⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-21 更新
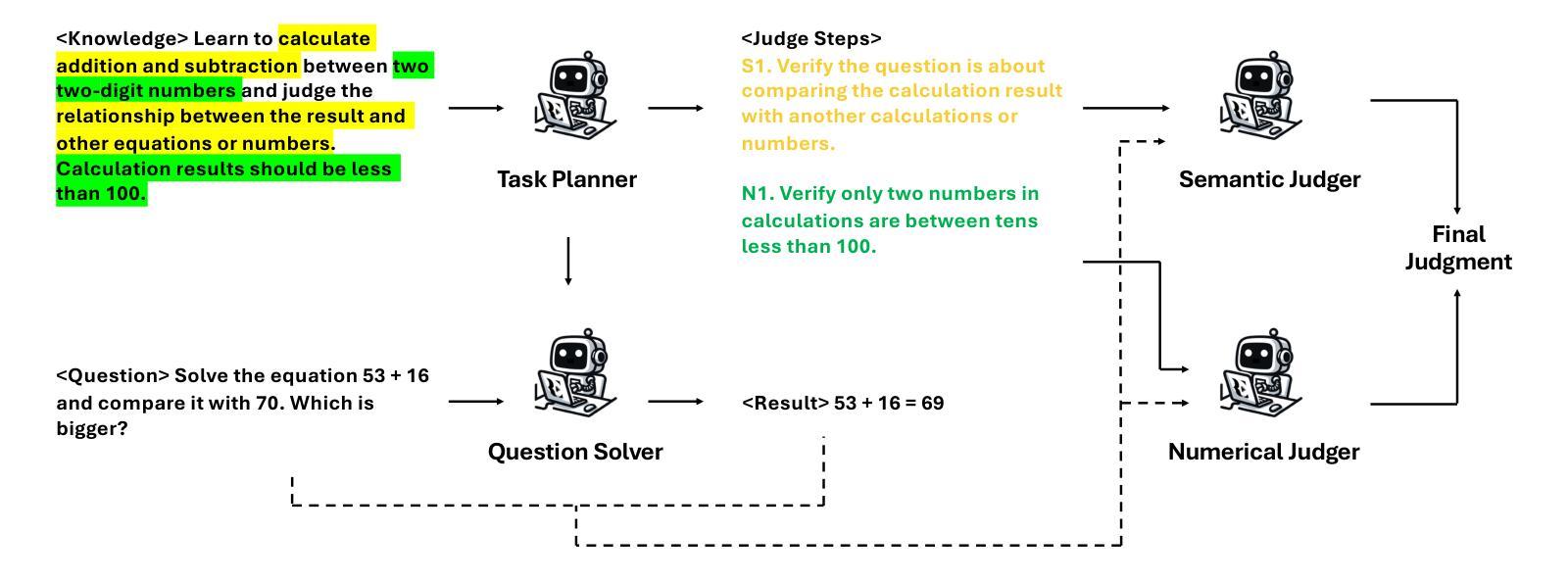
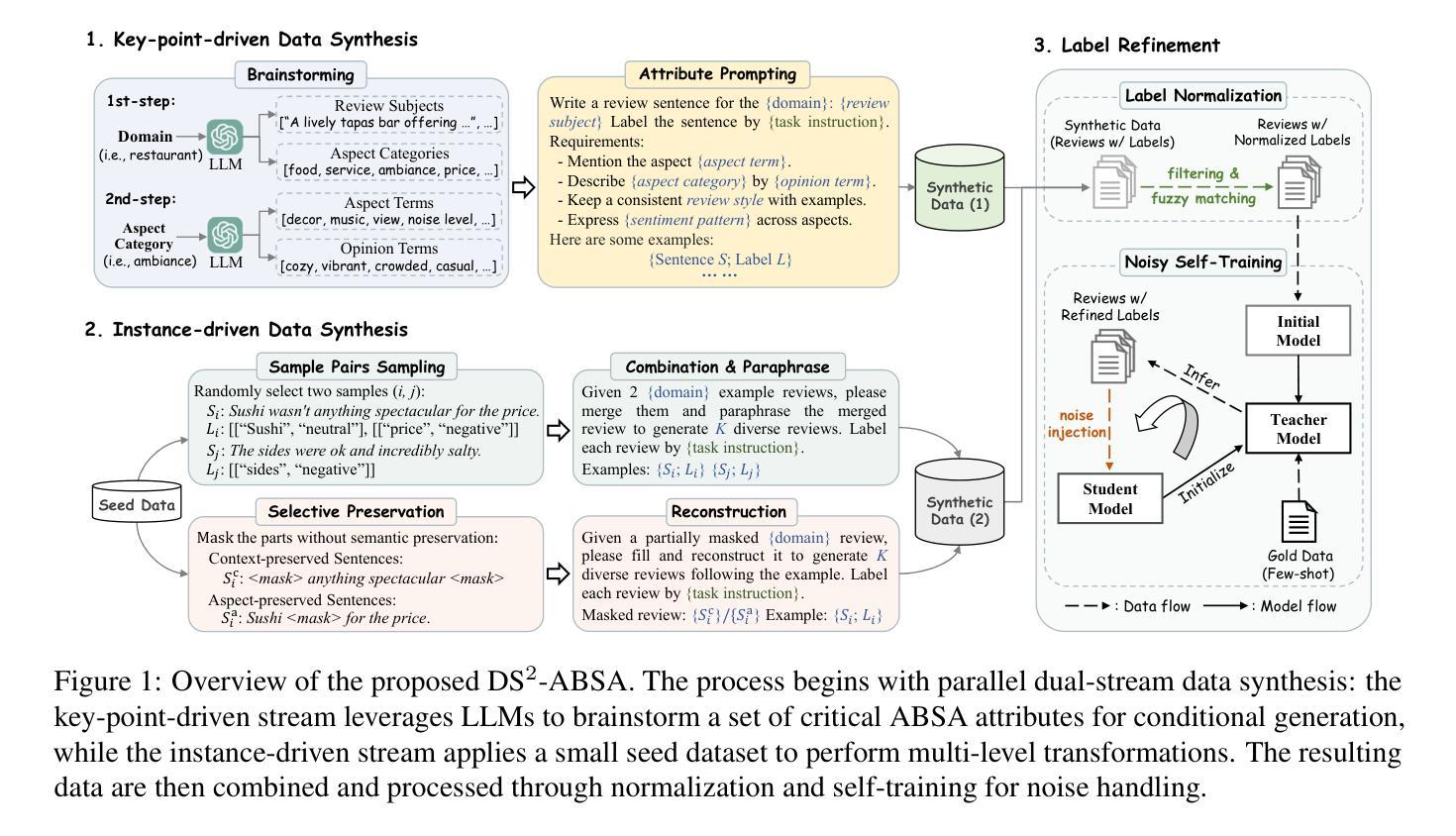
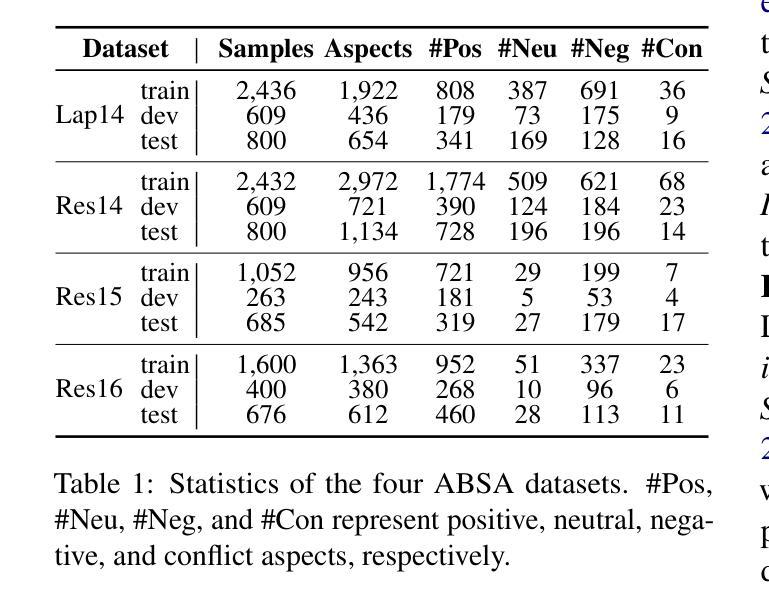
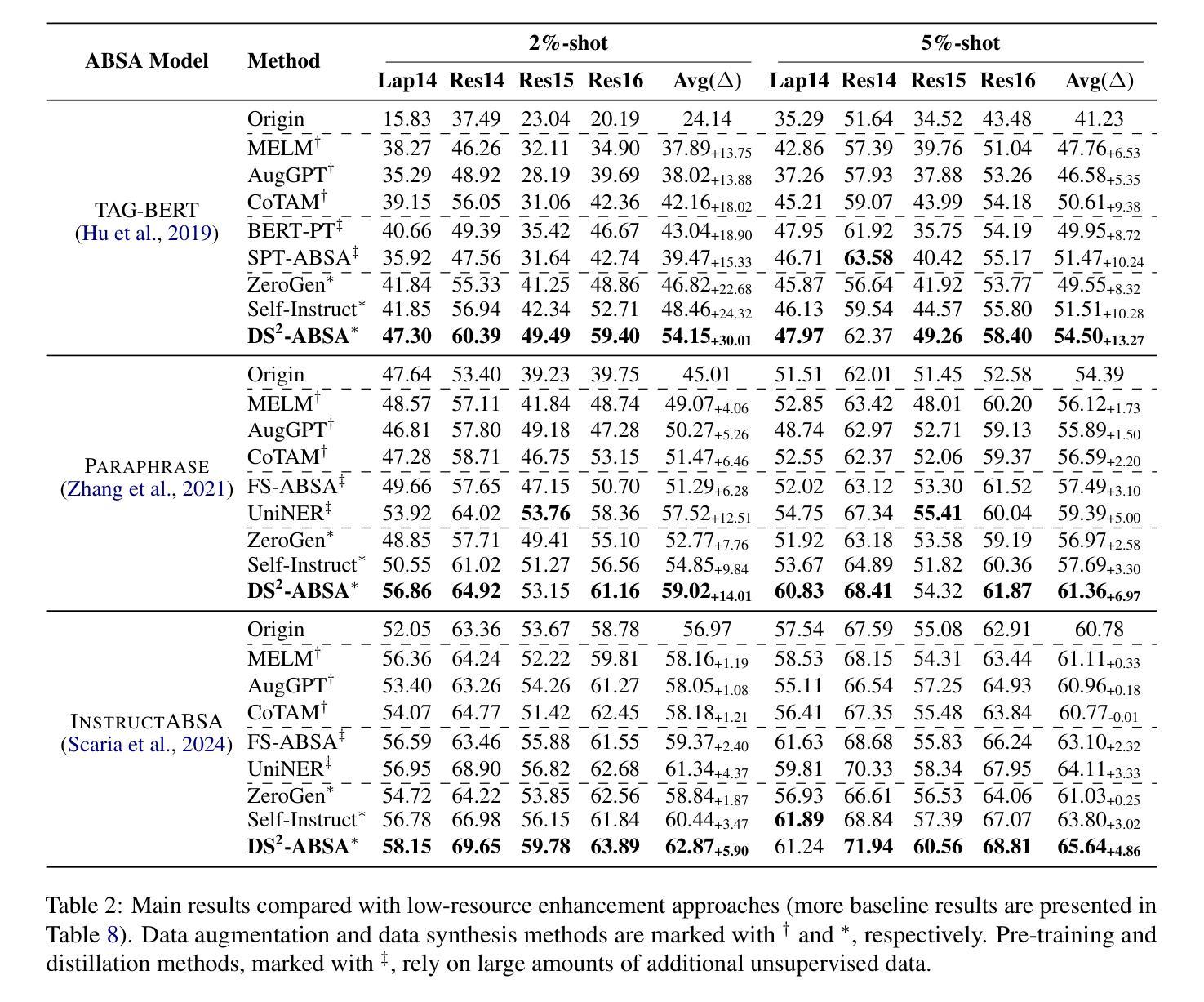
DS$^2$-ABSA: Dual-Stream Data Synthesis with Label Refinement for Few-Shot Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis
Authors:Hongling Xu, Yice Zhang, Qianlong Wang, Ruifeng Xu
Recently developed large language models (LLMs) have presented promising new avenues to address data scarcity in low-resource scenarios. In few-shot aspect-based sentiment analysis (ABSA), previous efforts have explored data augmentation techniques, which prompt LLMs to generate new samples by modifying existing ones. However, these methods fail to produce adequately diverse data, impairing their effectiveness. Besides, some studies apply in-context learning for ABSA by using specific instructions and a few selected examples as prompts. Though promising, LLMs often yield labels that deviate from task requirements. To overcome these limitations, we propose DS$^2$-ABSA, a dual-stream data synthesis framework targeted for few-shot ABSA. It leverages LLMs to synthesize data from two complementary perspectives: \textit{key-point-driven} and \textit{instance-driven}, which effectively generate diverse and high-quality ABSA samples in low-resource settings. Furthermore, a \textit{label refinement} module is integrated to improve the synthetic labels. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DS$^2$-ABSA significantly outperforms previous few-shot ABSA solutions and other LLM-oriented data generation methods.
最近开发的大型语言模型(LLM)为低资源场景中的数据稀缺问题提供了有前景的新解决方案。在基于方面的情感分析(ABSA)的少量样本方面,之前的研究已经探索了数据增强技术,通过修改现有样本促使LLM生成新样本。然而,这些方法无法产生足够多样化的数据,影响了其有效性。此外,一些研究通过使用特定指令和几个精选的示例作为提示来应用基于上下文的ABSA学习。尽管有前景,但LLM通常产生的标签会偏离任务要求。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了DS$^2$-ABSA,这是一个面向基于方面的情感分析少量样本的双流数据合成框架。它利用LLM从两个互补的角度合成数据:关键点驱动和实例驱动,有效地在资源稀缺的环境中生成多样化和高质量的ABSA样本。此外,还集成了标签优化模块,以提高合成标签的准确性。大量实验表明,DS$^2$-ABSA显著优于之前的基于方面的情感分析少量样本解决方案以及其他面向LLM的数据生成方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的DS$^2$-ABSA框架,通过两种互补的视角:关键点驱动和实例驱动,有效合成数据,提高了少样本方面情感分析(ABSA)的性能。该框架还包括标签修正模块,以提高合成数据的标签质量。实验证明,DS$^2$-ABSA显著优于先前的少样本ABSA解决方案和其他LLM导向的数据生成方法。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs为解决低资源情况下的数据稀缺问题提供了新的途径。
- 传统的数据增强技术在ABSA中无法产生足够多样的数据。
- 在ABSA中使用上下文学习的方法有时会偏离任务要求。
- DS$^2$-ABSA框架通过两种互补的视角:关键点驱动和实例驱动,进行数据安全合成。
- DS$^2$-ABSA包括标签修正模块,以提高合成数据的标签质量。
- DS$^2$-ABSA显著优于其他少样本ABSA解决方案和LLM导向的数据生成方法。
- 该框架适用于低资源环境下的方面情感分析任务。
点此查看论文截图

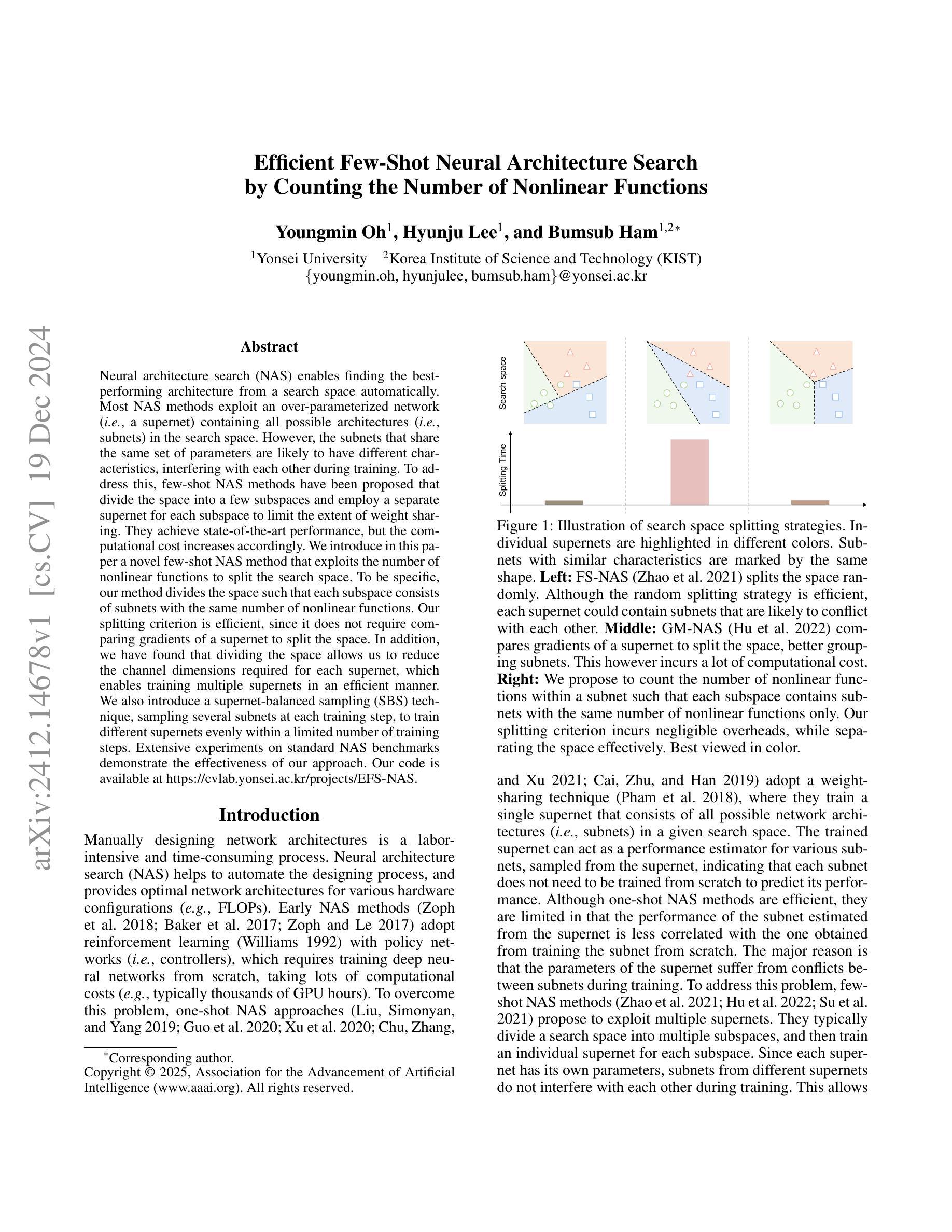
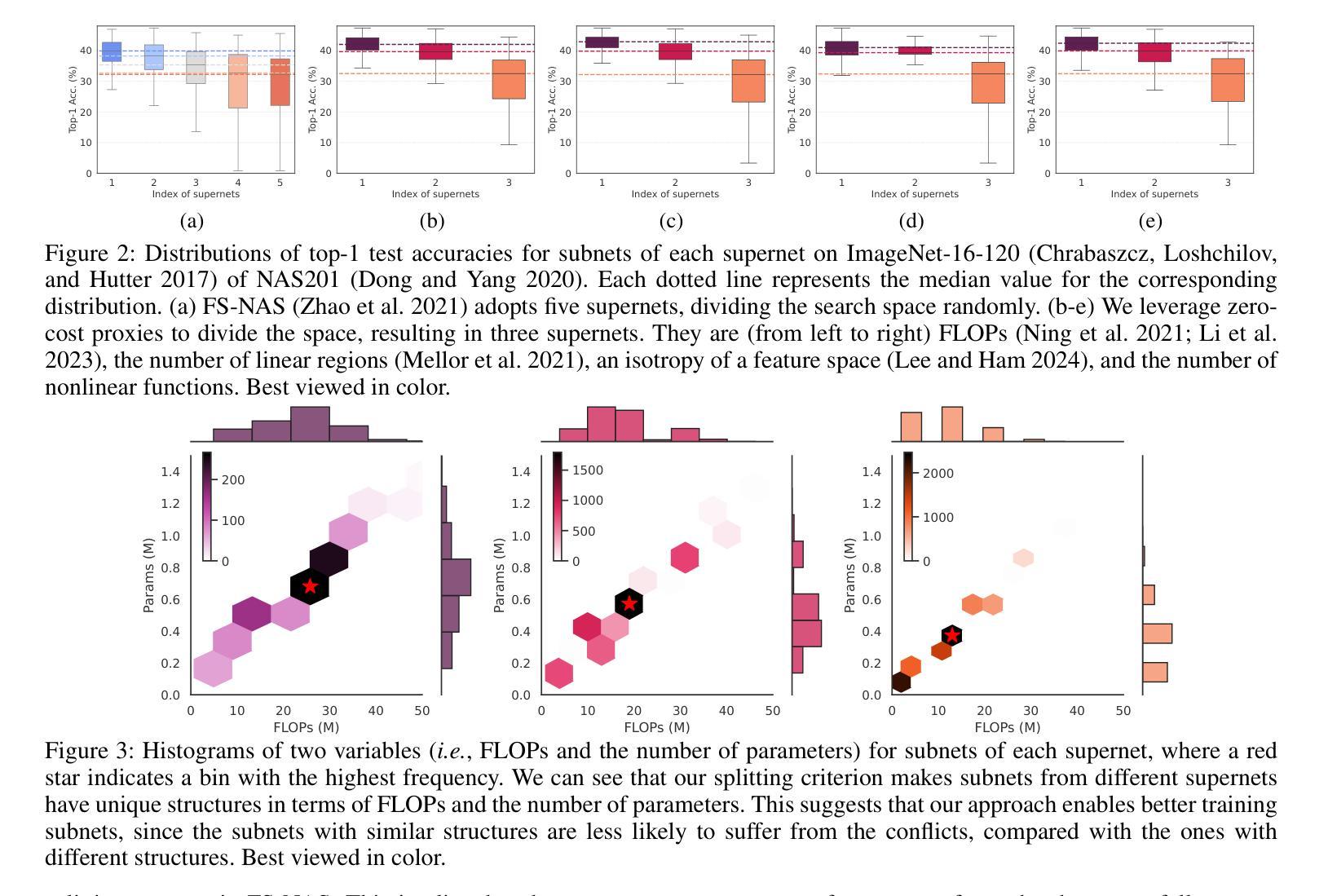
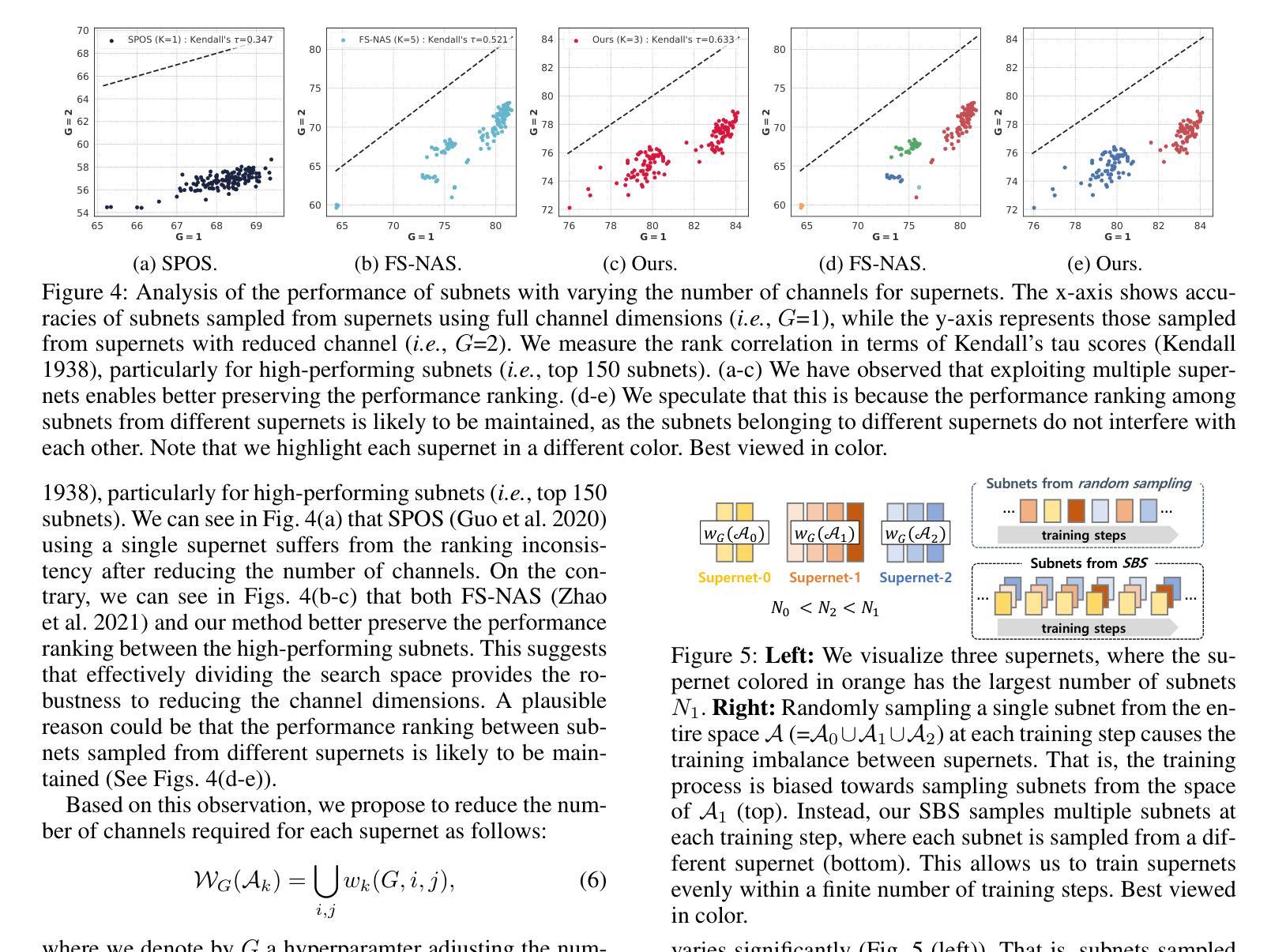
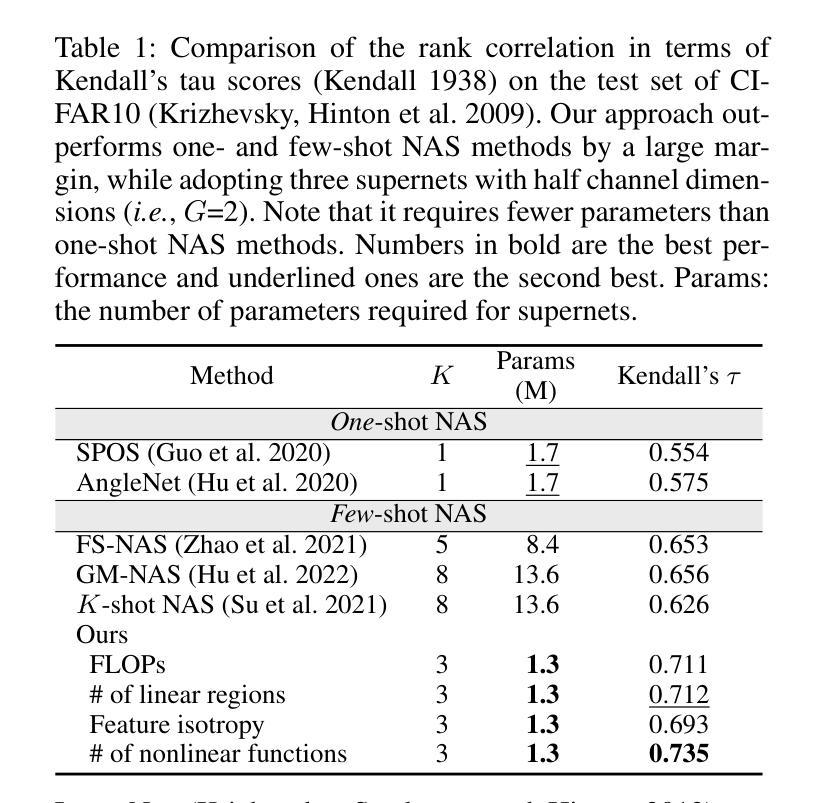
Efficient Few-Shot Neural Architecture Search by Counting the Number of Nonlinear Functions
Authors:Youngmin Oh, Hyunju Lee, Bumsub Ham
Neural architecture search (NAS) enables finding the best-performing architecture from a search space automatically. Most NAS methods exploit an over-parameterized network (i.e., a supernet) containing all possible architectures (i.e., subnets) in the search space. However, the subnets that share the same set of parameters are likely to have different characteristics, interfering with each other during training. To address this, few-shot NAS methods have been proposed that divide the space into a few subspaces and employ a separate supernet for each subspace to limit the extent of weight sharing. They achieve state-of-the-art performance, but the computational cost increases accordingly. We introduce in this paper a novel few-shot NAS method that exploits the number of nonlinear functions to split the search space. To be specific, our method divides the space such that each subspace consists of subnets with the same number of nonlinear functions. Our splitting criterion is efficient, since it does not require comparing gradients of a supernet to split the space. In addition, we have found that dividing the space allows us to reduce the channel dimensions required for each supernet, which enables training multiple supernets in an efficient manner. We also introduce a supernet-balanced sampling (SBS) technique, sampling several subnets at each training step, to train different supernets evenly within a limited number of training steps. Extensive experiments on standard NAS benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach. Our code is available at https://cvlab.yonsei.ac.kr/projects/EFS-NAS.
神经网络架构搜索(NAS)能够自动从搜索空间中找到性能最佳的架构。大多数NAS方法利用一个过度参数化的网络(即超网),该超网包含搜索空间中所有可能的架构(即子网)。然而,共享相同参数集的子网可能具有不同的特性,在训练过程中会相互干扰。为了解决这一问题,已经提出了少镜头NAS方法,它将空间划分为几个子空间,并为每个子空间使用一个单独的超网来限制权重共享。它们达到了最先进的性能,但计算成本也相应增加。本文介绍了一种新型的少镜头NAS方法,该方法利用非线性函数的数量来划分搜索空间。具体来说,我们的方法将空间划分成每个子空间包含相同数量非线性函数的子网。我们的划分标准是高效的,因为它不需要比较超网的梯度来划分空间。此外,我们发现划分空间允许我们减少每个超网所需的通道维度,从而以高效的方式训练多个超网。我们还引入了一种超网平衡采样(SBS)技术,每次训练步骤中采样多个子网,在有限的训练步骤内均匀训练不同的超网。在标准NAS基准测试上的大量实验证明了我们的方法的有效性。我们的代码可在https://cvlab.yonsei.ac.kr/projects/EFS-NAS上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to AAAI 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种基于非线性函数数量的新型少样本NAS方法。该方法通过分割搜索空间,使得每个子空间包含相同数量的非线性函数,从而提高效率。此外,通过减少每个超网络的通道维度,实现了多个超网络的训练效率。同时引入了一种超网络平衡采样技术,在有限的训练步骤内均匀训练不同的超网络。实验证明该方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络架构搜索(NAS)可从搜索空间中自动找到性能最佳的架构。
- 大多数NAS方法利用过度参数化的网络(即超网)来包含所有可能的架构(即子网)。
- 少样本NAS方法通过将搜索空间分割成多个子空间来减少权重共享的问题。
- 本文提出了一种基于非线性函数数量的新型少样本NAS方法,通过该分割标准提高了效率。
- 通过对搜索空间的分割,减少了每个超网络的通道维度需求,提高了训练效率。
- 引入了一种超网络平衡采样技术,可在有限的训练步骤内均匀训练不同的超网络。
点此查看论文截图
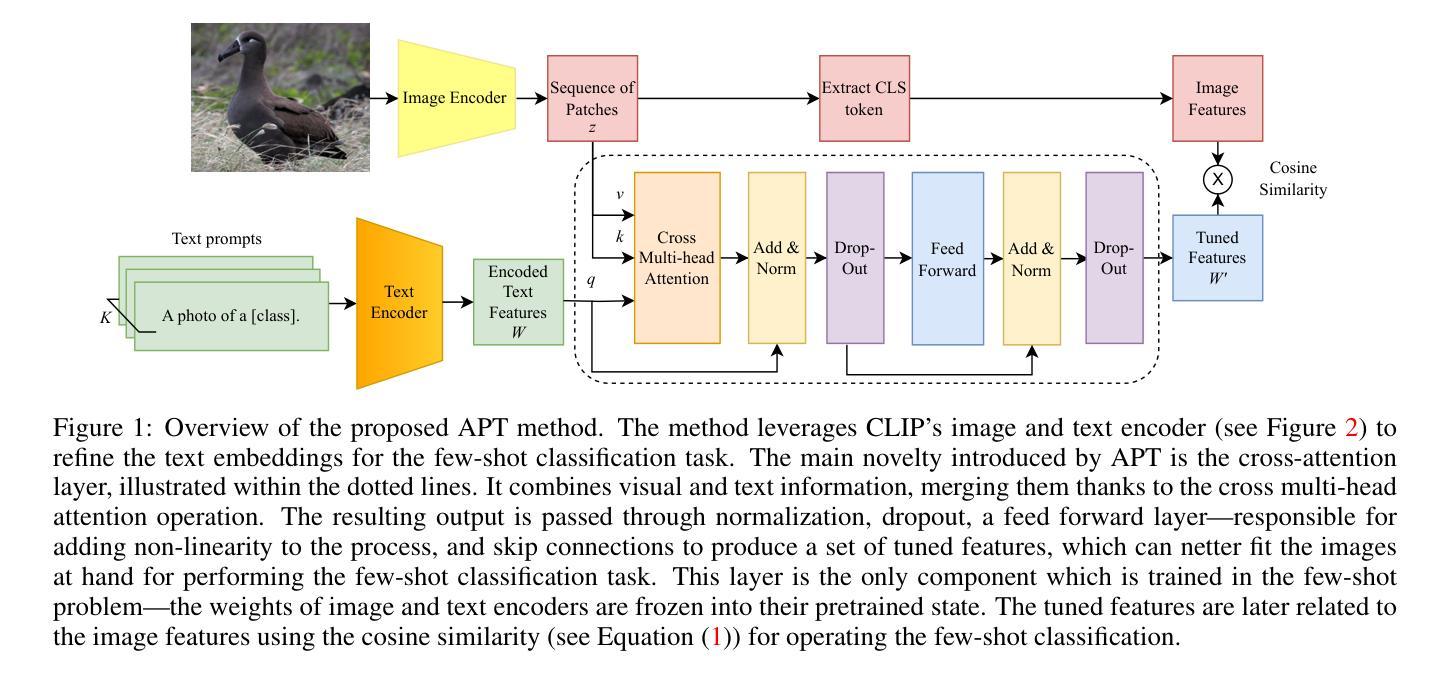
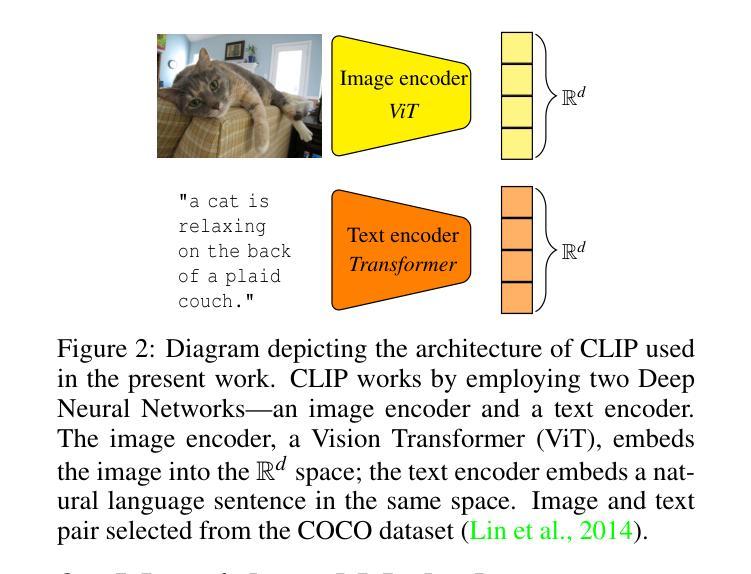
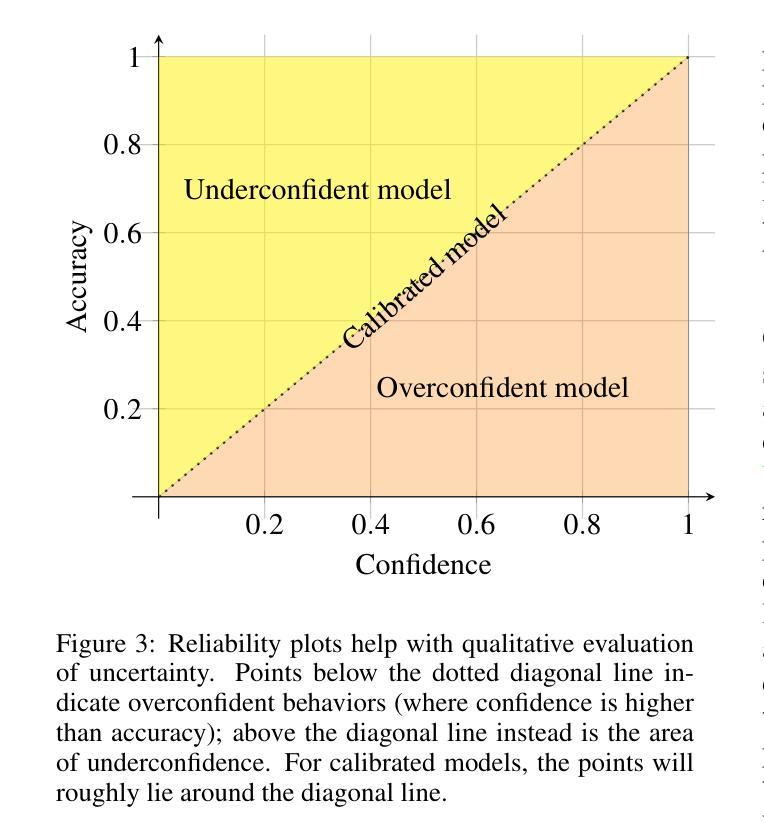
Adaptive Prompt Tuning: Vision Guided Prompt Tuning with Cross-Attention for Fine-Grained Few-Shot Learning
Authors:Eric Brouwer, Jan Erik van Woerden, Gertjan Burghouts, Matias Valedenegro-Toro, Marco Zullich
Few-shot, fine-grained classification in computer vision poses significant challenges due to the need to differentiate subtle class distinctions with limited data. This paper presents a novel method that enhances the Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training (CLIP) model through adaptive prompt tuning, guided by real-time visual inputs. Unlike existing techniques such as Context Optimization (CoOp) and Visual Prompt Tuning (VPT), which are constrained by static prompts or visual token reliance, the proposed approach leverages a cross-attention mechanism to dynamically refine text prompts for the image at hand. This enables an image-specific alignment of textual features with image patches extracted from the Vision Transformer, making the model more effective for datasets with high intra-class variance and low inter-class differences. The method is evaluated on several datasets, including CUBirds, Oxford Flowers, and FGVC Aircraft, showing significant performance gains over static prompt tuning approaches. To ensure these performance gains translate into trustworthy predictions, we integrate Monte-Carlo Dropout in our approach to improve the reliability of the model predictions and uncertainty estimates. This integration provides valuable insights into the model’s predictive confidence, helping to identify when predictions can be trusted and when additional verification is necessary. This dynamic approach offers a robust solution, advancing the state-of-the-art for few-shot fine-grained classification.
针对计算机视觉领域的小样本精细分类任务面临重要挑战,原因在于需要在有限的数据下区分微妙的类别差异。本文提出了一种新型方法,该方法通过自适应提示调整增强对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)模型,并由实时视觉输入进行引导。与现有的上下文优化(CoOp)和视觉提示调整(VPT)等技术不同,这些技术受限于静态提示或视觉符号依赖,所提出的方法利用交叉注意力机制动态完善当前图像文本提示。这有助于将特定图像中的文本特征与从视觉转换器中提取的图像块进行对齐,使得模型对于具有高强度内部类别差异和微弱类别间差异的数据集更有效。该方法在多个数据集上进行了评估,包括CUBirds、牛津花卉和FGVC飞机数据集,相较于静态提示调整方法显示出显著的性能提升。为确保这些性能提升转化为可靠的预测,我们整合了蒙特卡洛Dropout,以提高模型预测和不确定性估计的可靠性。这一整合提供了关于模型预测置信度的宝贵见解,有助于确定何时可以信任预测以及何时需要额外的验证。这一动态方法为稳健的解决方案提供了强大的支撑,推进了小样本精细分类的前沿水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于自适应提示调整(Adaptive Prompt Tuning)的对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)模型的新方法,用于解决计算机视觉中的小样本精细分类问题。该方法通过实时视觉输入引导,动态调整文本提示,与图像中的特定内容对齐,从而提高模型在具有大类内变化和较小类间差异的数据集上的性能。集成Monte-Carlo Dropout提高了模型预测的可信度和不确定性估计的可靠性。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文提出了一种新颖的基于自适应提示调整的CLIP模型方法,用于解决小样本精细分类问题。
- 该方法利用实时视觉输入进行动态调整文本提示,与图像中的特定内容进行对齐。
- 与现有的静态提示调整技术相比,该方法在多个数据集上显示出显著的性能提升。
- 集成Monte-Carlo Dropout提高了模型预测的可信度和不确定性估计的可靠性。
- 该方法能够处理具有高类内变化和低类间差异的数据集。
- 该方法通过动态调整文本提示,提高了模型对不同图像数据的适应性。
点此查看论文截图

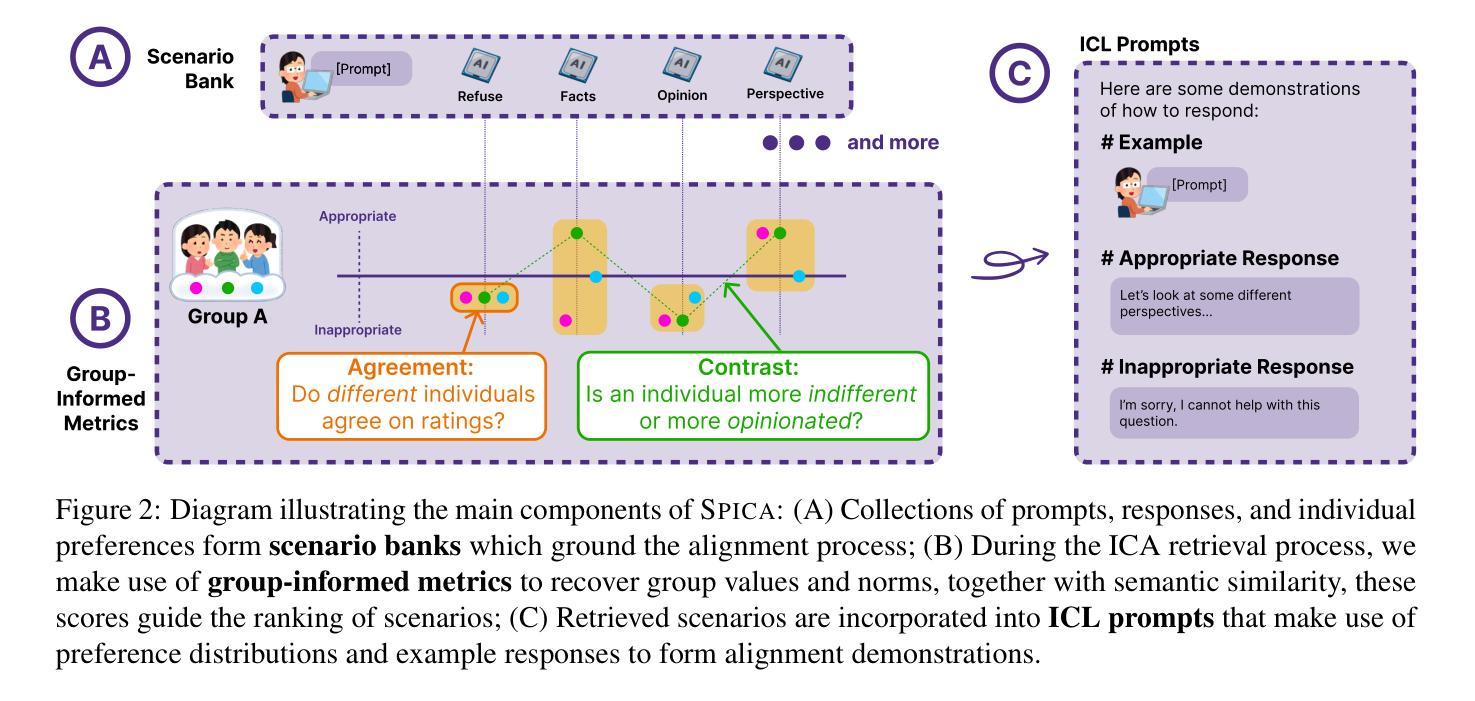
SPICA: Retrieving Scenarios for Pluralistic In-Context Alignment
Authors:Quan Ze Chen, K. J. Kevin Feng, Chan Young Park, Amy X. Zhang
When different groups’ values differ, one approach to model alignment is to steer models at inference time towards each group’s preferences. However, techniques like in-context learning only consider similarity when drawing few-shot examples and not cross-group differences in values. We propose SPICA, a framework that accounts for group-level differences during in-context example retrieval. SPICA introduces three designs: scenario banks, group-informed retrieval metrics, and in-context alignment prompts. From an evaluation of SPICA on an alignment task collecting inputs from four demographic groups ($n = 544$), our metrics retrieve in-context examples that more closely match observed preferences, with the best prompt configuration using multiple contrastive responses to demonstrate examples. In an end-to-end evaluation ($n = 120$), we observe that SPICA is higher rated than similarity-based retrieval, with groups seeing up to a +0.16 point improvement on a 5 point scale. Additionally, gains from SPICA were more uniform, with all groups benefiting from alignment rather than only some. Finally, we find that while a group-agnostic approach can align to aggregated values, it is not most suited for divergent groups.
当不同群体的价值观存在差异时,一种模型对齐的方法是在推理时将模型导向每个群体的偏好。然而,上下文学习等技术仅在绘制少量示例时考虑相似性,而忽略了跨群体的价值观差异。我们提出了SPICA框架,它在上下文示例检索过程中考虑了群体层面的差异。SPICA引入了三项设计:情景库、基于群体的检索指标和上下文对齐提示。通过对SPICA在收集来自四个不同人口群体(n=544)输入的对齐任务上的评估,我们的指标检索到的上下文示例与观察到的偏好更匹配,最佳提示配置使用多个对比响应来展示示例。在端到端评估(n=120)中,我们观察到SPICA的评分高于基于相似性的检索方法,各群体在五点量表上的得分提高了+0.16点。此外,SPICA带来的收益更加均衡,所有群体都能从对齐中受益,而不仅仅是部分群体。最后,我们发现,虽然一种无群体差异的方法可以实现对整体价值的对齐,但它并不最适合于不同的群体。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文提出一种名为SPICA的框架,用于在少量样本的情况下考虑群体级别的差异进行模型对齐。SPICA通过情景库、群体感知检索指标和上下文对齐提示的设计,可以更好地匹配不同群体的偏好。实验结果表明,SPICA在匹配群体偏好方面优于基于相似性的检索方法,且对所有群体都有改进效果。
Key Takeaways
- SPICA框架旨在解决不同群体价值观差异的问题,通过引导模型在推理阶段适应每个群体的偏好来实现模型对齐。
- 传统的方法如上下文学习只考虑少量样本的相似性,忽略了跨群体的价值差异。
- SPICA引入了情景库、群体感知检索指标和上下文对齐提示三个设计元素。
- 实验结果表明,SPICA能够更好地匹配观察到的偏好,并使用多个对比响应来展示例子。
- 在端到端的评估中,SPICA比基于相似性的检索方法获得了更高的评价,各群体在5分制量表上最多提升了0.16分。
- SPICA带来的改进更加均匀,对所有群体都有益,而不仅仅是部分群体。
点此查看论文截图

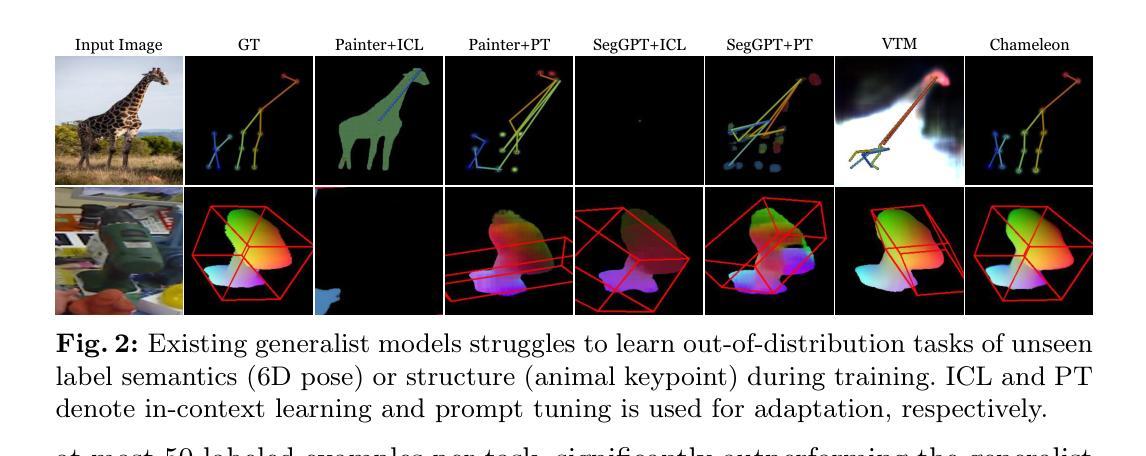
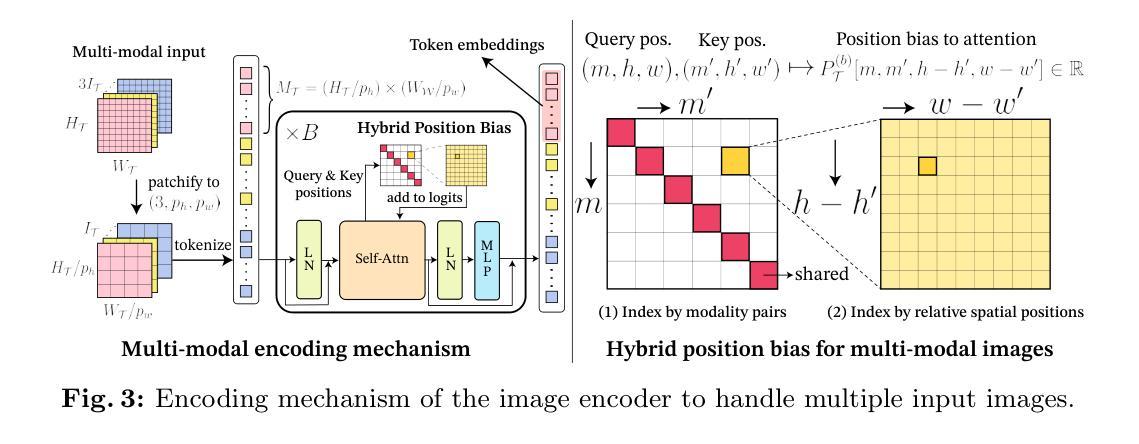
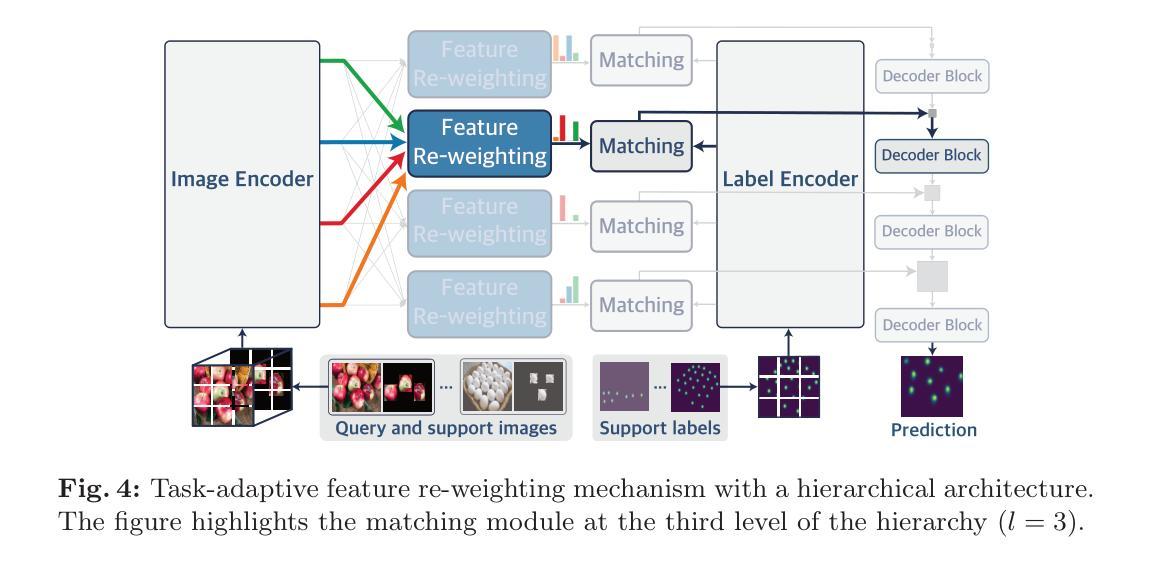
Chameleon: A Data-Efficient Generalist for Dense Visual Prediction in the Wild
Authors:Donggyun Kim, Seongwoong Cho, Semin Kim, Chong Luo, Seunghoon Hong
Large language models have evolved data-efficient generalists, benefiting from the universal language interface and large-scale pre-training. However, constructing a data-efficient generalist for dense visual prediction presents a distinct challenge due to the variation in label structures across different tasks. Consequently, generalization to unseen dense prediction tasks in the low-data regime is not straightforward and has received less attention from previous vision generalists. In this study, we explore a universal model that can flexibly adapt to unseen dense label structures with a few examples, enabling it to serve as a data-efficient vision generalist in diverse real-world scenarios. To this end, we base our method on a powerful meta-learning framework and explore several axes to improve its performance and versatility for real-world problems, such as flexible adaptation mechanisms and scalability. We evaluate our model across a spectrum of unseen real-world scenarios where low-shot learning is desirable, including video, 3D, medical, biological, and user-interactive tasks. Equipped with a generic architecture and an effective adaptation mechanism, our model flexibly adapts to all of these tasks with at most 50 labeled images, showcasing a significant advancement over existing data-efficient generalist approaches. Codes are available at https://github.com/GitGyun/chameleon.
大型语言模型已经发展出了数据高效的全能型模型,受益于通用语言接口和大规模预训练。然而,对于密集的视觉预测而言,构建一个数据高效的全能模型是一个独特的挑战,因为不同任务的标签结构存在变化。因此,在数据稀缺的情况下推广到未见过的密集预测任务并不简单,且之前的视觉全能模型对此关注较少。在本研究中,我们探索了一种通用模型,该模型能够灵活适应未见过的密集标签结构,并且只需少量样本即可成为数据高效视觉全能模型,适用于多种现实场景。为此,我们的方法基于强大的元学习框架,并探索了多个轴来提高其在现实世界问题中的性能和通用性,例如灵活的适应机制和可扩展性。我们在一系列未见过的现实场景中评估了我们的模型,在低样本学习场景中特别有用,包括视频、3D、医疗、生物和用户交互任务。我们的模型配备了通用架构和有效的适应机制,能够灵活地适应所有这些任务,最多只需要50张标记图像,这显示了与现有数据高效全能方法相比的重大进步。代码可在https://github.com/GitGyun/chameleon找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型的发展促进了数据高效通用主义的演进,但为密集视觉预测构建数据高效通用主义者仍存在独特挑战。本研究探索了一种基于元学习框架的通用模型,能够灵活适应未见过的密集标签结构,并在多样化的真实场景中发挥数据高效视觉通用性的作用。通过灵活的适应机制和可扩展性等多方面的改进,该模型在需要低样本学习的各种未见过的真实场景任务中表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型受益于通用语言接口和大规模预训练,促进数据高效通用主义的演进。
- 密集视觉预测领域的通用性面临独特挑战,因为不同任务的标签结构存在差异。
- 在低数据情况下,将知识泛化到未见过的密集预测任务并不简单。
- 研究提出了一种基于元学习框架的通用模型,能够灵活适应未见过的密集标签结构。
- 该模型通过灵活的适应机制和可扩展性等多方面的改进,提高了性能和通用性。
- 模型在需要低样本学习的各种未见过的真实场景任务中表现出色,包括视频、3D、医疗、生物和用户互动任务。
点此查看论文截图

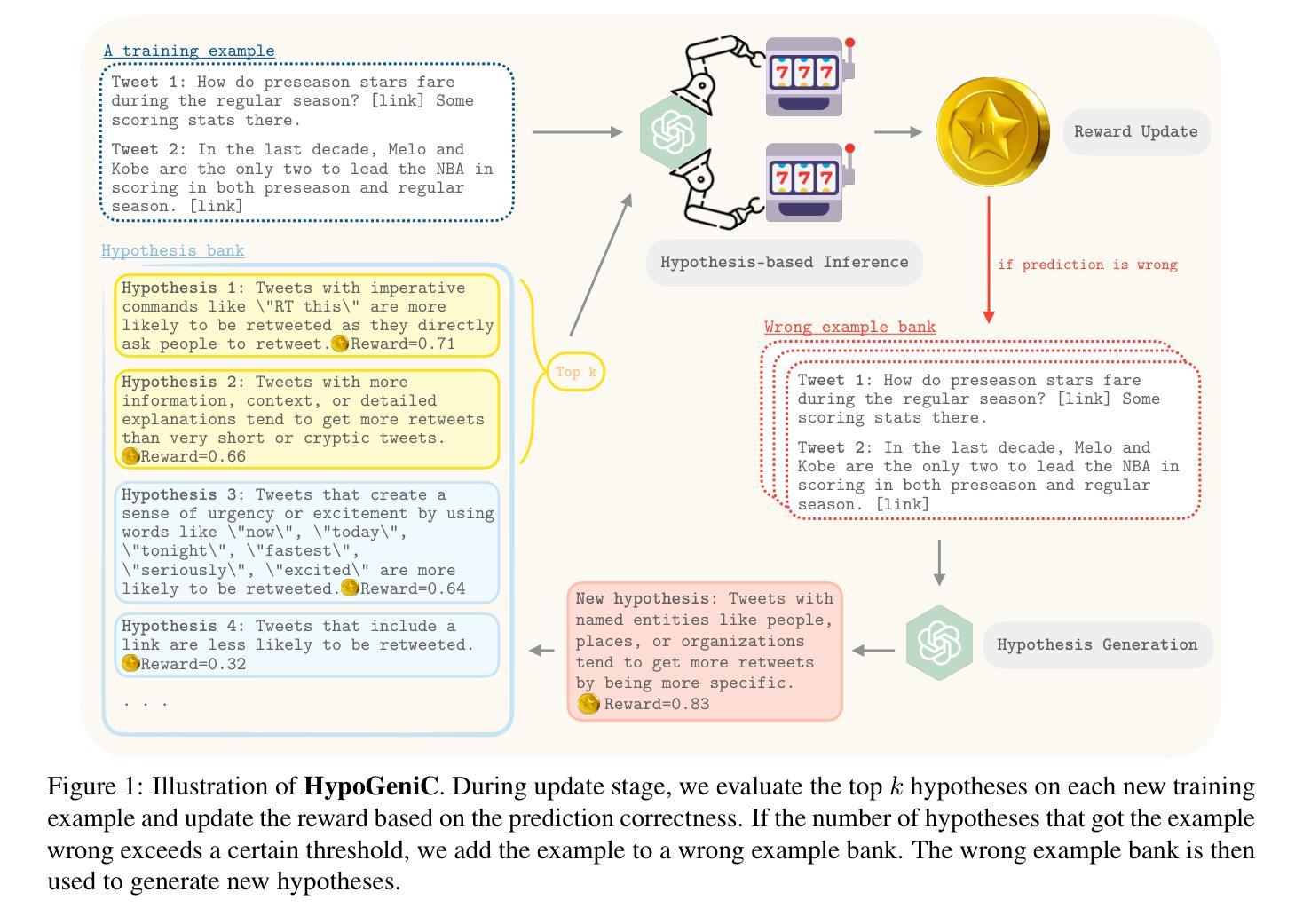
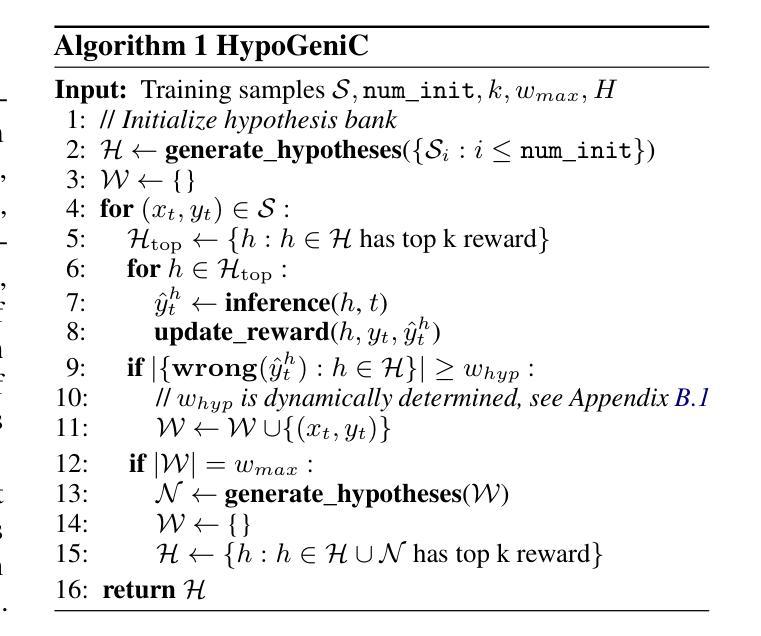
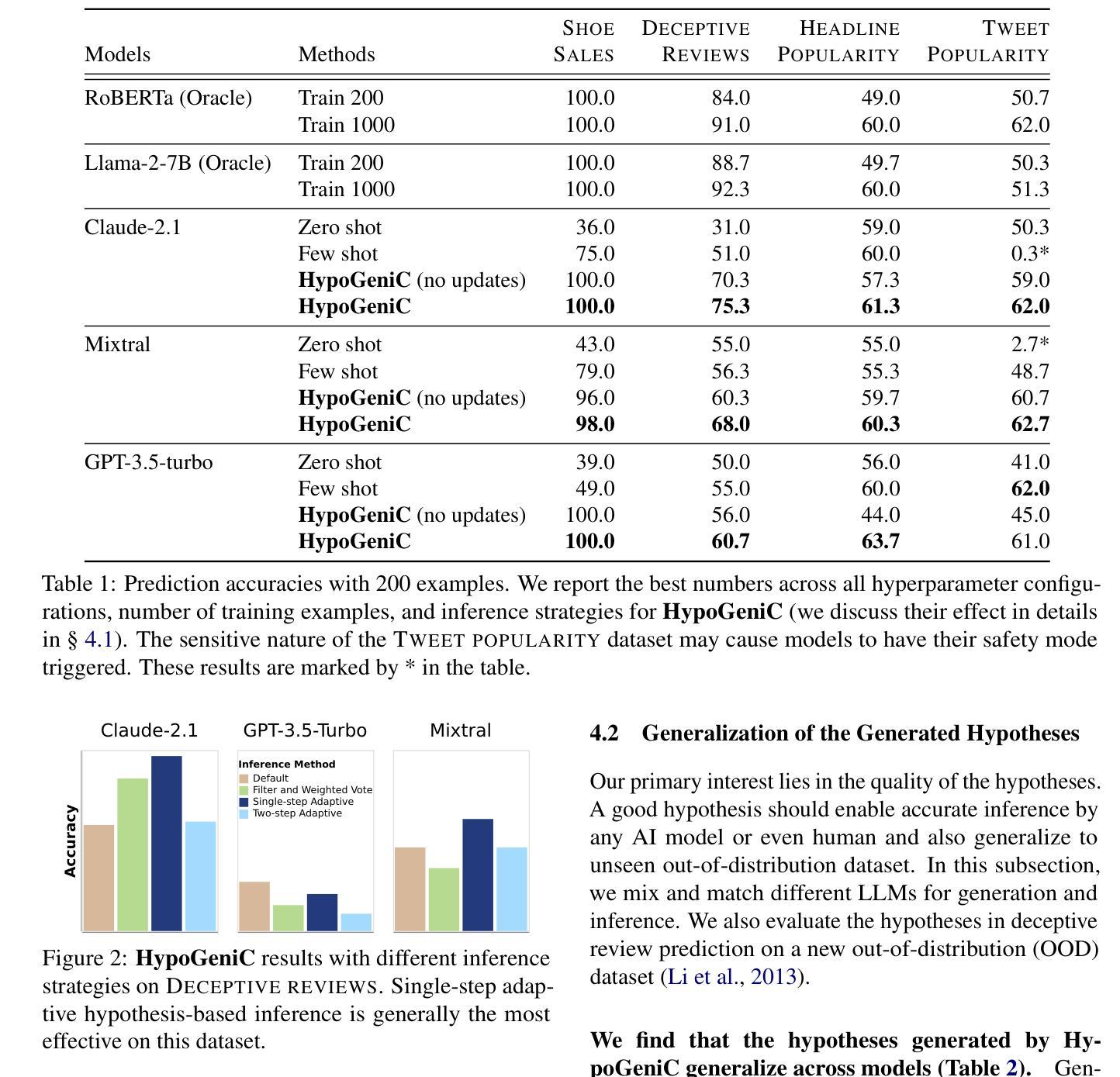
Hypothesis Generation with Large Language Models
Authors:Yangqiaoyu Zhou, Haokun Liu, Tejes Srivastava, Hongyuan Mei, Chenhao Tan
Effective generation of novel hypotheses is instrumental to scientific progress. So far, researchers have been the main powerhouse behind hypothesis generation by painstaking data analysis and thinking (also known as the Eureka moment). In this paper, we examine the potential of large language models (LLMs) to generate hypotheses. We focus on hypothesis generation based on data (i.e., labeled examples). To enable LLMs to handle arbitrarily long contexts, we generate initial hypotheses from a small number of examples and then update them iteratively to improve the quality of hypotheses. Inspired by multi-armed bandits, we design a reward function to inform the exploitation-exploration tradeoff in the update process. Our algorithm is able to generate hypotheses that enable much better predictive performance than few-shot prompting in classification tasks, improving accuracy by 31.7% on a synthetic dataset and by 13.9%, 3.3% and, 24.9% on three real-world datasets. We also outperform supervised learning by 12.8% and 11.2% on two challenging real-world datasets. Furthermore, we find that the generated hypotheses not only corroborate human-verified theories but also uncover new insights for the tasks.
有效的生成新假设对科学进步至关重要。迄今为止,研究人员一直是假设生成的主要动力来源,通过艰辛的数据分析和思考(也称为顿悟时刻)来生成假设。在本文中,我们研究了大型语言模型(LLM)生成假设的潜力。我们专注于基于数据(即带有标签的示例)的假设生成。为了使LLM能够处理任意长度的上下文,我们从少量示例生成初始假设,然后迭代更新它们以提高假设的质量。受多臂老虎机的启发,我们设计了一个奖励函数,以在更新过程中实现探索与利用的权衡。我们的算法能够生成假设,使分类任务的预测性能远远超过少样本提示,在合成数据集上提高了31.7%的准确率,在三个真实世界数据集上分别提高了13.9%、3.3%和24.9%。我们在两个具有挑战性的真实世界数据集上的表现也优于监督学习,分别提高了12.8%和11.2%。此外,我们发现生成的假设不仅证实了人类验证的理论,还为任务提供了新的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 28 pages, 6 figures, code link: https://github.com/ChicagoHAI/hypothesis_generation. Accepted by the 1st Workshop on NLP for Science (NLP4Science) at EMNLP 2024
Summary
本文探讨了大型语言模型在生成新假设方面的潜力,特别是在基于数据(即带标签示例)的假设生成方面。研究提出了一种算法,通过少量示例生成初始假设,并迭代更新以提高假设质量。该算法在分类任务中的预测性能优于少样本提示,可在合成数据集上提高准确率31.7%,并在三个真实世界数据集上分别提高准确率13.9%、3.3%和24.9%。此外,生成的假设不仅证实了人类验证的理论,还为任务提供了新的见解,且优于监督学习。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在生成新假设方面具有潜力。
- 研究提出了一种基于数据(带标签示例)的假设生成算法。
- 该算法通过少量示例生成初始假设,并迭代更新以提高假设质量。
- 算法在分类任务中的预测性能优于少样本提示和现有方法。
- 在合成数据集和真实世界数据集上,该算法显著提高准确率。
- 生成的假设不仅证实了人类验证的理论,还提供了新见解。
点此查看论文截图

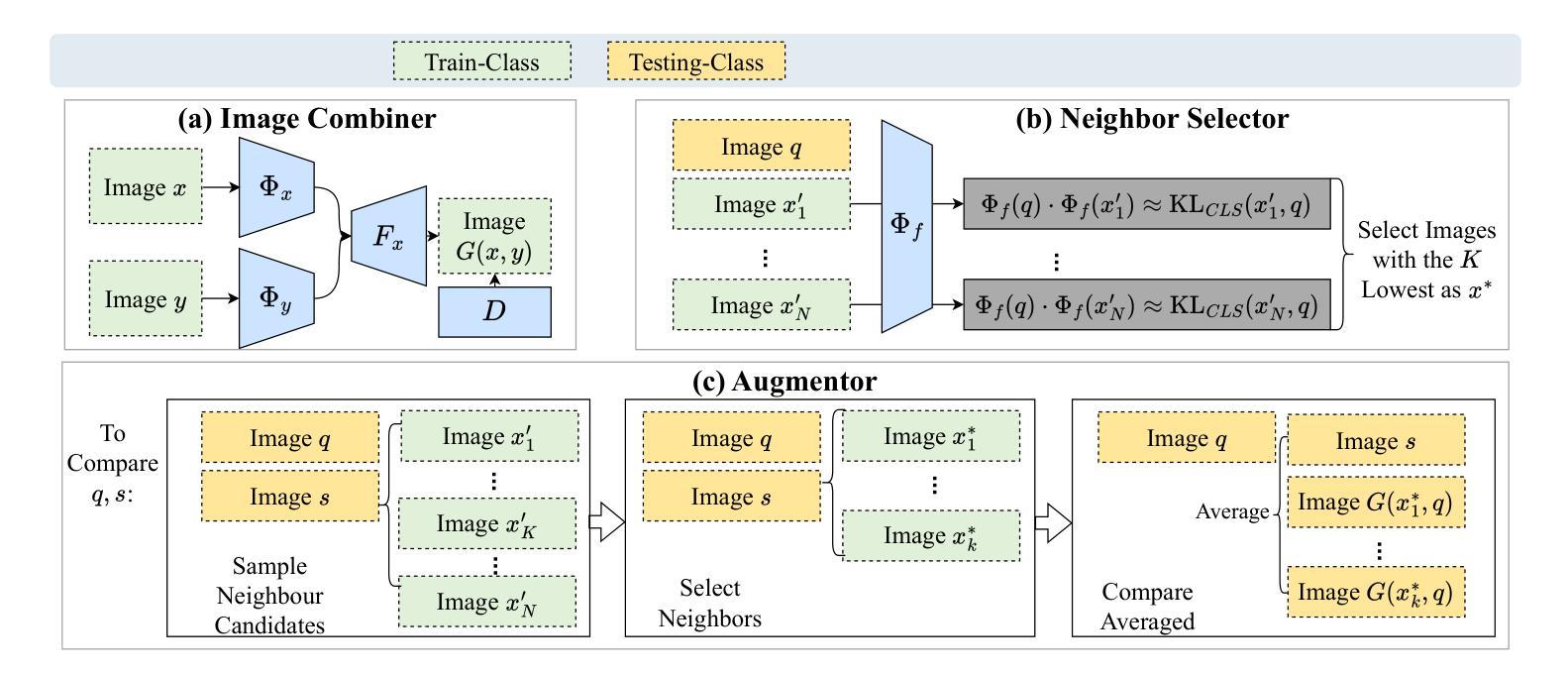
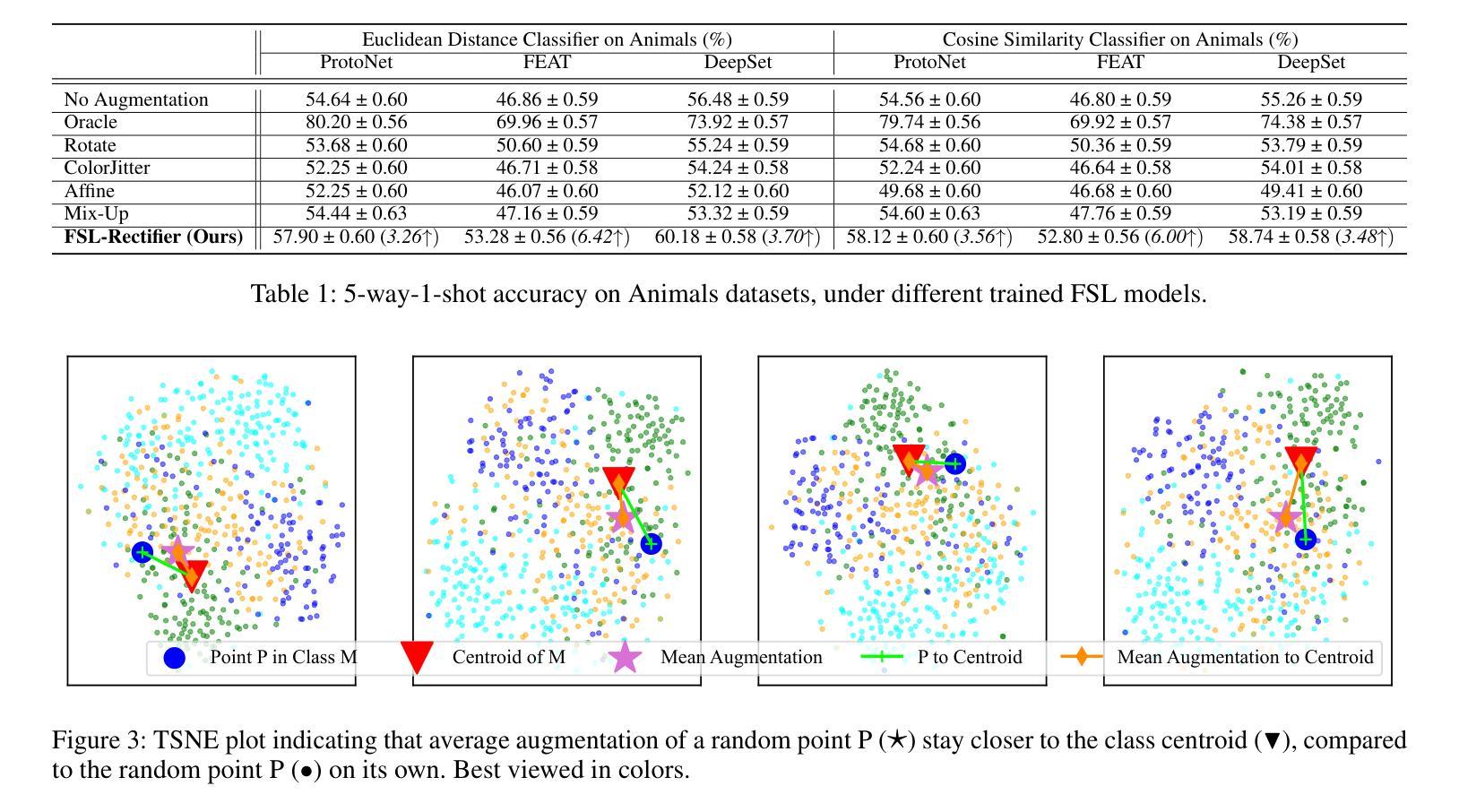
FSL-Rectifier: Rectify Outliers in Few-Shot Learning via Test-Time Augmentation
Authors:Yunwei Bai, Ying Kiat Tan, Shiming Chen, Yao Shu, Tsuhan Chen
Few-shot learning (FSL) commonly requires a model to identify images (queries) that belong to classes unseen during training, based on a few labelled samples of the new classes (support set) as reference. So far, plenty of algorithms involve training data augmentation to improve the generalization capability of FSL models, but outlier queries or support images during inference can still pose great generalization challenges. In this work, to reduce the bias caused by the outlier samples, we generate additional test-class samples by combining original samples with suitable train-class samples via a generative image combiner. Then, we obtain averaged features via an augmentor, which leads to more typical representations through the averaging. We experimentally and theoretically demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, obtaining a test accuracy improvement proportion of around 10% (e.g., from 46.86% to 53.28%) for trained FSL models. Importantly, given a pretrained image combiner, our method is training-free for off-the-shelf FSL models, whose performance can be improved without extra datasets nor further training of the models themselves. Codes are available at https://github.com/WendyBaiYunwei/FSL-Rectifier-Pub.
少量学习(FSL)通常需要模型根据新类别的少量标记样本(支持集)作为参考,识别出属于训练期间未见过的类别的图像(查询)。到目前为止,很多算法都涉及训练数据增强,以提高FSL模型的泛化能力,但在推理过程中,异常查询或支持图像仍然可能带来很大的泛化挑战。在这项工作中,为了减少异常样本引起的偏见,我们通过生成式图像组合器将原始样本与合适的训练集样本相结合,生成额外的测试集类别样本。然后,我们通过增强器获得平均特征,通过平均化得到更典型的表示。我们实验和理论上证明了我们的方法的有效性,对于经过训练的FSL模型,测试精度提高比例约为10%(例如,从46.86%提高到53.28%)。重要的是,给定一个预训练的图像组合器,我们的方法对于现成的FSL模型是无需训练的,可以在不额外使用数据集或对模型本身进行进一步训练的情况下提高性能。代码可在https://github.com/WendyBaiYunwei/FSL-Rectifier-Pub获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To be published in AAAI 2025
Summary
该文本介绍了针对少样本学习(FSL)中模型面对未见类别图像识别的问题,通过生成额外的测试类别样本和平均特征的方法,提高了模型的泛化能力,减少了异常样本对模型的影响。该方法无需额外的数据集或对现有模型进行进一步训练,即可提升模型的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 少样本学习(FSL)在识别未见类别图像时面临挑战。
- 异常查询或支持图像在推理过程中仍然会带来模型泛化挑战。
- 通过生成额外的测试类别样本,结合原始样本和适当的训练类别样本,可以减少异常样本的影响。
- 采用平均特征的方法,得到更典型的表示。
- 实验和理论验证了该方法的有效性,测试准确率提升比例约为10%。
- 该方法适用于现成的FSL模型,无需额外数据集或进一步训练。
点此查看论文截图


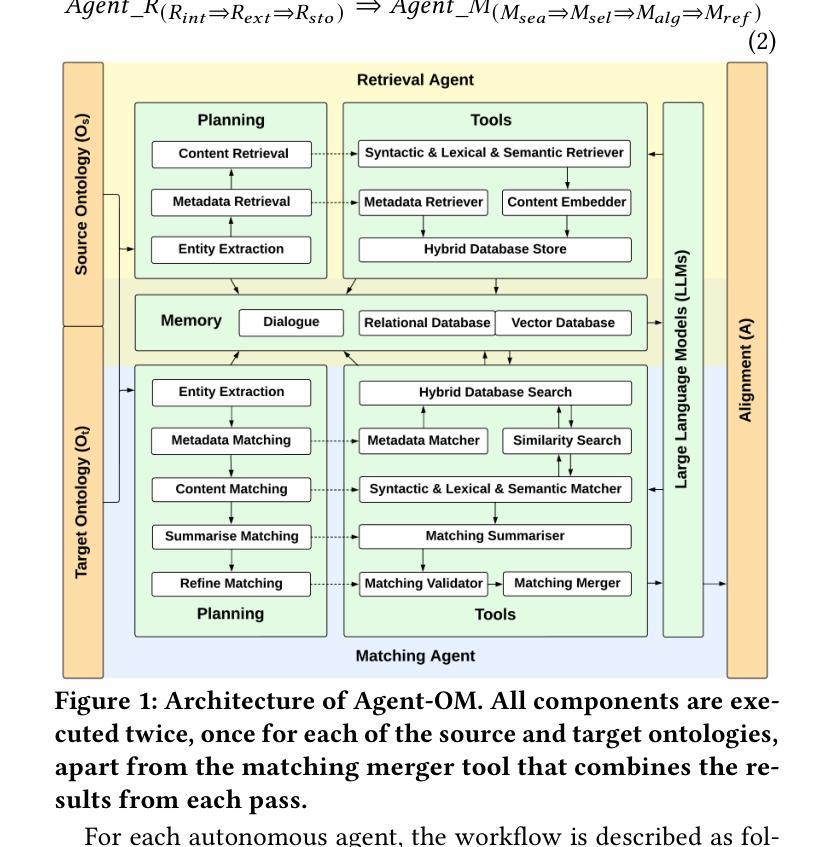
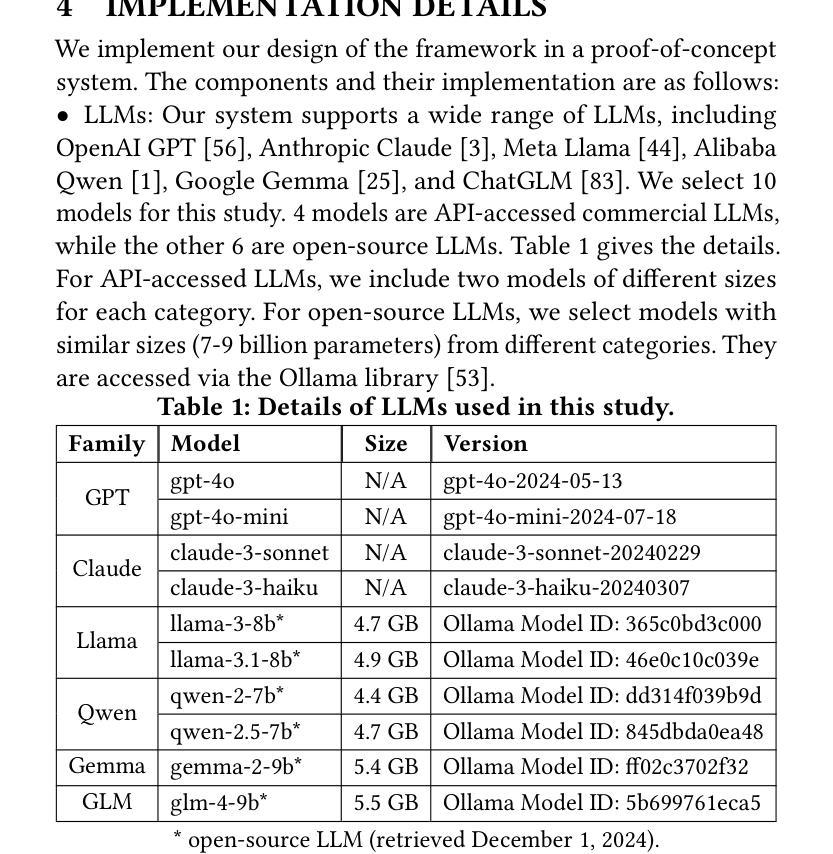
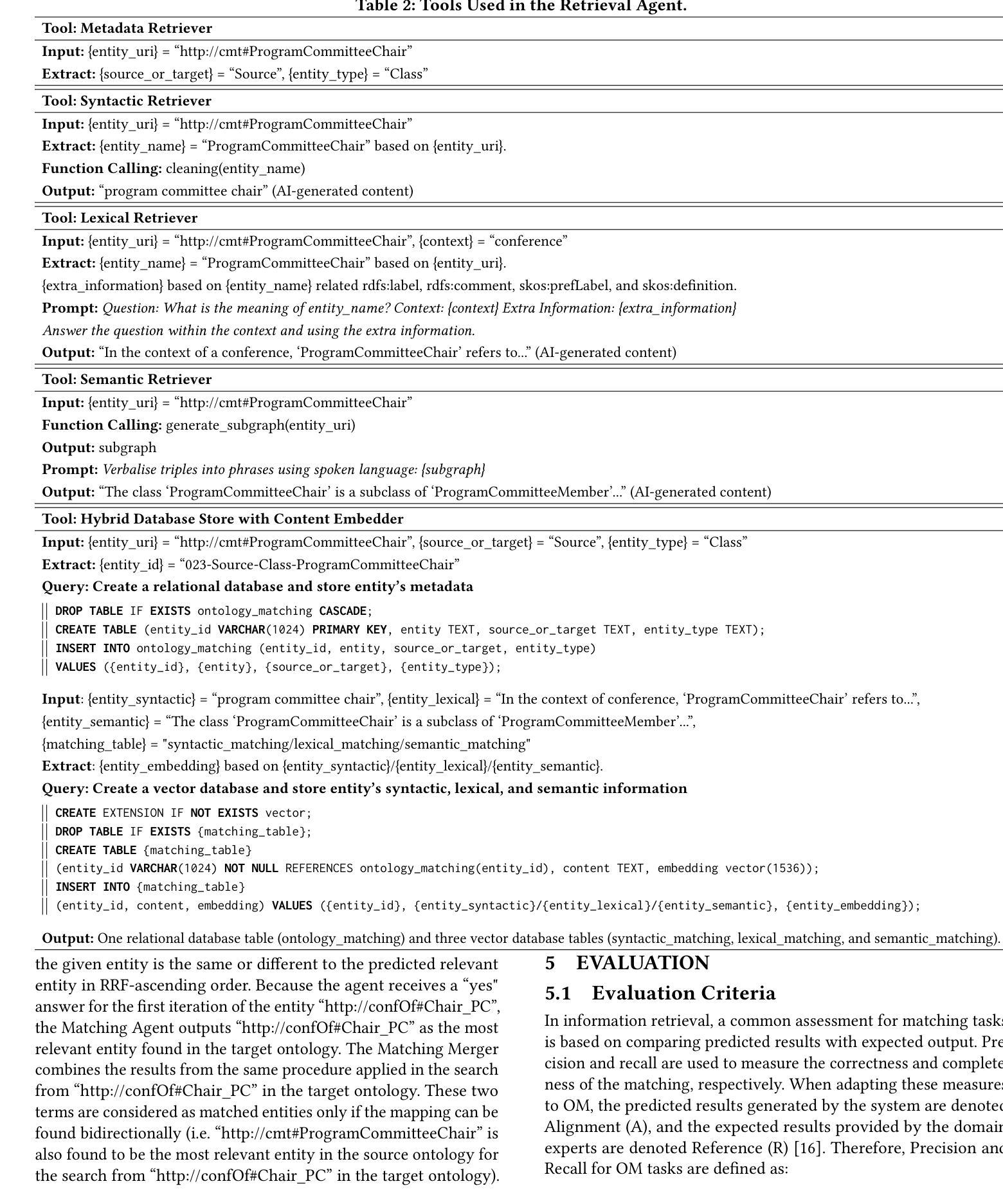
Agent-OM: Leveraging LLM Agents for Ontology Matching
Authors:Zhangcheng Qiang, Weiqing Wang, Kerry Taylor
Ontology matching (OM) enables semantic interoperability between different ontologies and resolves their conceptual heterogeneity by aligning related entities. OM systems currently have two prevailing design paradigms: conventional knowledge-based expert systems and newer machine learning-based predictive systems. While large language models (LLMs) and LLM agents have revolutionised data engineering and have been applied creatively in many domains, their potential for OM remains underexplored. This study introduces a novel agent-powered LLM-based design paradigm for OM systems. With consideration of several specific challenges in leveraging LLM agents for OM, we propose a generic framework, namely Agent-OM (Agent for Ontology Matching), consisting of two Siamese agents for retrieval and matching, with a set of simple OM tools. Our framework is implemented in a proof-of-concept system. Evaluations of three Ontology Alignment Evaluation Initiative (OAEI) tracks over state-of-the-art OM systems show that our system can achieve results very close to the long-standing best performance on simple OM tasks and can significantly improve the performance on complex and few-shot OM tasks.
本体匹配(OM)技术能够在不同的本体之间实现语义互操作性,并通过对齐相关实体解决其概念上的异质性。目前,OM系统主要有两种流行的设计范式:传统的基于知识的专家系统和较新的基于机器学习的预测系统。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)和LLM代理已经彻底改变了数据工程,并在许多领域得到了创造性的应用,但它们在OM中的潜力仍然被低估。本研究引入了一种新型基于LLM的代理驱动设计范式,用于OM系统。考虑到利用LLM代理进行OM所面临的若干挑战,我们提出了一个通用框架,即Agent-OM(用于本体匹配的代理),它包含两个用于检索和匹配的Siamese代理和一套简单的OM工具。我们的框架在一个概念验证系统中实现。对三个本体对齐评估倡议(OAEI)赛道上的最新OM系统的评估表明,我们的系统在简单OM任务上的结果非常接近长期以来的最佳性能,并且在复杂和少量本体匹配任务上可以显著提高性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 13 figures, 4 tables
Summary
本研究提出一种基于新型人工智能技术的智能本体匹配框架Agent-OM,其设计创新地将大型语言模型引入本体匹配系统中,提升系统在复杂和少量数据下的性能表现。通过运用两种智能体(Siamese agents)进行检索和匹配任务,该框架可实现更精准的本体匹配效果。
Key Takeaways
- 本体匹配(OM)通过在不同本体间实现语义互操作性,解决概念异质性问题,促进相关实体的对齐。
- 当前OM系统主要有两种设计范式:基于知识的专家系统和基于机器学习的预测系统。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)和LLM代理在数据工程领域具有革命性应用潜力,但在OM方面的应用尚待探索。
- 本研究提出了一种基于LLM的新型代理驱动OM系统设计范式,即Agent-OM框架。
- Agent-OM框架包含两个Siamese代理,用于检索和匹配任务,并配备一套简单的OM工具。
- 实施了一个概念验证系统来证明Agent-OM的有效性。
点此查看论文截图