⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-24 更新
Mask-RadarNet: Enhancing Transformer With Spatial-Temporal Semantic Context for Radar Object Detection in Autonomous Driving
Authors:Yuzhi Wu, Jun Liu, Guangfeng Jiang, Weijian Liu, Danilo Orlando
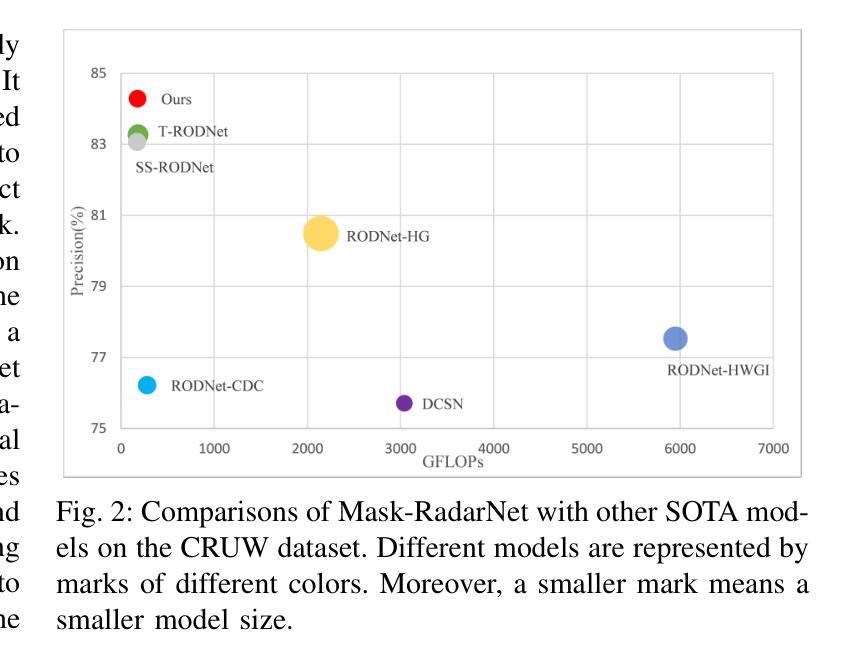
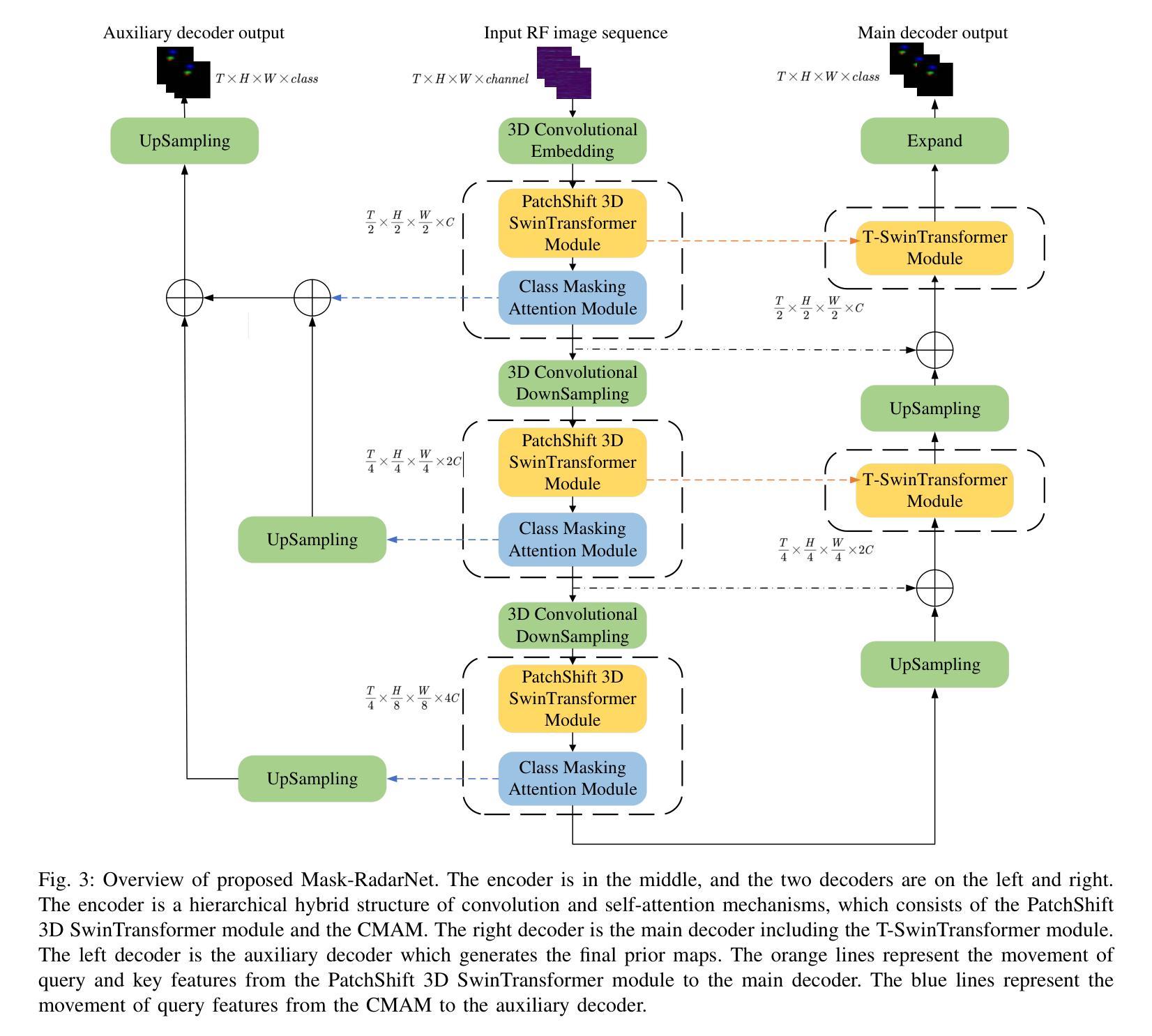
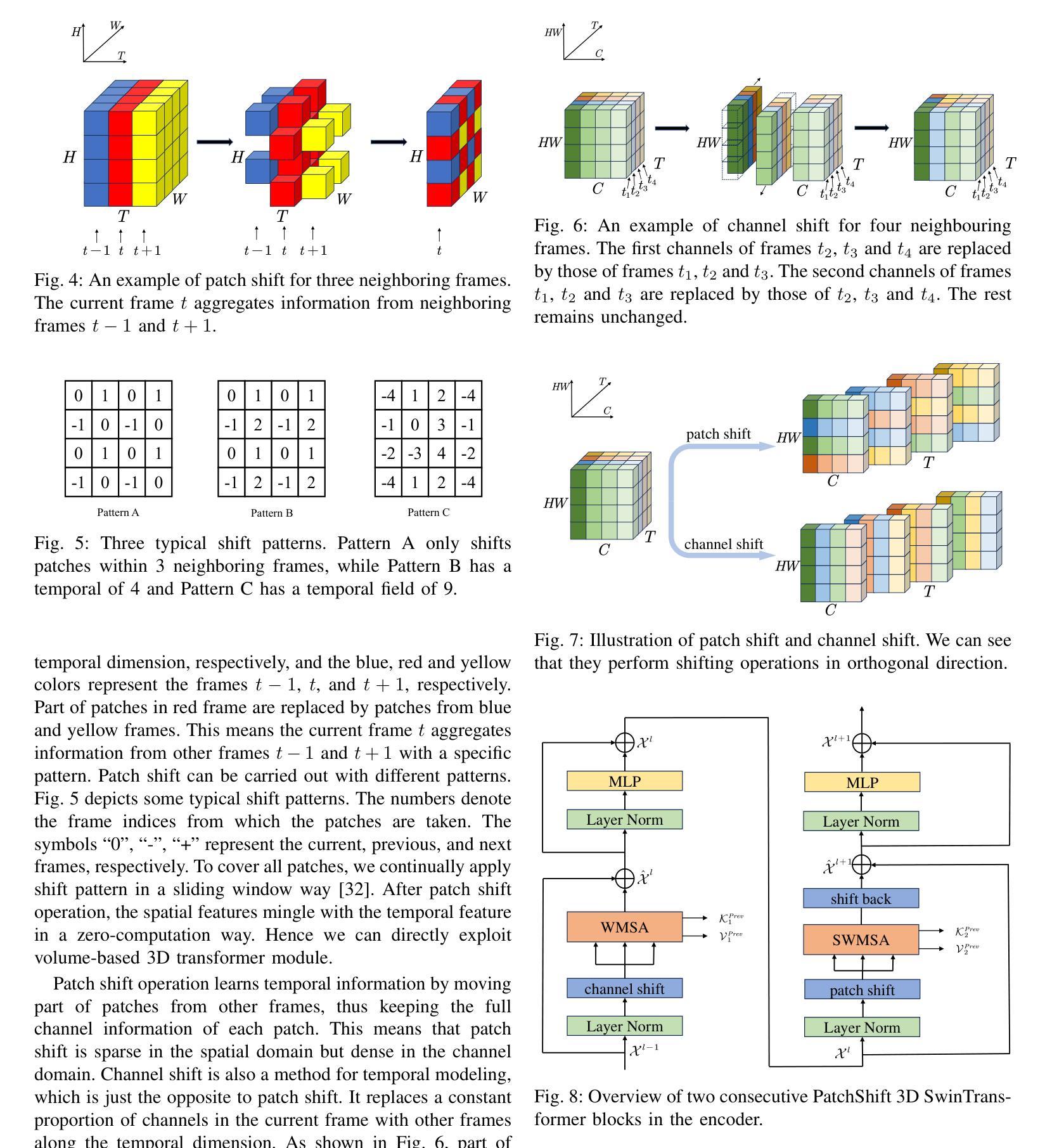
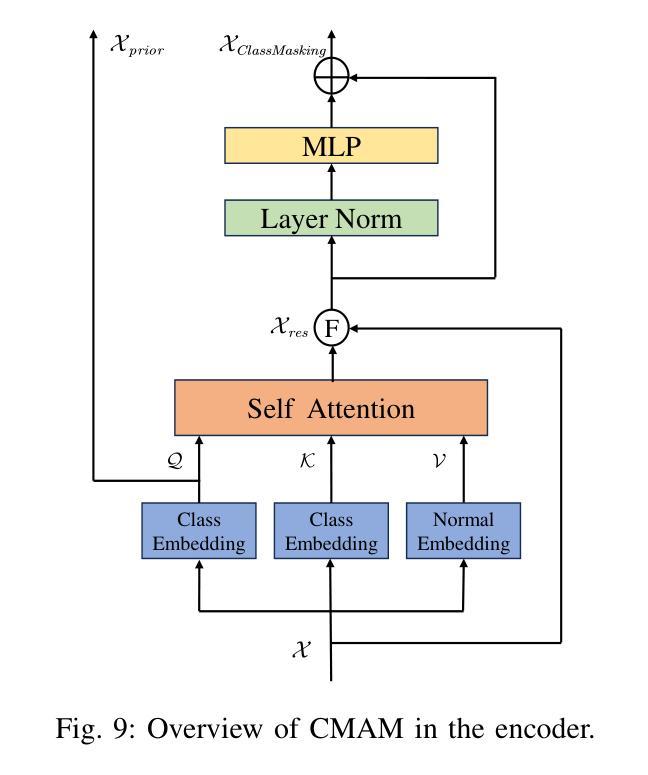
As a cost-effective and robust technology, automotive radar has seen steady improvement during the last years, making it an appealing complement to commonly used sensors like camera and LiDAR in autonomous driving. Radio frequency data with rich semantic information are attracting more and more attention. Most current radar-based models take radio frequency image sequences as the input. However, these models heavily rely on convolutional neural networks and leave out the spatial-temporal semantic context during the encoding stage. To solve these problems, we propose a model called Mask-RadarNet to fully utilize the hierarchical semantic features from the input radar data. Mask-RadarNet exploits the combination of interleaved convolution and attention operations to replace the traditional architecture in transformer-based models. In addition, patch shift is introduced to the Mask-RadarNet for efficient spatial-temporal feature learning. By shifting part of patches with a specific mosaic pattern in the temporal dimension, Mask-RadarNet achieves competitive performance while reducing the computational burden of the spatial-temporal modeling. In order to capture the spatial-temporal semantic contextual information, we design the class masking attention module (CMAM) in our encoder. Moreover, a lightweight auxiliary decoder is added to our model to aggregate prior maps generated from the CMAM. Experiments on the CRUW dataset demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method to some state-of-the-art radar-based object detection algorithms. With relatively lower computational complexity and fewer parameters, the proposed Mask-RadarNet achieves higher recognition accuracy for object detection in autonomous driving.
作为一种具有成本效益和稳健性的技术,汽车雷达在过去几年中一直在稳步改进,已成为自动驾驶中摄像头和激光雷达等常用传感器的吸引人的补充。富含语义信息的射频数据正越来越受到关注。当前大多数基于雷达的模型以射频图像序列作为输入。然而,这些模型严重依赖于卷积神经网络,并在编码阶段忽略了时空语义上下文。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种名为Mask-RadarNet的模型,以充分利用输入雷达数据的分层语义特征。Mask-RadarNet结合了交错卷积和注意力操作,以替代基于变压器模型的传统架构。此外,为了进行有效的时空特征学习,引入了斑块移位到Mask-RadarNet中。通过按时间维度以特定的马赛克模式移动部分斑块,Mask-RadarNet在降低时空建模的计算负担的同时实现了有竞争力的性能。为了捕获时空语义上下文信息,我们在编码器设计中了类掩蔽注意力模块(CMAM)。而且,我们模型中添加了一个轻量级的辅助解码器,以聚合由CMAM生成的先验图。在CRUW数据集上的实验表明,所提出的方法优于一些最先进的基于雷达的目标检测算法。所提出具有较低计算复杂度和更少参数的Mask-RadarNet在自动驾驶的目标检测中实现了更高的识别精度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
雷达技术因其成本效益和稳健性在自动驾驶领域受到广泛关注。为充分利用雷达数据的层次语义特征,提出一种名为Mask-RadarNet的模型,结合交错卷积和注意力操作,引入补丁移位进行高效时空特征学习,并设计类掩注意力模块以捕获时空语义上下文信息。实验证明,Mask-RadarNet在CRUW数据集上的表现优于其他先进的雷达目标检测算法,具有较低的计算复杂度和较少的参数,提高了自动驾驶中目标检测的识别精度。
Key Takeaways
- 雷达技术作为自动驾驶中的成本效益和稳健性技术,受到越来越多的关注。
- 当前雷达模型主要依赖卷积神经网络,但在编码阶段忽略了时空语义上下文。
- Mask-RadarNet模型旨在充分利用雷达数据的层次语义特征。
- Mask-RadarNet结合交错卷积和注意力操作,替代传统基于变压器的模型架构。
- 补丁移位被引入到Mask-RadarNet中,以实现高效的时空特征学习。
- 类掩注意力模块(CMAM)的设计用于捕获时空语义上下文信息。
点此查看论文截图

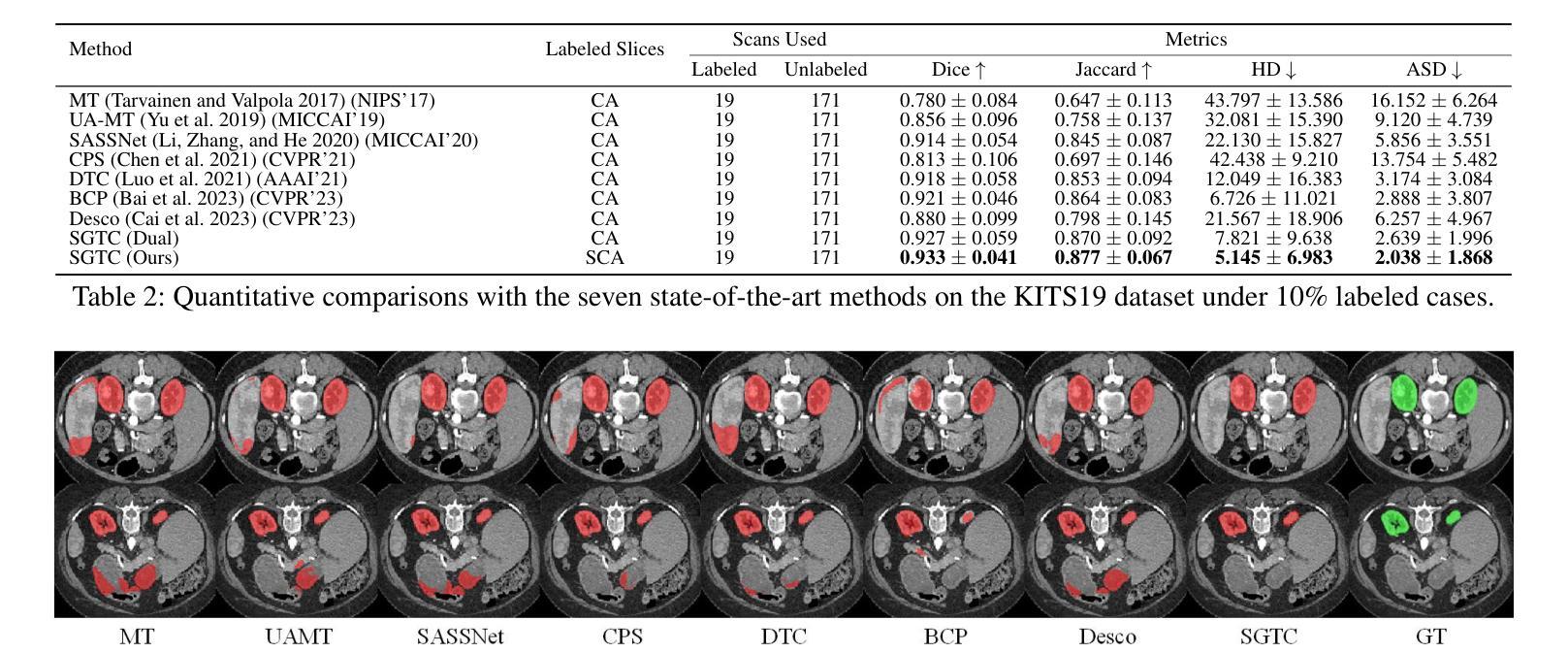
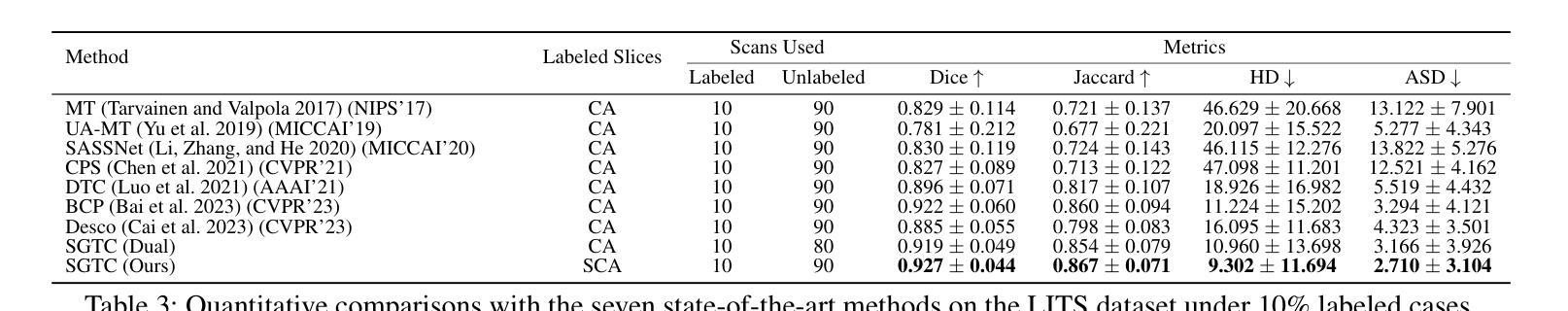
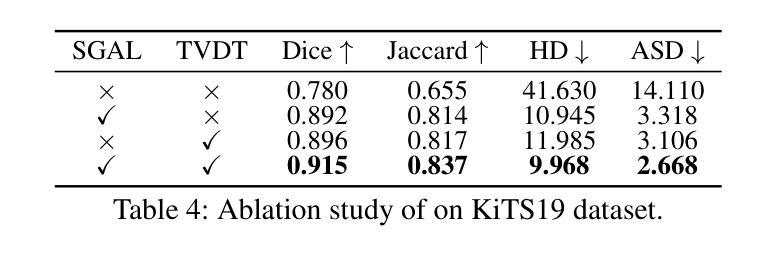
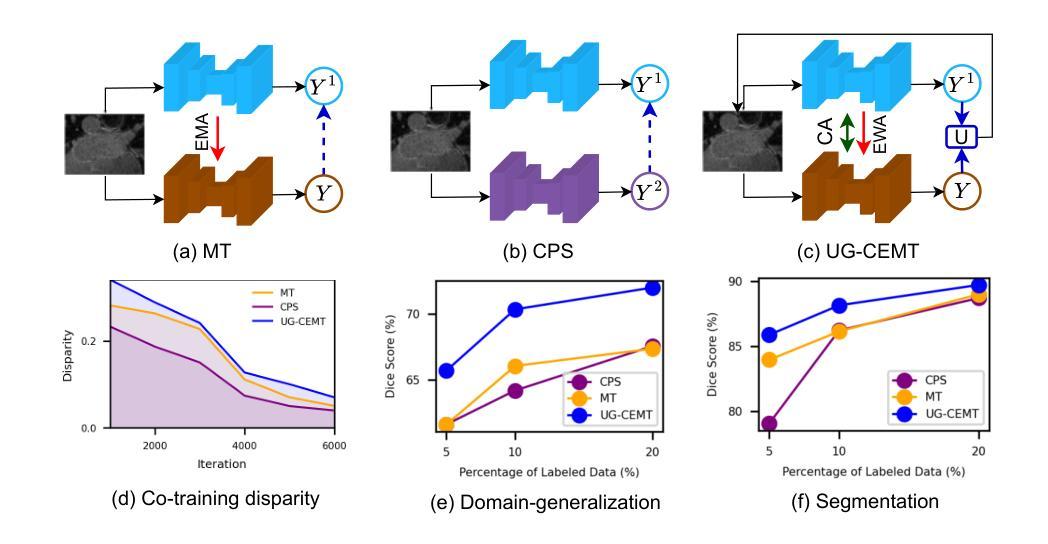
SGTC: Semantic-Guided Triplet Co-training for Sparsely Annotated Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Ke Yan, Qing Cai, Fan Zhang, Ziyan Cao, Zhi Liu
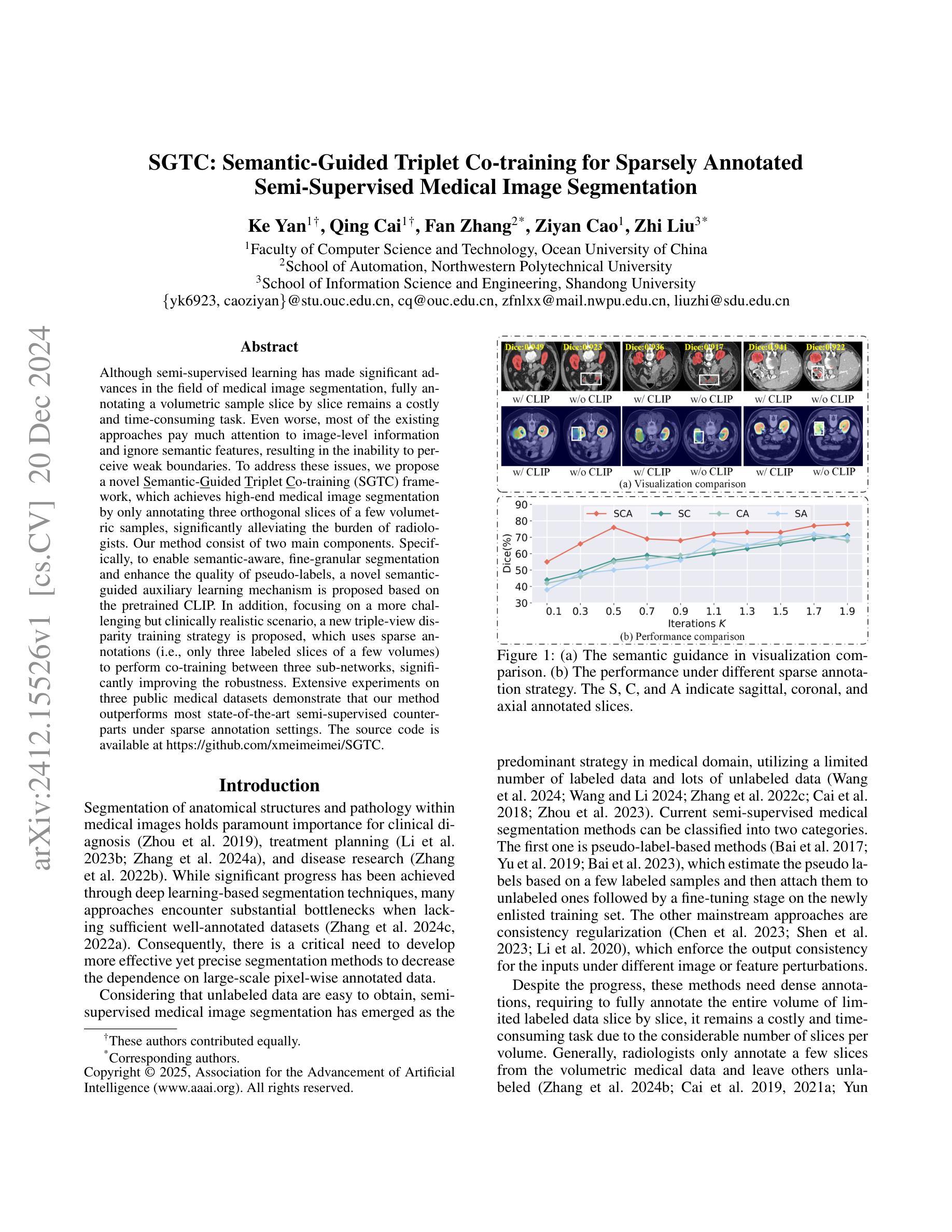
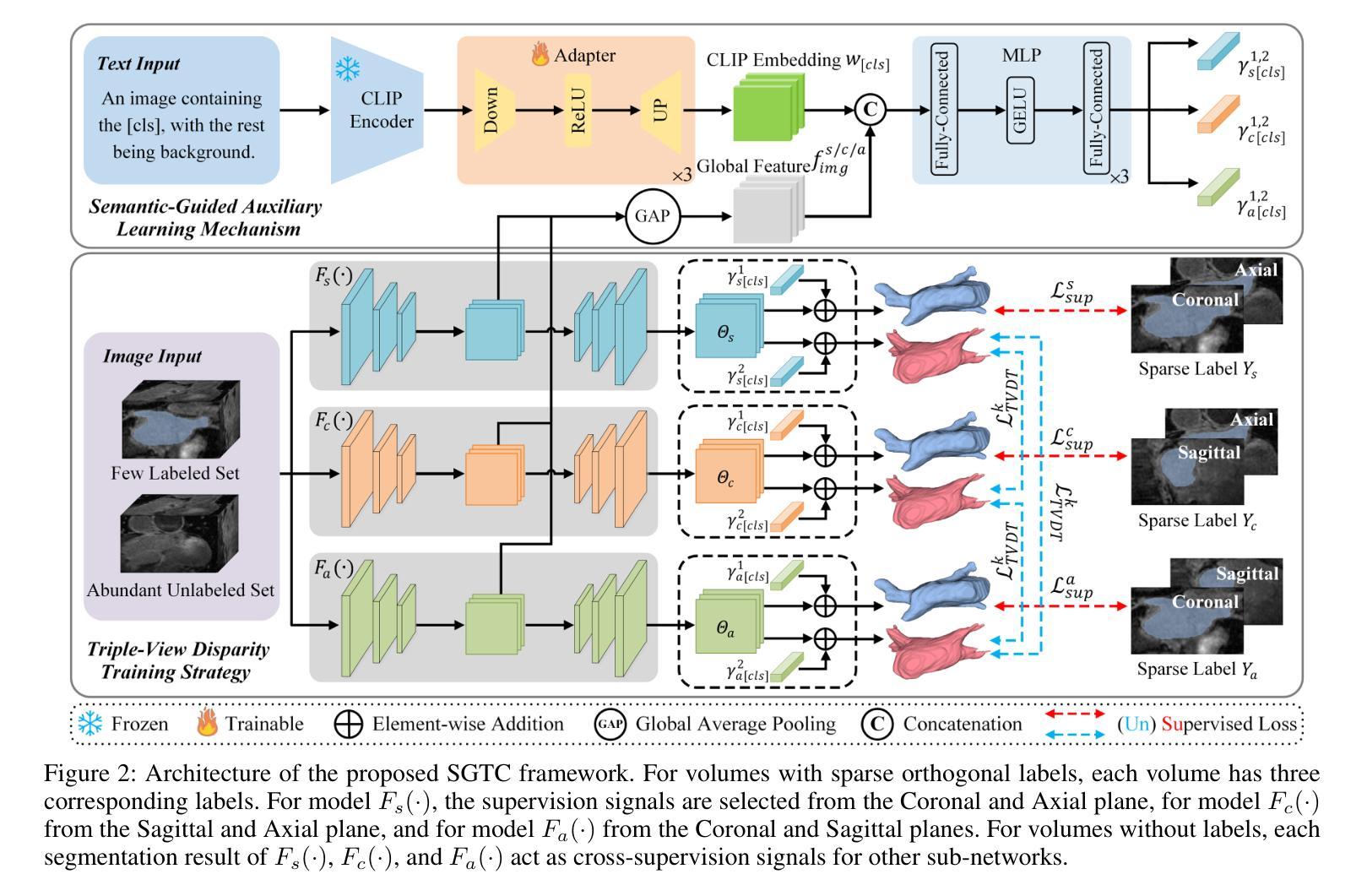
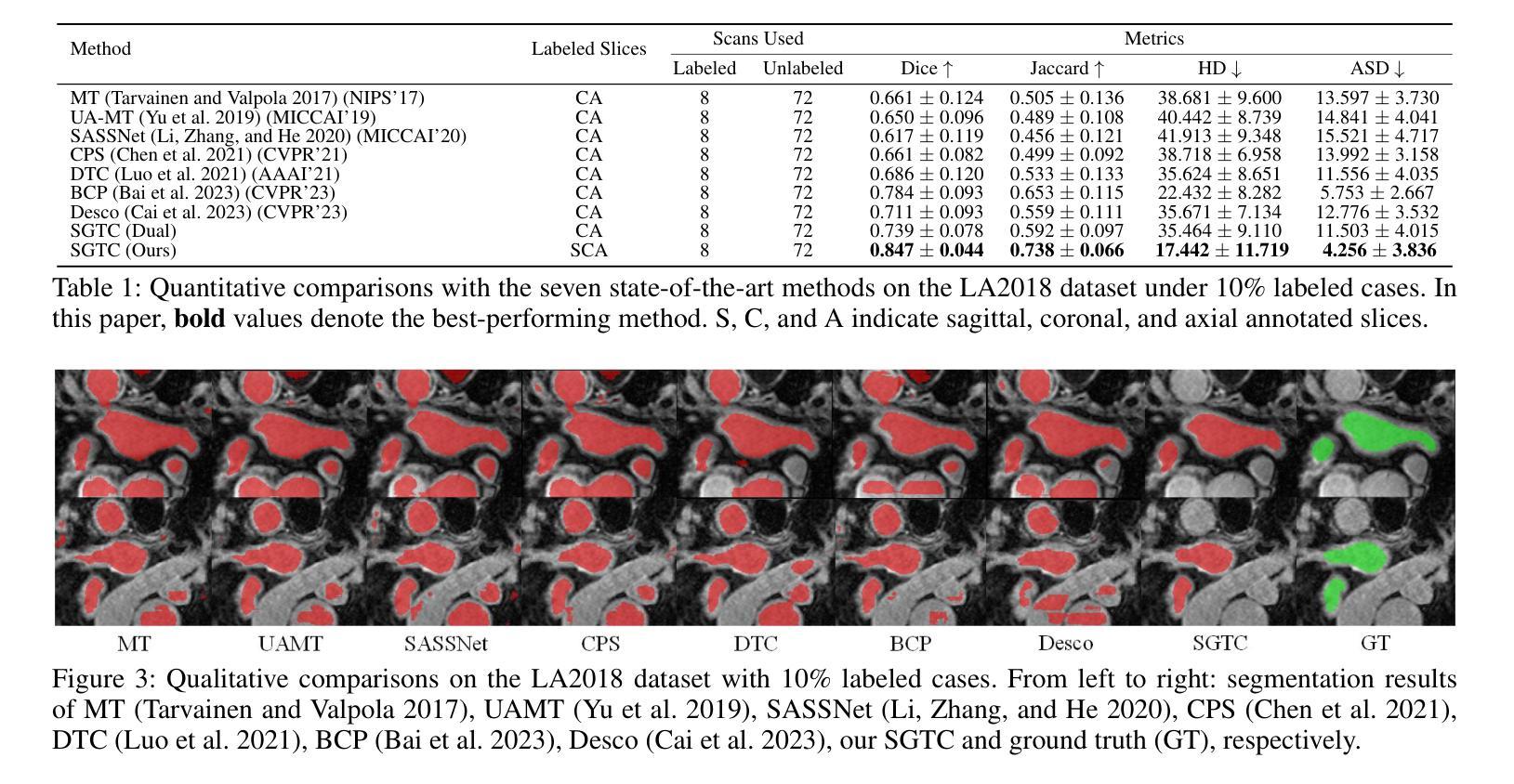
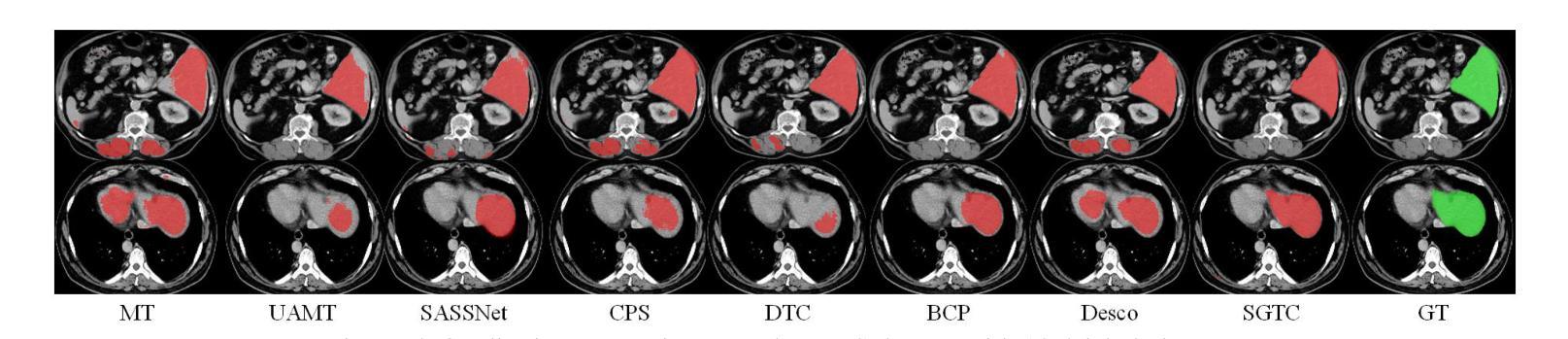
Although semi-supervised learning has made significant advances in the field of medical image segmentation, fully annotating a volumetric sample slice by slice remains a costly and time-consuming task. Even worse, most of the existing approaches pay much attention to image-level information and ignore semantic features, resulting in the inability to perceive weak boundaries. To address these issues, we propose a novel Semantic-Guided Triplet Co-training (SGTC) framework, which achieves high-end medical image segmentation by only annotating three orthogonal slices of a few volumetric samples, significantly alleviating the burden of radiologists. Our method consist of two main components. Specifically, to enable semantic-aware, fine-granular segmentation and enhance the quality of pseudo-labels, a novel semantic-guided auxiliary learning mechanism is proposed based on the pretrained CLIP. In addition, focusing on a more challenging but clinically realistic scenario, a new triple-view disparity training strategy is proposed, which uses sparse annotations (i.e., only three labeled slices of a few volumes) to perform co-training between three sub-networks, significantly improving the robustness. Extensive experiments on three public medical datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms most state-of-the-art semi-supervised counterparts under sparse annotation settings. The source code is available at https://github.com/xmeimeimei/SGTC.
尽管半监督学习在医学图像分割领域取得了重大进展,但逐层对体积样本进行完全标注仍然是一项成本高昂且耗时的任务。更糟糕的是,大多数现有方法过于关注图像级别的信息,而忽略了语义特征,导致无法感知到弱边界。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新型的语义引导三重共训练(SGTC)框架,只需对少数体积样本的三个正交切片进行标注,即可实现高端医学图像分割,显著减轻了放射科医生的负担。我们的方法主要包括两个组成部分。具体来说,为了实现语义感知的精细粒度分割并提高伪标签的质量,我们提出了一种基于预训练CLIP的的新型语义引导辅助学习机制。此外,为了应对更具挑战性但临床现实的场景,我们提出了一种新的三视图差异训练策略,该策略使用稀疏注释(即只有少数体积的三个标记切片)对三个子网络进行共训练,从而显著提高了稳健性。在三个公共医学数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在稀疏注释设置下超越了大多数最先进的半监督方法。源代码可在https://github.com/xmeimeimei/SGTC上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种新型的语义引导三元组联合训练(SGTC)框架,用于解决医学图像分割中面临的数据标注成本高昂、耗时以及忽视语义特征的问题。该框架仅通过标注少量体积样本的三个正交切片,即可实现高端医学图像分割,显著减轻了放射科医生的工作负担。SGTC框架包括两个主要部分:基于预训练CLIP模型的语义引导辅助学习机制和针对更具挑战性但临床更实际的三视图差异训练策略。实验表明,该方法在稀疏标注设置下,超越了大多数先进的半监督方法。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割中面临数据标注成本高昂和耗时的问题。
- 现有方法多关注图像级信息,忽视语义特征,导致无法识别弱边界。
- 提出的SGTC框架通过仅标注少量体积样本的三个正交切片,实现了高端医学图像分割。
- SGTC框架包括语义引导辅助学习机制和三视图差异训练策略。
- 语义引导辅助学习机制能够提高语义感知的精细粒度分割和伪标签质量。
- 三视图差异训练策略使用稀疏标注进行三个子网络之间的联合训练,提高了模型的稳健性。
点此查看论文截图