⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-24 更新
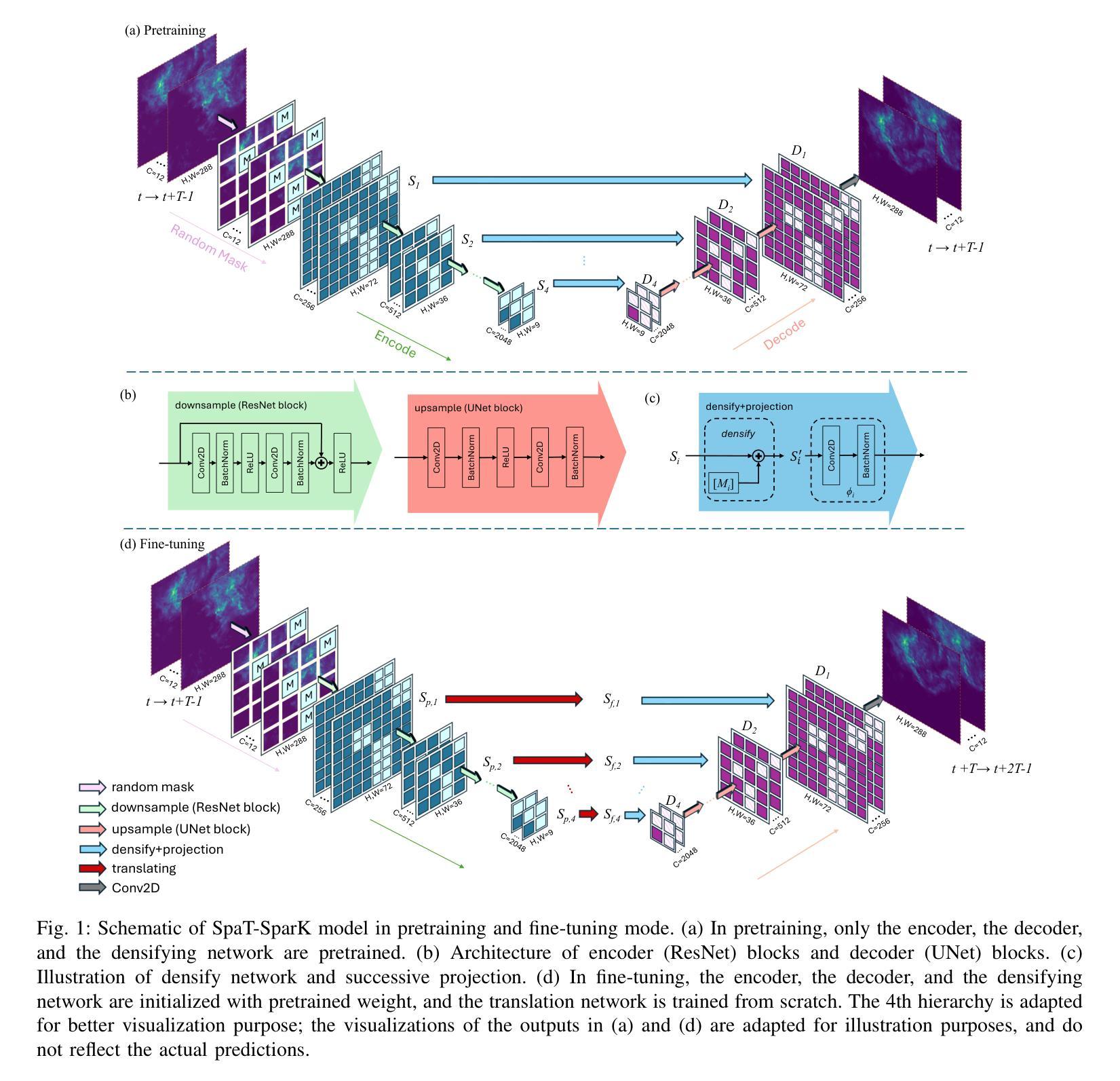
Self-supervised Spatial-Temporal Learner for Precipitation Nowcasting
Authors:Haotian Li, Arno Siebes, Siamak Mehrkanoon
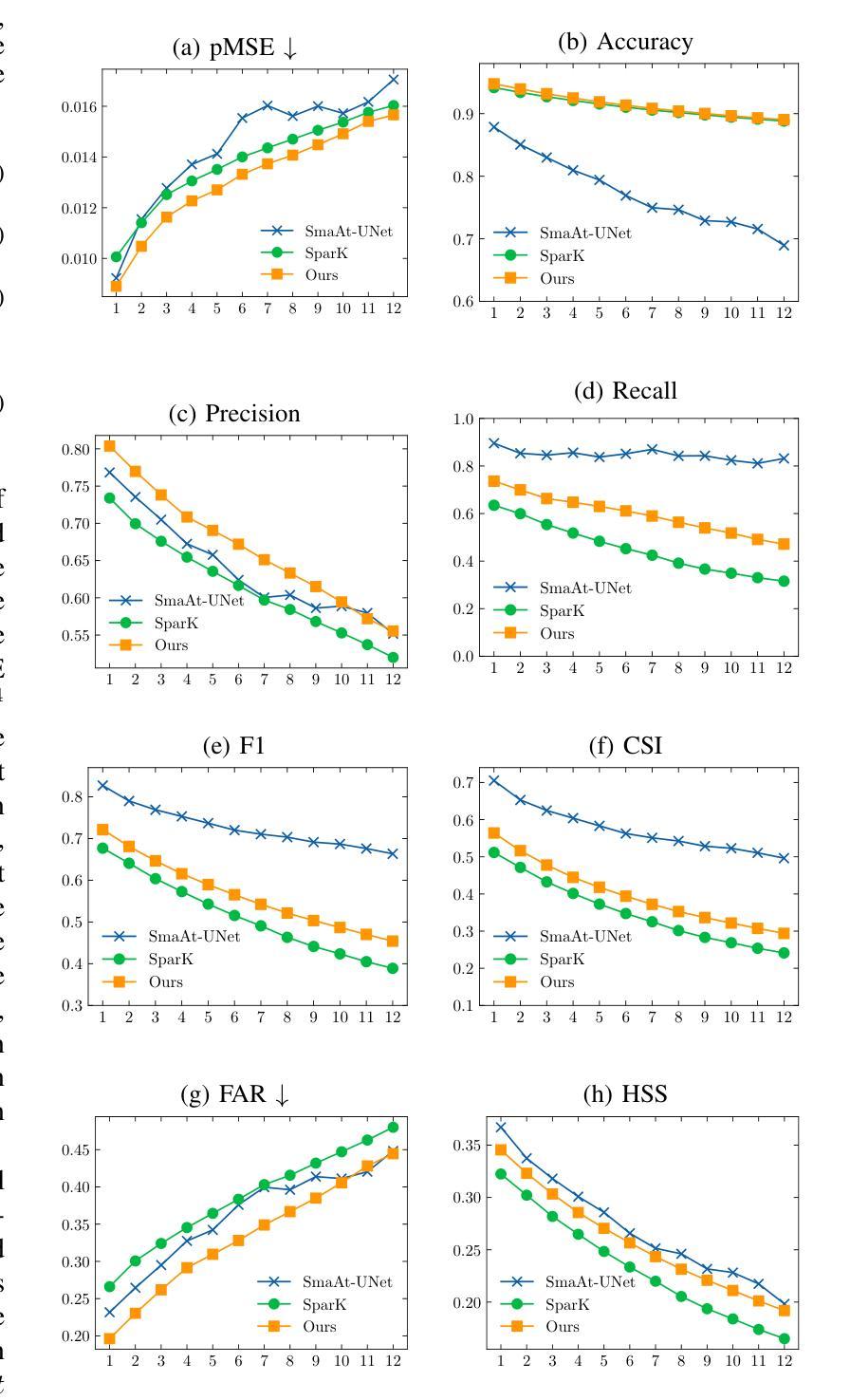
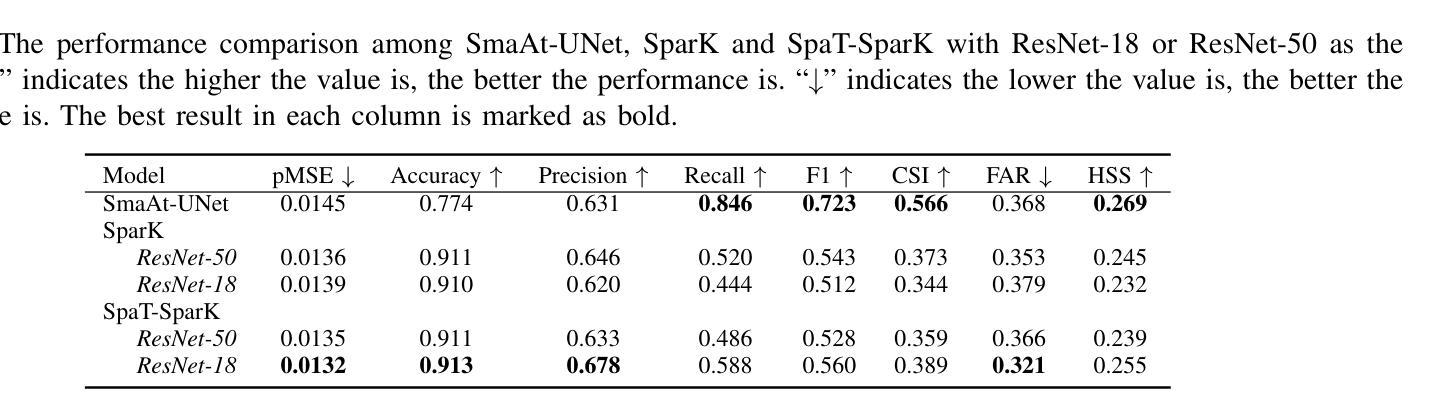
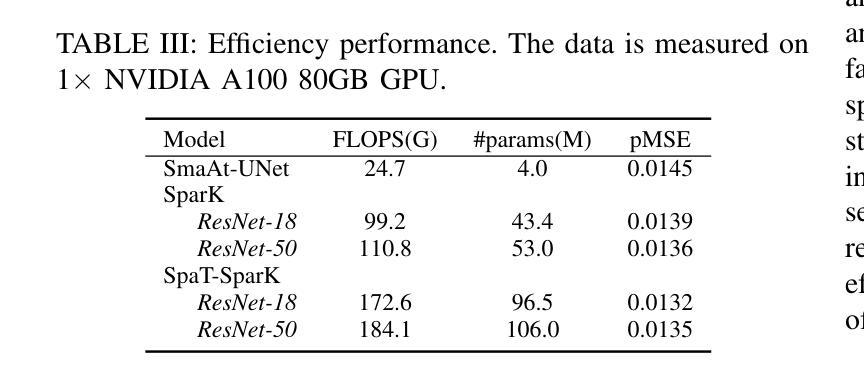
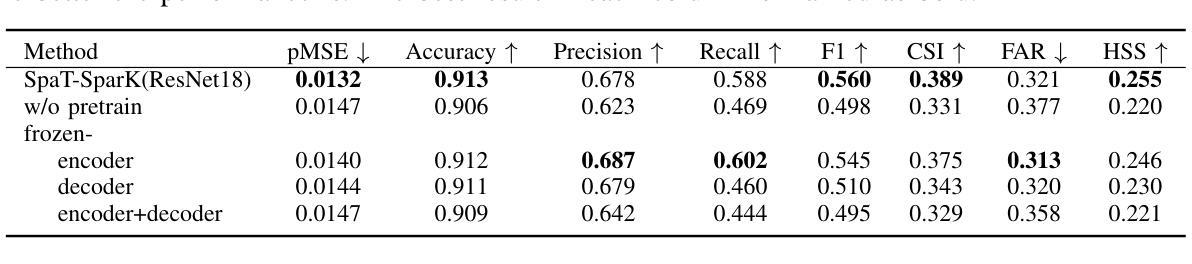
Nowcasting, the short-term prediction of weather, is essential for making timely and weather-dependent decisions. Specifically, precipitation nowcasting aims to predict precipitation at a local level within a 6-hour time frame. This task can be framed as a spatial-temporal sequence forecasting problem, where deep learning methods have been particularly effective. However, despite advancements in self-supervised learning, most successful methods for nowcasting remain fully supervised. Self-supervised learning is advantageous for pretraining models to learn representations without requiring extensive labeled data. In this work, we leverage the benefits of self-supervised learning and integrate it with spatial-temporal learning to develop a novel model, SpaT-SparK. SpaT-SparK comprises a CNN-based encoder-decoder structure pretrained with a masked image modeling (MIM) task and a translation network that captures temporal relationships among past and future precipitation maps in downstream tasks. We conducted experiments on the NL-50 dataset to evaluate the performance of SpaT-SparK. The results demonstrate that SpaT-SparK outperforms existing baseline supervised models, such as SmaAt-UNet, providing more accurate nowcasting predictions.
短期天气预报(即气象即时预报)对于及时和根据天气做出决策至关重要。具体而言,降水即时预报旨在预测未来6小时内当地的降水情况。此任务可以被构建为一个时空序列预测问题,深度学习在此类问题中表现出特别的效果。尽管自监督学习有所发展,但即时预报的最成功方法仍然是全监督的。自监督学习的优势在于,在没有大量标记数据的情况下,可以用于预训练模型以学习表示。在这项工作中,我们利用自监督学习的优势并将其与时空学习相结合,开发了一种新型模型SpaT-SparK。SpaT-SparK由基于CNN的编码器-解码器结构组成,采用掩码图像建模(MIM)任务进行预训练,并包含一个翻译网络,该网络能够捕捉下游任务中过去和未来的降水地图之间的时间关系。我们在NL-50数据集上进行了实验,以评估SpaT-SparK的性能。结果表明,SpaT-SparK优于现有的基线监督模型(如SmaAt-UNet),提供了更准确的即时预报预测。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 2 figures
Summary
天气现在预报是短期的天气预测,对制定及时的天气相关决策至关重要。研究中提出一个新的模型SpaT-SparK,它结合自监督学习与时空学习来预测未来6小时内的局部降水情况。模型使用基于CNN的编码器-解码器结构,并借助遮挡图像建模任务进行预训练。实验结果表明,SpaT-SparK相较于现有的监督模型,如SmaAt-UNet,在NL-50数据集上表现出更好的预测性能。
Key Takeaways
- 天气现在预报(Nowcasting)是对未来短时间内天气的预测,对决策有重要意义。
- 降水现在预报旨在预测未来6小时内的局部降水情况。
- 该任务可视为一个时空序列预测问题。
- 深度学习在此任务中特别有效。
- 尽管自监督学习有所发展,但现在大多数成功的预测方法仍然采用有监督学习。
- SpaT-SparK模型结合了自监督学习和时空学习,包括CNN编码器-解码器结构和预训练机制。
点此查看论文截图

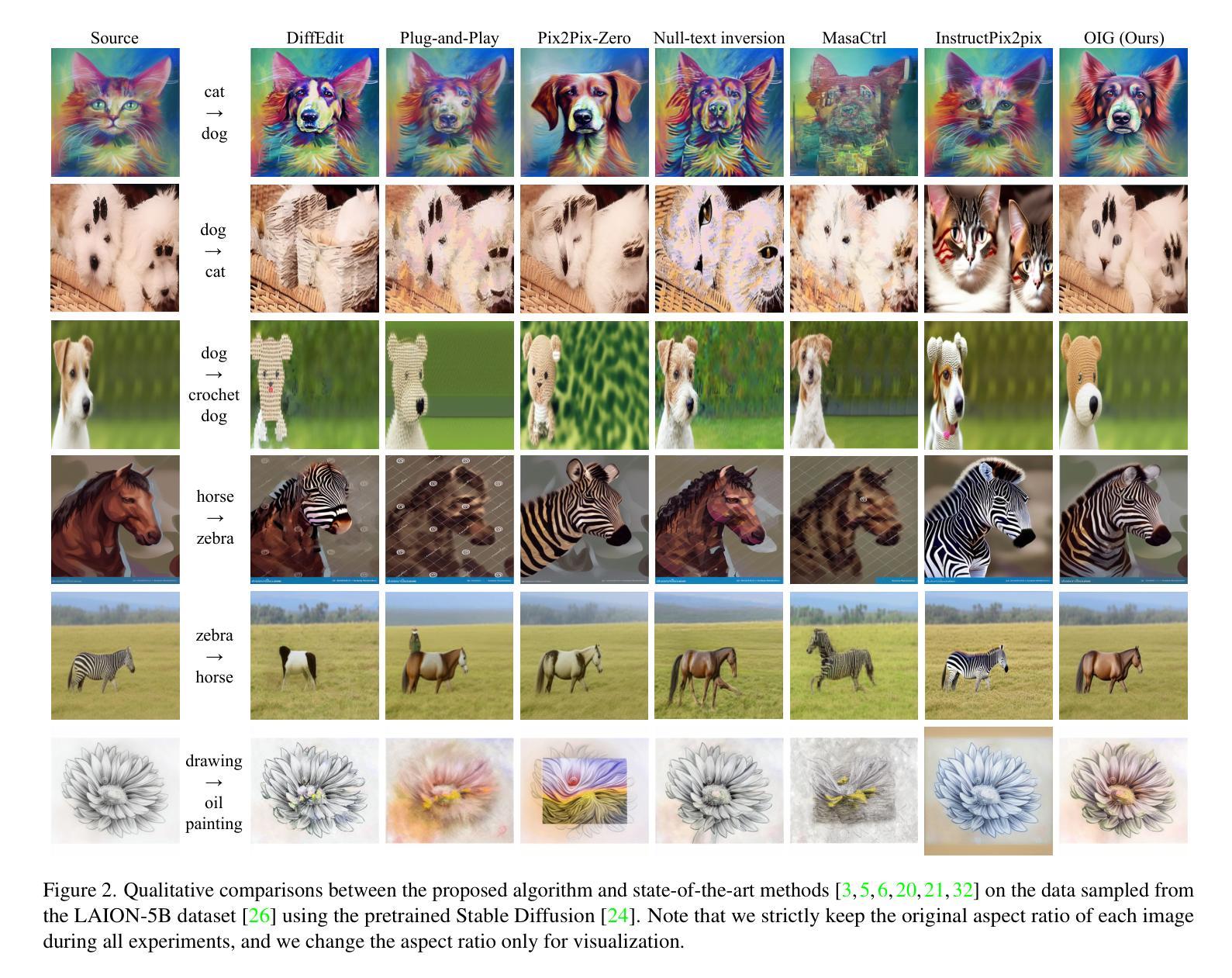
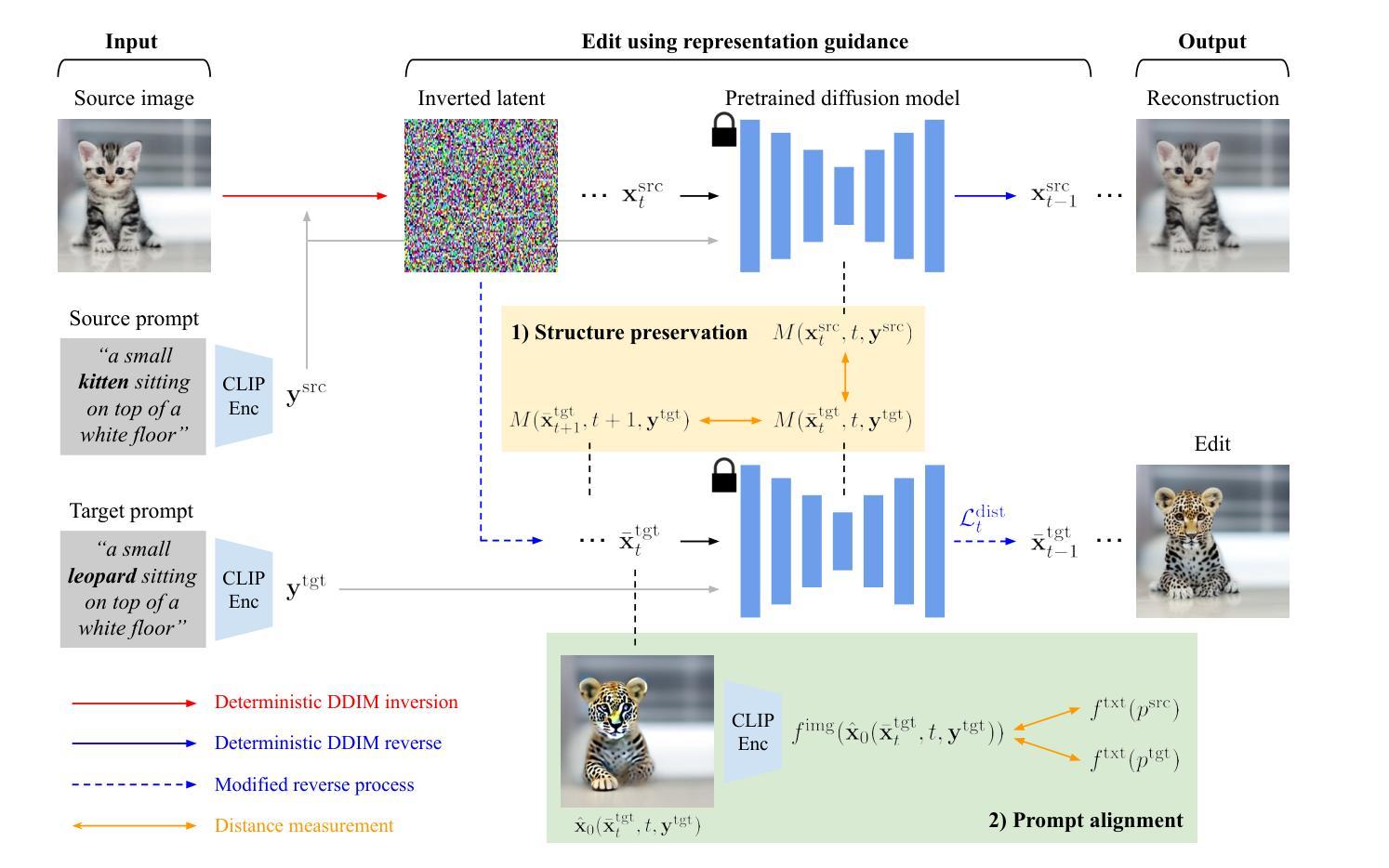
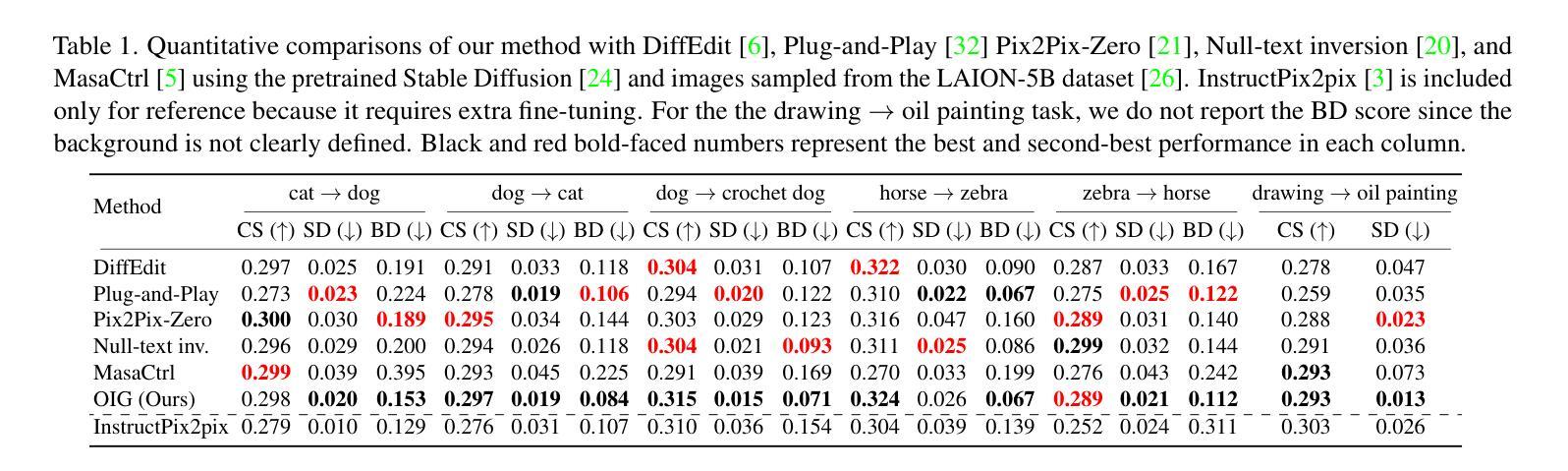
Diffusion-Based Conditional Image Editing through Optimized Inference with Guidance
Authors:Hyunsoo Lee, Minsoo Kang, Bohyung Han
We present a simple but effective training-free approach for text-driven image-to-image translation based on a pretrained text-to-image diffusion model. Our goal is to generate an image that aligns with the target task while preserving the structure and background of a source image. To this end, we derive the representation guidance with a combination of two objectives: maximizing the similarity to the target prompt based on the CLIP score and minimizing the structural distance to the source latent variable. This guidance improves the fidelity of the generated target image to the given target prompt while maintaining the structure integrity of the source image. To incorporate the representation guidance component, we optimize the target latent variable of diffusion model’s reverse process with the guidance. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves outstanding image-to-image translation performance on various tasks when combined with the pretrained Stable Diffusion model.
我们提出了一种简单而有效的无需训练的文字驱动图像到图像的翻译方法,该方法基于预训练的文本到图像的扩散模型。我们的目标是生成与目标任务对齐的图像,同时保留源图像的结构和背景。为此,我们通过结合两个目标来推导表示指导:基于CLIP分数的最大化与目标提示的相似性,以及最小化与源潜在变量的结构距离。这种指导提高了生成的目标图像对给定目标提示的保真度,同时保持了源图像的结构完整性。为了融入表示指导成分,我们优化扩散模型反向过程的目标潜在变量以得到指导。实验结果表明,当与预训练的Stable Diffusion模型结合时,我们的方法在各项任务上实现了出色的图像到图像的翻译性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF WACV 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于预训练文本到图像扩散模型的训练外文本驱动图像到图像转换的简单有效方法。该方法旨在生成与目标任务对齐的图像,同时保留源图像的结构和背景。通过结合两个目标——基于CLIP分数的最大化目标提示的相似性和最小化源潜在变量的结构距离,来改进生成的图像对给定目标提示的保真度,同时保持源图像的结构完整性。通过优化扩散模型反向过程中的目标潜在变量,将表示指导成分结合进来。实验结果表明,当与预训练的Stable Diffusion模型结合时,该方法在各项任务上均实现了出色的图像到图像的翻译性能。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种基于预训练文本到图像扩散模型的文本驱动图像翻译方法。
- 方法结合了最大化目标提示的相似性和最小化源潜在变量的结构距离作为表示指导。
- 通过优化扩散模型的反向过程中的目标潜在变量,将表示指导成分融入方法中。
- 该方法能够在生成与目标任务对齐的图像时,保留源图像的结构和背景。
- 方法实现了在多种任务上的出色图像到图像翻译性能。
- 与预训练的Stable Diffusion模型结合使用时,该方法表现尤为突出。
点此查看论文截图