⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-24 更新
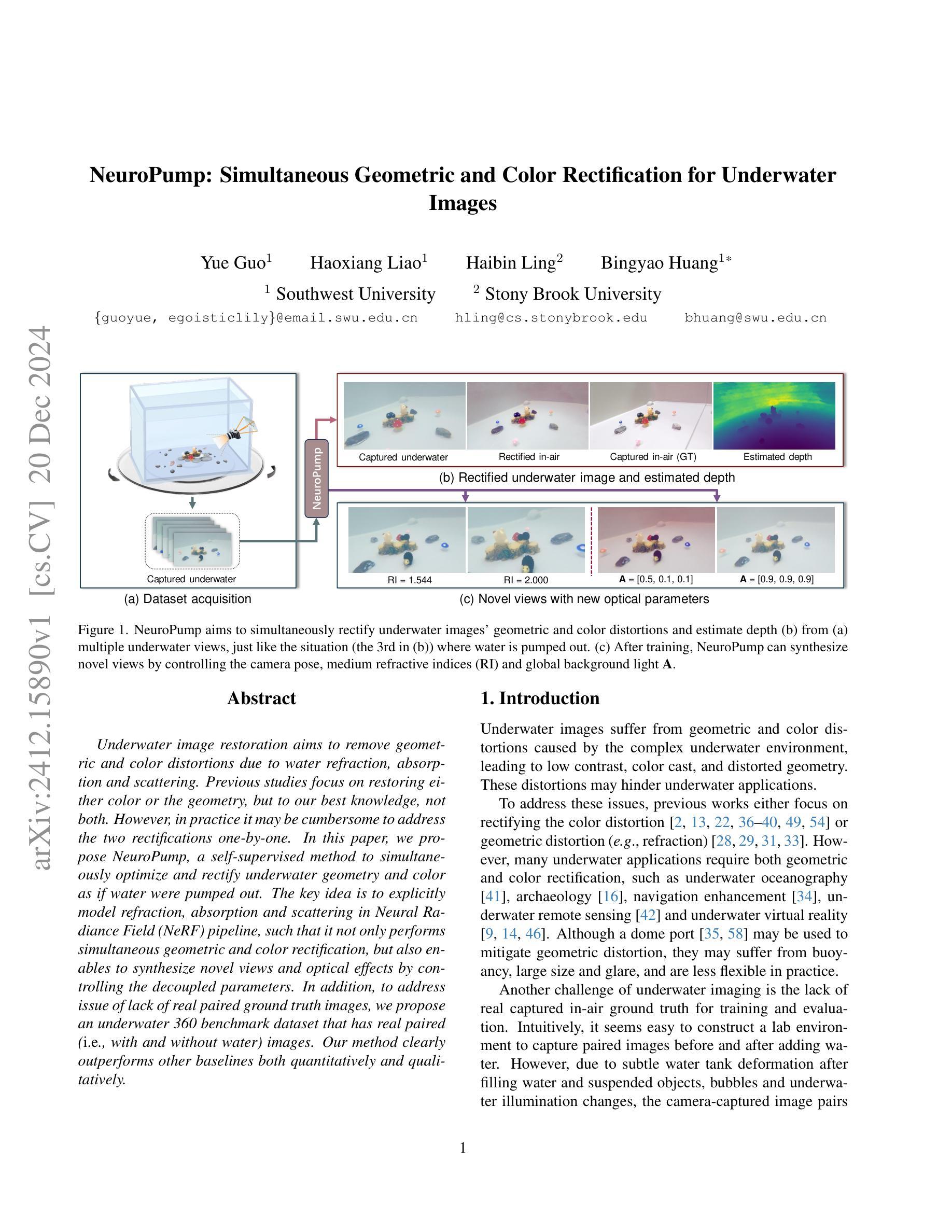
NeuroPump: Simultaneous Geometric and Color Rectification for Underwater Images
Authors:Yue Guo, Haoxiang Liao, Haibin Ling, Bingyao Huang
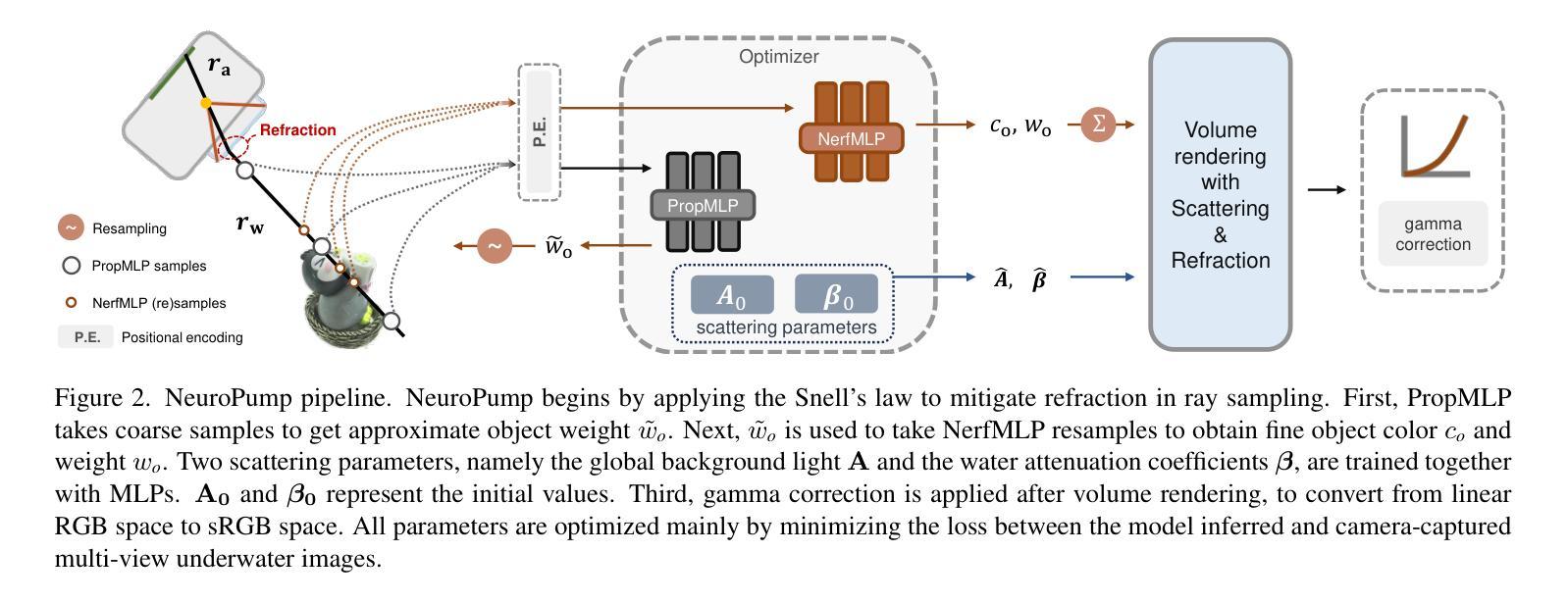
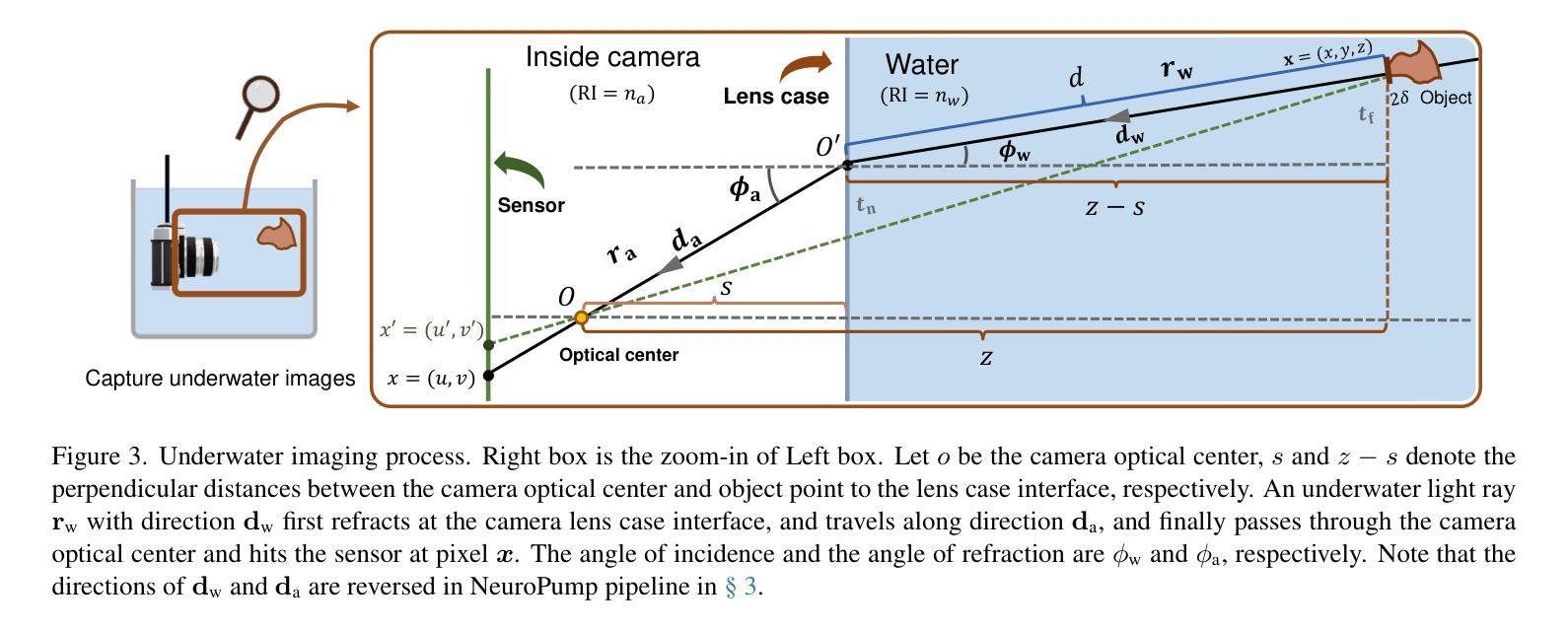
Underwater image restoration aims to remove geometric and color distortions due to water refraction, absorption and scattering. Previous studies focus on restoring either color or the geometry, but to our best knowledge, not both. However, in practice it may be cumbersome to address the two rectifications one-by-one. In this paper, we propose NeuroPump, a self-supervised method to simultaneously optimize and rectify underwater geometry and color as if water were pumped out. The key idea is to explicitly model refraction, absorption and scattering in Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) pipeline, such that it not only performs simultaneous geometric and color rectification, but also enables to synthesize novel views and optical effects by controlling the decoupled parameters. In addition, to address issue of lack of real paired ground truth images, we propose an underwater 360 benchmark dataset that has real paired (i.e., with and without water) images. Our method clearly outperforms other baselines both quantitatively and qualitatively.
水下图像恢复旨在消除由于水体的折射、吸收和散射引起的几何和色彩失真。先前的研究主要集中在恢复颜色或几何结构,但据我们了解,尚不能同时恢复两者。然而,实践中逐个解决这两种矫正可能很麻烦。在本文中,我们提出了NeuroPump,这是一种自监督方法,可同时优化和校正水下几何和颜色,就像将水抽出一样。关键思想是在神经辐射场(NeRF)管道中显式建模折射、吸收和散射,这样不仅可以同时进行几何和颜色校正,而且通过控制解耦的参数,还能合成新的视角和光学效果。此外,为了解决缺乏真实的配对基准图像的问题,我们提出了一个水下360度基准数据集,其中包含真实的配对(即,带水和不带水的)图像。我们的方法在定量和定性上均明显优于其他基线。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为NeuroPump的自监督方法,旨在同时优化和纠正水下图像的几何和颜色失真,就像将水排出一样。该方法的关键思想是在神经辐射场(NeRF)管道中显式建模折射、吸收和散射,实现几何和颜色的同时校正,并可通过控制解耦参数合成新视角和光学效果。为解决真实配对地面真实图像缺乏的问题,还提出了水下360基准数据集。该方法在定量和定性方面均优于其他基线。
Key Takeaways
- 水下图像恢复旨在消除由于水折射、吸收和散射引起的几何和颜色失真。
- 现有研究主要关注颜色或几何的恢复,但本文提出的方法可以同时优化和纠正两者。
- NeuroPump是一种自监督方法,显式建模折射、吸收和散射在神经辐射场(NeRF)中,实现几何和颜色的同时校正。
- 通过控制解耦参数,NeuroPump可以合成新视角和光学效果。
- 提出了水下360基准数据集,包含真实配对(有水和无水)的图像,以解决缺乏真实地面真实图像的问题。
- NeuroPump在定量和定性方面均优于其他基线方法。
点此查看论文截图
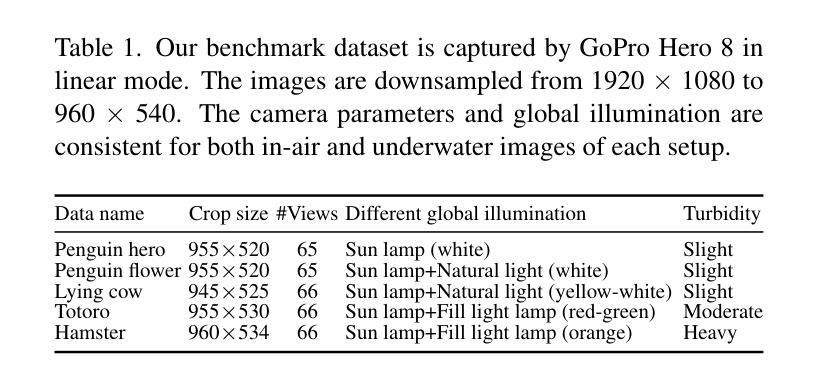
LiHi-GS: LiDAR-Supervised Gaussian Splatting for Highway Driving Scene Reconstruction
Authors:Pou-Chun Kung, Xianling Zhang, Katherine A. Skinner, Nikita Jaipuria
Photorealistic 3D scene reconstruction plays an important role in autonomous driving, enabling the generation of novel data from existing datasets to simulate safety-critical scenarios and expand training data without additional acquisition costs. Gaussian Splatting (GS) facilitates real-time, photorealistic rendering with an explicit 3D Gaussian representation of the scene, providing faster processing and more intuitive scene editing than the implicit Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs). While extensive GS research has yielded promising advancements in autonomous driving applications, they overlook two critical aspects: First, existing methods mainly focus on low-speed and feature-rich urban scenes and ignore the fact that highway scenarios play a significant role in autonomous driving. Second, while LiDARs are commonplace in autonomous driving platforms, existing methods learn primarily from images and use LiDAR only for initial estimates or without precise sensor modeling, thus missing out on leveraging the rich depth information LiDAR offers and limiting the ability to synthesize LiDAR data. In this paper, we propose a novel GS method for dynamic scene synthesis and editing with improved scene reconstruction through LiDAR supervision and support for LiDAR rendering. Unlike prior works that are tested mostly on urban datasets, to the best of our knowledge, we are the first to focus on the more challenging and highly relevant highway scenes for autonomous driving, with sparse sensor views and monotone backgrounds.
基于自主驾驶技术的光感逼真的三维场景重建具有重要的价值,它可以实现从已有的数据集生成新的数据,模拟关键安全场景,并且在无需额外采集成本的情况下扩充训练数据。高斯拼贴技术(GS)可实现场景实时的光感逼真的渲染,并拥有场景明确的三维高斯表达形式,相比于隐式的神经辐射场(NeRFs),它提供了更快的处理速度和更直观的场景编辑功能。尽管关于高斯拼贴技术的广泛研究已经在自主驾驶应用方面取得了有前景的进展,但它们忽略了两个关键方面:首先,现有的方法主要集中在低速且特征丰富的城市场景上,忽略了高速公路场景在自主驾驶中的重要作用。其次,虽然激光雷达在自主驾驶平台中很常见,但现有方法主要从图像中学习并仅将激光雷达用于初步估计或缺乏精确的传感器建模,从而没有充分利用激光雷达提供的丰富的深度信息,并限制了合成激光雷达数据的能力。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的高斯拼贴技术用于动态场景的合成和编辑,通过激光雷达的监督和改进的场景重建提高了场景的重建能力,并支持激光雷达的渲染。据我们所知,与之前主要在城区数据集上进行测试的工作不同,我们是首批专注于更具挑战性和高度相关的自主驾驶高速公路场景的团队,尤其是针对稀疏传感器视角和单色背景的场景。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了高斯拼贴(GS)在自主驾驶中的重要作用,它通过明确的3D高斯场景表示,实现了实时、逼真的渲染。然而,现有方法主要关注低速和特征丰富的城市场景,忽略了高速公路场景的重要性。本文提出了一种新的GS方法,通过激光雷达监督和改进的场景重建,支持激光雷达渲染,以应对更具挑战性和高度相关的高速公路场景。
Key Takeaways
- 高斯拼贴在自主驾驶中扮演重要角色,通过明确的3D高斯场景表示实现实时、逼真的渲染。
- 现有方法主要关注城市场景,忽略了高速公路场景在自主驾驶中的重要性。
- 激光雷达在自主驾驶中普及,但现有方法主要依赖图像学习,未充分利用激光雷达丰富的深度信息。
- 本文提出了一种新的高斯拼贴方法,用于动态场景合成和编辑,改进了场景重建。
- 该方法通过激光雷达监督和支持激光雷达渲染,可以更好地利用激光雷达数据。
- 与先前主要在城市数据集上测试的工作不同,本文专注于更具挑战性和高度相关的高速公路场景。
点此查看论文截图

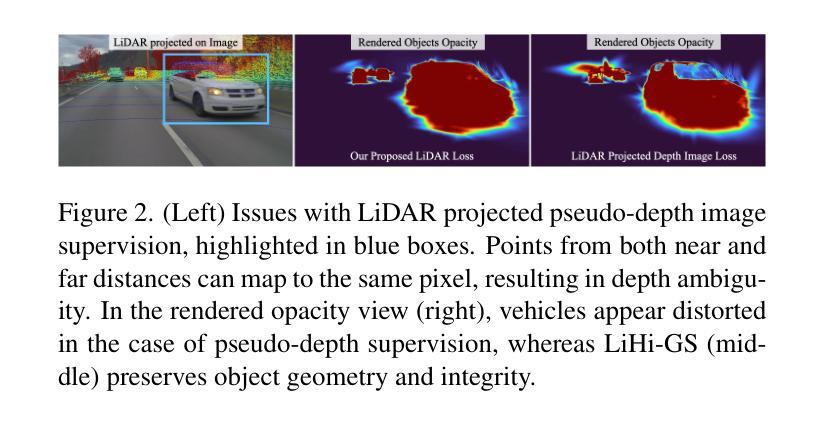
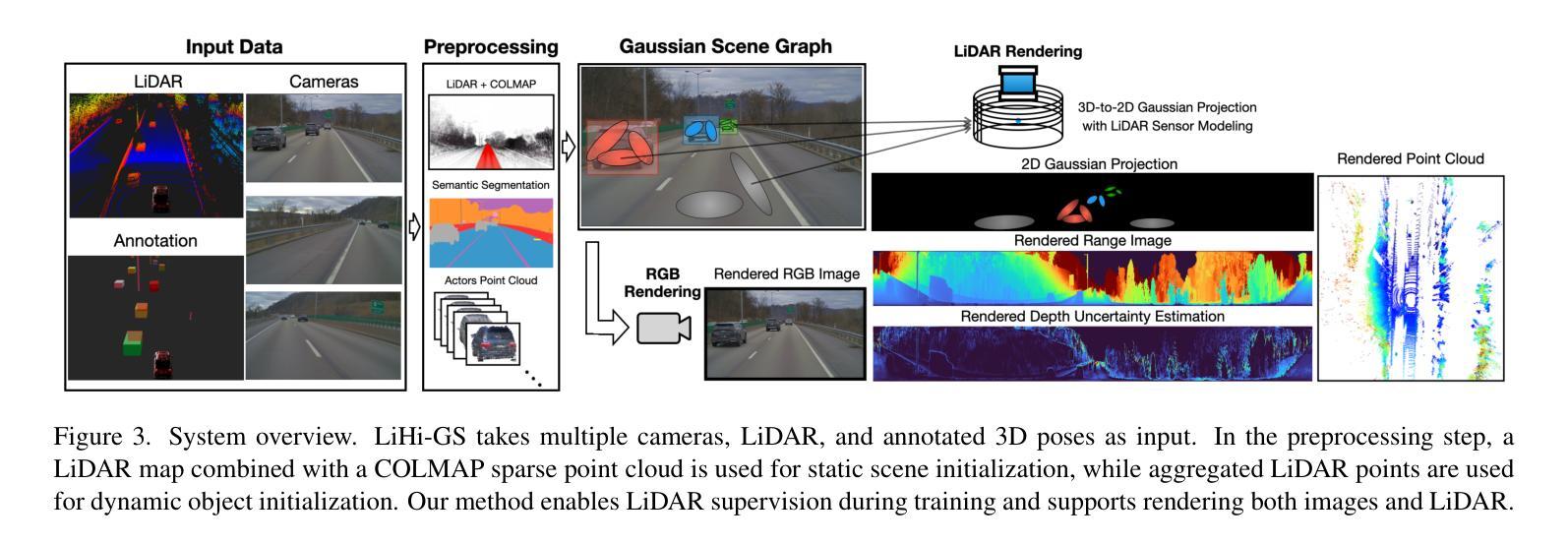
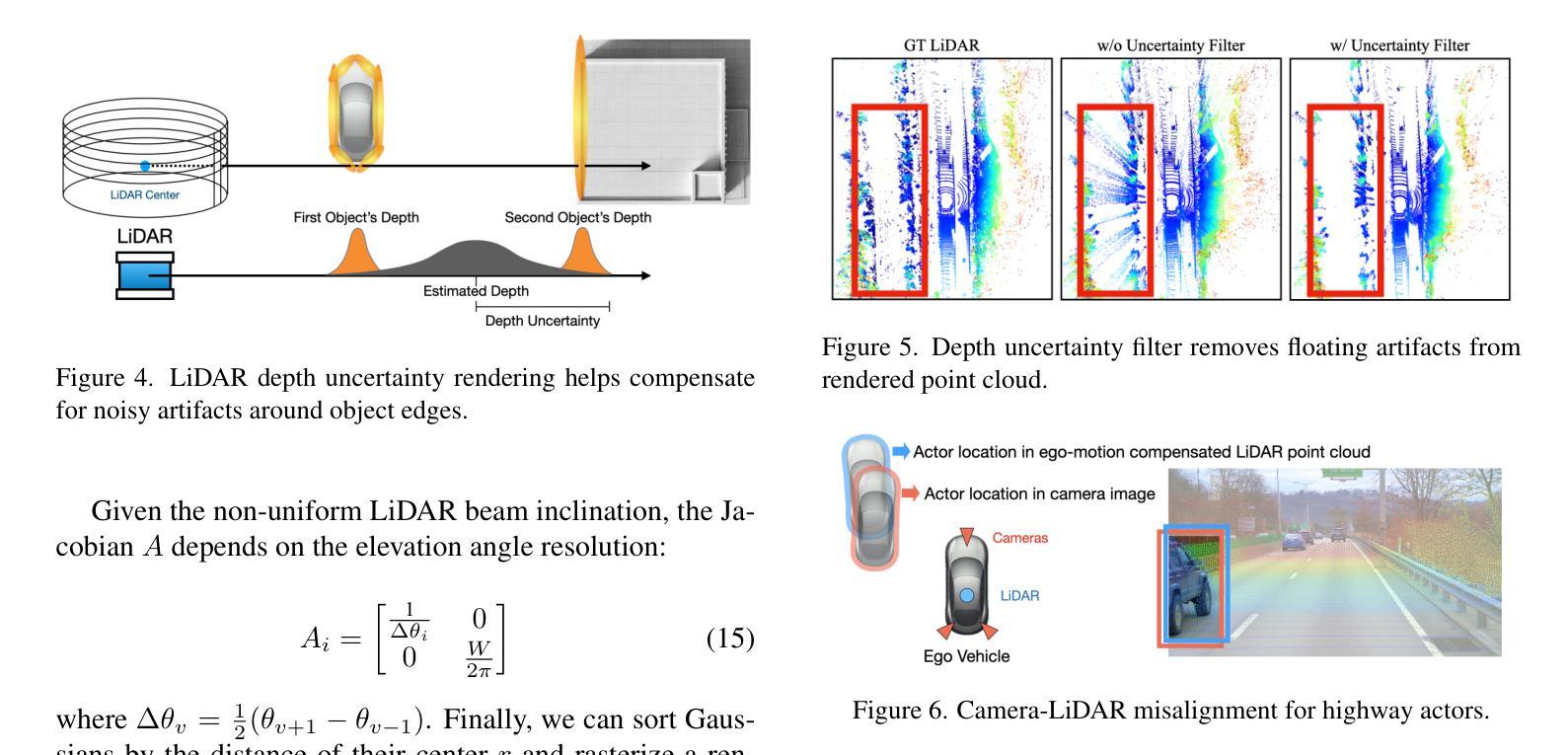
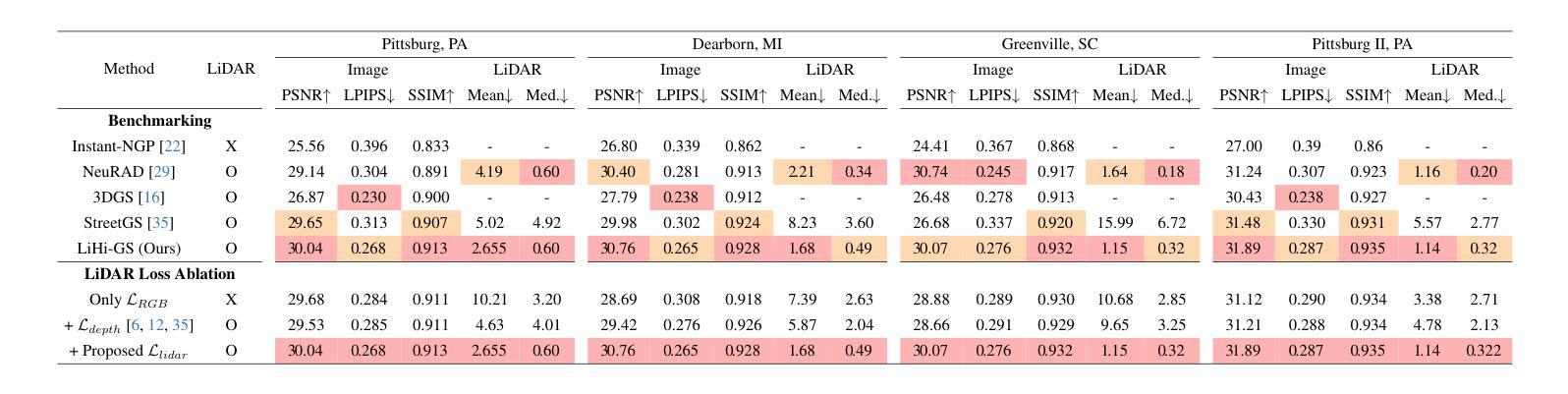
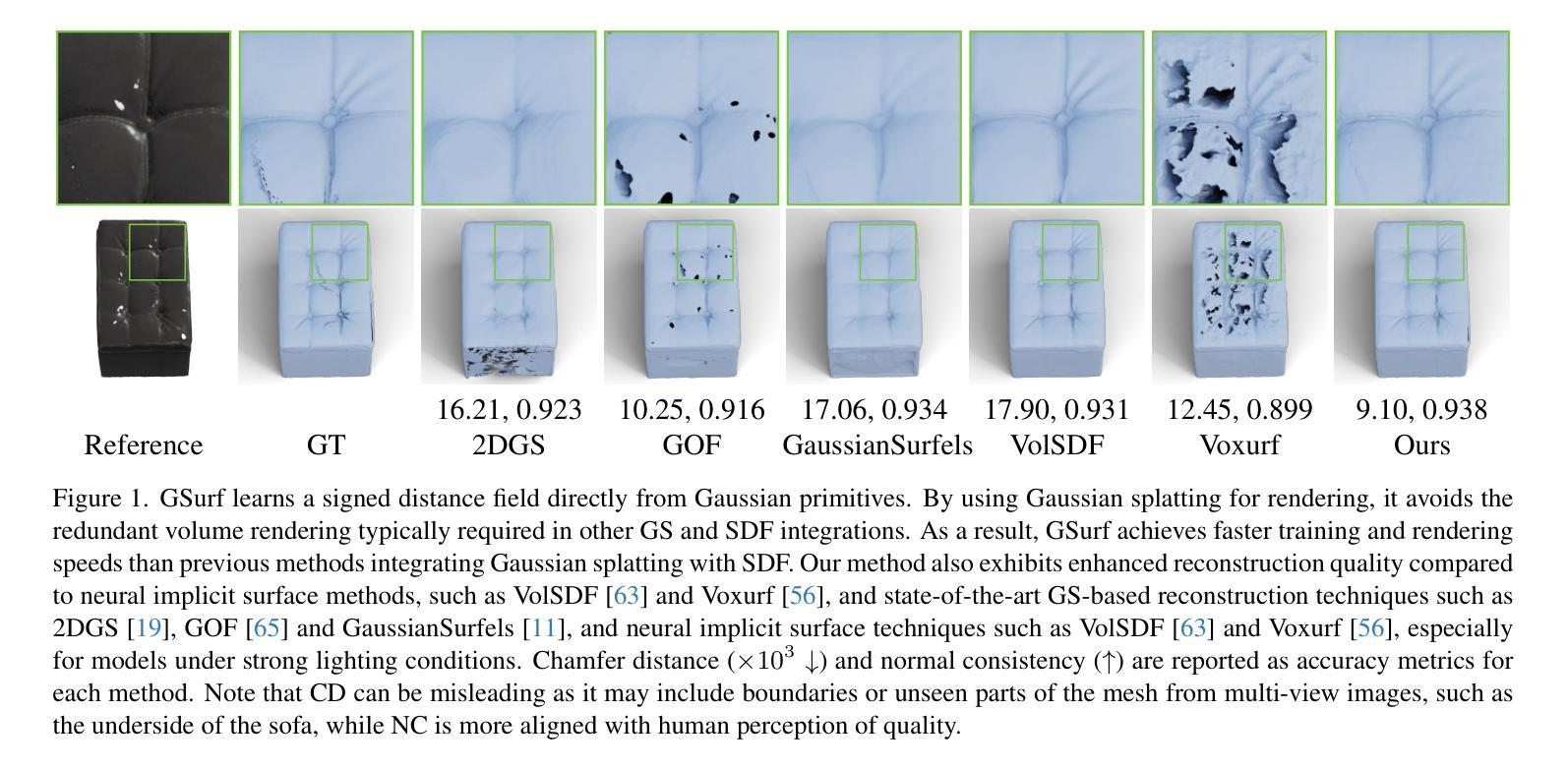
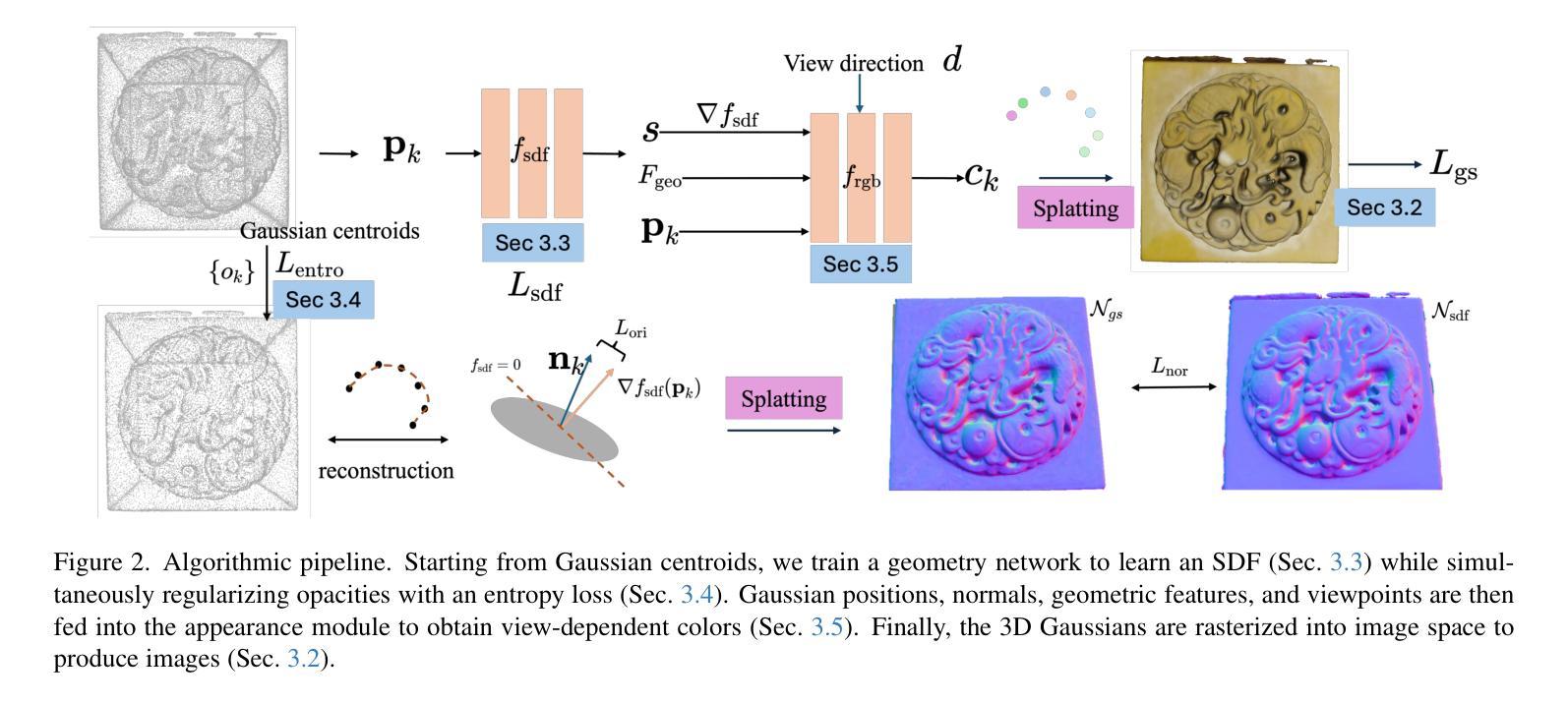
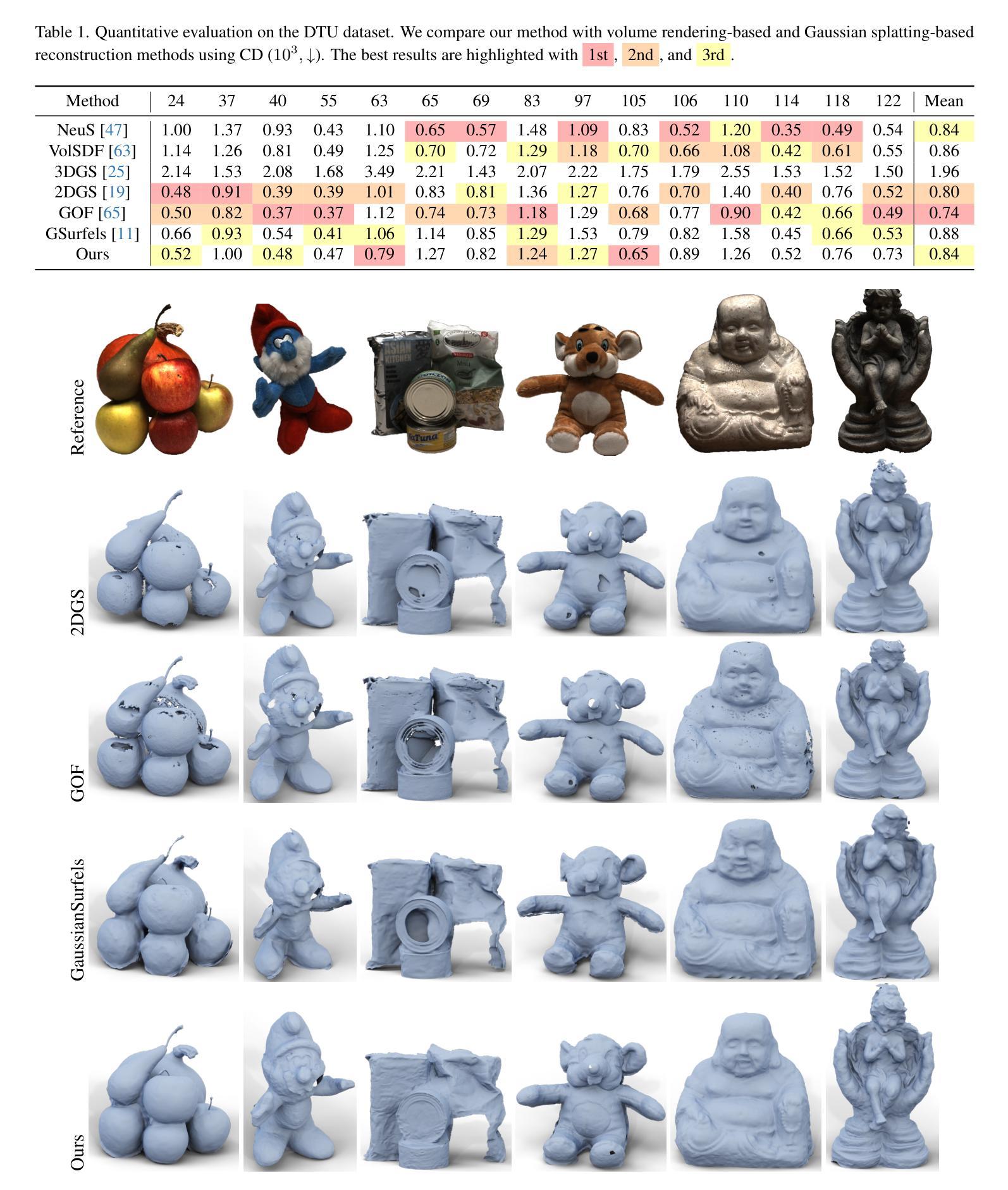
GSurf: 3D Reconstruction via Signed Distance Fields with Direct Gaussian Supervision
Authors:Baixin Xu, Jiangbei Hu, Jiaze Li, Ying He
Surface reconstruction from multi-view images is a core challenge in 3D vision. Recent studies have explored signed distance fields (SDF) within Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) to achieve high-fidelity surface reconstructions. However, these approaches often suffer from slow training and rendering speeds compared to 3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS). Current state-of-the-art techniques attempt to fuse depth information to extract geometry from 3DGS, but frequently result in incomplete reconstructions and fragmented surfaces. In this paper, we introduce GSurf, a novel end-to-end method for learning a signed distance field directly from Gaussian primitives. The continuous and smooth nature of SDF addresses common issues in the 3DGS family, such as holes resulting from noisy or missing depth data. By using Gaussian splatting for rendering, GSurf avoids the redundant volume rendering typically required in other GS and SDF integrations. Consequently, GSurf achieves faster training and rendering speeds while delivering 3D reconstruction quality comparable to neural implicit surface methods, such as VolSDF and NeuS. Experimental results across various benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in producing high-fidelity 3D reconstructions.
从多视角图像重建表面是3D视觉中的核心挑战之一。最近的研究探索了神经辐射场(NeRF)中的带符号距离场(SDF),以实现高保真表面重建。然而,与三维高斯贴片(3DGS)相比,这些方法通常存在训练和渲染速度较慢的问题。当前最先进的技术试图融合深度信息,以从3DGS中提取几何信息,但经常导致重建不完整和表面碎片化。在本文中,我们介绍了GSurf,这是一种新的端到端方法,用于直接从高斯原始数据中学习带符号的距离场。SDF的连续和平滑性质解决了3DGS家族中常见的问题,例如由于噪声或缺失的深度数据导致的空洞。通过使用高斯贴片进行渲染,GSurf避免了其他GS和SDF集成中通常需要的冗余体积渲染。因此,GSurf实现了更快的训练和渲染速度,同时提供了与神经隐式表面方法(如VolSDF和NeuS)相当的3D重建质量。在各种基准数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的方法在产生高保真3D重建方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF see https://github.com/xubaixinxbx/Gsurf
Summary
本文提出了一种基于高斯原始数据学习距离场的新方法GSurf,用于从多视角图像进行表面重建。GSurf直接利用高斯数据进行渲染,避免了冗余的体积渲染,提高了训练和渲染速度,同时保证了与神经隐式表面方法相当的3D重建质量。
Key Takeaways
- GSurf是一种新型的端到端方法,用于从高斯原始数据学习距离场进行表面重建。
- GSurf解决了3DGS常见的问题,如因噪声或缺失的深度数据导致的空洞。
- 通过使用高斯进行渲染,GSurf避免了其他GS和SDF集成所需的冗余体积渲染。
- GSurf实现了更快的训练和渲染速度。
- GSurf的重建质量可与神经隐式表面方法(如VolSDF和NeuS)相当。
- 跨多个基准数据集的实验结果证明了GSurf方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

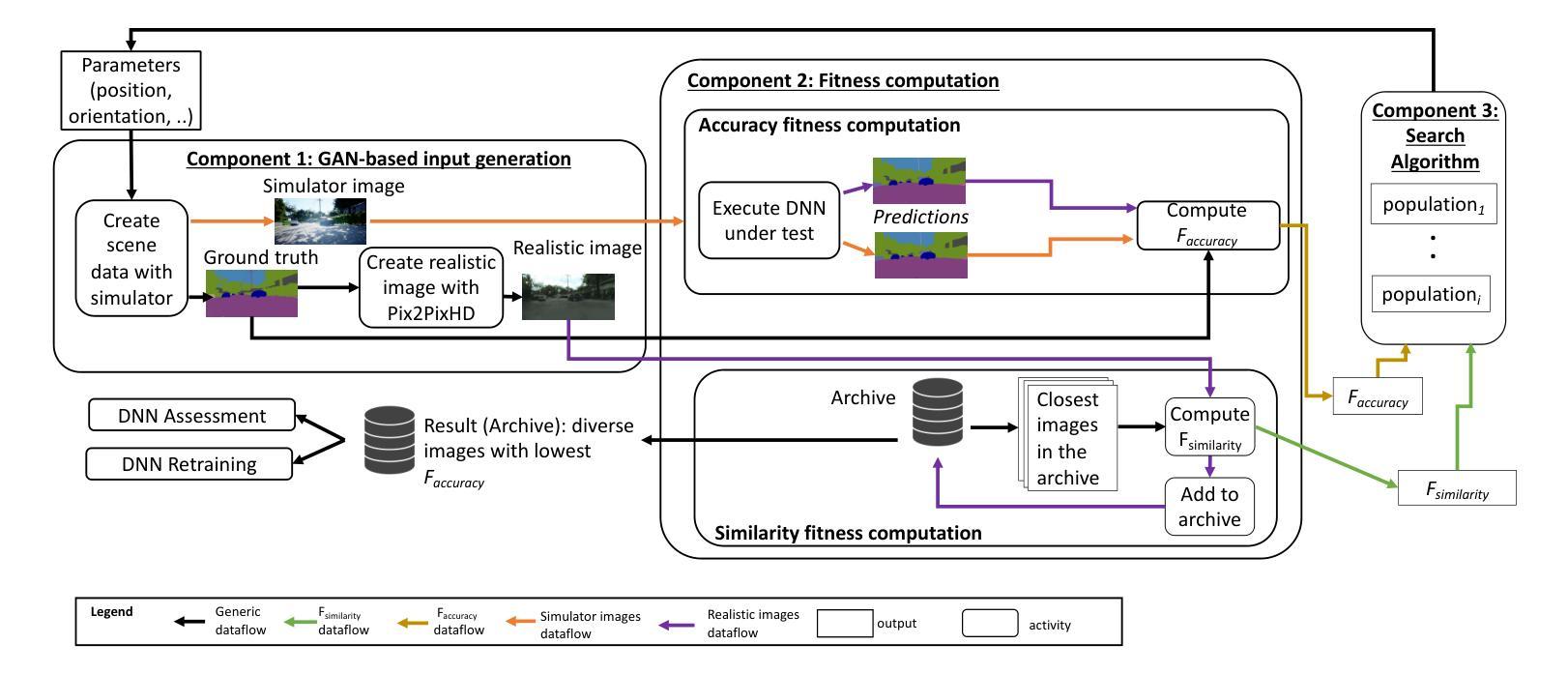
Search-based DNN Testing and Retraining with GAN-enhanced Simulations
Authors:Mohammed Oualid Attaoui, Fabrizio Pastore, Lionel Briand
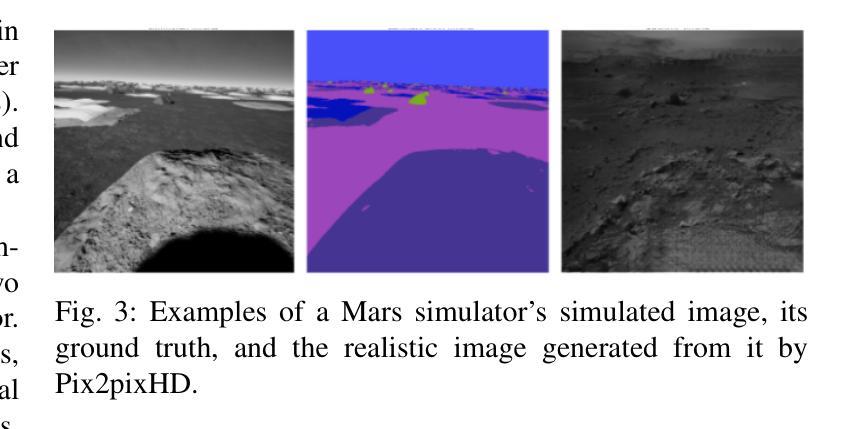
In safety-critical systems (e.g., autonomous vehicles and robots), Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) are becoming a key component for computer vision tasks, particularly semantic segmentation. Further, since the DNN behavior cannot be assessed through code inspection and analysis, test automation has become an essential activity to gain confidence in the reliability of DNNs. Unfortunately, state-of-the-art automated testing solutions largely rely on simulators, whose fidelity is always imperfect, thus affecting the validity of test results. To address such limitations, we propose to combine meta-heuristic search, used to explore the input space using simulators, with Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), to transform the data generated by simulators into realistic input images. Such images can be used both to assess the DNN performance and to retrain the DNN more effectively. We applied our approach to a state-of-the-art DNN performing semantic segmentation and demonstrated that it outperforms a state-of-the-art GAN-based testing solution and several baselines. Specifically, it leads to the largest number of diverse images leading to the worst DNN performance. Further, the images generated with our approach, lead to the highest improvement in DNN performance when used for retraining. In conclusion, we suggest to always integrate GAN components when performing search-driven, simulator-based testing.
在安全性关键系统(例如自动驾驶汽车和机器人)中,深度神经网络(DNN)已成为计算机视觉任务的关键组成部分,特别是在语义分割方面。此外,由于无法通过对代码的检查和分析来评估DNN的行为,因此测试自动化已成为对DNN可靠性建立信心的一项基本活动。然而,最先进的自动化测试解决方案在很大程度上依赖于模拟器,而模拟器的逼真度总是不完美的,从而影响测试结果的有效性。为了解决这些限制,我们提出将元启发式搜索(用于使用模拟器探索输入空间)与生成对抗网络(GAN)相结合,将模拟器生成的数据转换为逼真的输入图像。这些图像可用于评估DNN的性能并更有效地重新训练DNN。我们将该方法应用于执行语义分割的最先进的DNN,并证明其优于基于GAN的测试解决方案和几个基准测试。具体来说,它生成了导致DNN性能最差的最多样化图像数量最多的图像。此外,使用我们的方法生成的图像在用于重新训练时,对DNN性能的提高最大。总之,我们建议在执行基于搜索和模拟器的测试时始终集成GAN组件。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 5 figures, 13 tables
Summary
针对安全关键系统(如自动驾驶汽车和机器人)中的深度神经网络(DNN)在语义分割等计算机视觉任务中的应用,现有自动化测试解决方案主要依赖模拟器,但其逼真度有限影响测试结果的有效性。本研究结合元启发式搜索和生成对抗网络(GANs),将模拟器生成的数据转化为逼真的输入图像,用于评估DNN性能并更有效地对其进行再训练。实验证明,该方法优于现有GAN测试解决方案和其他基线方法,能生成更多导致DNN性能下降的图像,并显著提高DNN的重新训练效果。建议在进行基于搜索的模拟器测试时,应整合GAN组件。
Key Takeaways
- 安全关键系统中深度神经网络(DNN)在语义分割等计算机视觉任务中扮演重要角色。
- 当前自动化测试主要依赖模拟器,但其逼真度有限。
- 提出结合元启发式搜索和GANs的方法,将模拟器数据转化为逼真输入图像。
- 该方法不仅能有效评估DNN性能,还能用于更有效地再训练DNN。
- 该方法优于现有GAN测试解决方案和其他基线方法,生成更多导致DNN性能下降的图像。
- 使用该方法生成的图像进行再训练,能显著提高DNN性能。
点此查看论文截图