⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-25 更新
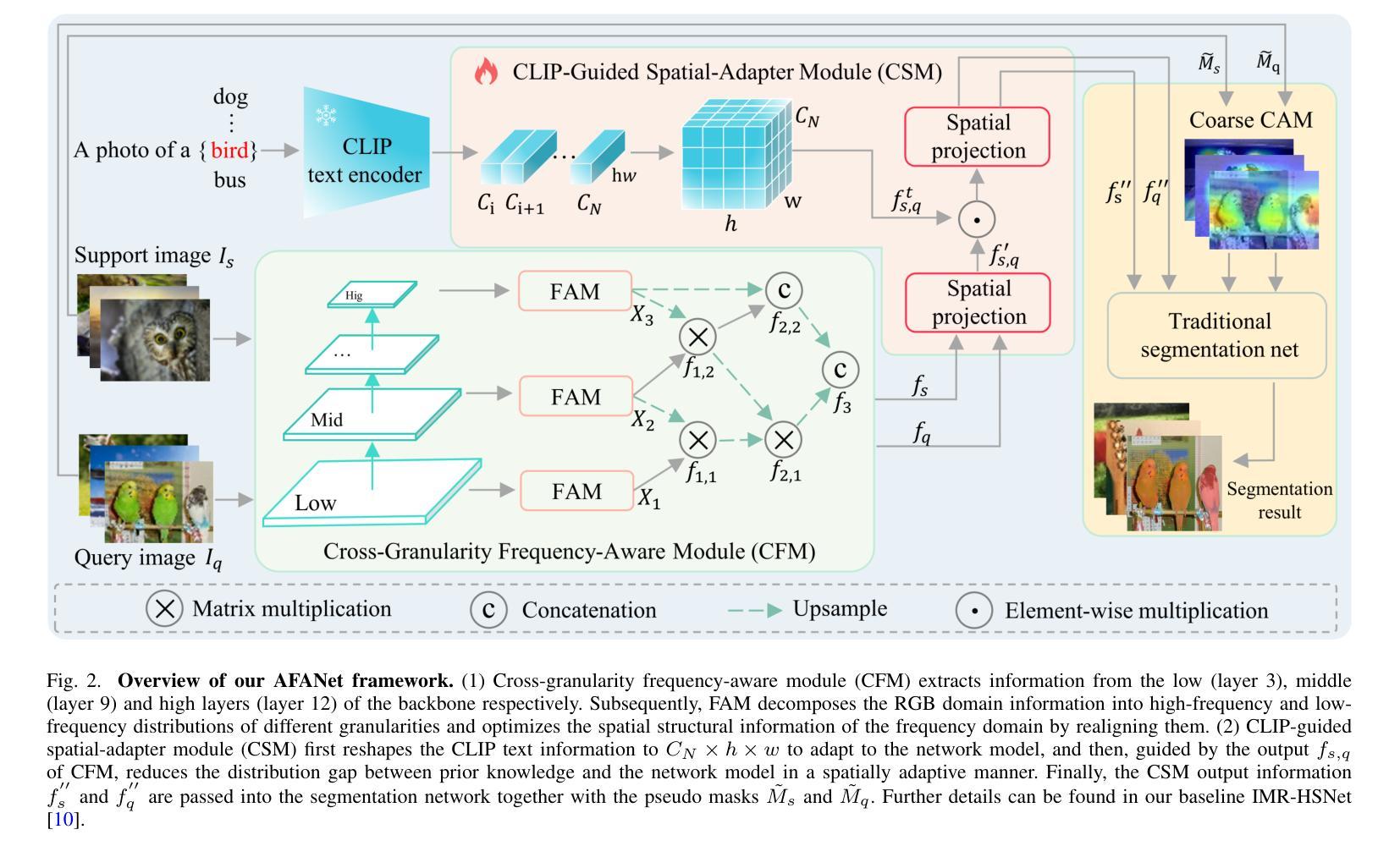
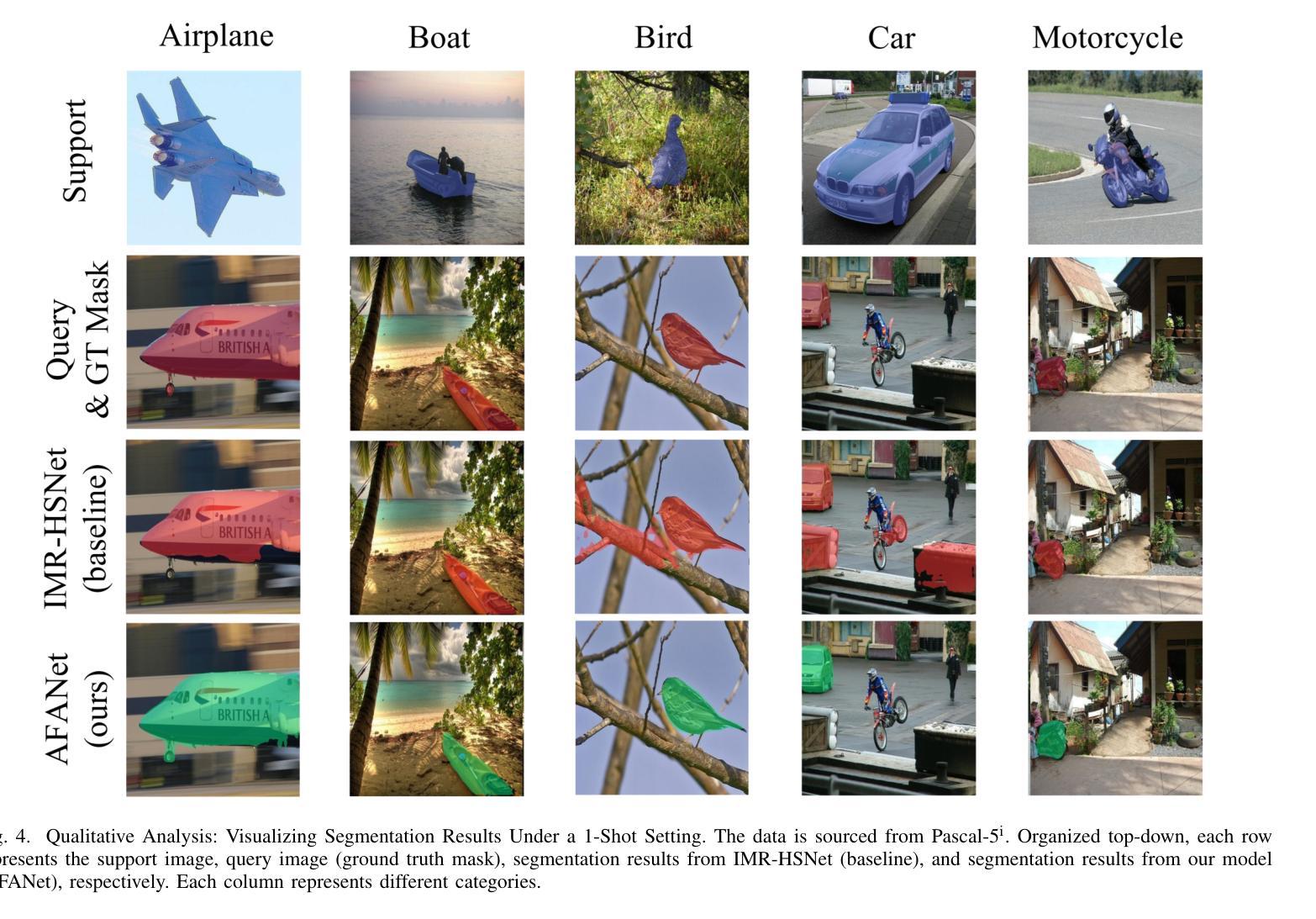
AFANet: Adaptive Frequency-Aware Network for Weakly-Supervised Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Jiaqi Ma, Guo-Sen Xie, Fang Zhao, Zechao Li
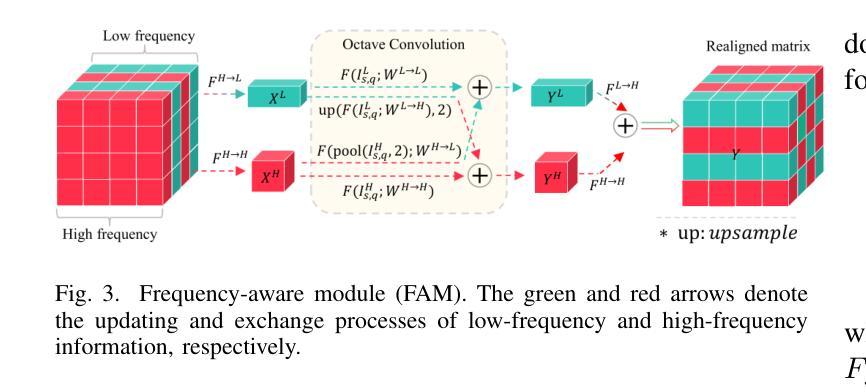
Few-shot learning aims to recognize novel concepts by leveraging prior knowledge learned from a few samples. However, for visually intensive tasks such as few-shot semantic segmentation, pixel-level annotations are time-consuming and costly. Therefore, in this paper, we utilize the more challenging image-level annotations and propose an adaptive frequency-aware network (AFANet) for weakly-supervised few-shot semantic segmentation (WFSS). Specifically, we first propose a cross-granularity frequency-aware module (CFM) that decouples RGB images into high-frequency and low-frequency distributions and further optimizes semantic structural information by realigning them. Unlike most existing WFSS methods using the textual information from the multi-modal language-vision model, e.g., CLIP, in an offline learning manner, we further propose a CLIP-guided spatial-adapter module (CSM), which performs spatial domain adaptive transformation on textual information through online learning, thus providing enriched cross-modal semantic information for CFM. Extensive experiments on the Pascal-5\textsuperscript{i} and COCO-20\textsuperscript{i} datasets demonstrate that AFANet has achieved state-of-the-art performance. The code is available at https://github.com/jarch-ma/AFANet.
少量学习旨在通过从少量样本中学习到的先验知识来识别新概念。然而,对于视觉密集型任务(如少量语义分割)来说,像素级注释既耗时又成本高昂。因此,本文利用更具挑战性的图像级注释,并提出一种自适应频率感知网络(AFANet)进行弱监督少量语义分割(WFSS)。具体来说,我们首先提出了跨粒度频率感知模块(CFM),它将RGB图像分解为高频和低频分布,并通过重新对齐进一步优化语义结构信息。与大多数现有的使用多模态语言视觉模型的文本信息的WFSS方法不同,例如以离线学习方式使用的CLIP,我们进一步提出了CLIP引导的空间适配器模块(CSM),该模块通过在线学习在文本信息上执行空间域自适应转换,从而为CFM提供丰富的跨模态语义信息。在Pascal-5i和COCO-20i数据集上的大量实验表明,AFANet已经达到了最新性能水平。代码可在https://github.com/jarch-ma/AFANet找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于自适应频率感知网络(AFANet)的弱监督少样本语义分割(WFSS)方法。该方法利用图像级标注,通过跨粒度频率感知模块(CFM)将图像分解为高频和低频分布,并重新对齐以优化语义结构信息。同时,引入CLIP引导的的空间适配器模块(CSM),通过在线学习对文本信息进行空间域自适应变换,为CFM提供丰富的跨模态语义信息。在Pascal-5i和COCO-20i数据集上的实验表明,AFANet达到了最新技术水平。
Key Takeaways
- 本文关注少样本语义分割问题,提出自适应频率感知网络(AFANet)解决方案。
- 利用图像级标注,避免像素级标注的时间成本和成本高昂问题。
- 引入跨粒度频率感知模块(CFM),分解图像为高频和低频分布,优化语义结构信息。
- 与大多数使用离线学习方式的WFSS方法不同,提出CLIP引导的的空间适配器模块(CSM),通过在线学习进行空间域自适应变换。
- CSAM模块富集了跨模态语义信息,为CFM提供更多上下文。
- 在Pascal-5i和COCO-20i数据集上的实验表明,AFANet性能达到最新技术水平。
点此查看论文截图

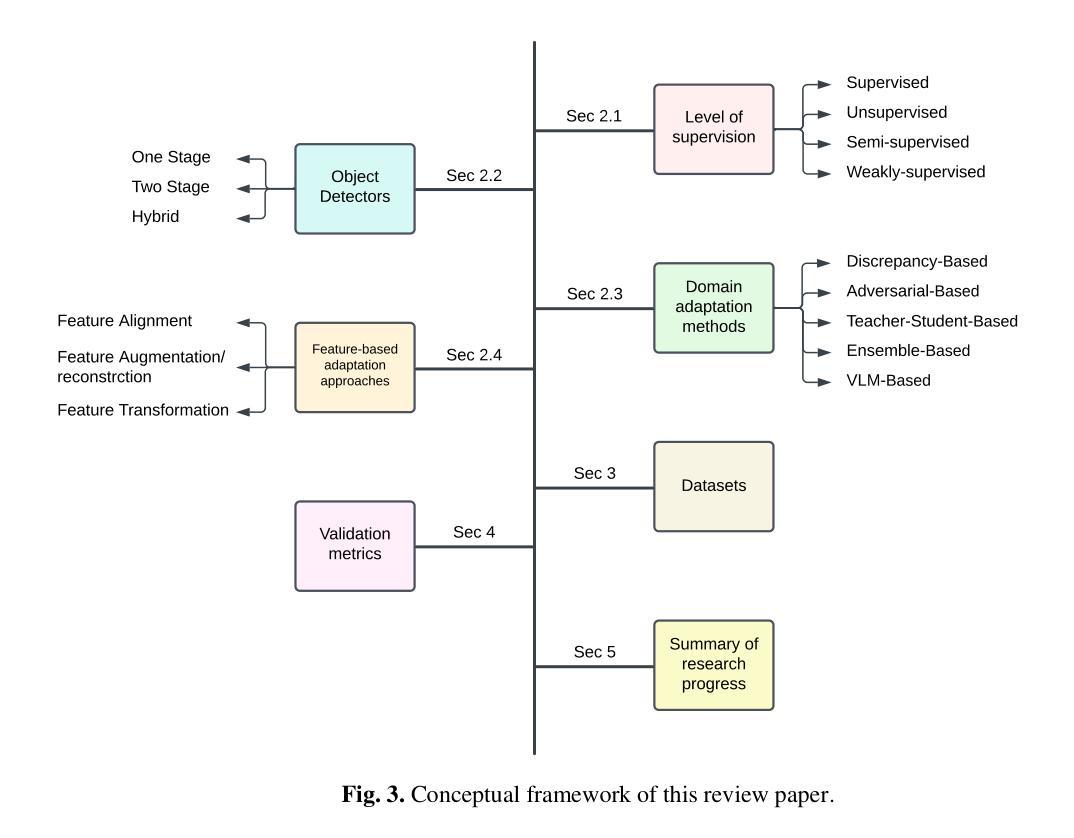
Feature Based Methods Domain Adaptation for Object Detection: A Review Paper
Authors:Helia Mohamadi, Mohammad Ali Keyvanrad, Mohammad Reza Mohammadi
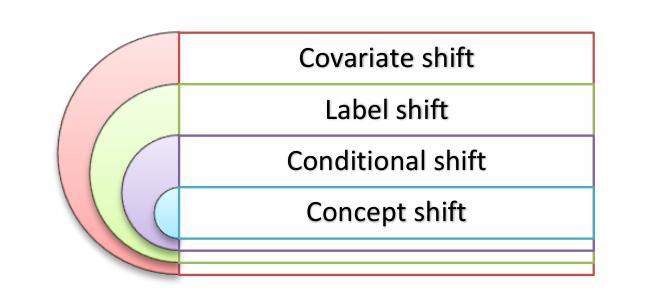
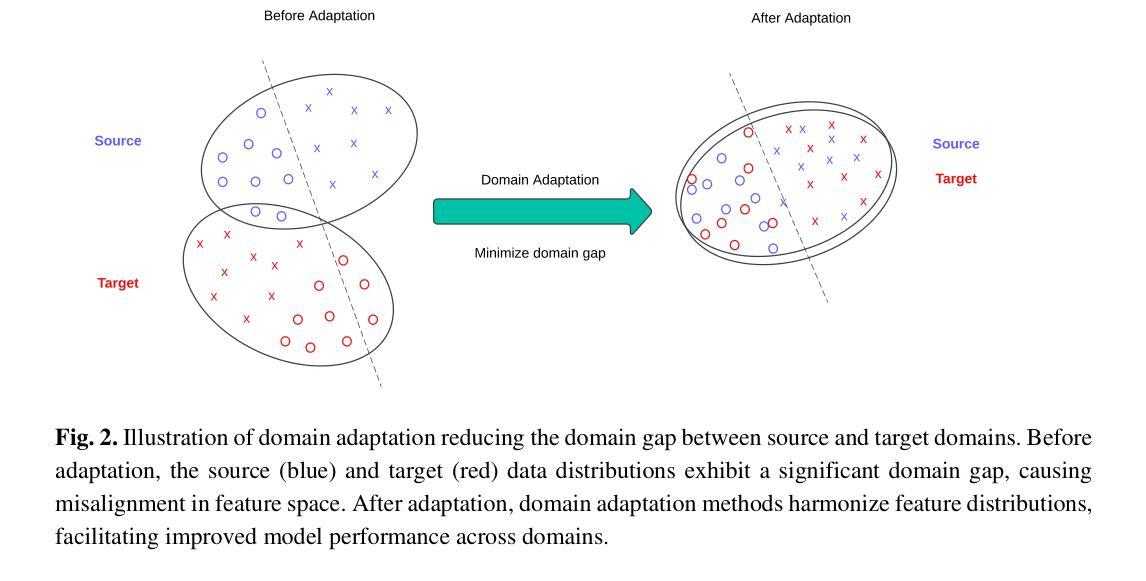
Domain adaptation, a pivotal branch of transfer learning, aims to enhance the performance of machine learning models when deployed in target domains with distinct data distributions. This is particularly critical for object detection tasks, where domain shifts (caused by factors such as lighting conditions, viewing angles, and environmental variations) can lead to significant performance degradation. This review delves into advanced methodologies for domain adaptation, including adversarial learning, discrepancy-based, multi-domain, teacher-student, ensemble, and VLM techniques, emphasizing their efficacy in reducing domain gaps and enhancing model robustness. Feature-based methods have emerged as powerful tools for addressing these challenges by harmonizing feature representations across domains. These techniques, such as Feature Alignment, Feature Augmentation/Reconstruction, and Feature Transformation, are employed alongside or as integral parts of other domain adaptation strategies to minimize domain gaps and improve model performance. Special attention is given to strategies that minimize the reliance on extensive labeled data and using unlabeled data, particularly in scenarios involving synthetic-to-real domain shifts. Applications in fields such as autonomous driving and medical imaging are explored, showcasing the potential of these methods to ensure reliable object detection in diverse and complex settings. By providing a thorough analysis of state-of-the-art techniques, challenges, and future directions, this work offers a valuable reference for researchers striving to develop resilient and adaptable object detection frameworks, advancing the seamless deployment of artificial intelligence in dynamic environments.
领域自适应是迁移学习的一个重要分支,旨在提高机器学习模型在具有不同数据分布的目标域中的性能。这对于对象检测任务尤为重要,因为域偏移(由光照条件、观看角度和环境变化等因素引起)可能导致性能显著下降。本文深入探讨了领域自适应的高级方法,包括对抗性学习、基于差异的方法、多域方法、师徒方法、集成方法和VLM技术,重点介绍了它们在减少域差距和提高模型稳健性方面的有效性。基于特征的方法已成为解决这些挑战的强大工具,通过协调不同领域的特征表示。这些方法,如特征对齐、特征增强/重建和特征变换等,与其他领域自适应策略一起使用或作为其不可或缺的一部分,以最小化领域差距并提高模型性能。在减少对大量标记数据的依赖和利用无标记数据方面给予了特别关注,特别是在涉及从合成到真实域的转移场景中。本文探讨了自动驾驶和医学影像等领域的应用,展示了这些方法在多样化和复杂环境中确保可靠对象检测的潜力。通过对最新技术、挑战和未来方向的深入分析,本文为那些努力开发具有弹性和适应性的对象检测框架的研究人员提供了宝贵的参考,推动了人工智能在动态环境中的无缝部署。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 46 pages, 13 figures, It will be submitted to a journal
Summary
本文综述了领域自适应技术在对象检测任务中的重要性,介绍了多种先进的领域自适应方法,如对抗性学习、差异法、多领域法、教师-学生法、集成法和VLM技术等,强调其在缩小领域差距和增强模型稳健性方面的作用。文中详细讨论了特征基方法,如特征对齐、特征增强/重建和特征变换等,这些方法作为其他领域自适应策略的补充或重要组成部分,用于最小化领域差距并提高模型性能。文章还重点关注了如何利用无标签数据减少依赖大量标签数据的方法,特别是在合成到真实领域转移的场景中。本文探讨了这些技术在自动驾驶和医学影像等领域的应用,展示了它们在确保在各种复杂环境中可靠对象检测方面的潜力。文章对最新技术、挑战和未来方向进行了深入分析,为开发具有弹性和适应性的对象检测框架的研究人员提供了宝贵的参考。
Key Takeaways
- 领域自适应是迁移学习的重要分支,旨在提高机器学习模型在数据分布不同的目标领域的性能。
- 对象检测任务中,领域偏移可能会导致性能显著下降。
- 先进的领域自适应方法包括对抗性学习、差异法、多领域法、教师-学生法、集成法和VLM技术等。
- 特征基方法,如特征对齐、特征增强/重建和特征变换等,是缩小领域差距和提高模型稳健性的有效工具。
- 利用无标签数据减少领域自适应中对标签数据的依赖是一个重要趋势。
- 领域自适应技术在自动驾驶和医学影像等领域有广泛应用。
点此查看论文截图

Object Detection Approaches to Identifying Hand Images with High Forensic Values
Authors:Thanh Thi Nguyen, Campbell Wilson, Imad Khan, Janis Dalins
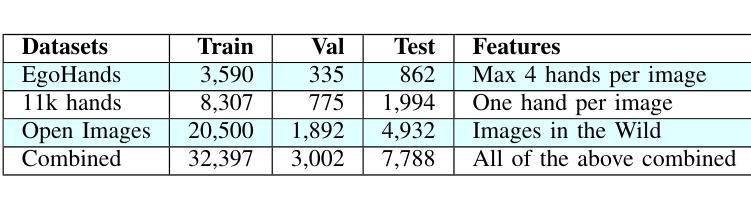
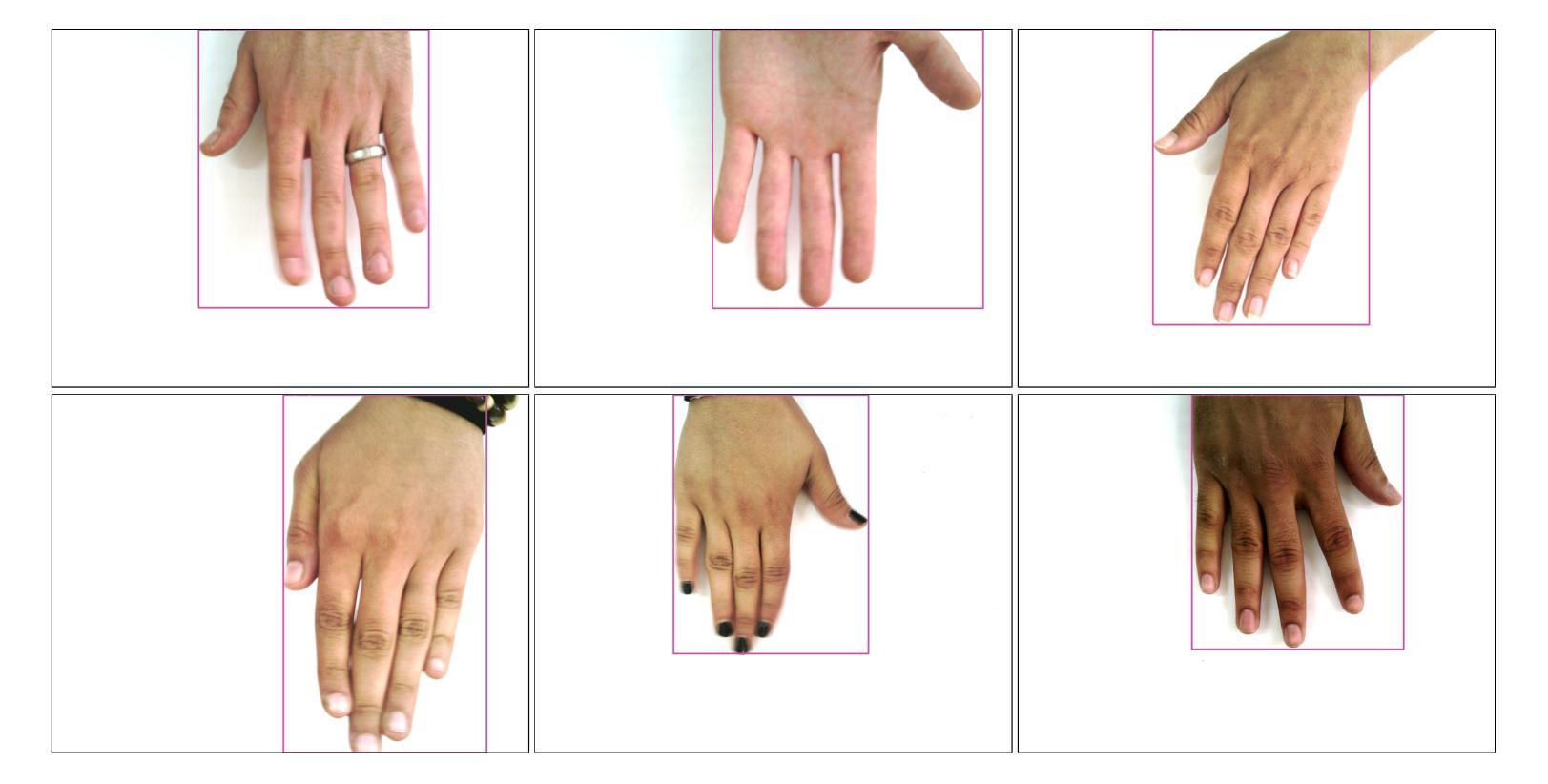
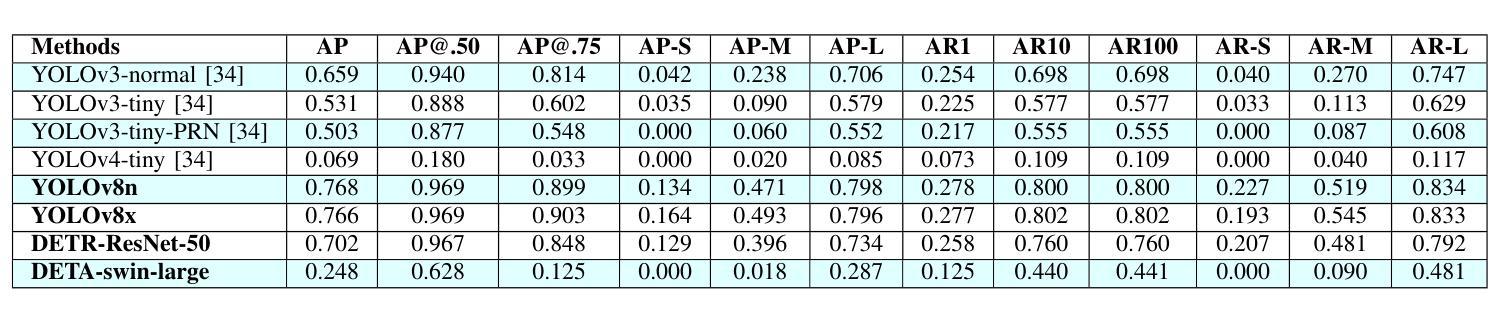
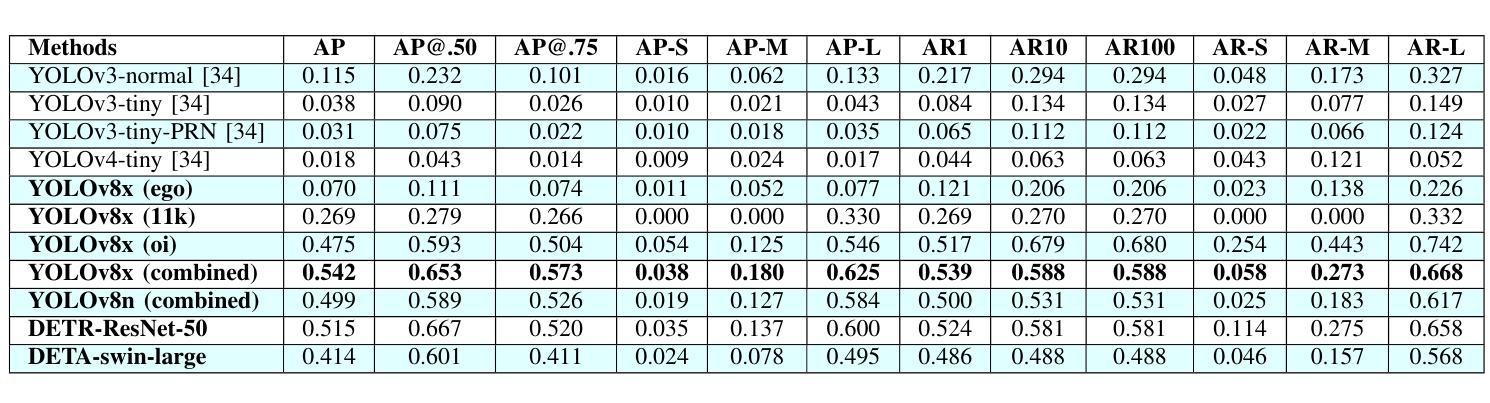
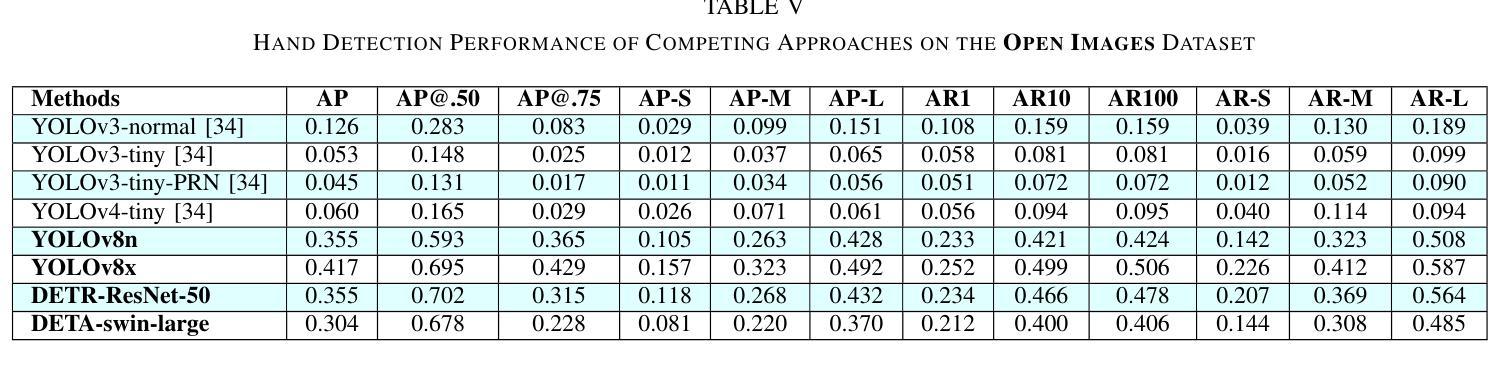
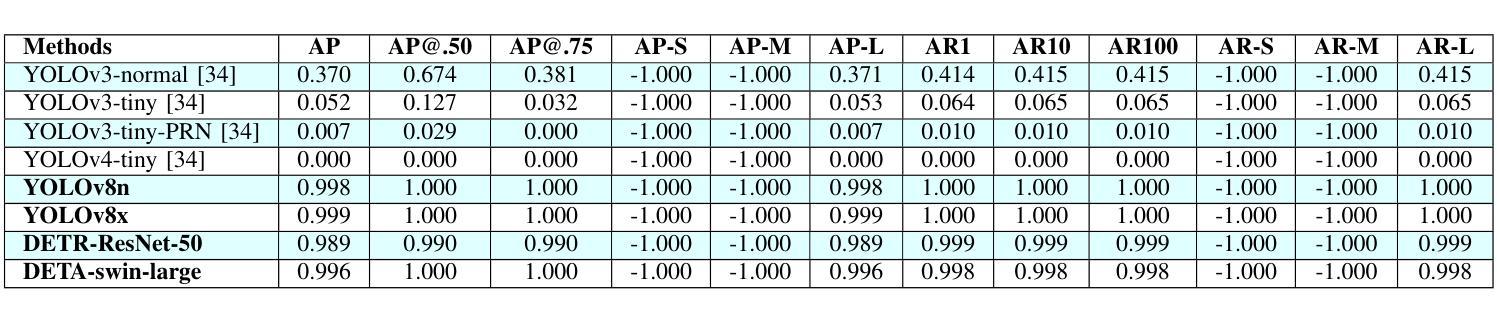
Forensic science plays a crucial role in legal investigations, and the use of advanced technologies, such as object detection based on machine learning methods, can enhance the efficiency and accuracy of forensic analysis. Human hands are unique and can leave distinct patterns, marks, or prints that can be utilized for forensic examinations. This paper compares various machine learning approaches to hand detection and presents the application results of employing the best-performing model to identify images of significant importance in forensic contexts. We fine-tune YOLOv8 and vision transformer-based object detection models on four hand image datasets, including the 11k hands dataset with our own bounding boxes annotated by a semi-automatic approach. Two YOLOv8 variants, i.e., YOLOv8 nano (YOLOv8n) and YOLOv8 extra-large (YOLOv8x), and two vision transformer variants, i.e., DEtection TRansformer (DETR) and Detection Transformers with Assignment (DETA), are employed for the experiments. Experimental results demonstrate that the YOLOv8 models outperform DETR and DETA on all datasets. The experiments also show that YOLOv8 approaches result in superior performance compared with existing hand detection methods, which were based on YOLOv3 and YOLOv4 models. Applications of our fine-tuned YOLOv8 models for identifying hand images (or frames in a video) with high forensic values produce excellent results, significantly reducing the time required by forensic experts. This implies that our approaches can be implemented effectively for real-world applications in forensics or related fields.
法医学在法律调查中发挥着至关重要的作用,使用先进技术,如基于机器学习方法的物体检测,可以提高法医学分析的效率和准确性。人手是独一无二的,可以留下独特的图案、痕迹或印记,可用于法医学检验。本文比较了各种机器学习在手部检测方面的应用方法,并展示了使用表现最佳的模型在法医学背景中识别具有重要意义的图像的应用结果。我们对YOLOv8和基于视觉变换器的物体检测模型进行了微调,使用了四个手部图像数据集,包括我们自己通过半自动方法标注边界框的包含1.1万张手部图像的数据集。实验采用了两种YOLOv8变体,即YOLOv8 nano(YOLOv8n)和YOLOv8 extra-large(YOLOv8x),以及两种视觉变换器变体,即DEtection TRansformer(DETR)和带有分配功能的Detection Transformers(DETA)。实验结果表明,YOLOv8模型在所有数据集上的表现优于DETR和DETA。实验还显示,与基于YOLOv3和YOLOv4模型的手部检测方法相比,YOLOv8方法具有更好的性能。我们微调后的YOLOv8模型在识别具有高法医学价值的手部图像(或视频中的帧)方面的应用取得了优异的结果,显著减少了法医学专家所需的时间。这意味着我们的方法可以有效地应用于法医学或相关领域的实际应用中。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at 2024 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC)
Summary
本文探讨了机器学习方法在法医学手印检测中的应用。通过对比不同的机器学习模型,如YOLOv8系列模型和视觉转换器模型,发现YOLOv8模型在手印检测方面表现出卓越性能,能够显著提高法医学分析的效率和准确性,有助于法医专家快速识别高价值的手印图像。
Key Takeaways
- 法医学中手印检测的重要性及其在提高调查效率与准确性方面的作用。
- 机器学习方法如YOLOv8模型和视觉转换器模型在手印检测中的应用。
- YOLOv8模型包括YOLOv8 nano和YOLOv8 extra-large两种变体,在手印检测方面表现优越。
- 对比实验显示YOLOv8模型相较于基于YOLOv3和YOLOv4模型的检测方法和视觉转换器模型具有更好的性能。
- YOLOv8模型的精细调整有助于快速识别高价值的手印图像或视频帧。
- 此研究能够为实现手印检测的有效应用奠定基础,尤其在法医学和相关领域。
点此查看论文截图

Cognition Transferring and Decoupling for Text-supervised Egocentric Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Zhaofeng Shi, Heqian Qiu, Lanxiao Wang, Fanman Meng, Qingbo Wu, Hongliang Li
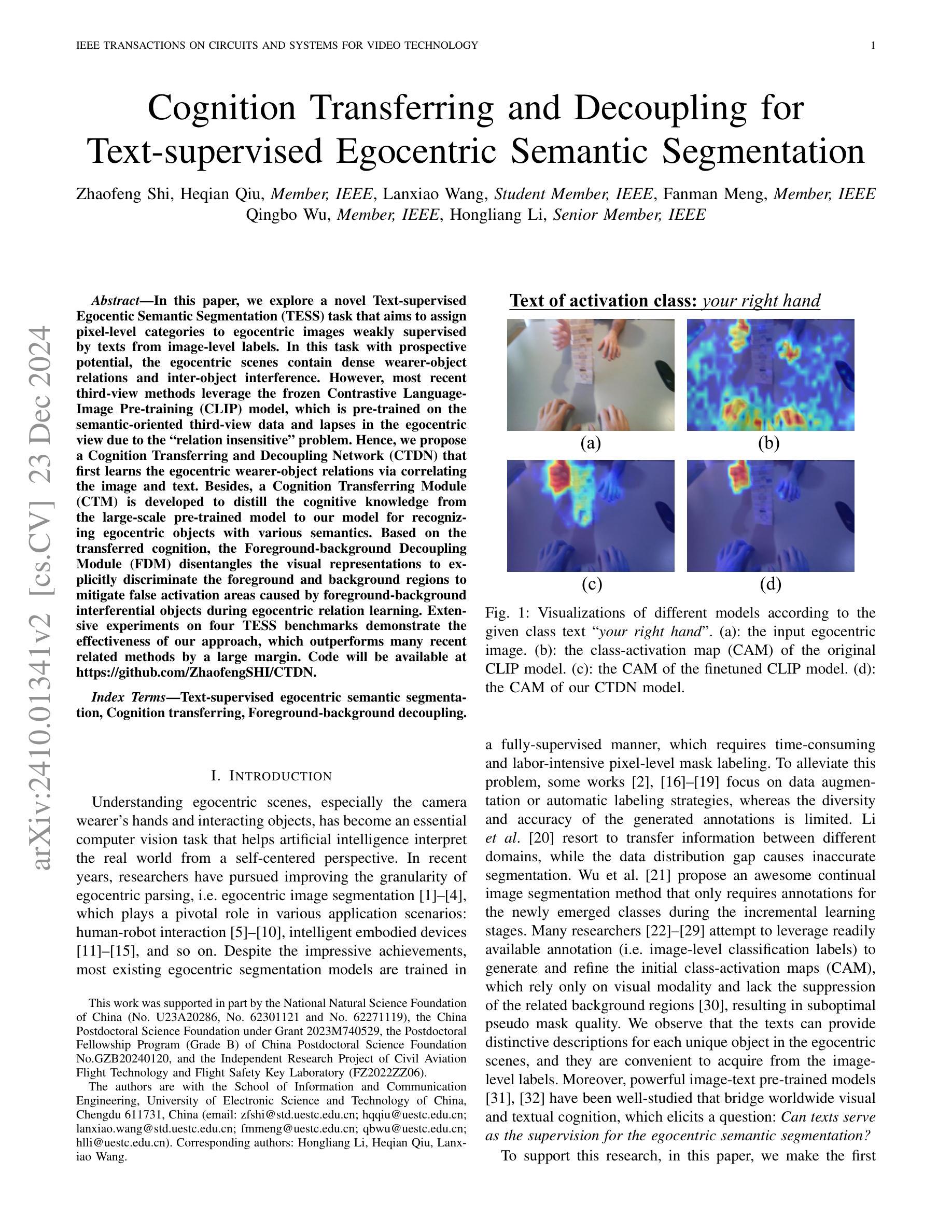
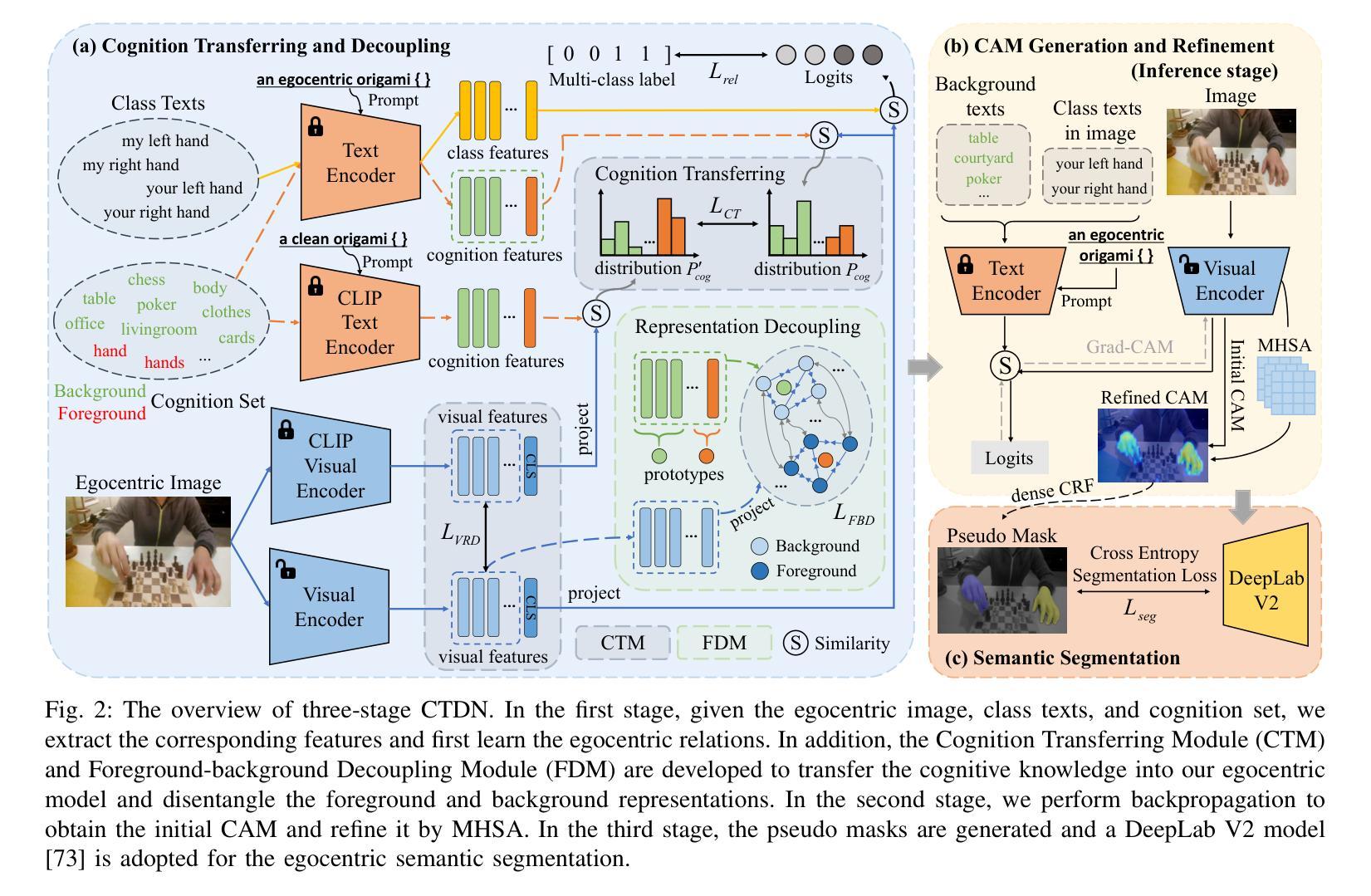
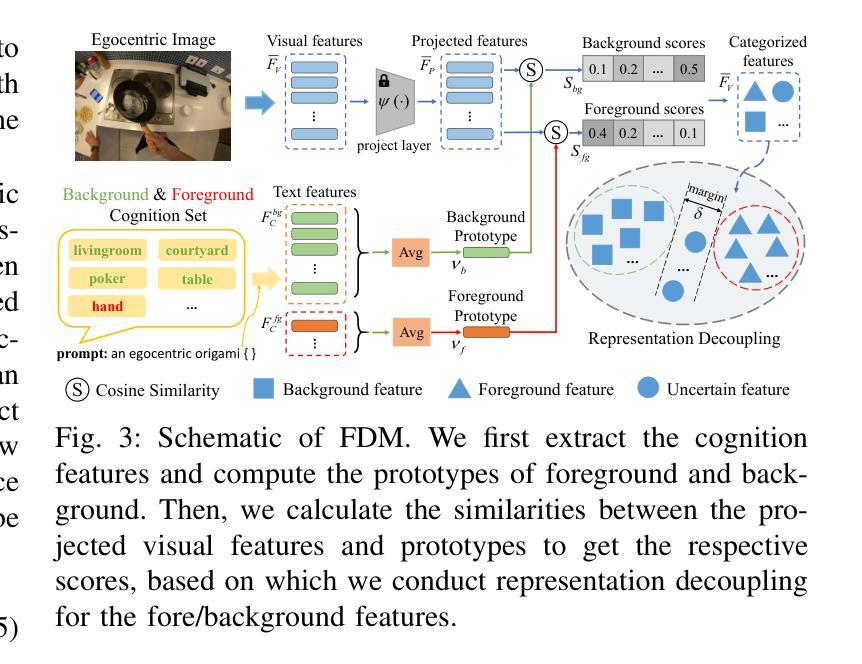
In this paper, we explore a novel Text-supervised Egocentic Semantic Segmentation (TESS) task that aims to assign pixel-level categories to egocentric images weakly supervised by texts from image-level labels. In this task with prospective potential, the egocentric scenes contain dense wearer-object relations and inter-object interference. However, most recent third-view methods leverage the frozen Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) model, which is pre-trained on the semantic-oriented third-view data and lapses in the egocentric view due to the ``relation insensitive” problem. Hence, we propose a Cognition Transferring and Decoupling Network (CTDN) that first learns the egocentric wearer-object relations via correlating the image and text. Besides, a Cognition Transferring Module (CTM) is developed to distill the cognitive knowledge from the large-scale pre-trained model to our model for recognizing egocentric objects with various semantics. Based on the transferred cognition, the Foreground-background Decoupling Module (FDM) disentangles the visual representations to explicitly discriminate the foreground and background regions to mitigate false activation areas caused by foreground-background interferential objects during egocentric relation learning. Extensive experiments on four TESS benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, which outperforms many recent related methods by a large margin. Code will be available at https://github.com/ZhaofengSHI/CTDN.
本文中,我们探索了一项新型的文本监督的以自我为中心的语义分割(TESS)任务,该任务旨在为以自我为中心的图像分配像素级类别,这些图像仅通过图像级标签的文本进行弱监督。在这个具有潜力的任务中,以自我为中心的场景包含密集的穿戴者-物体关系和物体间的相互干扰。然而,最近的大多数第三人称视角的方法都利用冻结的对比语言-图像预训练(CLIP)模型,该模型在语义导向的第三人称视角数据上进行预训练,并在以自我为中心的视角中存在“关系不敏感”问题。因此,我们提出了一种认知转移和解耦网络(CTDN),该网络首先通过图像和文本的相关性来学习以自我为中心的穿戴者-物体关系。此外,还开发了一种认知转移模块(CTM),用于从大规模预训练模型中提炼认知知识,以识别具有各种语义的以自我为中心的对象。基于转移的认知,前景-背景解耦模块(FDM)解开视觉表示,明确区分前景和背景区域,以减轻由前景-背景干扰物体引起的错误激活区域,从而促进以自我为中心的关联学习。在四个TESS基准测试上的大量实验表明,我们的方法效果显著,大大超越了最近的相关方法。代码将在https://github.com/ZhaofengSHI/CTDN上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (TCSVT)
Summary:
本文探索了一项新型的文本监督的以自我为中心的语义分割(TESS)任务,旨在利用图像级别的标签文本对以自我为中心的图像进行像素级别的类别分配。针对该任务中存在的穿戴者-物体关系密集和物体间干扰问题,提出了一种认知转移和解耦网络(CTDN)。通过关联图像和文本,学习以自我为中心的穿戴者-物体关系,并开发了一个认知转移模块(CTM),用于从大规模预训练模型中提炼认知知识,以识别具有不同语义的自我中心物体。基于转移的认知,前景-背景解耦模块(FDM)通过解析视觉表征来明确区分前景和背景区域,以减少由前景-背景干扰物体引起的错误激活区域。在四个TESS基准测试上的实验表明,该方法大大优于近期相关方法。
Key Takeaways:
- 介绍了文本监督的以自我为中心的语义分割(TESS)任务,该任务旨在利用图像级别的标签文本进行像素级别的类别分配。
- 针对TESS任务中存在的穿戴者-物体关系密集和物体间干扰问题,提出了认知转移和解耦网络(CTDN)。
- CTDN中的认知转移模块(CTM)能够从大规模预训练模型中提炼认知知识,用于识别具有不同语义的自我中心物体。
- CTDN中的前景-背景解耦模块(FDM)能够减少前景-背景干扰物体引起的错误激活区域。
- 在四个TESS基准测试上,CTDN的方法大大优于近期相关方法。
- 论文提供了有效的解决方案来解决“关系不敏感”问题,该问题在将预训练模型应用于自我中心视图时会出现。
点此查看论文截图
Enhanced Generative Data Augmentation for Semantic Segmentation via Stronger Guidance
Authors:Quang-Huy Che, Duc-Tri Le, Bich-Nga Pham, Duc-Khai Lam, Vinh-Tiep Nguyen
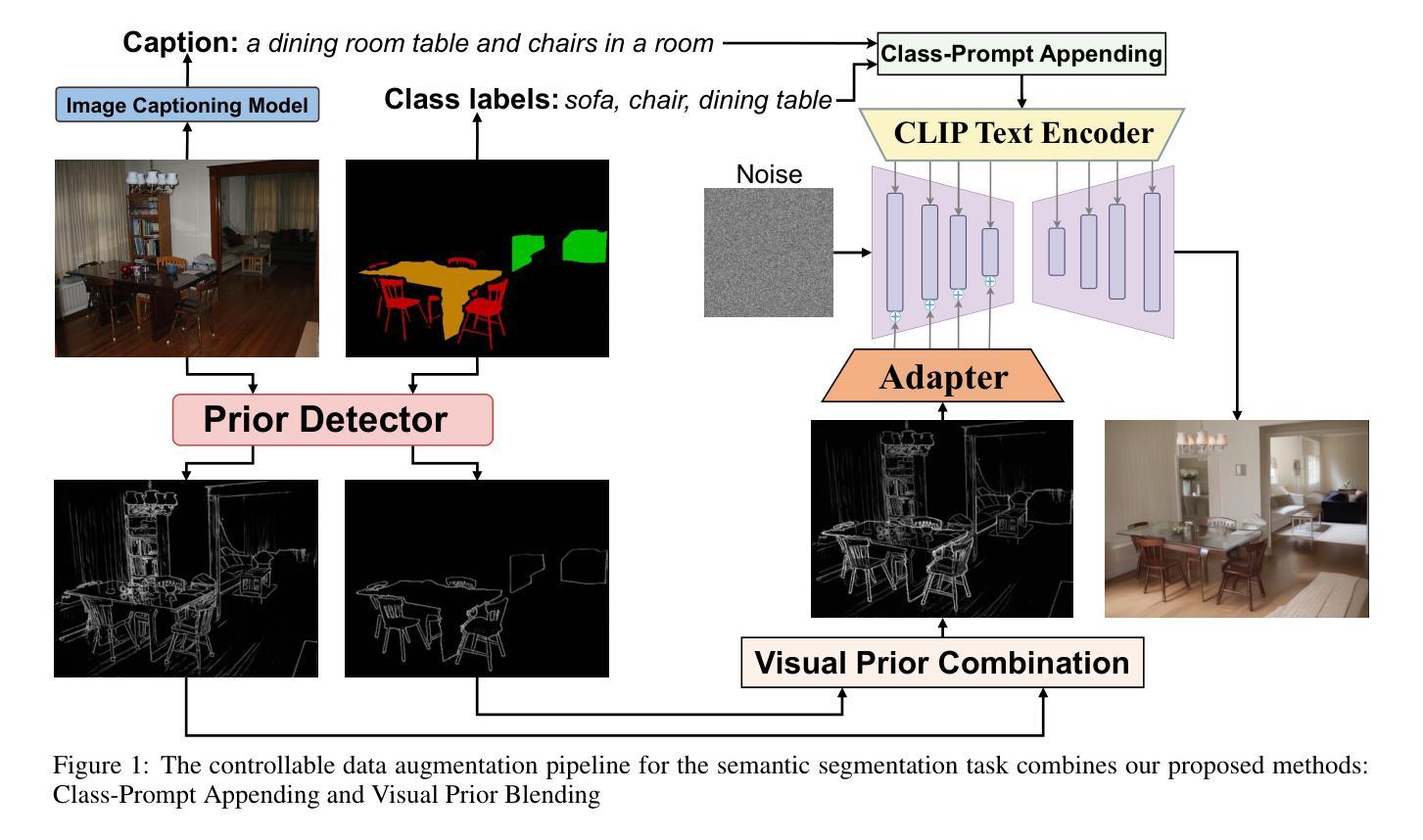
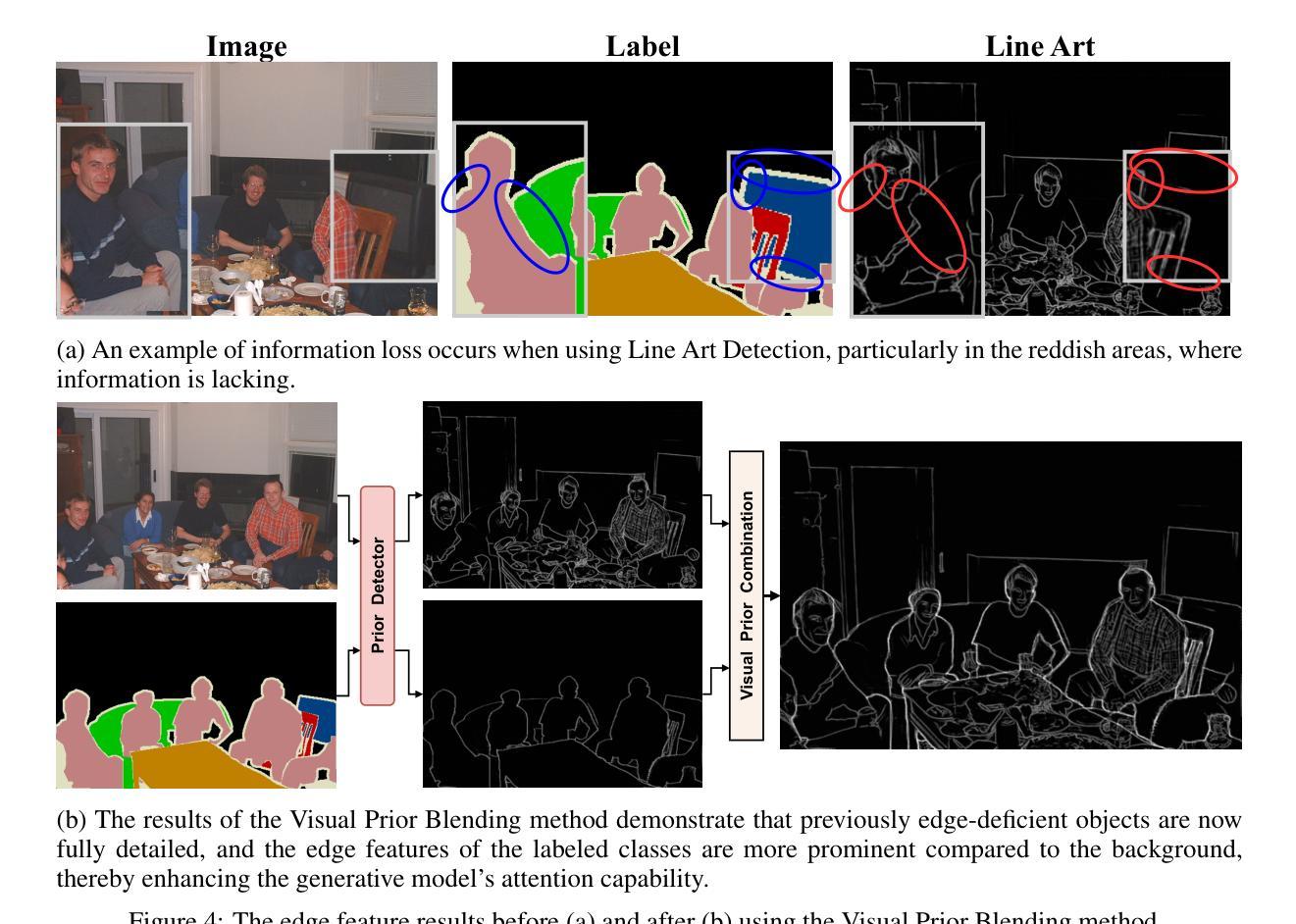
Data augmentation is crucial for pixel-wise annotation tasks like semantic segmentation, where labeling requires significant effort and intensive labor. Traditional methods, involving simple transformations such as rotations and flips, create new images but often lack diversity along key semantic dimensions and fail to alter high-level semantic properties. To address this issue, generative models have emerged as an effective solution for augmenting data by generating synthetic images. Controllable Generative models offer data augmentation methods for semantic segmentation tasks by using prompts and visual references from the original image. However, these models face challenges in generating synthetic images that accurately reflect the content and structure of the original image due to difficulties in creating effective prompts and visual references. In this work, we introduce an effective data augmentation pipeline for semantic segmentation using Controllable Diffusion model. Our proposed method includes efficient prompt generation using \textit{Class-Prompt Appending} and \textit{Visual Prior Blending} to enhance attention to labeled classes in real images, allowing the pipeline to generate a precise number of augmented images while preserving the structure of segmentation-labeled classes. In addition, we implement a \textit{class balancing algorithm} to ensure a balanced training dataset when merging the synthetic and original images. Evaluation on PASCAL VOC datasets, our pipeline demonstrates its effectiveness in generating high-quality synthetic images for semantic segmentation. Our code is available at \href{https://github.com/chequanghuy/Enhanced-Generative-Data-Augmentation-for-Semantic-Segmentation-via-Stronger-Guidance}{this https URL}.
数据增强对于像素级的标注任务,如语义分割,是至关重要的。语义分割需要投入大量的标注工作。传统的方法,如旋转和翻转等简单变换,可以创建新的图像,但往往在关键的语义维度上缺乏多样性,并且无法改变高级语义属性。为了解决这一问题,生成模型作为一种有效的数据增强方法应运而生,通过生成合成图像来增强数据。可控生成模型为语义分割任务提供了数据增强方法,通过使用原始图像的提示和视觉参考来生成新的数据。然而,这些模型在生成准确反映原始图像内容和结构的合成图像时面临挑战,因为创建有效的提示和视觉参考存在困难。在这项工作中,我们引入了使用可控扩散模型的语义分割有效数据增强管道。我们提出的方法包括使用“类提示附加”和“视觉先验混合”进行高效提示生成,以提高对真实图像中标记类的注意力,使管道能够在保留分割标记类结构的同时,生成精确数量的增强图像。此外,我们实现了“类别平衡算法”,以确保在合并合成图像和原始图像时,训练数据集保持平衡。在PASCAL VOC数据集上的评估表明,我们的管道在生成高质量合成图像进行语义分割方面非常有效。我们的代码位于:https://github.com/chequanghuy/Enhanced-Generative-Data-Augmentation-for-Semantic-Segmentation-via-Stronger-Guidance。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICPRAM 2025
Summary
数据增强对于像素级标注任务如语义分割至关重要,传统方法缺乏多样性并无法改变高级语义属性。为此,采用生成模型进行数据增强成为有效的解决方案。本研究提出了一种使用可控扩散模型进行数据增强的有效方法,利用“Class-Prompt Appending”和“Visual Prior Blending”等技术增强关注标注类别并生成精确的图像数量同时保持标注结构的完整性。实现类平衡算法确保合并数据集时平衡性。在PASCAL VOC数据集上的评估显示本方法有效生成高质量图像。相关代码可在提供的URL链接中查阅。
Key Takeaways
点此查看论文截图




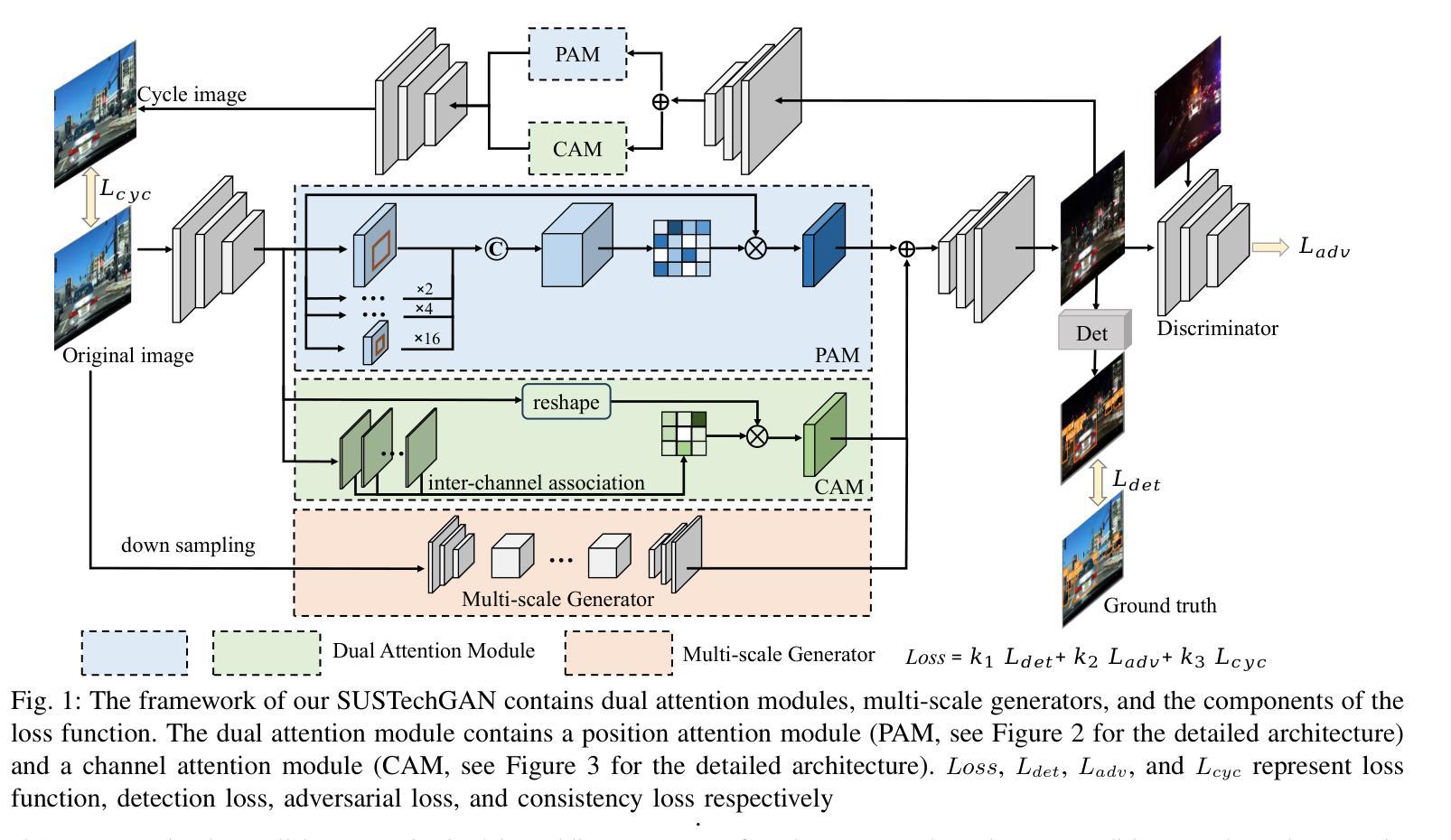
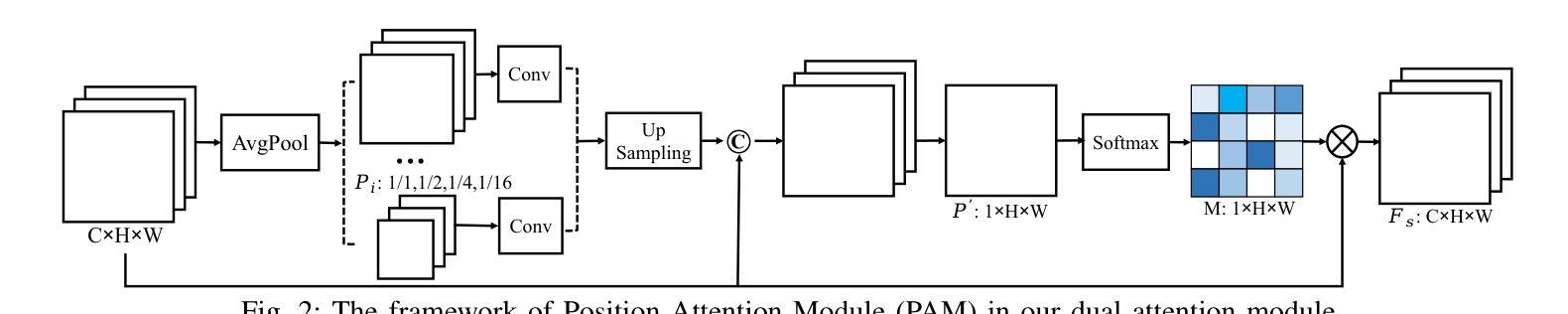
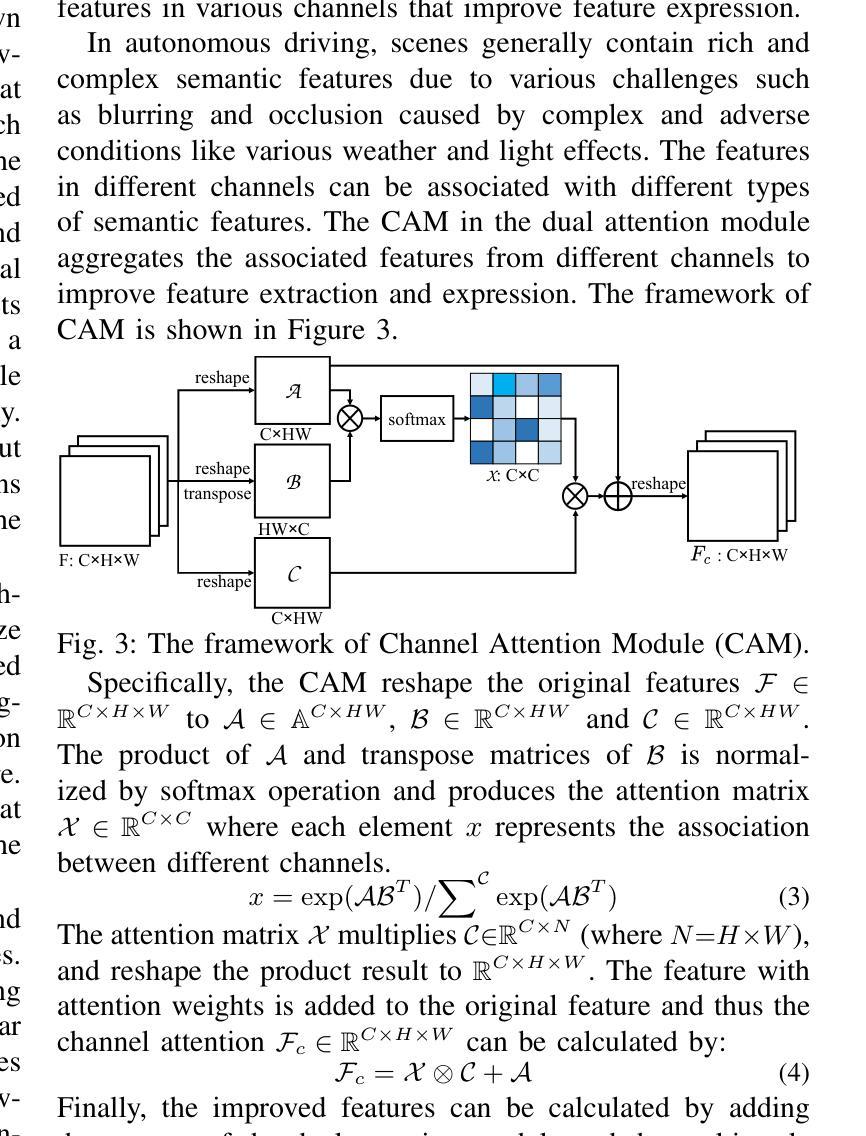
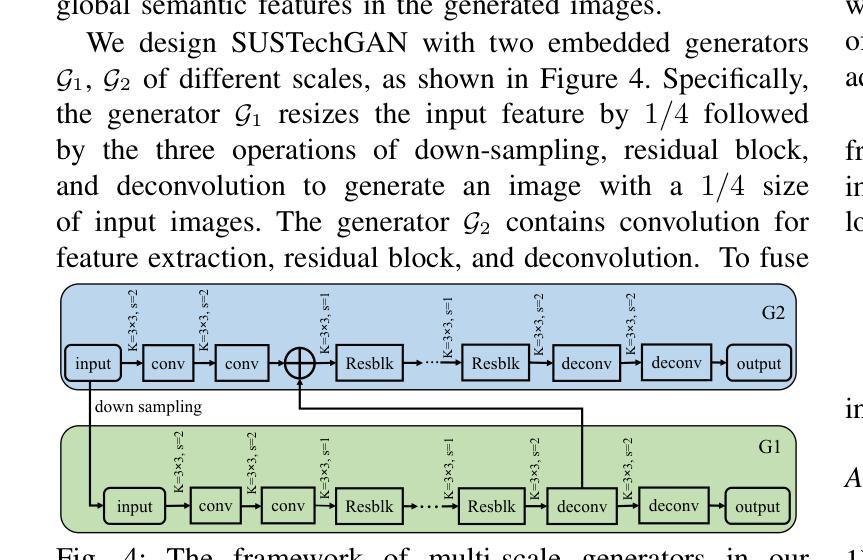
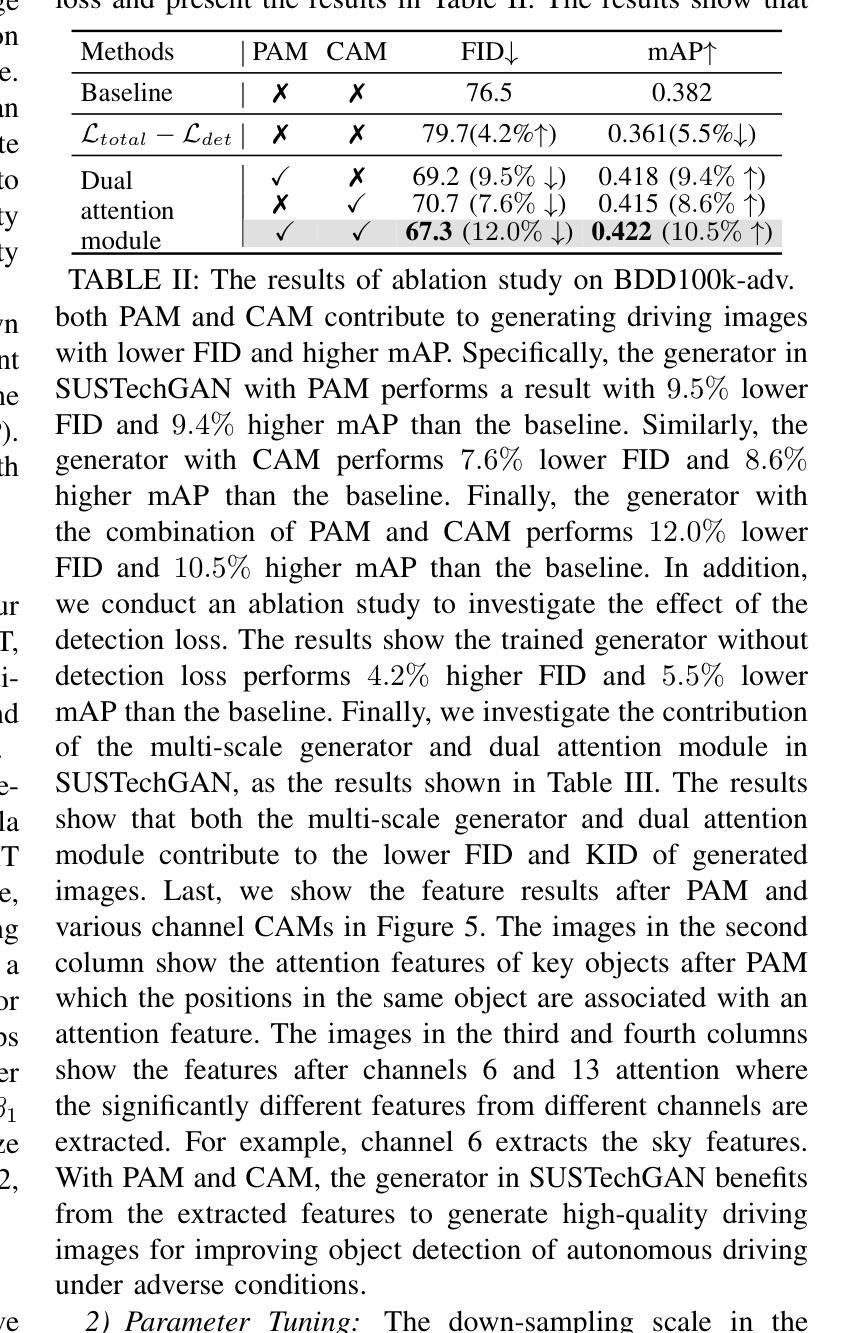
SUSTechGAN: Image Generation for Object Detection in Adverse Conditions of Autonomous Driving
Authors:Gongjin Lan, Yang Peng, Qi Hao, Chengzhong Xu
Autonomous driving significantly benefits from data-driven deep neural networks. However, the data in autonomous driving typically fits the long-tailed distribution, in which the critical driving data in adverse conditions is hard to collect. Although generative adversarial networks (GANs) have been applied to augment data for autonomous driving, generating driving images in adverse conditions is still challenging. In this work, we propose a novel framework, SUSTechGAN, with customized dual attention modules, multi-scale generators, and a novel loss function to generate driving images for improving object detection of autonomous driving in adverse conditions. We test the SUSTechGAN and the well-known GANs to generate driving images in adverse conditions of rain and night and apply the generated images to retrain object detection networks. Specifically, we add generated images into the training datasets to retrain the well-known YOLOv5 and evaluate the improvement of the retrained YOLOv5 for object detection in adverse conditions. The experimental results show that the generated driving images by our SUSTechGAN significantly improved the performance of retrained YOLOv5 in rain and night conditions, which outperforms the well-known GANs. The open-source code, video description and datasets are available on the page 1 to facilitate image generation development in autonomous driving under adverse conditions.
自动驾驶受益于数据驱动的深度神经网络。然而,自动驾驶中的数据通常符合长尾分布,其中在恶劣条件下的关键驾驶数据收集起来非常困难。虽然生成对抗网络(GANs)已被应用于增强自动驾驶的数据,但在恶劣条件下生成驾驶图像仍然具有挑战性。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型框架SUSTechGAN,它具有定制的双重注意力模块、多尺度生成器和新型损失函数,用于生成驾驶图像,以提高恶劣条件下的自动驾驶目标检测性能。我们对SUSTechGAN和著名的GANs进行了测试,以生成雨天和夜晚的驾驶图像,并将生成的图像用于重新训练目标检测网络。具体来说,我们将生成的图像添加到训练数据集中,以重新训练知名的YOLOv5网络,并评估重新训练的YOLOv5在恶劣条件下的目标检测性能的提升情况。实验结果表明,我们的SUSTechGAN生成的驾驶图像显著提高了重新训练的YOLOv5在雨天和夜晚条件下的性能,且优于已知的GANs。为了方便在恶劣条件下自动驾驶的图像生成开发,开源代码、视频描述和数据集均可在第1页上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 9 figures
Summary
数据驱动深度神经网络为自动驾驶带来了显著的利益,但由于关键驾驶数据的收集困难,如恶劣环境下的数据,实际应用中仍存在挑战。针对这一问题,本文提出了一种新型框架SUSTechGAN,包含定制化的双重注意力模块、多尺度生成器和新型损失函数,以生成恶劣环境下的驾驶图像,改善自动驾驶的目标检测性能。实验证明,使用SUSTechGAN生成的图像能显著提升YOLOv5在恶劣环境下的检测性能,优于其他知名GANs。
Key Takeaways
- 自动驾驶受益于数据驱动的深度神经网络,但恶劣环境下的数据收集是挑战。
- SUSTechGAN框架被提出,包含双重注意力模块、多尺度生成器和新型损失函数。
- SUSTechGAN能生成恶劣环境下的驾驶图像,如雨天和夜晚。
- 使用生成图像重训YOLOv5,在恶劣环境下显著提升目标检测性能。
- SUSTechGAN性能优于其他知名GANs。
- 开放源代码、视频描述和数据集,便于自动驾驶恶劣环境下的图像生成开发。
点此查看论文截图