⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-24 更新
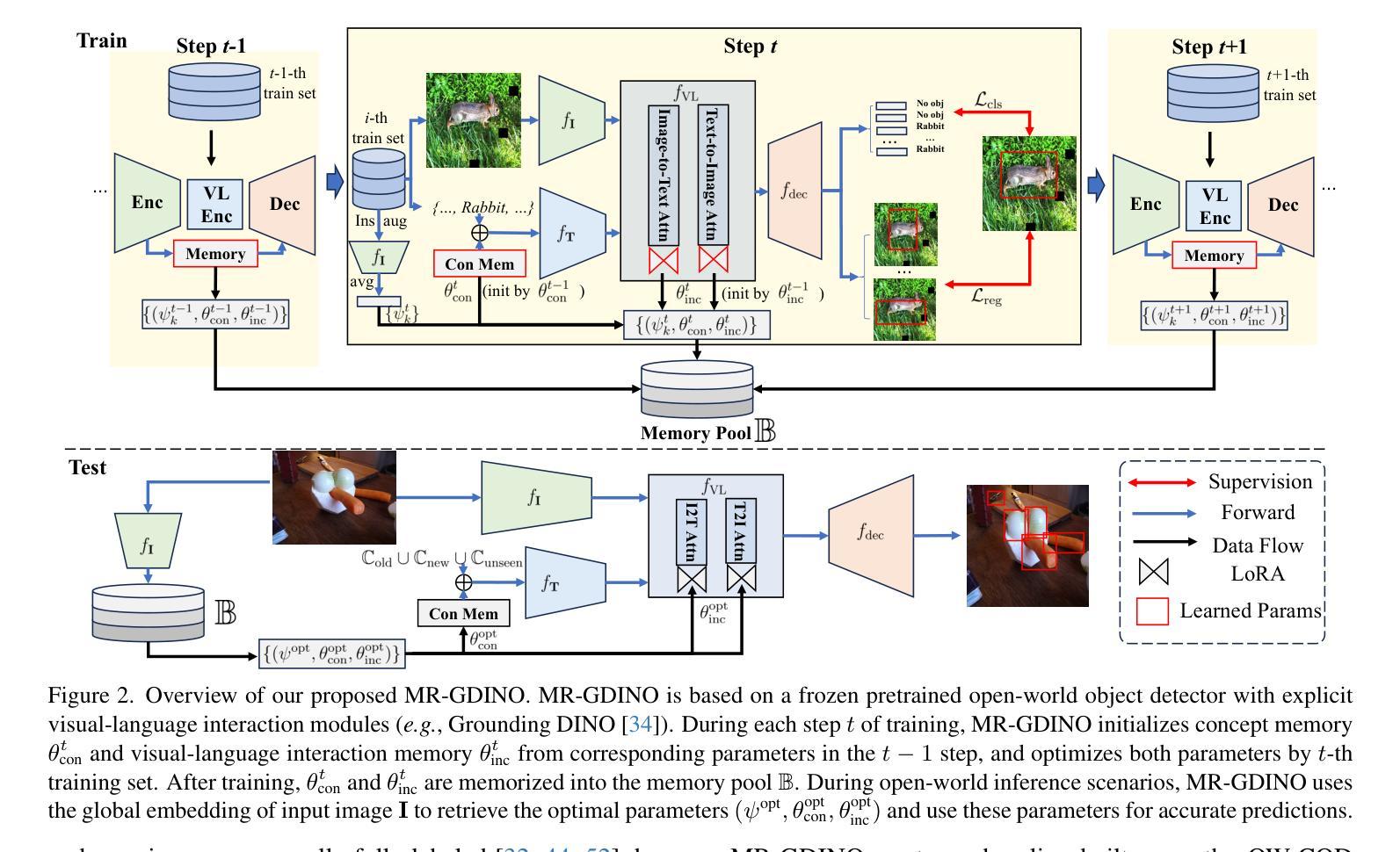
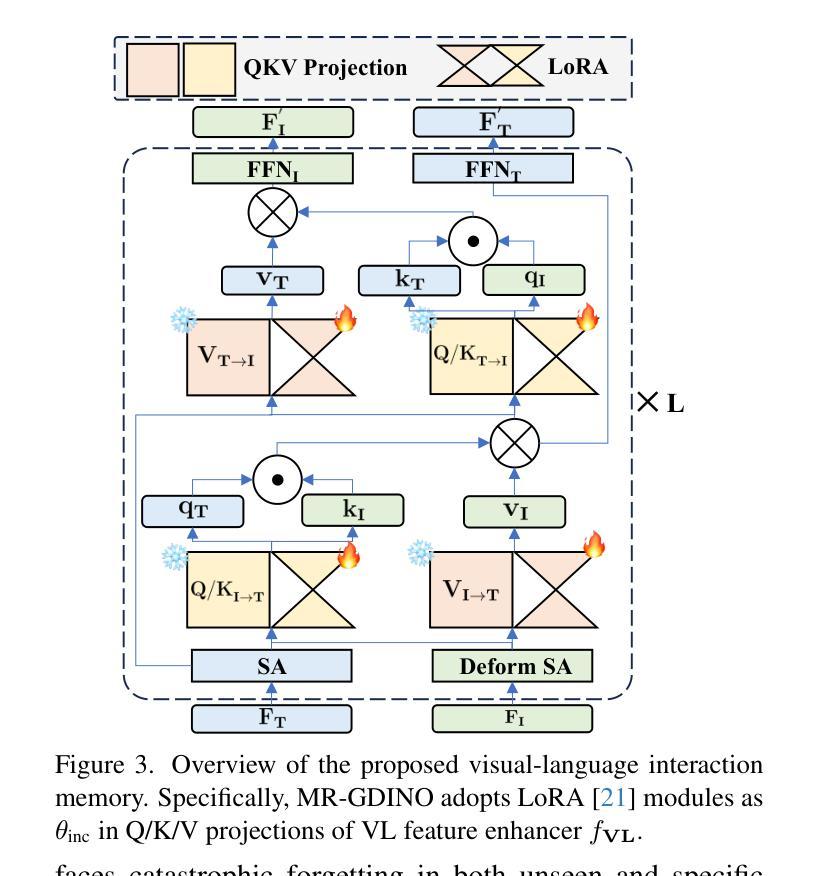
MR-GDINO: Efficient Open-World Continual Object Detection
Authors:Bowen Dong, Zitong Huang, Guanglei Yang, Lei Zhang, Wangmeng Zuo
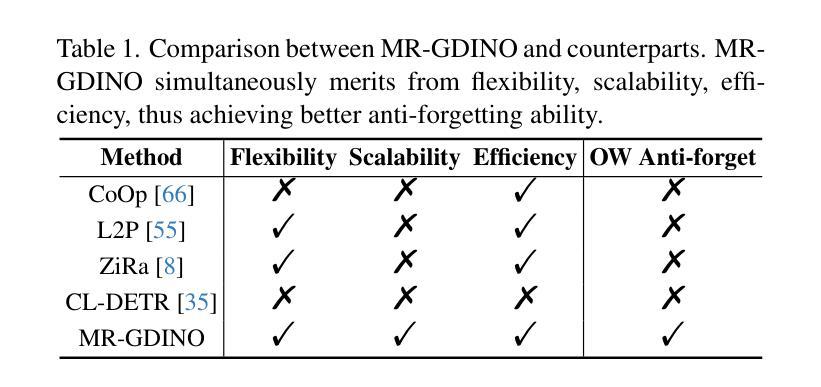
Open-world (OW) recognition and detection models show strong zero- and few-shot adaptation abilities, inspiring their use as initializations in continual learning methods to improve performance. Despite promising results on seen classes, such OW abilities on unseen classes are largely degenerated due to catastrophic forgetting. To tackle this challenge, we propose an open-world continual object detection task, requiring detectors to generalize to old, new, and unseen categories in continual learning scenarios. Based on this task, we present a challenging yet practical OW-COD benchmark to assess detection abilities. The goal is to motivate OW detectors to simultaneously preserve learned classes, adapt to new classes, and maintain open-world capabilities under few-shot adaptations. To mitigate forgetting in unseen categories, we propose MR-GDINO, a strong, efficient and scalable baseline via memory and retrieval mechanisms within a highly scalable memory pool. Experimental results show that existing continual detectors suffer from severe forgetting for both seen and unseen categories. In contrast, MR-GDINO largely mitigates forgetting with only 0.1% activated extra parameters, achieving state-of-the-art performance for old, new, and unseen categories.
开放世界(OW)识别和检测模型表现出强大的零样本和少样本适应力,这激发了它们作为初始化在持续学习方法中的使用,以提高性能。尽管在已知类别上取得了有前景的结果,但由于灾难性遗忘,这类OW模型在未知类别上的能力大大退化。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一个开放世界持续目标检测任务,要求检测器在持续学习场景中推广到旧、新和未知类别。基于这项任务,我们提出了一个具有挑战性但实用的OW-COD基准测试来评估检测能力。目标是激励OW检测器在保留已学类别、适应新类别和维持开放世界能力的同时,进行少样本适应。为了缓解对未知类别的遗忘,我们提出了MR-GDINO,这是一个强大的、高效的、可扩展的基线,通过内存和检索机制在一个高度可扩展的内存池内实现。实验结果表明,现有的持续检测器在已知和未知类别上都存在严重的遗忘问题。相比之下,MR-GDINO在很大程度上缓解了遗忘问题,只需激活0.1%的额外参数,即可实现对旧、新和未知类别的最佳性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Website: https://m1saka.moe/owcod/ . Code is available at: https://github.com/DongSky/MR-GDINO
Summary
开放世界(OW)识别与检测模型在零次和少次适应方面表现出强大的能力,在持续学习方法中作为初始化使用有助于提高性能。然而,对于未见类别,这种能力会大大退化,面临灾难性遗忘的问题。为解决这一挑战,本文提出了开放世界持续对象检测任务,要求检测器在持续学习场景中泛化到旧、新和未见类别。基于此任务,本文构建了一个具有挑战性且实用的OW-COD基准测试集,以评估检测能力。目标是激励OW检测器在少次适应的同时保留已学类别、适应新类别并保持开放世界的能力。为缓解未见类别的遗忘问题,本文提出了MR-GDINO,通过内存和检索机制构建了一个高度可扩展的内存池中的强效、高效且可扩展的基线。实验结果表明,现有的持续检测器在旧类别和新类别上都存在严重的遗忘问题。相比之下,MR-GDINO仅激活额外的0.1%参数即可大大缓解遗忘问题,并在旧、新和未见类别上实现最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 开放世界识别与检测模型具备强大的零次和少次适应能力,适用于持续学习场景。
- 在持续学习环境中,模型对未见类别的适应能力退化,面临灾难性遗忘问题。
- 提出开放世界持续对象检测任务,要求模型在持续学习场景中泛化到旧、新和未见类别。
- 构建OW-COD基准测试集以评估检测模型的性能。
- MR-GDINO通过内存和检索机制提出一种强效、高效且可扩展的基线解决方案。
- 现有持续检测器在旧类别和新类别上表现不佳,存在严重的遗忘问题。
点此查看论文截图

Enhancing Generalized Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation via Effective Knowledge Transfer
Authors:Xinyue Chen, Miaojing Shi, Zijian Zhou, Lianghua He, Sophia Tsoka
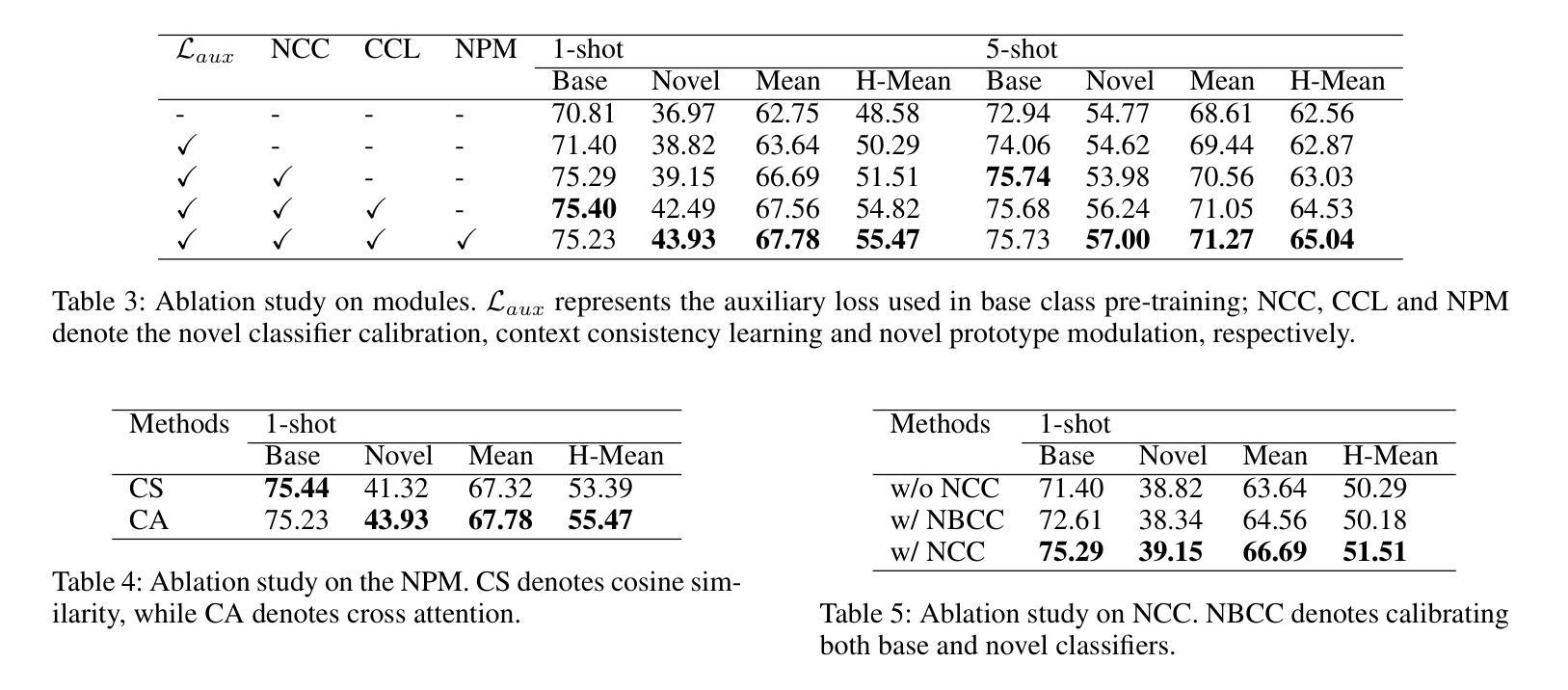
Generalized few-shot semantic segmentation (GFSS) aims to segment objects of both base and novel classes, using sufficient samples of base classes and few samples of novel classes. Representative GFSS approaches typically employ a two-phase training scheme, involving base class pre-training followed by novel class fine-tuning, to learn the classifiers for base and novel classes respectively. Nevertheless, distribution gap exists between base and novel classes in this process. To narrow this gap, we exploit effective knowledge transfer from base to novel classes. First, a novel prototype modulation module is designed to modulate novel class prototypes by exploiting the correlations between base and novel classes. Second, a novel classifier calibration module is proposed to calibrate the weight distribution of the novel classifier according to that of the base classifier. Furthermore, existing GFSS approaches suffer from a lack of contextual information for novel classes due to their limited samples, we thereby introduce a context consistency learning scheme to transfer the contextual knowledge from base to novel classes. Extensive experiments on PASCAL-5$^i$ and COCO-20$^i$ demonstrate that our approach significantly enhances the state of the art in the GFSS setting. The code is available at: https://github.com/HHHHedy/GFSS-EKT.
广义少样本语义分割(GFSS)旨在利用基础类别的充足样本和少量新类别的样本,对基础类别和新类别的对象进行分割。代表性的GFSS方法通常采用两阶段训练方案,包括基础类别预训练和新类别微调,以分别学习基础类别和新类别的分类器。然而,在此过程中,基础类别和新类别之间存在分布差距。为了缩小这一差距,我们从基础类别到新类别实现了有效的知识转移。首先,设计了一个新型原型调制模块,通过利用基础类别和新类别之间的相关性来调节新类别原型。其次,提出了一种新的分类器校准模块,根据基础分类器的权重分布校准新分类器的权重分布。此外,由于现有GFSS方法新类别样本有限,缺乏上下文信息,因此我们引入了一种上下文一致性学习方案,将上下文知识从基础类别转移到新类别。在PASCAL-5i和COCO-20i上的大量实验表明,我们的方法在GFSS设置中显著提高了现有技术水平。代码可在:https://github.com/HHHHedy/GFSS-EKT获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to AAAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了广义小样本语义分割(GFSS)的目标和方法。GFSS旨在利用基础类的充足样本和新颖类的少量样本对基础类和新颖类的对象进行分割。文章提出了一种有效的知识转移方法,缩小基础类和新颖类之间的分布差距。设计了一个新型原型调制模块,利用基础类和新颖类之间的相关性来调制新颖类原型。同时,提出了一个新型分类器校准模块,根据基础分类器的权重分布校准新颖分类器的权重分布。为了解决新颖类样本有限导致的缺乏上下文信息的问题,引入了上下文一致性学习方案,将上下文知识从基础类转移到新颖类。实验证明,该方法在PASCAL-5i和COCO-20i数据集上显著提高了GFSS的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 广义小样本语义分割(GFSS)旨在利用基础类的充足样本和新颖类的少量样本进行对象分割。
- 现有的GFSS方法存在基础类和新颖类之间的分布差距问题。
- 通过设计新型原型调制模块和分类器校准模块,实现有效知识从基础类到新颖类的转移,以缩小分布差距。
- 引入上下文一致性学习方案,解决新颖类样本有限导致的缺乏上下文信息的问题。
- 方法在PASCAL-5i和COCO-20i数据集上显著提高了GFSS的性能。
- 代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图


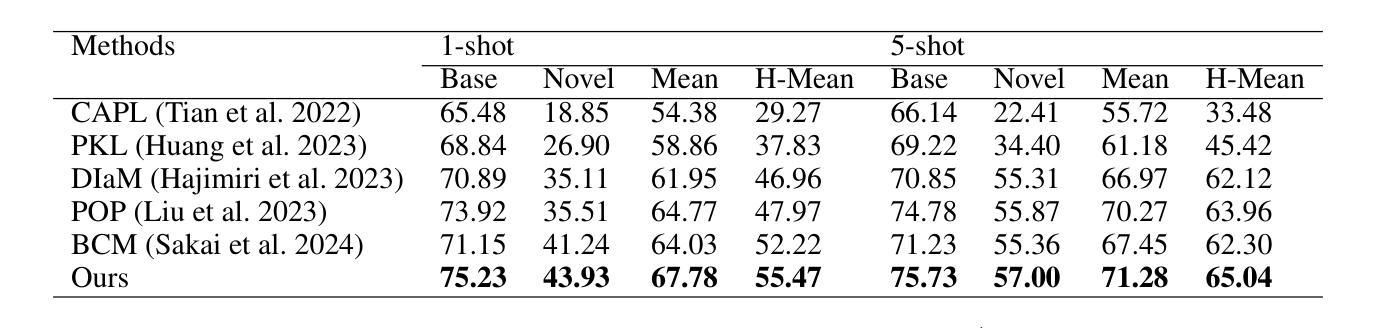
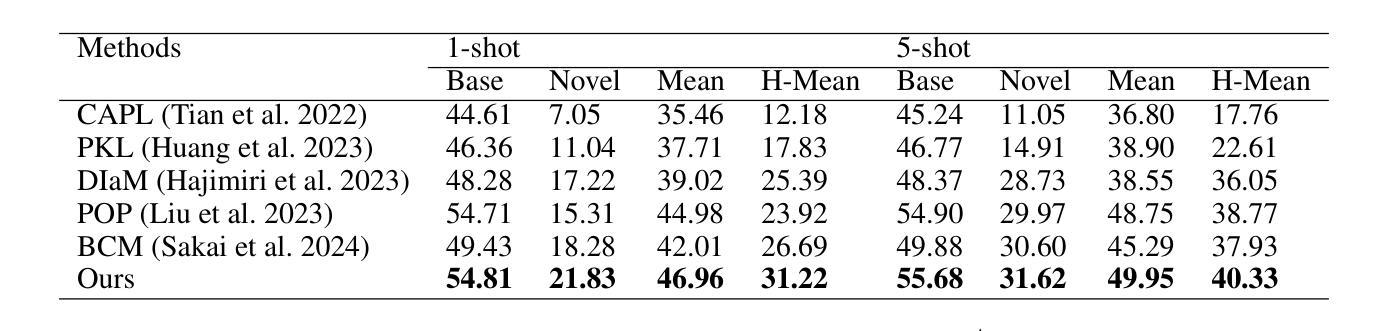
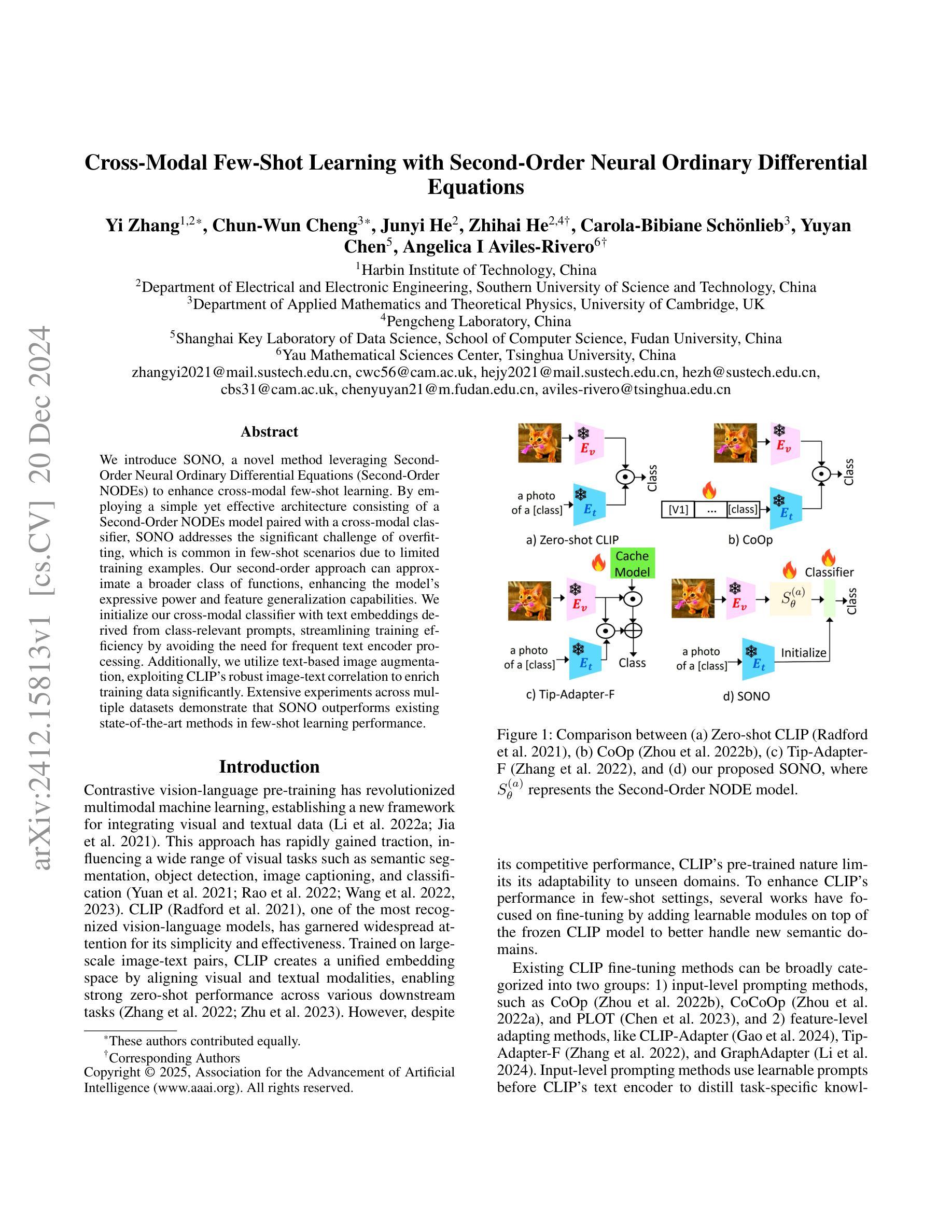
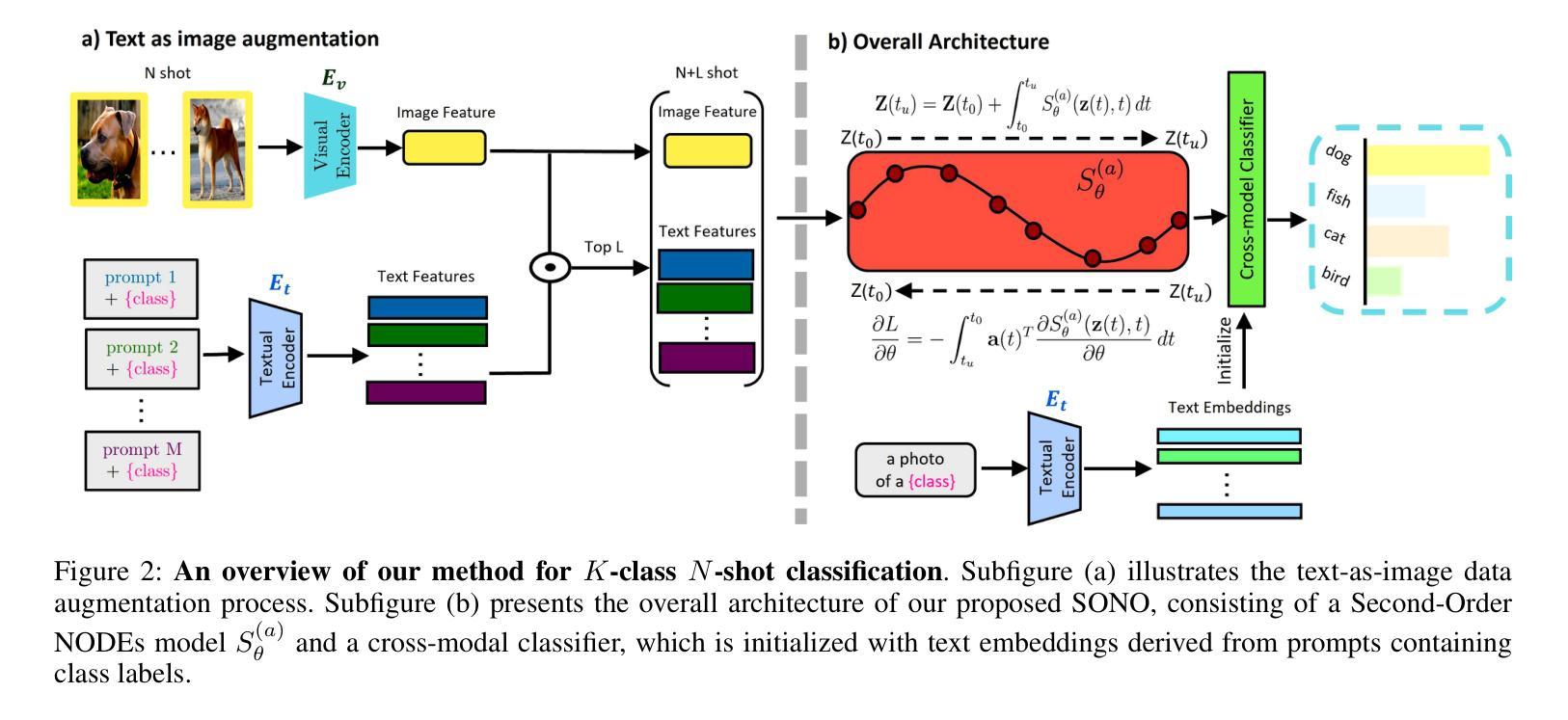
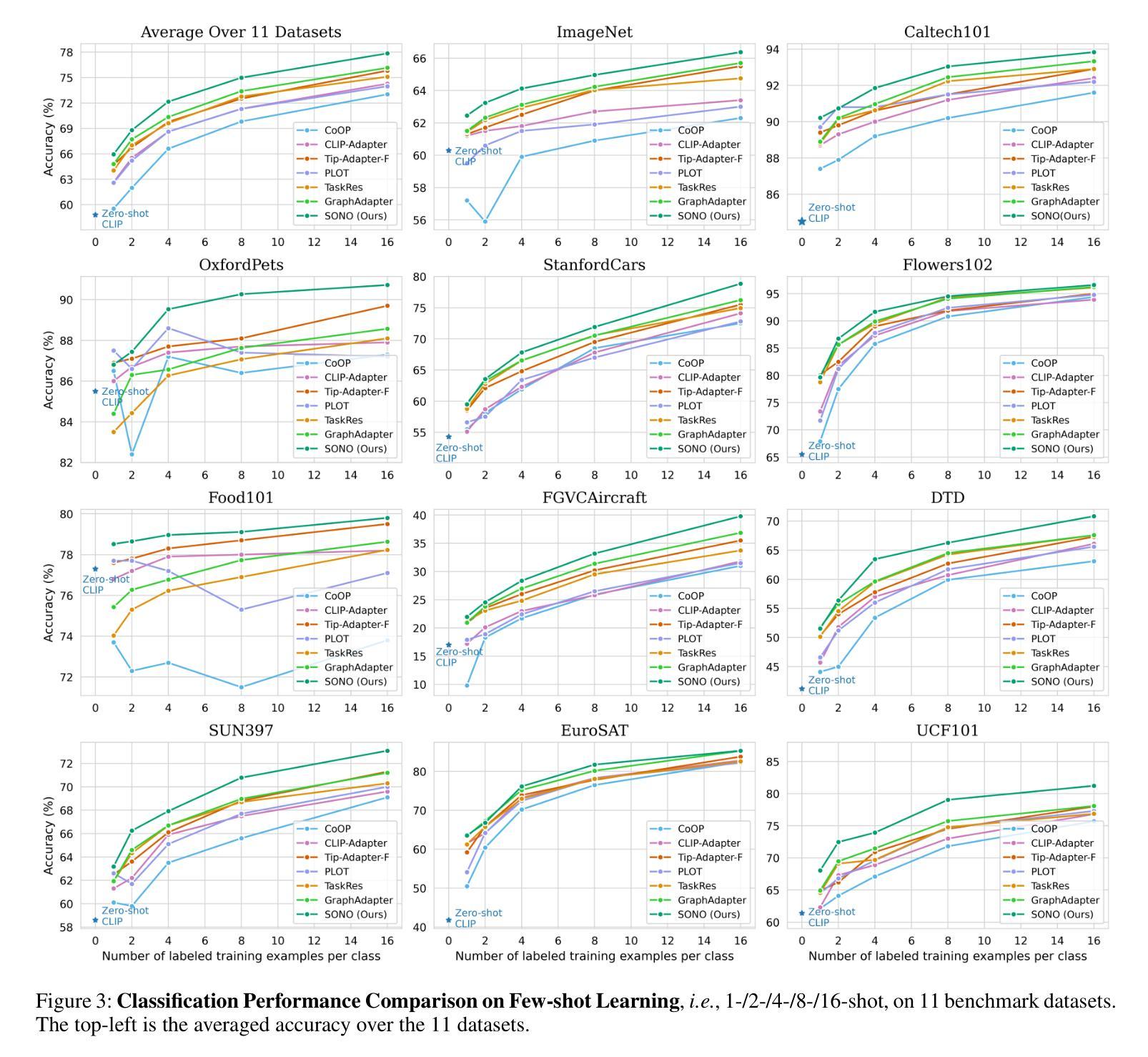
Cross-Modal Few-Shot Learning with Second-Order Neural Ordinary Differential Equations
Authors:Yi Zhang, Chun-Wun Cheng, Junyi He, Zhihai He, Carola-Bibiane Schönlieb, Yuyan Chen, Angelica I Aviles-Rivero
We introduce SONO, a novel method leveraging Second-Order Neural Ordinary Differential Equations (Second-Order NODEs) to enhance cross-modal few-shot learning. By employing a simple yet effective architecture consisting of a Second-Order NODEs model paired with a cross-modal classifier, SONO addresses the significant challenge of overfitting, which is common in few-shot scenarios due to limited training examples. Our second-order approach can approximate a broader class of functions, enhancing the model’s expressive power and feature generalization capabilities. We initialize our cross-modal classifier with text embeddings derived from class-relevant prompts, streamlining training efficiency by avoiding the need for frequent text encoder processing. Additionally, we utilize text-based image augmentation, exploiting CLIP’s robust image-text correlation to enrich training data significantly. Extensive experiments across multiple datasets demonstrate that SONO outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in few-shot learning performance.
我们介绍了一种新的方法SONO,它利用二阶神经常微分方程(Second-Order NODEs)增强跨模态小样本学习。SONO采用简单有效的架构,包括二阶NODEs模型和跨模态分类器,解决了小样本场景中常见的过拟合问题,这是由于训练样本有限所致。我们的二阶方法可以近似更广泛的函数,提高模型的表达能力和特征泛化能力。我们用与类别相关的提示生成的文本嵌入来初始化我们的跨模态分类器,避免了频繁使用文本编码器处理的需求,从而简化了训练效率。此外,我们利用基于文本的图像增强,利用CLIP强大的图像-文本相关性,显著丰富训练数据。在多个数据集上的广泛实验表明,SONO在少样本学习性能上超越了现有的最先进方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
SONO是一种利用二阶神经常微分方程(Second-Order NODEs)增强跨模态小样学习的新方法。它通过采用简单有效的架构,结合二阶神经常微分方程模型和跨模态分类器,解决了小样场景下因训练样本有限而导致的过拟合问题。二阶方法能更广泛地逼近各类函数,增强模型的表达能力和特征泛化能力。此外,SONO使用基于文本的图像增强技术,利用CLIP的图像文本相关性丰富训练数据。实验证明,SONO在少样本学习方面的性能优于现有先进技术。
Key Takeaways
- SONO利用二阶神经常微分方程(Second-Order NODEs)增强跨模态小样学习。
- 该方法通过结合二阶神经常微分方程模型和跨模态分类器,解决了小样场景中的过拟合问题。
- 二阶方法能够更广泛地逼近各类函数,提高模型的表达能力和特征泛化能力。
- SONO使用基于文本的图像嵌入初始化跨模态分类器,提高训练效率。
- 利用CLIP的图像文本相关性进行基于文本的图像增强。
- 通过丰富的实验验证,SONO在少样本学习方面性能优越。
点此查看论文截图
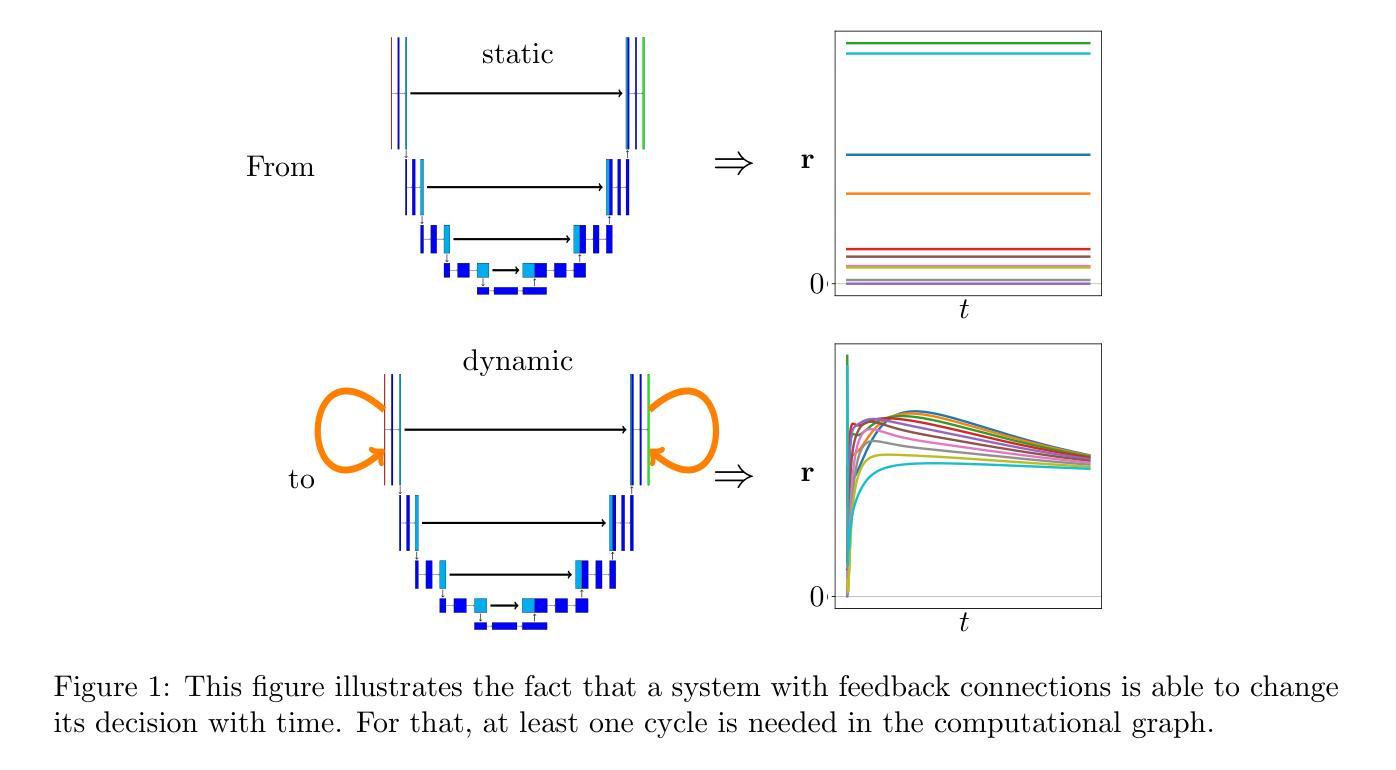
The Role of Recurrency in Image Segmentation for Noisy and Limited Sample Settings
Authors:David Calhas, João Marques, Arlindo L. Oliveira
The biological brain has inspired multiple advances in machine learning. However, most state-of-the-art models in computer vision do not operate like the human brain, simply because they are not capable of changing or improving their decisions/outputs based on a deeper analysis. The brain is recurrent, while these models are not. It is therefore relevant to explore what would be the impact of adding recurrent mechanisms to existing state-of-the-art architectures and to answer the question of whether recurrency can improve existing architectures. To this end, we build on a feed-forward segmentation model and explore multiple types of recurrency for image segmentation. We explore self-organizing, relational, and memory retrieval types of recurrency that minimize a specific energy function. In our experiments, we tested these models on artificial and medical imaging data, while analyzing the impact of high levels of noise and few-shot learning settings. Our results do not validate our initial hypothesis that recurrent models should perform better in these settings, suggesting that these recurrent architectures, by themselves, are not sufficient to surpass state-of-the-art feed-forward versions and that additional work needs to be done on the topic.
生物大脑为机器学习带来了诸多进步。然而,计算机视觉领域的大多数最新模型并不如人脑那样运作,原因仅仅在于它们无法基于更深入的分析来改变或改进其决策/输出。大脑是递归的,而这些模型并不是。因此,探索在现有最新架构中添加递归机制的影响,以及递归能否改进现有架构的问题,是十分重要的。为此,我们在前馈分割模型的基础上,探索了多种用于图像分割的递归类型。我们探索了最小化特定能量函数的自组织、关系和内存检索三种类型的递归。在实验中,我们对人工和医学成像数据进行了测试,同时分析了高噪声和少镜头学习设置的影响。我们的结果并未证实我们的初步假设,即递归模型在这些设置中的表现会更好,这表明这些递归架构本身不足以超越最新的前馈版本,并且还需要在此主题上投入额外的工作。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages
Summary
本文探索了将递归机制添加到现有最先进的架构中对图像分割的影响,实验了自我组织、关系和内存检索等多种递归类型。然而,实验结果并不支持初始假设,即递归模型在高噪声和少镜头学习环境中表现更好,表明仅依靠这些递归架构不足以超越现有最先进的前馈版本,需要在此主题上进一步开展工作。
Key Takeaways
- 递归机制在计算机视觉领域具有探索潜力。
- 研究人员尝试将递归机制添加到现有最先进的架构中进行图像分割。
- 实验包括自我组织、关系和内存检索等类型的递归。
- 实验在高噪声和少镜头学习环境下进行。
- 实验结果不支持假设递归模型会表现更好。
- 递归架构本身不足以超越现有最先进的馈送前版本。
点此查看论文截图


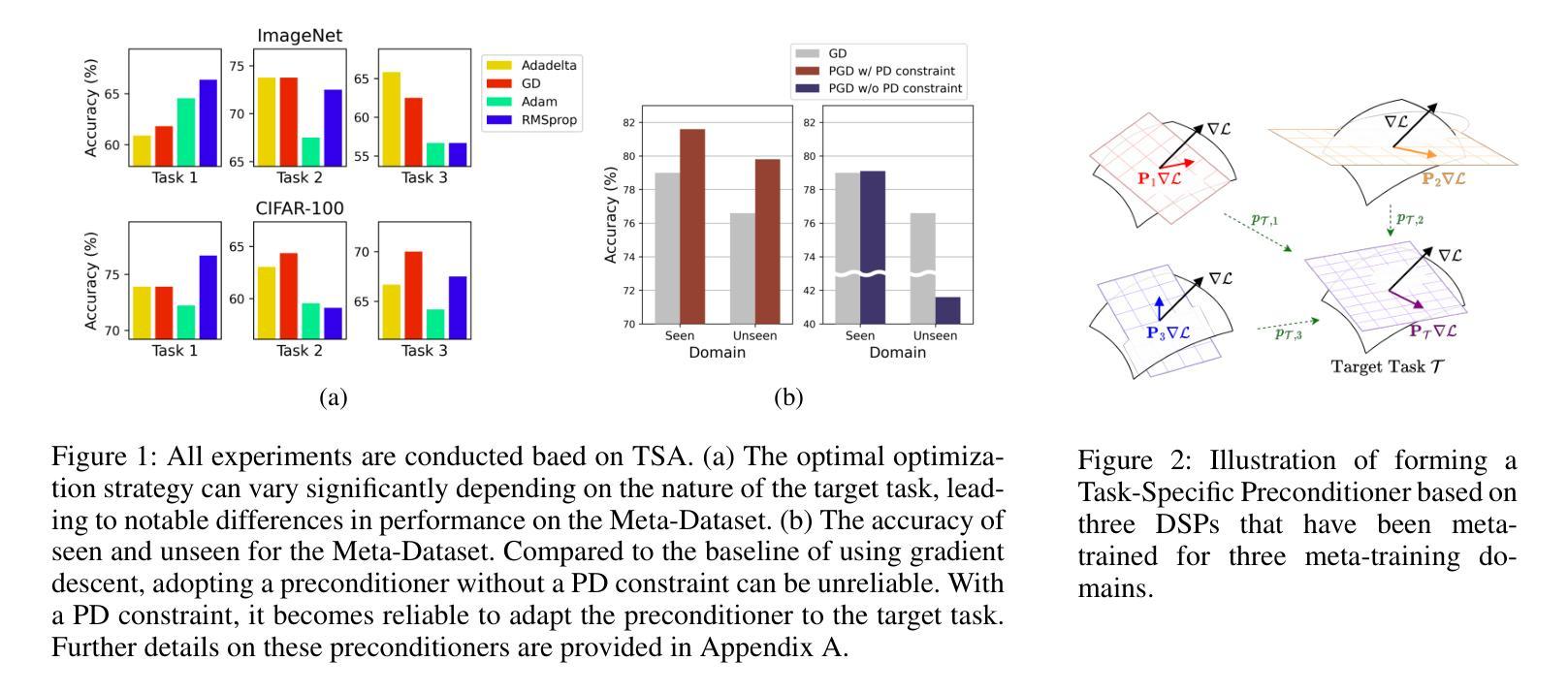
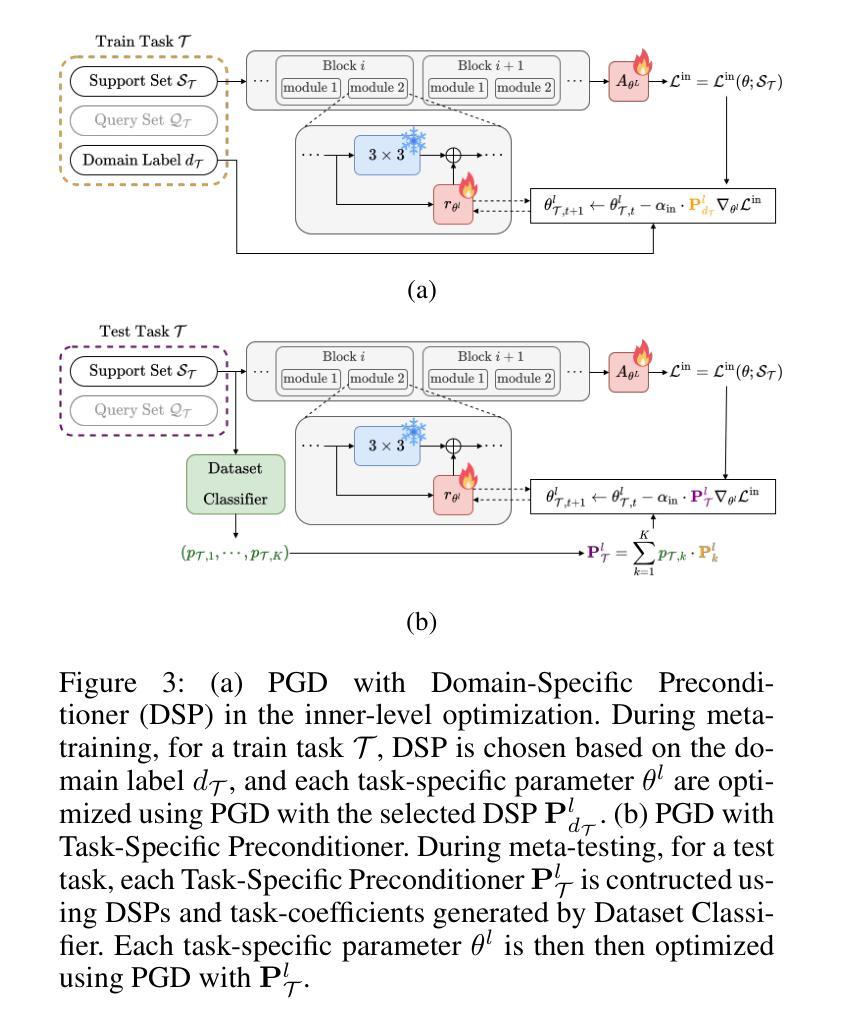
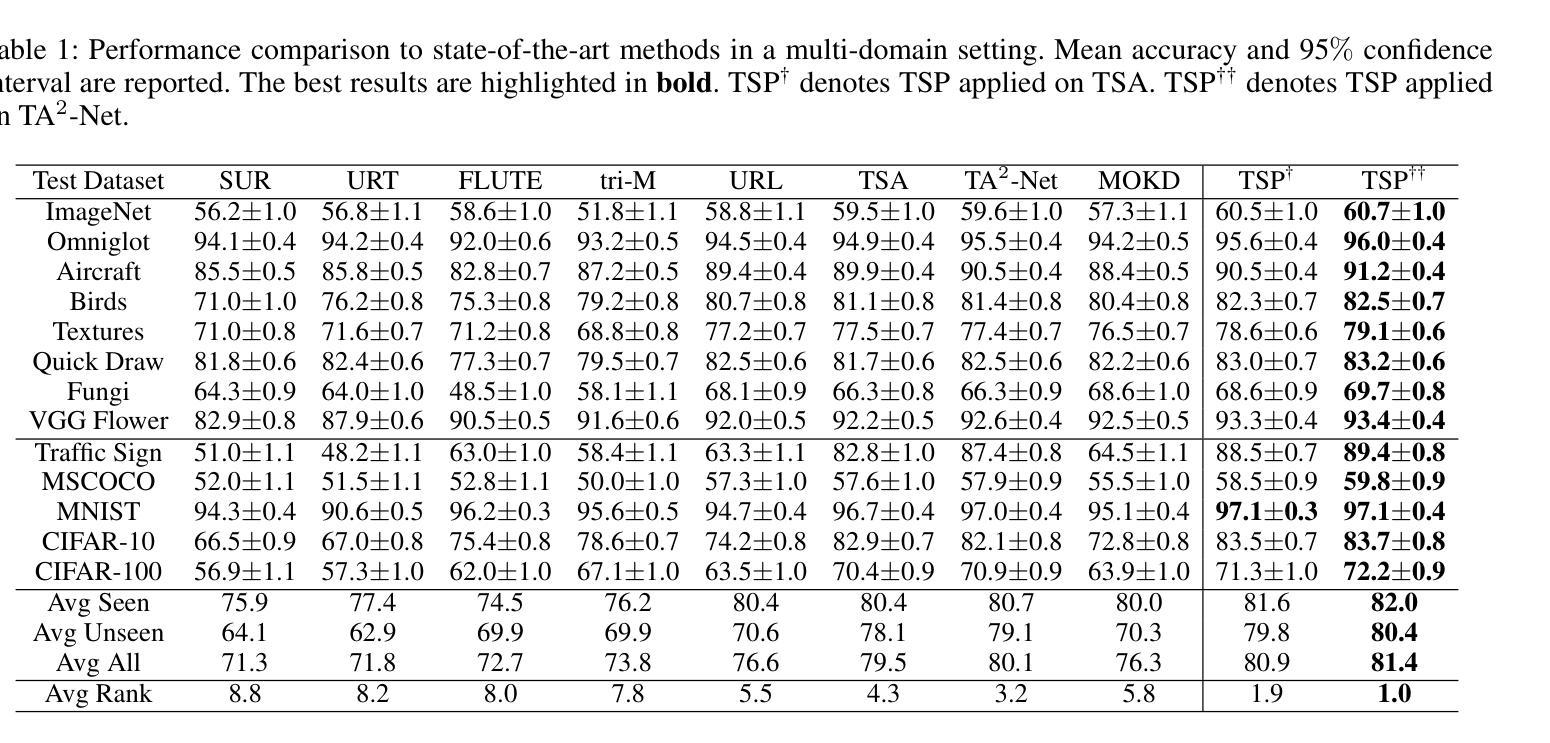
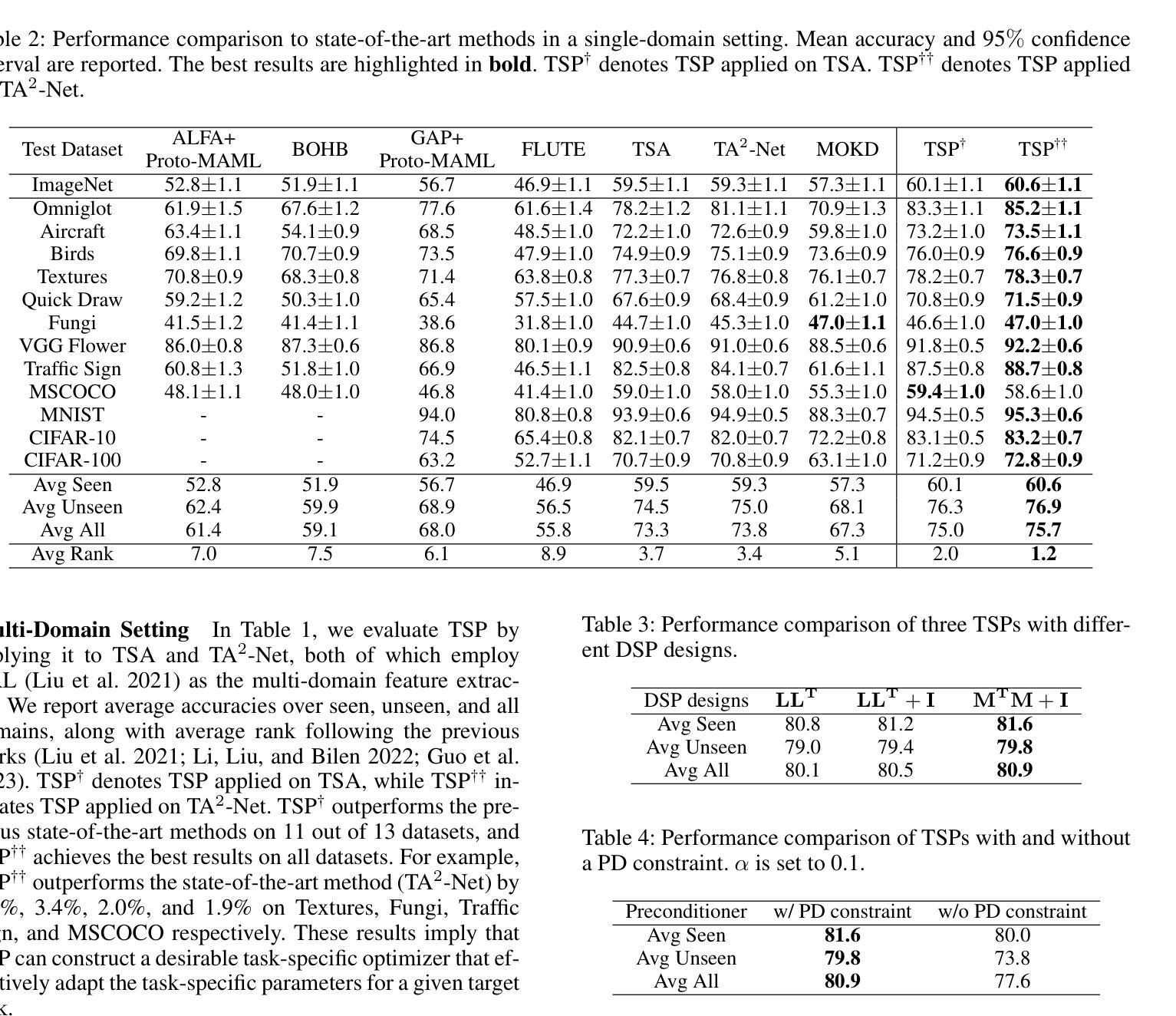
Task-Specific Preconditioner for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Learning
Authors:Suhyun Kang, Jungwon Park, Wonseok Lee, Wonjong Rhee
Cross-Domain Few-Shot Learning(CDFSL) methods typically parameterize models with task-agnostic and task-specific parameters. To adapt task-specific parameters, recent approaches have utilized fixed optimization strategies, despite their potential sub-optimality across varying domains or target tasks. To address this issue, we propose a novel adaptation mechanism called Task-Specific Preconditioned gradient descent(TSP). Our method first meta-learns Domain-Specific Preconditioners~(DSPs) that capture the characteristics of each meta-training domain, which are then linearly combined using task-coefficients to form the Task-Specific Preconditioner. The preconditioner is applied to gradient descent, making the optimization adaptive to the target task. We constrain our preconditioners to be positive definite, guiding the preconditioned gradient toward the direction of steepest descent. Empirical evaluations on the Meta-Dataset show that TSP achieves state-of-the-art performance across diverse experimental scenarios.
跨域小样本学习(CDFSL)方法通常使用任务通用参数和任务特定参数对模型进行参数化。为了调整任务特定参数,尽管不同的领域或目标任务可能存在潜在的最优性差异,但最近的方法仍采用了固定的优化策略。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种新的自适应机制,称为任务特定预调节梯度下降(TSP)。我们的方法首先通过元学习领域特定预调节器(DSP),捕捉每个元训练领域的特征,然后使用任务系数进行线性组合,形成任务特定预调节器。预调节器应用于梯度下降,使优化适应目标任务。我们将预调节器限制为正定矩阵,引导预调节梯度朝向最陡下降方向。在Meta-Dataset上的经验评估表明,TSP在多种实验场景中实现了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
文章提出了基于跨域的小样本学习(CDFSL)方法的一种改进自适应机制,称为任务特定预处理梯度下降(TSP)。TSP通过元学习领域特定预处理器(DSP)来捕获每个元训练领域的特征,然后使用任务系数进行线性组合形成任务特定预处理器。预处理器应用于梯度下降,使优化适应目标任务。在Meta-Dataset上的实证评估表明,TSP在多种实验场景下均达到最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 跨域小样本学习方法通常使用任务无关和任务特定的参数对模型进行参数化。
- 最近的方法使用固定的优化策略来适应任务特定参数,但这在不同领域或目标任务中可能表现不佳。
- 提出的TSP方法通过元学习领域特定预处理器(DSP)捕获每个元训练领域的特征。
- TSP使用线性组合和任务系数形成任务特定预处理器,用于梯度下降。
- 预处理器使优化适应目标任务的特性。
- 通过约束预处理器为正定矩阵,可以引导预处理梯度向最陡方向下降。
点此查看论文截图

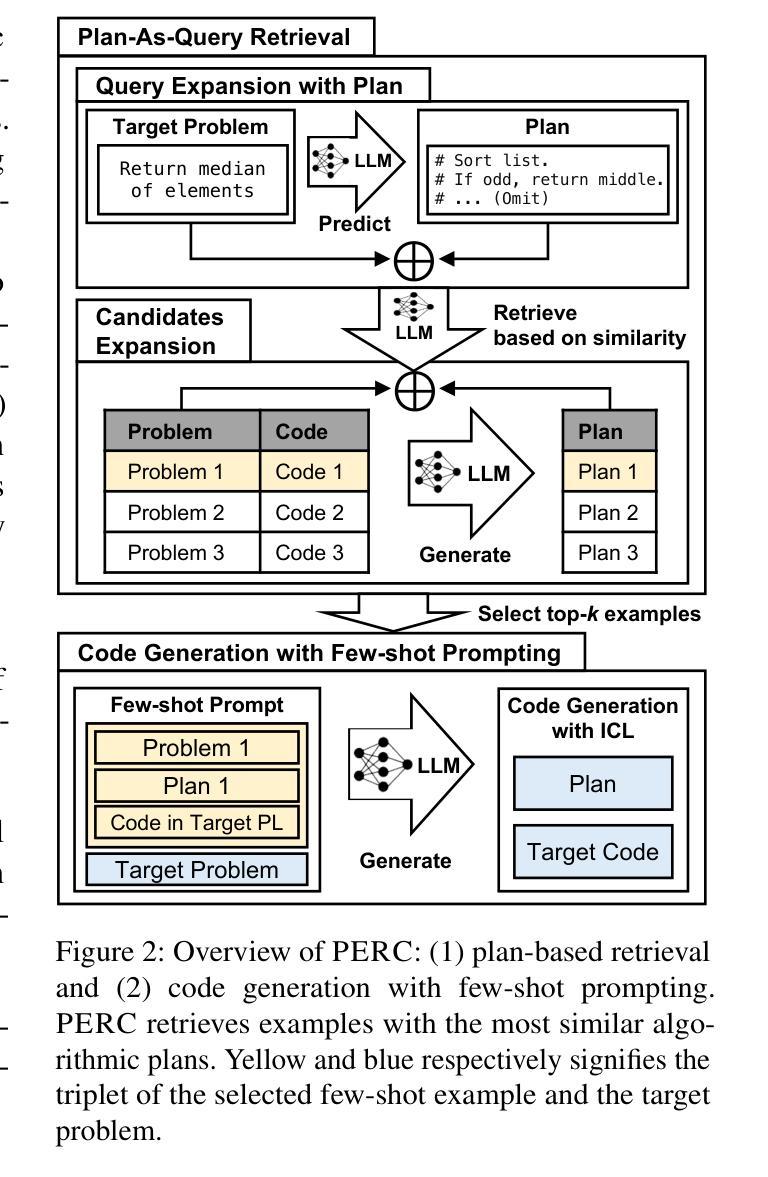
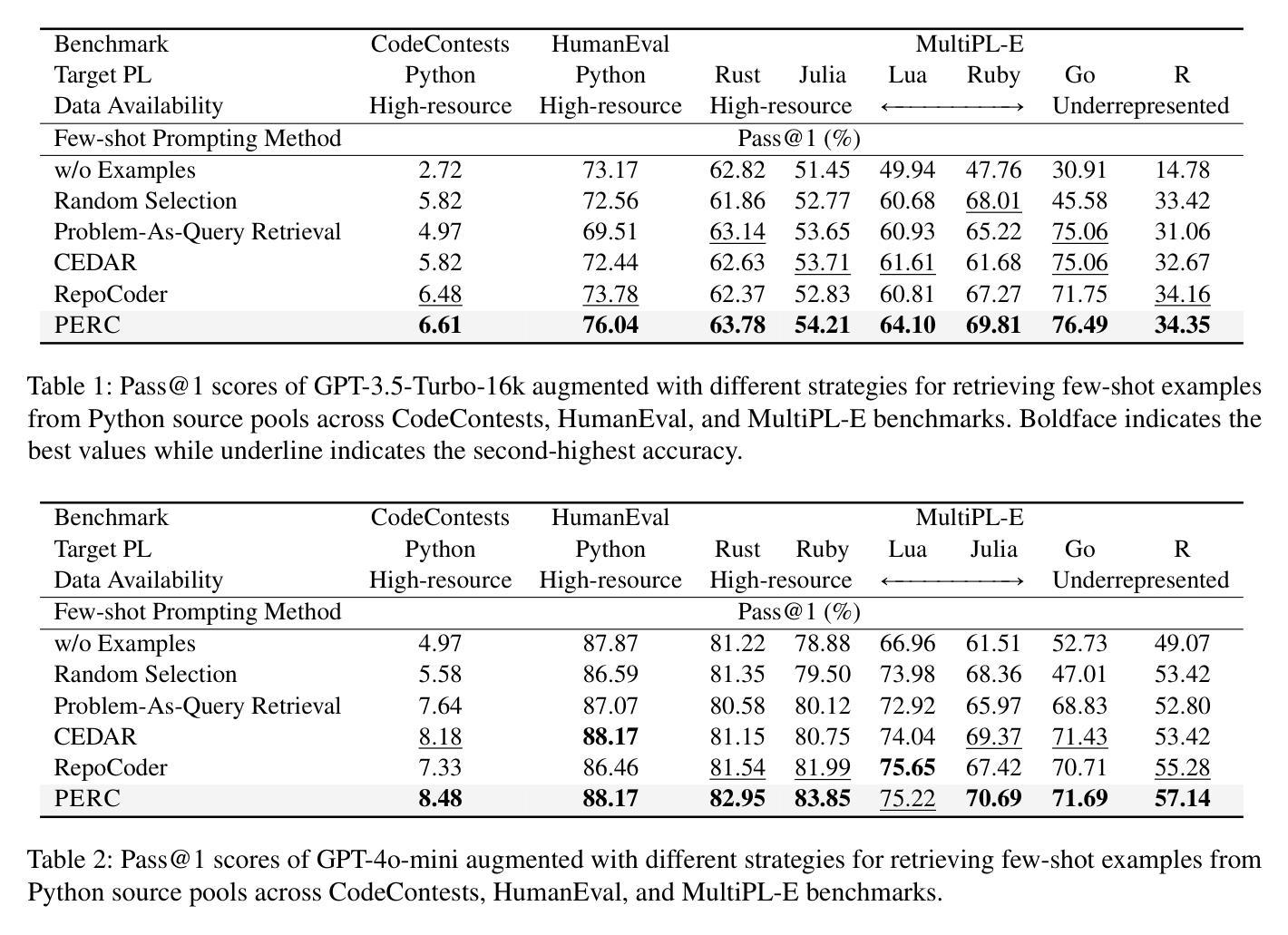
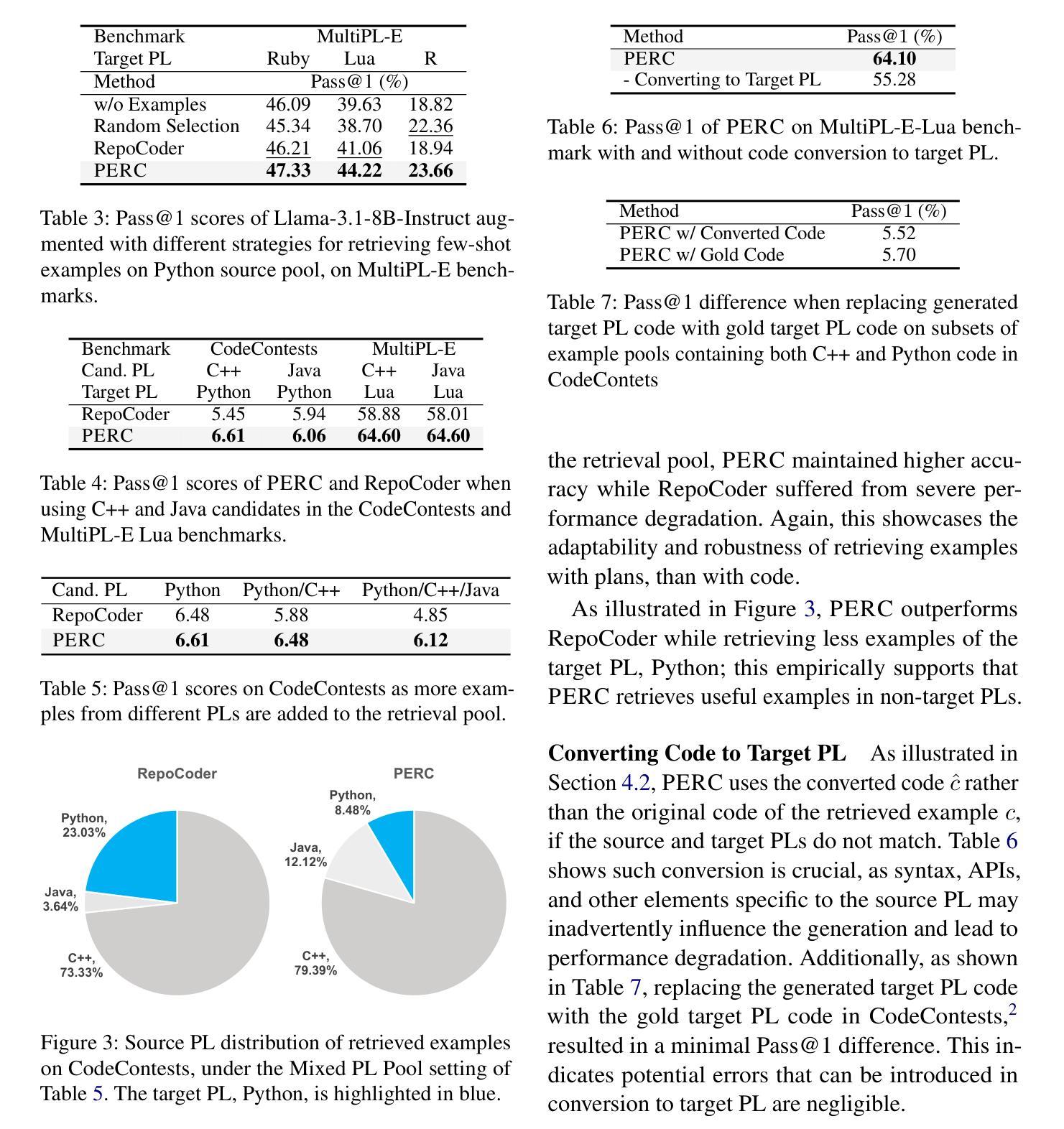
PERC: Plan-As-Query Example Retrieval for Underrepresented Code Generation
Authors:Jaeseok Yoo, Hojae Han, Youngwon Lee, Jaejin Kim, Seung-won Hwang
Code generation with large language models has shown significant promise, especially when employing retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) with few-shot examples. However, selecting effective examples that enhance generation quality remains a challenging task, particularly when the target programming language (PL) is underrepresented. In this study, we present two key findings: (1) retrieving examples whose presented algorithmic plans can be referenced for generating the desired behavior significantly improves generation accuracy, and (2) converting code into pseudocode effectively captures such algorithmic plans, enhancing retrieval quality even when the source and the target PLs are different. Based on these findings, we propose Plan-as-query Example Retrieval for few-shot prompting in Code generation (PERC), a novel framework that utilizes algorithmic plans to identify and retrieve effective examples. We validate the effectiveness of PERC through extensive experiments on the CodeContests, HumanEval and MultiPL-E benchmarks: PERC consistently outperforms the state-of-the-art RAG methods in code generation, both when the source and target programming languages match or differ, highlighting its adaptability and robustness in diverse coding environments.
代码生成与大型语言模型相结合已经展现出巨大的潜力,特别是在使用小样本检索增强生成(RAG)的情况下。然而,在选择能够提高生成质量的有效样本方面,仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务,尤其是在目标编程语言(PL)代表性不足的情况下。在这项研究中,我们发现了两个关键结果:(1)检索那些提供的算法计划可以作为生成所需行为的参考,可以显著提高生成准确性;(2)将代码转换为伪代码可以有效地捕获此类算法计划,即使在源语言和目标编程语言不同的情况下,也能提高检索质量。基于这些发现,我们提出了面向代码生成的小样本提示的“计划查询示例检索”(PERC)新框架,该框架利用算法计划来识别和检索有效示例。我们在CodeContests、HumanEval和MultiPL-E基准测试上对PERC的有效性进行了广泛实验验证:无论是在源语言和目标编程语言相匹配还是存在差异的情况下,PERC在代码生成方面始终优于最新RAG方法,突显其在多样化编码环境中的适应性和稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by COLING 2025 main conference
Summary
大型语言模型在代码生成方面展现出巨大潜力,特别是采用少量示例的检索增强生成(RAG)技术。本研究发现:一是检索能展示算法计划的例子能显著提高生成准确性;二是将代码转化为伪代码能有效捕捉算法计划,甚至在源语言和目标编程语言不同的情况下也能提高检索质量。基于这些发现,提出了基于算法计划检索有效示例的新框架——Plan-as-query Example Retrieval for few-shot prompting in Code generation(PERC)。在CodeContests、HumanEval和MultiPL-E基准测试上的实验表明,PERC在代码生成方面始终优于最新的RAG方法,无论是在源语言和目标编程语言相匹配还是不相匹配的情况下,都展现了其在多种编程环境中的适应性和稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 检索展示算法计划的例子能显著提高代码生成的准确性。
- 将代码转化为伪代码有助于提高检索质量,尤其在源语言和目标编程语言不同时。
- 提出了一种新的基于算法计划的检索框架PERC,用于在少量提示下进行代码生成。
- PERC在多个基准测试上表现优于最新的RAG方法。
- PERC在源语言和目标编程语言相匹配或不相匹配的情况下都能有效工作。
- PERC在多种编程环境中展现出适应性和稳健性。
- 代码生成是大型语言模型的一个重要应用领域,特别是在使用少量示例的情况下。
点此查看论文截图

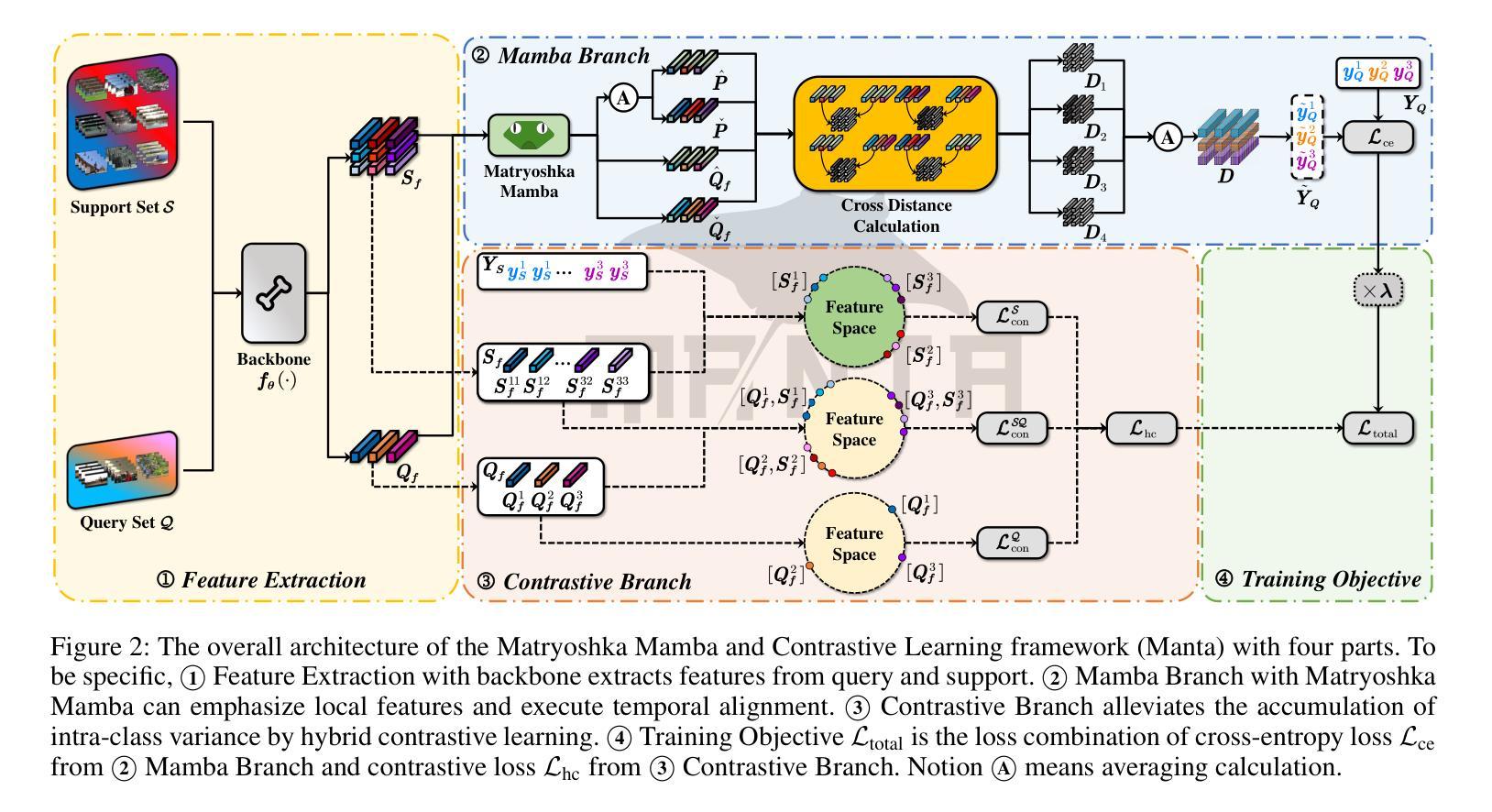
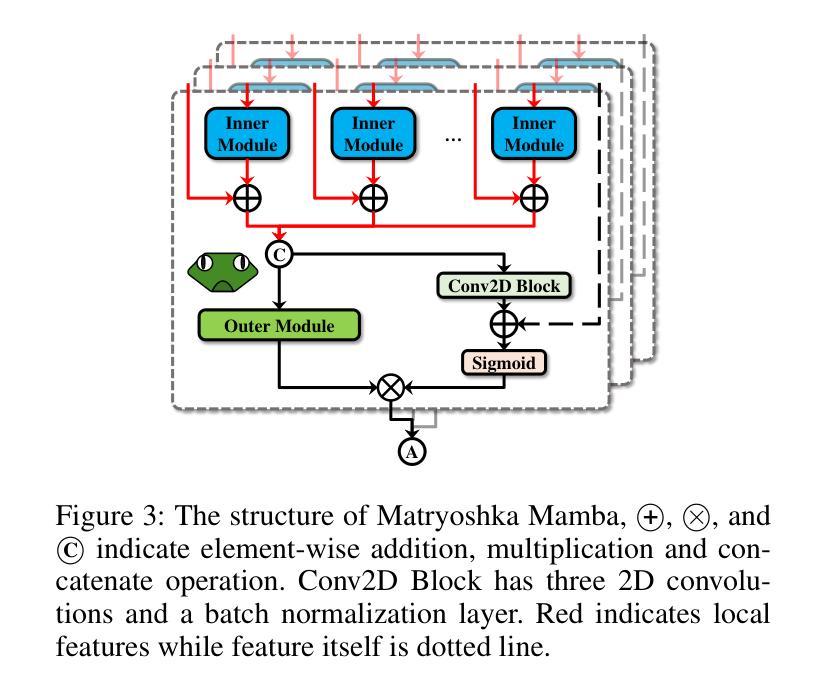
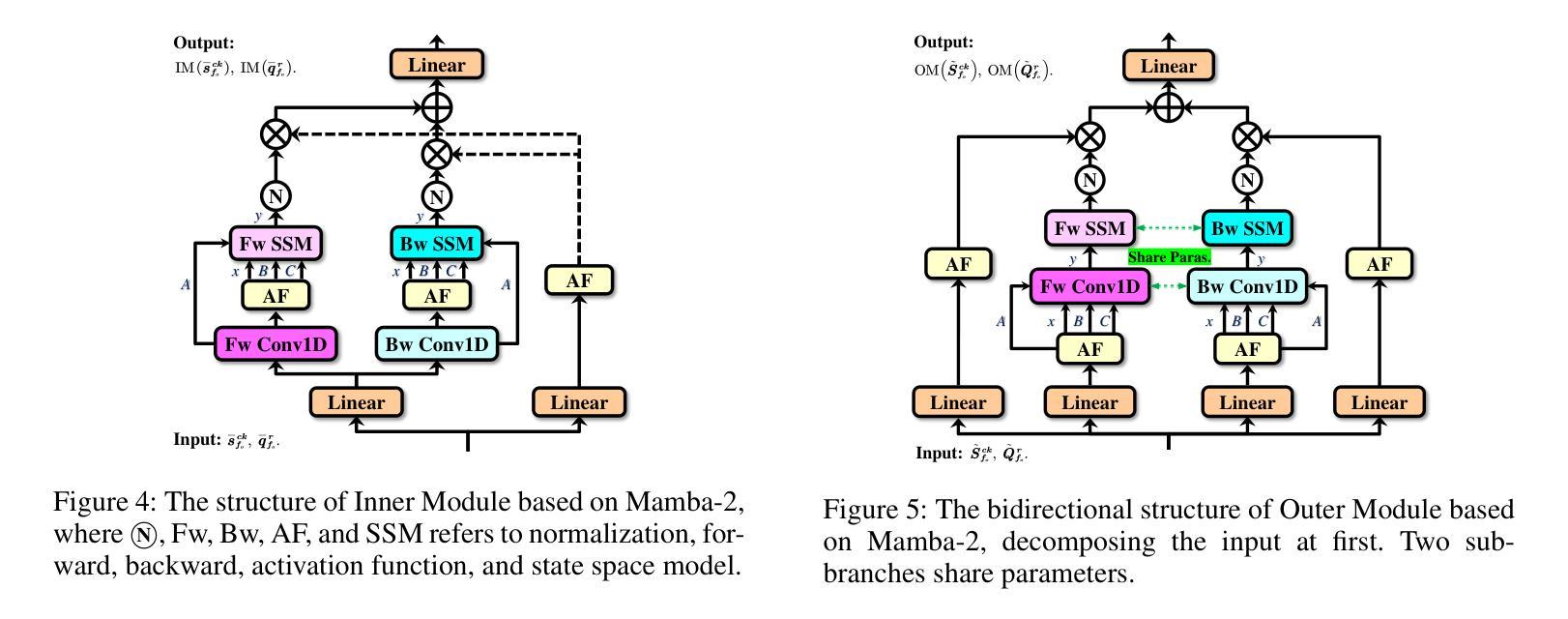
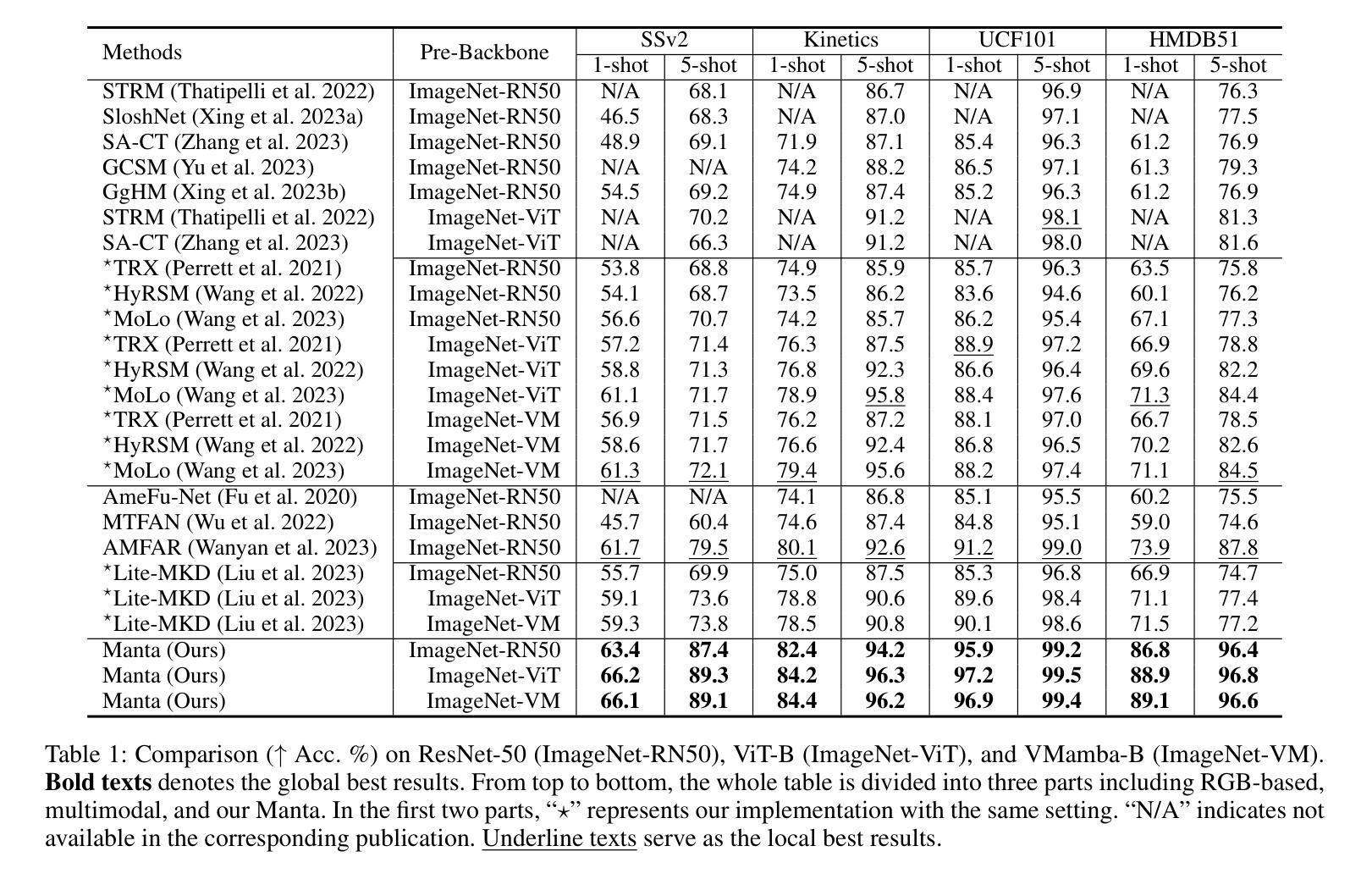
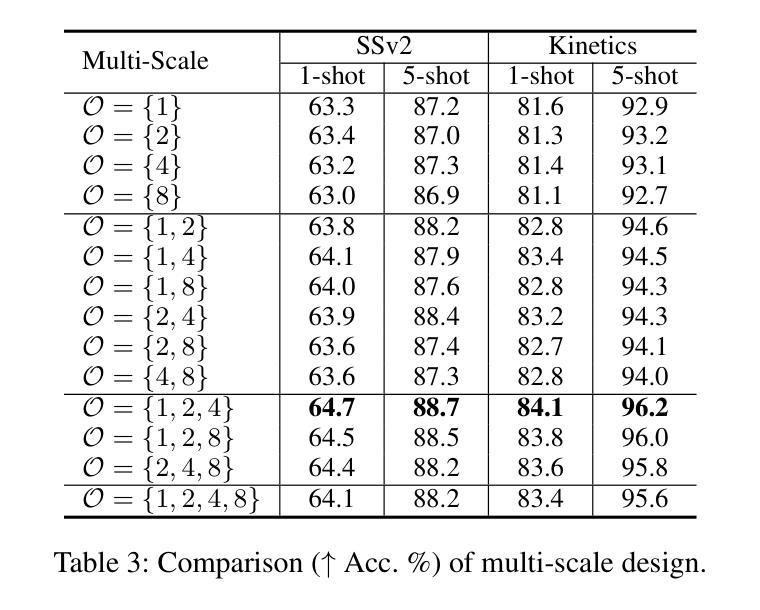
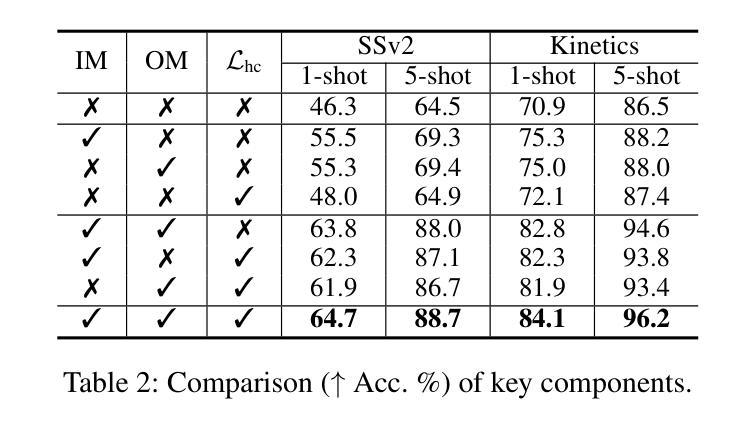
Manta: Enhancing Mamba for Few-Shot Action Recognition of Long Sub-Sequence
Authors:Wenbo Huang, Jinghui Zhang, Guang Li, Lei Zhang, Shuoyuan Wang, Fang Dong, Jiahui Jin, Takahiro Ogawa, Miki Haseyama
In few-shot action recognition (FSAR), long sub-sequences of video naturally express entire actions more effectively. However, the high computational complexity of mainstream Transformer-based methods limits their application. Recent Mamba demonstrates efficiency in modeling long sequences, but directly applying Mamba to FSAR overlooks the importance of local feature modeling and alignment. Moreover, long sub-sequences within the same class accumulate intra-class variance, which adversely impacts FSAR performance. To solve these challenges, we propose a Matryoshka MAmba and CoNtrasTive LeArning framework (Manta). Firstly, the Matryoshka Mamba introduces multiple Inner Modules to enhance local feature representation, rather than directly modeling global features. An Outer Module captures dependencies of timeline between these local features for implicit temporal alignment. Secondly, a hybrid contrastive learning paradigm, combining both supervised and unsupervised methods, is designed to mitigate the negative effects of intra-class variance accumulation. The Matryoshka Mamba and the hybrid contrastive learning paradigm operate in two parallel branches within Manta, enhancing Mamba for FSAR of long sub-sequence. Manta achieves new state-of-the-art performance on prominent benchmarks, including SSv2, Kinetics, UCF101, and HMDB51. Extensive empirical studies prove that Manta significantly improves FSAR of long sub-sequence from multiple perspectives.
在少量动作识别(FSAR)中,视频的长子序列更自然地表达了整个动作。然而,主流基于Transformer的方法的高计算复杂度限制了其应用。最近的Mamba在建模长序列方面展示了效率,但直接将Mamba应用于FSAR忽视了局部特征建模和对齐的重要性。此外,同一类别内的长子序列会累积类内差异,这对FSAR性能产生不利影响。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一个Matryoshka Mamba和对比学习框架(Manta)。首先,Matryoshka Mamba引入了多个内部模块来增强局部特征表示,而不是直接建模全局特征。外部模块捕获这些局部特征之间时间线的依赖性,进行隐式的时间对齐。其次,结合有监督和无监督方法的混合对比学习范式,旨在减轻类内差异积累带来的负面影响。Matryoshka Mamba和混合对比学习范式在Manta的两个并行分支中运行,增强了Mamba对长子序列的FSAR能力。Manta在包括SSv2、Kinetics、UCF101和HMDB51在内的主流基准测试上达到了最新状态的性能。大量的实证研究证明,Manta从多个角度显著提高了长子序列的FSAR性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了针对少样本动作识别(FSAR)的挑战,提出了一种名为Manta的新框架。Manta通过Matryoshka Mamba和混合对比学习的方法解决了长序列建模和局部特征对齐的问题,以及同类内方差积累带来的问题。Matryoshka Mamba通过引入多个内部模块增强局部特征表示,外部模块则捕捉这些局部特征的时间线依赖性以实现隐式时间对齐。混合对比学习范式结合监督和无监督方法,减轻了同类内方差积累的负面影响。Manta在SSv2、Kinetics、UCF101和HMDB51等主流基准测试中取得了最新状态的艺术性能。
Key Takeaways
- Manta框架解决了少样本动作识别(FSAR)中长序列建模的挑战。
- Matryoshka Mamba通过引入多个内部模块和外部模块,增强了局部特征表示和时间线依赖性捕捉。
- 混合对比学习范式结合监督和无监督方法,以减轻同类内方差积累的负面影响。
- Manta实现了对长序列的隐式时间对齐。
- Manta在多个主流基准测试中实现了最新状态的艺术性能。
- Matryoshka Mamba和混合对比学习范式在Manta框架中并行运作,增强了Mamba对FSAR长子序列的识别能力。
点此查看论文截图

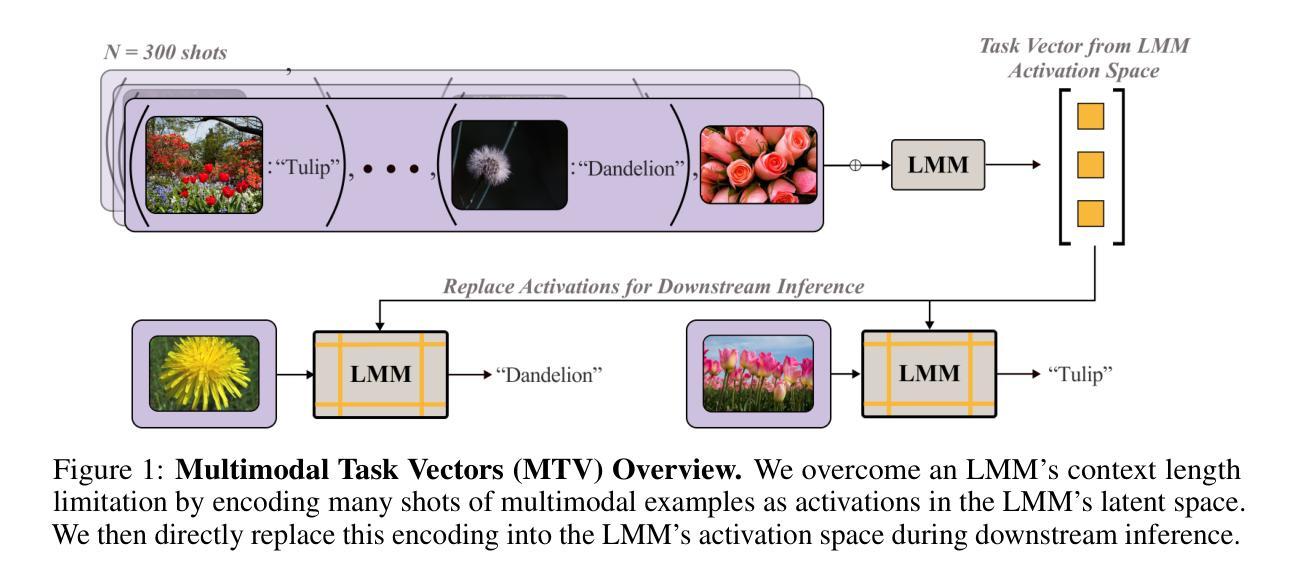
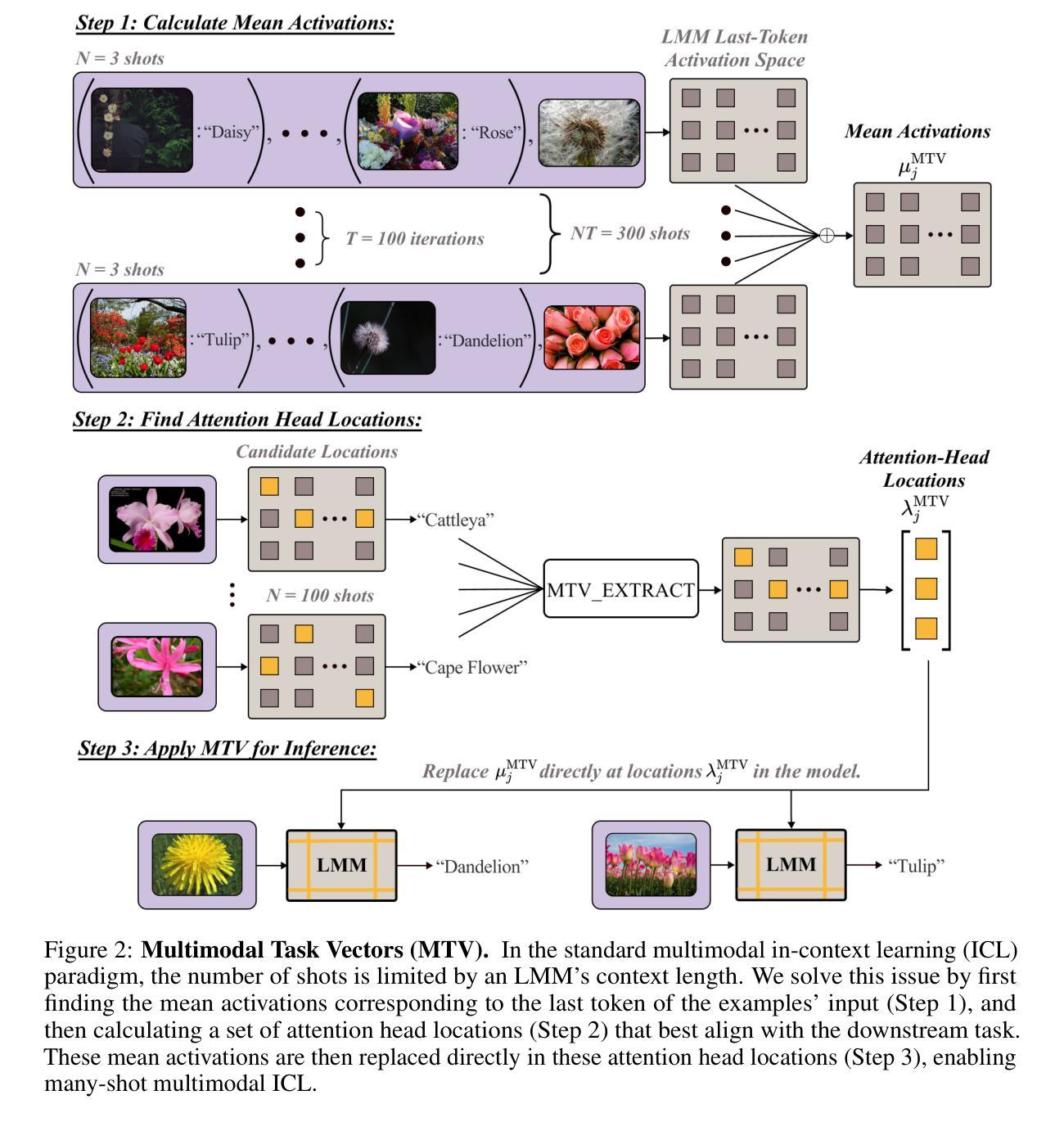
Multimodal Task Vectors Enable Many-Shot Multimodal In-Context Learning
Authors:Brandon Huang, Chancharik Mitra, Assaf Arbelle, Leonid Karlinsky, Trevor Darrell, Roei Herzig
The recent success of interleaved Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) in few-shot learning suggests that in-context learning (ICL) with many examples can be promising for learning new tasks. However, this many-shot multimodal ICL setting has one crucial problem: it is fundamentally limited by the model’s context length set at pretraining. The problem is especially prominent in the multimodal domain, which processes both text and images, requiring additional tokens. This motivates the need for a multimodal method to compress many shots into fewer tokens without finetuning. In this work, we enable LMMs to perform multimodal, many-shot in-context learning by leveraging Multimodal Task Vectors (MTV) – compact implicit representations of in-context examples compressed in the model’s attention heads. Specifically, we first demonstrate the existence of such MTV in LMMs and then leverage these extracted MTV to enable many-shot in-context learning for various vision-and-language tasks. Our experiments suggest that MTV can scale in performance with the number of compressed shots and generalize to similar out-of-domain tasks without additional context length for inference. Code: https://github.com/Brandon3964/MultiModal-Task-Vector
近期的穿插式大型多模态模型(LMMs)在少样本学习中的成功表明,使用多个例子的上下文学习(ICL)对于学习新任务可能是很有前景的。然而,这种多模态的许多例子上下文学习环境存在一个关键问题:它从根本上受到模型在预训练时设定的上下文长度的限制。这个问题在多模态领域尤为突出,该领域需要处理文本和图像,需要额外的标记符号。这促使需要一种多模态方法,将多个样本压缩成更少的标记符号,无需微调。在这项工作中,我们通过利用多模态任务向量(MTV)——压缩在模型注意力头中的上下文例子的紧凑隐式表示,使LMMs能够执行多模态、多例子的上下文学习。具体来说,我们首先证明这种MTV在LMMs中的存在性,然后利用这些提取的MTV来为各种视觉和语言任务提供多例子的上下文学习能力。我们的实验表明,随着压缩样本数量的增加,MTV的性能也可以提高,并能够推广到类似的域外任务,无需额外的推理上下文长度。代码:https://github.com/Brandon3964/MultiModal-Task-Vector
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in NeurIPS 2024
Summary
大模态模型(LMMs)在少样本学习中的成功表明,利用大量实例进行上下文学习(ICL)是有前景的。然而,多模态的上下文学习面临一个关键问题:模型预训练时的上下文长度限制。特别是在处理文本和图像的多模态领域,该问题尤为突出,需要额外的标记。因此,需要一种多模态方法将多个样本压缩成更少的标记,无需微调。本研究通过利用多任务向量(MTV),使LMMs能够进行多模态、多上下文学习,多任务向量是预训练模型中注意力头内压缩的上下文实例的紧凑隐式表示。实验表明,MTV在压缩样本数量增加时性能有所提升,并能推广到类似的外域任务,无需额外的推理上下文长度。
Key Takeaways
- 大模态模型(LMMs)在少样本学习中的成功表明上下文学习(ICL)潜力巨大。
- 多模态上下文学习面临预训练时的上下文长度限制问题。
- 多任务向量(MTV)是模型注意力头内的隐式表示,能解决多模态、多上下文学习问题。
- MTV通过压缩上下文实例,使LMMs能够处理更多的样本。
- MTV在压缩样本数量增加时性能提升,并适用于各种视觉和语言任务。
- MTV方法能够推广到类似的外域任务,无需额外的推理上下文长度。
点此查看论文截图