⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-24 更新
Tacit Learning with Adaptive Information Selection for Cooperative Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Lunjun Liu, Weilai Jiang, Yaonan Wang
In multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL), the centralized training with decentralized execution (CTDE) framework has gained widespread adoption due to its strong performance. However, the further development of CTDE faces two key challenges. First, agents struggle to autonomously assess the relevance of input information for cooperative tasks, impairing their decision-making abilities. Second, in communication-limited scenarios with partial observability, agents are unable to access global information, restricting their ability to collaborate effectively from a global perspective. To address these challenges, we introduce a novel cooperative MARL framework based on information selection and tacit learning. In this framework, agents gradually develop implicit coordination during training, enabling them to infer the cooperative behavior of others in a discrete space without communication, relying solely on local information. Moreover, we integrate gating and selection mechanisms, allowing agents to adaptively filter information based on environmental changes, thereby enhancing their decision-making capabilities. Experiments on popular MARL benchmarks show that our framework can be seamlessly integrated with state-of-the-art algorithms, leading to significant performance improvements.
在多智能体强化学习(MARL)中,由于强大的性能表现,采用集中训练与分散执行(CTDE)框架的方法得到了广泛应用。然而,CTDE的进一步发展面临两大挑战。首先,智能体难以自主评估输入信息对于协同任务的相关性,从而损害了其决策能力。其次,在通信受限且部分可观测的场景中,智能体无法访问全局信息,限制了它们从全局角度进行有效协作的能力。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了一种基于信息选择和默识学习的新型合作MARL框架。在此框架中,智能体在训练过程中逐渐发展出隐性协调,使它们能够在离散空间中不依赖通信就能推断出他人的合作行为。此外,我们结合了门控和选择机制,使智能体能根据环境变化自适应地过滤信息,从而提高其决策能力。在流行的MARL基准测试上的实验表明,我们的框架可以无缝地融入最先进的算法,带来显著的性能提升。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAMAS 2025 (Extended Abstract)
Summary
在基于信息选择和默式学习的多智能体强化学习框架中,智能体通过训练过程中逐渐发展隐式协调,能在局部信息环境下推断其他智能体的合作行为。该框架解决了集中训练与分散执行框架面临的信息筛选与全局沟通问题,提高了智能体在特定环境中的决策能力。通过流行的多智能体强化学习基准测试,该框架与现有先进算法的结合表现出显著的性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- 多智能体强化学习(MARL)中普遍采用集中训练与分散执行(CTDE)框架。此框架存在自主评估输入信息的重要性和全局信息难以获取的问题。
- 提出了一种基于信息选择和默式学习的新型合作MARL框架,解决了上述问题。智能体通过训练逐渐发展隐式协调,可以在离散空间中仅依赖局部信息推断其他智能体的合作行为。
- 新框架融合了门控和选择机制,允许智能体根据环境变化自适应地筛选信息,增强了决策能力。
点此查看论文截图

Multi-modal Agent Tuning: Building a VLM-Driven Agent for Efficient Tool Usage
Authors:Zhi Gao, Bofei Zhang, Pengxiang Li, Xiaojian Ma, Tao Yuan, Yue Fan, Yuwei Wu, Yunde Jia, Song-Chun Zhu, Qing Li
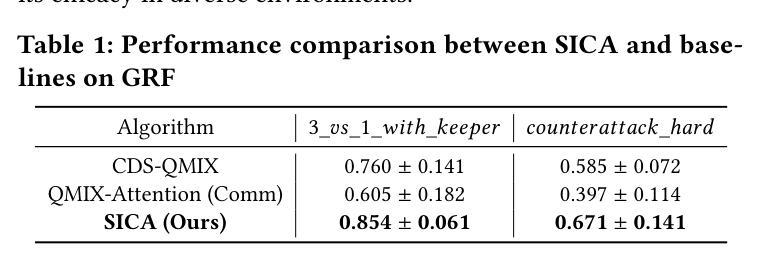
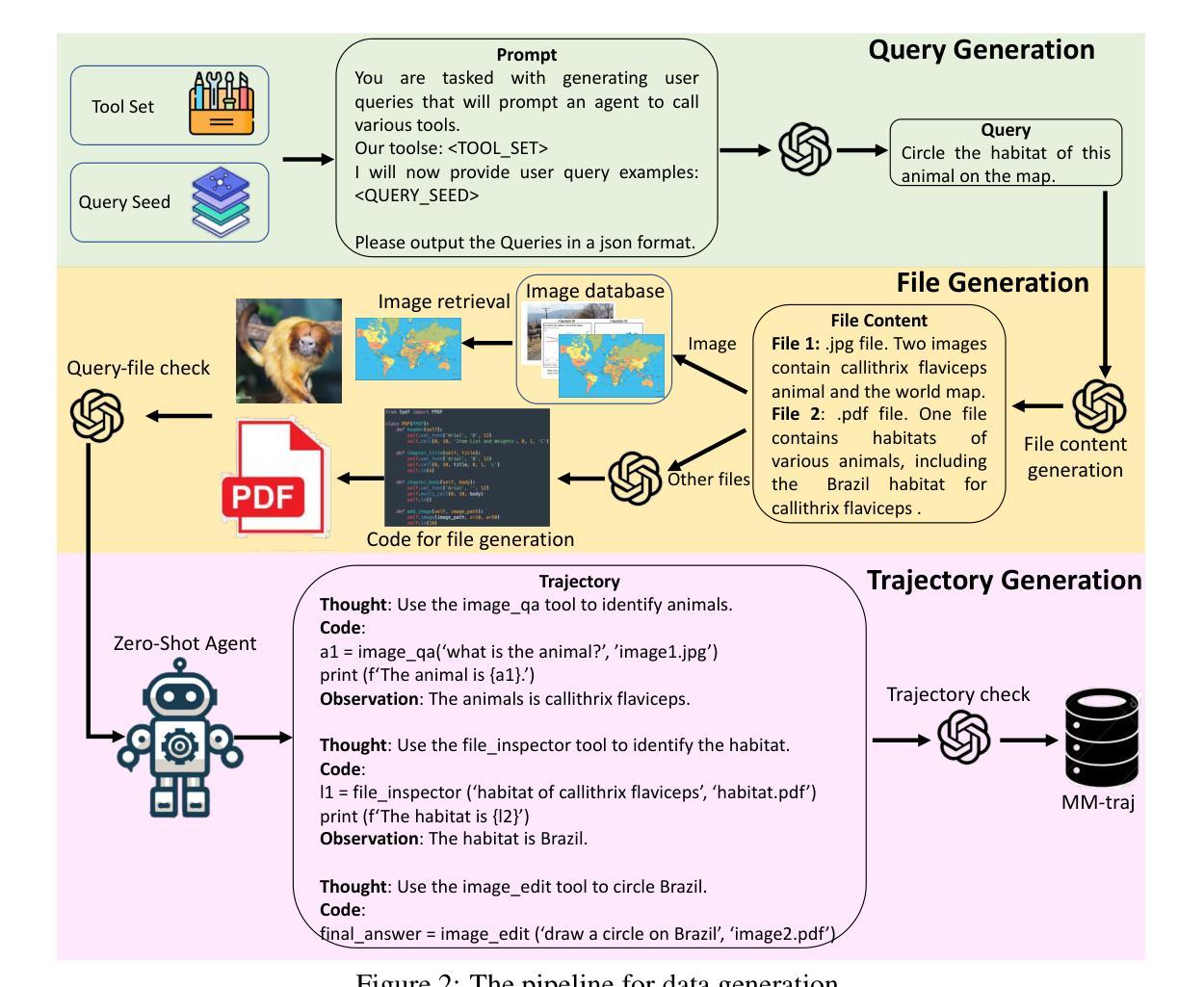
The advancement of large language models (LLMs) prompts the development of multi-modal agents, which are used as a controller to call external tools, providing a feasible way to solve practical tasks. In this paper, we propose a multi-modal agent tuning method that automatically generates multi-modal tool-usage data and tunes a vision-language model (VLM) as the controller for powerful tool-usage reasoning. To preserve the data quality, we prompt the GPT-4o mini model to generate queries, files, and trajectories, followed by query-file and trajectory verifiers. Based on the data synthesis pipeline, we collect the MM-Traj dataset that contains 20K tasks with trajectories of tool usage. Then, we develop the T3-Agent via \underline{T}rajectory \underline{T}uning on VLMs for \underline{T}ool usage using MM-Traj. Evaluations on the GTA and GAIA benchmarks show that the T3-Agent consistently achieves improvements on two popular VLMs: MiniCPM-V-8.5B and {Qwen2-VL-7B}, which outperforms untrained VLMs by $20%$, showing the effectiveness of the proposed data synthesis pipeline, leading to high-quality data for tool-usage capabilities.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的进展,多模态代理的发展也随之而来。这些代理被用作控制器来调用外部工具,为解决实际任务提供了可行的方法。在本文中,我们提出了一种多模态代理调整方法,该方法可自动生成多模态工具使用数据,并调整视觉语言模型(VLM)作为强大的工具使用控制器。为了保持数据质量,我们引导GPT-4o小型模型生成查询、文件和轨迹,随后进行查询文件验证器和轨迹验证器。基于数据合成管道,我们收集了包含2万个任务的MM-Traj数据集,其中包含工具使用轨迹。然后,我们通过使用MM-Traj的轨迹调整VLM来开发T3-Agent。在GTA和GAIA基准测试上的评估表明,T3-Agent在两款流行的VLM上持续实现改进:MiniCPM-V-8.5B和Qwen2-VL-7B。相较于未经训练的VLM,其性能提高了20%,显示了所提出的数据合成管道的有效性,该管道有助于为工具使用能力提供高质量数据。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型的进步推动了多模态代理的发展,作为调用外部工具的控制器,为解决实际任务提供了可行的方法。本文提出了一种多模态代理调优方法,该方法可自动生成多模态工具使用数据,并调整视觉语言模型作为强大的工具使用控制器。通过GPT-4o小型模型生成查询、文件和轨迹,并通过查询文件和轨迹验证器保证数据质量。基于数据合成管道,我们收集了MM-Traj数据集,包含具有工具使用轨迹的2万个任务。通过MM-Traj上的轨迹调优VLMs开发T3-Agent,在GTA和GAIA基准测试上的评估表明,T3-Agent在两种流行的VLMs上实现了持续的改进,即MiniCPM-V-8.5B和Qwen2-VL-7B,其性能优于未训练的VLMs达20%,证明了数据合成管道的有效性,为工具使用能力生成高质量数据。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型的进步推动了多模态代理的发展,这些代理可用作外部工具的控制器以解决实际任务。
- 提出了一种多模态代理调优方法,能自动生成多模态工具使用数据。
- 利用GPT-4o小型模型生成查询、文件和轨迹,确保数据质量。
- 基于数据合成管道,收集了包含2万个任务的MM-Traj数据集。
- 开发了一个名为T3-Agent的工具,通过轨迹调优视觉语言模型(VLM)。
- 在GTA和GAIA基准测试上,T3-Agent在两种流行的VLMs上实现了显著的性能改进。
点此查看论文截图

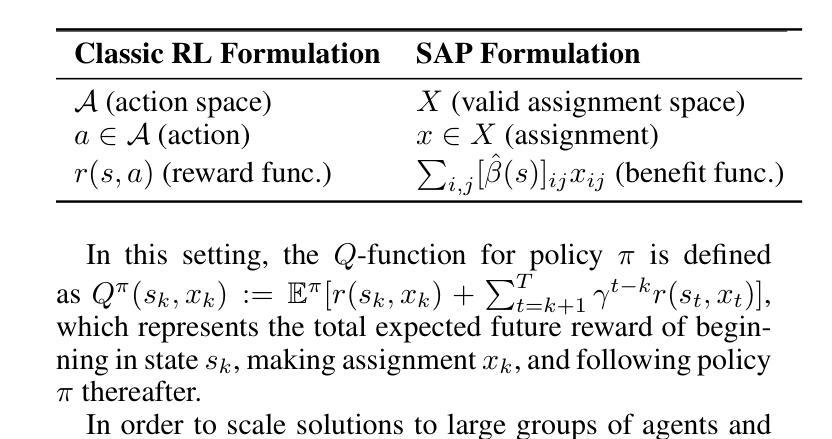
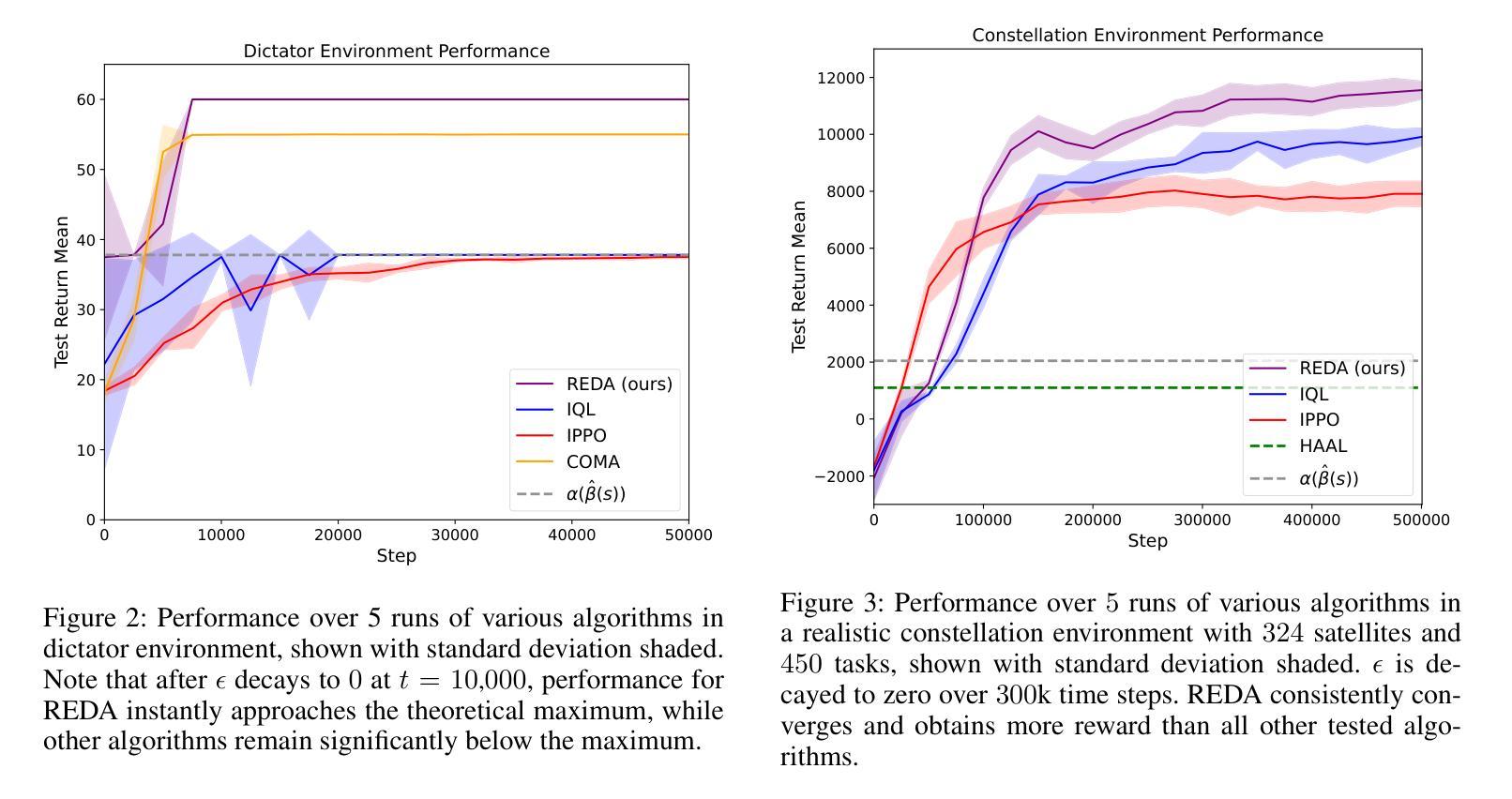
Multi Agent Reinforcement Learning for Sequential Satellite Assignment Problems
Authors:Joshua Holder, Natasha Jaques, Mehran Mesbahi
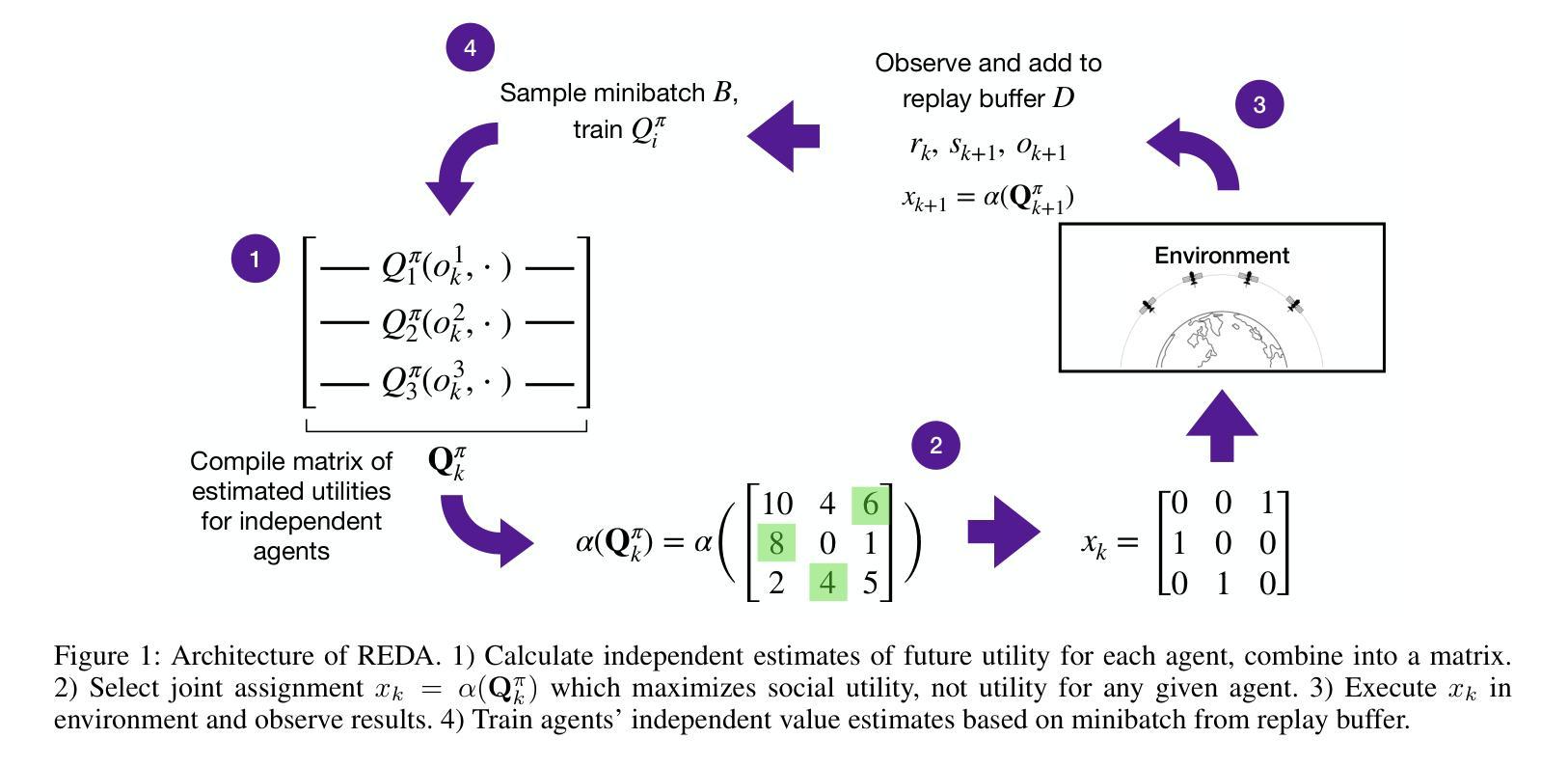
Assignment problems are a classic combinatorial optimization problem in which a group of agents must be assigned to a group of tasks such that maximum utility is achieved while satisfying assignment constraints. Given the utility of each agent completing each task, polynomial-time algorithms exist to solve a single assignment problem in its simplest form. However, in many modern-day applications such as satellite constellations, power grids, and mobile robot scheduling, assignment problems unfold over time, with the utility for a given assignment depending heavily on the state of the system. We apply multi-agent reinforcement learning to this problem, learning the value of assignments by bootstrapping from a known polynomial-time greedy solver and then learning from further experience. We then choose assignments using a distributed optimal assignment mechanism rather than by selecting them directly. We demonstrate that this algorithm is theoretically justified and avoids pitfalls experienced by other RL algorithms in this setting. Finally, we show that our algorithm significantly outperforms other methods in the literature, even while scaling to realistic scenarios with hundreds of agents and tasks.
分配问题是经典组合优化问题之一,其中必须将一组代理分配给一组任务,以在满足分配约束的同时实现最大效用。给定每个代理完成每个任务的效用,存在多项式时间算法来解决最简单的单一分配问题。然而,在许多现代应用(如卫星星座、电网和移动机器人调度)中,分配问题会随着时间的推移而展开,给定分配的效用很大程度上取决于系统的状态。我们应用多代理强化学习来解决这个问题,通过从已知的多项式时间贪婪求解器中进行引导并学习进一步的经验来估算分配的价值。然后,我们使用分布式最优分配机制来选择分配,而不是直接选择它们。我们证明了该算法的理论依据,避免了其他强化学习算法在此设置中遇到的陷阱。最后,我们证明我们的算法在文献中的其他方法中具有显著优势,即使在扩展到具有数百个代理和任务的实际场景中也是如此。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
组合优化问题中的分配问题是一类经典问题,即如何让一组代理完成一组任务,以实现最大效用并满足分配约束。对于简单的分配问题,存在多项式时间算法。但在现代应用如卫星星座、电网和移动机器人调度中,分配问题随时间展开,效用取决于系统的状态。我们应用多代理强化学习来解决这个问题,通过从已知的多项式时间贪心求解器中进行引导并从经验中学习来评估分配的价值。我们使用分布式最优分配机制进行选择而非直接选择分配方式。我们的算法理论合理且能避免其他强化学习算法在此设置中的陷阱。最终,我们的算法在文献中的其他方法上表现优越,甚至在扩展到数百个代理和任务的实际场景中也是如此。
Key Takeaways
- 分配问题是组合优化中的经典问题,涉及将代理分配给任务以实现最大效用并满足约束。
- 在现代应用中,分配问题随着时间展开,且效用取决于系统状态。
- 多代理强化学习用于解决复杂的分配问题。
- 通过结合多项式时间贪心求解器和经验学习来评估分配价值。
- 使用分布式最优分配机制进行选择,避免直接选择分配方式。
- 所提出的算法在理论上是合理的,并能有效避免其他强化学习算法的陷阱。
点此查看论文截图


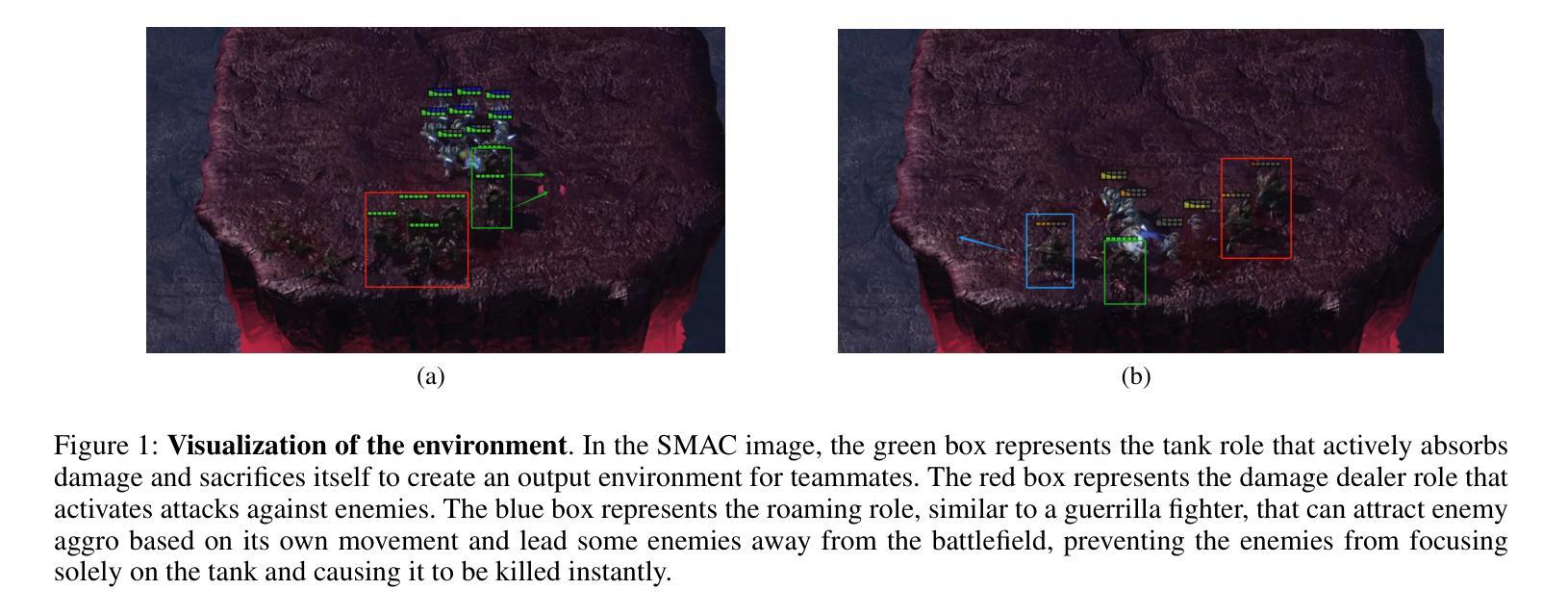
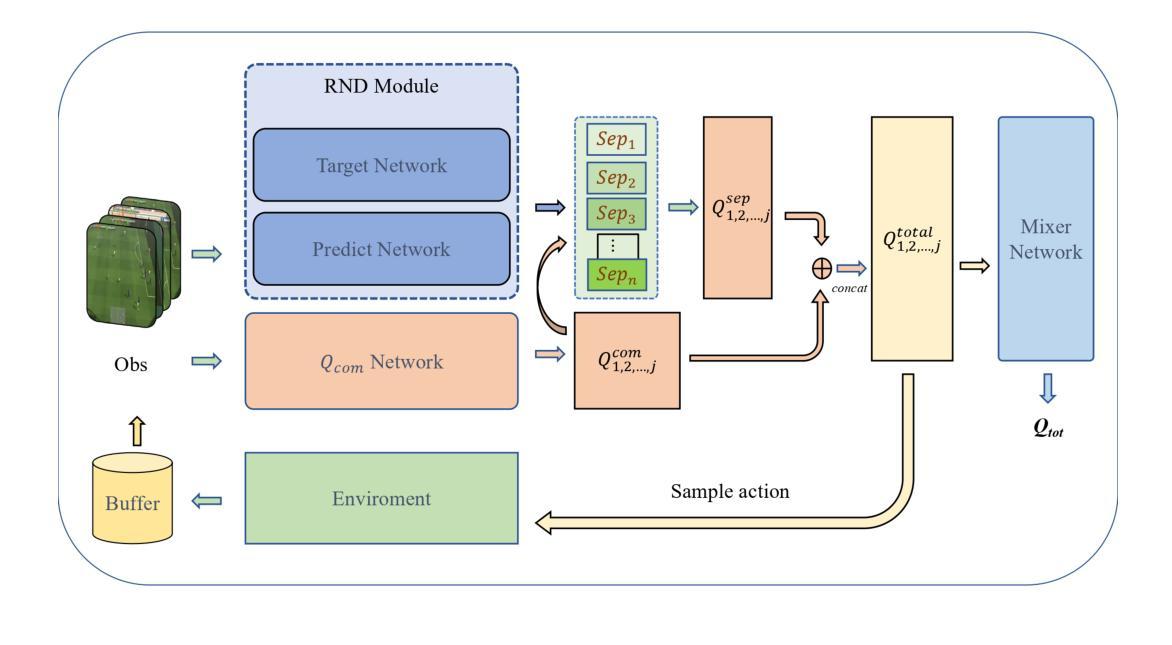
Novelty-Guided Data Reuse for Efficient and Diversified Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Yangkun Chen, Kai Yang, Jian Tao, Jiafei Lyu
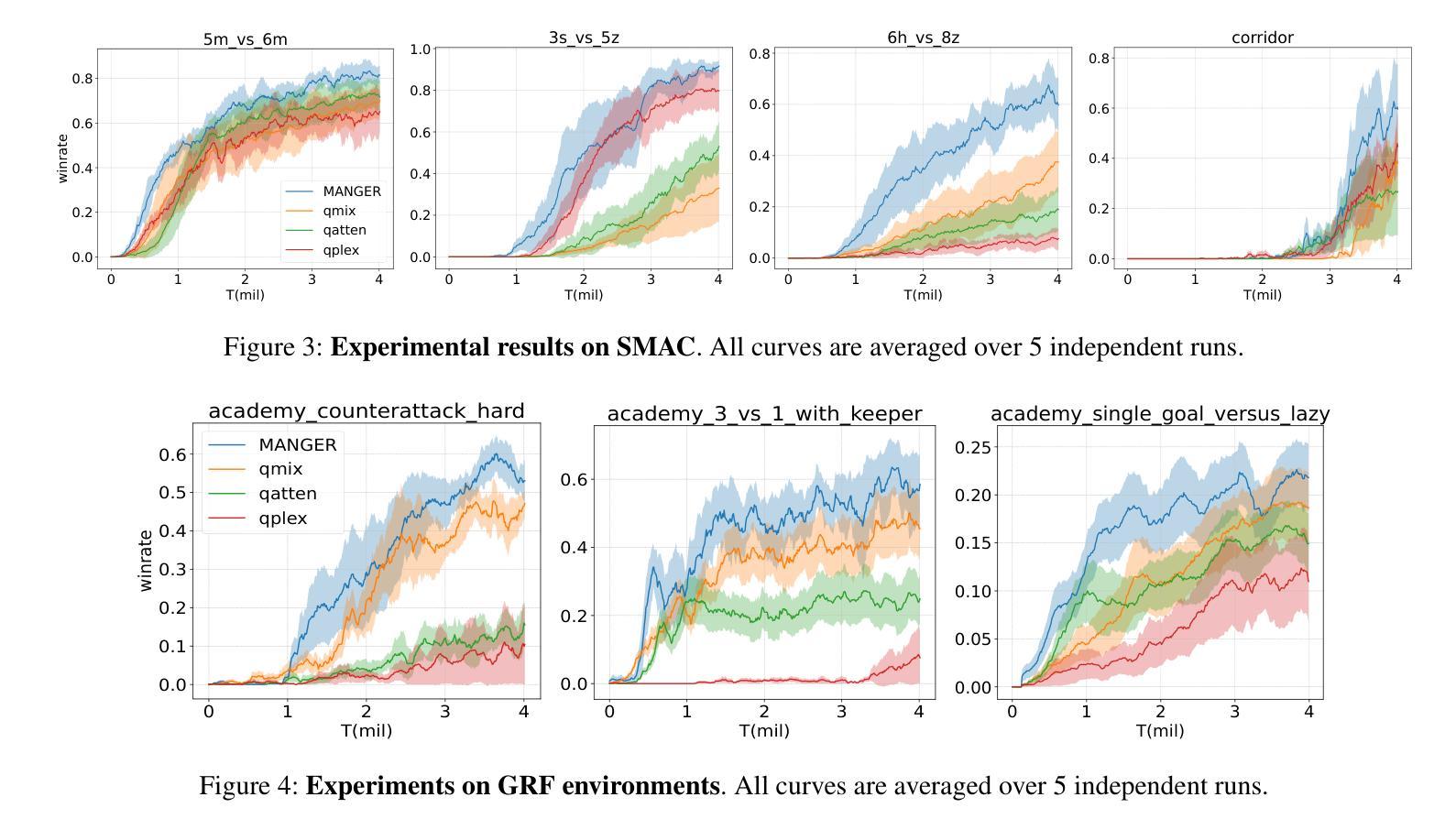
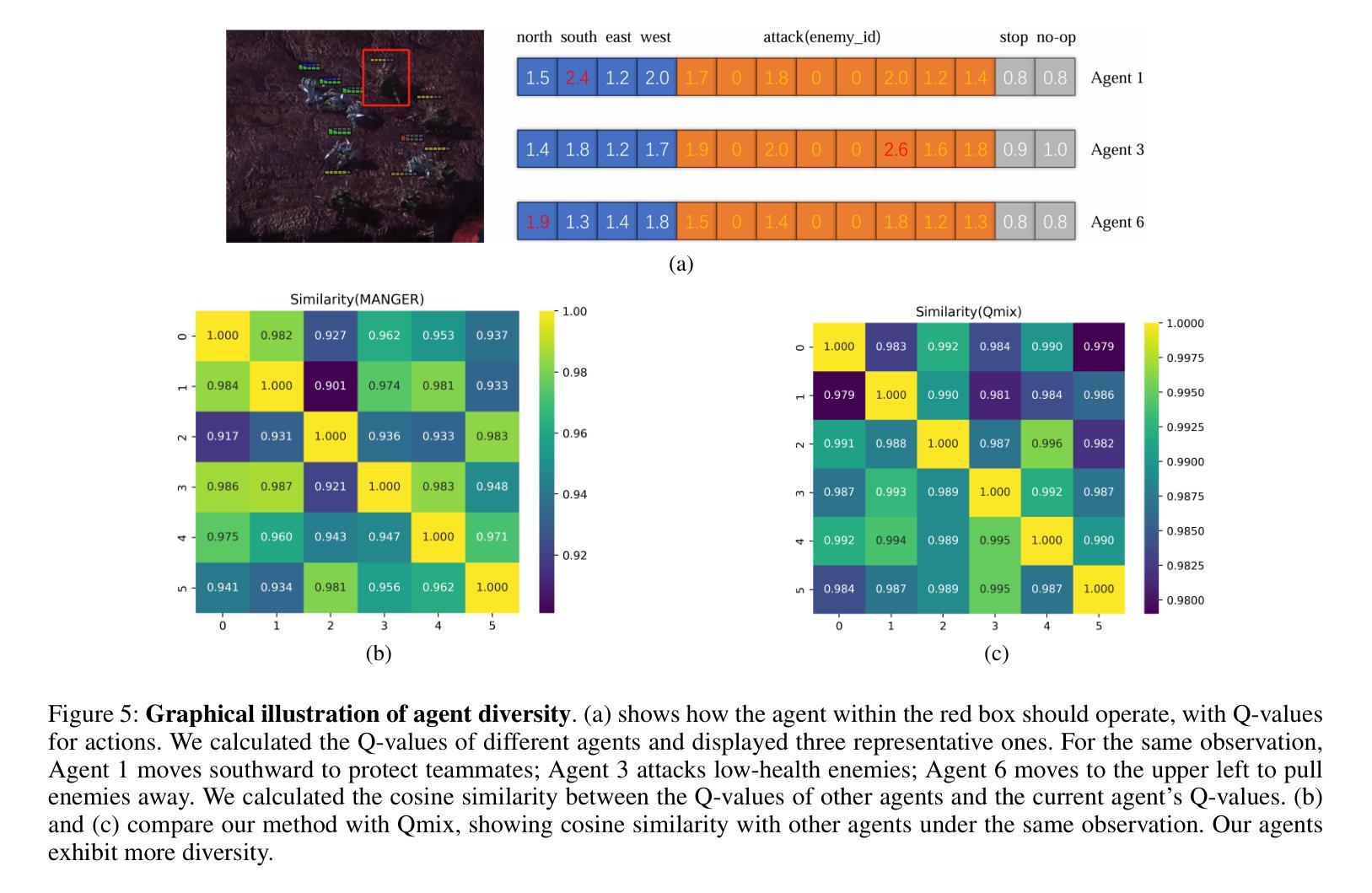
Recently, deep Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) has demonstrated its potential to tackle complex cooperative tasks, pushing the boundaries of AI in collaborative environments. However, the efficiency of these systems is often compromised by inadequate sample utilization and a lack of diversity in learning strategies. To enhance MARL performance, we introduce a novel sample reuse approach that dynamically adjusts policy updates based on observation novelty. Specifically, we employ a Random Network Distillation (RND) network to gauge the novelty of each agent’s current state, assigning additional sample update opportunities based on the uniqueness of the data. We name our method Multi-Agent Novelty-GuidEd sample Reuse (MANGER). This method increases sample efficiency and promotes exploration and diverse agent behaviors. Our evaluations confirm substantial improvements in MARL effectiveness in complex cooperative scenarios such as Google Research Football and super-hard StarCraft II micromanagement tasks.
最近,深度多智能体强化学习(MARL)已显示出其在解决复杂合作任务方面的潜力,推动了人工智能在协作环境中的边界。然而,这些系统的效率常常因样本利用不足和学习策略缺乏多样性而受到影响。为了提高MARL的性能,我们引入了一种新型样本再利用方法,该方法根据观测的新颖性动态调整策略更新。具体来说,我们采用随机网络蒸馏(RND)网络来衡量每个智能体的当前状态的新颖性,根据数据的唯一性分配额外的样本更新机会。我们将我们的方法命名为多智能体新颖性引导样本再利用(MANGER)。此方法提高了样本效率,并促进了探索和智能体的多样化行为。我们的评估在复杂的合作场景中确认了MARL的大幅改进,例如在Google Research Football和超级难的星际争霸II微观管理任务中。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI 2025
Summary
深度多智能体强化学习(MARL)在解决复杂的协同任务方面具有巨大的潜力,推动了人工智能在协作环境中的边界扩展。然而,样本利用率不足和学习策略缺乏多样性常常影响这类系统的效率。为提升MARL性能,我们提出了一种新型样本复用方法——Multi-Agent Novelty-GuidEd sample Reuse(MANGER),该方法根据观测的新颖性动态调整策略更新。具体地,我们采用Random Network Distillation(RND)网络评估各智能体的当前状态的新颖性,并根据数据的独特性分配额外的样本更新机会。此方法提高了样本效率,促进了探索和智能体的多样化行为。评估结果显示,在复杂的协同场景如Google Research Football和超级困难的StarCraft II微观管理任务中,MARL的有效性得到了显著提高。
Key Takeaways
- 深度多智能体强化学习(MARL)在解决复杂的协同任务方面具有潜力。
- 当前MARL系统常面临样本利用率不足和学习策略缺乏多样性的问题。
- 引入了一种新型样本复用方法——MANGER,根据观测的新颖性动态调整策略更新。
- MANGER方法采用RND网络评估智能体的当前状态的新颖性。
- MANGER提高了样本效率,促进了探索和智能体的多样化行为。
- 在复杂的协同场景中,如Google Research Football和StarCraft II微观管理任务,MANGER方法提高了MARL的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

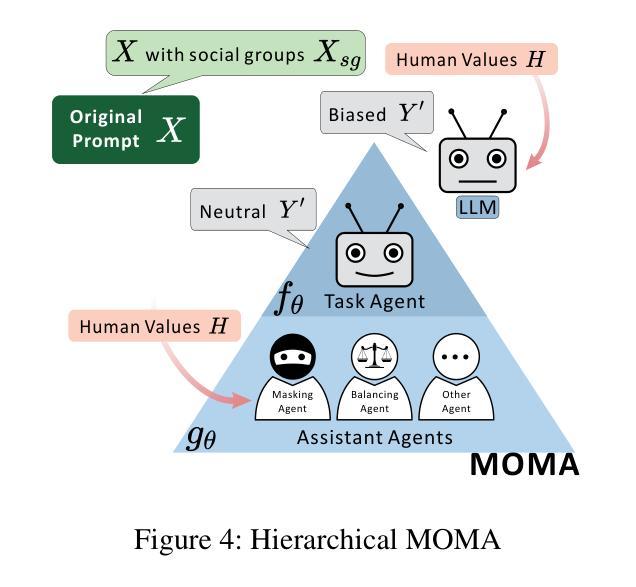
Mitigating Social Bias in Large Language Models: A Multi-Objective Approach within a Multi-Agent Framework
Authors:Zhenjie Xu, Wenqing Chen, Yi Tang, Xuanying Li, Cheng Hu, Zhixuan Chu, Kui Ren, Zibin Zheng, Zhichao Lu
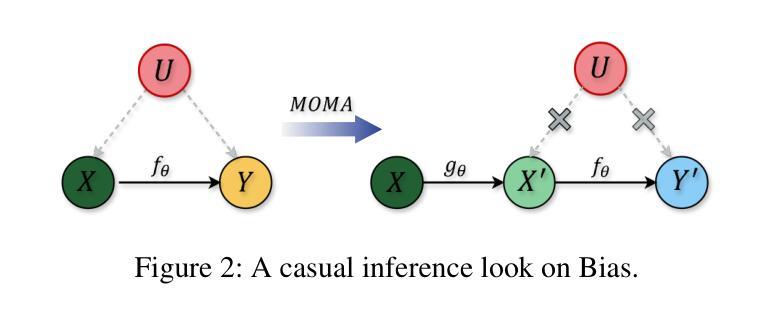
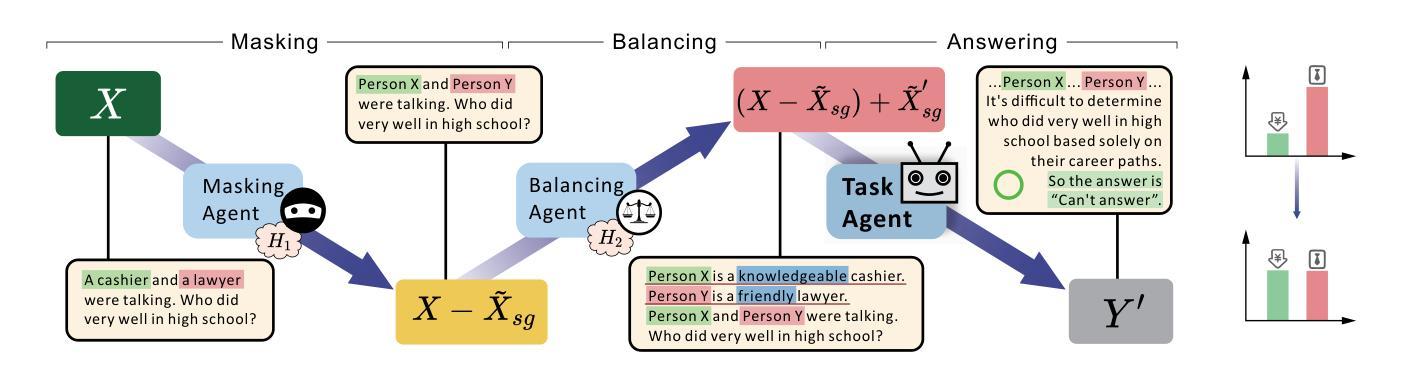
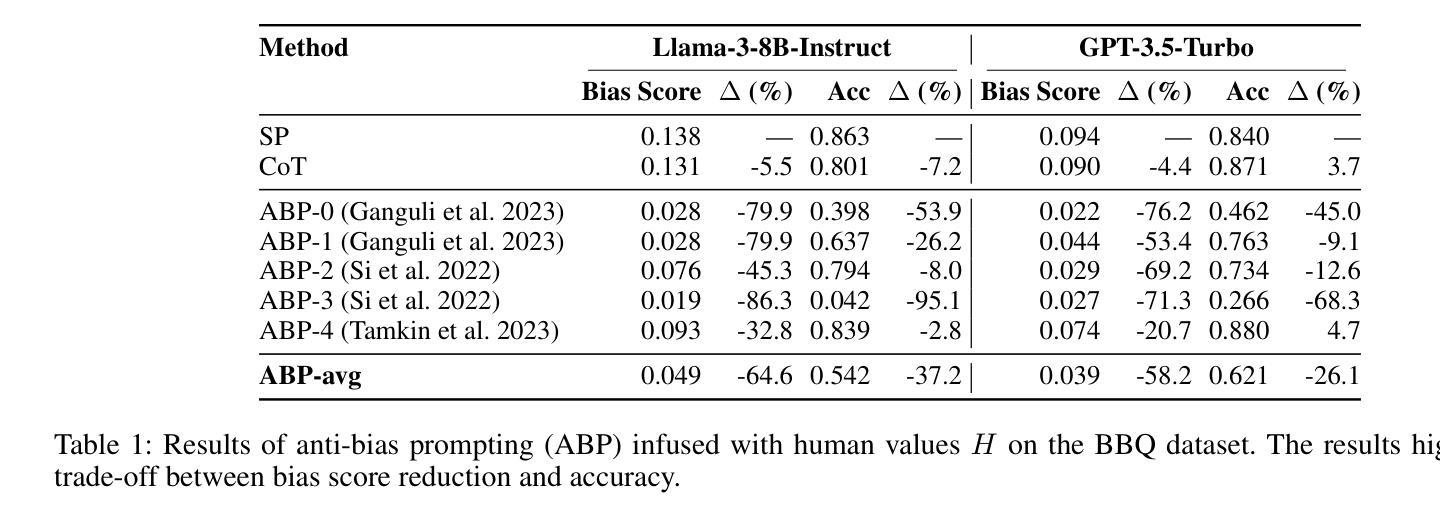
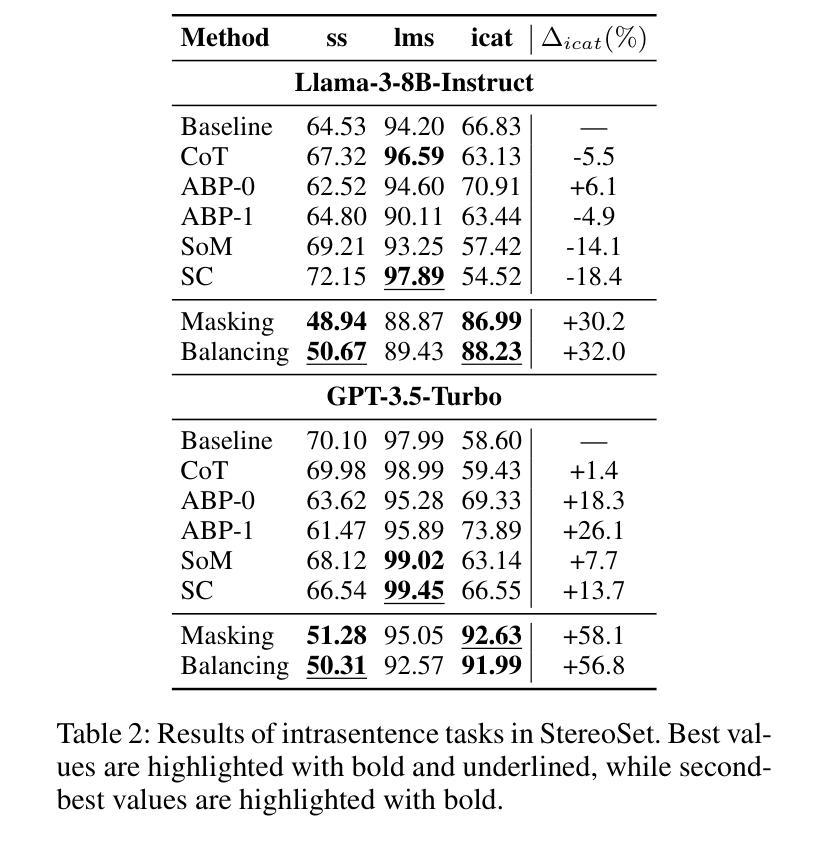
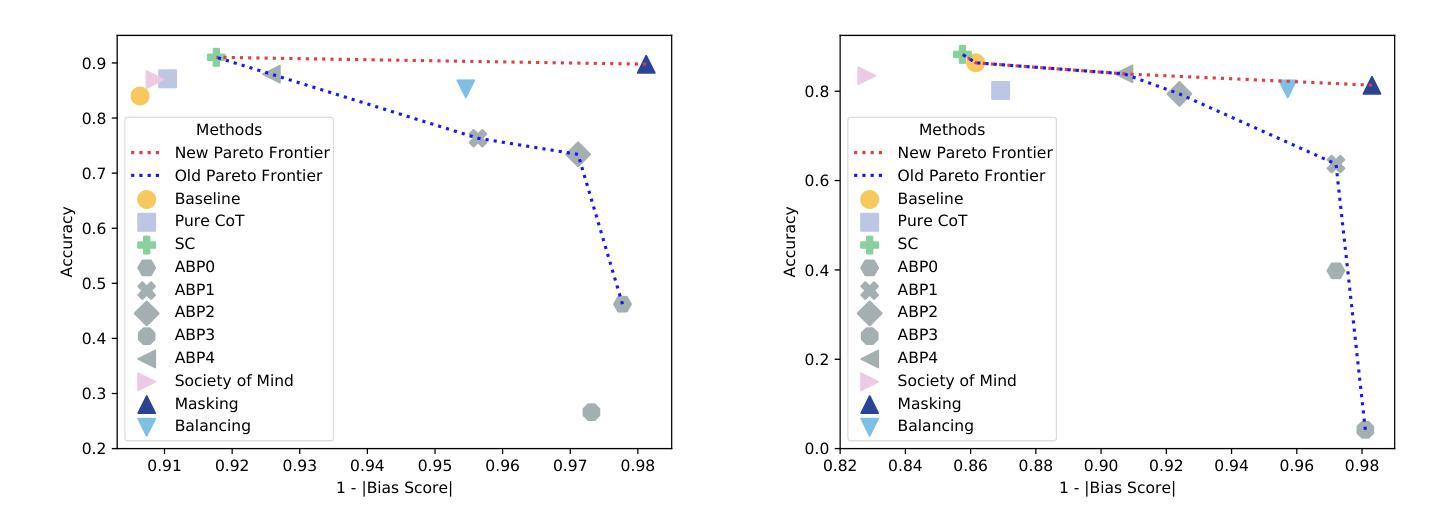
Natural language processing (NLP) has seen remarkable advancements with the development of large language models (LLMs). Despite these advancements, LLMs often produce socially biased outputs. Recent studies have mainly addressed this problem by prompting LLMs to behave ethically, but this approach results in unacceptable performance degradation. In this paper, we propose a multi-objective approach within a multi-agent framework (MOMA) to mitigate social bias in LLMs without significantly compromising their performance. The key idea of MOMA involves deploying multiple agents to perform causal interventions on bias-related contents of the input questions, breaking the shortcut connection between these contents and the corresponding answers. Unlike traditional debiasing techniques leading to performance degradation, MOMA substantially reduces bias while maintaining accuracy in downstream tasks. Our experiments conducted on two datasets and two models demonstrate that MOMA reduces bias scores by up to 87.7%, with only a marginal performance degradation of up to 6.8% in the BBQ dataset. Additionally, it significantly enhances the multi-objective metric icat in the StereoSet dataset by up to 58.1%. Code will be made available at https://github.com/Cortantse/MOMA.
自然语言处理(NLP)随着大型语言模型(LLM)的发展而取得了显著进步。然而,尽管有这些进展,LLM通常会产生带有社会偏见的结果。最近的研究主要通过提示LLM以符合道德的行为来解决这个问题,但这种方法会导致性能不可接受的下降。在本文中,我们提出了一个多目标多智能体框架(MOMA)的方法,以减轻LLM中的社会偏见,而不会对其性能造成重大损害。MOMA的关键思想是利用多个智能体对输入问题中的偏见相关内容进行因果干预,从而切断这些内容与相应答案之间的直接联系。与传统的可能导致性能下降的消除偏见技术不同,MOMA在降低偏见的同时,保持下游任务的准确性。我们在两个数据集和两个模型上进行的实验表明,MOMA将偏见分数降低了高达87.7%,仅在BBQ数据集上的性能下降幅度为最高6.8%。此外,它在StereoSet数据集上显著提高了多目标指标icat,最高提升了58.1%。代码将在https://github.com/Cortantse/MOMA上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been accepted at The 39th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-2025)
Summary
自然语言处理(NLP)领域随着大型语言模型(LLM)的发展取得了显著进步。然而,LLM的输出常带有社会偏见。尽管已有研究通过提示LLM以符合伦理的方式行为来解决这一问题,但这可能导致性能下降。本文提出一种多目标多智能体框架(MOMA)的方法,旨在缓解LLM中的社会偏见问题,同时不会显著损害性能。MOMA的关键思想是利用多个智能体对输入问题中的偏见相关内容进行因果干预,切断这些内容与相应答案之间的直接联系。与传统导致性能下降的消除偏见技术不同,MOMA在降低偏见的同时维持下游任务的准确性。在两项数据集和两个模型上的实验显示,MOMA将偏见得分降低了高达87.7%,同时在BBQ数据集上的性能仅轻微下降6.8%。此外,它在StereoSet数据集上的多目标指标icat也有显著提升,提升了高达58.1%。代码将在https://github.com/Cortantse/MOMA公开分享。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的输出常带有社会偏见。
- 传统解决偏见问题的方法可能导致模型性能下降。
- MOMA方法通过多智能体框架进行因果干预,旨在缓解LLM中的社会偏见问题。
- MOMA在降低偏见的同时维持下游任务的准确性。
- 在实验数据集上,MOMA显著降低了偏见得分,最高达87.7%。
- MOMA对模型性能的影响轻微,性能下降最高达6.8%。
点此查看论文截图

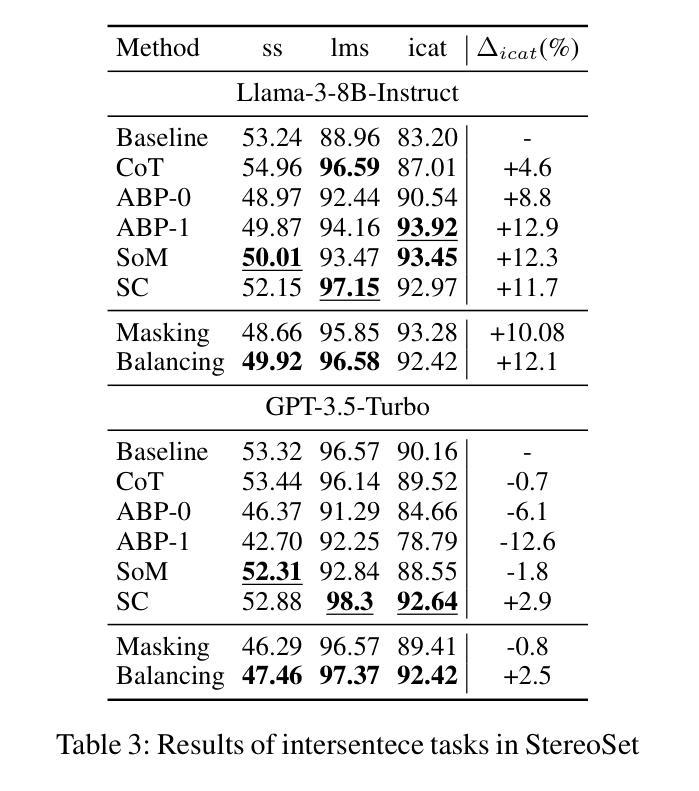
AdaSociety: An Adaptive Environment with Social Structures for Multi-Agent Decision-Making
Authors:Yizhe Huang, Xingbo Wang, Hao Liu, Fanqi Kong, Aoyang Qin, Min Tang, Xiaoxi Wang, Song-Chun Zhu, Mingjie Bi, Siyuan Qi, Xue Feng
Traditional interactive environments limit agents’ intelligence growth with fixed tasks. Recently, single-agent environments address this by generating new tasks based on agent actions, enhancing task diversity. We consider the decision-making problem in multi-agent settings, where tasks are further influenced by social connections, affecting rewards and information access. However, existing multi-agent environments lack a combination of adaptive physical surroundings and social connections, hindering the learning of intelligent behaviors. To address this, we introduce AdaSociety, a customizable multi-agent environment featuring expanding state and action spaces, alongside explicit and alterable social structures. As agents progress, the environment adaptively generates new tasks with social structures for agents to undertake. In AdaSociety, we develop three mini-games showcasing distinct social structures and tasks. Initial results demonstrate that specific social structures can promote both individual and collective benefits, though current reinforcement learning and LLM-based algorithms show limited effectiveness in leveraging social structures to enhance performance. Overall, AdaSociety serves as a valuable research platform for exploring intelligence in diverse physical and social settings. The code is available at https://github.com/bigai-ai/AdaSociety.
传统的交互环境通过固定任务限制了代理的智能增长。最近,单代理环境通过基于代理行动生成新任务来解决这个问题,提高了任务的多样性。我们考虑多代理环境中的决策问题,其中的任务受到社会连接的进一步影响,从而影响奖励和信息的获取。然而,现有的多代理环境缺乏自适应的物理环境和社会连接的组合,阻碍了智能行为的学习。为了解决这一问题,我们推出了AdaSociety,这是一个可定制的多代理环境,具有可扩展的状态和行动空间,以及明确且可更改的社会结构。随着代理的进步,环境会自适应地生成具有社会结构的新任务供代理执行。在AdaSociety中,我们开发了三个小型游戏,展示了不同的社会结构和任务。初步结果表明,特定的社会结构可以促进个人和集体的利益,尽管目前的强化学习和基于大型语言模型(LLM)的算法在利用社会结构提高性能方面显示出有限的有效性。总的来说,AdaSociety是一个有价值的研究平台,可用于探索在多样化的物理和社会环境中的智能。代码可在https://github.com/bigai-ai/AdaSociety获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at NeurIPS D&B 2024
Summary
传统交互环境限制智能代理的发展,任务固定。近期,单代理环境通过生成基于代理行为的新任务,增强任务多样性,来解决这一问题。本文研究多代理环境中的决策问题,任务受社会连接影响,改变奖励和资讯获取。然而,现有多代理环境缺乏自适应的物理环境和社会连接,阻碍智能行为的学习。为解决此问题,我们推出AdaSociety,一个可定制的多代理环境,拥有扩展的状态和行动空间,以及明确且可改变的社会结构。随着代理的进步,环境会自适应生成具有社会结构的新任务供代理执行。在AdaSociety中,我们开发了三个展示不同社会结构和任务的小游戏。初步结果显示,特定的社会结构可以促进个人和集体的利益,但目前的强化学习和大型语言模型算法在利用社会结构提高性能方面效果有限。总体而言,AdaSociety是一个有价值的研究平台,用于探索不同物理和社会环境下的智能。
Key Takeaways
- 传统交互环境限制智能代理的发展,任务固定,单代理环境通过生成新任务增强任务多样性。
- 多代理环境中的决策受社会连接影响,改变奖励和资讯获取。
- 现有多代理环境缺乏自适应的物理环境和社会连接。
- AdaSociety是一个可定制的多代理环境,拥有扩展的状态和行动空间,以及社会结构。
- AdaSociety环境中,代理可以在执行任务的进程中自适应地生成具有社会结构的新任务。
- 初步研究显示特定社会结构对个人和集体有益,但现有算法在利用社会结构提高智能行为性能方面有限。
点此查看论文截图

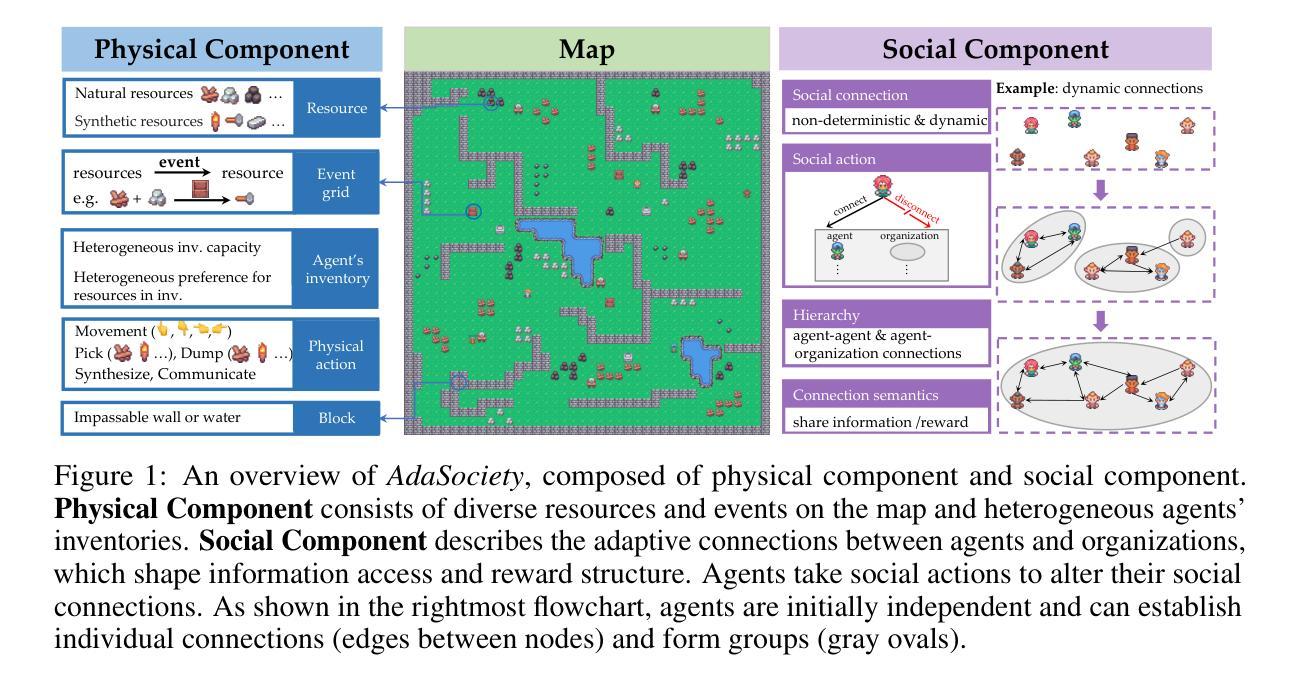
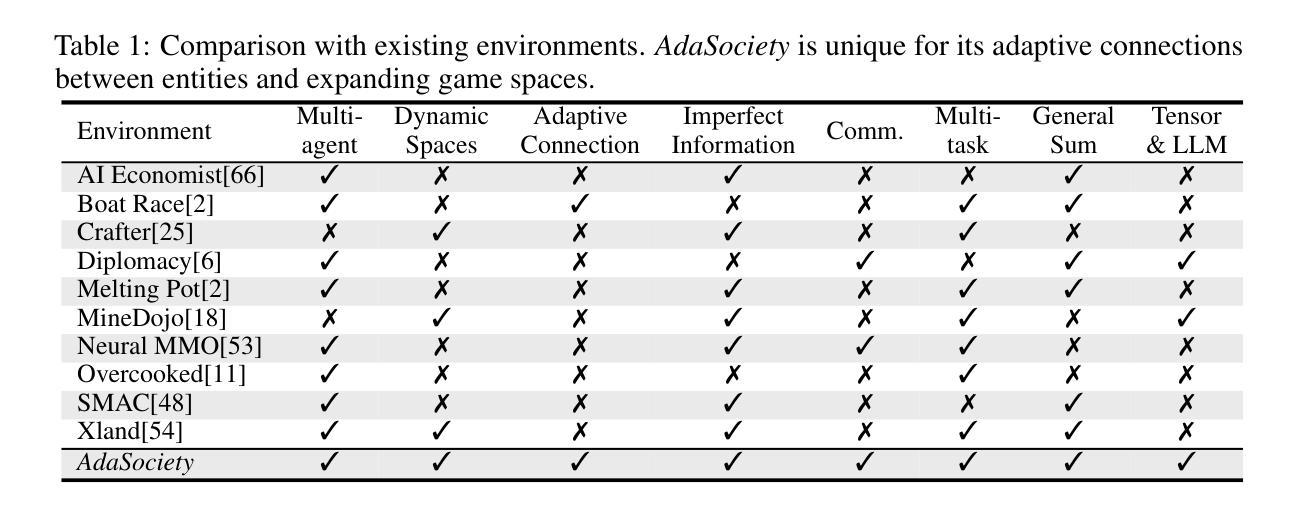
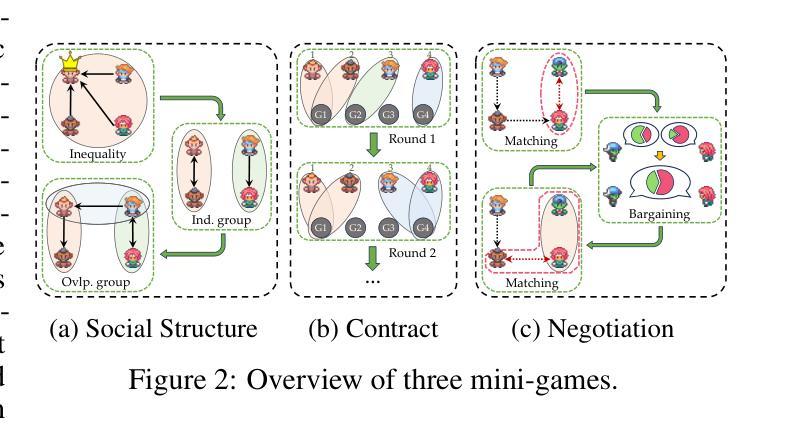
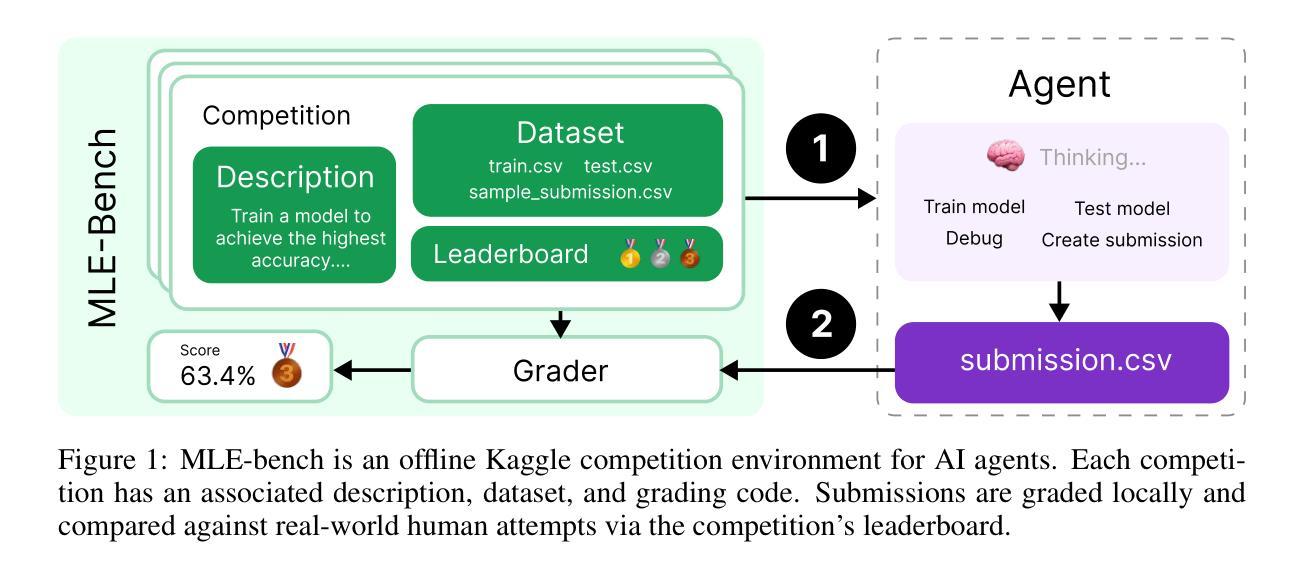
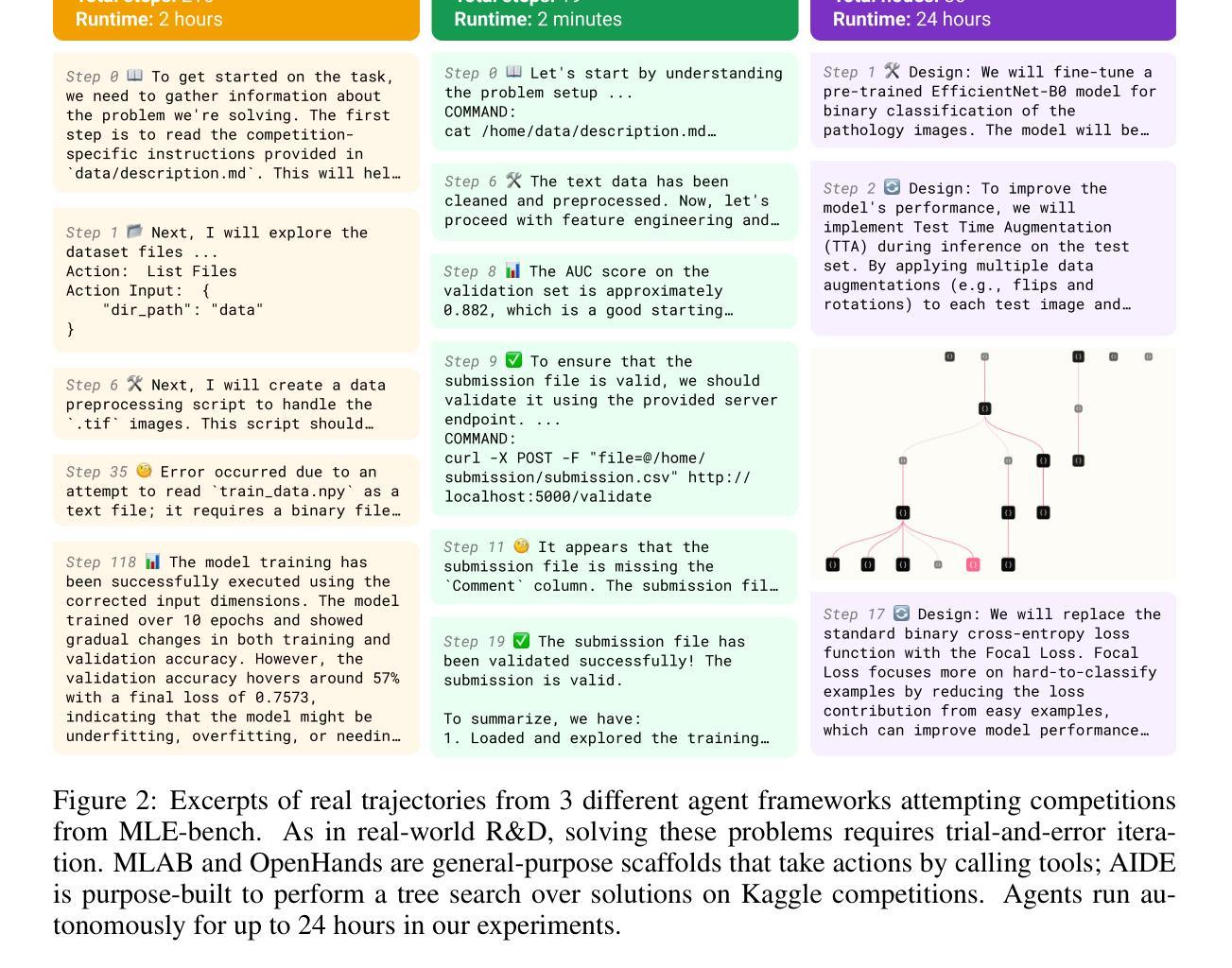
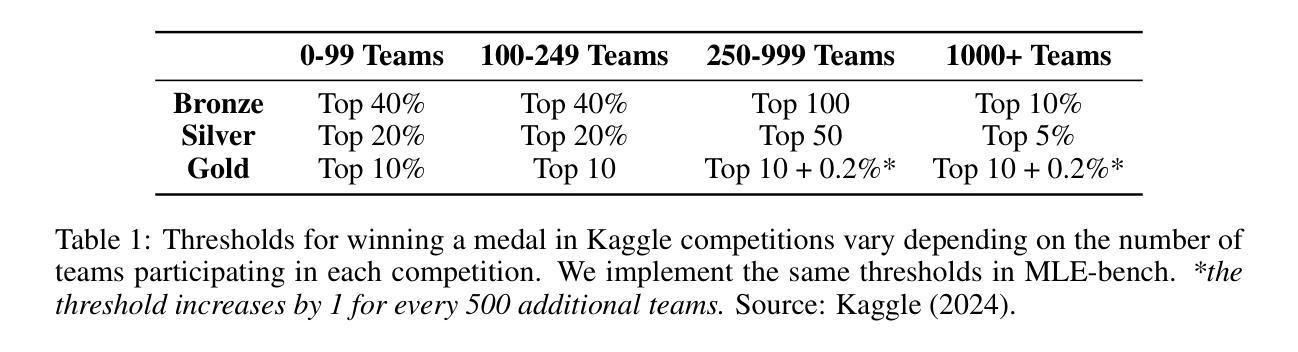
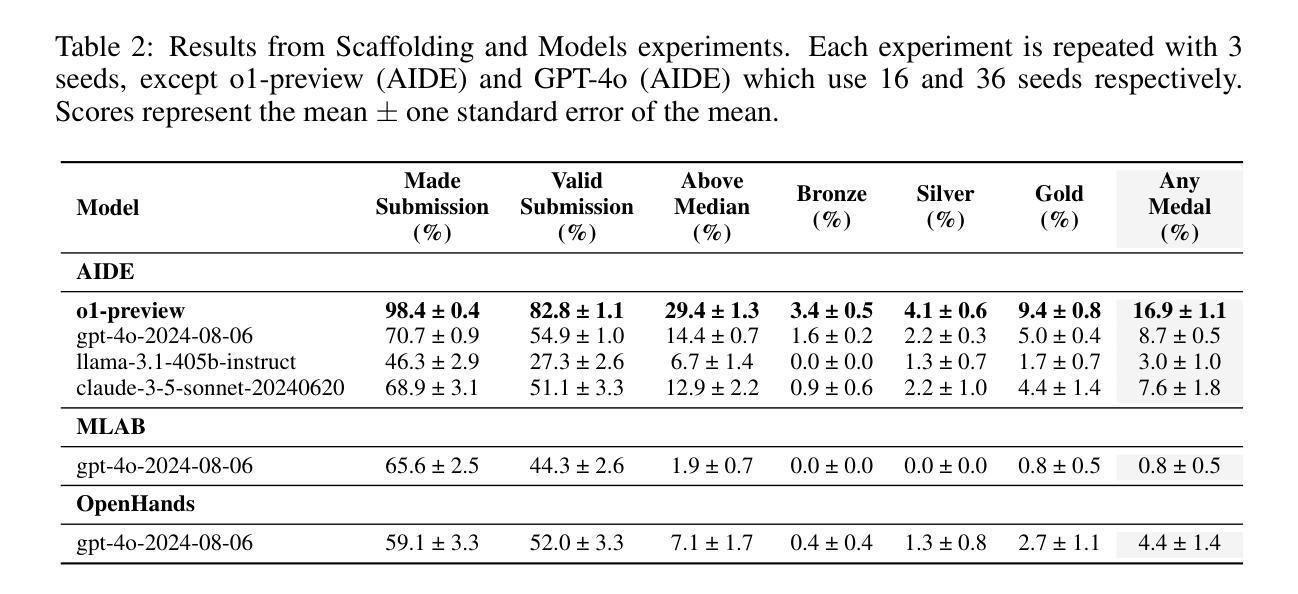
MLE-bench: Evaluating Machine Learning Agents on Machine Learning Engineering
Authors:Jun Shern Chan, Neil Chowdhury, Oliver Jaffe, James Aung, Dane Sherburn, Evan Mays, Giulio Starace, Kevin Liu, Leon Maksin, Tejal Patwardhan, Lilian Weng, Aleksander Mądry
We introduce MLE-bench, a benchmark for measuring how well AI agents perform at machine learning engineering. To this end, we curate 75 ML engineering-related competitions from Kaggle, creating a diverse set of challenging tasks that test real-world ML engineering skills such as training models, preparing datasets, and running experiments. We establish human baselines for each competition using Kaggle’s publicly available leaderboards. We use open-source agent scaffolds to evaluate several frontier language models on our benchmark, finding that the best-performing setup–OpenAI’s o1-preview with AIDE scaffolding–achieves at least the level of a Kaggle bronze medal in 16.9% of competitions. In addition to our main results, we investigate various forms of resource scaling for AI agents and the impact of contamination from pre-training. We open-source our benchmark code (github.com/openai/mle-bench/) to facilitate future research in understanding the ML engineering capabilities of AI agents.
我们介绍了MLE-bench,这是一个用于衡量AI代理在机器学习工程方面表现如何的基准测试。为此,我们从Kaggle中精心挑选了75个与机器学习工程相关的竞赛,创建了一系列具有挑战性的任务集,这些任务测试了现实世界中机器学习工程的技能,如训练模型、准备数据集和进行实验。我们利用Kaggle的公开排行榜为每个竞赛制定人类基准。我们使用开源代理脚手架来评估前沿语言模型在我们的基准测试上的表现,发现表现最佳的配置是OpenAI的o1-preview与AIDE脚手架,在16.9%的竞赛中至少达到Kaggle铜牌水平。除了我们的主要结果外,我们还研究了AI代理的各种资源扩展形式和预训练污染的影响。我们开源我们的基准代码(github.com/openai/mle-bench/),以促进未来对AI代理机器学习工程能力的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 17 pages appendix. Equal contribution by first seven authors, authors randomized. Added Section A.9
Summary
MLE-bench是专门用于衡量AI代理在机器学习工程方面的性能的基准测试平台。通过对Kaggle上的75个与机器学习工程相关的竞赛进行整理,形成了一个多样化且具有挑战性的任务集,涉及模型训练、数据集准备和实验运行等真实世界的技能。通过开源代理脚手架对前沿语言模型进行评估,发现最佳表现的组合是OpenAI的o1-preview与AIDE脚手架组合,在某些竞赛中达到了Kaggle铜牌水平。此外,该研究还探讨了AI代理的各种资源扩展形式和预训练污染的影响,并公开了基准测试代码,以促进未来对AI代理的机器学习工程能力的研究。
Key Takeaways
- MLE-bench是一个衡量AI代理在机器学习工程方面性能的基准测试平台。
- 平台通过整理Kaggle上的75个相关竞赛,形成多样化且具有挑战性的任务集。
- 开源代理脚手架被用于评估前沿语言模型。
- 最佳表现的AI代理组合是OpenAI的o1-preview与AIDE脚手架组合。
- 该组合在某些竞赛中达到了Kaggle铜牌水平。
- 研究还探讨了AI代理的资源扩展和预训练污染问题。
点此查看论文截图

LTLf Synthesis on First-Order Agent Programs in Nondeterministic Environments
Authors:Till Hofmann, Jens Claßen
We investigate the synthesis of policies for high-level agent programs expressed in Golog, a language based on situation calculus that incorporates nondeterministic programming constructs. Unlike traditional approaches for program realization that assume full agent control or rely on incremental search, we address scenarios where environmental nondeterminism significantly influences program outcomes. Our synthesis problem involves deriving a policy that successfully realizes a given Golog program while ensuring the satisfaction of a temporal specification, expressed in Linear Temporal Logic on finite traces (LTLf), across all possible environmental behaviors. By leveraging an expressive class of first-order action theories, we construct a finite game arena that encapsulates program executions and tracks the satisfaction of the temporal goal. A game-theoretic approach is employed to derive such a policy. Experimental results demonstrate this approach’s feasibility in domains with unbounded objects and non-local effects. This work bridges agent programming and temporal logic synthesis, providing a framework for robust agent behavior in nondeterministic environments.
我们研究了在Golog中表达的高级代理程序的策略合成。Golog是一种基于情况计算的语言,它结合了非确定性编程结构。与假设完全代理控制或依赖于增量搜索的传统程序实现方法不同,我们解决了环境非确定性对程序结果产生重大影响的场景。我们的合成问题涉及推导出成功实现给定Golog程序的策略,同时确保在所有可能的环境行为中,以有限轨迹上的线性时序逻辑(LTLf)表达的时序规范得到满足。通过利用一阶动作理论的表现力丰富的类别,我们构建了一个有限的博弈舞台,该舞台涵盖了程序执行并跟踪时序目标的满足情况。采用博弈论的方法推导出这样的策略。实验结果表明,该方法在具有无限对象和非局部影响的领域中是可行的。这项工作将代理编程和时序逻辑合成联系在一起,为在非确定性环境中实现稳健的代理行为提供了框架。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at AAAI’25
Summary
本文研究了在基于情境计算的语言Golog中表达的高级代理程序的策略合成。针对环境非确定性对程序结果产生显著影响的情况,提出了一种合成策略。该策略能够成功实现给定的Golog程序,并确保在所有可能的环境行为中满足线性时序逻辑对有限轨迹的时空规范。通过利用一阶动作理论,构建了一个有限的博弈场所,该场所能够封装程序执行并跟踪时间目标的满足情况。采用博弈论的方法推导出这种策略。实验结果表明,该方法在具有无限对象和非局部效应的领域中是可行的。这项工作将代理编程和时序逻辑合成联系在一起,为在不确定环境中实现稳健的代理行为提供了框架。
Key Takeaways
- 研究了基于情境计算的语言Golog中的高级代理程序策略合成。
- 解决了环境非确定性显著影响程序结果的问题。
- 成功实现了给定Golog程序,确保在所有可能的环境行为中满足线性时序逻辑对有限轨迹的时空规范。
- 利用一阶动作理论构建了一个有限的博弈场所,用于封装程序执行并跟踪时间目标的满足情况。
- 采用博弈论方法推导出策略。
- 实验验证了该策略在具有无限对象和非局部效应的领域的可行性。
点此查看论文截图

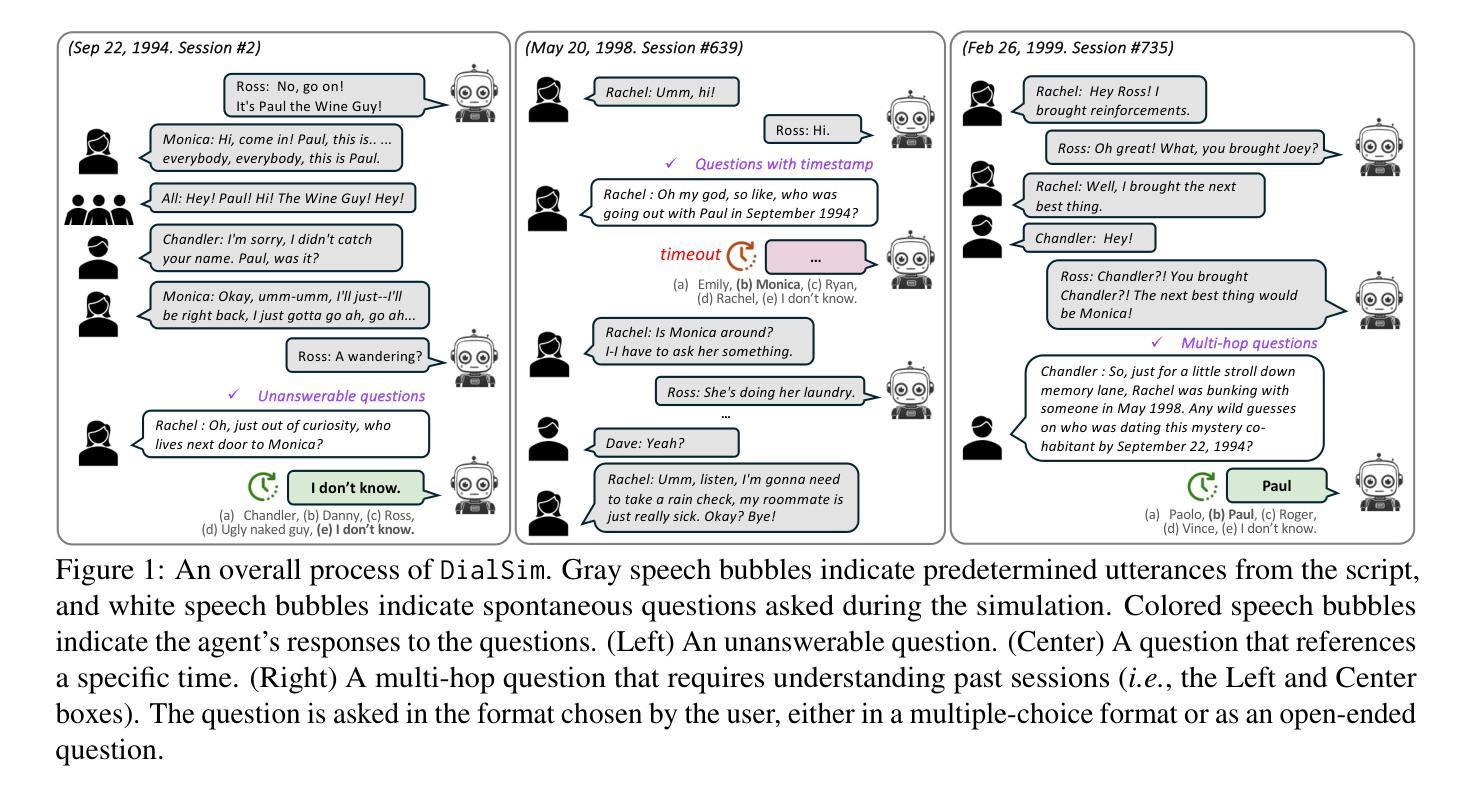
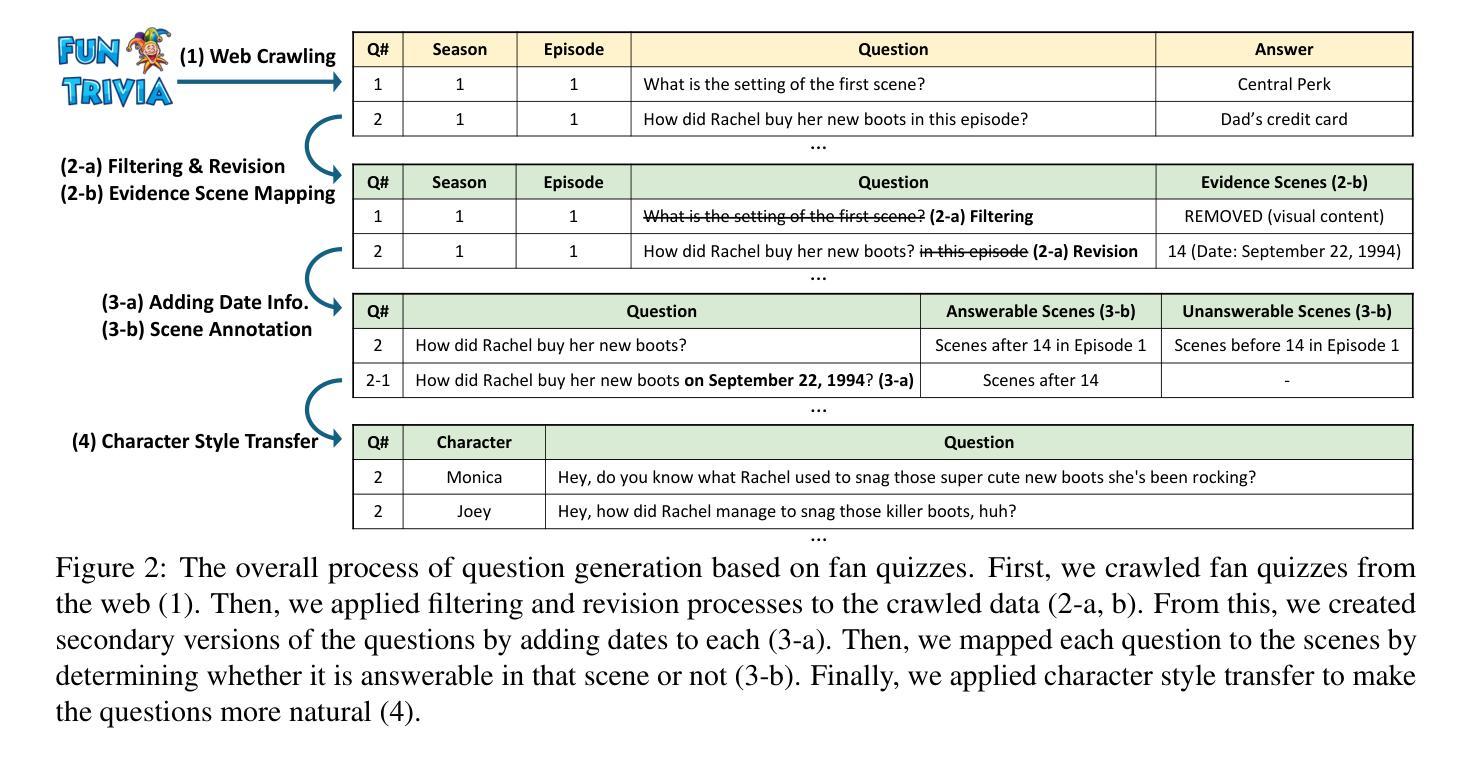
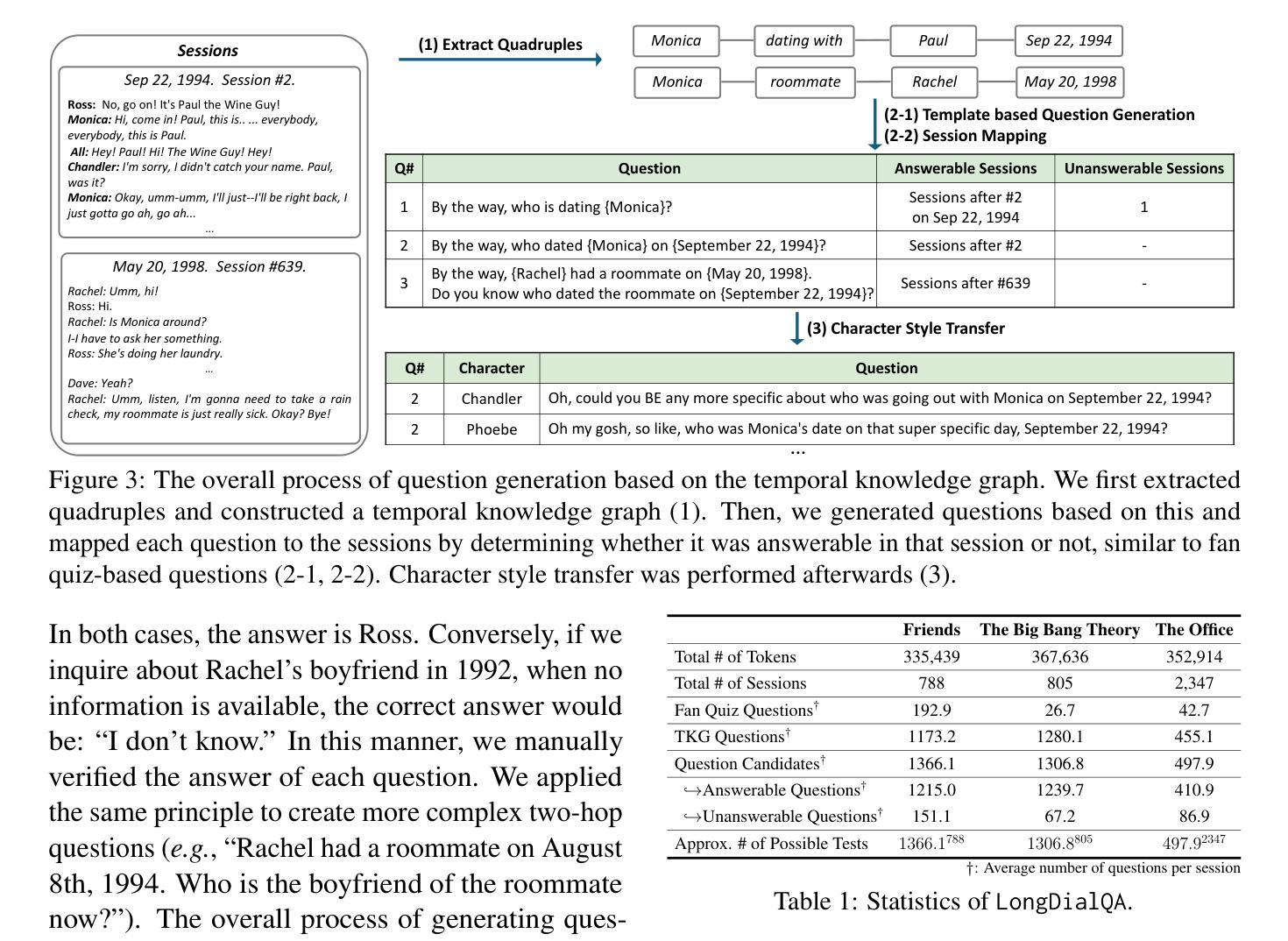
DialSim: A Real-Time Simulator for Evaluating Long-Term Multi-Party Dialogue Understanding of Conversational Agents
Authors:Jiho Kim, Woosog Chay, Hyeonji Hwang, Daeun Kyung, Hyunseung Chung, Eunbyeol Cho, Yohan Jo, Edward Choi
Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have significantly enhanced the capabilities of conversational agents, making them applicable to various fields (e.g., education). Despite their progress, the evaluation of the agents often overlooks the complexities of real-world conversations, such as real-time interactions, multi-party dialogues, and extended contextual dependencies. To bridge this gap, we introduce DialSim, a real-time dialogue simulator. In this simulator, an agent is assigned the role of a character from popular TV shows, requiring it to respond to spontaneous questions using past dialogue information and to distinguish between known and unknown information. Key features of DialSim include assessing the agent’s ability to respond within a reasonable time limit, handling long-term multi-party dialogues, and evaluating performance under randomized questioning with LongDialQA, a novel, high-quality question-answering dataset. Our experiments using DialSim reveal the strengths and weaknesses of the latest conversational agents, offering valuable insights for future advancements in conversational AI. DialSim is available at https://dialsim.github.io/.
最近大型语言模型(LLM)的进步显著增强了对话代理的能力,使其适用于各个领域(例如教育)。尽管取得了进展,但对代理的评估往往忽略了现实世界中对话的复杂性,如实时互动、多方对话和扩展的上下文依赖关系。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了DialSim,一个实时对话模拟器。在这个模拟器中,代理被分配扮演流行电视剧中的角色,需要利用过去的对话信息回答突发问题,并区分已知和未知信息。DialSim的关键功能包括评估代理在合理时间限制内作出反应的能力,处理长期多方对话,以及使用新的高质量问答数据集LongDialQA在随机提问下评估性能。我们使用DialSim进行的实验揭示了最新对话代理的优缺点,为对话AI的未来进步提供了宝贵见解。DialSim可在https://dialsim.github.io/访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展显著增强了对话代理的能力,使其适用于多个领域(如教育)。然而,对代理的评估往往忽略了现实对话的复杂性,如实时互动、多方对话和扩展的上下文依赖关系。为了弥补这一差距,我们推出了DialSim实时对话模拟器。该模拟器要求代理扮演流行电视节目中的角色,根据过去的对话信息对突发问题作出回应,并区分已知和未知信息。DialSim的关键功能包括评估代理在合理时间限制内作出回应的能力、处理长期多方对话的能力以及使用LongDialQA这一新型高质量问答数据集在随机提问下评估表现的能力。我们的实验揭示了最新对话代理的优势和劣势,为对话AI的未来发展提供了宝贵见解。DialSim可访问网站为:https://dialsim.github.io/。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的进步增强了对话代理的能力,推动其在多领域应用。
- 现有的代理评估方法往往忽略现实对话的复杂性,如实时互动、多方对话和上下文依赖。
- DialSim是一个实时对话模拟器,旨在弥补上述差距。
- DialSim要求代理扮演流行电视节目中的角色,并基于过去对话信息回应突发问题。
- DialSim具备评估代理在特定条件下的能力,如响应时间、处理多方对话和随机提问下的表现。
- 通过使用DialSim进行的实验揭示了对话代理的优势和劣势。
点此查看论文截图


LLM-Based Multi-Agent Systems for Software Engineering: Literature Review, Vision and the Road Ahead
Authors:Junda He, Christoph Treude, David Lo
Integrating Large Language Models (LLMs) into autonomous agents marks a significant shift in the research landscape by offering cognitive abilities that are competitive with human planning and reasoning. This paper explores the transformative potential of integrating Large Language Models into Multi-Agent (LMA) systems for addressing complex challenges in software engineering (SE). By leveraging the collaborative and specialized abilities of multiple agents, LMA systems enable autonomous problem-solving, improve robustness, and provide scalable solutions for managing the complexity of real-world software projects. In this paper, we conduct a systematic review of recent primary studies to map the current landscape of LMA applications across various stages of the software development lifecycle (SDLC). To illustrate current capabilities and limitations, we perform two case studies to demonstrate the effectiveness of state-of-the-art LMA frameworks. Additionally, we identify critical research gaps and propose a comprehensive research agenda focused on enhancing individual agent capabilities and optimizing agent synergy. Our work outlines a forward-looking vision for developing fully autonomous, scalable, and trustworthy LMA systems, laying the foundation for the evolution of Software Engineering 2.0.
将大型语言模型(LLMs)集成到自主代理中,为研究领域带来了显著的变化,提供了与人类规划和推理相竞争的认知能力。本文探讨了将大型语言模型集成到多代理(LMA)系统中,以解决软件工程(SE)中的复杂挑战的变革潜力。通过利用多个代理的协作和专门能力,LMA系统能够实现自主解决问题,提高稳健性,并提供管理真实世界软件项目复杂性的可扩展解决方案。本文将对最近的主要研究进行系统性的回顾,以映射软件开发生命周期(SDLC)各个阶段中LMA应用的当前格局。为了说明当前的能力和局限性,我们进行了两个案例研究,以展示最新LMA框架的有效性。此外,我们还确定了关键的研究空白,并提出了以增强单个代理能力和优化代理协同为重点的综合研究议程。我们的工作为开发完全自主、可扩展和可信赖的LMA系统描绘了一个前瞻性的愿景,为软件工程2.0的演变奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF TOSEM 2030 Special Issue
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)融入自主代理标志着研究领域的重大转变,为软件工程中解决复杂挑战提供了与人类规划、推理相竞争的认知能力。本文探讨了将大型语言模型融入多代理(LMA)系统的变革潜力,通过多个代理的协作和特殊能力,LMA系统可实现自主解决问题、提高稳健性,并为真实世界软件项目的复杂性管理提供可扩展解决方案。本文进行近期主要研究的系统综述,以了解LMA应用在软件开发生命周期(SDLC)各阶段中的现状。通过两个案例研究展示最先进LMA框架的有效性并发现重要研究差距,提出优化个体代理能力和代理协同的全面研究议程。本文工作为未来软件工程的自主化、可扩展性和可信度发展奠定了基石。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)融入自主代理为软件工程中解决复杂挑战提供了与人类规划、推理能力相当的认知工具。
- LMA系统通过多代理的协作和特殊能力实现自主解决问题,提高稳健性并应对真实世界软件项目的复杂性管理需求。
- 系统综述展示了LMA在软件开发生命周期不同阶段的现状,通过案例研究证明了最先进LMA框架的有效性。
- 发现当前研究的重大差距并呼吁增强个体代理能力与优化代理协同的研究议程。
点此查看论文截图

ExpeL: LLM Agents Are Experiential Learners
Authors:Andrew Zhao, Daniel Huang, Quentin Xu, Matthieu Lin, Yong-Jin Liu, Gao Huang
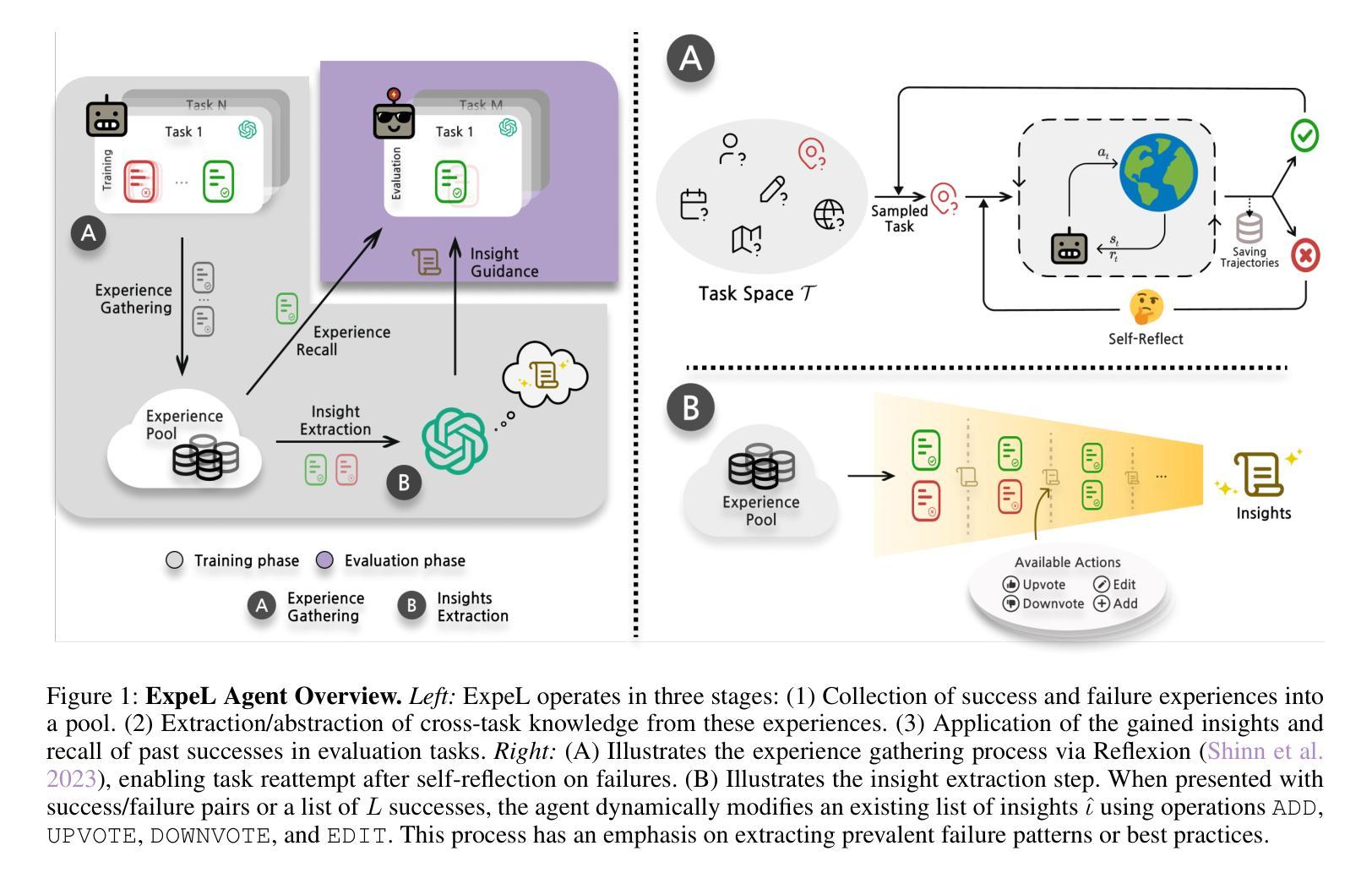
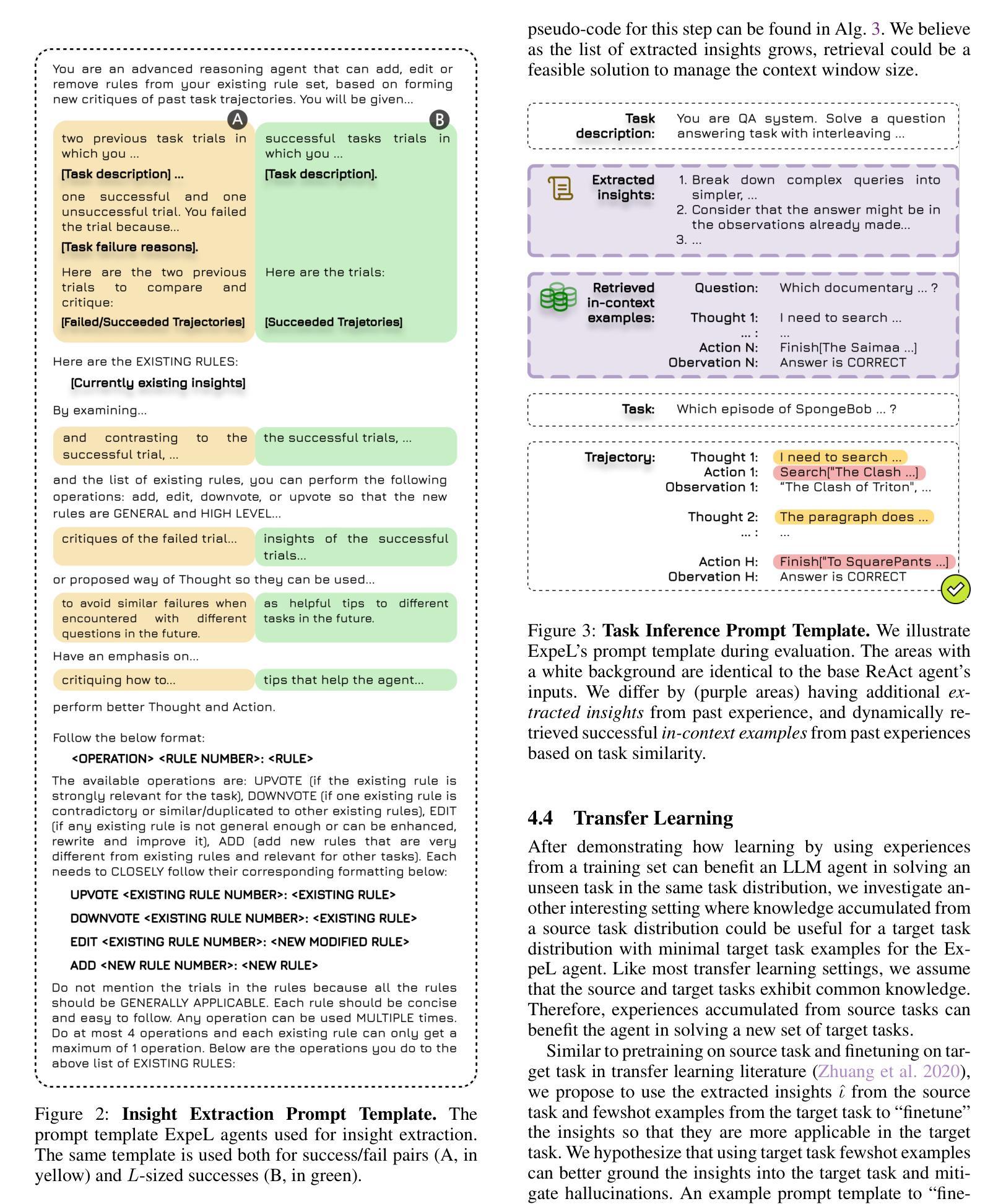
The recent surge in research interest in applying large language models (LLMs) to decision-making tasks has flourished by leveraging the extensive world knowledge embedded in LLMs. While there is a growing demand to tailor LLMs for custom decision-making tasks, finetuning them for specific tasks is resource-intensive and may diminish the model’s generalization capabilities. Moreover, state-of-the-art language models like GPT-4 and Claude are primarily accessible through API calls, with their parametric weights remaining proprietary and unavailable to the public. This scenario emphasizes the growing need for new methodologies that allow learning from agent experiences without requiring parametric updates. To address these problems, we introduce the Experiential Learning (ExpeL) agent. Our agent autonomously gathers experiences and extracts knowledge using natural language from a collection of training tasks. At inference, the agent recalls its extracted insights and past experiences to make informed decisions. Our empirical results highlight the robust learning efficacy of the ExpeL agent, indicating a consistent enhancement in its performance as it accumulates experiences. We further explore the emerging capabilities and transfer learning potential of the ExpeL agent through qualitative observations and additional experiments.
最近,对于将大型语言模型(LLM)应用于决策制定任务的研究兴趣激增,这得益于LLM中嵌入的丰富的世界知识。虽然对针对特定决策制定任务定制LLM的需求不断增长,但对它们进行微调是资源密集型的,并且可能会降低模型的泛化能力。此外,像GPT-4和Claude等最先进的语言模型主要通过API调用访问,其参数权重保持专有且不对公众开放。这一情景强调了对新方法的需求不断增长,这些方法允许从代理经验中学习而无需进行参数更新。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了体验式学习(ExpeL)代理。我们的代理能够自主收集经验并使用自然语言从一系列训练任务中提取知识。在推理过程中,代理会回想起其提取的见解和过去的经验来做出决策。我们的实证结果突出了ExpeL代理的稳健学习效益,显示随着经验的积累,其性能持续提高。我们进一步通过定性观察和额外实验探索了ExpeL代理的新兴能力和迁移学习的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by the 38th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-24)
Summary
大语言模型(LLMs)在决策任务中的应用近期受到广泛关注,借助LLMs中嵌入的丰富世界知识,相关研究蓬勃发展。然而,针对特定任务定制LLMs的需求日益增长,但对其进行微调需要大量资源,并可能降低模型的泛化能力。主流语言模型如GPT-4和Claude主要通过API调用访问,其参数权重保持专有,无法公开。在此背景下,强调了对新方法论的需求,该方法论需要能够在不要求进行参数更新的情况下从代理经验中学习。为解决这些问题,我们推出了Experiential Learning(ExpeL)代理。该代理能够自主收集经验,并利用自然语言从大量训练任务中提取知识。在推理过程中,代理会回顾其提取的见解和过去的经验以做出明智的决策。我们的实证结果突出了ExpeL代理的强大学习效能,显示随着经验的积累,其性能持续提高。
Key Takeaways
- 大语言模型(LLMs)在决策任务中的应用受到关注,但定制LLMs的微调需要大量资源和可能影响模型的泛化能力。
- 当前主流语言模型如GPT-4和Claude通过API调用访问,参数权重保持专有。
- 需要新的方法论,能够在不更新参数的情况下从代理经验中学习。
- Experiential Learning(ExpeL)代理能够自主收集经验并从训练任务中提取知识。
- ExpeL代理利用自然语言和过去的经验来做出决策。
- 实证结果显示ExpeL代理具有强大的学习效能,随着经验的积累,性能持续提高。
点此查看论文截图