⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-24 更新
CoCoGaussian: Leveraging Circle of Confusion for Gaussian Splatting from Defocused Images
Authors:Jungho Lee, Suhwan Cho, Taeoh Kim, Ho-Deok Jang, Minhyeok Lee, Geonho Cha, Dongyoon Wee, Dogyoon Lee, Sangyoun Lee
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has attracted significant attention for its high-quality novel view rendering, inspiring research to address real-world challenges. While conventional methods depend on sharp images for accurate scene reconstruction, real-world scenarios are often affected by defocus blur due to finite depth of field, making it essential to account for realistic 3D scene representation. In this study, we propose CoCoGaussian, a Circle of Confusion-aware Gaussian Splatting that enables precise 3D scene representation using only defocused images. CoCoGaussian addresses the challenge of defocus blur by modeling the Circle of Confusion (CoC) through a physically grounded approach based on the principles of photographic defocus. Exploiting 3D Gaussians, we compute the CoC diameter from depth and learnable aperture information, generating multiple Gaussians to precisely capture the CoC shape. Furthermore, we introduce a learnable scaling factor to enhance robustness and provide more flexibility in handling unreliable depth in scenes with reflective or refractive surfaces. Experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that CoCoGaussian achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple benchmarks.
三维高斯拼贴技术(3DGS)因其高质量的新型视角渲染而备受关注,并激发了对解决现实世界挑战的研究。虽然传统方法依赖于清晰的图像进行准确的场景重建,但现实世界场景往往受到有限景深造成的失焦模糊的影响,因此需要考虑现实的三维场景表示。在本研究中,我们提出了CoCoGaussian,这是一种基于模糊圆认知的高斯拼贴技术,它仅使用失焦图像就能实现精确的三维场景表示。CoCoGaussian通过摄影失焦的原理,采用物理基础的方法对模糊圆(CoC)进行建模,解决了失焦模糊的挑战。利用三维高斯,我们从深度和可学习的光圈信息计算出模糊圆的直径,生成多个高斯来精确捕捉模糊圆的形状。此外,我们还引入了一个可学习的缩放因子,以提高稳健性,并在处理具有反射或折射表面的场景中不可靠的深度时提供更多灵活性。在合成和真实数据集上的实验表明,CoCoGaussian在多个基准测试中达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://Jho-Yonsei.github.io/CoCoGaussian/
Summary
本文介绍了名为CoCoGaussian的新型三维高斯渲染技术。该技术采用模糊图像实现精确的三维场景表示,通过建模模糊圈(Circle of Confusion,CoC)解决了传统渲染方法对清晰图像的依赖问题。利用三维高斯模型,结合深度信息和可学习的光圈信息计算CoC直径,生成多个高斯模型来捕捉CoC形状。此外,引入可学习缩放因子以增强稳健性,并处理具有反射或折射表面的场景中深度不可靠的问题。实验证明,CoCoGaussian在多个基准测试中实现了卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS)在高质量新视角渲染方面受到关注。
- 传统方法依赖清晰图像进行准确场景重建,但现实世界场景中存在因景深有限导致的散焦模糊问题。
- CoCoGaussian技术解决了因散焦模糊导致的问题,通过物理基础的方法建模模糊圈(Circle of Confusion,CoC)。
- 利用三维高斯模型计算CoC直径,结合深度信息和可学习的光圈信息生成多个高斯模型来捕捉CoC形状。
- 引入可学习缩放因子以增强技术的稳健性,并处理具有反射或折射表面的场景中深度不可靠的问题。
- 在合成和真实数据集上的实验证明,CoCoGaussian在多个基准测试中实现了卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

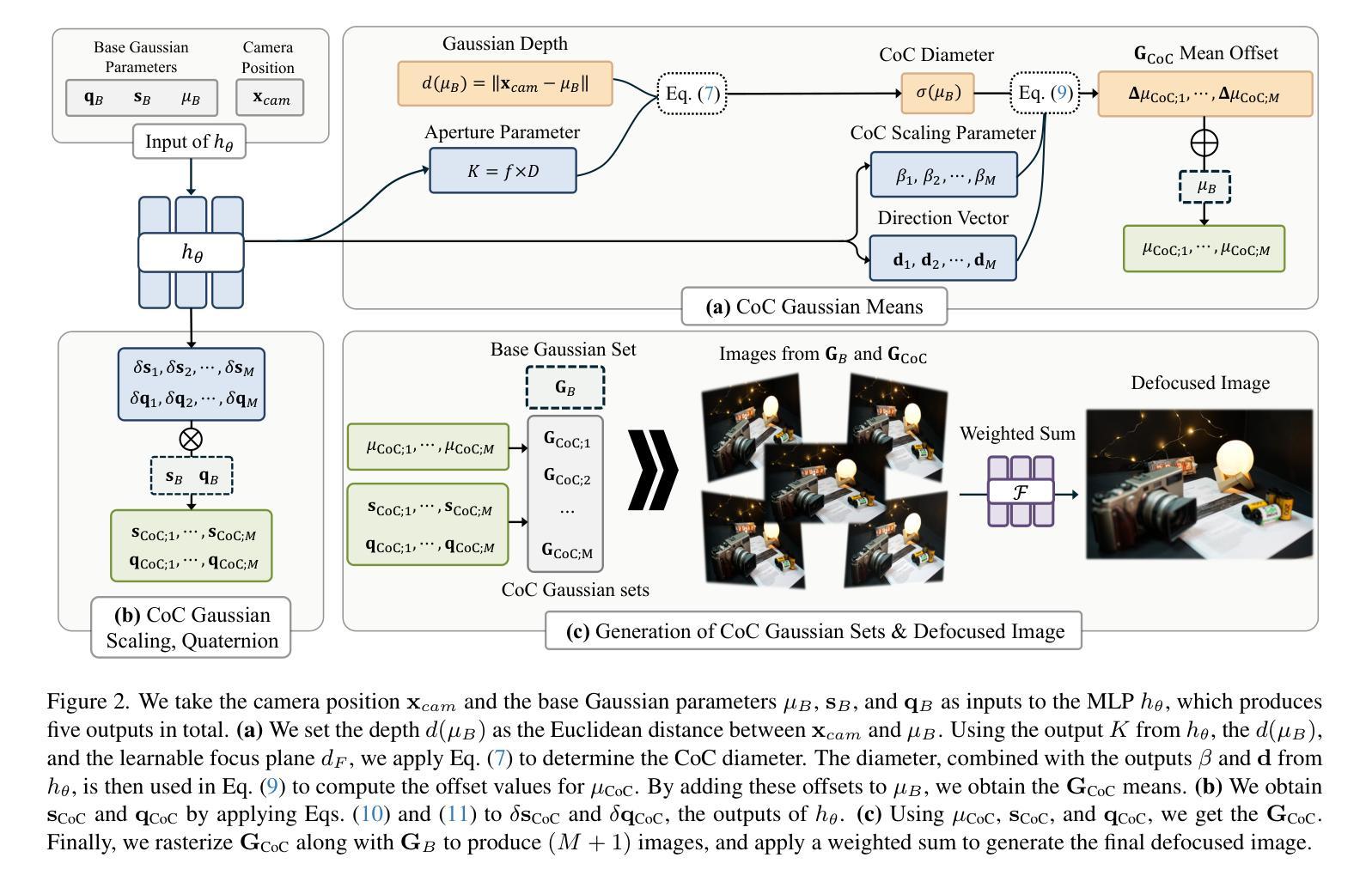
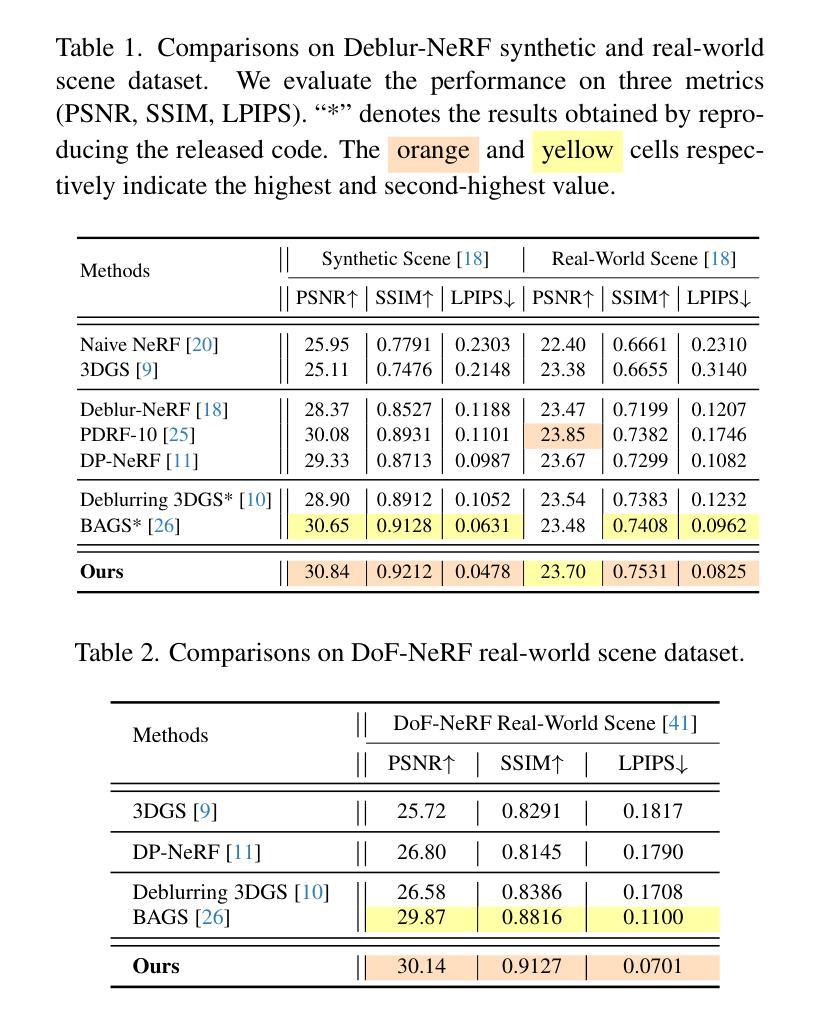
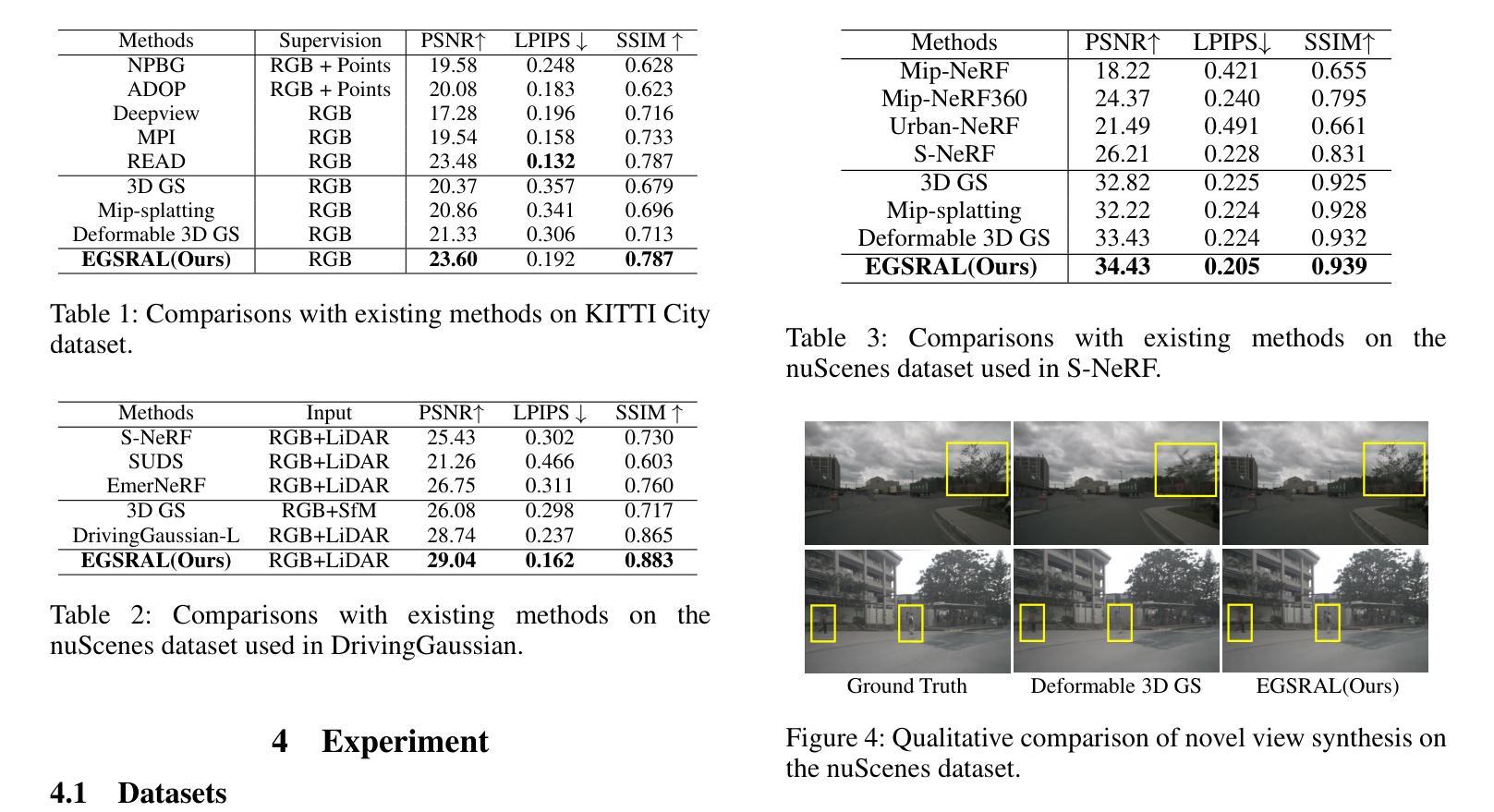
EGSRAL: An Enhanced 3D Gaussian Splatting based Renderer with Automated Labeling for Large-Scale Driving Scene
Authors:Yixiong Huo, Guangfeng Jiang, Hongyang Wei, Ji Liu, Song Zhang, Han Liu, Xingliang Huang, Mingjie Lu, Jinzhang Peng, Dong Li, Lu Tian, Emad Barsoum
3D Gaussian Splatting (3D GS) has gained popularity due to its faster rendering speed and high-quality novel view synthesis. Some researchers have explored using 3D GS for reconstructing driving scenes. However, these methods often rely on various data types, such as depth maps, 3D boxes, and trajectories of moving objects. Additionally, the lack of annotations for synthesized images limits their direct application in downstream tasks. To address these issues, we propose EGSRAL, a 3D GS-based method that relies solely on training images without extra annotations. EGSRAL enhances 3D GS’s capability to model both dynamic objects and static backgrounds and introduces a novel adaptor for auto labeling, generating corresponding annotations based on existing annotations. We also propose a grouping strategy for vanilla 3D GS to address perspective issues in rendering large-scale, complex scenes. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple datasets without any extra annotation. For example, the PSNR metric reaches 29.04 on the nuScenes dataset. Moreover, our automated labeling can significantly improve the performance of 2D/3D detection tasks. Code is available at https://github.com/jiangxb98/EGSRAL.
3D高斯绘制(3D GS)因其更快的渲染速度和高质量的新型视图合成而受到欢迎。一些研究人员已经探索了使用3D GS来重建驾驶场景。然而,这些方法通常依赖于各种数据类型,如深度图、3D框和移动物体的轨迹。此外,合成图像缺乏注释限制了它们在下游任务中的直接应用。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了EGSRAL,一种基于3D GS的方法,它仅依赖于训练图像,无需额外注释。EGSRAL增强了3D GS对动态对象和静态背景的建模能力,并引入了一种新型适配器进行自动标注,根据现有注释生成相应注释。我们还为普通3D GS提出了一种分组策略,以解决渲染大规模复杂场景时的透视问题。我们的方法在多个数据集上达到了最先进的性能,无需任何额外注释。例如,在nuScenes数据集上,PSNR指标达到29.04。此外,我们的自动标注可以显著提高2D/3D检测任务的性能。代码可在https://github.com/jiangxb98/EGSRAL找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI2025
Summary
基于3D高斯绘制技术(3D GS)的EGSRAL方法因其无需额外标注就能实现对驾驶场景的重建而受到关注。此方法不仅提高了渲染速度与合成图像质量,还通过自适应标签生成机制解决了标注问题,并采用了分组策略解决大规模复杂场景的透视问题。EGSRAL在多个数据集上实现了领先水平,例如nuScenes数据集上的PSNR指标达到29.04,可显著提高2D/3D检测任务性能。
Key Takeaways
- EGSRAL利用3D高斯绘制技术(3D GS)进行驾驶场景重建,提高了渲染速度和合成图像质量。
- EGSRAL仅依赖训练图像,无需额外标注,简化了操作流程。
- 通过自适应标签生成机制,EGSRAL解决了合成图像的标注问题。
- EGSRAL采用分组策略解决大规模复杂场景的透视问题,提升了场景重建的准确性。
- EGSRAL在多个数据集上实现了领先水平,如nuScenes数据集的PSNR指标达到29.04。
- EGSRAL可显著提高2D/3D检测任务性能,为自动驾驶等领域的应用提供了有力支持。
点此查看论文截图

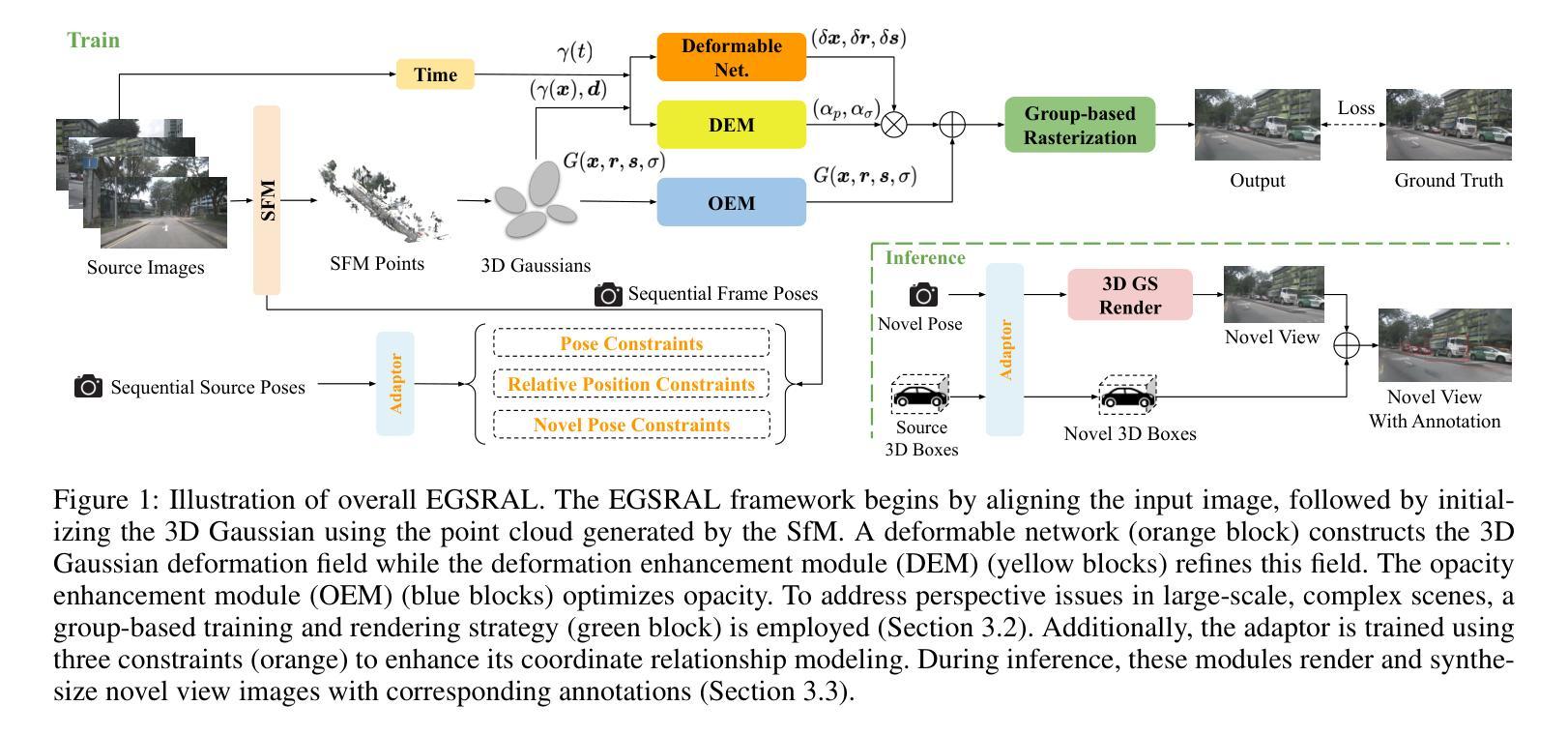
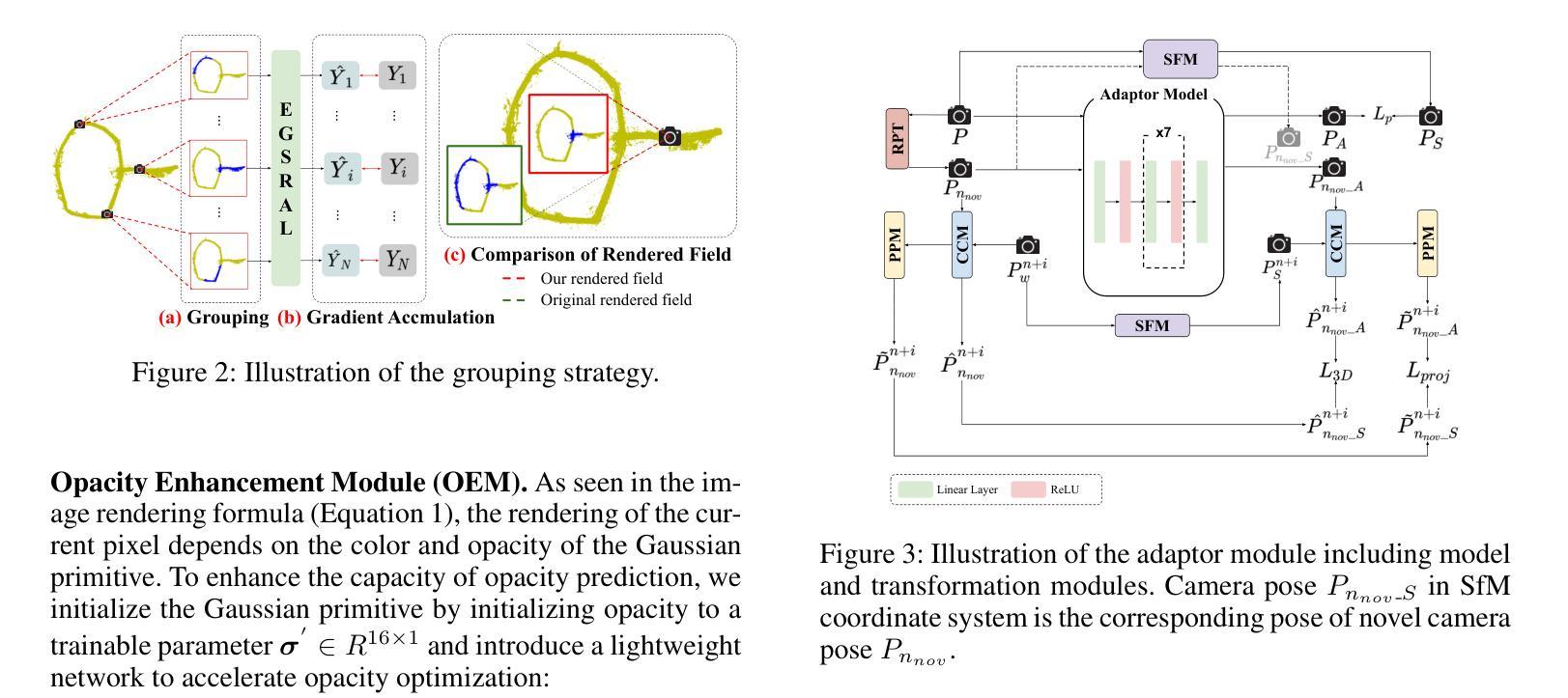
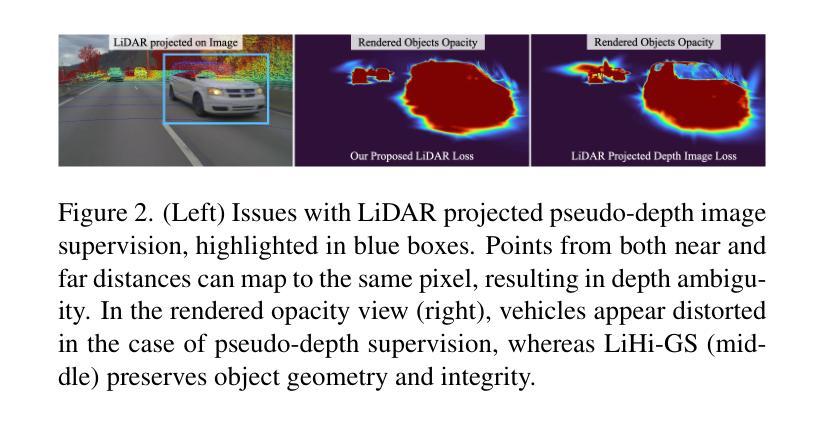
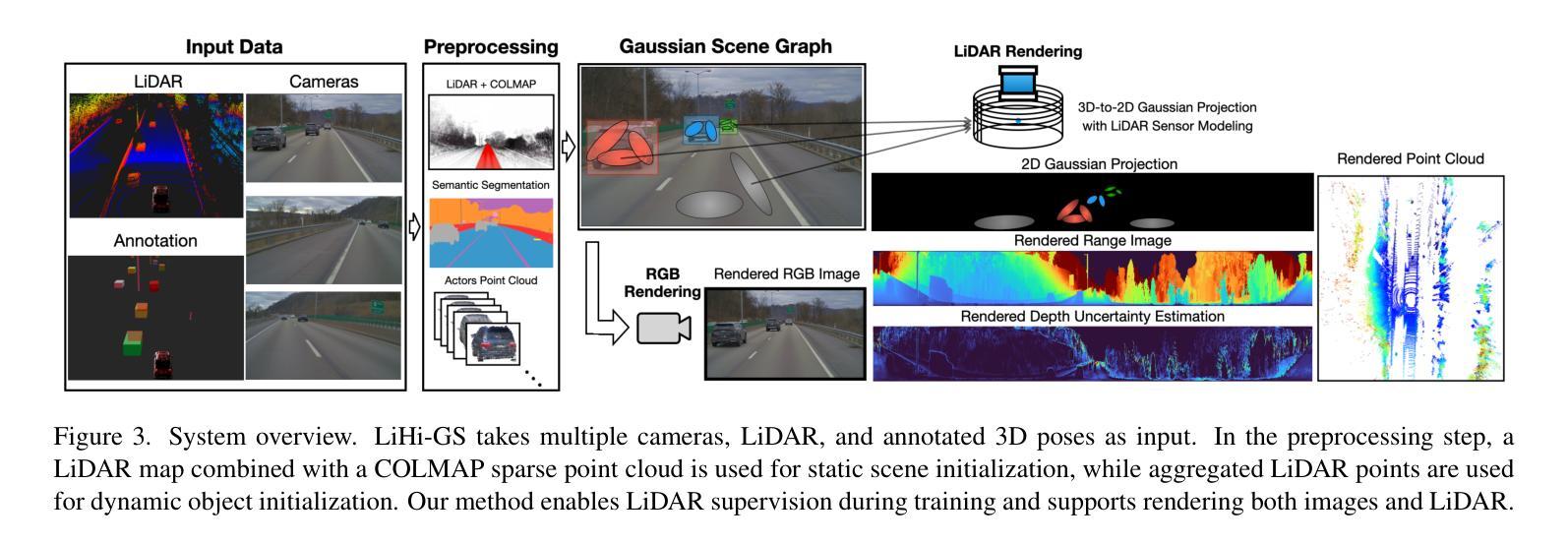
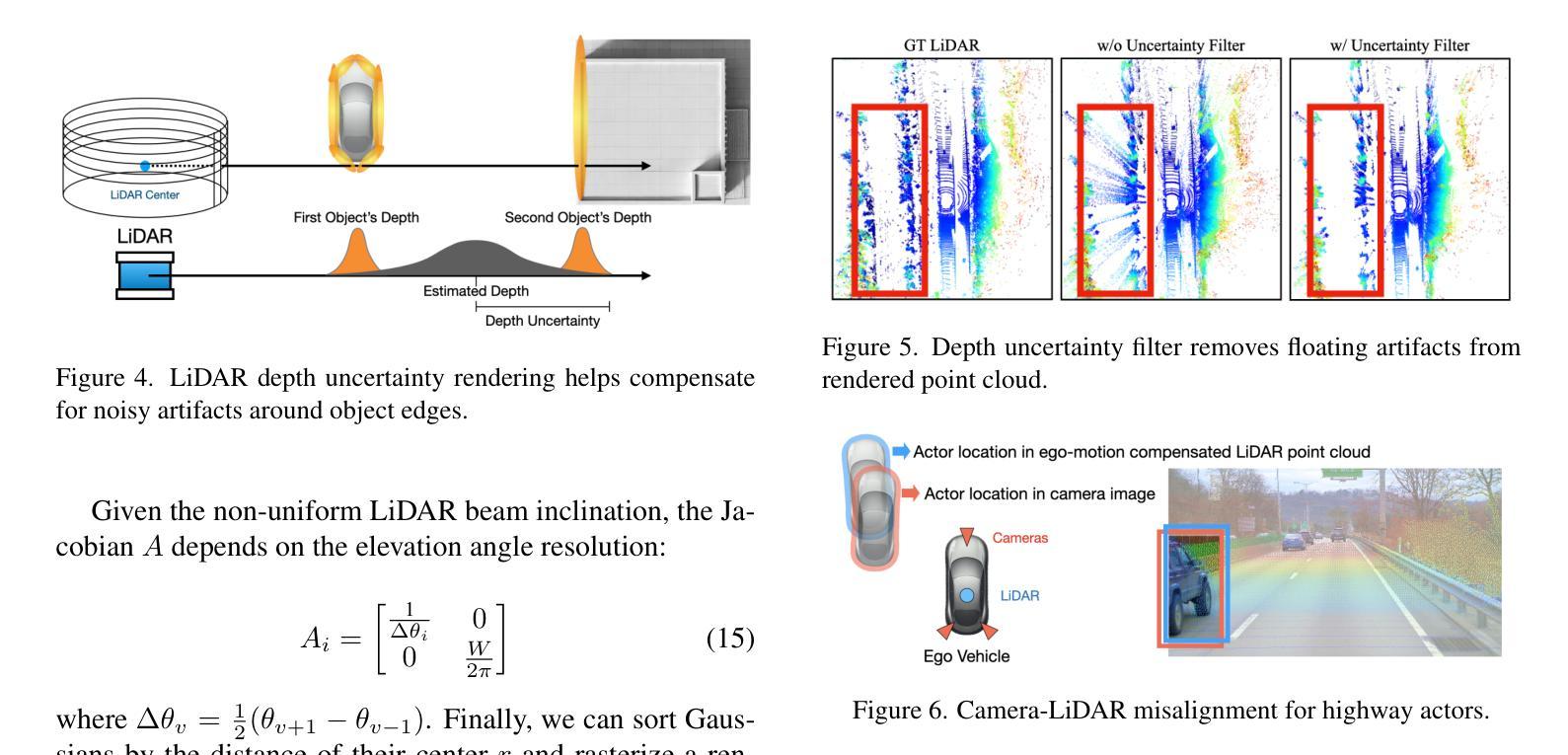
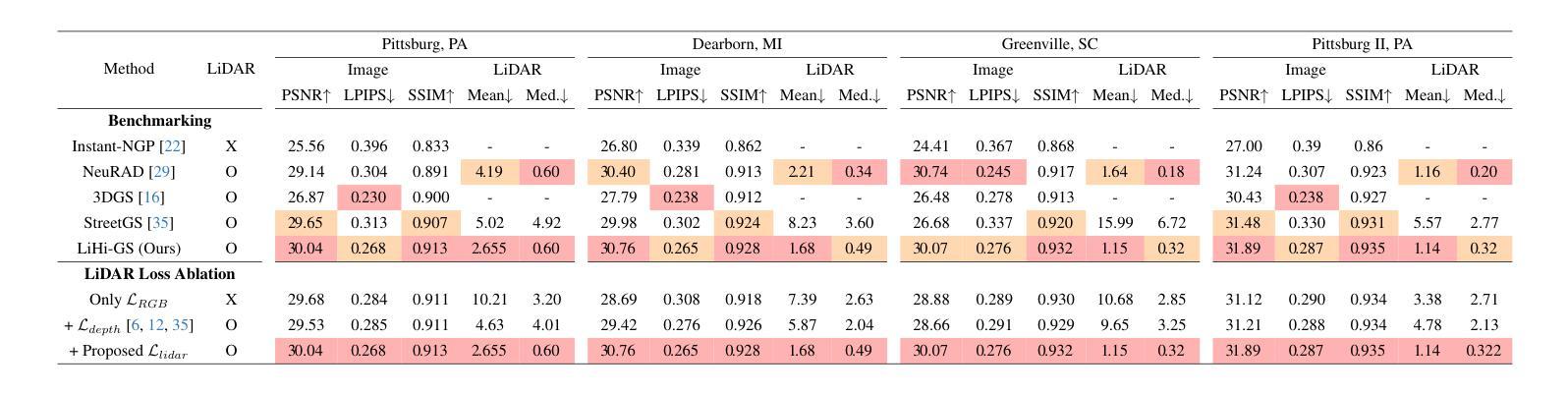
LiHi-GS: LiDAR-Supervised Gaussian Splatting for Highway Driving Scene Reconstruction
Authors:Pou-Chun Kung, Xianling Zhang, Katherine A. Skinner, Nikita Jaipuria
Photorealistic 3D scene reconstruction plays an important role in autonomous driving, enabling the generation of novel data from existing datasets to simulate safety-critical scenarios and expand training data without additional acquisition costs. Gaussian Splatting (GS) facilitates real-time, photorealistic rendering with an explicit 3D Gaussian representation of the scene, providing faster processing and more intuitive scene editing than the implicit Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs). While extensive GS research has yielded promising advancements in autonomous driving applications, they overlook two critical aspects: First, existing methods mainly focus on low-speed and feature-rich urban scenes and ignore the fact that highway scenarios play a significant role in autonomous driving. Second, while LiDARs are commonplace in autonomous driving platforms, existing methods learn primarily from images and use LiDAR only for initial estimates or without precise sensor modeling, thus missing out on leveraging the rich depth information LiDAR offers and limiting the ability to synthesize LiDAR data. In this paper, we propose a novel GS method for dynamic scene synthesis and editing with improved scene reconstruction through LiDAR supervision and support for LiDAR rendering. Unlike prior works that are tested mostly on urban datasets, to the best of our knowledge, we are the first to focus on the more challenging and highly relevant highway scenes for autonomous driving, with sparse sensor views and monotone backgrounds.
真实感三维场景重建在自动驾驶中扮演着重要角色。它可以从现有数据集中生成新数据,模拟安全关键场景,无需额外的采集成本即可扩展训练数据。高斯涂抹(GS)技术便于实现真实感的实时渲染,通过场景的三维高斯显式表示,与隐式神经辐射场(NeRFs)相比,提供了更快的处理和更直观的场景编辑。尽管关于高斯涂抹的广泛研究已经在自动驾驶应用中取得了有前景的进展,但它们忽略了两个关键方面:首先,现有方法主要集中在低速和特征丰富的城市场景上,忽视了高速公路场景在自动驾驶中的重要作用。其次,虽然激光雷达在自动驾驶平台中很普遍,但现有方法主要从图像中学习,仅将激光雷达用于初步估计或没有精确的传感器建模,从而错过了利用激光雷达提供的丰富深度信息的机会,并限制了合成激光雷达数据的能力。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的高斯涂抹方法,用于动态场景合成和编辑,通过激光雷达监督和改进的场景重建,支持激光雷达渲染。与主要测试于城市数据集的前期作品不同,据我们所知,我们是首个专注于更具挑战性和高度相关的自动驾驶高速公路场景的团队,具备稀疏传感器视角和单调背景。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在自动驾驶领域中,基于高斯贴图(GS)技术的真实感三维场景重建的重要性。通过生成新的数据集模拟关键安全场景,扩展训练数据且无需额外的采集成本。文章指出当前GS研究主要关注低速和特征丰富的城市场景,忽略了高速公路场景的重要性。此外,现有方法主要依赖图像学习,未充分利用激光雷达提供的丰富深度信息。本文提出一种新型的GS方法,支持动态场景合成与编辑,通过激光雷达监督改进场景重建,并支持激光雷达渲染。相较于之前主要关注城市数据集的研究,本文首次聚焦于更具挑战性和高度相关的高速公路场景,具有稀疏传感器视角和单调背景的特点。
Key Takeaways
- 高斯贴图(GS)技术对于自动驾驶中的真实感三维场景重建至关重要。
- 当前GS研究主要关注城市场景,忽略了高速公路场景的重要性。
- 现有方法主要依赖图像学习,未充分利用激光雷达(LiDAR)的深度信息。
- 本文提出一种新型的GS方法,支持动态场景合成与编辑。
- 该方法通过激光雷达监督改进场景重建,提高了场景重建的精度。
- 与之前的研究相比,本文首次聚焦于高速公路场景,这是更具挑战性和高度相关的研究领域。
点此查看论文截图

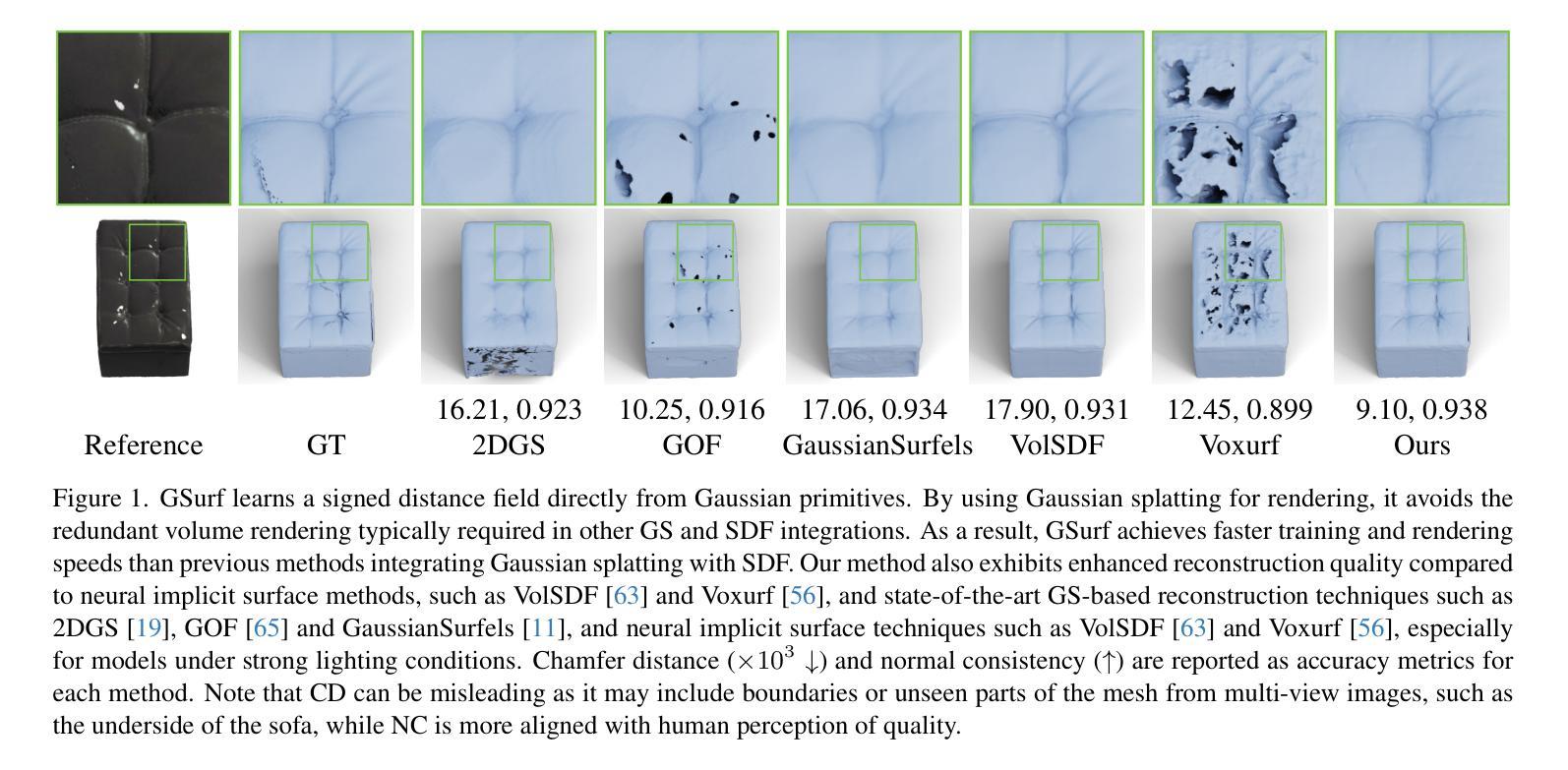
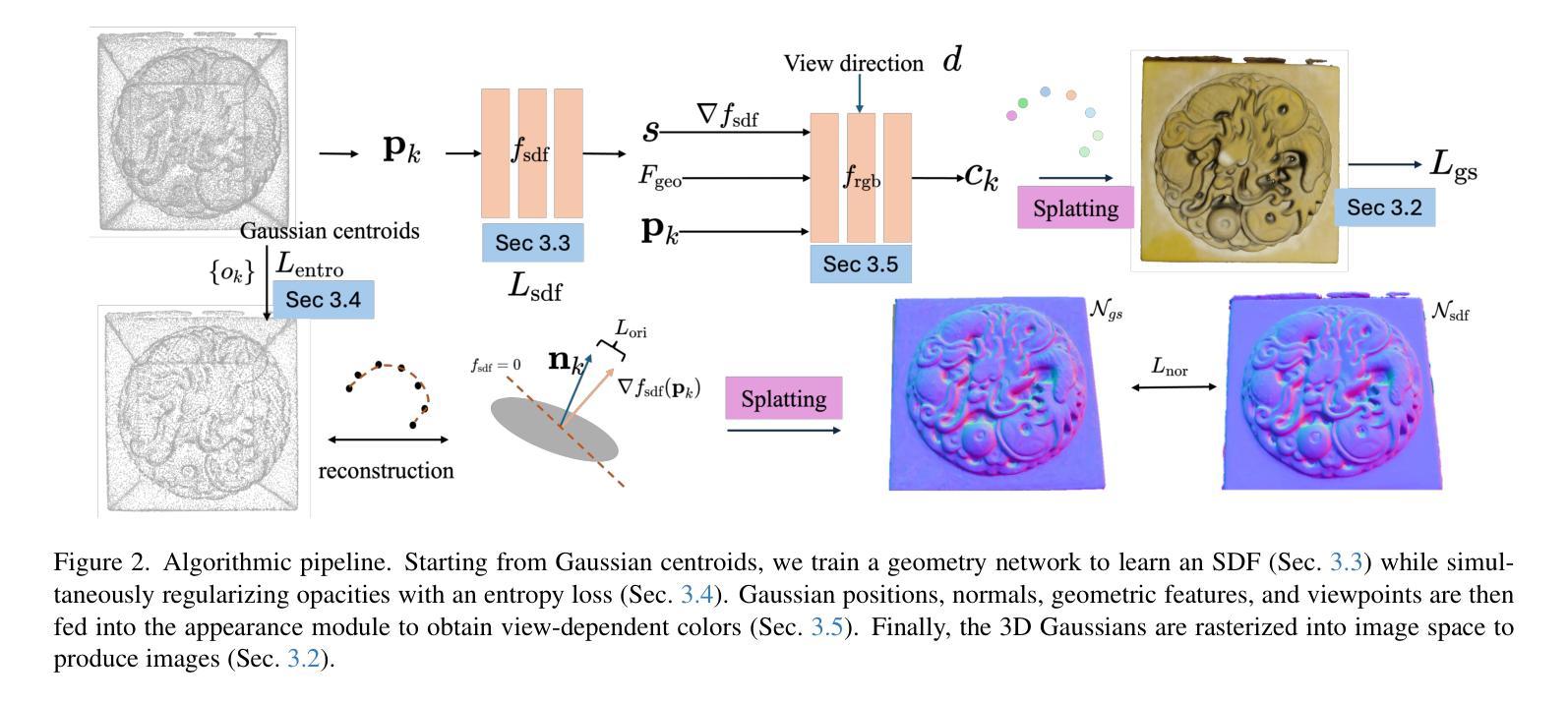
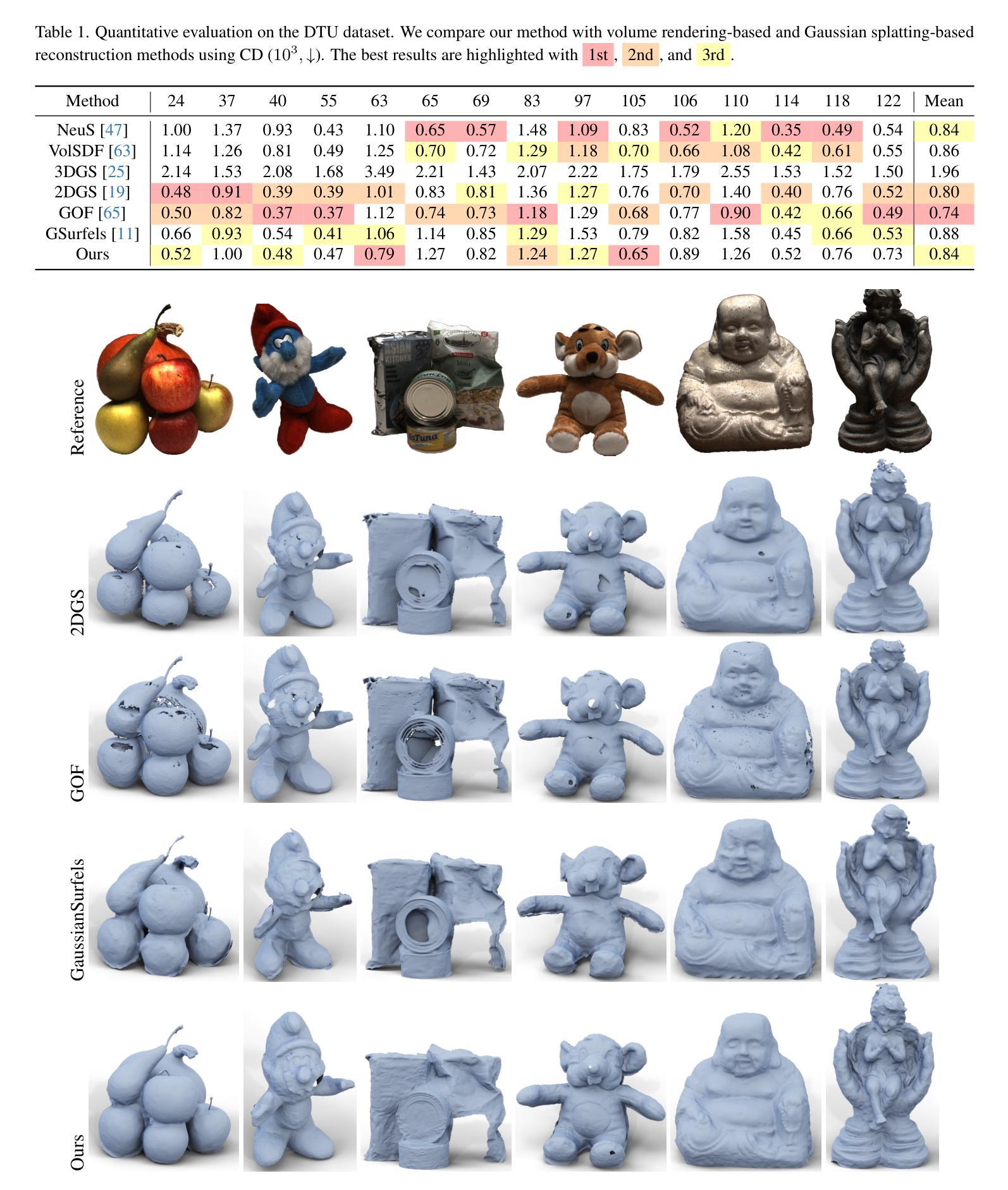
GSurf: 3D Reconstruction via Signed Distance Fields with Direct Gaussian Supervision
Authors:Baixin Xu, Jiangbei Hu, Jiaze Li, Ying He
Surface reconstruction from multi-view images is a core challenge in 3D vision. Recent studies have explored signed distance fields (SDF) within Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) to achieve high-fidelity surface reconstructions. However, these approaches often suffer from slow training and rendering speeds compared to 3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS). Current state-of-the-art techniques attempt to fuse depth information to extract geometry from 3DGS, but frequently result in incomplete reconstructions and fragmented surfaces. In this paper, we introduce GSurf, a novel end-to-end method for learning a signed distance field directly from Gaussian primitives. The continuous and smooth nature of SDF addresses common issues in the 3DGS family, such as holes resulting from noisy or missing depth data. By using Gaussian splatting for rendering, GSurf avoids the redundant volume rendering typically required in other GS and SDF integrations. Consequently, GSurf achieves faster training and rendering speeds while delivering 3D reconstruction quality comparable to neural implicit surface methods, such as VolSDF and NeuS. Experimental results across various benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in producing high-fidelity 3D reconstructions.
从多视角图像重建表面是3D视觉中的一项核心挑战。近期的研究探索了神经辐射场(NeRF)中的有向距离场(SDF),以实现高保真表面重建。然而,与三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)相比,这些方法通常存在训练和渲染速度较慢的问题。当前最先进的技术试图融合深度信息,以从3DGS中提取几何形状,但经常导致重建不完整和表面碎片化。在本文中,我们介绍了GSurf,这是一种新型端到端方法,用于直接从高斯原始数据中学习有向距离场。SDF的连续和平滑性质解决了3DGS系列中常见的问题,如由噪声或缺失的深度数据导致的空洞。通过使用高斯拼贴进行渲染,GSurf避免了其他GS和SDF集成通常需要的大量体积渲染。因此,GSurf实现了更快的训练和渲染速度,同时提供了与神经隐式表面方法(如VolSDF和NeuS)相当的3D重建质量。在多个基准数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的方法在产生高保真3D重建方面非常有效。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF see https://github.com/xubaixinxbx/Gsurf
摘要
本文介绍了一种新型端对端方法GSurf,该方法直接从高斯原始数据中学习有向距离场,用于从多视角图像进行表面重建。GSurf利用连续且平滑的有向距离场解决了三维高斯喷射技术(3DGS)家族中的常见问题,如因噪声或缺失深度数据导致的空洞。与其他GS和SDF集成方法相比,GSurf通过使用高斯喷射进行渲染避免了冗余的体积渲染。因此,GSurf实现了更快的训练和渲染速度,同时提供了与神经隐式表面方法(如VolSDF和NeuS)相当的3D重建质量。在多个基准数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法在生成高保真三维重建方面非常有效。
要点
- GSurf是一种新型端对端方法,用于从多视角图像进行表面重建,通过直接学习有向距离场来实现高保真表面重建。
- GSurf解决了三维高斯喷射技术(3DGS)中的常见问题,如因噪声或缺失深度数据导致的空洞。
- GSurf利用高斯喷射进行渲染,避免了其他方法中冗余的体积渲染,从而实现了更快的训练和渲染速度。
- GSurf的重建质量可以与神经隐式表面方法(如VolSDF和NeuS)相当。
- GSurf方法在多个基准数据集上进行了实验验证,证明了其在生成高保真三维重建方面的有效性。
- GSurf将有向距离场与高斯原始数据融合,提高了表面重建的完整性和连续性。
点此查看论文截图