⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-21 更新
Adaptive Prompt Tuning: Vision Guided Prompt Tuning with Cross-Attention for Fine-Grained Few-Shot Learning
Authors:Eric Brouwer, Jan Erik van Woerden, Gertjan Burghouts, Matias Valedenegro-Toro, Marco Zullich
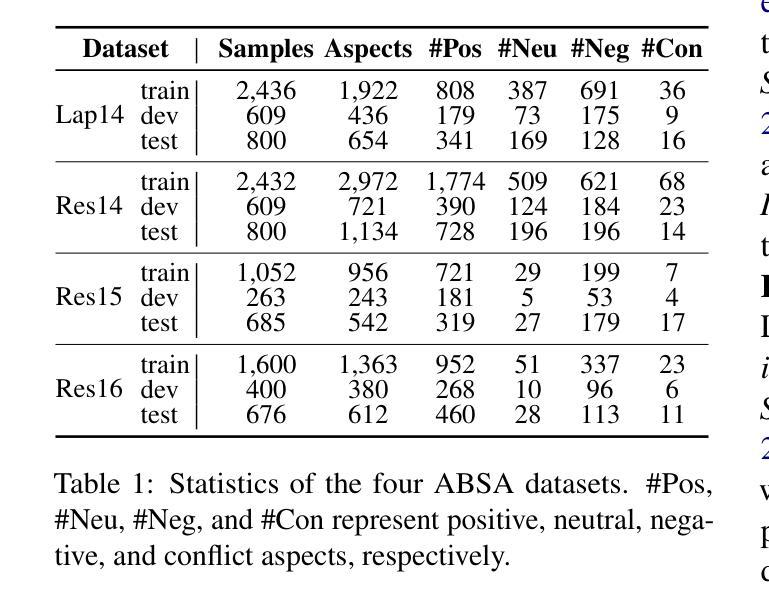
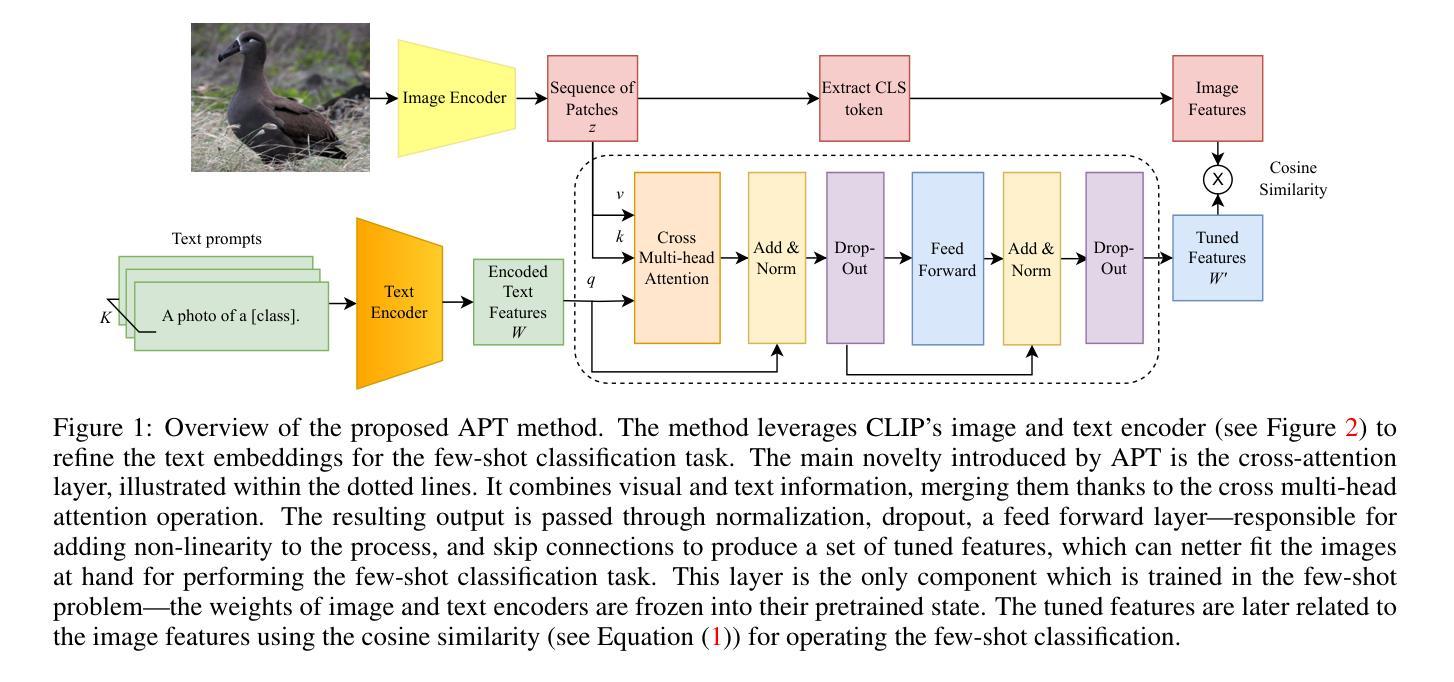
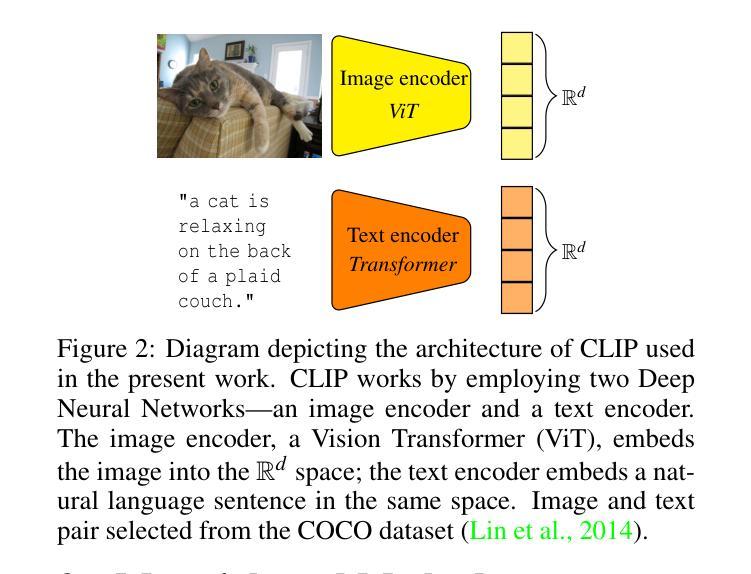
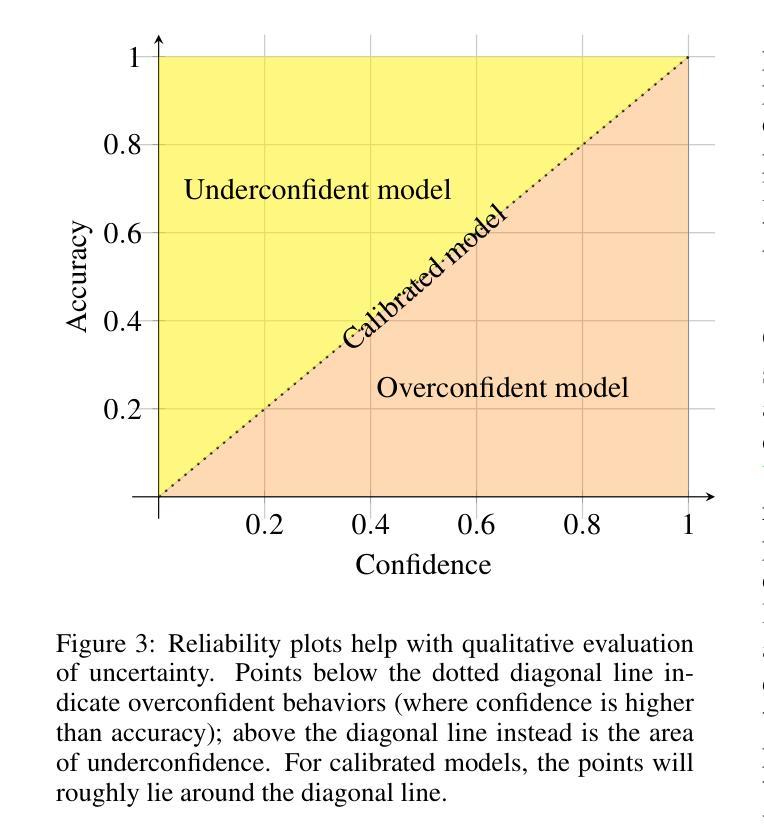
Few-shot, fine-grained classification in computer vision poses significant challenges due to the need to differentiate subtle class distinctions with limited data. This paper presents a novel method that enhances the Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training (CLIP) model through adaptive prompt tuning, guided by real-time visual inputs. Unlike existing techniques such as Context Optimization (CoOp) and Visual Prompt Tuning (VPT), which are constrained by static prompts or visual token reliance, the proposed approach leverages a cross-attention mechanism to dynamically refine text prompts for the image at hand. This enables an image-specific alignment of textual features with image patches extracted from the Vision Transformer, making the model more effective for datasets with high intra-class variance and low inter-class differences. The method is evaluated on several datasets, including CUBirds, Oxford Flowers, and FGVC Aircraft, showing significant performance gains over static prompt tuning approaches. To ensure these performance gains translate into trustworthy predictions, we integrate Monte-Carlo Dropout in our approach to improve the reliability of the model predictions and uncertainty estimates. This integration provides valuable insights into the model’s predictive confidence, helping to identify when predictions can be trusted and when additional verification is necessary. This dynamic approach offers a robust solution, advancing the state-of-the-art for few-shot fine-grained classification.
在计算机视觉领域,小样本精细分类面临重大挑战,因为需要在有限的数据下区分微妙的类别差异。本文针对此提出了一种新方法,它通过自适应提示调整增强对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)模型,并由实时视觉输入进行引导。与现有的上下文优化(CoOp)和视觉提示调整(VPT)等技术不同,这些方法受限于静态提示或视觉标记的依赖,本文提出的方法利用跨注意力机制来动态完善针对当前图像的文本提示。这使得文本特征与从视觉变压器中提取的图像块之间的图像特定对齐成为可能,使模型对于具有高的类内变化和低的类间差异的数据集更为有效。该方法在多个数据集上进行了评估,包括CUBirds、Oxford Flowers和FGVC Aircraft等数据集,显示出相较于静态提示调整方法显著的性能提升。为了确保这些性能提升转化为可靠的预测,我们还将蒙特卡洛Dropout集成到我们的方法中,以提高模型预测和不确定性估计的可靠性。这一集成提供了关于模型预测置信度的宝贵见解,有助于确定何时可以信任预测结果以及何时需要额外的验证。这种动态方法为精细分类的小样本问题提供了稳健的解决方案,并推动了当前的最佳水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于自适应提示调整(Adaptive Prompt Tuning)的对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)模型的新方法,用于解决计算机视觉中的小样本精细分类问题。该方法通过实时视觉输入引导,利用跨注意力机制动态调整文本提示,以提高模型对不同图像的特征对齐能力。在多个数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法在具有低类间差异和高类内差异的数据集上取得了显著的性能提升。同时,通过集成蒙特卡洛Dropout,提高了模型预测的可靠性和不确定性估计的可靠性。这是一种动态的方法,为少样本精细分类问题提供了稳健的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 该方法基于自适应提示调整增强了CLIP模型,解决了小样本精细分类中的挑战。
- 通过实时视觉输入引导,动态调整文本提示,提高模型对不同图像的特征对齐能力。
- 与现有的静态提示调整技术相比,该方法具有显著的性能提升。
- 在多个数据集上的实验验证了该方法的有效性。
- 集成蒙特卡洛Dropout提高了模型预测的可靠性及不确定性估计的可靠性。
- 该方法提供了一个动态解决方案,为少样本精细分类问题提供了稳健的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

Accelerated Patient-Specific Calibration via Differentiable Hemodynamics Simulations
Authors:Diego Renner, Georgios Kissas
One of the goals of personalized medicine is to tailor diagnostics to individual patients. Diagnostics are performed in practice by measuring quantities, called biomarkers, that indicate the existence and progress of a disease. In common cardiovascular diseases, such as hypertension, biomarkers that are closely related to the clinical representation of a patient can be predicted using computational models. Personalizing computational models translates to considering patient-specific flow conditions, for example, the compliance of blood vessels that cannot be a priori known and quantities such as the patient geometry that can be measured using imaging. Therefore, a patient is identified by a set of measurable and nonmeasurable parameters needed to well-define a computational model; else, the computational model is not personalized, meaning it is prone to large prediction errors. Therefore, to personalize a computational model, sufficient information needs to be extracted from the data. The current methods by which this is done are either inefficient, due to relying on slow-converging optimization methods, or hard to interpret, due to using black box deep-learning algorithms. We propose a personalized diagnostic procedure based on a differentiable 0D-1D Navier-Stokes reduced order model solver and fast parameter inference methods that take advantage of gradients through the solver. By providing a faster method for performing parameter inference and sensitivity analysis through differentiability while maintaining the interpretability of well-understood mathematical models and numerical methods, the best of both worlds is combined. The performance of the proposed solver is validated against a well-established process on different geometries, and different parameter inference processes are successfully performed.
个性化医疗的目标之一是针对个体患者进行定制化诊断。在实践中,诊断是通过测量称为生物标志物的数量来进行的,这些生物标志物可以指示疾病的存在和进展。在常见的心血管疾病,如高血压中,可以使用计算模型预测与患者的临床表现密切相关的生物标志物。个性化计算模型意味着要考虑患者特定的流动条件,例如事先不知道的血管顺应性以及可以使用成像测量的患者几何形状等数量。因此,一个患者通过一系列可测量和不可测量的参数来识别,这些参数用于很好地定义计算模型;否则,计算模型不是个性化的,这意味着它存在较大的预测误差。因此,为了个性化计算模型,需要从数据中提取足够的信息。当前完成此操作的方法要么效率低下,因为它们依赖于收敛缓慢的优化方法,要么难以解释,因为它们使用“黑箱”深度学习算法。我们提出了一种基于可微分的一维Navier-Stokes降阶模型求解器和快速参数推断方法的个性化诊断程序。该程序充分利用了求解器中的梯度来进行参数推断和敏感性分析,既提供了快速的方法,又保持了对数学模型和数值方法的理解的可解释性,实现了两者的最佳结合。所提出的求解器的性能在不同的几何形状和不同的参数推断过程中得到了验证,并成功进行了实践。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
个性化医学的目标之一是为患者量身定制诊断方案。通过测量与疾病存在和进展相关的生物标志物来进行诊断。在高血压等常见心血管疾病中,可以使用计算模型预测与病人临床表现密切相关的生物标志物。个性化计算模型需要考虑病人特定的血流条件,如血管顺应性等无法预先知道的因素以及可以通过成像测量的病人几何形状等因素。因此,一个病人通过一组可测量和不可测量的参数来定义计算模型,否则模型无法个性化,预测误差较大。当前从数据中提取信息的方法要么效率低下,依赖收敛缓慢的优化方法,要么难以解释,使用“黑箱”深度学习算法。我们提出了一种基于可微分的0D-1D Navier-Stokes降阶模型求解器和快速参数推断方法的个性化诊断程序,利用求解器的梯度优势进行参数推断和敏感性分析。该方法结合了快速的方法、可理解的数学模型和数值方法。
Key Takeaways
- 个性化医学旨在根据患者的具体情况定制诊断和治疗方案。
- 在心血管疾病中,可以使用计算模型预测与患者的临床表现密切相关的生物标志物。
- 真正的个性化计算模型需要考虑患者特定的血流条件和几何形状。
- 当前的参数提取方法存在效率不高和难以解释的问题。
- 提出的个性化诊断程序结合了快速的方法、可理解的数学模型和数值方法。
- 该方法基于可微分的0D-1D Navier-Stokes降阶模型求解器进行参数推断和敏感性分析。
点此查看论文截图