⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-25 更新
FaceLift: Single Image to 3D Head with View Generation and GS-LRM
Authors:Weijie Lyu, Yi Zhou, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Zhixin Shu
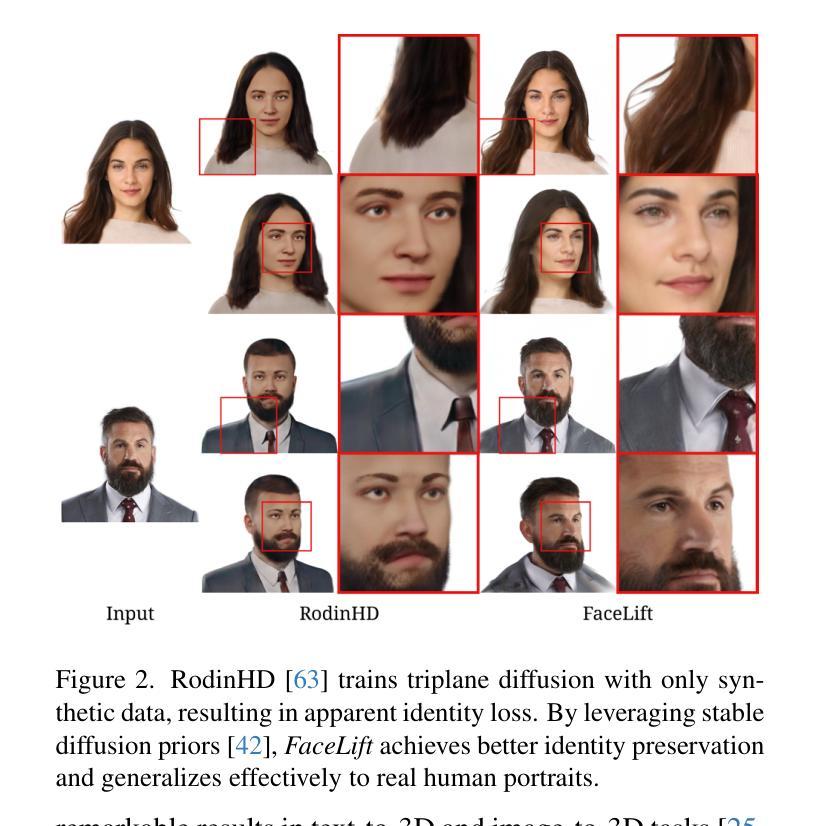
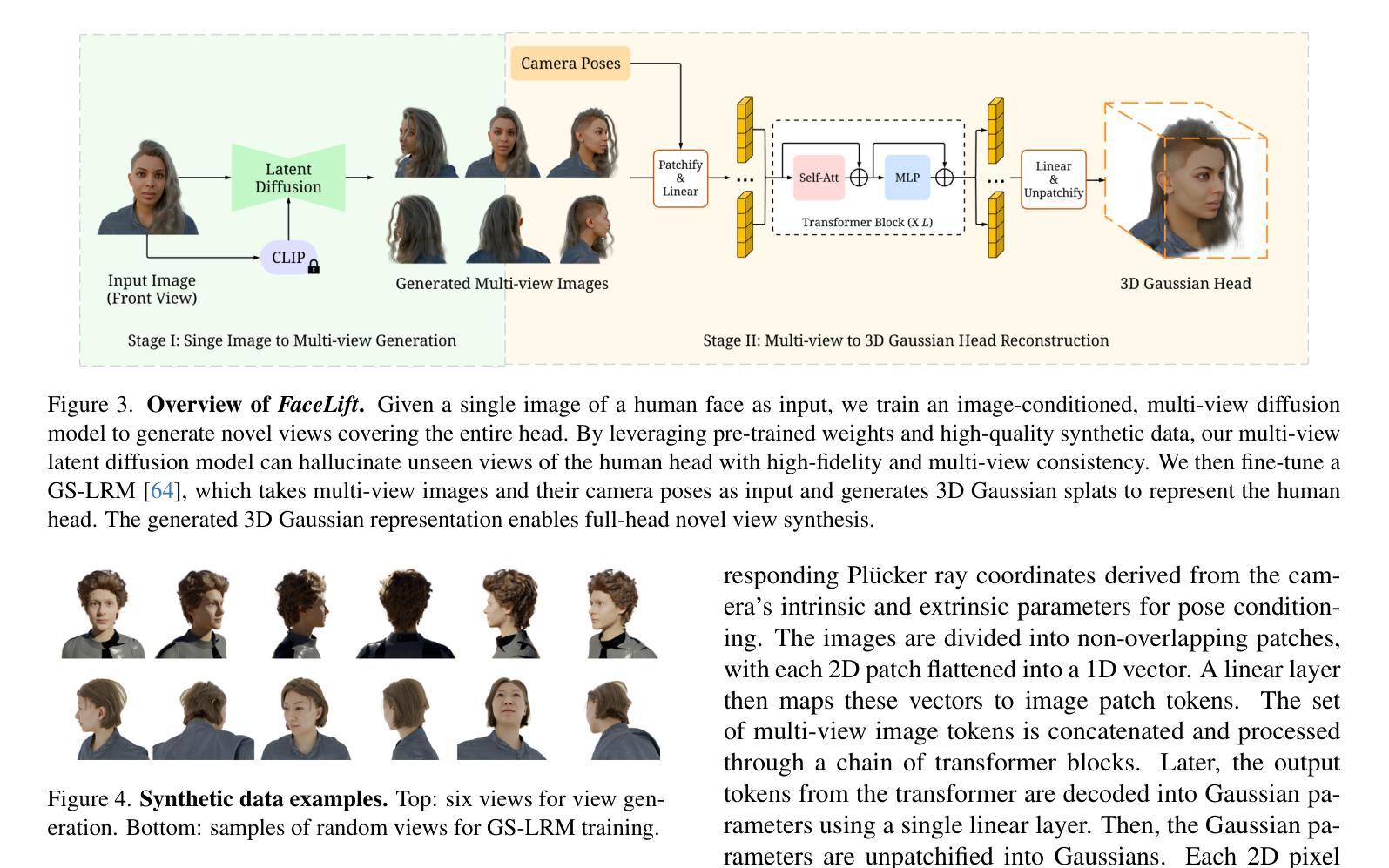
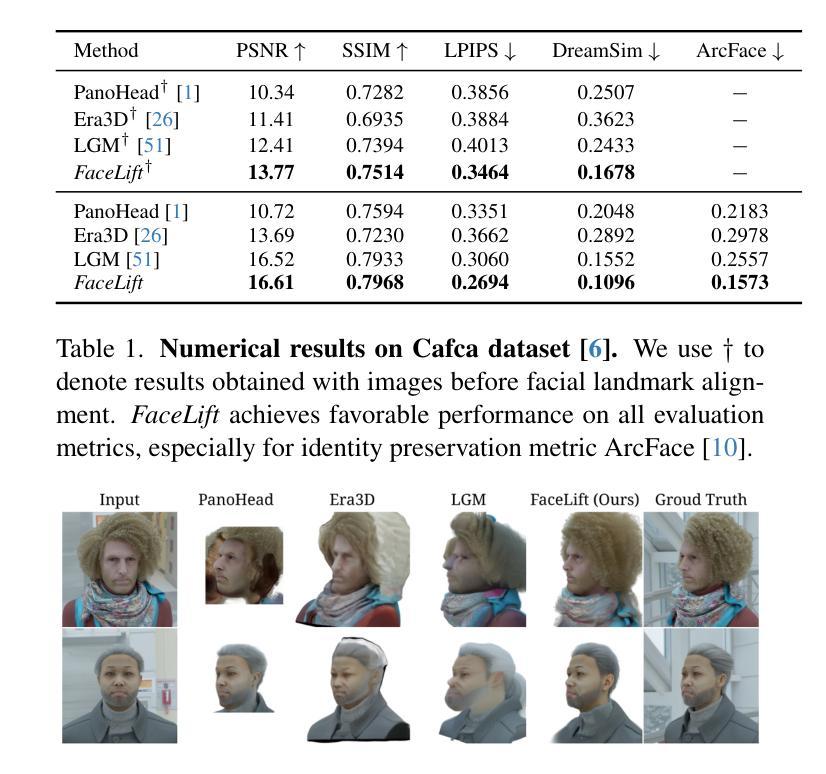
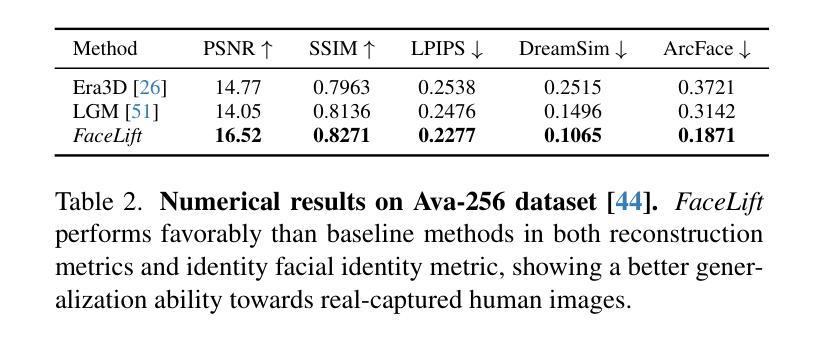
We present FaceLift, a feed-forward approach for rapid, high-quality, 360-degree head reconstruction from a single image. Our pipeline begins by employing a multi-view latent diffusion model that generates consistent side and back views of the head from a single facial input. These generated views then serve as input to a GS-LRM reconstructor, which produces a comprehensive 3D representation using Gaussian splats. To train our system, we develop a dataset of multi-view renderings using synthetic 3D human head as-sets. The diffusion-based multi-view generator is trained exclusively on synthetic head images, while the GS-LRM reconstructor undergoes initial training on Objaverse followed by fine-tuning on synthetic head data. FaceLift excels at preserving identity and maintaining view consistency across views. Despite being trained solely on synthetic data, FaceLift demonstrates remarkable generalization to real-world images. Through extensive qualitative and quantitative evaluations, we show that FaceLift outperforms state-of-the-art methods in 3D head reconstruction, highlighting its practical applicability and robust performance on real-world images. In addition to single image reconstruction, FaceLift supports video inputs for 4D novel view synthesis and seamlessly integrates with 2D reanimation techniques to enable 3D facial animation. Project page: https://weijielyu.github.io/FaceLift.
我们提出了FaceLift,这是一种前馈方法,可以从单张图像快速生成高质量、360度的头部重建。我们的流程首先采用多视角潜在扩散模型,根据单张面部输入生成一致的侧面和背面视角。这些生成的视角然后作为GS-LRM重建器的输入,使用高斯splat生成全面的3D表示。为了训练我们的系统,我们使用合成3D人头数据集开发了一个多视角渲染数据集。基于扩散的多视角生成器只接受合成头部图像进行训练,而GS-LRM重建器首先在Objaverse上进行初步训练,然后在合成头部数据上进行微调。FaceLift擅长在不同视角之间保持身份一致性和视角一致性。尽管只接受合成数据进行训练,但FaceLift在真实图像上表现出令人印象深刻的泛化能力。通过广泛的质量和数量评估,我们证明了FaceLift在3D头部重建方面优于最新技术,突出了其在真实图像上的实用性和稳健性能。除了单图像重建外,FaceLift还支持视频输入进行4D新颖视角合成,并与2D再动画技术无缝集成以实现3D面部动画。项目页面:https://weijielyu.github.io/FaceLift。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://weijielyu.github.io/FaceLift
Summary
FaceLift是一种基于前馈方法的快速高质量单图像360度头部重建技术。它通过多视角潜在扩散模型生成一致的侧面和背面视图,然后利用GS-LRM重建器生成全面的3D表示。尽管仅在合成数据上进行训练,FaceLift在真实图像上表现出卓越的通用化能力。此外,FaceLift还支持视频输入以实现4D新颖视图合成,并与2D动画技术无缝集成以实现3D面部动画。
Key Takeaways
- FaceLift是一种基于前馈方法的快速高质量头部重建技术。
- 通过多视角潜在扩散模型生成侧面和背面视图。
- GS-LRM重建器生成全面的3D表示。
- 仅用合成数据训练,但在真实图像上表现出良好的通用化能力。
- 支持视频输入以实现4D新颖视图合成。
- 与2D动画技术无缝集成以实现3D面部动画。
点此查看论文截图


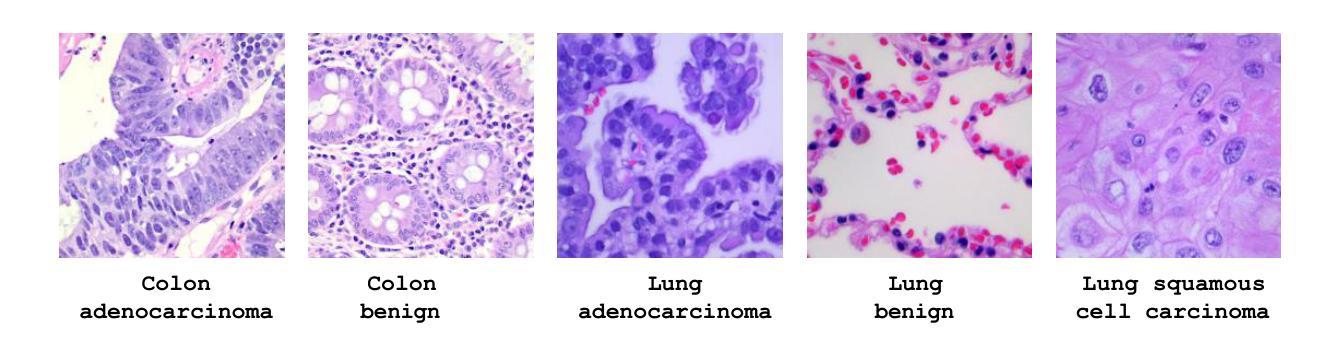
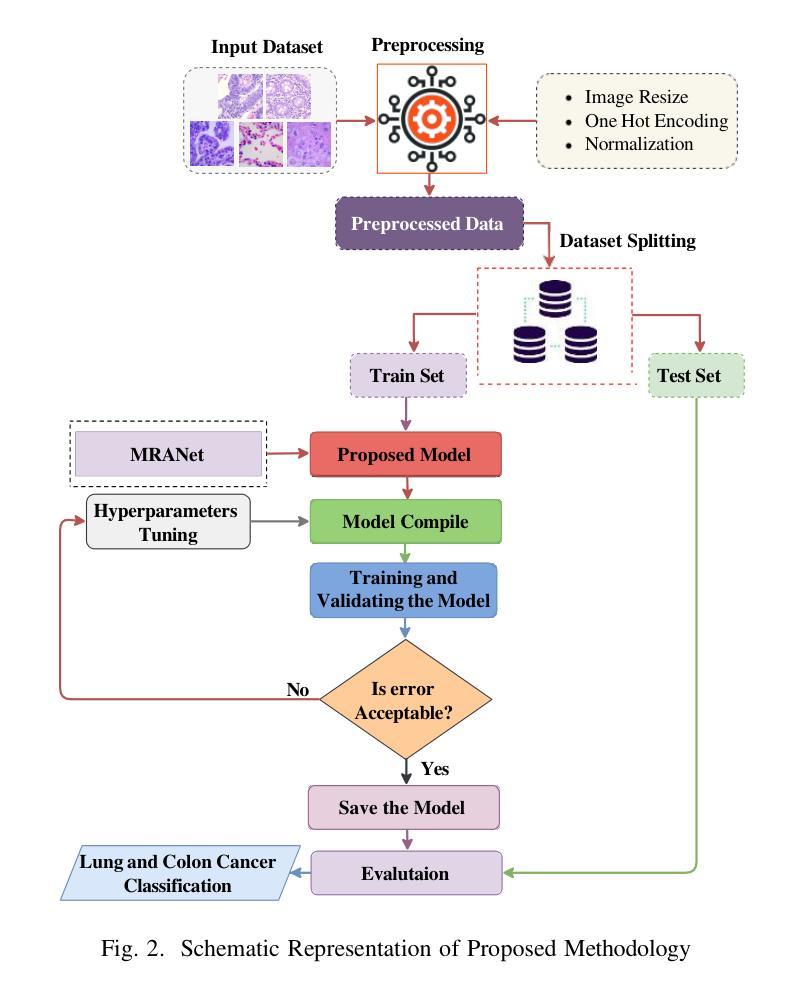
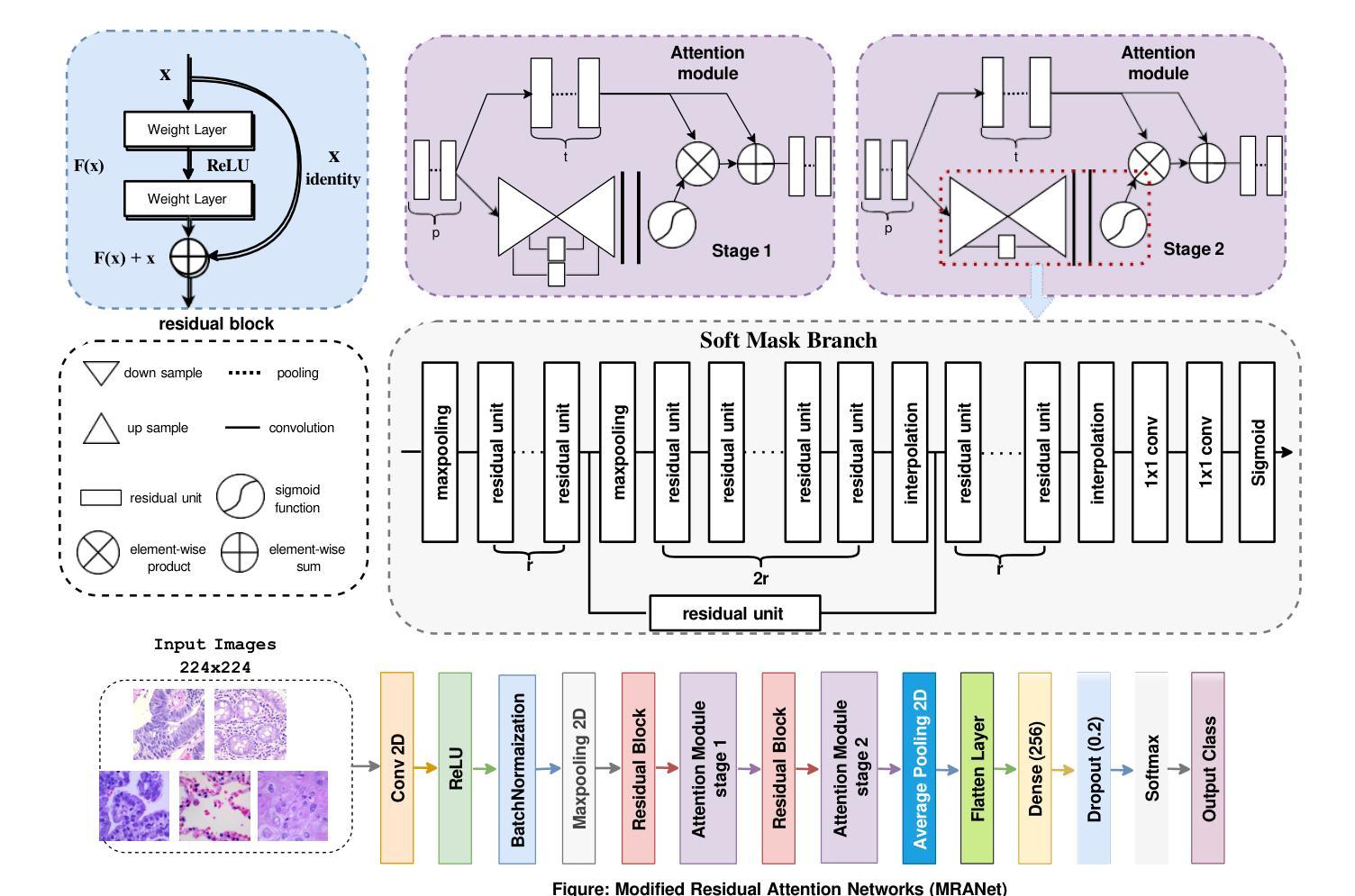
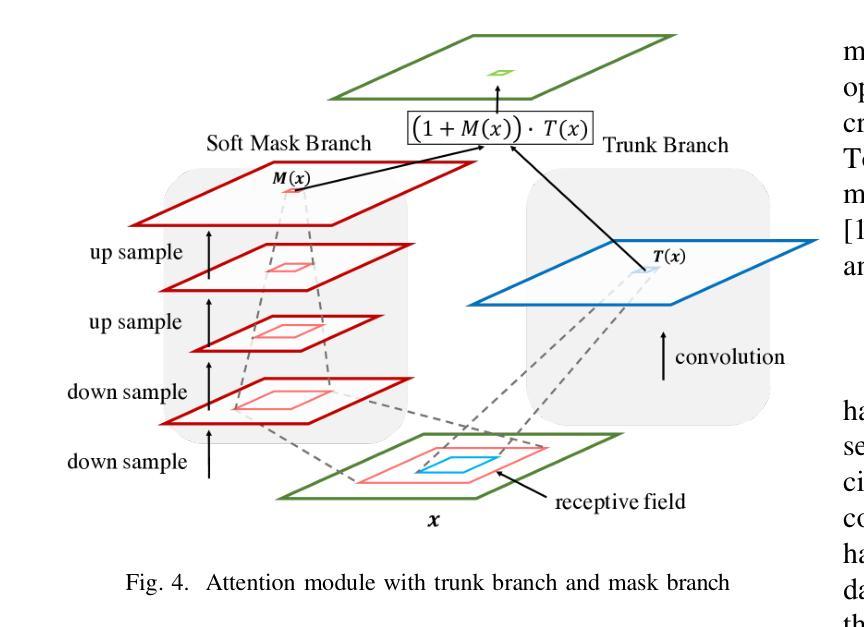
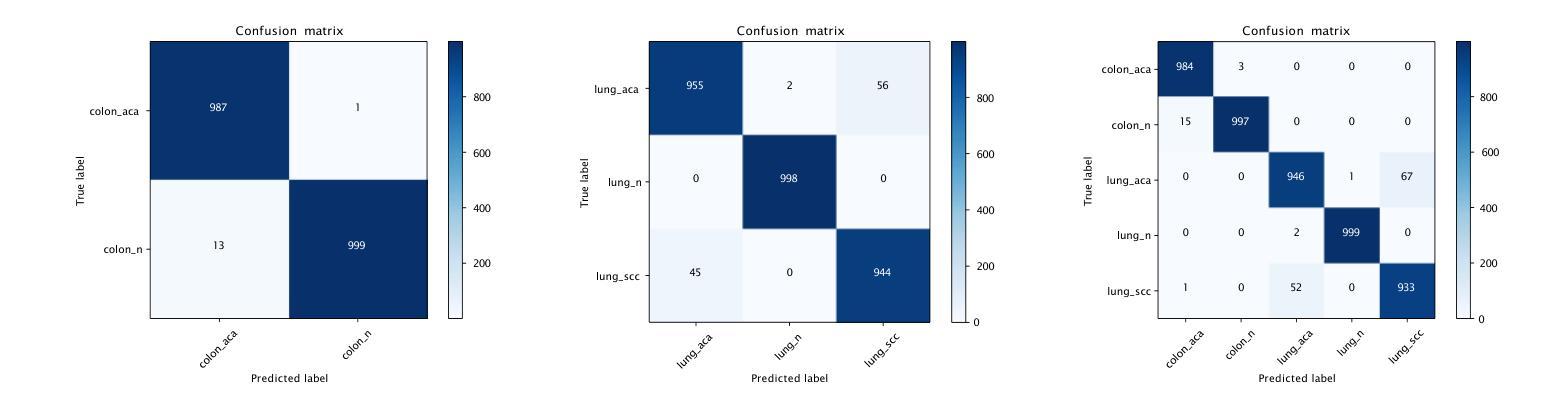
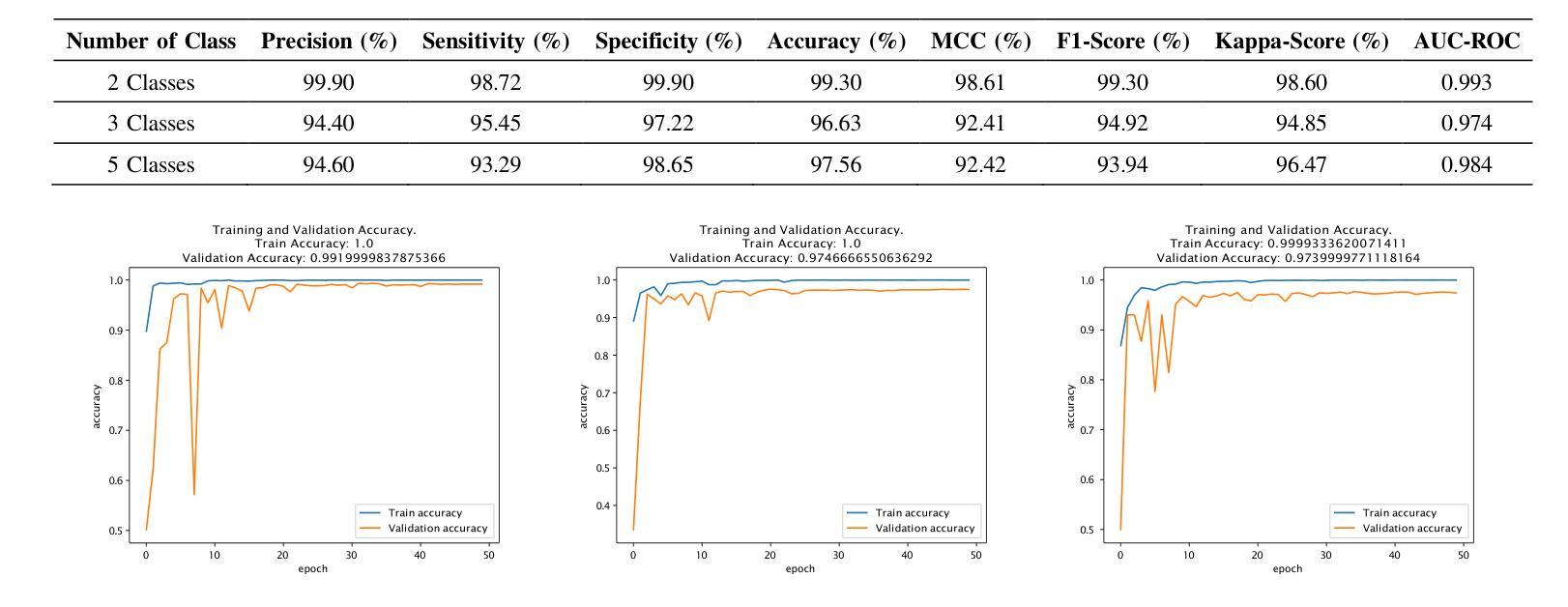
MRANet: A Modified Residual Attention Networks for Lung and Colon Cancer Classification
Authors:Diponkor Bala, S M Rakib Ul Karim, Rownak Ara Rasul
Lung and colon cancers are predominant contributors to cancer mortality. Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. By utilizing imaging technology in different image detection, learning models have shown promise in automating cancer classification from histopathological images. This includes the histopathological diagnosis, an important factor in cancer type identification. This research focuses on creating a high-efficiency deep-learning model for identifying lung and colon cancer from histopathological images. We proposed a novel approach based on a modified residual attention network architecture. The model was trained on a dataset of 25,000 high-resolution histopathological images across several classes. Our proposed model achieved an exceptional accuracy of 99.30%, 96.63%, and 97.56% for two, three, and five classes, respectively; those are outperforming other state-of-the-art architectures. This study presents a highly accurate deep learning model for lung and colon cancer classification. The superior performance of our proposed model addresses a critical need in medical AI applications.
肺癌和结肠癌是导致癌症死亡率较高的两种疾病,早期准确诊断对有效治疗至关重要。通过利用不同图像检测中的成像技术,学习模型在自动从组织病理学图像进行癌症分类方面显示出巨大的潜力,这包括组织病理学诊断,这是识别癌症类型的重要因素。本研究致力于创建一个高效的深度学习模型,用于从组织病理学图像中识别肺癌和结肠癌。我们提出了一种基于改进后的残差注意力网络架构的新方法。该模型在包含多个类别的25,000张高分辨率组织病理学图像数据集上进行训练。我们提出的模型在两个类别、三个类别和五个类别的准确率分别达到了惊人的99.30%、96.63%和97.56%,超过了其他先进的架构。本研究提出了一种用于肺癌和结肠癌分类的高精度深度学习模型。我们提出的模型的卓越性能满足了医疗人工智能应用中的关键需求。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
肺癌和结肠癌是癌症死亡的主要贡献者,早期准确诊断对有效治疗至关重要。利用图像检测中的成像技术,学习模型在自动从病理图像进行癌症分类方面显示出潜力。本文重点介绍了一种基于改进型残差注意力网络架构的高效深度学习模型,用于识别肺癌和结肠癌。该模型在多个类别的25000张高分辨率病理图像数据集上进行训练,对二、三、五类分类的准确率分别达到了99.30%、96.63%和97.56%,超过了其他最先进架构的性能。本研究为解决医学人工智能应用中的迫切需求提供了一个高度准确的深度学习模型。
Key Takeaways
- 肺癌和结肠癌是癌症死亡的主要原因,早期准确诊断对治疗至关重要。
- 深度学习模型在自动从病理图像进行癌症分类方面表现出潜力。
- 研究提出了一种基于改进型残差注意力网络架构的深度学习模型,用于识别肺癌和结肠癌。
- 模型在多个类别的病理图像数据集上进行训练,取得了高准确率。
- 模型性能超过了其他最先进架构,为解决医学人工智能应用中的需求提供了有效方法。
- 该模型的应用有助于提升癌症诊断的准确性和效率。
点此查看论文截图

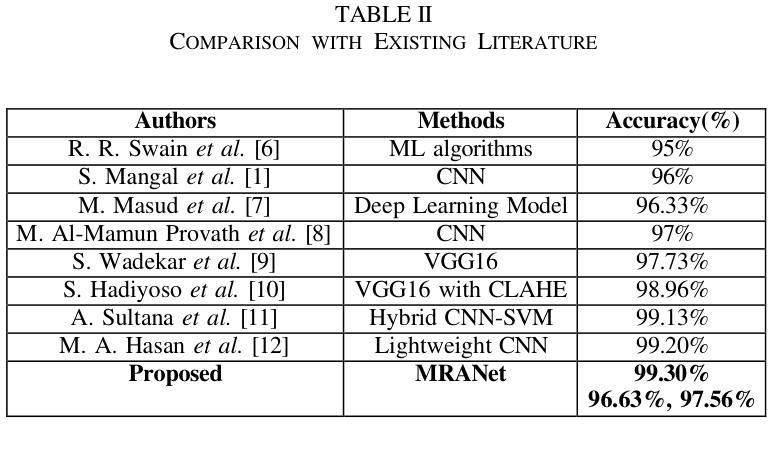
Assessment of Deep-Learning Methods for the Enhancement of Experimental Low Dose Dental CBCT Volumes
Authors:Louise Friot–Giroux, Françoise Peyrin, Voichiţa Maxim
Cone-beam tomography enables rapid 3D acquisitions, making it a suitable imaging modality for dental imaging. However, as with all X-ray techniques, the main challenge is to reduce the dose while maintaining good image quality. Moreover, dental reconstructions face a series of issues stemming from truncated projections as well as metal and cone beam artifacts. The aim here is to investigate the ability of neural networks to improve the quality of 3D CBCT dental images at low doses. We test different configurations of convolutional neural networks, trained in a supervised way to reduce artifacts and noise present in analytically reconstructed volumes. In a study on 32 experimental cone beam volumes, we show their capacity to preserve and enhance details while still reducing the artifacts. The best results are obtained with a 3D U-Net which compares advantageously with a TV regularized iterative method and is considerably faster.
锥形束断层扫描技术能够实现快速的三维采集,使其成为牙科成像的合适成像方式。然而,与所有X射线技术一样,主要挑战是在保持良好图像质量的同时减少剂量。此外,牙科重建还面临一系列由截断投影以及金属和锥形束伪影引起的问题。这里的目标是研究神经网络在提高低剂量三维锥形束CT牙科图像质量方面的能力。我们测试了不同配置的卷积神经网络,以监督学习的方式进行训练,以减少分析重建体积中存在的伪影和噪声。在32个实验性锥形束体积的研究中,我们展示了它们在保留和增强细节的同时减少伪影的能力。使用三维U-Net获得最佳结果,它较TV正则化迭代方法有明显的优势且速度更快。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学锥束层析技术可迅速实现三维成像,适合牙科成像。其挑战在于如何在保持良好图像质量的同时降低剂量。研究旨在探索神经网络对低剂量三维CBCT牙科图像质量提升的效果。测试了不同配置的卷积神经网络,通过监督学习的方式训练以减少解析重建体积中的伪影和噪声。在32个实验锥束体积的研究中,证明了这些网络在保留和增强细节的同时减少伪影的能力。最佳结果由三维U-Net获得,与TV正则化迭代方法相比具有优势,且速度更快。
Key Takeaways
- 锥束层析技术可实现快速三维成像,适用于牙科成像。
- 降低剂量同时保持良好图像质量是其主要挑战。
- 研究旨在探索神经网络在提升低剂量三维CBCT牙科图像质量方面的作用。
- 通过监督学习训练不同配置的卷积神经网络以减少解析重建体积中的伪影和噪声。
- 在实验研究中,神经网络能够保留和增强细节,同时减少伪影。
- 三维U-Net获得最佳结果,与现有方法相比具有优势。
点此查看论文截图

PointVoxelFormer – Reviving point cloud networks for 3D medical imaging
Authors:Mattias Paul Heinrich
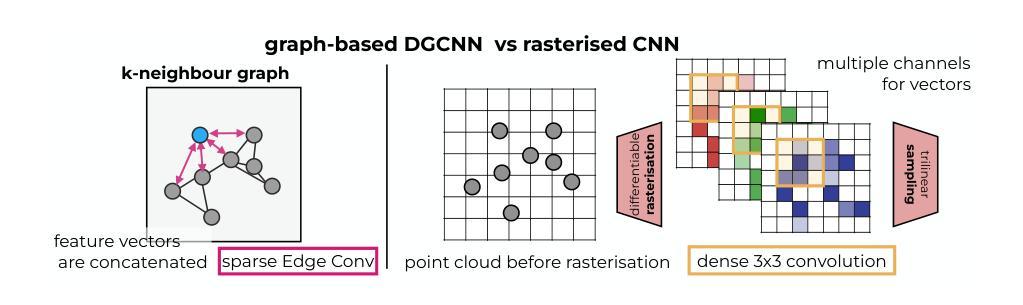
Point clouds are a very efficient way to represent volumetric data in medical imaging. First, they do not occupy resources for empty spaces and therefore can avoid trade-offs between resolution and field-of-view for voxel-based 3D convolutional networks (CNNs) - leading to smaller and robust models. Second, they provide a modality agnostic representation of anatomical surfaces and shapes to avoid domain gaps for generic geometric models. Third, they remove identifiable patient-specific information and may increase privacy preservation when publicly sharing data. Despite their benefits, point clouds are still underexplored in medical imaging compared to volumetric 3D CNNs and vision transformers. To date both datasets and stringent studies on comparative strengths and weaknesses of methodological choices are missing. Interactions and information exchange of spatially close points - e.g. through k-nearest neighbour graphs in edge convolutions or point transformations - within points clouds are crucial for learning geometrically meaningful features but may incur computational bottlenecks. This work presents a hybrid approach that combines point-wise operations with intermediate differentiable rasterisation and dense localised CNNs. For deformable point cloud registration, we devise an early fusion scheme for coordinate features that joins both clouds within a common reference frame and is coupled with an inverse consistent, two-step alignment architecture. Our extensive experiments on three different datasets for segmentation and registration demonstrate that our method, PointVoxelFormer, enables very compact models that excel with threefold speed-ups, fivefold memory reduction and over 30% registration error reduction against edge convolutions and other state-of-the-art models in geometric deep learning.
点云是医学成像中表示体积数据的一种非常高效的方式。首先,它们不占用空空间的资源,因此可以避免基于体素的3D卷积网络(CNN)在分辨率和视野之间的权衡,从而带来更小且更稳健的模型。其次,它们提供了一种通用的解剖表面和形状的表示方法,避免了通用几何模型的领域差异。第三,它们消除了可识别患者特定的信息,在公开共享数据时可能增加隐私保护。尽管点云具有诸多优点,但在医学成像中,与体积3D CNN和视觉变压器相比,对点云的研究仍然不足。到目前为止,缺少数据集以及对方法论选择比较优势和劣势的严格研究。点云内部空间上接近的点之间的交互和信息交换至关重要(例如,通过边缘卷积中的k最近邻图或点变换),这对于学习几何上有意义的特征可能是计算瓶颈。这项工作提出了一种结合点操作和中间可微分光栅化以及密集局部CNN的混合方法。对于可变形点云注册,我们为坐标特征设计了一种早期融合方案,该方案将两个云内嵌到一个共同参考框架中,并与逆向一致的两步对齐架构相结合。我们在三个不同数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,我们的PointVoxelFormer方法使模型非常紧凑,在分割和注册方面实现了三倍的速度提升、五倍的内存减少和超过30%的注册错误率降低,相较于边缘卷积和其他几何深度学习领域的最先进模型表现出色。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 4 figures
Summary
点云在医学成像中代表体积数据是一种非常高效的方式。它可避免对空空间的资源占用,为基于体素的3D卷积网络(CNN)带来更小、更稳健的模型。点云还提供了通用的几何模型表示,可避免领域差距,同时提高隐私保护。尽管点云在医学成像中的应用仍相对较少,但本文提出了一种结合点操作和中间可微分栅格化的混合方法,以及与可变形点云注册的早期融合方案。实验表明,该方法实现了非常紧凑的模型,具有三倍速度提升、五倍内存减少和超过30%的注册误差减少。
Key Takeaways
- 点云在医学成像中代表体积数据具有高效率。
- 点云可避免对空空间的资源占用,为基于体素的3D卷积网络带来更小、更稳健的模型。
- 点云提供了通用的几何模型表示,有助于避免领域差距和提高隐私保护。
- 与其他方法相比,点云在医学成像中的应用仍然相对较少。
- 本文提出了一种结合点操作和中间可微分栅格化的混合方法。
- 提出了与可变形点云注册的早期融合方案。
点此查看论文截图

QTSeg: A Query Token-Based Architecture for Efficient 2D Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Phuong-Nam Tran, Nhat Truong Pham, Duc Ngoc Minh Dang, Eui-Nam Huh, Choong Seon Hong
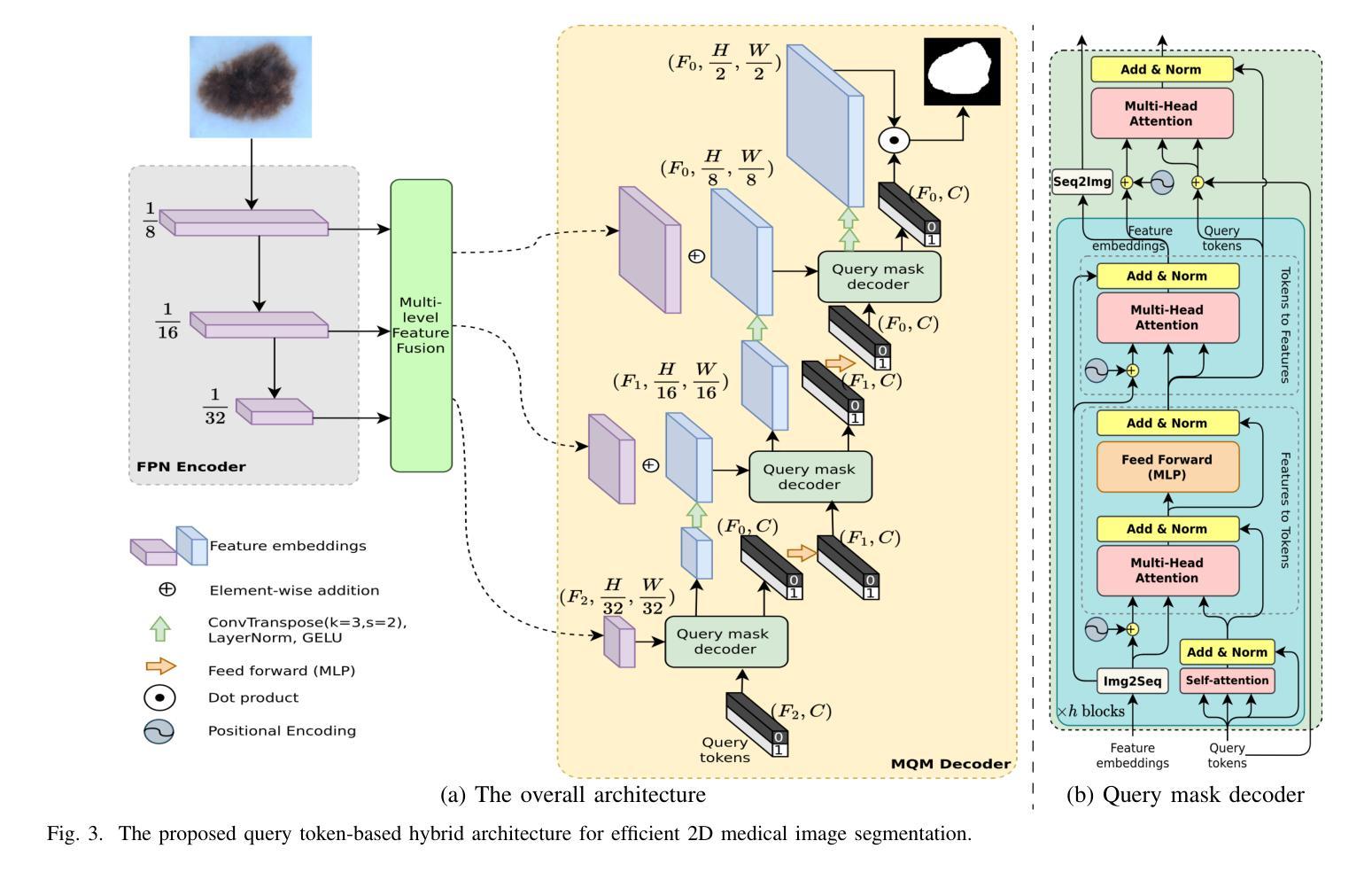
Medical image segmentation is crucial in assisting medical doctors in making diagnoses and enabling accurate automatic diagnosis. While advanced convolutional neural networks (CNNs) excel in segmenting regions of interest with pixel-level precision, they often struggle with long-range dependencies, which is crucial for enhancing model performance. Conversely, transformer architectures leverage attention mechanisms to excel in handling long-range dependencies. However, the computational complexity of transformers grows quadratically, posing resource-intensive challenges, especially with high-resolution medical images. Recent research aims to combine CNN and transformer architectures to mitigate their drawbacks and enhance performance while keeping resource demands low. Nevertheless, existing approaches have not fully leveraged the strengths of both architectures to achieve high accuracy with low computational requirements. To address this gap, we propose a novel architecture for 2D medical image segmentation (QTSeg) that leverages a feature pyramid network (FPN) as the image encoder, a multi-level feature fusion (MLFF) as the adaptive module between encoder and decoder and a multi-query mask decoder (MQM Decoder) as the mask decoder. In the first step, an FPN model extracts pyramid features from the input image. Next, MLFF is incorporated between the encoder and decoder to adapt features from different encoder stages to the decoder. Finally, an MQM Decoder is employed to improve mask generation by integrating query tokens with pyramid features at all stages of the mask decoder. Our experimental results show that QTSeg outperforms state-of-the-art methods across all metrics with lower computational demands than the baseline and the existing methods. Code is available at https://github.com/tpnam0901/QTSeg (v0.1.0)
医学图像分割对于协助医生进行诊断和实现准确的自动诊断至关重要。虽然先进的卷积神经网络(CNNs)在分割感兴趣区域方面具有像素级精度,但它们往往在处理长距离依赖关系方面表现挣扎,这对于提高模型性能至关重要。相反,transformer架构利用注意力机制在处理长距离依赖关系方面表现出色。然而,随着计算复杂度的增长,其复杂度呈现二次方的增长,特别是对于高分辨率医学图像来说资源密集型挑战更加明显。最近的研究旨在结合CNN和transformer架构以缓解它们的缺点并增强性能的同时保持低资源需求。然而,现有的方法尚未充分利用两种架构的优势来实现高准确性并满足低计算要求。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种用于二维医学图像分割(QTSeg)的新型架构,该架构利用特征金字塔网络(FPN)作为图像编码器,多级特征融合(MLFF)作为编码器与解码器之间的自适应模块,以及多查询掩膜解码器(MQM Decoder)作为掩膜解码器。首先,FPN模型从输入图像中提取金字塔特征。然后,MLFF被整合到编码器和解码器之间,以将不同编码器阶段的特征自适应到解码器。最后,使用MQM Decoder通过在与掩膜解码器所有阶段的查询令牌集成中改进掩膜生成。我们的实验结果表明,QTSeg在所有指标上均优于最新方法,并且相对于基线方法和现有方法的计算需求更低。代码可在https://github.com/tpnam0901/QTSeg(v0.1.0)找到。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
医学图像分割对于医生诊断和自动诊断的准确性至关重要。卷积神经网络(CNN)在像素级精确分割感兴趣区域方面表现出色,但在处理长距离依赖关系方面存在不足。相反,基于注意力机制的变压器架构擅长处理长距离依赖关系,但计算复杂度呈二次方增长,对于高分辨率医学图像尤其如此。最近的研究旨在结合CNN和变压器架构以取长补短,同时保持资源需求较低。然而,现有方法并未充分利用两者的优势,实现高准确率且计算量低的目标。为此,我们提出了一种新型的二维医学图像分割架构(QTSeg),它利用特征金字塔网络(FPN)作为图像编码器,多层次特征融合(MLFF)作为编码器和解码器之间的自适应模块,以及多查询掩膜解码器(MQM解码器)作为掩膜解码器。实验结果表明,QTSeg在所有指标上均优于现有先进技术方法,同时相较于基准方法和现有方法的计算需求更低。代码公开于https://github.com/tpnam0901/QTSeg(v0.1.0)。
关键见解
- 医学图像分割对医生诊断和自动诊断的重要性。
- 卷积神经网络(CNN)在处理医学图像分割时的优点和局限性。
- 变压器架构在处理长距离依赖关系方面的优势,及其在高分辨率医学图像中的挑战。
- 现有结合CNN和变压器的方法未能充分利用两者的优势。
- 提出的QTSeg架构包括特征金字塔网络(FPN)图像编码器、多层次特征融合(MLFF)自适应模块和多查询掩膜解码器(MQM解码器)。
- QTSeg在性能上优于现有技术方法,同时计算需求较低。
点此查看论文截图


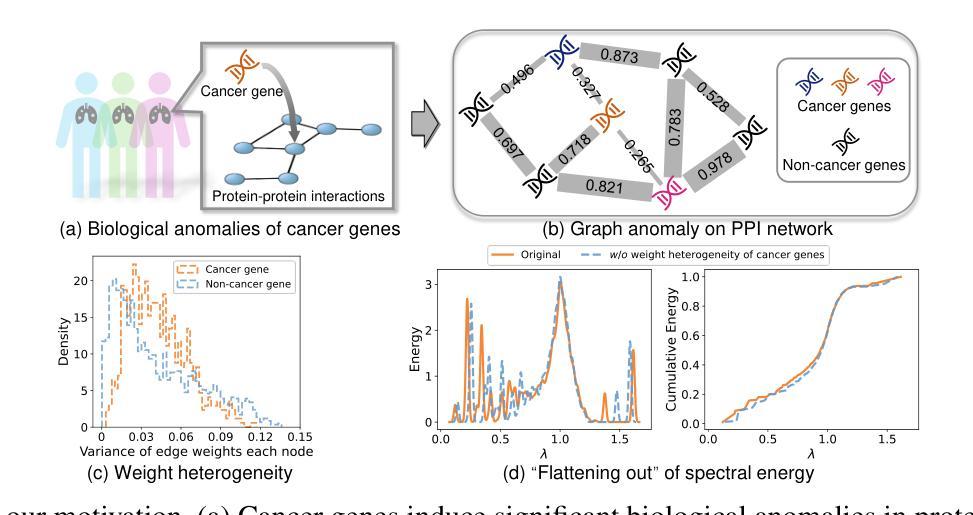
Rethinking Cancer Gene Identification through Graph Anomaly Analysis
Authors:Yilong Zang, Lingfei Ren, Yue Li, Zhikang Wang, David Antony Selby, Zheng Wang, Sebastian Josef Vollmer, Hongzhi Yin, Jiangning Song, Junhang Wu
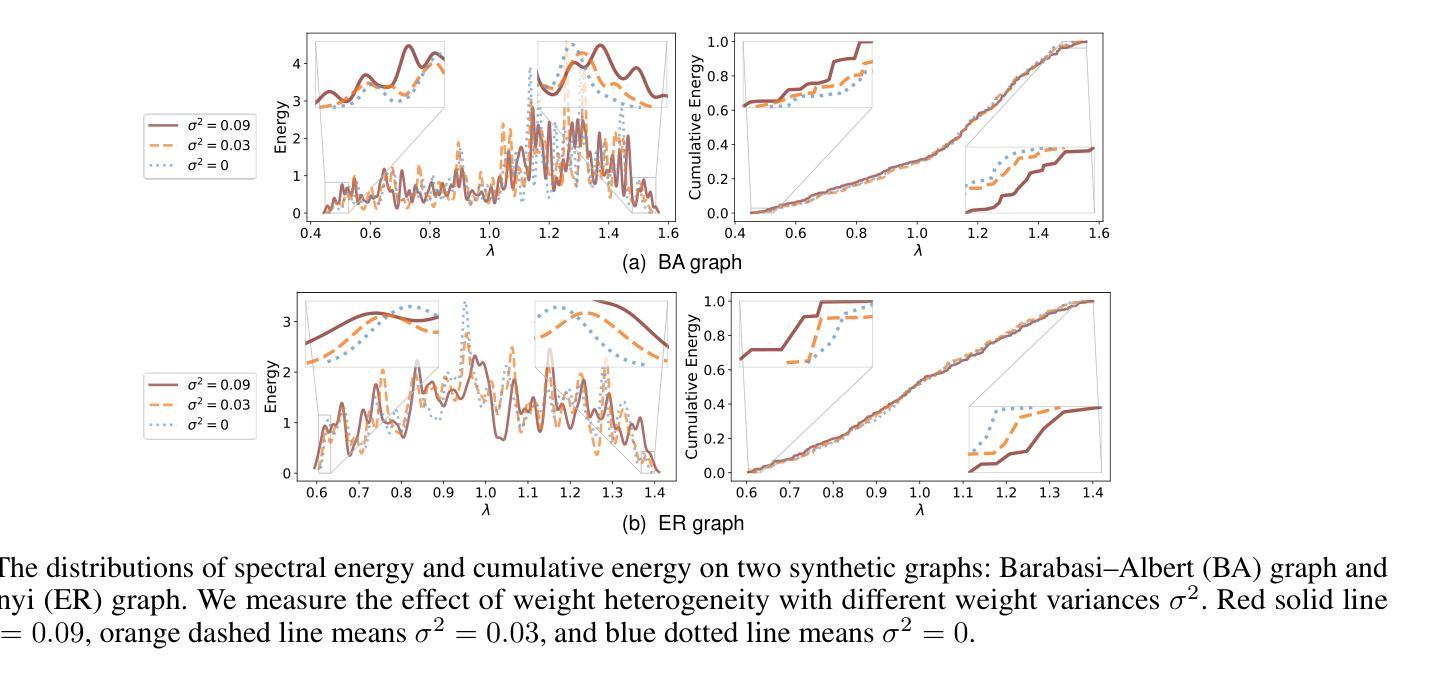
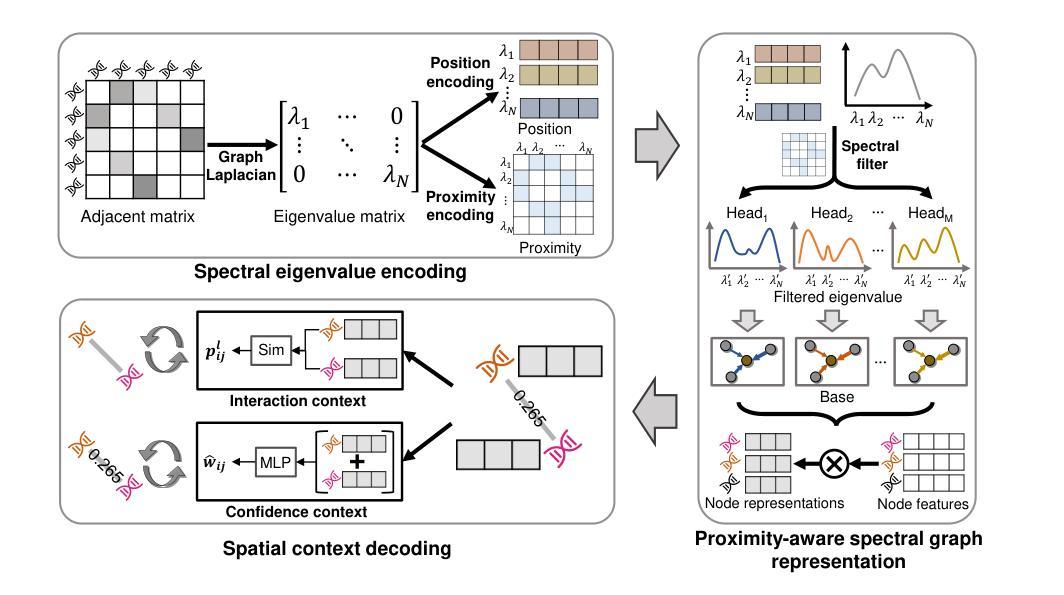
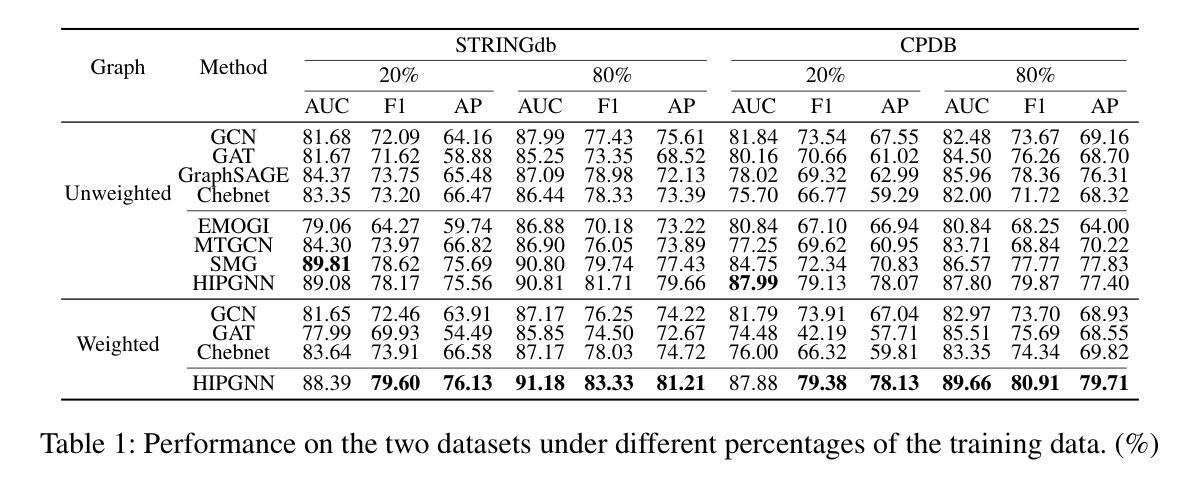
Graph neural networks (GNNs) have shown promise in integrating protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks for identifying cancer genes in recent studies. However, due to the insufficient modeling of the biological information in PPI networks, more faithfully depiction of complex protein interaction patterns for cancer genes within the graph structure remains largely unexplored. This study takes a pioneering step toward bridging biological anomalies in protein interactions caused by cancer genes to statistical graph anomaly. We find a unique graph anomaly exhibited by cancer genes, namely weight heterogeneity, which manifests as significantly higher variance in edge weights of cancer gene nodes within the graph. Additionally, from the spectral perspective, we demonstrate that the weight heterogeneity could lead to the “flattening out” of spectral energy, with a concentration towards the extremes of the spectrum. Building on these insights, we propose the HIerarchical-Perspective Graph Neural Network (HIPGNN) that not only determines spectral energy distribution variations on the spectral perspective, but also perceives detailed protein interaction context on the spatial perspective. Extensive experiments are conducted on two reprocessed datasets STRINGdb and CPDB, and the experimental results demonstrate the superiority of HIPGNN.
图神经网络(GNNs)在最近的研究中显示出在整合蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用(PPI)网络以识别癌症基因的潜力。然而,由于PPI网络中生物信息建模的不足,对图结构内癌症基因的复杂蛋白质相互作用模式的更真实描述仍然未被充分探索。本研究率先迈出一步,将蛋白质相互作用中的生物异常与由癌症基因引起的统计图异常联系起来。我们发现了一种特殊的癌症基因所表现出的图异常现象,即权重异质性,它表现为图中癌症基因节点边权重的方差显著增大。此外,从光谱的角度,我们证明了权重异质性可能导致光谱能量的“平坦化”,并集中在光谱的极端部分。基于这些见解,我们提出了分层视角图神经网络(HIPGNN),它不仅在光谱视角上确定光谱能量分布的变化,而且在空间视角上感知详细的蛋白质相互作用上下文。在两个经过处理的STRINGdb和CPDB数据集上进行了广泛的实验,实验结果表明HIPGNN的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF It has been accepted by the AAAI 2025 conference
Summary
该研究探索了图神经网络(GNNs)在整合蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用(PPI)网络中的潜力,以识别癌症基因。针对PPI网络中生物信息建模不足的问题,该研究首次将癌症基因引起的蛋白质相互作用中的生物学异常与图统计异常联系起来。研究发现癌症基因具有独特的图异常现象——权重异质性,表现为图中癌症基因节点边权重的方差显著增大。此外,从光谱角度,该研究展示了权重异质性可能导致光谱能量的“扁平化”,集中在光谱的极端部分。基于这些见解,该研究提出了分层视角图神经网络(HIPGNN),它不仅在光谱视角上确定了光谱能量分布的变化,还在空间视角上感知到了详细的蛋白质相互作用上下文。经过在两个重新处理的数据集STRINGdb和CPDB上的广泛实验,验证了HIPGNN的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 图神经网络(GNNs)在整合蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用(PPI)网络以识别癌症基因方面展现出潜力。
- PPI网络中生物信息建模不足,需要更真实地描绘癌症基因在图形结构中的复杂相互作用模式。
- 癌症基因具有独特的图异常现象——权重异质性,表现为图中癌症基因节点边权重的方差增大。
- 权重异质性可能导致光谱能量的“扁平化”,集中在光谱的极端部分。
- 分层视角图神经网络(HIPGNN)结合了光谱与空间视角,能感知详细的蛋白质相互作用上下文。
- HIPGNN不仅确定了光谱能量分布的变化,还在实验上表现出优越性。
点此查看论文截图

MatchMiner-AI: An Open-Source Solution for Cancer Clinical Trial Matching
Authors:Ethan Cerami, Pavel Trukhanov, Morgan A. Paul, Michael J. Hassett, Irbaz B. Riaz, James Lindsay, Emily Mallaber, Harry Klein, Gufran Gungor, Matthew Galvin, Stephen C. Van Nostrand, Joyce Yu, Tali Mazor, Kenneth L. Kehl
Clinical trials drive improvements in cancer treatments and outcomes. However, most adults with cancer do not participate in trials, and trials often fail to enroll enough patients to answer their scientific questions. Artificial intelligence could accelerate matching of patients to appropriate clinical trials. Here, we describe the development and evaluation of the MatchMiner-AI pipeline for clinical trial searching and ranking. MatchMiner-AI focuses on matching patients to potential trials based on core criteria describing clinical “spaces,” or disease contexts, targeted by a trial. It aims to accelerate the human work of identifying potential matches, not to fully automate trial screening. The pipeline includes modules for extraction of key information from a patient’s longitudinal electronic health record; rapid ranking of candidate trial-patient matches based on embeddings in vector space; and classification of whether a candidate match represents a reasonable clinical consideration. Code and synthetic data are available at https://huggingface.co/ksg-dfci/MatchMiner-AI . Model weights based on synthetic data are available at https://huggingface.co/ksg-dfci/TrialSpace and https://huggingface.co/ksg-dfci/TrialChecker . A simple cancer clinical trial search engine to demonstrate pipeline components is available at https://huggingface.co/spaces/ksg-dfci/trial_search_alpha .
临床试验推动了癌症治疗和结果的改进。然而,大多数癌症患者并没有参与到临床试验中,而且试验往往无法招募到足够的患者来回答其科学问题。人工智能可以加速患者与合适的临床试验的匹配。在这里,我们描述了MatchMiner-AI管道的临床试验搜索和排名的开发与评价。MatchMiner-AI专注于根据描述临床试验所针对的临床“空间”或疾病背景的核心标准,为患者匹配潜在的试验。它的目标是为了加速识别潜在匹配的人工工作,而不是完全自动化试验筛选。该管道包括从患者的纵向电子健康记录中提取关键信息的模块;基于向量空间中的嵌入快速排列候选试验患者匹配;以及分类候选匹配是否代表合理的临床考虑。代码和合成数据可在https://huggingface.co/ksg-dfci/MatchMiner-AI上找到。基于合成数据的模型权重可在https://huggingface.co/ksg-dfci/TrialSpace和https://huggingface.co/ksg-dfci/TrialChecker上找到。一个简单的癌症临床试验搜索引擎,用于展示管道组件,可在https://huggingface.co/spaces/ksg-dfci/trial_search_alpha上访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人工智能匹配患者与合适的临床试验可加速癌症治疗与成果的改进。MatchMiner-AI管道的开发与评估用于临床试验搜索与排名。其重点是根据描述临床试验核心标准的临床“空间”或疾病背景,为患者匹配潜在试验。旨在加速人类识别潜在匹配的工作,而非完全自动化试验筛选。包括从患者纵向电子病历中提取关键信息的模块、基于向量空间嵌入快速排名试验患者匹配以及分类候选匹配是否代表合理的临床考量。相关资源和模型权重可通过特定链接获取。
Key Takeaways
- 临床试验对癌症治疗与成果的改进至关重要,但患者参与度不足和患者招募困难是常见问题。
- MatchMiner-AI旨在通过人工智能加速患者与合适临床试验的匹配过程。
- MatchMiner-AI管道包括从患者电子病历中提取关键信息的模块。
- 该系统基于向量空间嵌入进行试验患者匹配的快速排名。
- MatchMiner-AI旨在辅助人类识别潜在匹配,而非完全自动化试验筛选。
- 合理利用人工智能的技术和资源可通过https://huggingface.co/ksg-dfci/MatchMiner-AI等链接获取。
点此查看论文截图



The Potential of Convolutional Neural Networks for Cancer Detection
Authors:Hossein Molaeian, Kaveh Karamjani, Sina Teimouri, Saeed Roshani, Sobhan Roshani
Early detection of cancer is critical in improving treatment outcomes and increasing survival rates, particularly for common cancers such as lung, breast, and prostate which collectively contribute to a significant global mortality burden. With advancements in imaging technologies and data processing, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have emerged as a powerful tool for analyzing and classifying medical images, enabling more precise cancer detection. This paper provides a comprehensive review of recent studies leveraging CNN models for detecting ten different types of cancer. Each study employs distinct CNN architectures to identify patterns associated with these cancers, utilizing diverse datasets. Key differences and strengths of these architectures are meticulously compared and analyzed, highlighting their efficacy in improving early detection. Beyond reviewing the performance and limitations of CNN-based cancer detection methods, this study explores the feasibility of integrating CNNs into clinical settings as an early detection tool, potentially complementing or replacing traditional methods. Despite significant progress, challenges remain, including data diversity, result interpretation, and ethical considerations. By identifying the best-performing CNN architectures and providing a comparative analysis, this study aims to contribute a comprehensive perspective on the application of CNNs in cancer detection and their role in advancing diagnostic capabilities in healthcare.
癌症的早期发现对于提高治疗效果和增加存活率至关重要,特别是对于肺癌、乳腺癌和前列腺癌等常见癌症,它们共同造成了全球大量的死亡负担。随着成像技术和数据处理的发展,卷积神经网络(CNNs)已经成为分析和分类医学图像的强大工具,使癌症检测更加精确。本文全面回顾了最近利用CNN模型检测十种不同类型癌症的研究。每项研究采用不同的CNN架构来识别与这些癌症相关的模式,并利用各种数据集。本文仔细比较和分析这些架构的主要差异和优点,突出其在提高早期检测方面的有效性。除了回顾基于CNN的癌症检测方法的性能和局限性外,本研究还探讨了将CNN集成到临床环境中作为早期检测工具的可行性,可能补充或替代传统方法。尽管取得了显著进展,但仍存在挑战,包括数据多样性、结果解释和伦理考虑。通过确定表现最佳的CNN架构并提供比较分析,本研究旨在为CNN在癌症检测中的应用及其在提高医疗诊断能力中的作用提供全面视角。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文综述了利用卷积神经网络(CNN)模型检测包括肺癌、乳腺癌和前列腺癌在内的十种不同类型癌症的最新研究。研究比较分析了不同CNN架构的优缺点,并强调了它们在提高早期检测方面的有效性。除了回顾CNN在癌症检测中的应用及其局限性,本文还探讨了将CNN集成到临床环境中作为早期检测工具的可行性。本文旨在为CNN在癌症检测中的应用提供一个全面的视角,推动医疗诊断能力的提高。
Key Takeaways
- CNN模型被广泛应用于分析和分类医学图像,为癌症检测提供更精确的方法。
- 不同类型的癌症检测采用了多种CNN架构,以识别与癌症相关的模式。
- CNN架构之间的关键差异和优势得到了详细比较和分析。
- CNN在癌症检测中的有效性和局限性得到了评估。
- 将CNN集成到临床环境作为早期检测工具的可行性得到了探讨。
- 尽管有显著进展,但CNN在癌症检测中仍面临数据多样性、结果解读和伦理考虑等挑战。
点此查看论文截图

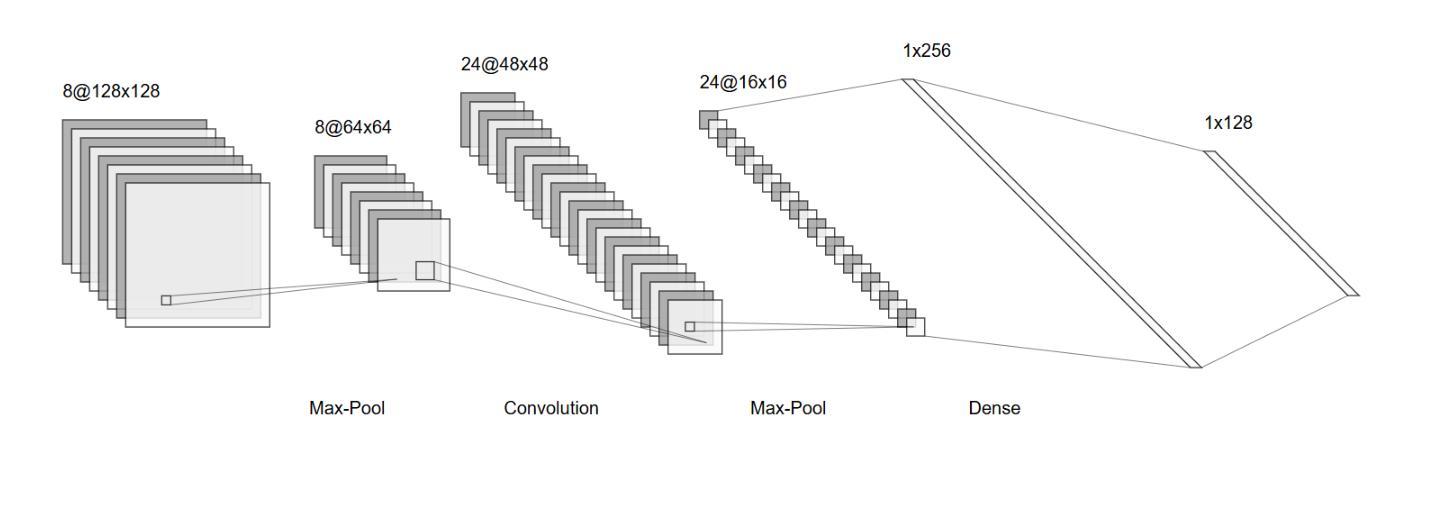
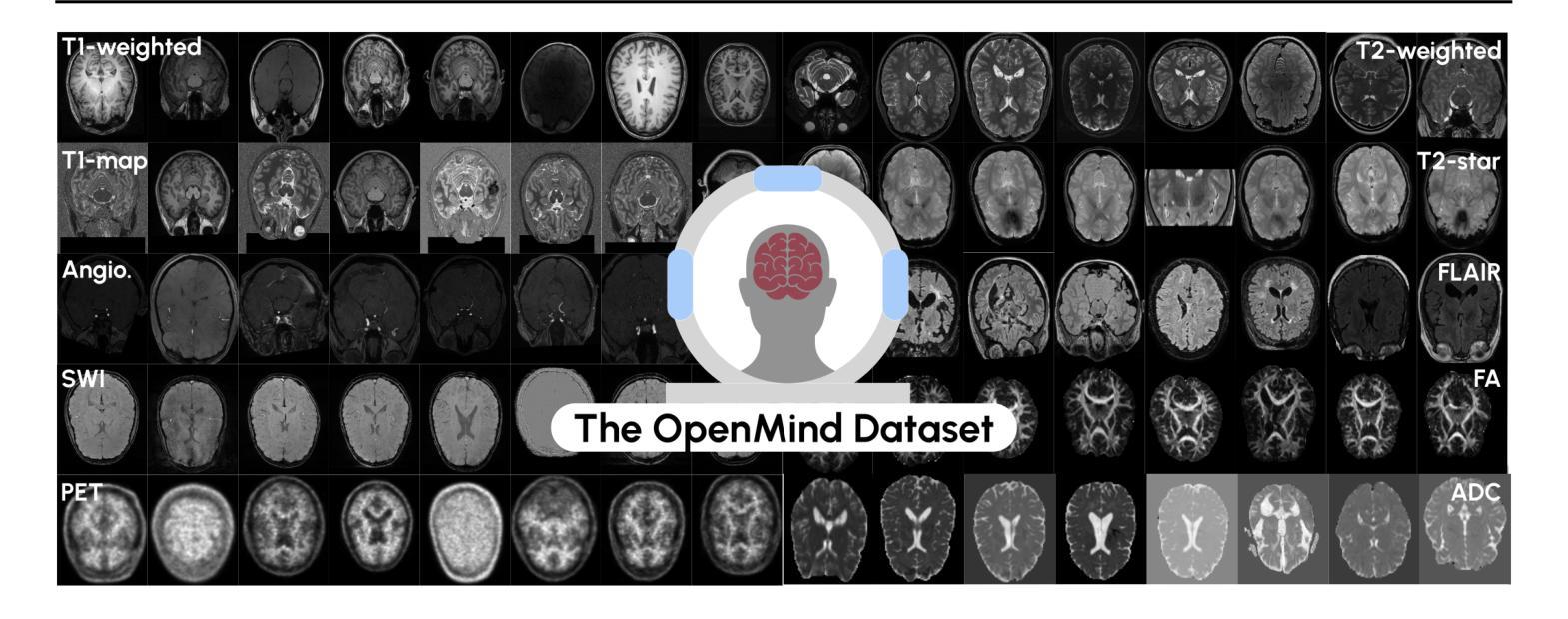
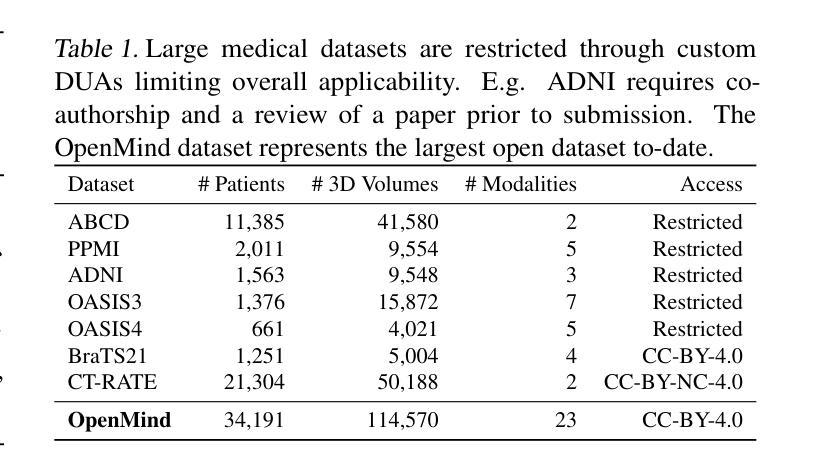
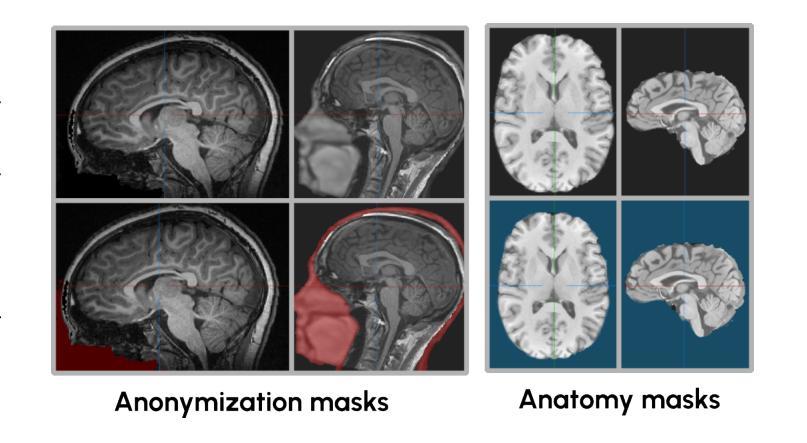
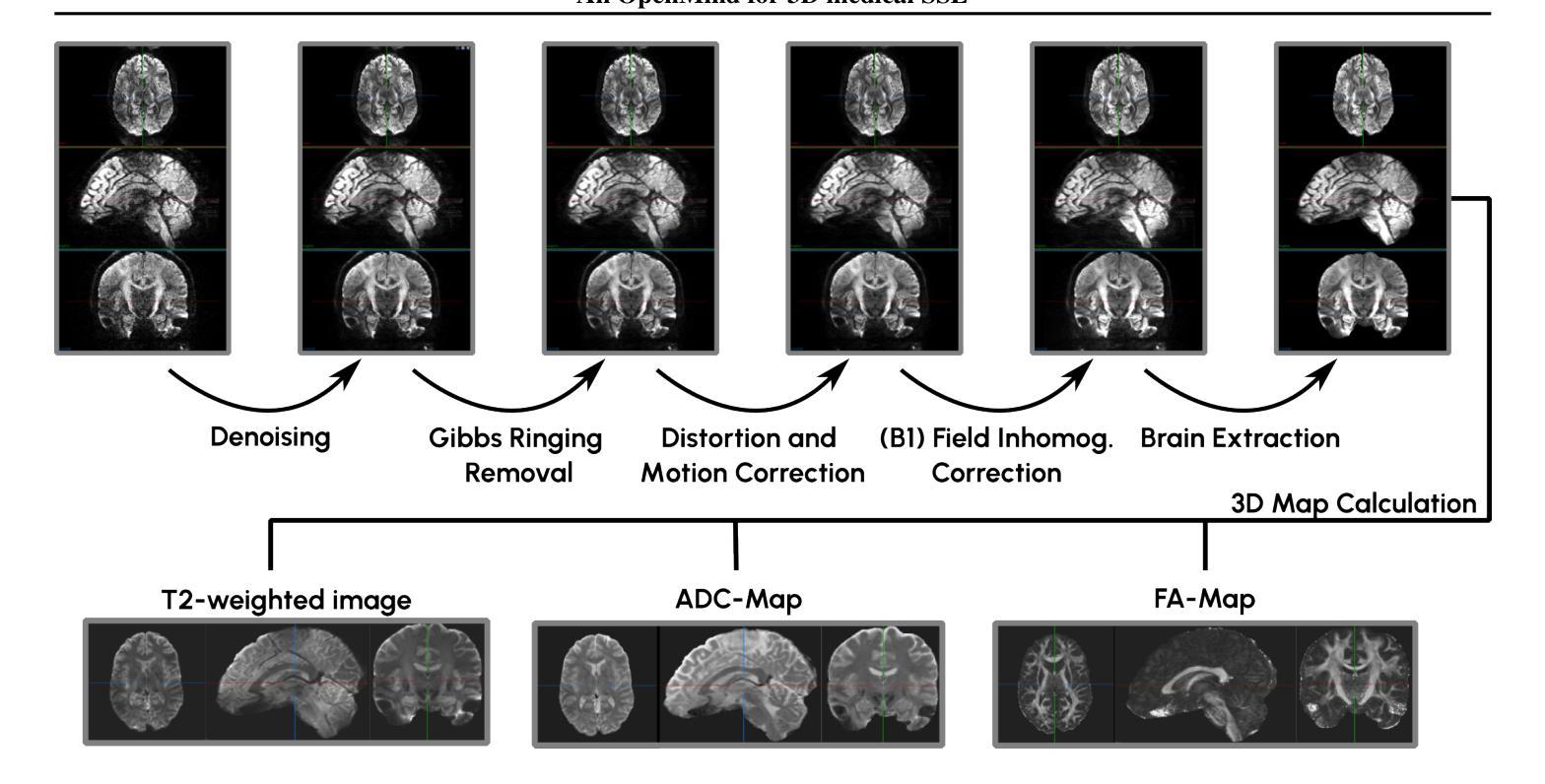
An OpenMind for 3D medical vision self-supervised learning
Authors:Tassilo Wald, Constantin Ulrich, Jonathan Suprijadi, Michal Nohel, Robin Peretzke, Klaus H. Maier-Hein
The field of 3D medical vision self-supervised learning lacks consistency and standardization. While many methods have been developed it is impossible to identify the current state-of-the-art, due to i) varying and small pre-training datasets, ii) varying architectures, and iii) being evaluated on differing downstream datasets. In this paper we bring clarity to this field and lay the foundation for further method advancements: We a) publish the largest publicly available pre-training dataset comprising 114k 3D brain MRI volumes and b) benchmark existing SSL methods under common architectures and c) provide the code of our framework publicly to facilitate rapid adoption and reproduction. This pre-print \textit{only describes} the dataset contribution (a); Data, benchmark, and codebase will be made available shortly.
医学三维视觉自监督学习领域缺乏一致性和标准化。虽然已经开发了许多方法,但由于i)预训练数据集大小不一且各异,ii)架构各异,以及iii)在下游数据集上的评估存在差异,因此无法确定当前的最佳方法。在本文中,我们使该领域更加清晰,并为进一步的方法发展奠定基础:我们a)公布了最大的公开预训练数据集,包含11.4万份三维脑MRI数据卷;b)对现有SSL方法在通用架构上进行了基准测试;c)公开我们的框架代码,以促进快速采用和复制。这篇预打印论文仅描述数据集贡献部分(a);数据、基准和代码库将在近期发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Pre-Print for Challenge proposal; Dataset, Benchmark and Codebase will be made available shortly once Benchmarking concludes
Summary
医学三维视觉自监督学习领域缺乏一致性和标准化。本文为解决此问题做出贡献,公开了最大的预训练数据集,包含11.4万份三维脑部MRI体积数据,为现有自监督学习方法提供了基准测试,并公开了代码框架,以促进快速采用和复现。
Key Takeaways
- 医学三维视觉自监督学习领域缺乏一致性和标准化。
- 现有方法难以识别当前最佳实践,原因在于预训练数据集大小不一、架构各异、下游数据集评估不同。
- 本文公开了最大的预训练数据集,包含11.4万份三维脑部MRI体积数据。
- 为现有自监督学习方法提供了基准测试。
- 公开了代码框架,以促进快速采用和复现。
- 本文仅描述了数据集贡献部分。
点此查看论文截图

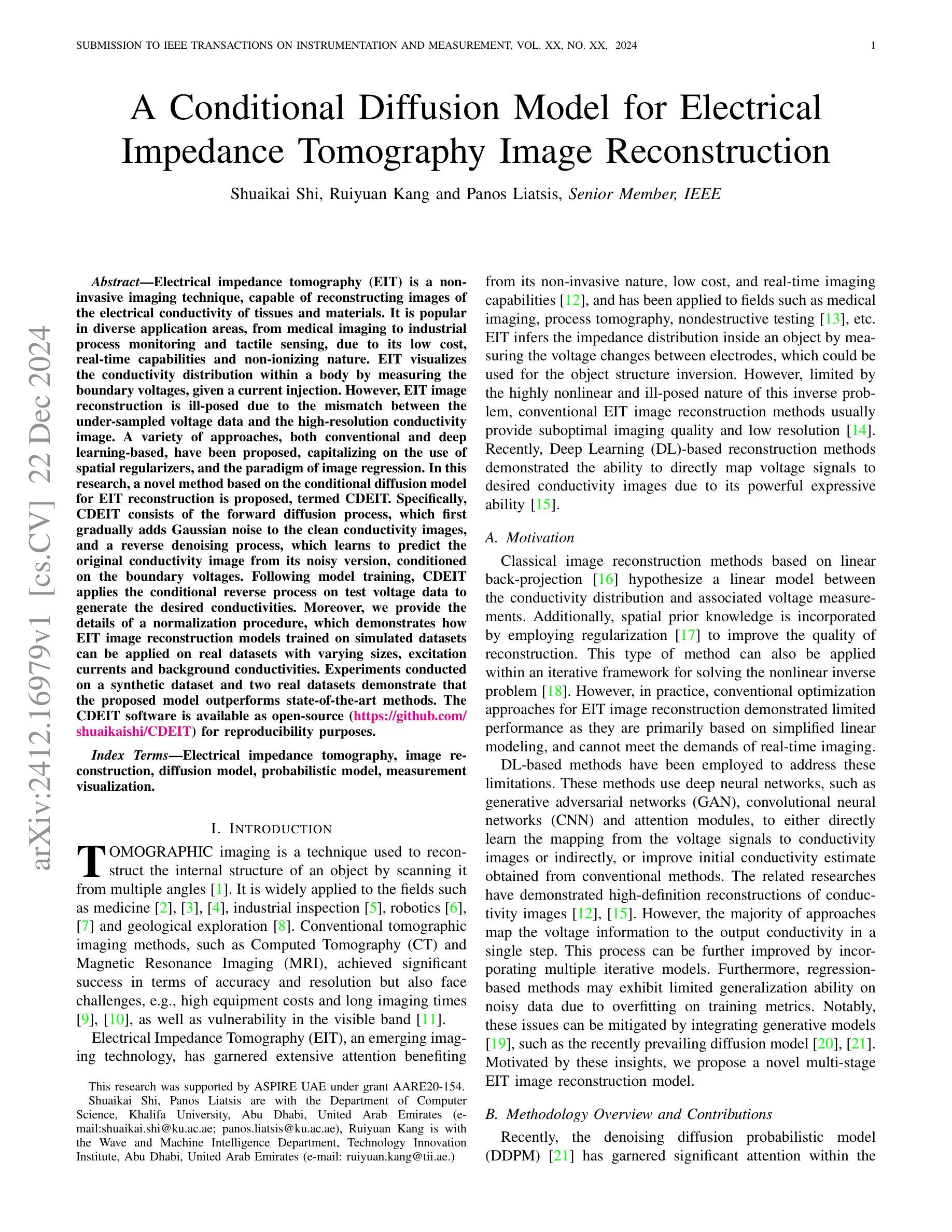
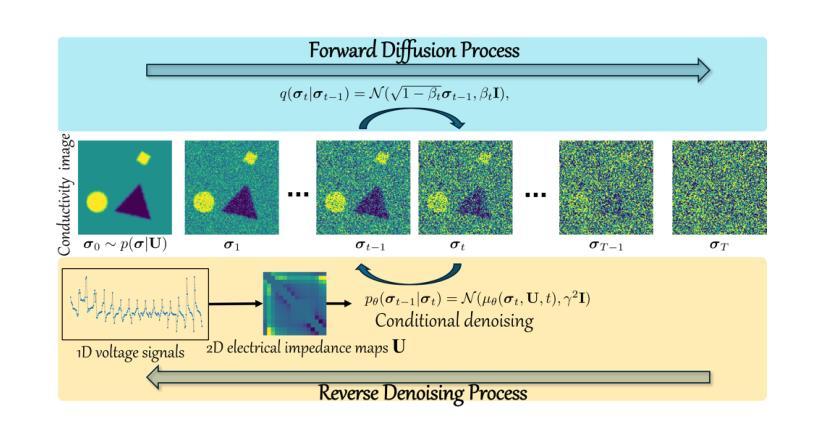
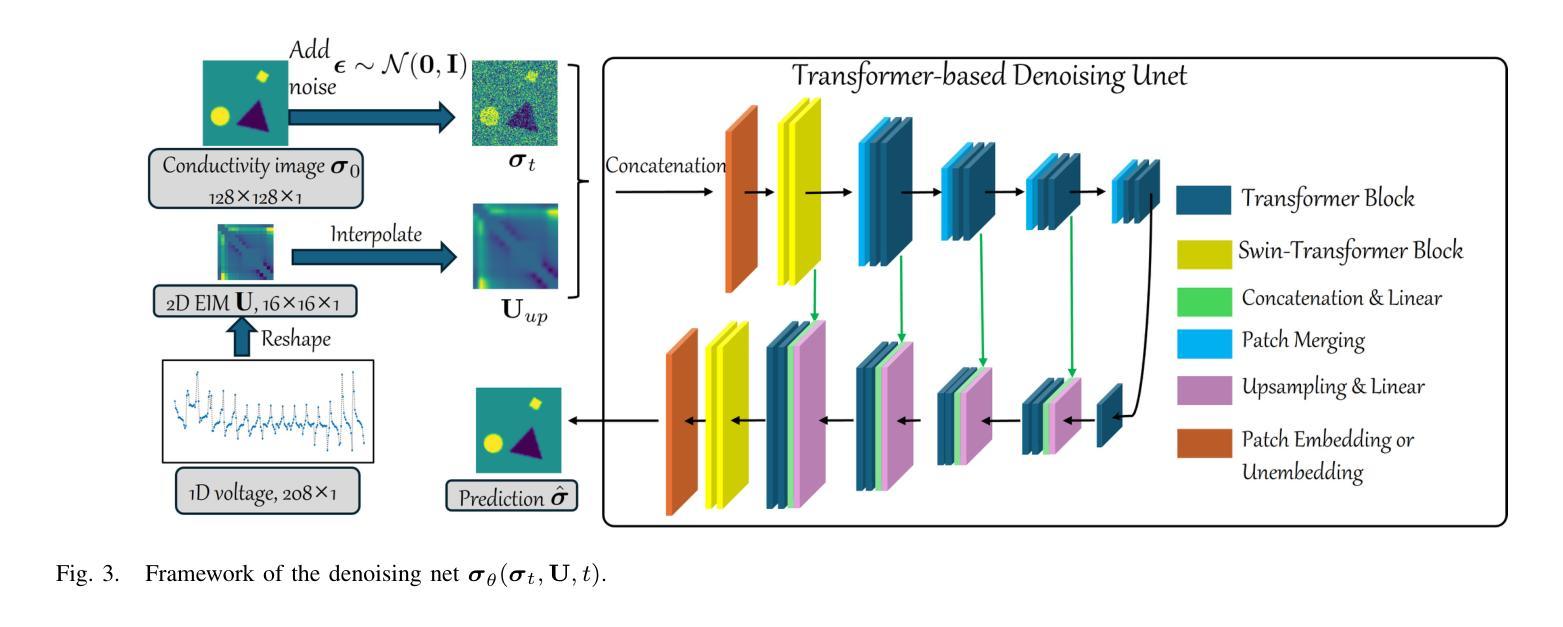
A Conditional Diffusion Model for Electrical Impedance Tomography Image Reconstruction
Authors:Shuaikai Shi, Ruiyuan Kang, Panos Liatsis
Electrical impedance tomography (EIT) is a non-invasive imaging technique, capable of reconstructing images of the electrical conductivity of tissues and materials. It is popular in diverse application areas, from medical imaging to industrial process monitoring and tactile sensing, due to its low cost, real-time capabilities and non-ionizing nature. EIT visualizes the conductivity distribution within a body by measuring the boundary voltages, given a current injection. However, EIT image reconstruction is ill-posed due to the mismatch between the under-sampled voltage data and the high-resolution conductivity image. A variety of approaches, both conventional and deep learning-based, have been proposed, capitalizing on the use of spatial regularizers, and the paradigm of image regression. In this research, a novel method based on the conditional diffusion model for EIT reconstruction is proposed, termed CDEIT. Specifically, CDEIT consists of the forward diffusion process, which first gradually adds Gaussian noise to the clean conductivity images, and a reverse denoising process, which learns to predict the original conductivity image from its noisy version, conditioned on the boundary voltages. Following model training, CDEIT applies the conditional reverse process on test voltage data to generate the desired conductivities. Moreover, we provide the details of a normalization procedure, which demonstrates how EIT image reconstruction models trained on simulated datasets can be applied on real datasets with varying sizes, excitation currents and background conductivities. Experiments conducted on a synthetic dataset and two real datasets demonstrate that the proposed model outperforms state-of-the-art methods. The CDEIT software is available as open-source (https://github.com/shuaikaishi/CDEIT) for reproducibility purposes.
电阻抗成像(EIT)是一种非侵入性的成像技术,能够重建组织和材料的电导率图像。由于其成本低、实时性能强和非电离性质,EIT在医学成像、工业过程监控和触觉感知等多样化应用领域广受欢迎。EIT通过测量电流注入时的边界电压来可视化体内的电导率分布。然而,由于采样不足的电压数据与高分辨率电导率图像之间的不匹配,EIT图像重建是一个适定性问题。已经提出了许多传统和基于深度学习的方法,利用空间正则化和图像回归范式。本研究提出了一种基于条件扩散模型的EIT重建新方法,称为CDEIT。具体来说,CDEIT包括正向扩散过程,该过程首先在干净的电导率图像上逐渐添加高斯噪声,以及反向去噪过程,该过程学会根据边界电压预测原始电导率图像。模型训练完成后,CDEIT将条件反向过程应用于测试电压数据,生成所需的电导率。此外,我们还提供了归一化流程的详细信息,展示了如何在不同大小、激励电流和背景电导率的真实数据集上应用经过模拟数据集训练的EIT图像重建模型。在合成数据集和两个真实数据集上进行的实验表明,所提出的方法优于现有技术。CDEIT软件作为开源软件(https://github.com/shuaikaishi/CDEIT)提供,以供可重复实验之用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
EIT(电气阻抗成像技术)是一种非侵入性的成像技术,能重建组织和材料的电导率图像。由于其低成本、实时性和非电离性质,EIT广泛应用于医学成像、工业过程监控和触觉感知等领域。本研究提出了一种基于条件扩散模型的EIT重建新方法,称为CDEIT。该方法包括正向扩散过程(向干净的电导率图像逐渐添加高斯噪声)和反向去噪过程(学习从含噪版本预测原始电导率图像)。经过模型训练后,CDEIT应用于测试电压数据生成所需的导电率。此外,还提供了一种归一化程序,该程序展示了如何将EIT图像重建模型从模拟数据集应用到具有不同大小、激发电流和背景电导率的真实数据集上。实验表明,该方法优于现有技术,CDEIT软件作为开源软件可供使用。
Key Takeaways
- EIT是一种非侵入性的成像技术,可重建组织和材料的电导率图像。
- EIT在医学成像、工业过程监控和触觉感知等领域有广泛应用。
- CDEIT是一种基于条件扩散模型的EIT重建新方法。
- CDEIT包括正向扩散过程和反向去噪过程。
- CDEIT模型在合成数据集和真实数据集上的实验表现优于现有技术。
- CDEIT软件作为开源软件可供使用,有助于提高研究的可重复性。
点此查看论文截图
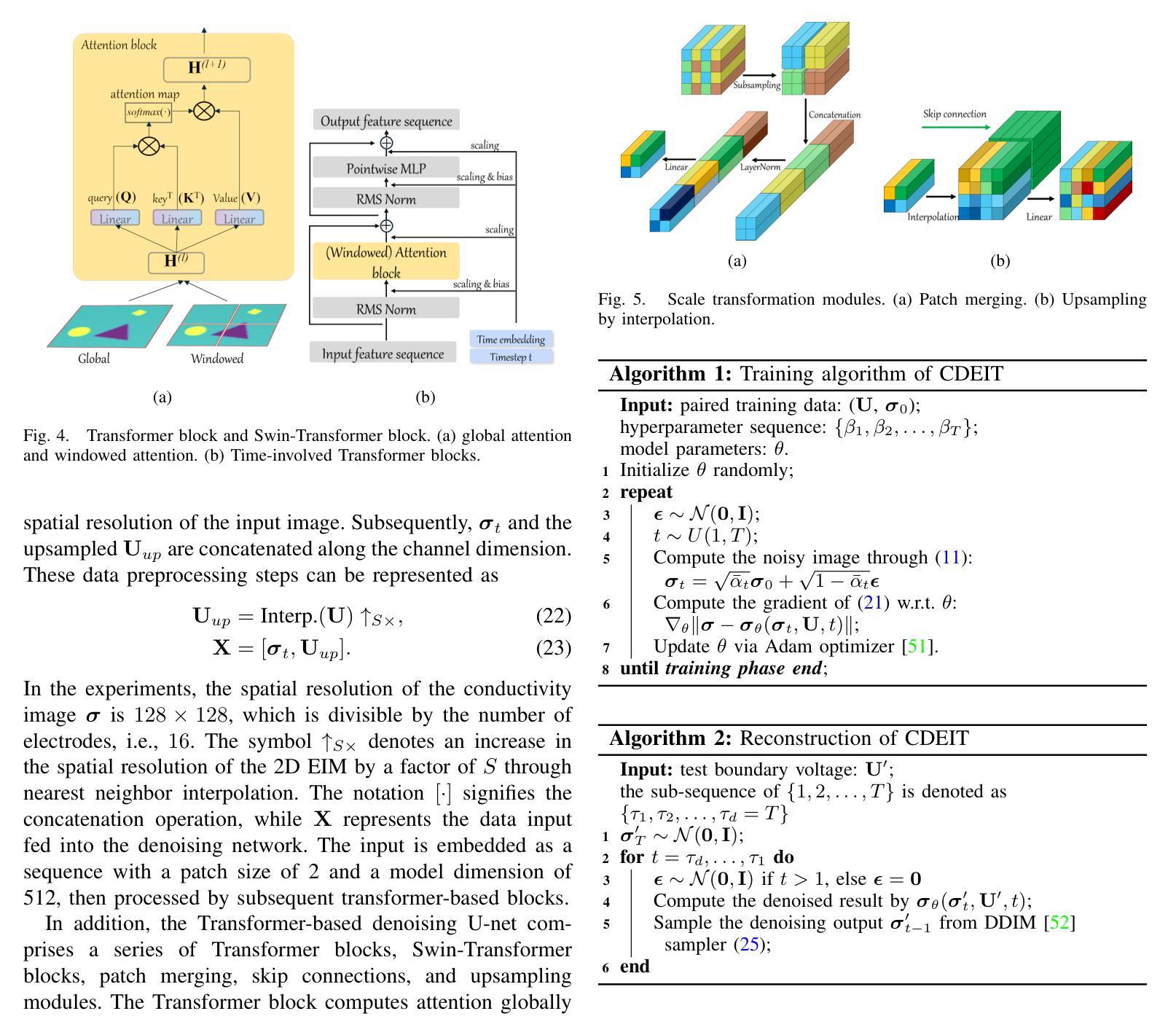
PINN-EMFNet: PINN-based and Enhanced Multi-Scale Feature Fusion Network for Breast Ultrasound Images Segmentation
Authors:Jiajun Ding, Beiyao Zhu, Wenjie Wang, Shurong Zhang, Dian Zhua, Zhao Liua
With the rapid development of deep learning and computer vision technologies, medical image segmentation plays a crucial role in the early diagnosis of breast cancer. However, due to the characteristics of breast ultrasound images, such as low contrast, speckle noise, and the highly diverse morphology of tumors, existing segmentation methods exhibit significant limitations in terms of accuracy and robustness. To address these challenges, this study proposes a PINN-based and Enhanced Multi-Scale Feature Fusion Network. The network introduces a Hierarchical Aggregation Encoder in the backbone, which efficiently integrates and globally models multi-scale features through several structural innovations and a novel PCAM module. In the decoder section, a Multi-Scale Feature Refinement Decoder is employed, which, combined with a Multi-Scale Supervision Mechanism and a correction module, significantly improves segmentation accuracy and adaptability. Additionally, the loss function incorporating the PINN mechanism introduces physical constraints during the segmentation process, enhancing the model’s ability to accurately delineate tumor boundaries. Comprehensive evaluations on two publicly available breast ultrasound datasets, BUSIS and BUSI, demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms previous segmentation approaches in terms of segmentation accuracy and robustness, particularly under conditions of complex noise and low contrast, effectively improving the accuracy and reliability of tumor segmentation. This method provides a more precise and robust solution for computer-aided diagnosis of breast ultrasound images.
随着深度学习和计算机视觉技术的快速发展,医学图像分割在乳腺癌的早期诊断中扮演着至关重要的角色。然而,由于乳腺超声图像的特性,如对比度低、斑点噪声和肿瘤形态高度多样,现有的分割方法在准确性和稳健性方面表现出显著局限性。为解决这些挑战,本研究提出了一种基于PINN的增强多尺度特征融合网络。该网络在主干中引入分层聚合编码器,通过若干结构创新和新型PCAM模块,有效地整合和全局建模多尺度特征。在解码器部分,采用多尺度特征细化解码器,结合多尺度监督机制和校正模块,显著提高分割精度和适应性。此外,损失函数结合PINN机制,在分割过程中引入物理约束,增强了模型准确勾勒肿瘤边界的能力。对两个公开可用的乳腺超声数据集BUSIS和BUSI的综合评估表明,所提出的方法在分割准确性和稳健性方面优于先前的分割方法,特别是在复杂噪声和低对比度条件下,有效提高肿瘤分割的准确性和可靠性。该方法为计算机辅助诊断乳腺超声图像提供了更精确和稳健的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
基于深度学习及计算机视觉技术,医学图像分割在乳腺癌早期诊断中起到关键作用。但由于乳腺超声图像特点,如对比度低、斑点噪声及肿瘤形态多样性,现有分割方法在准确性与稳健性上存在显著局限。本研究提出一种基于PINN和增强多尺度特征融合网络的解决方案。网络在主干中引入分层聚合编码器,通过若干结构创新和新型PCAM模块,有效整合并全局建模多尺度特征。解码器部分采用多尺度特征细化解码器,结合多尺度监督机制和校正模块,显著提高分割准确性和适应性。此外,损失函数结合PINN机制,在分割过程中引入物理约束,增强模型精确描绘肿瘤边界的能力。在公开可用的两个乳腺超声数据集BUSIS和BUSI上的综合评估表明,该方法在分割准确性和稳健性方面优于先前的分割方法,特别是在复杂噪声和低对比度条件下,有效提高肿瘤分割的准确性和可靠性。为计算机辅助诊断乳腺超声图像提供更精确和稳健的解决方案。
关键见解
- 医学图像分割在乳腺癌早期诊断中起关键作用。
- 现有乳腺超声图像分割方法面临准确性与稳健性挑战。
- 研究提出一种基于PINN和增强多尺度特征融合网络的解决方案。
- 网络引入分层聚合编码器和多尺度特征细化解码器以提高性能。
- PINN机制结合物理约束提高模型精确描绘肿瘤边界的能力。
- 在公开数据集上的评估显示,该方法在分割准确性和稳健性上优于先前方法。
点此查看论文截图

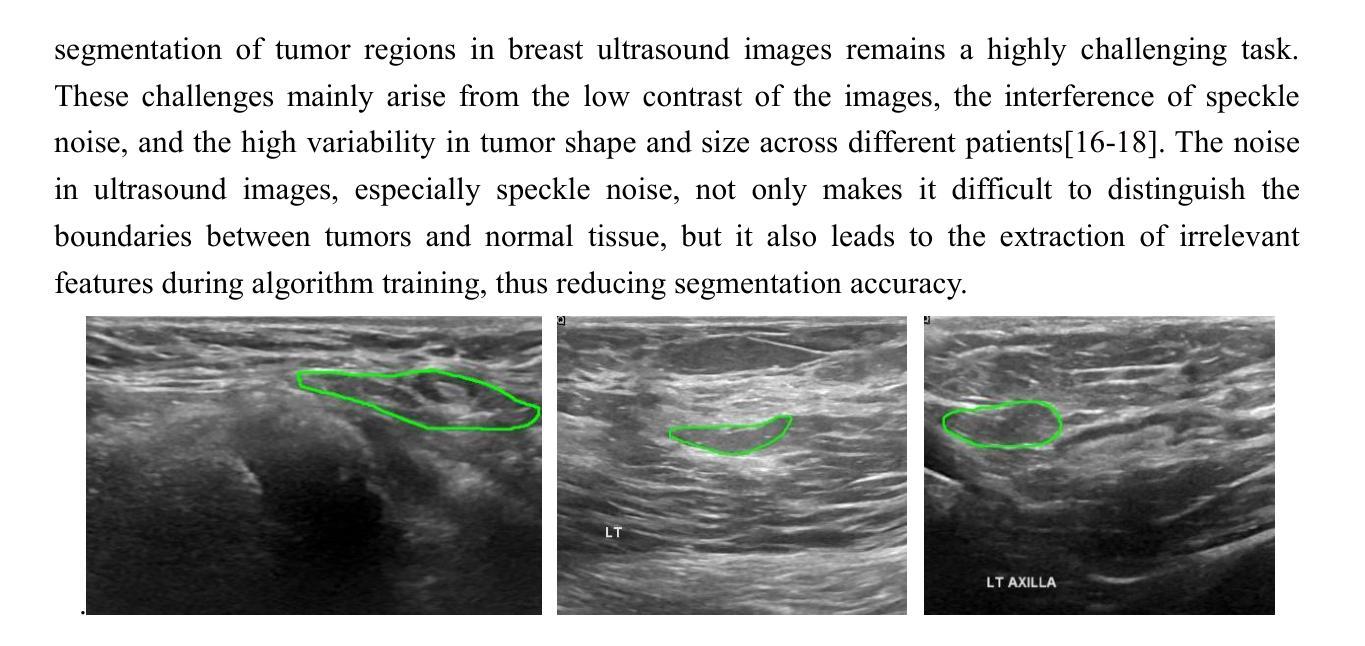
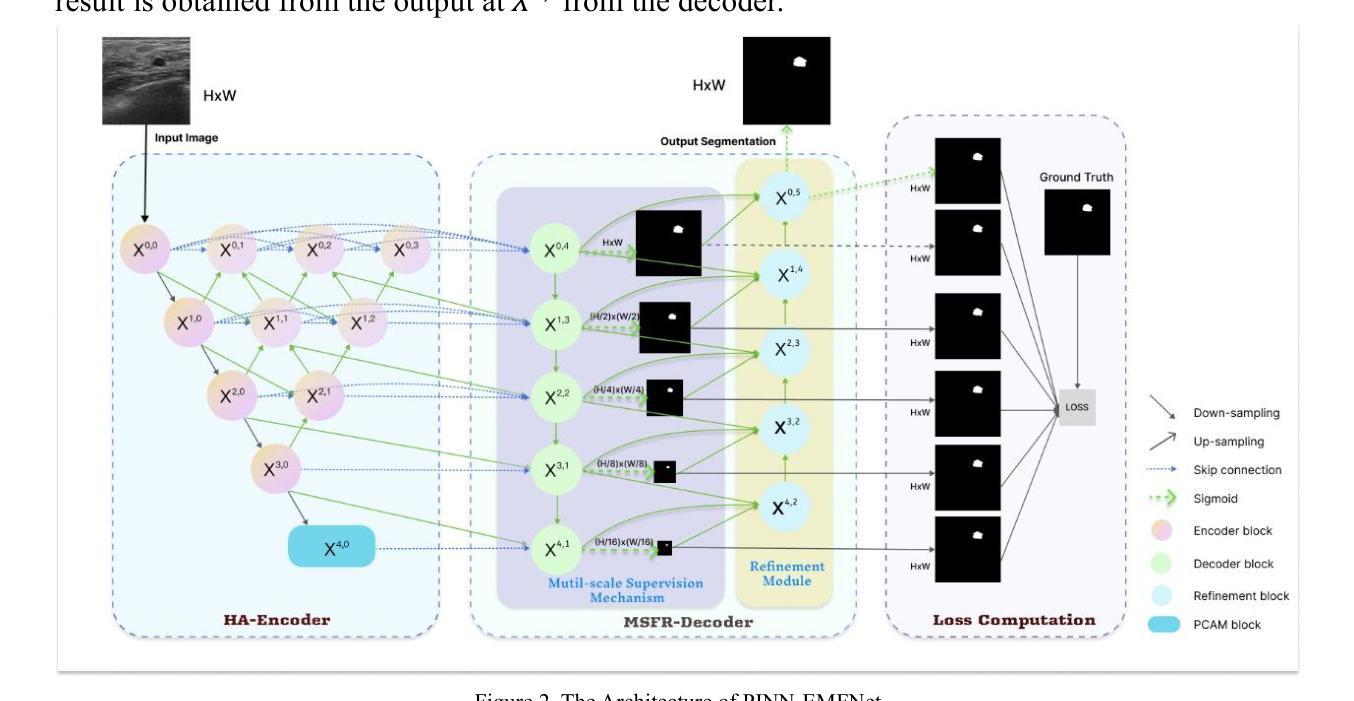
Evaluation of radiomic feature harmonization techniques for benign and malignant pulmonary nodules
Authors:Claire Huchthausen, Menglin Shi, Gabriel L. A. de Sousa, Jonathan Colen, Emery Shelley, James Larner, Krishni Wijesooriya
BACKGROUND: Radiomics provides quantitative features of pulmonary nodules (PNs) which could aid lung cancer diagnosis, but medical image acquisition variability is an obstacle to clinical application. Acquisition effects may differ between radiomic features from benign vs. malignant PNs. PURPOSE: We evaluated how to account for differences between benign and malignant PNs when correcting radiomic features’ acquisition dependency. METHODS: We used 567 chest CT scans grouped as benign, malignant, or lung cancer screening (mixed benign, malignant). ComBat harmonization was applied to extracted features for variation in 4 acquisition parameters. We compared: harmonizing without distinction, harmonizing with a covariate to preserve distinctions between subgroups, and harmonizing subgroups separately. Significant ($p\le0.05$) Kruskal-Wallis tests showed whether harmonization removed acquisition dependency. A LASSO-SVM pipeline was trained on successfully harmonized features to predict malignancy. To evaluate predictive information in these features, the trained harmonization estimators and predictive model were applied to unseen test sets. Harmonization and predictive performance were assessed for 10 trials of 5-fold cross-validation. RESULTS: An average 2.1% of features (95% CI:1.9-2.4%) were acquisition-independent when harmonized without distinction, 27.3% (95% CI:25.7-28.9%) when harmonized with a covariate, and 90.9% (95% CI:90.4-91.5%) when harmonized separately. Data harmonized separately or with a covariate trained models with higher ROC-AUC for screening scans than data harmonized without distinction between benign and malignant PNs (Delong test, adjusted $p\le0.05$). CONCLUSIONS: Radiomic features of benign and malignant PNs need different corrective transformations to recover acquisition-independent distributions. This can be done by harmonizing separately or with a covariate.
背景:放射组学提供了肺结节(PNs)的定量特征,这有助于肺癌的诊断,但医学图像采集的变异性是临床应用中的障碍。良性和恶性肺结节之间的放射学特征可能存在采集效果上的差异。目的:我们评估了如何在校正放射学特征的采集依赖性时考虑良性和恶性肺结节之间的差异。方法:我们使用567张胸部CT扫描图像,按良性、恶性或肺癌筛查(混合良性和恶性)进行分组。应用ComBat和谐法对提取的特征进行变异校正,变异涉及4个采集参数。我们比较了以下三种方法:无区别的和谐法、使用协变量保留亚组间差异的和协法,以及分别和谐亚组的方法。Kruskal-Wallis检验(p≤0.05)显示和谐化是否消除了采集依赖性。使用成功和谐化的特征训练LASSO-SVM管道以预测恶性。为了评估这些特征中的预测信息,将经过训练的和谐化估计器和预测模型应用于未见过的测试集。和谐化和预测性能均经过10次5折交叉验证的试验进行评估。结果:当无区别和谐化时,平均有2.1%(95%置信区间:1.9-2.4%)的特征与采集无关;当使用协变量和谐化时,平均有27.3%(95%置信区间:25.7-28.9%)的特征与采集无关;当分别和谐化时,平均有90.9%(95%置信区间:90.4-91.5%)的特征与采集无关。对于筛查扫描,与在良性和恶性肺结节之间无区别地和谐化数据相比,分别和谐化或与协变量一起和谐化的数据训练模型的ROC-AUC更高(经调整的Delong检验,p≤0.05)。结论:良性和恶性肺结节的放射学特征需要不同的校正转换来恢复与采集无关的分布。这可以通过分别和谐化或使用协变量的方法来实现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 3 figures, plus supplemental material
Summary
本文研究了放射组学特征在肺结节诊断中的应用,探讨了如何校正放射组学特征采集过程中的差异,特别是针对良恶性肺结节之间的差异。通过应用ComBat和谐化技术,研究发现分别对良恶性肺结节进行和谐化处理或用一个协变量进行和谐化处理可以更好地去除采集参数的差异,提高预测模型的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 放射组学特征对于肺结节的良恶性诊断有重要作用,但医学图像采集过程中的差异是一个挑战。
- 使用ComBat和谐化技术可以消除放射组学特征采集过程中的差异。
- 良恶性肺结节的放射组学特征需要不同的校正转换以恢复独立于采集的分布。
- 分别和谐化良恶性肺结节数据或使用协变量可以提高预测模型的性能。
- 文中提到了三种和谐化方法:无区别的和谐化、使用协变量的和谐化、以及分别和谐化不同子群体。
- 通过对模型进行10次5倍交叉验证,发现使用分别和谐化或带有协变量的和谐化方法可以更好地去除采集依赖性。
点此查看论文截图

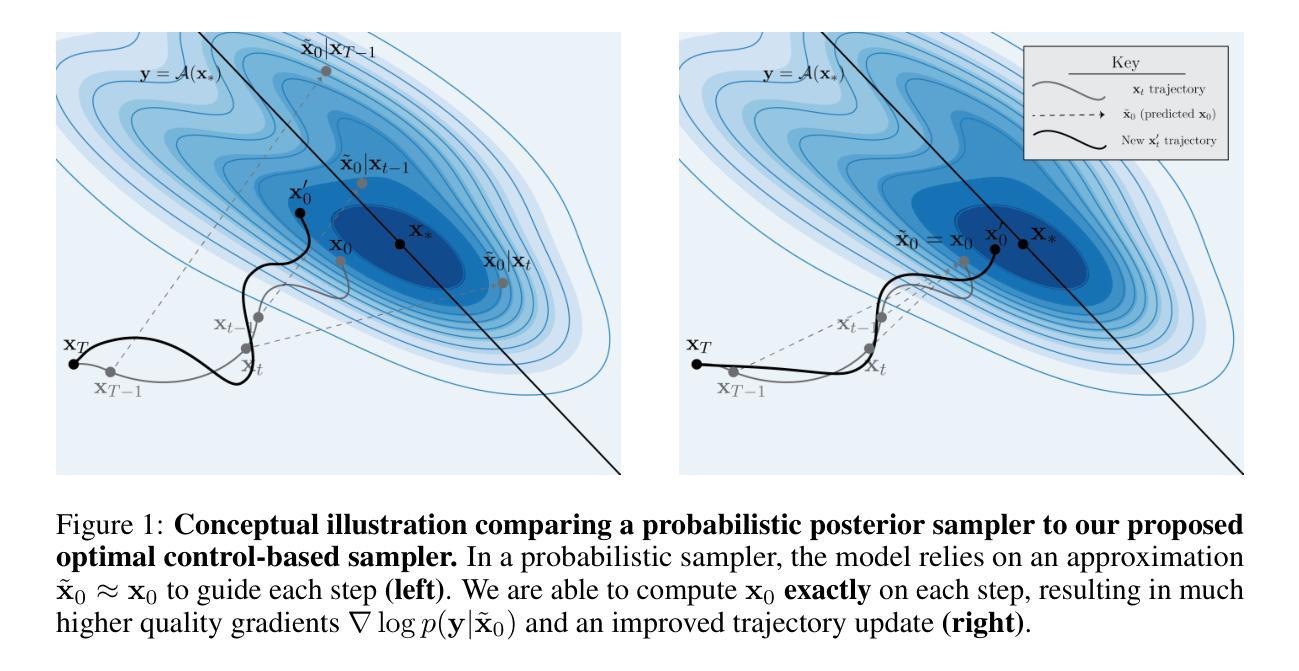
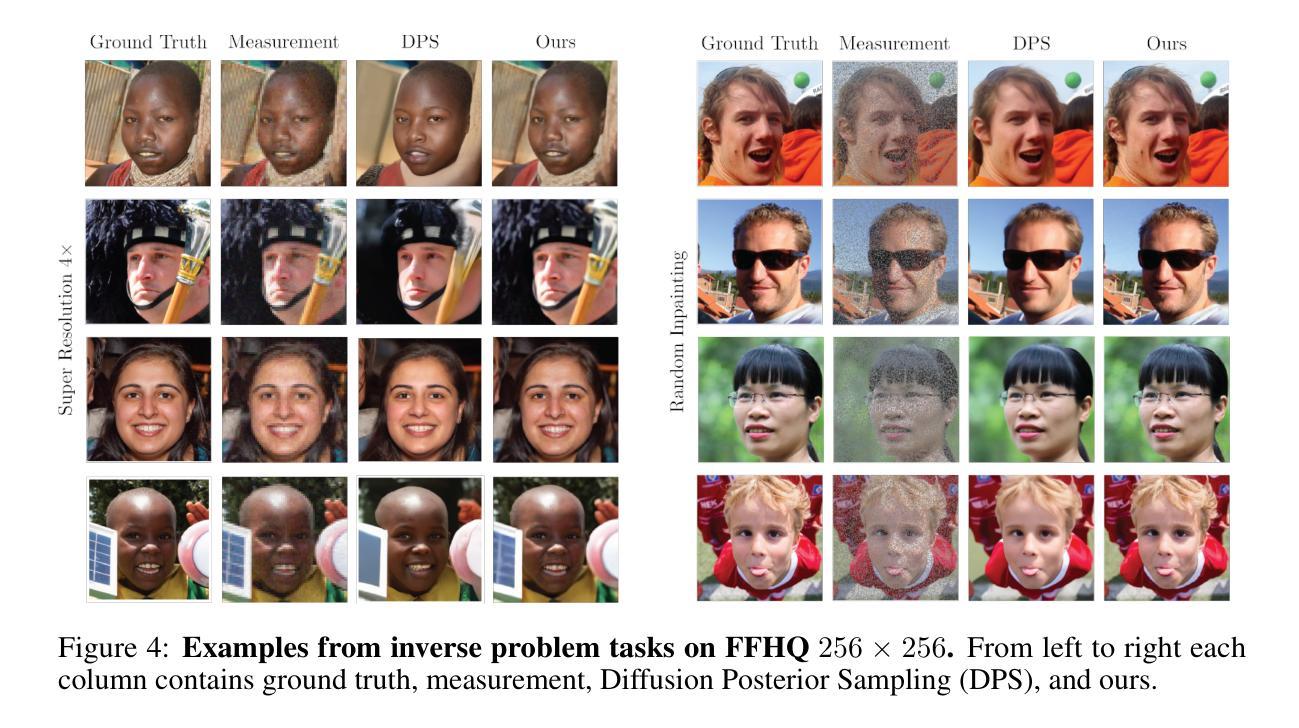
Solving Inverse Problems via Diffusion Optimal Control
Authors:Henry Li, Marcus Pereira
Existing approaches to diffusion-based inverse problem solvers frame the signal recovery task as a probabilistic sampling episode, where the solution is drawn from the desired posterior distribution. This framework suffers from several critical drawbacks, including the intractability of the conditional likelihood function, strict dependence on the score network approximation, and poor $\mathbf{x}_0$ prediction quality. We demonstrate that these limitations can be sidestepped by reframing the generative process as a discrete optimal control episode. We derive a diffusion-based optimal controller inspired by the iterative Linear Quadratic Regulator (iLQR) algorithm. This framework is fully general and able to handle any differentiable forward measurement operator, including super-resolution, inpainting, Gaussian deblurring, nonlinear deblurring, and even highly nonlinear neural classifiers. Furthermore, we show that the idealized posterior sampling equation can be recovered as a special case of our algorithm. We then evaluate our method against a selection of neural inverse problem solvers, and establish a new baseline in image reconstruction with inverse problems.
现有的基于扩散的逆问题求解方法将信号恢复任务构建为概率采样事件,其中解是从期望的后验分布中得出的。这一框架存在几个关键缺点,包括条件似然函数的不易处理性、对评分网络近似的严格依赖性以及糟糕的$\mathbf{x}_0$预测质量。我们证明,通过重新构建生成过程作为离散最优控制事件,可以规避这些限制。我们受到迭代线性二次调节器(iLQR)算法的启发,推导出了基于扩散的最优控制器。这一框架通用性十足,能够处理任何可区分的正向测量算子,包括超分辨率、图像补全、高斯去模糊、非线性去模糊,甚至是高度非线性的神经网络分类器。此外,我们还证明理想化的后验采样方程可以作为我们算法的一个特例进行恢复。然后,我们对一系列神经逆问题求解器进行了评估,并在逆问题图像重建中建立了新的基准。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Presented at NeurIPS 2024
Summary
本文介绍了基于扩散的逆问题求解器的新方法,该方法将生成过程重新构建为离散最优控制事件,克服了现有方法的局限性,如条件概率函数的不可计算性、对评分网络近似的严格依赖以及预测质量不佳等问题。新方法采用基于迭代线性二次调节器(iLQR)算法的最优控制器,可处理任何可微的前向测量算子,包括超分辨率、图像补全、高斯去模糊、非线性去模糊甚至高度非线性的神经网络分类器。在评估中,该方法建立了新的图像重建逆问题基准。
Key Takeaways
- 现有扩散逆问题求解方法将信号恢复任务视为概率采样事件,从期望的后验分布中抽取解决方案。
- 这种方法存在关键缺点,如条件概率函数不可计算、依赖评分网络近似和预测质量不佳。
- 本文通过将生成过程重新构建为离散最优控制事件来解决这些限制。
- 提出了一种基于迭代线性二次调节器(iLQR)算法的最优控制器。
- 该方法可处理各种可微的前向测量算子,包括超分辨率、图像补全、去模糊和神经网络分类器。
- 理想化后验采样方程可作为该算法的一种特殊情况。
点此查看论文截图



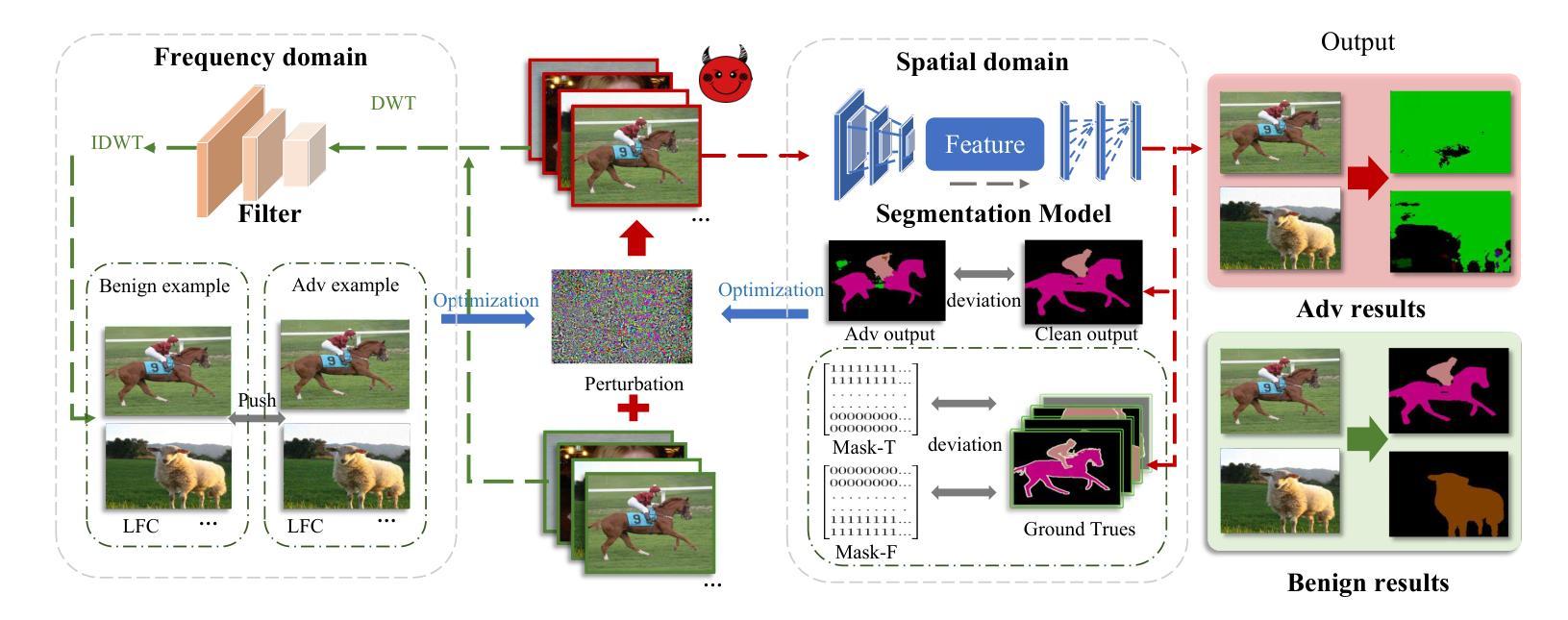
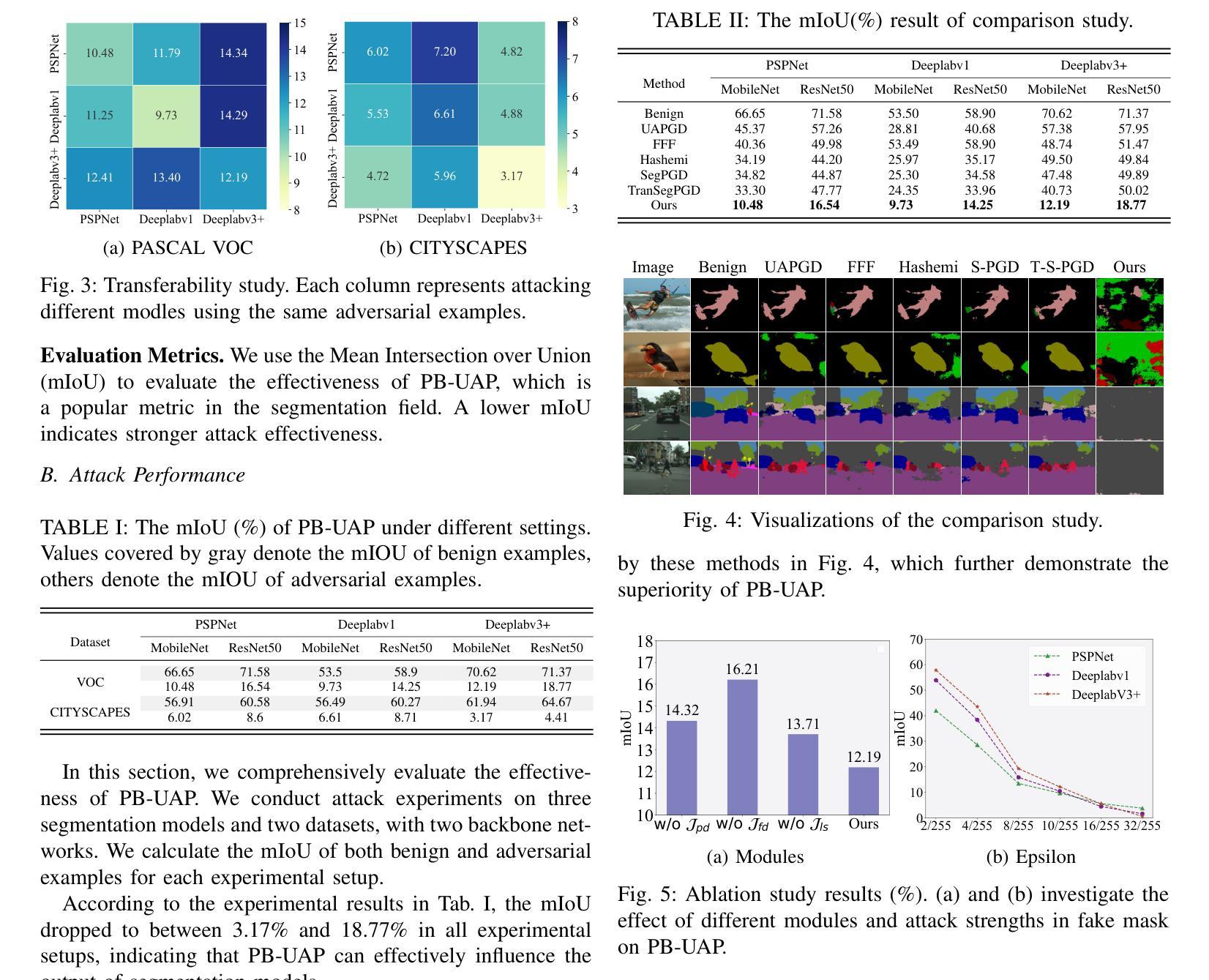
PB-UAP: Hybrid Universal Adversarial Attack For Image Segmentation
Authors:Yufei Song, Ziqi Zhou, Minghui Li, Xianlong Wang, Menghao Deng, Wei Wan, Shengshan Hu, Leo Yu Zhang
With the rapid advancement of deep learning, the model robustness has become a significant research hotspot, \ie, adversarial attacks on deep neural networks. Existing works primarily focus on image classification tasks, aiming to alter the model’s predicted labels. Due to the output complexity and deeper network architectures, research on adversarial examples for segmentation models is still limited, particularly for universal adversarial perturbations. In this paper, we propose a novel universal adversarial attack method designed for segmentation models, which includes dual feature separation and low-frequency scattering modules. The two modules guide the training of adversarial examples in the pixel and frequency space, respectively. Experiments demonstrate that our method achieves high attack success rates surpassing the state-of-the-art methods, and exhibits strong transferability across different models.
随着深度学习的快速发展,模型的稳健性已成为一个重要的研究热点,即对深度神经网络进行对抗性攻击。现有的工作主要集中在图像分类任务上,旨在改变模型的预测标签。由于输出复杂性和更深的网络架构,关于分割模型的对抗性示例的研究仍然有限,特别是对通用对抗性扰动的研究。在本文中,我们提出了一种针对分割模型的新型通用对抗性攻击方法,包括双特征分离和低频散射模块。这两个模块分别在像素和频率空间指导对抗性示例的训练。实验表明,我们的方法实现了较高的攻击成功率,超越了最先进的方法,并且在不同模型之间表现出强大的迁移性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICASSP 2025
Summary
随着深度学习的高速发展,模型稳健性已成为研究热点,特别是在对抗性攻击方面的深度神经网络。目前,大部分研究关注图像分类任务,致力于改变模型预测标签。由于输出复杂和网络架构较深,针对分割模型的对抗性例子研究仍然有限,特别是通用对抗性扰动。本文提出一种针对分割模型的新型通用对抗性攻击方法,包括双特征分离和低频散射模块。这两个模块分别在像素和频率空间指导对抗性示例的训练。实验证明,该方法攻击成功率高超现有方法,且在不同模型间展现出强大的迁移性。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习模型稳健性成为研究热点,特别是在对抗性攻击方面。
- 当前研究主要关注图像分类任务的对抗性攻击,改变模型预测标签。
- 分割模型的对抗性例子研究仍然有限,尤其是通用对抗性扰动。
- 本文提出一种新型通用对抗性攻击方法,适用于分割模型。
- 该方法包括双特征分离和低频散射两个模块,分别在像素和频率空间指导训练。
- 实验证明,该方法攻击成功率高超出现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

Optimal dosing of anti-cancer treatment under drug-induced plasticity
Authors:Einar Bjarki Gunnarsson, Benedikt Vilji Magnússon, Jasmine Foo
While cancer has traditionally been considered a genetic disease, mounting evidence indicates an important role for non-genetic (epigenetic) mechanisms. Common anti-cancer drugs have recently been observed to induce the adoption of reversible drug-tolerant cell states, thereby accelerating the evolution of drug resistance. Determining how to optimally balance the competing goals of killing the tumor bulk and delaying resistance evolution in this scenario is a nontrivial question of high clinical importance. In this work, we use a combined mathematical and computational approach to study optimal dosing of anti-cancer drug treatment under drug-induced cell plasticity. Our results show that the optimal treatment steers the tumor into a fixed equilibrium composition while balancing the trade-off between cell kill and tolerance induction in a precisely quantifiable way. Under linear induction of tolerance, a low-dose constant strategy is optimal in equilibrium, while under uniform induction of tolerance, alternating between a large dose and no dose is best. The directionality of drug induction, whether the drug elevates transitions from sensitivity to tolerance or inhibits transitions back, significantly affects optimal dosing. To demonstrate the applicability of our approach, we use it to identify an optimal low-dose strategy for colorectal cancer using publicly available in vitro data.
虽然癌症历来被视为一种遗传性疾病,但越来越多的证据表明非遗传(表观遗传)机制也发挥着重要作用。最近观察到常用的抗癌药物会诱导产生可逆的耐药细胞状态,从而加速药物抵抗性的进化。在这种情况下,如何在杀死肿瘤主体和延缓抵抗性进化这两个相互竞争的目标之间找到最佳平衡,是一个具有重要临床意义的非简单问题。在这项工作中,我们采用数学和计算相结合的方法,研究药物诱导的细胞可塑性下的抗癌药物治疗的最佳剂量。我们的结果表明,最佳治疗策略将肿瘤引导到一个固定的平衡状态,同时以可量化的方式平衡细胞杀伤和诱导耐受之间的权衡。在耐受性的线性诱导下,在平衡状态下,低剂量恒定策略是最优的;而在均匀诱导耐受性下,大剂量与无剂量之间的交替交替效果最好。药物诱导的方向性,即药物是促使从敏感状态向耐受状态的转变还是抑制反向转变,都会显著影响最佳剂量。为了证明我们方法的应用性,我们使用它来根据公开的体外数据为结肠癌确定最佳低剂量策略。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 46 pages, 10 figures
Summary
本摘要介绍了一种新的抗癌药物治疗方式的研究。研究指出,传统的抗癌药物可能会诱导药物耐受性细胞状态的出现,从而加速药物抵抗的演化。本研究采用数学与计算相结合的方法,研究了药物诱导的细胞可塑性下的最优抗癌药物剂量。结果表明,最优治疗方案能够使肿瘤达到固定的平衡状态,在细胞杀伤和耐受诱导之间取得精确的可量化的平衡。
Key Takeaways
- 癌症不仅仅是一种遗传性疾病,非遗传(表观遗传)机制也起着重要作用。
- 常见抗癌药物会诱导可逆的药物耐受性细胞状态,从而加速药物抵抗的演化。
- 平衡杀死肿瘤主体和延缓抵抗演化的目标是一个重要的临床问题。
- 研究采用数学和计算结合的方法,研究了药物诱导的细胞可塑性下的最优抗癌药物剂量。
- 最优治疗方案能使肿瘤达到固定平衡状态,在细胞杀伤和耐受诱导之间取得精确平衡。
- 药物诱导的方向性,即药物是否提高了从敏感状态到耐受状态的过渡,或是否抑制了从耐受状态回到敏感状态的过渡,会显著影响最优药物剂量。
点此查看论文截图

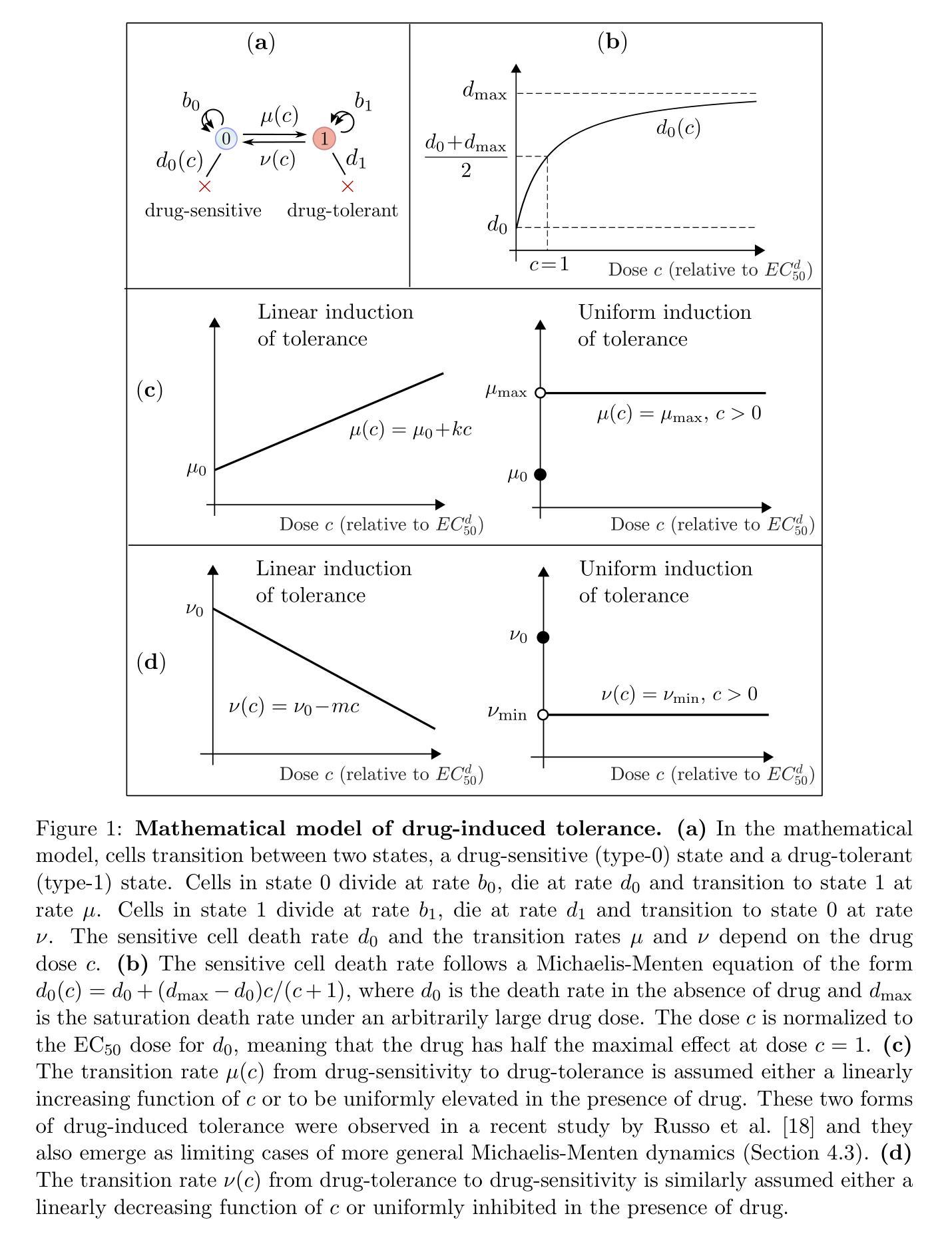
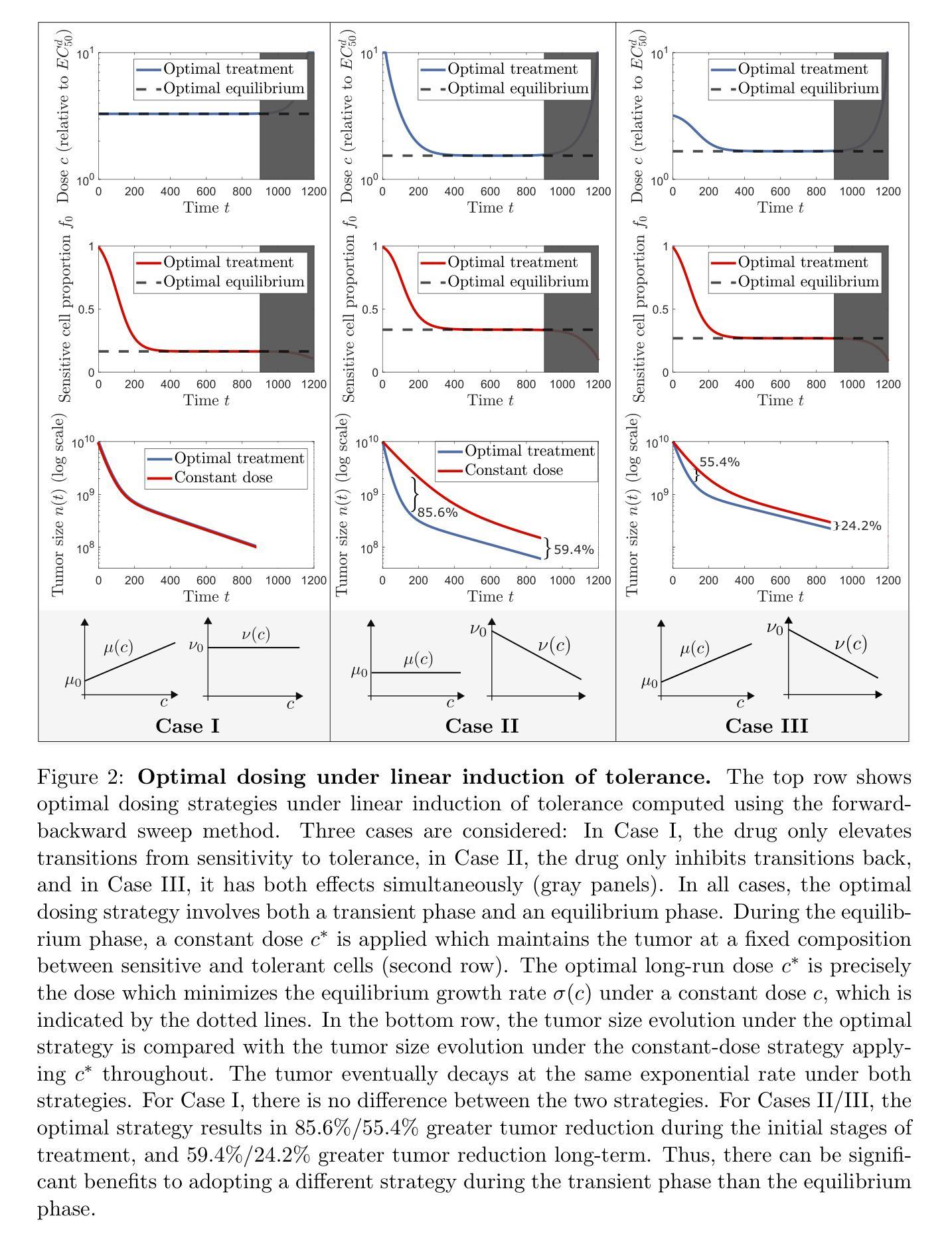
VerSe: Integrating Multiple Queries as Prompts for Versatile Cardiac MRI Segmentation
Authors:Bangwei Guo, Meng Ye, Yunhe Gao, Bingyu Xin, Leon Axel, Dimitris Metaxas
Despite the advances in learning-based image segmentation approach, the accurate segmentation of cardiac structures from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) remains a critical challenge. While existing automatic segmentation methods have shown promise, they still require extensive manual corrections of the segmentation results by human experts, particularly in complex regions such as the basal and apical parts of the heart. Recent efforts have been made on developing interactive image segmentation methods that enable human-in-the-loop learning. However, they are semi-automatic and inefficient, due to their reliance on click-based prompts, especially for 3D cardiac MRI volumes. To address these limitations, we propose VerSe, a Versatile Segmentation framework to unify automatic and interactive segmentation through mutiple queries. Our key innovation lies in the joint learning of object and click queries as prompts for a shared segmentation backbone. VerSe supports both fully automatic segmentation, through object queries, and interactive mask refinement, by providing click queries when needed. With the proposed integrated prompting scheme, VerSe demonstrates significant improvement in performance and efficiency over existing methods, on both cardiac MRI and out-of-distribution medical imaging datasets. The code is available at https://github.com/bangwayne/Verse.
尽管基于学习的图像分割方法取得了进展,但从磁共振成像(MRI)准确分割心脏结构仍然是一个巨大的挑战。虽然现有的自动分割方法显示出了一定的前景,但它们仍然需要专家对分割结果进行大量手动修正,特别是在心脏底部和顶部等复杂区域。近期已经开发出交互式图像分割方法,实现了人类环内学习。然而,它们是半自动的且效率不高,因为它们依赖于基于点击的提示,特别是对于3D心脏MRI体积。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了VerSe,一个通用分割框架,通过多个查询统一自动和交互式分割。我们的关键创新在于联合学习对象和点击查询,作为共享分割骨干的提示。VerSe既支持通过对象查询进行完全自动分割,也支持在需要时通过点击查询提供交互式蒙版细化。通过提出的集成提示方案,VerSe在心脏MRI和离群分布的医学成像数据集上,相较于现有方法,性能和效率均得到了显著提升。代码可访问https://github.com/bangwayne/Verse。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
心脏磁共振成像(MRI)的精准分割仍是学习基础的图像分割方法的一大挑战。尽管现有自动分割方法具有潜力,但仍需专家对分割结果进行大量手动修正,特别是在心脏基部和顶部等复杂区域。为改善此情况,研究者提出了VerSe(Versatile Segmentation)框架,通过多查询统一自动和交互式分割。其关键创新在于对象查询和点击查询的联合学习,为共享分割骨干提供提示。VerSe既支持完全自动分割(通过对象查询),又支持在需要时通过点击查询进行交互式掩膜细化。与现有方法相比,VerSe在心脏MRI和离散医学影像数据集上的性能和效率均有显著提高。相关代码已发布在https://github.com/bangwayne/Verse。
Key Takeaways
- 心脏MRI的精准分割仍然是一个挑战,需要开发更高效和准确的方法。
- 现有自动分割方法在复杂区域如心脏基部和顶部仍需要手动修正。
- VerSe框架结合了自动和交互式分割,通过多查询进行统一处理。
- VerSe的关键创新在于联合学习对象查询和点击查询,为分割提供提示。
- VerSe支持全自动和交互式掩膜细化,适应不同需求。
- 与现有方法相比,VerSe在心脏MRI和其他医学影像数据集上的性能和效率有显著提高。
点此查看论文截图

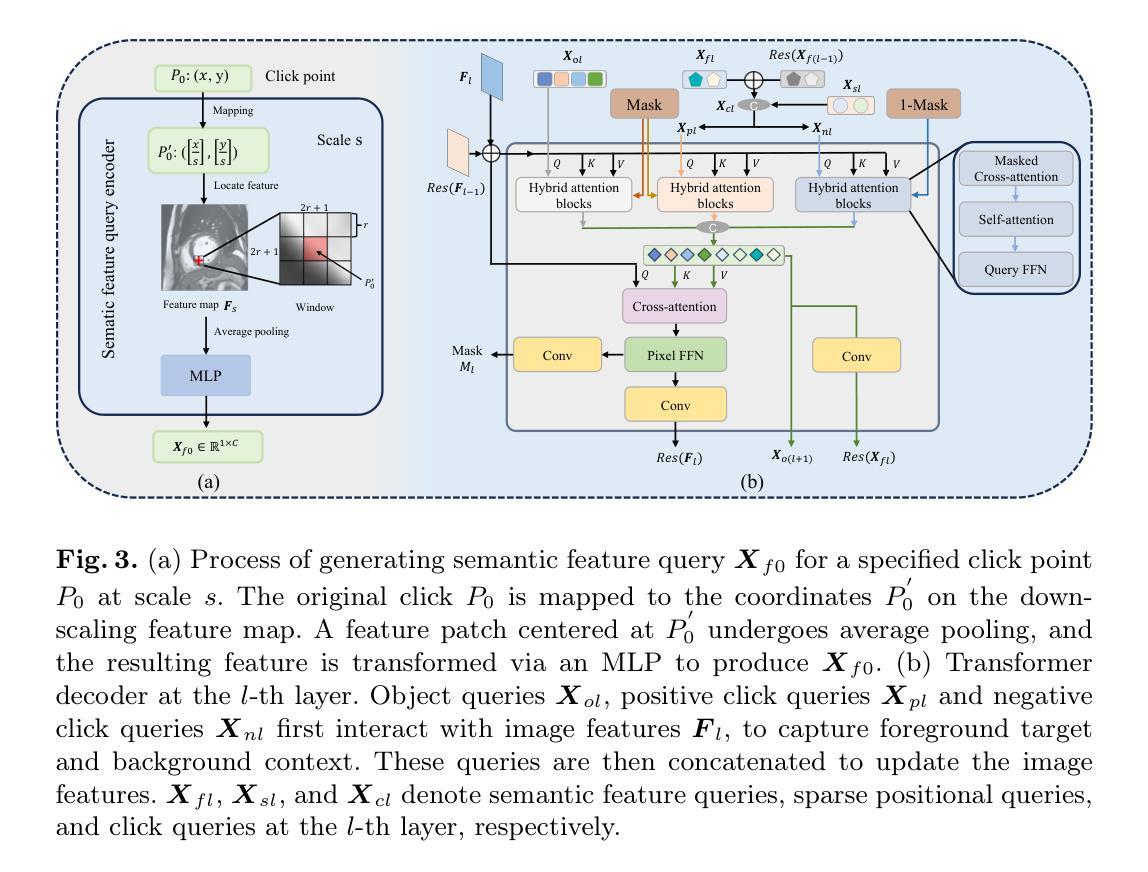
DAMPER: A Dual-Stage Medical Report Generation Framework with Coarse-Grained MeSH Alignment and Fine-Grained Hypergraph Matching
Authors:Xiaofei Huang, Wenting Chen, Jie Liu, Qisheng Lu, Xiaoling Luo, Linlin Shen
Medical report generation is crucial for clinical diagnosis and patient management, summarizing diagnoses and recommendations based on medical imaging. However, existing work often overlook the clinical pipeline involved in report writing, where physicians typically conduct an initial quick review followed by a detailed examination. Moreover, current alignment methods may lead to misaligned relationships. To address these issues, we propose DAMPER, a dual-stage framework for medical report generation that mimics the clinical pipeline of report writing in two stages. In the first stage, a MeSH-Guided Coarse-Grained Alignment (MCG) stage that aligns chest X-ray (CXR) image features with medical subject headings (MeSH) features to generate a rough keyphrase representation of the overall impression. In the second stage, a Hypergraph-Enhanced Fine-Grained Alignment (HFG) stage that constructs hypergraphs for image patches and report annotations, modeling high-order relationships within each modality and performing hypergraph matching to capture semantic correlations between image regions and textual phrases. Finally,the coarse-grained visual features, generated MeSH representations, and visual hypergraph features are fed into a report decoder to produce the final medical report. Extensive experiments on public datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of DAMPER in generating comprehensive and accurate medical reports, outperforming state-of-the-art methods across various evaluation metrics.
医学报告生成对临床诊断和治疗管理至关重要,它是基于医学成像对诊断和建议进行汇总的关键环节。然而,现有工作往往忽略了报告写作中涉及的临床流程,医生通常先进行初步快速审查,然后进行详细检查。此外,当前的对齐方法可能导致关系错位。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了DAMPER,这是一个用于医学报告生成的双阶段框架,它模仿了两阶段报告写作的临床流程。在第一阶段,采用MeSH指导的粗粒度对齐(MCG)阶段,将胸部X光(CXR)图像特征与医学主题词表(MeSH)特征对齐,生成整体印象的粗略关键词表示。在第二阶段,采用超图增强细粒度对齐(HFG)阶段,为图像补丁和报告注释构建超图,对每种模态内部的高阶关系进行建模,并执行超图匹配以捕获图像区域和文本短语之间的语义相关性。最后,将粗粒度视觉特征、生成的MeSH表示和视觉超图特征输入报告解码器,以生成最终的医学报告。在公共数据集上的大量实验表明,DAMPER在生成全面准确的医学报告方面非常有效,在各项评估指标上均优于最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了医学报告生成的重要性及其在临床诊断和治疗患者管理中的作用。针对现有方法忽略临床报告写作流程和可能导致的对齐问题,提出了DAMPER双阶段框架,模仿临床报告写作流程,包括MeSH指导的粗粒度对齐和超图增强的细粒度对齐,并实现了在公共数据集上的优良表现。
Key Takeaways
- 医学报告生成在临床诊断和治疗患者管理中起到重要作用。
- 现有方法忽略了临床报告写作流程,通常分为初步审查和详细检查两个阶段。
- DAMPER框架模仿临床报告写作流程,分为两个阶段:MeSH指导的粗粒度对齐和Hypergraph增强的细粒度对齐。
- MeSH指导的粗粒度对齐阶段将CXR图像特征与MeSH特征对齐,生成整体印象的关键短语表示。
- Hypergraph增强的细粒度对齐阶段构建图像补丁和报告注释的超图,建立每种模态内的高阶关系,并通过超图匹配捕捉图像区域和文本短语之间的语义关联。
- DAMPER框架实现了在公共数据集上的优良表现,生成的医学报告全面且准确。
点此查看论文截图

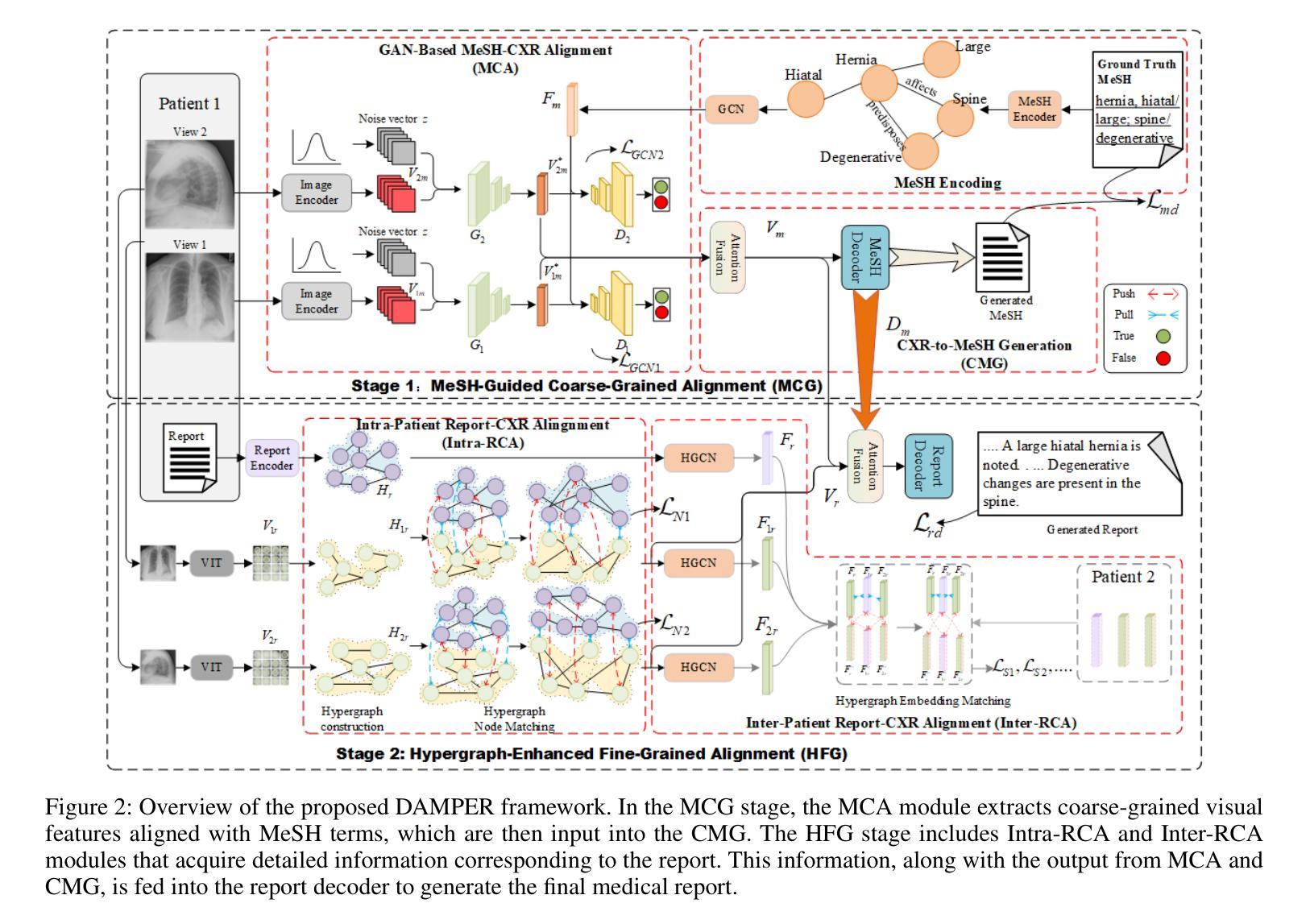
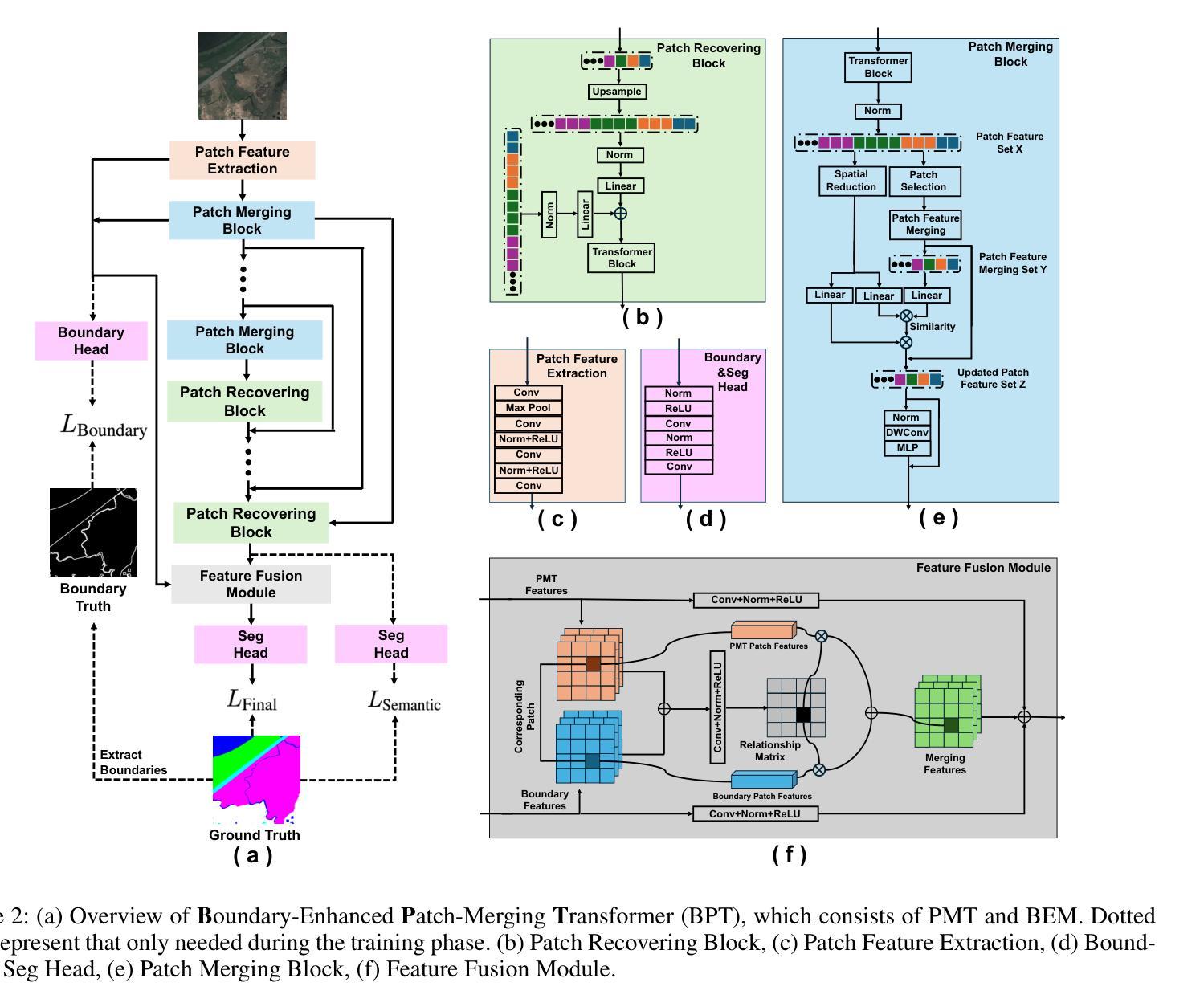
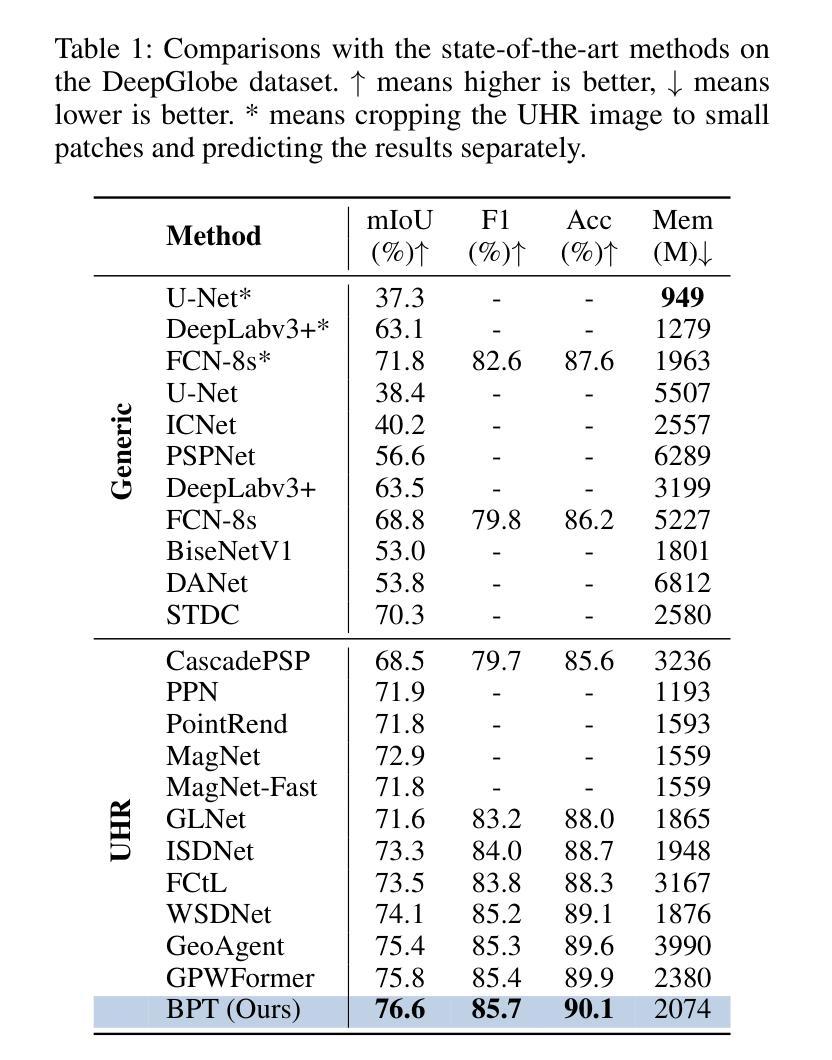
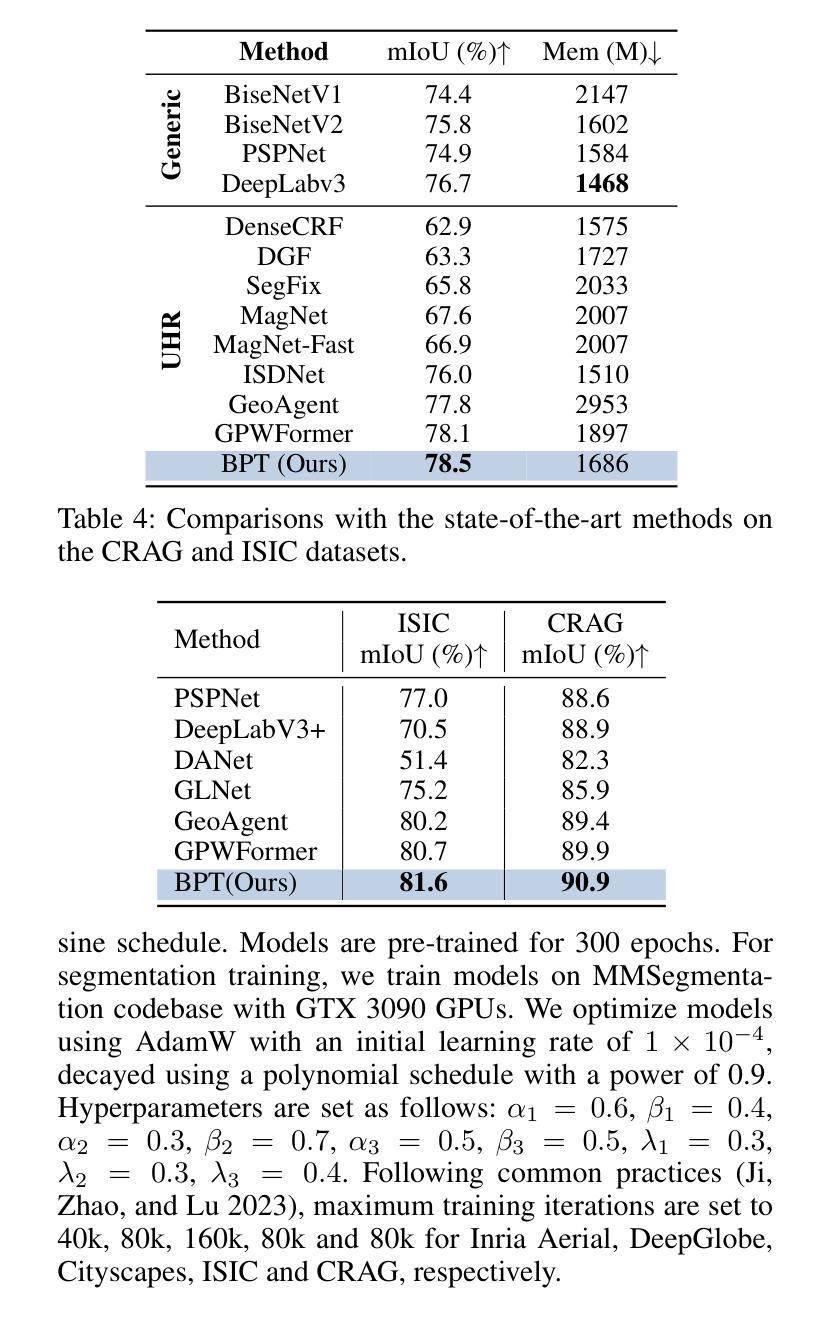
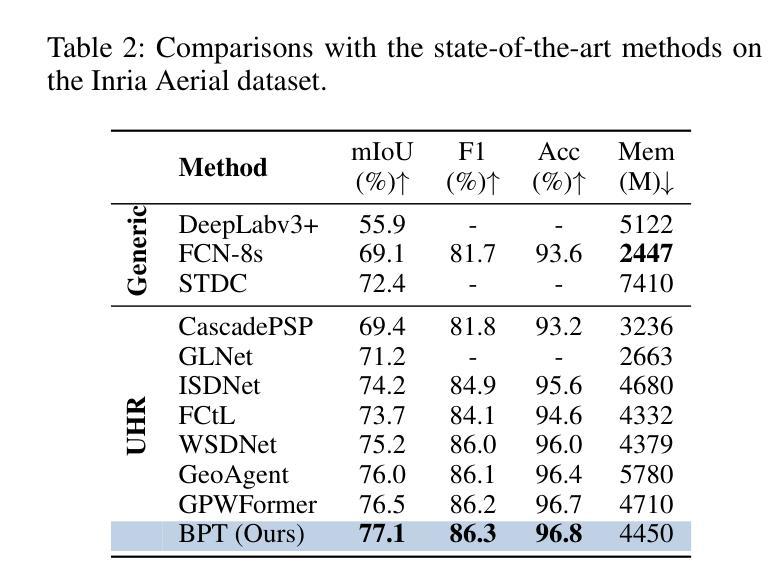
Ultra-High Resolution Segmentation via Boundary-Enhanced Patch-Merging Transformer
Authors:Haopeng Sun, Yingwei Zhang, Lumin Xu, Sheng Jin, Yiqiang Chen
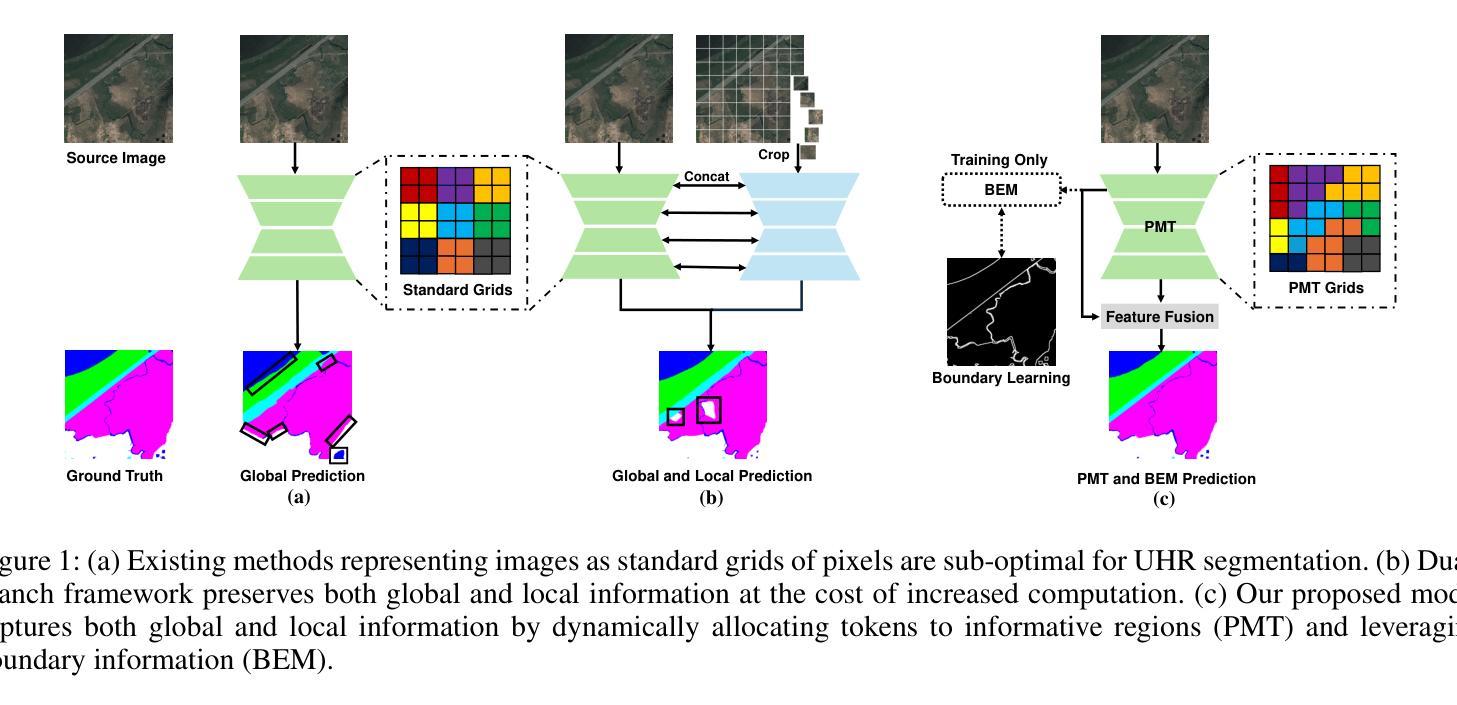
Segmentation of ultra-high resolution (UHR) images is a critical task with numerous applications, yet it poses significant challenges due to high spatial resolution and rich fine details. Recent approaches adopt a dual-branch architecture, where a global branch learns long-range contextual information and a local branch captures fine details. However, they struggle to handle the conflict between global and local information while adding significant extra computational cost. Inspired by the human visual system’s ability to rapidly orient attention to important areas with fine details and filter out irrelevant information, we propose a novel UHR segmentation method called Boundary-enhanced Patch-merging Transformer (BPT). BPT consists of two key components: (1) Patch-Merging Transformer (PMT) for dynamically allocating tokens to informative regions to acquire global and local representations, and (2) Boundary-Enhanced Module (BEM) that leverages boundary information to enrich fine details. Extensive experiments on multiple UHR image segmentation benchmarks demonstrate that our BPT outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods without introducing extra computational overhead. Codes will be released to facilitate research.
超高分辨率(UHR)图像分割是一个具有许多应用的关键任务,但由于其高空间分辨率和丰富的细节而面临重大挑战。最近的方法采用双分支架构,其中全局分支学习长程上下文信息,而局部分支捕获细节。然而,它们在处理全局和局部信息之间的冲突时遇到困难,同时增加了相当大的额外计算成本。受人类视觉系统能够快速将注意力定向到具有细节的重要区域并过滤掉无关信息的能力的启发,我们提出了一种新的UHR分割方法,称为边界增强补丁合并转换器(BPT)。BPT由两个关键组件组成:(1)补丁合并转换器(PMT),用于动态分配令牌以获取全局和局部表示信息的有意义区域;(2)边界增强模块(BEM),利用边界信息来丰富细节。在多个UHR图像分割基准测试上的广泛实验表明,我们的BPT方法在没有任何额外计算开销的情况下优于以前的最先进方法。我们将发布代码以促进研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted by AAAI 2025, 10 pages, 4 figures
Summary
超高分辨率(UHR)图像分割是一项具有许多应用的关键任务,但由于高空间分辨率和丰富的细节而面临挑战。最近的方法采用双分支架构,全局分支学习长范围上下文信息,局部分支捕捉细节。然而,它们难以处理全局和局部信息之间的冲突,并增加了额外的计算成本。受人类视觉系统能够快速将注意力集中在具有细节的重要区域并过滤掉无关信息的能力的启发,我们提出了一种新的UHR分割方法,称为边界增强补丁合并转换器(BPT)。BPT由两个关键组件组成:(1)补丁合并转换器(PMT)用于动态分配令牌以获取全局和局部表示;(2)边界增强模块(BEM)利用边界信息来丰富细节。在多个UHR图像分割基准测试上的广泛实验表明,我们的BPT在不需要引入额外计算开销的情况下优于以前的最先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- 超高分辨率(UHR)图像分割是一项具有挑战性的任务,需要处理高空间分辨率和丰富细节。
- 现有方法采用双分支架构,但难以平衡全局和局部信息,且计算成本较高。
- 提出的Boundary-enhanced Patch-merging Transformer(BPT)方法受到人类视觉系统的启发,能够动态分配注意力到重要区域。
- BPT包含两个关键组件:Patch-Merging Transformer(PMT)和Boundary-Enhanced Module(BEM)。
- PMT用于获取全局和局部表示,而BEM利用边界信息来增强细节。
- 在多个UHR图像分割基准测试上,BPT表现出优异的性能,优于其他最先进的方法。
点此查看论文截图


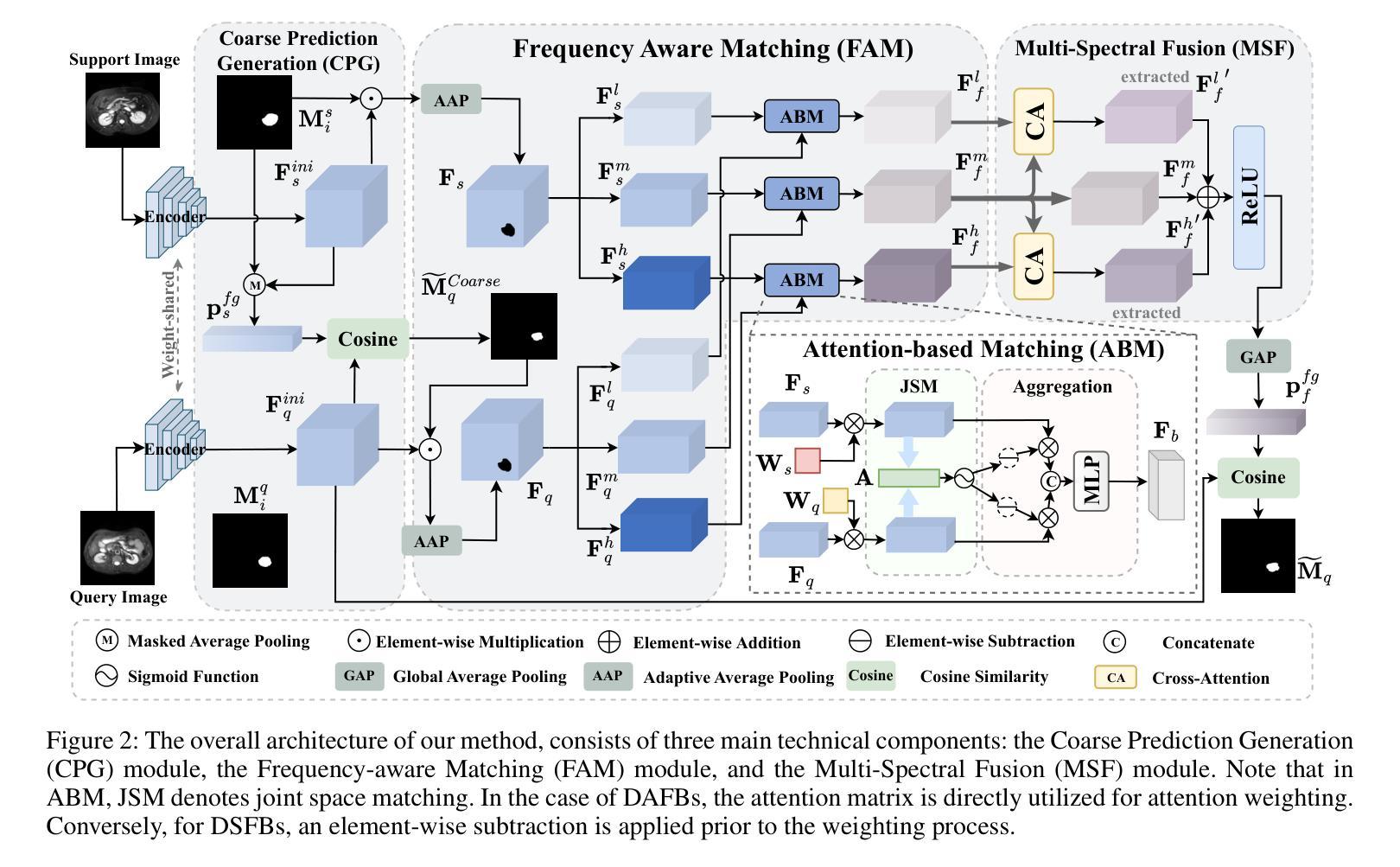
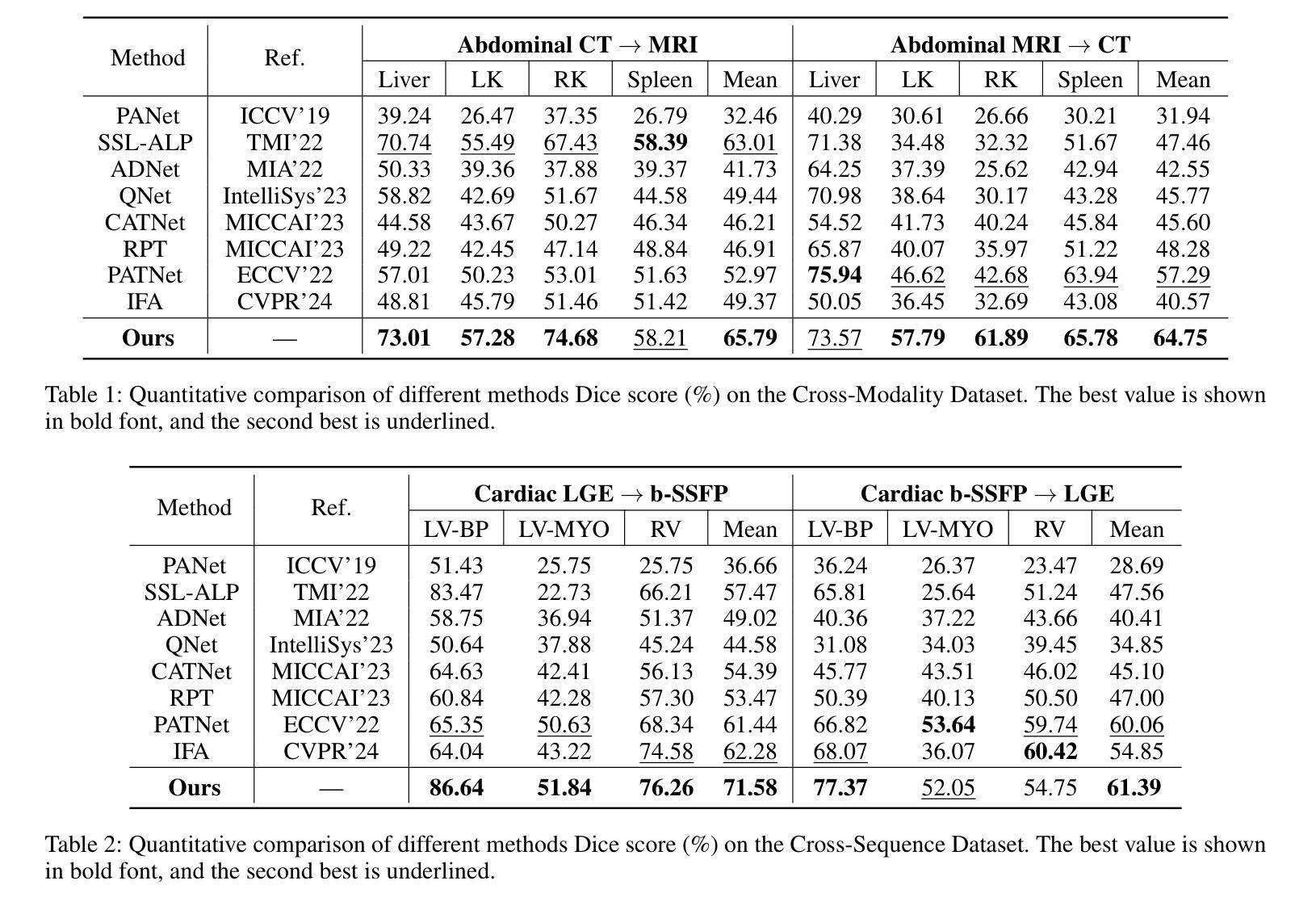
FAMNet: Frequency-aware Matching Network for Cross-domain Few-shot Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Yuntian Bo, Yazhou Zhu, Lunbo Li, Haofeng Zhang
Existing few-shot medical image segmentation (FSMIS) models fail to address a practical issue in medical imaging: the domain shift caused by different imaging techniques, which limits the applicability to current FSMIS tasks. To overcome this limitation, we focus on the cross-domain few-shot medical image segmentation (CD-FSMIS) task, aiming to develop a generalized model capable of adapting to a broader range of medical image segmentation scenarios with limited labeled data from the novel target domain. Inspired by the characteristics of frequency domain similarity across different domains, we propose a Frequency-aware Matching Network (FAMNet), which includes two key components: a Frequency-aware Matching (FAM) module and a Multi-Spectral Fusion (MSF) module. The FAM module tackles two problems during the meta-learning phase: 1) intra-domain variance caused by the inherent support-query bias, due to the different appearances of organs and lesions, and 2) inter-domain variance caused by different medical imaging techniques. Additionally, we design an MSF module to integrate the different frequency features decoupled by the FAM module, and further mitigate the impact of inter-domain variance on the model’s segmentation performance. Combining these two modules, our FAMNet surpasses existing FSMIS models and Cross-domain Few-shot Semantic Segmentation models on three cross-domain datasets, achieving state-of-the-art performance in the CD-FSMIS task.
现有的一些医学图像分割模型的少数拍摄场景无法应对医学成像中的一个实际问题:由于不同成像技术造成的领域偏移问题,限制了其在当前医学图像分割任务中的应用。为了克服这一局限性,我们专注于跨域医学图像分割模型的少数拍摄场景(CD-FSMIS任务),旨在开发一种通用模型,能够在有限的新目标域标记数据的情况下适应更广泛的医学图像分割场景。受不同领域之间频域相似性特征的启发,我们提出了一种频率感知匹配网络(FAMNet),它包括两个关键组件:频率感知匹配(FAM)模块和多光谱融合(MSF)模块。FAM模块解决了元学习阶段的两个问题:1)由于器官和病变的不同外观导致的内在支撑查询偏差所造成的领域内方差;以及由不同医学成像技术引起的领域间方差。此外,我们设计了一个MSF模块来整合由FAM模块分离的不同的频率特征,并进一步减轻领域间方差对模型分割性能的影响。结合这两个模块,我们的FAMNet在三个跨域数据集上的表现超过了现有的FSMIS模型和跨域少数拍摄语义分割模型,在CD-FSMIS任务中达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by the 39th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-25)
Summary
针对现有医疗图像分割模型因不同成像技术导致的领域偏移问题,提出一种频率感知匹配网络(FAMNet),包含频率感知匹配和多光谱融合两个关键组件,以提升模型对多种医疗图像分割场景的适应性。FAMNet成功超越了现有的FSMIS模型和跨域少数语义分割模型,在三个跨域数据集上实现了CD-FSMIS任务的最新性能。
Key Takeaways
- 领域偏移问题是医疗图像分割中的一个实际问题,由于不同成像技术导致的。
- 频率感知匹配网络(FAMNet)旨在解决跨域少数医疗图像分割(CD-FSMIS)任务。
- FAMNet包含两个关键组件:频率感知匹配(FAM)模块和多光谱融合(MSF)模块。
- FAM模块解决了元学习阶段的域内和域间方差问题。
- MSF模块用于集成由FAM模块分离的不同频率特征,并减少域间方差对模型分割性能的影响。
- FAMNet在三个跨域数据集上的表现超越了现有的FSMIS模型和跨域少数语义分割模型。
- FAMNet在CD-FSMIS任务上实现了最新性能。
点此查看论文截图

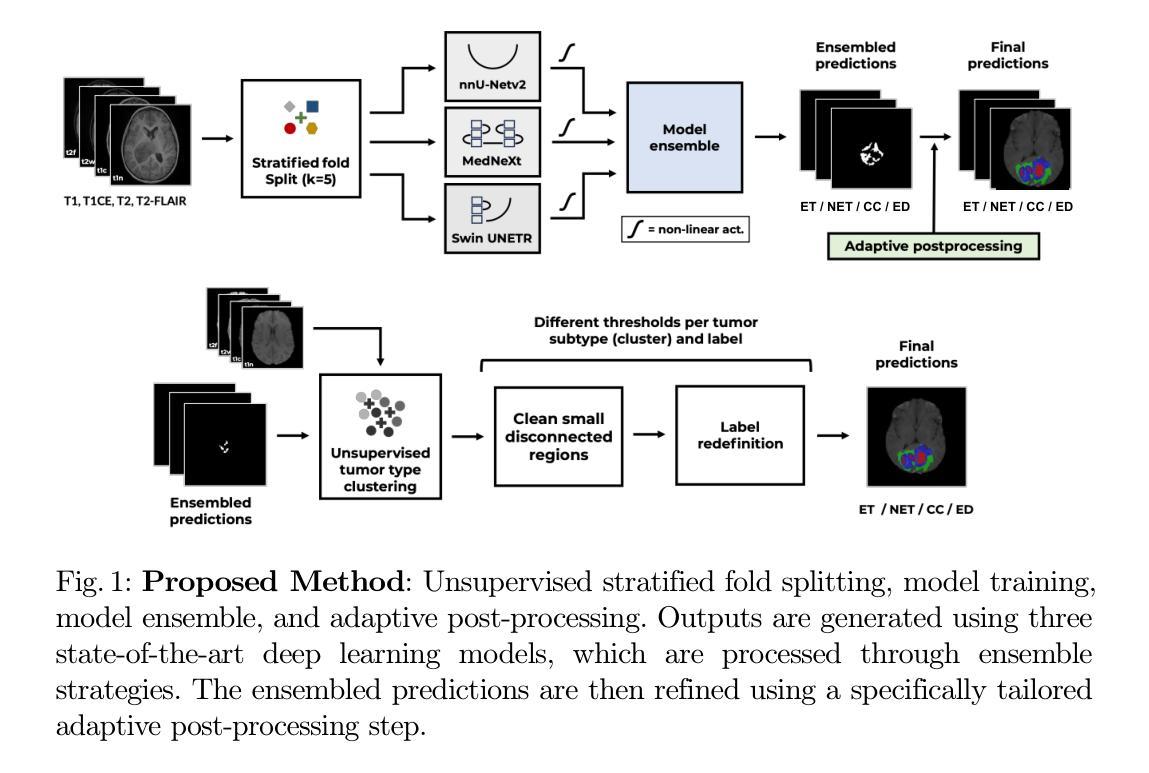
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Feature-Based Subtyping and Model Ensemble for Enhanced Brain Tumor Segmentation
Authors:Zhifan Jiang, Daniel Capellán-Martín, Abhijeet Parida, Austin Tapp, Xinyang Liu, María J. Ledesma-Carbayo, Syed Muhammad Anwar, Marius George Linguraru
Accurate and automatic segmentation of brain tumors in multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) is essential for quantitative measurements, which play an increasingly important role in clinical diagnosis and prognosis. The International Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) Challenge 2024 offers a unique benchmarking opportunity, including various types of brain tumors in both adult and pediatric populations, such as pediatric brain tumors (PED), meningiomas (MEN-RT) and brain metastases (MET), among others. Compared to previous editions, BraTS 2024 has implemented changes to substantially increase clinical relevance, such as refined tumor regions for evaluation. We propose a deep learning-based ensemble approach that integrates state-of-the-art segmentation models. Additionally, we introduce innovative, adaptive pre- and post-processing techniques that employ MRI-based radiomic analyses to differentiate tumor subtypes. Given the heterogeneous nature of the tumors present in the BraTS datasets, this approach enhances the precision and generalizability of segmentation models. On the final testing sets, our method achieved mean lesion-wise Dice similarity coefficients of 0.926, 0.801, and 0.688 for the whole tumor in PED, MEN-RT, and MET, respectively. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in improving segmentation performance and generalizability for various brain tumor types. The source code of our implementation is available at https://github.com/Precision-Medical-Imaging-Group/HOPE-Segmenter-Kids. Additionally, an open-source web-application is accessible at https://segmenter.hope4kids.io/ which uses the docker container aparida12/brats-peds-2024:v20240913 .
在多参数磁共振成像(mpMRI)中,对脑肿瘤进行准确、自动分割对于定量测量非常重要,这在临床诊断和预后中发挥着越来越重要的作用。2024年国际脑肿瘤分割(BraTS)挑战赛提供了一个独特的基准测试机会,包括成人和儿童人群中的各种脑肿瘤类型,如儿童脑肿瘤(PED)、脑膜瘤(MEN-RT)和脑转移(MET)等。与之前的版本相比,BraTS 2024实施了变化,以大大增加临床相关性,例如对评估肿瘤区域的精细划分。我们提出了一种基于深度学习的集成方法,该方法集成了最先进的分割模型。此外,我们引入了创新、自适应的预处理和后处理技巧,采用基于MRI的放射组学分析来区分肿瘤亚型。鉴于BraTS数据集中存在的肿瘤的异质性,这种方法提高了分割模型的精度和通用性。在最终测试集上,我们的方法实现了PED、MEN-RT和MET全肿瘤的病变级平均Dice相似系数分别为0.926、0.801和0.688。这些结果证明了我们方法在改进各种脑肿瘤类型的分割性能和通用性方面的有效性。我们实现的源代码可在[https://github.com/Precision-Medical-Imaging-Group/HOPE-Segmenter-Kids获取。此外,一个开源的web应用程序可在[https://segmenter.hope4kids.io/上使用,该应用程序使用docker容器aparida12/brats-peds-2024:v20240913。](https://segmenter.hope4kids.io/%E4%B8%8A%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8%EF%BC%8C%E8%AF%A5%E7%9A%84%E5%AE%BE%E7%BD%AE%E5%B9%B3%E5%AE%B9aparida12/brats-peds-2024:v20240913%E3%80%82)
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 4 figures, 3 tables. This paper was accepted at MICCAI-BraTS 2024
Summary
本文提出一种基于深度学习的集成方法,用于多参数磁共振成像(mpMRI)中的脑肿瘤准确自动分割。该方法结合最先进的分割模型,并引入创新的预处理和后处理技术,以区分肿瘤亚型。在BraTS 2024挑战数据集上,该方法提高了分割性能和模型的泛化能力,对不同类型的脑肿瘤如PED、MEN-RT和MET的整瘤Dice相似系数分别达到0.926、0.801和0.688。源代码已发布在GitHub上,并有一个开放源码的web应用程序可供使用。
Key Takeaways
- BraTS 2024挑战提供了独特的基准测试机会,包含成人和儿童的多种类型的脑肿瘤。
- 与之前的版本相比,BraTS 2024增加了临床相关性更高的改进,如更精细的肿瘤区域评估。
- 本文提出了一种基于深度学习的集成方法,整合最先进的分割模型进行脑肿瘤分割。
- 引入创新的预处理和后处理技术,利用MRI的放射组学分析区分肿瘤亚型。
- 该方法在BraTS 2024数据集上实现了较高的分割性能,特别是对于不同类型的脑肿瘤。
- 公开的源代码包括一个GitHub链接和一个web应用程序,方便使用。
点此查看论文截图