⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-21 更新
Unified Image Restoration and Enhancement: Degradation Calibrated Cycle Reconstruction Diffusion Model
Authors:Minglong Xue, Jinhong He, Shivakumara Palaiahnakote, Mingliang Zhou
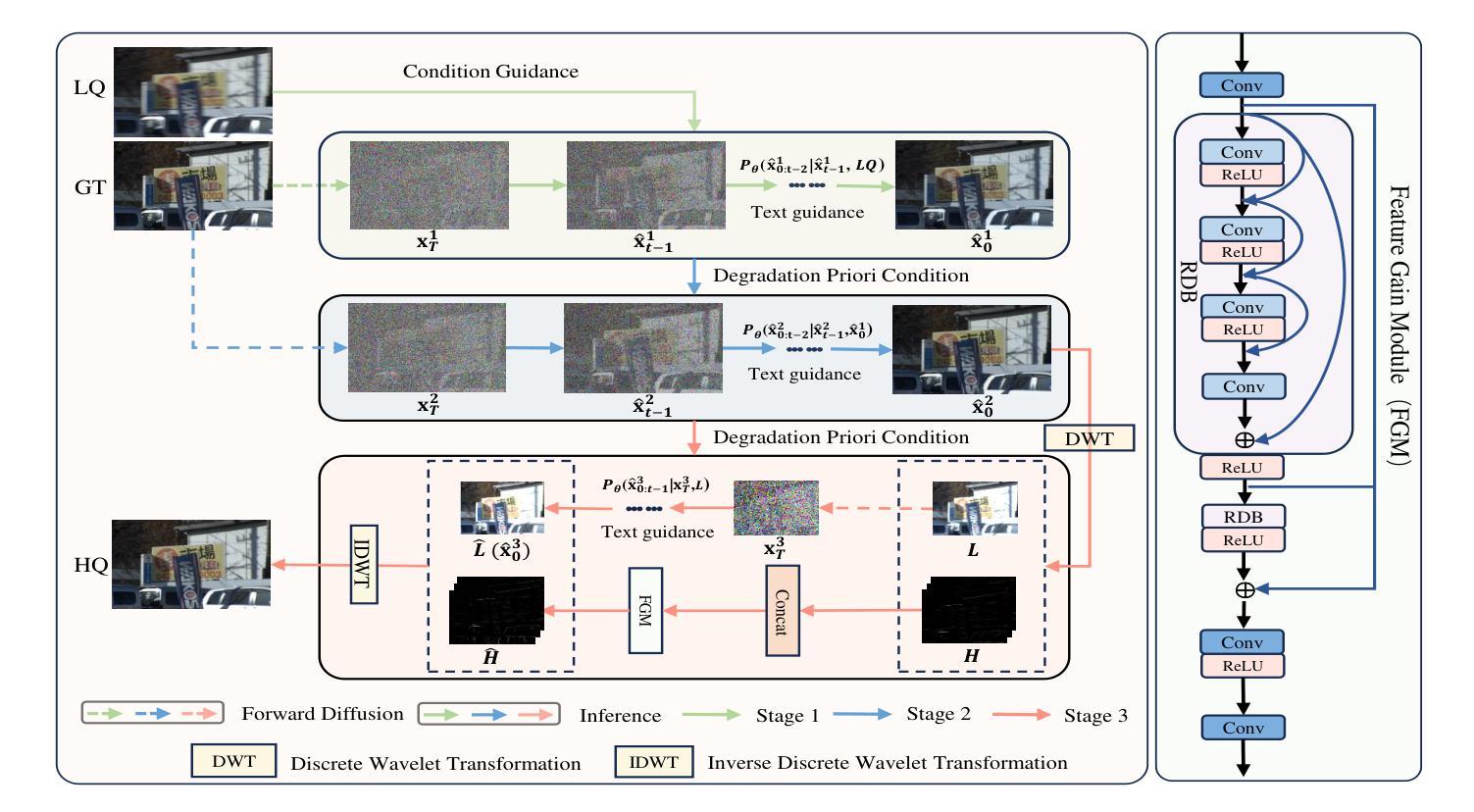
Image restoration and enhancement are pivotal for numerous computer vision applications, yet unifying these tasks efficiently remains a significant challenge. Inspired by the iterative refinement capabilities of diffusion models, we propose CycleRDM, a novel framework designed to unify restoration and enhancement tasks while achieving high-quality mapping. Specifically, CycleRDM first learns the mapping relationships among the degraded domain, the rough normal domain, and the normal domain through a two-stage diffusion inference process. Subsequently, we transfer the final calibration process to the wavelet low-frequency domain using discrete wavelet transform, performing fine-grained calibration from a frequency domain perspective by leveraging task-specific frequency spaces. To improve restoration quality, we design a feature gain module for the decomposed wavelet high-frequency domain to eliminate redundant features. Additionally, we employ multimodal textual prompts and Fourier transform to drive stable denoising and reduce randomness during the inference process. After extensive validation, CycleRDM can be effectively generalized to a wide range of image restoration and enhancement tasks while requiring only a small number of training samples to be significantly superior on various benchmarks of reconstruction quality and perceptual quality. The source code will be available at https://github.com/hejh8/CycleRDM.
图像修复与增强对于众多计算机视觉应用至关重要,然而如何有效地统一这两项任务仍然是一个巨大挑战。受扩散模型的迭代细化能力的启发,我们提出了CycleRDM这一新型框架,旨在统一修复和增强任务,同时实现高质量映射。具体来说,CycleRDM首先通过两阶段扩散推理过程学习退化域、粗略正常域和正常域之间的映射关系。随后,我们通过离散小波变换将最终的校准过程转移到小波低频域,利用任务特定的频率空间,从频率域的角度进行精细校准。为了提高修复质量,我们为分解的小波高频域设计了一个特征增益模块,以消除冗余特征。此外,我们还采用多模式文本提示和傅里叶变换,以驱动稳定的去噪,减少推理过程中的随机性。经过广泛验证,CycleRDM可有效地推广至多种图像修复和增强任务,仅需少量训练样本即可在各种重建质量和感知质量的基准测试中表现卓越。源代码将发布在https://github.com/hejh8/CycleRDM。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
图像修复与增强对于众多计算机视觉应用至关重要,但统一这些任务并高效完成仍是挑战。受扩散模型的启发,我们提出CycleRDM框架,旨在统一修复与增强任务,同时实现高质量映射。它通过两阶段扩散推断学习退化域、粗略正常域和正常域之间的映射关系。随后,通过离散小波变换将最终校准过程转移到小波低频域,利用特定任务的频率空间进行精细校准。为提高修复质量,我们设计针对小波高频域的特征增益模块,消除冗余特征。此外,我们使用多模态文本提示和傅里叶变换推动稳定去噪,减少推断过程中的随机性。CycleRDM可广泛应用于多种图像修复与增强任务,仅需少量训练样本即可在各种重建质量和感知质量基准测试中表现卓越。
Key Takeaways
- CycleRDM框架结合了图像修复和增强的任务,实现了高效的高质量映射。
- 通过两阶段扩散推断学习不同域之间的映射关系。
- 最终校准过程通过离散小波变换转移到小波低频域进行精细校准。
- 框架包含针对小波高频域的特征增益模块以提高修复质量。
- 使用多模态文本提示和傅里叶变换以增强去噪的稳定性并减少推断过程中的随机性。
- CycleRDM可广泛应用于多种图像修复与增强任务,具有强大的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图


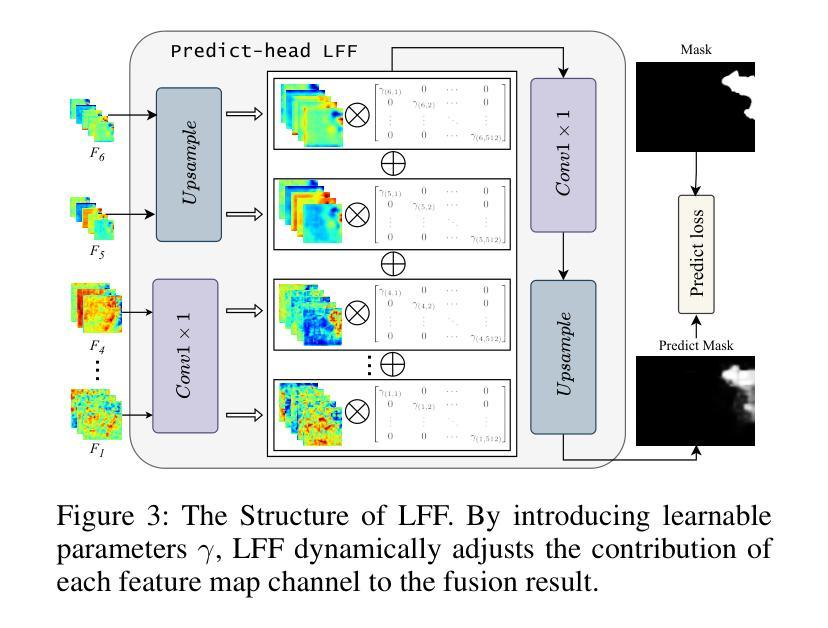
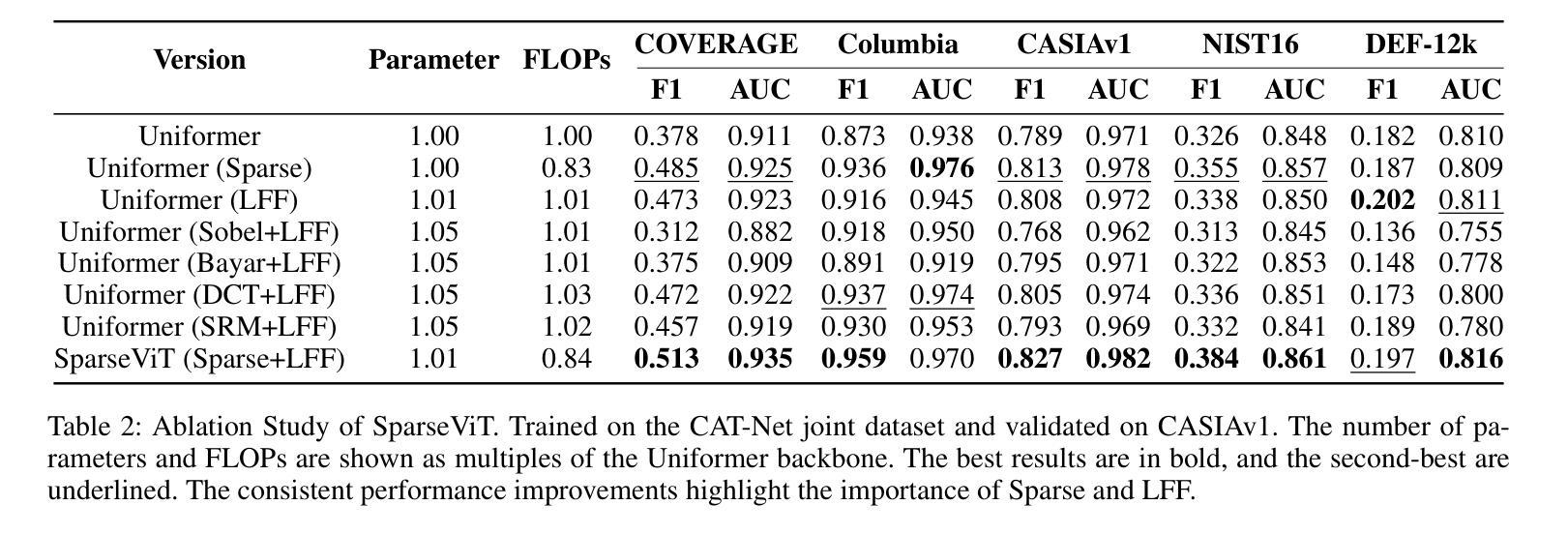
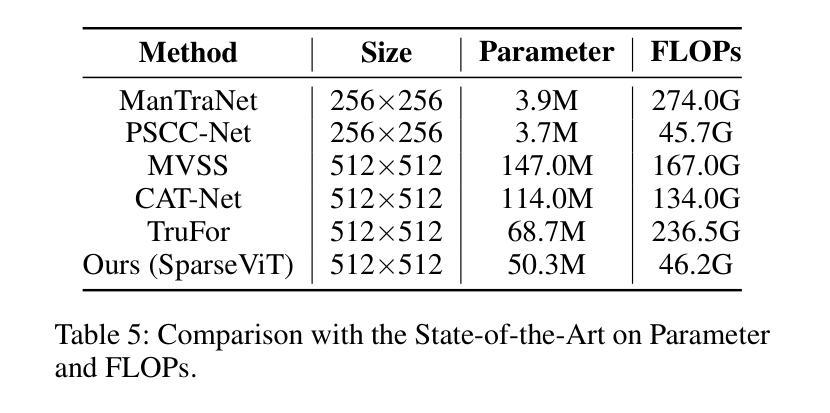
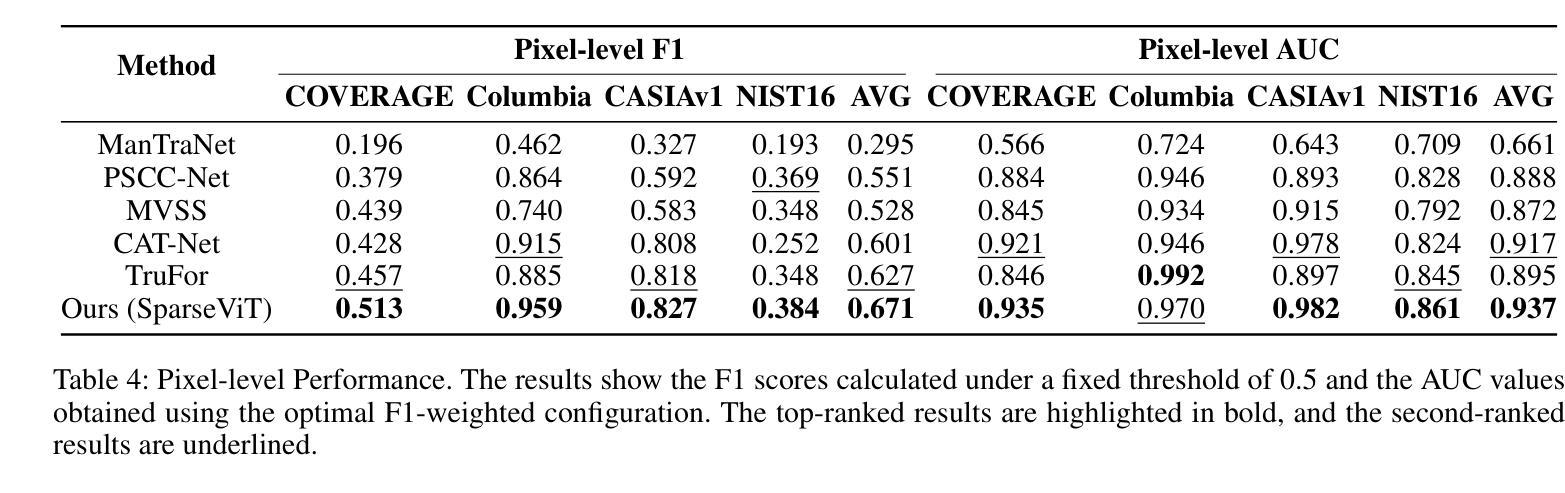
Can We Get Rid of Handcrafted Feature Extractors? SparseViT: Nonsemantics-Centered, Parameter-Efficient Image Manipulation Localization Through Spare-Coding Transformer
Authors:Lei Su, Xiaochen Ma, Xuekang Zhu, Chaoqun Niu, Zeyu Lei, Ji-Zhe Zhou
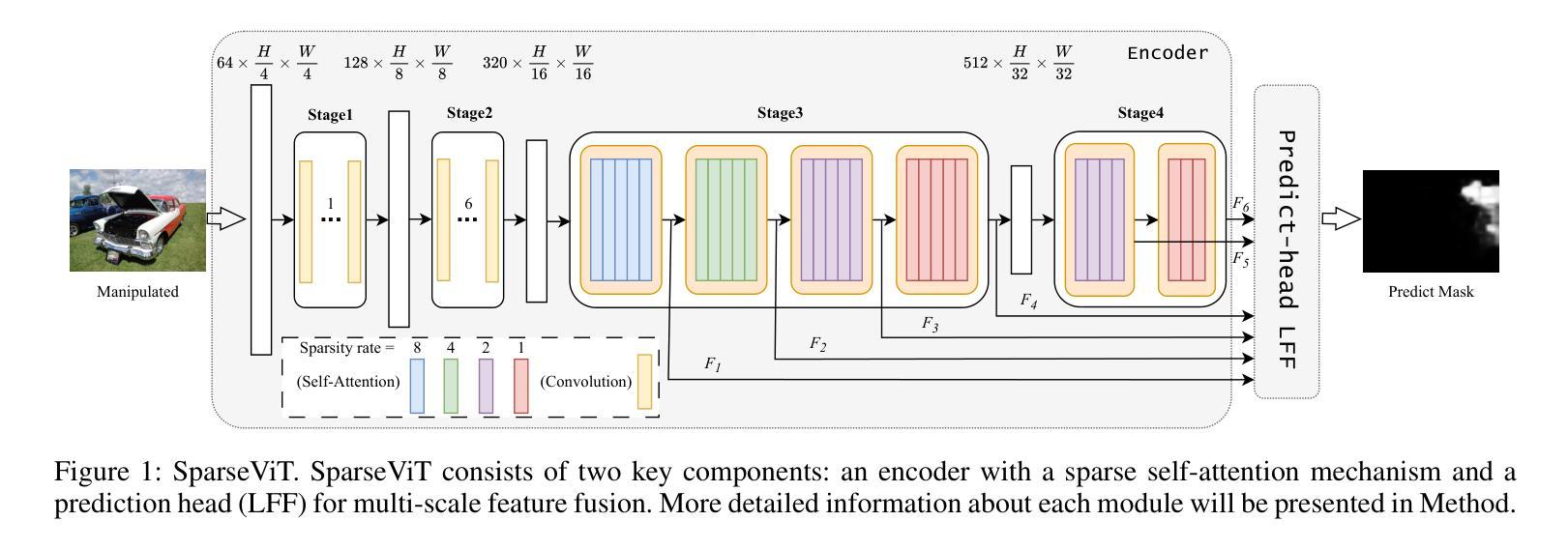
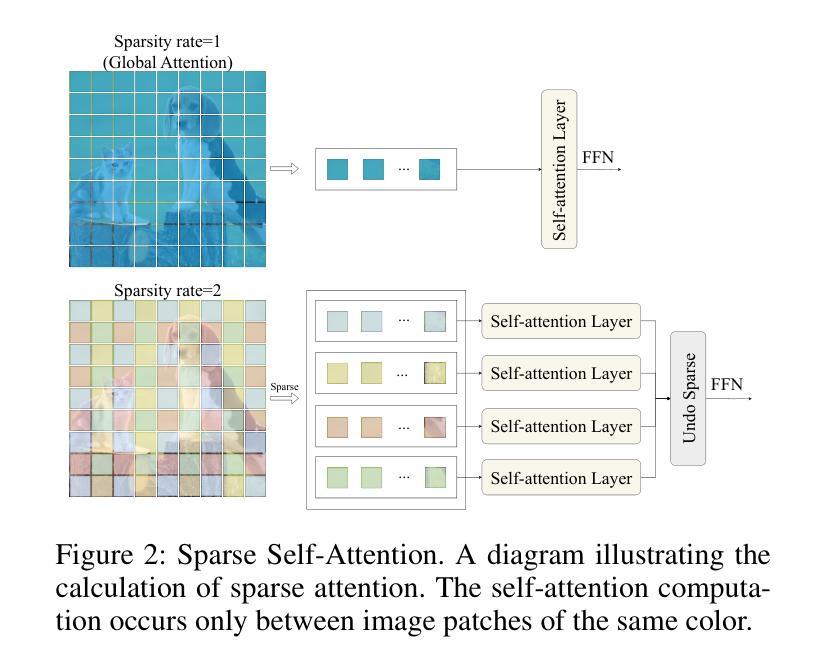
Non-semantic features or semantic-agnostic features, which are irrelevant to image context but sensitive to image manipulations, are recognized as evidential to Image Manipulation Localization (IML). Since manual labels are impossible, existing works rely on handcrafted methods to extract non-semantic features. Handcrafted non-semantic features jeopardize IML model’s generalization ability in unseen or complex scenarios. Therefore, for IML, the elephant in the room is: How to adaptively extract non-semantic features? Non-semantic features are context-irrelevant and manipulation-sensitive. That is, within an image, they are consistent across patches unless manipulation occurs. Then, spare and discrete interactions among image patches are sufficient for extracting non-semantic features. However, image semantics vary drastically on different patches, requiring dense and continuous interactions among image patches for learning semantic representations. Hence, in this paper, we propose a Sparse Vision Transformer (SparseViT), which reformulates the dense, global self-attention in ViT into a sparse, discrete manner. Such sparse self-attention breaks image semantics and forces SparseViT to adaptively extract non-semantic features for images. Besides, compared with existing IML models, the sparse self-attention mechanism largely reduced the model size (max 80% in FLOPs), achieving stunning parameter efficiency and computation reduction. Extensive experiments demonstrate that, without any handcrafted feature extractors, SparseViT is superior in both generalization and efficiency across benchmark datasets.
非语义特征或语义无关特征,虽然与图像上下文无关,但对图像操作很敏感,被公认为是图像操作定位(IML)的证据。由于手动标签是不可能的,现有工作依赖于手工方法提取非语义特征。手工非语义特征会损害IML模型在未见或复杂场景中的泛化能力。因此,对于IML来说,关键问题是:如何自适应地提取非语义特征?非语义特征是上下文无关且对操作敏感的。也就是说,在一张图像内,除非发生操作,否则它们在各个补丁中是一致的。然后,图像补丁之间的稀疏离散交互足以提取非语义特征。然而,不同补丁上的图像语义差异很大,需要密集连续的图像补丁交互来学习语义表示。因此,本文提出了一种稀疏视觉转换器(SparseViT),它将ViT中的密集全局自注意力重新制定为稀疏离散方式。这种稀疏自注意力打破了图像语义,并迫使SparseViT自适应地提取图像的非语义特征。此外,与现有的IML模型相比,稀疏自注意力机制大大减少了模型大小(最多减少80%的浮点运算),实现了惊人的参数效率和计算减少。大量实验表明,无需任何手工特征提取器,SparseViT在基准数据集上在泛化和效率方面都更优越。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 page, 8 figures, published to AAAI
Summary
非语义特征对于图像上下文无关但对图像操作敏感,被视为图像操作定位(IML)的证据。现有作品依赖手工方法提取非语义特征,这损害了IML模型的未见场景和复杂场景的泛化能力。因此,对于IML来说,如何自适应地提取非语义特征是关键问题。本文提出Sparse Vision Transformer(SparseViT),将ViT中的密集全局自注意力改革为稀疏离散方式,打破图像语义并迫使SparseViT自适应提取非语义特征。相比现有IML模型,SparseViT的稀疏自注意力机制大大减少了模型规模,实现了惊人的参数效率和计算减少。
Key Takeaways
- 非语义特征对于图像操作定位(IML)至关重要,但对图像上下文不敏感。
- 现有IML模型依赖手工方法提取非语义特征,这限制了其在未见或复杂场景中的泛化能力。
- Sparse Vision Transformer(SparseViT)被提出以解决上述问题,将密集全局自注意力转化为稀疏离散方式。
- SparseViT能够自适应提取非语义特征,有助于提高IML模型的性能。
- SparseViT的稀疏自注意力机制大大减少了模型规模,提高了参数效率和计算效率。
- 相比其他IML模型,SparseViT在基准数据集上表现出优异的泛化能力和效率。
点此查看论文截图


GenHMR: Generative Human Mesh Recovery
Authors:Muhammad Usama Saleem, Ekkasit Pinyoanuntapong, Pu Wang, Hongfei Xue, Srijan Das, Chen Chen
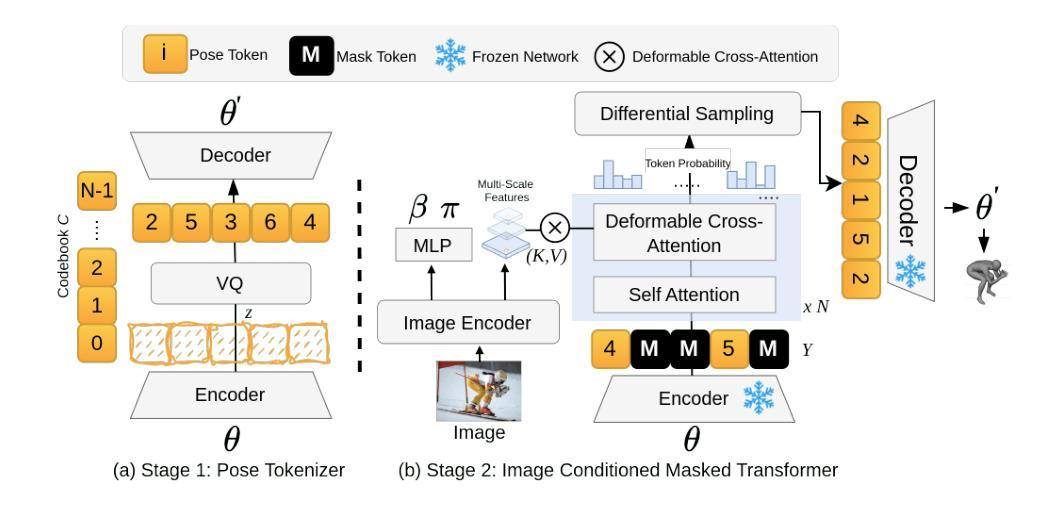
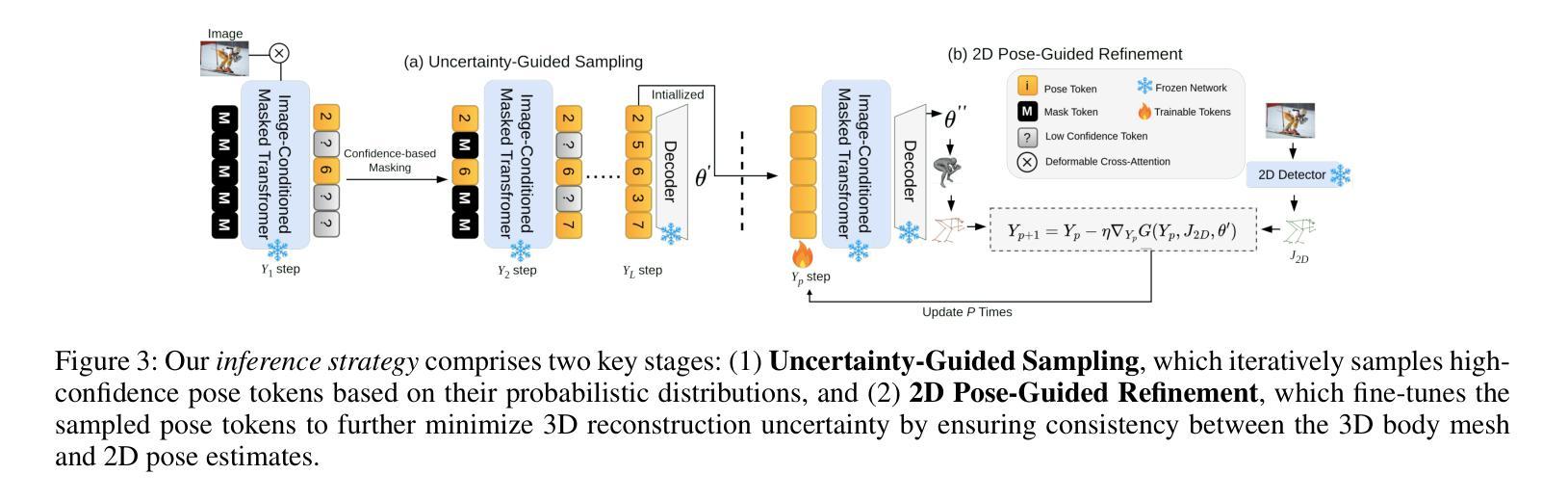
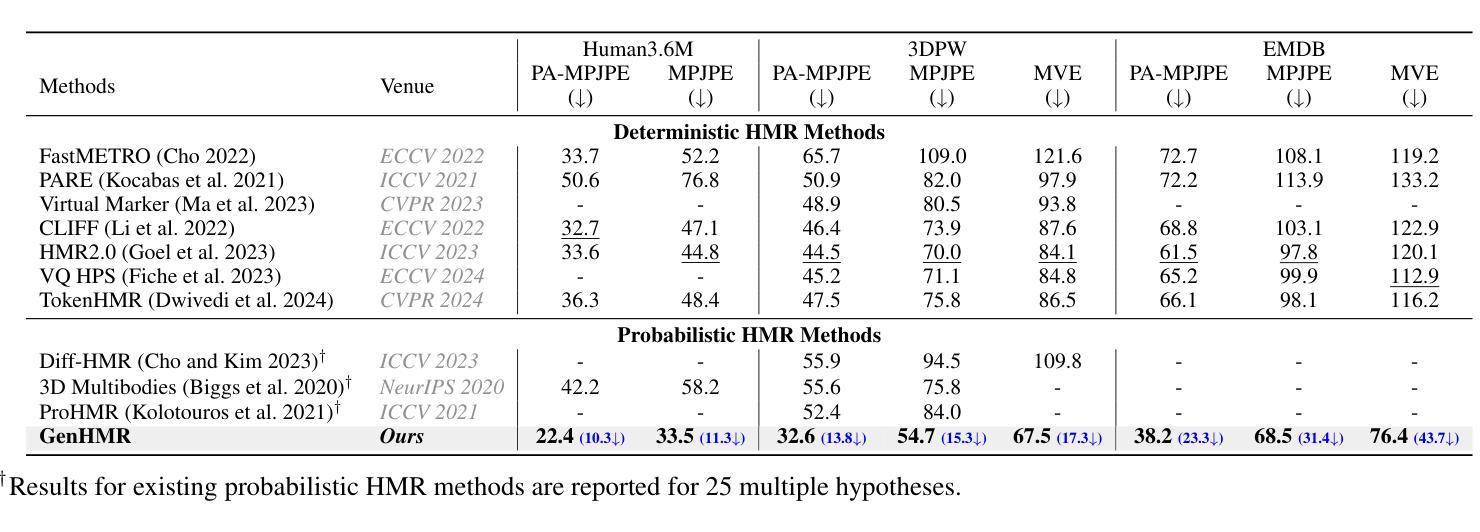
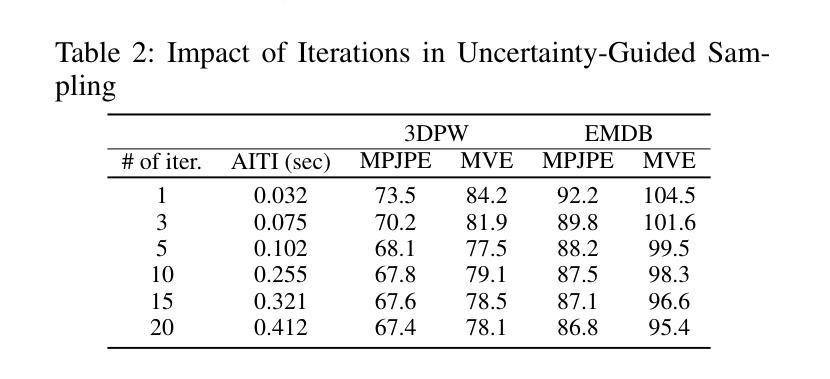
Human mesh recovery (HMR) is crucial in many computer vision applications; from health to arts and entertainment. HMR from monocular images has predominantly been addressed by deterministic methods that output a single prediction for a given 2D image. However, HMR from a single image is an ill-posed problem due to depth ambiguity and occlusions. Probabilistic methods have attempted to address this by generating and fusing multiple plausible 3D reconstructions, but their performance has often lagged behind deterministic approaches. In this paper, we introduce GenHMR, a novel generative framework that reformulates monocular HMR as an image-conditioned generative task, explicitly modeling and mitigating uncertainties in the 2D-to-3D mapping process. GenHMR comprises two key components: (1) a pose tokenizer to convert 3D human poses into a sequence of discrete tokens in a latent space, and (2) an image-conditional masked transformer to learn the probabilistic distributions of the pose tokens, conditioned on the input image prompt along with randomly masked token sequence. During inference, the model samples from the learned conditional distribution to iteratively decode high-confidence pose tokens, thereby reducing 3D reconstruction uncertainties. To further refine the reconstruction, a 2D pose-guided refinement technique is proposed to directly fine-tune the decoded pose tokens in the latent space, which forces the projected 3D body mesh to align with the 2D pose clues. Experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that GenHMR significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods. Project website can be found at https://m-usamasaleem.github.io/publication/GenHMR/GenHMR.html
人体网格恢复(HMR)在许多计算机视觉应用中至关重要,从健康到艺术和娱乐等各个领域都有应用。从单目图像进行HMR研究主要采用的是确定性方法,对给定的2D图像输出单一预测结果。然而,从单张图像进行HMR是一个适定不良的问题,因为存在深度模糊和遮挡。概率方法试图通过生成和融合多种可能的3D重建来解决这个问题,但它们的性能往往落后于确定性方法。在本文中,我们介绍了GenHMR,这是一种新的生成性框架,它将单目HMR重新制定为图像条件生成任务,显式地建模和缓解2D到3D映射过程中的不确定性。GenHMR包含两个关键组件:(1)姿态分词器,将3D人体姿态转换为潜在空间中的一系列离散令牌序列;(2)图像条件掩码变压器,学习姿态令牌的概率分布,该分布受输入图像提示和随机掩码令牌序列的影响。在推理过程中,模型从学习的条件分布中进行采样,以迭代解码高置信度的姿态令牌,从而降低3D重建的不确定性。为了进一步改进重建效果,提出了一种2D姿态引导细化技术,直接在潜在空间中微调解码后的姿态令牌,这强制投影的3D人体网格与2D姿态线索对齐。在基准数据集上的实验表明,GenHMR显著优于最新方法。项目网站地址为:https://m-usamasaleem.github.io/publication/GenHMR/GenHMR.html。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了GenHMR,一种新型生成式框架,用于解决单目人体网格恢复(HMR)问题。通过姿态令牌化和图像条件掩蔽变压器,GenHMR显式建模并缓解2D到3D映射过程中的不确定性。该框架采用迭代解码高置信姿态令牌的方式,进一步细化重建结果,并与二维姿态线索对齐。在基准数据集上的实验表明,GenHMR显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- GenHMR是一个新型生成式框架,用于解决单目人体网格恢复(HMR)。
- GenHMR通过姿态令牌化和图像条件掩蔽变压器,显式建模并缓解2D到3D映射过程中的不确定性。
- 该框架采用迭代解码方式,从学习的条件分布中采样高置信姿态令牌,减少3D重建的不确定性。
- GenHMR采用二维姿态引导细化技术,直接微调解码姿态令牌,使投影的3D人体网格与二维姿态线索对齐。
- GenHMR在基准数据集上的实验表现显著优于现有方法。
- GenHMR的框架包括姿态令牌化模块和图像条件掩蔽变压器模块。这两个模块协同工作,共同处理不确定性和细节重建的问题。
点此查看论文截图

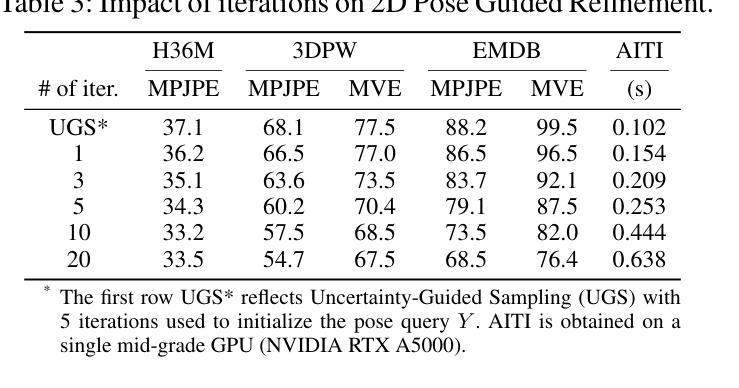
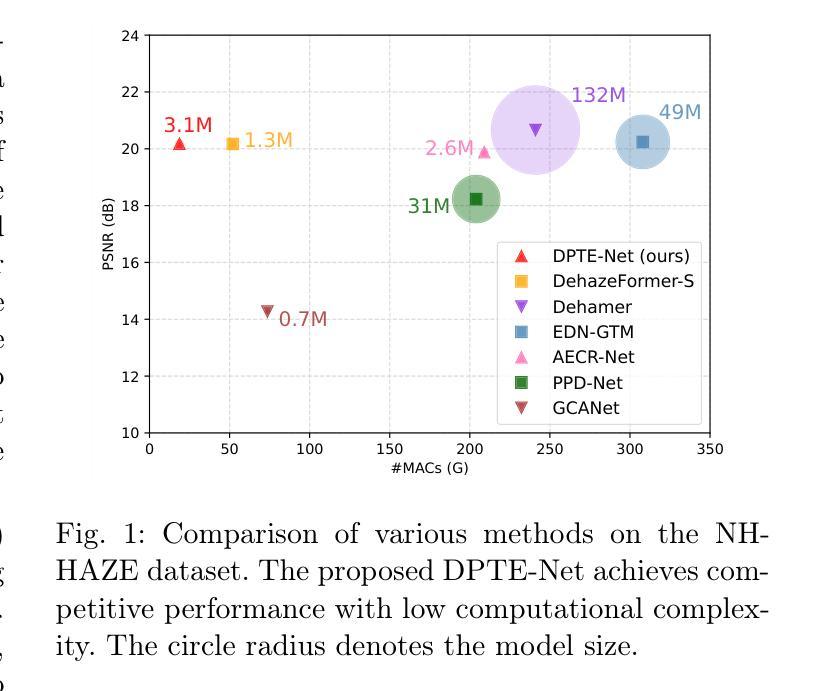
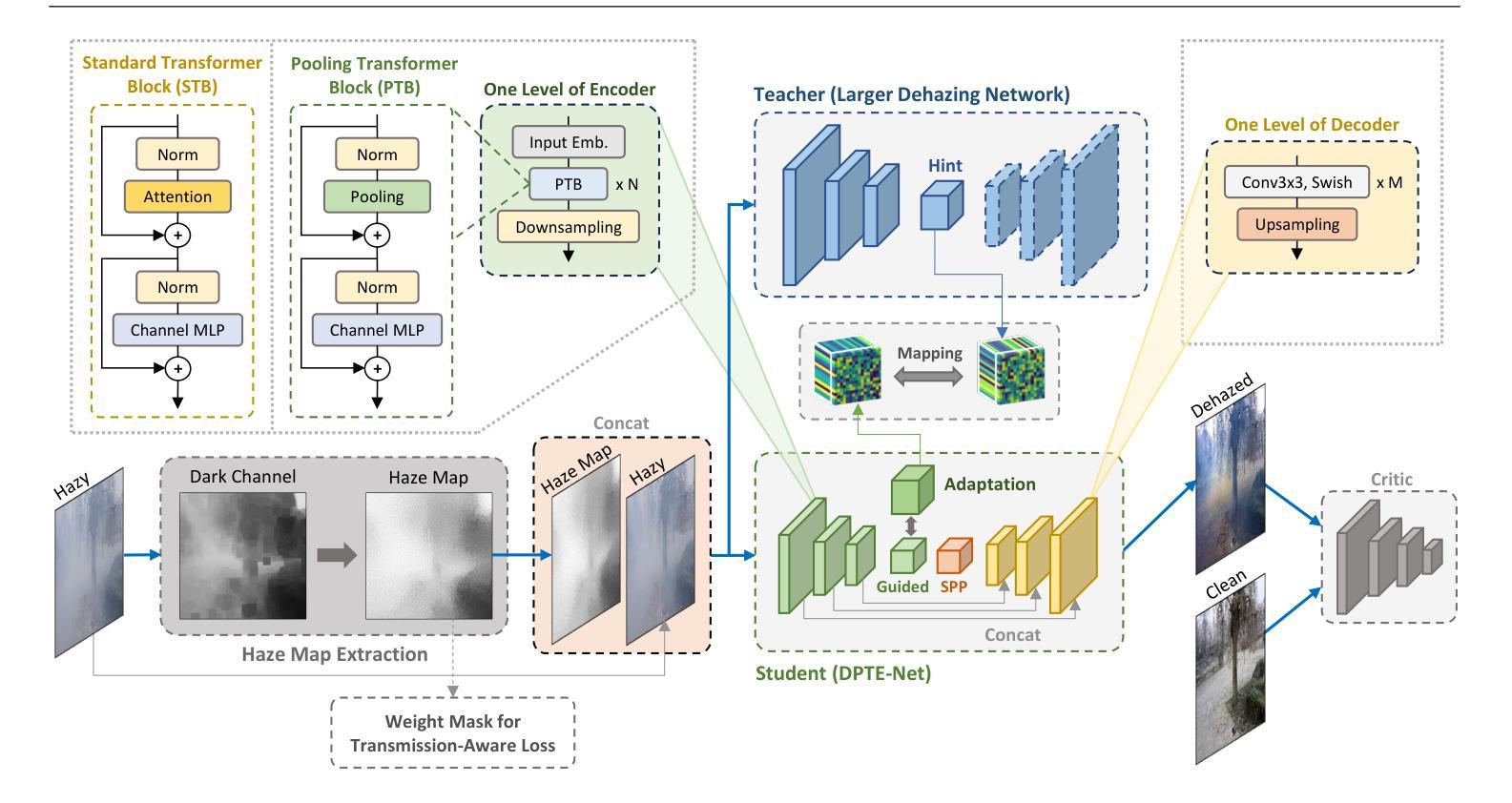
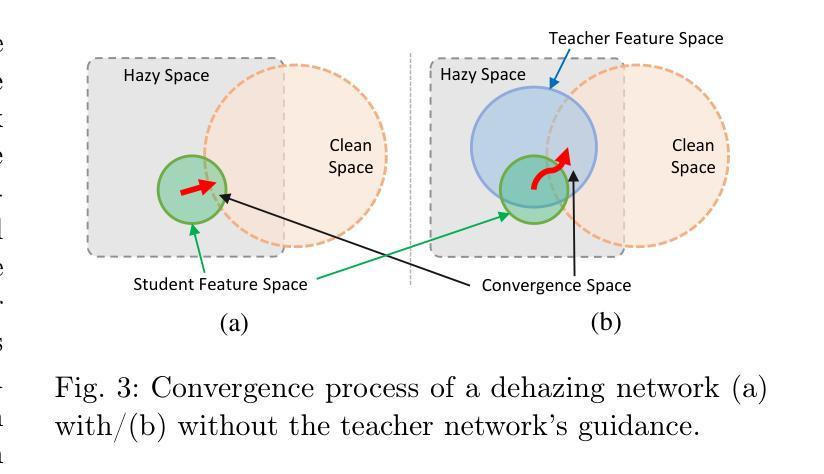
Distilled Pooling Transformer Encoder for Efficient Realistic Image Dehazing
Authors:Le-Anh Tran, Dong-Chul Park
This paper proposes a lightweight neural network designed for realistic image dehazing, utilizing a Distilled Pooling Transformer Encoder, named DPTE-Net. Recently, while vision transformers (ViTs) have achieved great success in various vision tasks, their self-attention (SA) module’s complexity scales quadratically with image resolution, hindering their applicability on resource-constrained devices. To overcome this, the proposed DPTE-Net substitutes traditional SA modules with efficient pooling mechanisms, significantly reducing computational demands while preserving ViTs’ learning capabilities. To further enhance semantic feature learning, a distillation-based training process is implemented which transfers rich knowledge from a larger teacher network to DPTE-Net. Additionally, DPTE-Net is trained within a generative adversarial network (GAN) framework, leveraging the strong generalization of GAN in image restoration, and employs a transmission-aware loss function to dynamically adapt to varying haze densities. Experimental results on various benchmark datasets have shown that the proposed DPTE-Net can achieve competitive dehazing performance when compared to state-of-the-art methods while maintaining low computational complexity, making it a promising solution for resource-limited applications. The code of this work is available at https://github.com/tranleanh/dpte-net.
本文提出了一种为现实图像去雾设计的轻量级神经网络,该网络利用蒸馏池化变压器编码器(Distilled Pooling Transformer Encoder,简称DPTE-Net)。尽管视觉变压器(ViTs)在各种视觉任务中取得了巨大成功,但其自注意力(SA)模块的复杂性会随图像分辨率的平方而增加,这在资源受限的设备上限制了其适用性。为了克服这一问题,所提出的DPTE-Net用高效的池化机制替代了传统的自注意力模块,在保持ViTs学习能力的同时,大大降低了计算需求。为了进一步增强语义特征学习,实施了一种基于蒸馏的训练过程,该过程将大型教师网络中的丰富知识转移到DPTE-Net。此外,DPTE-Net在一个生成对抗网络(GAN)框架内进行训练,利用GAN在图像恢复中的强大泛化能力,并采用一种传输感知损失函数来动态适应不同的雾霾密度。在各种基准数据集上的实验结果表明,与最新方法相比,所提出的DPTE-Net在去雾性能方面表现良好,同时保持较低的计算复杂度,成为资源受限应用的有前途的解决方案。该工作的代码可在https://github.com/tranleanh/dpte-net上获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 17 figures
Summary
本文提出了一种用于现实图像去雾的轻量级神经网络,名为蒸馏池化变压器编码器(DPTE-Net)。针对视觉变压器(ViT)在资源受限设备上应用时自注意力(SA)模块计算复杂度较高的问题,DPTE-Net采用高效的池化机制替代传统SA模块,显著降低了计算需求同时保留了ViTs的学习能力。为进一步提升语义特征学习,实施了一种基于蒸馏的训练过程,从较大的教师网络向DPTE-Net转移丰富知识。此外,DPTE-Net在一个生成对抗网络(GAN)框架下训练,利用其强大的图像恢复泛化能力,并采用传输感知损失函数来适应不同的雾霾密度。实验结果表明,相比现有最佳方法,DPTE-Net在去雾性能上表现有竞争力且计算复杂度较低,使其成为资源受限应用的可行解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- DPTE-Net是一个轻量级的神经网络,专为现实图像去雾设计。
- 利用池化机制替代传统的自注意力模块以降低计算复杂度。
- 实施基于蒸馏的训练过程,从大型教师网络转移知识到DPTE-Net。
- 在GAN框架下训练DPTE-Net,利用其在图像恢复中的强大泛化能力。
- 采用传输感知损失函数来适应不同雾霾密度。
- 在多个基准数据集上的实验结果表明DPTE-Net具有竞争力的去雾性能。
点此查看论文截图


One Pixel is All I Need
Authors:Deng Siqin, Zhou Xiaoyi
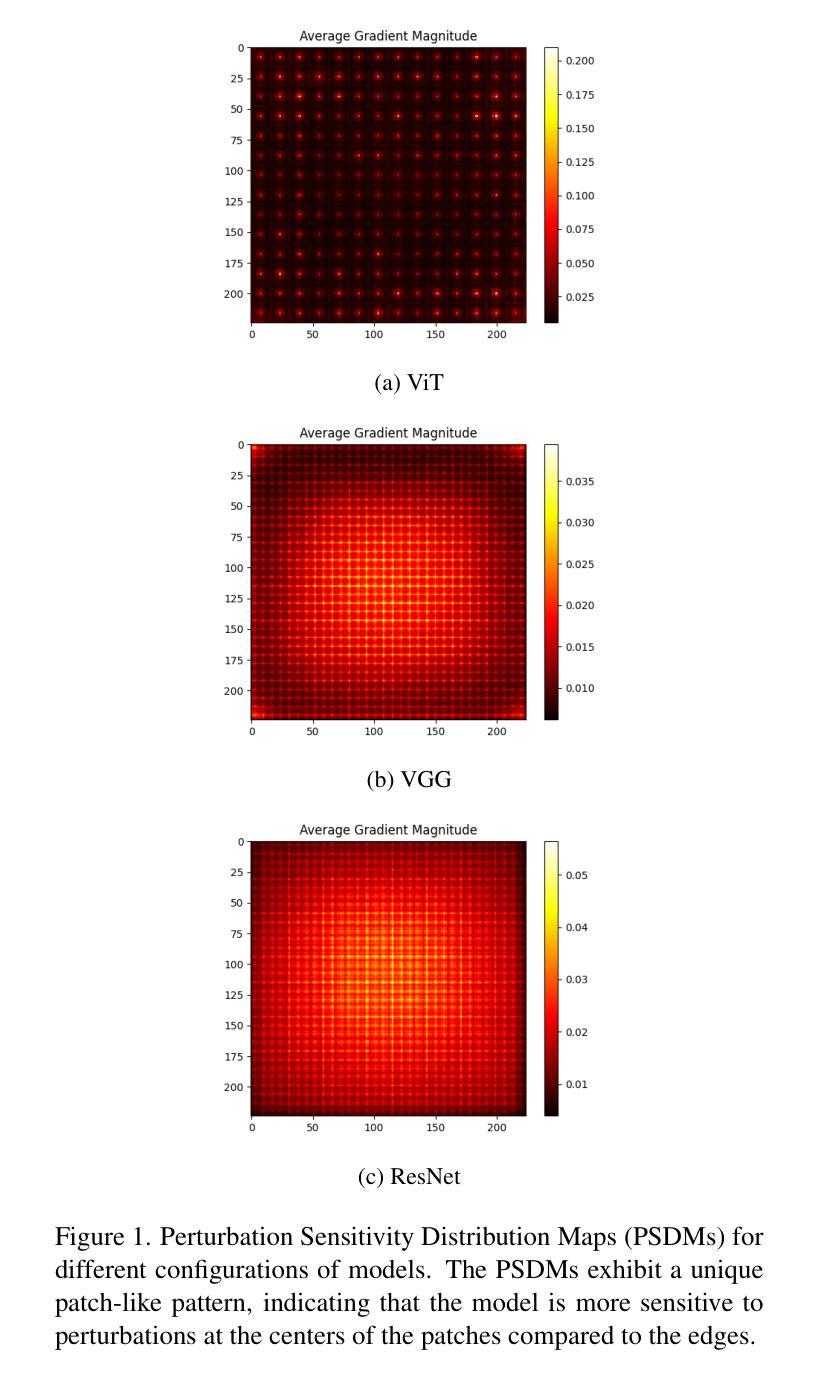
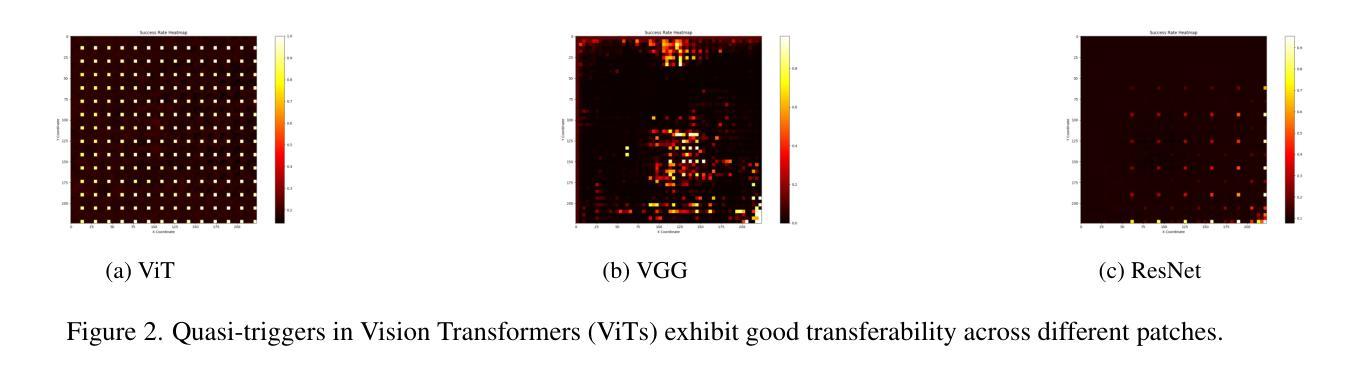
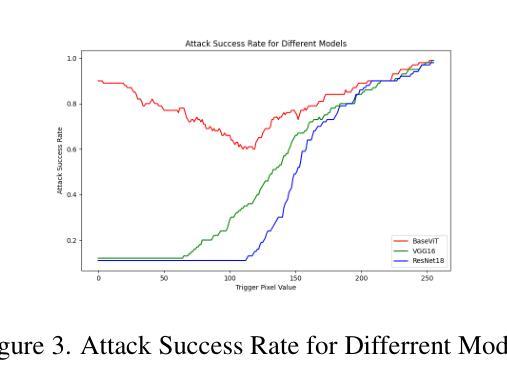
Vision Transformers (ViTs) have achieved record-breaking performance in various visual tasks. However, concerns about their robustness against backdoor attacks have grown. Backdoor attacks involve associating a specific trigger with a target label, causing the model to predict the attacker-specified label when the trigger is present, while correctly identifying clean images.We found that ViTs exhibit higher attack success rates for quasi-triggers(patterns different from but similar to the original training triggers)compared to CNNs. Moreover, some backdoor features in clean samples can suppress the original trigger, making quasi-triggers more effective.To better understand and exploit these vulnerabilities, we developed a tool called the Perturbation Sensitivity Distribution Map (PSDM). PSDM computes and sums gradients over many inputs to show how sensitive the model is to small changes in the input. In ViTs, PSDM reveals a patch-like pattern where central pixels are more sensitive than edges. We use PSDM to guide the creation of quasi-triggers.Based on these findings, we designed “WorstVIT,” a simple yet effective data poisoning backdoor for ViT models. This attack requires an extremely low poisoning rate, trains for just one epoch, and modifies a single pixel to successfully attack all validation images.
视觉Transformer(ViTs)在各种视觉任务中取得了突破性的性能。然而,人们对它们对抗后门攻击的稳健性越来越担忧。后门攻击涉及将特定触发因素与目标标签相关联,当存在触发因素时,导致模型预测攻击者指定的标签,同时正确识别干净图像。我们发现,与CNN相比,ViT对类似但不同于原始训练触发的准触发(模式)表现出更高的攻击成功率。此外,干净样本中的一些后门特征可以抑制原始触发,使准触发更加有效。为了更好地利用这些漏洞,我们开发了一个名为扰动敏感性分布图(PSDM)的工具。PSDM计算并汇总多个输入的梯度,以显示模型对输入微小变化的敏感性。在ViTs中,PSDM呈现了一种类似补丁的模式,其中中央像素比边缘更敏感。我们使用PSDM来指导准触发的创建。基于这些发现,我们为ViT模型设计了名为“WorstVIT”的简单而有效的数据中毒后门。这种攻击需要极低的中毒率,只需一个训练周期,并修改单个像素即可成功攻击所有验证图像。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
ViT模型在视觉任务中表现出卓越性能,但其对后门攻击的鲁棒性引发关注。研究发现,ViT对类触发式攻击(quasi-triggers)的防御较弱,且清洁样本中的后门特征可能增强类触发式攻击的效果。为探究这些漏洞,研究团队提出扰动敏感性分布图(PSDM),揭示ViT模型在中央像素与边缘像素的敏感性差异,并据此指导类触发式攻击的设计。基于这些发现,团队开发出针对ViT模型的“WorstVIT”攻击方法,其仅需极低的感染率、短期训练,并只需修改单一像素即可成功攻击所有验证图像。
Key Takeaways
- ViT模型对后门攻击(尤其是类触发式攻击)的防御能力较弱。
- 与CNN相比,ViT模型在面临类触发式攻击时表现出更高的攻击成功率。
- 清洁样本中的后门特征可能增强类触发式攻击的效果。
- PSDM能有效展示模型对输入微小变化的敏感性,揭示ViT模型的补丁状模式,即中央像素比边缘像素更敏感。
- PSDM用于指导类触发式攻击的设计。
- “WorstVIT”攻击方法针对ViT模型,具有低感染率、短期训练、单一像素修改的特点。
- “WorstVIT”攻击能成功影响所有验证图像。
点此查看论文截图