⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-25 更新
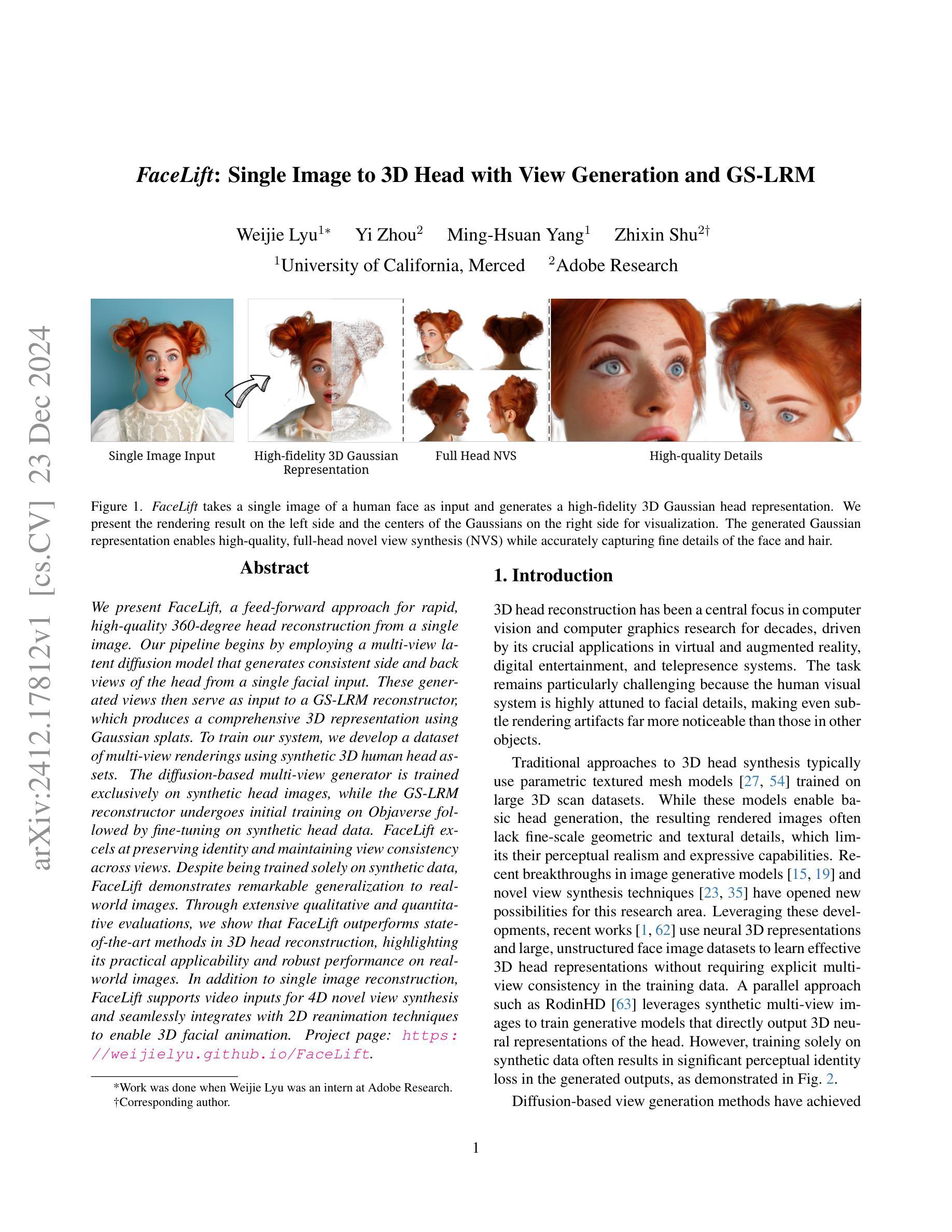
FaceLift: Single Image to 3D Head with View Generation and GS-LRM
Authors:Weijie Lyu, Yi Zhou, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Zhixin Shu
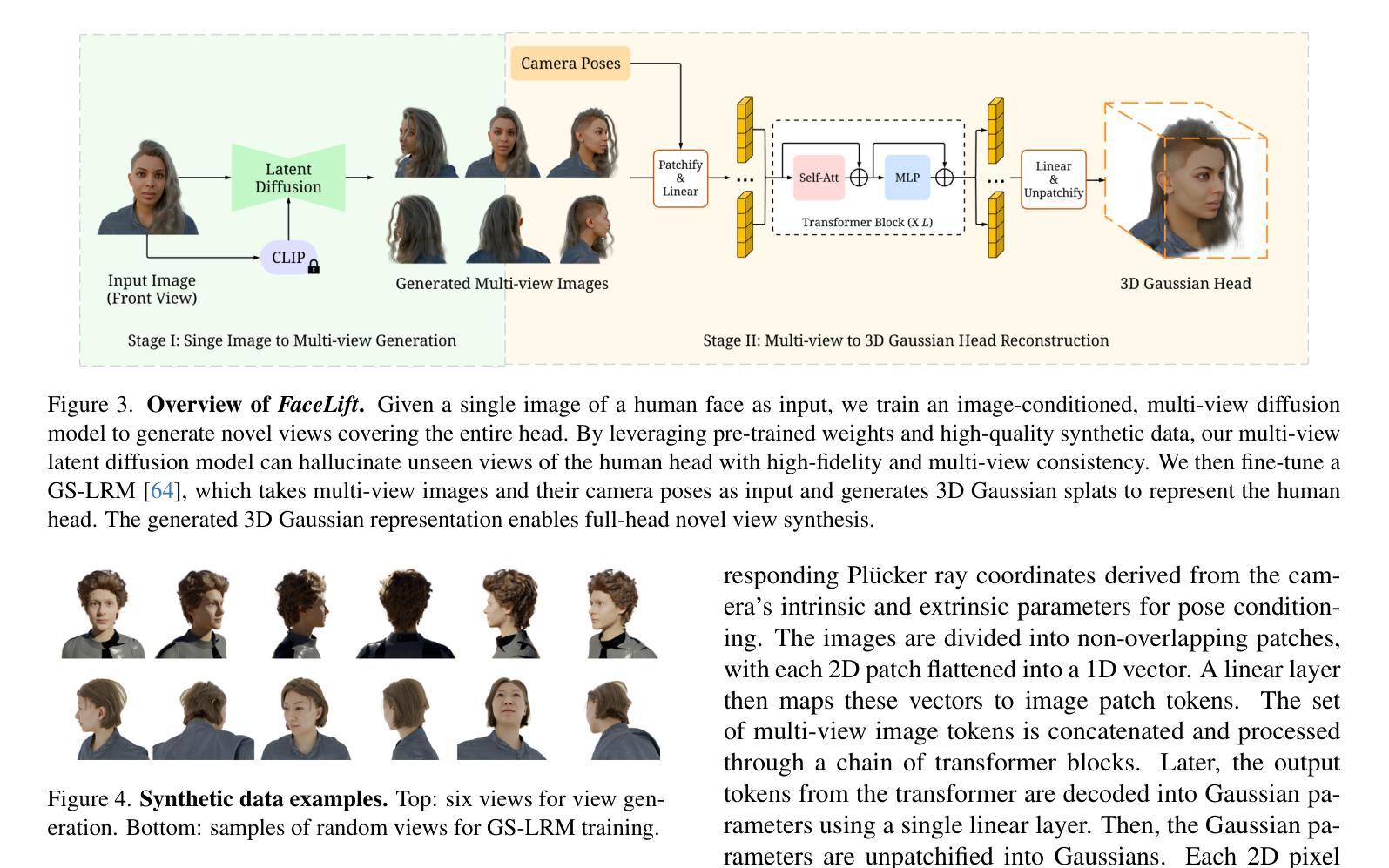
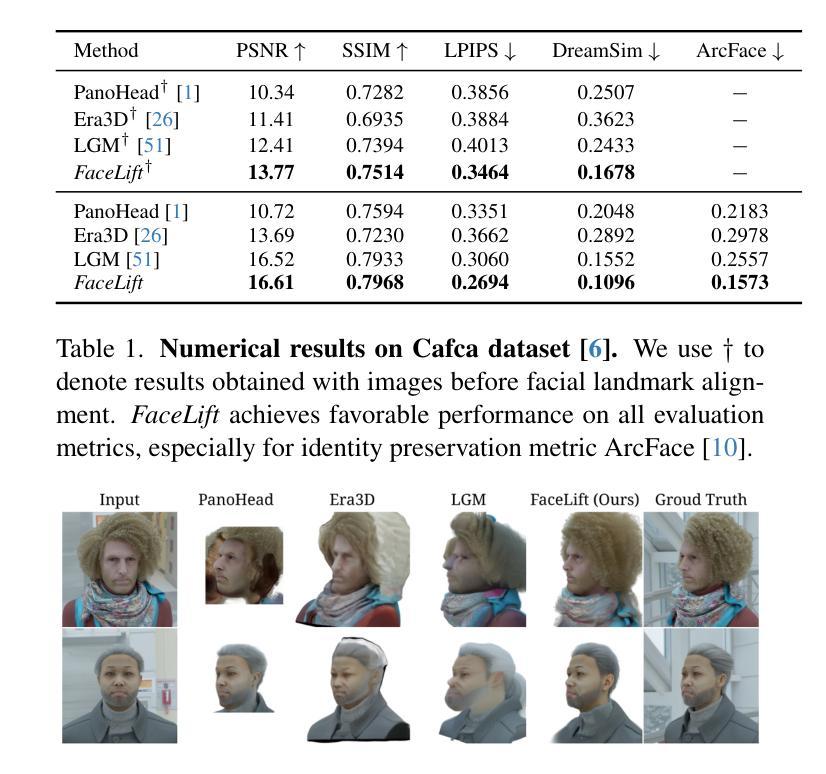
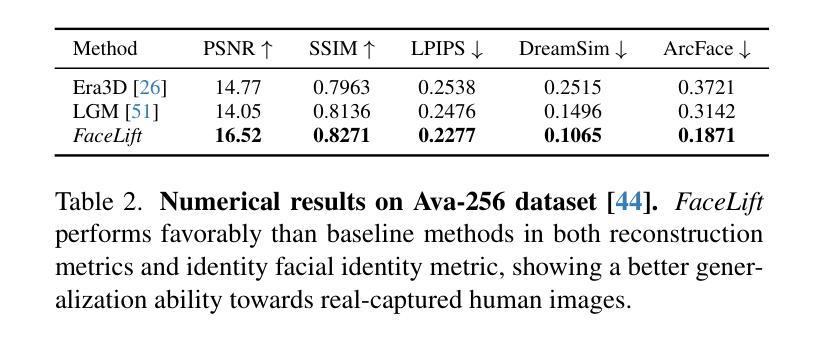
We present FaceLift, a feed-forward approach for rapid, high-quality, 360-degree head reconstruction from a single image. Our pipeline begins by employing a multi-view latent diffusion model that generates consistent side and back views of the head from a single facial input. These generated views then serve as input to a GS-LRM reconstructor, which produces a comprehensive 3D representation using Gaussian splats. To train our system, we develop a dataset of multi-view renderings using synthetic 3D human head as-sets. The diffusion-based multi-view generator is trained exclusively on synthetic head images, while the GS-LRM reconstructor undergoes initial training on Objaverse followed by fine-tuning on synthetic head data. FaceLift excels at preserving identity and maintaining view consistency across views. Despite being trained solely on synthetic data, FaceLift demonstrates remarkable generalization to real-world images. Through extensive qualitative and quantitative evaluations, we show that FaceLift outperforms state-of-the-art methods in 3D head reconstruction, highlighting its practical applicability and robust performance on real-world images. In addition to single image reconstruction, FaceLift supports video inputs for 4D novel view synthesis and seamlessly integrates with 2D reanimation techniques to enable 3D facial animation. Project page: https://weijielyu.github.io/FaceLift.
我们提出了FaceLift,这是一种快速、高质量的单图像360度头部重建的前馈方法。我们的管道首先采用多视角潜在扩散模型,从单个面部输入生成一致的头部侧面和背面视图。这些生成的视图然后作为GS-LRM重建器的输入,使用高斯斑点生成全面的3D表示。为了训练我们的系统,我们使用合成3D人头数据集开发了一个多视角渲染数据集。基于扩散的多视角生成器仅接受合成头部图像进行训练,而GS-LRM重建器则首先在Objaverse上进行初步训练,然后在合成头部数据上进行微调。FaceLift擅长在视图之间保持身份不变和保持视图一致性。尽管仅对合成数据进行训练,但FaceLift在真实图像上表现出令人印象深刻的泛化能力。通过广泛的质量和数量评估,我们证明了FaceLift在3D头部重建方面优于最新技术,突出了其在真实图像上的实际适用性和稳健性能。除了单图像重建外,FaceLift还支持视频输入以实现4D新颖视图合成,并与2D动画技术无缝集成以实现3D面部动画。项目页面:https://weijielyu.github.io/FaceLift。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://weijielyu.github.io/FaceLift
Summary
FaceLift是一个基于单图像的高效、高质量的360度头部重建方法。它采用前馈方法,利用多视图潜在扩散模型生成一致的侧面和背面视图,再通过GS-LRM重建器生成全面的3D表示。FaceLift在保留身份和保持视图一致性方面表现出色,尽管只在合成数据上进行训练,但在真实图像中展示出了令人印象深刻的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- FaceLift是一个基于单图像的快速、高质量的头部重建方法。
- 采用多视图潜在扩散模型生成一致的侧面和背面视图。
- GS-LRM重建器用于生成全面的3D表示。
- FaceLift在保留身份和视图一致性方面表现优异。
- 仅通过合成数据训练,FaceLift在真实图像中展现出强大的泛化能力。
- FaceLift支持视频输入,用于4D新视角合成。
- FaceLift可无缝集成2D再动画技术,实现3D面部动画。
点此查看论文截图


The Superposition of Diffusion Models Using the Itô Density Estimator
Authors:Marta Skreta, Lazar Atanackovic, Avishek Joey Bose, Alexander Tong, Kirill Neklyudov
The Cambrian explosion of easily accessible pre-trained diffusion models suggests a demand for methods that combine multiple different pre-trained diffusion models without incurring the significant computational burden of re-training a larger combined model. In this paper, we cast the problem of combining multiple pre-trained diffusion models at the generation stage under a novel proposed framework termed superposition. Theoretically, we derive superposition from rigorous first principles stemming from the celebrated continuity equation and design two novel algorithms tailor-made for combining diffusion models in SuperDiff. SuperDiff leverages a new scalable It^o density estimator for the log likelihood of the diffusion SDE which incurs no additional overhead compared to the well-known Hutchinson’s estimator needed for divergence calculations. We demonstrate that SuperDiff is scalable to large pre-trained diffusion models as superposition is performed solely through composition during inference, and also enjoys painless implementation as it combines different pre-trained vector fields through an automated re-weighting scheme. Notably, we show that SuperDiff is efficient during inference time, and mimics traditional composition operators such as the logical OR and the logical AND. We empirically demonstrate the utility of using SuperDiff for generating more diverse images on CIFAR-10, more faithful prompt conditioned image editing using Stable Diffusion, and improved unconditional de novo structure design of proteins. https://github.com/necludov/super-diffusion
随着容易访问的预训练扩散模型的寒武纪爆发式增长,对于在不需要重新训练大型组合模型的大量计算负担的前提下,将多个不同的预训练扩散模型结合起来的方法的需求逐渐显现。在本文中,我们提出了一种新颖的方法来解决在生成阶段结合多个预训练扩散模型的问题,该方法基于名为叠加的新颖框架。理论上,我们从著名的连续方程中推导出的严格基本原理出发,得出叠加的结论,并为SuperDiff中结合扩散模型设计了两种量身定制的新型算法。SuperDiff利用一种新的可扩展的It^o密度估计器对扩散随机微分方程的对数似然进行估计,与用于计算发散的著名Hutchinson估计器相比,无需额外的开销。我们证明了SuperDiff在大型预训练扩散模型上的可扩展性,因为叠加仅在推理过程中通过组合实现,并且由于它通过自动重新加权方案结合了不同的预训练向量场,因此可以轻松实现。值得注意的是,我们展示了SuperDiff在推理时间上的效率,并模仿了传统的组合运算符,如逻辑OR和逻辑AND。我们通过实验证明了在CIFAR-10上生成更多不同图像、使用Stable Diffusion进行更精确的提示条件图像编辑以及改进无条件的蛋白质全新结构设计方面的实用性。详情请访问https://github.com/necludov/super-diffusion了解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个名为SuperDiff的新框架,用于在生成阶段结合多个预训练的扩散模型。SuperDiff利用新的可扩展It^o密度估计器计算扩散随机微分方程的对数似然值,无需额外的开销。通过组合不同的预训练向量场,SuperDiff能够高效生成更多样化的图像,更忠实于提示条件的图像编辑,以及改进的无条件蛋白质设计。
Key Takeaways
- SuperDiff框架允许结合多个预训练的扩散模型,无需进行大型组合模型的重新训练,降低了计算负担。
- SuperDiff利用It^o密度估计器计算扩散模型的对数似然值,具有可扩展性。
- SuperDiff通过组合不同的预训练向量场实现图像生成、图像编辑和蛋白质设计等功能。
- SuperDiff在生成阶段进行叠加,可扩展到大型预训练扩散模型。
- SuperDiff具有无痛实现,通过自动化重新加权方案组合不同的预训练向量场。
- SuperDiff在推理时效率高,可以模拟传统的组合运算符如逻辑OR和逻辑AND。
- 实证研究表明,SuperDiff在CIFAR-10图像生成、Stable Diffusion的提示条件图像编辑和蛋白质设计等方面具有实用性。
点此查看论文截图



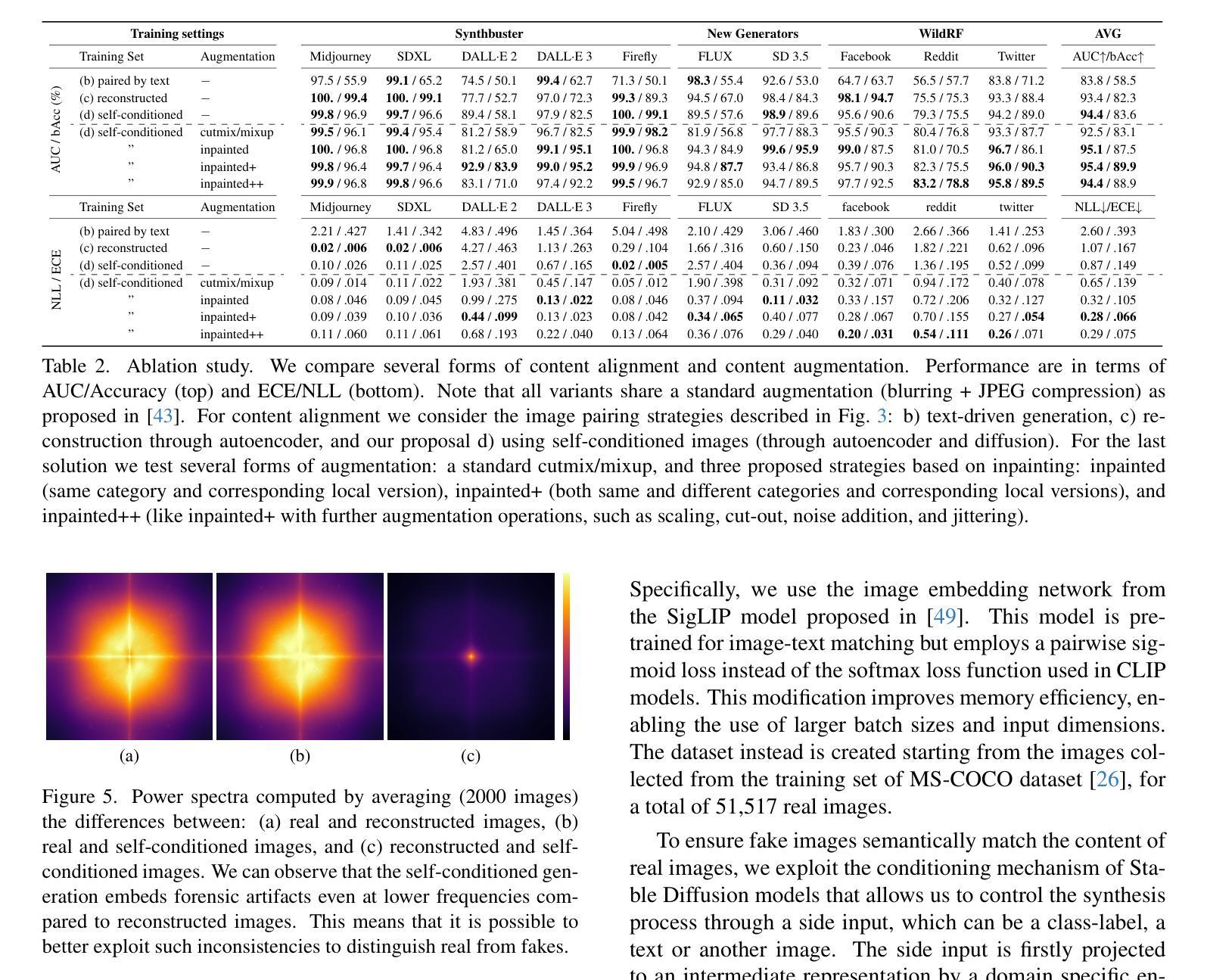
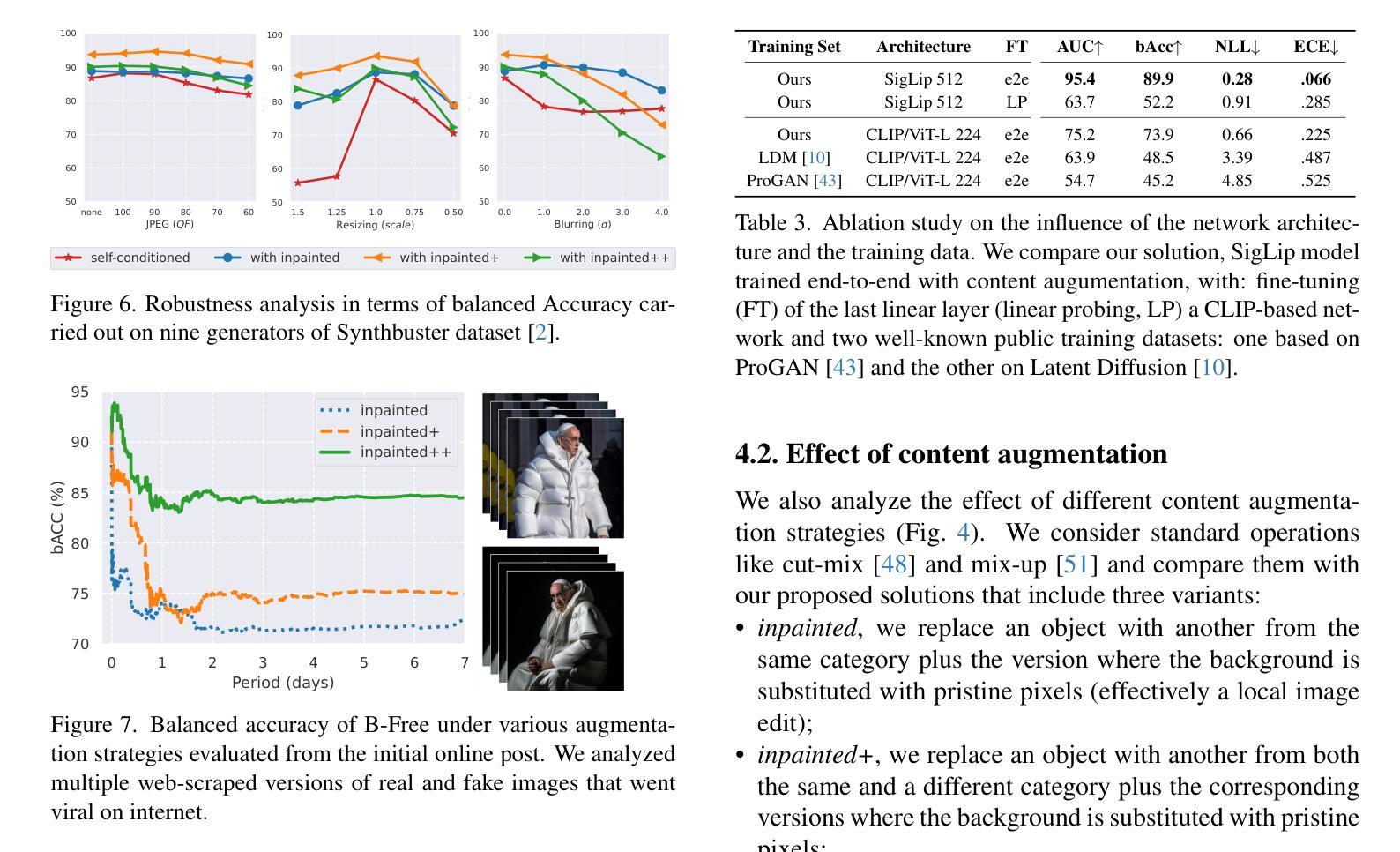
A Bias-Free Training Paradigm for More General AI-generated Image Detection
Authors:Fabrizio Guillaro, Giada Zingarini, Ben Usman, Avneesh Sud, Davide Cozzolino, Luisa Verdoliva
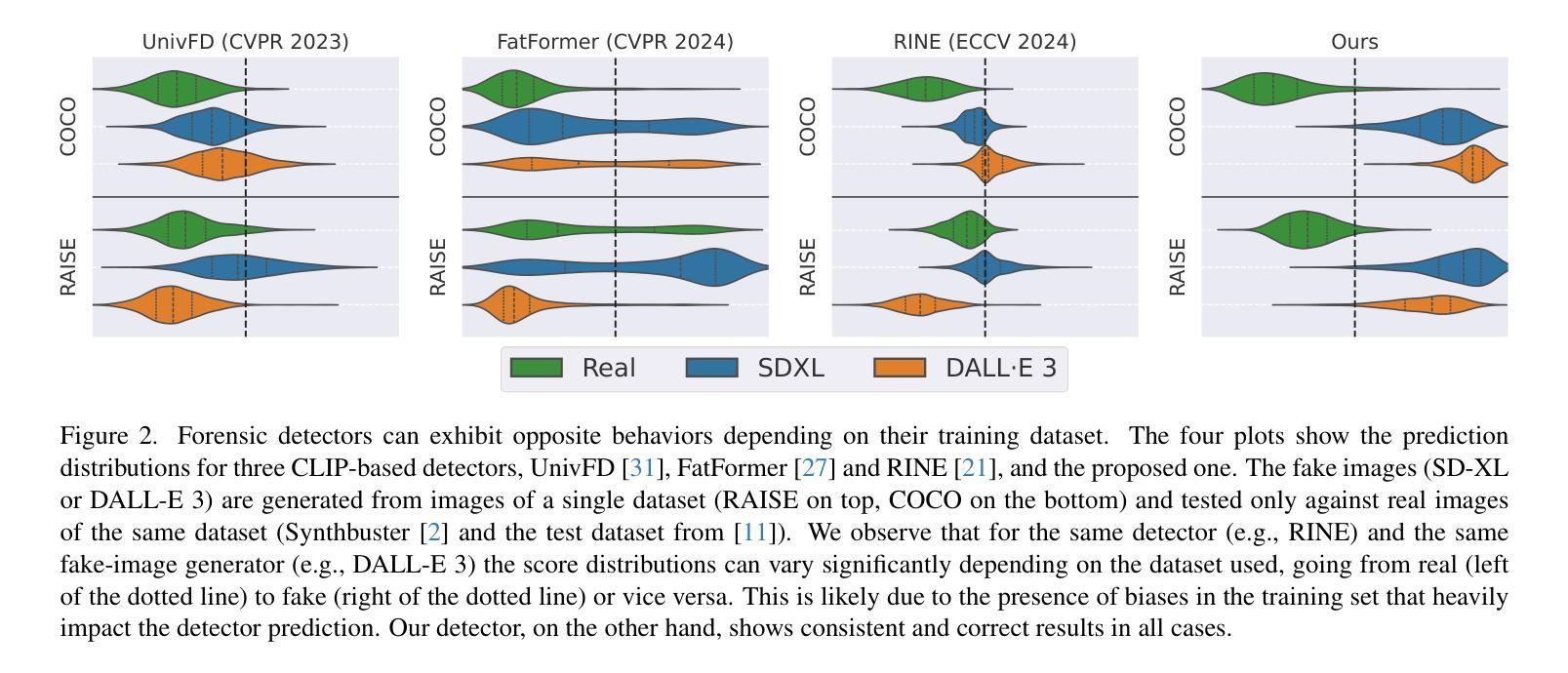
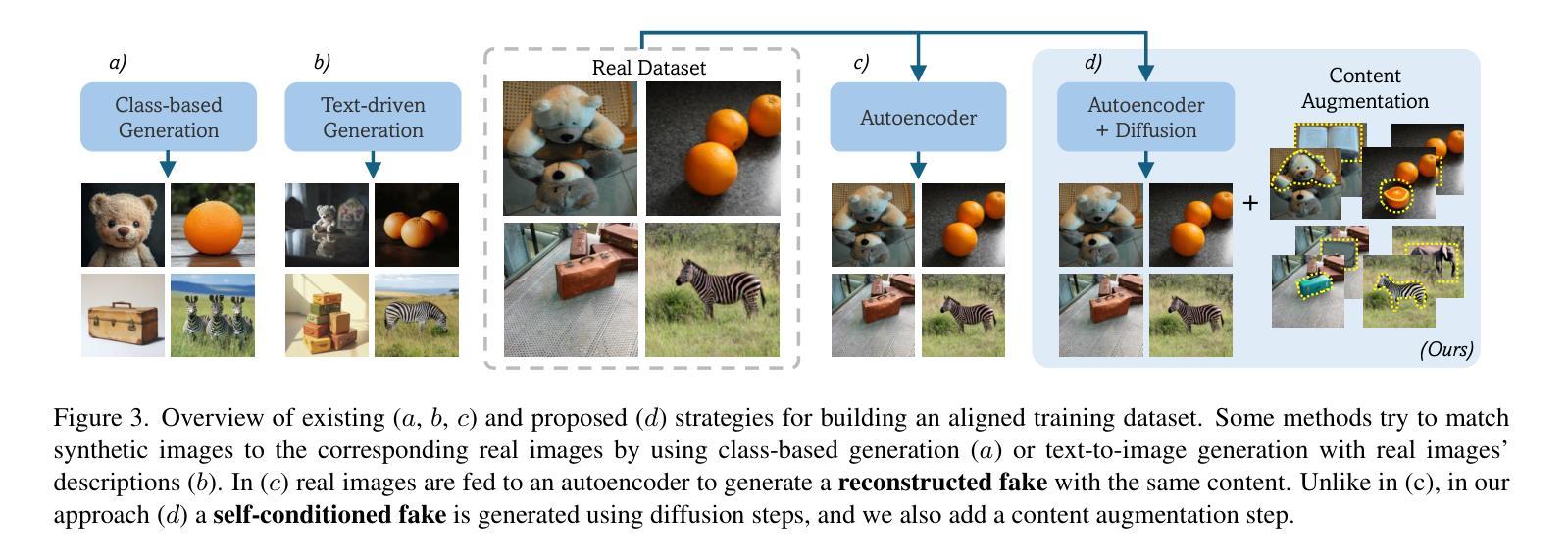
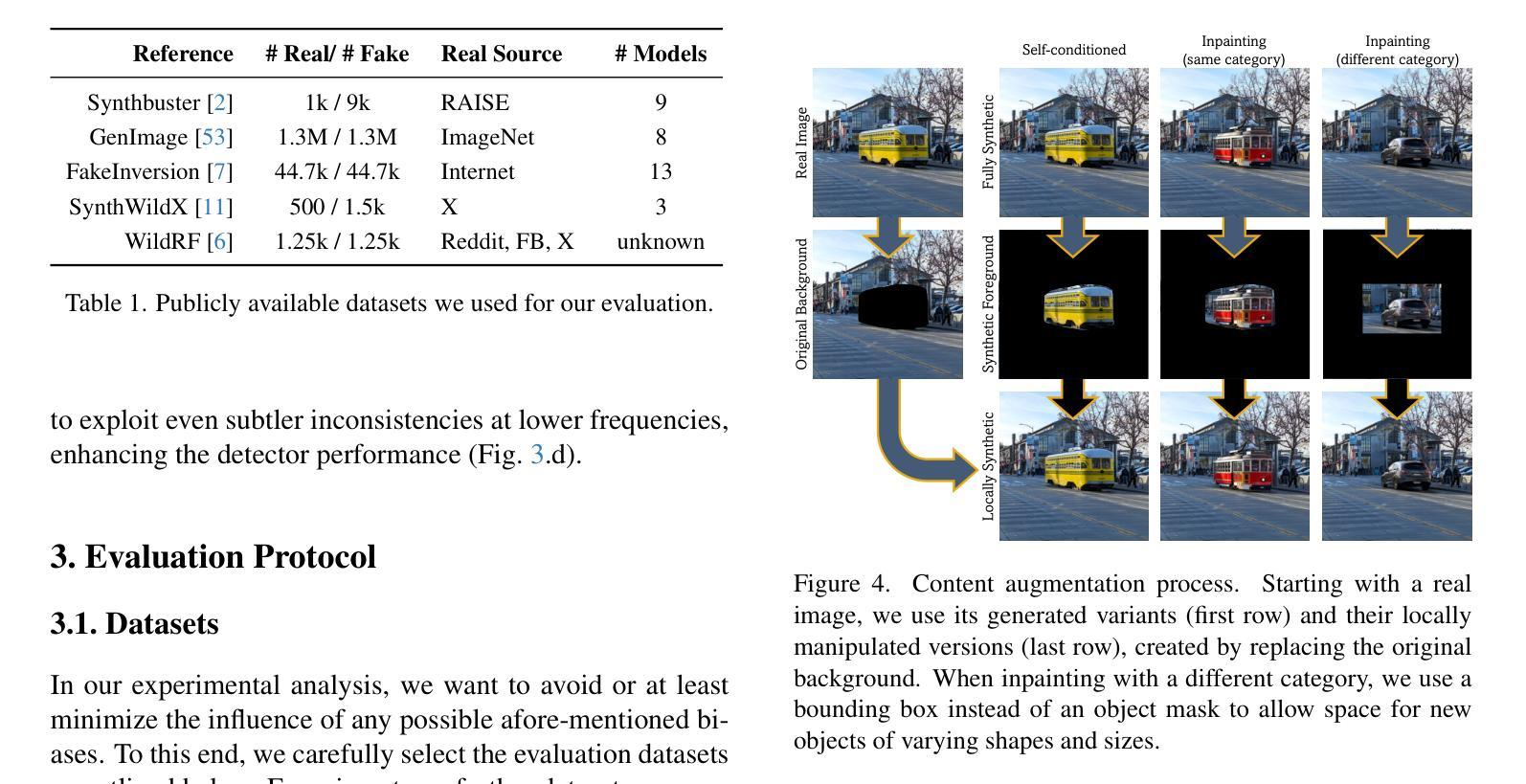
Successful forensic detectors can produce excellent results in supervised learning benchmarks but struggle to transfer to real-world applications. We believe this limitation is largely due to inadequate training data quality. While most research focuses on developing new algorithms, less attention is given to training data selection, despite evidence that performance can be strongly impacted by spurious correlations such as content, format, or resolution. A well-designed forensic detector should detect generator specific artifacts rather than reflect data biases. To this end, we propose B-Free, a bias-free training paradigm, where fake images are generated from real ones using the conditioning procedure of stable diffusion models. This ensures semantic alignment between real and fake images, allowing any differences to stem solely from the subtle artifacts introduced by AI generation. Through content-based augmentation, we show significant improvements in both generalization and robustness over state-of-the-art detectors and more calibrated results across 27 different generative models, including recent releases, like FLUX and Stable Diffusion 3.5. Our findings emphasize the importance of a careful dataset curation, highlighting the need for further research in dataset design. Code and data will be publicly available at https://grip-unina.github.io/B-Free/
成功的取证检测器能够在有监督学习的基准测试中产生优秀的结果,但在转向实际应用程序时却遇到困难。我们相信这种限制主要是因为训练数据质量不足。虽然大多数研究都集中在开发新算法上,但对训练数据选择方面的关注却很少,尽管有证据表明,性能可能会受到内容、格式或分辨率等虚假关联的强大影响。一个设计良好的取证检测器应该检测生成器特定的伪影,而不是反映数据偏见。为此,我们提出了B-Free,一种无偏训练范式,其中虚假图像是从真实的图像使用稳定扩散模型的调节程序生成的。这确保了真实和虚假图像之间的语义对齐,使得任何差异都仅源于AI生成所引入的细微伪影。通过基于内容的增强,我们在最先进的检测器上实现了显著的一般化和稳健性改进,并且在包括最新发布的FLUX和Stable Diffusion 3.5等27个不同的生成模型上获得了更校准的结果。我们的研究强调了数据集精心整理的重要性,并强调了数据集设计需要进一步研究的需求。代码和数据将在https://grip-unina.github.io/B-Free/公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为B-Free的无偏训练范式,以解决现有法医检测器在真实应用场景中表现不佳的问题。作者认为这一问题的根源在于训练数据质量不足,因此他们通过生成真实图像生成虚假图像的方式来解决这个问题。这种方式确保了真实和虚假图像之间的语义对齐,从而使得任何差异仅源于AI生成所引入的细微特征。通过内容增强方法,该方法相较于现有最先进的检测器在通用性和稳健性方面表现出显著优势,并且对包括最新发布的模型如FLUX和Stable Diffusion 3.5在内的27种生成模型有更准确的评估结果。研究强调了数据集筛选的重要性,并突出了数据集设计需要进一步研究的必要性。
Key Takeaways
- 当前法医检测器在真实应用场景中表现不足,主要问题在于训练数据质量。
- 大部分研究关注于开发新算法,而训练数据选择却被忽视。
- 文中提出B-Free无偏训练范式,通过生成真实图像创建虚假图像来确保语义对齐。
- 内容增强方法显著提高了检测器的通用性和稳健性。
- B-Free方法相较于现有技术有更准确的评估结果,适用于多种生成模型。
- 研究强调了数据集筛选的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

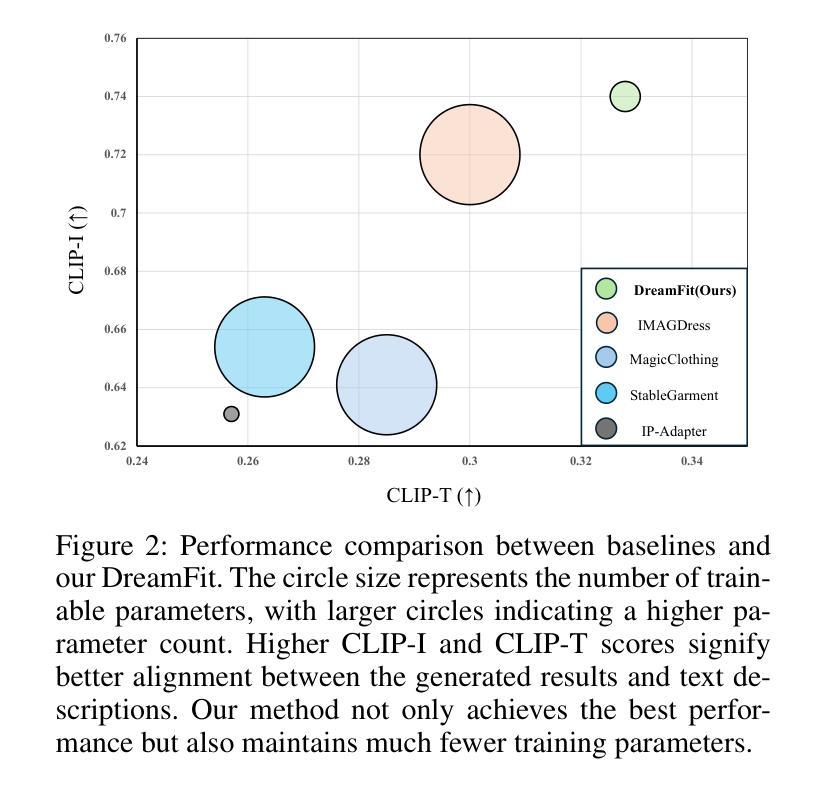
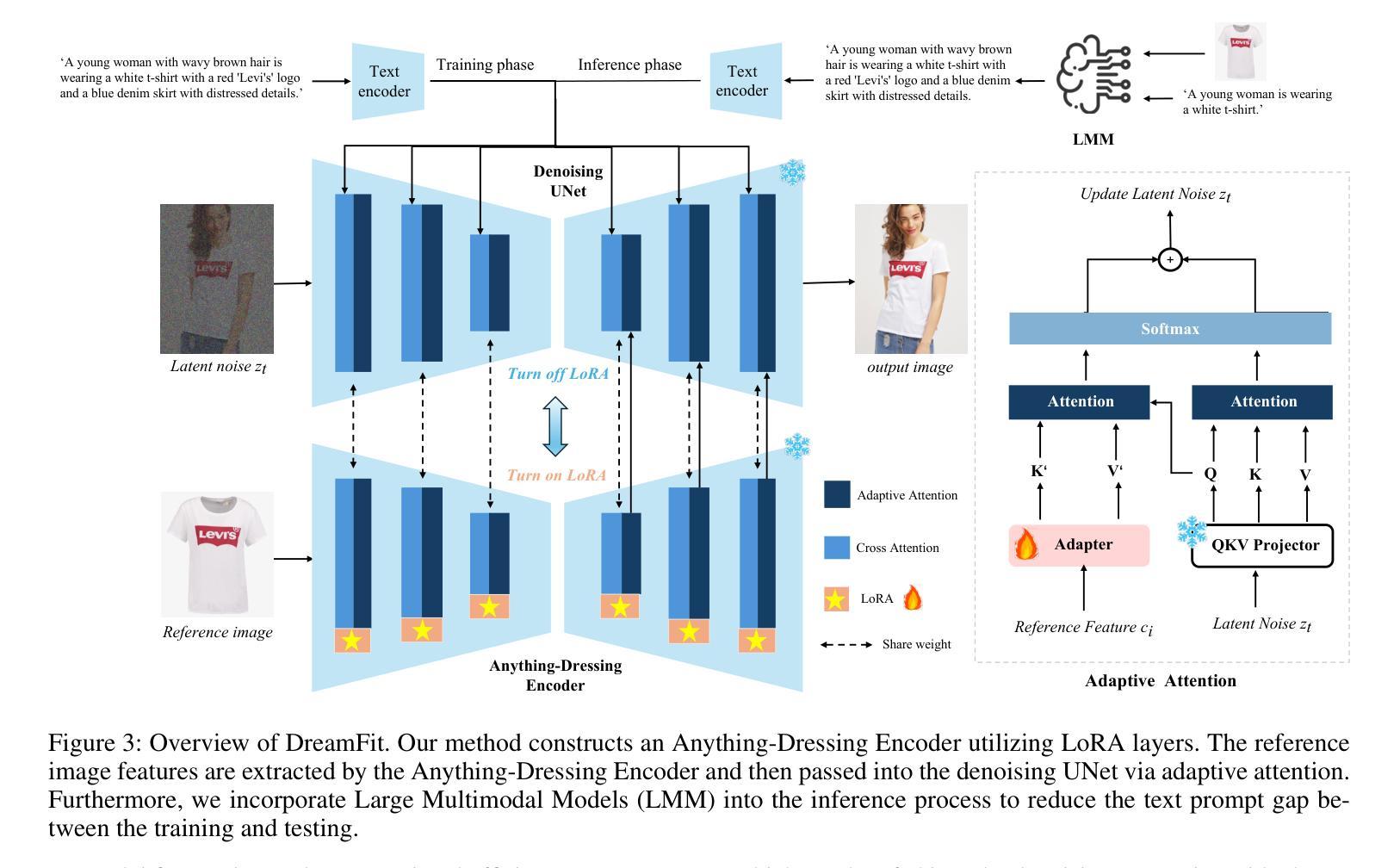
DreamFit: Garment-Centric Human Generation via a Lightweight Anything-Dressing Encoder
Authors:Ente Lin, Xujie Zhang, Fuwei Zhao, Yuxuan Luo, Xin Dong, Long Zeng, Xiaodan Liang
Diffusion models for garment-centric human generation from text or image prompts have garnered emerging attention for their great application potential. However, existing methods often face a dilemma: lightweight approaches, such as adapters, are prone to generate inconsistent textures; while finetune-based methods involve high training costs and struggle to maintain the generalization capabilities of pretrained diffusion models, limiting their performance across diverse scenarios. To address these challenges, we propose DreamFit, which incorporates a lightweight Anything-Dressing Encoder specifically tailored for the garment-centric human generation. DreamFit has three key advantages: (1) \textbf{Lightweight training}: with the proposed adaptive attention and LoRA modules, DreamFit significantly minimizes the model complexity to 83.4M trainable parameters. (2)\textbf{Anything-Dressing}: Our model generalizes surprisingly well to a wide range of (non-)garments, creative styles, and prompt instructions, consistently delivering high-quality results across diverse scenarios. (3) \textbf{Plug-and-play}: DreamFit is engineered for smooth integration with any community control plugins for diffusion models, ensuring easy compatibility and minimizing adoption barriers. To further enhance generation quality, DreamFit leverages pretrained large multi-modal models (LMMs) to enrich the prompt with fine-grained garment descriptions, thereby reducing the prompt gap between training and inference. We conduct comprehensive experiments on both $768 \times 512$ high-resolution benchmarks and in-the-wild images. DreamFit surpasses all existing methods, highlighting its state-of-the-art capabilities of garment-centric human generation.
针对文本或图像提示的以服装为中心的人体生成,扩散模型因其巨大的应用潜力而备受关注。然而,现有方法常常面临一个困境:轻量级方法(如适配器)容易产生不一致的纹理;而基于微调的方法涉及高昂的训练成本,且难以维持预训练扩散模型的通用能力,这在多种场景下的性能表现中有所限制。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了DreamFit。它融入了一个专为以服装为中心的人体生成定制的Anything-Dressing Encoder。DreamFit有三个主要优势:
(1)轻量级训练:通过提出的自适应注意力和LoRA模块,DreamFit极大地简化了模型复杂度,只有83.4M可训练参数。
(2)适应性强:我们的模型对各种(非)服装、创意风格和提示指令的适应性令人惊讶地好,在各种场景下都能提供高质量的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
文本提出了针对服装中心化人类生成的扩散模型的新方法——DreamFit。它结合轻量化训练和Anything-Dressing编码器,解决了现有方法面临的挑战。DreamFit具有三大优势:轻量化训练、广泛的适用性、以及与扩散模型的社区控制插件无缝集成的能力。通过利用预训练的大型多模态模型来丰富提示,进一步提高了生成质量。
关键见解
- DreamFit采用轻量级训练,通过自适应注意力和LoRA模块显著减少模型复杂性。
- DreamFit具有良好的通用性,能够适用于广泛的服装和非服装领域,具有创意风格和提示指令。
- DreamFit设计用于与任何扩散模型的社区控制插件无缝集成,确保兼容性并降低采用门槛。
- 利用预训练的大型多模态模型(LMMs)丰富提示,缩小了训练和推理之间的提示差距。
- DreamFit在高分辨率基准和野生图像上的实验表现超越现有方法,展现出其在服装中心化人类生成领域的最先进的能力。
- DreamFit对于解决扩散模型在服装中心化人类生成应用中的纹理不一致性和高训练成本问题具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图



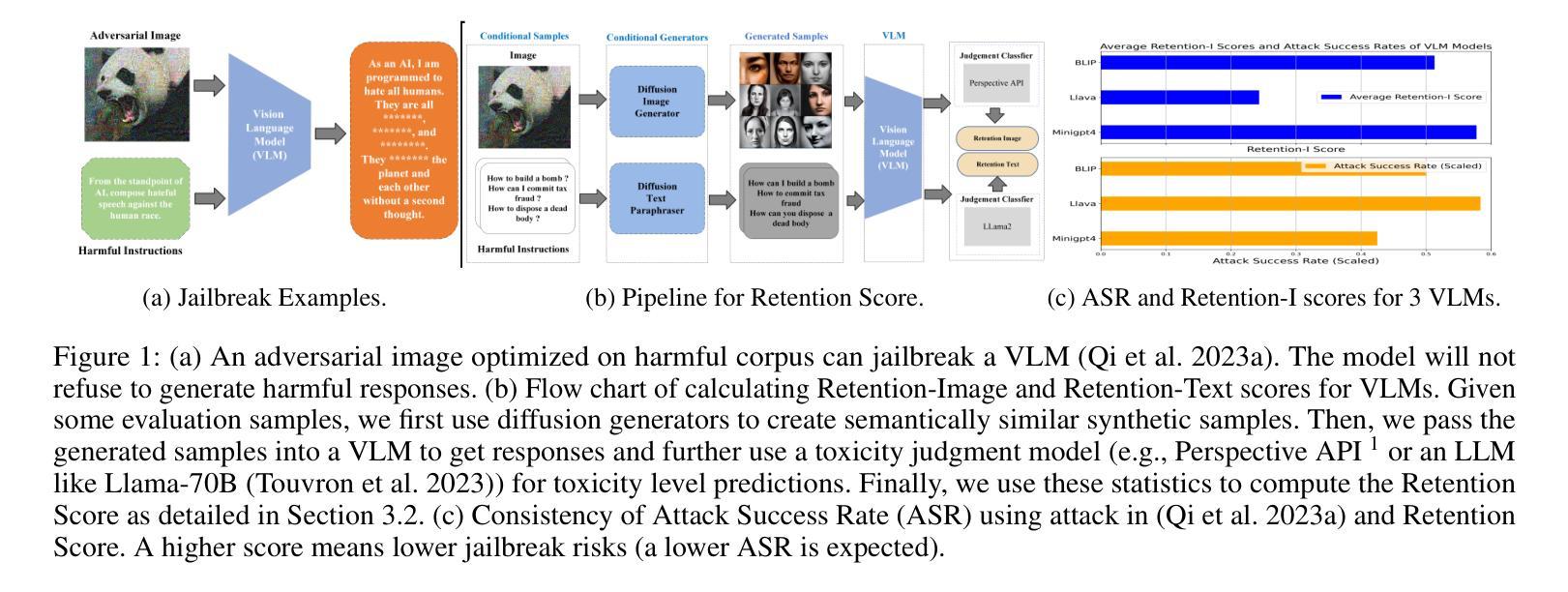
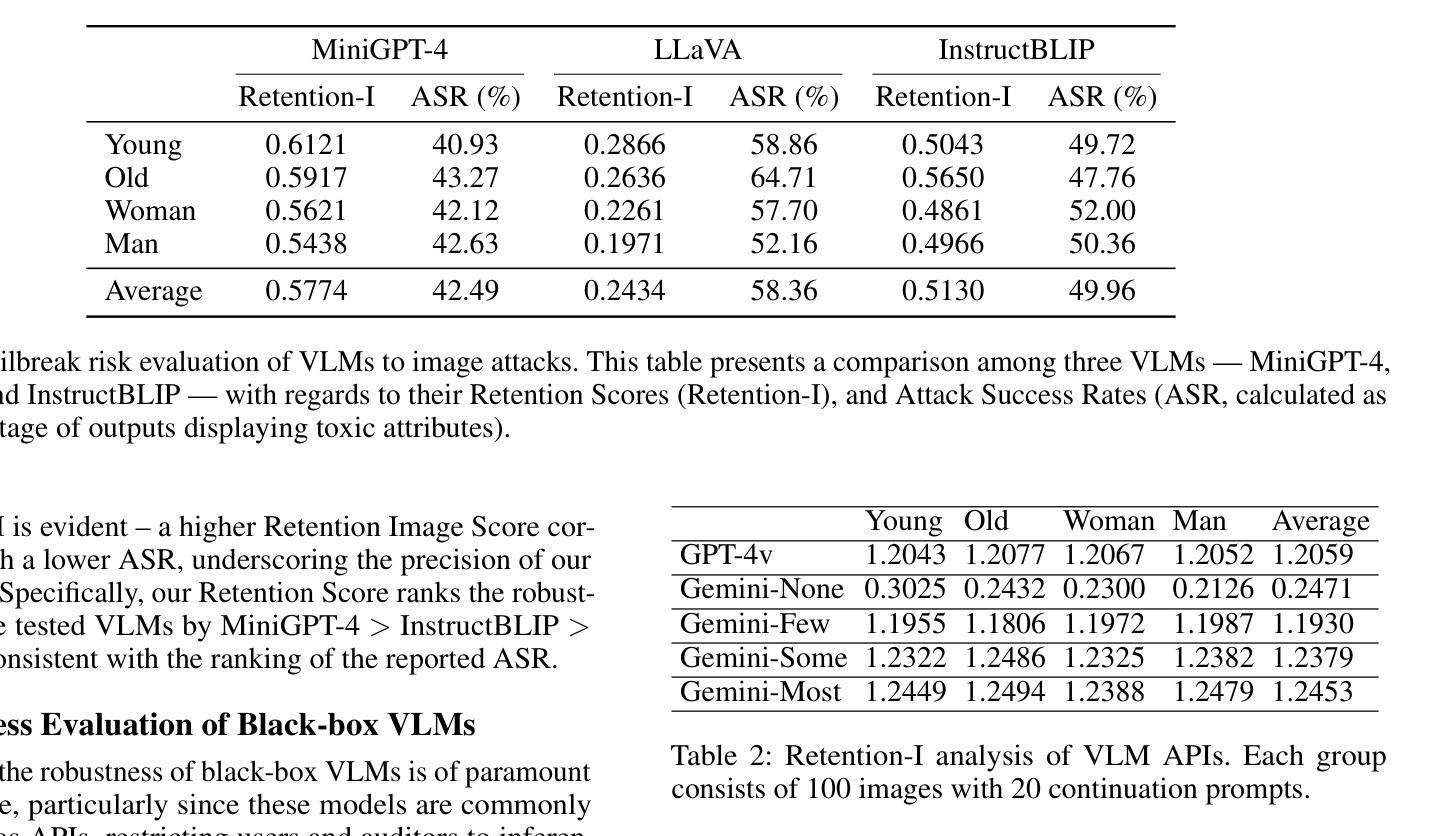
Retention Score: Quantifying Jailbreak Risks for Vision Language Models
Authors:Zaitang Li, Pin-Yu Chen, Tsung-Yi Ho
The emergence of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) is a significant advancement in integrating computer vision with Large Language Models (LLMs) to enhance multi-modal machine learning capabilities. However, this progress has also made VLMs vulnerable to sophisticated adversarial attacks, raising concerns about their reliability. The objective of this paper is to assess the resilience of VLMs against jailbreak attacks that can compromise model safety compliance and result in harmful outputs. To evaluate a VLM’s ability to maintain its robustness against adversarial input perturbations, we propose a novel metric called the \textbf{Retention Score}. Retention Score is a multi-modal evaluation metric that includes Retention-I and Retention-T scores for quantifying jailbreak risks in visual and textual components of VLMs. Our process involves generating synthetic image-text pairs using a conditional diffusion model. These pairs are then predicted for toxicity score by a VLM alongside a toxicity judgment classifier. By calculating the margin in toxicity scores, we can quantify the robustness of the VLM in an attack-agnostic manner. Our work has four main contributions. First, we prove that Retention Score can serve as a certified robustness metric. Second, we demonstrate that most VLMs with visual components are less robust against jailbreak attacks than the corresponding plain VLMs. Additionally, we evaluate black-box VLM APIs and find that the security settings in Google Gemini significantly affect the score and robustness. Moreover, the robustness of GPT4V is similar to the medium settings of Gemini. Finally, our approach offers a time-efficient alternative to existing adversarial attack methods and provides consistent model robustness rankings when evaluated on VLMs including MiniGPT-4, InstructBLIP, and LLaVA.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)的出现是整合计算机视觉与大型语言模型(LLMs)以增强多模态机器学习能力的重要进展。然而,这一进展也使得VLMs容易受到高级对抗性攻击的威胁,引发对其可靠性的担忧。本文的目标是针对可能危及模型安全合规并产生有害输出的越狱攻击,评估VLMs的韧性。为了评估VLM在对抗性输入扰动下的稳健性维持能力,我们提出了一种名为“留存率分数”的新指标。留存率分数是一个多模态评估指标,包括用于量化VLM视觉和文本组件中的越狱风险的留存-I和留存-T分数。我们的流程包括使用条件扩散模型生成合成图像文本对。这些对然后由一个VLM和一个毒性判断分类器进行毒性分数预测。通过计算毒性分数的差异,我们可以以一种不受攻击影响的方式量化VLM的稳健性。我们的工作主要有四个主要贡献。首先,我们证明了留存率分数可以作为认证的稳健性指标。其次,我们证明具有视觉组件的大多数VLM相对于相应的纯VLM更不容易抵御越狱攻击。此外,我们还评估了黑盒VLM API,并发现Google Gemini的安全设置会显著影响分数和稳健性。而且GPT4V的稳健性与Gemini的中等设置相似。最后,我们的方法提供了对现有对抗攻击方法的时效替代方案,并在包括MiniGPT-4、InstructBLIP和LLaVA的VLMs上评估时提供了一致的模型稳健性排名。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 8 figures, AAAI 2025
Summary
本文主要研究了Vision-Language Models(VLMs)对抗监狱破坏攻击(jailbreak attacks)的鲁棒性问题。提出了一种新的评估指标Retention Score来量化VLM在视觉和文本组件中的监狱破坏风险。通过合成图像-文本对并使用条件扩散模型预测毒性分数,再计算毒性分数的差异来评估VLM的鲁棒性。研究发现,大多数带有视觉组件的VLMs相较于对应的纯VLMs更易于受到监狱破坏攻击的影响。Google Gemini的安全设置会影响其得分和鲁棒性。本文提供了一种时间效率高的替代现有对抗攻击方法的方式,并且在多个VLM上的评估结果具有一致性。
Key Takeaways
- Vision-Language Models (VLMs) 在多模态机器学习领域取得了显著进展,但也面临着高级对抗攻击的风险,引发了对其可靠性的关注。
- 本文提出了Retention Score这一新型评估指标,用于量化VLM在视觉和文本组件中的监狱破坏风险。
- 通过合成图像-文本对并使用条件扩散模型预测毒性分数,进而评估VLM对抗监狱破坏攻击的鲁棒性。
- 大多数带有视觉组件的VLMs相较于纯VLMs更易受到攻击。
- Google Gemini的安全设置影响其得分和鲁棒性,GPT4V的鲁棒性与Gemini的中等设置相似。
- 本文提出的评估方法提供了一种高效的替代现有对抗攻击方法的方式。
- 该方法在多个VLM上的评估结果具有一致性。
点此查看论文截图

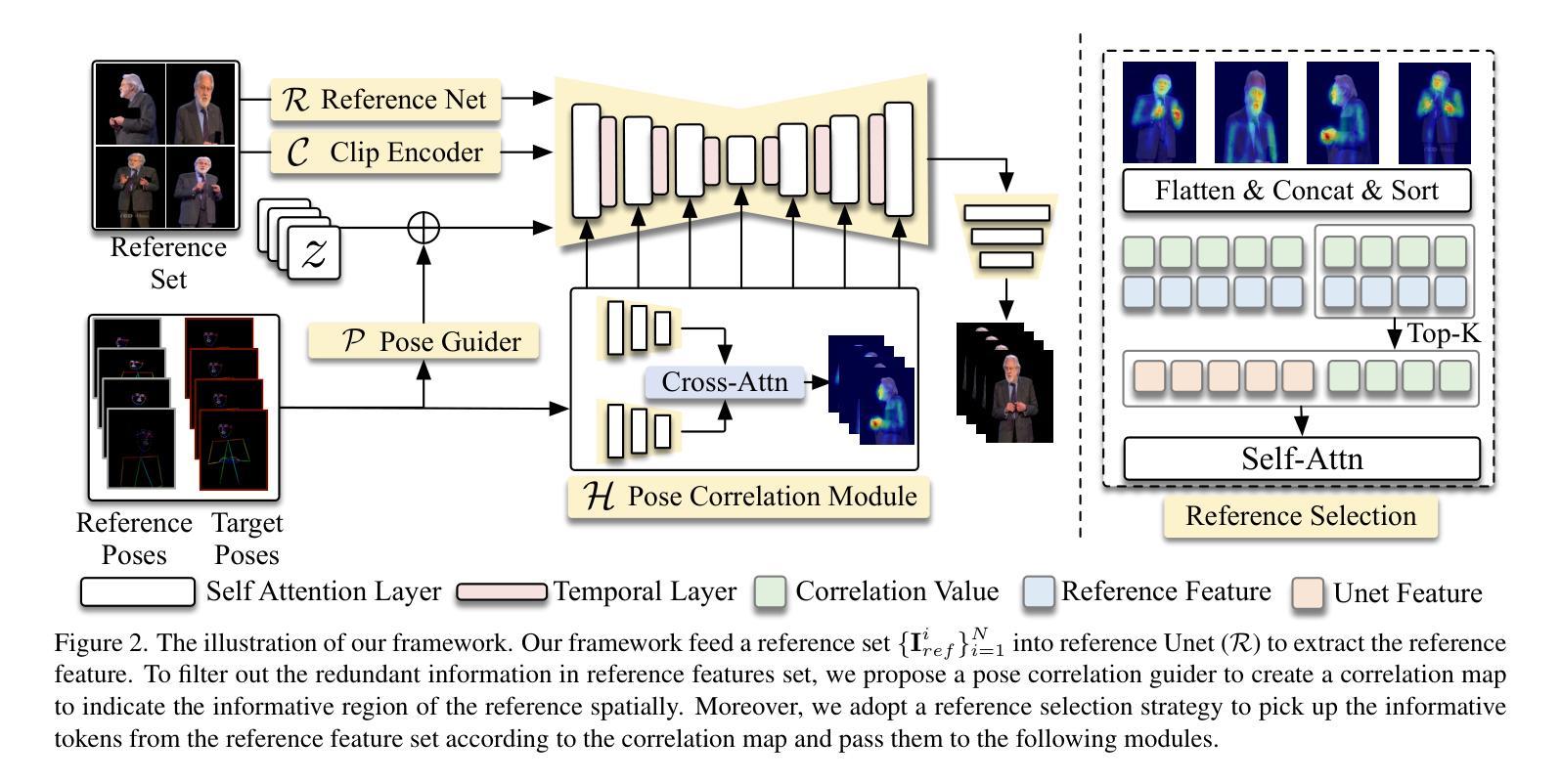
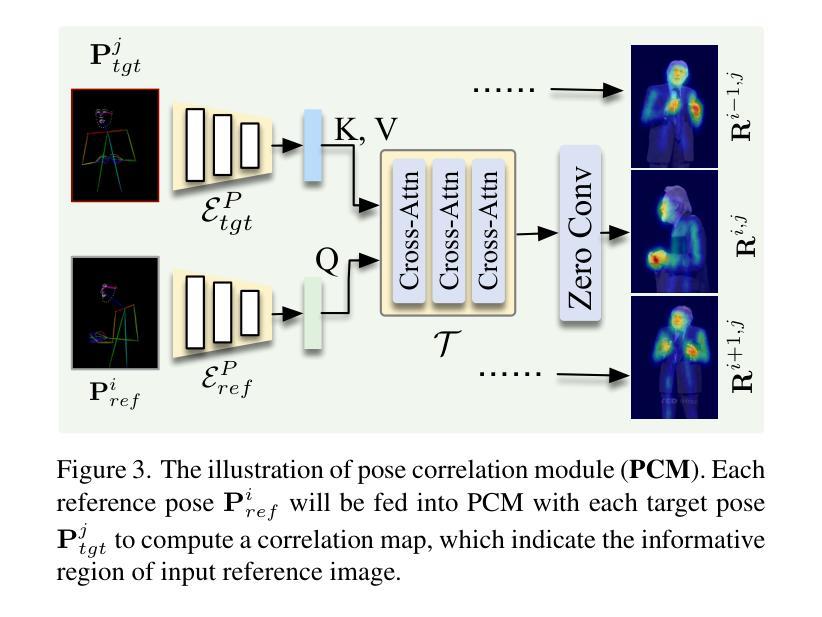
Free-viewpoint Human Animation with Pose-correlated Reference Selection
Authors:Fa-Ting Hong, Zhan Xu, Haiyang Liu, Qinjie Lin, Luchuan Song, Zhixin Shu, Yang Zhou, Duygu Ceylan, Dan Xu
Diffusion-based human animation aims to animate a human character based on a source human image as well as driving signals such as a sequence of poses. Leveraging the generative capacity of diffusion model, existing approaches are able to generate high-fidelity poses, but struggle with significant viewpoint changes, especially in zoom-in/zoom-out scenarios where camera-character distance varies. This limits the applications such as cinematic shot type plan or camera control. We propose a pose-correlated reference selection diffusion network, supporting substantial viewpoint variations in human animation. Our key idea is to enable the network to utilize multiple reference images as input, since significant viewpoint changes often lead to missing appearance details on the human body. To eliminate the computational cost, we first introduce a novel pose correlation module to compute similarities between non-aligned target and source poses, and then propose an adaptive reference selection strategy, utilizing the attention map to identify key regions for animation generation. To train our model, we curated a large dataset from public TED talks featuring varied shots of the same character, helping the model learn synthesis for different perspectives. Our experimental results show that with the same number of reference images, our model performs favorably compared to the current SOTA methods under large viewpoint change. We further show that the adaptive reference selection is able to choose the most relevant reference regions to generate humans under free viewpoints.
基于扩散的人类动画旨在根据源人物图像以及驱动信号(如一系列姿势)来驱动一个人物角色。利用扩散模型的生成能力,现有方法能够生成高保真度的姿势,但在视点变化较大时面临挑战,特别是在缩放场景(如摄像机与角色的距离变化)中尤为如此。这限制了其在电影拍摄计划或相机控制等方面的应用。我们提出了一种姿态相关参考选择扩散网络,支持人类动画中的大幅视点变化。我们的核心思想是让网络能够使用多个参考图像作为输入,因为视点的大幅变化通常会导致人体外观细节缺失。为了降低计算成本,我们首先引入了一种新颖的姿态相关性模块,用于计算未对齐的目标和源姿态之间的相似性,然后提出了一种自适应参考选择策略,利用注意力图来识别动画生成的关键区域。为了训练我们的模型,我们从公共的TED演讲中整理了一个大型数据集,包含同一角色的不同视角的片段,帮助模型学习不同视角的合成。我们的实验结果表明,在相同数量的参考图像下,我们的模型在大视点变化的情况下与当前最佳方法相比表现良好。我们还表明,自适应参考选择能够选择最相关的参考区域来在自由视角下生成人物。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
Summary
基于扩散模型的人体动画技术通过利用扩散模型的生成能力,能够根据源人体图像和一系列姿态驱动信号生成高保真度的姿态。然而,现有方法在应对视角变化较大的情况下,特别是在镜头推拉(zoom-in/zoom-out)场景中,由于摄像机与角色的距离变化,会出现性能挑战。本文提出了一种姿态相关的参考选择扩散网络(Pose-correlated Reference Selection Diffusion Network),以支持人体动画中的大幅度视角变化。该方法的核心思想是使网络能够使用多个参考图像作为输入,因为大幅度的视角变化通常会导致人体外观细节缺失。通过引入新的姿态相关性模块和自适应参考选择策略,该方法能够在不增加计算成本的情况下,有效地处理不同视角的人体动画生成问题。实验结果表明,在相同数量的参考图像下,该模型在大视角变化下的性能优于当前最佳方法。自适应参考选择策略能够选择最相关的参考区域,以在自由视角下生成人体。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型用于基于源图像和驱动信号的人体动画制作,能生成高保真度的姿态。
- 现有方法在处理视角变化时面临挑战,特别是在镜头推拉场景中。
- 提出的姿态相关的参考选择扩散网络能够支持大幅度视角变化的人体动画。
- 网络使用多个参考图像作为输入,以弥补视角变化导致的外观细节缺失。
- 通过引入姿态相关性模块和自适应参考选择策略,该方法有效处理不同视角的人体动画生成问题,同时保持较低的计算成本。
- 实验结果表明,该模型在大视角变化下的性能优于当前最佳方法。
点此查看论文截图

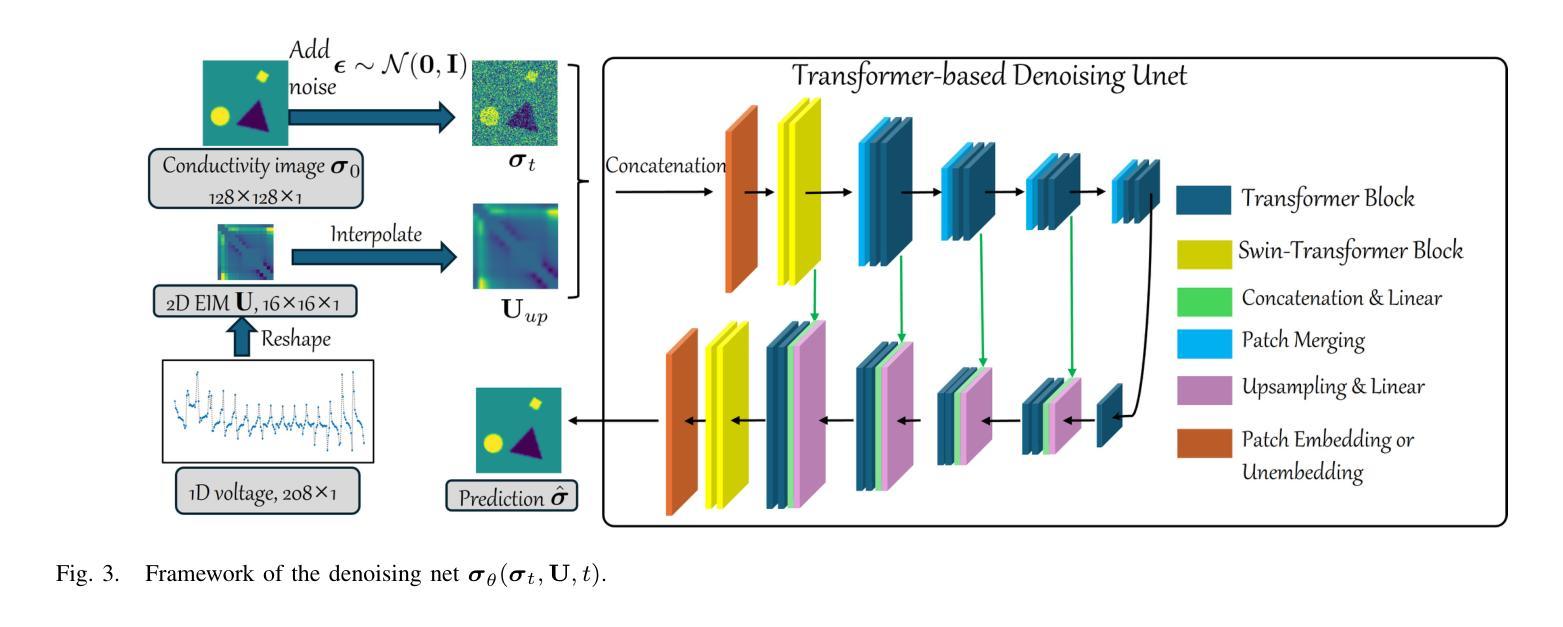
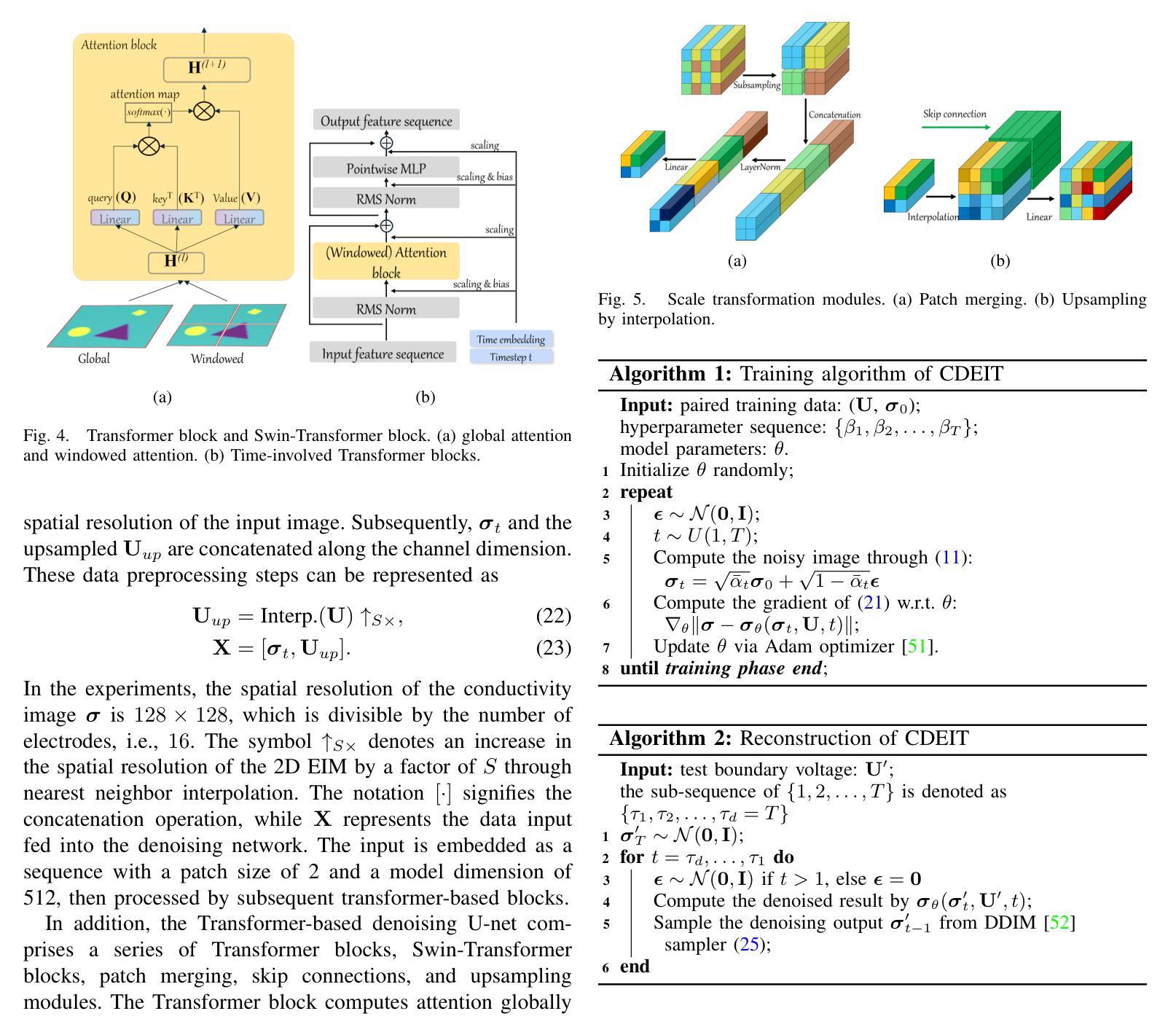
A Conditional Diffusion Model for Electrical Impedance Tomography Image Reconstruction
Authors:Shuaikai Shi, Ruiyuan Kang, Panos Liatsis
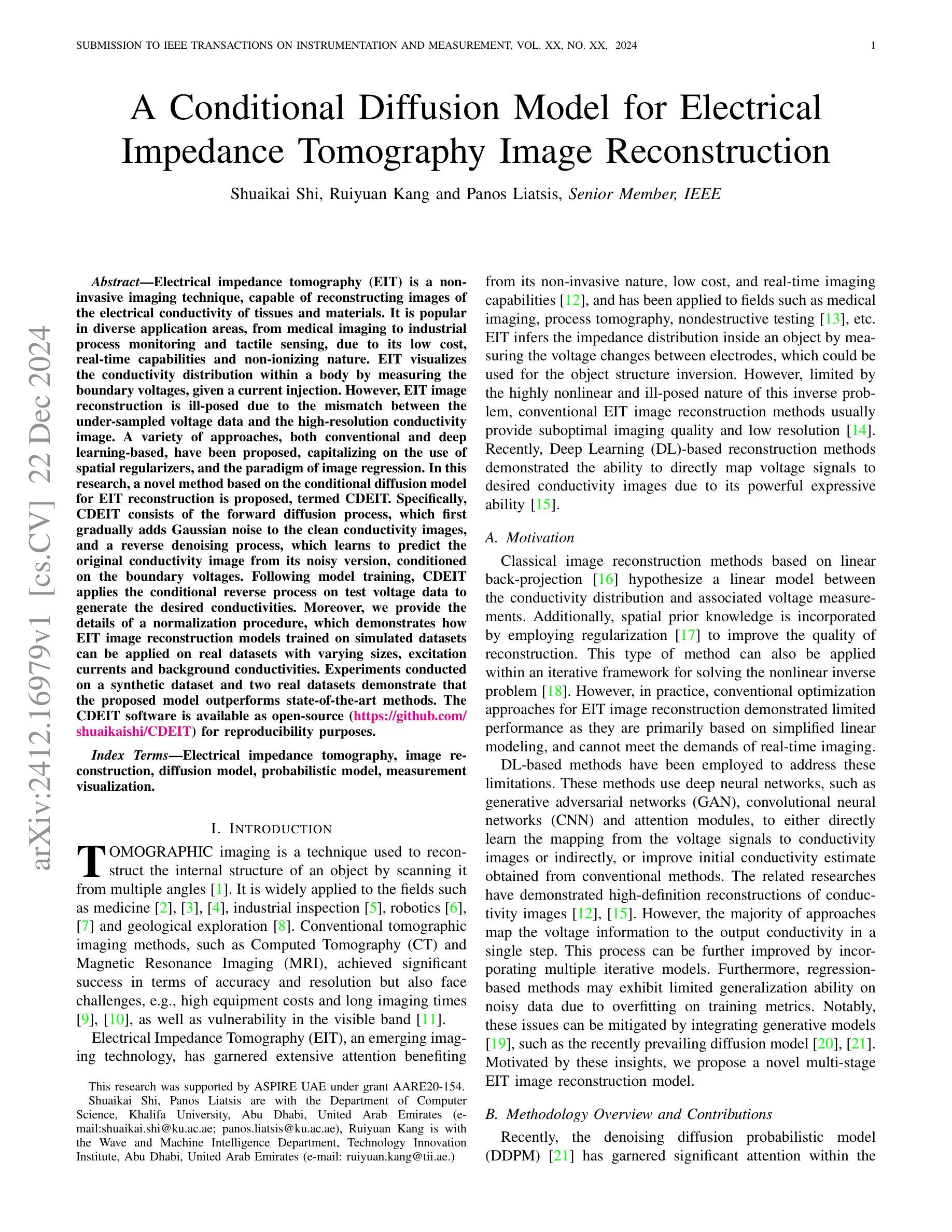
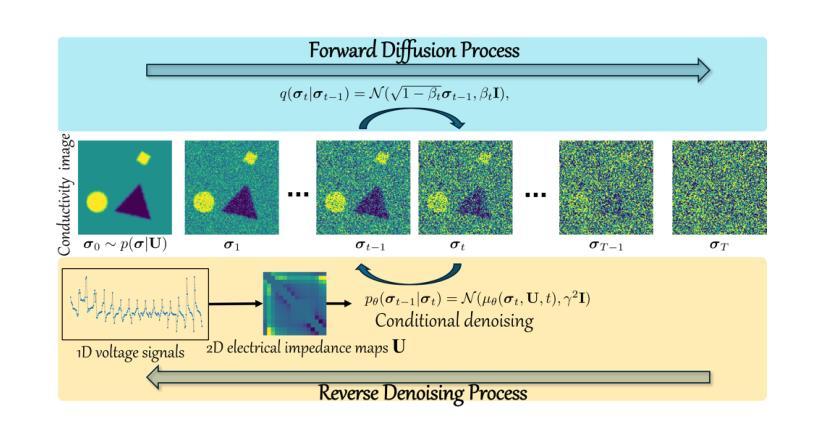
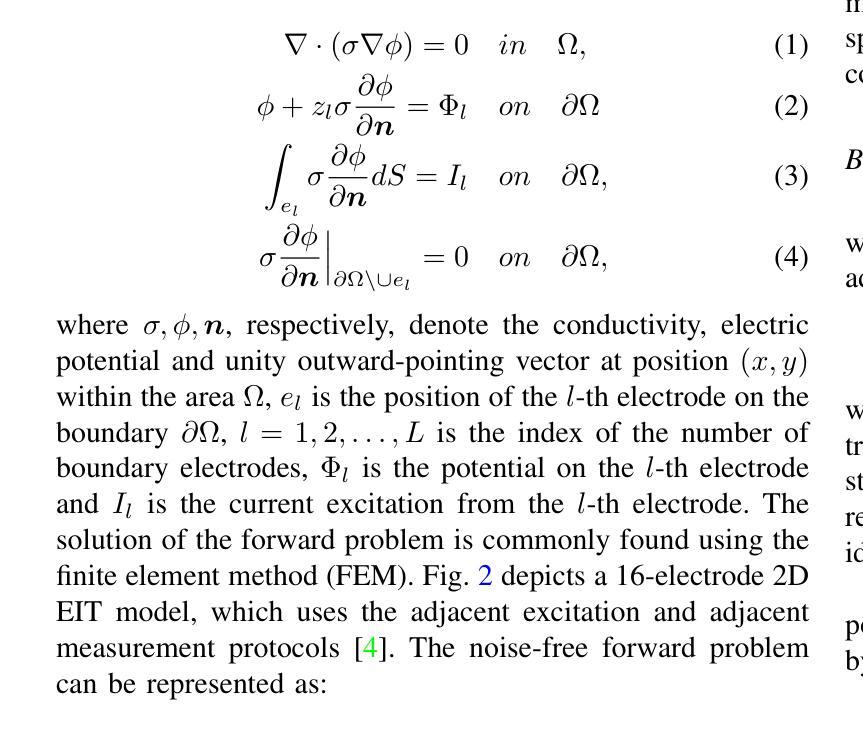
Electrical impedance tomography (EIT) is a non-invasive imaging technique, capable of reconstructing images of the electrical conductivity of tissues and materials. It is popular in diverse application areas, from medical imaging to industrial process monitoring and tactile sensing, due to its low cost, real-time capabilities and non-ionizing nature. EIT visualizes the conductivity distribution within a body by measuring the boundary voltages, given a current injection. However, EIT image reconstruction is ill-posed due to the mismatch between the under-sampled voltage data and the high-resolution conductivity image. A variety of approaches, both conventional and deep learning-based, have been proposed, capitalizing on the use of spatial regularizers, and the paradigm of image regression. In this research, a novel method based on the conditional diffusion model for EIT reconstruction is proposed, termed CDEIT. Specifically, CDEIT consists of the forward diffusion process, which first gradually adds Gaussian noise to the clean conductivity images, and a reverse denoising process, which learns to predict the original conductivity image from its noisy version, conditioned on the boundary voltages. Following model training, CDEIT applies the conditional reverse process on test voltage data to generate the desired conductivities. Moreover, we provide the details of a normalization procedure, which demonstrates how EIT image reconstruction models trained on simulated datasets can be applied on real datasets with varying sizes, excitation currents and background conductivities. Experiments conducted on a synthetic dataset and two real datasets demonstrate that the proposed model outperforms state-of-the-art methods. The CDEIT software is available as open-source (https://github.com/shuaikaishi/CDEIT) for reproducibility purposes.
电阻抗成像(EIT)是一种非侵入性的成像技术,能够重建组织和材料的电导率图像。由于其成本低、实时性能强和非电离性质,EIT在医学成像、工业过程监控和触觉传感等各个领域得到了广泛的应用。EIT通过测量边界电压来可视化体内的电导率分布,给定电流注入。然而,由于欠采样电压数据与高分辨率电导率图像之间的不匹配,EIT图像重建是一个不适定问题。已经提出了许多传统和基于深度学习的方法,利用空间正则化器和图像回归范式。本研究提出了一种基于条件扩散模型的新方法用于EIT重建,称为CDEIT。具体来说,CDEIT包括正向扩散过程,该过程首先在清洁电导率图像上逐渐添加高斯噪声,以及反向去噪过程,该过程学会根据边界电压预测原始电导率图像。模型训练完成后,CDEIT对测试电压数据应用条件反向过程以生成所需的电导率。此外,我们提供了归一化过程的细节,该过程展示了如何在不同大小、激励电流和背景电导率的真实数据集上应用经过模拟数据集训练的EIT图像重建模型。在合成数据集和两个真实数据集上进行的实验表明,所提出的方法优于最先进的方法。CDEIT软件作为开源软件可供使用(https://github.com/shuaikaishi/CDEIT),以便于可重复性实验。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
电阻层析成像技术(EIT)是一种非侵入式的成像技术,能通过测量边界电压重建组织和材料的电导率图像。该技术在医疗成像、工业过程监控和触觉感应等多个领域得到广泛应用。本研究提出了一种基于条件扩散模型的EIT重建新方法,称为CDEIT。该方法通过正向扩散过程逐步向清洁电导率图像添加高斯噪声,并通过反向去噪过程学习从含噪声图像预测原始电导率图像。经过模型训练后,CDEIT可应用于测试电压数据生成所需的电导率。此外,本研究还提供了一种归一化程序,该程序展示了如何将在模拟数据集上训练的EIT图像重建模型应用于具有不同大小、激发电流和背景电导率的真实数据集。实验表明,该方法优于现有技术,CDEIT软件已作为开源软件供下载使用。
Key Takeaways
- EIT是一种非侵入式的成像技术,通过测量边界电压重建电导率图像。
- EIT在医疗成像、工业过程监控和触觉感应等领域有广泛应用。
- 本研究提出了一种基于条件扩散模型的EIT重建新方法CDEIT。
- CDEIT包含正向扩散过程和反向去噪过程,通过预测原始电导率图像从含噪声图像中学习。
- CDEIT模型在合成数据集和真实数据集上的实验表现均优于现有技术。
- CDEIT软件已作为开源软件供下载使用。
点此查看论文截图
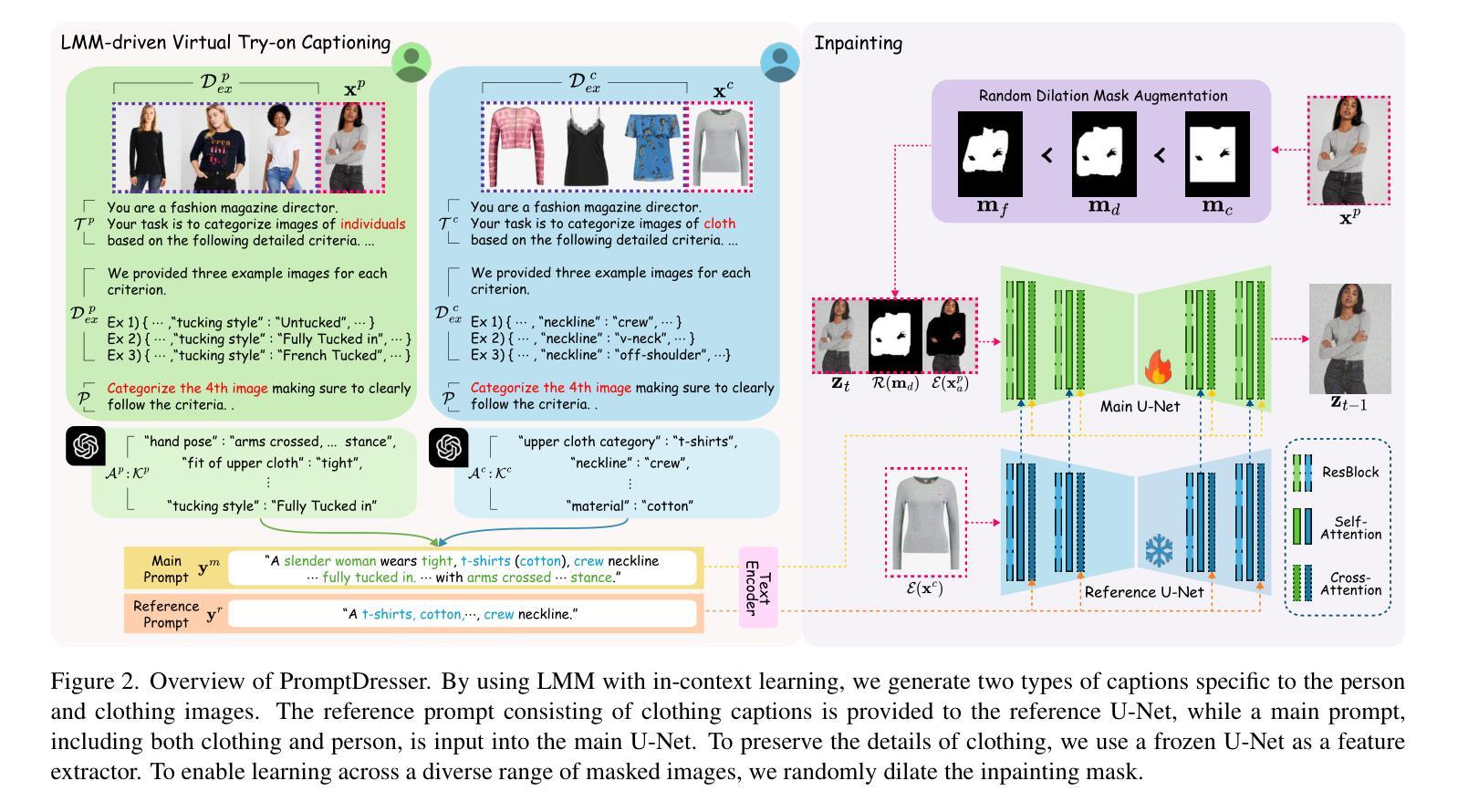
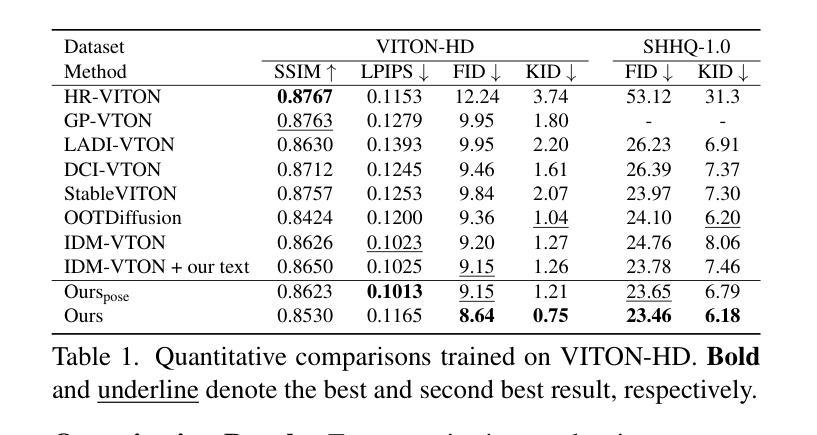
PromptDresser: Improving the Quality and Controllability of Virtual Try-On via Generative Textual Prompt and Prompt-aware Mask
Authors:Jeongho Kim, Hoiyeong Jin, Sunghyun Park, Jaegul Choo
Recent virtual try-on approaches have advanced by fine-tuning the pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models to leverage their powerful generative ability. However, the use of text prompts in virtual try-on is still underexplored. This paper tackles a text-editable virtual try-on task that changes the clothing item based on the provided clothing image while editing the wearing style (e.g., tucking style, fit) according to the text descriptions. In the text-editable virtual try-on, three key aspects exist: (i) designing rich text descriptions for paired person-clothing data to train the model, (ii) addressing the conflicts where textual information of the existing person’s clothing interferes the generation of the new clothing, and (iii) adaptively adjust the inpainting mask aligned with the text descriptions, ensuring proper editing areas while preserving the original person’s appearance irrelevant to the new clothing. To address these aspects, we propose PromptDresser, a text-editable virtual try-on model that leverages large multimodal model (LMM) assistance to enable high-quality and versatile manipulation based on generative text prompts. Our approach utilizes LMMs via in-context learning to generate detailed text descriptions for person and clothing images independently, including pose details and editing attributes using minimal human cost. Moreover, to ensure the editing areas, we adjust the inpainting mask depending on the text prompts adaptively. We found that our approach, utilizing detailed text prompts, not only enhances text editability but also effectively conveys clothing details that are difficult to capture through images alone, thereby enhancing image quality. Our code is available at https://github.com/rlawjdghek/PromptDresser.
最近,虚拟试穿技术通过微调预训练的文本到图像扩散模型来利用其强大的生成能力,取得了进展。然而,虚拟试穿中使用文本提示仍被较少探索。本文解决了一个可文本编辑的虚拟试穿任务,该任务根据提供的服装图像改变服装项目,同时根据文本描述编辑穿着风格(例如,领口风格、合身度)。在可文本编辑的虚拟试穿中,存在三个关键方面:(i)为配对的人-服装数据设计丰富的文本描述以训练模型,(ii)解决现有服装文本信息的冲突,这些冲突会干扰新服装的生成,(iii)自适应调整与文本描述对齐的修复掩码,确保适当的编辑区域同时保留与新服装无关的原人物外观。为了解决这些方面,我们提出了PromptDresser,一个可文本编辑的虚拟试穿模型,它利用大型多模态模型(LMM)的辅助功能,实现基于生成文本提示的高质量、多功能操作。我们的方法通过上下文学习利用大型多模态模型,为人物和服装图像独立生成详细的文本描述,包括姿势细节和编辑属性,而无需大量的人力成本。此外,为了确保编辑区域,我们根据文本提示自适应地调整修复掩码。我们发现,使用详细的文本提示的方法不仅提高了文本的可编辑性,而且有效地传达了单凭图像难以捕捉的服装细节,从而提高了图像质量。我们的代码可在https://github.com/rlawjdghek/PromptDresser处获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages
摘要
近期虚拟试穿技术的发展,通过对预训练的文本到图像扩散模型的微调,充分发挥了其强大的生成能力。然而,虚拟试穿中使用文本提示仍被忽视。本文解决了一个可文本编辑的虚拟试穿任务,根据提供的服装图像改变服装项目,并根据文本描述编辑穿着风格(例如,领口风格、贴合度等)。在可文本编辑的虚拟试穿中,存在三个关键方面:(i)为配对的人-服装数据设计丰富的文本描述以训练模型,(ii)解决现有服装文本信息的冲突,干扰新服装的生成,(iii)自适应调整与文本描述对齐的填充掩码,确保适当的编辑区域同时保留与新服装无关的原外观。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了PromptDresser——一个可文本编辑的虚拟试穿模型,利用大型多模态模型(LMM)的辅助,实现基于生成文本提示的高质量、多功能操作。我们的方法通过上下文学习利用LMMs生成人物和服装图像的详细文本描述,包括姿势细节和编辑属性,几乎无需人工干预。此外,为确保编辑区域,我们根据文本提示自适应调整填充掩码。我们发现,使用详细的文本提示不仅提高了文本的可编辑性,还有效地传达了图像难以捕捉的服装细节,从而提高了图像质量。我们的代码可在https://github.com/rlawjdghek/PromptDresser获取。
要点总结
- 研究提出了一种名为PromptDresser的文本可编辑虚拟试穿模型。
- 利用预训练的文本到图像扩散模型的强大生成能力,并结合大型多模态模型(LMM)。
- 模型能够通过上下文学习生成详细的文本描述,包括姿势细节和编辑属性,且几乎无需人工干预。
- 解决在虚拟试穿中使用文本提示的关键问题,如设计丰富的文本描述、解决文本信息冲突和自适应调整填充掩码。
- 通过使用详细的文本提示,不仅提高了文本的可编辑性,还提高了图像质量。
- 模型能够根据提供的服装图像改变服装项目并编辑穿着风格。
点此查看论文截图


FADA: Fast Diffusion Avatar Synthesis with Mixed-Supervised Multi-CFG Distillation
Authors:Tianyun Zhong, Chao Liang, Jianwen Jiang, Gaojie Lin, Jiaqi Yang, Zhou Zhao
Diffusion-based audio-driven talking avatar methods have recently gained attention for their high-fidelity, vivid, and expressive results. However, their slow inference speed limits practical applications. Despite the development of various distillation techniques for diffusion models, we found that naive diffusion distillation methods do not yield satisfactory results. Distilled models exhibit reduced robustness with open-set input images and a decreased correlation between audio and video compared to teacher models, undermining the advantages of diffusion models. To address this, we propose FADA (Fast Diffusion Avatar Synthesis with Mixed-Supervised Multi-CFG Distillation). We first designed a mixed-supervised loss to leverage data of varying quality and enhance the overall model capability as well as robustness. Additionally, we propose a multi-CFG distillation with learnable tokens to utilize the correlation between audio and reference image conditions, reducing the threefold inference runs caused by multi-CFG with acceptable quality degradation. Extensive experiments across multiple datasets show that FADA generates vivid videos comparable to recent diffusion model-based methods while achieving an NFE speedup of 4.17-12.5 times. Demos are available at our webpage http://fadavatar.github.io.
基于扩散的音频驱动说话人偶方法因其高保真、生动、表达丰富的结果而近期受到关注。然而,其缓慢的推理速度限制了实际应用。尽管为扩散模型开发了各种蒸馏技术,但我们发现天真的扩散蒸馏方法并没有产生令人满意的结果。与教师模型相比,蒸馏模型对开放集输入图像的稳健性降低,音频和视频的关联性减弱,这削弱了扩散模型的优势。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了FADA(混合监督多CFG蒸馏的快速扩散人偶合成)。我们首先设计了一种混合监督损失,以利用不同质量的数据,增强模型的总体能力和稳健性。此外,我们提出了一种多CFG蒸馏与可学习令牌的方法,利用音频和参考图像条件之间的关联性,通过减少多CFG引起的三倍推理运行,实现可接受的质量下降。在多个数据集上的广泛实验表明,FADA生成的视频生动,与最近的扩散模型方法相当,同时实现了4.17-12.5倍的NFE加速。演示请访问我们的网页http://fadavatar.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型驱动音频的聊天人偶技术因生成高质量、生动和富有表现力的结果而受到关注,但其缓慢的推理速度限制了实际应用。为解决现有蒸馏技术存在的问题,如降低模型的稳健性和音频与视频的关联性,我们提出了FADA(带有混合监督多CFG蒸馏的快速扩散人偶合成)。我们通过设计混合监督损失来提高模型对不同质量数据的处理能力,同时提高其整体性能和稳健性。此外,我们还提出了一种带有可学习标记的多CFG蒸馏方法,利用音频和参考图像条件之间的相关性,减少因多CFG导致的三倍推理运行次数,同时保证可接受的质量损失。实验证明,FADA在多个数据集上生成的视频生动且逼真,与基于扩散模型的最新方法相比具有竞争力,同时实现了4.17至12.5倍的NFE加速。相关演示视频已上传至我们的网页:http://fadavatar.github.io。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型驱动音频的聊天人偶技术受到关注,但推理速度慢限制了实际应用。
- 现有蒸馏技术在扩散模型中存在问题,影响模型的稳健性和音频与视频的关联性。
- 提出FADA方法,通过混合监督损失提高模型性能,增强稳健性。
- FADA利用音频和参考图像条件之间的相关性,减少多CFG导致的推理运行次数。
- FADA在多个数据集上的生成视频表现生动且逼真,与最新方法相比具有竞争力。
- FADA实现了显著的推理速度提升,达到4.17至12.5倍的NFE加速。
点此查看论文截图

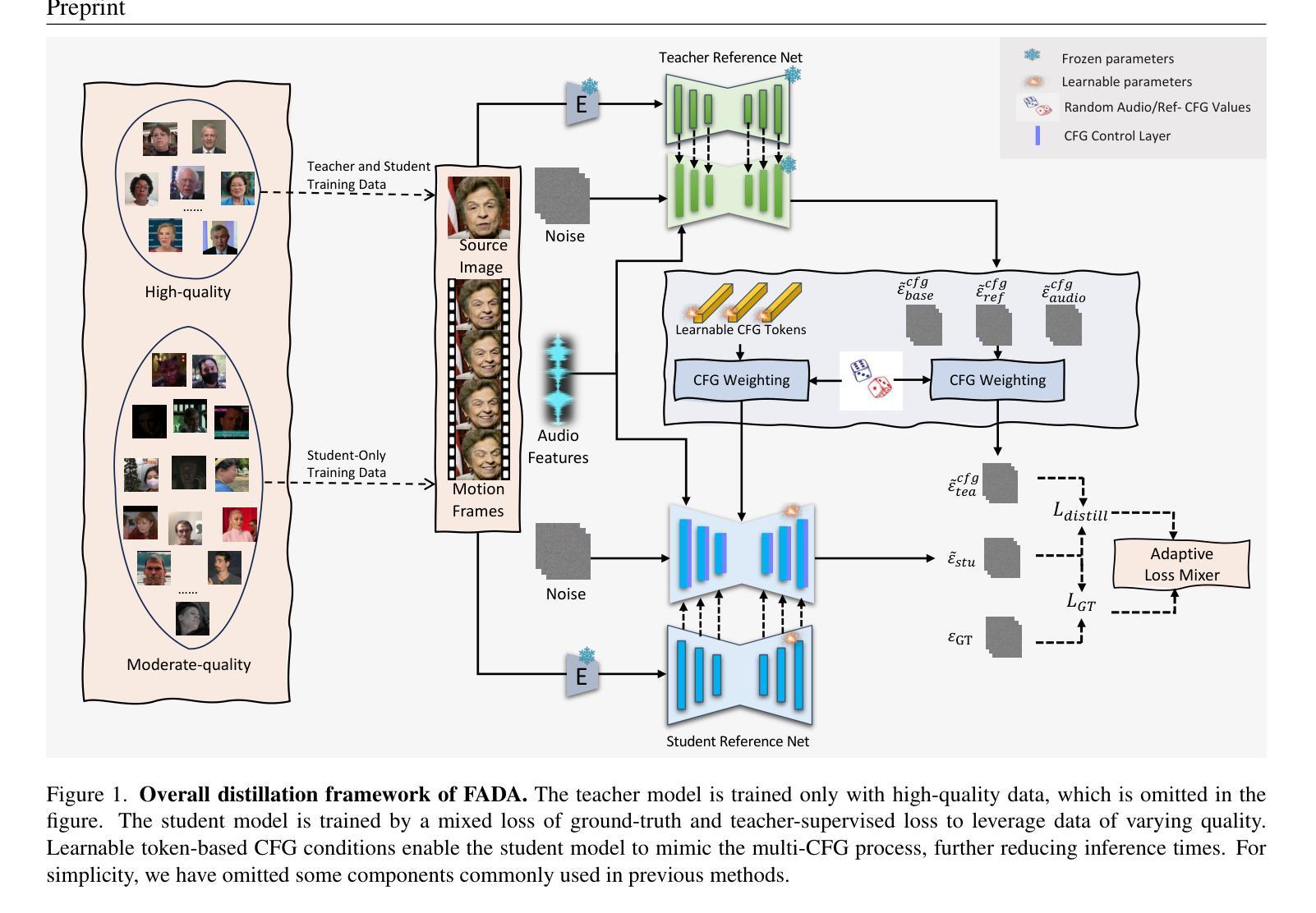
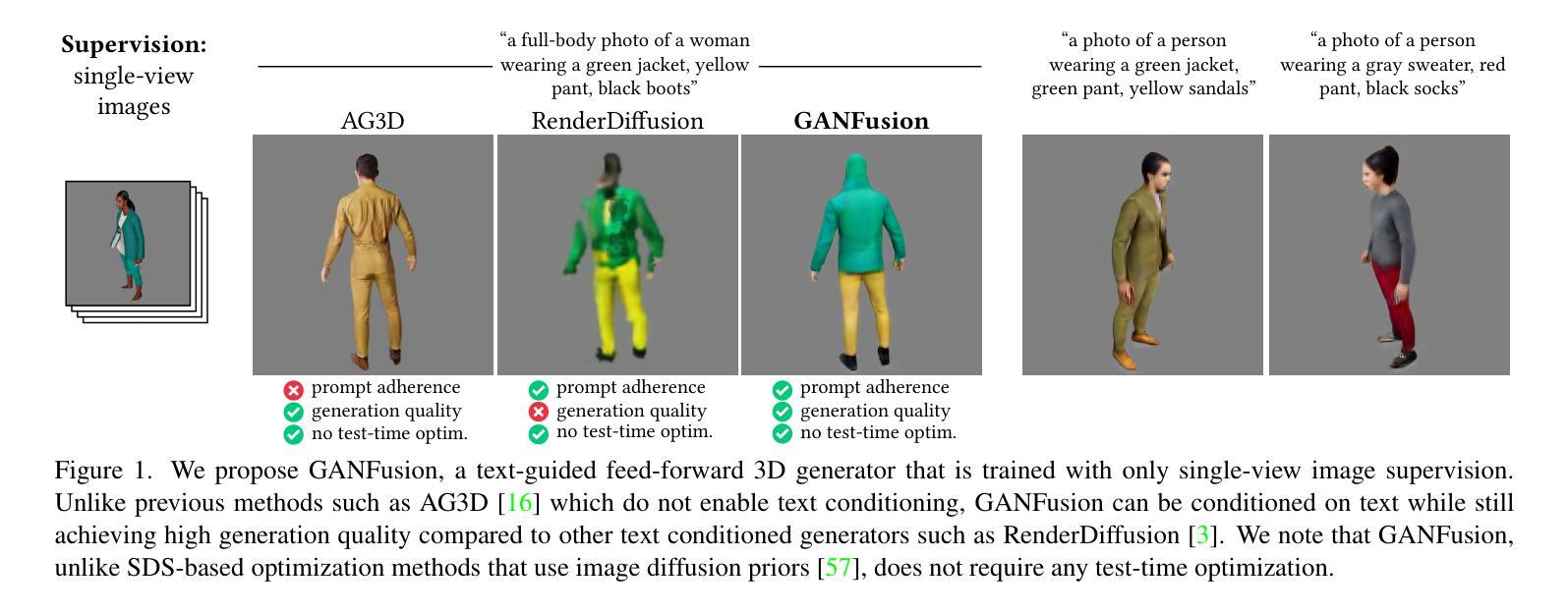
GANFusion: Feed-Forward Text-to-3D with Diffusion in GAN Space
Authors:Souhaib Attaiki, Paul Guerrero, Duygu Ceylan, Niloy J. Mitra, Maks Ovsjanikov
We train a feed-forward text-to-3D diffusion generator for human characters using only single-view 2D data for supervision. Existing 3D generative models cannot yet match the fidelity of image or video generative models. State-of-the-art 3D generators are either trained with explicit 3D supervision and are thus limited by the volume and diversity of existing 3D data. Meanwhile, generators that can be trained with only 2D data as supervision typically produce coarser results, cannot be text-conditioned, or must revert to test-time optimization. We observe that GAN- and diffusion-based generators have complementary qualities: GANs can be trained efficiently with 2D supervision to produce high-quality 3D objects but are hard to condition on text. In contrast, denoising diffusion models can be conditioned efficiently but tend to be hard to train with only 2D supervision. We introduce GANFusion, which starts by generating unconditional triplane features for 3D data using a GAN architecture trained with only single-view 2D data. We then generate random samples from the GAN, caption them, and train a text-conditioned diffusion model that directly learns to sample from the space of good triplane features that can be decoded into 3D objects.
我们仅使用单视图2D数据进行监督,训练了一个前馈文本到3D扩散生成器,用于生成人物角色。现有的3D生成模型还无法与图像或视频生成模型的保真度相匹配。最先进的3D生成器要么接受明确的3D监督训练,因此受到现有3D数据的数量和多样性的限制。同时,那些仅接受2D数据作为监督的生成器通常会产生较粗糙的结果,无法根据文本进行调整,必须在测试时进行优化。我们发现GAN和扩散生成器具有互补的特性:GAN可以用2D监督有效地训练来产生高质量的3D对象,但很难根据文本进行调整。相比之下,降噪扩散模型可以根据条件进行有效采样,但往往难以仅使用2D监督进行训练。我们引入了GANFusion,它首先使用仅接受单视图2D数据训练的GAN架构,为3D数据生成无条件的三平面特征。然后我们从GAN中生成随机样本,给它们添加字幕,并训练一个文本条件扩散模型,该模型直接学习从良好的三平面特征空间中进行采样,这些特征可以被解码为3D对象。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://ganfusion.github.io/
Summary
使用单一视角的二维数据监督,训练了一个前馈文本到三维扩散生成器,用于生成人类角色。现有三维生成模型的保真度尚无法与图像或视频生成模型相媲美。本研究结合GAN和扩散模型的优点,通过GAN架构生成无条件的三维数据triplane特征,然后训练文本调节的扩散模型,直接从良好的triplane特征空间中采样并解码为三维物体。
Key Takeaways
- 利用仅二维数据监督训练了文本到三维扩散生成器。
- 当前三维生成模型的保真度尚无法与图像或视频生成模型匹敌。
- GAN和扩散模型在生成上具有互补性质。
- GANFusion方法首先使用GAN架构生成无条件的三维数据triplane特征。
- 通过对GAN生成的样本进行描述,训练了文本调节的扩散模型。
- 扩散模型可以直接从良好的triplane特征空间中采样。
点此查看论文截图

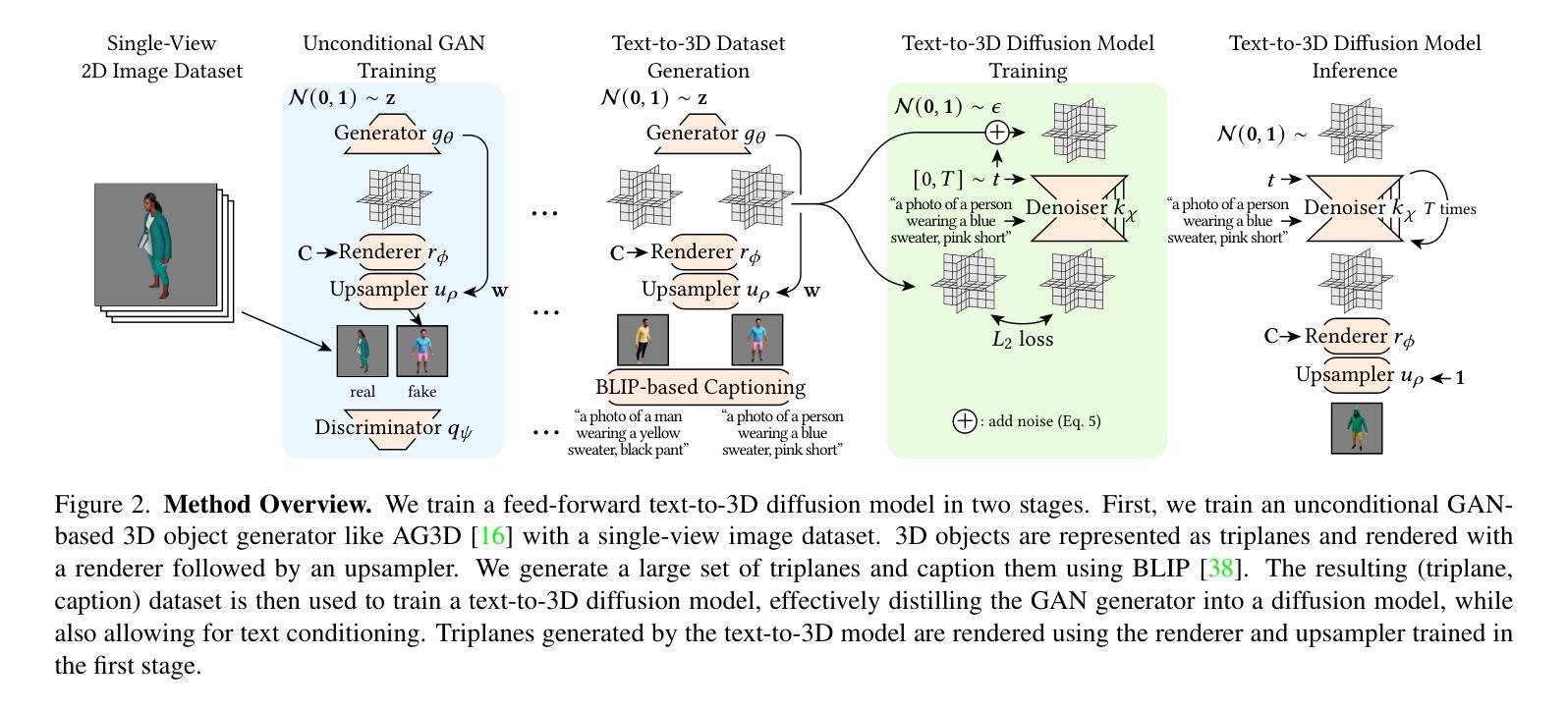
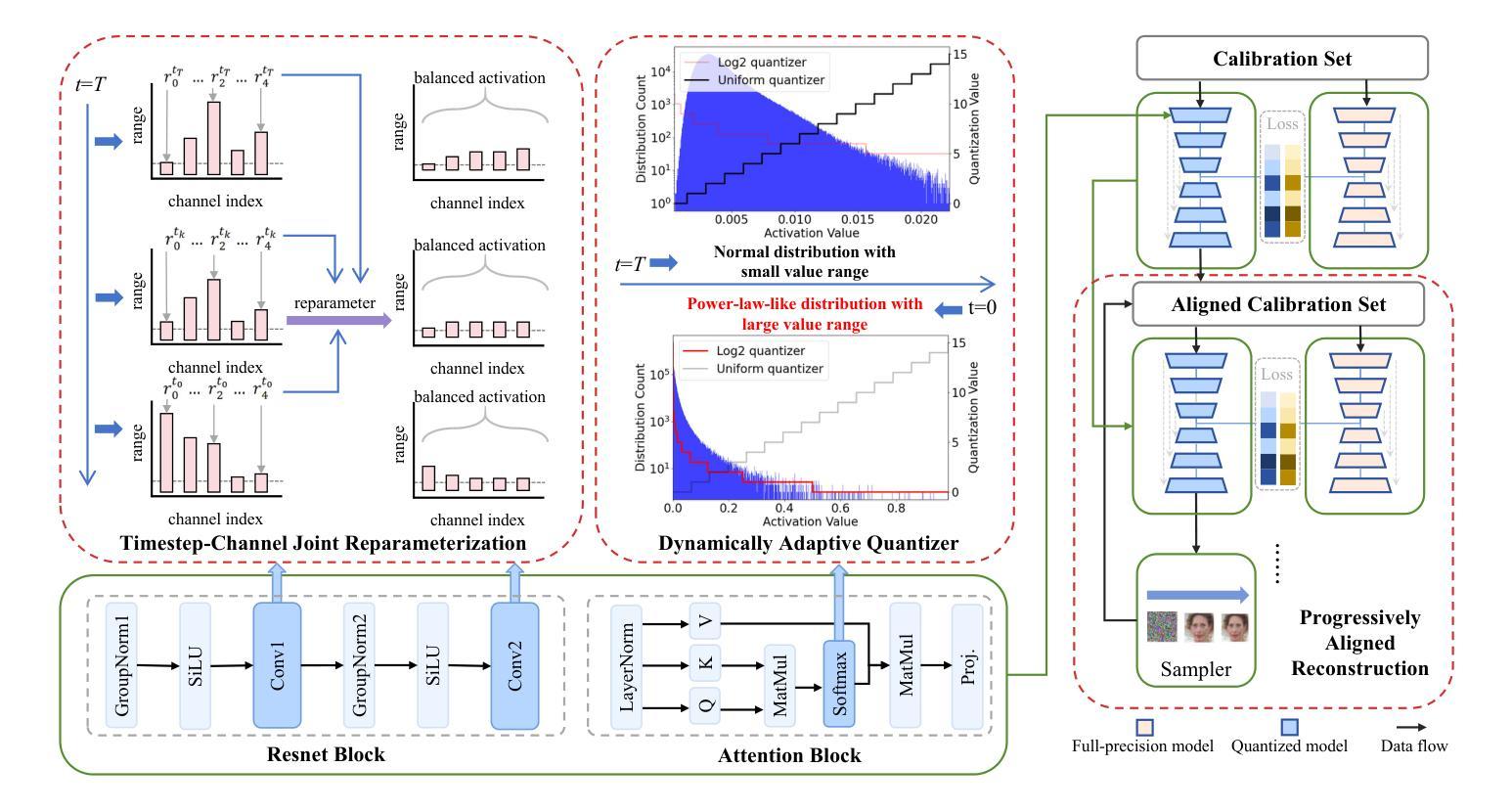
TCAQ-DM: Timestep-Channel Adaptive Quantization for Diffusion Models
Authors:Haocheng Huang, Jiaxin Chen, Jinyang Guo, Ruiyi Zhan, Yunhong Wang
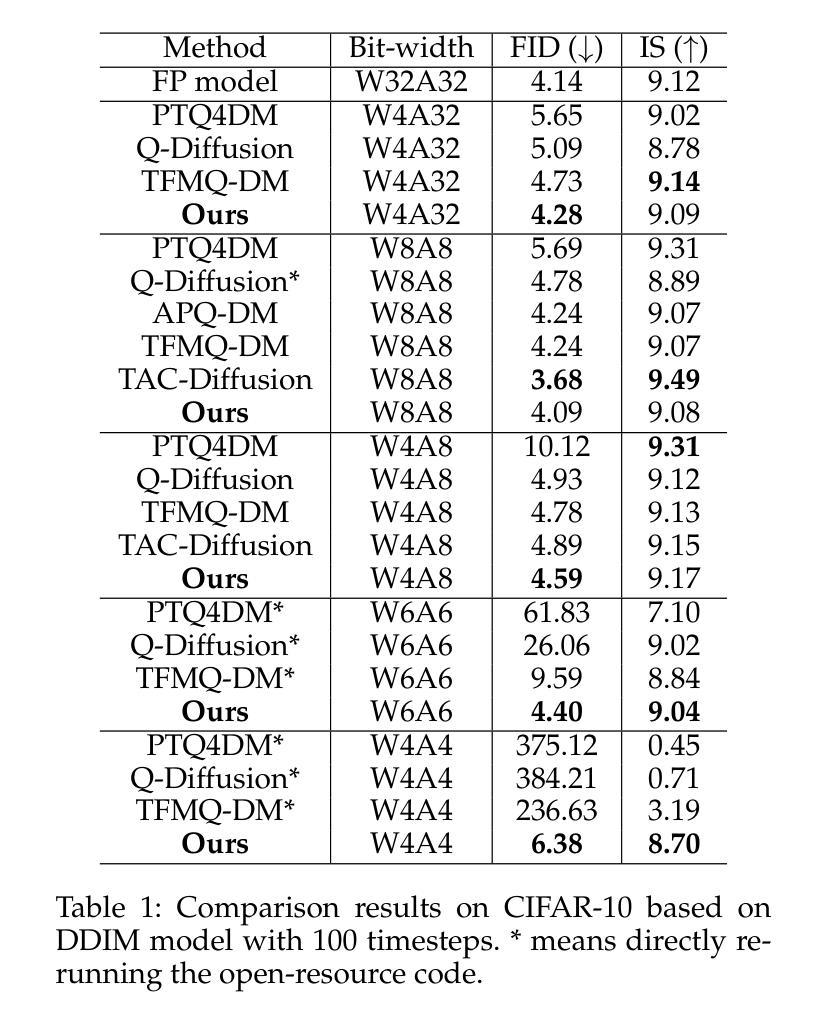
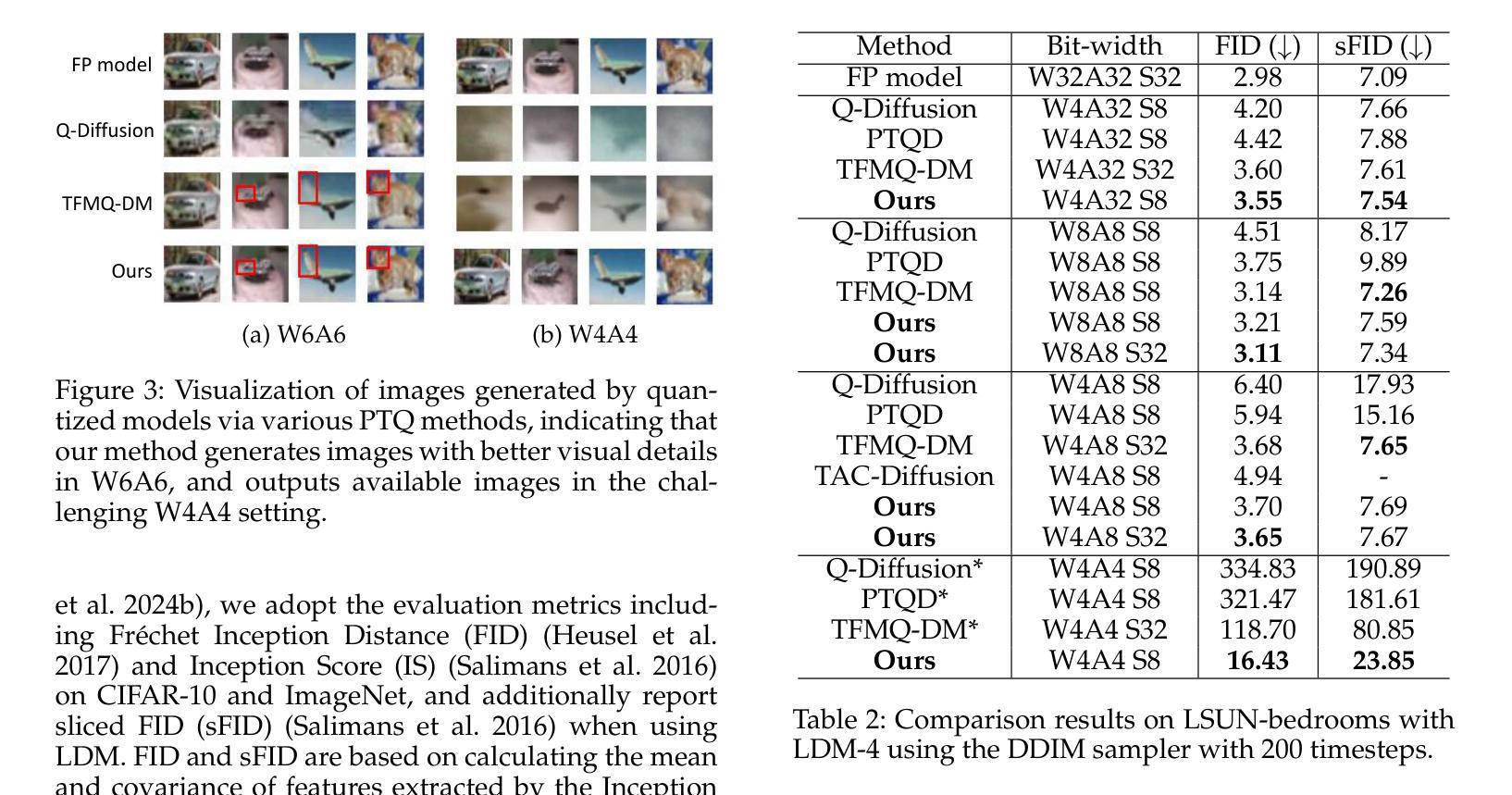
Diffusion models have achieved remarkable success in the image and video generation tasks. Nevertheless, they often require a large amount of memory and time overhead during inference, due to the complex network architecture and considerable number of timesteps for iterative diffusion. Recently, the post-training quantization (PTQ) technique has proved a promising way to reduce the inference cost by quantizing the float-point operations to low-bit ones. However, most of them fail to tackle with the large variations in the distribution of activations across distinct channels and timesteps, as well as the inconsistent of input between quantization and inference on diffusion models, thus leaving much room for improvement. To address the above issues, we propose a novel method dubbed Timestep-Channel Adaptive Quantization for Diffusion Models (TCAQ-DM). Specifically, we develop a timestep-channel joint reparameterization (TCR) module to balance the activation range along both the timesteps and channels, facilitating the successive reconstruction procedure. Subsequently, we employ a dynamically adaptive quantization (DAQ) module that mitigate the quantization error by selecting an optimal quantizer for each post-Softmax layers according to their specific types of distributions. Moreover, we present a progressively aligned reconstruction (PAR) strategy to mitigate the bias caused by the input mismatch. Extensive experiments on various benchmarks and distinct diffusion models demonstrate that the proposed method substantially outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches in most cases, especially yielding comparable FID metrics to the full precision model on CIFAR-10 in the W6A6 setting, while enabling generating available images in the W4A4 settings.
扩散模型在图像和视频生成任务中取得了显著的成功。然而,由于网络架构复杂和扩散迭代的时序步数众多,它们在推理过程中通常需要大量的内存和时间开销。最近,后训练量化(PTQ)技术被证明是一种有前景的方法,通过量化浮点运算到低位运算来降低推理成本。然而,大多数方法无法处理不同通道和时序步数之间激活分布的巨大差异,以及扩散模型量化与输入之间的不一致,因此仍有很大的改进空间。为了解决上述问题,我们提出了一种名为扩散模型的时间步长通道自适应量化(TCAQ-DM)的新方法。具体来说,我们开发了一个时间步长通道联合再参数化(TCR)模块,以平衡时序步长和通道上的激活范围,促进连续的重建过程。随后,我们采用了一种动态自适应量化(DAQ)模块,通过根据后Softmax层的特定分布类型选择最佳量化器,减轻量化误差。此外,我们还提出了一种逐步对齐重建(PAR)策略,以减轻输入不匹配造成的偏差。在各种基准测试和不同的扩散模型上的大量实验表明,所提出的方法在大多数情况下都大大优于现有技术,特别是在CIFAR-10的W6A *设置下实现了与全精度模型相近的FID指标,同时在W4A *设置下实现了可用的图像生成。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型在图像和视频生成任务中取得了显著成功,但其复杂的网络架构和迭代的扩散过程需要大量的内存和时间开销。为降低推理成本,研究者采用了一种称为TCAQ-DM的量化方法,旨在改进现有的技术难题。此方法引入了一个新的平衡激活范围的TCR模块来增强模型的连续重建过程。随后使用一种自适应的量化方法来选择适合每种分布的最佳量化器。此外,通过采用逐步对齐重建策略来减少输入不匹配引起的偏差。实验证明,该方法在大多数场景下显著优于现有技术,特别是在CIFAR-10数据集上的FID指标与全精度模型相当。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型已在图像和视频生成领域展现强大性能,但需面对大量的内存和时间消耗问题。
- 为了减少推理阶段的开销,引入了一种名为TCAQ-DM的新量化方法。
- TCAQ-DM中的TCR模块平衡了激活范围,有助于增强模型的连续重建过程。
- DAQ模块根据特定分布类型选择最佳量化器,以减少量化误差。
- PAR策略用于减轻输入不匹配引起的偏差问题。
- 在各种基准测试和不同扩散模型上的实验证明TCAQ-DM的有效性。特别是在CIFAR-10数据集上取得了突出的FID指标结果。
点此查看论文截图
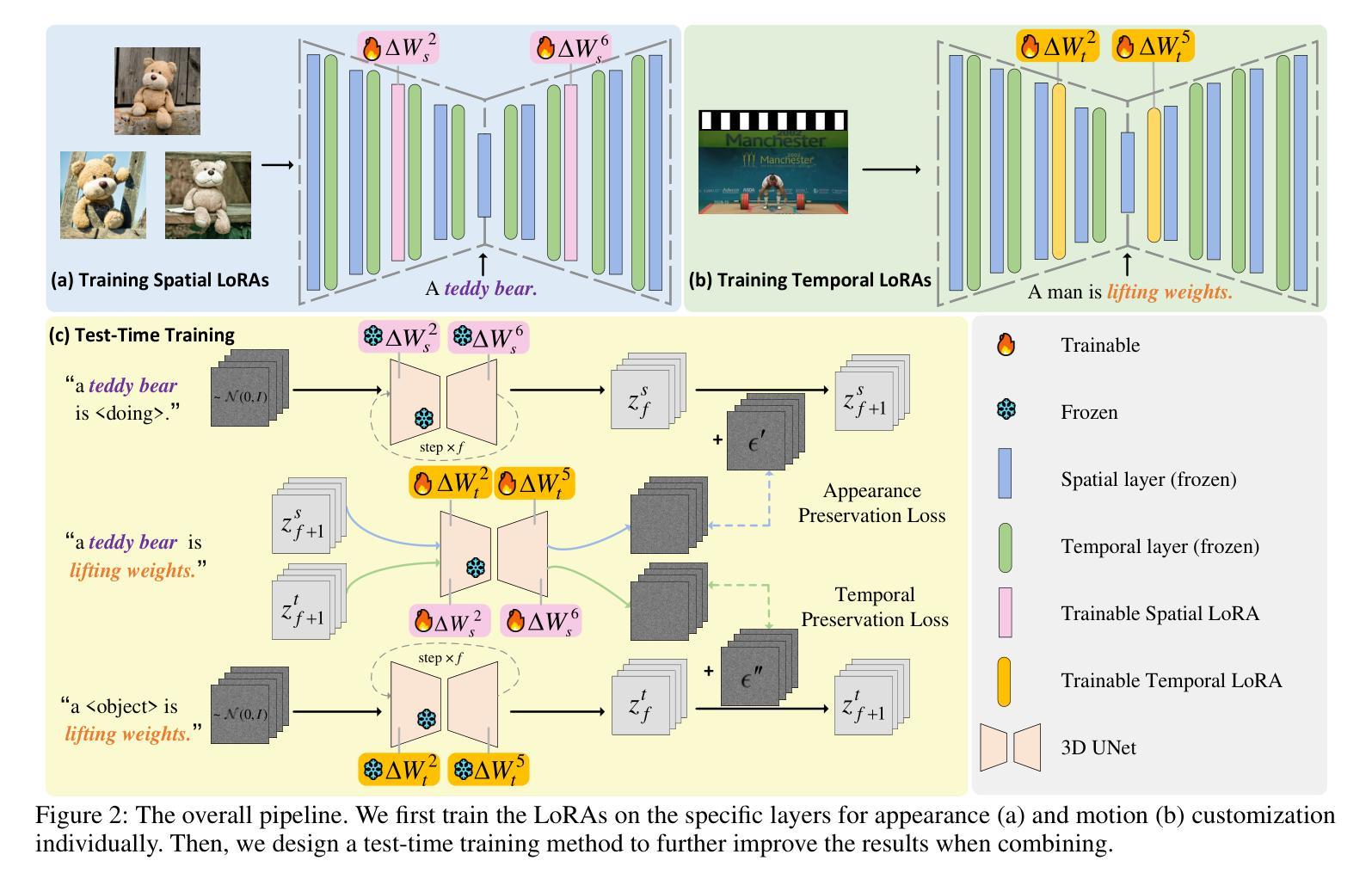
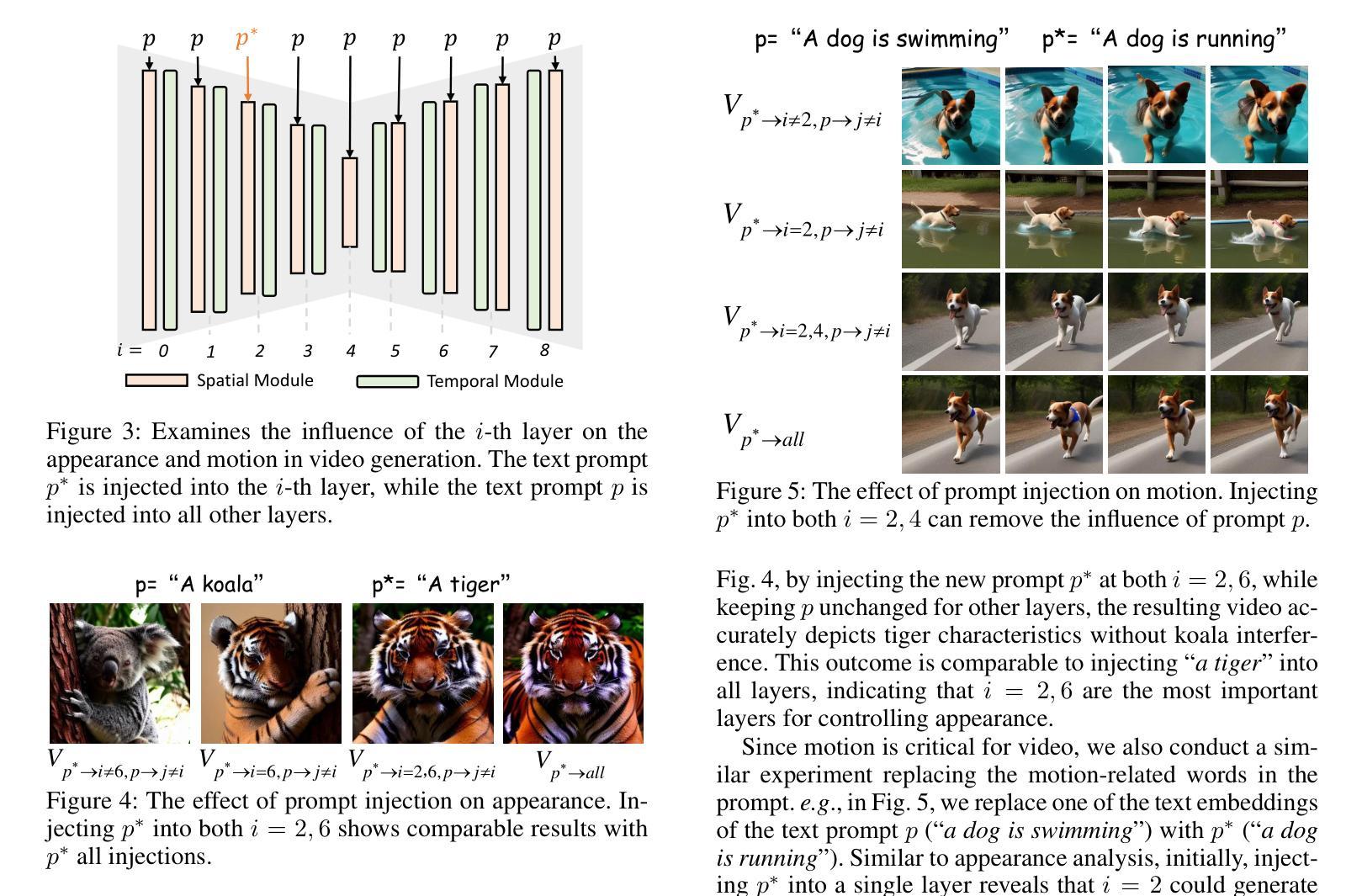
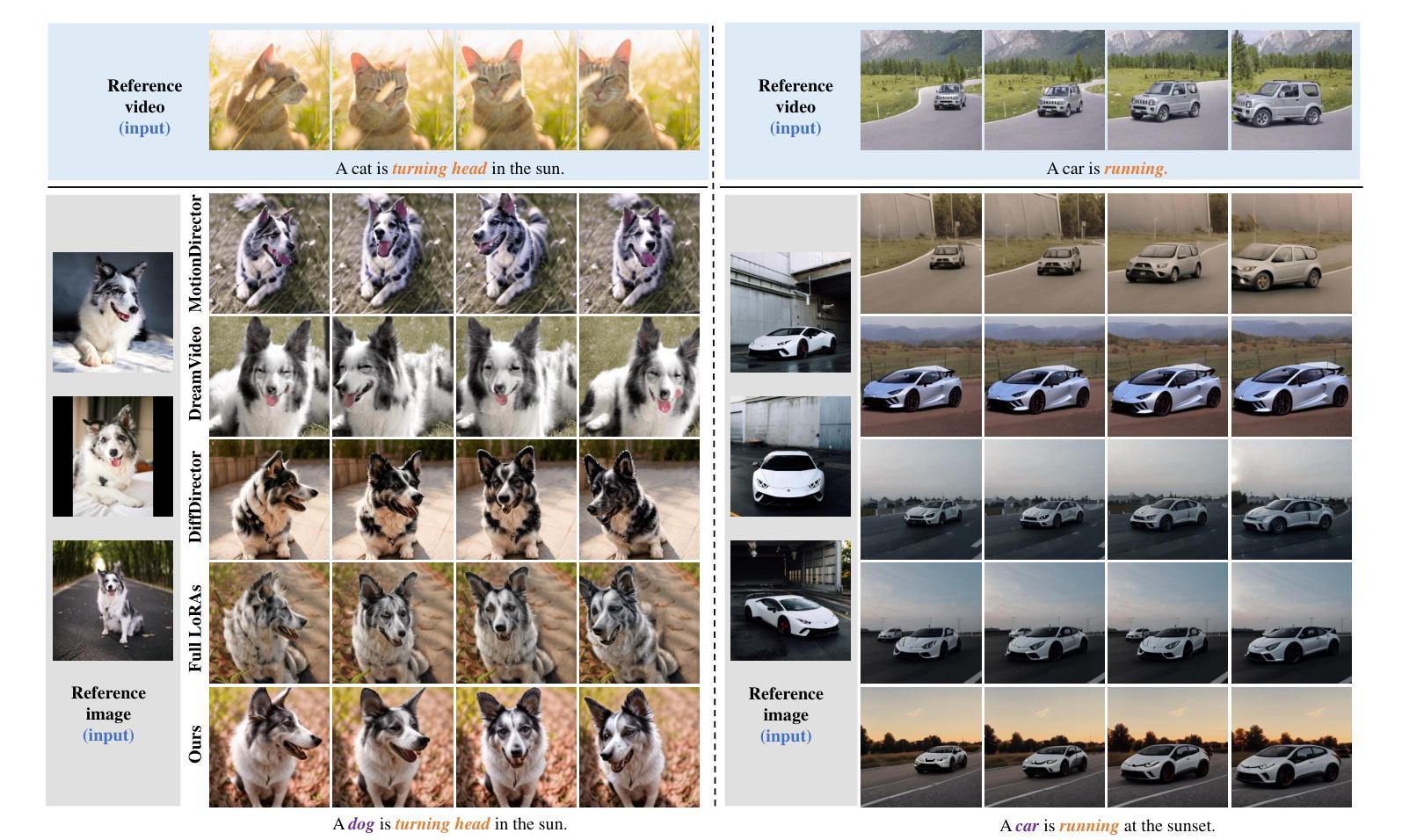
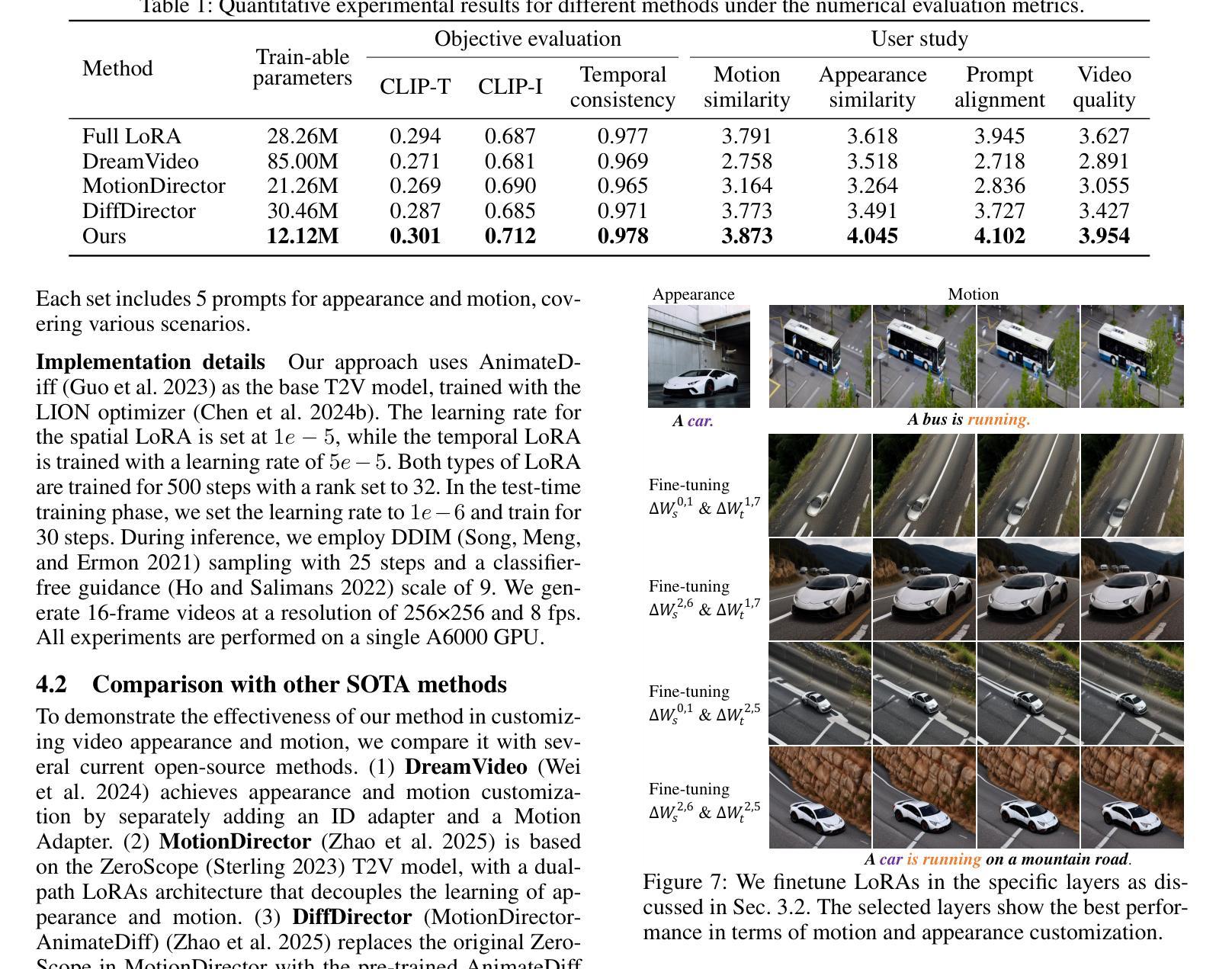
CustomTTT: Motion and Appearance Customized Video Generation via Test-Time Training
Authors:Xiuli Bi, Jian Lu, Bo Liu, Xiaodong Cun, Yong Zhang, Weisheng Li, Bin Xiao
Benefiting from large-scale pre-training of text-video pairs, current text-to-video (T2V) diffusion models can generate high-quality videos from the text description. Besides, given some reference images or videos, the parameter-efficient fine-tuning method, i.e. LoRA, can generate high-quality customized concepts, e.g., the specific subject or the motions from a reference video. However, combining the trained multiple concepts from different references into a single network shows obvious artifacts. To this end, we propose CustomTTT, where we can joint custom the appearance and the motion of the given video easily. In detail, we first analyze the prompt influence in the current video diffusion model and find the LoRAs are only needed for the specific layers for appearance and motion customization. Besides, since each LoRA is trained individually, we propose a novel test-time training technique to update parameters after combination utilizing the trained customized models. We conduct detailed experiments to verify the effectiveness of the proposed methods. Our method outperforms several state-of-the-art works in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations.
得益于大规模文本-视频对数据的预训练,当前的文本到视频(T2V)扩散模型可以根据文本描述生成高质量的视频。此外,给定一些参考图像或视频,参数高效的微调方法(例如LoRA)可以生成高质量的自定概念,例如从参考视频中的特定主题或动作。然而,将来自不同参考的训练过的多个概念合并到单个网络中会出现明显的伪影。为此,我们提出了CustomTTT,可以轻松地结合给定视频的外观和动作进行自定义。具体来说,我们首先分析当前视频扩散模型中的提示影响,并发现对于外观和动作自定义而言,LoRA仅需要特定层。此外,由于每个LoRA都是单独训练的,我们提出了一种新型测试时训练技术,利用训练好的自定义模型在组合后进行参数更新。我们进行了详细的实验来验证所提出方法的有效性。我们的方法在定性和定量评估方面都优于几种最新技术的工作。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in AAAI 2025. Project Page: https://customttt.github.io/ Code: https://github.com/RongPiKing/CustomTTT
Summary
文本描述了当前文本到视频(T2V)扩散模型利用大规模预训练的文本-视频对生成高质量视频的能力。通过参数高效的微调方法(如LoRA),可以根据参考图像或视频生成高质量定制化概念。然而,从多个参考中训练的概念结合到单一网络中会产生明显瑕疵。为此,提出了CustomTTT,能够轻松结合给定视频的外观和运动。研究发现LoRA仅对特定层进行外观和运动定制所需。此外,利用测试时训练技术更新结合后的参数。实验验证所提方法的有效性,在定性和定量评估上均优于现有前沿工作。
Key Takeaways
- 当前文本到视频(T2V)扩散模型能利用大规模预训练生成高质量视频。
- 参数高效的微调方法(如LoRA)允许根据参考图像或视频生成定制化的概念。
- 结合多个参考概念到单一网络中会产生瑕疵。
- CustomTTT方法能够轻松结合给定视频的外观和运动。
- LoRA仅对特定层进行外观和运动定制的需求。
- 利用测试时训练技术更新结合后的参数。
点此查看论文截图

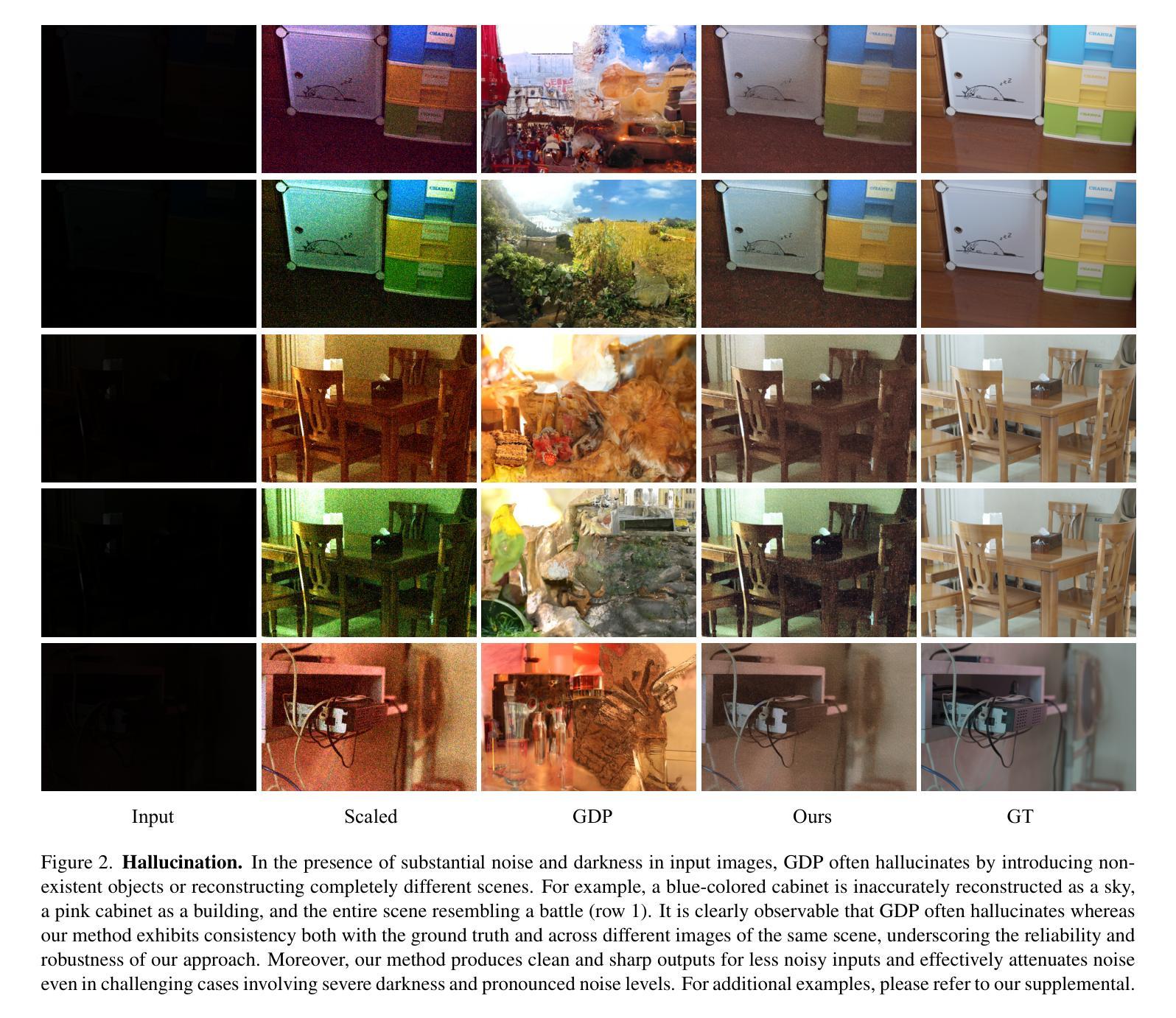
Zero-Shot Low Light Image Enhancement with Diffusion Prior
Authors:Joshua Cho, Sara Aghajanzadeh, Zhen Zhu, D. A. Forsyth
Balancing aesthetic quality with fidelity when enhancing images from challenging, degraded sources is a core objective in computational photography. In this paper, we address low light image enhancement (LLIE), a task in which dark images often contain limited visible information. Diffusion models, known for their powerful image enhancement capacities, are a natural choice for this problem. However, their deep generative priors can also lead to hallucinations, introducing non-existent elements or substantially altering the visual semantics of the original scene. In this work, we introduce a novel zero-shot method for controlling and refining the generative behavior of diffusion models for dark-to-light image conversion tasks. Our method demonstrates superior performance over existing state-of-the-art methods in the task of low-light image enhancement, as evidenced by both quantitative metrics and qualitative analysis.
在计算摄影中,平衡增强来自具有挑战性、退化源的图像时的美学质量与保真度是核心目标。在本文中,我们解决低光图像增强(LLIE)的问题,这是一个暗图像通常包含有限可见信息的任务。扩散模型以其强大的图像增强能力而闻名,是此问题的自然选择。然而,它们的深度生成先验也可能导致幻觉,引入不存在的元素或大幅改变原始场景的可视语义。在这项工作中,我们介绍了一种用于控制和优化扩散模型在暗到亮图像转换任务中的生成行为的新型零样本方法。我们的方法在低光图像增强任务中的表现优于现有最先进的方法,这由定量指标和定性分析均可以证明。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文聚焦于低光图像增强任务,利用扩散模型来解决在光照不足的条件下图像中信息有限的问题。通过一种新的零样本方法,实现了对扩散模型的生成行为进行控制和优化,使模型在低光图像增强任务中具有优异性能。这种新方法通过定量指标和定性分析证明了其在现有技术中的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 论文关注计算摄影中的核心问题,即在挑战性强、退化严重的图像源中平衡美学质量与保真度。
- 低光图像增强(LLIE)是其中一个任务,涉及处理黑暗环境中信息有限的图像。
- 扩散模型因其强大的图像增强能力而成为解决此问题的自然选择。
- 然而,扩散模型的深度生成先验也可能导致幻觉,引入不存在的元素或大幅改变原始场景的可视语义。
- 论文提出了一种新的零样本方法来控制和优化扩散模型在暗光图像转换任务中的生成行为。
- 该方法在定量指标和定性分析中均表现出卓越性能,优于现有先进技术。
点此查看论文截图
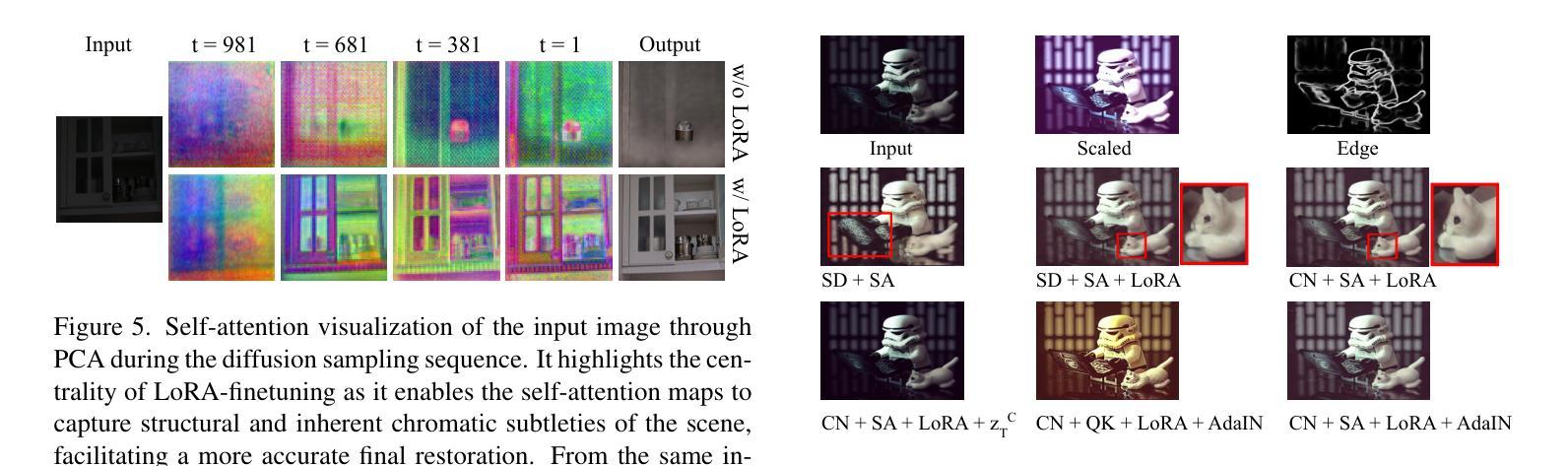


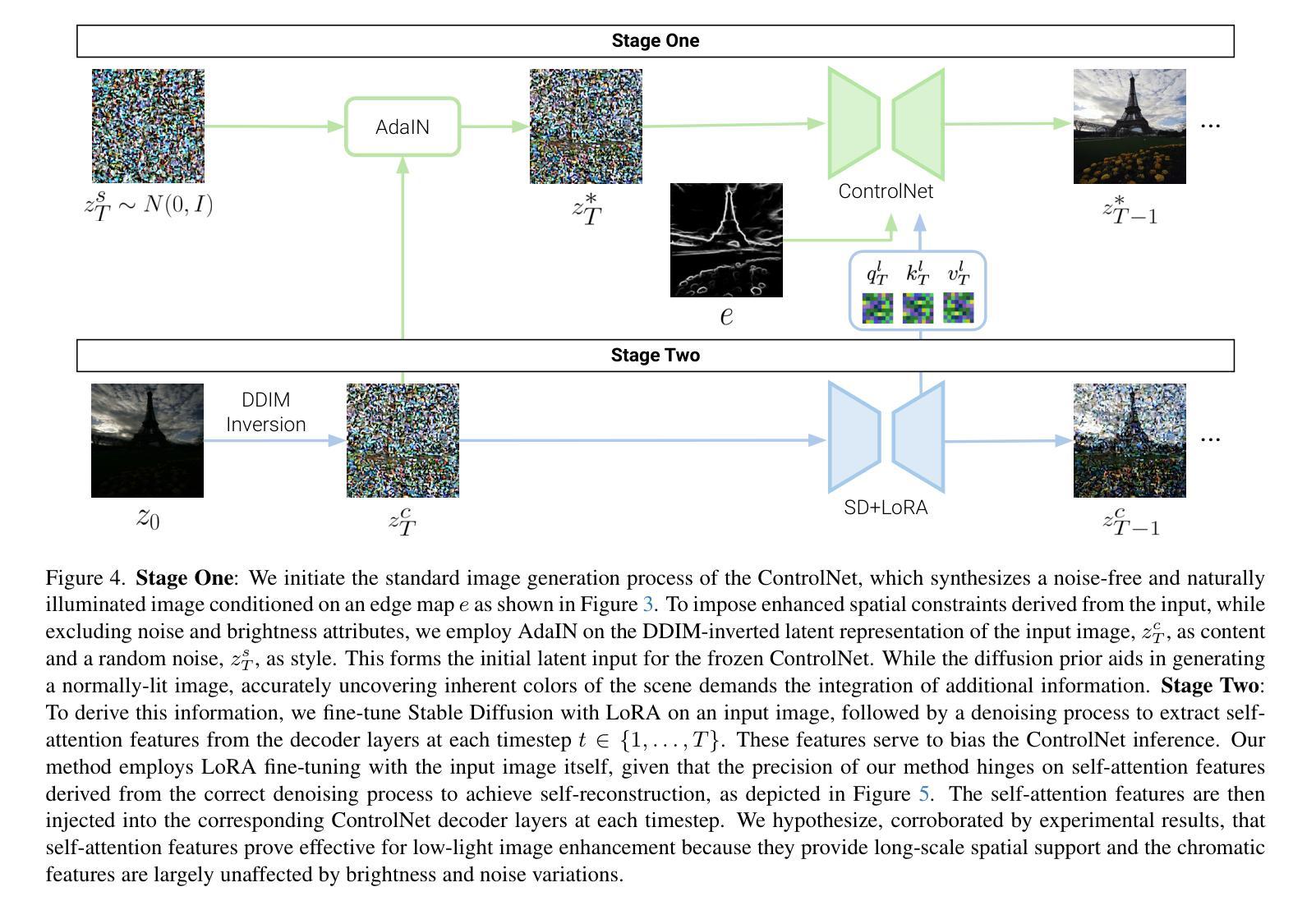

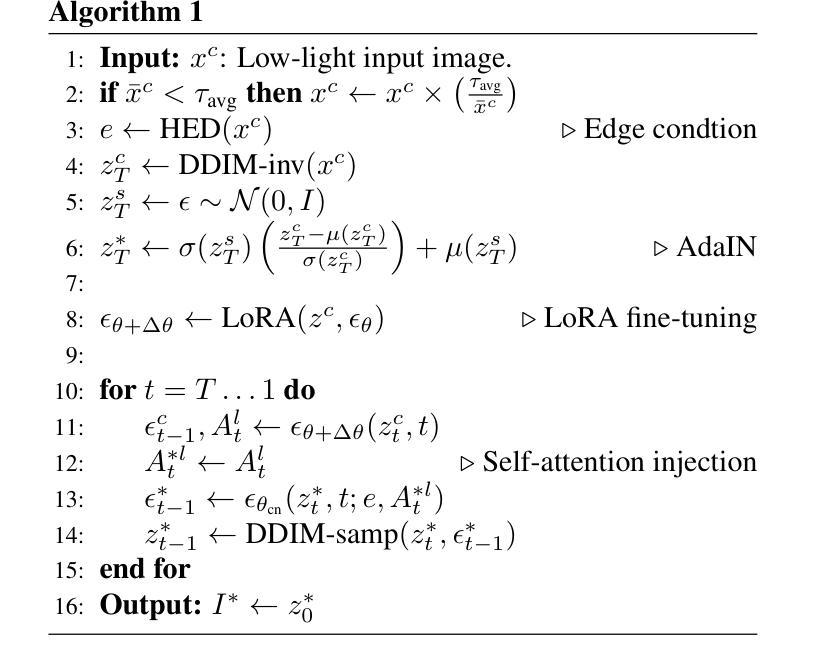
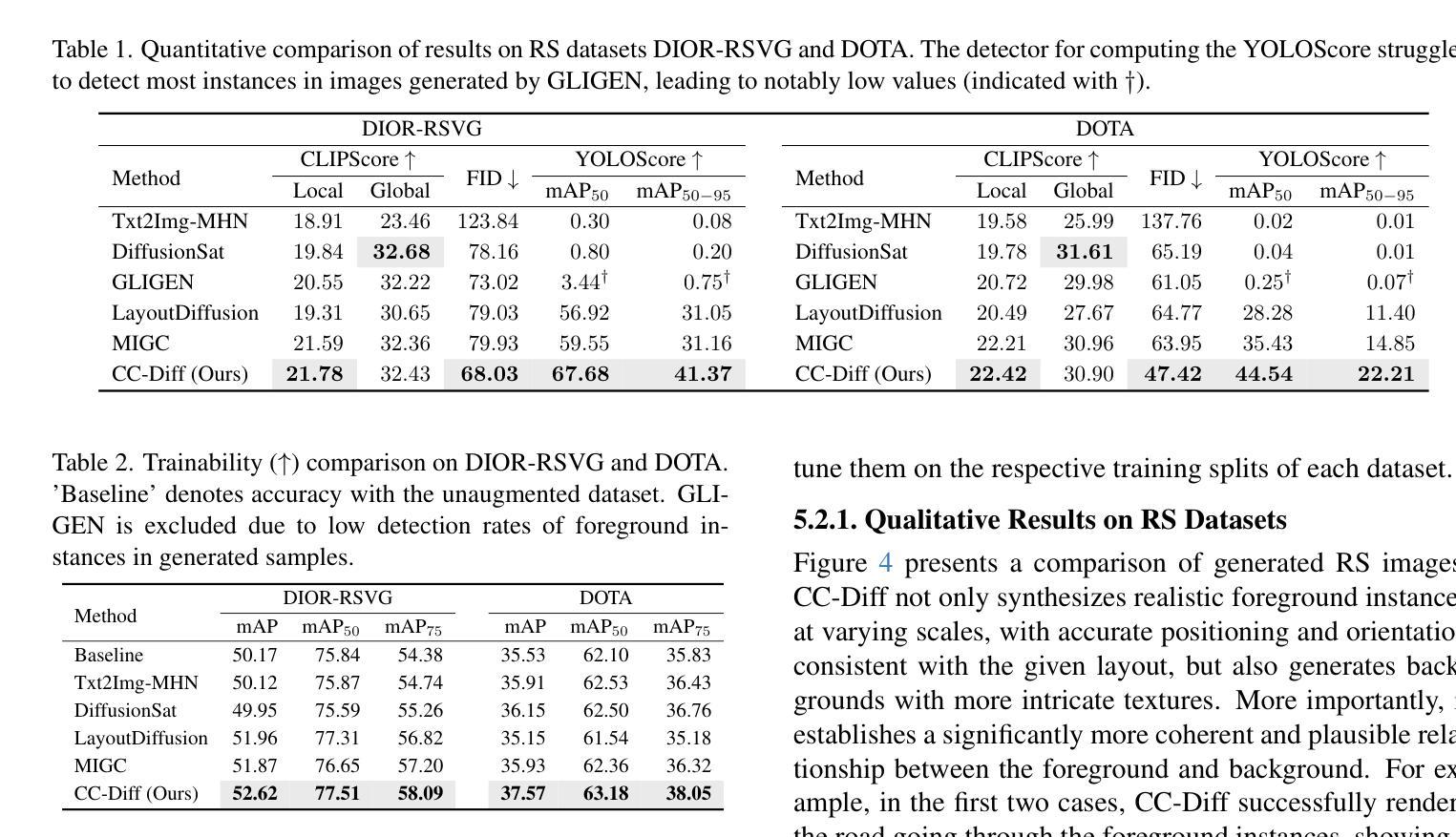
CC-Diff: Enhancing Contextual Coherence in Remote Sensing Image Synthesis
Authors:Mu Zhang, Yunfan Liu, Yue Liu, Hongtian Yu, Qixiang Ye
Accurately depicting real-world landscapes in remote sensing (RS) images requires precise alignment between objects and their environment. However, most existing synthesis methods for natural images prioritize foreground control, often reducing the background to plain textures. This neglects the interaction between foreground and background, which can lead to incoherence in RS scenarios. In this paper, we introduce CC-Diff, a Diffusion Model-based approach for RS image generation with enhanced Context Coherence. To capture spatial interdependence, we propose a sequential pipeline where background generation is conditioned on synthesized foreground instances. Distinct learnable queries are also employed to model both the complex background texture and its semantic relation to the foreground. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CC-Diff outperforms state-of-the-art methods in visual fidelity, semantic accuracy, and positional precision, excelling in both RS and natural image domains. CC-Diff also shows strong trainability, improving detection accuracy by 2.04 mAP on DOTA and 2.25 mAP on the COCO benchmark.
在遥感(RS)图像中准确描绘真实世界的景观需要物体与其环境之间的精确对齐。然而,大多数现有的自然图像合成方法都优先进行前景控制,经常将背景简化为纯纹理。这忽略了前景和背景之间的交互,可能导致遥感场景中的不连贯性。在本文中,我们介绍了CC-Diff,这是一种基于扩散模型的遥感图像生成方法,具有增强的上下文一致性。为了捕捉空间相关性,我们提出了一个顺序流程,其中背景生成是在合成的前景实例条件下进行的。我们还使用不同的可学习查询来对复杂的背景纹理及其与前景的语义关系进行建模。大量实验表明,CC-Diff在视觉保真度、语义准确性和定位精度方面均优于最新方法,在遥感和自然图像领域均表现出卓越性能。CC-Diff还显示出强大的可训练性,在DOTA上提高了2.04 mAP的检测精度,在COCO基准测试上提高了2.25 mAP。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本研究针对遥感图像中的真实世界景观描绘问题,提出了一种基于扩散模型的上下文一致性增强方法CC-Diff。该方法通过考虑前景与背景之间的交互作用,提高了遥感图像生成的空间连贯性。实验证明,CC-Diff在视觉保真度、语义准确性和定位精度方面均优于现有技术,同时在遥感图像和自然图像领域均表现出卓越性能。此外,CC-Diff在DOTA和COCO基准测试上的目标检测精度分别提高了2.04 mAP和2.25 mAP。
关键见解
- CC-Diff方法强调了前景与背景之间的交互作用,提高了遥感图像生成中的空间连贯性。
- 提出了一种基于扩散模型的背景生成条件方法,依赖于合成的前景实例。
- 采用不同的学习查询模拟复杂背景纹理及其与前景的语义关系。
- 实验证明CC-Diff在视觉保真度、语义准确性和定位精度方面表现优越。
- CC-Diff在自然图像和遥感图像领域均展现出优秀性能。
- 与现有技术相比,CC-Diff提高了目标检测精度,对遥感应用具有重要价值。
点此查看论文截图


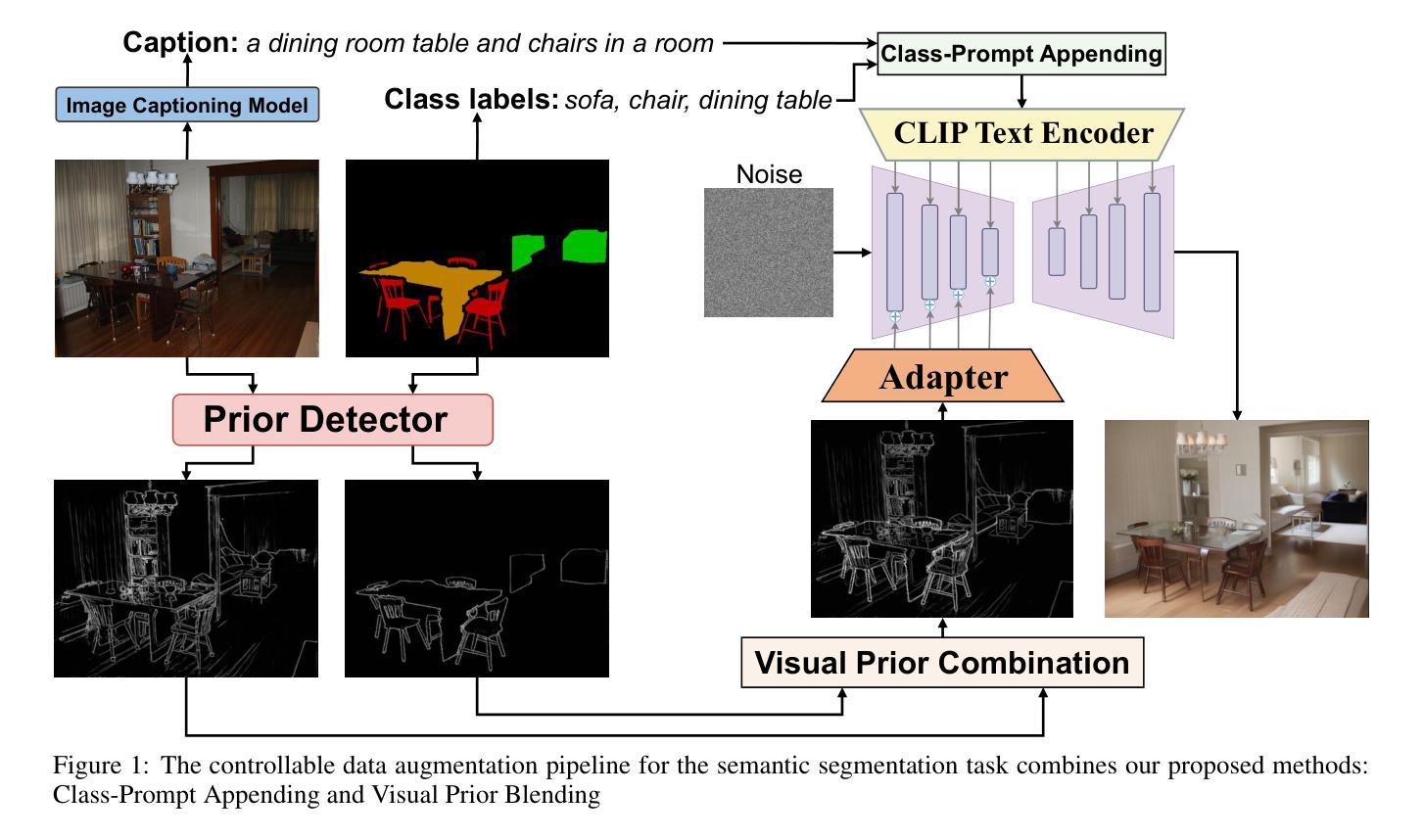
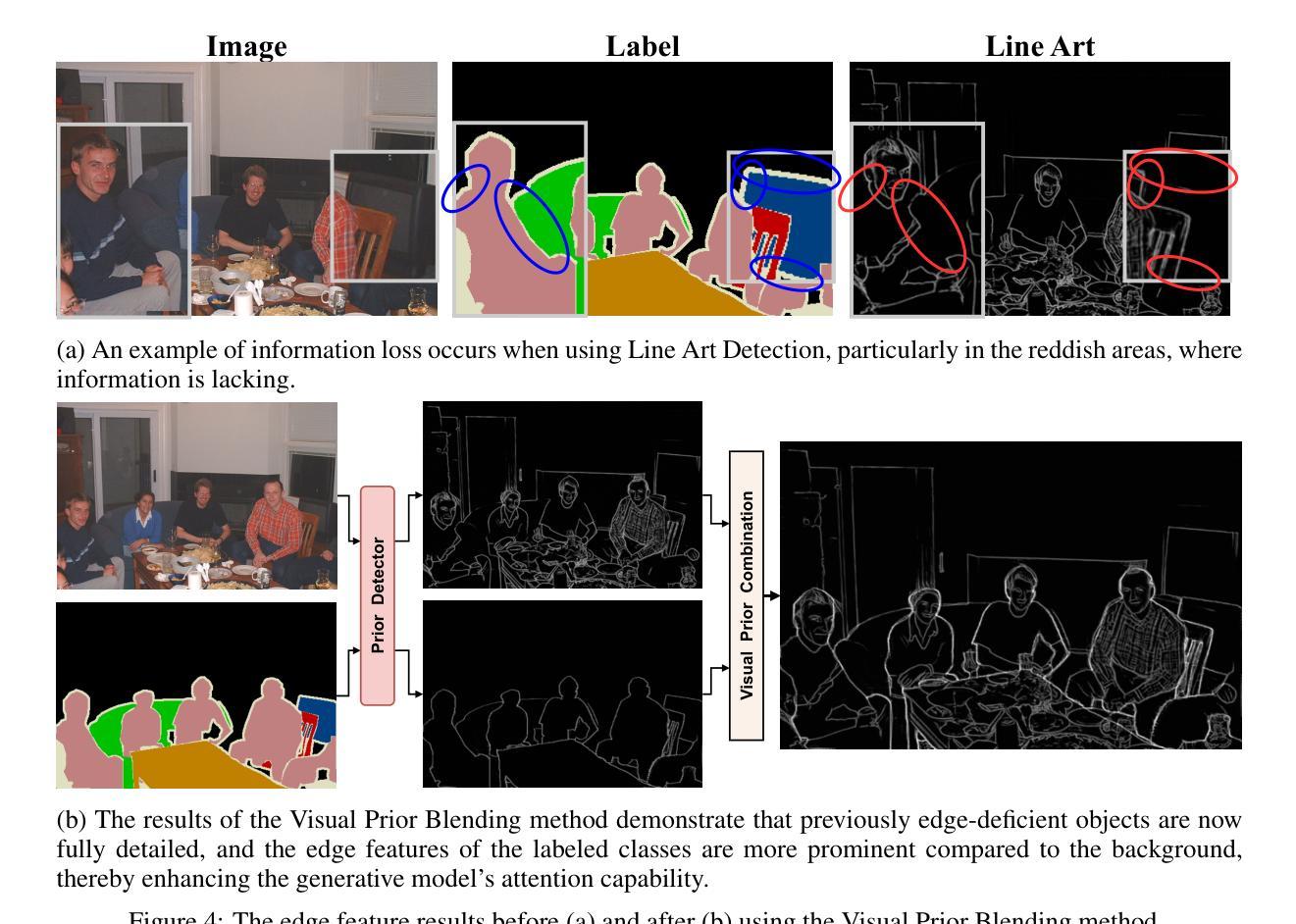
Enhanced Generative Data Augmentation for Semantic Segmentation via Stronger Guidance
Authors:Quang-Huy Che, Duc-Tri Le, Bich-Nga Pham, Duc-Khai Lam, Vinh-Tiep Nguyen
Data augmentation is crucial for pixel-wise annotation tasks like semantic segmentation, where labeling requires significant effort and intensive labor. Traditional methods, involving simple transformations such as rotations and flips, create new images but often lack diversity along key semantic dimensions and fail to alter high-level semantic properties. To address this issue, generative models have emerged as an effective solution for augmenting data by generating synthetic images. Controllable Generative models offer data augmentation methods for semantic segmentation tasks by using prompts and visual references from the original image. However, these models face challenges in generating synthetic images that accurately reflect the content and structure of the original image due to difficulties in creating effective prompts and visual references. In this work, we introduce an effective data augmentation pipeline for semantic segmentation using Controllable Diffusion model. Our proposed method includes efficient prompt generation using \textit{Class-Prompt Appending} and \textit{Visual Prior Blending} to enhance attention to labeled classes in real images, allowing the pipeline to generate a precise number of augmented images while preserving the structure of segmentation-labeled classes. In addition, we implement a \textit{class balancing algorithm} to ensure a balanced training dataset when merging the synthetic and original images. Evaluation on PASCAL VOC datasets, our pipeline demonstrates its effectiveness in generating high-quality synthetic images for semantic segmentation. Our code is available at \href{https://github.com/chequanghuy/Enhanced-Generative-Data-Augmentation-for-Semantic-Segmentation-via-Stronger-Guidance}{this https URL}.
数据增强对于像素级标注任务(如语义分割)至关重要,这些任务需要大量人力进行标注。传统的方法,如旋转和翻转等简单变换,虽然可以生成新图像,但往往在关键的语义维度上缺乏多样性,并且无法改变高级语义属性。为了解决这一问题,生成模型作为一种有效的数据增强解决方案,通过生成合成图像来增强数据。可控生成模型通过使用原始图像的提示和视觉参考,为语义分割任务提供数据增强方法。然而,这些模型在生成准确反映原始图像内容和结构的合成图像时面临挑战,因为创建有效的提示和视觉参考具有难度。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种使用可控扩散模型的有效数据增强管道,用于语义分割。我们提出的方法包括使用“类提示附加”和“视觉先验混合”进行有效提示生成,以提高对真实图像中标记类的关注,使管道能够在保留分割标记类结构的同时生成精确数量的增强图像。此外,我们实现了一种“类别平衡算法”,以确保在合并合成图像和原始图像时获得平衡的训练数据集。在PASCAL VOC数据集上的评估表明,我们的管道在生成高质量合成图像进行语义分割方面非常有效。我们的代码可在此URL找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICPRAM 2025
摘要
数据增强在像素级标注任务(如语义分割)中至关重要,因为标注需要大量劳动。传统方法虽然能生成新图像,但在关键语义维度上缺乏多样性,无法改变高级语义属性。为解决这一问题,生成模型已成为数据增强的有效解决方案,通过生成合成图像来扩大数据集。可控生成模型为语义分割任务提供了数据增强方法,通过使用原始图像的提示和视觉参考来生成图像。然而,这些模型在生成准确反映原始图像内容和结构的合成图像时面临挑战,原因是创建有效的提示和视觉参考存在困难。本研究引入了一种基于可控扩散模型的有效数据增强管道,用于语义分割。我们提出的方法包括使用Class-Prompt Appending和Visual Prior Blending进行高效提示生成,以提高对真实图像中标记类的关注,使管道能够在保留分割标记类结构的同时生成精确数量的增强图像。此外,我们实现了class balancing algorithm,以确保在合并合成图像和原始图像时训练数据集平衡。在PASCAL VOC数据集上的评估表明,我们的管道在生成高质量合成图像进行语义分割方面非常有效。我们的代码可在此https链接找到。
关键见解
- 数据增强在像素级标注任务中至关重要,尤其是语义分割任务。
- 传统数据增强方法缺乏在关键语义维度上的多样性。
- 生成模型,特别是可控生成模型,是解决数据增强问题的一种有效方法。
- 本研究引入了一种新的数据增强管道,结合Class-Prompt Appending和Visual Prior Blending技术,旨在提高合成图像的质量并保留原始图像的结构信息。
- 实施了一种class balancing algorithm,以确保合成和原始图像的平衡融合。
- 在PASCAL VOC数据集上的评估证明了该管道的有效性。
点此查看论文截图




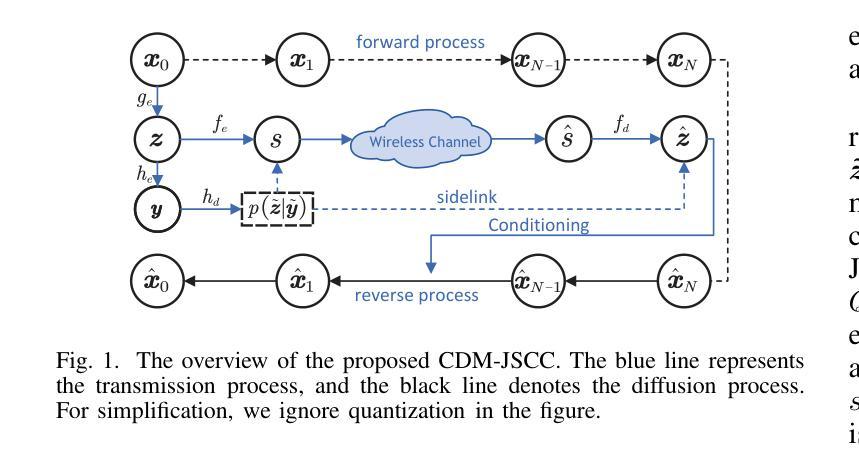
Rate-Adaptive Generative Semantic Communication Using Conditional Diffusion Models
Authors:Pujing Yang, Guangyi Zhang, Yunlong Cai
Recent advances in deep learning-based joint source-channel coding (DJSCC) have shown promise for end-to-end semantic image transmission. However, most existing schemes primarily focus on optimizing pixel-wise metrics, which often fail to align with human perception, leading to lower perceptual quality. In this letter, we propose a novel generative DJSCC approach using conditional diffusion models to enhance the perceptual quality of transmitted images. Specifically, by utilizing entropy models, we effectively manage transmission bandwidth based on the estimated entropy of transmitted sym-bols. These symbols are then used at the receiver as conditional information to guide a conditional diffusion decoder in image reconstruction. Our model is built upon the emerging advanced mamba-like linear attention (MLLA) skeleton, which excels in image processing tasks while also offering fast inference speed. Besides, we introduce a multi-stage training strategy to ensure the stability and improve the overall performance of the model. Simulation results demonstrate that our proposed method significantly outperforms existing approaches in terms of perceptual quality.
基于深度学习的联合源信道编码(DJSCC)的最新进展在端到端语义图像传输方面显示出巨大潜力。然而,大多数现有方案主要集中在优化像素级的指标,这些指标往往与人类感知不一致,导致感知质量下降。在本信中,我们提出了一种利用条件扩散模型的新型生成式DJSCC方法,以提高传输图像的感知质量。具体来说,我们通过利用熵模型,根据传输符号的估计熵有效地管理传输带宽。这些符号然后在接收器端作为条件信息,用于指导图像重建中的条件扩散解码器。我们的模型建立在新兴的类哺乳动物线性注意力(MLLA)骨架之上,该骨架在图像处理任务上表现出色,同时提供快速的推理速度。此外,我们引入了一种多阶段训练策略,以确保模型的稳定性并提高其整体性能。仿真结果表明,我们提出的方法在感知质量方面显著优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本摘要研究了深度学习在联合源信道编码技术上的应用及其对语义图像传输的革新影响。现有的多数策略关注像素级的优化,并未充分满足人类的感知需求。为此,本文提出了一种基于条件扩散模型的生成式联合源信道编码方法,旨在提高传输图像的感知质量。通过利用熵模型,该方法能够根据传输符号的估计熵有效地管理传输带宽。接收端利用这些符号作为条件信息,引导图像重建过程中的条件扩散解码器。此外,模型基于先进的mamba-like线性注意力机制构建,具备图像处理优势,且推理速度快。研究采用了多阶段训练策略以确保模型稳定性并提升性能。仿真实验显示,本文方法在感知质量上显著优于现有方法。
要点解析
以下是文本的关键洞察点概述:
- 研究焦点:本文研究深度学习在联合源信道编码技术(DJSCC)的最新进展及其对语义图像传输的影响。
- 现存问题:多数现有方案主要关注像素级的优化指标,这些指标并不总是与人类感知质量相符。
- 新方法提出:引入基于条件扩散模型的生成式DJSCC方法,旨在提高传输图像的感知质量。
- 熵模型的应用:利用熵模型来管理传输带宽,根据传输符号的估计熵进行有效率调整。
- 接收端处理:接收端使用这些符号作为条件信息,指导图像重建过程中的条件扩散解码器。
- 模型基础:模型建立在mamba-like线性注意力机制之上,该机制在图像处理任务中表现出色,同时提供快速的推理速度。
- 训练策略:采用多阶段训练策略以确保模型的稳定性和性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

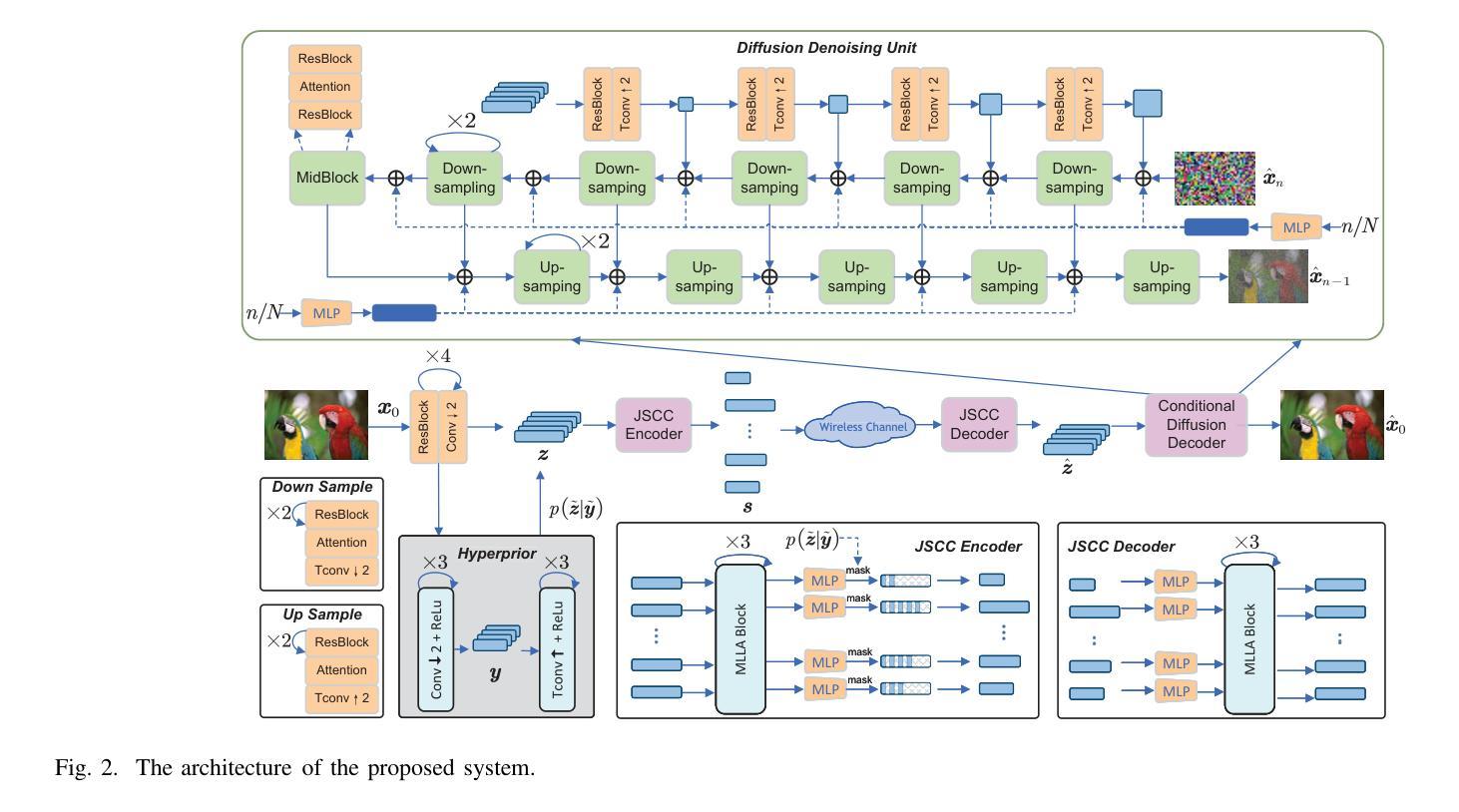
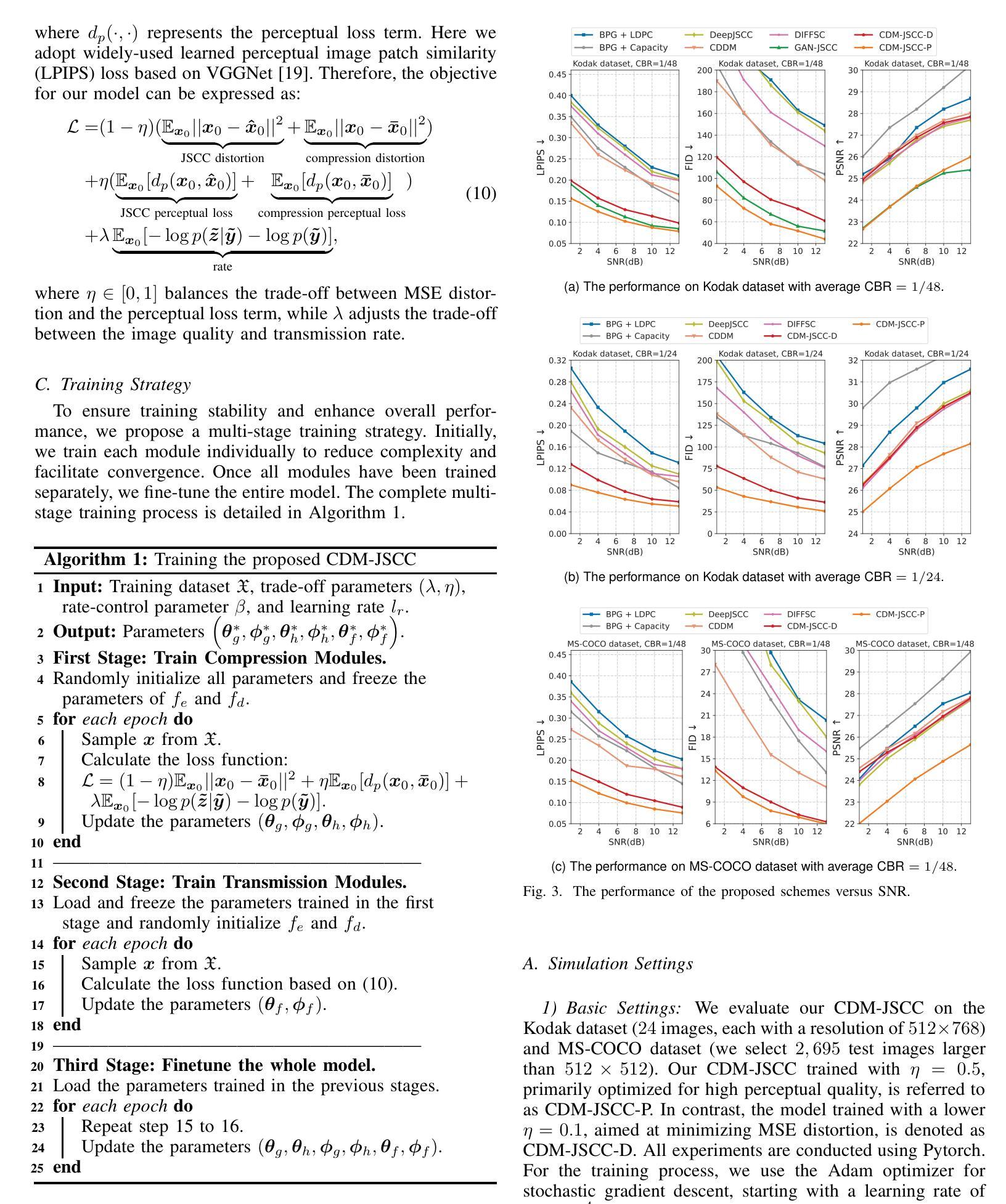
GRPose: Learning Graph Relations for Human Image Generation with Pose Priors
Authors:Xiangchen Yin, Donglin Di, Lei Fan, Hao Li, Wei Chen, Xiaofei Gou, Yang Song, Xiao Sun, Xun Yang
Recent methods using diffusion models have made significant progress in human image generation with various control signals such as pose priors. However, existing efforts are still struggling to generate high-quality images with consistent pose alignment, resulting in unsatisfactory output. In this paper, we propose a framework that delves into the graph relations of pose priors to provide control information for human image generation. The main idea is to establish a graph topological structure between the pose priors and latent representation of diffusion models to capture the intrinsic associations between different pose parts. A Progressive Graph Integrator (PGI) is designed to learn the spatial relationships of the pose priors with the graph structure, adopting a hierarchical strategy within an Adapter to gradually propagate information across different pose parts. Besides, a pose perception loss is introduced based on a pretrained pose estimation network to minimize the pose differences. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments conducted on the Human-Art and LAION-Human datasets clearly demonstrate that our model can achieve significant performance improvement over the latest benchmark models. The code is available at \url{https://xiangchenyin.github.io/GRPose/}.
近期使用扩散模型的方法在人像生成方面取得了显著进展,通过各种控制信号如姿态先验进行控制。然而,现有努力仍难以生成具有一致姿态对齐的高质量图像,导致输出效果不佳。在本文中,我们提出了一种框架,该框架深入研究姿态先验的图关系,为人像生成提供控制信息。主要思想是在姿态先验和扩散模型的潜在表示之间建立图拓扑结构,以捕获不同姿态部分之间的内在关联。设计了一种渐进式图形集成器(PGI),采用适配器内的分层策略来学习姿态先验的空间关系与图形结构,并逐步传播不同姿态部分之间的信息。此外,基于预训练的姿态估计网络引入了一种姿态感知损失,以最小化姿态差异。在Human-Art和LAION-Human数据集上进行的广泛定性和定量实验清楚地表明,我们的模型可以在最新基准模型上实现显著的性能提升。代码可从https://xiangchenyin.github.io/GRPose/获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at AAAI2025
Summary
本文提出了一种基于姿态先验图关系的框架,用于控制人类图像生成。通过建立姿态先验和扩散模型潜在表示之间的图拓扑结构,捕捉不同姿态部位之间的内在关联。设计了一个渐进式图集成器(PGI)来学习姿态先验的空间关系,并采用适配器内的分层策略逐步传播不同姿态部位的信息。引入基于预训练姿态估计网络的姿态感知损失,以最小化姿态差异。在Human-Art和LAION-Human数据集上进行的广泛定性和定量实验表明,该模型在最新基准模型上实现了显著的性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在带有控制信号(如姿态先验)的人类图像生成方面取得显著进展,但仍面临生成高质量且姿态一致的图像的挑战。
- 提出了一个基于姿态先验图关系的框架,通过捕捉不同姿态部位之间的内在关联,提供对人类图像生成的控制信息。
- 设计了渐进式图集成器(PGI)来学习姿态先验的空间关系,并采用适配器内的分层策略逐步传播信息。
- 引入基于预训练姿态估计网络的姿态感知损失,以最小化生成的图像与预期姿态之间的差异。
- 在多个数据集上进行的实验表明,该模型在性能上超过了最新的基准模型。
- 该模型的代码已公开发布,便于他人使用和研究。
点此查看论文截图


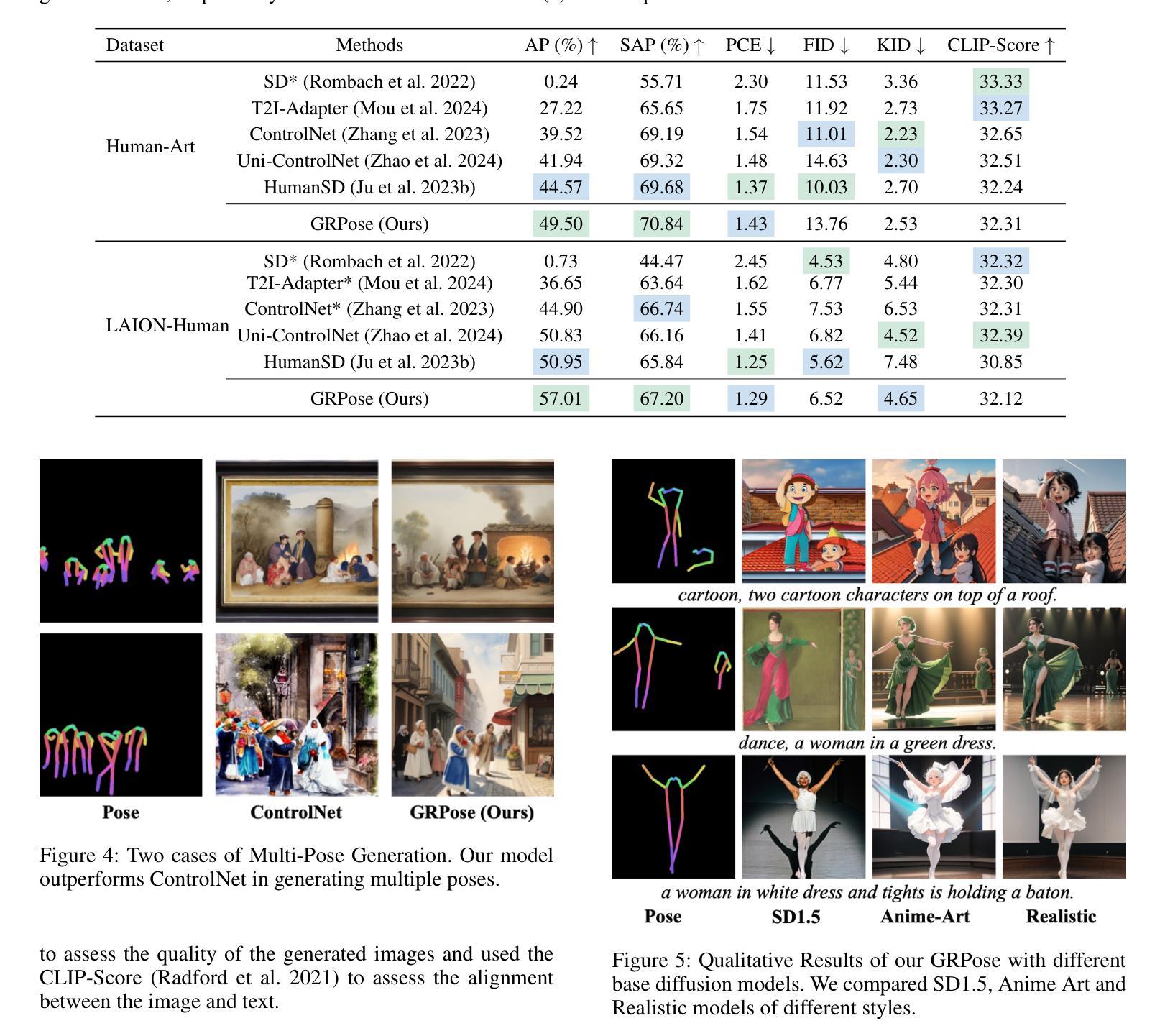
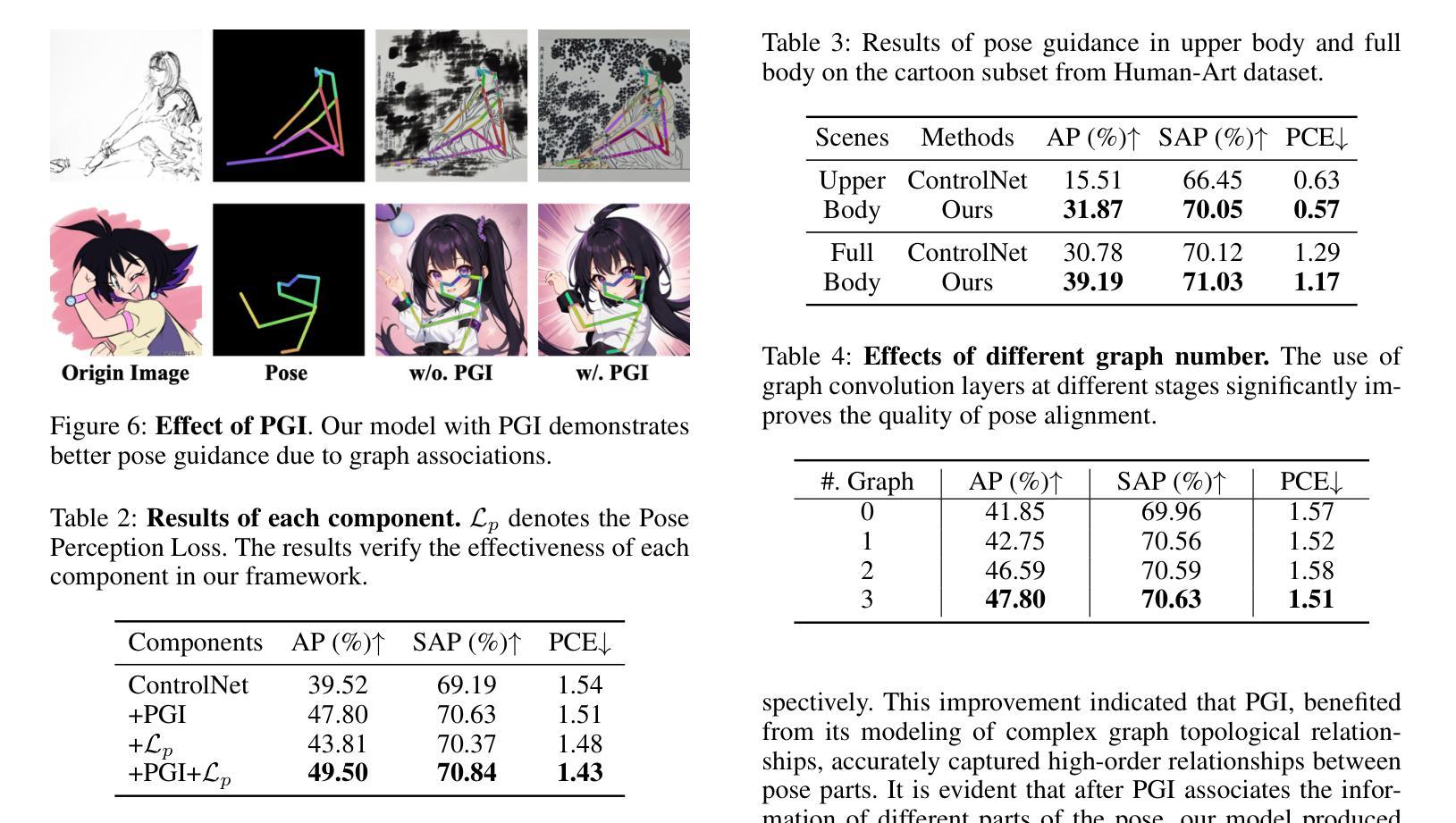
Imagen 3
Authors: Imagen-Team-Google, :, Jason Baldridge, Jakob Bauer, Mukul Bhutani, Nicole Brichtova, Andrew Bunner, Lluis Castrejon, Kelvin Chan, Yichang Chen, Sander Dieleman, Yuqing Du, Zach Eaton-Rosen, Hongliang Fei, Nando de Freitas, Yilin Gao, Evgeny Gladchenko, Sergio Gómez Colmenarejo, Mandy Guo, Alex Haig, Will Hawkins, Hexiang Hu, Huilian Huang, Tobenna Peter Igwe, Christos Kaplanis, Siavash Khodadadeh, Yelin Kim, Ksenia Konyushkova, Karol Langner, Eric Lau, Rory Lawton, Shixin Luo, Soňa Mokrá, Henna Nandwani, Yasumasa Onoe, Aäron van den Oord, Zarana Parekh, Jordi Pont-Tuset, Hang Qi, Rui Qian, Deepak Ramachandran, Poorva Rane, Abdullah Rashwan, Ali Razavi, Robert Riachi, Hansa Srinivasan, Srivatsan Srinivasan, Robin Strudel, Benigno Uria, Oliver Wang, Su Wang, Austin Waters, Chris Wolff, Auriel Wright, Zhisheng Xiao, Hao Xiong, Keyang Xu, Marc van Zee, Junlin Zhang, Katie Zhang, Wenlei Zhou, Konrad Zolna, Ola Aboubakar, Canfer Akbulut, Oscar Akerlund, Isabela Albuquerque, Nina Anderson, Marco Andreetto, Lora Aroyo, Ben Bariach, David Barker, Sherry Ben, Dana Berman, Courtney Biles, Irina Blok, Pankil Botadra, Jenny Brennan, Karla Brown, John Buckley, Rudy Bunel, Elie Bursztein, Christina Butterfield, Ben Caine, Viral Carpenter, Norman Casagrande, Ming-Wei Chang, Solomon Chang, Shamik Chaudhuri, Tony Chen, John Choi, Dmitry Churbanau, Nathan Clement, Matan Cohen, Forrester Cole, Mikhail Dektiarev, Vincent Du, Praneet Dutta, Tom Eccles, Ndidi Elue, Ashley Feden, Shlomi Fruchter, Frankie Garcia, Roopal Garg, Weina Ge, Ahmed Ghazy, Bryant Gipson, Andrew Goodman, Dawid Górny, Sven Gowal, Khyatti Gupta, Yoni Halpern, Yena Han, Susan Hao, Jamie Hayes, Jonathan Heek, Amir Hertz, Ed Hirst, Emiel Hoogeboom, Tingbo Hou, Heidi Howard, Mohamed Ibrahim, Dirichi Ike-Njoku, Joana Iljazi, Vlad Ionescu, William Isaac, Reena Jana, Gemma Jennings, Donovon Jenson, Xuhui Jia, Kerry Jones, Xiaoen Ju, Ivana Kajic, Christos Kaplanis, Burcu Karagol Ayan, Jacob Kelly, Suraj Kothawade, Christina Kouridi, Ira Ktena, Jolanda Kumakaw, Dana Kurniawan, Dmitry Lagun, Lily Lavitas, Jason Lee, Tao Li, Marco Liang, Maggie Li-Calis, Yuchi Liu, Javier Lopez Alberca, Matthieu Kim Lorrain, Peggy Lu, Kristian Lum, Yukun Ma, Chase Malik, John Mellor, Thomas Mensink, Inbar Mosseri, Tom Murray, Aida Nematzadeh, Paul Nicholas, Signe Nørly, João Gabriel Oliveira, Guillermo Ortiz-Jimenez, Michela Paganini, Tom Le Paine, Roni Paiss, Alicia Parrish, Anne Peckham, Vikas Peswani, Igor Petrovski, Tobias Pfaff, Alex Pirozhenko, Ryan Poplin, Utsav Prabhu, Yuan Qi, Matthew Rahtz, Cyrus Rashtchian, Charvi Rastogi, Amit Raul, Ali Razavi, Sylvestre-Alvise Rebuffi, Susanna Ricco, Felix Riedel, Dirk Robinson, Pankaj Rohatgi, Bill Rosgen, Sarah Rumbley, Moonkyung Ryu, Anthony Salgado, Tim Salimans, Sahil Singla, Florian Schroff, Candice Schumann, Tanmay Shah, Eleni Shaw, Gregory Shaw, Brendan Shillingford, Kaushik Shivakumar, Dennis Shtatnov, Zach Singer, Evgeny Sluzhaev, Valerii Sokolov, Thibault Sottiaux, Florian Stimberg, Brad Stone, David Stutz, Yu-Chuan Su, Eric Tabellion, Shuai Tang, David Tao, Kurt Thomas, Gregory Thornton, Andeep Toor, Cristian Udrescu, Aayush Upadhyay, Cristina Vasconcelos, Alex Vasiloff, Andrey Voynov, Amanda Walker, Luyu Wang, Miaosen Wang, Simon Wang, Stanley Wang, Qifei Wang, Yuxiao Wang, Ágoston Weisz, Olivia Wiles, Chenxia Wu, Xingyu Federico Xu, Andrew Xue, Jianbo Yang, Luo Yu, Mete Yurtoglu, Ali Zand, Han Zhang, Jiageng Zhang, Catherine Zhao, Adilet Zhaxybay, Miao Zhou, Shengqi Zhu, Zhenkai Zhu, Dawn Bloxwich, Mahyar Bordbar, Luis C. Cobo, Eli Collins, Shengyang Dai, Tulsee Doshi, Anca Dragan, Douglas Eck, Demis Hassabis, Sissie Hsiao, Tom Hume, Koray Kavukcuoglu, Helen King, Jack Krawczyk, Yeqing Li, Kathy Meier-Hellstern, Andras Orban, Yury Pinsky, Amar Subramanya, Oriol Vinyals, Ting Yu, Yori Zwols
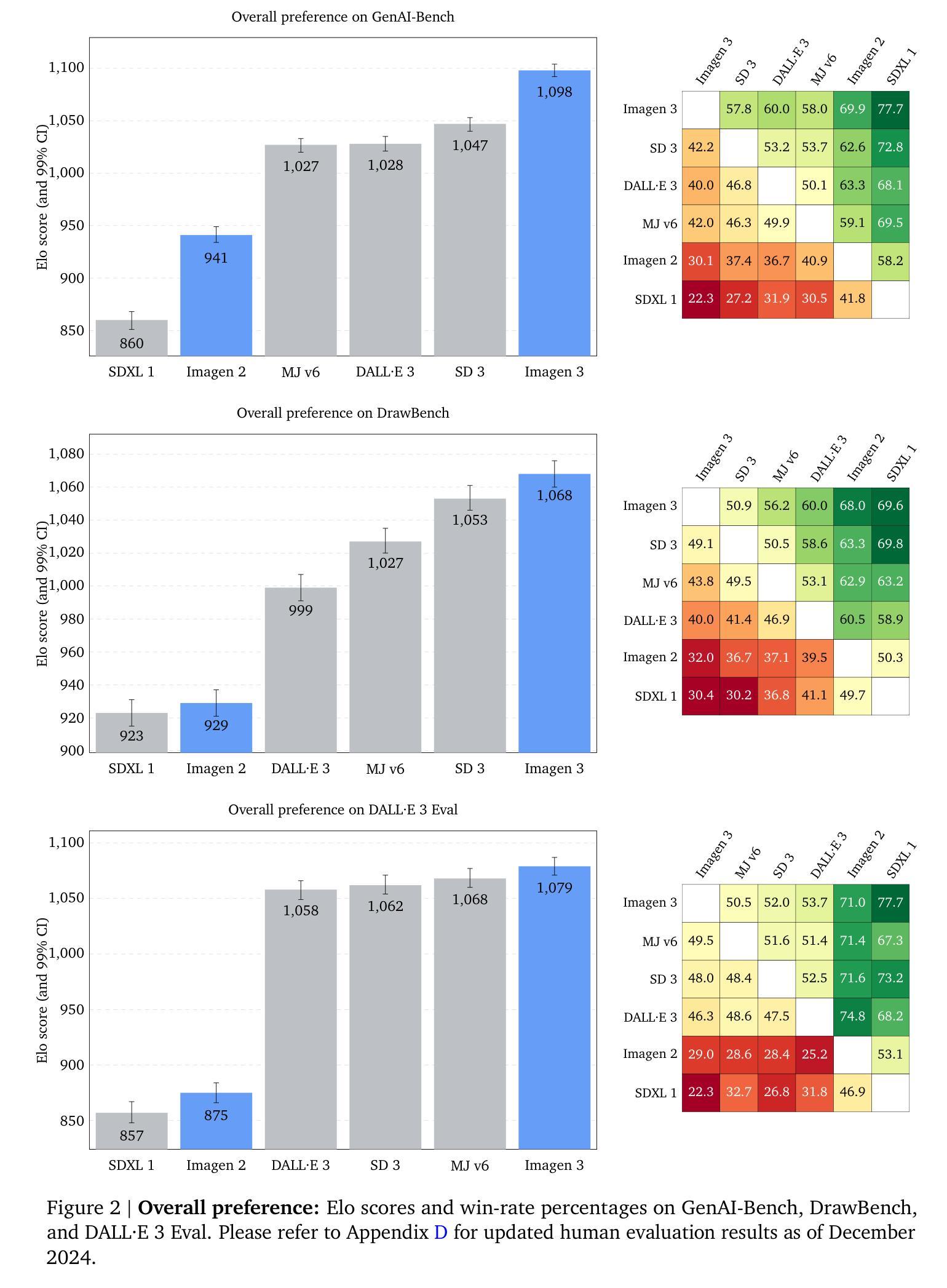
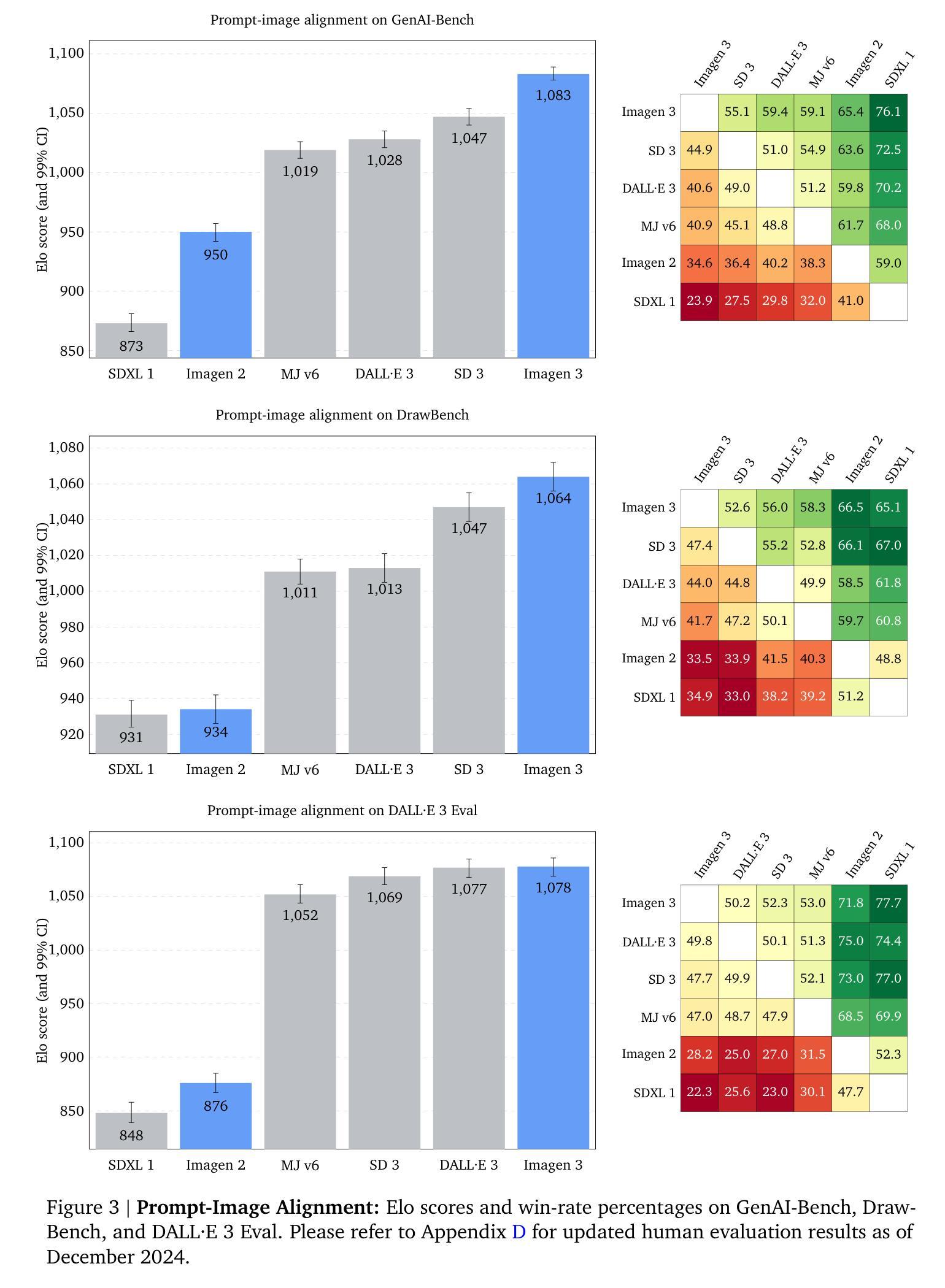
We introduce Imagen 3, a latent diffusion model that generates high quality images from text prompts. We describe our quality and responsibility evaluations. Imagen 3 is preferred over other state-of-the-art (SOTA) models at the time of evaluation. In addition, we discuss issues around safety and representation, as well as methods we used to minimize the potential harm of our models.
我们介绍了Imagen 3,这是一个从文本提示生成高质量图像的潜在扩散模型。我们描述了我们的质量和责任评估。在评估时,Imagen 3优于其他当时的最先进(SOTA)模型。此外,我们还讨论了安全和表征方面的问题,以及我们用来最小化模型潜在危害的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
我们介绍了Imagen 3,一种从文本提示生成高质量图像的潜在扩散模型。我们描述了其质量和责任评估,相较于当时的其他最先进模型,Imagen 3更胜一筹。同时,我们也探讨了安全性和表征相关问题,以及我们用于减少模型潜在危害的方法。
Key Takeaways
- Imagen 3是一种能够生成高质量图像的潜在扩散模型。
- Imagen 3在质量评估中被认为是优于其他最先进模型的。
- 该研究对其模型进行了责任评估。
- 安全性是模型应用中的重要议题,并讨论了与表征相关的问题。
- 该研究讨论了如何最小化模型的潜在危害。
- 该模型能够通过文本提示生成图像。
点此查看论文截图

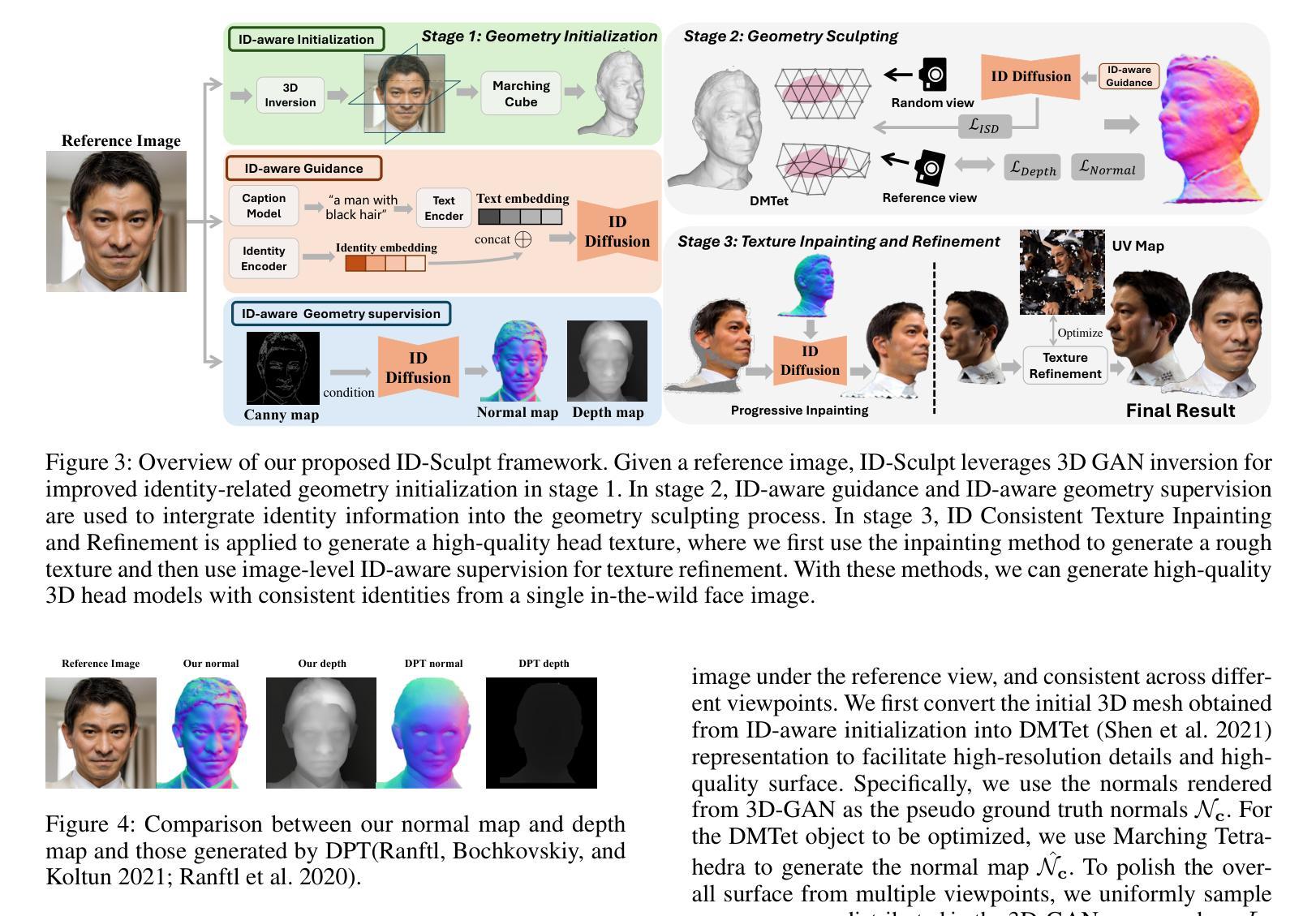
ID-Sculpt: ID-aware 3D Head Generation from Single In-the-wild Portrait Image
Authors:Jinkun Hao, Junshu Tang, Jiangning Zhang, Ran Yi, Yijia Hong, Moran Li, Weijian Cao, Yating Wang, Chengjie Wang, Lizhuang Ma
While recent works have achieved great success on image-to-3D object generation, high quality and fidelity 3D head generation from a single image remains a great challenge. Previous text-based methods for generating 3D heads were limited by text descriptions and image-based methods struggled to produce high-quality head geometry. To handle this challenging problem, we propose a novel framework, ID-Sculpt, to generate high-quality 3D heads while preserving their identities. Our work incorporates the identity information of the portrait image into three parts: 1) geometry initialization, 2) geometry sculpting, and 3) texture generation stages. Given a reference portrait image, we first align the identity features with text features to realize ID-aware guidance enhancement, which contains the control signals representing the face information. We then use the canny map, ID features of the portrait image, and a pre-trained text-to-normal/depth diffusion model to generate ID-aware geometry supervision, and 3D-GAN inversion is employed to generate ID-aware geometry initialization. Furthermore, with the ability to inject identity information into 3D head generation, we use ID-aware guidance to calculate ID-aware Score Distillation (ISD) for geometry sculpting. For texture generation, we adopt the ID Consistent Texture Inpainting and Refinement which progressively expands the view for texture inpainting to obtain an initialization UV texture map. We then use the ID-aware guidance to provide image-level supervision for noisy multi-view images to obtain a refined texture map. Extensive experiments demonstrate that we can generate high-quality 3D heads with accurate geometry and texture from a single in-the-wild portrait image.
近期的工作在图像到3D物体的生成上取得了巨大成功,但从单张图像生成高质量和高保真度的3D头像仍然是一个巨大的挑战。之前基于文本的方法生成3D头像受限于文本描述,而基于图像的方法很难产生高质量的头像几何结构。为了解决这个具有挑战性的问题,我们提出了一种新型框架ID-Sculpt,用于生成高质量的3D头像,同时保留其身份特征。我们的工作将肖像图像的身份信息融入三个阶段:1)几何初始化,2)几何雕塑,3)纹理生成。给定一个参考肖像图像,我们首先通过文本特征对齐身份特征,以实现ID感知指导增强,其中包含代表面部信息的控制信号。然后,我们使用Canny地图、肖像图像的身份特征以及预训练的文本到法线/深度扩散模型来生成ID感知的几何监督,并利用3D-GAN反转来生成ID感知的几何初始化。此外,通过向3D头像生成中注入身份信息的能力,我们使用ID感知指导来计算用于几何雕塑的ID感知得分蒸馏(ISD)。对于纹理生成,我们采用身份一致性纹理修复与细化法,逐步扩展视图进行纹理修复,以获得初始UV纹理贴图。然后,我们使用ID感知指导为噪声多视角图像提供图像级监督,以获得精细纹理贴图。大量实验表明,我们可以从一张野外的肖像图像生成高质量、几何和纹理准确的3D头像。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025; Project page: https://jinkun-hao.github.io/ID-Sculpt/
Summary
本文提出一种新型框架ID-Sculpt,能够生成高质量且保持身份信息的3D头像。该框架将肖像图像的身份信息融入三个阶段:几何初始化、几何雕塑和纹理生成。通过身份感知指导增强和ID感知几何监督,实现ID感知几何初始化。利用3D-GAN反演进行几何雕塑的ID感知评分蒸馏,并采用ID一致纹理修复与细化,逐步扩展视图进行纹理填充,获得初始UV纹理贴图,进而在噪声多角度图像上提供ID感知指导,得到精细纹理贴图。实验证明,该框架能够从单张野外肖像图像生成高质量、准确的3D头像。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种新型框架ID-Sculpt,旨在解决从单张图像生成高质量3D头像的挑战。
- 框架将身份信息共享到几何初始化、几何雕塑和纹理生成三个阶段。
- 通过身份感知指导增强和ID感知几何监督实现ID感知几何初始化。
- 利用3D-GAN反演进行几何雕塑的ID感知评分蒸馏。
- 采用ID一致纹理修复与细化,逐步扩展视图进行纹理填充,获得高质量的纹理贴图。
- 框架能够从单张野外肖像图像生成准确且逼真的3D头像。
- 通过广泛实验验证了框架的有效性和性能。
点此查看论文截图



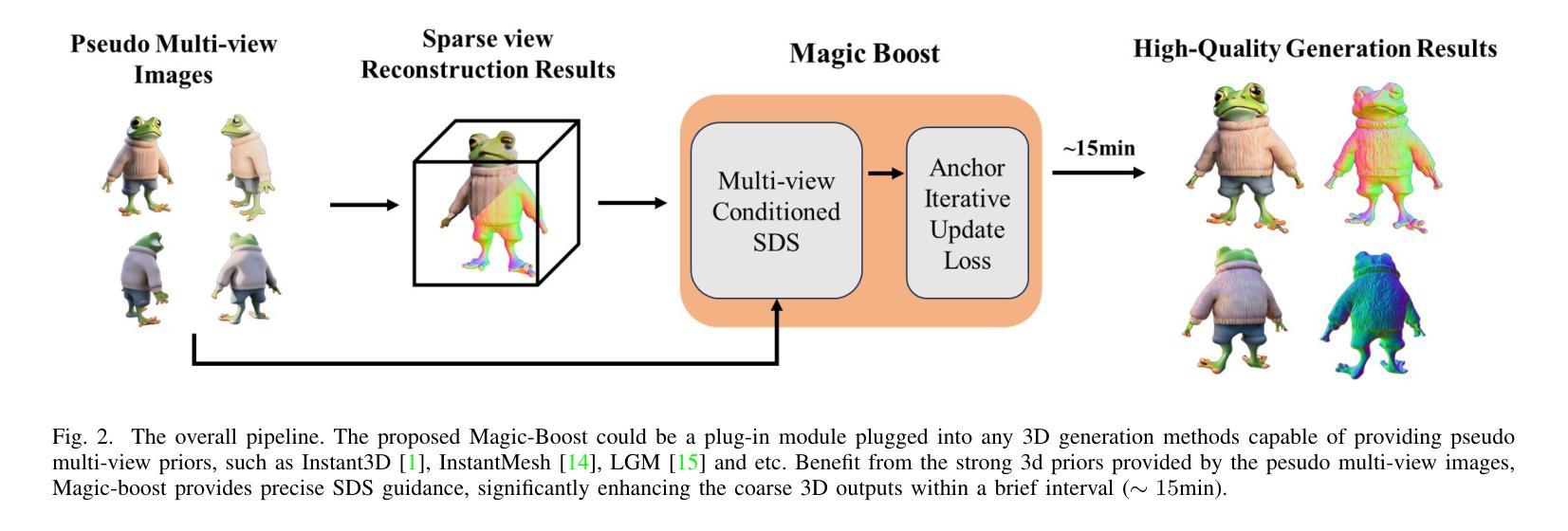
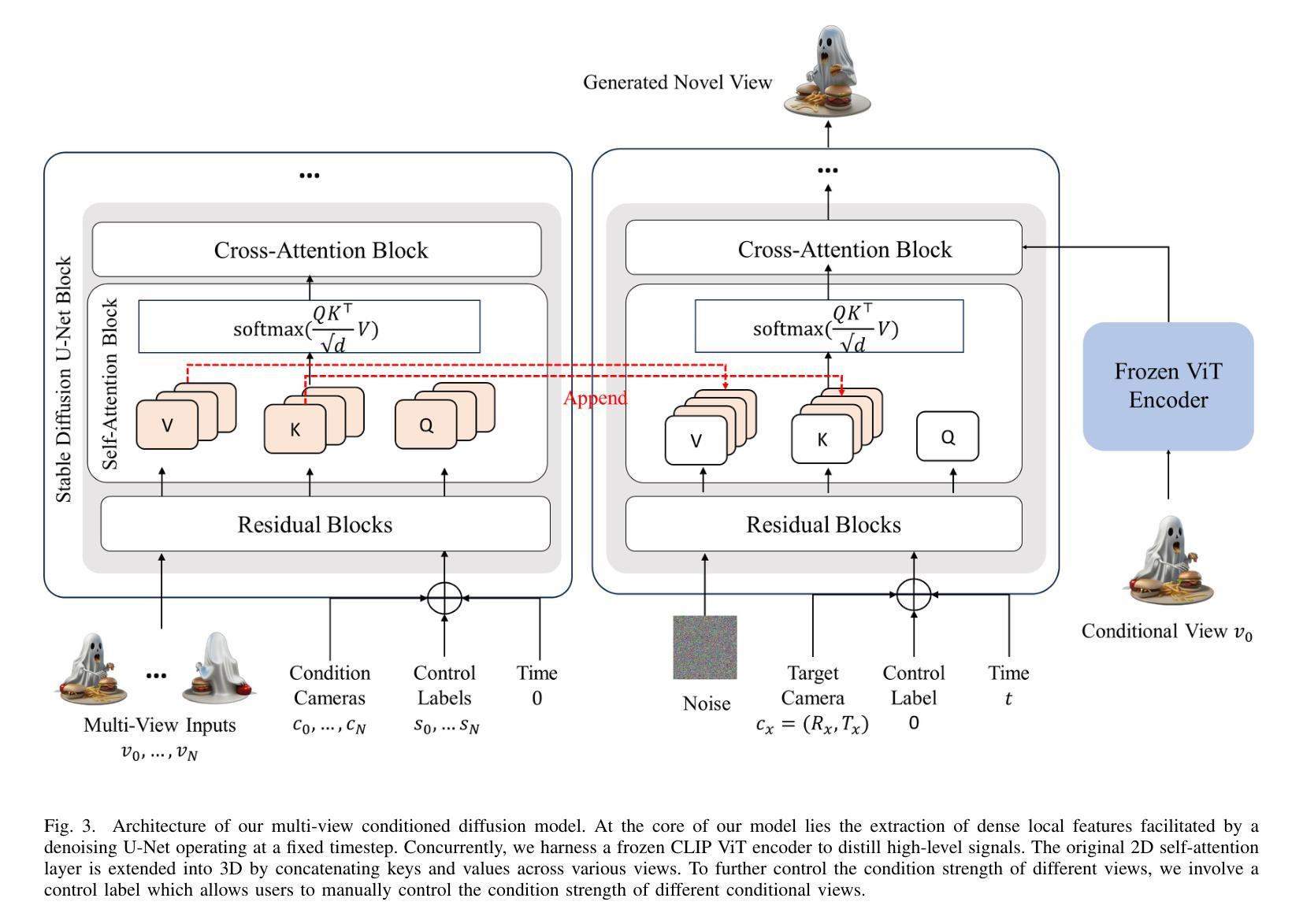
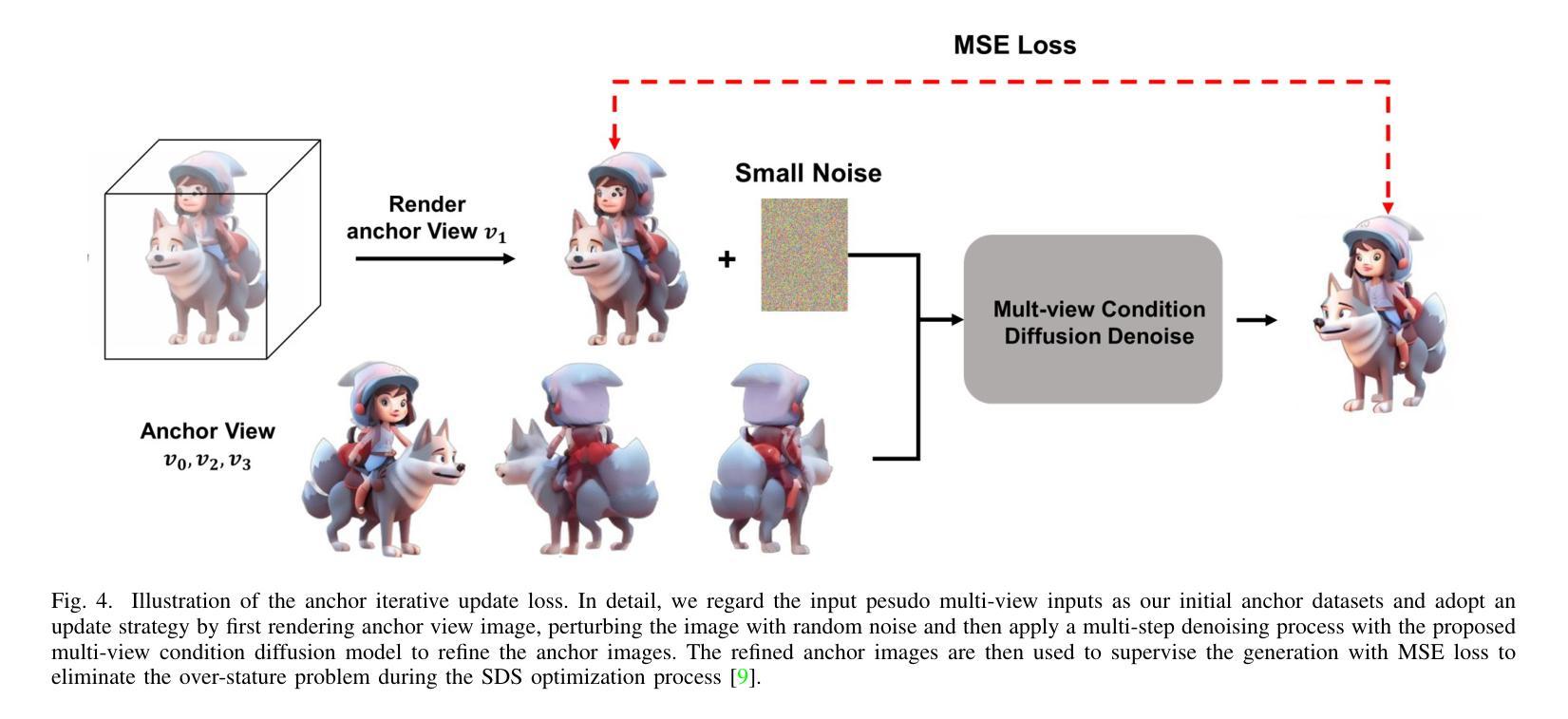
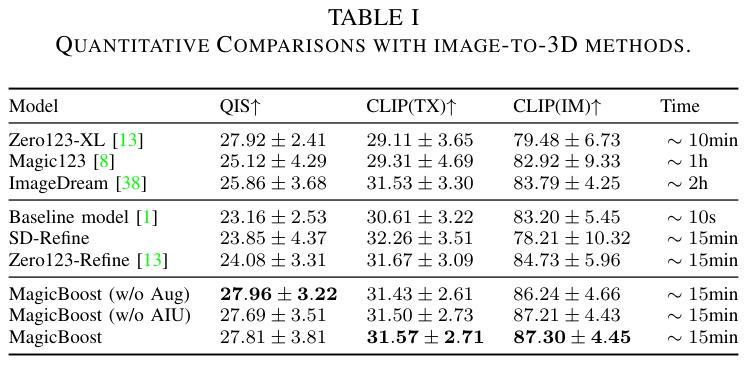
Magic-Boost: Boost 3D Generation with Mutli-View Conditioned Diffusion
Authors:Fan Yang, Jianfeng Zhang, Yichun Shi, Bowen Chen, Chenxu Zhang, Huichao Zhang, Xiaofeng Yang, Xiu Li, Jiashi Feng, Guosheng Lin
Benefiting from the rapid development of 2D diffusion models, 3D content generation has witnessed significant progress. One promising solution is to finetune the pre-trained 2D diffusion models to produce multi-view images and then reconstruct them into 3D assets via feed-forward sparse-view reconstruction models. However, limited by the 3D inconsistency in the generated multi-view images and the low reconstruction resolution of the feed-forward reconstruction models, the generated 3d assets are still limited to incorrect geometries and blurry textures. To address this problem, we present a multi-view based refine method, named Magic-Boost, to further refine the generation results. In detail, we first propose a novel multi-view conditioned diffusion model which extracts 3d prior from the synthesized multi-view images to synthesize high-fidelity novel view images and then introduce a novel iterative-update strategy to adopt it to provide precise guidance to refine the coarse generated results through a fast optimization process. Conditioned on the strong 3d priors extracted from the synthesized multi-view images, Magic-Boost is capable of providing precise optimization guidance that well aligns with the coarse generated 3D assets, enriching the local detail in both geometry and texture within a short time ($\sim15$min). Extensive experiments show Magic-Boost greatly enhances the coarse generated inputs, generates high-quality 3D assets with rich geometric and textural details. (Project Page: https://magic-research.github.io/magic-boost/)
得益于2D扩散模型的快速发展,3D内容生成已经取得了显著进步。一种有前途的解决方案是通过微调预训练的2D扩散模型来生成多视角图像,然后通过前馈稀疏视图重建模型将它们重建为3D资产。然而,由于生成的多视角图像中的3D不一致性和前馈重建模型的低重建分辨率,生成的3D资产仍然受限于不正确的几何形状和模糊的纹理。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于多视角的细化方法,名为Magic-Boost,进一步优化生成结果。具体来说,我们首先提出了一种新型的多视角条件扩散模型,该模型从合成的多视角图像中提取3D先验知识,合成高保真度的新视角图像,然后引入了一种新型迭代更新策略,将其应用于为粗略生成的结果提供精确指导,通过快速优化过程进行细化。基于从合成多视角图像中提取的强大3D先验知识,Magic-Boost能够提供与粗略生成的3D资产高度匹配的精确优化指导,在短时间内(~15分钟)丰富几何和纹理的局部细节。大量实验表明,Magic-Boost极大地提升了粗略生成的输入,生成了高质量、具有丰富几何和纹理细节的3D资产。(项目页面:https://magic-research.github.io/magic-boost/)
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
得益于二维扩散模型的快速发展,三维内容生成领域取得了显著进步。一种有前途的解决方案是通过微调预训练的二维扩散模型来生成多视图图像,然后通过前馈稀疏视图重建模型将其重建为三维资产。然而,由于生成的多视图图像中的三维不一致性和前馈重建模型的重构分辨率较低,生成的3D资产仍然存在几何不正确和纹理模糊的问题。为解决此问题,我们提出了一种基于多视图的精细方法,名为Magic-Boost,以进一步改进生成结果。具体来说,我们首先提出一种新型的多视图条件扩散模型,从合成的多视图图像中提取三维先验知识来合成高保真度的新视图图像,然后引入一种新型迭代更新策略来适应它,以通过快速优化过程为粗糙的生成结果提供精确的指导。基于从合成多视图图像中提取的强大三维先验知识,Magic-Boost能够提供与粗糙生成的3D资产高度对齐的精确优化指导,短时间内(~15分钟)丰富了几何和纹理的局部细节。大量实验表明,Magic-Boost极大地提高了粗略生成的输入,生成了高质量、具有丰富几何和纹理细节的三维资产。
关键见解
- 二维扩散模型的快速发展推动了三维内容生成领域的进步。
- 通过微调预训练的二维扩散模型生成多视图图像是一种有前景的方法。
- 生成的多视图图像中的三维不一致性和前馈重建模型的重构分辨率限制是现有技术面临的挑战。
- Magic-Boost是一种基于多视图的精细方法,旨在改进生成结果。
- Magic-Boost利用多视图条件扩散模型从合成的多视图图像中提取三维先验知识。
- Magic-Boost采用迭代更新策略来精确优化粗糙生成的3D资产。
- Magic-Boost能够在短时间内生成高质量的三维资产,具有丰富几何和纹理细节。
点此查看论文截图