⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-24 更新
Convolutional Deep Operator Networks for Learning Nonlinear Focused Ultrasound Wave Propagation in Heterogeneous Spinal Cord Anatomy
Authors:Avisha Kumar, Xuzhe Zhi, Zan Ahmad, Minglang Yin, Amir Manbachi
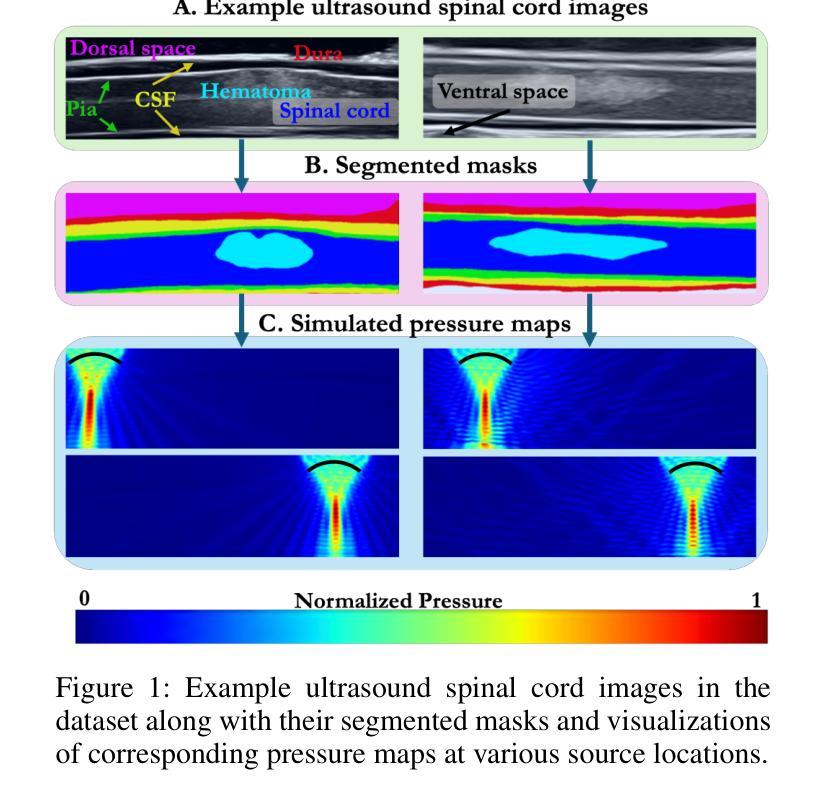
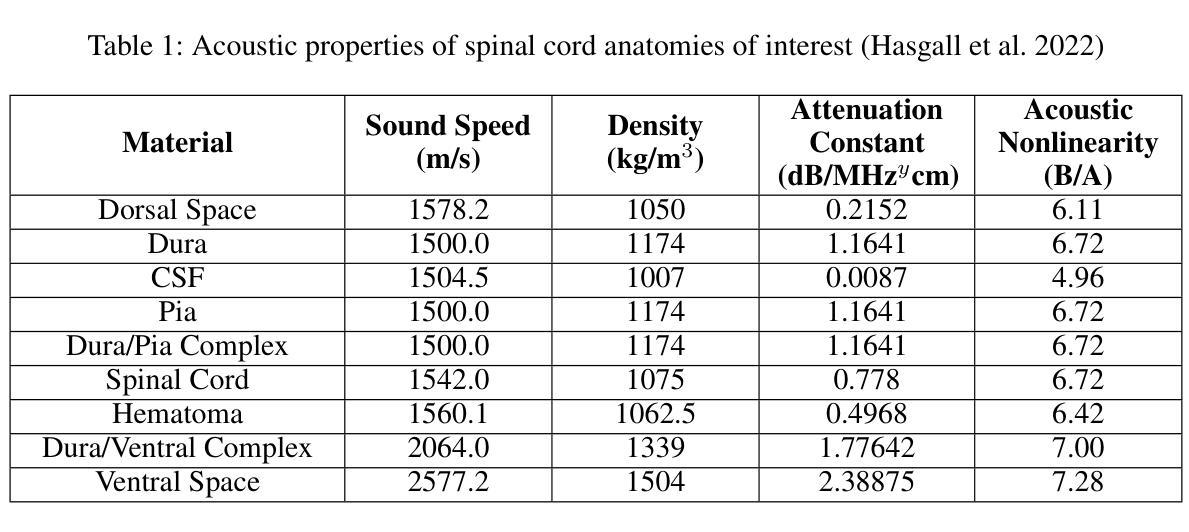
Focused ultrasound (FUS) therapy is a promising tool for optimally targeted treatment of spinal cord injuries (SCI), offering submillimeter precision to enhance blood flow at injury sites while minimizing impact on surrounding tissues. However, its efficacy is highly sensitive to the placement of the ultrasound source, as the spinal cord’s complex geometry and acoustic heterogeneity distort and attenuate the FUS signal. Current approaches rely on computer simulations to solve the governing wave propagation equations and compute patient-specific pressure maps using ultrasound images of the spinal cord anatomy. While accurate, these high-fidelity simulations are computationally intensive, taking up to hours to complete parameter sweeps, which is impractical for real-time surgical decision-making. To address this bottleneck, we propose a convolutional deep operator network (DeepONet) to rapidly predict FUS pressure fields in patient spinal cords. Unlike conventional neural networks, DeepONets are well equipped to approximate the solution operator of the parametric partial differential equations (PDEs) that govern the behavior of FUS waves with varying initial and boundary conditions (i.e., new transducer locations or spinal cord geometries) without requiring extensive simulations. Trained on simulated pressure maps across diverse patient anatomies, this surrogate model achieves real-time predictions with only a 2% loss on the test set, significantly accelerating the modeling of nonlinear physical systems in heterogeneous domains. By facilitating rapid parameter sweeps in surgical settings, this work provides a crucial step toward precise and individualized solutions in neurosurgical treatments.
聚焦超声(FUS)疗法对脊髓损伤(SCI)的精准治疗具有巨大潜力。这一技术能以亚毫米精度提升损伤部位的血流,同时尽量减少对周围组织的冲击。然而,其疗效对超声源的位置极为敏感,因为脊髓的复杂几何结构和声学异质性会干扰和减弱FUS信号。目前的方法依赖于计算机模拟来解决主导波传播的方程,并使用脊髓解剖的超声图像计算患者特定的压力图。虽然这些高保真模拟非常准确,但它们计算量大,完成参数扫描可能需要数小时,这对于实时手术决策来说不太实际。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种卷积深度操作网络(DeepONet)来快速预测患者脊髓中的FUS压力场。与传统的神经网络不同,DeepONets能够很好地逼近解决参数偏微分方程(PDEs)的解决方案算子,这些偏微分方程主导了在不同初始和边界条件下(即新的换能器位置或脊髓几何形状)FUS波的行为,无需进行大量模拟。该代理模型经过多种患者解剖结构的模拟压力图训练,测试集上仅损失2%,即可实现实时预测,显著加速了异质领域中非线性物理系统的建模。通过促进手术环境中的快速参数扫描,这项工作为神经手术治疗的精确和个性化解决方案提供了关键一步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for oral presentation at AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence: AI for Accelerating Science and Engineering Workshop 2025
Summary
基于超声波图像的病患脊髓DeepONet压力场预测模型研究。该研究利用深度学习技术,通过构建DeepONet模型快速预测患者脊髓中的超声波压力场,以优化脊髓损伤治疗的超声源定位,同时简化高保真模拟的耗时计算,促进手术决策的快速实施。模型的构建有助于提高手术治疗的神经科学个性化精确性和效率。
Key Takeaways
- Focused ultrasound(FUS)疗法针对脊髓损伤(SCI)具有精准治疗潜力。
- FUS疗法对超声源的放置位置要求极高,需精确至亚毫米级别。
- 当前依赖计算机模拟解决声波传播方程的问题,通过计算患者的个性化压力图谱分析脊髓解剖的超声波图像。这些模拟虽准确但计算量大。
点此查看论文截图

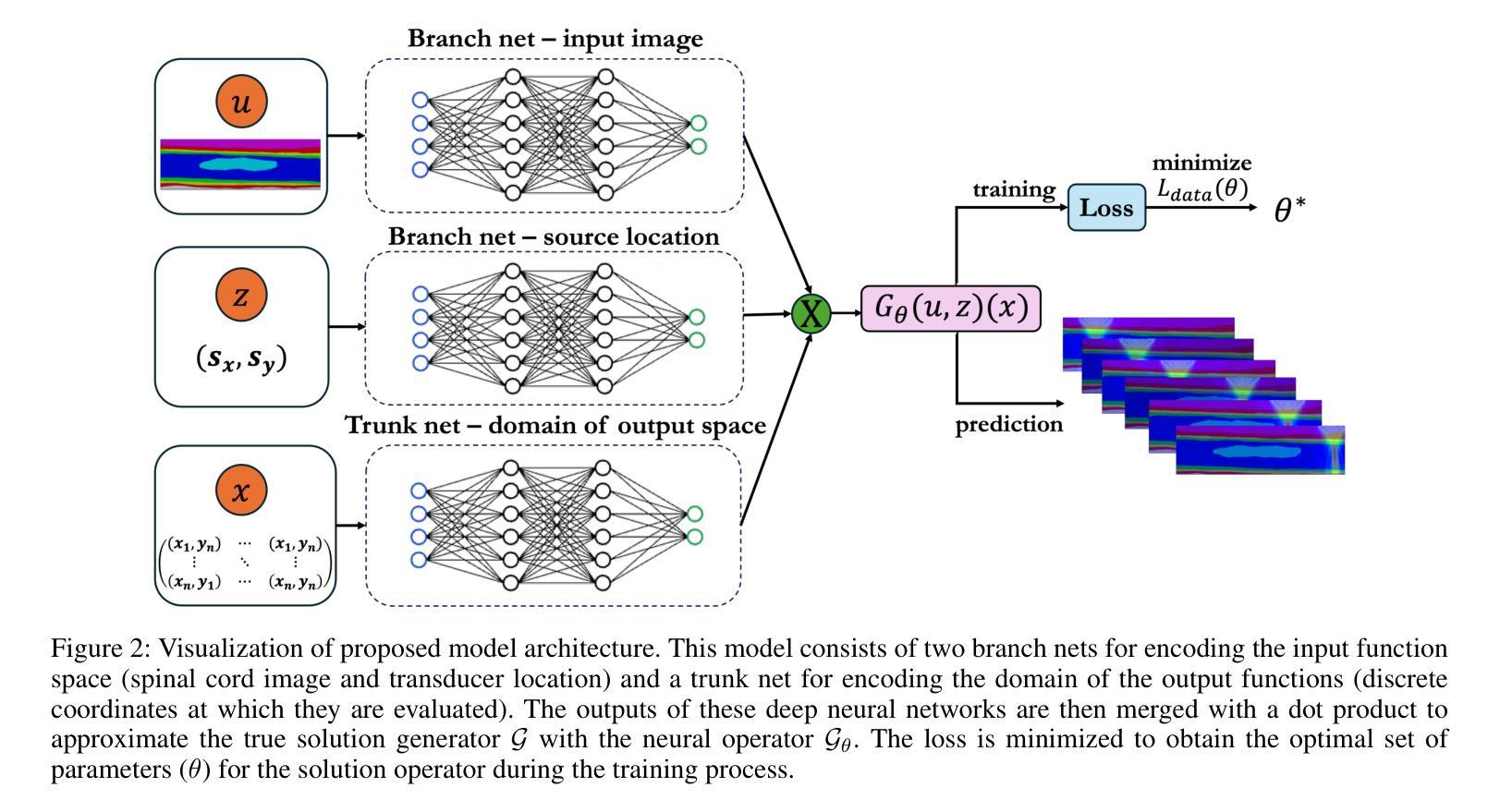
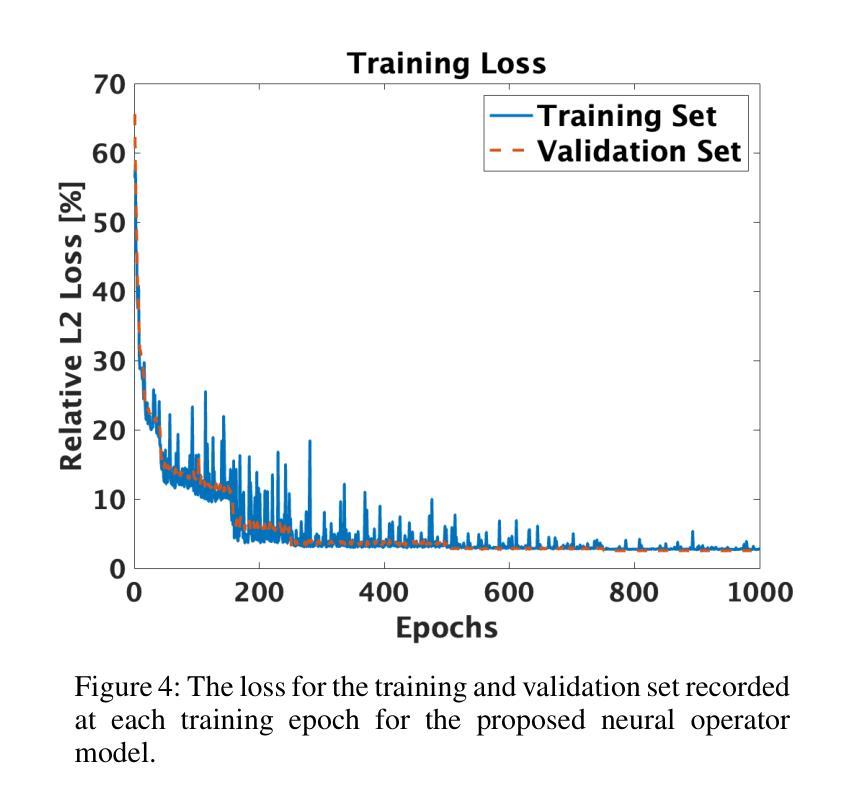
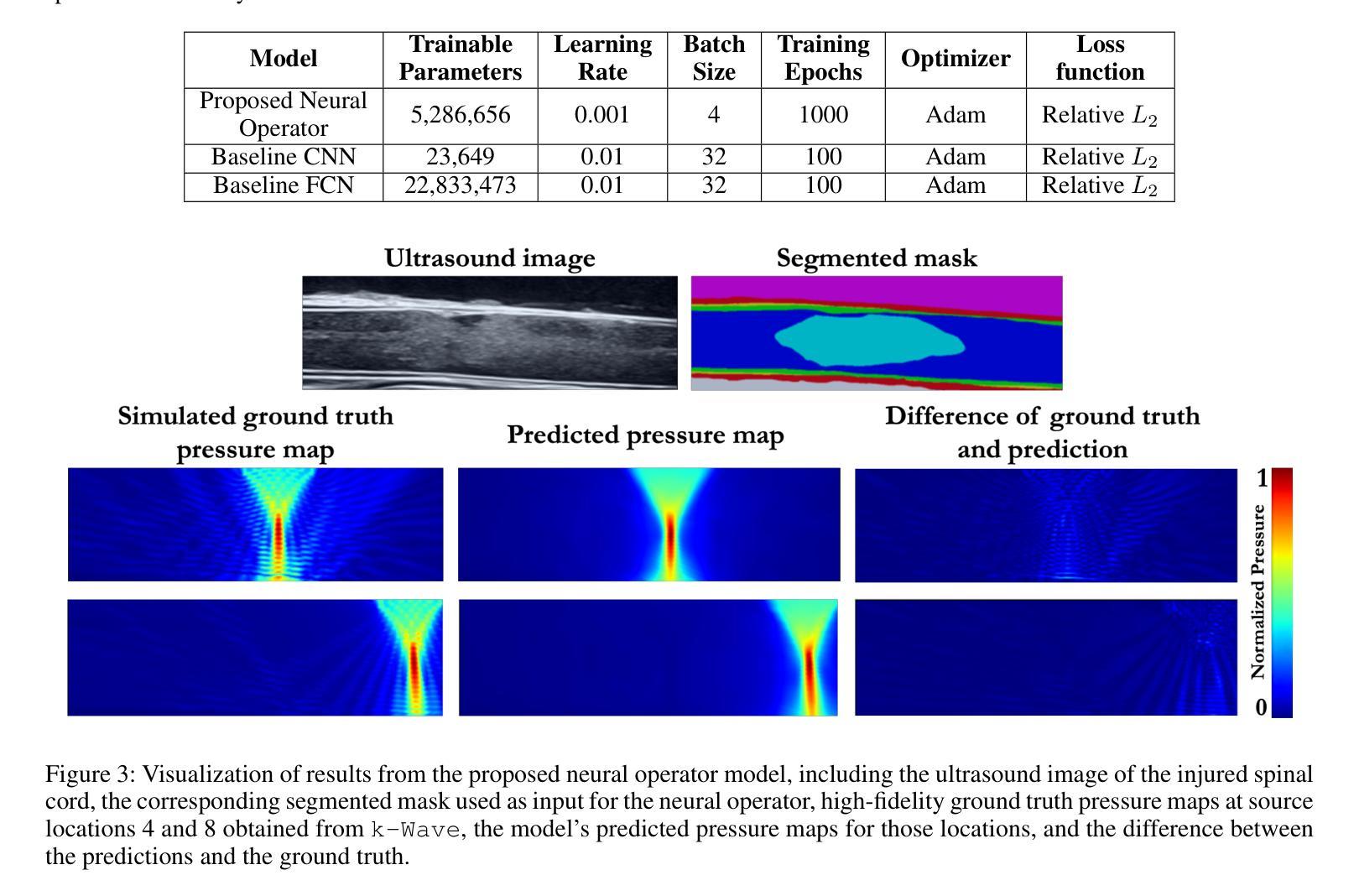
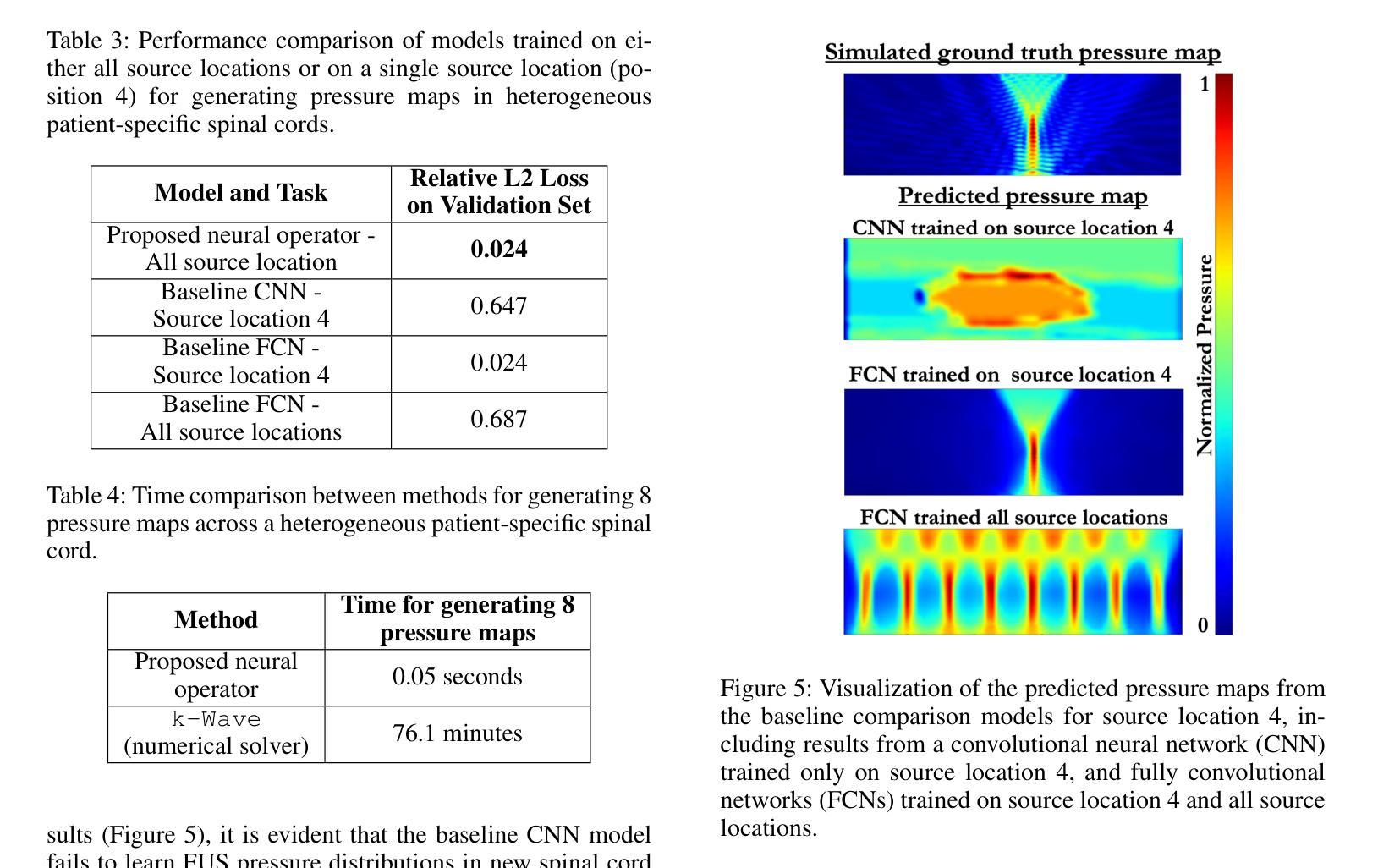
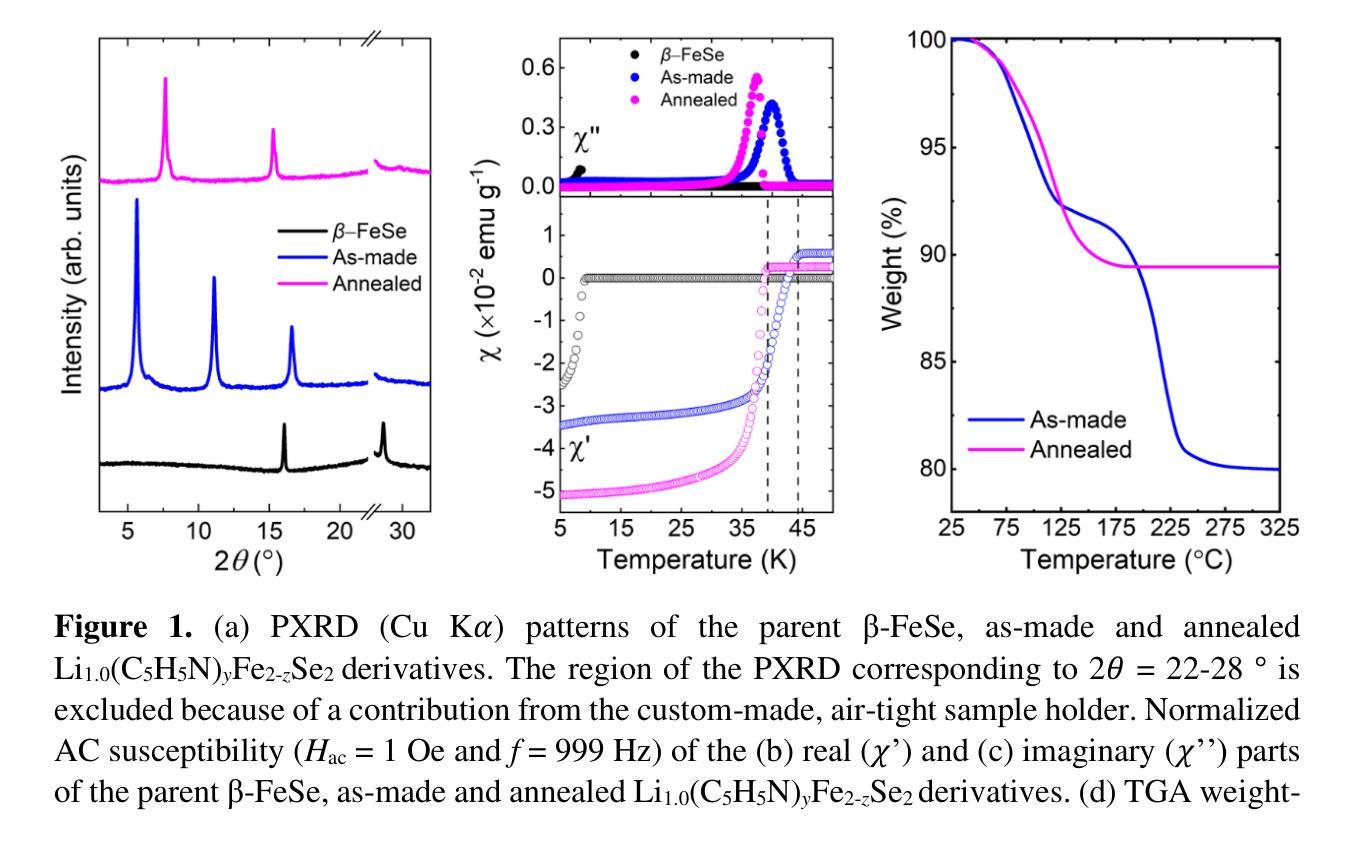
Local structure and phonon states mediated by intercalation-driven doping in superconducting $Li_{1.0}(C_5H_5N)yFe{2-z}Se_2$
Authors:Alexandros Deltsidis, Myrsini Kaitatzi, Laura Simonelli, Chris Stock, David Voneshen, Alexandros Lappas
Intercalation of two-dimensional (2D) iron chalcogenides with molecular species requires disentangling electronic and structural contributions to understand the puzzling limit to superconducting transition temperature ($T_c$) at the frontier of long interlayer separations. Here, synchrotron X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) at the Se K-edge sheds light on the impact of carrier-doping on the local structure of the high-$T_c$ (39 K) $Li_{1.0}(C_5H_5N)yFe{2-z}Se_2$ phase. This material is derived by annealing the structurally related as-made derivative ($T_c$ 44 K), with layers being primed apart by [alkali-molecule] guests. Metrics, such as, a reduced filling of Se $4p$ orbitals and shorter Fe-Se bonds in the annealed phase, corroborate to a lower electron doping level with respect to the as-made one. Analysis of the metal-ligand thermal motion, based on the correlated Debye model, further relates the higher $T_c$ intercalates with the softening of the local Fe-Se bond. Beyond electronic effects, intercalation brings forth host-guest interactions that mediate the dynamics of the bulk crystal structure. For this, neutron time-of-flight spectroscopy on the annealed derivative, corroborates to the Se-Fe-Se layer being sensitive to chemical pressure effects imposed by the confined organic guests. This reflects in the phonon density of states, where harder low-energy transverse acoustic matrix phonons and molecular vibrations are witnessed, with respect to the pristine inorganic ($\beta$-FeSe) and organic ($C_5D_5N$) counterparts. On cooling through $T_c$, these excitations arrive without a collective magnetic-resonance mode - essential in unconventional, spin-mediated mechanisms - enquiring about deviations from optimal doping. The work highlights that when the Fe-square planes are tuned far apart, carrier-doping leveraged by intercalation plays a key role in the $T_c$ parametrization.
插层二维(2D)铁硫属化物与分子物种需要对电子和结构贡献进行梳理,以理解超导转变温度($T_c$)的极限,这在长层间分离的前沿是一个令人困惑的问题。这里,同步加速器X射线吸收光谱(XAS)在Se K边对载体掺杂对局部结构的影响进行了阐明,影响对象是高$T_c$(约39K)的$Li_{1.0}(C_5H_5N)yFe{2-z}Se_2$相。这种材料是通过退火结构相关的即时衍生($T_c$ ~ 44 K)而得到的,层间由[碱金属分子]客体隔开。指标显示,退火相中Se $4p$轨道填充减少和Fe-Se键缩短,证实了与即时衍生相比,退火相的电子掺杂水平较低。基于相关Debye模型的金属配体热运动分析进一步表明,较高的$T_c$插层与局部Fe-Se键的软化有关。除了电子效应外,插层还带来了主体与客体之间的相互作用,这些相互作用介导了主体晶体结构的动力学变化。为此,对退火衍生物的飞行时间中子光谱证实了Se-Fe-Se层对由受限有机客体产生的化学压力效应敏感。这反映在态密度声子中,与原始无机(β-FeSe)和有机($C_5D_5N$)相比,观察到更硬的低能横向声学基阵阵列声子和分子振动。在通过$T_c$冷却时,这些激发不伴随集体磁共振模式出现,这在非传统的自旋介导机制中是至关重要的,引发了偏离最佳掺杂的疑问。这项工作强调,当Fe平面被调谐远离时,通过插层调节载体掺杂在$T_c$参数化中起关键作用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MAIN text: 19 pages, 5 figures; Supplemental Material: 7 pages, 3 figures
Summary
本文研究了二维铁硫族化合物与分子物种的掺杂过程中电子与结构因素对超导转变温度($T_c$)的影响。通过同步辐射X射线吸收光谱(XAS)研究,发现载流子掺杂对高$T_c$(约39K)的$Li_{1.0}(C_5H_5N)yFe{2-z}Se_2$相局部结构的影响。分析表明,退火处理降低了电子掺杂水平,同时与金属配体的热运动有关,提高了超导转变温度与局部Fe-Se键软化之间的关系。此外,该工作还强调了插层过程中载流子掺杂在调节Fe平面间距以影响$T_c$方面的关键作用。
Key Takeaways
- 通过同步辐射X射线吸收光谱(XAS)研究载流子掺杂对二维铁硫族化合物超导性能的影响。
- 退火处理通过降低电子掺杂水平和影响金属配体的热运动来提高超导转变温度。
- 插层过程通过载流子掺杂在调节Fe平面间距方面发挥关键作用。
- 高温超导材料中的Fe-Se键软化与更高的超导转变温度相关联。
- 主客相互作用对插层后晶体结构的动态变化有影响。
- 通过中子飞行时间光谱法观察到插层衍生物的Se-Fe-Se层对化学压力敏感,表现出特定的振动模式变化。
点此查看论文截图

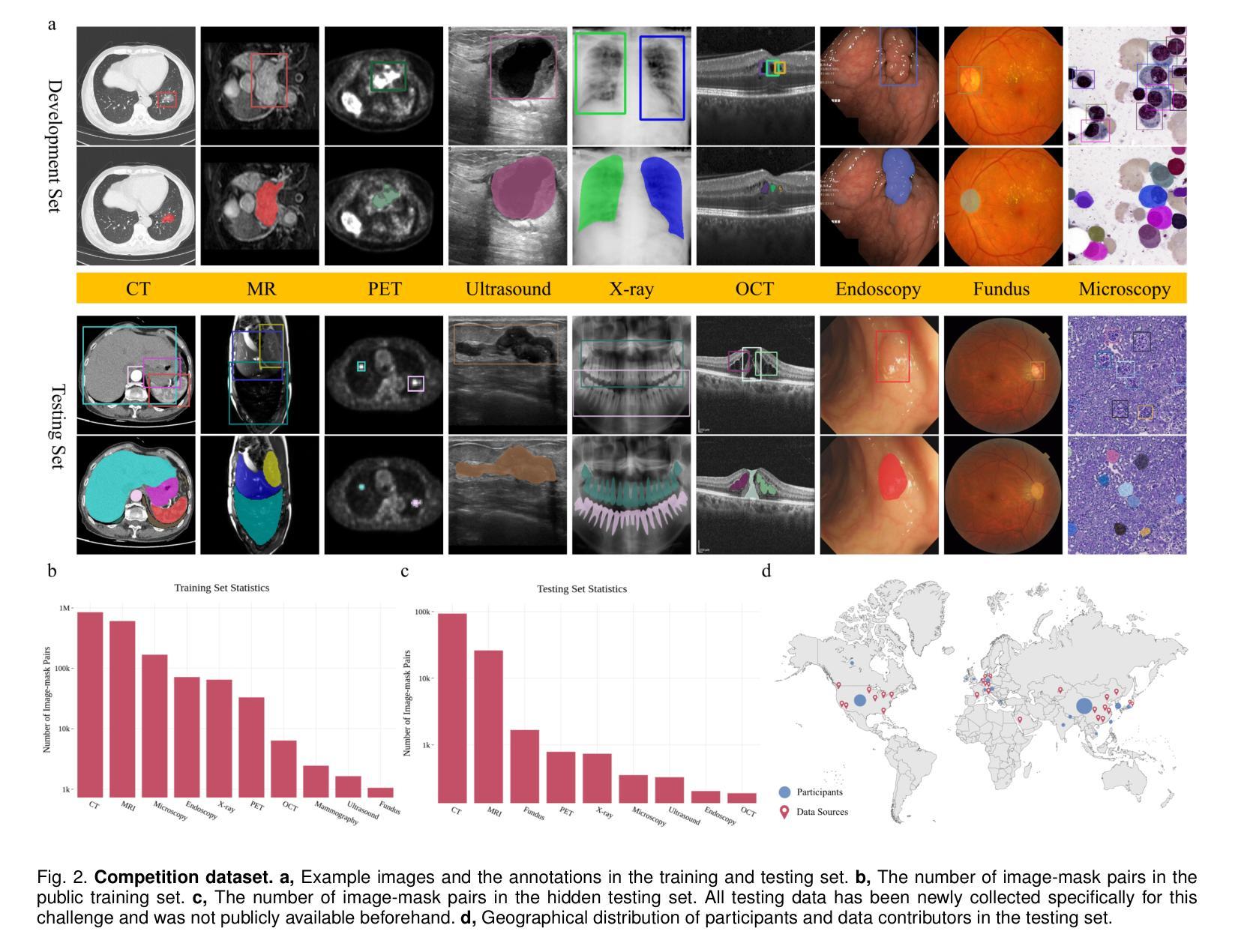
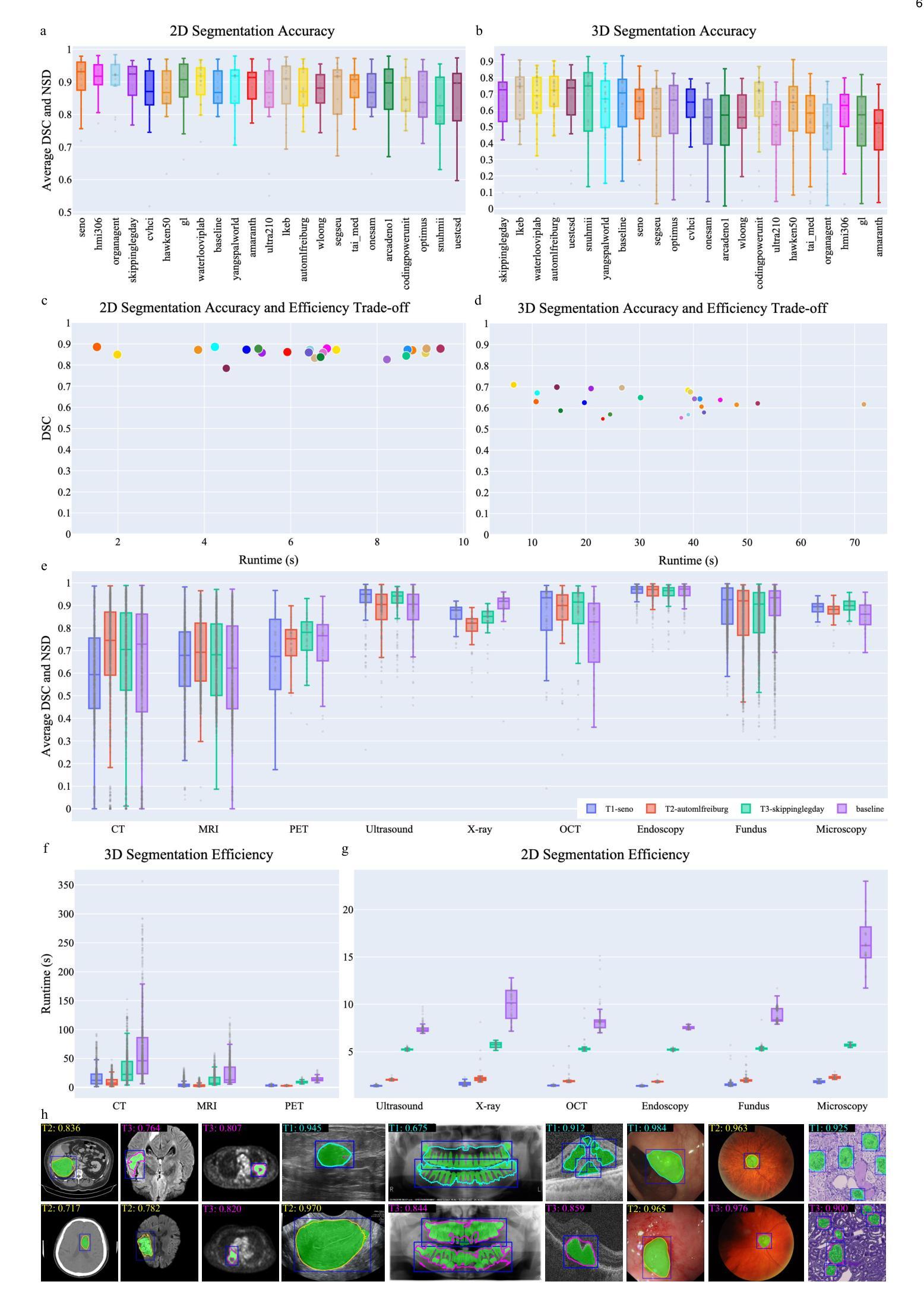
Efficient MedSAMs: Segment Anything in Medical Images on Laptop
Authors:Jun Ma, Feifei Li, Sumin Kim, Reza Asakereh, Bao-Hiep Le, Dang-Khoa Nguyen-Vu, Alexander Pfefferle, Muxin Wei, Ruochen Gao, Donghang Lyu, Songxiao Yang, Lennart Purucker, Zdravko Marinov, Marius Staring, Haisheng Lu, Thuy Thanh Dao, Xincheng Ye, Zhi Li, Gianluca Brugnara, Philipp Vollmuth, Martha Foltyn-Dumitru, Jaeyoung Cho, Mustafa Ahmed Mahmutoglu, Martin Bendszus, Irada Pflüger, Aditya Rastogi, Dong Ni, Xin Yang, Guang-Quan Zhou, Kaini Wang, Nicholas Heller, Nikolaos Papanikolopoulos, Christopher Weight, Yubing Tong, Jayaram K Udupa, Cahill J. Patrick, Yaqi Wang, Yifan Zhang, Francisco Contijoch, Elliot McVeigh, Xin Ye, Shucheng He, Robert Haase, Thomas Pinetz, Alexander Radbruch, Inga Krause, Erich Kobler, Jian He, Yucheng Tang, Haichun Yang, Yuankai Huo, Gongning Luo, Kaisar Kushibar, Jandos Amankulov, Dias Toleshbayev, Amangeldi Mukhamejan, Jan Egger, Antonio Pepe, Christina Gsaxner, Gijs Luijten, Shohei Fujita, Tomohiro Kikuchi, Benedikt Wiestler, Jan S. Kirschke, Ezequiel de la Rosa, Federico Bolelli, Luca Lumetti, Costantino Grana, Kunpeng Xie, Guomin Wu, Behrus Puladi, Carlos Martín-Isla, Karim Lekadir, Victor M. Campello, Wei Shao, Wayne Brisbane, Hongxu Jiang, Hao Wei, Wu Yuan, Shuangle Li, Yuyin Zhou, Bo Wang
Promptable segmentation foundation models have emerged as a transformative approach to addressing the diverse needs in medical images, but most existing models require expensive computing, posing a big barrier to their adoption in clinical practice. In this work, we organized the first international competition dedicated to promptable medical image segmentation, featuring a large-scale dataset spanning nine common imaging modalities from over 20 different institutions. The top teams developed lightweight segmentation foundation models and implemented an efficient inference pipeline that substantially reduced computational requirements while maintaining state-of-the-art segmentation accuracy. Moreover, the post-challenge phase advanced the algorithms through the design of performance booster and reproducibility tasks, resulting in improved algorithms and validated reproducibility of the winning solution. Furthermore, the best-performing algorithms have been incorporated into the open-source software with a user-friendly interface to facilitate clinical adoption. The data and code are publicly available to foster the further development of medical image segmentation foundation models and pave the way for impactful real-world applications.
可提示的分割基础模型已经作为一种变革性的方法,解决了医学图像中多样化的需求,但大多数现有模型需要昂贵的计算资源,这成为在临床实践中采用它们的巨大障碍。在这项工作中,我们组织了首届专门针对可提示医学图像分割的国际竞赛,使用来自20多个不同机构的涵盖九种常见成像模式的大规模数据集。顶尖团队开发了轻量级的分割基础模型,并实现了高效的推理流程,在保持最先进的分割精度的同时,大大降低了计算需求。此外,挑战赛后的阶段通过设计性能提升器和可重复性任务,推动了算法的进步,从而改进了算法并验证了获胜解决方案的可重复性。此外,最佳性能的算法已被集成到具有用户友好界面的开源软件中,以促进其在临床中的应用。数据和代码公开可用,以促进医学图像分割基础模型的进一步发展,并为实际世界的重大影响应用铺平道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2024 MedSAM on Laptop Competition Summary: https://www.codabench.org/competitions/1847/
Summary
基于提示的医学图像分割基础模型的出现,为解决医疗实践中多样化的图像需求带来了变革性的方法。但大多数现有模型需要高昂的计算成本,成为临床应用中的一大障碍。本研究组织了首个针对基于提示的医学图像分割的国际竞赛,使用来自超过20个不同机构的涵盖九种常见成像模式的大规模数据集。竞赛顶尖团队开发了轻量级的分割基础模型,并实现了高效的推理管道,大幅降低了计算需求的同时保持了先进的分割精度。此外,竞赛后阶段通过设计性能提升和可重复任务进一步推进了算法的发展,提升了算法性能并验证了获胜解决方案的可重复性。表现最佳的算法已被集成到具有用户友好界面的开源软件中,以促进临床采用。数据和代码公开可用,以推动医学图像分割基础模型的进一步发展,为实际应用开辟道路。
Key Takeaways
- 基于提示的医学图像分割基础模型能满足多样化的医疗图像需求。
- 现有模型高昂的计算成本是临床应用的主要障碍。
- 国际竞赛使用了涵盖九种常见成像模式的大规模数据集。
- 顶尖团队开发了轻量级分割基础模型和高效推理管道以降低计算需求并保持高分割精度。
- 竞赛后阶段通过设计性能提升和可重复任务进一步推进了算法发展。
- 最佳性能的算法已被集成到开源软件中,具有用户友好界面,促进临床采用。
点此查看论文截图

Coherent Interactions of Free Electrons and Matter: Toward Tunable Compact X-ray Sources
Authors:Amnon Balanov, Alexey Gorlach, Vladimir Baryshevsky, Ilya Feranchuk, Hideo Nitta, Yasushi Hayakawa, Alexander Shchagin, Yuichi Takabayashi, Yaron Danon, Liang Jie Wong, Ido Kaminer
Compact laboratory-scale X-ray sources still rely on the same fundamental principles as in the first X-ray tubes developed more than a century ago. In recent years, significant research and development have focused on large-scale X-ray sources such as synchrotrons and free-electron lasers, leading to the generation of high-brightness coherent X-rays. However, the large size and high costs of such sources prevent their widespread use. The quest for a compact and coherent Xray source has long been a critical objective in modern physics, gaining further importance in recent years for industrial applications and fundamental scientific research. Here, we review the physical mechanisms governing compact coherent X-ray generation. Of current interest are coherent periodic interactions of free electrons in crystalline materials, creating hard X-rays via a mechanism known as parametric X-ray radiation (PXR). Over the past decade, X-ray sources leveraging this mechanism have demonstrated state-of-the-art tunability, directionality, and broad spatial coherence, enabling X-ray phase-contrast imaging on a compact scale. The coming years are expected to show substantial miniaturization of compact X-ray sources, facilitated by progress in electron beam technologies. This review compares the most promising mechanisms used for hard-X-ray generation, contrasting parametric X-ray radiation with inverse Compton scattering and characteristic radiation from a liquid-jet anode. We cover the most recent advancements, including the development of new materials, innovative geometrical designs, and specialized optimization techniques, aiming toward X-ray flux levels suitable for medical imaging and X-ray spectroscopy in compact scales.
紧凑的实验室规模X射线源仍然依赖于与一个多世纪前开发的第一代X射线管相同的基本原理。近年来,大量研究重点集中在大型X射线源上,如同步辐射器和自由电子激光器,产生了高亮度相干X射线。然而,这些光源体积庞大、成本高昂,阻碍了其广泛应用。寻找紧凑且相干性强的X射线源一直是现代物理学的重要目标,近年来在工业应用和基础科学研究中的重要性日益增强。在这里,我们回顾了控制紧凑相干X射线产生的物理机制。目前感兴趣的是晶体材料中自由电子的相干周期性相互作用,通过一种称为参数化X射线辐射(PXR)的机制产生硬X射线。在过去的十年中,利用这种机制的X射线源已经表现出了最先进的可调谐性、方向性和广泛的空间相干性,能够在紧凑规模上实现X射线相位对比成像。未来几年预计紧凑型X射线源将实现重大小型化,得益于电子束技术的进步。本文比较了最具前途的硬X射线产生机制,将参数化X射线辐射与逆康普顿散射和液体喷射阳极的特征辐射进行了对比。我们涵盖了最近的最新进展,包括新材料的发展、创新的几何设计和专门的优化技术,旨在实现适合医学成像和紧凑规模X射线光谱的X射线通量水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文综述了小型化相干X射线源的物理机制,特别关注了通过参数化X射线辐射(PXR)机制生成硬X射线的研究进展。文章讨论了近期在材料开发、几何设计优化和技术创新方面的进展,旨在实现适合医学成像和X射线光谱学的小型化X射线源。对于未来小型化X射线源的发展前景进行了分析,期待通过电子束技术的进步实现重大突破。总体来看,该技术向着紧凑型和应用广泛的道路上迈出了一大步。这一研究成果有望进一步推动医学和工业应用领域的实际应用和发展。这一综述展示了参数化X射线辐射相较于逆康普顿散射和液态喷射阳极特征辐射等机制的潜力。尽管小型化相干X射线源研究面临的挑战依然很大,但是上述内容值得更多研究和进一步推动这些领域的后续工作方向研究的基础背景支持意义很重大。希望在研究人员的努力下能够早日实现医学和工业领域的大规模应用。这些努力将有助于改善我们的生活质量,并推动科学技术的发展。该领域的前景值得期待。同时本文指出了实现这一目标需要解决的若干关键问题和挑战,也为我们未来研究和改进指明了方向。综上所述,小型化相干X射线源研究的重要性和前景非常值得期待。文中对于各种机制和技术的深入剖析也为读者提供了一个全面且深入的视角,让我们对该领域的研究进展有了更为清晰的认识。
Key Takeaways
- 实验室规模的X光射线源仍基于一个多世纪前开发的原理,而目前研究的焦点已转向大型X射线源如同步加速器与自由电子激光器等。
- 小型化相干X射线源是现代物理学的重要目标之一,特别是在工业应用和基础科学研究领域具有广泛应用前景。
- 参数化X射线辐射(PXR)是当前研究的一种硬X射线生成机制,展现出优秀的调谐性、方向性和空间相干性,有望应用于紧凑尺度上的X射线相位对比成像技术。
- 电子束技术的进步促进了小型化X射线源的发展前景预期将有显著的缩小成果展示出来了明显的可能性比较小但同时要解决一些重要的关键问题和挑战譬如开发新型材料几何设计的创新优化技术等创新科技都提升了此领域的飞速进展相关理论和应用的提出对于我们更好地理解和掌握此技术并实现进一步的提升和应用推广大有裨益是值得我们深入研究和探索的重要领域之一 。
- 未来小型化相干X射线源的发展有望推动医学成像和X射线光谱学等领域的进步和发展应用前景值得期待 。
- 文章对比了参数化X射线辐射与逆康普顿散射以及液态喷射阳极特征辐射等机制展示了参数化机制的潜力优势同时也指出了实现小型化相干X射线源所面临的挑战和需要解决的关键问题 。
点此查看论文截图

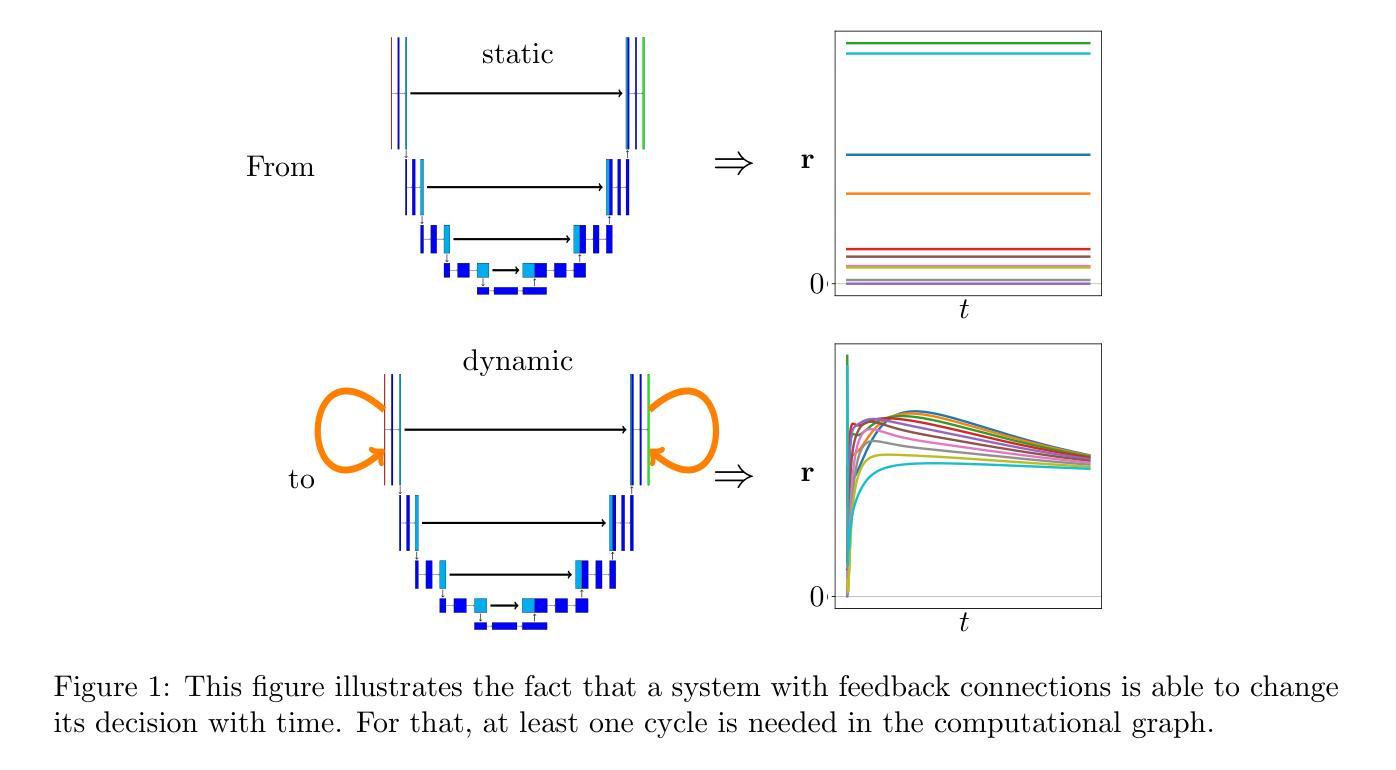
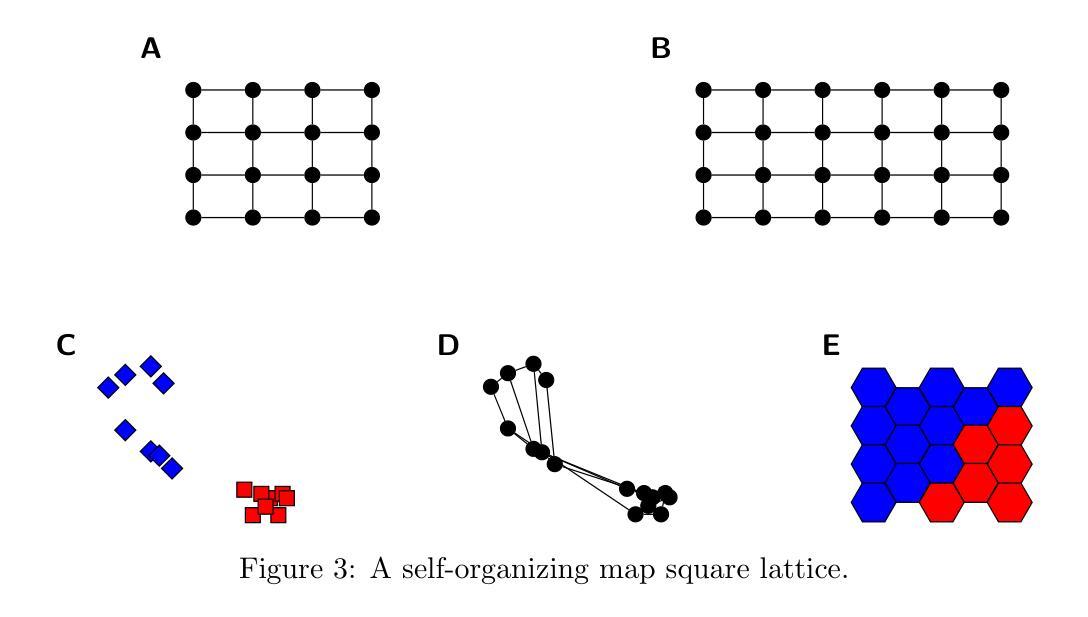
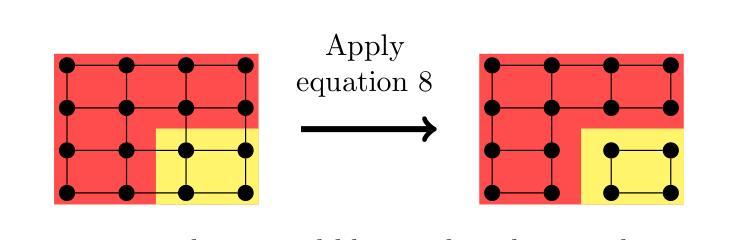
The Role of Recurrency in Image Segmentation for Noisy and Limited Sample Settings
Authors:David Calhas, João Marques, Arlindo L. Oliveira
The biological brain has inspired multiple advances in machine learning. However, most state-of-the-art models in computer vision do not operate like the human brain, simply because they are not capable of changing or improving their decisions/outputs based on a deeper analysis. The brain is recurrent, while these models are not. It is therefore relevant to explore what would be the impact of adding recurrent mechanisms to existing state-of-the-art architectures and to answer the question of whether recurrency can improve existing architectures. To this end, we build on a feed-forward segmentation model and explore multiple types of recurrency for image segmentation. We explore self-organizing, relational, and memory retrieval types of recurrency that minimize a specific energy function. In our experiments, we tested these models on artificial and medical imaging data, while analyzing the impact of high levels of noise and few-shot learning settings. Our results do not validate our initial hypothesis that recurrent models should perform better in these settings, suggesting that these recurrent architectures, by themselves, are not sufficient to surpass state-of-the-art feed-forward versions and that additional work needs to be done on the topic.
生物大脑已经激发了机器学习领域的多项进展。然而,最先进的计算机视觉模型并不能像人脑那样运作,原因很简单,它们无法基于更深入的分析来改变或提高自己的决策/输出。大脑是递归的,而这些模型却不是。因此,探索在现有最先进的架构中添加递归机制将会产生什么影响,以及递归是否能改进现有架构,这是非常重要的。为此,我们在前馈分割模型的基础上,探索了多种递归方式用于图像分割。我们探索了自我组织、关系和记忆检索等递归类型,这些类型能够最小化特定的能量函数。在我们的实验中,我们在人工和医学成像数据上测试了这些模型,同时分析了高噪声水平和少镜头学习设置的影响。我们的结果并没有验证我们最初的假设,即递归模型应该在这些设置中表现得更好,这表明这些递归架构本身不足以超越最先进的前馈版本,还需要在这个主题上做出额外的工作。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages
Summary
本文探索了将递归机制添加到现有最先进的架构中对于图像分割的影响,实验了自组织、关系和记忆检索等类型的递归,但最终结果显示递归模型并未在噪声高或少量学习的情况下表现更好,因此仍需进一步探讨。
Key Takeaways
- 生物学大脑对机器学习产生了多领域的启发。
- 当前最先进的计算机视觉模型在决策和输出上无法像人脑那样进行深度分析并做出改变。
- 人脑具有递归性,而现有模型缺乏此特性。
- 研究者基于前馈分割模型,探索了多种递归类型(如自组织、关系和记忆检索)用于图像分割。
- 实验在人工和医学成像数据上进行了测试,并分析了高噪声和少量学习场景下的影响。
- 结果并未验证初始假设,即递归模型在这些场景中表现更好。
点此查看论文截图

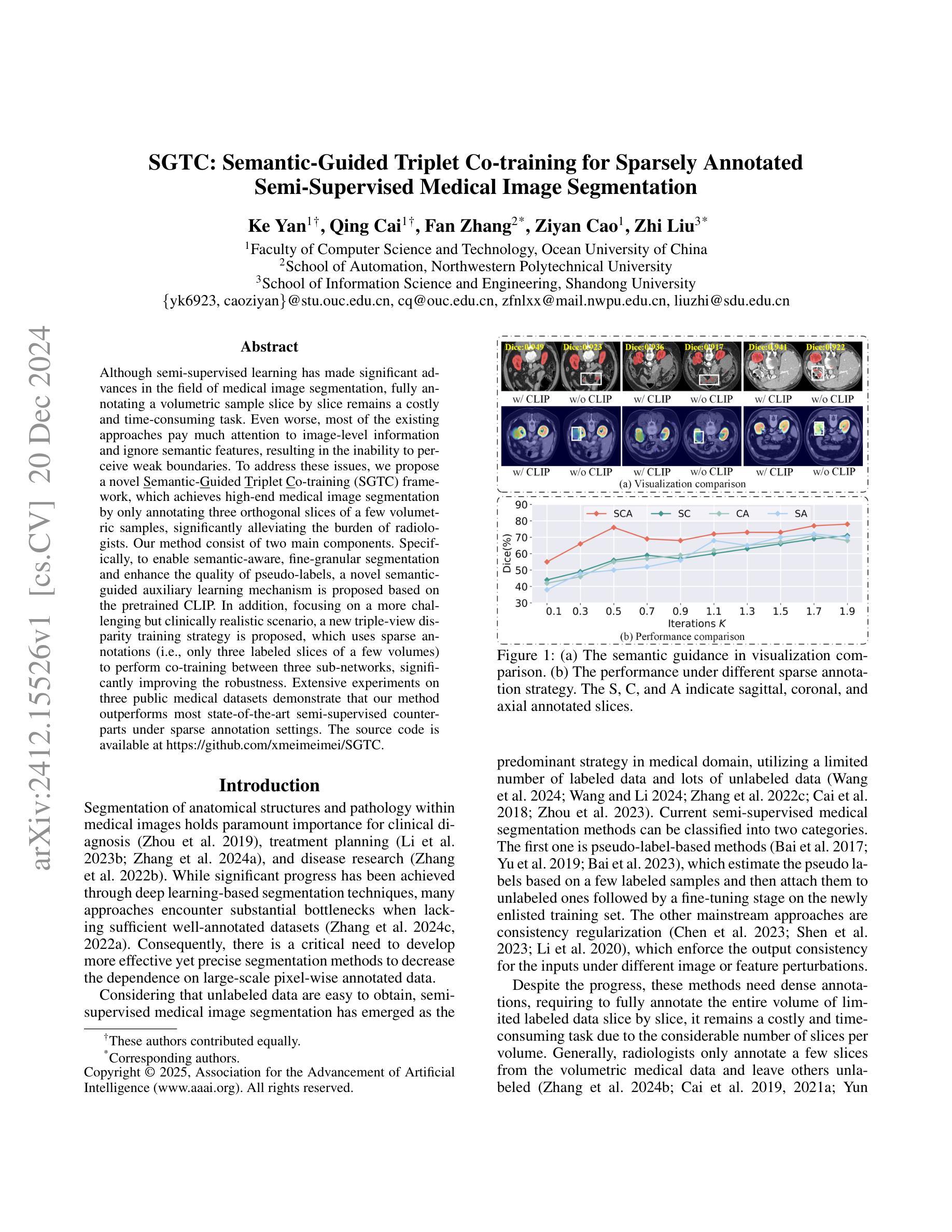
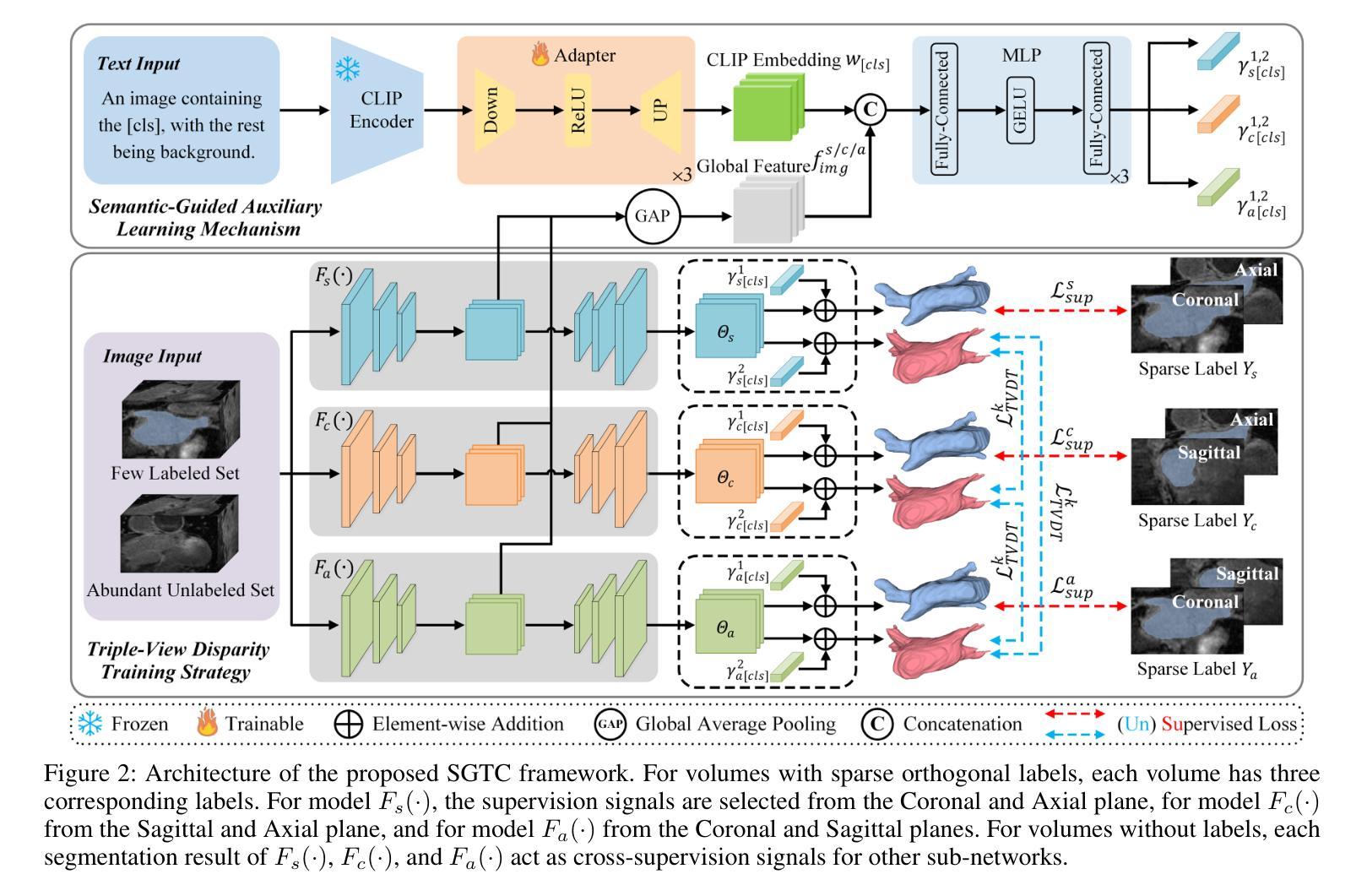
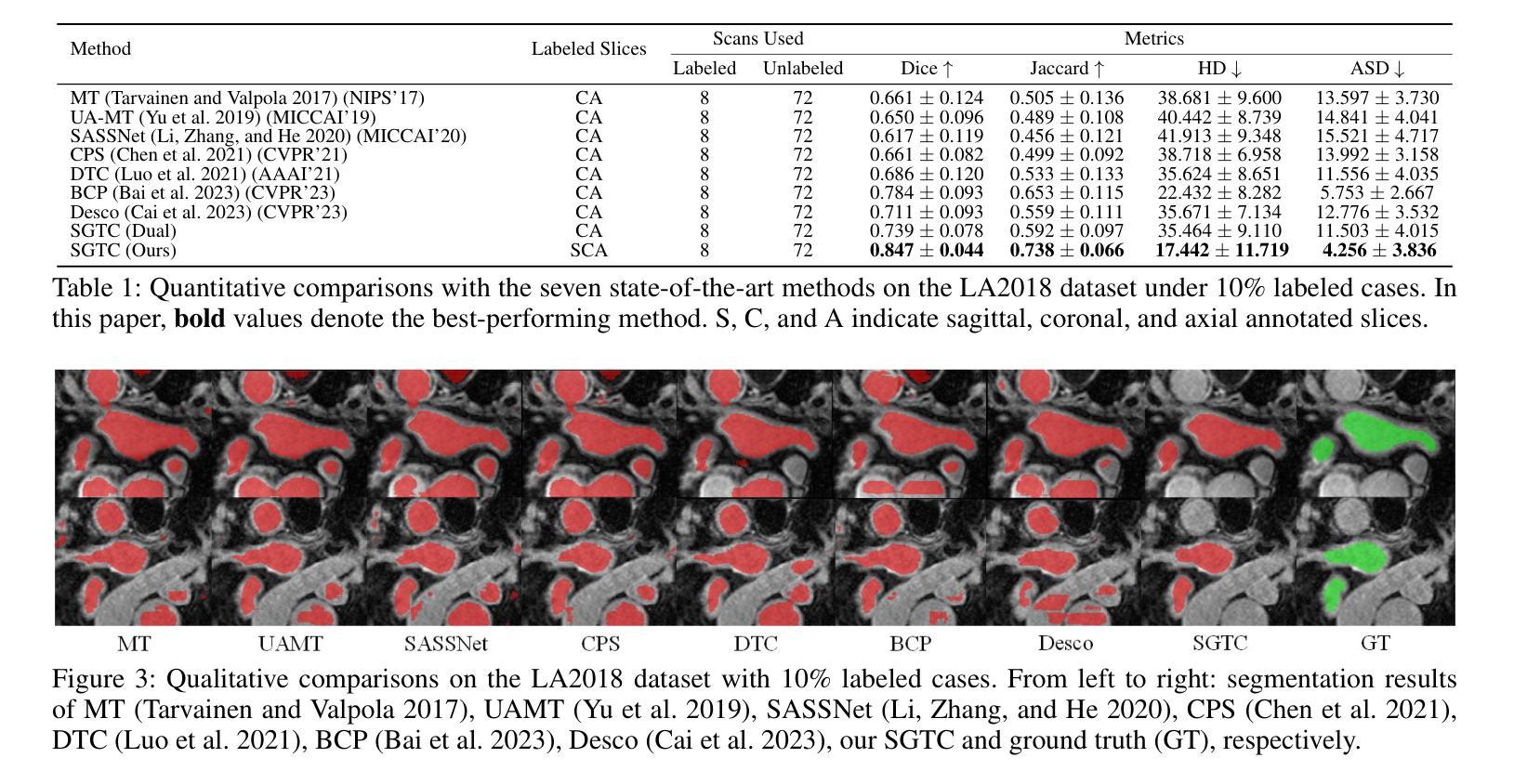
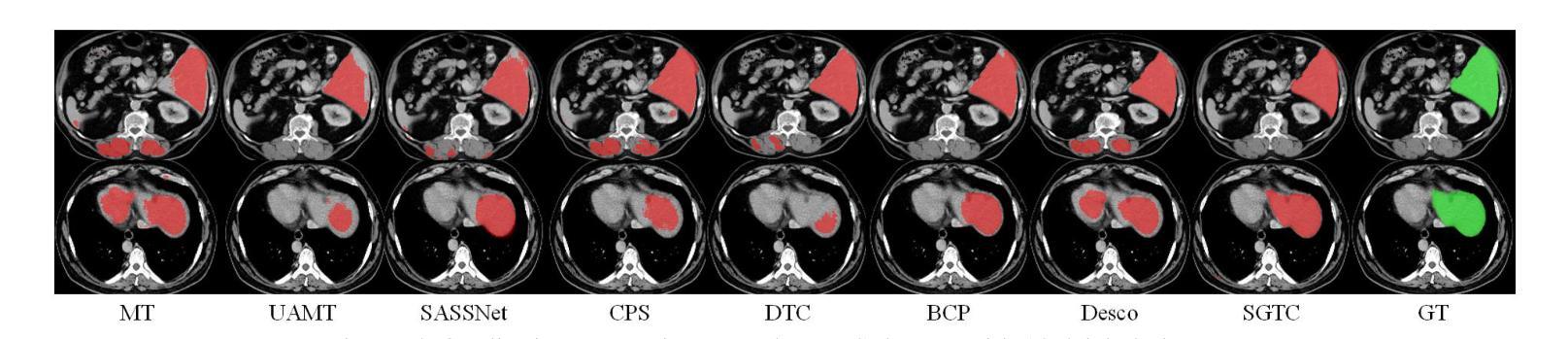
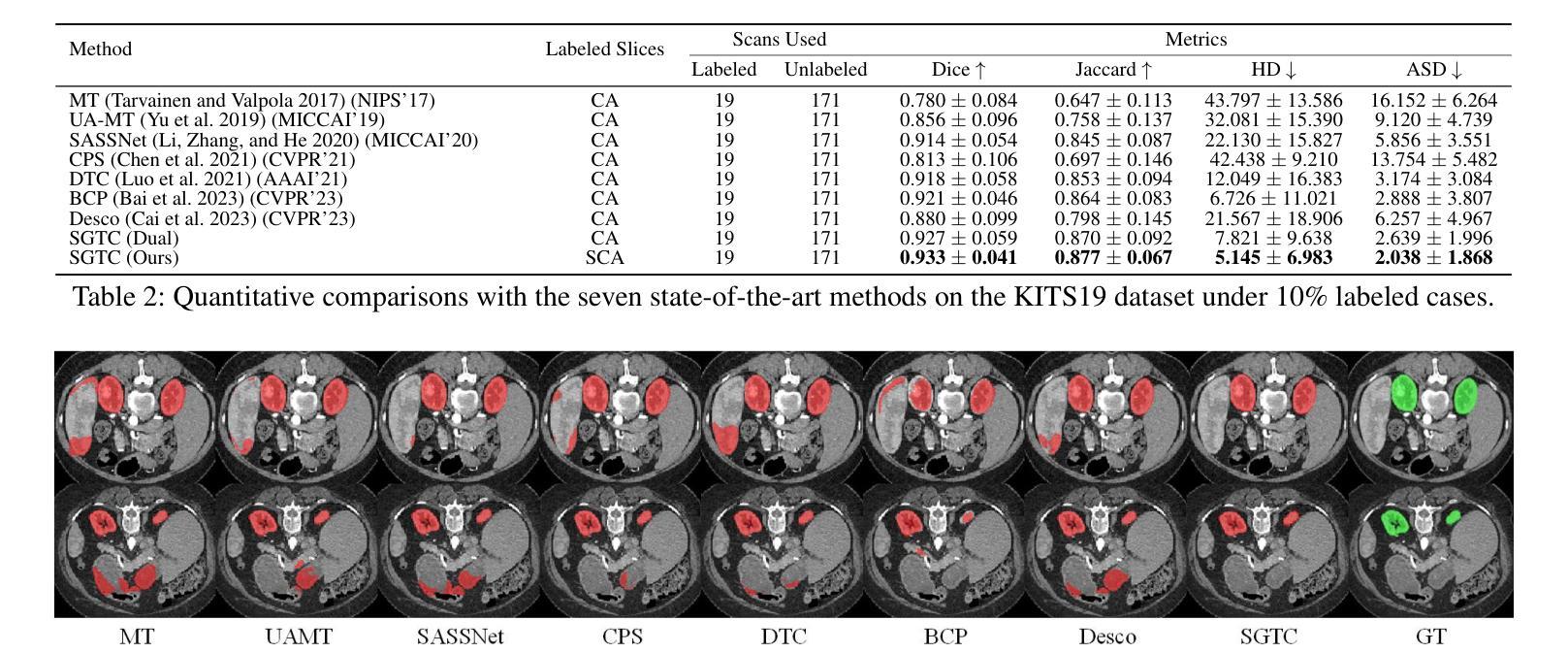
SGTC: Semantic-Guided Triplet Co-training for Sparsely Annotated Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Ke Yan, Qing Cai, Fan Zhang, Ziyan Cao, Zhi Liu
Although semi-supervised learning has made significant advances in the field of medical image segmentation, fully annotating a volumetric sample slice by slice remains a costly and time-consuming task. Even worse, most of the existing approaches pay much attention to image-level information and ignore semantic features, resulting in the inability to perceive weak boundaries. To address these issues, we propose a novel Semantic-Guided Triplet Co-training (SGTC) framework, which achieves high-end medical image segmentation by only annotating three orthogonal slices of a few volumetric samples, significantly alleviating the burden of radiologists. Our method consist of two main components. Specifically, to enable semantic-aware, fine-granular segmentation and enhance the quality of pseudo-labels, a novel semantic-guided auxiliary learning mechanism is proposed based on the pretrained CLIP. In addition, focusing on a more challenging but clinically realistic scenario, a new triple-view disparity training strategy is proposed, which uses sparse annotations (i.e., only three labeled slices of a few volumes) to perform co-training between three sub-networks, significantly improving the robustness. Extensive experiments on three public medical datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms most state-of-the-art semi-supervised counterparts under sparse annotation settings. The source code is available at https://github.com/xmeimeimei/SGTC.
尽管半监督学习在医学图像分割领域取得了重大进展,但完全对体积样本逐片进行标注仍然是一项成本高昂且耗时的任务。更糟糕的是,大多数现有方法过于关注图像级别的信息,而忽略了语义特征,导致无法感知到弱边界。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新颖的语义引导三重协同训练(SGTC)框架,仅通过标注少量体积样本的三个正交切片,就能实现高端医学图像分割,显著减轻了放射科医师的负担。我们的方法主要包括两个组成部分。具体来说,为了进行语义感知的精细粒度分割并提高伪标签的质量,我们提出了一种基于预训练CLIP的新的语义引导辅助学习机制。此外,为了应对更具挑战性但临床现实的场景,我们提出了一种新的三视图差异训练策略,该策略使用稀疏注释(即只有少数体积的三个标记切片)来对三个子网络进行协同训练,从而显著提高了稳健性。在三个公共医学数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法在稀疏注释设置下超越了大多数最先进的半监督方法。源代码可访问 https://github.com/xmeimeimei/SGTC。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
本文提出一种名为SGTC的半监督学习框架,通过仅标注少数体积样本的三个正交切片,实现高端医学图像分割。该框架包含两个主要组件:基于预训练CLIP的语义引导辅助学习机制和针对更具挑战性但临床现实的三视图差异训练策略。实验表明,该方法在稀疏标注设置下优于大多数先进的半监督方法。
Key Takeaways
- SGTC框架实现了高端医学图像分割,通过仅标注少数体积样本的三个正交切片,减轻了医生的工作负担。
- 框架包含两个主要组件:语义引导辅助学习机制和三视图差异训练策略。
- 语义引导辅助学习机制能提高语义感知的精细粒度分割和伪标签的质量。
- 三视图差异训练策略利用稀疏标注进行三个子网络之间的协同训练,提高了模型的稳健性。
- 该方法在三个公开医学数据集上的实验结果表明,其性能优于大多数先进的半监督方法。
- 框架的源代码已公开发布在GitHub上。
点此查看论文截图
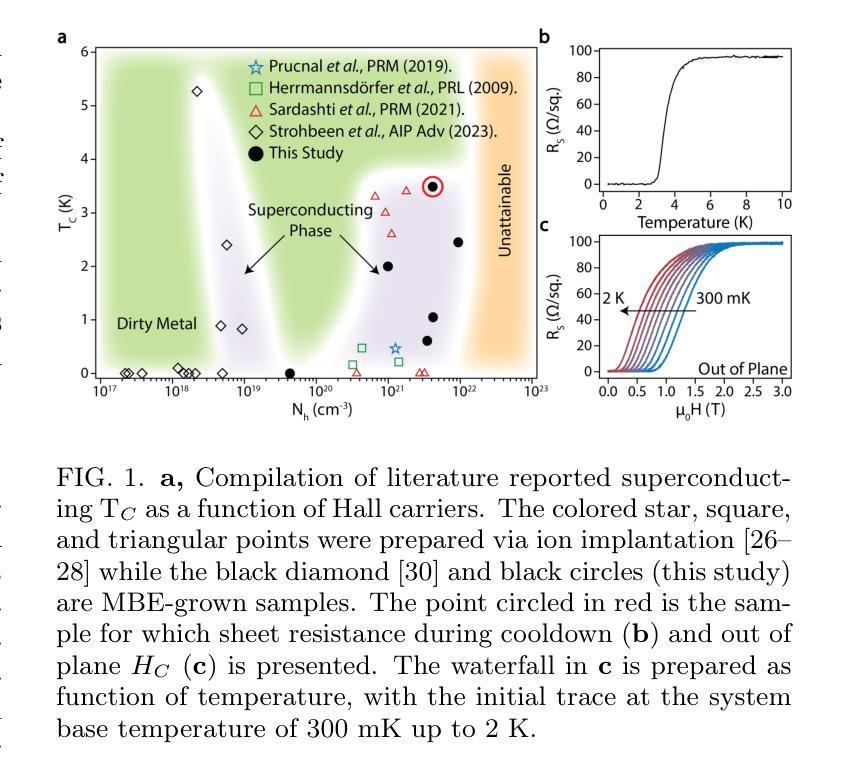
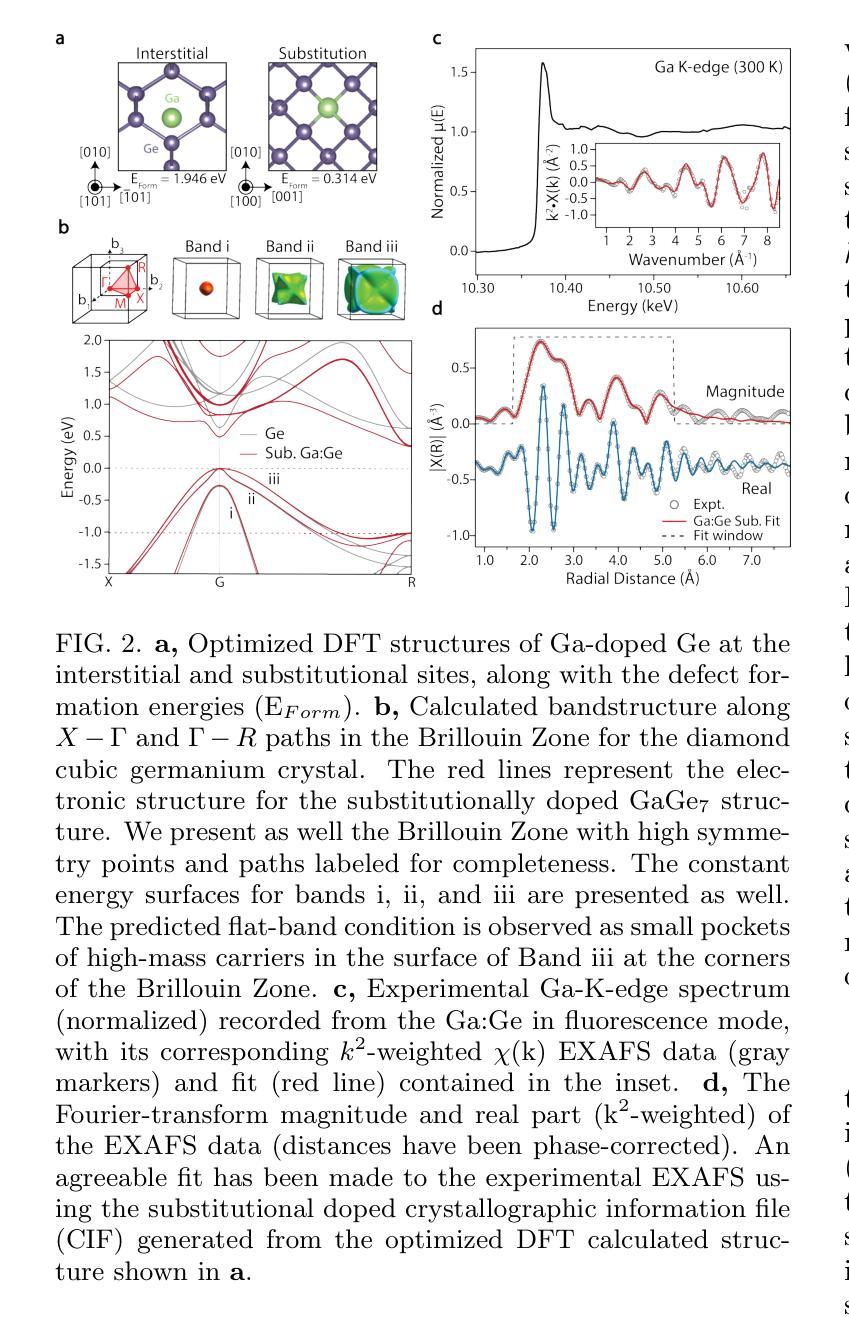
Superconductivity in Epitaxial SiGe for Cryogenic Electronics
Authors:Julian A. Steele, Patrick J. Strohbeen, Carla Verdi, Ardeshir Baktash, Alisa Danilenko, Yi-Hsun Chen, Jechiel van Dijk, Lianzhou Wang, Eugene Demler, Salva Salmani-Rezaie, Peter Jacobson, Javad Shabani
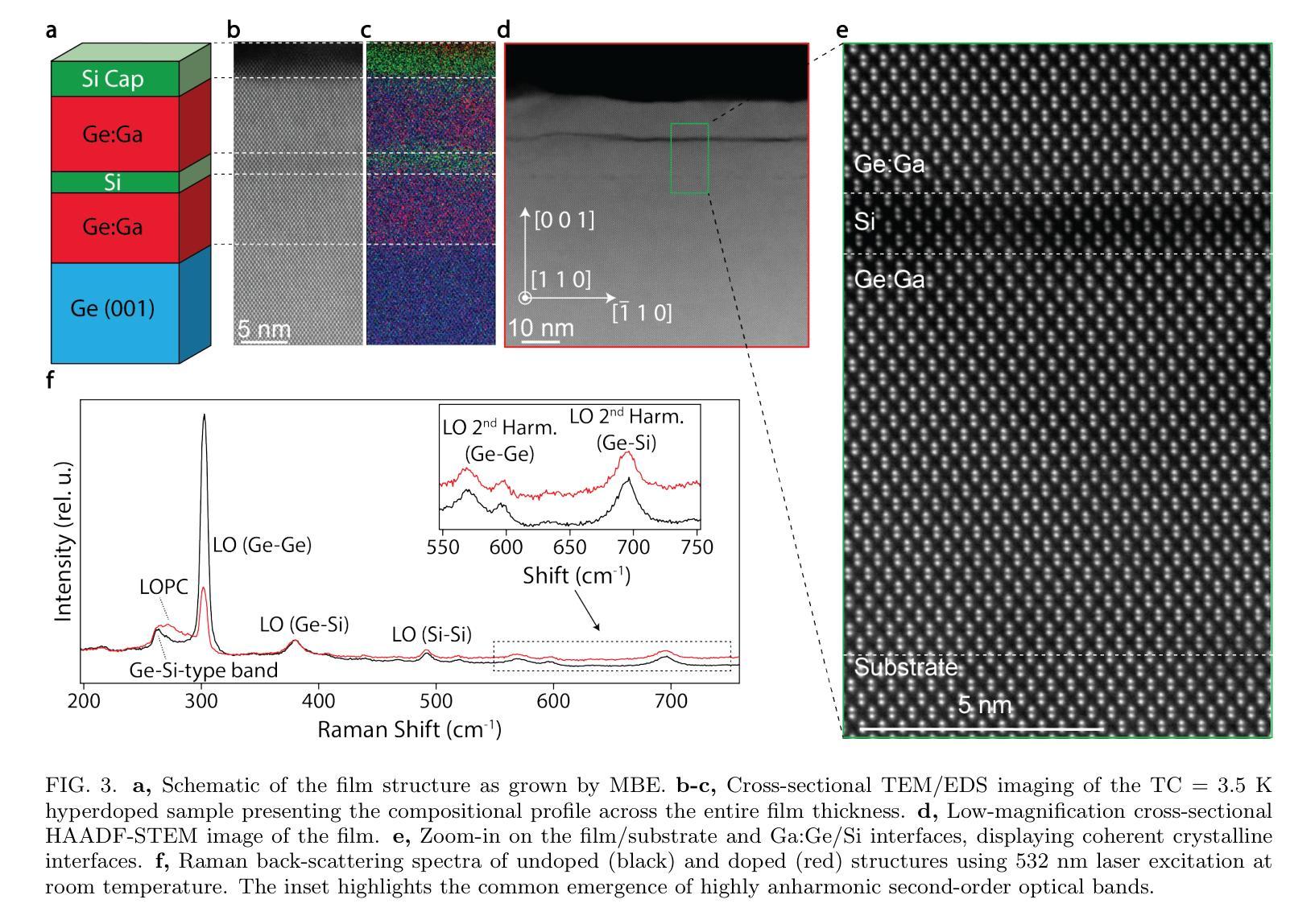
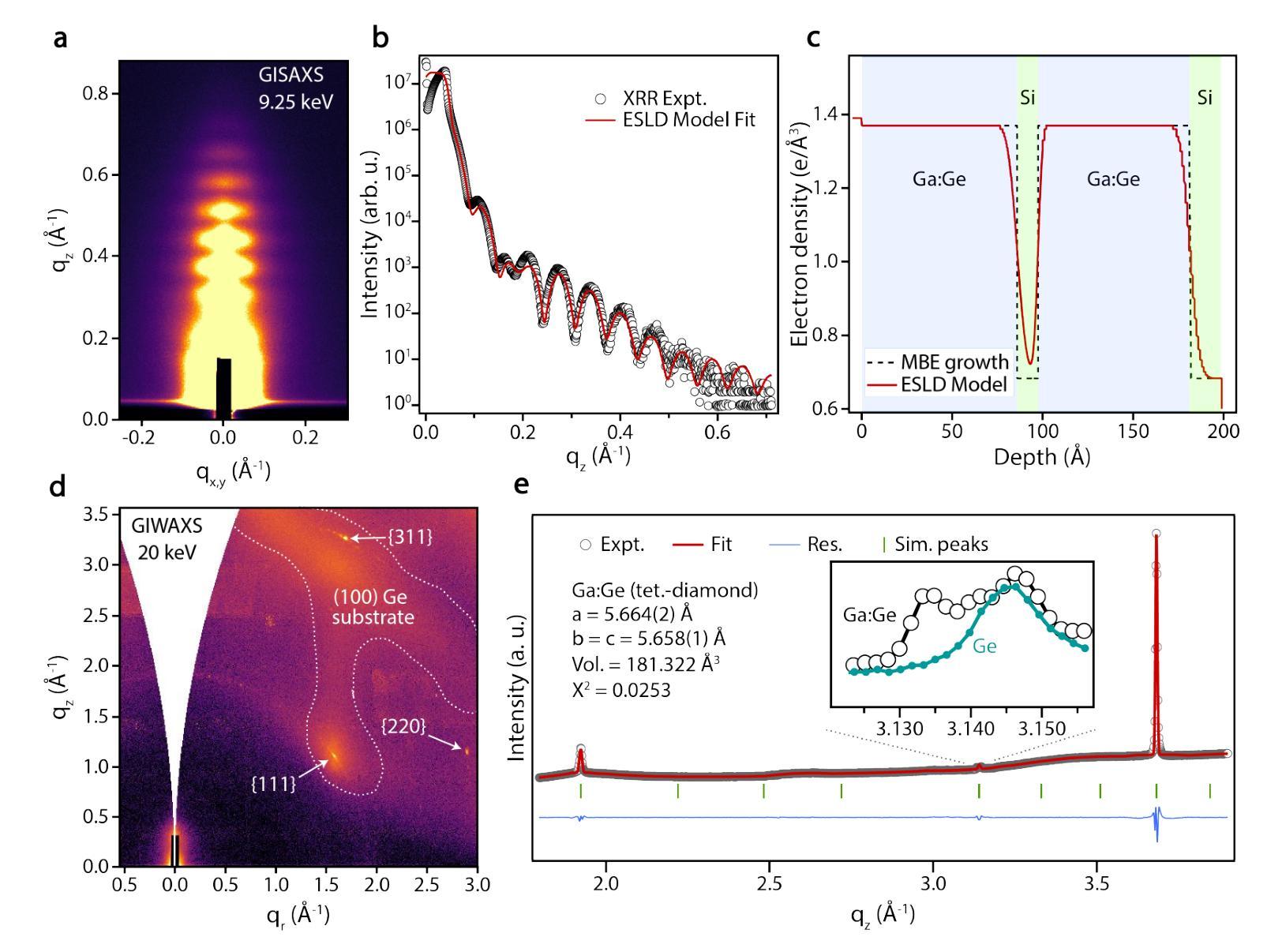
Introducing superconductivity into group IV elements by doping has long promised a pathway to introduce quantum functionalities into well-established semiconductor technologies. The non-equilibrium hyperdoping of group III atoms into Si or Ge has successfully shown superconductivity can be achieved, however, the origin of superconductivity has been obscured by structural disorder and dopant clustering. Here, we report the epitaxial growth of hyperdoped Ga:Ge films by molecular beam epitaxy with extreme hole concentrations (n${h}$ = 4.15 $\times$ 10$^{21}$ cm$^{-3}$, ~17.9% Ga substitution) that yield superconductivity with a critical temperature of T${C}$ = 3.5 K, and an out-of-plane critical field of 1 T at 270 mK. Synchrotron-based X-ray absorption and scattering methods reveal that Ga dopants are substitutionally incorporated within the Ge lattice, introducing a tetragonal distortion to the crystal unit cell. Our findings, corroborated by first-principles calculations, suggest that the structural order of Ga dopants creates a flat band for the emergence of superconductivity in Ge, establishing hyperdoped Ga:Ge as a low-disorder, epitaxial superconductor-semiconductor platform.
将超导性引入第四族元素通过掺杂长期以来为实现将量子功能引入成熟的半导体技术提供了途径。通过III族原子对Si或Ge的非平衡超掺杂已经成功显示出可以实现超导性,然而,超导性的起源被结构无序和掺杂剂聚集所掩盖。在这里,我们通过分子束外延技术报告了超掺杂Ga:Ge薄膜的外延生长,具有极高的空穴浓度(nh = 4.15 × 10^{21} cm^{-3},约17.9%的Ga替代),产生超导性,临界温度为Tc = 3.5 K,在270 mK时的离面临界场为1 T。基于同步辐射的X射线吸收和散射方法表明,Ga掺杂剂被替代性地掺入Ge晶格中,导致晶胞产生四方畸变。我们的发现得到第一性原则计算的证实,表明Ga掺杂剂的结构顺序为Ge中出现超导性创造了平坦带,确立了超掺杂Ga:Ge作为低无序、外延的超导体-半导体平台。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
引入掺杂超导性进入第四组元素长期以来为实现量子功能融入成熟的半导体技术提供了途径。通过非平衡超掺杂III族原子进入硅或锗已经成功展示了超导性的实现,然而其起源被结构无序和掺杂剂聚集所掩盖。我们报告了通过分子束外延技术外延生长超掺杂Ga:Ge薄膜的结果,获得了极高的空穴浓度(nh = 4.15 × 10^21 cm^-3,约17.9%的Ga替代),产生超导性,临界温度Tc = 3.5 K,在270 mK时的垂直临界场为1 T。同步辐射X射线吸收和散射方法显示Ga掺杂剂在Ge晶格中的取代位置引入了四方晶格畸变。我们的研究结果与第一性原则计算结果相符,表明Ga掺杂剂的结构有序性为Ge中出现超导性创造了平坦带,确立了超掺杂Ga:Ge作为低无序、外延生长的半导体-超导体平台。
Key Takeaways
- 通过掺杂方式将超导性引入群IV元素,是实现量子功能与传统半导体技术融合的重要途径。
- 非平衡超掺杂III族原子进入锗(Ge)已经成功展示超导性。
- 高浓度Ga掺杂的Ge薄膜通过分子束外延技术实现外延生长,表现出超导性。
- Ga掺杂剂在Ge晶格中的取代位置引入了四方晶格畸变。
- Ga掺杂剂的结构有序性是超导性在Ge中出现的关键因素。
- 超掺杂Ga:Ge平台具有低无序、外延生长的半导体-超导体特性。
点此查看论文截图

Uncertainty-Guided Cross Attention Ensemble Mean Teacher for Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Meghana Karri, Amit Soni Arya, Koushik Biswas, Nicol`o Gennaro, Vedat Cicek, Gorkem Durak, Yuri S. Velichko, Ulas Bagci
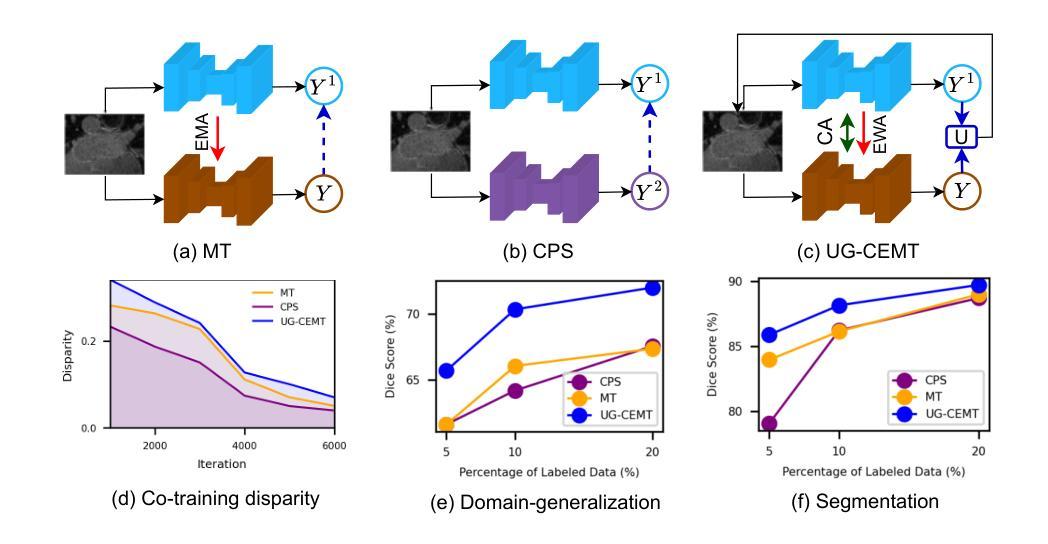
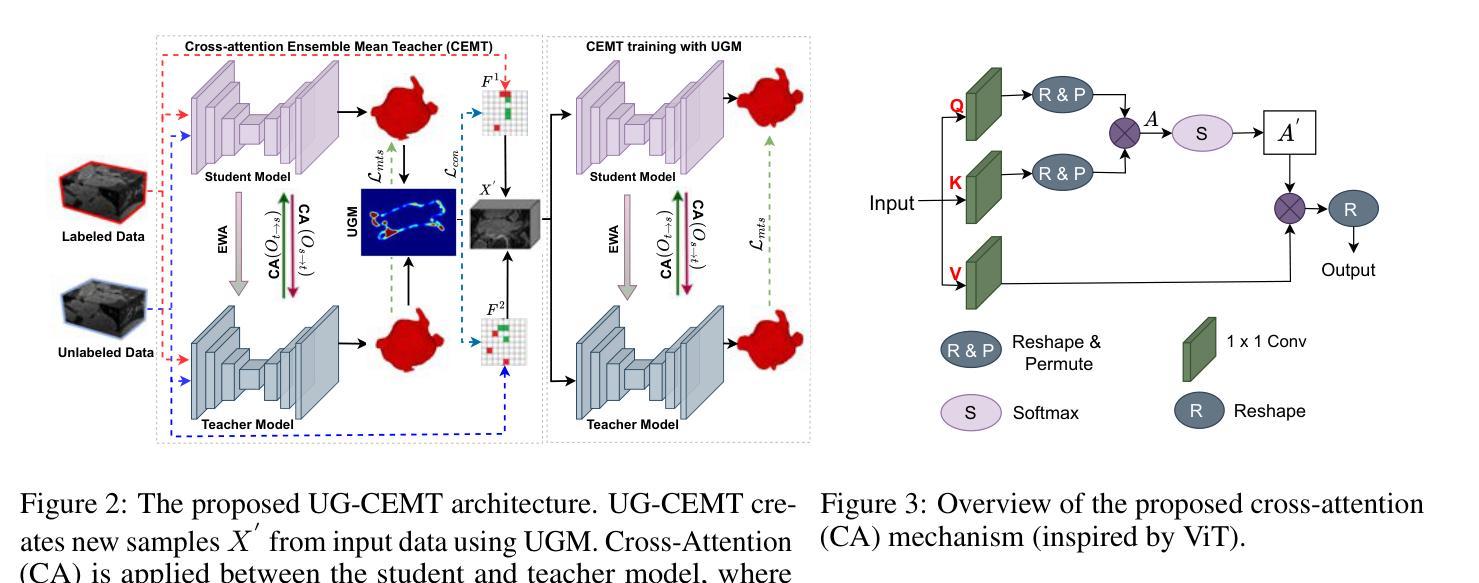
This work proposes a novel framework, Uncertainty-Guided Cross Attention Ensemble Mean Teacher (UG-CEMT), for achieving state-of-the-art performance in semi-supervised medical image segmentation. UG-CEMT leverages the strengths of co-training and knowledge distillation by combining a Cross-attention Ensemble Mean Teacher framework (CEMT) inspired by Vision Transformers (ViT) with uncertainty-guided consistency regularization and Sharpness-Aware Minimization emphasizing uncertainty. UG-CEMT improves semi-supervised performance while maintaining a consistent network architecture and task setting by fostering high disparity between sub-networks. Experiments demonstrate significant advantages over existing methods like Mean Teacher and Cross-pseudo Supervision in terms of disparity, domain generalization, and medical image segmentation performance. UG-CEMT achieves state-of-the-art results on multi-center prostate MRI and cardiac MRI datasets, where object segmentation is particularly challenging. Our results show that using only 10% labeled data, UG-CEMT approaches the performance of fully supervised methods, demonstrating its effectiveness in exploiting unlabeled data for robust medical image segmentation. The code is publicly available at \url{https://github.com/Meghnak13/UG-CEMT}
本文提出了一种新型框架,名为不确定性引导交叉注意力集成均值教师(UG-CEMT),旨在在半监督医学图像分割领域实现最新性能。UG-CEMT结合了协同训练和知识蒸馏的优点,通过将受视觉转换器(ViT)启发的交叉注意力集成均值教师(CEMT)框架与不确定性引导的一致性正则化和锐度感知最小化相结合,以强调不确定性。UG-CEMT在促进子网之间的高差异的同时,维持网络架构和任务设置的连贯性,从而提高了半监督性能。实验表明,与Mean Teacher和交叉伪监督等现有方法相比,UG-CEMT在差异性、域泛化和医学图像分割性能等方面具有显著优势。UG-CEMT在多中心前列腺MRI和心脏MRI数据集上实现了最新结果,这些数据集的对象分割特别具有挑战性。我们的结果表明,仅使用10%的标记数据,UG-CEMT就能接近全监督方法的表现,证明了其在利用无标签数据进行稳健医学图像分割方面的有效性。代码已公开在https://github.com/Meghnak13/UG-CEMT。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in WACV 2025
Summary
医学图像分割领域提出一种新型框架UG-CEMT,融合交叉注意力集平均教师模型,利用不确定性引导的一致性正则化和清晰度感知最小化策略。该框架能提高半监督性能并保持一致的网络架构和任务设置,实验显示其在多中心前列腺MRI和心脏MRI数据集上的医学图像分割性能优于现有方法,如平均教师和交叉伪监督方法。使用仅10%的标签数据即可接近全监督方法的性能。
Key Takeaways
- UG-CEMT是一个用于医学图像分割的半监督学习框架。
- 结合交叉注意力集平均教师模型(CEMT)与不确定性引导的策略。
- CEMT借鉴了视觉转换器(ViT)的灵感。
- UG-CEMT通过促进子网之间的高差异性来提高半监督性能。
- 实验结果显示UG-CEMT在医学图像分割方面优于现有方法。
- UG-CEMT在多中心前列腺MRI和心脏MRI数据集上实现了最佳结果。
- 使用少量标签数据即可达到接近全监督方法的性能。
点此查看论文截图

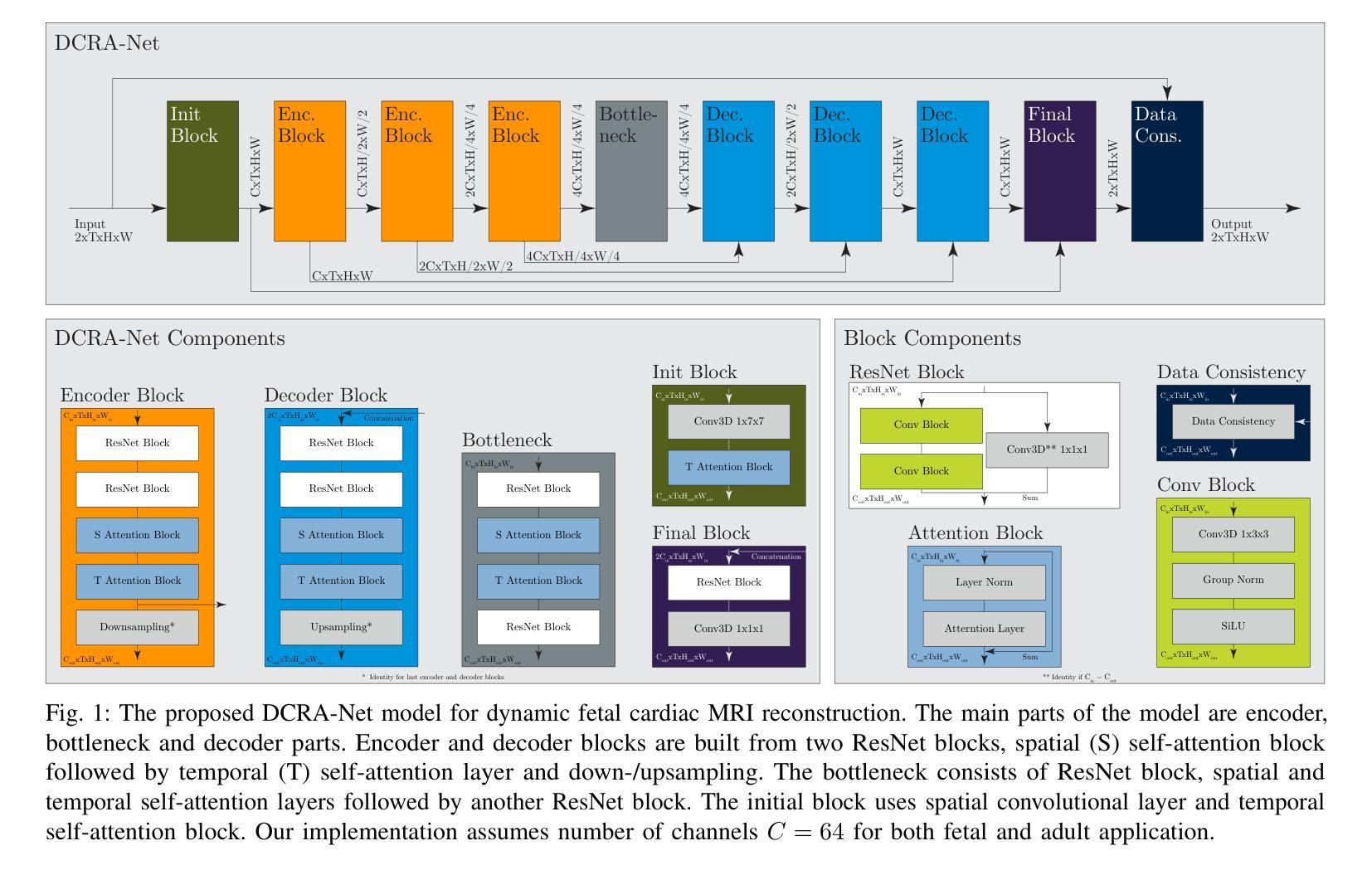
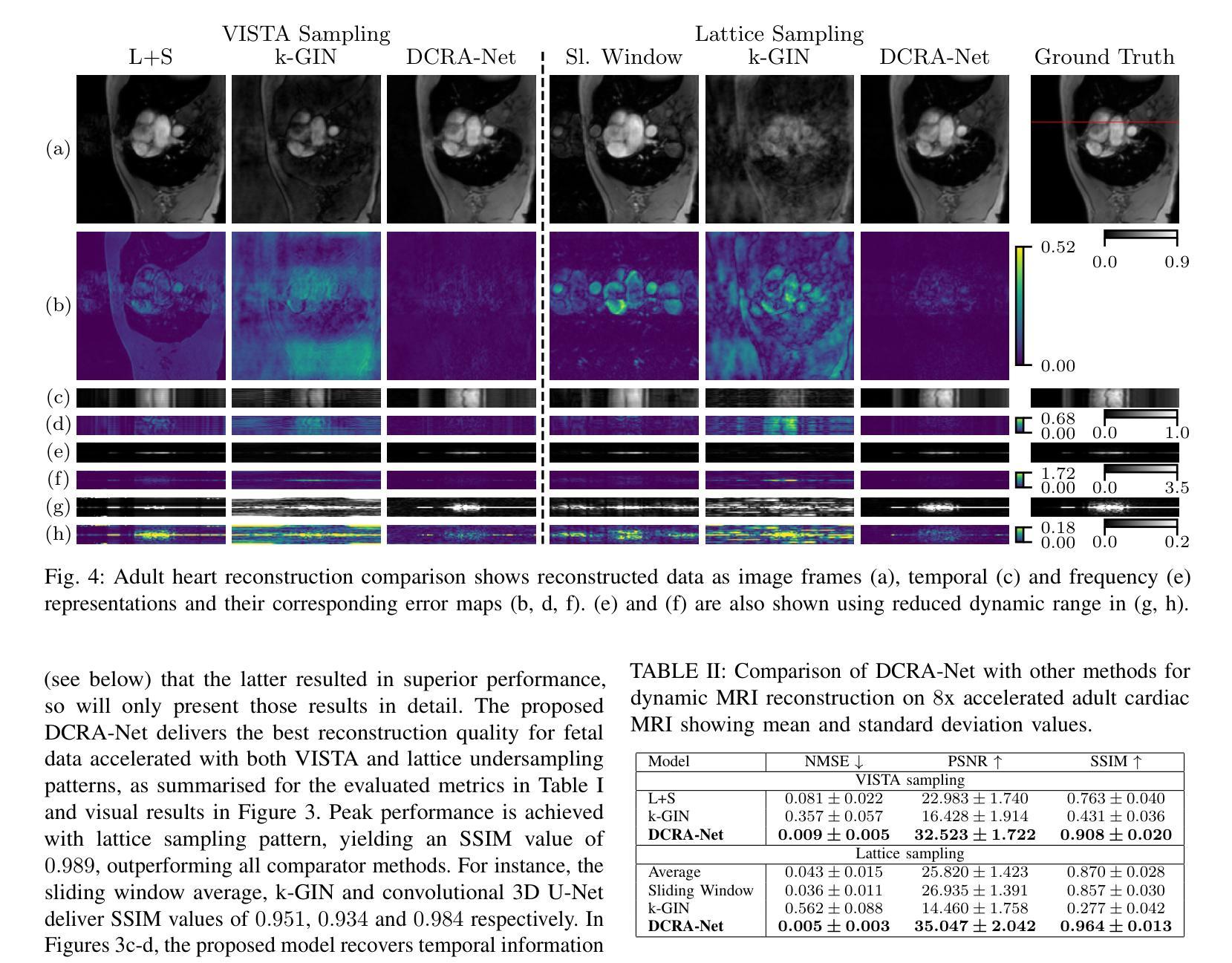
DCRA-Net: Attention-Enabled Reconstruction Model for Dynamic Fetal Cardiac MRI
Authors:Denis Prokopenko, David F. A. Lloyd, Amedeo Chiribiri, Daniel Rueckert, Joseph V. Hajnal
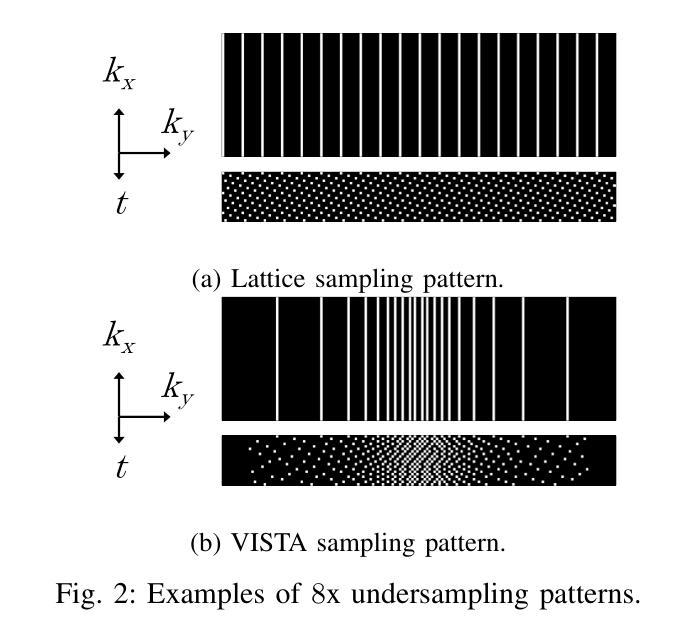
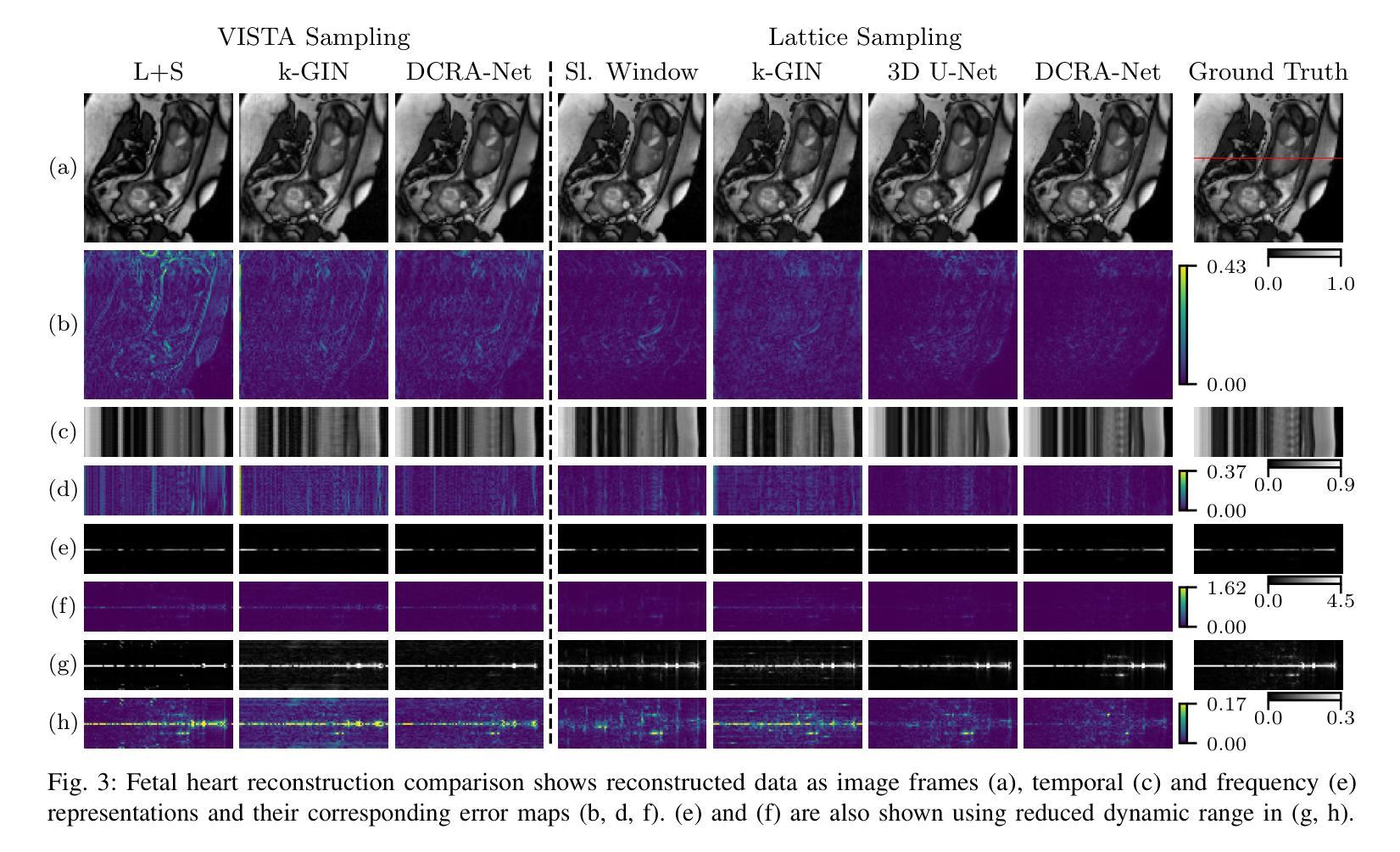
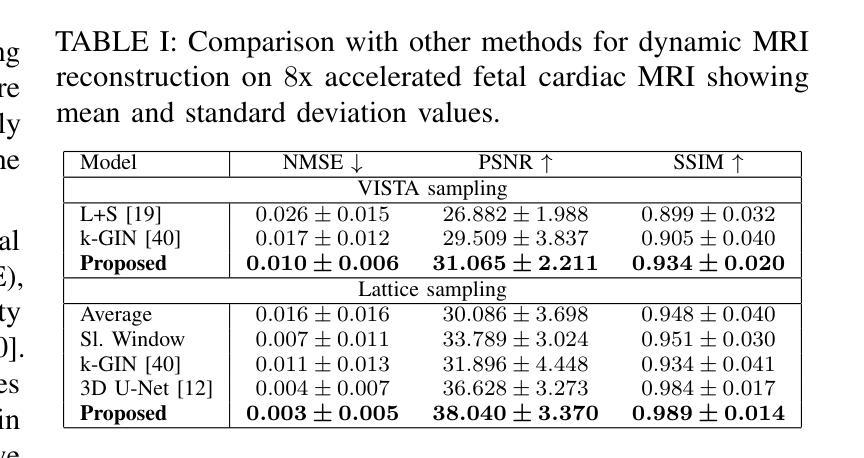
Dynamic fetal heart magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) presents unique challenges due to the fast heart rate of the fetus compared to adult subjects and uncontrolled fetal motion. This requires high temporal and spatial resolutions over a large field of view, in order to encompass surrounding maternal anatomy. In this work, we introduce Dynamic Cardiac Reconstruction Attention Network (DCRA-Net) - a novel deep learning model that employs attention mechanisms in spatial and temporal domains and temporal frequency representation of data to reconstruct the dynamics of the fetal heart from highly accelerated free-running (non-gated) MRI acquisitions. DCRA-Net was trained on retrospectively undersampled complex-valued cardiac MRIs from 42 fetal subjects and separately from 153 adult subjects, and evaluated on data from 14 fetal and 39 adult subjects respectively. Its performance was compared to L+S and k-GIN methods in both fetal and adult cases for an undersampling factor of 8x. The proposed network performed better than the comparators for both fetal and adult data, for both regular lattice and centrally weighted random undersampling. Aliased signals due to the undersampling were comprehensively resolved, and both the spatial details of the heart and its temporal dynamics were recovered with high fidelity. The highest performance was achieved when using lattice undersampling, data consistency and temporal frequency representation, yielding PSNR of 38 for fetal and 35 for adult cases. Our method is publicly available at https://github.com/denproc/DCRA-Net.
动态胎儿心脏磁共振成像(MRI)面临着独特的挑战,这是因为胎儿的心率与成人相比更快,且胎儿的运动不受控制。这需要在较大的视野范围内实现高时间分辨率和高空间分辨率,以包含周围母体的结构。在这项工作中,我们引入了动态心脏重建注意力网络(DCRA-Net)——一种新型深度学习模型,该模型采用空间和时间域的注意力机制以及数据的时频表示,从高度加速的自由运行(非门控)MRI采集重建胎儿心脏的动力学。DCRA-Net接受了来自42个胎儿和另外153个成人主体的回顾性下采样复数心脏MRI的训练,并在分别来自14个胎儿和39个成人主体的数据上进行了评估。其性能与胎儿和成人病例中以8倍下采样率的L+S和k-GIN方法进行了比较。所提出网络在胎儿和成人数据上均优于比较对象,无论是常规晶格还是中心加权随机下采样皆是如此。由于下采样导致的别名信号得到了全面的解决,心脏的空间细节及其时间动态以高保真度恢复。使用晶格下采样、数据一致性和时频表示时,取得了最佳性能,胎儿和成人病例的峰值信噪比(PSNR)分别为38和35。我们的方法在https://github.com/denproc/DCRA-Net公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型的深度学习模型——动态心脏重建注意力网络(DCRA-Net),用于动态胎儿心脏磁共振成像。该模型解决了胎儿心率快速和无法控制的胎儿运动带来的挑战,通过空间和时间域的注意力机制和数据的时序频率表示,重建胎儿心脏的动态过程。模型在胎儿和成人数据上的表现均优于其他方法,成功解决由于欠采样导致的别名信号问题,并恢复心脏的空间细节和时间动态。最佳性能在网格欠采样、数据一致性和时序频率表示下达到峰值信噪比(PSNR)为38(胎儿)和35(成人)。
Key Takeaways
- 动态胎儿心脏磁共振成像面临胎儿心率快速和无法控制的胎儿运动的挑战。
- 新型的深度学习模型——动态心脏重建注意力网络(DCRA-Net)解决了这些问题。
- DCRA-Net通过空间和时间域的注意力机制和数据的时序频率表示,重建胎儿心脏的动态过程。
- 模型在高度加速的自由运行(非门控)MRI采集数据上进行训练,并成功解决由于欠采样导致的别名信号问题。
- DCRA-Net在胎儿和成人数据上的表现均优于其他方法,恢复心脏的空间细节和时间动态。
- 最佳性能在网格欠采样、数据一致性和时序频率表示下达到较高的峰值信噪比(PSNR)。
点此查看论文截图

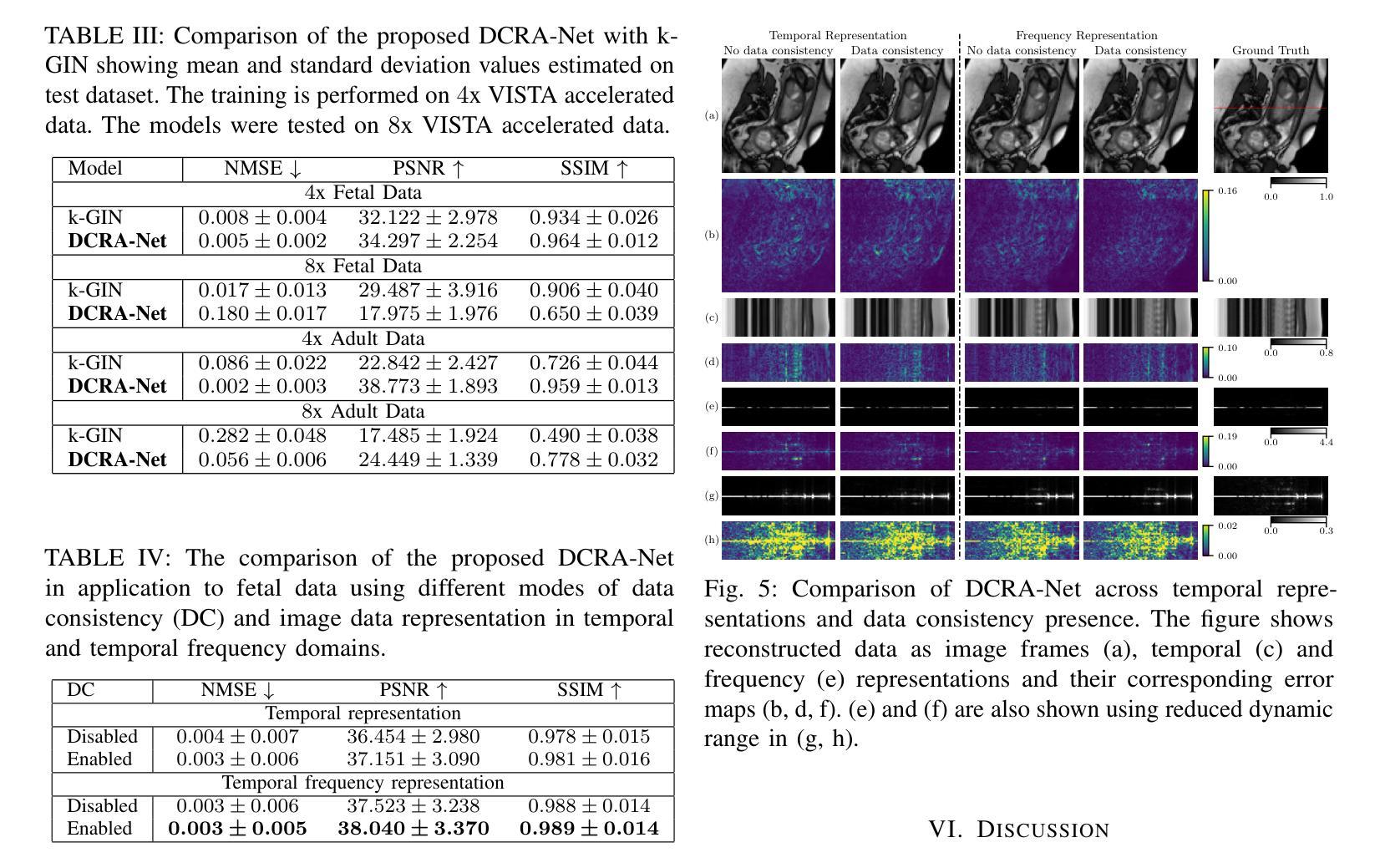
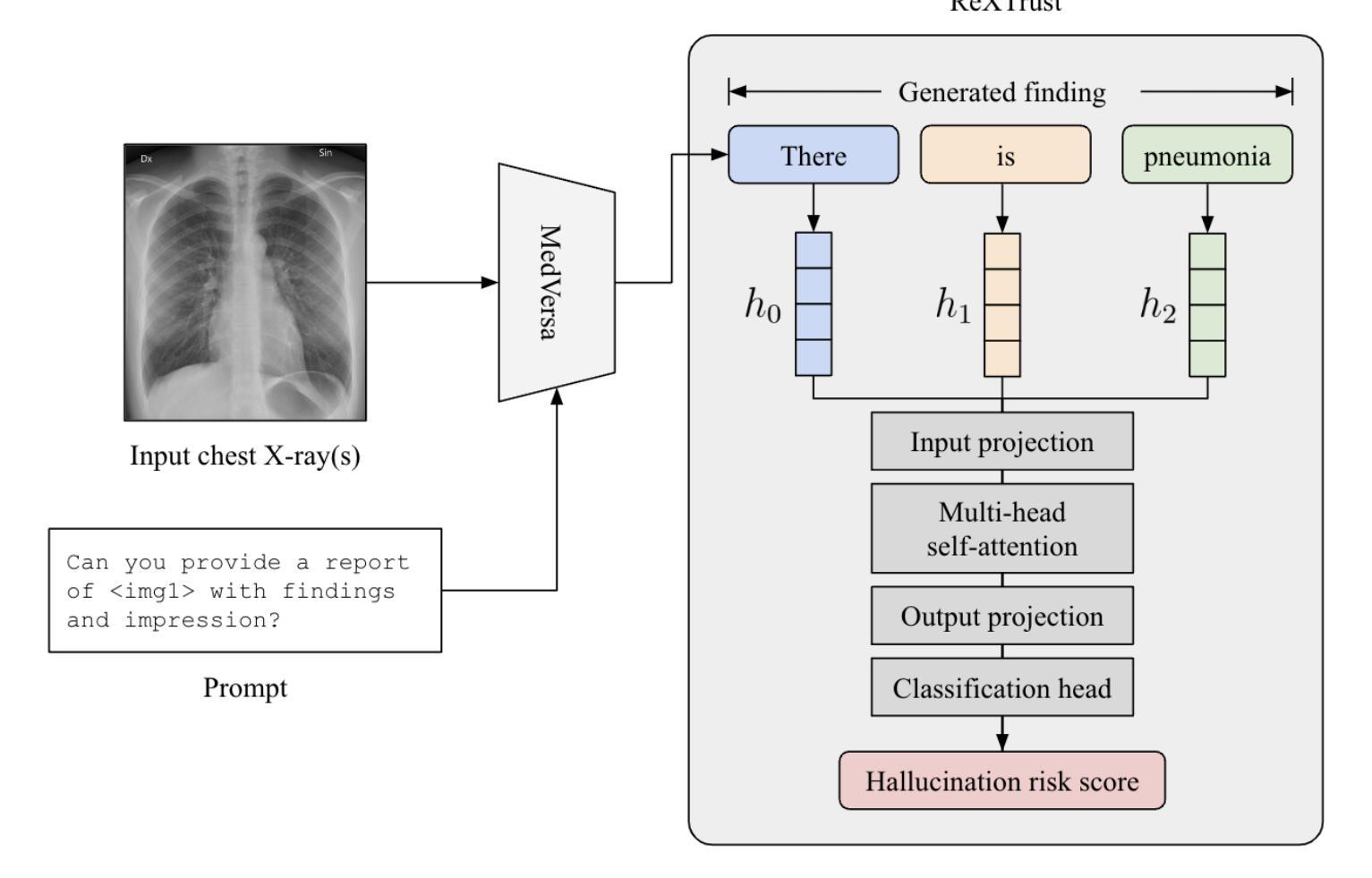
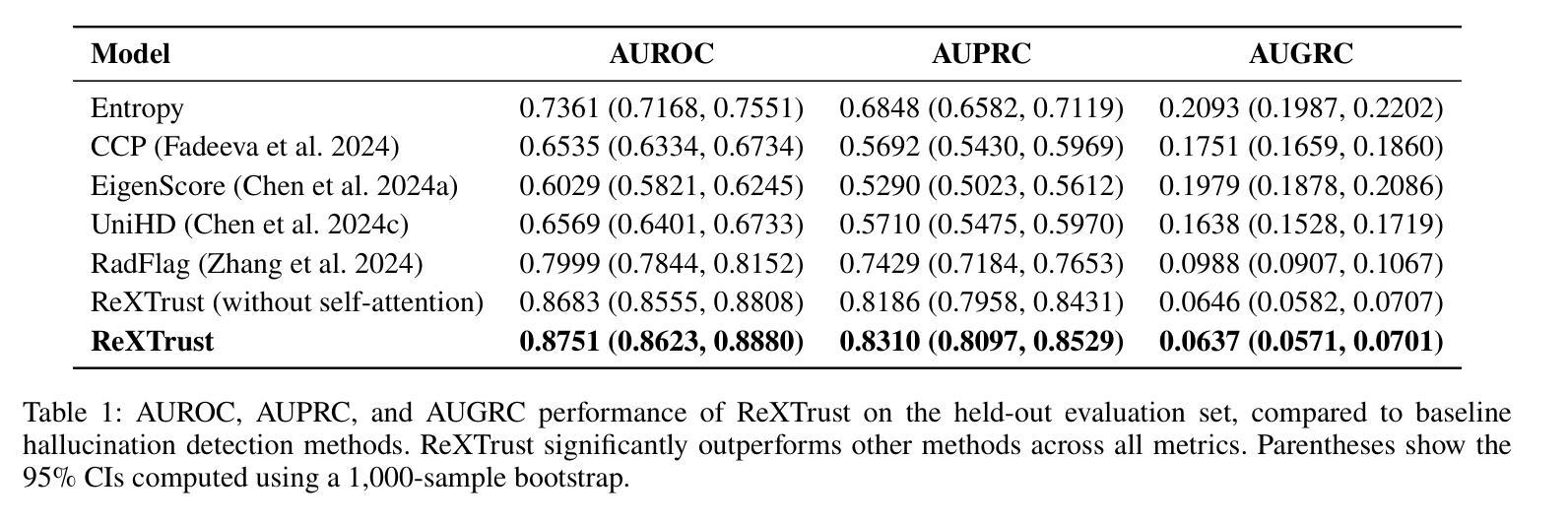
ReXTrust: A Model for Fine-Grained Hallucination Detection in AI-Generated Radiology Reports
Authors:Romain Hardy, Sung Eun Kim, Pranav Rajpurkar
The increasing adoption of AI-generated radiology reports necessitates robust methods for detecting hallucinations–false or unfounded statements that could impact patient care. We present ReXTrust, a novel framework for fine-grained hallucination detection in AI-generated radiology reports. Our approach leverages sequences of hidden states from large vision-language models to produce finding-level hallucination risk scores. We evaluate ReXTrust on a subset of the MIMIC-CXR dataset and demonstrate superior performance compared to existing approaches, achieving an AUROC of 0.8751 across all findings and 0.8963 on clinically significant findings. Our results show that white-box approaches leveraging model hidden states can provide reliable hallucination detection for medical AI systems, potentially improving the safety and reliability of automated radiology reporting.
随着AI生成的放射学报告越来越受到欢迎,我们需要可靠的方法来检测幻觉——可能会影响患者护理的虚假或毫无根据的陈述。我们提出了ReXTrust,这是一个用于AI生成的放射学报告中精细粒度幻觉检测的新框架。我们的方法利用大型视觉语言模型的隐藏状态序列来生成发现级别的幻觉风险分数。我们在MIMIC-CXR数据集的一个子集上评估了ReXTrust,并展示了相较于现有方法的优越性能,在所有发现上的AUROC达到0.8751,在具有临床意义上的发现上达到0.8963。我们的结果表明,利用模型隐藏状态的white-box方法可以为医疗AI系统提供可靠的幻觉检测,可能提高自动放射学报告的安全性和可靠性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to AIMedHealth 10 pages, 5 figures
Summary
基于人工智能生成的医学影像报告逐渐普及,对其中可能出现的幻觉(即可能影响患者诊疗的虚假或无根据的陈述)进行检测的方法日益受到关注。本研究提出一种新型精细幻觉检测框架ReXTrust,利用大型视觉语言模型的隐藏状态序列来生成发现级别的幻觉风险评分。在MIMIC-CXR数据集的一个子集上评估ReXTrust,相较于现有方法展现出卓越性能,所有发现的AUROC达到0.8751,临床重要发现的AUROC达到0.8963。结果表明,利用模型隐藏状态的透明方法可为医学影像AI系统提供可靠的幻觉检测,有望提高自动报告的安全性及可靠性。
Key Takeaways
- AI生成的医学影像报告普及导致需要检测潜在的幻觉陈述。
- ReXTrust是一种新型的精细幻觉检测框架。
- ReXTrust利用大型视觉语言模型的隐藏状态序列生成幻觉风险评分。
- ReXTrust在MIMIC-CXR数据集上的性能评估显示出优越表现。
- ReXTrust在所有发现上的AUROC为0.8751,临床重要发现的AUROC更高,达到0.8963。
- 利用模型隐藏状态的透明方法能提供可靠的医学影像AI系统幻觉检测。
点此查看论文截图

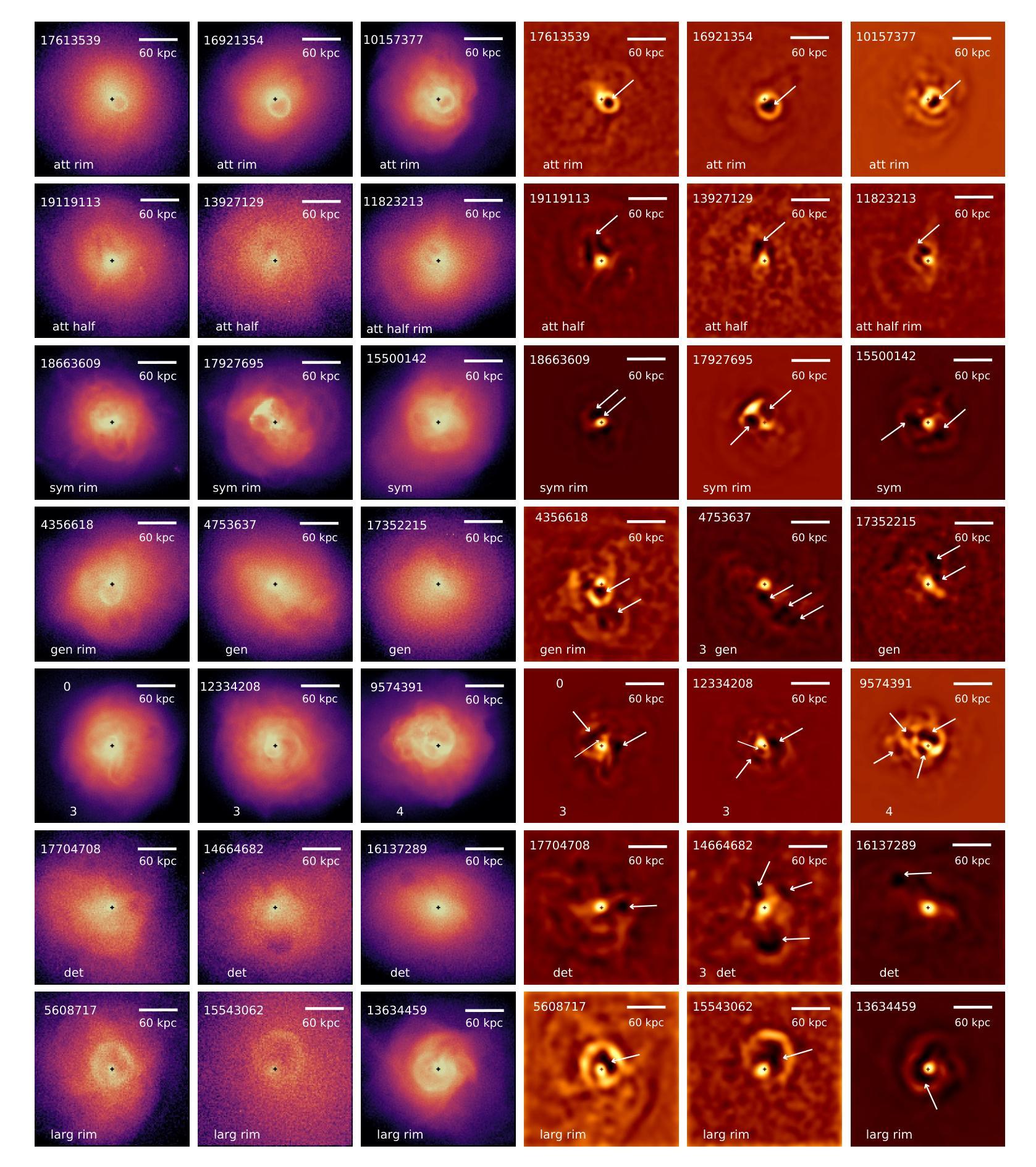
X-ray cavities in TNG-Cluster: AGN phenomena in the full cosmological context
Authors:Marine Prunier, Julie Hlavacek-Larrondo, Annalisa Pillepich, Katrin Lehle, Dylan Nelson
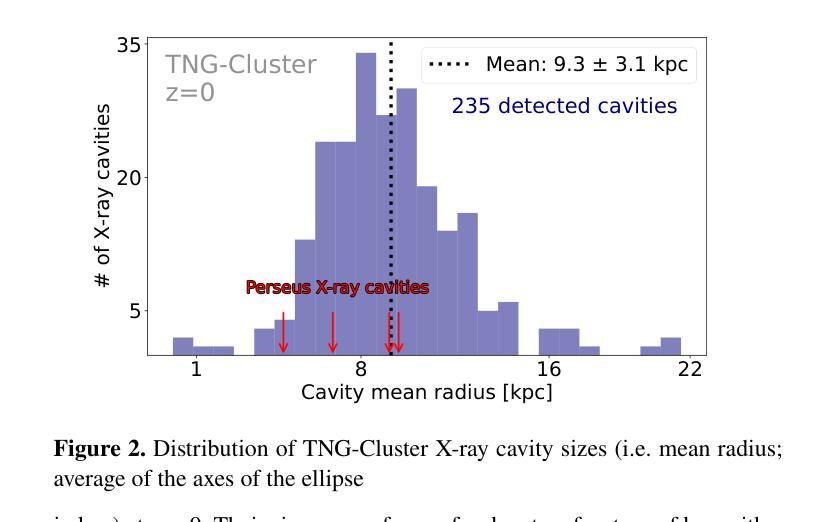
Active galactic nuclei (AGN) feedback from supermassive black holes (SMBHs) at the centers of galaxy clusters plays a key role in regulating star formation and shaping the intracluster medium (ICM), often manifesting through prominent X-ray cavities embedded in the cluster’s hot atmosphere. Here we show that X-ray cavities arise naturally due to AGN feedback in TNG-Cluster. This is a new suite of magnetohydrodynamic cosmological simulations of galaxy formation and evolution, and hence of galaxy clusters, whereby cold dark matter, baryon dynamics, galactic astrophysics, and magnetic fields are evolved together consistently. We construct mock Chandra X-ray observations of the central regions of the 352 simulated clusters at $z=0$ and find that $\sim$39 per cent contain X-ray cavities. Identified X-ray cavities vary in configuration (single, pairs, or multiples), with some still attached to SMBHs, while others have buoyantly risen. Their size ranges from a few to several tens of kpc. In terms of gas physical properties, TNG-Cluster X-ray cavities are underdense compared to the surrounding halo and filled with hot gas ($\sim$10$^8$K); 25 per cent of them are surrounded by an X-ray bright and compressed rim associated with a weak shock (Mach number $\sim 1.5$). Clusters exhibiting X-ray cavities are preferentially strong or weak cool-cores, are dynamically relaxed, and host SMBHs accreting at low Eddington rates. We show that TNG-Cluster X-ray cavities originate from episodic, wind-like energy injections from central AGN. Our results illustrate the existence and diversity of X-ray cavities simulated in state-of-the-art models within realistic cosmological environments and show that these can form without necessarily invoking bipolar, collimated, or relativistic jets.
活动星系核(AGN)反馈来自星系团中心的超大质量黑洞(SMBH),在调节恒星形成和塑造星系团内介质(ICM)方面起着关键作用,通常表现为嵌入在星系团热大气中的突出X射线空洞。在这里,我们展示了TNG-Cluster中的X射线空洞是由于超大质量黑洞(SMBH)的活动性产生的。这是一个新的磁流体动力学宇宙学模拟套件,模拟星系的形成和演化,因此对星系团进行了连贯一致的模拟,其中包括冷暗物质、重子动力学、星系天体物理学和磁场。我们构建了模拟集群中心区域的模拟钱德拉X射线观测结果,这些集群共有352个在z=0时的模拟集群,我们发现约39%的集群存在X射线空洞。所确定的X射线空洞的形态各异(单个、成对或多重),其中一些仍然与SMBH相连,而其他则已上浮。它们的大小范围从几到几十kpc。就气体物理性质而言,TNG-Cluster的X射线空洞与周围的晕相比密度较低,并充满热气体(约10^8K);其中25%被X射线明亮的压缩边缘包围,与弱冲击波相关(马赫数约为1.5)。表现出X射线空洞的集群通常是强或弱的冷核,处于动态平衡状态,并宿主着低爱丁顿率的SMBH。我们表明,TNG-Cluster的X射线空洞源于中央类星体的间歇性、类似风的能量注入。我们的结果说明了在先进的模型中模拟的X射线空洞的存在和多样性,这些空洞可以在现实的宇宙学环境中形成,而不需要一定假设为双极、定向或相对论性喷流。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to MNRAS. See further TNG-Cluster papers from Eric Rohr, and Urmila Chadayammuri over the next days, and on the TNG-Cluster website: https://www.tng-project.org/cluster/
Summary
超大质量黑洞(SMBh)位于星系团中心的活跃星系核(AGN)反馈对于调节恒星形成和塑造星系团内介质(ICM)起着关键作用,通常表现为嵌入在星系团热大气中的突出X射线空洞。本研究通过TNG-Cluster模拟显示,X射线空洞是由于宇宙学中超大质量黑洞的活跃星系核反馈自然产生的。该模拟是一套新的磁流体动力学宇宙学模拟,包含冷暗物质、重子动力学、星系天体物理学和磁场的协同演化。通过对模拟星系团中央区域的模拟观察,发现约39%存在X射线空洞。这些空洞在配置上有所不同(单个、成对或多重),有些仍与SMBh相连,而另一些则表现出浮力上升现象。它们的大小范围从几到几十kpc不等。在气体物理性质方面,TNG-Cluster的X射线空洞与其周围的光晕相比密度较低,充满热气体(约10$^8$K);其中25%被X射线明亮的压缩边缘包围,与弱冲击波相关(马赫数约为1.5)。表现出X射线空洞的星系团更喜欢强或弱的冷却核心,处于动态平衡状态,并宿主低艾丁顿率下的SMBh吸积。本研究表明,TNG-Cluster的X射线空洞源于中央活跃星系核的间歇性风能量注入。我们的结果展示了在真实宇宙学环境中先进模型模拟的X射线空洞的存在和多样性,并表明这些空洞的形成不一定需要两极、定向或相对论性射流。
Key Takeaways
- TNG-Cluster模拟显示活跃星系核(AGN)反馈产生X射线空洞。
- X射线空洞在配置、大小和物理性质上存在差异。
- 约39%的模拟星系团存在X射线空洞。
- X射线空洞与超大质量黑洞(SMBh)有关,并表现出浮力上升现象。
- TNG-Cluster模拟的X射线空洞可能由中央AGN的间歇性风能量注入形成。
- 存在X射线空洞的星系团倾向于具有强或弱的冷却核心,处于动态平衡状态。
点此查看论文截图

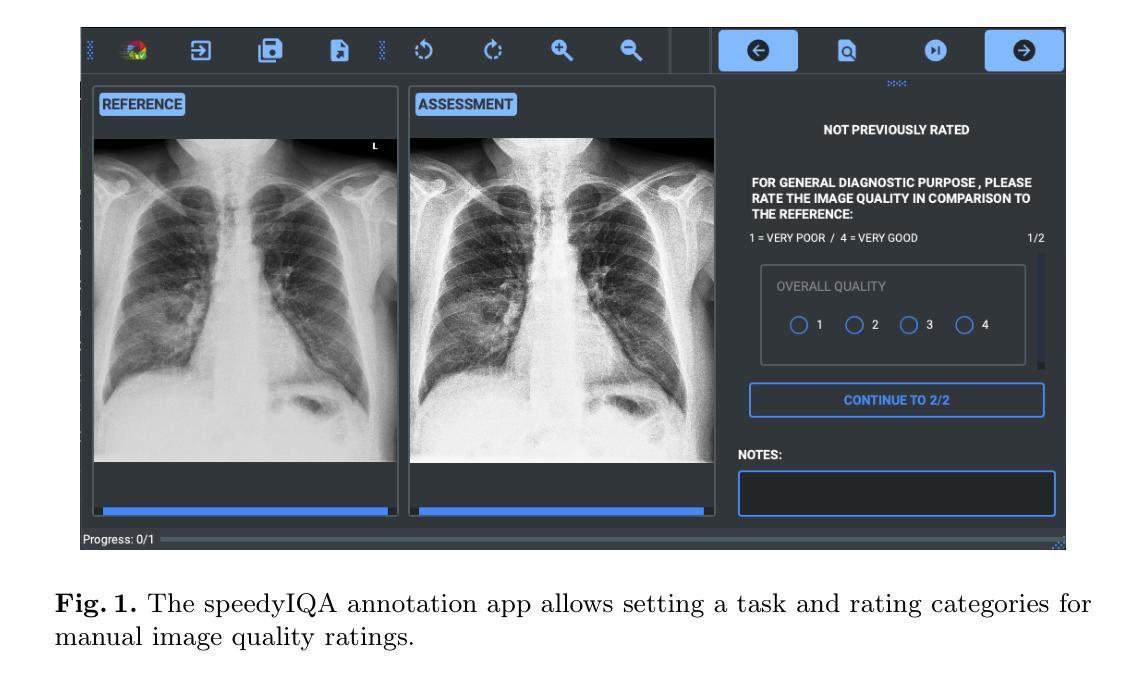
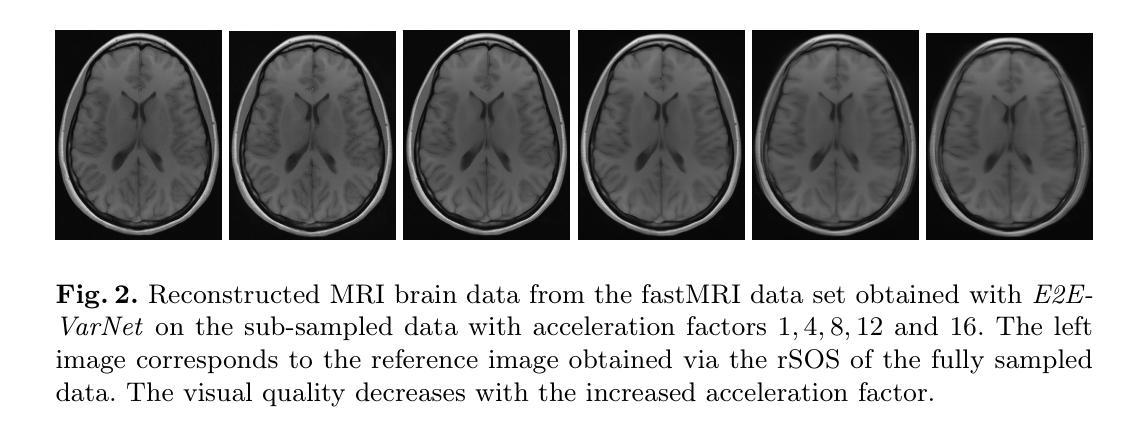
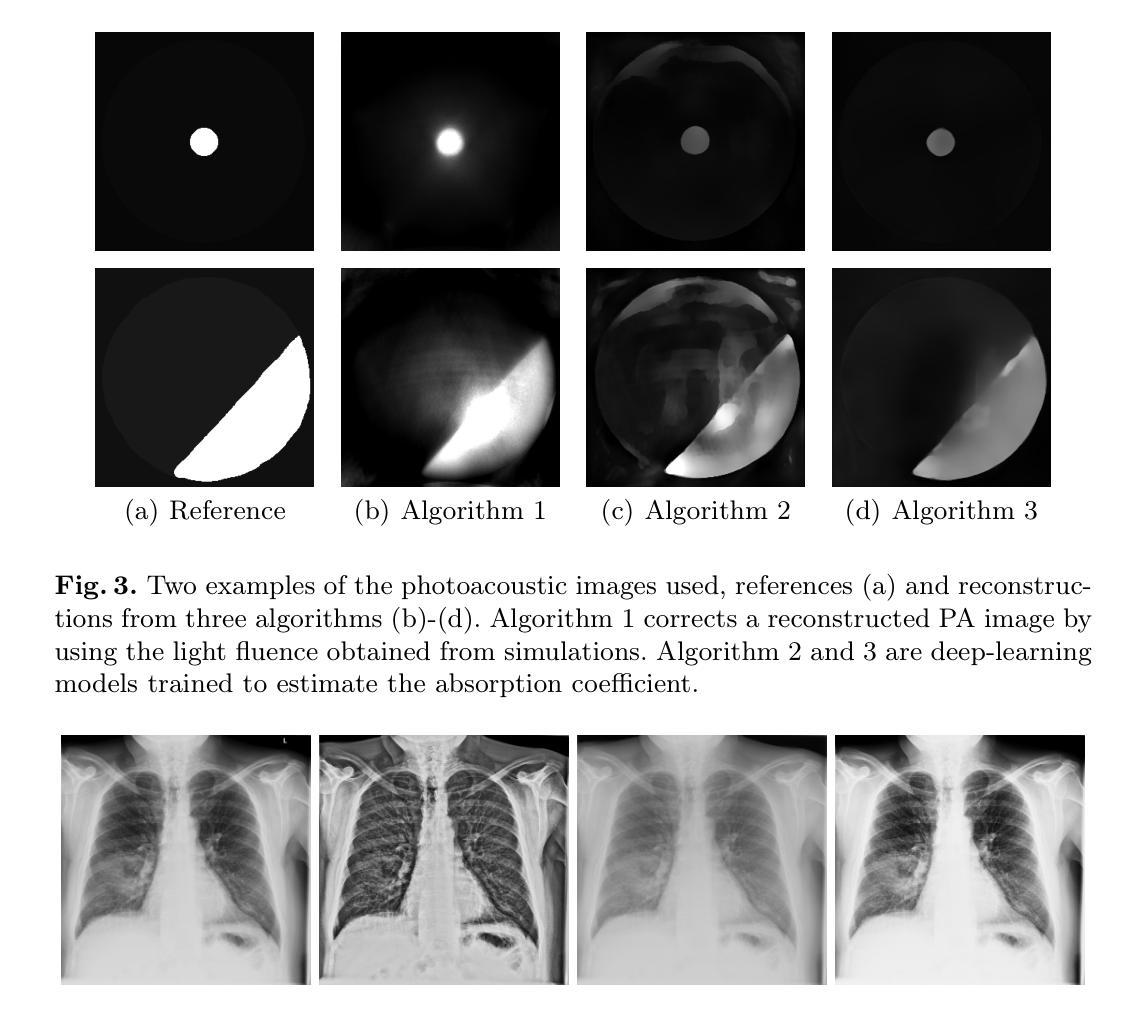
A study on the adequacy of common IQA measures for medical images
Authors:Anna Breger, Clemens Karner, Ian Selby, Janek Gröhl, Sören Dittmer, Edward Lilley, Judith Babar, Jake Beckford, Thomas R Else, Timothy J Sadler, Shahab Shahipasand, Arthikkaa Thavakumar, Michael Roberts, Carola-Bibiane Schönlieb
Image quality assessment (IQA) is standard practice in the development stage of novel machine learning algorithms that operate on images. The most commonly used IQA measures have been developed and tested for natural images, but not in the medical setting. Reported inconsistencies arising in medical images are not surprising, as they have different properties than natural images. In this study, we test the applicability of common IQA measures for medical image data by comparing their assessment to manually rated chest X-ray (5 experts) and photoacoustic image data (2 experts). Moreover, we include supplementary studies on grayscale natural images and accelerated brain MRI data. The results of all experiments show a similar outcome in line with previous findings for medical images: PSNR and SSIM in the default setting are in the lower range of the result list and HaarPSI outperforms the other tested measures in the overall performance. Also among the top performers in our experiments are the full reference measures FSIM, LPIPS and MS-SSIM. Generally, the results on natural images yield considerably higher correlations, suggesting that additional employment of tailored IQA measures for medical imaging algorithms is needed.
图像质量评估(IQA)是图像操作的新型机器学习算法开发阶段的标准实践。最常用的IQA措施是为自然图像开发和测试的,而不是在医疗环境中。医疗图像中出现的报告不一致性并不奇怪,因为它们的属性与自然图像不同。在这项研究中,我们通过将其评估与手动评分的胸部X射线(5位专家)和光声图像数据(2位专家)进行比较,测试了常见IQA措施在医学图像数据中的适用性。此外,我们还进行了关于灰度自然图像和加速脑部MRI数据的补充研究。所有实验的结果均显示与先前对医学图像的研究结果一致:PSNR和SSIM在默认设置下的结果排名较低,HaarPSI在总体性能上优于其他测试措施。此外,在我们的实验中表现最好的还有全参考措施FSIM、LPIPS和MS-SSIM。总体而言,自然图像的结果显示出较高的相关性,这表明需要额外采用针对医学成像算法的定制IQA措施。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了图像质量评估(IQA)在医学图像领域的应用。实验结果显示,针对医学图像数据的常见IQA措施表现不一,特别是在胸部X射线和光声图像数据上。研究还发现,与传统的自然图像相比,医学图像的结果关联度较低,可能需要采用针对医学成像算法的定制IQA措施。
Key Takeaways
- 图像质量评估(IQA)在医学图像领域具有重要性。
- 常见IQA措施在医学图像数据上的表现存在差异。
- 针对医学图像的IQA研究结果显示,PSNR和SSIM在默认设置下的表现较低。
- HaarPSI在总体性能上超越了其他测试措施。
- 全参考措施FSIM、LPIPS和MS-SSIM在实验中表现较好。
- 与自然图像相比,医学图像的结果关联度较低。
点此查看论文截图

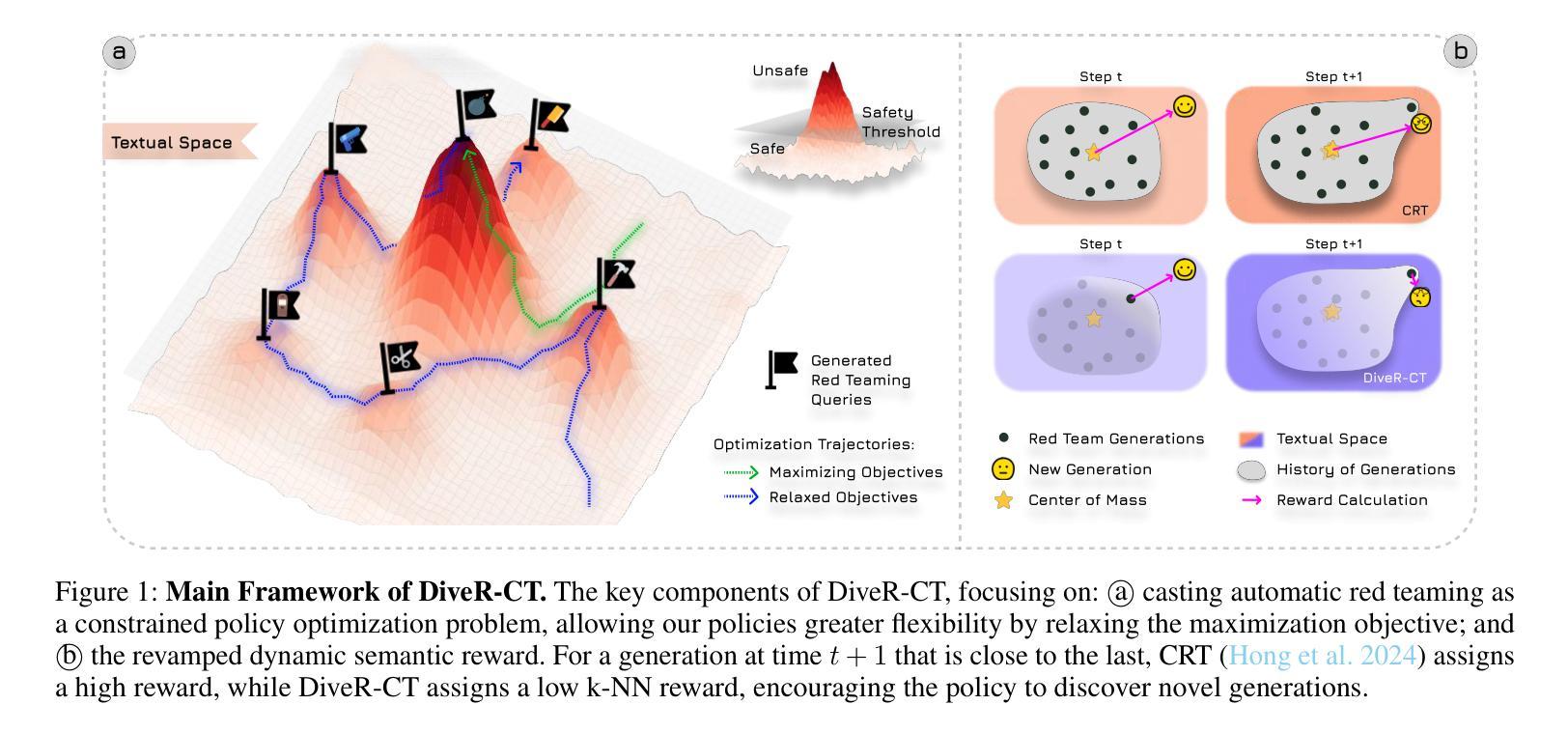
DiveR-CT: Diversity-enhanced Red Teaming Large Language Model Assistants with Relaxing Constraints
Authors:Andrew Zhao, Quentin Xu, Matthieu Lin, Shenzhi Wang, Yong-jin Liu, Zilong Zheng, Gao Huang
Recent advances in large language model assistants have made them indispensable, raising significant concerns over managing their safety. Automated red teaming offers a promising alternative to the labor-intensive and error-prone manual probing for vulnerabilities, providing more consistent and scalable safety evaluations. However, existing approaches often compromise diversity by focusing on maximizing attack success rate. Additionally, methods that decrease the cosine similarity from historical embeddings with semantic diversity rewards lead to novelty stagnation as history grows. To address these issues, we introduce DiveR-CT, which relaxes conventional constraints on the objective and semantic reward, granting greater freedom for the policy to enhance diversity. Our experiments demonstrate DiveR-CT’s marked superiority over baselines by 1) generating data that perform better in various diversity metrics across different attack success rate levels, 2) better-enhancing resiliency in blue team models through safety tuning based on collected data, 3) allowing dynamic control of objective weights for reliable and controllable attack success rates, and 4) reducing susceptibility to reward overoptimization. Overall, our method provides an effective and efficient approach to LLM red teaming, accelerating real-world deployment.
近年来,大型语言模型助理的进展使其变得不可或缺,这引发了人们对如何管理其安全性的重大关注。自动红队测试作为一种替代方法,具有替代劳动密集型和易出错的手动探测漏洞的潜力,可以提供更一致和可扩展的安全评估。然而,现有的方法往往通过专注于最大化攻击成功率来牺牲多样性。此外,通过减少历史嵌入的余弦相似度来增加语义多样性的奖励随着历史的增长会导致新奇度的停滞。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了DiveR-CT,它放宽了目标和语义奖励的常规约束,为策略提供了更大的自由度以增强多样性。我们的实验表明,DiveR-CT在以下方面显示出明显优于基线:1)生成在各种攻击成功率级别上表现优异的数据,同时在各种多样性指标上表现出更高的得分;2)基于收集的数据进行安全调整,更好地增强蓝队模型的韧性;3)允许动态控制目标权重以实现可靠且可控的攻击成功率;4)减少易受奖励过度优化的影响。总的来说,我们的方法为LLM红队测试提供了一种有效且高效的方法,加速了其在现实世界中的部署。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by the 39th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-25)
Summary
大型语言模型助理的近期进展使其变得不可或缺,引发了关于其安全管理的重大关注。自动红队通过为劳动密集型和易出错的手动探测提供有希望的替代方案,提供了更一致和可扩展的安全评估。然而,现有方法常常在最大化攻击成功率时牺牲了多样性。此外,随着历史数据的增长,减少与具有语义多样性奖励的历史嵌入之间的余弦相似度的方法会导致新颖性的停滞。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了DiveR-CT,它放松了客观性和语义奖励的传统约束,为策略提供了更大的自由以增强多样性。实验证明,相较于基线方法,DiveR-CT具有显著优势:能够在不同的攻击成功率级别上在各种多样性指标上表现更好、通过基于收集数据的安全调整增强蓝队模型的恢复能力、允许动态控制目标权重以实现可靠和可控的攻击成功率,并减少奖励过度优化的易感性。总体而言,我们的方法为LLM红队提供了有效且高效的方法,加速了其在现实世界中的部署。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型助理的安全问题引发了关注,自动红队提供了一种有前景的替代方案进行安全评估。
- 现有方法过于注重最大化攻击成功率,牺牲了多样性。
- 减少与具有语义多样性奖励的历史嵌入之间的余弦相似度可能导致新颖性停滞。
- DiveR-CT方法旨在解决这些问题,通过放松客观性和语义奖励的传统约束增强多样性。
- DiveR-CT实验证明其在多个方面优于基线方法。
- DiveR-CT允许动态控制攻击成功率,并减少奖励过度优化的风险。
点此查看论文截图


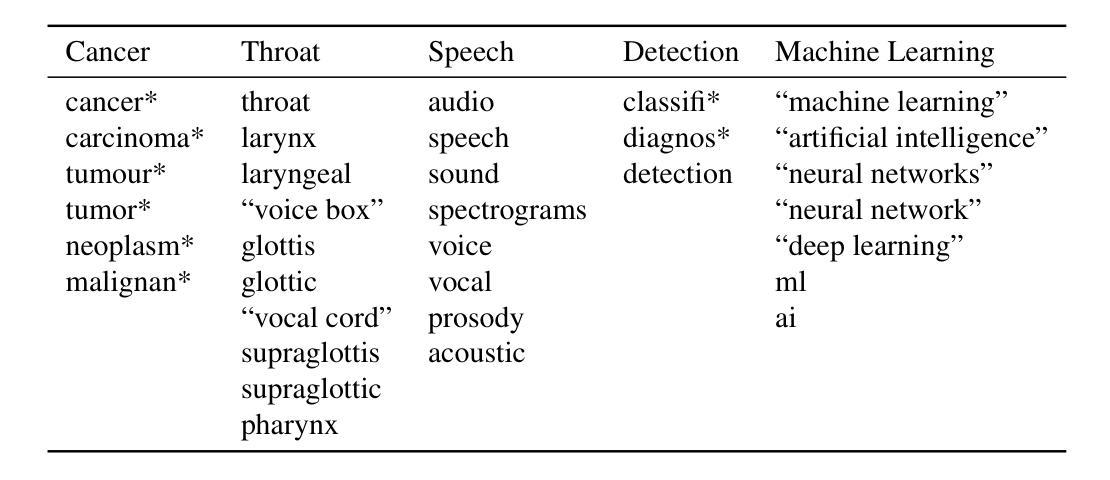
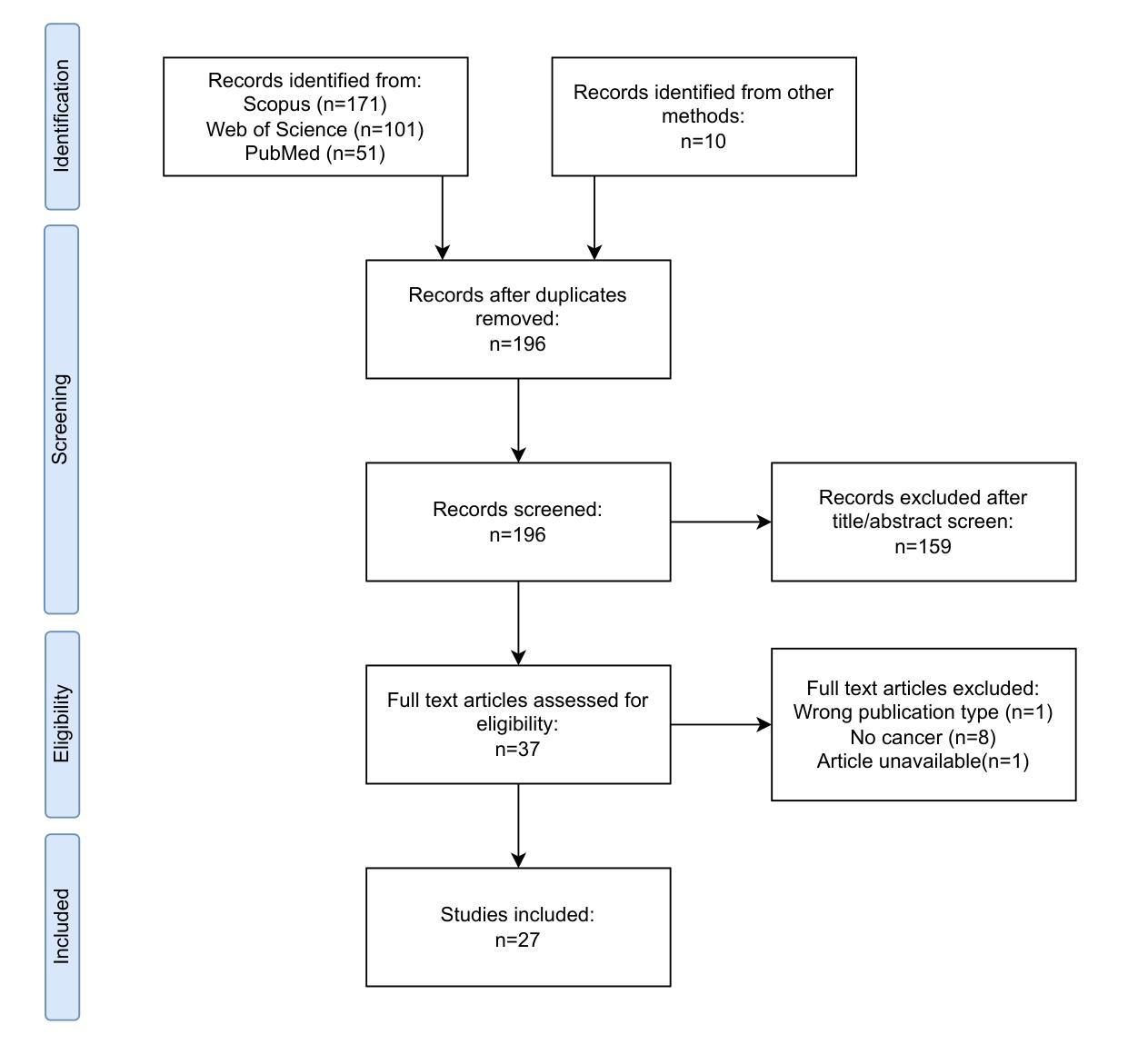
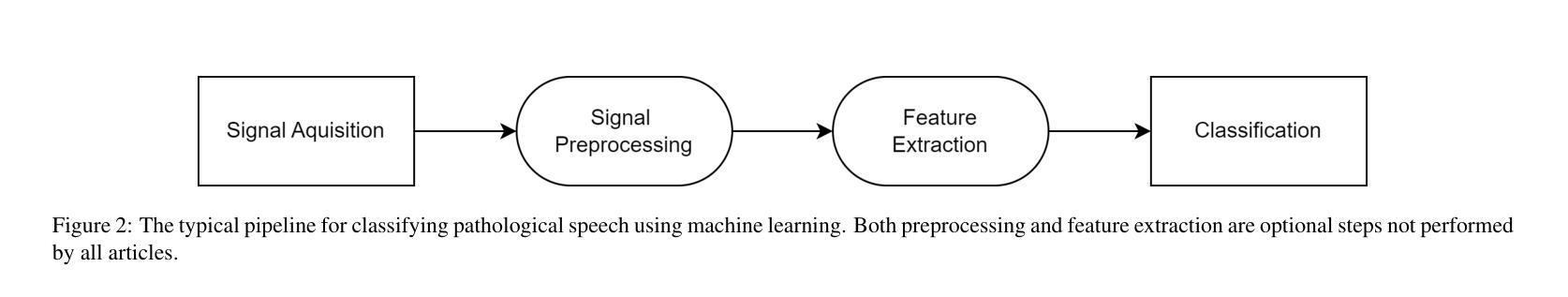
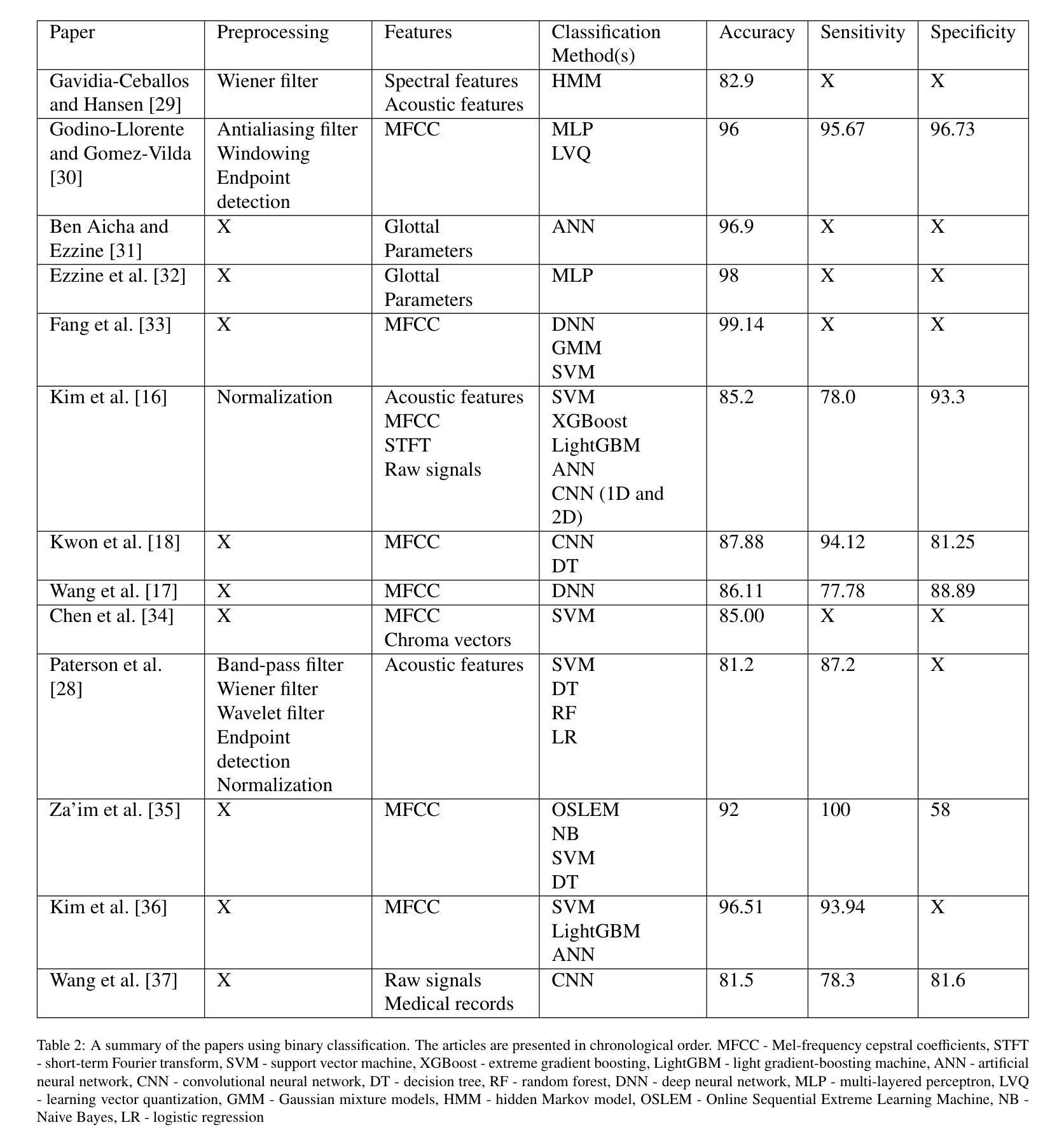
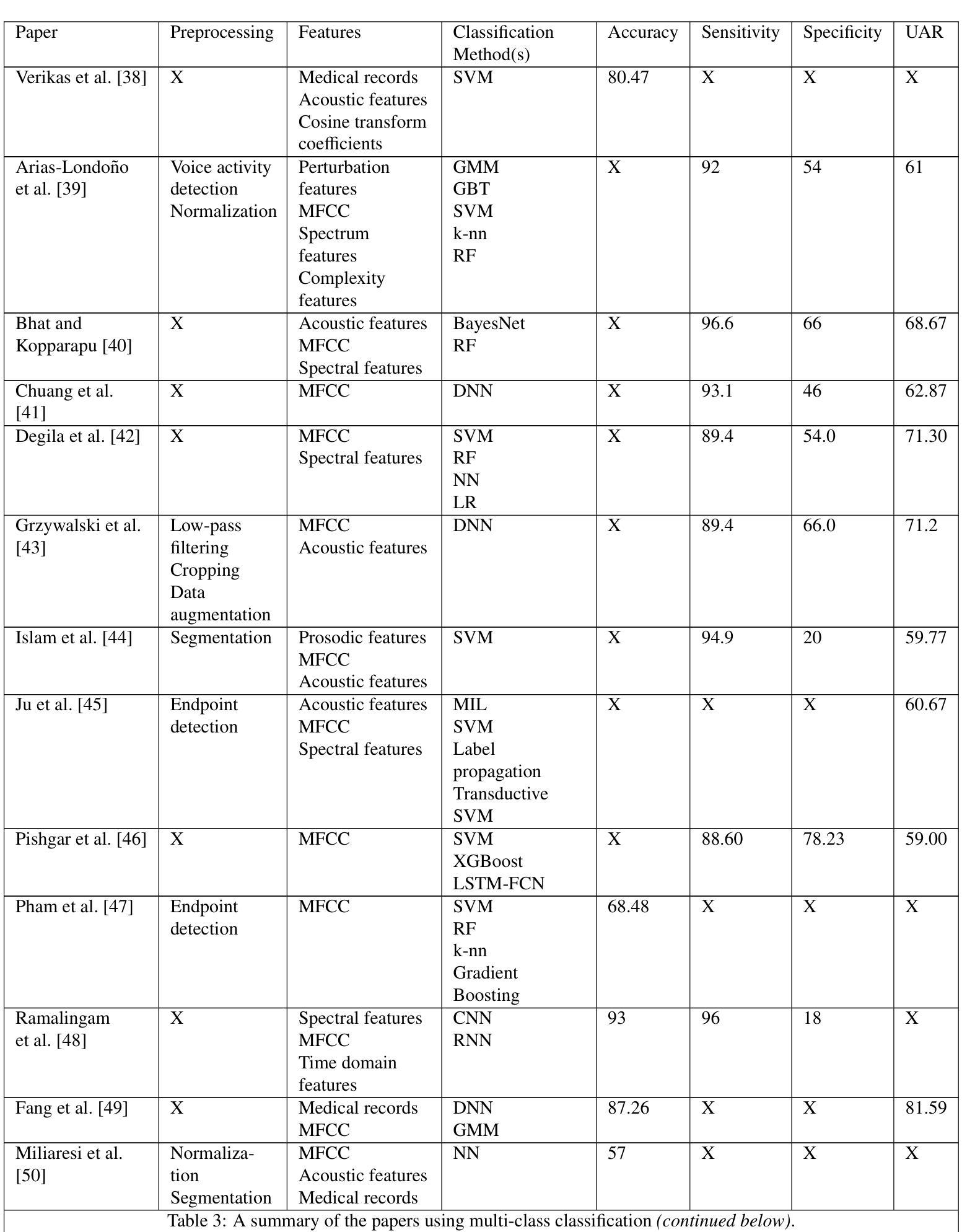
Detecting Throat Cancer from Speech Signals using Machine Learning: A Scoping Literature Review
Authors:Mary Paterson, James Moor, Luisa Cutillo
Introduction: Cases of throat cancer are rising worldwide. With survival decreasing significantly at later stages, early detection is vital. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have the potential to detect throat cancer from patient speech, facilitating earlier diagnosis and reducing the burden on overstretched healthcare systems. However, no comprehensive review has explored the use of AI and ML for detecting throat cancer from speech. This review aims to fill this gap by evaluating how these technologies perform and identifying issues that need to be addressed in future research. Materials and Methods: We conducted a scoping literature review across three databases: Scopus, Web of Science, and PubMed. We included articles that classified speech using machine learning and specified the inclusion of throat cancer patients in their data. Articles were categorized based on whether they performed binary or multi-class classification. Results: We found 27 articles fitting our inclusion criteria, 12 performing binary classification, 13 performing multi-class classification, and two that do both binary and multiclass classification. The most common classification method used was neural networks, and the most frequently extracted feature was mel-spectrograms. We also documented pre-processing methods and classifier performance. We compared each article against the TRIPOD-AI checklist, which showed a significant lack of open science, with only one article sharing code and only three using open-access data. Conclusion: Open-source code is essential for external validation and further development in this field. Our review indicates that no single method or specific feature consistently outperforms others in detecting throat cancer from speech. Future research should focus on standardizing methodologies and improving the reproducibility of results.
引言:全球喉癌病例数量正在上升。由于后期生存率显著降低,早期发现至关重要。人工智能(AI)和机器学习(ML)有潜力通过患者的语音检测喉癌,有助于更早诊断,减轻过度劳累的医疗卫生系统的负担。然而,还没有一篇全面的综述探讨使用AI和ML从语音中检测喉癌的情况。本综述旨在填补这一空白,评估这些技术的表现,并确定未来研究中需要解决的问题。
材料与方法:我们在三个数据库(Scopus、Web of Science和PubMed)中进行了文献范围综述。我们纳入了使用机器学习对语音进行分类的文章,并指定在数据中包含喉癌患者。文章根据是否进行二分类或多类分类进行分类。
结果:我们发现符合我们纳入标准的27篇文章,其中12篇进行二分类,13篇进行多类分类,2篇同时进行二分类和多类分类。使用最普遍的分类方法是神经网络,最常提取的特征是梅尔频谱图。我们还记录了预处理方法和分类器性能。我们根据TRIPOD-AI清单对比了每篇文章,结果显示开放科学严重缺乏,只有一篇文章分享代码,三篇文章使用开放获取数据。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 12 figures, 5 tables
摘要
喉癌病例全球范围内不断上升,后期生存率显著下降,因此早期发现至关重要。人工智能(AI)和机器学习(ML)在患者语音中检测喉癌方面具有巨大潜力,有助于更早诊断,减轻医疗系统的负担。然而,尚未有全面的综述探讨使用AI和ML通过语音检测喉癌的情况。本综述旨在评价这些技术的应用情况,并确定未来研究中需要解决的问题。
要点
- 喉癌病例全球上升,早期发现至关重要。
- AI和ML在语音中检测喉癌具有潜力。
- 本综述旨在全面评估AI和ML在喉癌检测中的应用。
- 通过文献综述,发现27篇文章符合纳入标准。
- 神经网络是最常用的分类方法,mel-spectrograms是最常提取的特征。
- 大多数研究缺乏公开科学,只有少数分享代码和使用开放获取数据。
- 建议未来研究应关注方法标准化和提高结果的可重复性。
点此查看论文截图