⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-25 更新
Editing Implicit and Explicit Representations of Radiance Fields: A Survey
Authors:Arthur Hubert, Gamal Elghazaly, Raphael Frank
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) revolutionized novel view synthesis in recent years by offering a new volumetric representation, which is compact and provides high-quality image rendering. However, the methods to edit those radiance fields developed slower than the many improvements to other aspects of NeRF. With the recent development of alternative radiance field-based representations inspired by NeRF as well as the worldwide rise in popularity of text-to-image models, many new opportunities and strategies have emerged to provide radiance field editing. In this paper, we deliver a comprehensive survey of the different editing methods present in the literature for NeRF and other similar radiance field representations. We propose a new taxonomy for classifying existing works based on their editing methodologies, review pioneering models, reflect on current and potential new applications of radiance field editing, and compare state-of-the-art approaches in terms of editing options and performance.
神经辐射场(NeRF)为体积表示法提供了一种新的形式,这种形式紧凑且能提供高质量图像渲染,从而彻底改变了近年来的新视角合成技术。然而,编辑这些辐射场的方法的发展速度比NeRF其他方面改进的速度要慢。随着最近受NeRF启发的其他辐射场表示方法的发展以及全球文本到图像模型的普及,出现了许多新的机会和策略来提供辐射场编辑功能。在本文中,我们对文献中针对NeRF和其他类似辐射场表示的不同编辑方法进行了全面的调查。我们基于编辑方法论提出了新的分类法来分类现有作品,回顾了开创性模型,思考了辐射场编辑的当前和潜在新应用,并在编辑选项和性能方面比较了最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
NeRF的神经网络辐射场为新型视图合成提供了高质量图像渲染的紧凑体积表示,但其编辑方法发展较慢。随着受NeRF启发的其他辐射场表示方法的出现以及文本到图像模型的普及,新兴的策略和机会涌现,用于编辑辐射场。本文全面综述了文献中针对NeRF和其他类似辐射场表示的不同编辑方法,提出了基于编辑方法的新分类法,回顾了开创性模型,思考了辐射场编辑的当前和潜在应用,并比较了编辑选项和性能方面的最新先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF通过其神经网络辐射场为新型视图合成提供了高质量图像渲染的紧凑体积表示。
- NeRF的编辑方法发展相对较慢,但新的辐射场表示方法和文本到图像模型的普及为其带来了新的机遇。
- 本文全面综述了针对NeRF和其他辐射场表示的编辑方法,并提出了基于编辑方法的新分类法。
- 文章回顾了一些开创性的模型在辐射场编辑领域的应用。
- 当前和未来的辐射场编辑应用被探讨,包括可能的新的使用场景和趋势。
- 文章比较了不同编辑方法的性能以及它们在编辑选项方面的优势。
点此查看论文截图

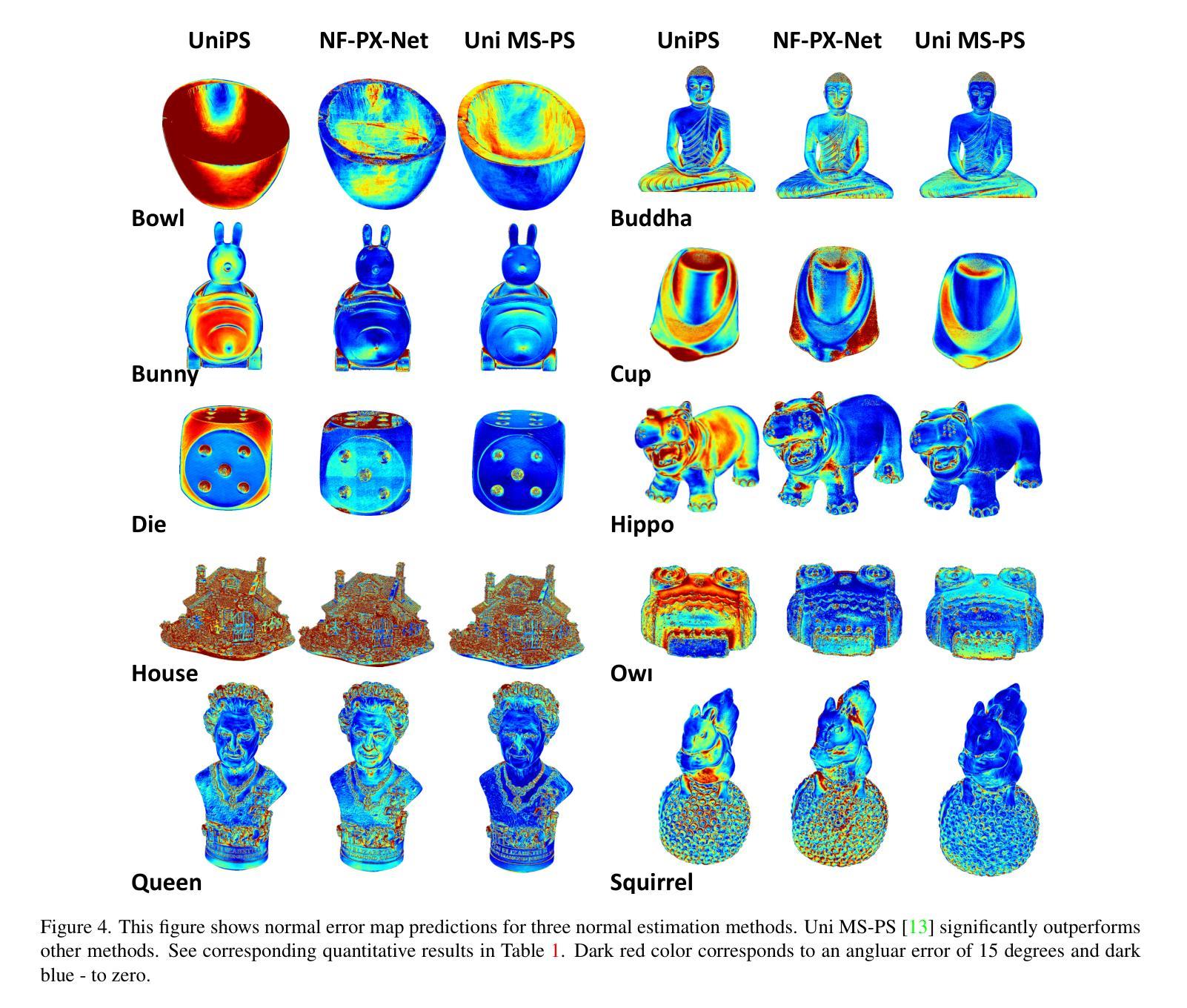
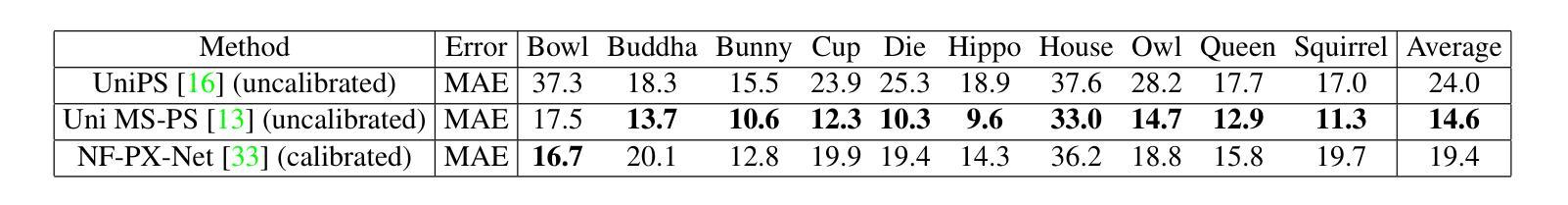
LUCES-MV: A Multi-View Dataset for Near-Field Point Light Source Photometric Stereo
Authors:Fotios Logothetis, Ignas Budvytis, Stephan Liwicki, Roberto Cipolla
The biggest improvements in Photometric Stereo (PS) field has recently come from adoption of differentiable volumetric rendering techniques such as NeRF or Neural SDF achieving impressive reconstruction error of 0.2mm on DiLiGenT-MV benchmark. However, while there are sizeable datasets for environment lit objects such as Digital Twin Catalogue (DTS), there are only several small Photometric Stereo datasets which often lack challenging objects (simple, smooth, untextured) and practical, small form factor (near-field) light setup. To address this, we propose LUCES-MV, the first real-world, multi-view dataset designed for near-field point light source photometric stereo. Our dataset includes 15 objects with diverse materials, each imaged under varying light conditions from an array of 15 LEDs positioned 30 to 40 centimeters from the camera center. To facilitate transparent end-to-end evaluation, our dataset provides not only ground truth normals and ground truth object meshes and poses but also light and camera calibration images. We evaluate state-of-the-art near-field photometric stereo algorithms, highlighting their strengths and limitations across different material and shape complexities. LUCES-MV dataset offers an important benchmark for developing more robust, accurate and scalable real-world Photometric Stereo based 3D reconstruction methods.
近期光度立体视觉(PS)领域最大的进展主要来自于采用可微分体积渲染技术,如NeRF或Neural SDF,在DiLiGenT-MV基准测试上实现了令人印象深刻的重建误差为0.2毫米。然而,虽然有大量针对环境照明物体的数据集,如数字孪生目录(DTS),但光度立体视觉数据集仅有少数几个,这些数据集通常缺乏具有挑战性的物体(简单、光滑、无纹理)以及实用、小尺寸的近场光照设置。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了LUCES-MV,这是专为近场点光源光度立体视觉设计的第一份现实世界多视角数据集。我们的数据集包含15个不同材质的对象,每个对象都在不同的光照条件下,由一组距离相机中心30至40厘米的15个LED拍摄。为了方便端到端的透明评估,我们的数据集不仅提供了地面真实法线、地面真实物体网格和姿态,还提供了光和相机的校准图像。我们评估了最先进的近场光度立体视觉算法,突出了它们在不同材质和形状复杂度上的优势和局限性。LUCES-MV数据集为开发更稳健、准确和可扩展的现实世界光度立体视觉基于3D重建方法提供了重要基准。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
神经网络体积渲染技术(NeRF)和数字孪生目录(DTS)数据集的发展促进了光度立体视觉领域的进展。针对近场光度立体视觉缺乏挑战性和实用性问题,提出LUCES-MV数据集,包含多种材质物体和复杂的近场光源配置,促进更稳健、准确、可扩展的光度立体视觉方法的发展。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF等可微分体积渲染技术在重建误差方面取得了显著进展。
- 目前存在大型环境照明物体数据集如Digital Twin Catalogue(DTS),但针对近场光度立体视觉的数据集较少且缺乏挑战性。
- LUCES-MV数据集是首个针对近场点光源光度立体的真实世界多视角数据集。
- LUCES-MV包含多种材质物体,在变化的光照条件下进行成像。
- 数据集提供地面真实法线、物体网格、姿态以及光和相机校准图像。
- LUCES-MV数据集为近场光度立体视觉算法提供了重要的基准测试。
点此查看论文截图


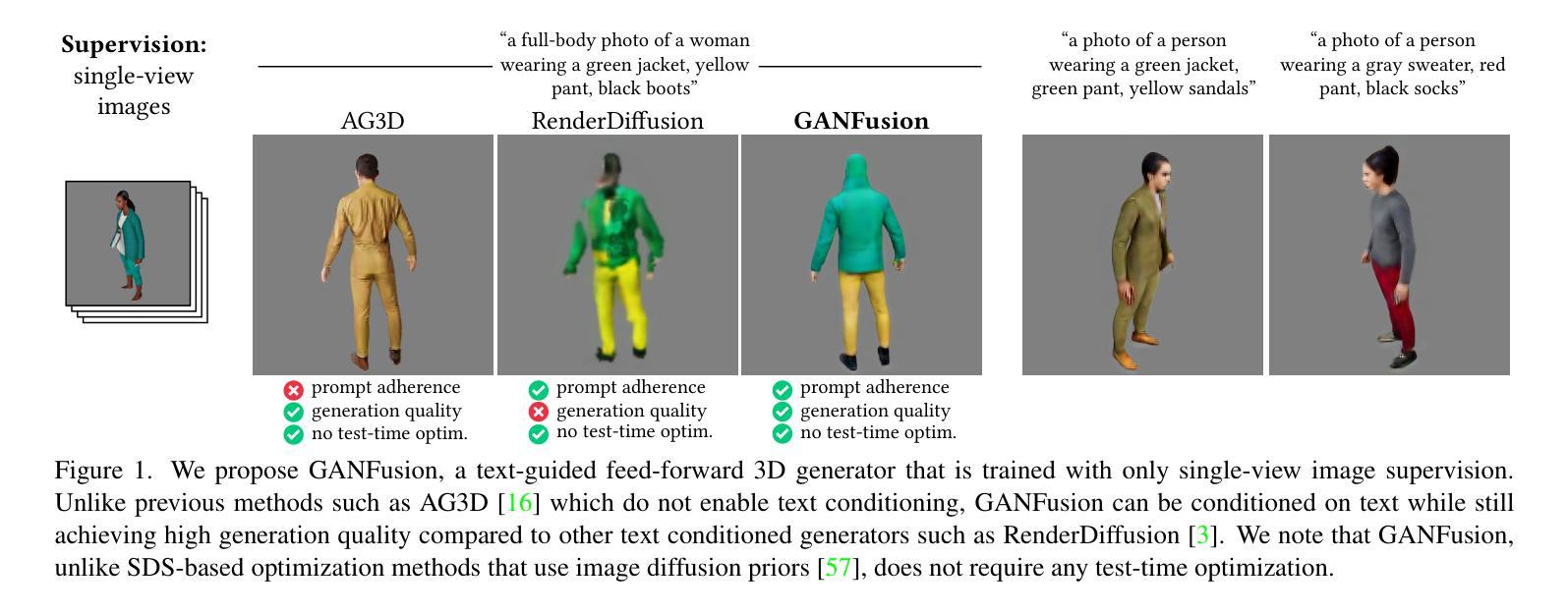
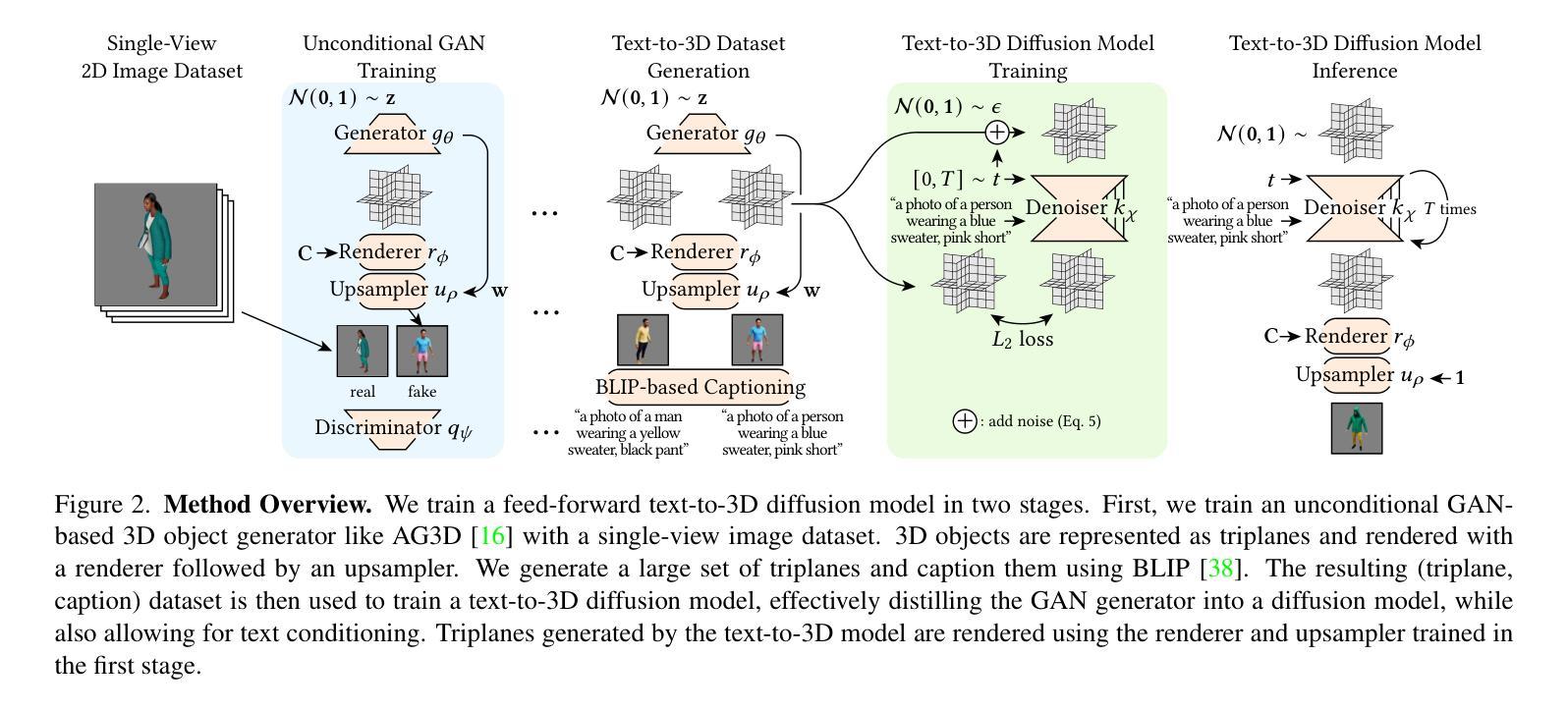
GANFusion: Feed-Forward Text-to-3D with Diffusion in GAN Space
Authors:Souhaib Attaiki, Paul Guerrero, Duygu Ceylan, Niloy J. Mitra, Maks Ovsjanikov
We train a feed-forward text-to-3D diffusion generator for human characters using only single-view 2D data for supervision. Existing 3D generative models cannot yet match the fidelity of image or video generative models. State-of-the-art 3D generators are either trained with explicit 3D supervision and are thus limited by the volume and diversity of existing 3D data. Meanwhile, generators that can be trained with only 2D data as supervision typically produce coarser results, cannot be text-conditioned, or must revert to test-time optimization. We observe that GAN- and diffusion-based generators have complementary qualities: GANs can be trained efficiently with 2D supervision to produce high-quality 3D objects but are hard to condition on text. In contrast, denoising diffusion models can be conditioned efficiently but tend to be hard to train with only 2D supervision. We introduce GANFusion, which starts by generating unconditional triplane features for 3D data using a GAN architecture trained with only single-view 2D data. We then generate random samples from the GAN, caption them, and train a text-conditioned diffusion model that directly learns to sample from the space of good triplane features that can be decoded into 3D objects.
我们仅使用单视图2D数据进行监督,训练了一个前馈文本到3D扩散生成器,用于生成人物角色。现有的3D生成模型还无法与图像或视频生成模型的保真度相匹配。最先进的3D生成器要么接受明确的3D监督训练,因此受到现有3D数据量和多样性的限制。同时,只能接受2D数据作为监督训练的生成器通常会产生较粗糙的结果,无法根据文本进行调整,或在测试时需要进行优化。我们发现基于GAN和扩散的生成器具有互补的特性:GAN可以仅通过2D监督有效地训练,产生高质量的3D对象,但很难根据文本进行调整。相比之下,降噪扩散模型可以根据文本进行高效的条件生成,但仅用2D数据进行训练时往往很难训练。我们引入了GANFusion,它首先使用仅接受单视图2D数据训练的GAN架构,为3D数据生成无条件triplane特征。然后我们从GAN生成随机样本,进行描述,并训练一个文本条件扩散模型,该模型直接学习从可以解码为3D对象的良好triplane特征空间中进行采样。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://ganfusion.github.io/
Summary
本文训练了一个前馈文本到三维扩散生成器,用于生成人物角色,仅使用单视图二维数据进行监督。现有的三维生成模型尚无法匹配图像或视频生成模型的保真度。本研究结合了GAN和扩散模型的优点,通过GAN架构生成无条件的三维数据triplane特征,然后使用文本条件扩散模型进行训练,直接学习从良好的triplane特征空间中进行采样,这些特征可以被解码为三维对象。
Key Takeaways
- 研究训练了一个前馈文本到三维扩散生成器,利用单视图二维数据进行监督。
- 当前三维生成模型的保真度尚未达到图像或视频生成模型的水平。
- GAN和扩散模型各有优点,研究尝试结合两者。
- GAN架构用于生成无条件的三维数据triplane特征。
- 文本条件扩散模型直接学习从良好的triplane特征空间中进行采样。
- 这种结合方法能够利用二维数据监督生成高质量的三维对象。
点此查看论文截图

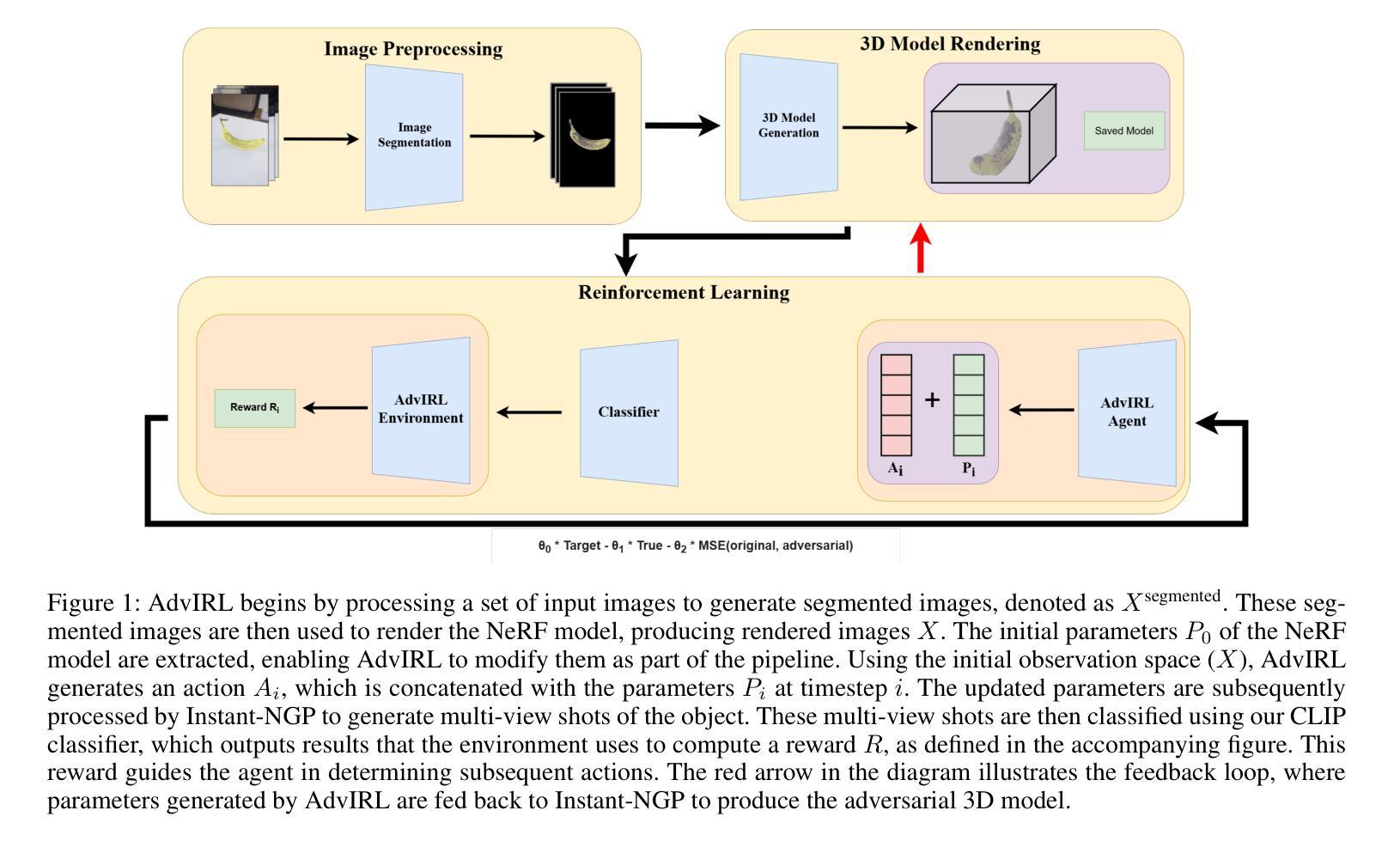
AdvIRL: Reinforcement Learning-Based Adversarial Attacks on 3D NeRF Models
Authors:Tommy Nguyen, Mehmet Ergezer, Christian Green
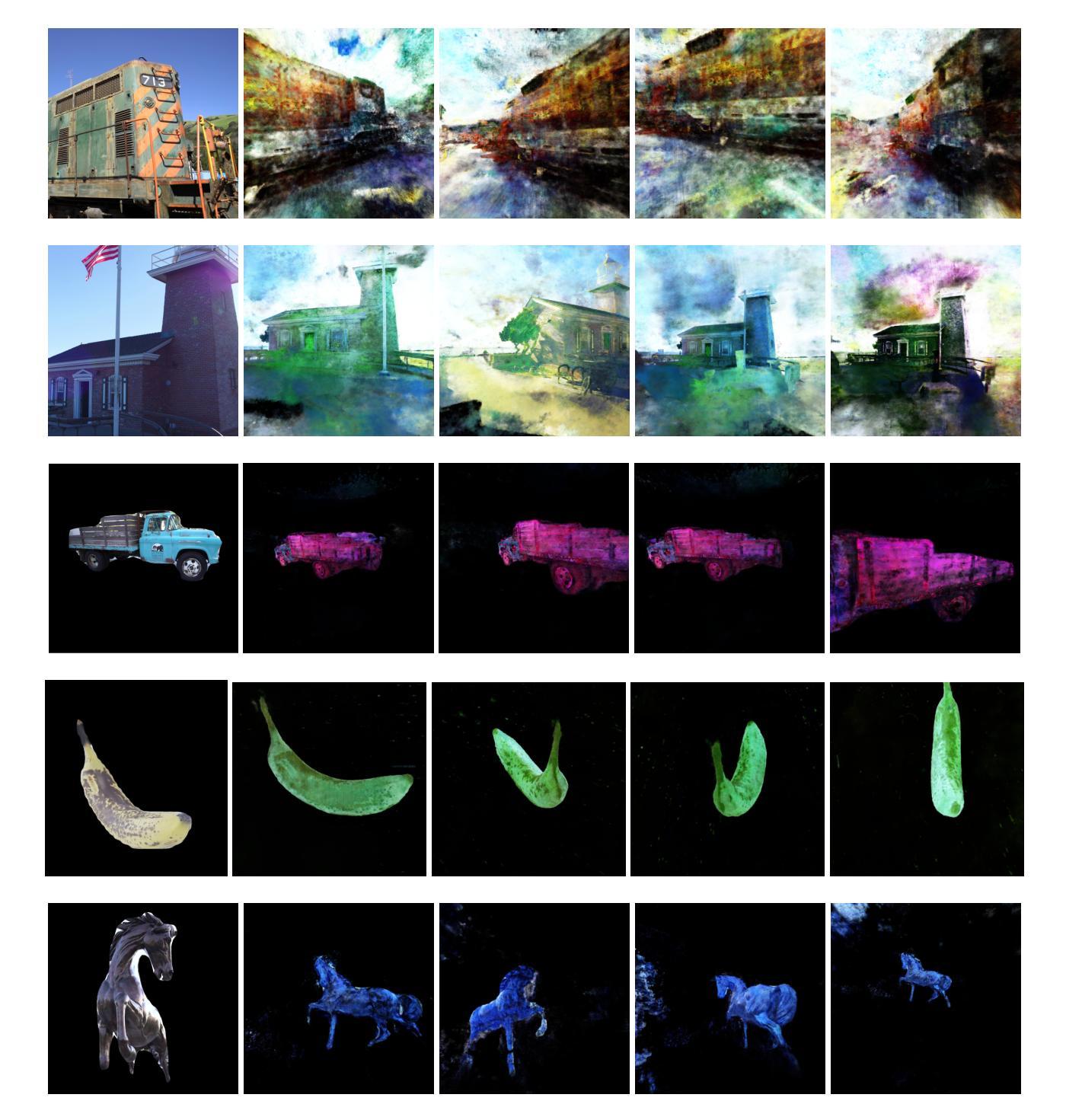
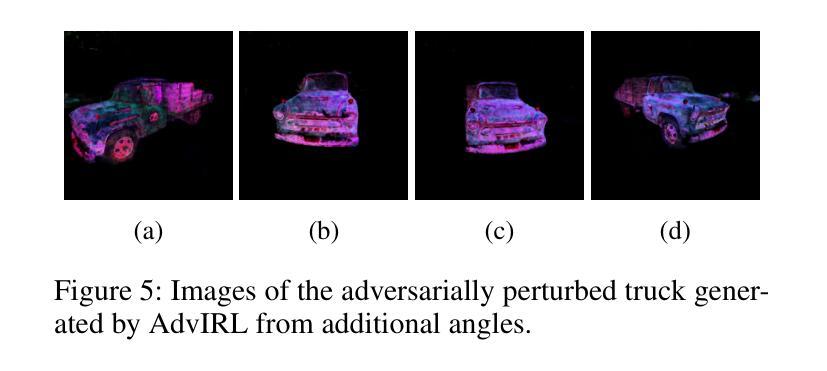
The increasing deployment of AI models in critical applications has exposed them to significant risks from adversarial attacks. While adversarial vulnerabilities in 2D vision models have been extensively studied, the threat landscape for 3D generative models, such as Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), remains underexplored. This work introduces \textit{AdvIRL}, a novel framework for crafting adversarial NeRF models using Instant Neural Graphics Primitives (Instant-NGP) and Reinforcement Learning. Unlike prior methods, \textit{AdvIRL} generates adversarial noise that remains robust under diverse 3D transformations, including rotations and scaling, enabling effective black-box attacks in real-world scenarios. Our approach is validated across a wide range of scenes, from small objects (e.g., bananas) to large environments (e.g., lighthouses). Notably, targeted attacks achieved high-confidence misclassifications, such as labeling a banana as a slug and a truck as a cannon, demonstrating the practical risks posed by adversarial NeRFs. Beyond attacking, \textit{AdvIRL}-generated adversarial models can serve as adversarial training data to enhance the robustness of vision systems. The implementation of \textit{AdvIRL} is publicly available at \url{https://github.com/Tommy-Nguyen-cpu/AdvIRL/tree/MultiView-Clean}, ensuring reproducibility and facilitating future research.
随着人工智能模型在关键应用中的部署越来越多,它们遭受敌对攻击的风险也显著上升。虽然二维视觉模型中的敌对脆弱性已经得到了广泛的研究,但针对三维生成模型(如神经辐射场(NeRF))的威胁态势仍被低估。本研究引入了名为AdvIRL的新框架,该框架使用即时神经图形原始(Instant-NGP)和强化学习来制作敌对NeRF模型。与先前的方法不同,AdvIRL生成的敌对噪声在多种三维变换(包括旋转和缩放)下保持稳健,从而在现实场景中实现了有效的黑盒攻击。我们的方法经过各种场景的验证,从小型物体(例如香蕉)到大型环境(例如灯塔)都有涵盖。值得注意的是,有针对性的攻击实现了高置信度的误分类,例如将香蕉标记为蛞蝓,将卡车标记为大炮,这显示了敌对NeRFs带来的实际风险。除了攻击之外,AdvIRL生成的敌对模型还可以作为对抗训练数据,以增强视觉系统的稳健性。AdvIRL的实现可在https://github.com/Tommy-Nguyen-cpu/AdvIRL/tree/MultiView-Clean公开访问,以确保可重复性并促进未来研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to The AAAI-25 Workshop on Artificial Intelligence for Cyber Security (AICS)
Summary
该文本介绍了针对三维生成模型(如神经辐射场NeRF)对抗性攻击的威胁。文章提出了一种名为AdvIRL的新框架,用于创建对抗性NeRF模型,使用即时神经图形原语(Instant-NGP)和强化学习。AdvIRL生成能够在多种三维变换(包括旋转和缩放)下保持稳定的对抗噪声,可实现现实世界场景中的有效黑盒攻击。该方法在不同场景(从小型物体到大型环境)中得到了验证,并且有针对性的攻击取得了高置信度的误分类结果。除了攻击功能外,AdvIRL生成的对抗模型还可以用作对抗训练数据,以提高视觉系统的鲁棒性。
Key Takeaways
- 对抗性攻击对三维生成模型(如NeRF)构成重大风险,而针对这些模型的威胁景观仍被低估。
- AdvIRL框架是一种针对NeRF模型的新型对抗攻击方法,结合了Instant-NGP和强化学习。
- AdvIRL能够在多种三维变换下生成稳健的对抗噪声,实现有效的黑盒攻击。
- AdvIRL在多种场景中进行了验证,包括小型物体和大型环境,并展示了高置信度的误分类结果。
- AdvIRL不仅可用于攻击,还可生成对抗模型作为训练数据,提高视觉系统的鲁棒性。
- AdvIRL的实施公开可用,确保了可重复性和未来研究的便利。
点此查看论文截图



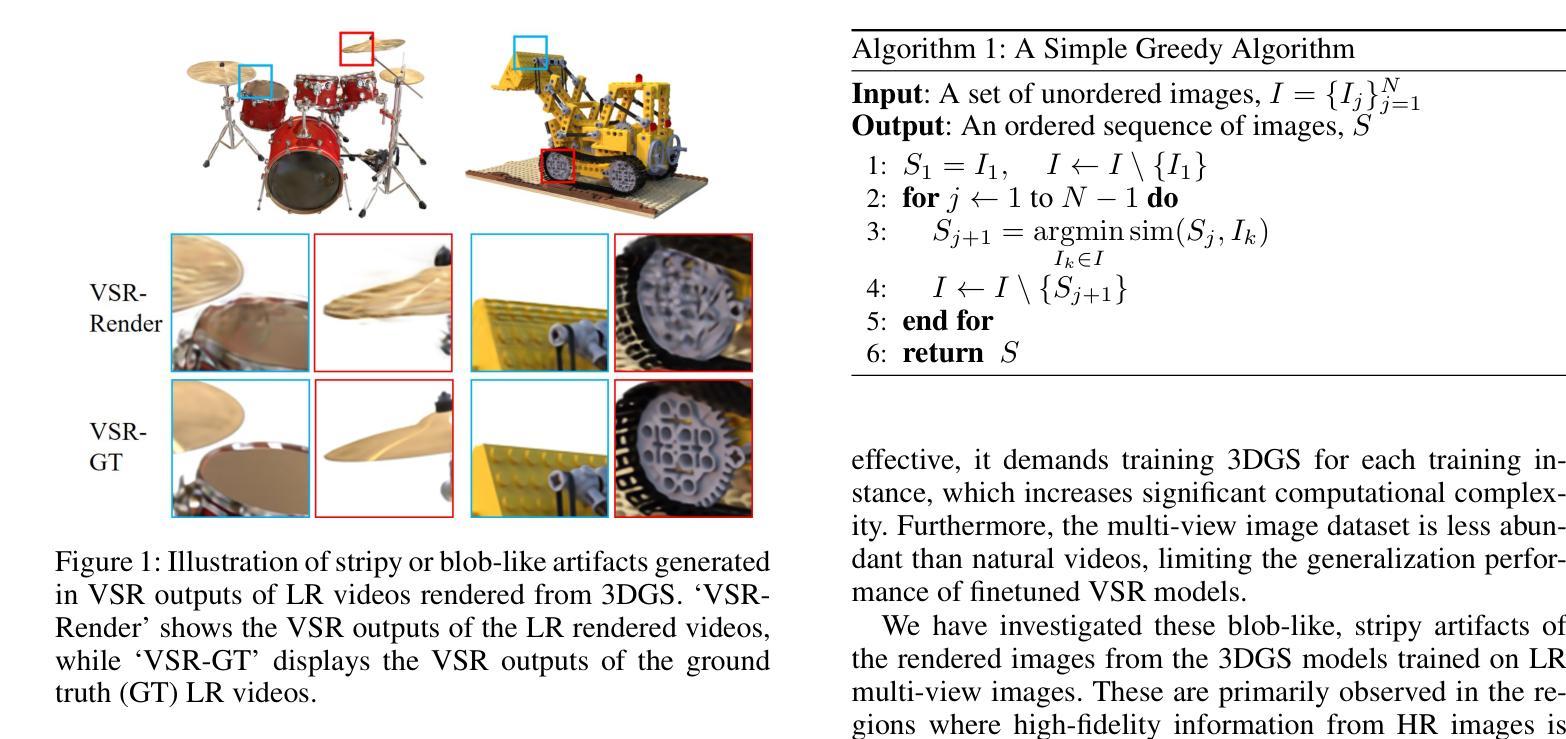
Sequence Matters: Harnessing Video Models in 3D Super-Resolution
Authors:Hyun-kyu Ko, Dongheok Park, Youngin Park, Byeonghyeon Lee, Juhee Han, Eunbyung Park
3D super-resolution aims to reconstruct high-fidelity 3D models from low-resolution (LR) multi-view images. Early studies primarily focused on single-image super-resolution (SISR) models to upsample LR images into high-resolution images. However, these methods often lack view consistency because they operate independently on each image. Although various post-processing techniques have been extensively explored to mitigate these inconsistencies, they have yet to fully resolve the issues. In this paper, we perform a comprehensive study of 3D super-resolution by leveraging video super-resolution (VSR) models. By utilizing VSR models, we ensure a higher degree of spatial consistency and can reference surrounding spatial information, leading to more accurate and detailed reconstructions. Our findings reveal that VSR models can perform remarkably well even on sequences that lack precise spatial alignment. Given this observation, we propose a simple yet practical approach to align LR images without involving fine-tuning or generating ‘smooth’ trajectory from the trained 3D models over LR images. The experimental results show that the surprisingly simple algorithms can achieve the state-of-the-art results of 3D super-resolution tasks on standard benchmark datasets, such as the NeRF-synthetic and MipNeRF-360 datasets. Project page: https://ko-lani.github.io/Sequence-Matters
三维超分辨率旨在从低分辨率(LR)多视角图像重建高保真三维模型。早期研究主要集中在单图像超分辨率(SISR)模型上,将LR图像上采样为高分辨率图像。然而,这些方法通常缺乏视角一致性,因为它们独立地处理每张图像。尽管已经广泛探索了各种后处理技术来缓解这些不一致性,但它们尚未完全解决这些问题。
在本文中,我们通过对利用视频超分辨率(VSR)模型的3D超分辨率进行深入研究。通过利用VSR模型,我们确保了更高的空间一致性,并且可以引用周围的空间信息,从而导致更精确和详细的重建。我们的研究结果表明,即使在缺乏精确空间对齐的序列上,VSR模型也可以表现出非常出色的性能。鉴于此观察结果,我们提出了一种简单而实用的方法来对齐LR图像,而无需进行微调或从训练的3D模型中对LR图像生成“平滑”轨迹。实验结果表明,这些出人意料的简单算法可以在标准基准数据集(如NeRF-synthetic和MipNeRF-360数据集)上实现3D超分辨率任务的最新结果。项目页面:https://ko-lani.github.io/Sequence-Matters
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://ko-lani.github.io/Sequence-Matters
摘要
本文探讨了利用视频超分辨率(VSR)模型进行3D超分辨率重建的方法。通过利用VSR模型,研究确保了更高的空间一致性,并能引用周围的空间信息,从而实现了更准确和详细的重建。研究发现在缺乏精确空间对齐的序列上,VSR模型也能表现出色。提出了一种简单实用的方法,无需微调或生成基于训练好的三维模型的平滑轨迹,就能实现对低分辨率图像的对齐。实验结果表明,这种出人意料的简单算法在标准数据集上实现了三维超分辨率任务的最新结果。
关键见解
- 研究采用了视频超分辨率(VSR)模型进行3D超分辨率重建,保证了更高的空间一致性。
- 通过引用周围的空间信息,VSR模型能提供更准确和详细的重建结果。
- VSR模型在缺乏精确空间对齐的序列上也能展现出卓越性能。
- 提出了一种简单实用的低分辨率图像对齐方法,无需复杂操作如微调或生成平滑轨迹。
- 该方法能够在标准数据集上实现出色的三维超分辨率重建结果。
- 研究采用了广泛的实验验证,证明了该方法在标准数据集上的优越性。
点此查看论文截图


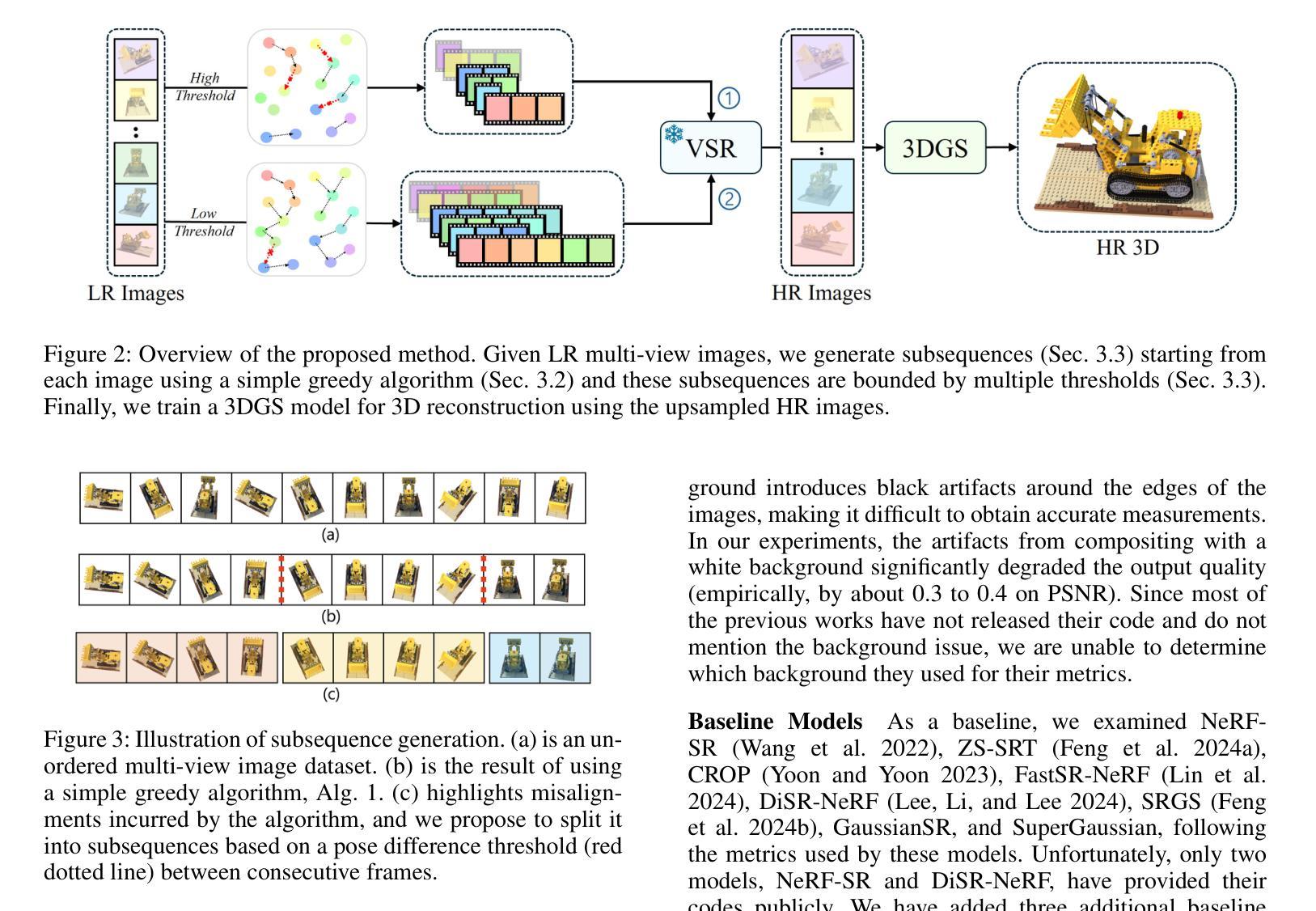
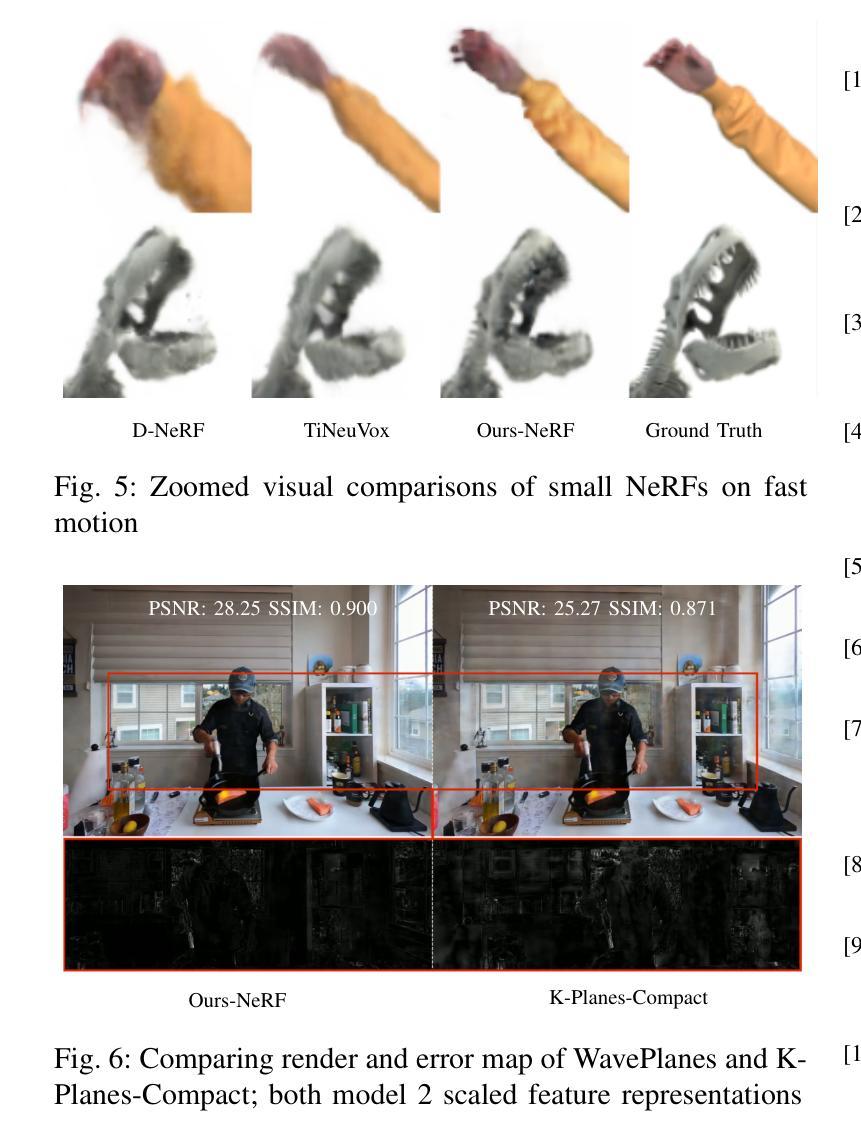
WavePlanes: Compact Hex Planes for Dynamic Novel View Synthesis
Authors:Adrian Azzarelli, Nantheera Anantrasirichai, David R Bull
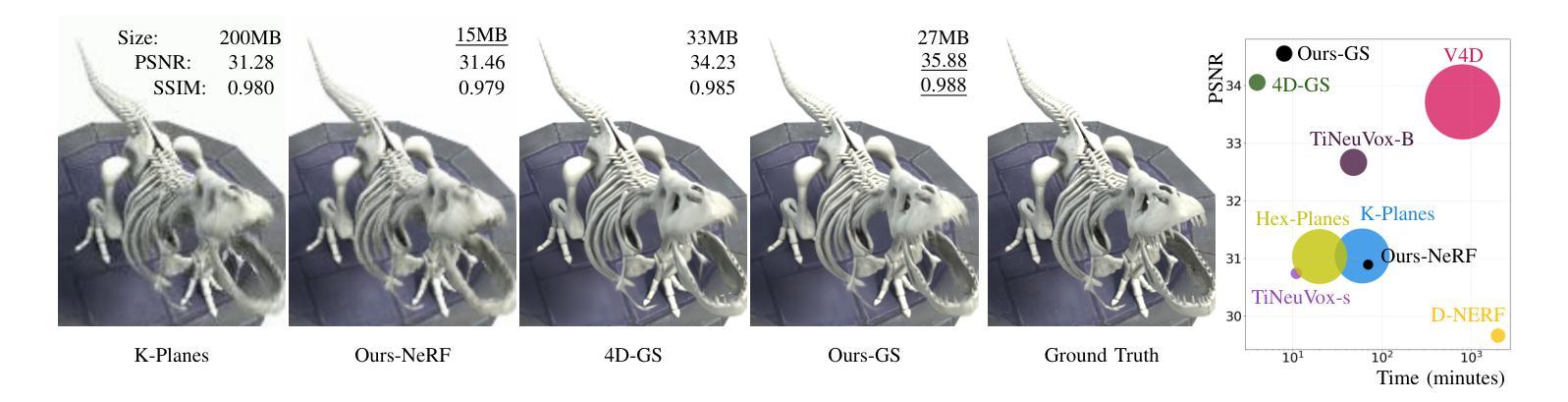
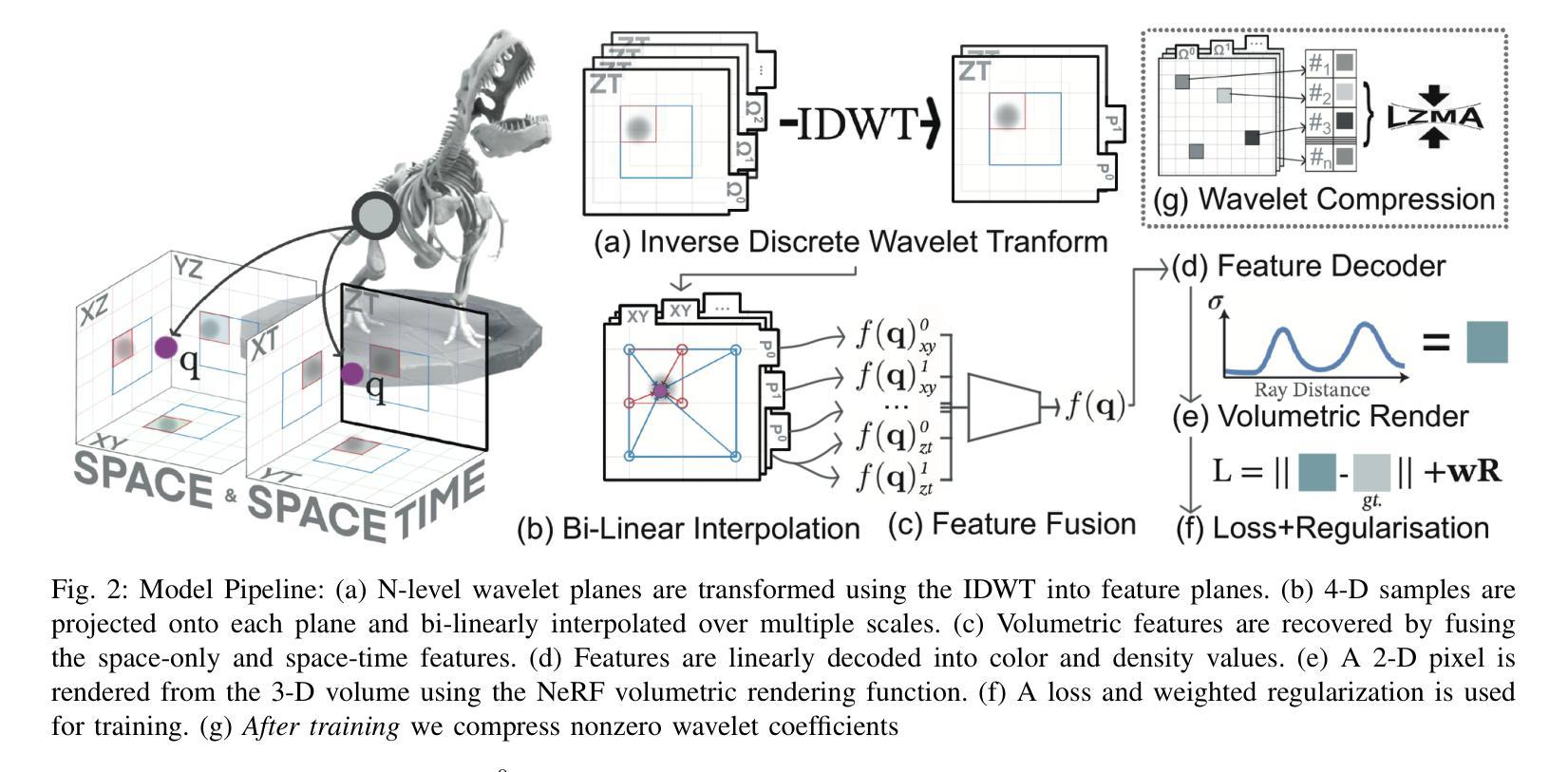
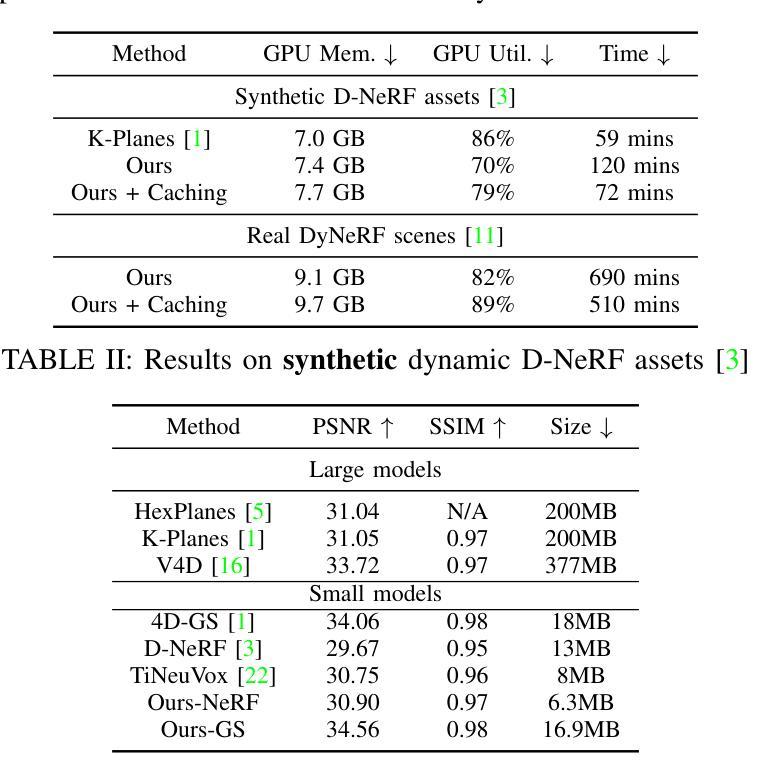
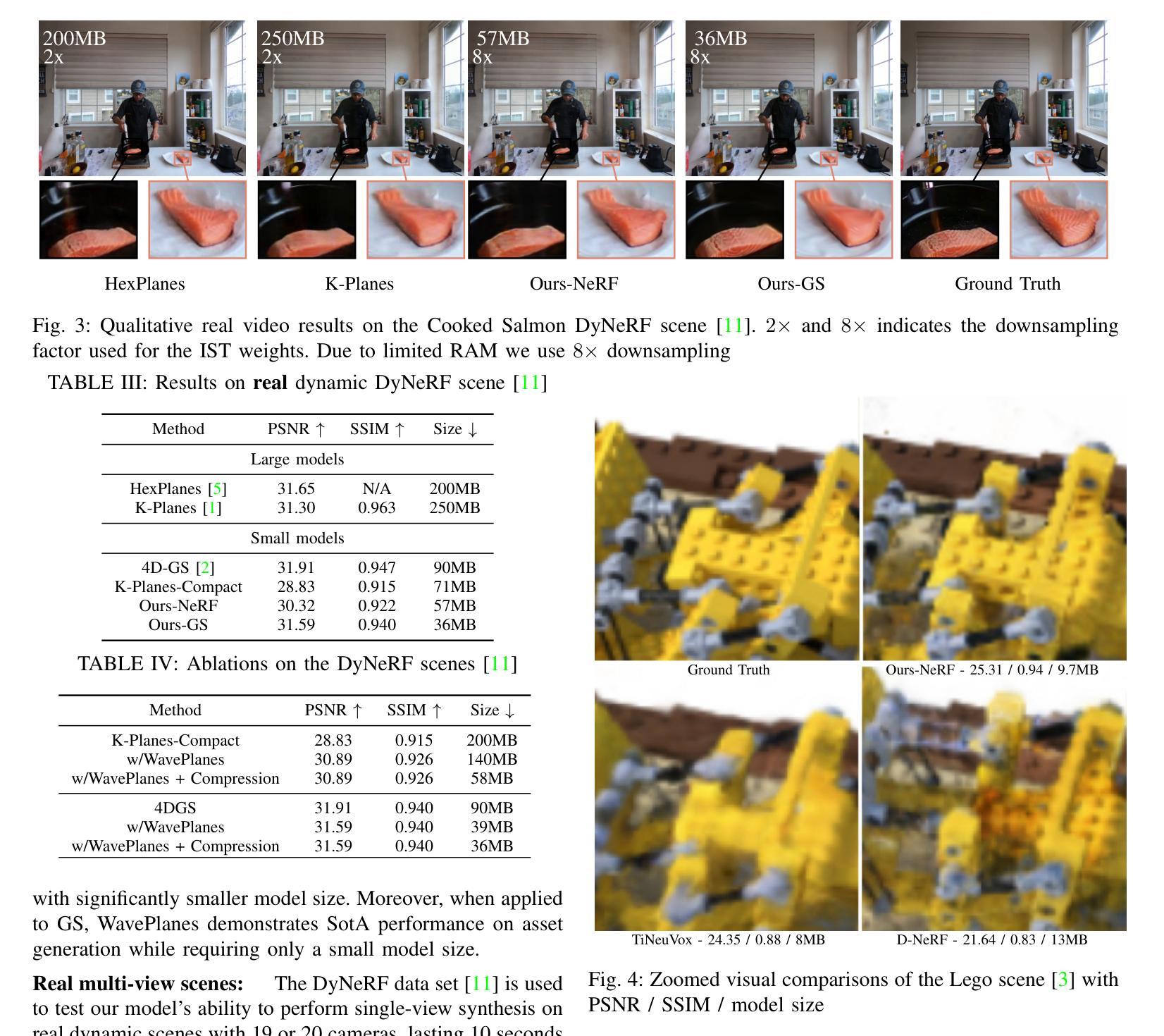
Dynamic Novel View Synthesis (Dynamic NVS) enhances NVS technologies to model moving 3-D scenes. However, current methods are resource intensive and challenging to compress. To address this, we present WavePlanes, a fast and more compact hex plane representation, applicable to both Neural Radiance Fields and Gaussian Splatting methods. Rather than modeling many feature scales separately (as done previously), we use the inverse discrete wavelet transform to reconstruct features at varying scales. This leads to a more compact representation and allows us to explore wavelet-based compression schemes for further gains. The proposed compression scheme exploits the sparsity of wavelet coefficients, by applying hard thresholding to the wavelet planes and storing nonzero coefficients and their locations on each plane in a Hash Map. Compared to the state-of-the-art (SotA), WavePlanes is significantly smaller, less resource demanding and competitive in reconstruction quality. Compared to small SotA models, WavePlanes outperforms methods in both model size and quality of novel views.
动态Novel View Synthesis(Dynamic NVS)技术增强了NVS技术,以模拟移动的3D场景。然而,当前的方法资源密集且压缩具有挑战性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了WavePlanes,这是一种快速且更紧凑的六平面表示方法,适用于神经辐射场和高斯喷涂方法。我们并不单独建模许多特征尺度(如以前所做的那样),而是使用逆离散小波变换来重建不同尺度的特征。这导致了更紧凑的表示形式,并允许我们进一步探索基于小波压缩方案以获得更多收益。所提出的压缩方案通过应用硬阈值处理小波平面并利用哈希映射存储每个平面上的非零系数及其位置来利用小波系数的稀疏性。与最新技术相比,WavePlanes体积更小、资源消耗更低并且在重建质量方面具有很强的竞争力。与小型最新技术模型相比,WavePlanes在模型大小和新颖视角的质量方面都表现出卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
动态场景的新型视图合成技术(Dynamic NVS)对NVS技术进行了增强,可以建模移动的3D场景。然而,当前的方法资源消耗大且压缩困难。为解决这一问题,我们提出了WavePlanes,这是一种快速且更紧凑的六平面表示法,适用于神经网络辐射场和高斯溅射方法。我们利用逆离散小波变换来重建不同尺度的特征,而不是像过去那样分别建模许多特征尺度。这导致了更紧凑的表示形式,并允许我们进一步探索基于小波压缩方案以获得更多收益。所提出的压缩方案利用小波系数的稀疏性,通过对小波平面应用硬阈值处理并存储每个平面上的非零系数及其位置哈希映射来实现压缩。与最新技术相比,WavePlanes体积更小、资源消耗更低、重建质量更具竞争力。相较于小型最新技术模型,WavePlanes在模型大小和新视图的质量方面都表现出优越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 动态场景的新型视图合成技术(Dynamic NVS)增强了NVS技术,使其能够建模移动的3D场景。
- 当前方法存在资源消耗大且压缩困难的问题。
- WavePlanes是一种适用于神经网络辐射场和高斯溅射方法的快速且更紧凑的六平面表示法。
- 利用逆离散小波变换进行特征重建,实现了更紧凑的模型表示。
- 提出了基于小波压缩方案的压缩策略,利用小波系数的稀疏性进行硬阈值处理。
- 与现有技术相比,WavePlanes具有更小的体积、更低的资源消耗和更具竞争力的重建质量。
点此查看论文截图