⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-25 更新
HumanVBench: Exploring Human-Centric Video Understanding Capabilities of MLLMs with Synthetic Benchmark Data
Authors:Ting Zhou, Daoyuan Chen, Qirui Jiao, Bolin Ding, Yaliang Li, Ying Shen
In the domain of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), achieving human-centric video understanding remains a formidable challenge. Existing benchmarks primarily emphasize object and action recognition, often neglecting the intricate nuances of human emotions, behaviors, and speech visual alignment within video content. We present HumanVBench, an innovative benchmark meticulously crafted to bridge these gaps in the evaluation of video MLLMs. HumanVBench comprises 17 carefully designed tasks that explore two primary dimensions: inner emotion and outer manifestations, spanning static and dynamic, basic and complex, as well as single-modal and cross-modal aspects. With two advanced automated pipelines for video annotation and distractor-included QA generation, HumanVBench utilizes diverse state-of-the-art (SOTA) techniques to streamline benchmark data synthesis and quality assessment, minimizing human annotation dependency tailored to human-centric multimodal attributes. A comprehensive evaluation across 16 SOTA video MLLMs reveals notable limitations in current performance, especially in cross-modal and temporal alignment, underscoring the necessity for further refinement toward achieving more human-like understanding. HumanVBench is open-sourced to facilitate future advancements and real-world applications in video MLLMs.
在多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)领域,实现以人类为中心的视频理解仍然是一项艰巨的挑战。现有基准测试主要强调对象和动作识别,往往忽视了视频内容中人类情绪、行为和语音视觉对齐的细微差别。我们推出了HumanVBench,这是一个精心设计的创新基准测试,旨在弥补视频MLLM评估中的这些差距。HumanVBench包含17个精心设计的任务,探索两个主要维度:内在情绪和外在表现,涵盖静态和动态、基本和复杂以及单模态和跨模态方面。HumanVBench使用两个先进的自动化管道进行视频注释和包含干扰项的QA生成,利用多种最新技术优化基准测试数据合成和质量评估,减少对人类注释的依赖,专门针对以人类为中心的多模态属性。对16种最新视频MLLM的全面评估显示,当前性能存在显著局限性,尤其在跨模态和时间对齐方面,这强调了对进一步改进实现更人性化的理解的必要性。HumanVBench开源,以促进视频MLLM的未来发展和实际应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 24 figures, 4 tables
Summary
HumanVBench是多模态大语言模型领域中的一项新型基准测试,专门用于解决以人类为中心的视频理解的挑战性问题。现有的基准测试通常忽略人类情绪的复杂性和细微差别以及语音与视频内容对齐,HumanVBench弥补了这一缺口,具有多层次评估系统,涉及17项精心设计的任务,全面涵盖了从情感感知到外在表现的各方面评估内容。它通过视频注释自动化管道以及包括干扰项在内的问答生成管道,实现了数据合成和质量控制流程的自动化。对现有顶尖视频大模型的全面评估显示,在跨模态和时序对齐方面仍存在明显局限性。该项目旨在促进更贴近人类的视频理解的发展。其已经开源以供将来在该领域改进进步和未来在真实世界的应用场景使用。
Key Takeaways
- HumanVBench填补了视频理解领域中以人类为中心的多模态大语言模型基准测试的空白。
- 它涵盖了多个层次的任务,包括情感感知和外在表现等方面。
- HumanVBench具有自动化的数据合成和质量控制流程,以减少人工注释的依赖。
- 该基准测试揭示了现有顶尖视频大模型在跨模态和时序对齐方面的局限性。
- HumanVBench专注于视频内容中的情绪、行为和语音视觉对齐等复杂细微之处。
- 该项目已开源,旨在促进未来的发展和在真实世界的应用场景中使用。
点此查看论文截图

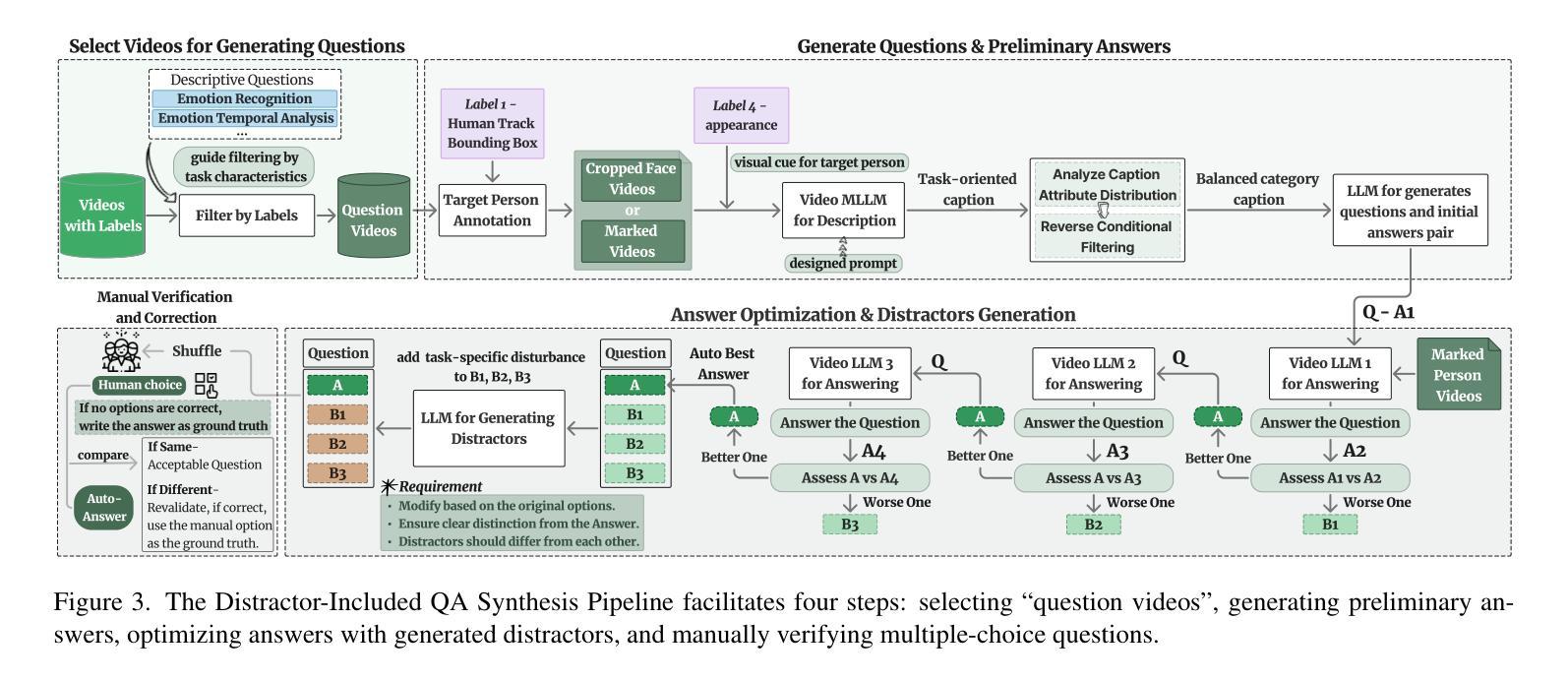
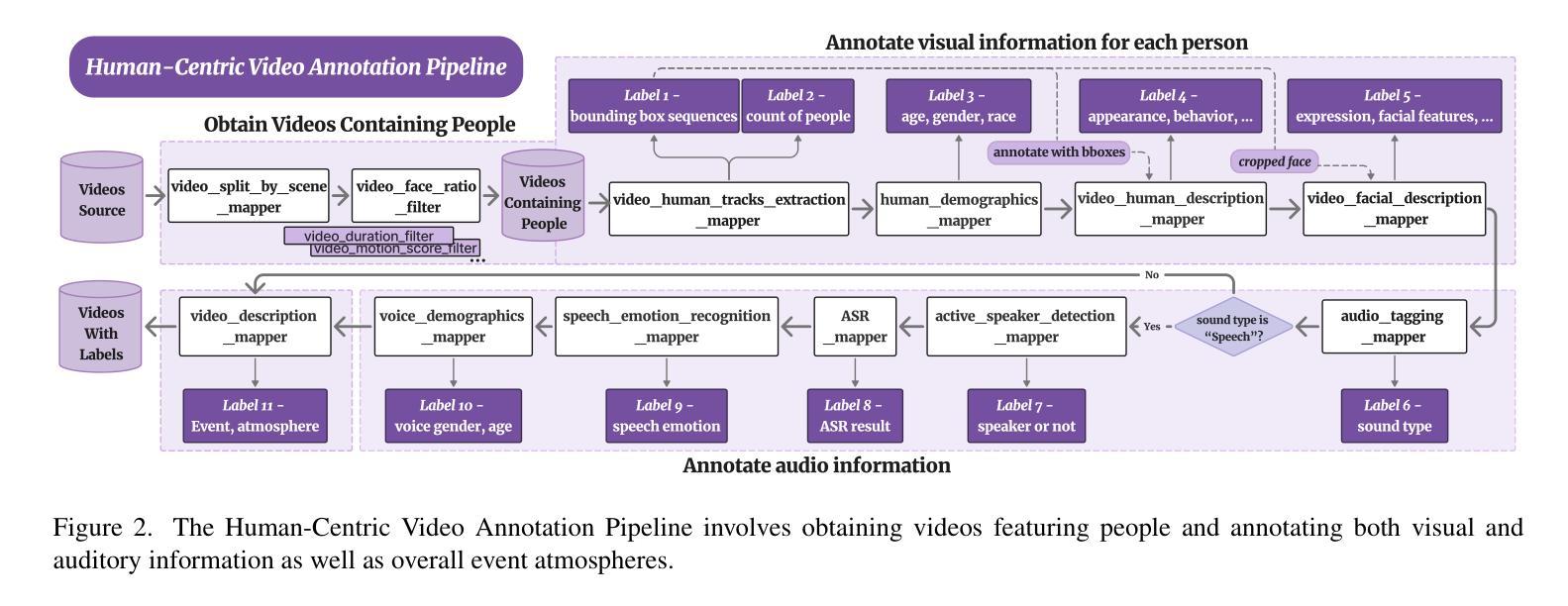
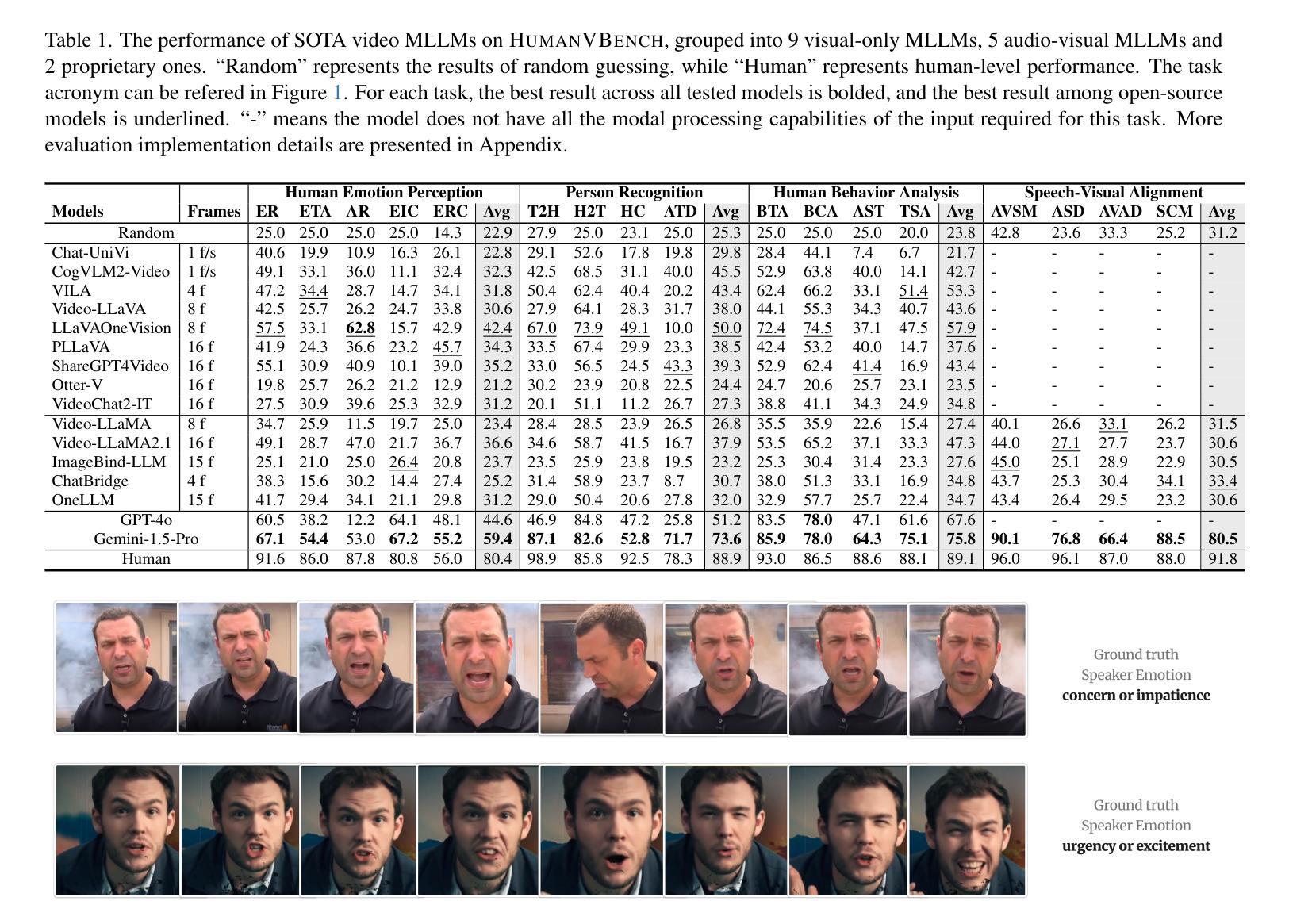
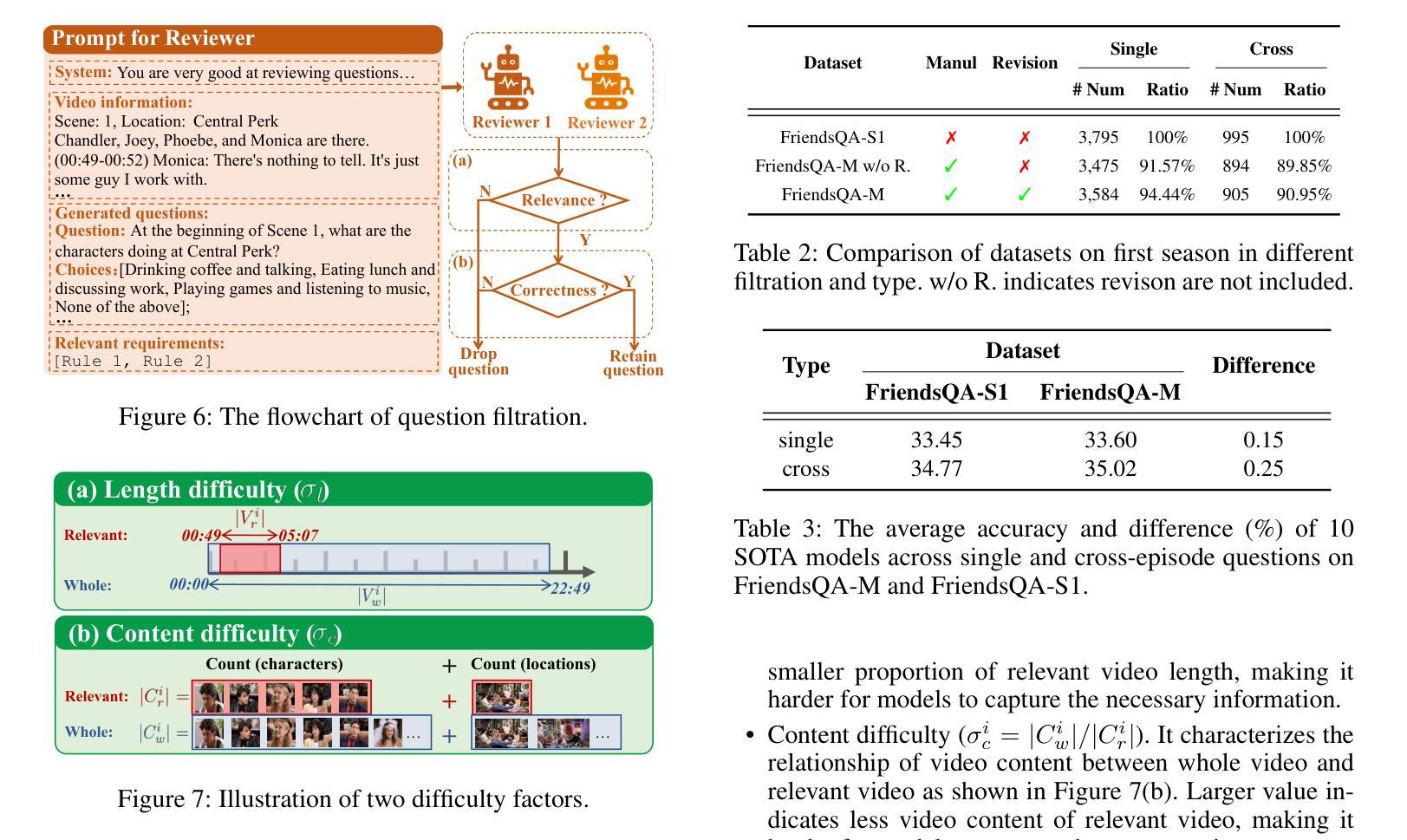
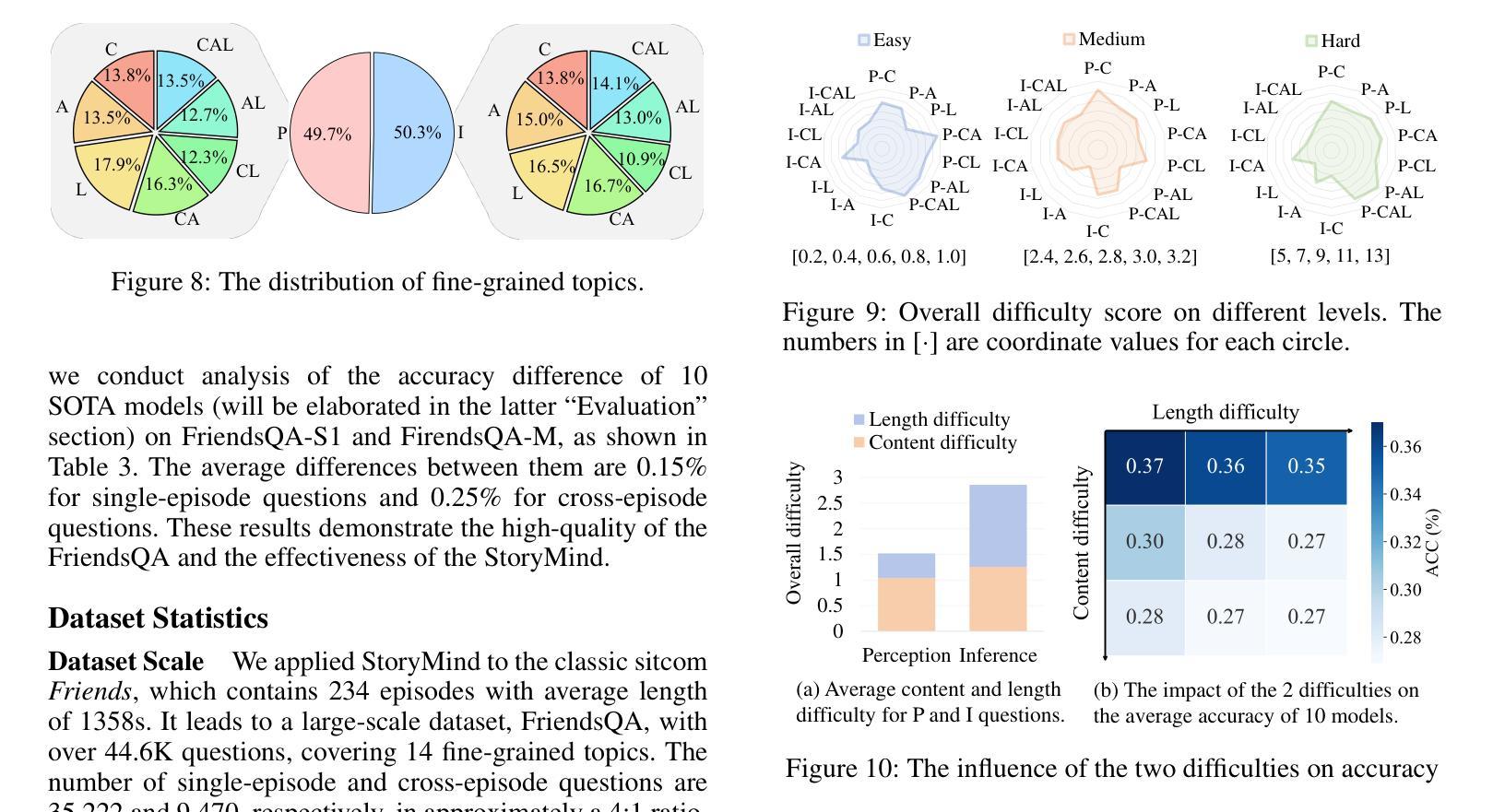
FriendsQA: A New Large-Scale Deep Video Understanding Dataset with Fine-grained Topic Categorization for Story Videos
Authors:Zhengqian Wu, Ruizhe Li, Zijun Xu, Zhongyuan Wang, Chunxia Xiao, Chao Liang
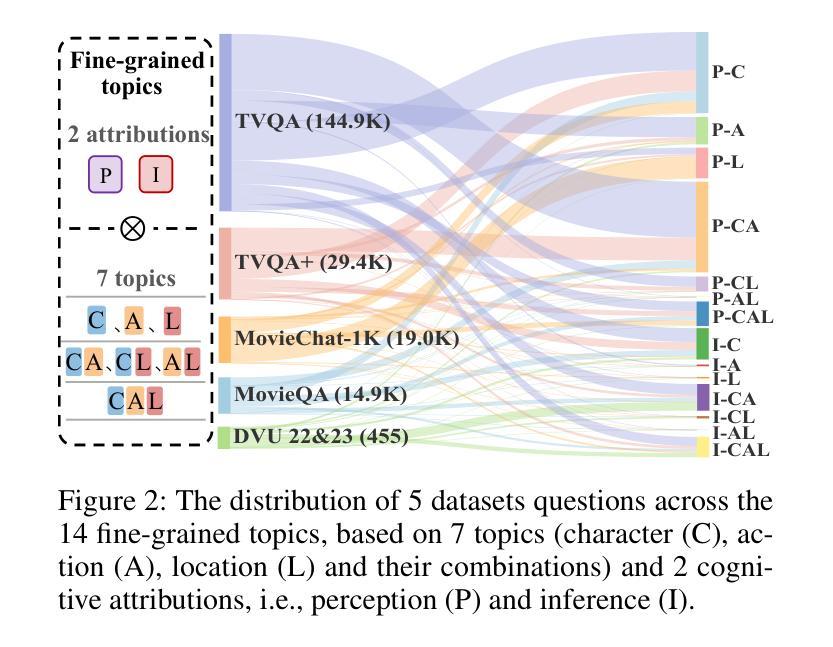
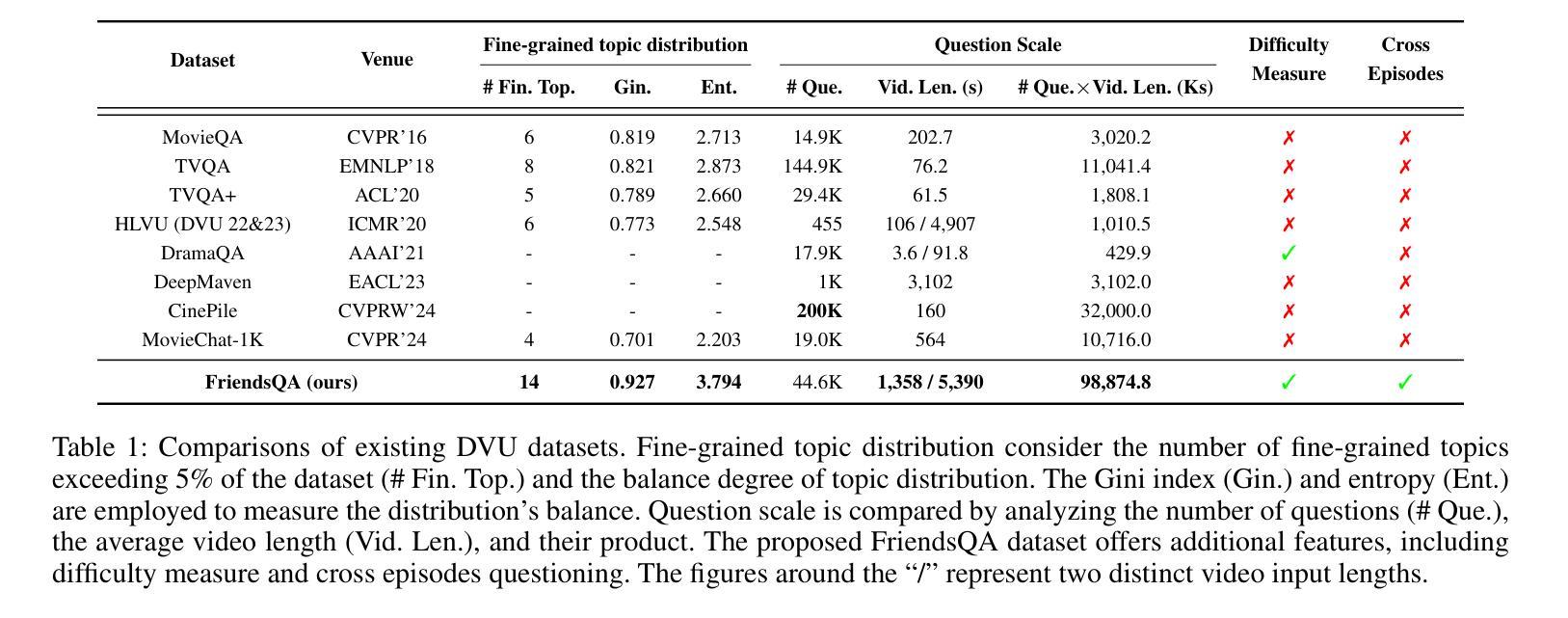
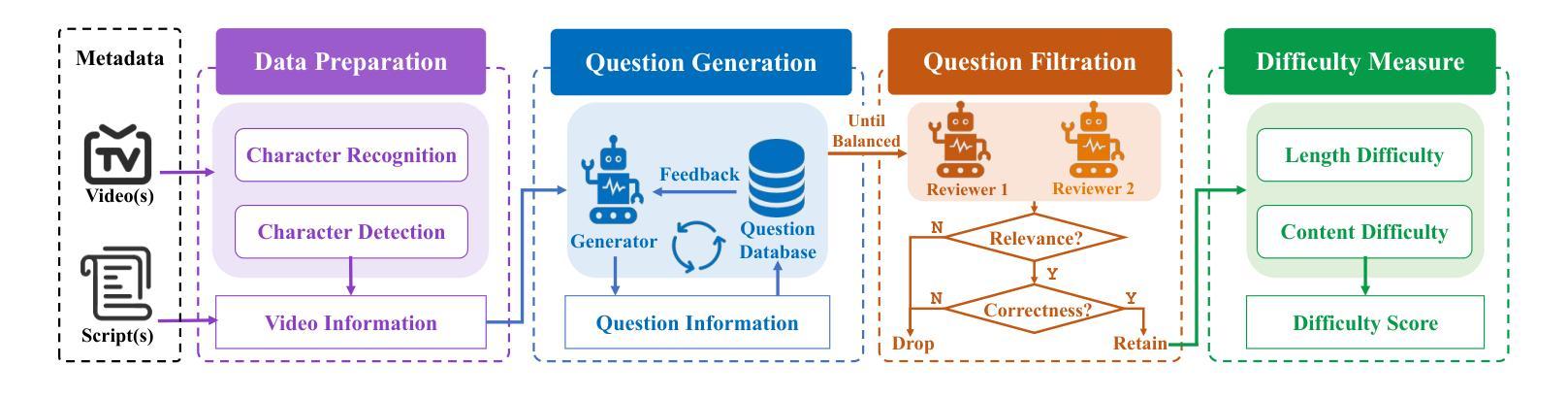
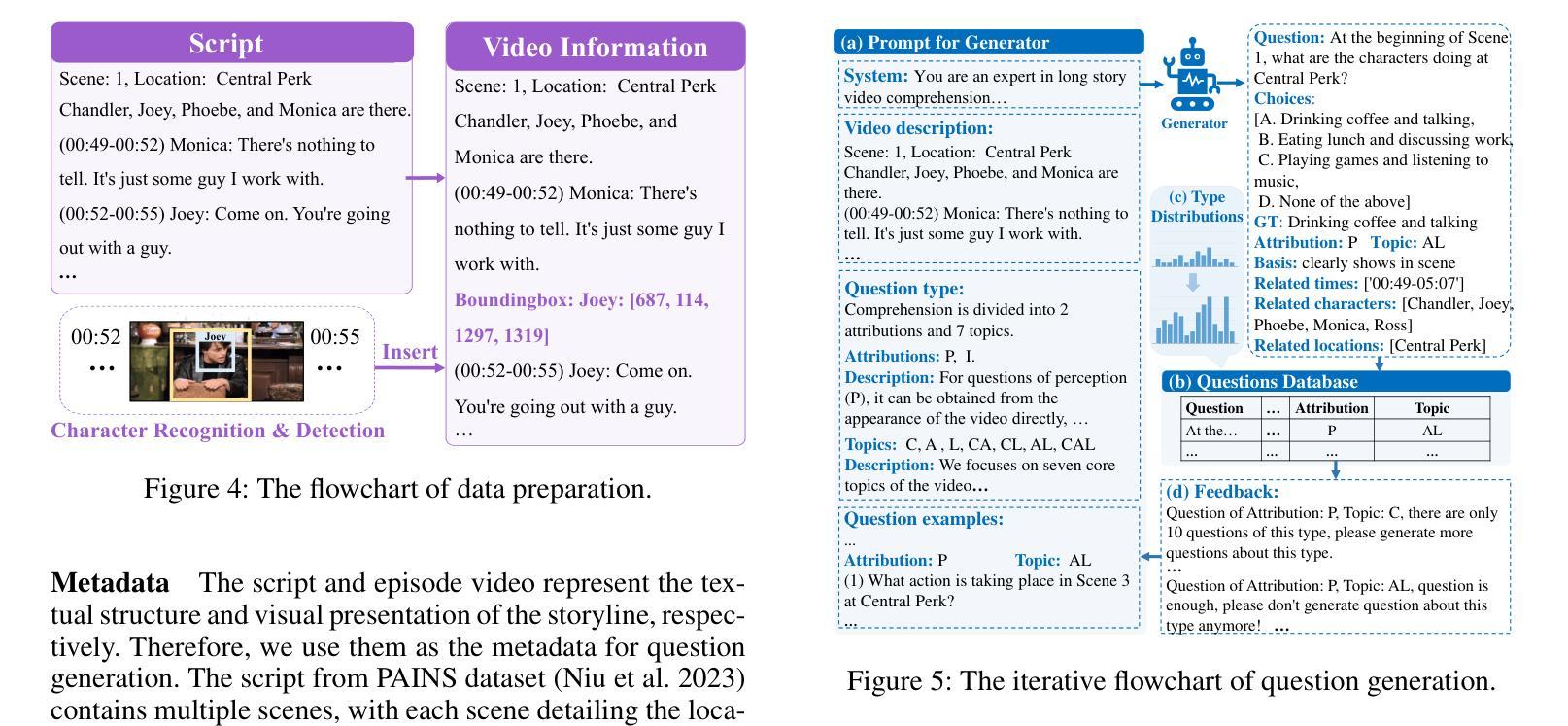
Video question answering (VideoQA) aims to answer natural language questions according to the given videos. Although existing models perform well in the factoid VideoQA task, they still face challenges in deep video understanding (DVU) task, which focuses on story videos. Compared to factoid videos, the most significant feature of story videos is storylines, which are composed of complex interactions and long-range evolvement of core story topics including characters, actions and locations. Understanding these topics requires models to possess DVU capability. However, existing DVU datasets rarely organize questions according to these story topics, making them difficult to comprehensively assess VideoQA models’ DVU capability of complex storylines. Additionally, the question quantity and video length of these dataset are limited by high labor costs of handcrafted dataset building method. In this paper, we devise a large language model based multi-agent collaboration framework, StoryMind, to automatically generate a new large-scale DVU dataset. The dataset, FriendsQA, derived from the renowned sitcom Friends with an average episode length of 1,358 seconds, contains 44.6K questions evenly distributed across 14 fine-grained topics. Finally, We conduct comprehensive experiments on 10 state-of-the-art VideoQA models using the FriendsQA dataset.
视频问答(VideoQA)旨在根据给定的视频回答自然语言问题。尽管现有模型在事实类VideoQA任务中表现良好,但它们在面对深度视频理解(DVU)任务时仍面临挑战,该任务专注于故事视频。与事实视频相比,故事视频的最显著特点是其故事情节,由复杂的交互和核心故事主题(如角色、动作和地点)的长期演变组成。理解这些主题需要模型具备DVU能力。然而,现有的DVU数据集很少根据这些故事主题来组织问题,这使得它们难以全面评估VideoQA模型对复杂故事情节的DVU能力。此外,这些数据集的题目数量和视频长度都受到手工构建数据集的高成本劳动的限制。在本文中,我们设计了一个基于大型语言模型的多智能体协作框架StoryMind,以自动生成一个新的大规模DVU数据集。该数据集来源于著名情景喜剧《老友记》,平均每集长度为1358秒,包含均匀分布在14个精细主题中的44.6K个问题。最后,我们使用FriendsQA数据集对10种最新VideoQA模型进行了全面的实验。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary:
视频问答(VideoQA)旨在根据给定视频回答自然语言问题。尽管现有模型在事实类VideoQA任务上表现良好,但在深度视频理解(DVU)任务上仍面临挑战,尤其是针对故事视频的理解。故事视频的核心是复杂交互和核心故事主题(如角色、动作和地点)的长期演变。现有DVU数据集很少根据这些故事主题组织问题,使得难以全面评估VideoQA模型的复杂故事线理解能力。本文设计了一个基于大型语言模型的多智能体协作框架StoryMind,自动生成大规模DVU数据集FriendsQA。该数据集源自著名情景喜剧《老友记》,平均每集长度为1358秒,包含均匀分布在14个精细主题中的44.6K个问题。最后,我们在FriendsQA数据集上对10款最先进的VideoQA模型进行了综合实验。
Key Takeaways:
- 视频问答(VideoQA)需要理解和解答关于视频的问题。
- 故事视频相比事实类视频包含了更复杂的交互和故事主题长期演变。
- 现有DVU数据集在评估模型理解复杂故事线的能力上存在局限性。
- StoryMind框架用于自动生成大规模DVU数据集FriendsQA。
- FriendsQA数据集源自《老友记》,包含大量问题,均匀分布在多个精细主题上。
- 在FriendsQA数据集上进行了全面的VideoQA模型实验。
点此查看论文截图