⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-25 更新
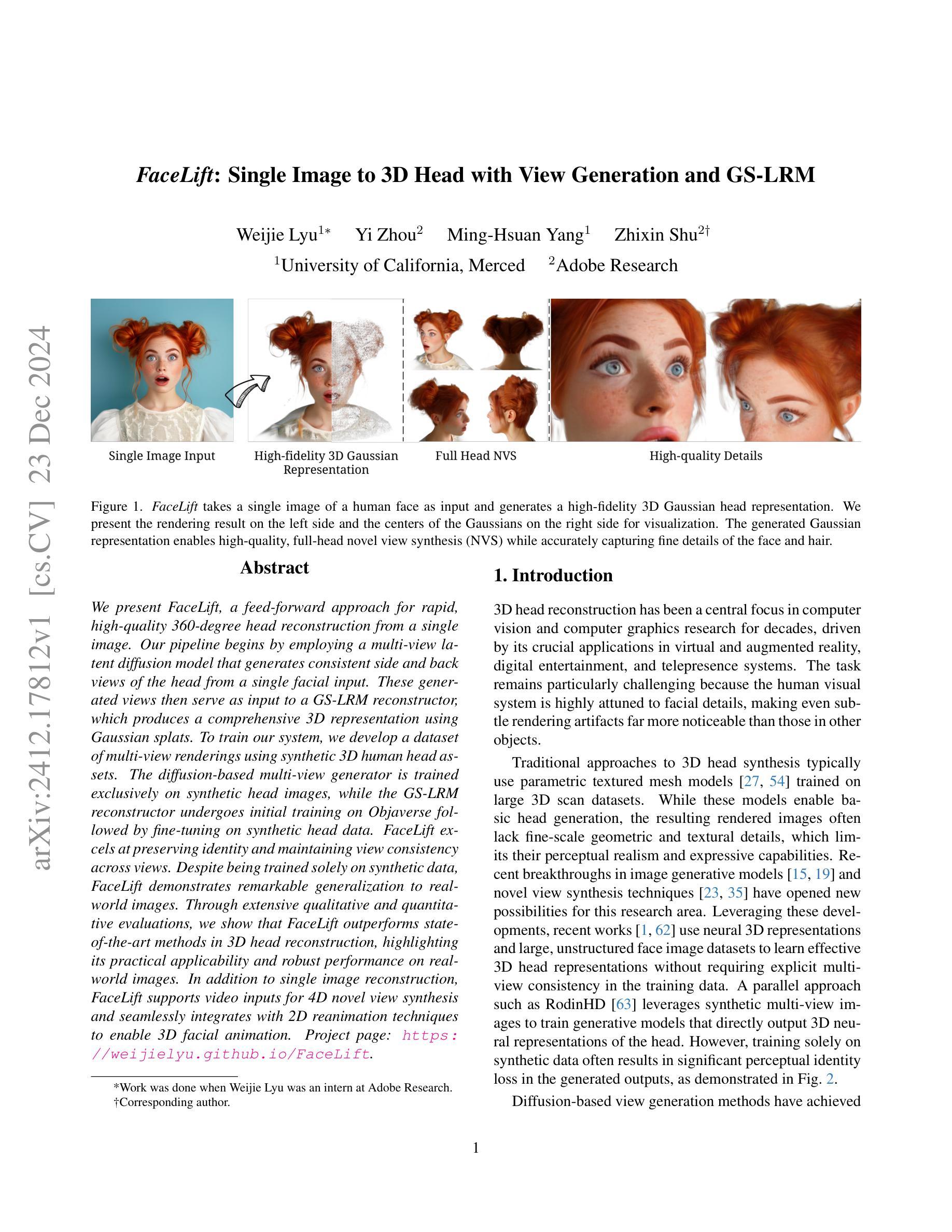
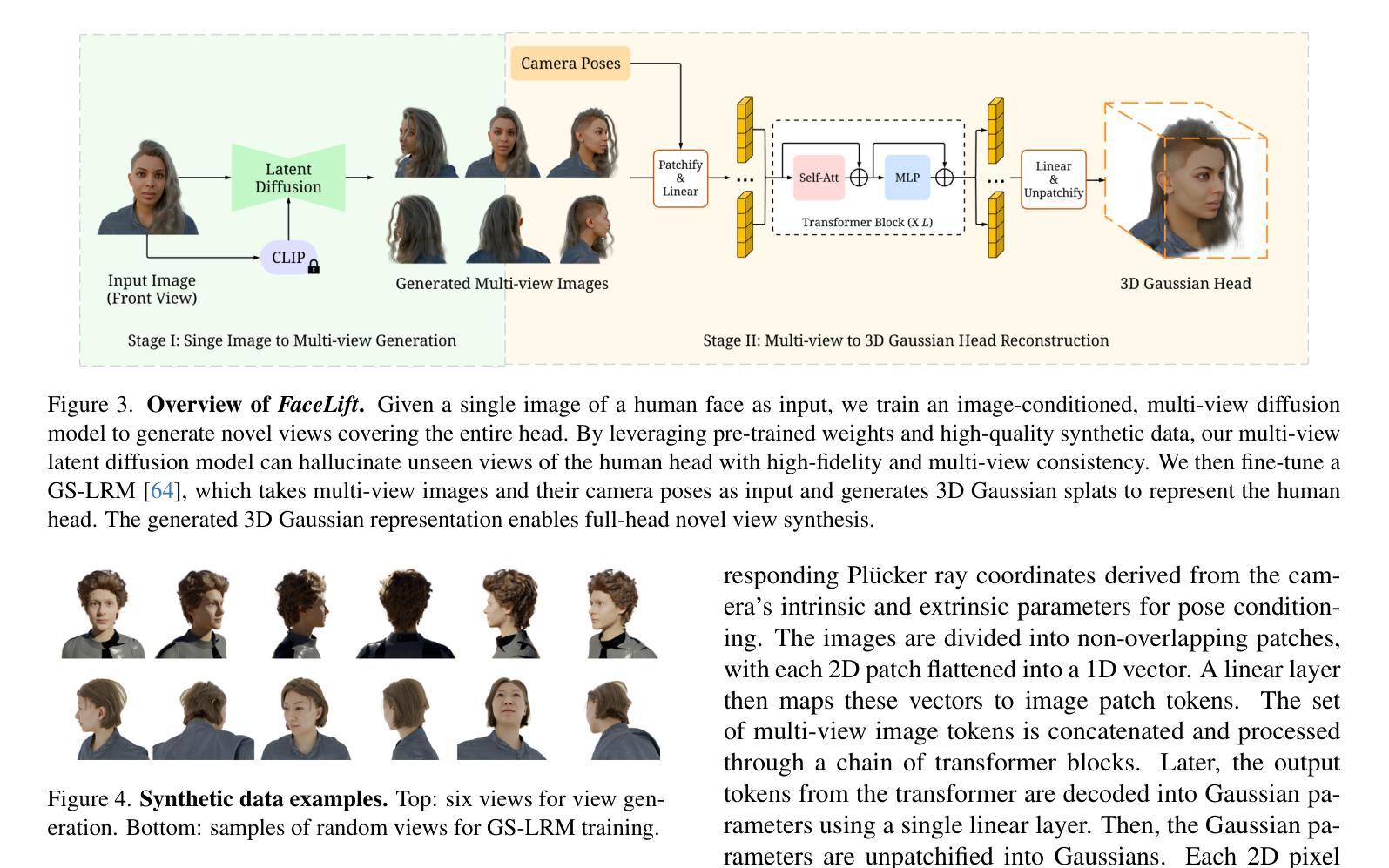
FaceLift: Single Image to 3D Head with View Generation and GS-LRM
Authors:Weijie Lyu, Yi Zhou, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Zhixin Shu
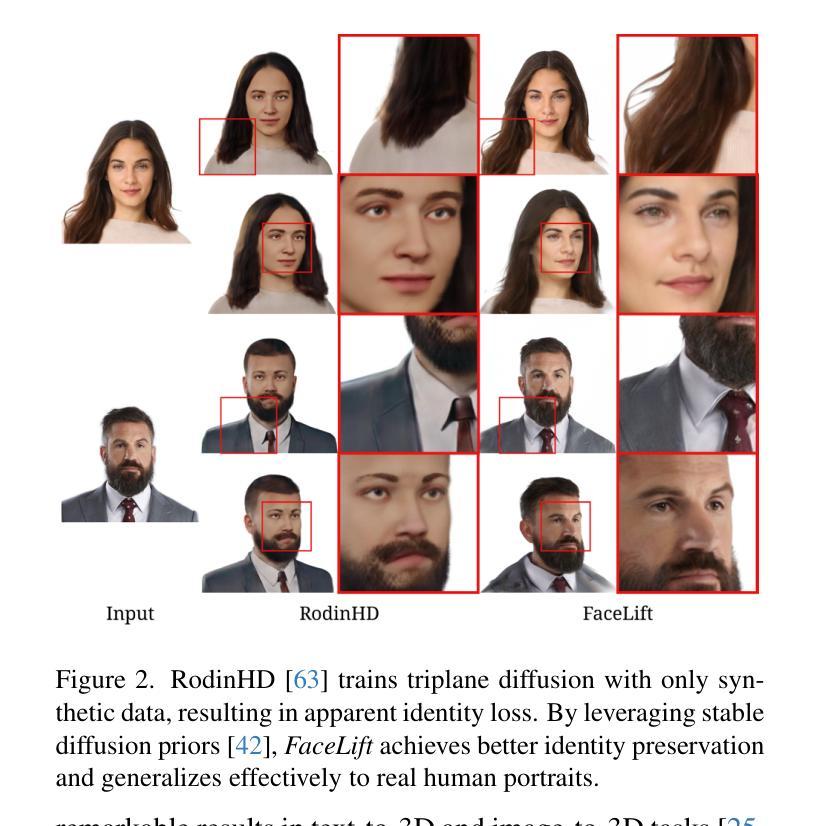
We present FaceLift, a feed-forward approach for rapid, high-quality, 360-degree head reconstruction from a single image. Our pipeline begins by employing a multi-view latent diffusion model that generates consistent side and back views of the head from a single facial input. These generated views then serve as input to a GS-LRM reconstructor, which produces a comprehensive 3D representation using Gaussian splats. To train our system, we develop a dataset of multi-view renderings using synthetic 3D human head as-sets. The diffusion-based multi-view generator is trained exclusively on synthetic head images, while the GS-LRM reconstructor undergoes initial training on Objaverse followed by fine-tuning on synthetic head data. FaceLift excels at preserving identity and maintaining view consistency across views. Despite being trained solely on synthetic data, FaceLift demonstrates remarkable generalization to real-world images. Through extensive qualitative and quantitative evaluations, we show that FaceLift outperforms state-of-the-art methods in 3D head reconstruction, highlighting its practical applicability and robust performance on real-world images. In addition to single image reconstruction, FaceLift supports video inputs for 4D novel view synthesis and seamlessly integrates with 2D reanimation techniques to enable 3D facial animation. Project page: https://weijielyu.github.io/FaceLift.
我们提出了FaceLift,这是一种前馈方法,可以从单张图像快速进行高质量、360度的头部重建。我们的流程首先采用多视角潜在扩散模型,从单张面部输入生成一致的头部侧面和背面视图。这些生成的视图然后作为GS-LRM重建器的输入,使用高斯球斑技术产生全面的3D表示。为了训练我们的系统,我们使用合成3D人头数据集开发了一个多视角渲染数据集。基于扩散的多视角生成器仅在合成头部图像上进行训练,而GS-LRM重建器首先在Objaverse上进行初步训练,然后在合成头部数据上进行微调。FaceLift擅长于保持身份一致性并维持视角的一致性。尽管只在合成数据上进行训练,FaceLift在真实世界图像上表现出了惊人的泛化能力。通过广泛的质量和数量评估,我们证明了FaceLift在3D头部重建方面优于最新技术,突出了其在真实世界图像上的实用性和稳健性能。除了单图像重建外,FaceLift还支持视频输入用于4D新颖视图合成,并与2D动画技术无缝集成以实现3D面部动画。项目页面:https://weijielyu.github.io/FaceLift。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://weijielyu.github.io/FaceLift
Summary
FaceLift是一种基于前馈方法的快速高质量单图像360度头部重建技术。它通过多视角潜在扩散模型生成一致的头侧和背面视图,然后利用GS-LRM重建器生成全面的3D表示。FaceLift在合成数据集上训练,能在真实世界图像中展现出良好的泛化性能,并在单图像重建和视频输入的新型视图合成方面表现出优异性能,还支持3D面部动画。
Key Takeaways
- FaceLift是一种快速、高质量的头部重建方法,能够从单一图像实现360度头部重建。
- FaceLift使用多视角潜在扩散模型生成一致的头侧和背面视图。
- GS-LRM重建器用于生成全面的3D表示。
- FaceLift在合成数据集上进行训练,但能在真实世界图像中展现出良好的泛化性能。
- FaceLift在单图像重建和视频输入的新型视图合成方面表现出优异性能。
- FaceLift支持3D面部动画。
点此查看论文截图

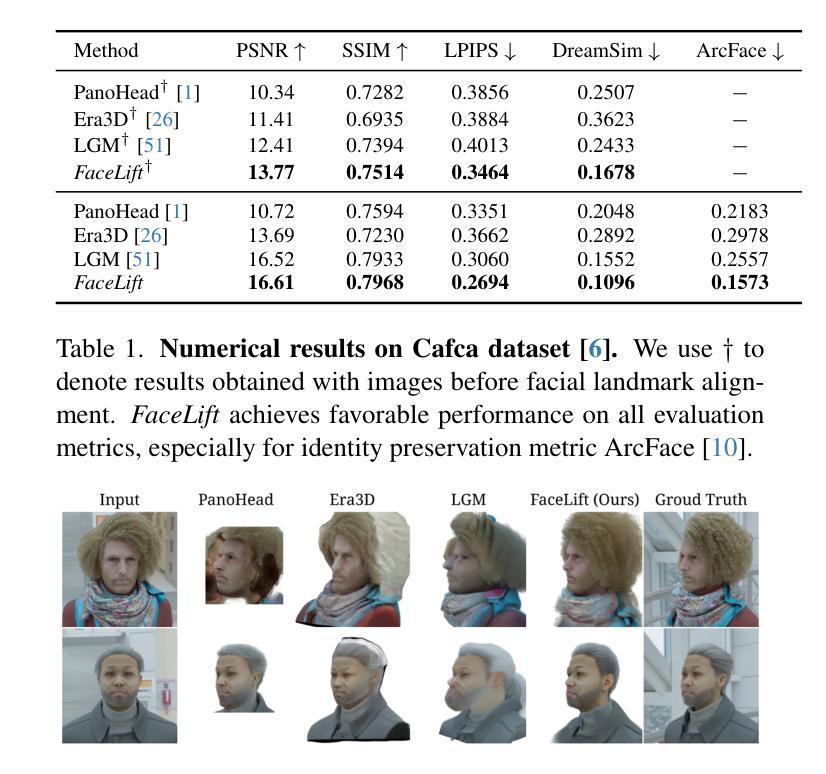
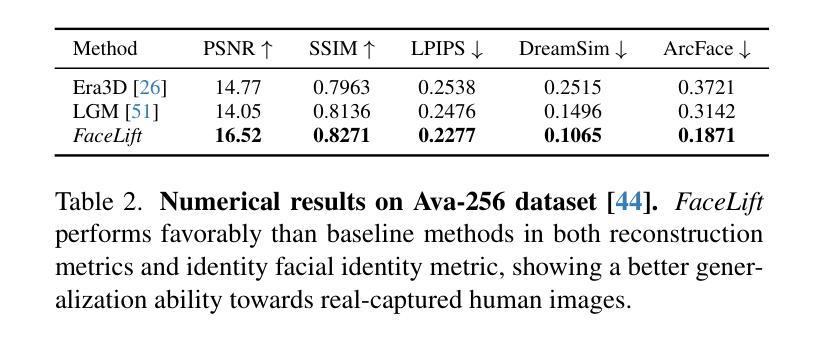

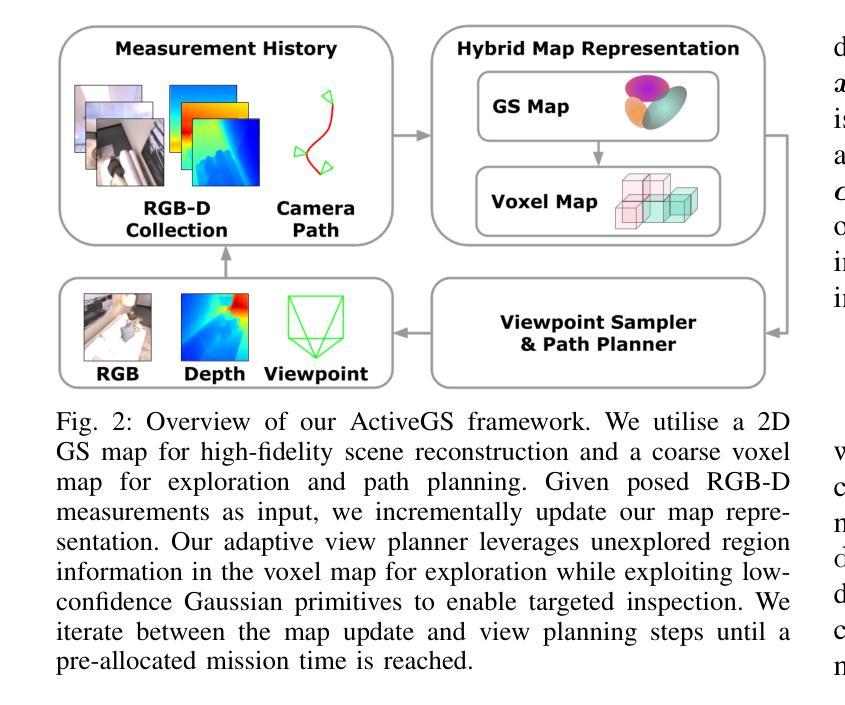
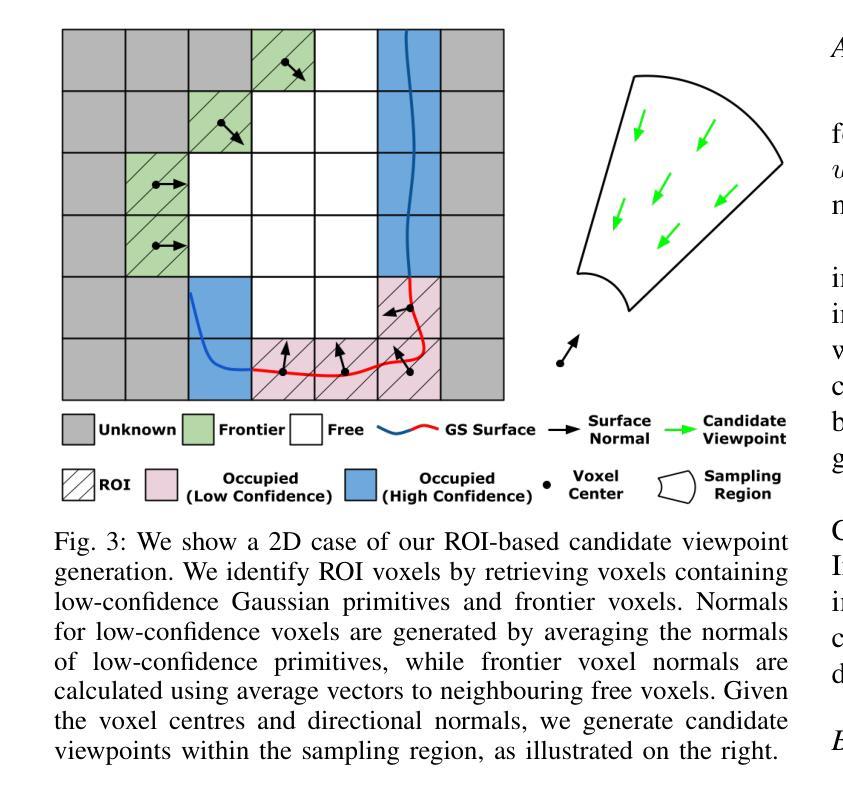
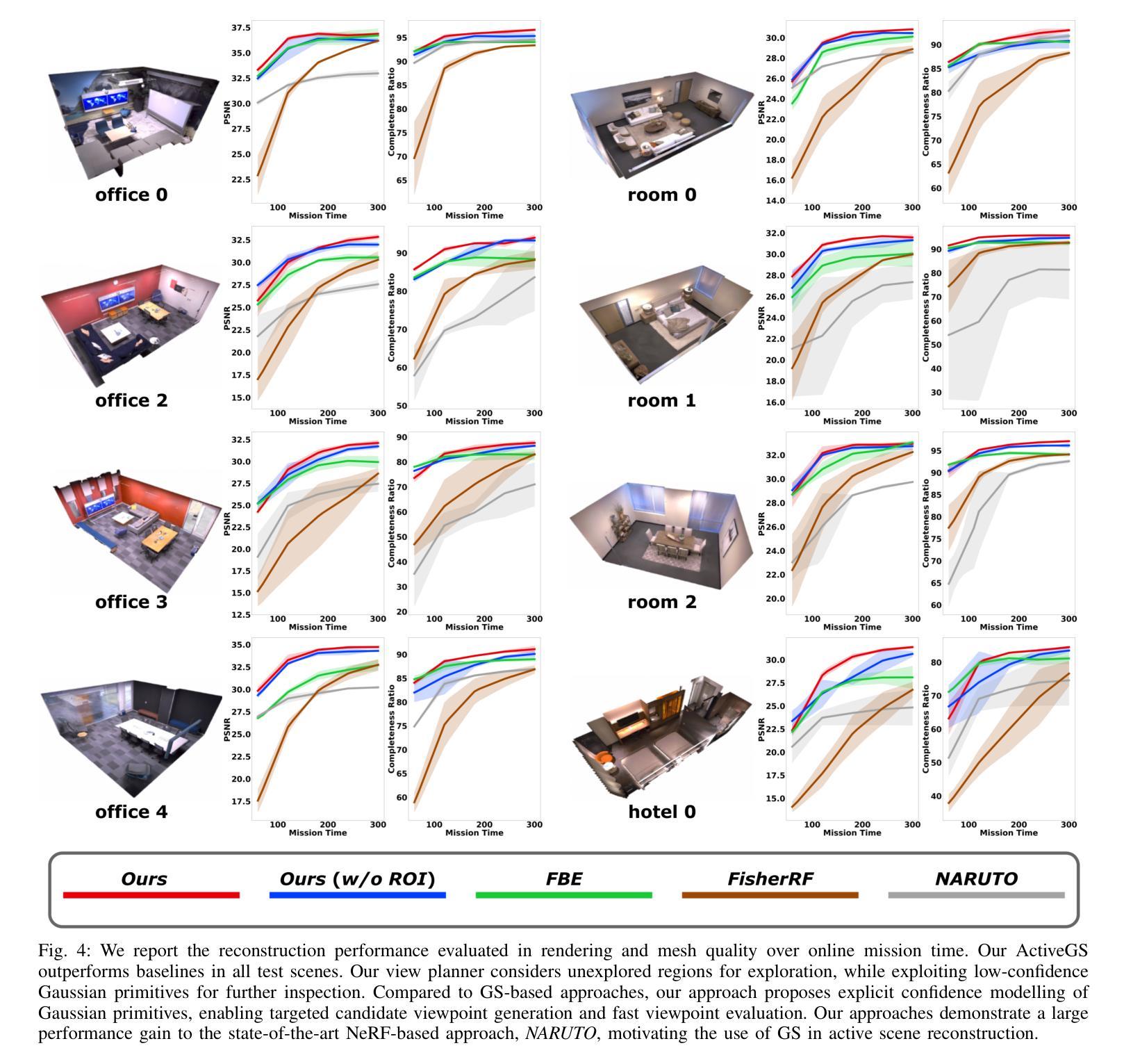
ActiveGS: Active Scene Reconstruction using Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Liren Jin, Xingguang Zhong, Yue Pan, Jens Behley, Cyrill Stachniss, Marija Popović
Robotics applications often rely on scene reconstructions to enable downstream tasks. In this work, we tackle the challenge of actively building an accurate map of an unknown scene using an on-board RGB-D camera. We propose a hybrid map representation that combines a Gaussian splatting map with a coarse voxel map, leveraging the strengths of both representations: the high-fidelity scene reconstruction capabilities of Gaussian splatting and the spatial modelling strengths of the voxel map. The core of our framework is an effective confidence modelling technique for the Gaussian splatting map to identify under-reconstructed areas, while utilising spatial information from the voxel map to target unexplored areas and assist in collision-free path planning. By actively collecting scene information in under-reconstructed and unexplored areas for map updates, our approach achieves superior Gaussian splatting reconstruction results compared to state-of-the-art approaches. Additionally, we demonstrate the applicability of our active scene reconstruction framework in the real world using an unmanned aerial vehicle.
机器人应用通常依赖于场景重建来实现后续任务。在这项工作中,我们解决了使用车载RGB-D相机主动构建未知场景精确地图的挑战。我们提出了一种混合地图表示方法,结合了高斯拼贴地图和粗糙体素地图,利用两者的优势:高斯拼贴的高保真场景重建能力和体素地图的空间建模优势。我们框架的核心是对高斯拼贴地图进行置信建模的有效技术,以识别未重建区域,同时利用体素地图的空间信息进行针对性探索,并辅助实现无碰撞路径规划。通过主动收集未重建和探索区域的场景信息进行地图更新,我们的方法与最先进的方法相比,实现了优越的高斯拼贴重建结果。此外,我们还使用无人机在实际世界中展示了我们的主动场景重建框架的适用性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文解决的是使用机载RGB-D相机对未知场景进行精确地图构建的挑战。文章提出了一种混合地图表示方法,结合了高斯喷绘地图和粗糙体素地图的优势。该框架的核心是一种有效的置信度建模技术,用于识别高斯喷绘地图的未重建区域,同时利用体素地图的空间信息来定位未探索的区域,辅助无碰撞路径规划。通过主动收集未重建和未探索区域的场景信息进行地图更新,该方法实现了优于现有技术的高斯喷绘重建结果,并在无人机上展示了其实际应用性。
Key Takeaways
- 文章解决了使用RGB-D相机对未知场景进行主动精确地图构建的挑战。
- 提出了一种混合地图表示方法,结合了高斯喷绘地图和体素地图的优势。
- 置信度建模技术用于识别高斯喷绘地图的未重建区域。
- 利用体素地图的空间信息来定位未探索的区域,辅助无碰撞路径规划。
- 通过主动收集场景信息更新地图,实现了优越的高斯喷绘重建结果。
- 文章展示了该方法在无人机上的实际应用性。
点此查看论文截图

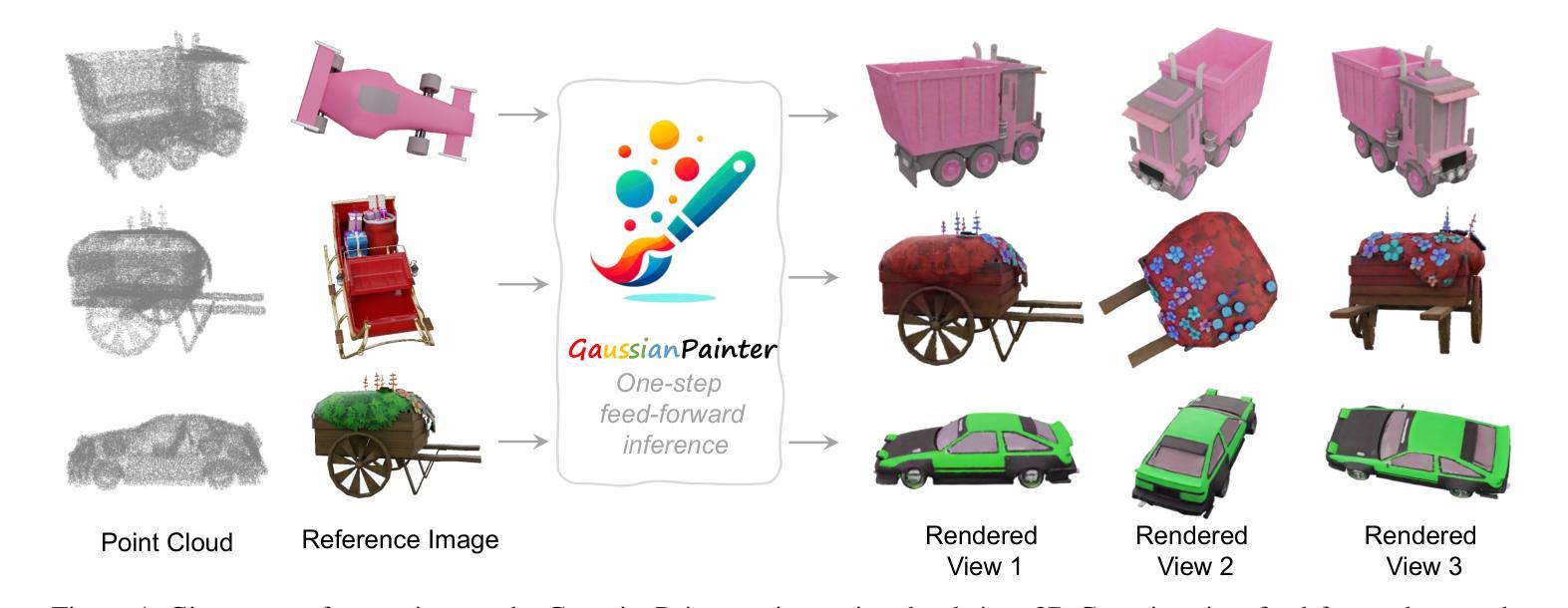
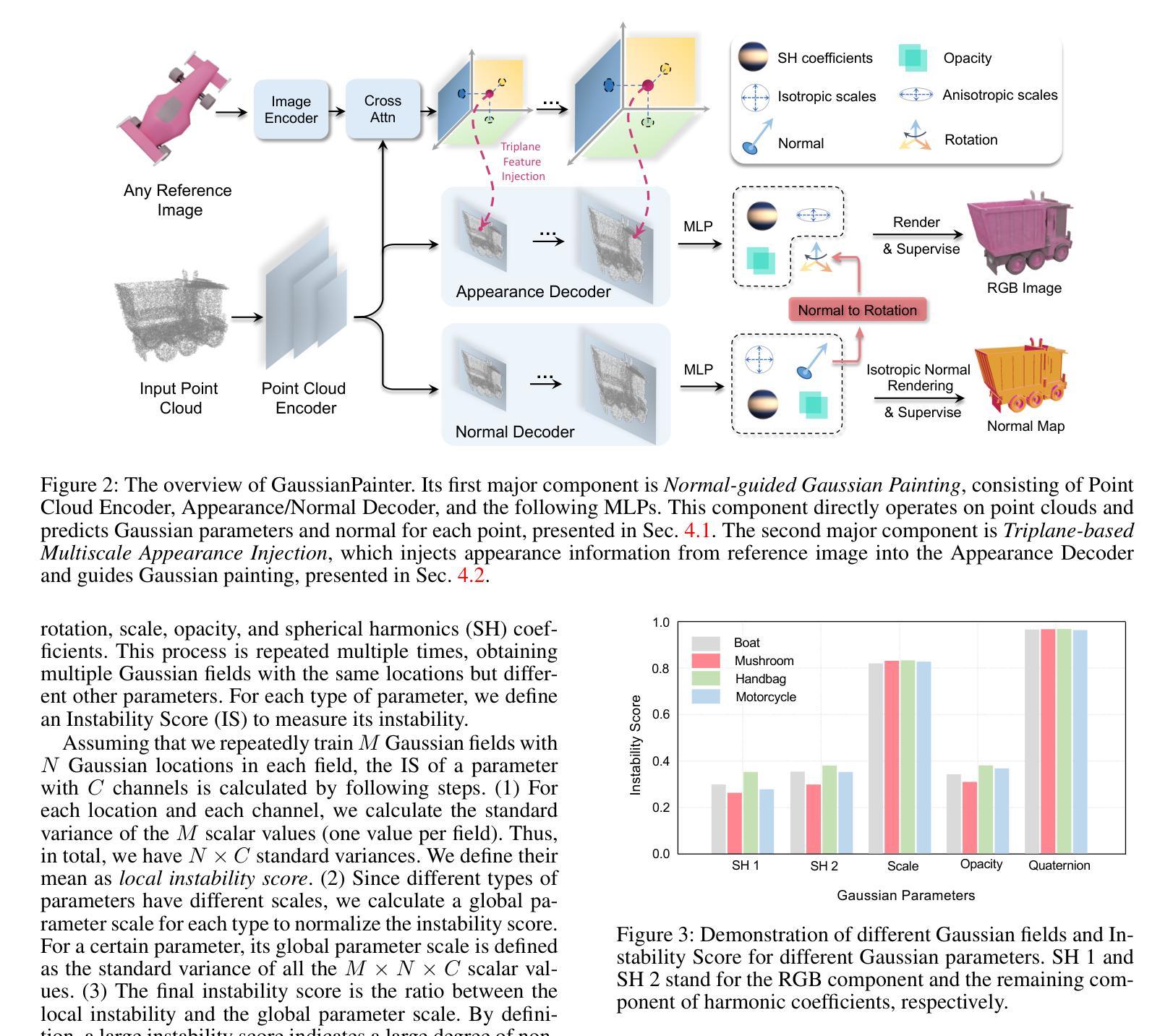
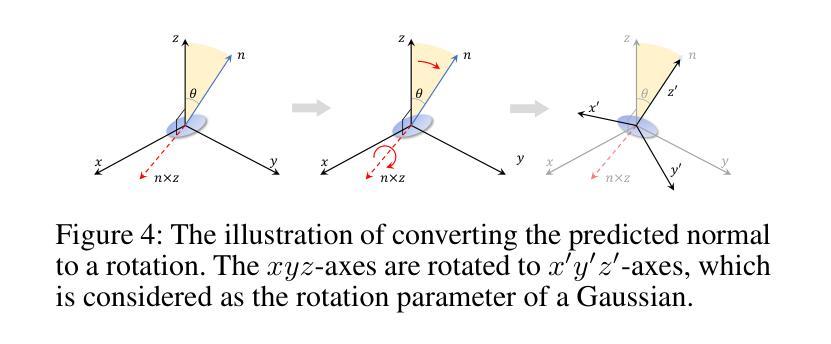
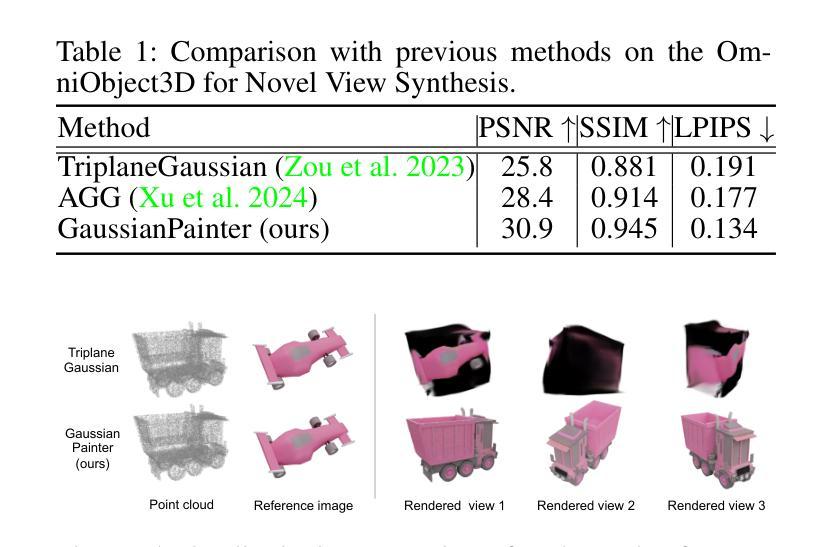
GaussianPainter: Painting Point Cloud into 3D Gaussians with Normal Guidance
Authors:Jingqiu Zhou, Lue Fan, Xuesong Chen, Linjiang Huang, Si Liu, Hongsheng Li
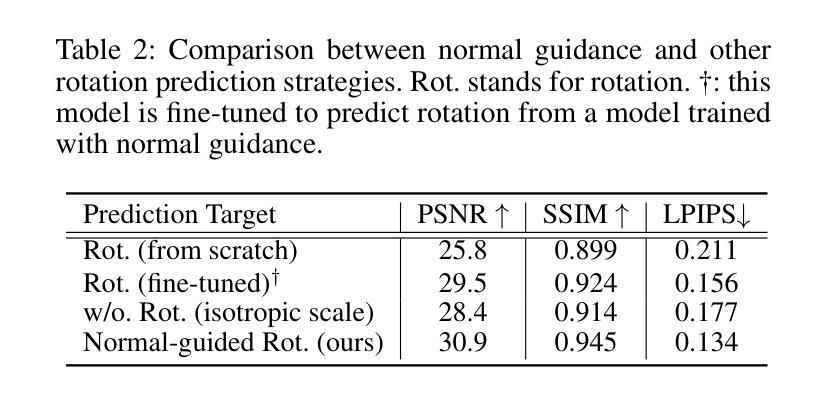
In this paper, we present GaussianPainter, the first method to paint a point cloud into 3D Gaussians given a reference image. GaussianPainter introduces an innovative feed-forward approach to overcome the limitations of time-consuming test-time optimization in 3D Gaussian splatting. Our method addresses a critical challenge in the field: the non-uniqueness problem inherent in the large parameter space of 3D Gaussian splatting. This space, encompassing rotation, anisotropic scales, and spherical harmonic coefficients, introduces the challenge of rendering similar images from substantially different Gaussian fields. As a result, feed-forward networks face instability when attempting to directly predict high-quality Gaussian fields, struggling to converge on consistent parameters for a given output. To address this issue, we propose to estimate a surface normal for each point to determine its Gaussian rotation. This strategy enables the network to effectively predict the remaining Gaussian parameters in the constrained space. We further enhance our approach with an appearance injection module, incorporating reference image appearance into Gaussian fields via a multiscale triplane representation. Our method successfully balances efficiency and fidelity in 3D Gaussian generation, achieving high-quality, diverse, and robust 3D content creation from point clouds in a single forward pass.
本文介绍了GaussianPainter,这是一种将点云绘制成三维高斯体的新方法,只需提供一张参考图像即可。GaussianPainter引入了一种创新的前馈方法,克服了三维高斯涂抹中耗时测试优化的局限性。我们的方法解决了该领域的一个关键挑战:三维高斯涂抹的大参数空间所固有的非唯一性问题。这个空间包括旋转、各向异性尺度和球面谐波系数,从实质上不同的高斯场渲染相似图像的挑战。因此,前馈网络在尝试直接预测高质量高斯场时面临不稳定问题,难以在给定输出上收敛于一致参数。为了解决这一问题,我们提出为每个点估计法线以确定其高斯旋转。这一策略使网络能够在约束空间中有效地预测剩余的高斯参数。我们进一步通过外观注入模块增强了我们的方法,该模块通过多尺度triplane表示将参考图像外观融入到高斯场中。我们的方法在三维高斯生成中成功实现了效率和保真度的平衡,单次前向传递即可实现高质量、多样化和稳健的3D内容创建。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To appear in AAAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了GaussianPainter方法,该方法能够将点云绘制成3D高斯图像给定参考图像。GaussianPainter采用创新的前馈方法,克服了3D高斯喷涂中耗时的时间优化方法的局限性。该方法解决了领域中的一个关键挑战:3D高斯喷涂参数空间中的非唯一性问题。此空间包含旋转、各向异性尺度和谐波系数等问题,使得从实质上不同的高斯场渲染相似图像变得困难。为解决这一问题,我们提出为每个点估算表面法线以确定其高斯旋转。此策略使网络能够在约束空间中有效预测其余的高斯参数。我们进一步通过外观注入模块增强我们的方法,通过多尺度triplane表示法将参考图像外观融入高斯场。我们的方法在效率和保真度之间取得了平衡,在单次前向传递中实现了高质量、多样化和稳健的3D内容创建。
Key Takeaways
- GaussianPainter是第一个能将点云绘制成3D高斯图像的方法,给定一个参考图像。
- 该方法采用前馈方法,克服了3D高斯喷涂中的时间优化难题。
- 解决了3D高斯喷涂参数空间中的非唯一性问题,该空间包含旋转、各向异性尺度和谐波系数等问题。
- 通过估算每个点的表面法线来解决非唯一性问题,从而确定高斯旋转。
- 引入外观注入模块,通过多尺度triplane表示法将参考图像融入高斯场。
- 该方法在效率和保真度之间取得了平衡。
点此查看论文截图

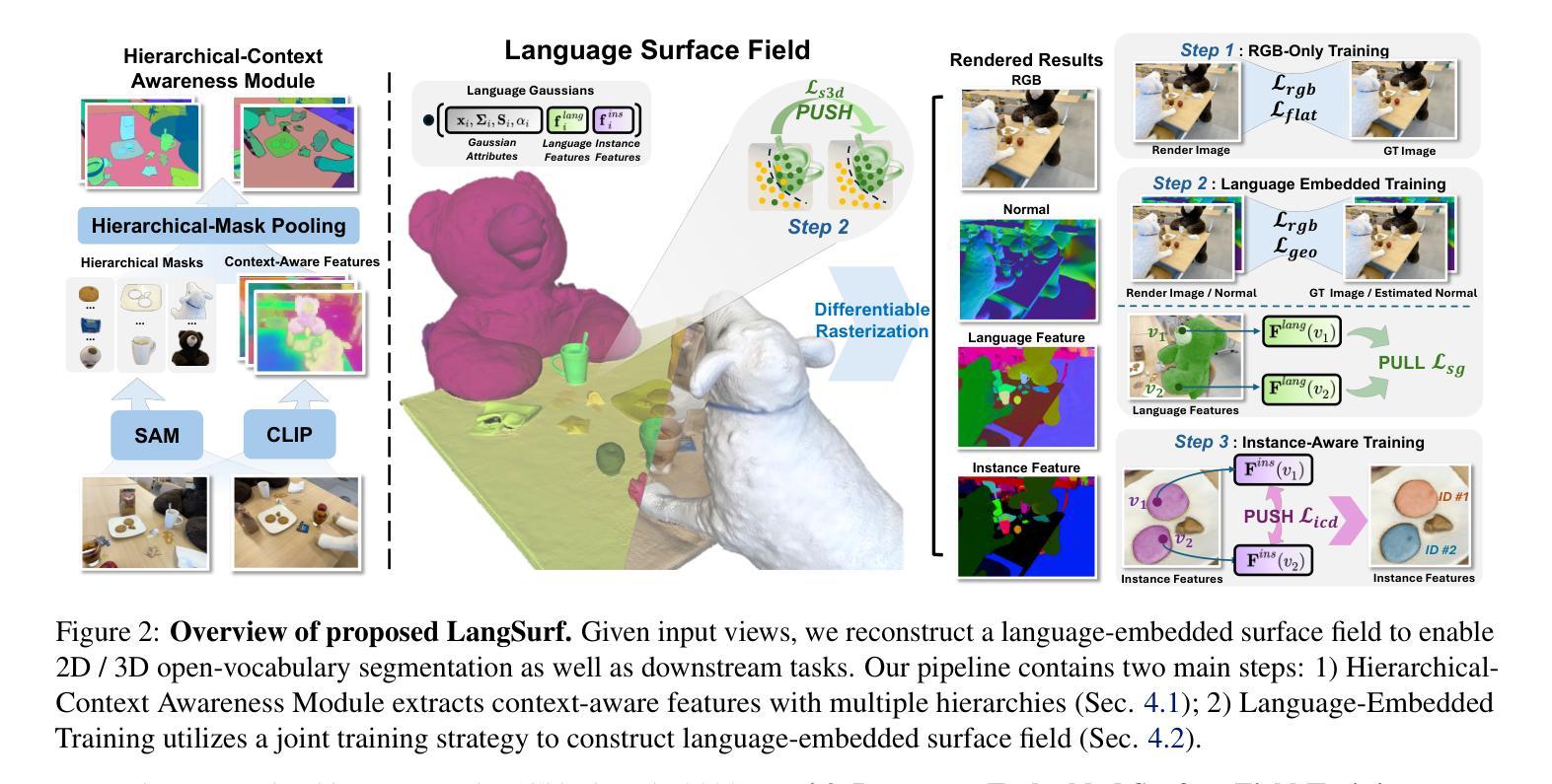
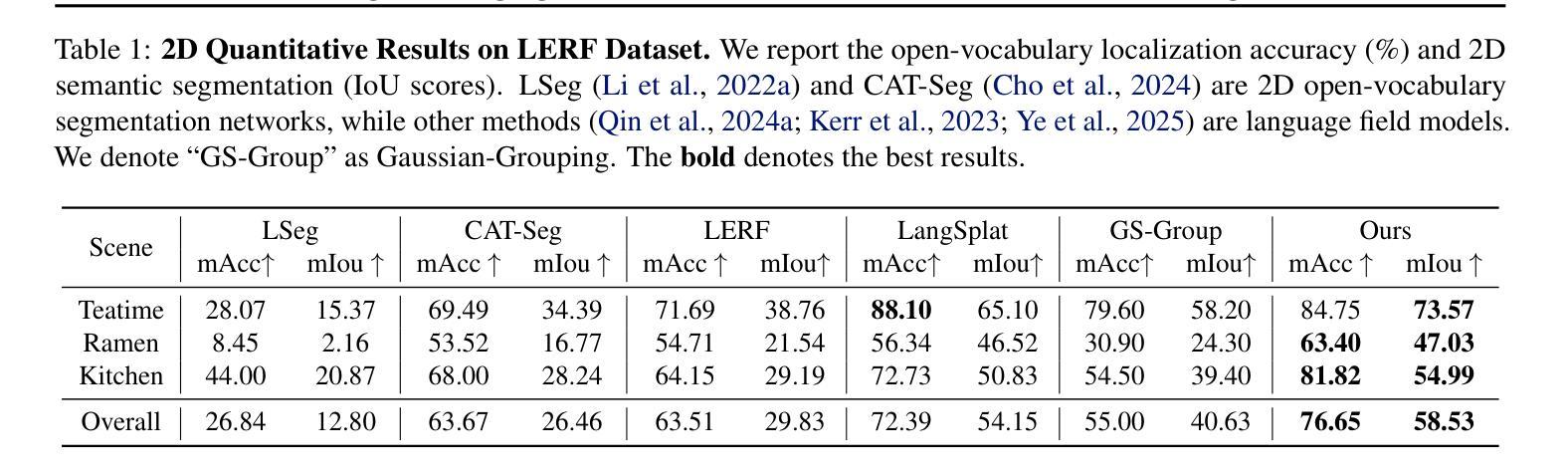
LangSurf: Language-Embedded Surface Gaussians for 3D Scene Understanding
Authors:Hao Li, Roy Qin, Zhengyu Zou, Diqi He, Bohan Li, Bingquan Dai, Dingewn Zhang, Junwei Han
Applying Gaussian Splatting to perception tasks for 3D scene understanding is becoming increasingly popular. Most existing works primarily focus on rendering 2D feature maps from novel viewpoints, which leads to an imprecise 3D language field with outlier languages, ultimately failing to align objects in 3D space. By utilizing masked images for feature extraction, these approaches also lack essential contextual information, leading to inaccurate feature representation. To this end, we propose a Language-Embedded Surface Field (LangSurf), which accurately aligns the 3D language fields with the surface of objects, facilitating precise 2D and 3D segmentation with text query, widely expanding the downstream tasks such as removal and editing. The core of LangSurf is a joint training strategy that flattens the language Gaussian on the object surfaces using geometry supervision and contrastive losses to assign accurate language features to the Gaussians of objects. In addition, we also introduce the Hierarchical-Context Awareness Module to extract features at the image level for contextual information then perform hierarchical mask pooling using masks segmented by SAM to obtain fine-grained language features in different hierarchies. Extensive experiments on open-vocabulary 2D and 3D semantic segmentation demonstrate that LangSurf outperforms the previous state-of-the-art method LangSplat by a large margin. As shown in Fig.~\ref{fig:teaser}, our method is capable of segmenting objects in 3D space, thus boosting the effectiveness of our approach in instance recognition, removal, and editing, which is also supported by comprehensive experiments. \url{https://langsurf.github.io}{Project Page}.
将高斯摊铺应用于3D场景理解的感知任务越来越受欢迎。现有的大多数工作主要集中在从新颖视角渲染2D特征图,这导致3D语言场存在离群值语言,最终无法将对象对齐到三维空间中。这些方法通过利用遮罩图像进行特征提取,也缺乏必要的上下文信息,导致特征表示不准确。因此,我们提出了语言嵌入表面场(LangSurf),它能够准确地将3D语言场与物体表面对齐,便于通过文本查询进行精确的二维和三维分割,并广泛扩展下游任务,如移除和编辑。LangSurf的核心是一种联合训练策略,它通过几何监督和对比损失将语言的Gaussian摊在物体表面,为物体的Gaussians分配准确的语言特征。此外,我们还引入了层次上下文感知模块,以在图像级别提取特征以获得上下文信息,然后使用SAM分割的遮罩进行分层遮罩池化,以在不同层次上获得精细的语言特征。在开放词汇的二维和三维语义分割方面的广泛实验表明,LangSurf明显优于之前的最先进方法LangSplat。如图~\ref{fig:teaser}所示,我们的方法能够在三维空间中对物体进行分割,从而提高了在实例识别、移除和编辑方面的方法的有效性,这也是由综合实验所支持的。项目页面。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF \url{https://langsurf.github.io}{Project Page}
摘要
基于高斯喷溅技术,提出一种语言嵌入表面场(LangSurf),用于精准对齐3D语言场与物体表面,实现通过文本查询进行精确的2D和3D分割,并大大扩展了如下游任务,如移除和编辑。核心在于采用联合训练策略,通过几何监督和对比损失,将语言特征准确分配给物体的高斯图。引入层次上下文感知模块,提取图像级别的特征进行上下文信息,然后使用层次掩膜池化获得不同层次的精细语言特征。在开放词汇表的2D和3D语义分割实验中,LangSurf显著优于之前的最新方法LangSplat。如图《fig:teaser》所示,该方法能够分割3D空间中的物体,提高了在实例识别、移除和编辑中的有效性。
关键见解
- 提出了一种新的方法LangSurf,基于高斯喷溅技术,用于改善3D场景理解中的感知任务。
- LangSurf能够精准对齐3D语言场与物体表面,实现通过文本查询进行精确的2D和3D分割。
- 引入联合训练策略,通过几何监督和对比损失,以分配准确的语言特征到物体的高斯图。
- 引入了层次上下文感知模块来提取图像级别的特征,并通过层次掩膜池化获取不同层次的精细语言特征。
- LangSurf在开放词汇表的2D和3D语义分割实验中显著优于之前的最新方法。
- 该方法能够分割3D空间中的物体,提高了实例识别、移除和编辑的有效性。
- 提供了项目页面链接,可以进一步了解该方法的相关细节和实现。
点此查看论文截图

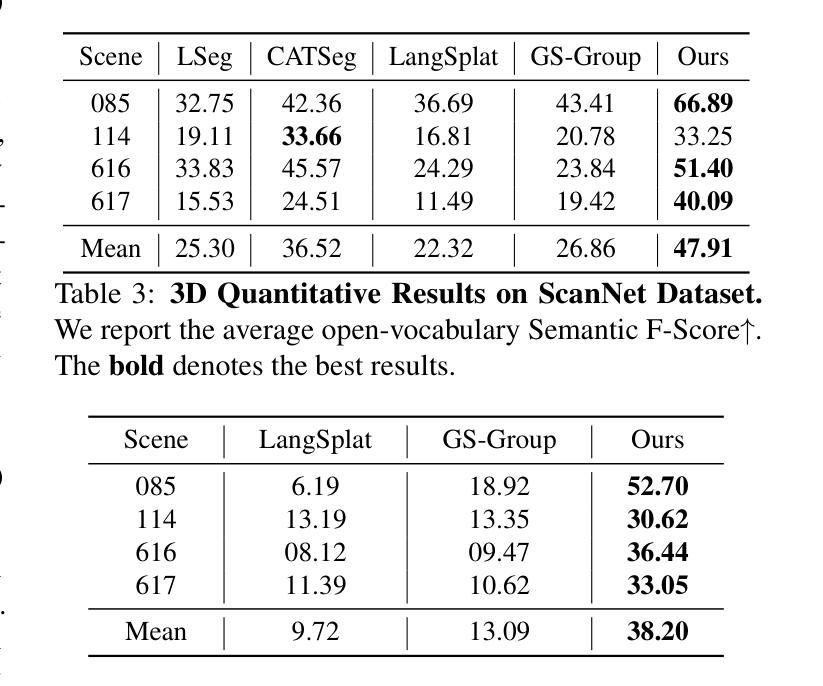

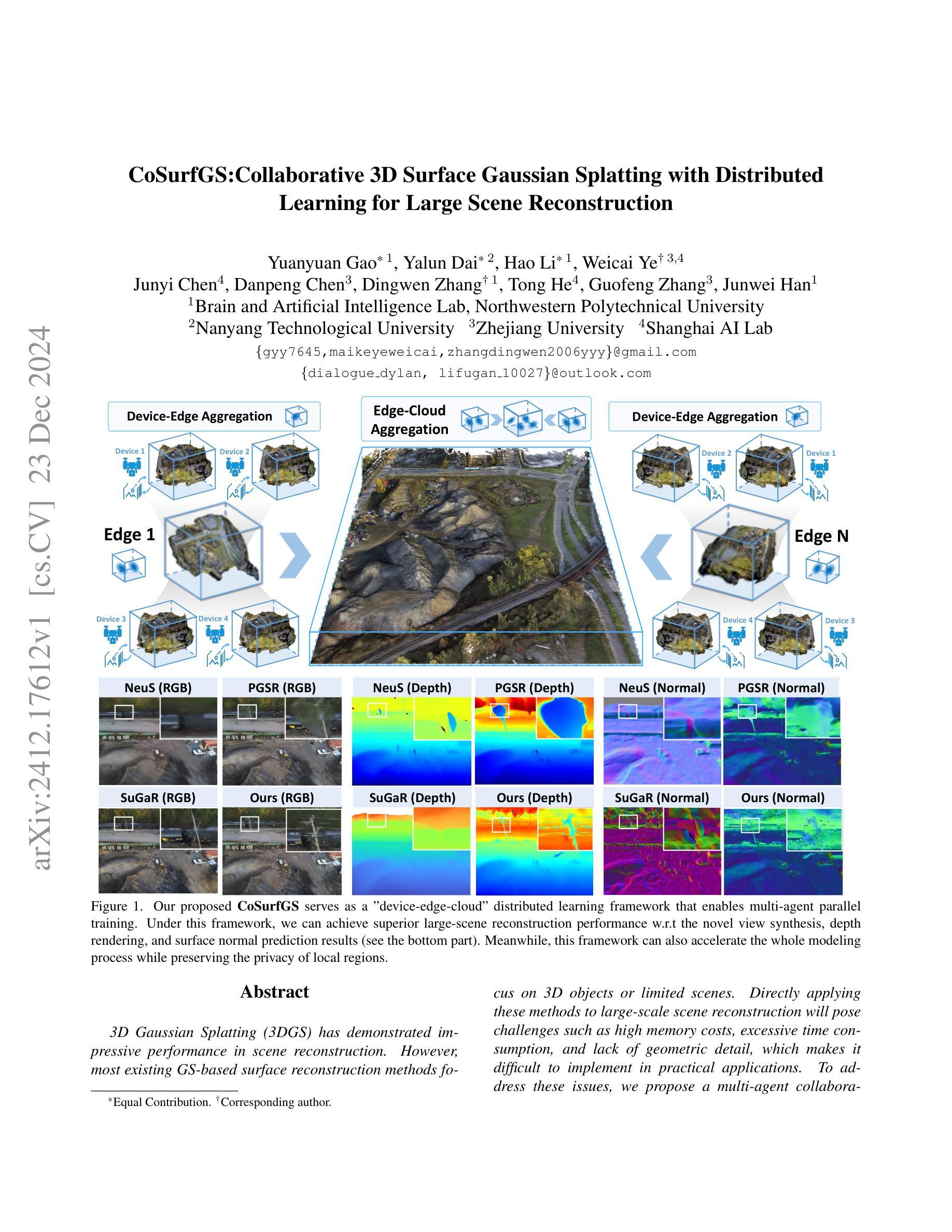
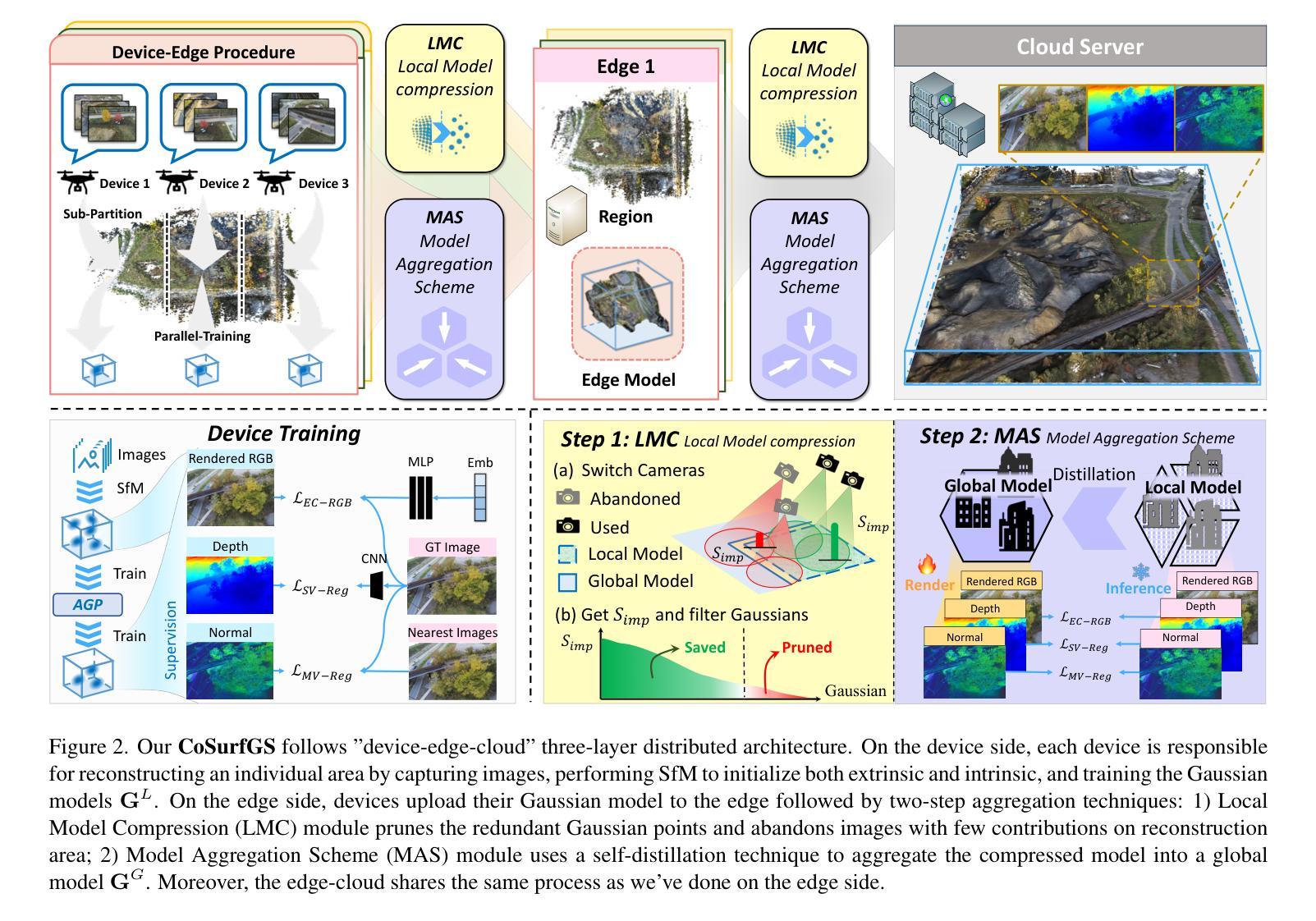
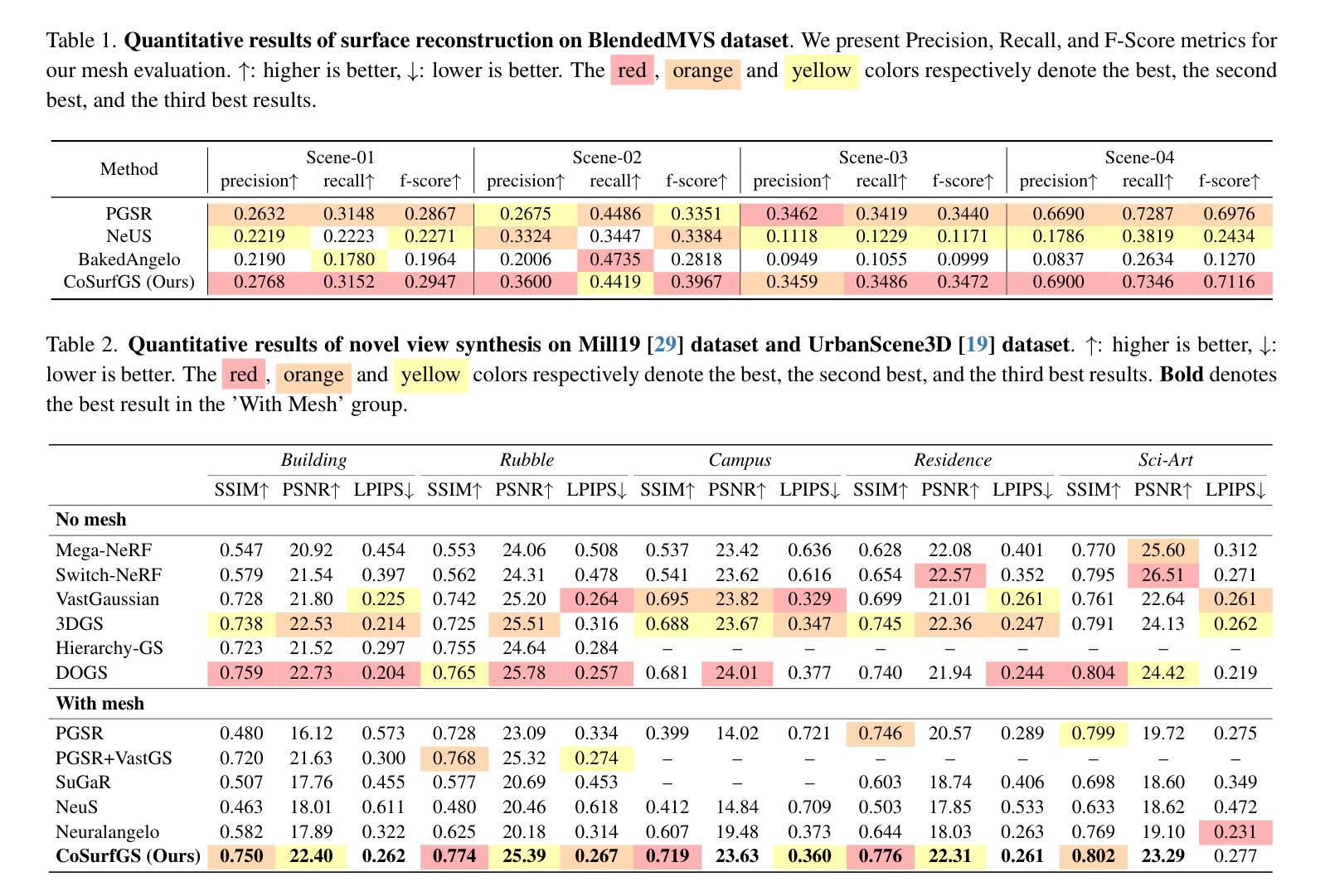
CoSurfGS:Collaborative 3D Surface Gaussian Splatting with Distributed Learning for Large Scene Reconstruction
Authors:Yuanyuan Gao, Yalun Dai, Hao Li, Weicai Ye, Junyi Chen, Danpeng Chen, Dingwen Zhang, Tong He, Guofeng Zhang, Junwei Han
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has demonstrated impressive performance in scene reconstruction. However, most existing GS-based surface reconstruction methods focus on 3D objects or limited scenes. Directly applying these methods to large-scale scene reconstruction will pose challenges such as high memory costs, excessive time consumption, and lack of geometric detail, which makes it difficult to implement in practical applications. To address these issues, we propose a multi-agent collaborative fast 3DGS surface reconstruction framework based on distributed learning for large-scale surface reconstruction. Specifically, we develop local model compression (LMC) and model aggregation schemes (MAS) to achieve high-quality surface representation of large scenes while reducing GPU memory consumption. Extensive experiments on Urban3d, MegaNeRF, and BlendedMVS demonstrate that our proposed method can achieve fast and scalable high-fidelity surface reconstruction and photorealistic rendering. Our project page is available at \url{https://gyy456.github.io/CoSurfGS}.
3D高斯混合(3DGS)在场景重建中展现了令人印象深刻的性能。然而,大多数现有的基于GS的表面重建方法主要关注于3D对象或有限的场景。直接将这些方法应用于大规模场景重建将面临高内存成本、时间消耗过多以及缺乏几何细节等挑战,这使得在实际应用中难以实现。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种基于分布式学习的多智能体协作快速3DGS表面重建框架,用于大规模表面重建。具体来说,我们开发了本地模型压缩(LMC)和模型聚合方案(MAS),以实现大型场景的高质量表面表示,同时降低GPU内存消耗。在Urban3d、MegaNeRF和BlendedMVS上的大量实验表明,我们提出的方法可以实现快速、可扩展的高保真表面重建和逼真的渲染。我们的项目页面可通过网址https://gyy456.github.io/CoSurfGS访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Our project page is available at \url{https://gyy456.github.io/CoSurfGS}
Summary
3DGS在场景重建中表现优异,但现有方法主要关注于小规模的3D对象或场景,难以直接应用于大规模场景重建。针对此问题,我们提出基于多智能体协作的快速三维高斯展开表面重建框架,利用分布式学习实现大规模表面重建。通过开发本地模型压缩和模型聚合方案,实现高质量的场景表面表示,同时降低GPU内存消耗。实验证明,该方法可实现快速、可扩展的高保真表面重建和逼真的渲染。
Key Takeaways
- 现有基于高斯展开的重建方法面临大规模场景重建的挑战。
- 提出基于多智能体协作的快速三维高斯展开表面重建框架,适用于大规模场景。
- 通过本地模型压缩和模型聚合方案实现高质量的场景表面表示。
- 方法能降低GPU内存消耗,提高表面重建的效率。
- 在Urban3d、MegaNeRF和BlendedMVS等数据集上进行了广泛的实验验证。
- 实验证明该方法可实现快速、可扩展的高保真表面重建和逼真的渲染。
点此查看论文截图
GSemSplat: Generalizable Semantic 3D Gaussian Splatting from Uncalibrated Image Pairs
Authors:Xingrui Wang, Cuiling Lan, Hanxin Zhu, Zhibo Chen, Yan Lu
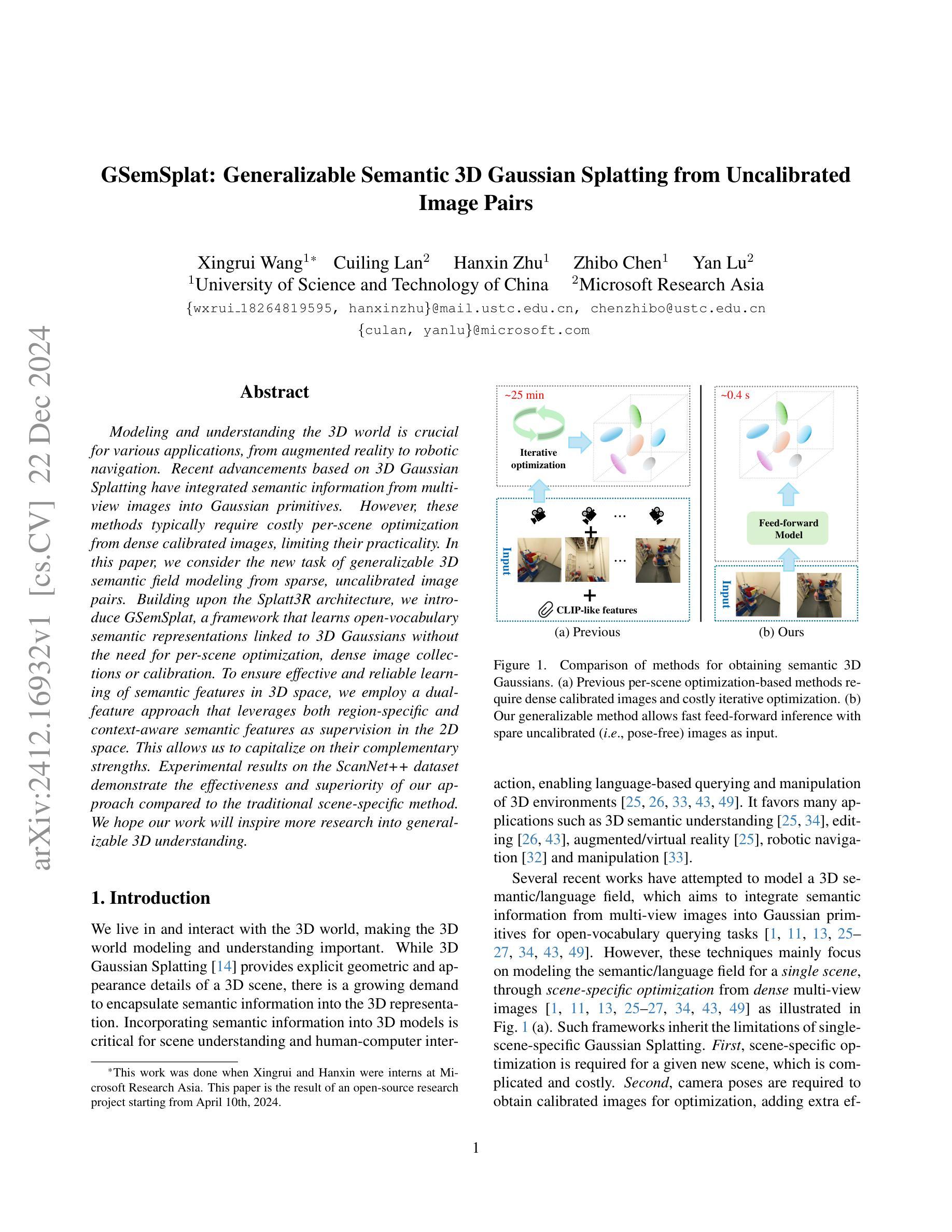
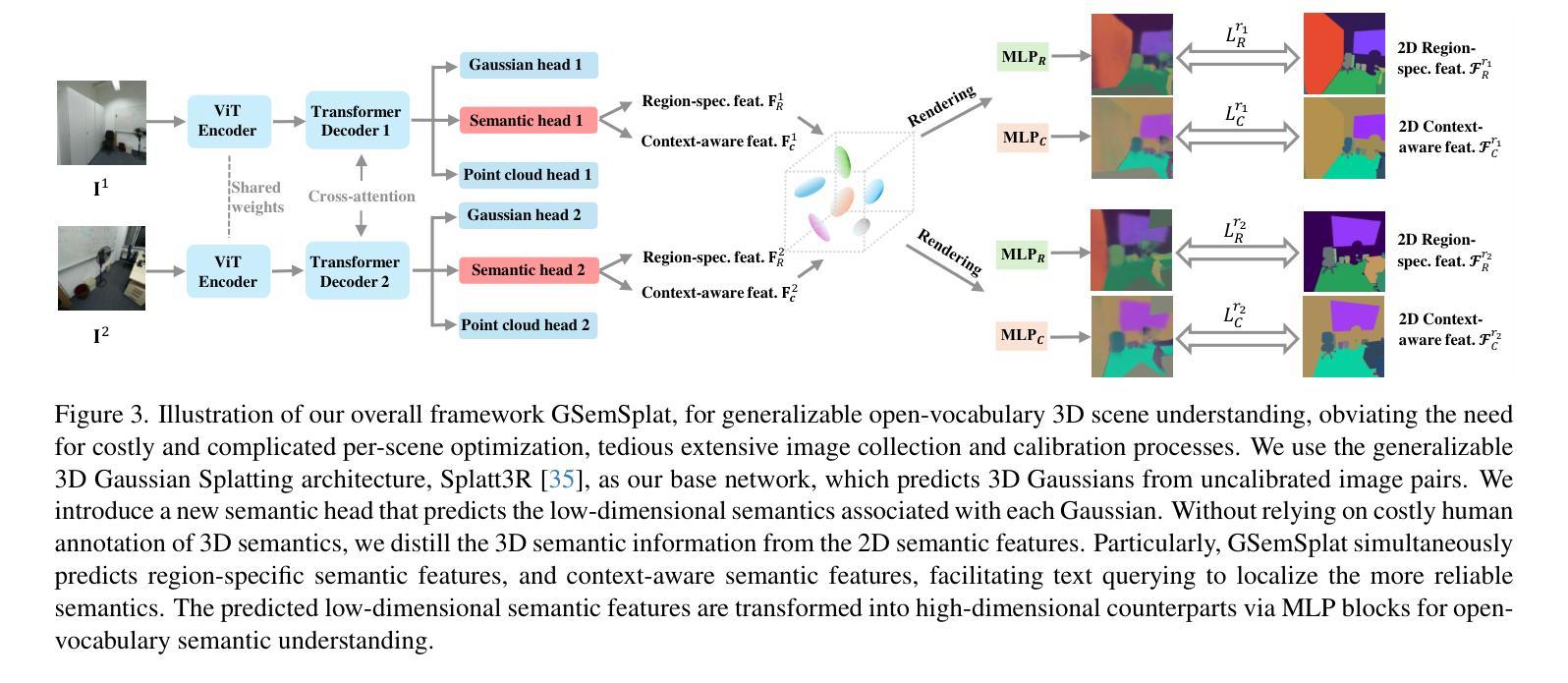
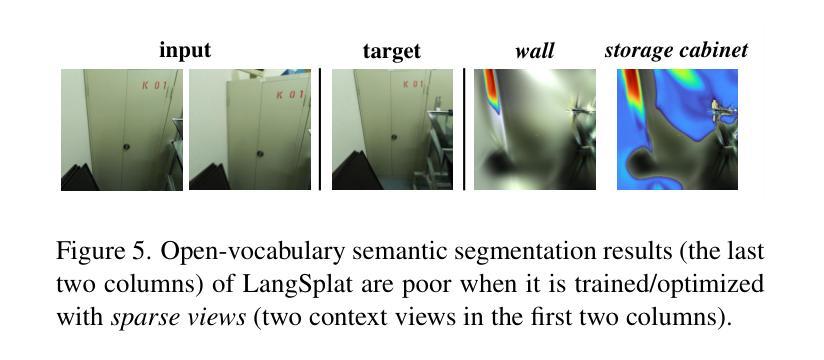
Modeling and understanding the 3D world is crucial for various applications, from augmented reality to robotic navigation. Recent advancements based on 3D Gaussian Splatting have integrated semantic information from multi-view images into Gaussian primitives. However, these methods typically require costly per-scene optimization from dense calibrated images, limiting their practicality. In this paper, we consider the new task of generalizable 3D semantic field modeling from sparse, uncalibrated image pairs. Building upon the Splatt3R architecture, we introduce GSemSplat, a framework that learns open-vocabulary semantic representations linked to 3D Gaussians without the need for per-scene optimization, dense image collections or calibration. To ensure effective and reliable learning of semantic features in 3D space, we employ a dual-feature approach that leverages both region-specific and context-aware semantic features as supervision in the 2D space. This allows us to capitalize on their complementary strengths. Experimental results on the ScanNet++ dataset demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our approach compared to the traditional scene-specific method. We hope our work will inspire more research into generalizable 3D understanding.
对三维世界的建模和理解对于各种应用至关重要,从增强现实到机器人导航都是如此。最近基于三维高斯贴图技术的进展已经将多视角图像中的语义信息集成到高斯基本元素中。然而,这些方法通常需要昂贵的场景优化步骤,依赖密集的校准图像,限制了其实际应用性。在本文中,我们提出了稀疏、未经校准的图像对的一般性三维语义场建模的新任务。在Splatt3R架构的基础上,我们引入了GSemSplat框架,它能够在无需进行场景优化、密集的图像集或校准的情况下学习开放词汇的语义表示,并将其链接到三维高斯图上。为了保证在三维空间中有效地学习语义特征,我们采用了一种双重特征方法,在二维空间中利用特定区域和上下文感知语义特征作为监督,这让我们可以充分利用两者的互补优势。在ScanNet++数据集上的实验结果表明,与传统针对特定场景的方法相比,我们的方法具有有效性和优越性。我们希望这项工作能激发更多关于通用三维理解的研究灵感。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于3D高斯喷溅技术的最新进展,已经能够将多视角图像的语义信息集成到高斯基本单元中。然而,这些方法通常需要密集校准图像的昂贵场景优化,限制了其实用性。本研究考虑从稀疏、未校准的图像对中建立通用的3D语义场模型的新任务。基于Splatt3R架构,我们引入了GSemSplat框架,能够无需场景优化、密集图像集合或校准,直接关联开放式词汇语义表示与3D高斯分布。为确保在3D空间中有效可靠地学习语义特征,我们采用双重特征方法,利用区域特定和上下文感知的语义特征在二维空间中进行监督,充分发挥其互补优势。在ScanNet++数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的方法相较于传统场景特定方法更为有效和优越。
Key Takeaways
- 3D世界建模对于增强现实和机器人导航等应用至关重要。
- 最新研究采用基于3D高斯喷溅的技术集成多视角图像的语义信息。
- 当前方法需要密集校准图像的昂贵场景优化,限制了实用性。
- 研究提出了一种新的任务:从稀疏、未校准的图像对中进行通用3D语义场建模。
- 引入GSemSplat框架,无需场景优化或密集图像集合即可关联开放式词汇语义表示与3D高斯分布。
- 采用双重特征方法,结合区域特定和上下文感知的语义特征在二维空间中进行监督。
点此查看论文截图


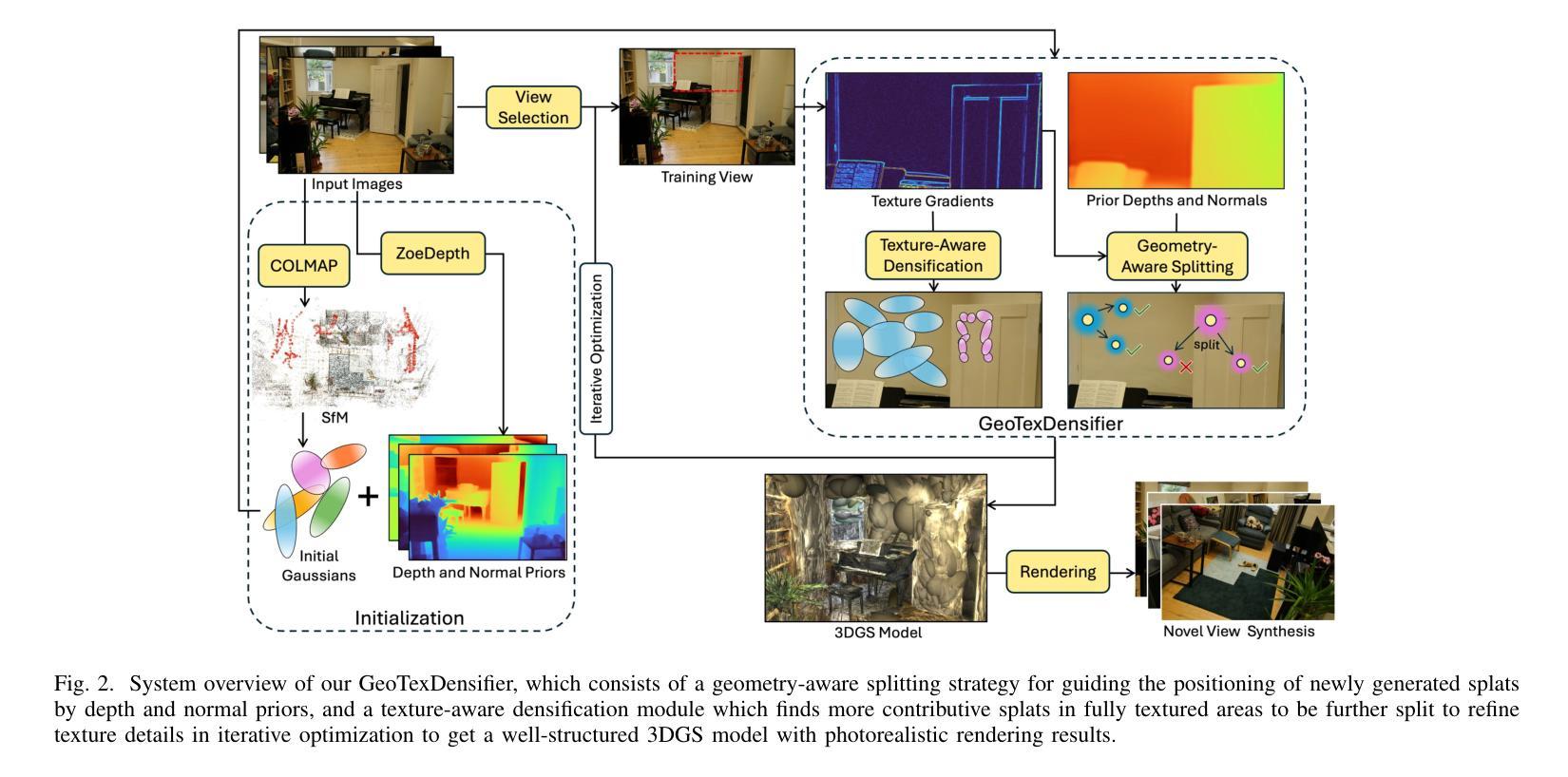
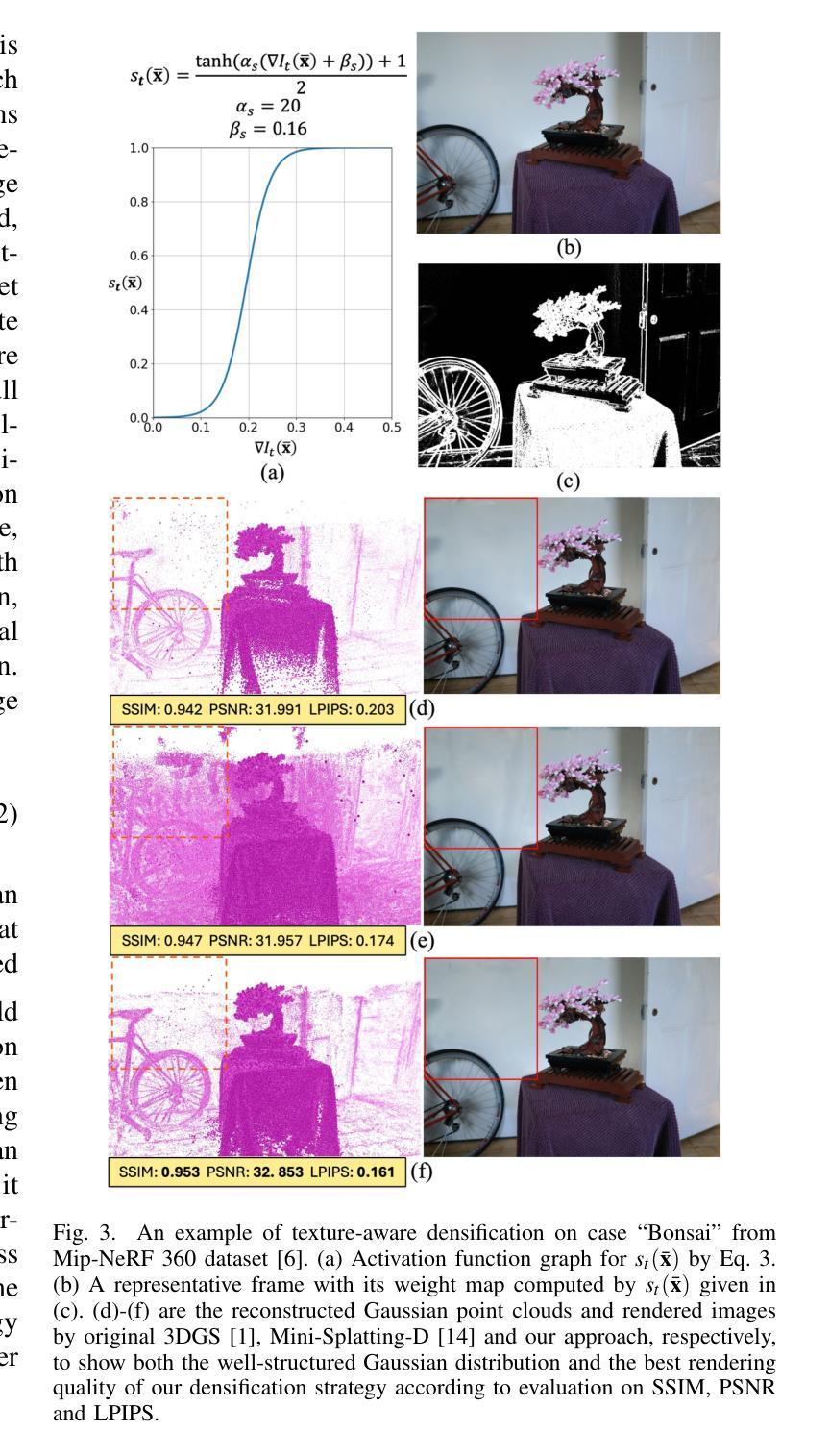
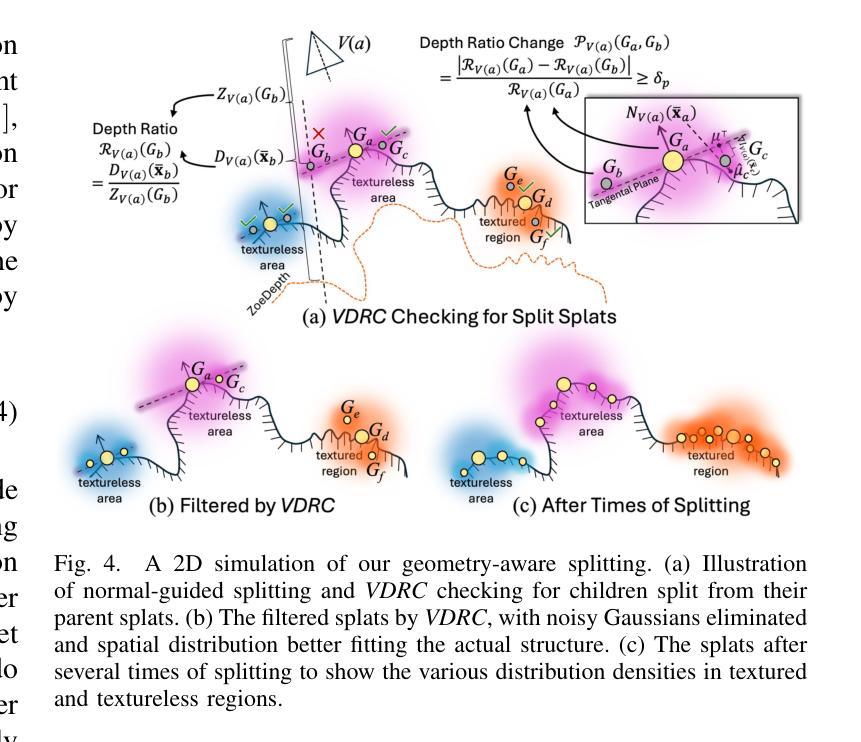
GeoTexDensifier: Geometry-Texture-Aware Densification for High-Quality Photorealistic 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Hanqing Jiang, Xiaojun Xiang, Han Sun, Hongjie Li, Liyang Zhou, Xiaoyu Zhang, Guofeng Zhang
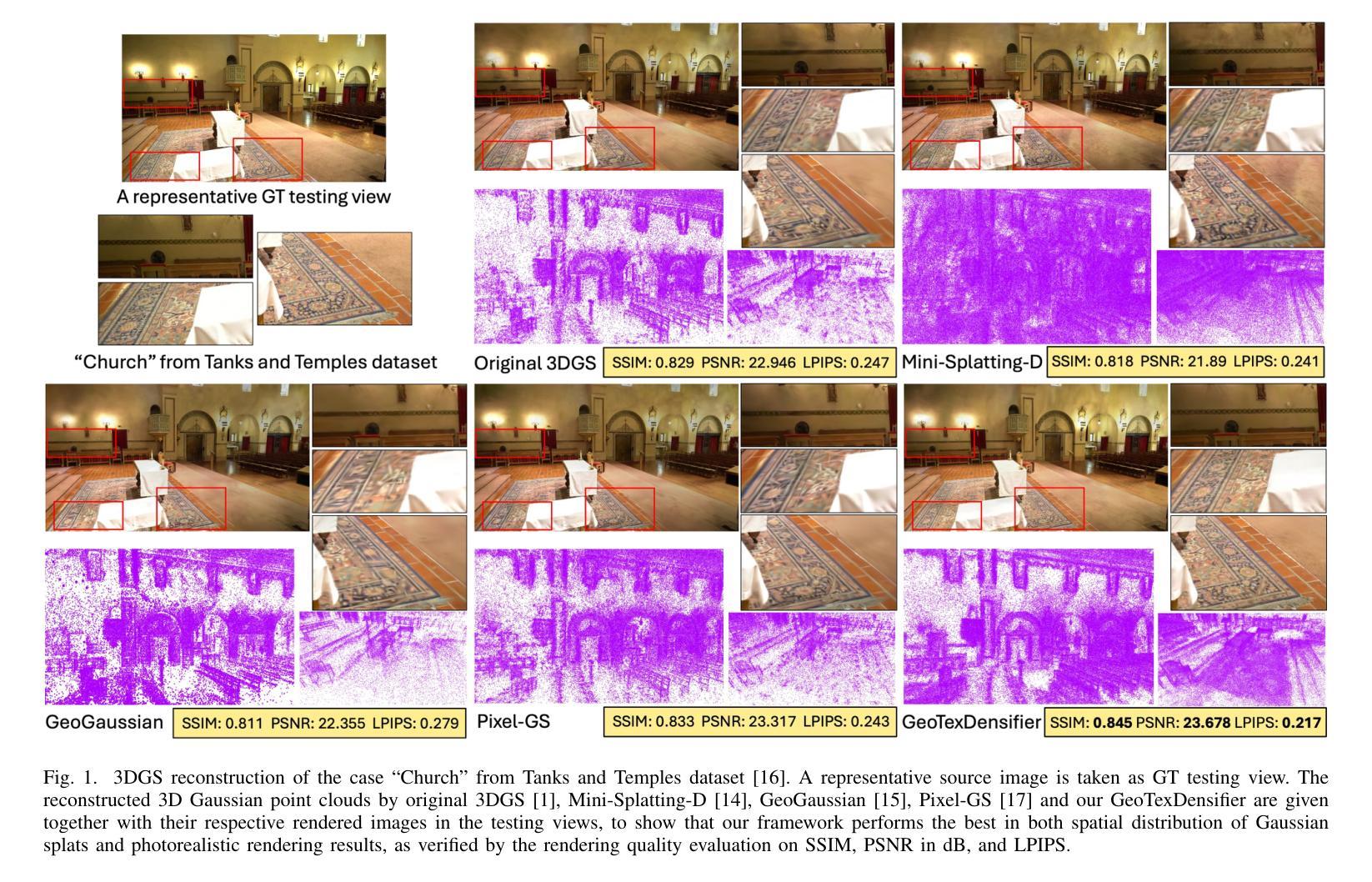
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has recently attracted wide attentions in various areas such as 3D navigation, Virtual Reality (VR) and 3D simulation, due to its photorealistic and efficient rendering performance. High-quality reconstrution of 3DGS relies on sufficient splats and a reasonable distribution of these splats to fit real geometric surface and texture details, which turns out to be a challenging problem. We present GeoTexDensifier, a novel geometry-texture-aware densification strategy to reconstruct high-quality Gaussian splats which better comply with the geometric structure and texture richness of the scene. Specifically, our GeoTexDensifier framework carries out an auxiliary texture-aware densification method to produce a denser distribution of splats in fully textured areas, while keeping sparsity in low-texture regions to maintain the quality of Gaussian point cloud. Meanwhile, a geometry-aware splitting strategy takes depth and normal priors to guide the splitting sampling and filter out the noisy splats whose initial positions are far from the actual geometric surfaces they aim to fit, under a Validation of Depth Ratio Change checking. With the help of relative monocular depth prior, such geometry-aware validation can effectively reduce the influence of scattered Gaussians to the final rendering quality, especially in regions with weak textures or without sufficient training views. The texture-aware densification and geometry-aware splitting strategies are fully combined to obtain a set of high-quality Gaussian splats. We experiment our GeoTexDensifier framework on various datasets and compare our Novel View Synthesis results to other state-of-the-art 3DGS approaches, with detailed quantitative and qualitative evaluations to demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in producing more photorealistic 3DGS models.
3D高斯摊铺(3DGS)因其逼真的高效渲染性能,在诸如3D导航、虚拟现实(VR)和3D模拟等领域引起了广泛关注。高质量的3DGS重建依赖于足够的摊片和这些摊片的合理分布,以拟合真实几何表面和纹理细节,这证明是一个具有挑战性的问题。我们提出了GeoTexDensifier,这是一种新型几何纹理感知的密集化策略,用于重建高质量的高斯摊片,更好地符合场景的几何结构和纹理丰富性。具体来说,我们的GeoTexDensifier框架采用辅助纹理感知密集化方法,在有纹理的区域产生更密集的摊片分布,同时在低纹理区域保持稀疏性,以保持高斯点云的质量。同时,几何感知分割策略采用深度和法线先验来指导分割采样,并过滤掉初始位置远离其拟合的实际几何表面的噪声摊片,进行深度比率变化检查。借助相对的单眼深度先验,这样的几何感知验证可以有效地减少散射高斯对最终渲染质量的影响,特别是在纹理较弱或缺乏足够训练视图的区域。纹理感知密集化和几何感知分割策略充分结合,获得一组高质量的高斯摊片。我们在各种数据集上实验了GeoTexDensifier框架,并将我们的新型视图合成结果与其他最先进的3DGS方法进行比较,通过详细的定量和定性评估,证明我们的方法在生成更逼真的3DGS模型方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 8 figures, 1 table
Summary
本文介绍了3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)技术在三维导航、虚拟现实和三维仿真等领域中的广泛应用,以及其面临的高质量问题挑战。提出了一种新型的几何纹理感知密化策略GeoTexDensifier,通过辅助纹理感知密化方法和几何感知分割策略,能够在充分纹理的区域产生更密集的splat分布,同时保持低纹理区域的稀疏性,从而提高高斯点云的质量。该策略通过深度和预先的几何感知验证,减少了散射高斯对最终渲染质量的影响,尤其是在纹理较弱或缺乏足够训练视图的区域。通过实验验证,该框架能够有效生成更逼真的3DGS模型。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS技术在多个领域得到广泛应用,但高质量重建面临挑战。
- GeoTexDensifier框架采用几何纹理感知密化策略解决此问题。
- 辅助纹理感知密化方法用于产生更密集的splat分布,特别是在纹理丰富的区域。
- 几何感知分割策略利用深度和预先的几何感知验证来优化分裂采样并过滤远离实际几何表面的噪声splat。
- 该策略有效减少了散射高斯对最终渲染质量的影响,特别是在纹理较弱或无足够训练视图的区域。
- GeoTexDensifier框架在各种数据集上的实验验证了其有效性。
点此查看论文截图

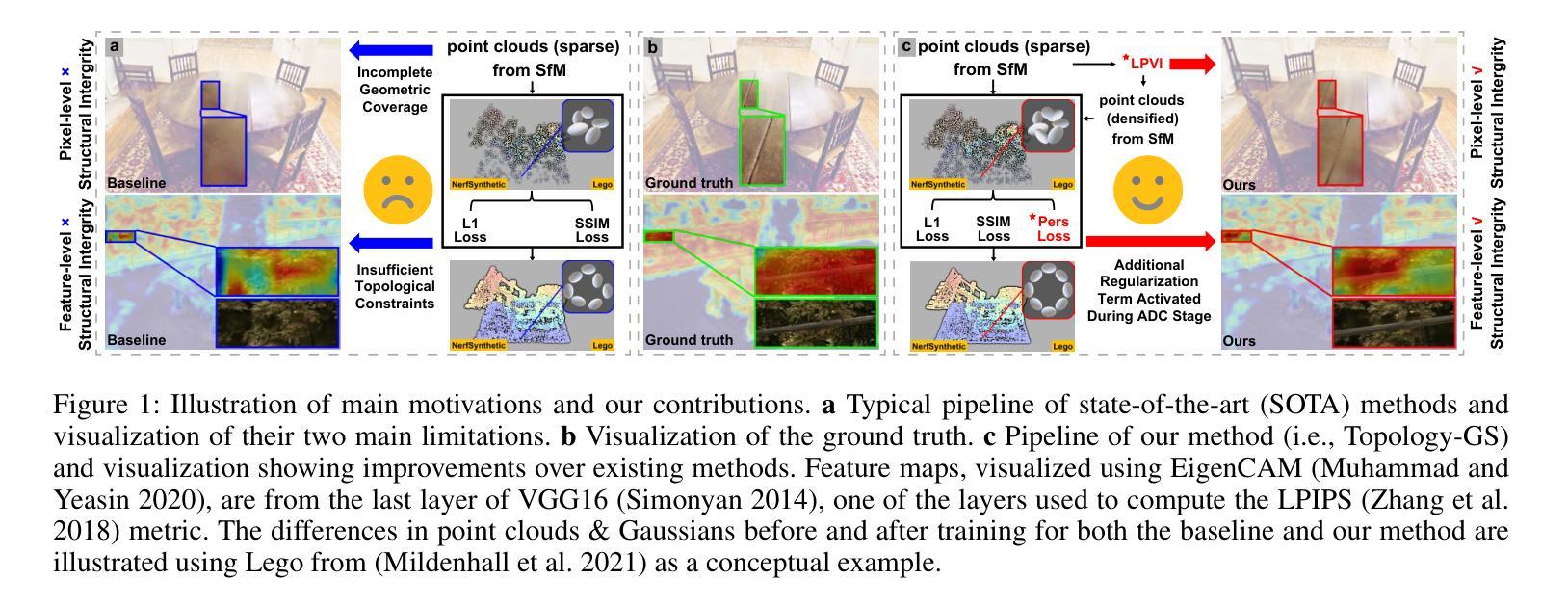
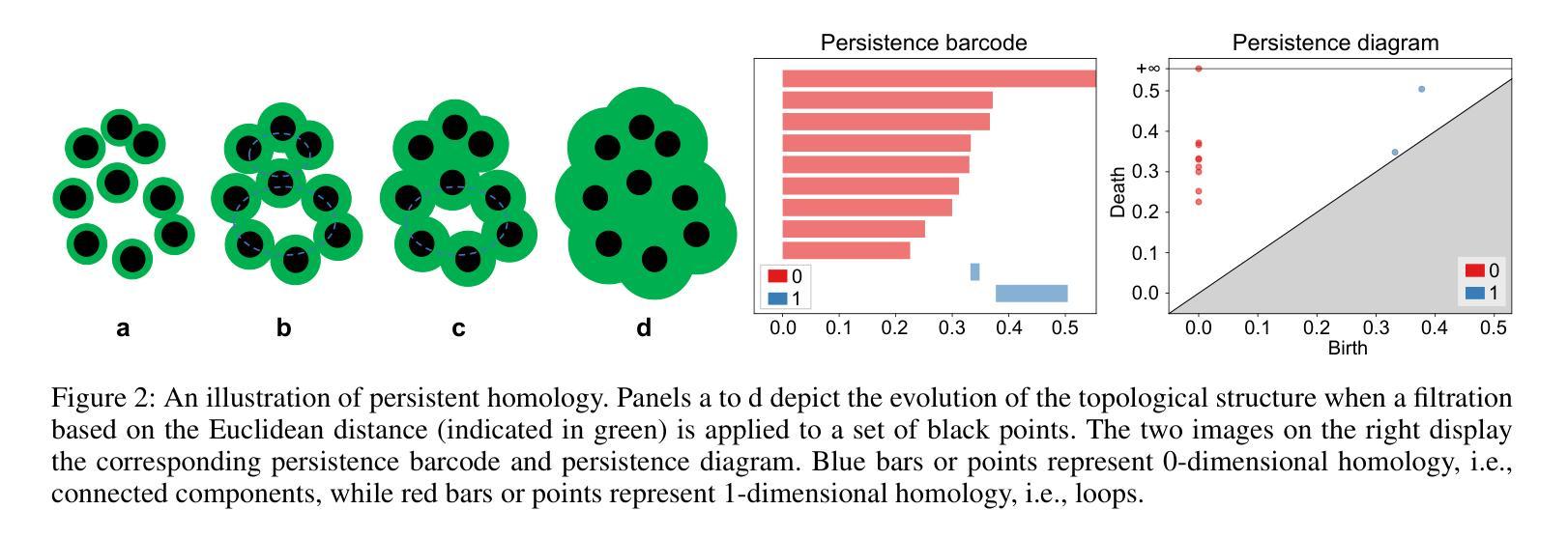
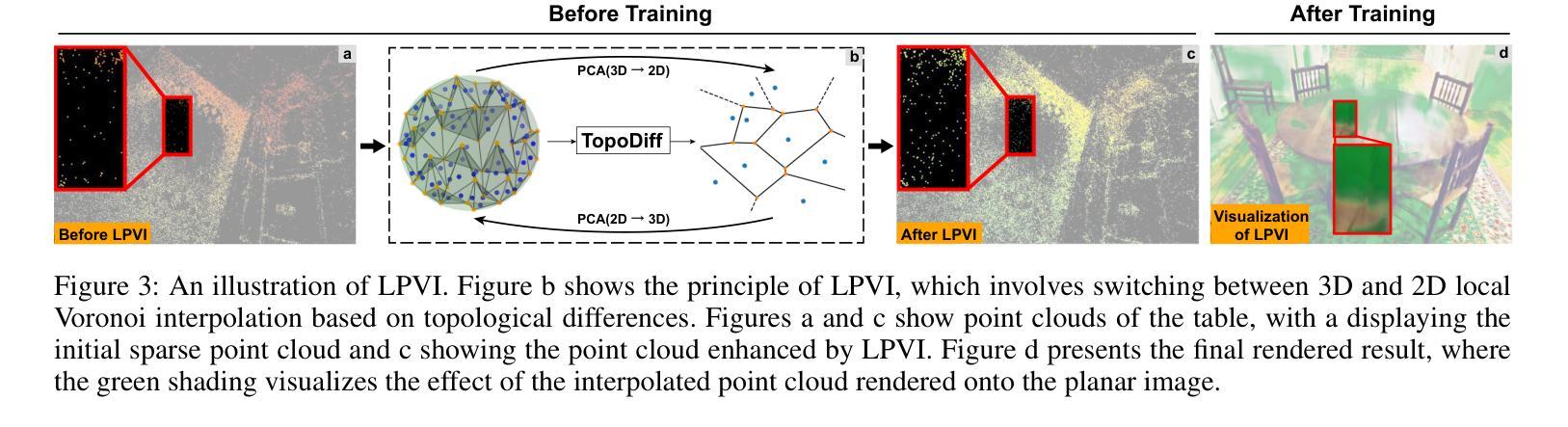
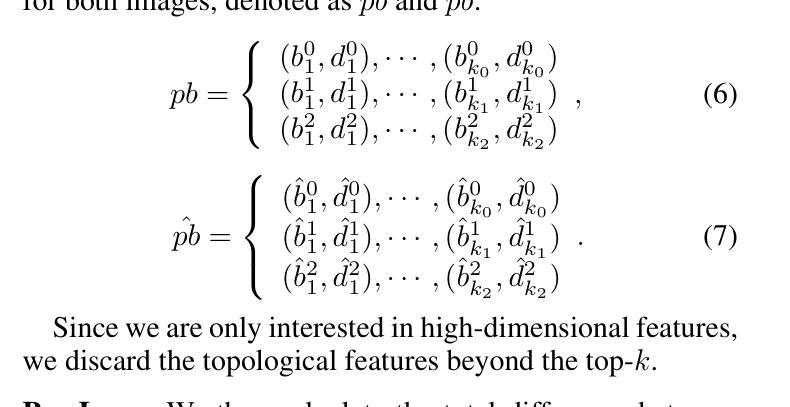
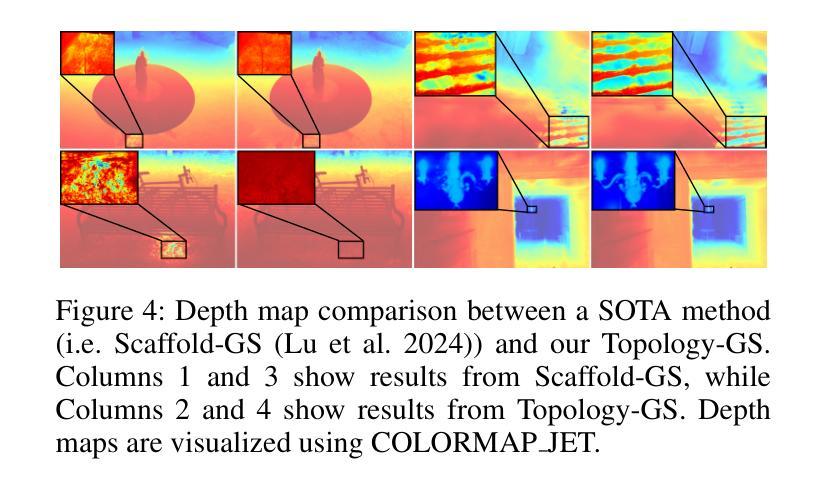
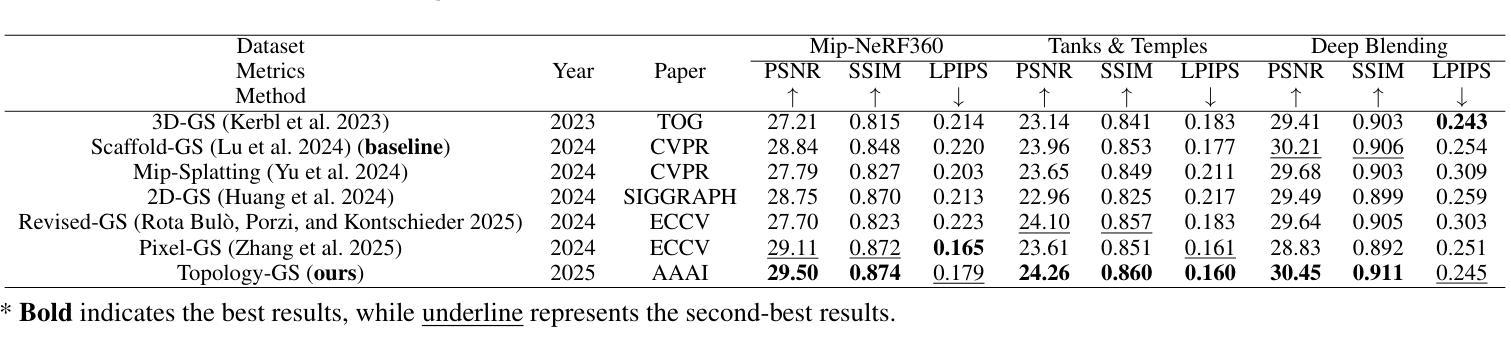
Topology-Aware 3D Gaussian Splatting: Leveraging Persistent Homology for Optimized Structural Integrity
Authors:Tianqi Shen, Shaohua Liu, Jiaqi Feng, Ziye Ma, Ning An
Gaussian Splatting (GS) has emerged as a crucial technique for representing discrete volumetric radiance fields. It leverages unique parametrization to mitigate computational demands in scene optimization. This work introduces Topology-Aware 3D Gaussian Splatting (Topology-GS), which addresses two key limitations in current approaches: compromised pixel-level structural integrity due to incomplete initial geometric coverage, and inadequate feature-level integrity from insufficient topological constraints during optimization. To overcome these limitations, Topology-GS incorporates a novel interpolation strategy, Local Persistent Voronoi Interpolation (LPVI), and a topology-focused regularization term based on persistent barcodes, named PersLoss. LPVI utilizes persistent homology to guide adaptive interpolation, enhancing point coverage in low-curvature areas while preserving topological structure. PersLoss aligns the visual perceptual similarity of rendered images with ground truth by constraining distances between their topological features. Comprehensive experiments on three novel-view synthesis benchmarks demonstrate that Topology-GS outperforms existing methods in terms of PSNR, SSIM, and LPIPS metrics, while maintaining efficient memory usage. This study pioneers the integration of topology with 3D-GS, laying the groundwork for future research in this area.
高斯采样(GS)已经成为表示离散体积辐射场的关键技术。它利用独特的参数化方法,以减轻场景优化中的计算需求。本文介绍了拓扑感知三维高斯采样(Topology-GS),解决了当前方法的两个主要局限性:由于初始几何覆盖不完整而损害像素级结构完整性,以及在优化过程中由于拓扑约束不足而导致特征级完整性不足。为了克服这些局限性,Topology-GS融入了一种新型插值策略——局部持久Voronoi插值(LPVI)和一种基于持久条形码的拓扑重点正则化术语,称为PersLoss。LPVI利用持久同源性引导自适应插值,在低曲率区域增强点覆盖的同时保持拓扑结构。PersLoss通过约束渲染图像与真实图像之间拓扑特征的距离,使渲染图像的视觉感知相似性符合真实情况。在三个全新视图合成基准测试上的综合实验表明,Topology-GS在PSNR、SSIM和LPIPS指标上优于现有方法,同时保持有效的内存使用。本研究首创了拓扑与3D-GS的集成,为未来该领域的研究奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
拓扑感知三维高斯投点法(Topology-GS)是一种针对离散体积辐射场表示的关键技术,它通过独特的参数化方法减轻了场景优化中的计算负担。该方法解决了现有方法的两个关键问题:由于初始几何覆盖不完整导致的像素级结构完整性受损,以及在优化过程中由于拓扑约束不足导致的特征级完整性不足。为此,Topology-GS引入了一种新的插值策略——局部持久冯诺伊曼插值(LPVI)和基于持久条形码的拓扑重点正则化术语PersLoss。LPVI利用持久同源性引导自适应插值,增强低曲率区域的点覆盖,同时保持拓扑结构。PersLoss通过对拓扑特征之间的距离进行约束,使渲染图像的视觉感知与地面真实情况保持一致。在三个全新视图合成基准测试上的综合实验表明,Topology-GS在PSNR、SSIM和LPIPS指标上优于现有方法,同时保持高效的内存使用。
Key Takeaways
- Topology-GS解决了当前方法中由于初始几何覆盖不足和拓扑约束不足导致的问题。
- LPVI利用持久同源性进行自适应插值,提升点覆盖并维持拓扑结构。
- PersLoss约束了渲染图像与真实图像在拓扑特征上的距离,提高了视觉感知的相似性。
- Topology-GS在新型视图合成基准测试中表现优越,优于其他方法,且内存使用效率高。
点此查看论文截图


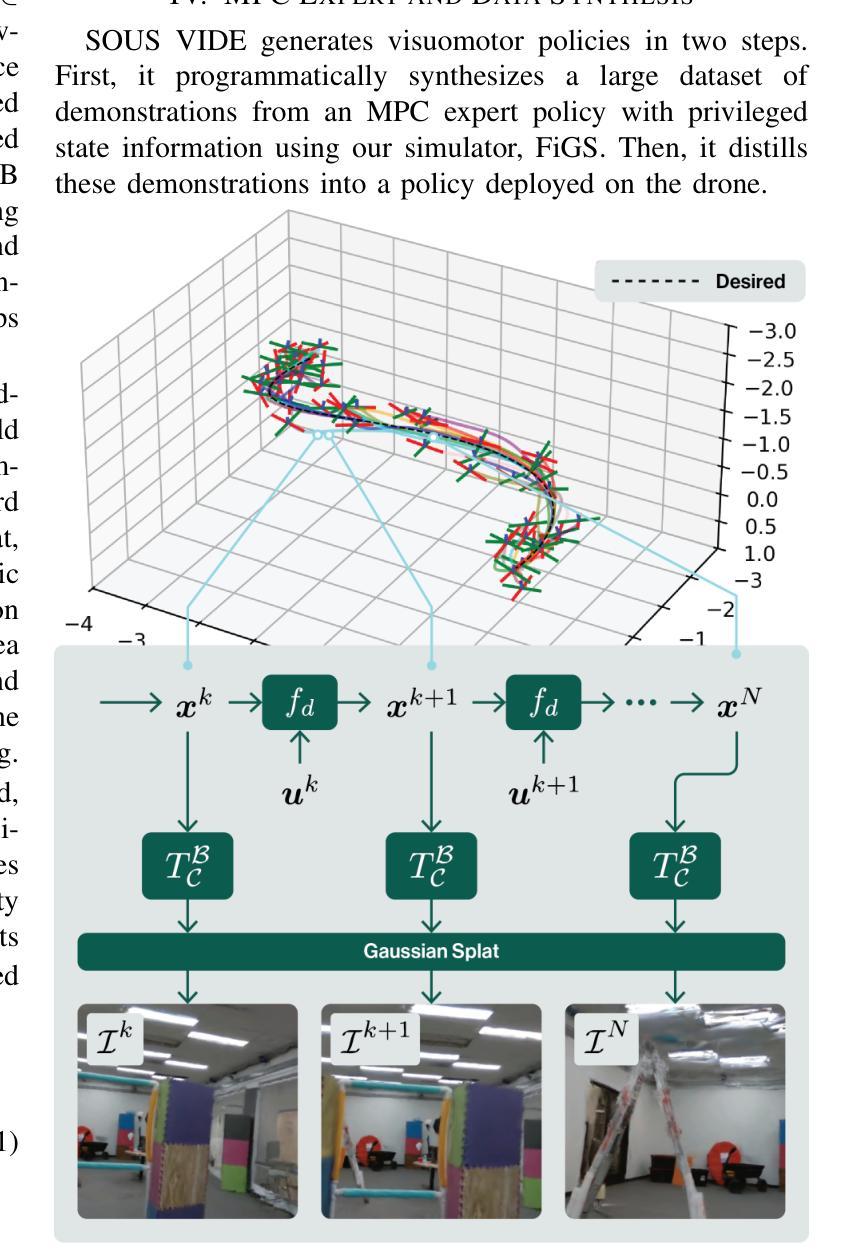
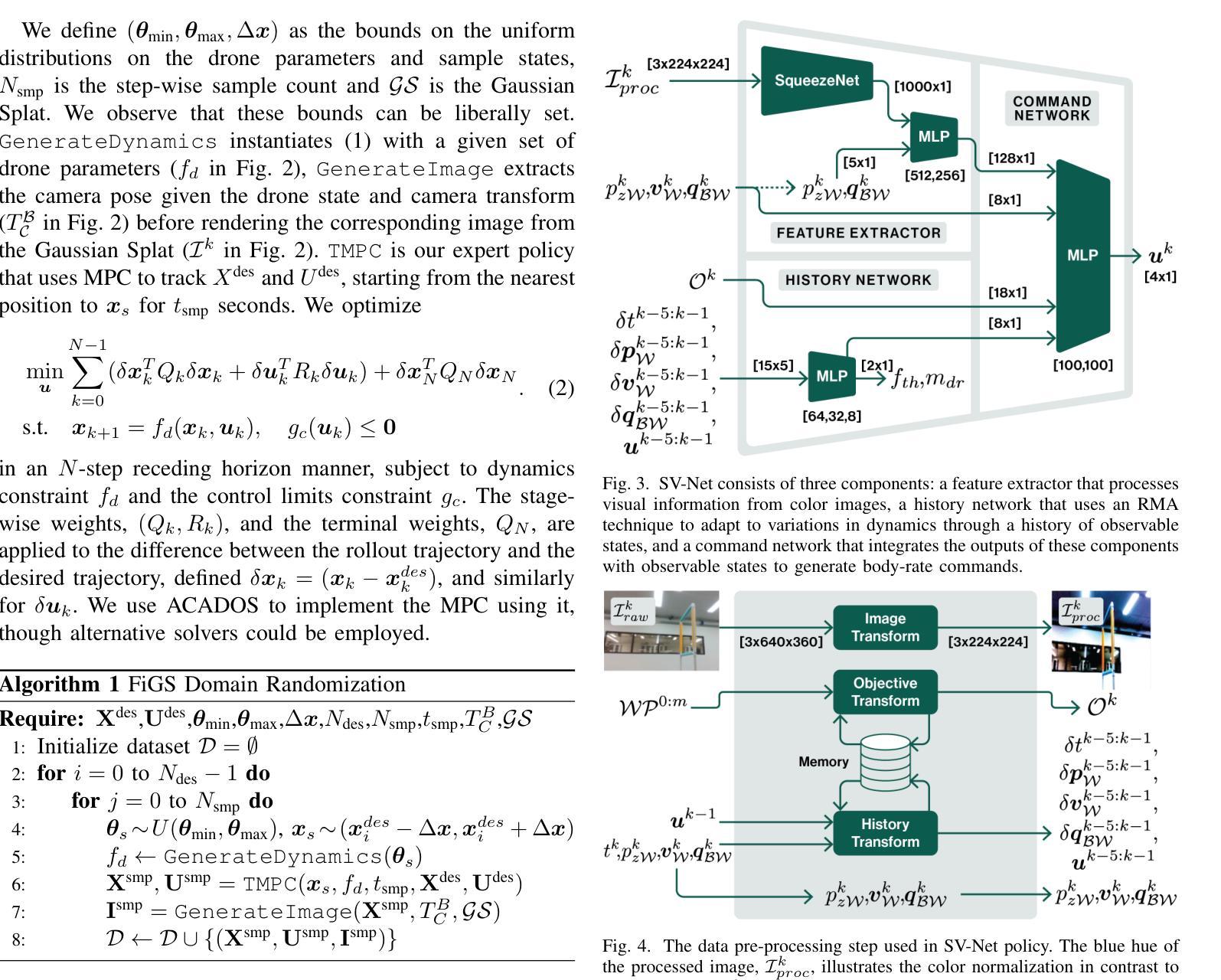
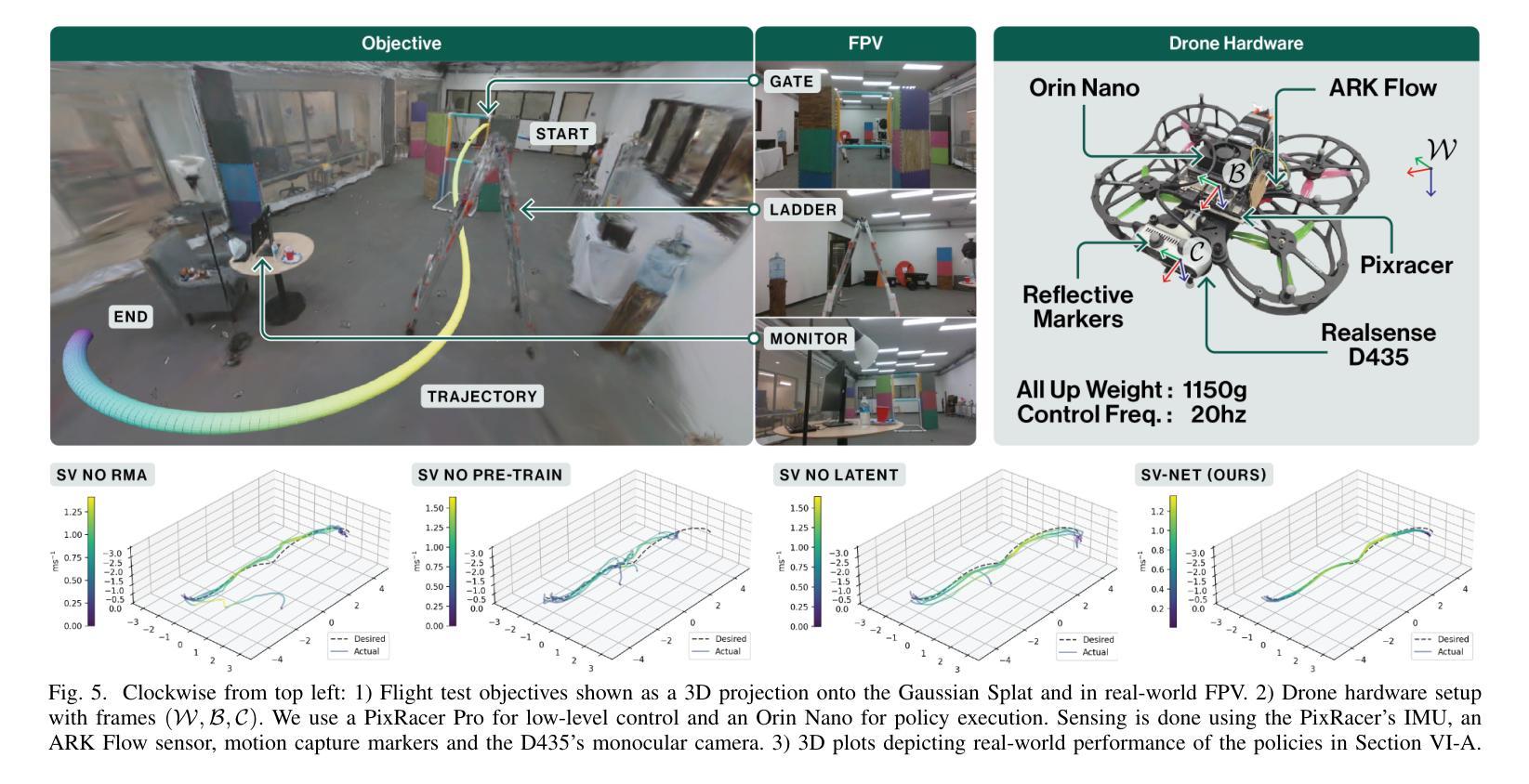
SOUS VIDE: Cooking Visual Drone Navigation Policies in a Gaussian Splatting Vacuum
Authors:JunEn Low, Maximilian Adang, Javier Yu, Keiko Nagami, Mac Schwager
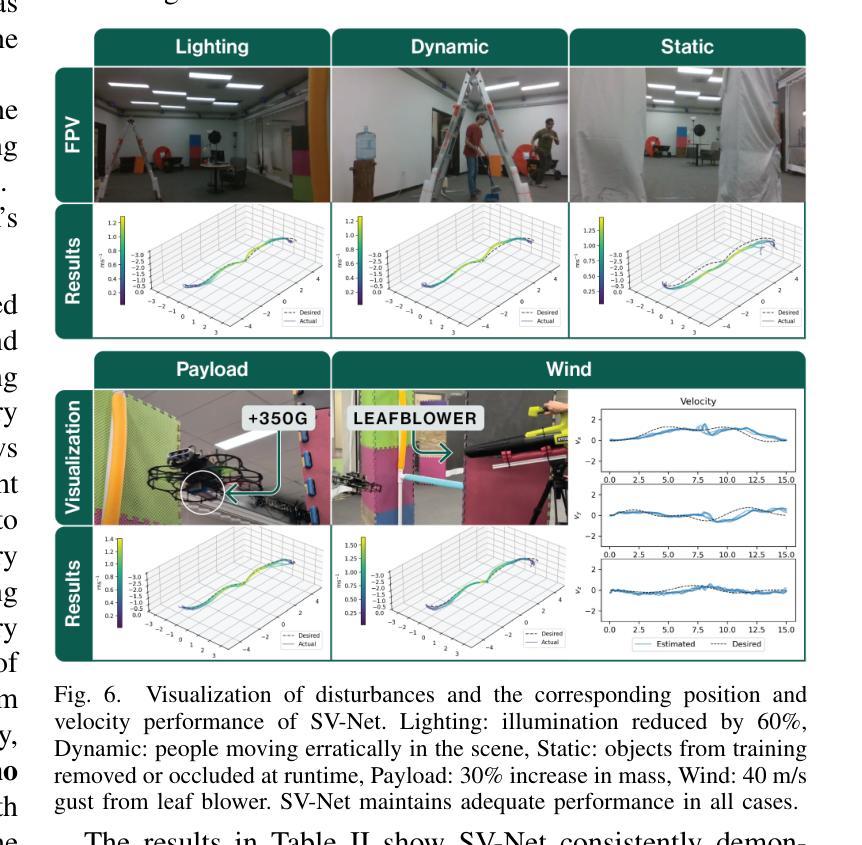
We propose a new simulator, training approach, and policy architecture, collectively called SOUS VIDE, for end-to-end visual drone navigation. Our trained policies exhibit zero-shot sim-to-real transfer with robust real-world performance using only on-board perception and computation. Our simulator, called FiGS, couples a computationally simple drone dynamics model with a high visual fidelity Gaussian Splatting scene reconstruction. FiGS can quickly simulate drone flights producing photorealistic images at up to 130 fps. We use FiGS to collect 100k-300k observation-action pairs from an expert MPC with privileged state and dynamics information, randomized over dynamics parameters and spatial disturbances. We then distill this expert MPC into an end-to-end visuomotor policy with a lightweight neural architecture, called SV-Net. SV-Net processes color image, optical flow and IMU data streams into low-level body rate and thrust commands at 20Hz onboard a drone. Crucially, SV-Net includes a Rapid Motor Adaptation (RMA) module that adapts at runtime to variations in drone dynamics. In a campaign of 105 hardware experiments, we show SOUS VIDE policies to be robust to 30% mass variations, 40 m/s wind gusts, 60% changes in ambient brightness, shifting or removing objects from the scene, and people moving aggressively through the drone’s visual field. Code, data, and experiment videos can be found on our project page: https://stanfordmsl.github.io/SousVide/.
我们提出了一种新的模拟器、训练方法和策略架构,统称为SOUS VIDE,用于端到端的视觉无人机导航。我们训练的策略表现出零样本仿真到现实的迁移能力,仅使用机载感知和计算功能就能实现稳健的现实世界性能。我们的模拟器名为FiGS,它将计算简单的无人机动力学模型与高斯拼贴场景重建的高视觉保真度相结合。FiGS能够迅速模拟无人机飞行,以高达130帧/秒的速度生成逼真的图像。我们使用FiGS收集来自拥有特权状态和动力学信息的专家MPC的10万至30万观察行动对,在动力学参数和空间干扰上进行随机化。然后我们将这个专家MPC蒸馏成一个具有轻量级神经网络架构的端到端视觉运动策略,称为SV-Net。SV-Net处理彩色图像、光流和IMU数据流,生成低级别的机体速率和推力指令,在无人机上达到20Hz。关键的是,SV-Net包含一个快速电机适应(RMA)模块,该模块在运行时能够适应无人机动力学的变化。在105次硬件实验活动中,我们展示了SOUS VIDE策略对于30%的质量变化、40米/秒的风暴、环境亮度变化60%、场景中物体移动或移除以及人们在无人机视野中激烈移动等情况具有稳健性。代码、数据和实验视频可以在我们的项目页面找到:https://stanfordmsl.github.io/SousVide/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了名为SOUS VIDE的端到端视觉无人机导航模拟器、训练方法和政策架构。该模拟器使用FiGS,结合简单的无人机动力学模型和高视觉保真度的Gaussian Splatting场景重建,能快速模拟无人机飞行并生成高达130帧/秒的照片级图像。通过收集专家MPC的观察行动对并随机化其动力学参数和空间干扰,研究者蒸馏出端到端的视觉运动政策SV-Net。SV-Net能处理彩色图像、光流和IMU数据流,生成低级别的机体速率和推力指令,并在无人机上实现20Hz的运行频率。关键的是,SV-Net包含运行时适应无人机动力学变化的快速电机适应模块。通过一系列硬件实验验证,SOUS VIDE政策在多种场景下表现出稳健性,包括质量变化、风速干扰、亮度变化、场景物体移动以及视觉场内人员动态移动等。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了名为SOUS VIDE的端到端视觉无人机导航系统,包括新模拟器FiGS、训练方法和政策架构。
- FiGS模拟器结合了简单无人机动力学模型和高视觉保真度的场景重建。
- FiGS能高效模拟无人机飞行,生成高质量图像,最高达130帧/秒。
- 通过专家MPC数据,研究者训练出名为SV-Net的视听觉运动政策网络。
- SV-Net能处理多种数据输入并输出低级别指令,具备20Hz的运行频率。
- SV-Net包含快速电机适应模块,能适应无人机动力学变化。
点此查看论文截图

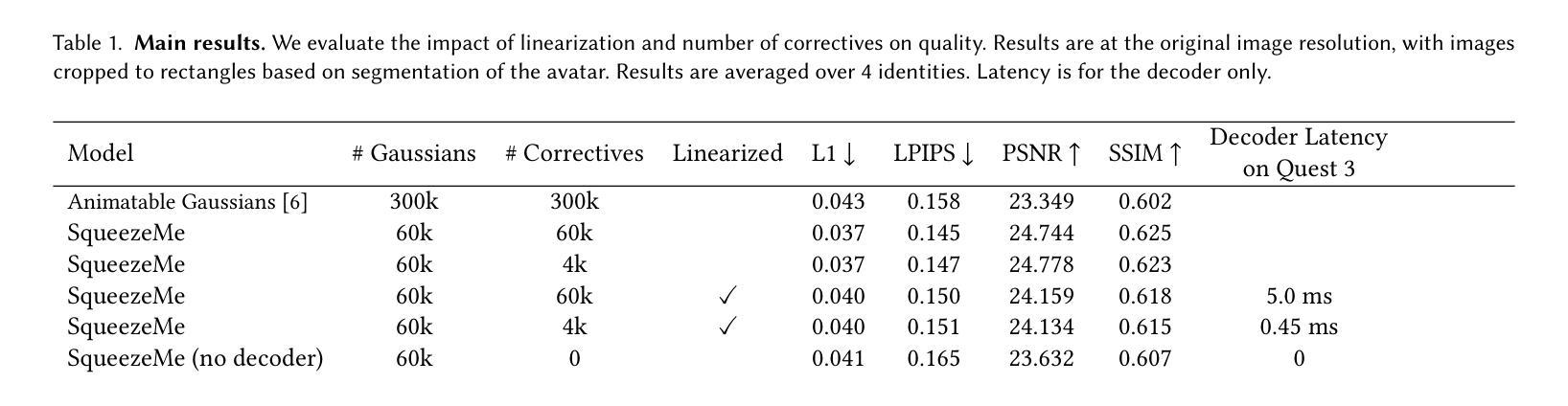
SqueezeMe: Efficient Gaussian Avatars for VR
Authors:Shunsuke Saito, Stanislav Pidhorskyi, Igor Santesteban, Forrest Iandola, Divam Gupta, Anuj Pahuja, Nemanja Bartolovic, Frank Yu, Emanuel Garbin, Tomas Simon
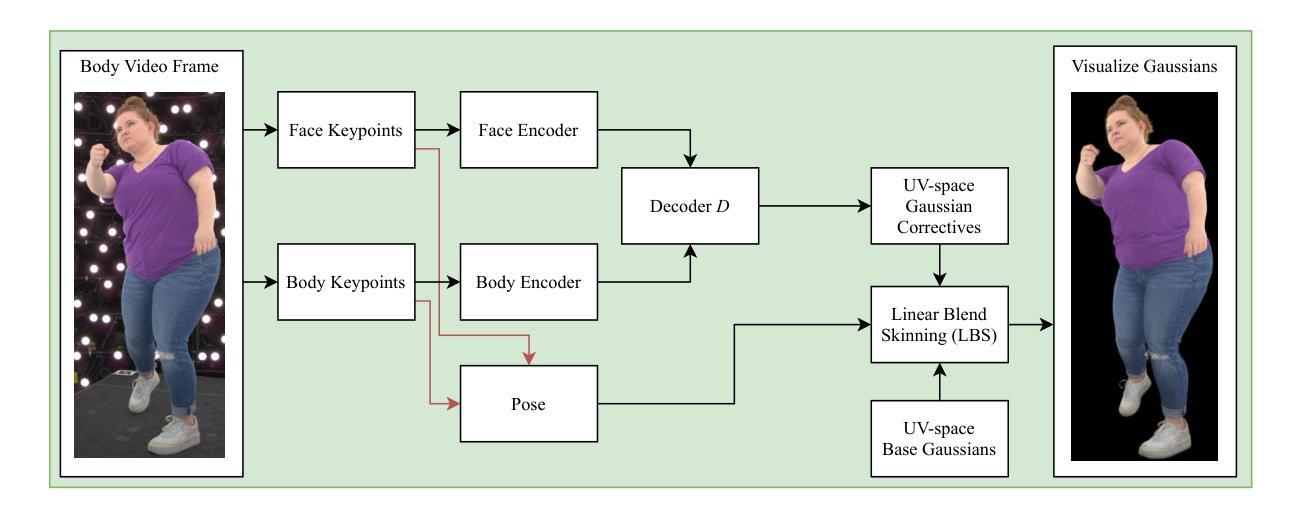
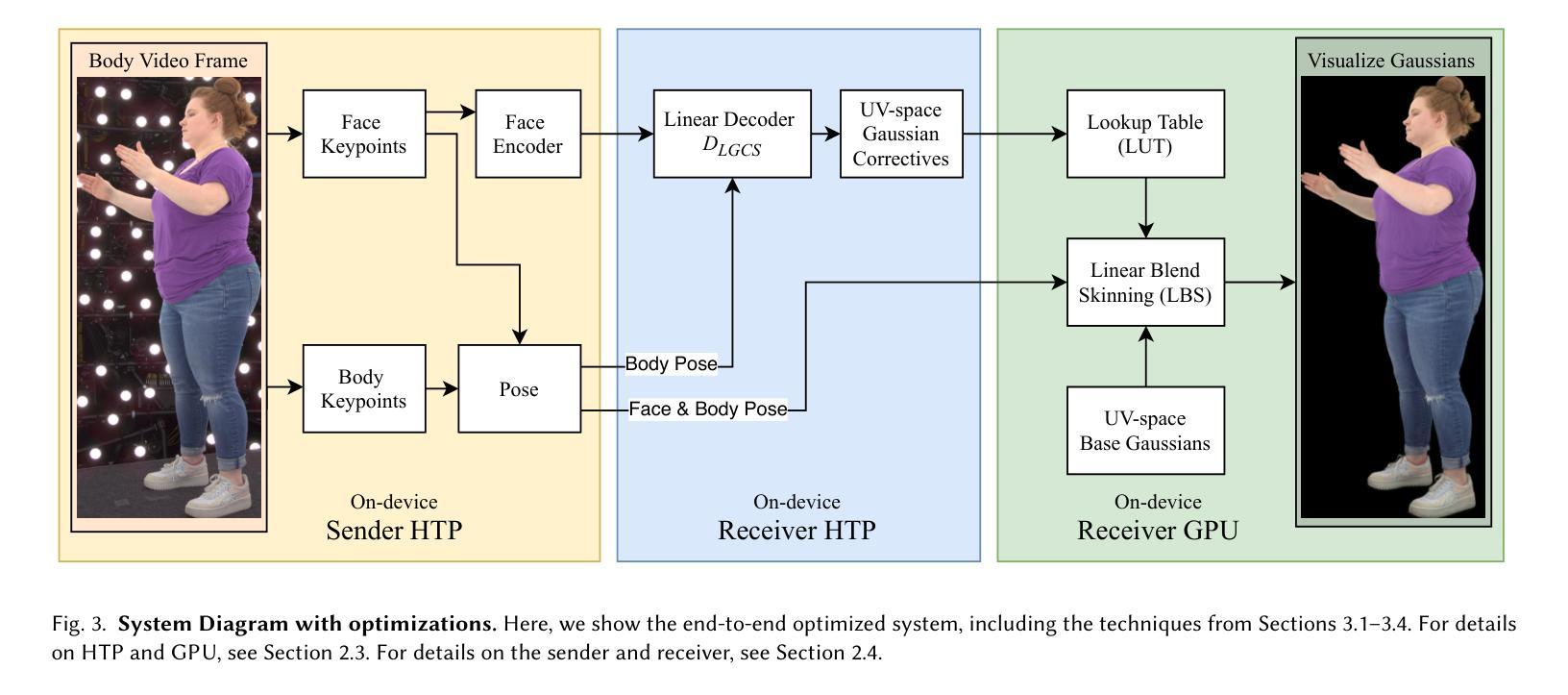
Gaussian Splatting has enabled real-time 3D human avatars with unprecedented levels of visual quality. While previous methods require a desktop GPU for real-time inference of a single avatar, we aim to squeeze multiple Gaussian avatars onto a portable virtual reality headset with real-time drivable inference. We begin by training a previous work, Animatable Gaussians, on a high quality dataset captured with 512 cameras. The Gaussians are animated by controlling base set of Gaussians with linear blend skinning (LBS) motion and then further adjusting the Gaussians with a neural network decoder to correct their appearance. When deploying the model on a Meta Quest 3 VR headset, we find two major computational bottlenecks: the decoder and the rendering. To accelerate the decoder, we train the Gaussians in UV-space instead of pixel-space, and we distill the decoder to a single neural network layer. Further, we discover that neighborhoods of Gaussians can share a single corrective from the decoder, which provides an additional speedup. To accelerate the rendering, we develop a custom pipeline in Vulkan that runs on the mobile GPU. Putting it all together, we run 3 Gaussian avatars concurrently at 72 FPS on a VR headset. Demo videos are at https://forresti.github.io/squeezeme.
高斯拼贴技术为实时3D人类化身带来了前所未有的视觉品质。虽然之前的方法需要桌面GPU来进行单个化身实时推理,我们的目标是将多个高斯化身挤压到便携式虚拟现实头盔上,实现实时驱动推理。我们首先训练一个以前的工作“可动画高斯”,使用由512台相机捕获的高质量数据集。高斯通过控制基础高斯集进行动画渲染,使用线性混合蒙皮(LBS)运动对高斯进行动画处理,然后通过神经网络解码器进一步调整高斯以校正其外观。在Meta Quest 3 VR头盔上部署模型时,我们发现两个主要的计算瓶颈:解码器和渲染器。为了加速解码器,我们在UV空间而不是像素空间训练高斯,并将解码器蒸馏到单个神经网络层。此外,我们发现邻近的高斯可以从解码器共享单个校正,这提供了额外的加速。为了加速渲染器,我们在Vulkan中开发了一个自定义管道,该管道在移动GPU上运行。综上所述,我们在VR头盔上同时运行三个高斯化身,帧速率为每秒72帧。演示视频请访问:[https://forresti.github.io/squeezeme/] 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF v2
Summary
基于高斯技术的新进展,研究团队实现了可以在VR头显中以实时驱动渲染的高逼真度实时动态3D人类角色。其通过对以往工作进行了改进和创新训练过程,在VR头显上实现了多角色同时渲染,解决了渲染和模型解码两大瓶颈问题。此技术不仅提升了视觉效果,还实现了便携性。相关演示视频可在相关网站找到。
Key Takeaways
- 高斯技术用于创建高逼真度的实时动态3D人类角色。
- 研究人员成功将多个高斯角色挤压到便携式VR头显上,实现实时驱动渲染。
- 研究团队对旧有技术进行改进和创新训练过程,利用线性混合蒙皮动画技术对高斯角色进行动画设计,并利用神经网络解码器校正其外观。
- 模型解码和渲染是该技术的两大瓶颈问题,研究团队针对这两个问题提出了解决方案。
- 研究人员通过在UV空间而非像素空间训练高斯角色,并简化了神经网络解码器以加速解码过程。邻近的高斯角色可以共享解码器的校正结果,进一步提高了效率。
- 研究团队开发了一个自定义的Vulkan渲染管线,能在移动GPU上运行,解决了VR头显上的渲染瓶颈问题。
点此查看论文截图


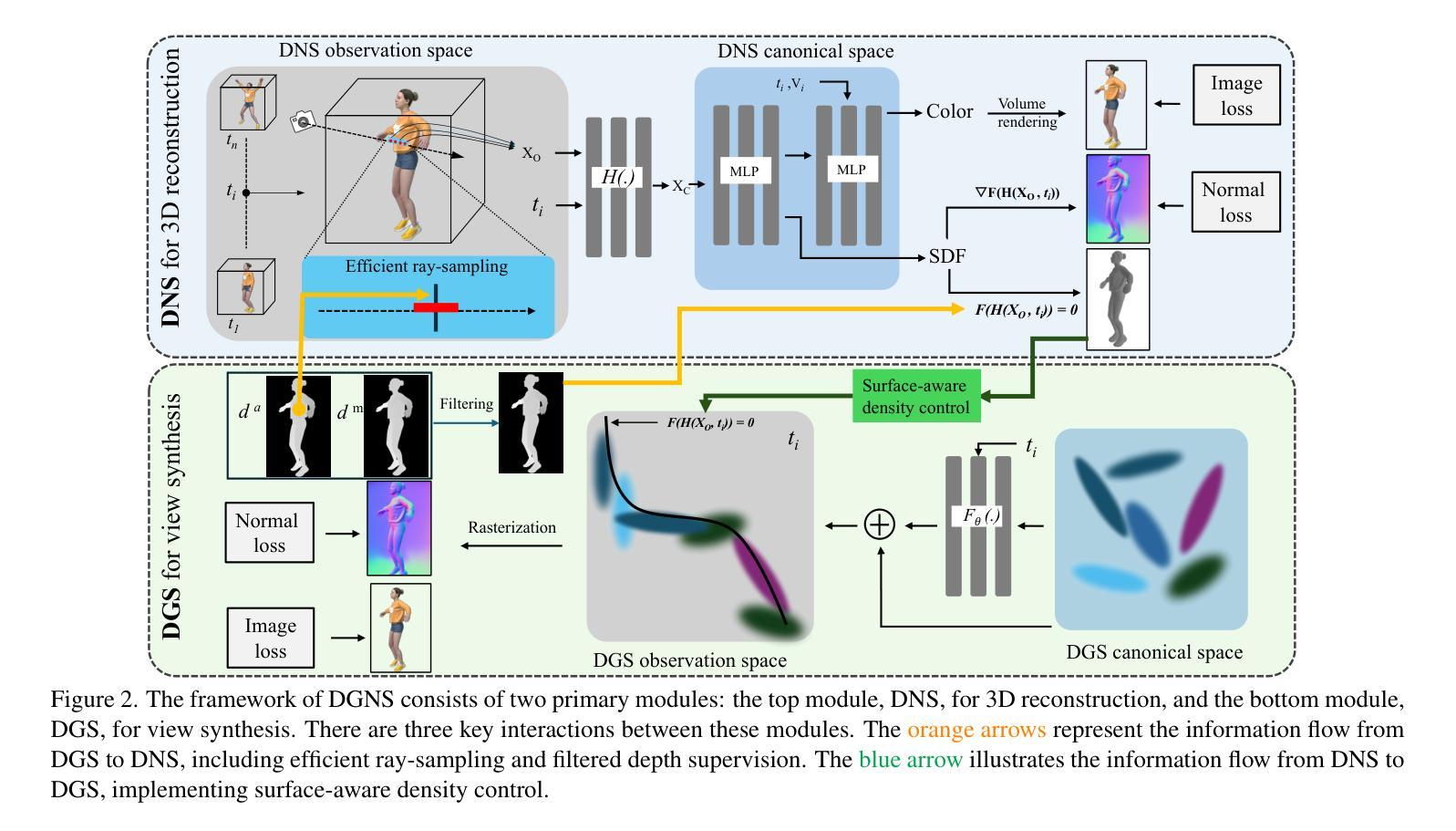
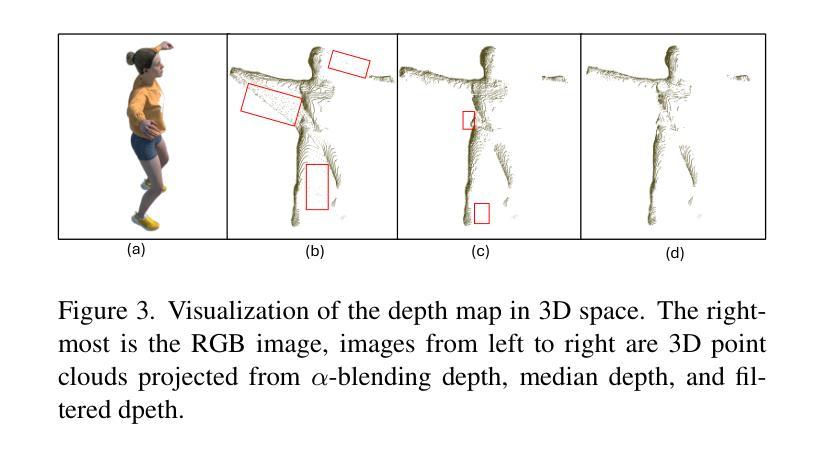
DGNS: Deformable Gaussian Splatting and Dynamic Neural Surface for Monocular Dynamic 3D Reconstruction
Authors:Xuesong Li, Jinguang Tong, Jie Hong, Vivien Rolland, Lars Petersson
Dynamic scene reconstruction from monocular video is critical for real-world applications. This paper tackles the dual challenges of dynamic novel-view synthesis and 3D geometry reconstruction by introducing a hybrid framework: Deformable Gaussian Splatting and Dynamic Neural Surfaces (DGNS), in which both modules can leverage each other for both tasks. During training, depth maps generated by the deformable Gaussian splatting module guide the ray sampling for faster processing and provide depth supervision within the dynamic neural surface module to improve geometry reconstruction. Simultaneously, the dynamic neural surface directs the distribution of Gaussian primitives around the surface, enhancing rendering quality. To further refine depth supervision, we introduce a depth-filtering process on depth maps derived from Gaussian rasterization. Extensive experiments on public datasets demonstrate that DGNS achieves state-of-the-art performance in both novel-view synthesis and 3D reconstruction.
从单目视频中重建动态场景对实际应用至关重要。本文通过引入混合框架——可变形高斯喷涂和动态神经网络表面(DGNS),解决了动态新视角合成和3D几何重建的双重挑战。在该框架中,两个模块可以相互利用,共同完成这两个任务。在训练过程中,可变形高斯喷涂模块生成的深度图引导光线采样,加快处理速度,并在动态神经网络模块内提供深度监督,以改进几何重建。同时,动态神经网络引导高斯原始元素在表面周围的分布,提高渲染质量。为了进一步优化深度监督,我们在从高斯栅格化派生的深度图上实施了深度过滤过程。在公共数据集上的大量实验表明,DGNS在新视角合成和3D重建方面都达到了最新技术水平。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
DGNS混合框架通过利用可变形的高斯喷涂模块和动态神经网络模块,解决了动态场景重建中的新视角合成和三维几何重建双重挑战。训练过程中,深度图指导光线采样以提高处理速度,同时为动态神经网络模块提供深度监督以改善几何重建。此外,动态神经网络引导高斯原始数据在表面周围的分布,提高渲染质量。对公共数据集的大量实验表明,DGNS在新型视角合成和三维重建方面均达到最佳性能。
关键见解
- DGNS混合框架解决了动态场景重建中的新视角合成和三维几何重建双重挑战。
- DGNS利用可变形的高斯喷涂模块生成深度图,指导光线采样并改善几何重建。
- 动态神经网络模块通过利用深度图提供的深度监督,提高了渲染质量。
- DGNS引入了深度过滤过程,对由高斯光栅化生成的深度图进行进一步优化。
- DGNS在训练过程中两个模块可以相互促进,共同提高性能。
- 大量在公共数据集上的实验验证了DGNS框架的有效性和优越性。
点此查看论文截图

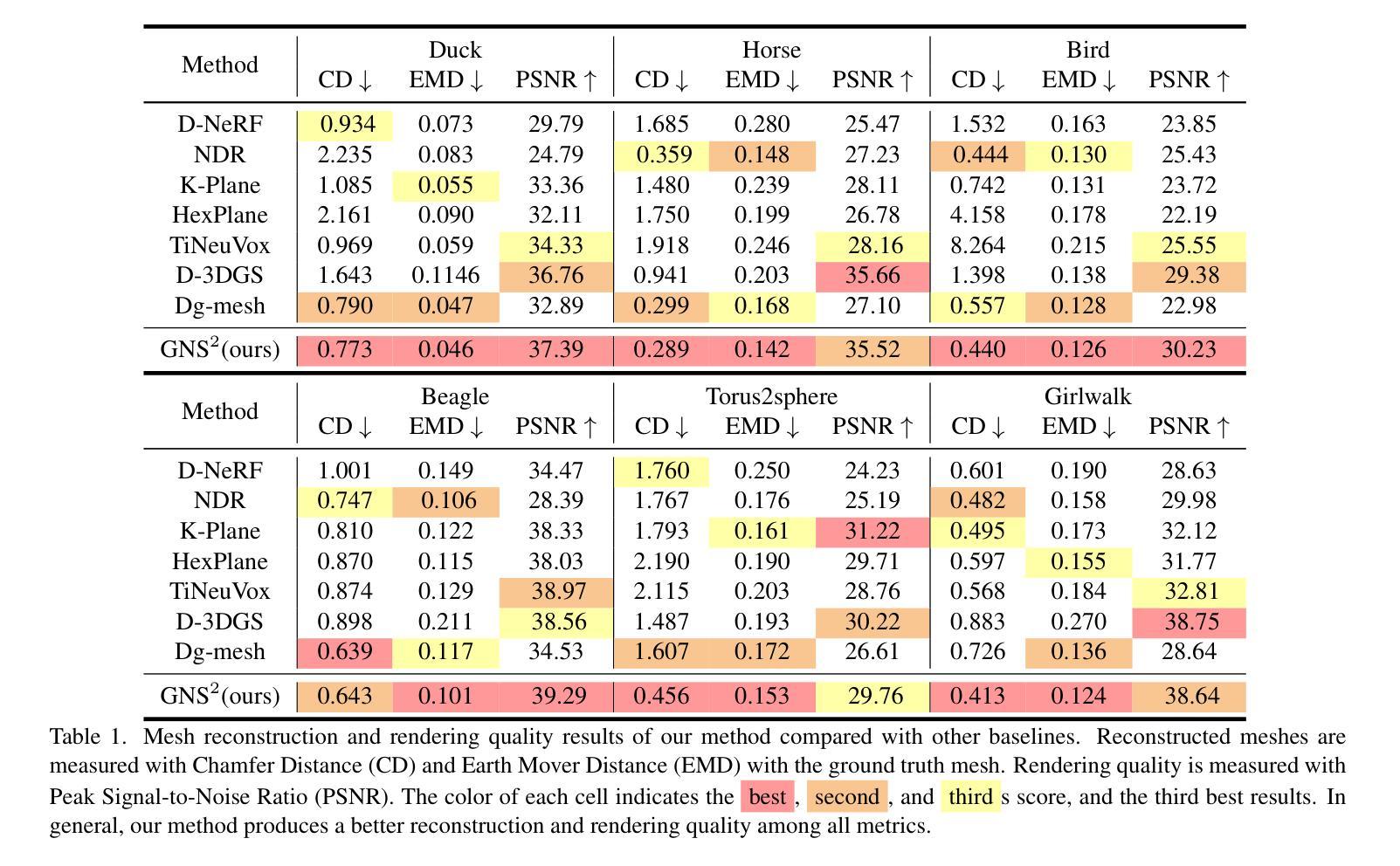
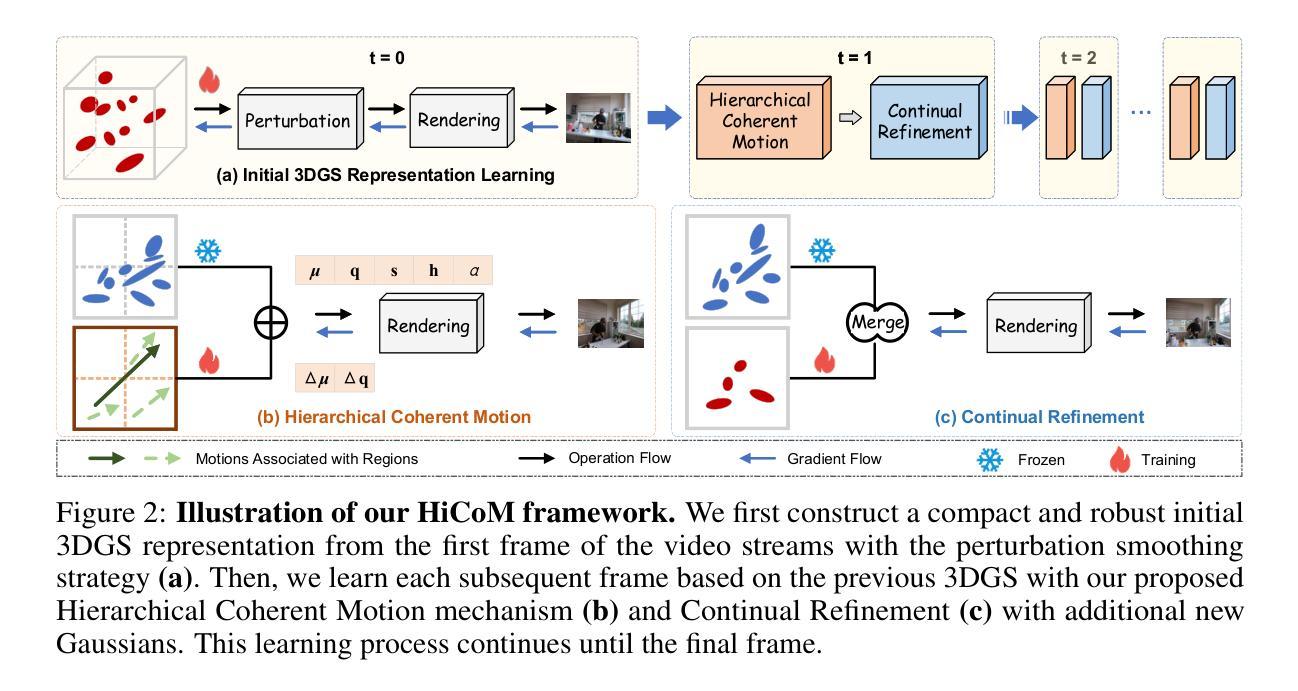
HiCoM: Hierarchical Coherent Motion for Streamable Dynamic Scene with 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Qiankun Gao, Jiarui Meng, Chengxiang Wen, Jie Chen, Jian Zhang
The online reconstruction of dynamic scenes from multi-view streaming videos faces significant challenges in training, rendering and storage efficiency. Harnessing superior learning speed and real-time rendering capabilities, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has recently demonstrated considerable potential in this field. However, 3DGS can be inefficient in terms of storage and prone to overfitting by excessively growing Gaussians, particularly with limited views. This paper proposes an efficient framework, dubbed HiCoM, with three key components. First, we construct a compact and robust initial 3DGS representation using a perturbation smoothing strategy. Next, we introduce a Hierarchical Coherent Motion mechanism that leverages the inherent non-uniform distribution and local consistency of 3D Gaussians to swiftly and accurately learn motions across frames. Finally, we continually refine the 3DGS with additional Gaussians, which are later merged into the initial 3DGS to maintain consistency with the evolving scene. To preserve a compact representation, an equivalent number of low-opacity Gaussians that minimally impact the representation are removed before processing subsequent frames. Extensive experiments conducted on two widely used datasets show that our framework improves learning efficiency of the state-of-the-art methods by about $20%$ and reduces the data storage by $85%$, achieving competitive free-viewpoint video synthesis quality but with higher robustness and stability. Moreover, by parallel learning multiple frames simultaneously, our HiCoM decreases the average training wall time to $<2$ seconds per frame with negligible performance degradation, substantially boosting real-world applicability and responsiveness.
从多视角流视频中在线重建动态场景面临着训练、渲染和存储效率方面的重大挑战。凭借卓越的学习速度和实时渲染能力,3D高斯喷绘(3DGS)在该领域展示了巨大的潜力。然而,3DGS在存储方面可能效率低下,并且由于高斯过度增长而容易过度拟合,特别是在视角有限的情况下。本文提出了一个高效的框架,称为HiCoM,包含三个关键组件。首先,我们使用扰动平滑策略构建紧凑且稳健的初始3DGS表示。其次,我们引入了一种分层一致运动机制,该机制利用3D高斯本身的非均匀分布和局部一致性,快速准确地学习帧之间的运动。最后,我们继续使用额外的高斯对3DGS进行持续优化,然后将这些高斯合并到初始的3DGS中,以保持与不断变化的场景的一致性。为了保持紧凑的表示形式,在处理后续帧之前,会移除对表示影响最小的等效数量的低透明度高斯。在广泛使用的两个数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,我们的框架提高了现有方法的学习效率约20%,并减少了数据存储量高达85%,达到了具有竞争力的自由视点视频合成质量,但具有更高的稳健性和稳定性。此外,通过并行学习多个帧,我们的HiCoM将平均训练时间减少到每帧小于2秒,且性能几乎没有下降,大大提高了实际应用的适用性和响应速度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to NeurIPS 2024; Code is avaliable at https://github.com/gqk/HiCoM
摘要
针对在线动态场景重建面临的挑战,利用强大的学习速度和实时渲染能力,论文提出了一种高效的框架HiCoM,利用三维高斯喷绘技术实现多视角流媒体视频的在线重建。该框架具有紧凑且稳健的初始三维高斯喷绘表示,引入层次化协同运动机制,并利用高斯分布的非均匀分布和局部一致性,实现快速准确的学习运动过程。此外,通过不断精炼三维高斯喷绘技术,利用融合策略优化模型,最终提升了模型的性能和适应性。实验证明,HiCoM框架可提高学习效率约20%,减少数据存储空间高达85%,实现了竞争性的自由视角视频合成质量。同时,HiCoM支持并行学习多个帧,平均训练时间缩短至每帧小于2秒,提高了实际应用中的响应速度和可用性。
关键见解
- 多视角流媒体视频的在线重建面临多方面的挑战。采用先进的训练、渲染和存储效率策略。
- 三维高斯喷绘技术在处理此类任务时具有显著潜力。然而,它也存在存储效率低和过度拟合的问题。
- HiCoM框架通过构建紧凑且稳健的三维高斯喷绘初始表示来解决上述问题。采用扰动平滑策略实现初始表示。
- 引入层次化协同运动机制,利用高斯分布的非均匀性和局部一致性,提高学习运动的准确性和速度。
- 通过不断精炼和优化三维高斯喷绘技术来提高模型的性能和适应性。采用合并策略来处理新增的高斯数据以保持模型一致性。
- 实验证明HiCoM框架在提升学习效率和减少数据存储方面表现出显著优势。相较于现有技术,学习效率提高约20%,存储空间减少高达85%。同时实现了高质量的视频合成效果。
点此查看论文截图

UW-GS: Distractor-Aware 3D Gaussian Splatting for Enhanced Underwater Scene Reconstruction
Authors:Haoran Wang, Nantheera Anantrasirichai, Fan Zhang, David Bull
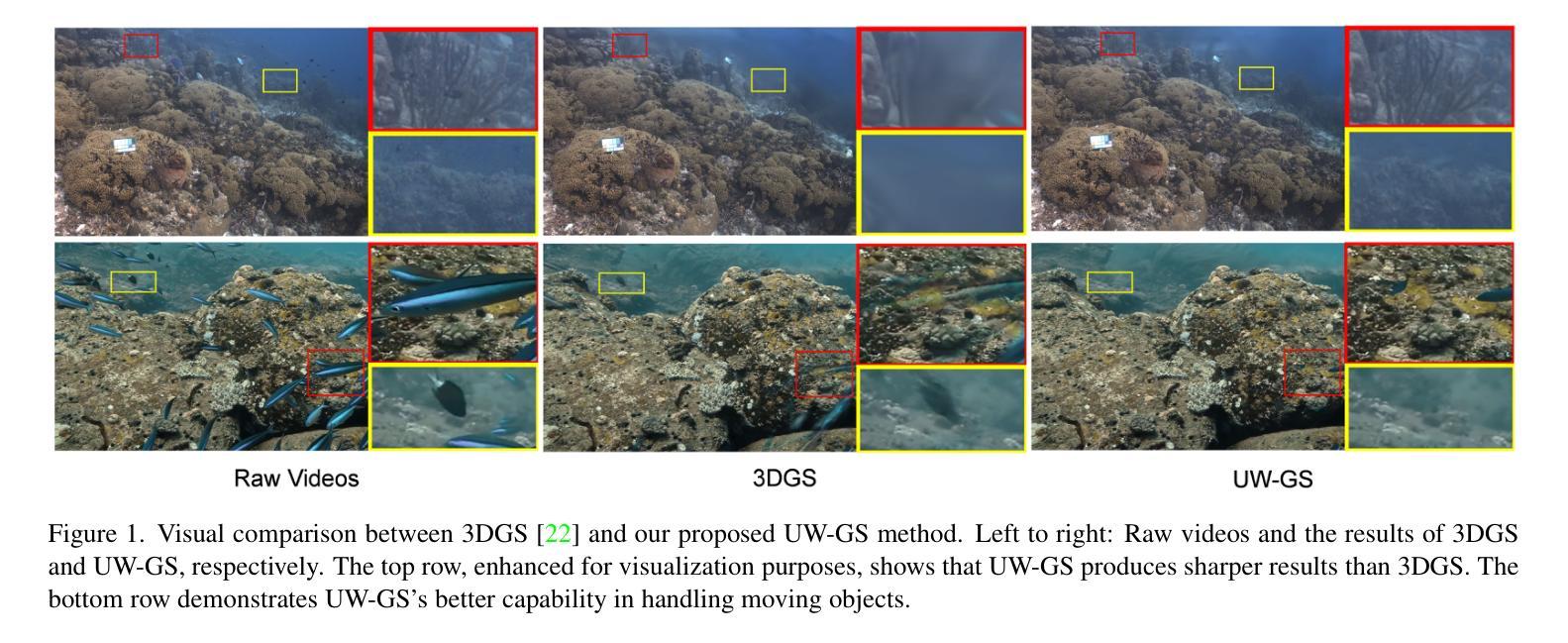
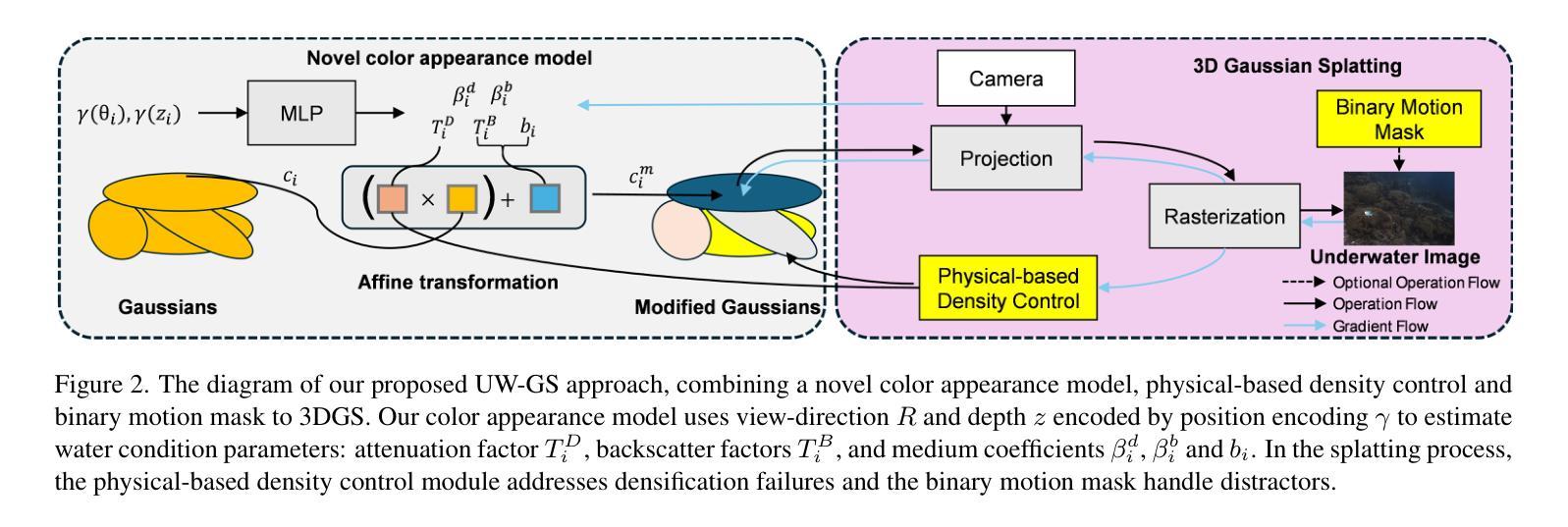
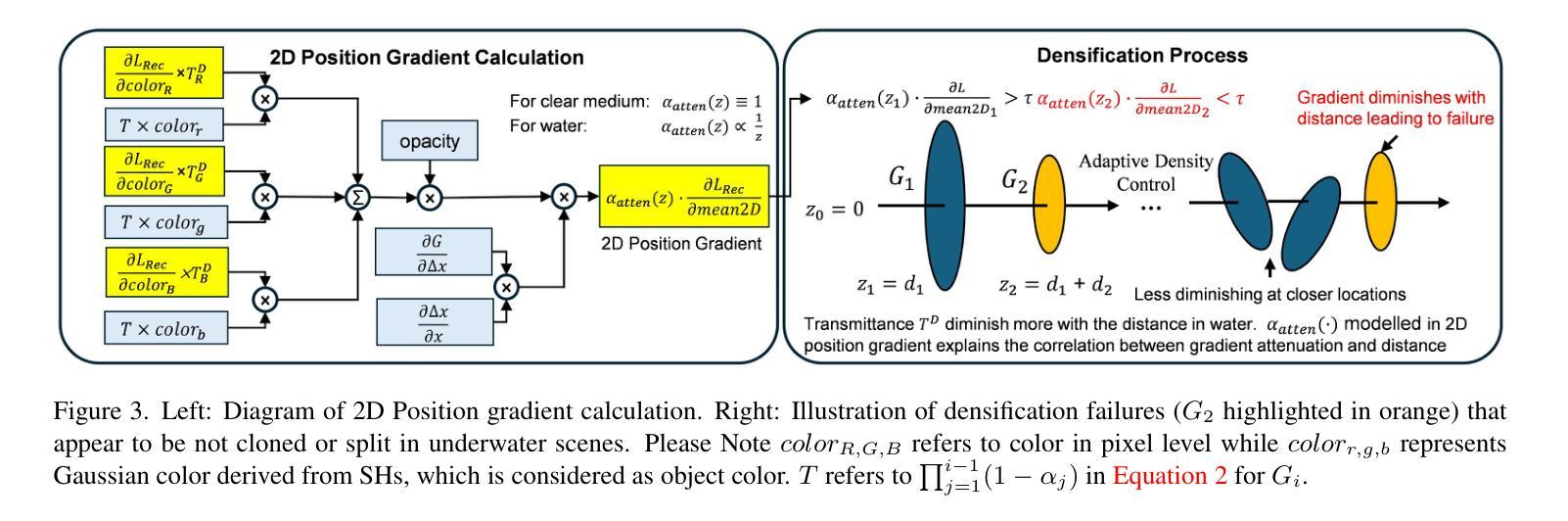
3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS) offers the capability to achieve real-time high quality 3D scene rendering. However, 3DGS assumes that the scene is in a clear medium environment and struggles to generate satisfactory representations in underwater scenes, where light absorption and scattering are prevalent and moving objects are involved. To overcome these, we introduce a novel Gaussian Splatting-based method, UW-GS, designed specifically for underwater applications. It introduces a color appearance that models distance-dependent color variation, employs a new physics-based density control strategy to enhance clarity for distant objects, and uses a binary motion mask to handle dynamic content. Optimized with a well-designed loss function supporting for scattering media and strengthened by pseudo-depth maps, UW-GS outperforms existing methods with PSNR gains up to 1.26dB. To fully verify the effectiveness of the model, we also developed a new underwater dataset, S-UW, with dynamic object masks.
3D高斯喷涂技术(3DGS)可以实现实时高质量3D场景渲染。然而,3DGS假设场景处于清晰的介质环境中,对于水下场景,由于光线吸收和散射普遍存在以及涉及移动物体,它难以产生令人满意的表示。为了克服这一问题,我们引入了一种基于高斯喷涂的新方法UW-GS,专门用于水下应用。它引入了一种颜色外观,该颜色外观模拟与距离相关的颜色变化,采用了一种基于物理的新型密度控制策略来提高远距离物体的清晰度,并使用二进制运动蒙版来处理动态内容。通过精心设计的损失函数支持散射介质,并通过伪深度图增强,UW-GS的性能优于现有方法,峰值信噪比提高高达1.26dB。为了充分验证模型的有效性,我们还开发了一个新的水下数据集S-UW,其中包含动态对象蒙版。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IEEE/CVF WACV 2025
摘要
本文探讨了使用改进后的水下场景的高斯立体溅散(UW-GS)方法进行实时高质量三维场景渲染。针对水下场景中的光线吸收和散射问题以及动态物体的问题,UW-GS引入了基于高斯溅散的方法,考虑了距离依赖的颜色变化模型,采用了新的基于物理的密度控制策略,提高了远距离物体的清晰度,并使用二进制运动掩膜处理动态内容。通过设计支持散射介质的损失函数和增强伪深度图,UW-GS在性能上优于现有方法,峰值信噪比增益高达1.26dB。同时为了验证模型的有效性,我们还开发了新的水下数据集S-UW,包含动态物体掩膜。
要点摘要
- 3DGS在清晰介质环境下可实现高质量的三维场景渲染。
- 水下场景中的光线吸收和散射使得3DGS难以生成满意的效果。
- 提出了一种基于高斯溅散的新方法UW-GS,专门用于水下应用。
- 考虑距离依赖的颜色变化模型,增强远距离物体的清晰度。
- 采用新的基于物理的密度控制策略优化远距离物体渲染。
- 使用二进制运动掩膜处理动态内容。
- 通过设计支持散射介质的损失函数和增强伪深度图优化模型性能。
点此查看论文截图

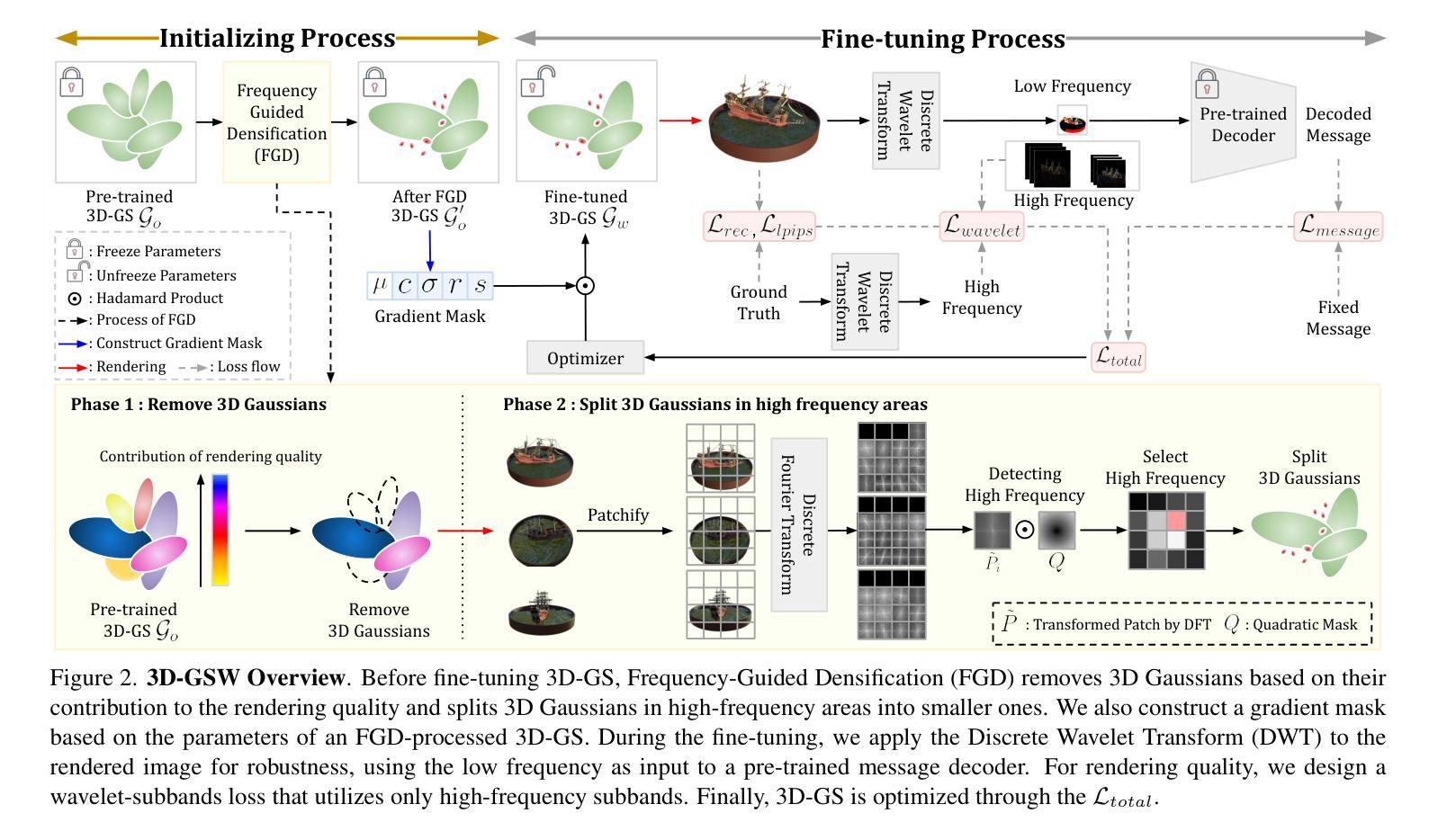
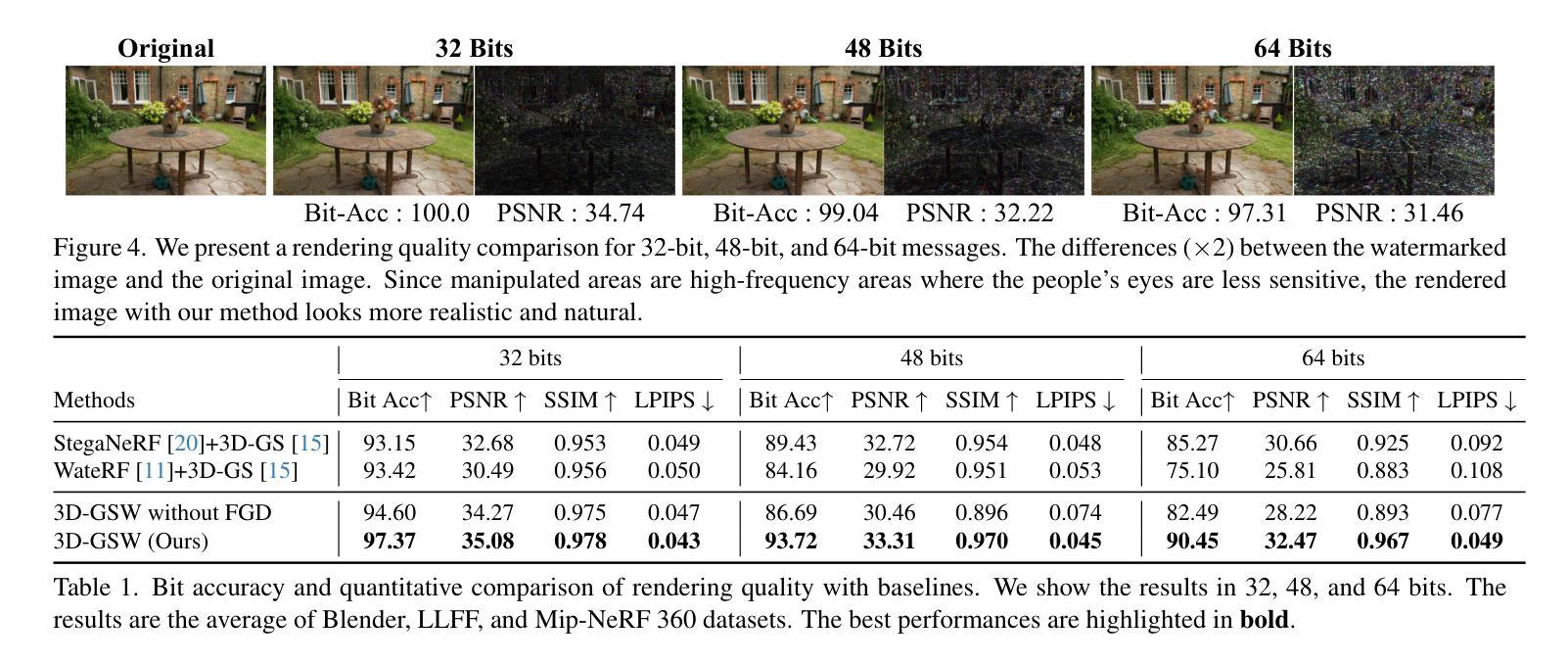
3D-GSW: 3D Gaussian Splatting for Robust Watermarking
Authors:Youngdong Jang, Hyunje Park, Feng Yang, Heeju Ko, Euijin Choo, Sangpil Kim
As 3D Gaussian Splatting(3D-GS) gains significant attention and its commercial usage increases, the need for watermarking technologies to prevent unauthorized use of the 3D-GS models and rendered images has become increasingly important. In this paper, we introduce a robust watermarking method for 3D-GS that secures ownership of both the model and its rendered images. Our proposed method remains robust against distortions in rendered images and model attacks while maintaining high rendering quality. To achieve these objectives, we present Frequency-Guided Densification(FGD), which removes 3D Gaussians based on their contribution to rendering quality, enhancing real-time rendering and the robustness of the message. FGD utilizes Discrete Fourier Transform to split 3D Gaussians in high-frequency areas, improving rendering quality. Furthermore, we employ a gradient mask for 3D Gaussians and design a wavelet-subband loss to enhance rendering quality. Our experiments show that our method embeds the message in the rendered images invisibly and robustly against various attacks, including model distortion. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance. Project page: https://kuai-lab.github.io/3dgsw2024/
随着三维高斯混合技术(3DGS)受到越来越多的关注,其商业应用也在不断增加。为了防止未经授权的3DGS模型和渲染图像的使用,水印技术的需求变得越来越重要。在本文中,我们为三维高斯混合提出了一种稳健的水印方法,该方法既保护模型的所有权,又保护其渲染图像的所有权。所提出的方法对于渲染图像的畸变和模型攻击具有很强的鲁棒性,同时保持了高质量的渲染效果。为了实现这些目标,我们提出了频率引导致密化(FGD)的方法,该方法根据其对渲染质量的贡献去除三维高斯,从而提高实时渲染和信息内容的稳健性。FGD利用离散傅里叶变换将三维高斯在高频区域进行分割,以提高渲染质量。此外,我们对三维高斯进行了梯度掩膜处理,并设计了一种小波子带损失来提高渲染质量。实验表明,我们的方法将信息嵌入到渲染图像中,对各种攻击具有不可见性和稳健性,包括模型畸变。我们的方法达到了最先进的性能。项目页面:https://kuai-lab.github.io/3dgsw2024/。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
随着3D高斯展铺(3D-GS)受到广泛关注及商业应用的增加,防止未经授权使用3D-GS模型和渲染图像的需求日益重要。本文介绍了一种针对3D-GS的稳健水印方法,确保模型和渲染图像的所有权安全。该方法对渲染图像的失真和模型攻击具有鲁棒性,同时保持高质量的渲染。通过提出频率引导密实化(FGD)实现这一目标,该方法根据其对渲染质量的贡献去除3D高斯,提高实时渲染和信息鲁棒性。FGD利用离散傅里叶变换将3D高斯分裂为高频区域,提高渲染质量。此外,我们对3D高斯采用梯度掩膜,并设计小波子带损失来提高渲染质量。实验表明,该方法将信息嵌入渲染图像中,对各种攻击具有隐形和鲁棒性,包括模型失真。该方法达到最新性能水平。
要点
- 随着3D-GS受到关注及商业应用增长,保护3D模型及渲染图像所有权的需求增强。
- 引入一种针对3D-GS的稳健水印方法,确保模型和渲染图像的所有权。
- 提出频率引导密实化(FGD)方法,根据对渲染质量的贡献处理3D高斯。
- FGD利用离散傅里叶变换分裂3D高斯为高频区域,提高渲染质量。
- 采用梯度掩膜及小波子带损失增强渲染质量。
- 实验显示,该方法能隐形且稳健地将信息嵌入渲染图像,对抗包括模型失真在内的各种攻击。
点此查看论文截图


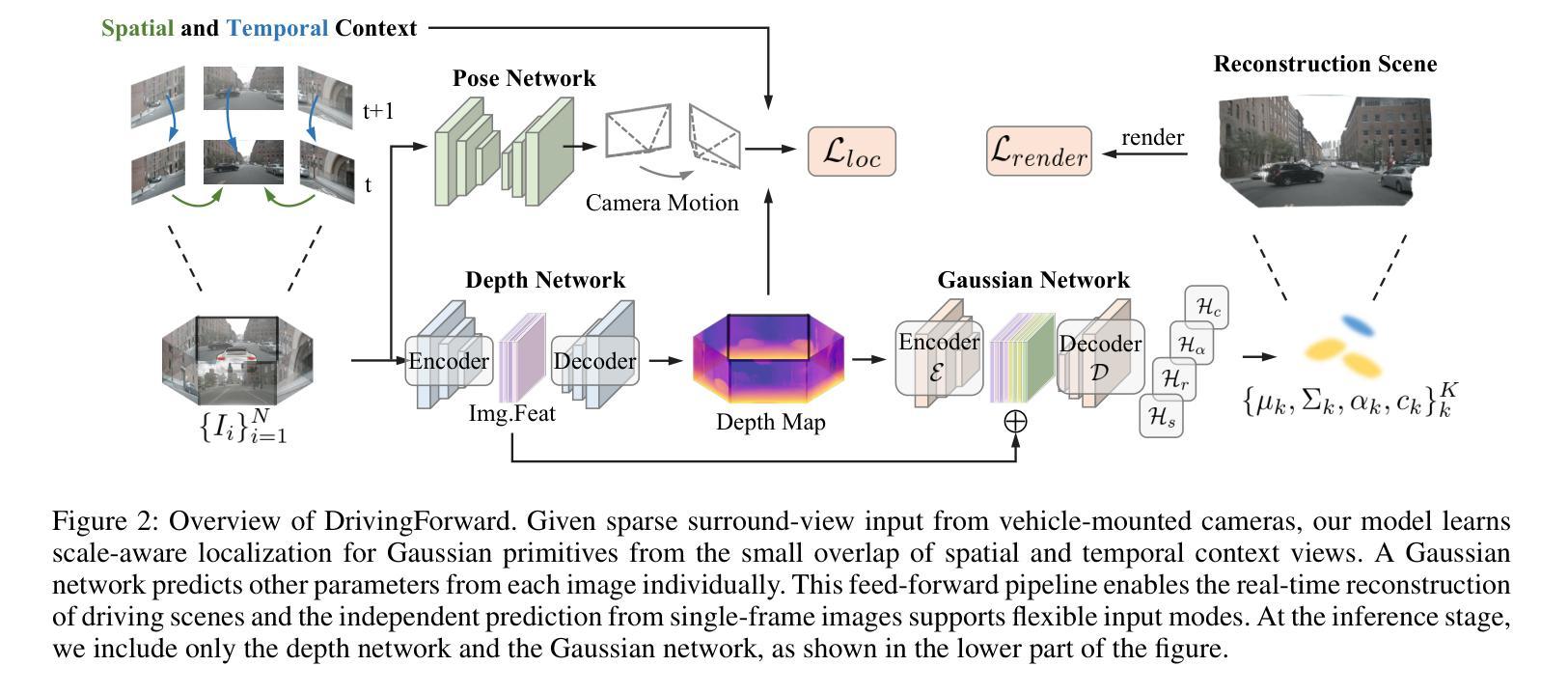
DrivingForward: Feed-forward 3D Gaussian Splatting for Driving Scene Reconstruction from Flexible Surround-view Input
Authors:Qijian Tian, Xin Tan, Yuan Xie, Lizhuang Ma
We propose DrivingForward, a feed-forward Gaussian Splatting model that reconstructs driving scenes from flexible surround-view input. Driving scene images from vehicle-mounted cameras are typically sparse, with limited overlap, and the movement of the vehicle further complicates the acquisition of camera extrinsics. To tackle these challenges and achieve real-time reconstruction, we jointly train a pose network, a depth network, and a Gaussian network to predict the Gaussian primitives that represent the driving scenes. The pose network and depth network determine the position of the Gaussian primitives in a self-supervised manner, without using depth ground truth and camera extrinsics during training. The Gaussian network independently predicts primitive parameters from each input image, including covariance, opacity, and spherical harmonics coefficients. At the inference stage, our model can achieve feed-forward reconstruction from flexible multi-frame surround-view input. Experiments on the nuScenes dataset show that our model outperforms existing state-of-the-art feed-forward and scene-optimized reconstruction methods in terms of reconstruction.
我们提出了DrivingForward这一前馈高斯拼贴模型,该模型能够从灵活的多视角输入重建驾驶场景。车载相机拍摄的驾驶场景图像通常稀疏且重叠有限,车辆的运动进一步增加了获取相机外部参数的难度。为了应对这些挑战并实现实时重建,我们联合训练了一个姿态网络、一个深度网络和一个高斯网络,以预测代表驾驶场景的高斯基本体。姿态网络和深度网络以自我监督的方式确定高斯基本体的位置,在训练过程中不使用深度真实值和相机外部参数。高斯网络独立地从每个输入图像预测基本体参数,包括协方差、不透明度和球面谐波系数。在推理阶段,我们的模型可以从灵活的多视角输入实现前馈重建。在nuScenes数据集上的实验表明,我们的模型在重建方面优于现有的最先进的前馈和场景优化重建方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accept by AAAI 2025. Project Page: https://fangzhou2000.github.io/projects/drivingforward/
摘要
提出了一种名为DrivingForward的向前传递高斯涂斑模型,该模型能够从灵活的环绕视图输入重建驾驶场景。针对车载相机拍摄的驾驶场景图像稀疏、重叠有限,以及车辆运动导致相机外部参数获取困难等问题,我们联合训练了一个姿态网络、深度网络和高斯网络,以预测代表驾驶场景的高斯基元。姿态网络和深度网络以自我监督的方式确定高斯基元的位置,训练过程中无需使用深度地面真实值和相机外部参数。高斯网络独立预测每个输入图像的高斯基元参数,包括协方差、不透明度和球面谐波系数。在推理阶段,我们的模型能够实现从灵活的多帧环绕视图输入的向前重建。在nuScenes数据集上的实验表明,我们的模型在重建方面优于现有的最先进的向前传递和场景优化重建方法。
要点
- 提出一种名为DrivingForward的向前传递高斯涂斑模型,能够从灵活的环绕视图输入重建驾驶场景。
- 联合训练姿态网络、深度网络和高斯网络,以预测代表驾驶场景的高斯基元。
- 姿态网络和深度网络以自我监督的方式工作,无需深度地面真实值和相机外部参数。
- 高斯网络预测每个输入图像的高斯基元参数,包括协方差、不透明度和球面谐波系数。
- 模型在推理阶段能够实现多帧环绕视图输入的向前重建。
- 在nuScenes数据集上的实验表明,该模型在重建性能上优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

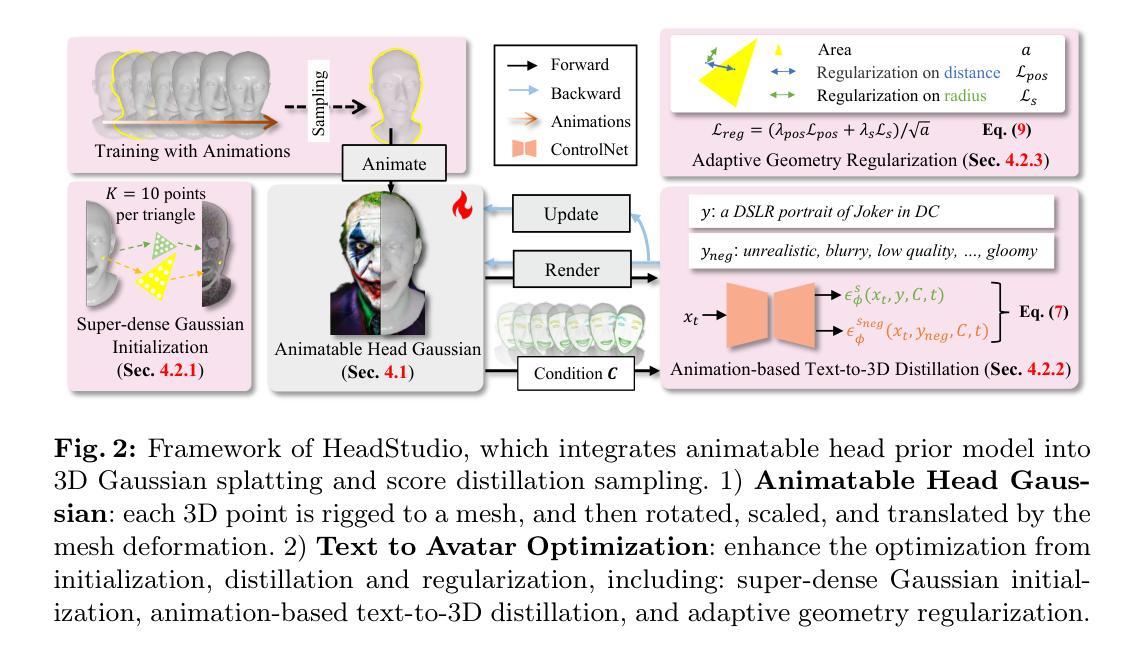
HeadStudio: Text to Animatable Head Avatars with 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Zhenglin Zhou, Fan Ma, Hehe Fan, Zongxin Yang, Yi Yang
Creating digital avatars from textual prompts has long been a desirable yet challenging task. Despite the promising results achieved with 2D diffusion priors, current methods struggle to create high-quality and consistent animated avatars efficiently. Previous animatable head models like FLAME have difficulty in accurately representing detailed texture and geometry. Additionally, high-quality 3D static representations face challenges in semantically driving with dynamic priors. In this paper, we introduce \textbf{HeadStudio}, a novel framework that utilizes 3D Gaussian splatting to generate realistic and animatable avatars from text prompts. Firstly, we associate 3D Gaussians with animatable head prior model, facilitating semantic animation on high-quality 3D representations. To ensure consistent animation, we further enhance the optimization from initialization, distillation, and regularization to jointly learn the shape, texture, and animation. Extensive experiments demonstrate the efficacy of HeadStudio in generating animatable avatars from textual prompts, exhibiting appealing appearances. The avatars are capable of rendering high-quality real-time ($\geq 40$ fps) novel views at a resolution of 1024. Moreover, These avatars can be smoothly driven by real-world speech and video. We hope that HeadStudio can enhance digital avatar creation and gain popularity in the community. Code is at: https://github.com/ZhenglinZhou/HeadStudio.
从文本提示创建数字化身一直是一项令人向往但具有挑战性的任务。尽管二维扩散先验取得了有前景的结果,但当前的方法仍然难以高效地创建高质量且连贯的动画化身。像FLAME这样的先前可动画头部模型在准确表示精细纹理和几何结构方面存在困难。此外,高质量的三维静态表示在语义驱动的动态先验方面也面临挑战。在本文中,我们介绍了HeadStudio,这是一个利用三维高斯拼贴法从文本提示生成逼真且可动画的化身的新型框架。首先,我们将三维高斯与可动画头部先验模型相关联,促进高质量三维表示上的语义动画。为了确保连贯的动画,我们进一步增强了从初始化、蒸馏和正则化开始的优化,以联合学习形状、纹理和动画。大量实验表明,HeadStudio在从文本提示生成可动画化身方面非常有效,具有吸引人的外观。这些化身能够以高于或等于40帧/秒的速度呈现高质量实时(≥40帧/秒)的新视角,分辨率高达1024。此外,这些化身可以被现实世界中的语音和视频流畅驱动。我们希望HeadStudio能增强数字化身的创建并在社区中广受欢迎。代码地址为:https://github.com/ZhenglinZhou/HeadStudio。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 26 pages, 18 figures, accepted by ECCV 2024
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为HeadStudio的新型框架,它利用3D高斯涂斑技术从文本提示生成真实且可动画的头像。HeadStudio结合可动画的头部先验模型与3D高斯,实现在高质量3D表示上的语义动画。通过优化初始化、蒸馏和正则化,联合学习形状、纹理和动画。实验表明,HeadStudio能从未加工的文本中生成可动画的头像,展现吸引人的外观,并以高质量实时渲染。
Key Takeaways
- HeadStudio利用3D高斯涂斑技术生成真实且可动画的头像。
- 结合可动画的头部先验模型与3D高斯,实现高质量3D表示上的语义动画。
- 通过优化初始化、蒸馏和正则化,联合学习形状、纹理和动画,确保动画的一致性。
- HeadStudio可从文本提示生成可动画的头像,展现吸引人的外观。
- 生成的头像能以高质量实时渲染,渲染速度达到或超过40帧每秒。
- 这些头像可以被真实世界的语音和视频流畅驱动。
点此查看论文截图


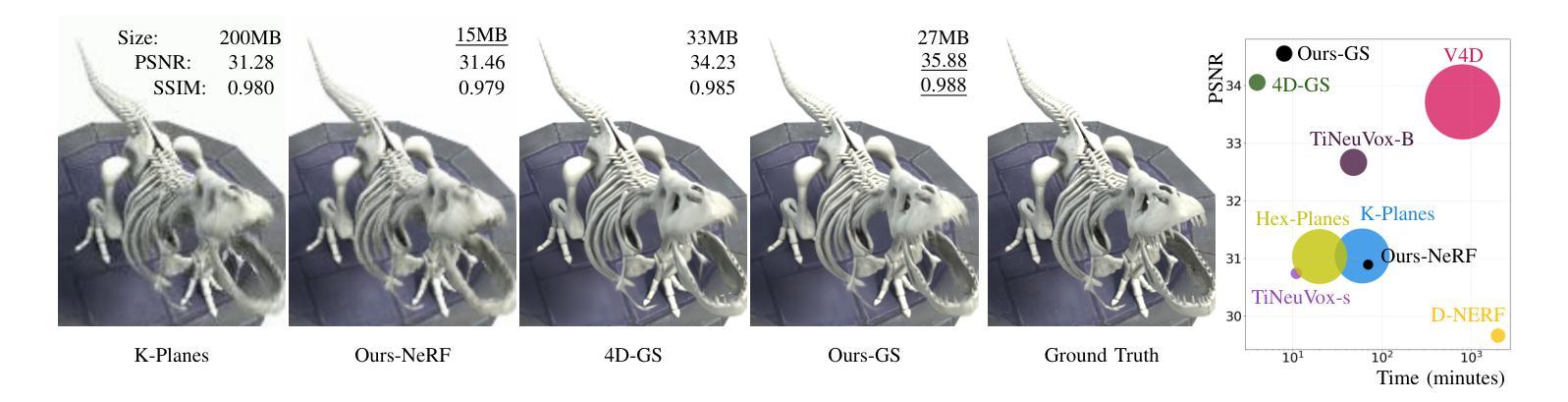
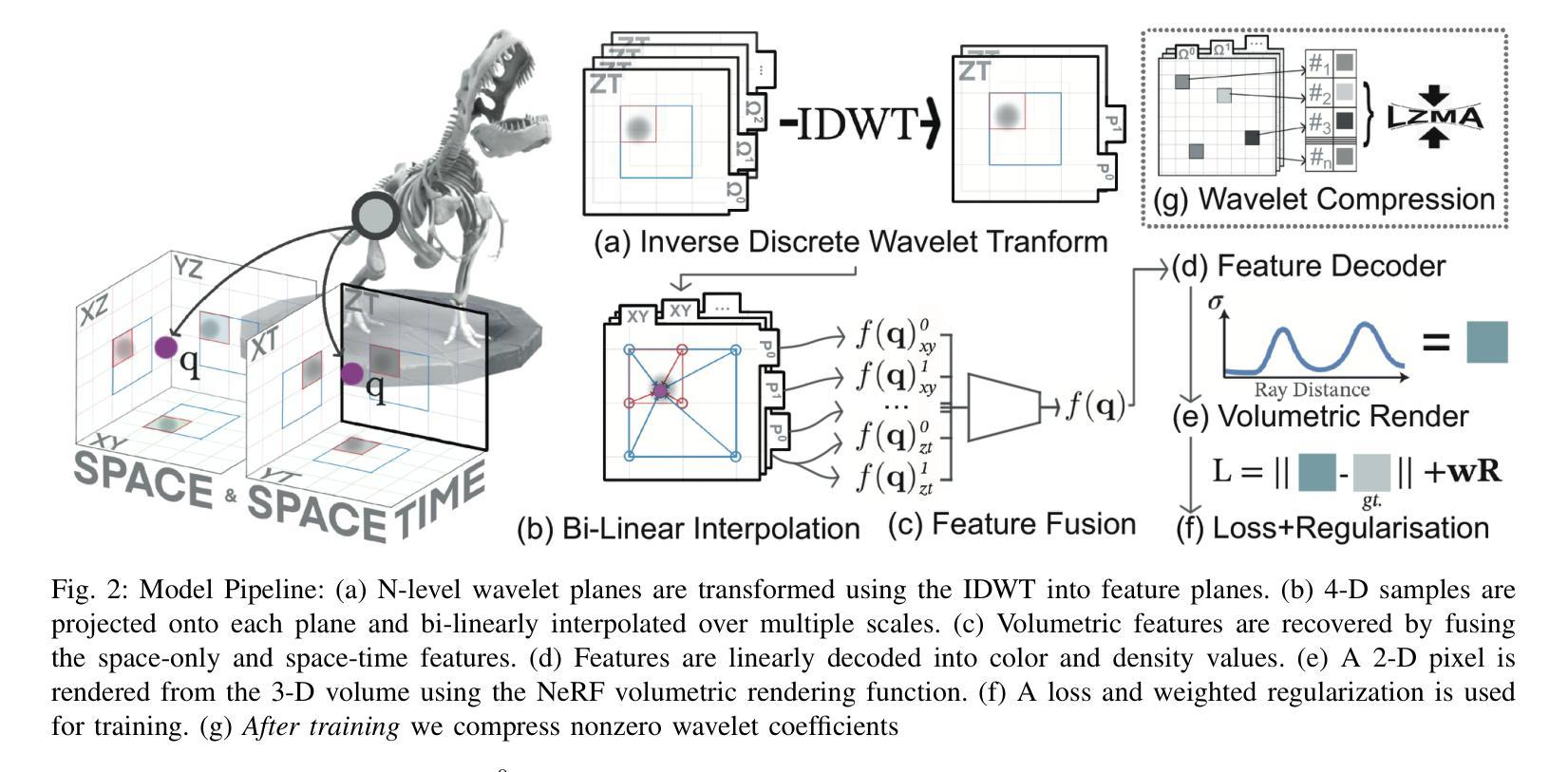
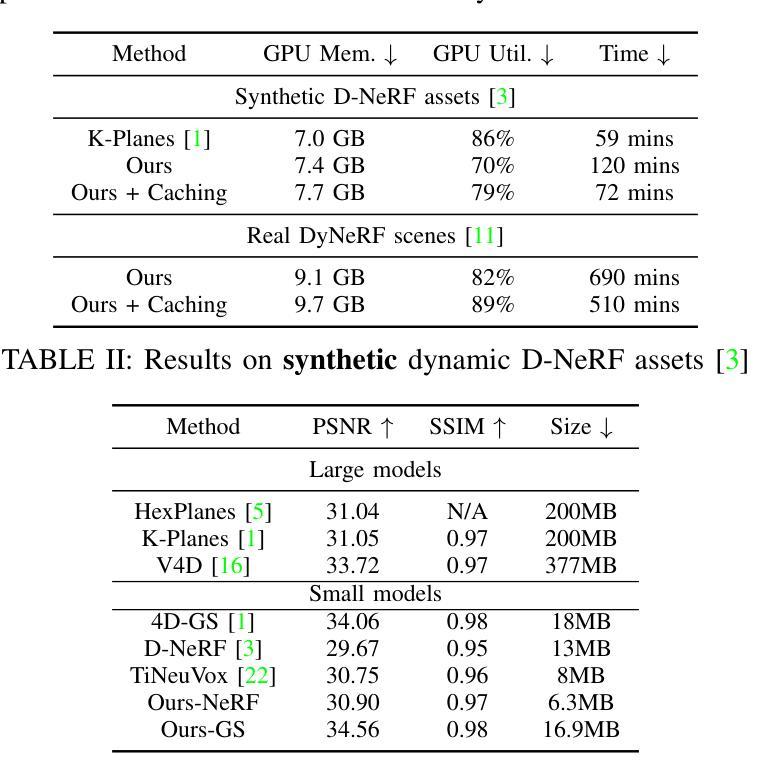
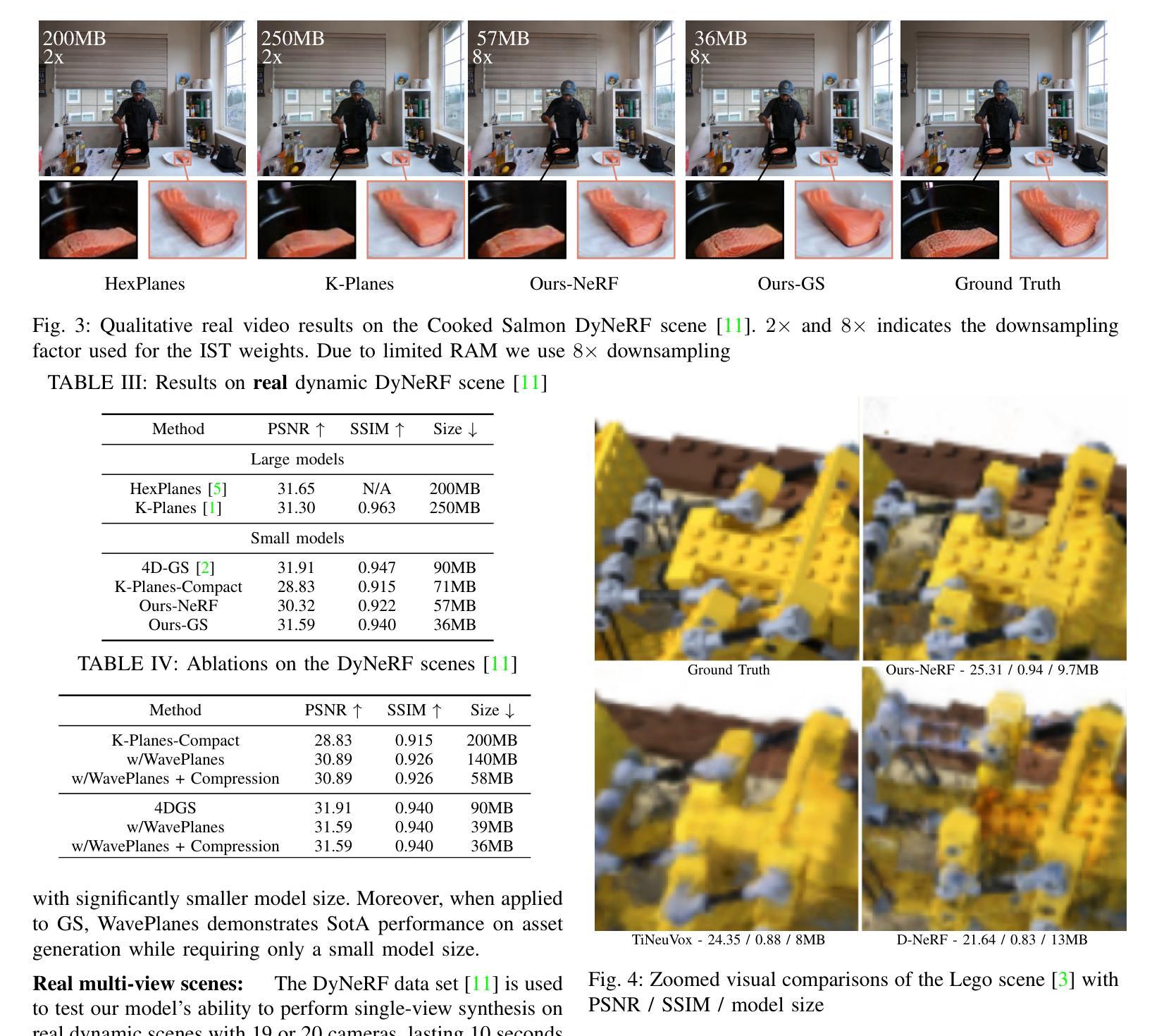
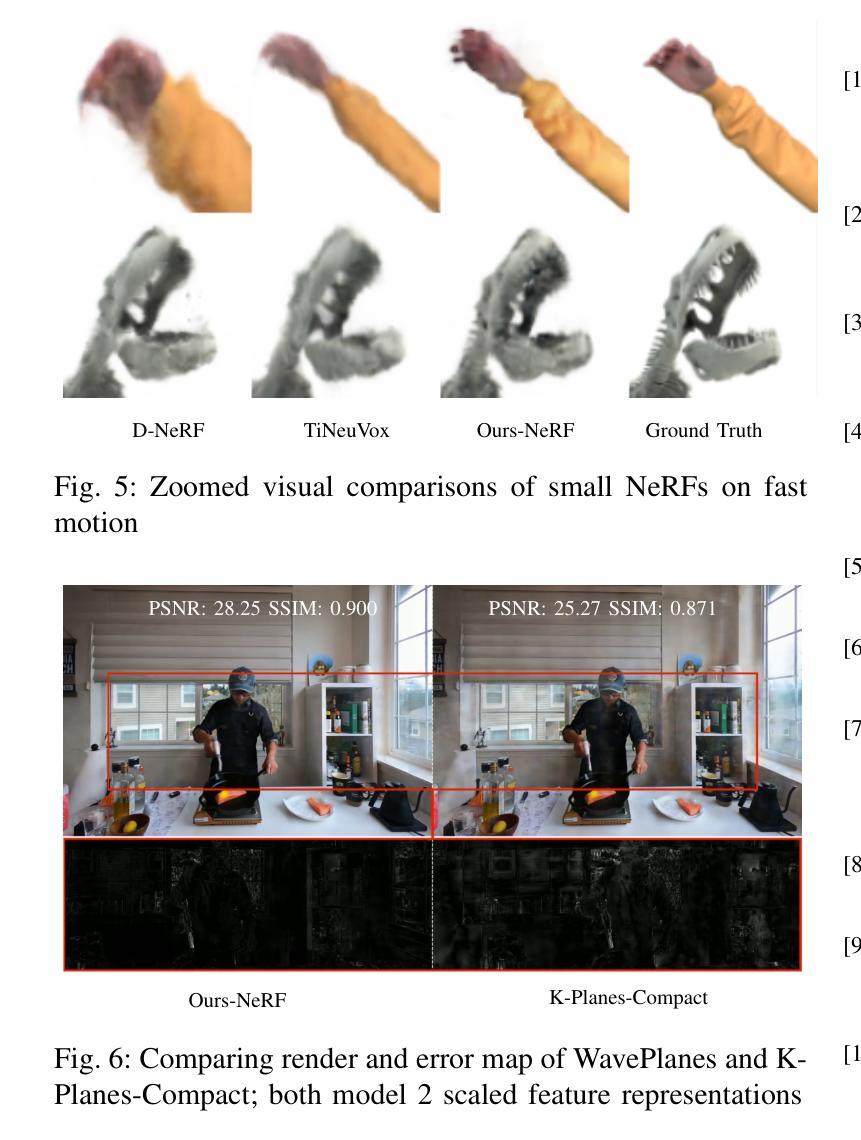
WavePlanes: Compact Hex Planes for Dynamic Novel View Synthesis
Authors:Adrian Azzarelli, Nantheera Anantrasirichai, David R Bull
Dynamic Novel View Synthesis (Dynamic NVS) enhances NVS technologies to model moving 3-D scenes. However, current methods are resource intensive and challenging to compress. To address this, we present WavePlanes, a fast and more compact hex plane representation, applicable to both Neural Radiance Fields and Gaussian Splatting methods. Rather than modeling many feature scales separately (as done previously), we use the inverse discrete wavelet transform to reconstruct features at varying scales. This leads to a more compact representation and allows us to explore wavelet-based compression schemes for further gains. The proposed compression scheme exploits the sparsity of wavelet coefficients, by applying hard thresholding to the wavelet planes and storing nonzero coefficients and their locations on each plane in a Hash Map. Compared to the state-of-the-art (SotA), WavePlanes is significantly smaller, less resource demanding and competitive in reconstruction quality. Compared to small SotA models, WavePlanes outperforms methods in both model size and quality of novel views.
动态场景视图合成技术(Dynamic Novel View Synthesis,简称Dynamic NVS)旨在增强NVS技术在模拟移动三维场景方面的能力。然而,当前的方法资源消耗大且压缩具有挑战性。针对这一问题,我们提出了WavePlanes,这是一种快速且更紧凑的六平面表示法,适用于神经网络辐射场和高斯贴图方法。我们不再像过去那样单独建模许多特征尺度,而是使用逆离散小波变换来重建不同尺度的特征。这导致了更紧凑的表示形式,并允许我们进一步探索基于小波压缩方案以获得更多收益。所提出的压缩方案通过利用小波系数的稀疏性,对小波平面应用硬阈值处理,并在哈希表中存储每个平面上的非零系数及其位置。与现有技术相比,WavePlanes体积更小、资源消耗更低且在重建质量方面具有竞争力。相较于小型现有技术模型,WavePlanes在模型大小和新视图质量方面都表现出优越性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
动态场景建模技术动态小说视图合成(Dynamic NVS)提高了NVS技术的性能,但当前方法资源密集且压缩困难。本研究提出了WavePlanes,一种快速且更紧凑的六平面表示方法,适用于神经辐射场和高斯溅射方法。我们利用逆离散小波变换重构不同尺度的特征,实现了更紧凑的表示,并探索了基于小波的更高效的压缩方案。压缩方案利用小波系数的稀疏性,通过对小波平面应用硬阈值处理并存储每个平面上的非零系数及其位置来实现高效的存储。与最新技术相比,WavePlanes体积更小、资源需求更低,在重建质量方面具有竞争力;在小模型方面,WavePlanes在模型大小和质量上均表现出优势。
Key Takeaways
- 动态场景建模技术中的Dynamic NVS面临资源密集和压缩困难的问题。
- WavePlanes是一种新的六平面表示方法,适用于神经辐射场和高斯溅射方法。
- 利用逆离散小波变换重构不同尺度的特征,实现更紧凑的模型表示。
- 基于小波系数的稀疏性,提出了高效的压缩方案。
- 通过硬阈值处理小波平面并存储非零系数及其位置来实现存储优化。
- 与现有技术相比,WavePlanes模型更小、资源需求更低,在重建质量方面具有竞争力。
点此查看论文截图