at the level of style and instance, respectively. Comprehensive evaluations across multiple benchmarks demonstrate that DiffSim achieves state-of-the-art performance, providing a robust tool for measuring visual coherence in generative models.
扩散模型已经从根本上改变了生成模型领域,评估定制模型输出和参考输入之间的相似性变得至关重要。然而,传统的感知相似性度量主要工作在像素和补丁级别,比较低级的颜色和纹理,但无法捕捉中级相似性以及图像布局、物体姿态和语义内容的差异。基于对比学习的CLIP和基于自监督学习的DINO通常用于测量语义相似性,但它们会高度压缩图像特征,对外观细节评估不足。本文首次发现可以利用预训练的扩散模型来测量视觉相似性,并引入了DiffSim方法,解决了传统指标在捕获定制生成任务中的感知一致性方面的局限性。通过对齐去噪U-Net注意层中的特征,DiffSim评估外观和风格相似性,与人类视觉偏好高度一致。此外,我们还引入了Sref和IP基准来分别在风格和实例级别评估视觉相似性。在多个基准上的综合评估表明,DiffSim实现了最先进的性能,为生成模型中视觉一致性的测量提供了可靠的工具。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
扩散模型已经彻底改变了生成模型领域,因此对定制化模型输出与参考输入之间的相似性评估变得至关重要。然而,传统的感知相似性度量主要侧重于像素和斑块层面,比较低级的颜色和纹理,而无法捕捉中级的相似性以及图像布局、物体姿态和语义内容的差异。虽然对比学习基础上的CLIP和自监督学习基础上的DINO常用于衡量语义相似性,但它们高度压缩图像特征,对外观细节评估不足。本文首次发现可以利用预训练的扩散模型来测量视觉相似性,并引入了DiffSim方法,解决了传统度量方法在定制生成任务中捕捉感知一致性的局限性。通过对齐去噪U-Net注意力层中的特征,DiffSim评估外观和风格相似性,与人类视觉偏好高度一致。此外,我们还引入了Sref和IP基准来分别在风格和实例层面评估视觉相似性。在多个基准的综合性评估中,DiffSim实现了卓越的性能,为生成模型中视觉一致性的测量提供了稳健的工具。
关键见解
- 扩散模型对生成模型领域产生了根本性影响,使得评估定制化模型输出与参考输入之间的相似性至关重要。
- 传统感知相似性度量主要关注像素和斑块层面,难以捕捉中级相似性及图像布局、物体姿态和语义内容的差异。
- 预训练的扩散模型可用于测量视觉相似性,引入的DiffSim方法解决了传统度量方法的局限性。
- DiffSim通过对齐去噪U-Net注意力层中的特征,能够评估外观和风格相似性,与人类视觉偏好高度一致。
- Sref和IP基准的引入分别用于评估视觉相似性的风格和实例层面。
- DiffSim在多个基准测试中实现了卓越性能,为生成模型中视觉一致性的测量提供了有力工具。
- DiffSim的引入有望推动生成模型领域的发展,促进更准确的模型评估和定制生成任务的优化。
点此查看论文截图


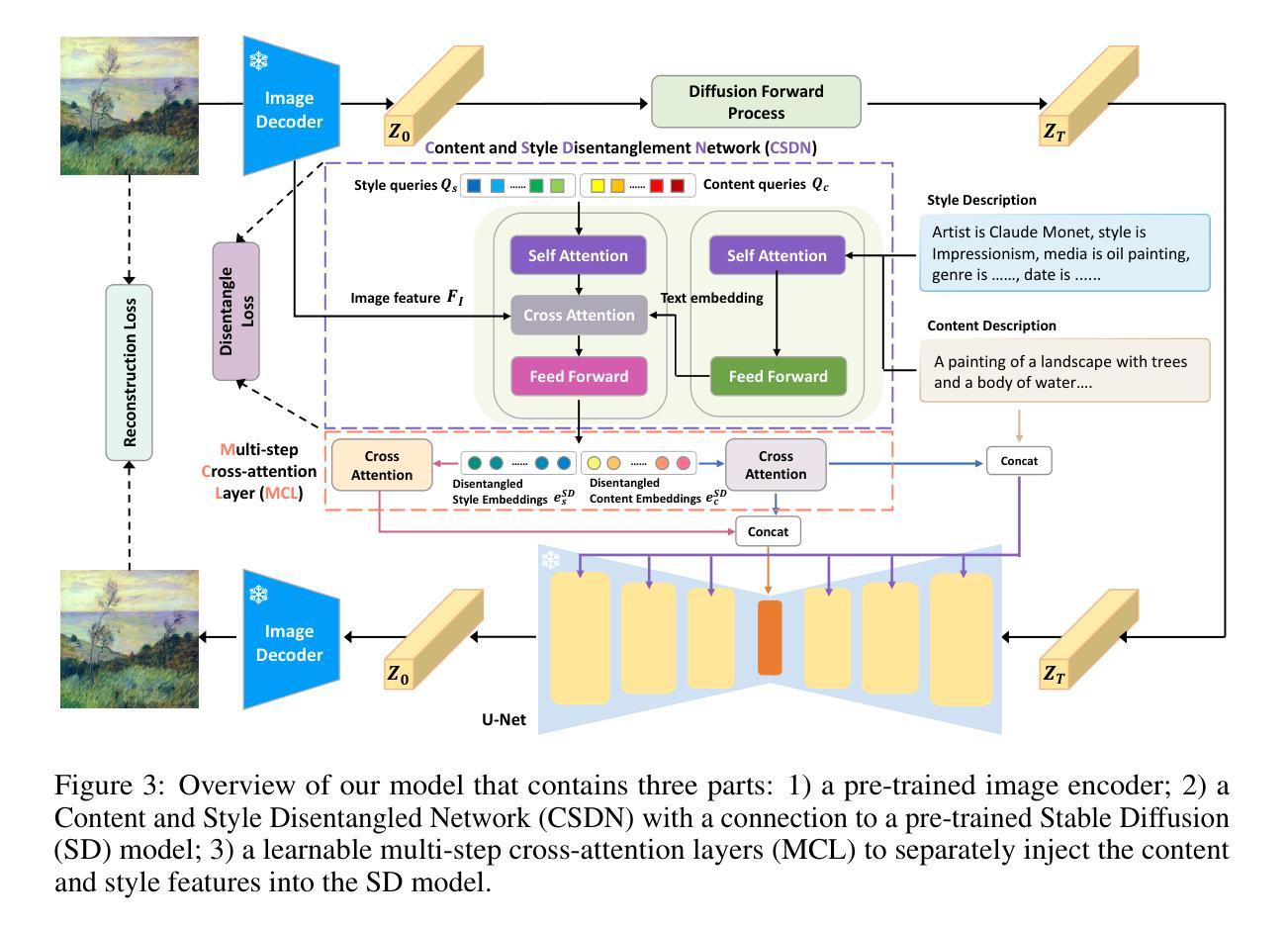
Content-style disentangled representation for controllable artistic image stylization and generation
Authors:Ma Zhuoqi, Zhang Yixuan, You Zejun, Tian Long, Liu Xiyang
Controllable artistic image stylization and generation aims to render the content provided by text or image with the learned artistic style, where content and style decoupling is the key to achieve satisfactory results. However, current methods for content and style disentanglement primarily rely on image information for supervision, which leads to two problems: 1) models can only support one modality for style or content input;2) incomplete disentanglement resulting in semantic interference from the reference image. To address the above issues, this paper proposes a content-style representation disentangling method for controllable artistic image stylization and generation. We construct a WikiStyle+ dataset consists of artworks with corresponding textual descriptions for style and content. Based on the multimodal dataset, we propose a disentangled content and style representations guided diffusion model. The disentangled representations are first learned by Q-Formers and then injected into a pre-trained diffusion model using learnable multi-step cross-attention layers for better controllable stylization. This approach allows model to accommodate inputs from different modalities. Experimental results show that our method achieves a thorough disentanglement of content and style in reference images under multimodal supervision, thereby enabling a harmonious integration of content and style in the generated outputs, successfully producing style-consistent and expressive stylized images.
可控的艺术图像风格化和生成旨在用提供的文本或图像内容呈现所学的艺术风格,而内容和风格的解耦是获得满意结果的关键。然而,当前的内容和风格分离方法主要依赖于图像信息进行监督,这导致了两个问题:1)模型只能支持一种风格或内容输入的模态;2)由于参考图像存在语义干扰,导致解耦不完全。为了解决上述问题,本文提出了一种可控艺术图像风格化和生成的内容与风格表示分离方法。我们构建了WikiStyle+数据集,其中包含艺术品及其相应的文本描述风格和内容。基于多模态数据集,我们提出了一个分离的内容和风格表示指导的扩散模型。首先通过Q-Formers学习解耦的表示,然后将其注入预训练的扩散模型中,使用可学习的多步交叉注意层实现更好的可控风格化。这种方法允许模型接受来自不同模态的输入。实验结果表明,我们的方法在多种模态监督下实现了参考图像内容和风格的彻底分离,从而能够在生成的输出中和谐地融合内容和风格,成功生成风格一致、表现力强的图像。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于多模态数据集的内容与风格表示分离方法,用于可控的艺术图像风格化和生成。通过构建包含艺术作品及其相应文本描述的WikiStyle+数据集,以及采用分离的内容与风格表示引导扩散模型,实现了对不同模态输入的支持,并彻底解耦了参考图像中的内容和风格,从而生成风格一致、富有表现力的图像。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文旨在通过内容与风格解耦的方法实现艺术图像的可控风格化和生成。
- 现有方法主要依赖图像信息进行监督,导致只能支持单一模态的输入和不完整的解耦。
- 论文构建了WikiStyle+数据集,包含艺术作品及其相应的文本描述,用于风格和内容的表示。
- 提出了基于多模态数据集的内容与风格表示分离方法。
- 通过Q-Formers学习解耦后的表示,然后注入预训练的扩散模型中,使用可学习的多步交叉注意层实现更好的可控风格化。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在多模态监督下彻底解耦了参考图像中的内容和风格。
点此查看论文截图



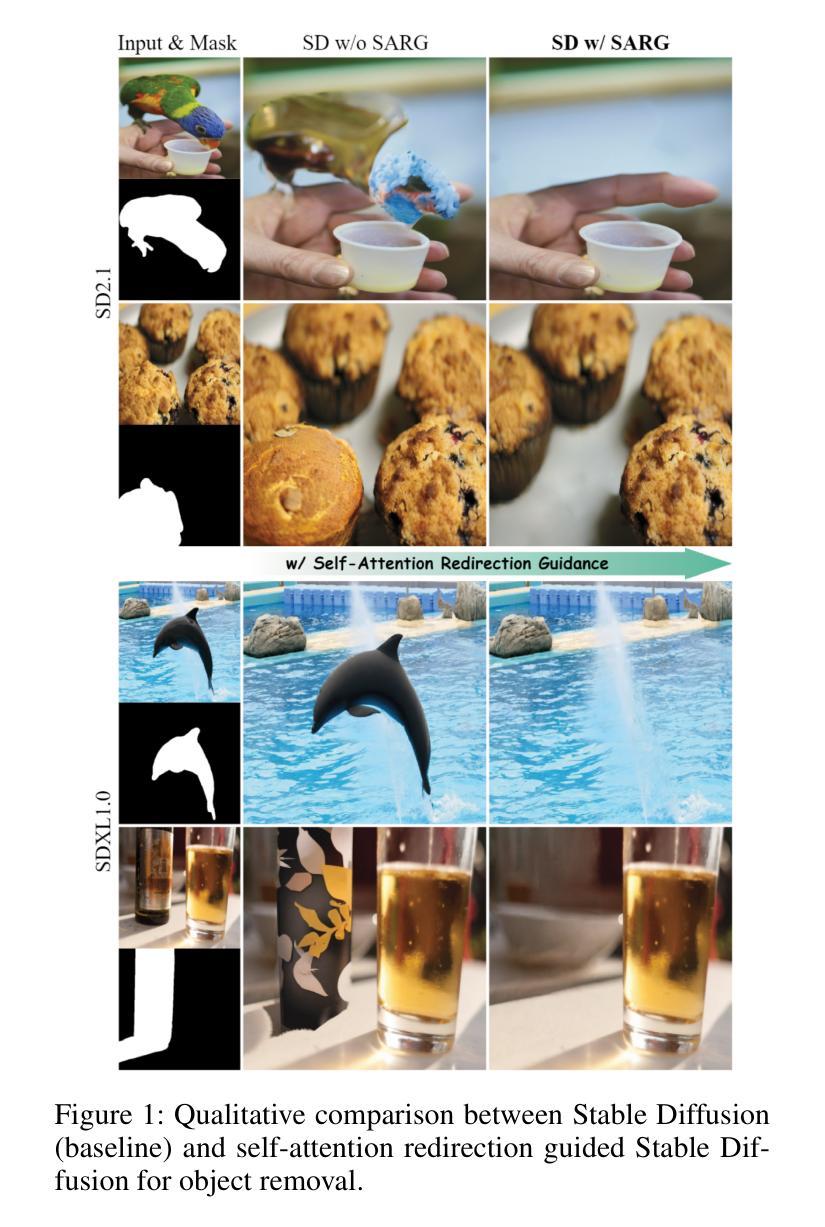
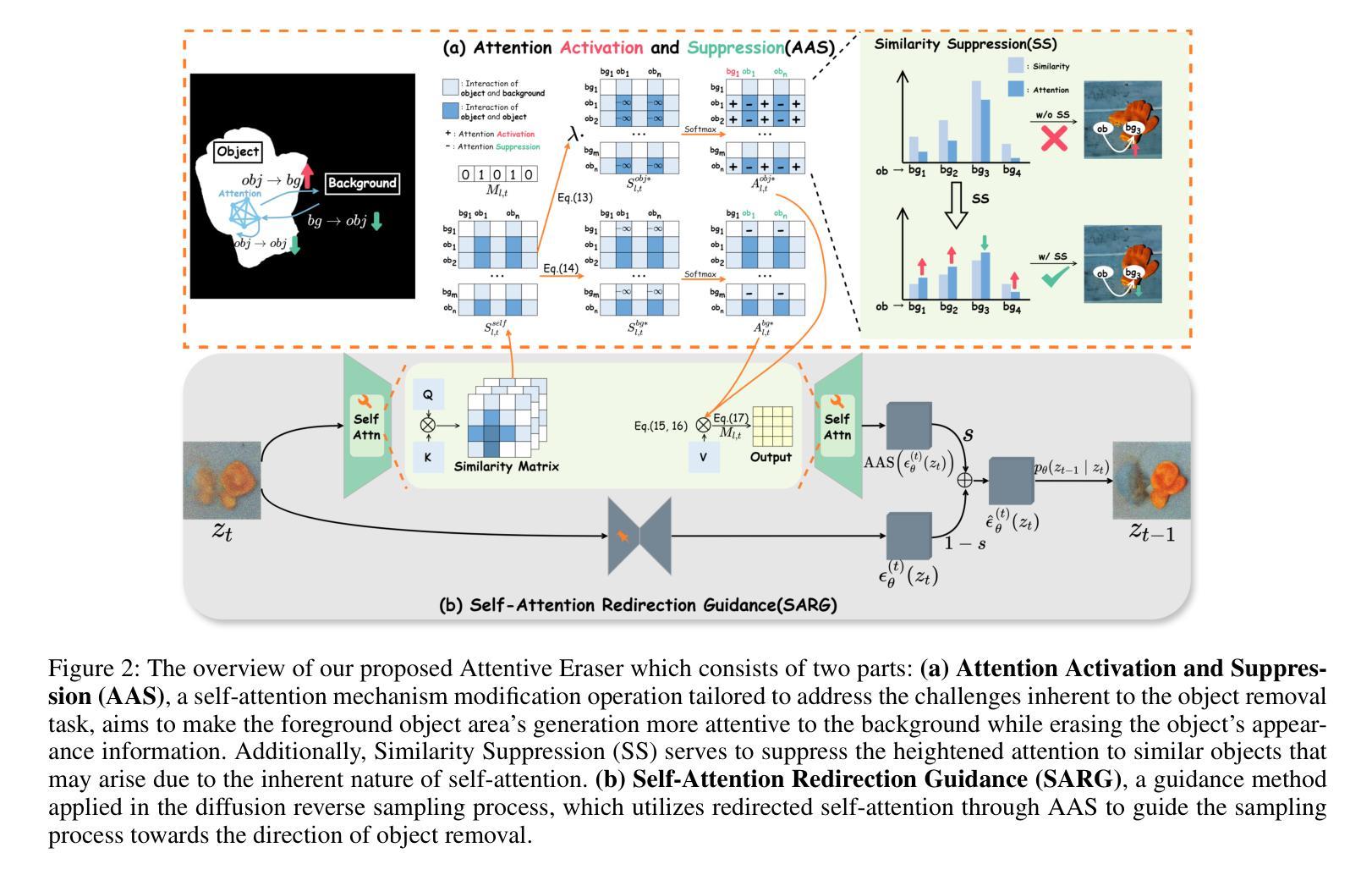
Attentive Eraser: Unleashing Diffusion Model’s Object Removal Potential via Self-Attention Redirection Guidance
Authors:Wenhao Sun, Benlei Cui, Xue-Mei Dong, Jingqun Tang
Recently, diffusion models have emerged as promising newcomers in the field of generative models, shining brightly in image generation. However, when employed for object removal tasks, they still encounter issues such as generating random artifacts and the incapacity to repaint foreground object areas with appropriate content after removal. To tackle these problems, we propose Attentive Eraser, a tuning-free method to empower pre-trained diffusion models for stable and effective object removal. Firstly, in light of the observation that the self-attention maps influence the structure and shape details of the generated images, we propose Attention Activation and Suppression (ASS), which re-engineers the self-attention mechanism within the pre-trained diffusion models based on the given mask, thereby prioritizing the background over the foreground object during the reverse generation process. Moreover, we introduce Self-Attention Redirection Guidance (SARG), which utilizes the self-attention redirected by ASS to guide the generation process, effectively removing foreground objects within the mask while simultaneously generating content that is both plausible and coherent. Experiments demonstrate the stability and effectiveness of Attentive Eraser in object removal across a variety of pre-trained diffusion models, outperforming even training-based methods. Furthermore, Attentive Eraser can be implemented in various diffusion model architectures and checkpoints, enabling excellent scalability. Code is available at https://github.com/Anonym0u3/AttentiveEraser.
近期,扩散模型作为生成模型领域的新晋热门,在图像生成方面表现出色。然而,当用于目标移除任务时,它们仍面临一些问题,例如产生随机伪影和在移除后无法重新绘制前景对象区域以填充适当的内容。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了“Attentive Eraser”方法,这是一种无需调整即可增强预训练扩散模型进行稳定和有效目标移除的方法。首先,基于观察到自注意力图会影响生成图像的结构和形状细节,我们提出了注意力激活和抑制(ASS),该方法根据给定的掩膜重新设计预训练扩散模型内的自注意力机制,从而在反向生成过程中优先处理背景而非前景目标。此外,我们引入了自注意力重定向指导(SARG),它利用ASS引导的自注意力来指导生成过程,从而在掩膜内有效地移除前景目标,同时生成既合理又连贯的内容。实验表明,Attentive Eraser在不同预训练的扩散模型中表现稳定且有效,甚至超越了基于训练的方法。此外,Attentive Eraser可应用于各种扩散模型架构和检查点,具有良好的可扩展性。相关代码可访问https://github.com/Anonym0u3/AttentiveEraser。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
扩散模型在生成模型领域崭露头角,尤其在图像生成方面表现出色。然而,在处理对象移除任务时仍存在问题,如生成随机伪影和在移除前景对象后无法重新绘制适当内容。为此,我们提出无需调整的“Attentive Eraser”方法,使预训练的扩散模型能够进行稳定有效的对象移除。我们通过利用自注意力重定向引导(SARG)和注意力激活与抑制(ASS),重新设计预训练扩散模型内的自注意力机制,优先处理背景而非前景对象。该方法在对象移除方面表现出色,超越了许多训练型方法,适用于各种预训练扩散模型和检查点。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在生成模型领域具有广阔的应用前景,尤其在图像生成方面表现优异。
- 对象移除任务中,扩散模型面临生成随机伪影和无法重新绘制移除对象后的适当内容的问题。
- 提出了一种名为“Attentive Eraser”的方法,该方法能够赋能预训练的扩散模型进行稳定有效的对象移除。
- 通过Attention Activation and Suppression(ASS)技术,重新设计预训练扩散模型内的自注意力机制。
- 引入Self-Attention Redirection Guidance(SARG),有效去除前景对象并生成合理连贯的内容。
- Attentive Eraser方法在各种预训练扩散模型中表现出稳定性与高效性,且优于许多训练型方法。
点此查看论文截图

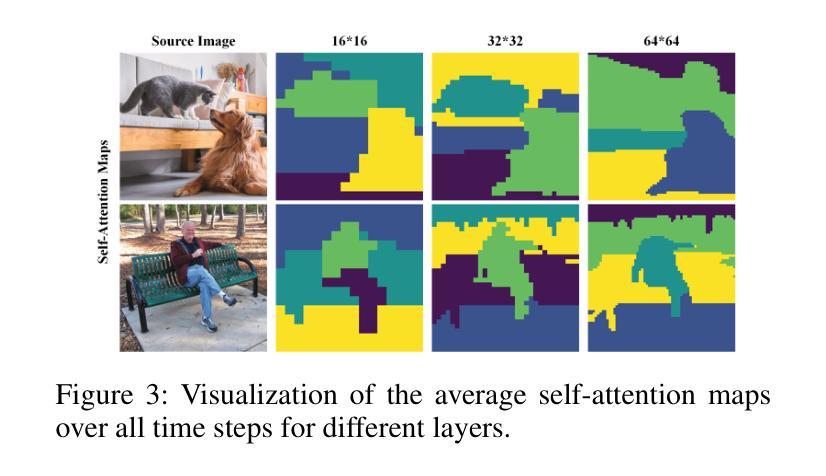
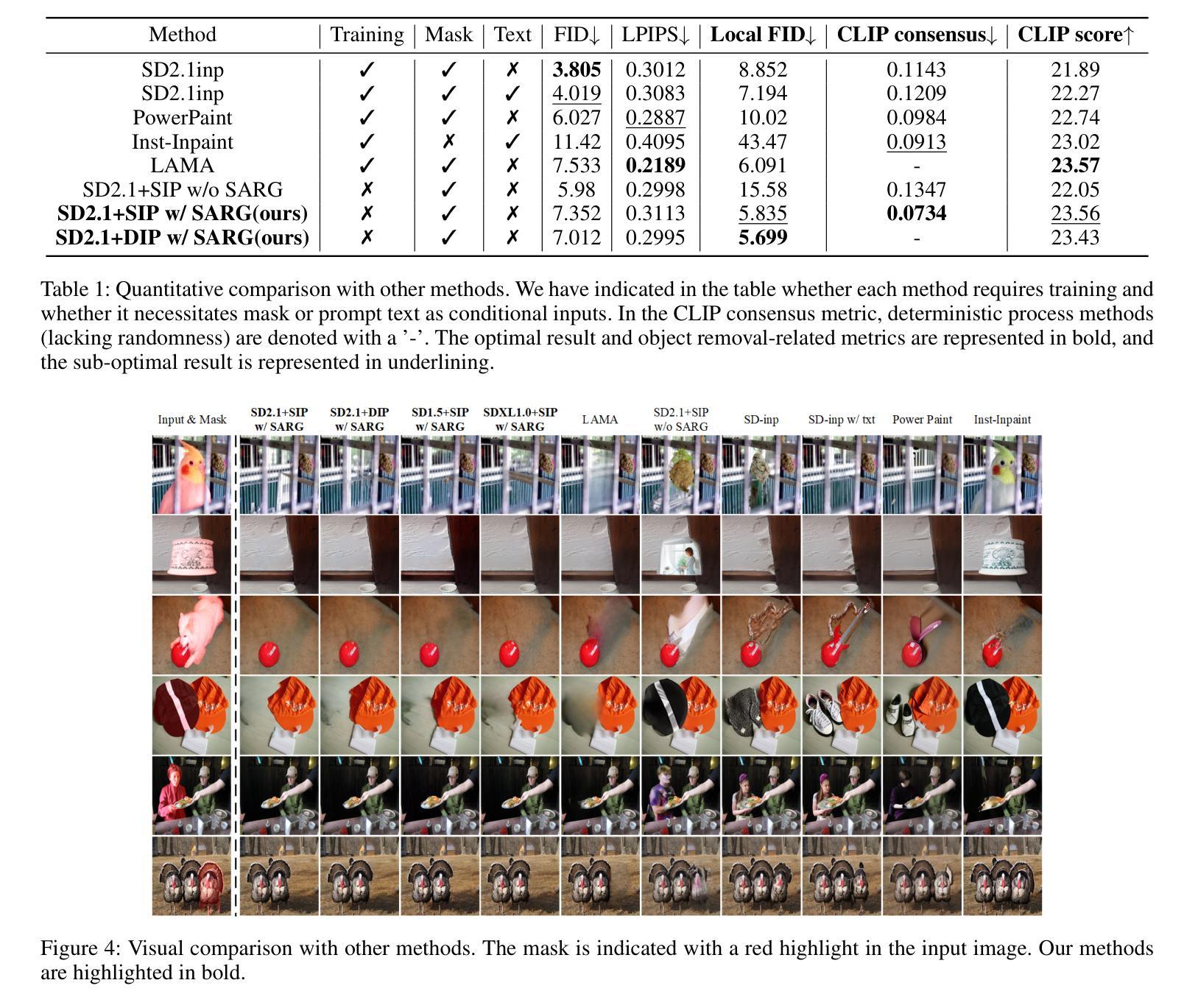

RAD: Region-Aware Diffusion Models for Image Inpainting
Authors:Sora Kim, Sungho Suh, Minsik Lee
Diffusion models have achieved remarkable success in image generation, with applications broadening across various domains. Inpainting is one such application that can benefit significantly from diffusion models. Existing methods either hijack the reverse process of a pretrained diffusion model or cast the problem into a larger framework, \ie, conditioned generation. However, these approaches often require nested loops in the generation process or additional components for conditioning. In this paper, we present region-aware diffusion models (RAD) for inpainting with a simple yet effective reformulation of the vanilla diffusion models. RAD utilizes a different noise schedule for each pixel, which allows local regions to be generated asynchronously while considering the global image context. A plain reverse process requires no additional components, enabling RAD to achieve inference time up to 100 times faster than the state-of-the-art approaches. Moreover, we employ low-rank adaptation (LoRA) to fine-tune RAD based on other pretrained diffusion models, reducing computational burdens in training as well. Experiments demonstrated that RAD provides state-of-the-art results both qualitatively and quantitatively, on the FFHQ, LSUN Bedroom, and ImageNet datasets.
扩散模型在图像生成方面取得了显著的成功,其应用正在各个领域不断扩展。图像修复是其中一个可以从扩散模型中大大受益的应用。现有方法要么劫持预训练扩散模型的反向过程,要么将问题转化为更大的框架,即条件生成。然而,这些方法通常需要在生成过程中使用嵌套循环或额外的组件来进行条件处理。在本文中,我们提出了用于图像修复的区域感知扩散模型(RAD),这是对原始扩散模型的简单而有效的重新表述。RAD为每个像素使用不同的噪声方案,这允许局部区域在考虑全局图像上下文的同时进行异步生成。简单的反向过程不需要额外的组件,使RAD的推理时间达到最新方法的100倍。此外,我们采用了低秩适应(LoRA)方法来对RAD进行微调,基于其他预训练的扩散模型,减轻了训练中的计算负担。实验表明,RAD在FFHQ、LSUN卧室和ImageNet数据集上在定性和定量方面都提供了最新结果。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出了基于扩散模型的区域感知图像修复方法(RAD)。该方法通过简单的调整实现了扩散模型的异步局部区域生成,并利用不同的噪声调度策略考虑了全局图像上下文。RAD无需额外的组件,只需使用普通的反向过程,即可实现比现有技术更快的推理速度。此外,通过使用低秩适应(LoRA)技术微调RAD模型,降低了训练的计算负担。实验表明,RAD在FFHQ、LSUN卧室和ImageNet数据集上均达到了最先进的性能。
关键见解
- 扩散模型在图像生成方面取得了显著的成功,其应用领域正在不断扩展,包括图像修复。
- 现有方法通常需要复杂的生成过程或额外的组件来实现条件生成。
- RAD通过简单的调整实现了扩散模型的区域感知图像修复,利用不同的噪声调度策略为每个像素生成局部区域,同时考虑全局图像上下文。
- RAD在推理速度方面表现出显著的优势,比现有技术快100倍。
- RAD模型通过使用低秩适应(LoRA)技术进行微调,降低了训练的计算负担。
- 实验结果表明,RAD在多个数据集上实现了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

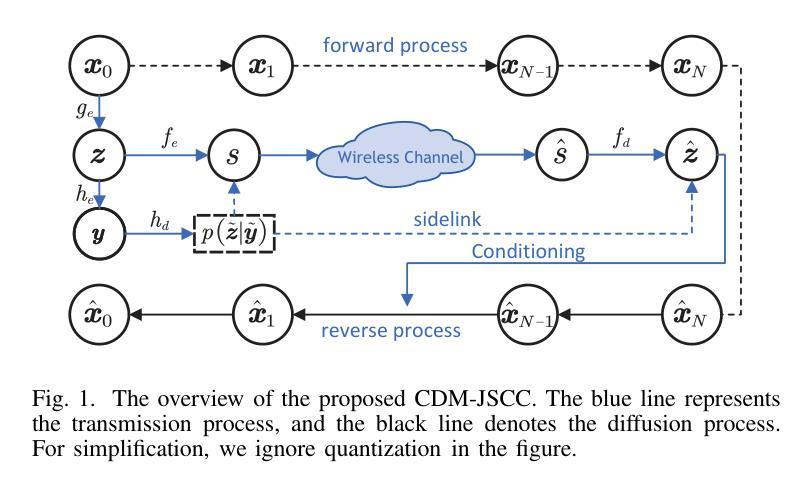
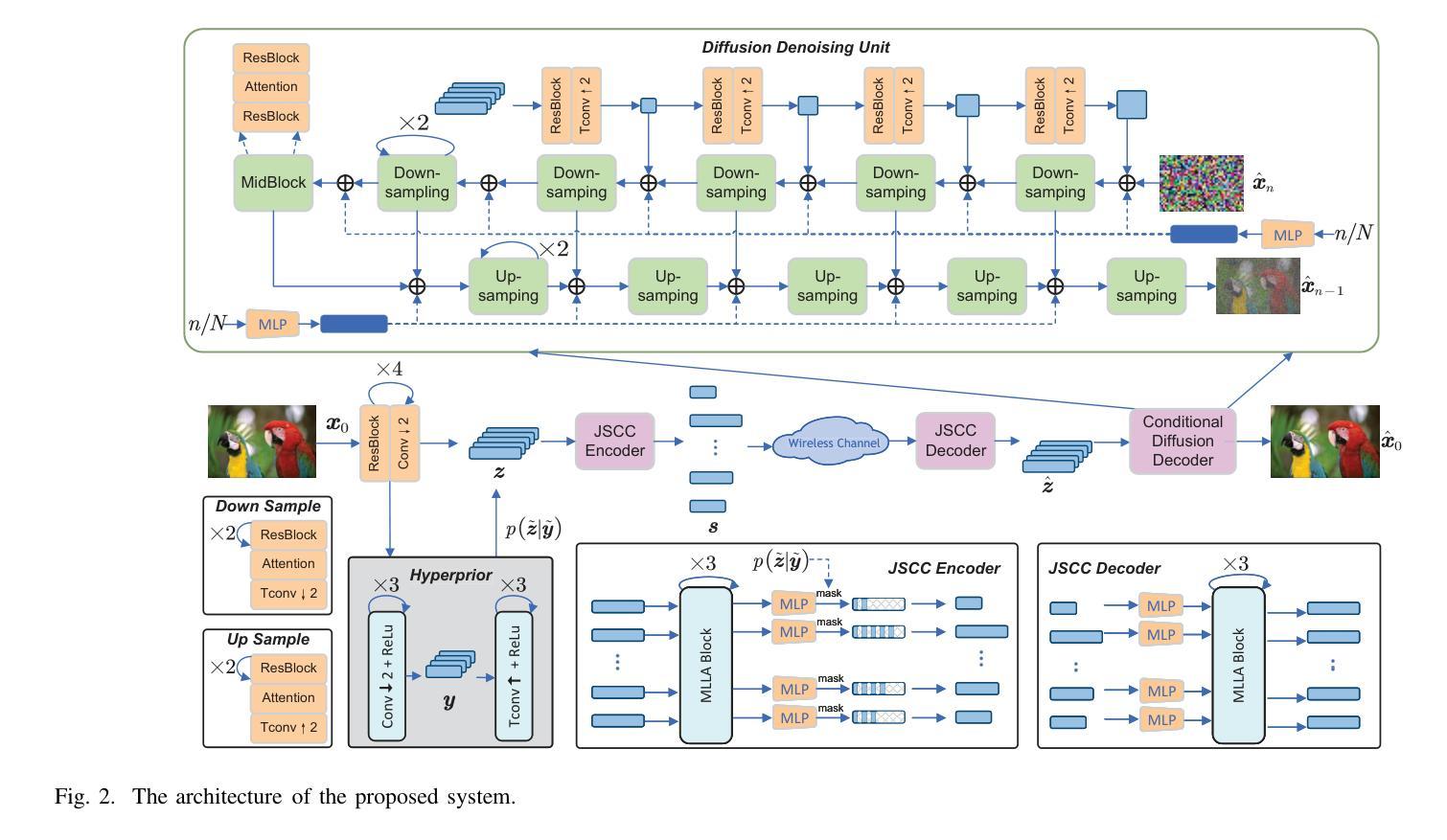
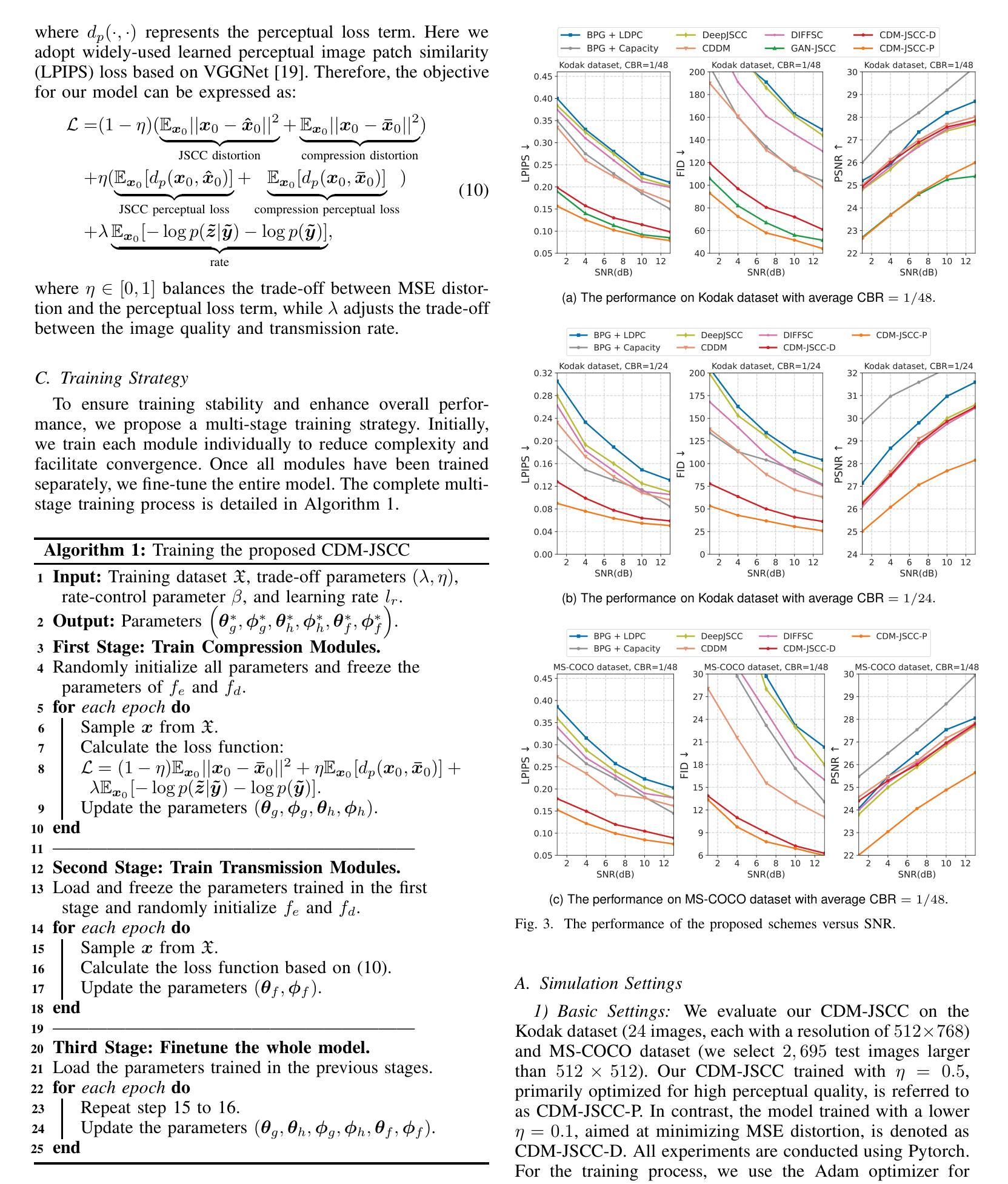
Rate-Adaptive Generative Semantic Communication Using Conditional Diffusion Models
Authors:Pujing Yang, Guangyi Zhang, Yunlong Cai
Recent advances in deep learning-based joint source-channel coding (DJSCC) have shown promise for end-to-end semantic image transmission. However, most existing schemes primarily focus on optimizing pixel-wise metrics, which often fail to align with human perception, leading to lower perceptual quality. In this letter, we propose a novel generative DJSCC approach using conditional diffusion models to enhance the perceptual quality of transmitted images. Specifically, by utilizing entropy models, we effectively manage transmission bandwidth based on the estimated entropy of transmitted sym-bols. These symbols are then used at the receiver as conditional information to guide a conditional diffusion decoder in image reconstruction. Our model is built upon the emerging advanced mamba-like linear attention (MLLA) skeleton, which excels in image processing tasks while also offering fast inference speed. Besides, we introduce a multi-stage training strategy to ensure the stability and improve the overall performance of the model. Simulation results demonstrate that our proposed method significantly outperforms existing approaches in terms of perceptual quality.
近年来,基于深度学习的联合源信道编码(DJSCC)的最新进展为端到端的语义图像传输展示了前景。然而,大多数现有方案主要关注像素级的指标优化,这通常与人类感知不吻合,导致感知质量下降。在这篇文章中,我们提出了一种新的基于条件扩散模型的生成式DJSCC方法,以提高传输图像的感知质量。具体来说,我们利用熵模型,根据传输符号的估计熵有效地管理传输带宽。这些符号然后作为接收端时的条件信息,用于指导图像重建中的条件扩散解码器。我们的模型建立在新兴的马姆巴式线性注意力(MLLA)骨架之上,该骨架在图像处理任务中表现出色,同时提供快速的推理速度。此外,我们引入了一种多阶段训练策略,以确保模型的稳定性并提高其整体性能。仿真结果表明,我们提出的方法在感知质量方面显著优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于条件扩散模型的新型深度联合源信道编码(DJSCC)方法,旨在提高传输图像的感知质量。该方法利用熵模型估算传输符号的熵,实现有效带宽管理,并在接收端使用这些符号作为条件信息来指导图像重建的条件扩散解码器。该模型基于先进的mamba-like线性注意力(MLLA)骨架,具有图像处理任务出色和快速推理速度的优点。同时,引入多阶段训练策略以确保模型的稳定性和提高整体性能。仿真结果表明,该方法在感知质量方面显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种新型深度联合源信道编码(DJSCC)方法,利用条件扩散模型增强图像传输的感知质量。
- 利用熵模型估算传输符号的熵,实现带宽的有效管理。
- 在接收端使用条件信息来指导图像重建的条件扩散解码器。
- 模型基于先进的mamba-like线性注意力(MLLA)骨架,具有快速推理速度和优秀的图像处理性能。
- 引入多阶段训练策略以提高模型的稳定性和整体性能。
- 仿真结果表明,该方法在感知质量上显著优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

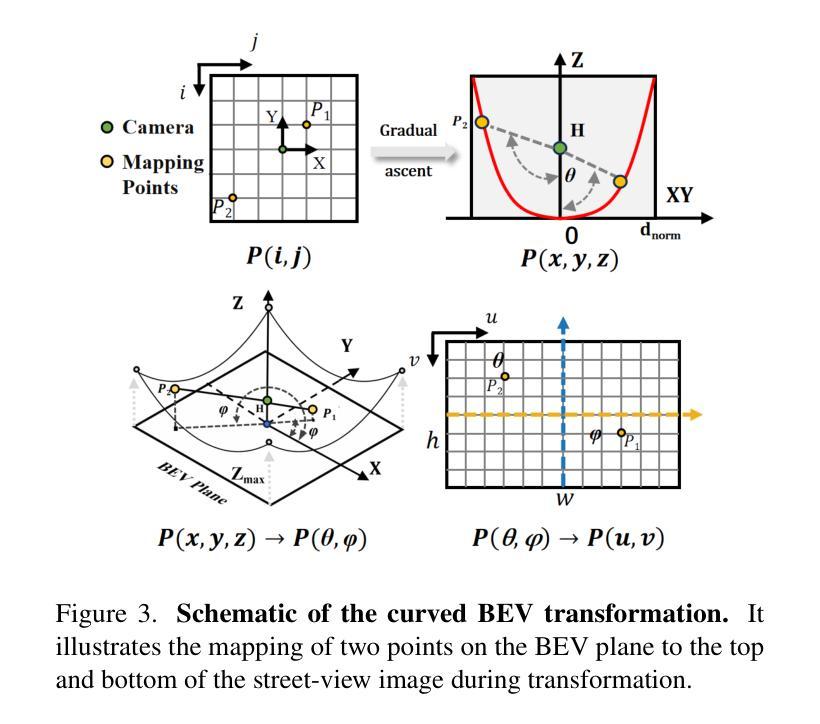
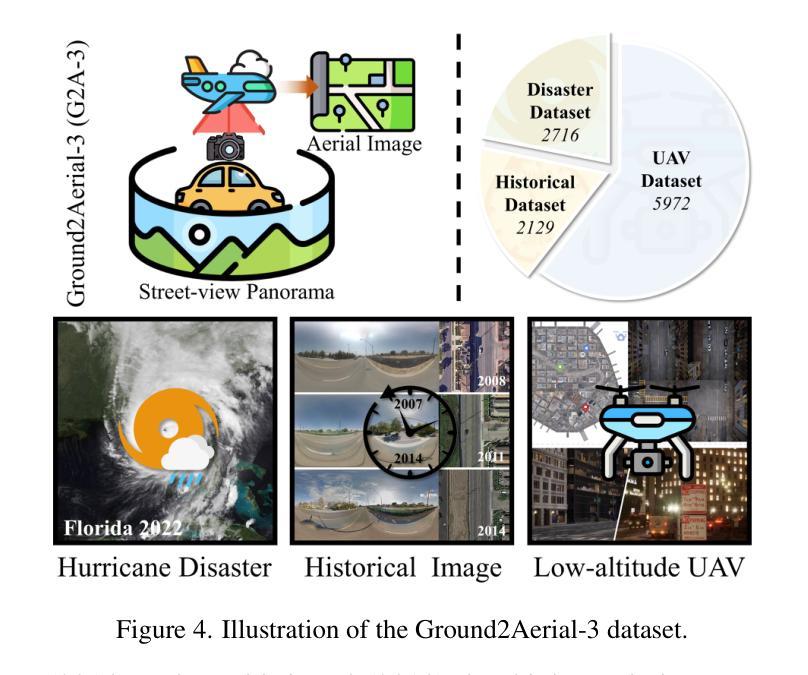
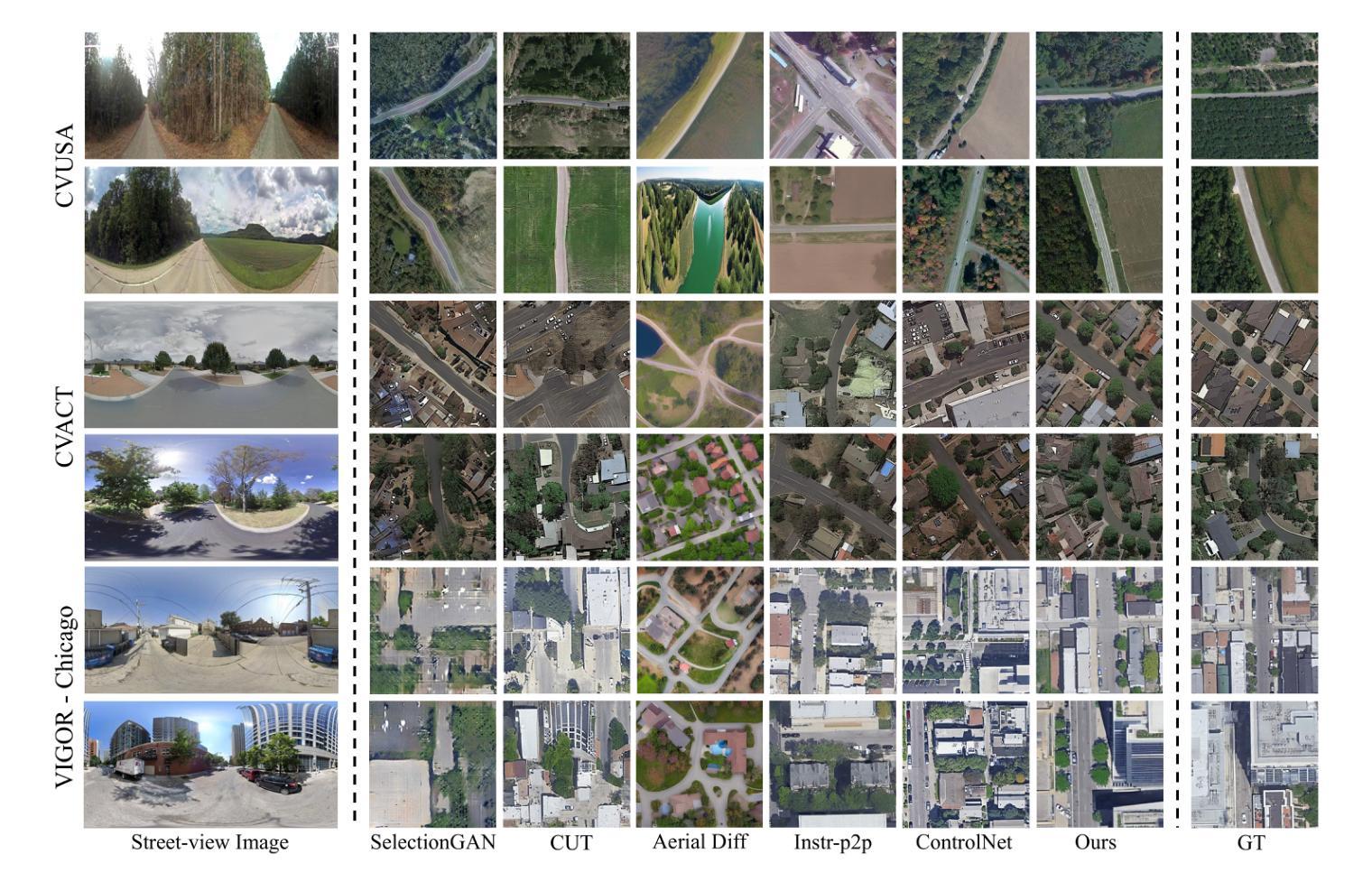
SkyDiffusion: Ground-to-Aerial Image Synthesis with Diffusion Models and BEV Paradigm
Authors:Junyan Ye, Jun He, Weijia Li, Zhutao Lv, Yi Lin, Jinhua Yu, Haote Yang, Conghui He
Ground-to-aerial image synthesis focuses on generating realistic aerial images from corresponding ground street view images while maintaining consistent content layout, simulating a top-down view. The significant viewpoint difference leads to domain gaps between views, and dense urban scenes limit the visible range of street views, making this cross-view generation task particularly challenging. In this paper, we introduce SkyDiffusion, a novel cross-view generation method for synthesizing aerial images from street view images, utilizing a diffusion model and the Bird’s-Eye View (BEV) paradigm. The Curved-BEV method in SkyDiffusion converts street-view images into a BEV perspective, effectively bridging the domain gap, and employs a “multi-to-one” mapping strategy to address occlusion issues in dense urban scenes. Next, SkyDiffusion designed a BEV-guided diffusion model to generate content-consistent and realistic aerial images. Additionally, we introduce a novel dataset, Ground2Aerial-3, designed for diverse ground-to-aerial image synthesis applications, including disaster scene aerial synthesis, historical high-resolution satellite image synthesis, and low-altitude UAV image synthesis tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that SkyDiffusion outperforms state-of-the-art methods on cross-view datasets across natural (CVUSA), suburban (CVACT), urban (VIGOR-Chicago), and various application scenarios (G2A-3), achieving realistic and content-consistent aerial image generation. More result and dataset information can be found at https://opendatalab.github.io/skydiffusion/ .
地面到空中的图像合成专注于从相应的地面街景图像生成逼真的空中图像,同时保持内容布局的一致性,模拟从上到下的视角。显著的视点差异导致了不同视角之间的领域差距,而密集的城区场景限制了街景的可见范围,这使得跨视图生成任务特别具有挑战性。在本文中,我们介绍了SkyDiffusion,这是一种从街景图像合成空中图像的新型跨视图生成方法,它利用扩散模型和鸟瞰图(BEV)范式。SkyDiffusion中的Curved-BEV方法将街景图像转换为BEV透视,有效地弥补了领域差距,并采用“多到一”的映射策略来解决密集城市场景中的遮挡问题。接下来,SkyDiffusion设计了一个BEV引导的扩散模型,以生成内容一致且逼真的空中图像。此外,我们还引入了一个新型数据集Ground2Aerial-3,该数据集专为多样化的地面到空中图像合成应用而设计,包括灾害场景空中合成、高分辨率历史卫星图像合成以及低空无人机图像合成任务等。实验结果表明,SkyDiffusion在跨视图数据集(如自然场景(CVUSA)、郊区场景(CVACT)、城市场景(VIGOR-Chicago)以及多种应用场景(G2A-3))上的表现均优于最先进的方法,实现了逼真且内容一致的天空图像生成。更多结果和数据集信息可在https://opendatalab.github.io/skydiffusion/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 7 figures
Summary
基于地面视角生成真实感强烈的空中图像是一个充满挑战的任务,因为视点差异导致领域鸿沟以及城市景观的遮挡问题。本文提出了SkyDiffusion方法,通过扩散模型和鸟瞰图(BEV)范式实现这一任务。SkyDiffusion创新性地引入了Curved-BEV方法,有效缩短了领域差距并解决了遮挡问题。同时,设计了一种受鸟瞰图指导的扩散模型来生成内容连贯且真实的空中图像。此外,还推出了一个新的数据集Ground2Aerial-3,用于地面到空中的图像合成应用。实验结果显示,SkyDiffusion在自然、郊区、城市和多种应用情境的数据集上表现均优于其他先进技术。有关结果和详细信息可参见网址:https://opendatalab.github.io/skydiffusion/。
Key Takeaways
- SkyDiffusion是一种新颖的跨视角生成方法,用于从街头视角的图像合成空中图像。
- 引入Curved-BEV方法,有效桥接地面与空中视角的域差距。
- 采用“多到一”的映射策略来解决密集城市景观中的遮挡问题。
- 设计了受鸟瞰图指导的扩散模型来生成连贯且真实的空中图像。
- 推出新的数据集Ground2Aerial-3,适用于多种地面到空中的图像合成应用。
- SkyDiffusion在多个数据集上的表现优于其他先进技术。
点此查看论文截图

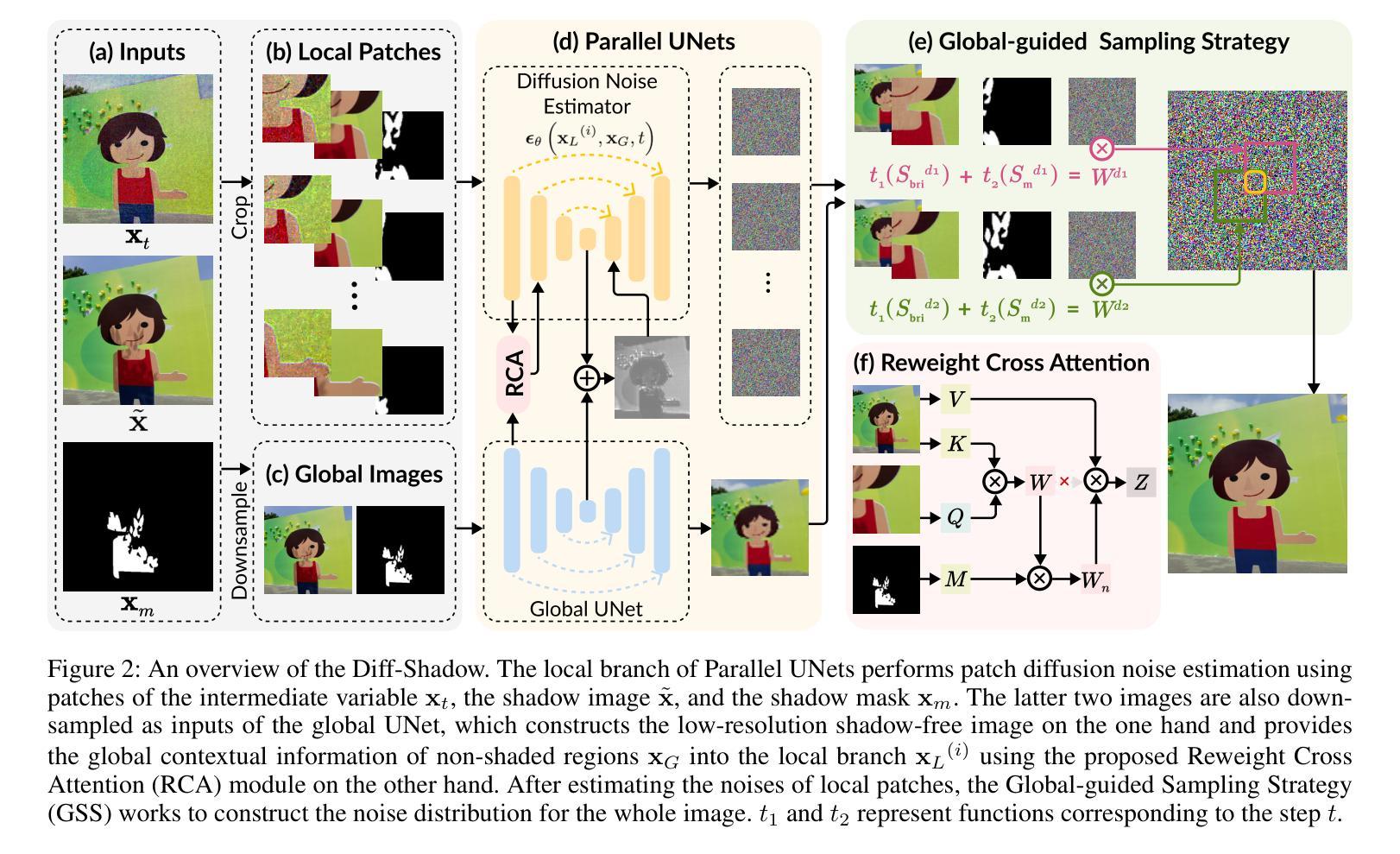
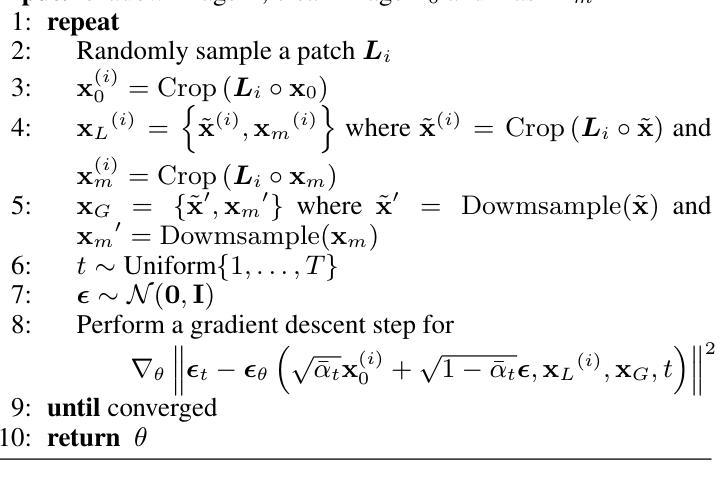
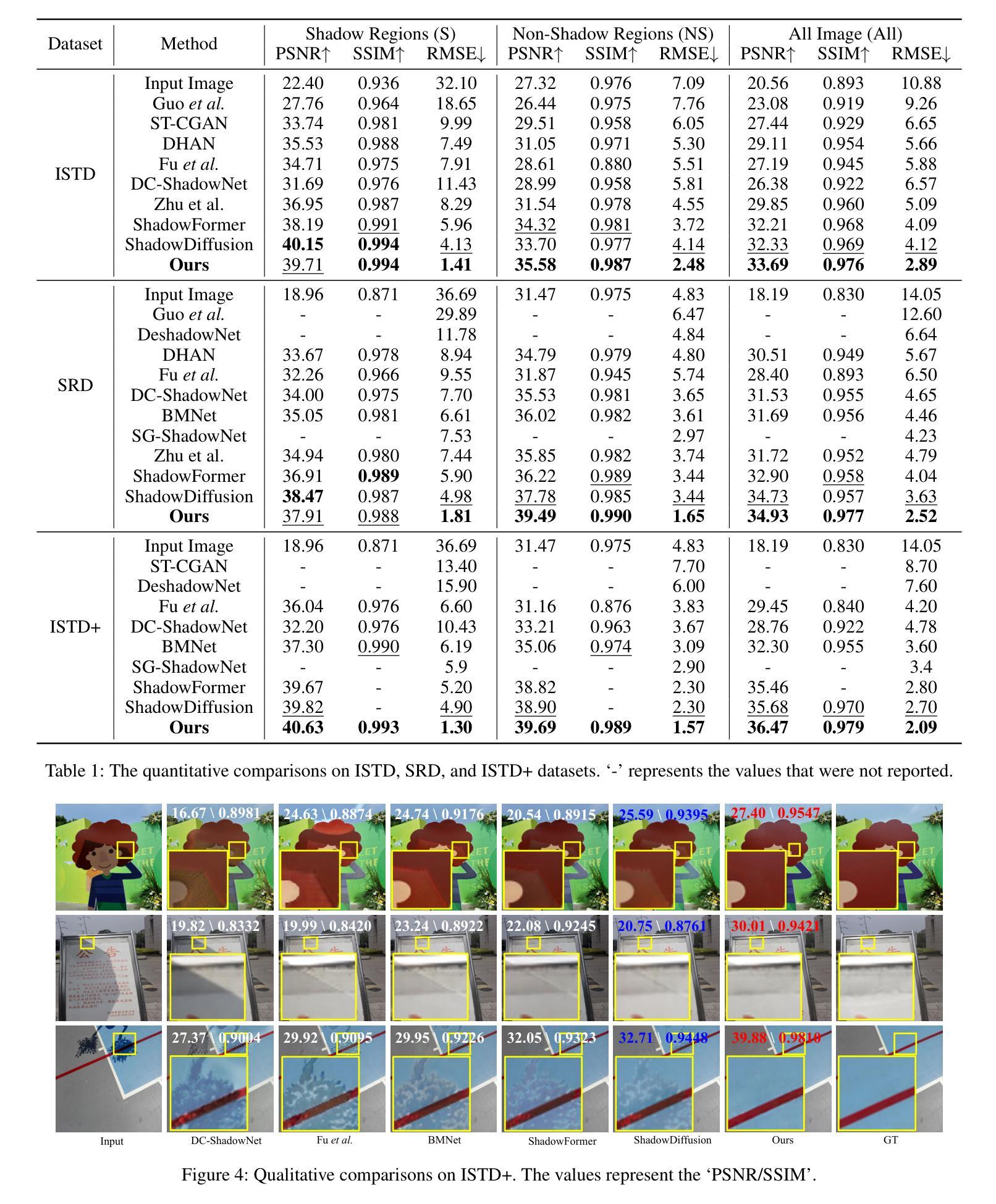
Diff-Shadow: Global-guided Diffusion Model for Shadow Removal
Authors:Jinting Luo, Ru Li, Chengzhi Jiang, Xiaoming Zhang, Mingyan Han, Ting Jiang, Haoqiang Fan, Shuaicheng Liu
We propose Diff-Shadow, a global-guided diffusion model for shadow removal. Previous transformer-based approaches can utilize global information to relate shadow and non-shadow regions but are limited in their synthesis ability and recover images with obvious boundaries. In contrast, diffusion-based methods can generate better content but they are not exempt from issues related to inconsistent illumination. In this work, we combine the advantages of diffusion models and global guidance to achieve shadow-free restoration. Specifically, we propose a parallel UNets architecture: 1) the local branch performs the patch-based noise estimation in the diffusion process, and 2) the global branch recovers the low-resolution shadow-free images. A Reweight Cross Attention (RCA) module is designed to integrate global contextual information of non-shadow regions into the local branch. We further design a Global-guided Sampling Strategy (GSS) that mitigates patch boundary issues and ensures consistent illumination across shaded and unshaded regions in the recovered image. Comprehensive experiments on datasets ISTD, ISTD+, and SRD have demonstrated the effectiveness of Diff-Shadow. Compared to state-of-the-art methods, our method achieves a significant improvement in terms of PSNR, increasing from 32.33dB to 33.69dB on the ISTD dataset.
我们提出了Diff-Shadow,这是一种用于阴影去除的全局引导扩散模型。之前的基于transformer的方法可以利用全局信息来关联阴影和非阴影区域,但它们在合成能力方面有限,恢复的图像具有明显的边界。相比之下,基于扩散的方法可以生成更好的内容,但它们也存在光照不一致的问题。在这项工作中,我们结合了扩散模型和全局引导的优点,实现了无阴影的恢复。具体来说,我们提出了一种并行U-Net架构:1)局部分支执行扩散过程中的基于补丁的噪声估计;2)全局分支恢复无阴影的低分辨率图像。设计了一种重加权交叉注意力(RCA)模块,将非阴影区域的全局上下文信息集成到局部分支中。我们还设计了一种全局引导采样策略(GSS),可以缓解补丁边界问题,并确保恢复图像中的阴影和非阴影区域之间光照一致。在ISTD、ISTD+和SRD数据集上的综合实验证明了Diff-Shadow的有效性。与最先进的方法相比,我们的方法在PSNR方面取得了显著改进,在ISTD数据集上从32.33dB提高到33.69dB。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Proceedings of the 39th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence
Summary
基于扩散模型的阴影去除技术Diff-Shadow研究。结合扩散模型的优点和全局指导策略,实现了阴影去除的图像恢复。采用并行UNets架构,局部分支进行基于补丁的噪声估计,全局分支恢复无阴影的低分辨率图像。设计重权交叉注意力模块(RCA)整合非阴影区域的全局上下文信息到局部分支,并设计全局引导采样策略(GSS)减少补丁边界问题并确保恢复图像中的阴影和未阴影区域的照明一致性。在ISTD、ISTD+和SRD数据集上的实验验证了Diff-Shadow的有效性,相较于最新方法,在ISTD数据集上的PSNR值从32.33dB显著提高至33.69dB。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了基于扩散模型的阴影去除方法Diff-Shadow,结合了扩散模型和全局指导策略的优势。
- 采用并行UNets架构,包括局部和全局两个分支,分别进行噪声估计和无阴影图像恢复。
- 设计了重权交叉注意力模块(RCA),用于整合全局上下文信息。
- 提出了全局引导采样策略(GSS),解决补丁边界问题,确保照明一致性。
- 在多个数据集上的实验验证了Diff-Shadow的有效性。
- 与现有方法相比,Diff-Shadow在ISTD数据集上的PSNR值有显著提高。
点此查看论文截图



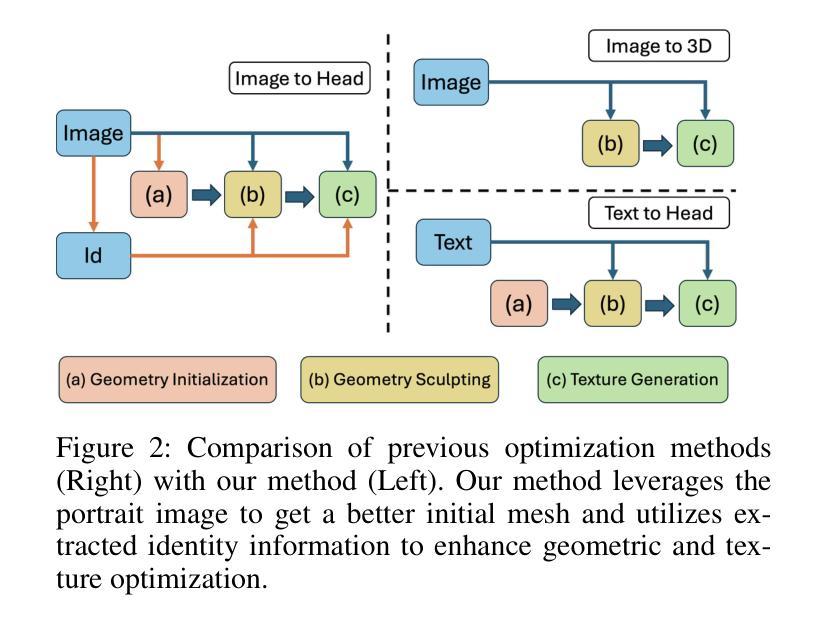
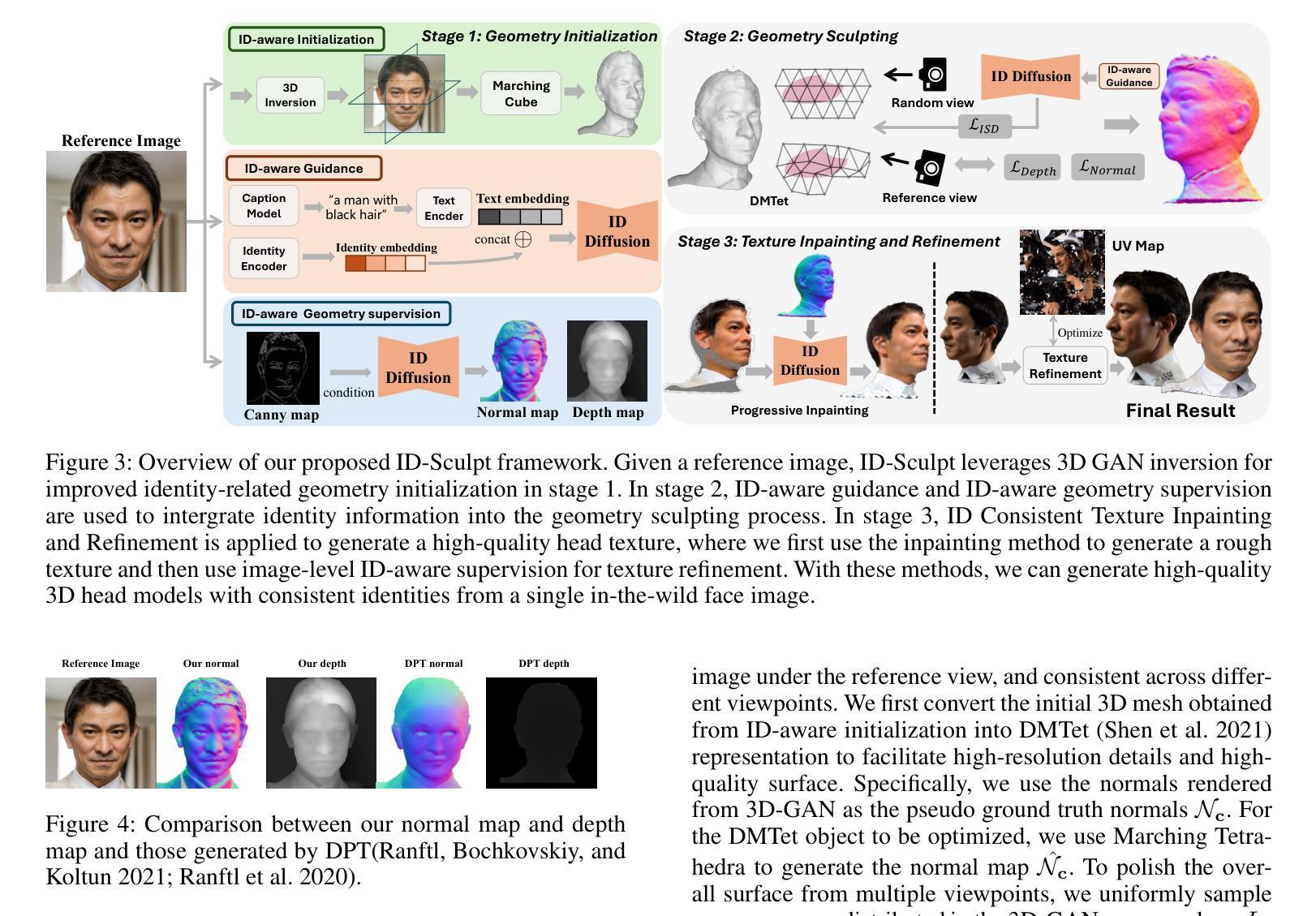
ID-Sculpt: ID-aware 3D Head Generation from Single In-the-wild Portrait Image
Authors:Jinkun Hao, Junshu Tang, Jiangning Zhang, Ran Yi, Yijia Hong, Moran Li, Weijian Cao, Yating Wang, Chengjie Wang, Lizhuang Ma
While recent works have achieved great success on image-to-3D object generation, high quality and fidelity 3D head generation from a single image remains a great challenge. Previous text-based methods for generating 3D heads were limited by text descriptions and image-based methods struggled to produce high-quality head geometry. To handle this challenging problem, we propose a novel framework, ID-Sculpt, to generate high-quality 3D heads while preserving their identities. Our work incorporates the identity information of the portrait image into three parts: 1) geometry initialization, 2) geometry sculpting, and 3) texture generation stages. Given a reference portrait image, we first align the identity features with text features to realize ID-aware guidance enhancement, which contains the control signals representing the face information. We then use the canny map, ID features of the portrait image, and a pre-trained text-to-normal/depth diffusion model to generate ID-aware geometry supervision, and 3D-GAN inversion is employed to generate ID-aware geometry initialization. Furthermore, with the ability to inject identity information into 3D head generation, we use ID-aware guidance to calculate ID-aware Score Distillation (ISD) for geometry sculpting. For texture generation, we adopt the ID Consistent Texture Inpainting and Refinement which progressively expands the view for texture inpainting to obtain an initialization UV texture map. We then use the ID-aware guidance to provide image-level supervision for noisy multi-view images to obtain a refined texture map. Extensive experiments demonstrate that we can generate high-quality 3D heads with accurate geometry and texture from a single in-the-wild portrait image.
虽然近期的工作在图像到3D物体的生成上取得了巨大的成功,但从单张图像生成高质量和高保真度的3D头像仍然是一个巨大的挑战。之前基于文本的方法生成3D头像受限于文本描述,而基于图像的方法难以产生高质量的头像几何结构。为了处理这个具有挑战性的问题,我们提出了一种新型框架ID-Sculpt,用于生成高质量的3D头像,同时保留其身份特征。我们的工作将肖像图像的身份信息融入三个阶段:1)几何初始化,2)几何雕塑,3)纹理生成。给定一个参考肖像图像,我们首先通过文本特征与身份特征的对齐,实现ID感知引导增强,其中包含代表面部信息的控制信号。然后,我们使用Canny地图、肖像图像的身份特征以及预训练的文本到法线/深度扩散模型来生成ID感知的几何监督,并利用3D-GAN反转来生成ID感知的几何初始化。此外,通过向3D头像生成中注入身份信息的能力,我们使用ID感知指导来计算用于几何雕塑的ID感知分数蒸馏(ISD)。对于纹理生成,我们采用ID一致纹理填充和细化方法,逐步扩展视图以进行纹理填充,以获得初始UV纹理贴图。然后,我们使用ID感知指导为噪声多视角图像提供图像级监督,以获得精细的纹理贴图。大量实验表明,我们可以从一张野外的肖像图像生成高质量、几何和纹理准确的3D头像。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025; Project page: https://jinkun-hao.github.io/ID-Sculpt/
Summary
该文本介绍了一种新型框架ID-Sculpt,用于从单幅图像生成高质量的三维头像,同时保留其身份特征。该框架将身份信息融入三个阶段:几何初始化、几何雕刻和纹理生成。通过ID感知指导增强、Canny地图、预训练的文本到法线/深度扩散模型等技术,实现了高质量的三维头像生成。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新型框架ID-Sculpt,旨在解决从单幅图像生成高质量三维头像的挑战。
- 框架将身份信息融入三个阶段:几何初始化、几何雕刻和纹理生成。
- 通过ID感知指导增强,实现了身份特征和文本特征的融合。
- 利用Canny地图、预训练的文本到法线/深度扩散模型和3D-GAN反转,生成ID感知的几何监督。
- ID感知指导用于计算几何雕刻的ID感知分数蒸馏(ISD)。
- 采用ID一致纹理补全与细化方法,逐步扩展视图进行纹理补全,获得初始UV纹理贴图。
点此查看论文截图


Guiding a Diffusion Model with a Bad Version of Itself
Authors:Tero Karras, Miika Aittala, Tuomas Kynkäänniemi, Jaakko Lehtinen, Timo Aila, Samuli Laine
The primary axes of interest in image-generating diffusion models are image quality, the amount of variation in the results, and how well the results align with a given condition, e.g., a class label or a text prompt. The popular classifier-free guidance approach uses an unconditional model to guide a conditional model, leading to simultaneously better prompt alignment and higher-quality images at the cost of reduced variation. These effects seem inherently entangled, and thus hard to control. We make the surprising observation that it is possible to obtain disentangled control over image quality without compromising the amount of variation by guiding generation using a smaller, less-trained version of the model itself rather than an unconditional model. This leads to significant improvements in ImageNet generation, setting record FIDs of 1.01 for 64x64 and 1.25 for 512x512, using publicly available networks. Furthermore, the method is also applicable to unconditional diffusion models, drastically improving their quality.
在图像生成扩散模型中,主要的关注点在于图像质量、结果变化的程度以及结果如何符合给定的条件,例如类别标签或文本提示。流行的无分类器引导方法使用无条件模型来引导有条件模型,这导致了提示对齐更好和图像质量更高,但代价是变化减少。这些效果似乎固有地纠缠在一起,因此难以控制。我们意外地发现,通过使用模型本身的更小、训练较少的版本来指导生成,可以在不损害变化量的同时获得对图像质量的分离控制。这导致在ImageNet生成方面取得了显著改进,使用公开可用的网络,以64x64和512x512的分辨率分别设置了记录FID得分1.01和1.25。此外,该方法也适用于无条件扩散模型,大大提高了其质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2024
Summary
本文探讨了图像生成扩散模型中的关键方面,如图像质量、结果多样性和对齐特定条件的能力。通过指导模型的方法可以改进模型表现,即利用无条件的模型引导条件模型以获得更好的提示对齐和更高的图像质量,但同时也降低了多样性。本文观察到可以通过利用较小的未完全训练版本模型进行引导来分离控制图像质量而不牺牲多样性,这在ImageNet生成上取得了显著改进,并在公开网络上设置了新的FID记录。此方法同样适用于无条件扩散模型,可大幅提高模型质量。
Key Takeaways
- 图像生成扩散模型的核心关注点包括图像质量、结果多样性和与给定条件对齐的能力。
- 使用无条件模型引导条件模型的方法可以同时提高提示对齐和图像质量,但会降低多样性。
- 利用较小的未完全训练版本模型进行引导可以分离控制图像质量而不牺牲多样性。
- 此方法在ImageNet生成上取得了显著改进,并设置了新的FID记录。
- 该方法适用于无条件扩散模型,可以大幅提高模型质量。
- 该研究提供了一种有效的策略来控制图像生成过程中的关键因素。
点此查看论文截图