⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-25 更新
Investigating Prosodic Signatures via Speech Pre-Trained Models for Audio Deepfake Source Attribution
Authors:Orchid Chetia Phukan, Drishti Singh, Swarup Ranjan Behera, Arun Balaji Buduru, Rajesh Sharma
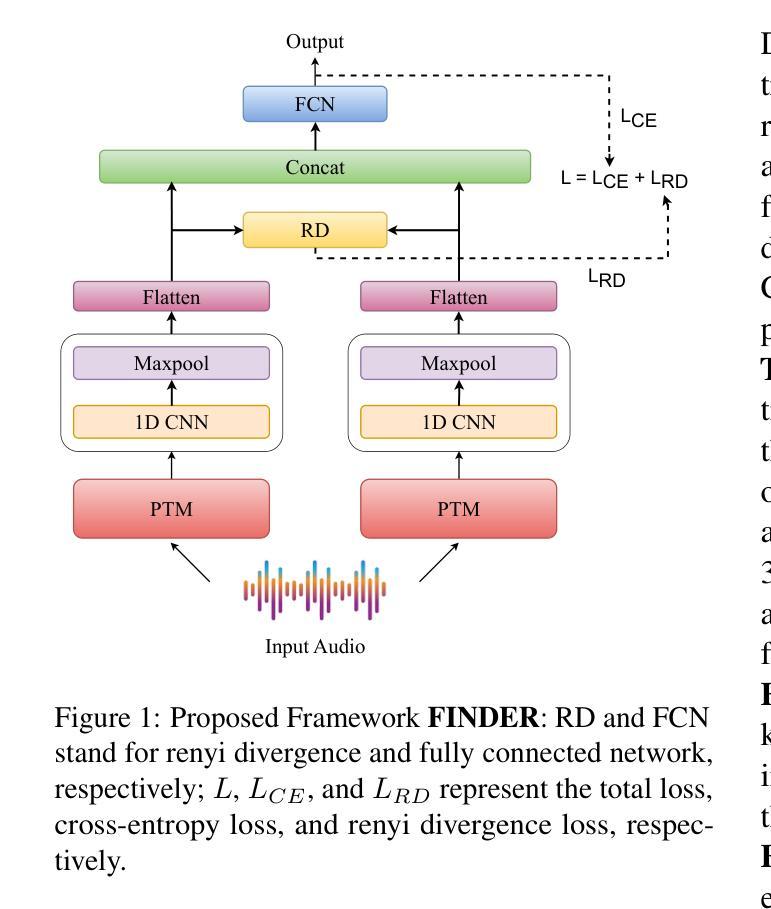
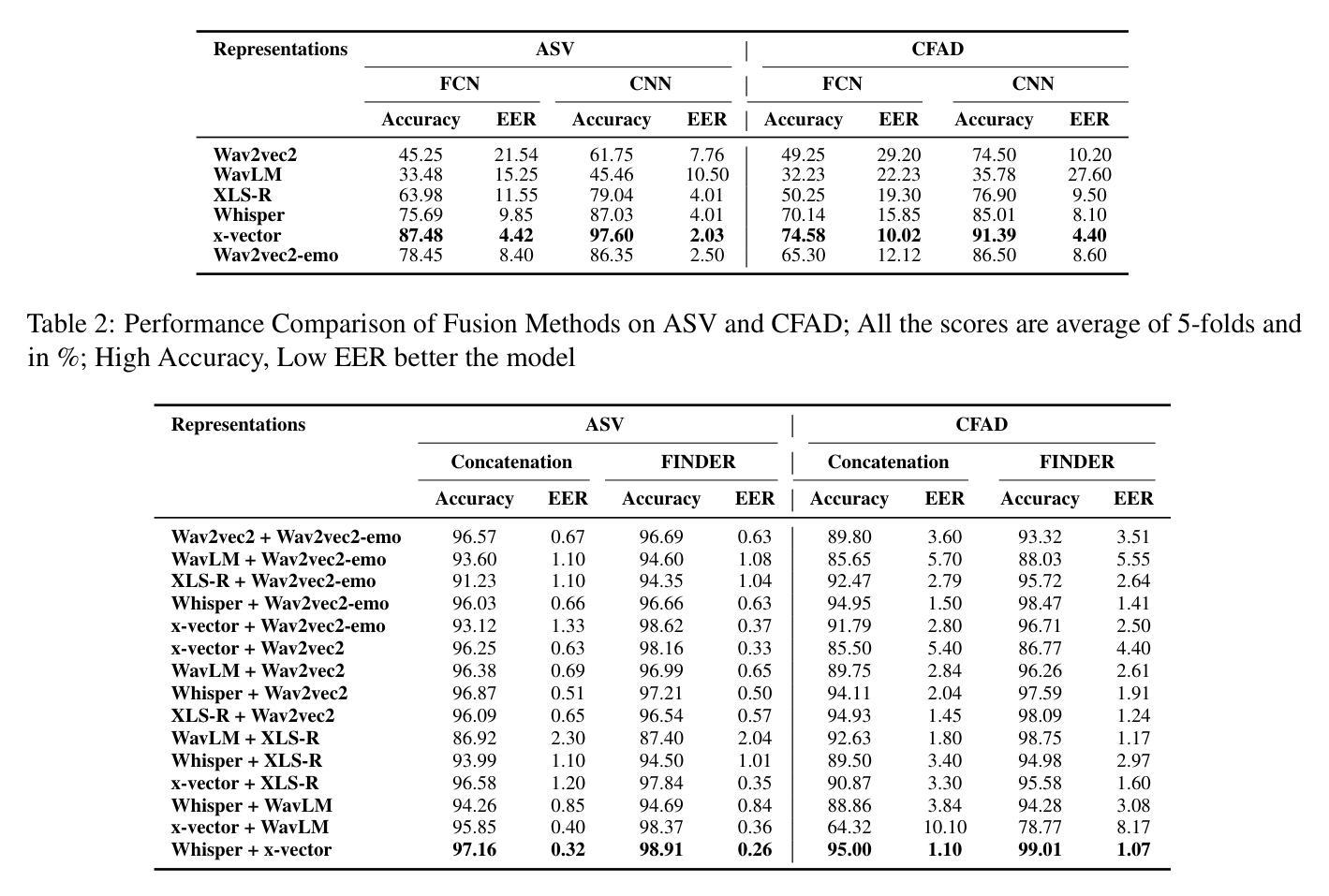
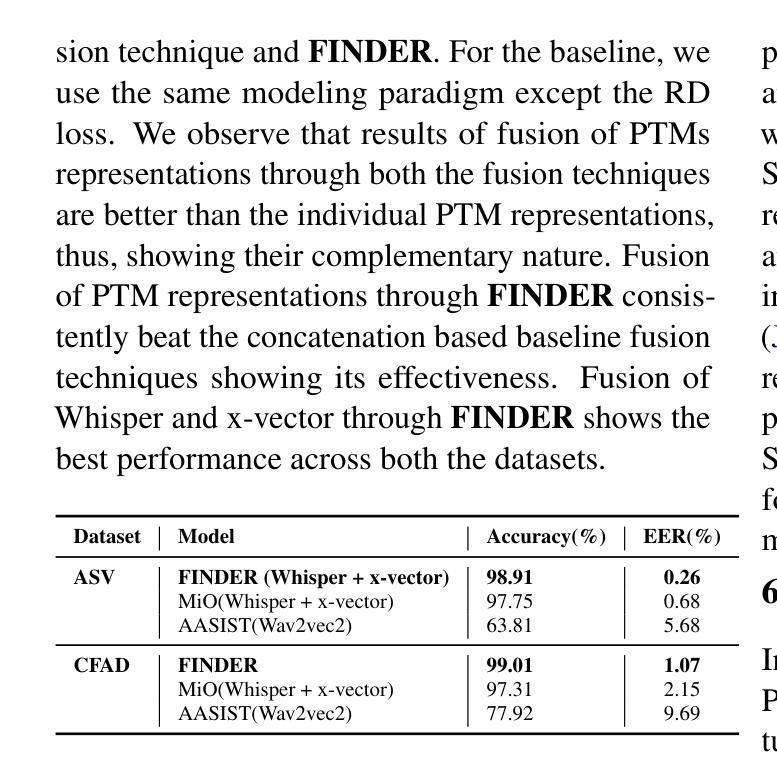
In this work, we investigate various state-of-the-art (SOTA) speech pre-trained models (PTMs) for their capability to capture prosodic signatures of the generative sources for audio deepfake source attribution (ADSD). These prosodic characteristics can be considered one of major signatures for ADSD, which is unique to each source. So better is the PTM at capturing prosodic signs better the ADSD performance. We consider various SOTA PTMs that have shown top performance in different prosodic tasks for our experiments on benchmark datasets, ASVSpoof 2019 and CFAD. x-vector (speaker recognition PTM) attains the highest performance in comparison to all the PTMs considered despite consisting lowest model parameters. This higher performance can be due to its speaker recognition pre-training that enables it for capturing unique prosodic characteristics of the sources in a better way. Further, motivated from tasks such as audio deepfake detection and speech recognition, where fusion of PTMs representations lead to improved performance, we explore the same and propose FINDER for effective fusion of such representations. With fusion of Whisper and x-vector representations through FINDER, we achieved the topmost performance in comparison to all the individual PTMs as well as baseline fusion techniques and attaining SOTA performance.
在这项工作中,我们研究了多种最新前沿的语音预训练模型(PTM),以评估它们在捕获音频深度伪造源归因(ADSD)的生成源语的韵律特征方面的能力。这些韵律特征可视为ADSD的主要特征之一,每个源都有其独特性。因此,PTM在捕捉韵律符号方面的能力越强,ADSD的性能就越好。我们在基准数据集ASVSpoof 2019和CFAD上进行了实验,考虑了在不同韵律任务中表现最佳的多种最新前沿PTM。相比之下,x-vector(语音识别PTM)尽管模型参数最少,但取得了最高性能。这种高性能可能是由于其语音识别的预训练功能,使其能够更好地捕捉源的独特韵律特征。此外,受音频深度伪造检测和语音识别等任务的启发,融合PTM表示可以提高性能,因此我们探索了同样的方法,并提出了FINDER,以实现此类表示的有效融合。通过FINDER融合Whisper和x-vector表示,与所有单个PTM以及基线融合技术相比,我们取得了最佳性能,并达到了最新前沿水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了先进的语音预训练模型在捕捉音频深度伪造源归因的韵律特征方面的能力。这些韵律特征是每个源的独特标志,因此预训练模型在捕捉韵律特征方面的能力越强,ADSD性能越好。本文考虑了多个在基准数据集上表现突出的先进预训练模型进行实验,发现x-vector(语音识别预训练模型)相较于其他模型表现最佳,这可能是由于其语音识别预训练能更好地捕捉源独特韵律特征所致。此外,受音频深度伪造检测和语音识别任务的启发,通过融合多种预训练模型的表示形式可以提高性能,因此本文提出了FINDER进行有效融合。通过融合Whisper和x-vector的表示形式,相较于所有单个预训练模型和基准融合技术,取得了最佳性能,达到了目前最先进的技术水平。
Key Takeaways
- 研究了先进语音预训练模型在捕捉音频深度伪造源归因的韵律特征方面的能力。
- 韵律特征是每个源的独特标志,对ADSD性能至关重要。
- x-vector在多个预训练模型中表现最佳,这得益于其语音识别预训练能更好地捕捉源的独特韵律特征。
- 融合多种预训练模型的表示形式可以提高性能,受音频深度伪造检测和语音识别任务的启发。
- 提出了FINDER方法,用于有效融合预训练模型的表示形式。
- 通过融合Whisper和x-vector的表示形式,取得了最佳性能,达到了目前最先进的技术水平。
点此查看论文截图

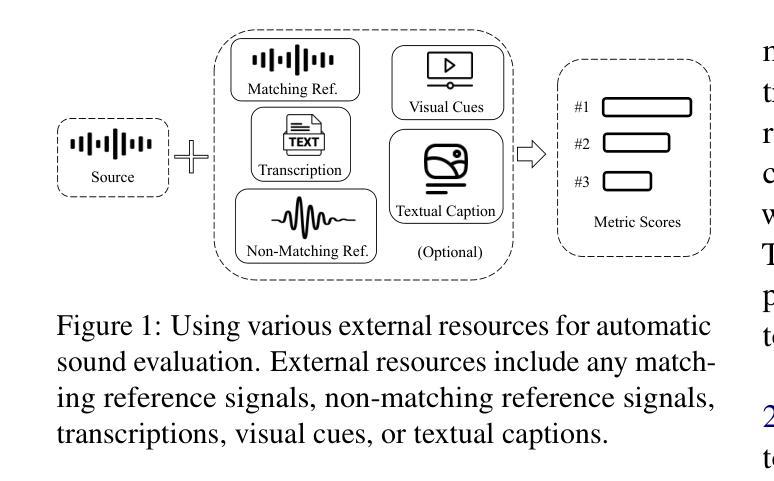
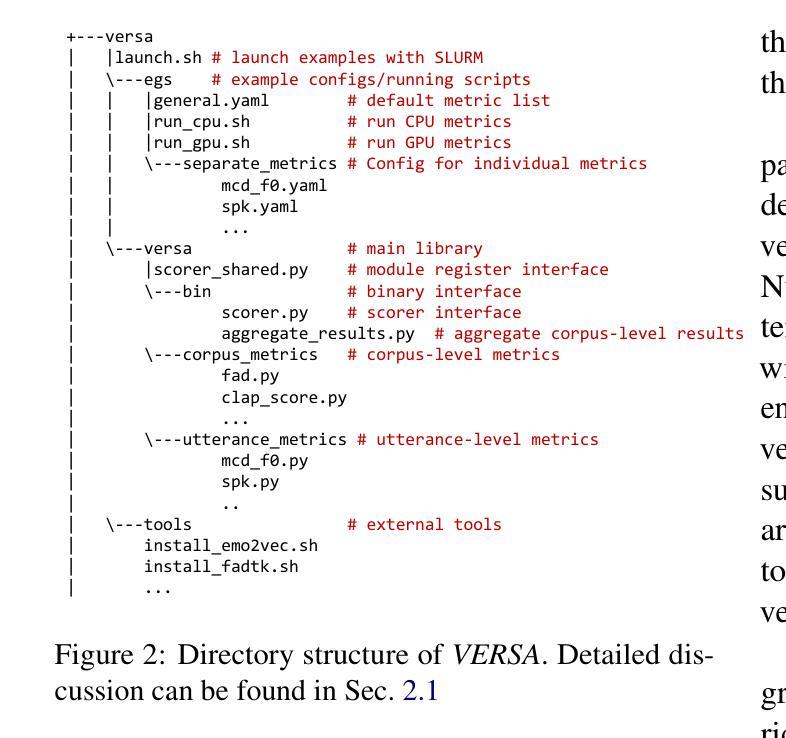
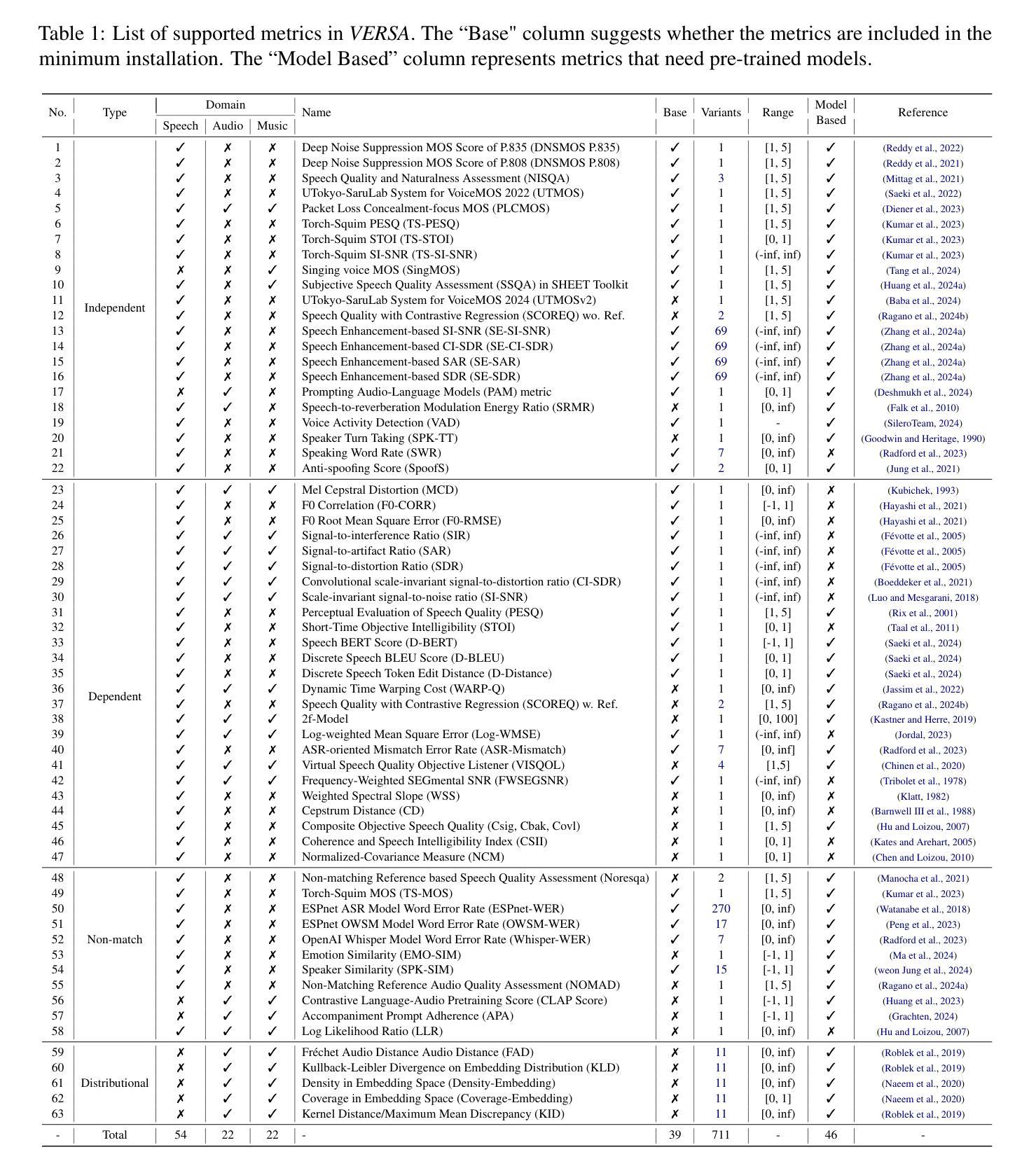
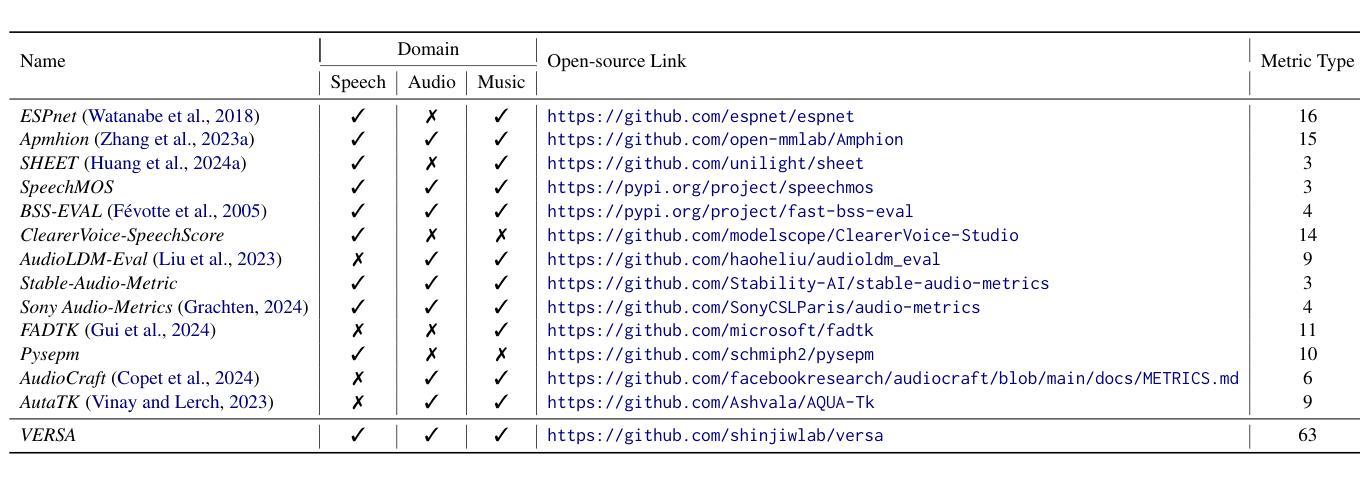
VERSA: A Versatile Evaluation Toolkit for Speech, Audio, and Music
Authors:Jiatong Shi, Hye-jin Shim, Jinchuan Tian, Siddhant Arora, Haibin Wu, Darius Petermann, Jia Qi Yip, You Zhang, Yuxun Tang, Wangyou Zhang, Dareen Safar Alharthi, Yichen Huang, Koichi Saito, Jionghao Han, Yiwen Zhao, Chris Donahue, Shinji Watanabe
In this work, we introduce VERSA, a unified and standardized evaluation toolkit designed for various speech, audio, and music signals. The toolkit features a Pythonic interface with flexible configuration and dependency control, making it user-friendly and efficient. With full installation, VERSA offers 63 metrics with 711 metric variations based on different configurations. These metrics encompass evaluations utilizing diverse external resources, including matching and non-matching reference audio, text transcriptions, and text captions. As a lightweight yet comprehensive toolkit, VERSA is versatile to support the evaluation of a wide range of downstream scenarios. To demonstrate its capabilities, this work highlights example use cases for VERSA, including audio coding, speech synthesis, speech enhancement, singing synthesis, and music generation. The toolkit is available at https://github.com/shinjiwlab/versa.
在这项工作中,我们介绍了VERSA,这是一个为各种语音、音频和音乐信号设计的统一、标准化的评估工具包。该工具包具有Python风格的接口,具有灵活的配置和依赖控制,使其易于使用且高效。完成安装后,VERSA提供基于不同配置的63种指标和711种指标变体。这些指标包括利用多种外部资源的评估,包括匹配和非匹配的参考音频、文本转录和文本标题。作为一个轻便而全面的工具包,VERSA支持对各种下游场景的评估。为了展示其能力,这项工作重点介绍了VERSA的示例用例,包括音频编码、语音合成、语音增强、歌唱合成和音乐生成。该工具包可在https://github.com/shinjiwlab/versa找到。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
该工作推出VERSA工具包,一个统一标准化的用于语音、音频和音乐信号的评估工具包。该工具包采用Python接口,配置灵活,依赖控制性强,使用方便且效率高。完成安装后,根据配置不同,VERSA提供63种指标的711种变化。这些指标涵盖利用多种外部资源的评估,包括匹配和非匹配参考音频、文本转录和文本字幕等。作为一个轻便而全面的工具包,VERSA支持多种下游场景的评估,包括音频编码、语音合成、语音增强、歌唱合成和音乐生成等。相关资源可在https://github.com/shinjiwlab/versa获取。
要点掌握
- VERSA是一个统一标准化的评价工具包,适用于多种语音、音频和音乐信号的评估。
- VERSA提供Pythonic接口,配置灵活,依赖控制性强,方便用户使用。
- 根据不同的配置,VERSA提供丰富的评价指标。
- VERSA涵盖多种外部资源的评估,如匹配和非匹配参考音频、文本转录和文本字幕等。
- VERSA支持多种下游场景的评估,如音频编码、语音合成等。
- VERSA在GitHub上有详细的资源和相关链接,方便获取和使用。
点此查看论文截图

HumanVBench: Exploring Human-Centric Video Understanding Capabilities of MLLMs with Synthetic Benchmark Data
Authors:Ting Zhou, Daoyuan Chen, Qirui Jiao, Bolin Ding, Yaliang Li, Ying Shen
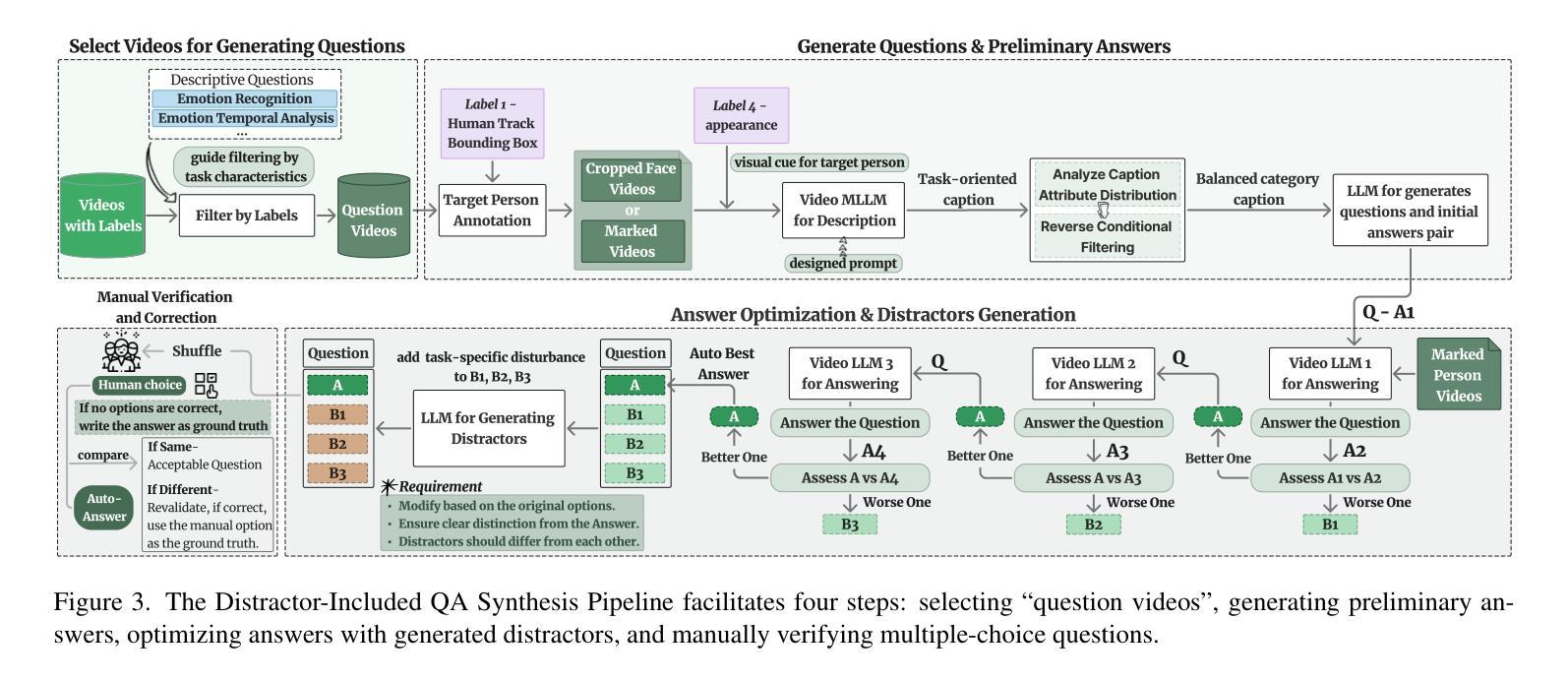
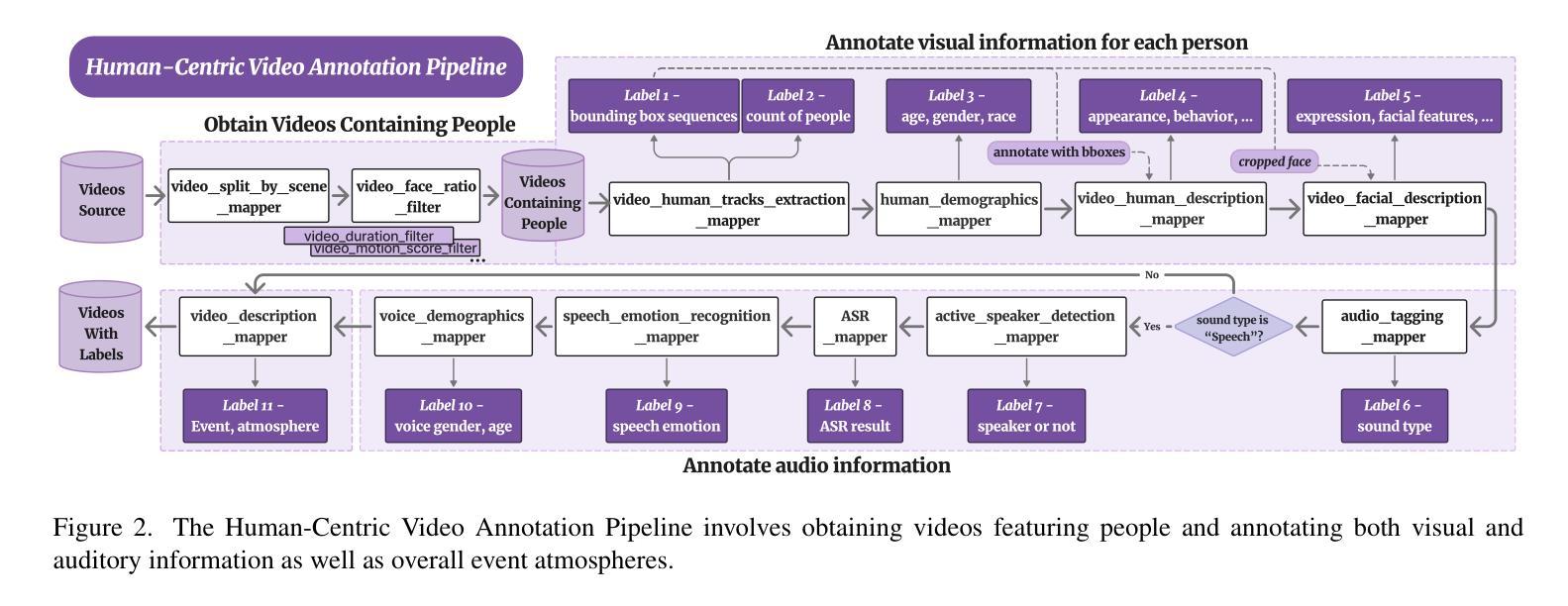
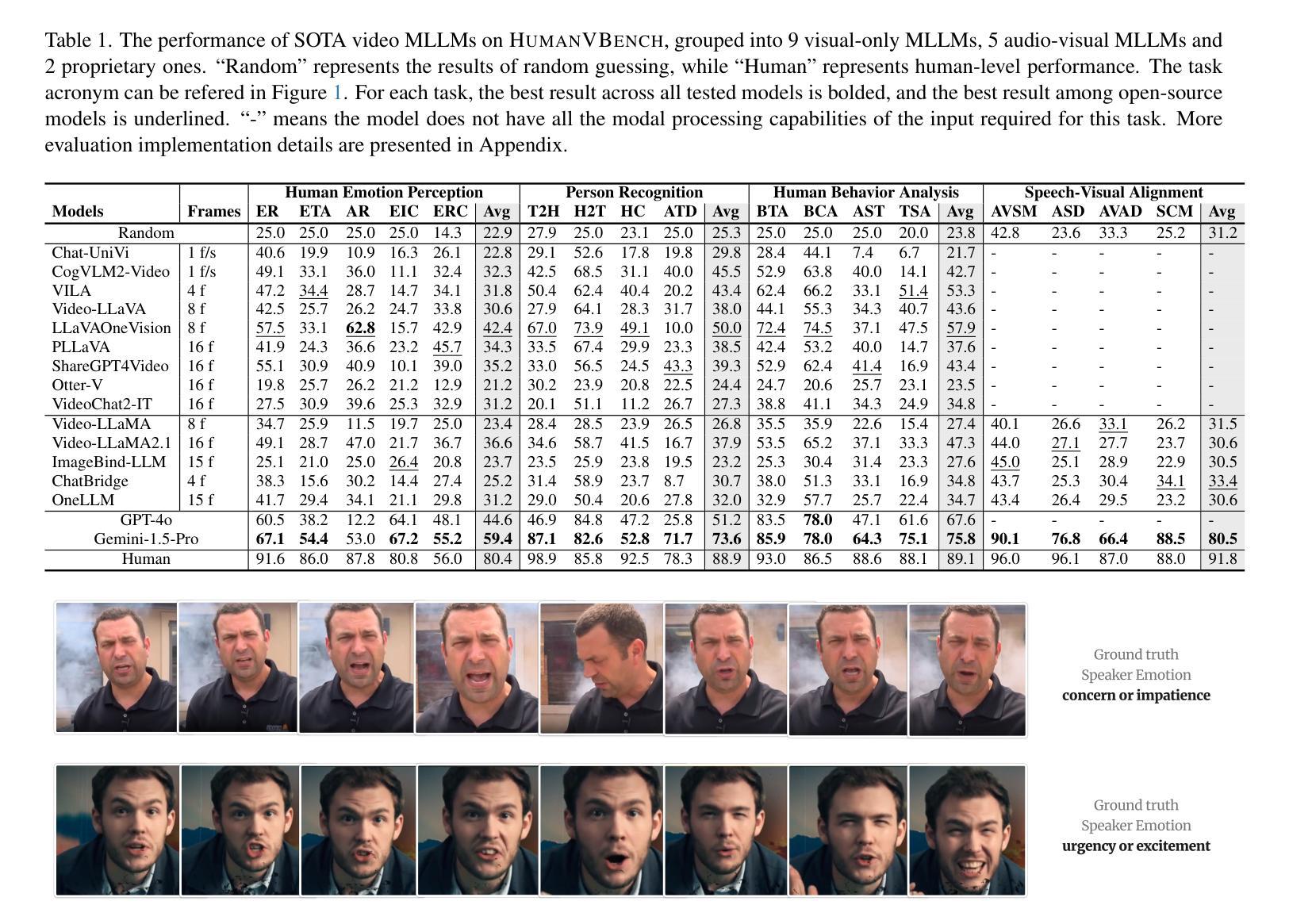
In the domain of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), achieving human-centric video understanding remains a formidable challenge. Existing benchmarks primarily emphasize object and action recognition, often neglecting the intricate nuances of human emotions, behaviors, and speech visual alignment within video content. We present HumanVBench, an innovative benchmark meticulously crafted to bridge these gaps in the evaluation of video MLLMs. HumanVBench comprises 17 carefully designed tasks that explore two primary dimensions: inner emotion and outer manifestations, spanning static and dynamic, basic and complex, as well as single-modal and cross-modal aspects. With two advanced automated pipelines for video annotation and distractor-included QA generation, HumanVBench utilizes diverse state-of-the-art (SOTA) techniques to streamline benchmark data synthesis and quality assessment, minimizing human annotation dependency tailored to human-centric multimodal attributes. A comprehensive evaluation across 16 SOTA video MLLMs reveals notable limitations in current performance, especially in cross-modal and temporal alignment, underscoring the necessity for further refinement toward achieving more human-like understanding. HumanVBench is open-sourced to facilitate future advancements and real-world applications in video MLLMs.
在多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)领域,实现以人类为中心的视频理解仍然是一项艰巨的挑战。现有的基准测试主要强调对象和动作识别,往往忽视了视频内容中人类情绪、行为和语音视觉对齐的细微差别。我们提出了HumanVBench,这是一个精心设计的基准测试,旨在弥补视频MLLMs评估中的这些差距。HumanVBench包含17项精心设计的任务,探索两个主要维度:内在情绪和外在表现,涵盖静态和动态、基本和复杂以及单模态和跨模态方面。HumanVBench采用两个先进的自动化管道进行视频标注和包含干扰项的QA生成,利用多种最新技术优化基准数据合成和质量评估,减少对人类标注的依赖,专门针对以人类为中心的多模态属性。对16种最新视频MLLMs的综合评估显示,当前性能存在显著局限性,尤其在跨模态和时间对齐方面,这强调了对进一步改进实现更人性化的理解的必要性。HumanVBench开源,以促进视频MLLMs的未来发展和实际应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 24 figures, 4 tables
Summary
在多媒体大型语言模型领域(MLLMs),实现以人类为中心的视频理解仍然是一项挑战。现有基准测试主要侧重于对象和动作识别,往往忽视了人类情绪、行为和视频内语音视觉对齐的细微差别。本文提出了HumanVBench,这是一个精心设计的基准测试,旨在弥补视频MLLM评估中的这些差距。HumanVBench包含17个精心设计的任务,探索两个主要维度:内在情绪和外在表现,涵盖静态和动态、基本和复杂以及单模态和跨模态方面。它采用两个先进的自动化管道进行视频注释和包含干扰项的QA生成,利用多种最先进技术来简化基准测试数据合成和质量评估,减少人工注释的依赖,专注于以人类为中心的多模态属性。对16个最新视频MLLM的全面评估显示,在跨模态和时间对齐方面存在显著局限性,强调需要进一步改进才能实现更人性化的理解。HumanVBench已开源,以促进视频MLLM的未来发展和实际应用。
Key Takeaways
- Human-centric video understanding remains a challenge in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs).
- 现有基准测试主要关注对象和动作识别,忽视了人类情绪、行为和语音视觉对齐的细微差别。
- HumanVBench是一个新的基准测试,旨在弥补视频MLLM评估中的差距。
- HumanVBench包含17个任务,探索内在情绪和外在表现两个主要维度。
- 该基准测试采用自动化管道进行视频注释和QA生成,减少人工注释的依赖。
- 最新视频MLLM在跨模态和时间对齐方面存在局限性。
点此查看论文截图

UME: Upcycling Mixture-of-Experts for Scalable and Efficient Automatic Speech Recognition
Authors:Li Fu, Shanyong Yu, Siqi Li, Lu Fan, Youzheng Wu, Xiaodong He
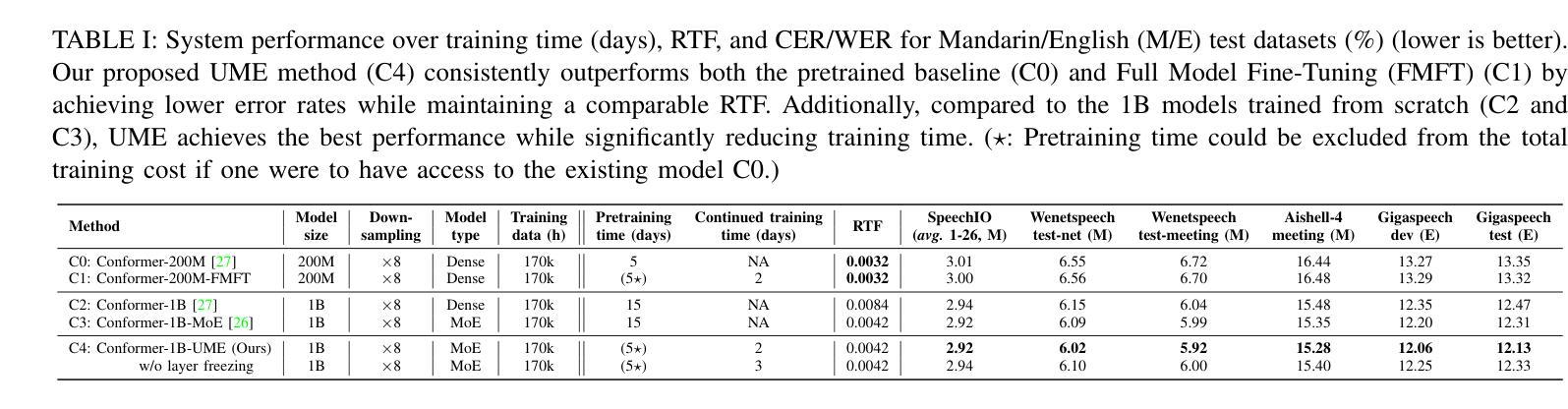
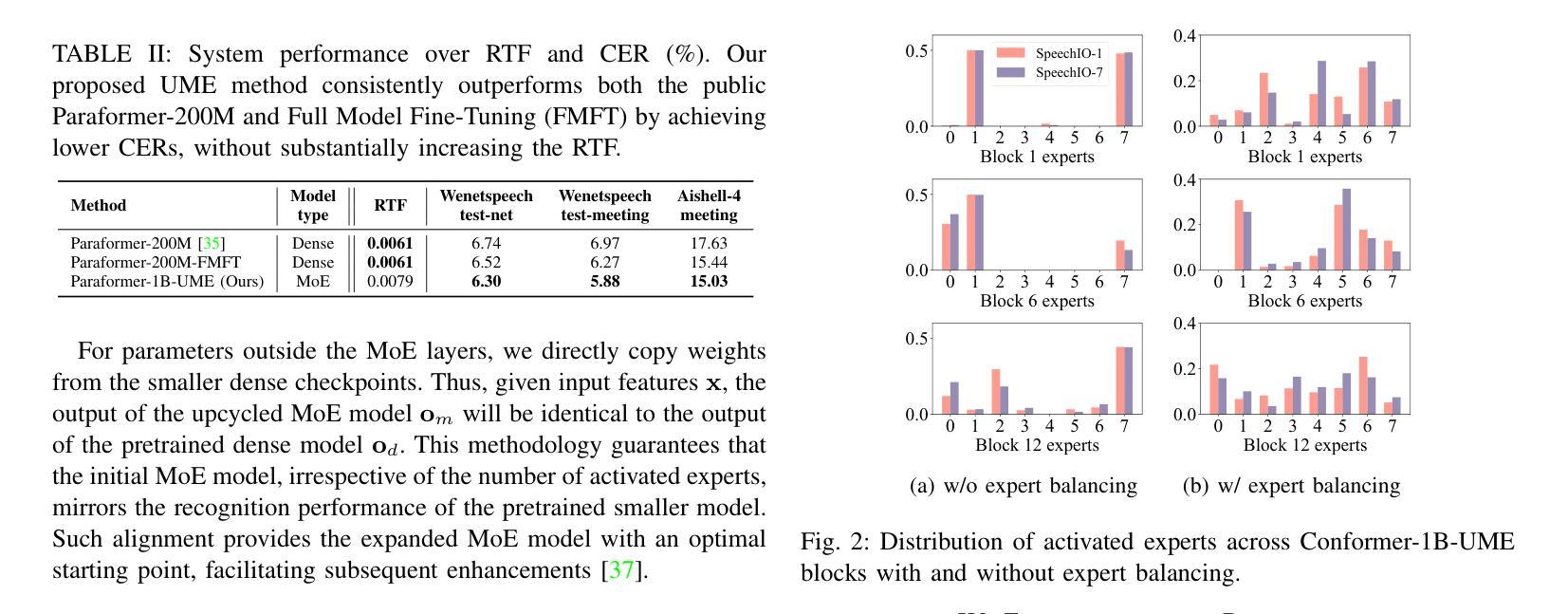
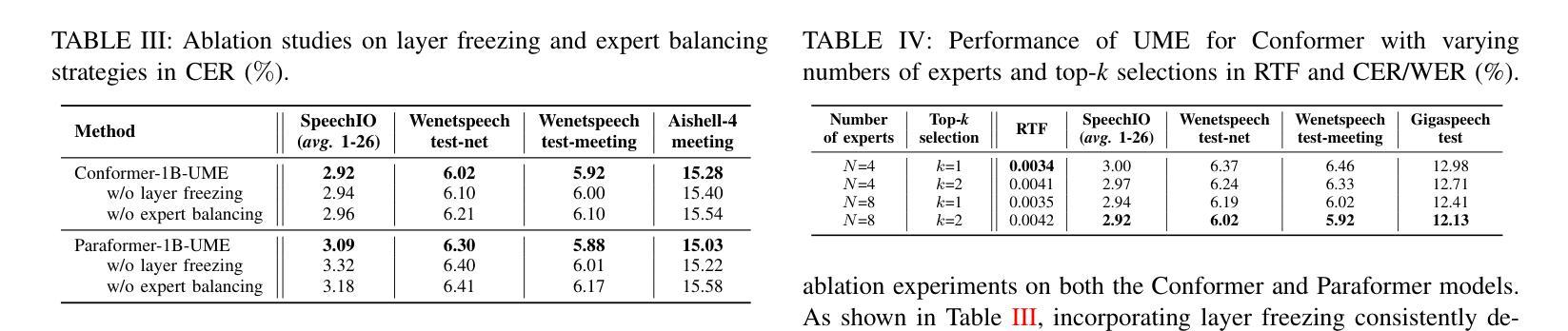
Recent advancements in scaling up models have significantly improved performance in Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) tasks. However, training large ASR models from scratch remains costly. To address this issue, we introduce UME, a novel method that efficiently Upcycles pretrained dense ASR checkpoints into larger Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures. Initially, feed-forward networks are converted into MoE layers. By reusing the pretrained weights, we establish a robust foundation for the expanded model, significantly reducing optimization time. Then, layer freezing and expert balancing strategies are employed to continue training the model, further enhancing performance. Experiments on a mixture of 170k-hour Mandarin and English datasets show that UME: 1) surpasses the pretrained baseline by a margin of 11.9% relative error rate reduction while maintaining comparable latency; 2) reduces training time by up to 86.7% and achieves superior accuracy compared to training models of the same size from scratch.
最近模型扩展方面的进展显著提高了自动语音识别(ASR)任务的性能。然而,从头开始训练大型ASR模型成本仍然很高。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了UME,一种将预训练的密集ASR检查点高效升级为更大的混合专家(MoE)架构的新方法。最初,前馈网络被转换为MoE层。通过重用预训练权重,我们为扩展模型建立了稳健的基础,显著减少了优化时间。然后,采用层冻结和专家平衡策略继续训练模型,进一步提高性能。在170k小时的普通话和英语数据集混合进行的实验表明,UME:1)相对于预训练基线,相对误差率降低了11.9%,同时保持可比较的延迟;2)训练时间最多减少86.7%,并且在相同大小的模型中实现了优于从头开始训练的准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICASSP 2025
Summary
ASR模型扩展的新方法UME通过将预训练的密集ASR检查点高效地转化为更大的混合专家架构(MoE)来解决从头训练大型ASR模型的成本问题。该方法先将前馈网络转换为MoE层并利用预训练权重进行模型扩展,从而减少优化时间。再通过冻结层和专家平衡策略进一步提升模型性能。实验表明,UME在保持延迟的同时,相对于预训练基线降低了11.9%的相对误差率,同时减少了高达86.7%的训练时间,并在相同规模的模型中实现了更高的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- UME是一种解决ASR模型训练成本高昂的新方法,它通过有效地将预训练的密集ASR检查点升级为更大的混合专家架构来实现这一点。
- UME通过将前馈网络转化为MoE层并利用预训练权重建立稳固基础来优化模型性能,减少优化时间。
- 在冻结层和采用专家平衡策略后,模型的性能得到进一步提升。
- 实验表明,UME在保持延迟不变的情况下,相对于预训练基线降低了显著比例的相对误差率。
- UME显著减少了训练时间,相比从头开始训练相同规模的模型,其效率更高。
- UME方法结合了预训练权重和混合专家架构的优势,实现了高性能和高效能的结合。
点此查看论文截图

Uncovering the Visual Contribution in Audio-Visual Speech Recognition
Authors:Zhaofeng Lin, Naomi Harte
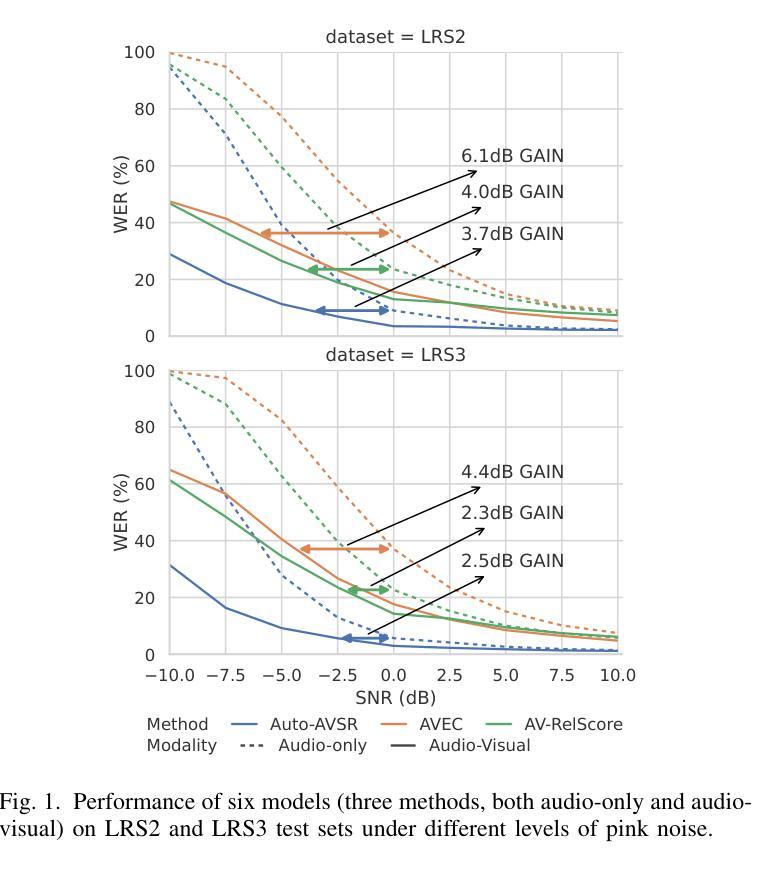
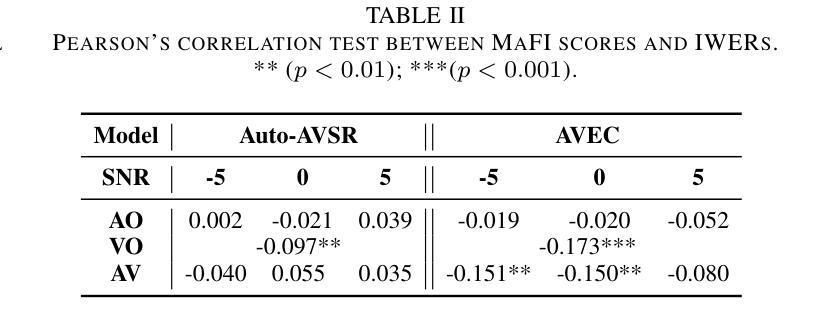
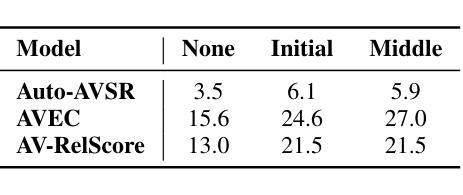
Audio-Visual Speech Recognition (AVSR) combines auditory and visual speech cues to enhance the accuracy and robustness of speech recognition systems. Recent advancements in AVSR have improved performance in noisy environments compared to audio-only counterparts. However, the true extent of the visual contribution, and whether AVSR systems fully exploit the available cues in the visual domain, remains unclear. This paper assesses AVSR systems from a different perspective, by considering human speech perception. We use three systems: Auto-AVSR, AVEC and AV-RelScore. We first quantify the visual contribution using effective SNR gains at 0 dB and then investigate the use of visual information in terms of its temporal distribution and word-level informativeness. We show that low WER does not guarantee high SNR gains. Our results suggest that current methods do not fully exploit visual information, and we recommend future research to report effective SNR gains alongside WERs.
视听语音识别(AVSR)结合了听觉和视觉语音线索,以提高语音识别系统的准确性和稳健性。与仅使用音频的同行相比,AVSR的最新进展在嘈杂环境中表现出更高的性能。然而,视觉贡献的真正程度,以及AVSR系统是否充分利用视觉领域中的可用线索,仍然不清楚。本文通过考虑人类语音感知,从不同角度评估AVSR系统。我们使用三种系统:Auto-AVSR、AVEC和AV-RelScore。我们首先使用有效信噪比增益(在0分贝处)量化视觉贡献,然后研究视觉信息的使用与其时间分布和词级信息量有关。我们表明,低词错误率并不保证高信噪比增益。我们的结果表明,当前方法并没有充分利用视觉信息,我们建议未来的研究在报告词错误率的同时,也要报告有效的信噪比增益。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 2 figures. Accepted to ICASSP 2025
Summary
音视频语音识别(AVSR)结合了听觉和视觉语音线索,提高了语音识别系统的准确性和稳健性。最新进展表明,AVSR在嘈杂环境中的性能优于仅使用音频的系统。然而,视觉信息的真正贡献以及AVSR系统是否充分利用视觉领域的可用线索仍不明确。本文采用自动AVSR、AVEC和AV-RelScore三个系统进行评估,首先量化视觉贡献,然后研究视觉信息的时序分布和词级信息量。研究表明,低词错误率并不保证高信噪比增益。当前方法未充分利用视觉信息,建议未来研究在报告词错误率的同时也要报告有效的信噪比增益。
Key Takeaways
- AVSR结合了听觉和视觉语音线索,提高了语音识别系统的准确性。
- 最新AVSR技术改进了在嘈杂环境中的性能。
- 视觉信息对AVSR的贡献尚未完全明确。
- 通过使用三个系统(Auto-AVSR、AVEC和AV-RelScore)进行评估,发现视觉信息的量化是重要的研究方向。
- 研究表明,低词错误率并不保证高信噪比增益,这暗示当前方法未充分利用视觉信息。
- 视觉信息在时空分布和词级信息量方面的使用是评估AVSR系统性能的关键。
点此查看论文截图


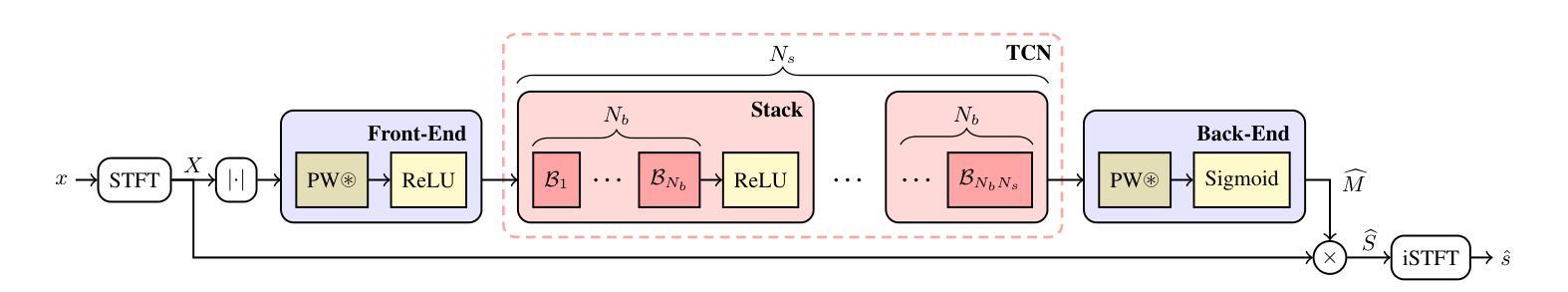
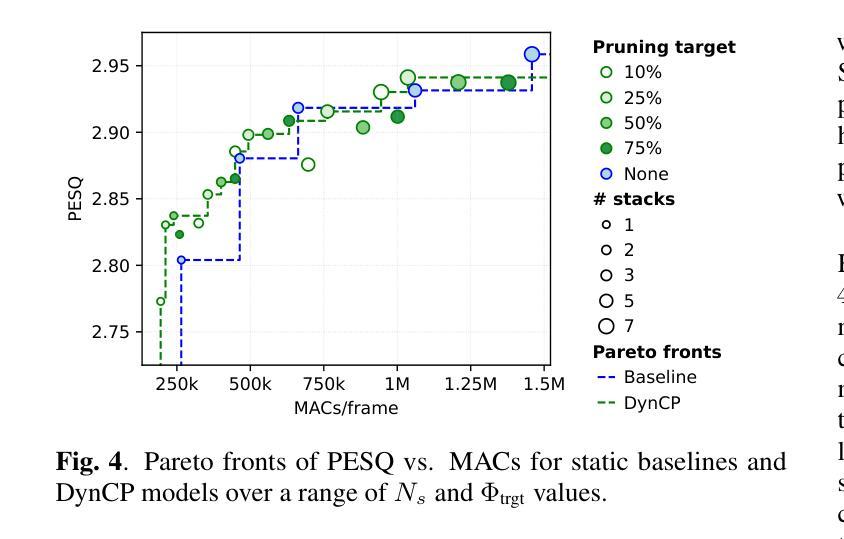
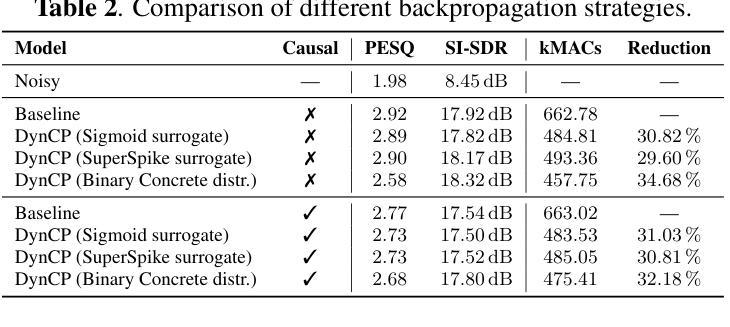
Scalable Speech Enhancement with Dynamic Channel Pruning
Authors:Riccardo Miccini, Clement Laroche, Tobias Piechowiak, Luca Pezzarossa
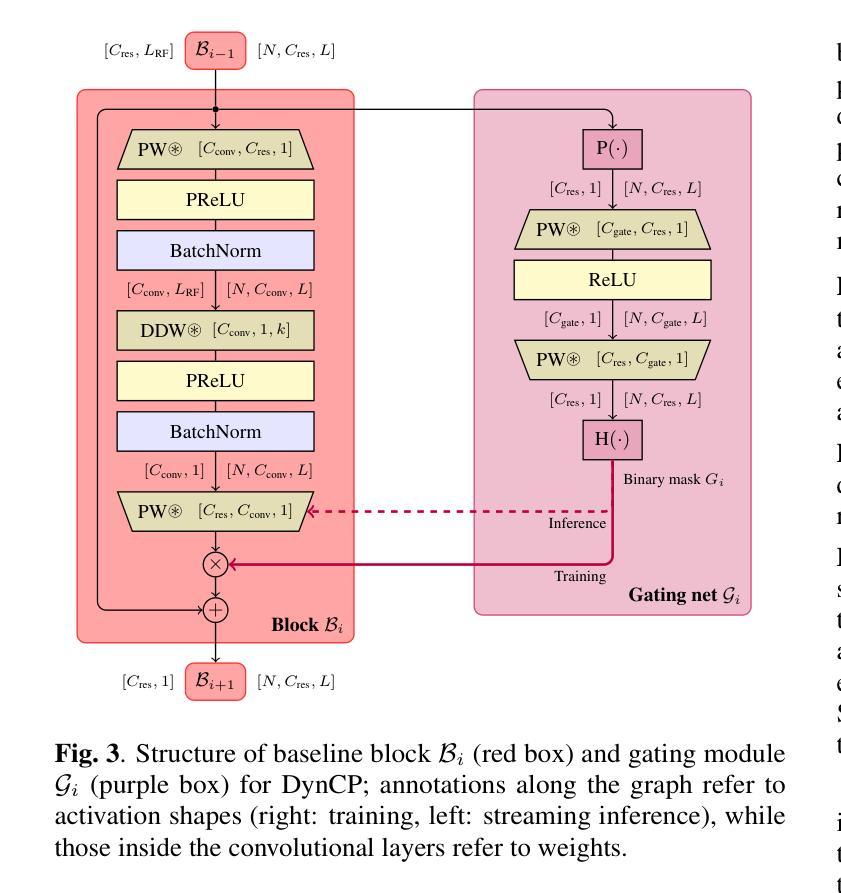
Speech Enhancement (SE) is essential for improving productivity in remote collaborative environments. Although deep learning models are highly effective at SE, their computational demands make them impractical for embedded systems. Furthermore, acoustic conditions can change significantly in terms of difficulty, whereas neural networks are usually static with regard to the amount of computation performed. To this end, we introduce Dynamic Channel Pruning to the audio domain for the first time and apply it to a custom convolutional architecture for SE. Our approach works by identifying unnecessary convolutional channels at runtime and saving computational resources by not computing the activations for these channels and retrieving their filters. When trained to only use 25% of channels, we save 29.6% of MACs while only causing a 0.75% drop in PESQ. Thus, DynCP offers a promising path toward deploying larger and more powerful SE solutions on resource-constrained devices.
语音增强(SE)对于提高远程协作环境中的生产力至关重要。尽管深度学习模型在SE方面非常有效,但其计算需求使其不适用于嵌入式系统。此外,声学条件在难度方面可能会发生重大变化,而神经网络通常在进行计算时保持静态。为此,我们首次将动态通道裁剪引入到音频领域,并将其应用于用于SE的自定义卷积架构。我们的方法通过在运行时识别不必要的卷积通道,并通过不计算这些通道的激活和检索其过滤器来节省计算资源。当仅训练使用25%的通道时,我们在节省29.6%的乘加操作的同时,仅导致PESQ下降0.75%。因此,DynCP为在资源受限设备上部署更大、更强大的SE解决方案提供了一条有前途的道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP)
总结
文章介绍了针对远程协作环境中的语音增强(SE)问题,虽然深度学习模型效果显著,但在嵌入式系统中因计算需求过高而不实用。为解决这一问题,首次将动态通道裁剪技术引入音频领域,并应用于定制的卷积架构进行SE。该方法在运行过程中识别不必要的卷积通道,通过不计算这些通道的激活和检索其过滤器来节省计算资源。当训练仅使用25%的通道时,可在降低0.75%的PESQ的同时,节省29.6%的MACs。动态通道裁剪技术为实现资源受限设备上部署更大、更强大的SE解决方案提供了可行的路径。
关键见解
- 语音增强(SE)在远程协作环境中对提升生产力至关重要。
- 深度学习模型在SE方面效果显著,但在嵌入式系统中因计算需求过高而不实用。
- 引入动态通道裁剪技术,首次将其应用于音频领域的卷积架构进行SE。
- 该方法通过识别并忽略不必要的卷积通道来节省计算资源。
- 使用仅25%的通道进行训练,可以在降低少许性能损失(0.74%)的前提下,实现显著的资源节约(节省29.6%的MACs)。
- 动态通道裁剪技术为资源受限设备上的SE解决方案部署提供了可行的路径。
点此查看论文截图


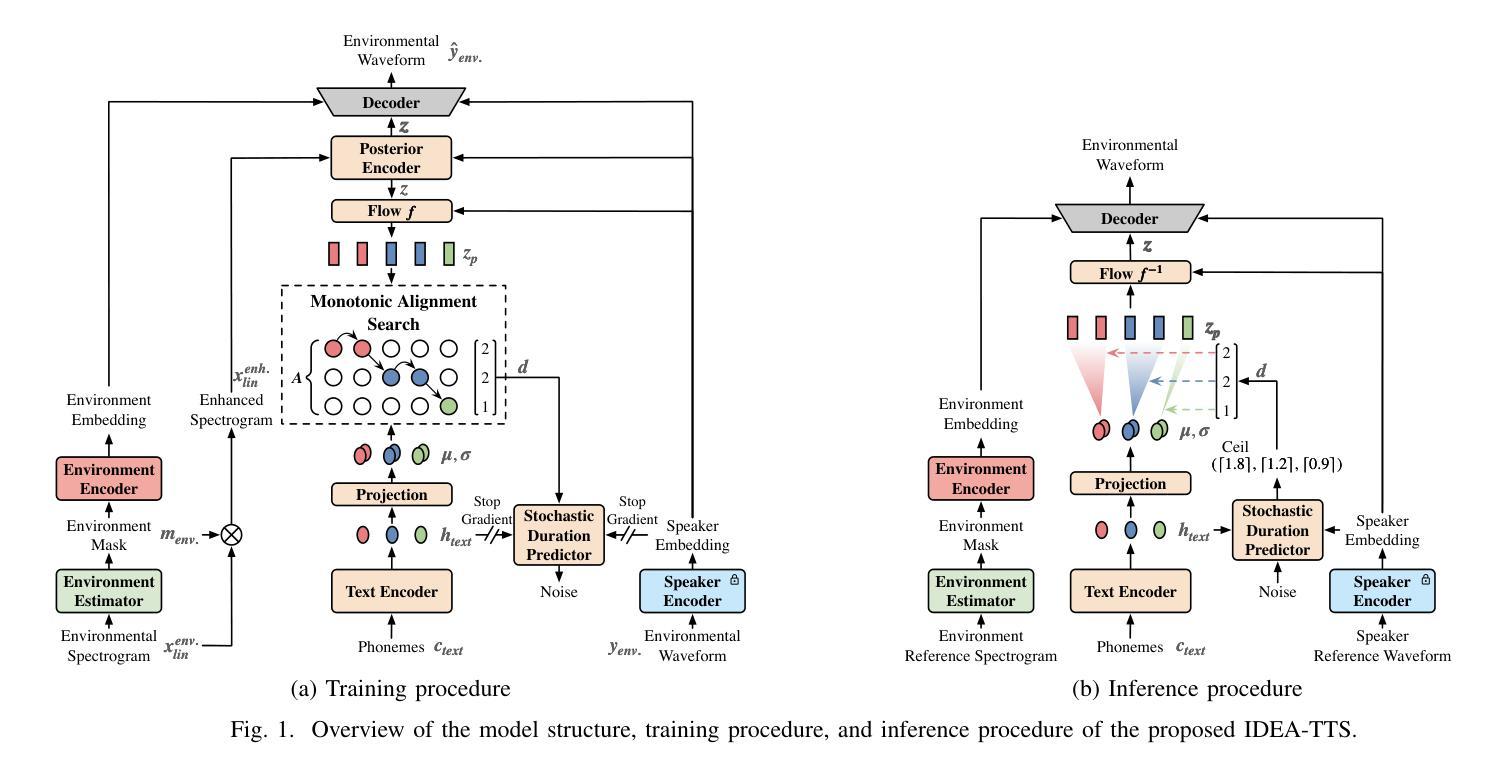
Incremental Disentanglement for Environment-Aware Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech Synthesis
Authors:Ye-Xin Lu, Hui-Peng Du, Zheng-Yan Sheng, Yang Ai, Zhen-Hua Ling
This paper proposes an Incremental Disentanglement-based Environment-Aware zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) method, dubbed IDEA-TTS, that can synthesize speech for unseen speakers while preserving the acoustic characteristics of a given environment reference speech. IDEA-TTS adopts VITS as the TTS backbone. To effectively disentangle the environment, speaker, and text factors, we propose an incremental disentanglement process, where an environment estimator is designed to first decompose the environmental spectrogram into an environment mask and an enhanced spectrogram. The environment mask is then processed by an environment encoder to extract environment embeddings, while the enhanced spectrogram facilitates the subsequent disentanglement of the speaker and text factors with the condition of the speaker embeddings, which are extracted from the environmental speech using a pretrained environment-robust speaker encoder. Finally, both the speaker and environment embeddings are conditioned into the decoder for environment-aware speech generation. Experimental results demonstrate that IDEA-TTS achieves superior performance in the environment-aware TTS task, excelling in speech quality, speaker similarity, and environmental similarity. Additionally, IDEA-TTS is also capable of the acoustic environment conversion task and achieves state-of-the-art performance.
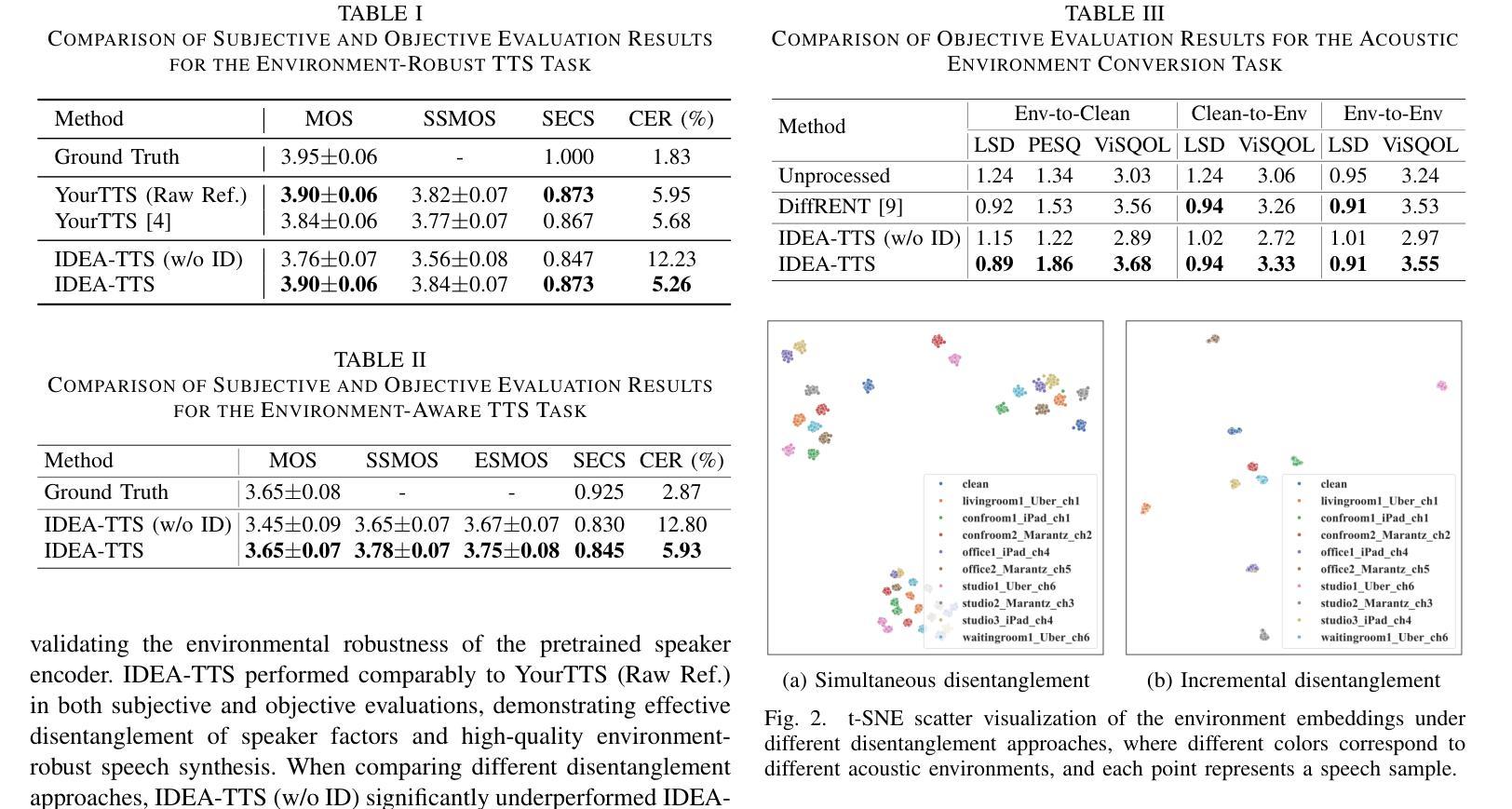
本文提出了一种基于增量解耦的环境感知零样本文本到语音(TTS)方法,称为IDEA-TTS。该方法可以在为未见过的说话人合成语音的同时,保留给定环境参考语音的声学特征。IDEA-TTS采用VITS作为TTS的骨干。为了有效地解开环境、说话人和文本因素,我们提出了一个增量解耦过程,其中环境估计器被设计用来首先将环境光谱图分解成环境掩膜和增强光谱图。然后,环境掩膜被环境编码器处理以提取环境嵌入,而增强光谱图有助于在环境语音的说话人嵌入的条件下,随后解开说话人和文本因素,这些嵌入是从环境语音中使用预训练的环境稳健说话人编码器提取的。最后,说话人和环境嵌入都被输入到解码器中,以进行环境感知的语音生成。实验结果表明,IDEA-TTS在环境感知TTS任务上取得了优越的性能,在语音质量、说话人相似度和环境相似度方面都表现出色。此外,IDEA-TTS还具备声音环境转换任务的能力,并达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICASSP 2025
摘要
本文提出了一种基于增量解耦的环境感知零样本文本到语音(TTS)方法,名为IDEA-TTS。该方法能够在未见过说话人的情况下合成语音,同时保留给定环境参考语音的声学特征。IDEA-TTS采用VITS作为TTS骨架。为了有效地解开环境、说话人和文本因素,我们提出了一个增量解耦过程,其中环境估计器被设计来首先分解环境光谱图成一个环境掩膜和一个增强光谱图。环境掩膜随后被环境编码器处理以提取环境嵌入,同时增强光谱图有助于随后解开说话人和文本因素,以说话人嵌入为条件,这些嵌入是从带有预训练的环境稳健说话人编码器从环境语音中提取的。最后,说话人和环境嵌入都被输入到解码器中进行环境感知的语音生成。实验结果表明,IDEA-TTS在环境感知TTS任务上取得了优越的性能,在语音质量、说话人相似性和环境相似性方面表现出色。此外,IDEA-TTS还具备声音环境转换任务的能力,并实现了最先进的性能。
关键见解
- IDEA-TTS是一种基于增量解耦的环境感知零样本文本到语音(TTS)方法。
- IDEA-TTS能够合成未见过说话人的语音,同时保留给定环境参考语音的声学特征。
- 环境估计器用于分解环境光谱图,产生环境掩膜和增强光谱图。
- 环境编码器用于提取环境嵌入。
- IDEA-TTS利用预训练的说话人编码器从环境语音中提取说话人嵌入。
- IDEA-TTS在环境感知TTS任务上取得了显著的性能提升,特别是在语音质量、说话人相似性、环境相似性方面。
点此查看论文截图

Temporal-Frequency State Space Duality: An Efficient Paradigm for Speech Emotion Recognition
Authors:Jiaqi Zhao, Fei Wang, Kun Li, Yanyan Wei, Shengeng Tang, Shu Zhao, Xiao Sun
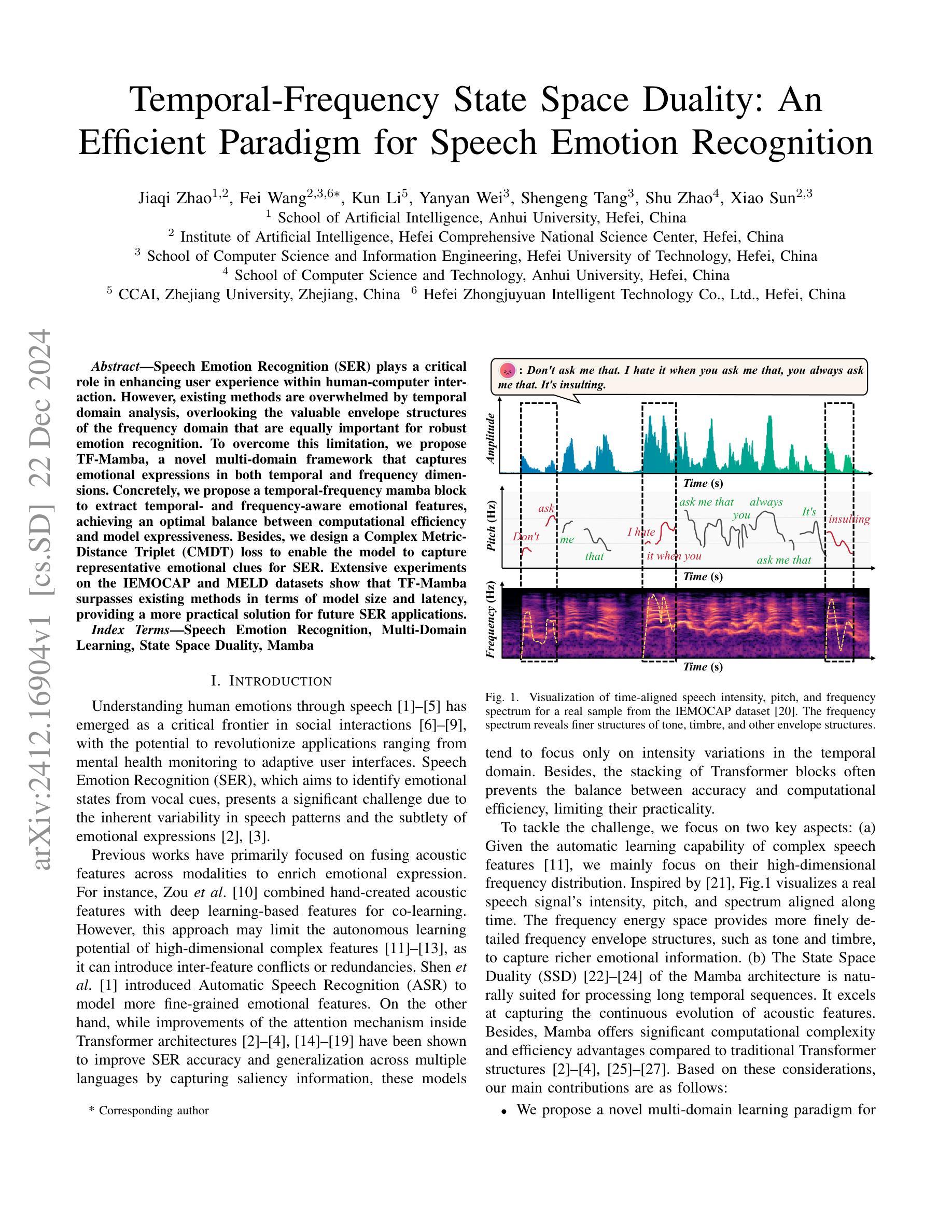
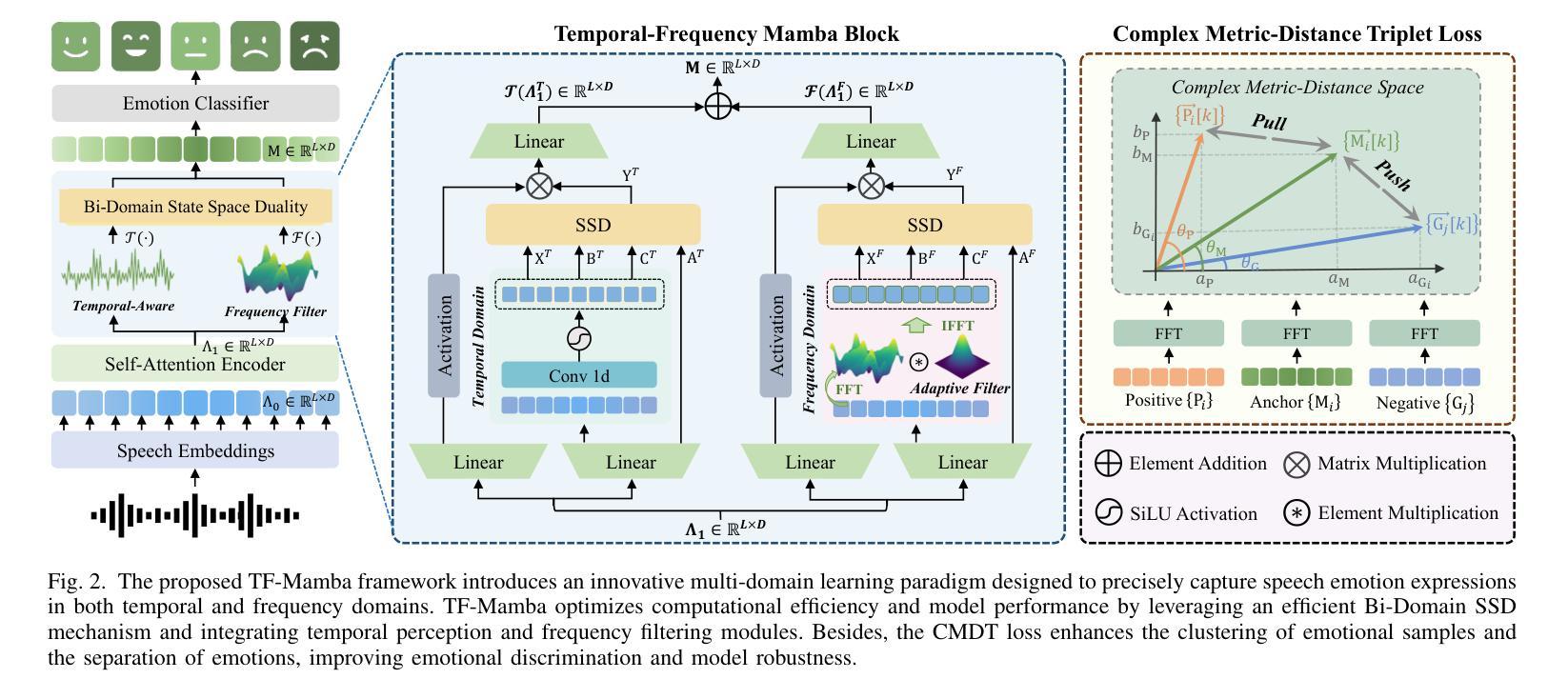
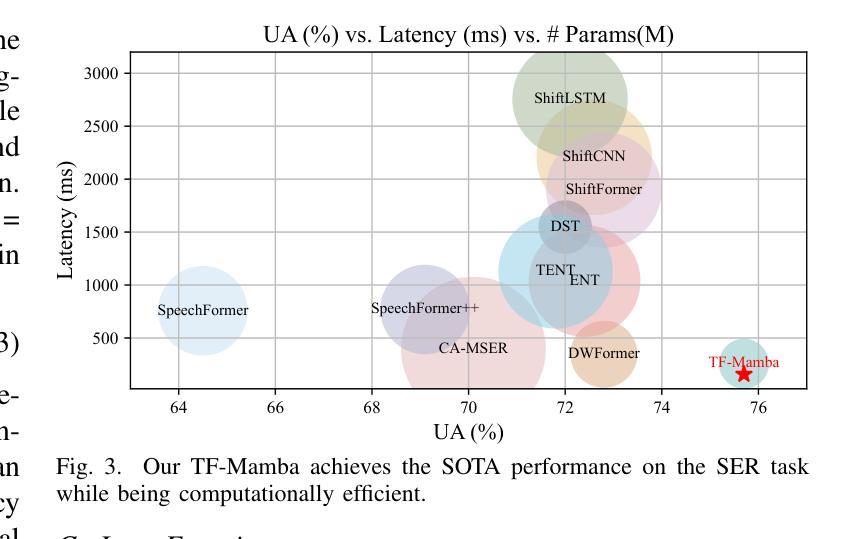
Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) plays a critical role in enhancing user experience within human-computer interaction. However, existing methods are overwhelmed by temporal domain analysis, overlooking the valuable envelope structures of the frequency domain that are equally important for robust emotion recognition. To overcome this limitation, we propose TF-Mamba, a novel multi-domain framework that captures emotional expressions in both temporal and frequency dimensions.Concretely, we propose a temporal-frequency mamba block to extract temporal- and frequency-aware emotional features, achieving an optimal balance between computational efficiency and model expressiveness. Besides, we design a Complex Metric-Distance Triplet (CMDT) loss to enable the model to capture representative emotional clues for SER. Extensive experiments on the IEMOCAP and MELD datasets show that TF-Mamba surpasses existing methods in terms of model size and latency, providing a more practical solution for future SER applications.
语音情绪识别(SER)在人机交互中提升用户体验方面起着关键作用。然而,现有方法被时间域分析所困扰,忽略了频率域的宝贵包络结构,这些结构对于稳健的情绪识别同样重要。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了TF-Mamba,这是一种新的多域框架,能够在时间和频率两个维度上捕捉情绪表达。具体来说,我们提出了一种时空mamba块,以提取时空情感特征,在计算效率和模型表现力之间达到最优平衡。此外,我们设计了一种复杂度量距离三元组(CMDT)损失,使模型能够捕获用于SER的典型情感线索。在IEMOCAP和MELD数据集上的大量实验表明,TF-Mamba在模型大小和延迟方面超过了现有方法,为未来SER应用提供了更实用的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICASSP 2025
Summary
语音情感识别(SER)在人机交互中对于提升用户体验具有重要作用。现有方法过于注重时域分析,忽略了频域包络结构对于稳健情感识别的同等重要性。为此,我们提出了TF-Mamba这一新型多域框架,能够同时在时域和频域捕捉情感表达。我们设计了一个时频mamba模块,以提取时频情感特征,在计算效率和模型表现力之间达到最优平衡。此外,我们还设计了复杂度量距离三元组(CMDT)损失,使模型能够捕捉代表性的情感线索用于SER。在IEMOCAP和MELD数据集上的实验表明,TF-Mamba在模型大小和延迟方面超越了现有方法,为未来SER应用提供了更实用的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 语音情感识别(SER)对提升人机交互中的用户体验至关重要。
- 现有SER方法过于依赖时域分析,忽略了频域的重要性。
- TF-Mamba是一个新型多域框架,旨在同时捕捉时域和频域的情感表达。
- TF-Mamba通过时频mamba模块提取时频情感特征,实现计算效率和模型表现力的平衡。
- CMDT损失的设计使模型能够捕捉代表性的情感线索,提高SER性能。
- 在IEMOCAP和MELD数据集上,TF-Mamba的表现优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图
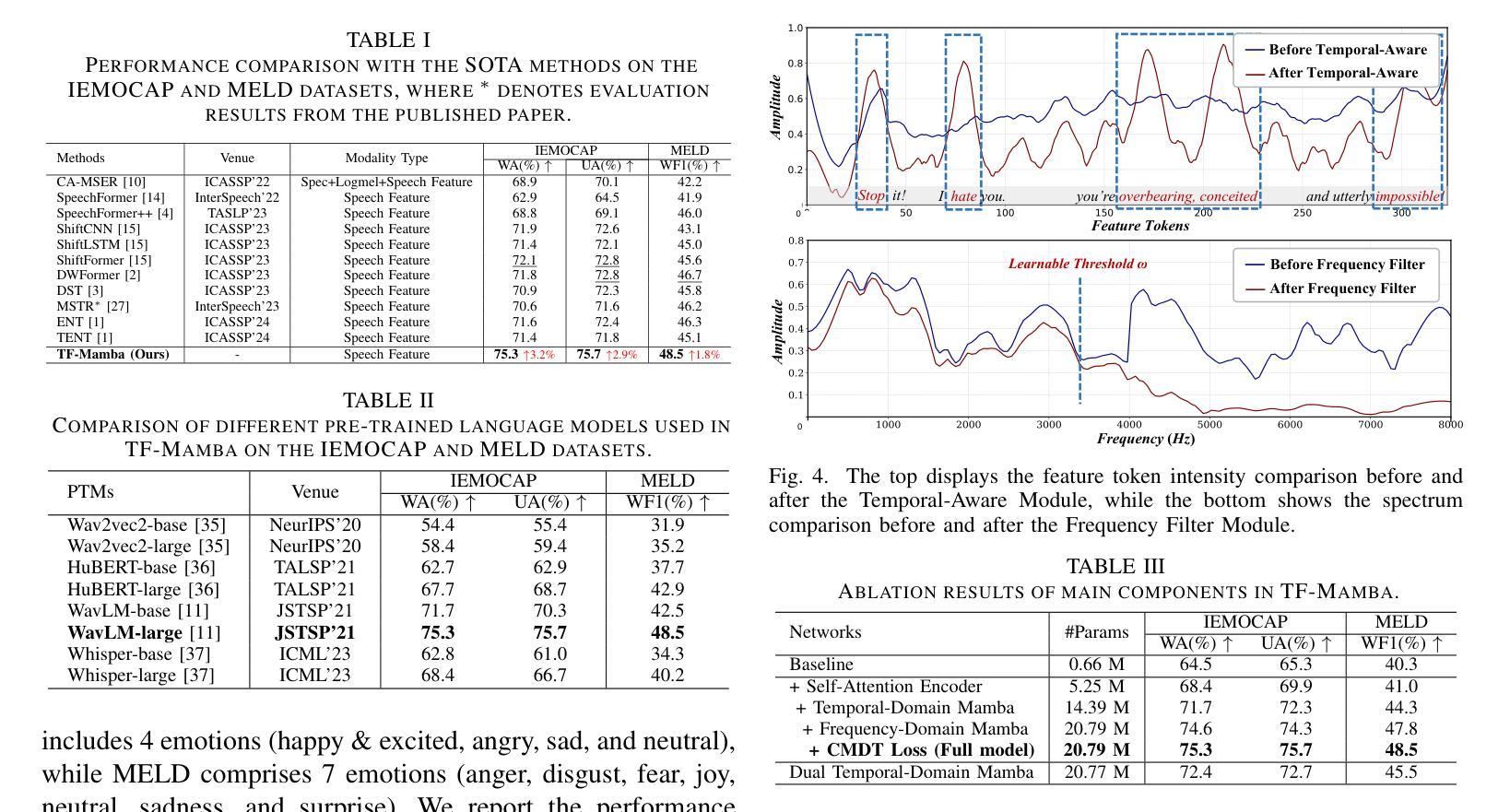
Time-Graph Frequency Representation with Singular Value Decomposition for Neural Speech Enhancement
Authors:Tingting Wang, Tianrui Wang, Meng Ge, Qiquan Zhang, Zirui Ge, Zhen Yang
Time-frequency (T-F) domain methods for monaural speech enhancement have benefited from the success of deep learning. Recently, focus has been put on designing two-stream network models to predict amplitude mask and phase separately, or, coupling the amplitude and phase into Cartesian coordinates and constructing real and imaginary pairs. However, most methods suffer from the alignment modeling of amplitude and phase (real and imaginary pairs) in a two-stream network framework, which inevitably incurs performance restrictions. In this paper, we introduce a graph Fourier transform defined with the singular value decomposition (GFT-SVD), resulting in real-valued time-graph representation for neural speech enhancement. This real-valued representation-based GFT-SVD provides an ability to align the modeling of amplitude and phase, leading to avoiding recovering the target speech phase information. Our findings demonstrate the effects of real-valued time-graph representation based on GFT-SVD for neutral speech enhancement. The extensive speech enhancement experiments establish that the combination of GFT-SVD and DNN outperforms the combination of GFT with the eigenvector decomposition (GFT-EVD) and magnitude estimation UNet, and outperforms the short-time Fourier transform (STFT) and DNN, regarding objective intelligibility and perceptual quality. We release our source code at: https://github.com/Wangfighting0015/GFT\_project.
对于单声道语音增强的时频域(T-F)方法,深度学习已经取得了巨大的成功。最近的研究重点主要放在设计双流网络模型上,以分别预测振幅掩模和相位,或者将振幅和相位耦合到笛卡尔坐标中并构建实虚对。然而,大多数方法在双流网络框架下的振幅和相位(实虚对)对齐建模方面存在困难,这不可避免地导致了性能限制。在本文中,我们引入了一种基于奇异值分解(SVD)定义的图傅里叶变换(GFT-SVD),从而实现了用于神经语音增强的实数时间图表示。基于实数表示的GFT-SVD提供了对齐振幅和相位建模的能力,避免了恢复目标语音相位信息。我们的研究结果表明,基于GFT-SVD的实数时间图表示对于中性语音增强具有显著效果。大量的语音增强实验证实,GFT-SVD与深度神经网络(DNN)的结合优于GFT与特征向量分解(GFT-EVD)的结合以及幅度估计UNet,并且在客观可懂度和感知质量方面优于短时傅里叶变换(STFT)和DNN。我们在以下链接发布了我们的源代码:https://github.com/Wangfighting0015/GFT_project。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 4 figures
Summary
基于深度学习的时频域方法在单声道语音增强方面取得了成功。近期研究多集中于设计双流网络模型以分别预测幅度掩码和相位掩码。但大部分方法受到双流网络中幅度与相位建模对位不良的影响,存在性能限制。本文引入基于奇异值分解的图傅里叶变换(GFT-SVD),产生用于神经语音增强的实值时间图表示。这种实值表示法能够良好地解决幅度与相位的建模对位问题,避免目标语音相位信息的恢复。实验证明,基于实值时间图表示的GFT-SVD方法能提升中性语音增强的效果,且在客观可理解性和感知质量方面表现优秀。相关研究代码已发布于GitHub。
Key Takeaways
- 双流网络模型广泛应用于单声道语音增强中的时频域方法。
- 双流网络模型面临幅度与相位建模的对位问题,影响性能。
- 引入基于奇异值分解的图傅里叶变换(GFT-SVD),生成实值时间图表示用于解决幅度与相位建模问题。
- 该方法能提高语音增强性能,尤其表现在客观可理解性和感知质量上。
点此查看论文截图

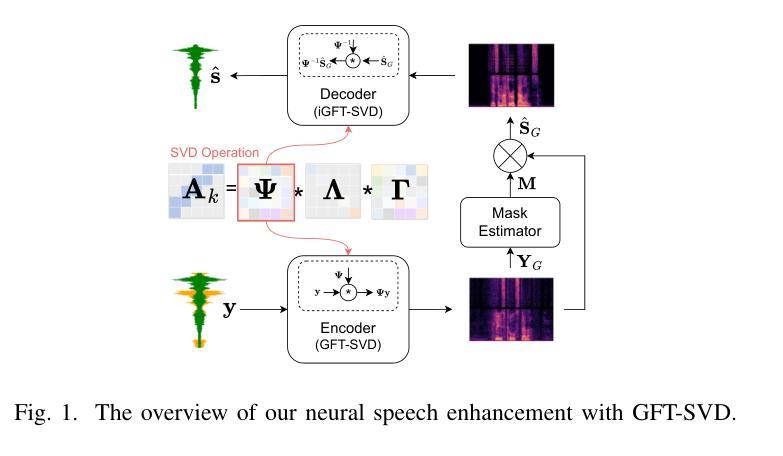
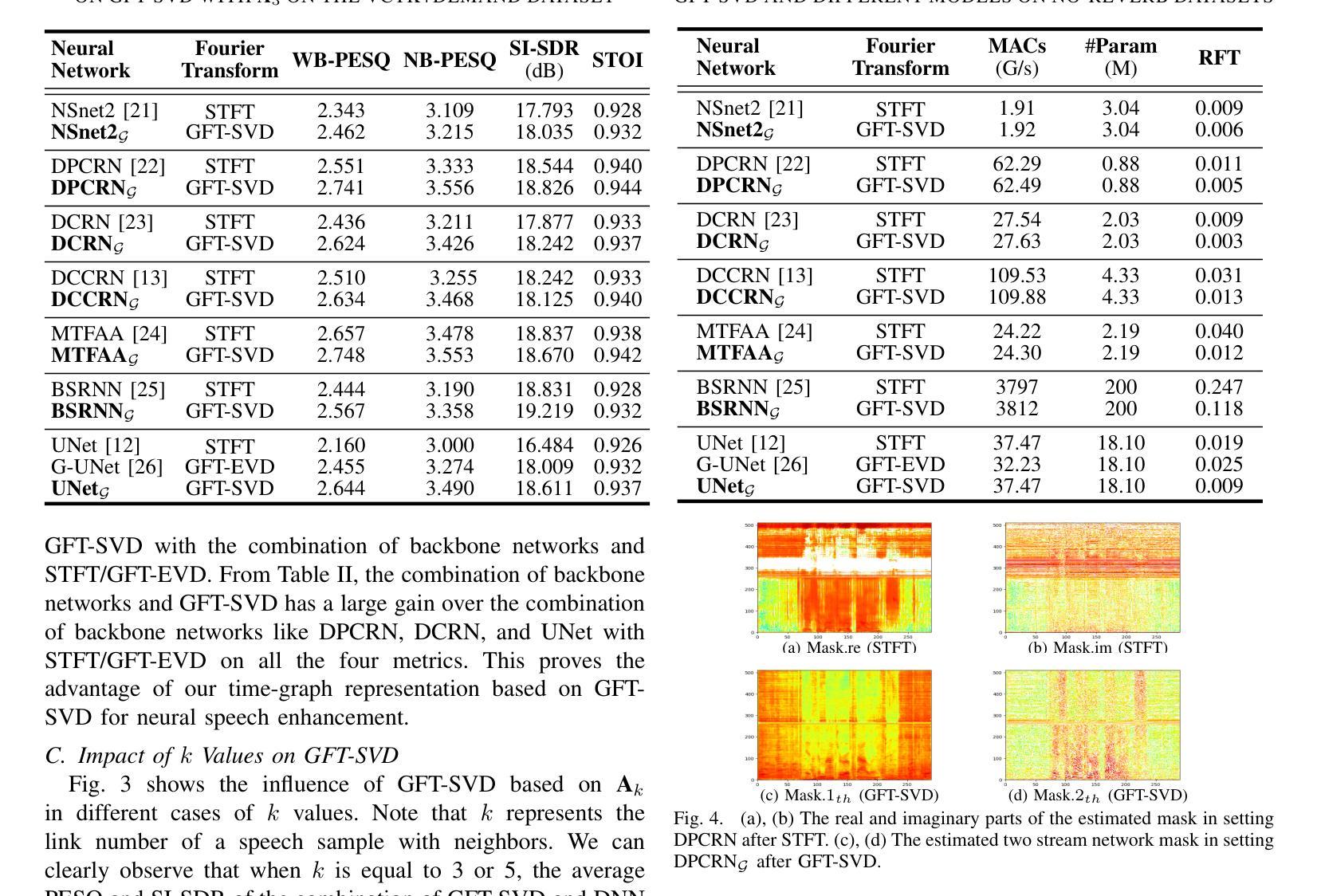
SilVar: Speech Driven Multimodal Model for Reasoning Visual Question Answering and Object Localization
Authors:Tan-Hanh Pham, Hoang-Nam Le, Phu-Vinh Nguyen, Chris Ngo, Truong-Son Hy
Visual Language Models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across tasks, including visual question answering and image captioning. However, most models rely on text-based instructions, limiting their effectiveness in human-machine interactions. Moreover, the quality of language models depends on reasoning and prompting techniques, such as COT, which remain underexplored when using speech instructions. To address these challenges, we propose SilVar, a novel end-to-end multimodal model that uses speech instructions for reasoning in visual question answering. In addition, we investigate reasoning techniques with levels including conversational, simple, and complex speech instruction. SilVar is built upon CLIP, Whisper, and LLaMA 3.1-8B, enabling intuitive interactions by allowing users to provide verbal or text instructions. To this end, we introduce a dataset designed to challenge models with speech-based reasoning tasks for object localization. This dataset enhances the model ability to process and explain visual scenes from spoken input, moving beyond object recognition to reasoning-based interactions. The experiments show that SilVar achieves SOTA performance on the MMMU and ScienceQA benchmarks despite the challenge of speech-based instructions. We believe SilVar will inspire next-generation multimodal reasoning models, toward expert artificial general intelligence. Our code and dataset are available here.
视觉语言模型在视觉问答和图像描述等任务中展现出卓越的能力。然而,大多数模型依赖于文本指令,这在人机交互中限制了其有效性。此外,语言模型的质量依赖于推理和提示技术,如COT(认知理论),在使用语音指令时仍被探索不足。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了SilVar,这是一种新型端到端的跨模态模型,它使用语音指令进行视觉问答中的推理。此外,我们研究了包括对话、简单和复杂语音指令在内的推理技术。SilVar建立在CLIP、Whisper和LLaMA 3.1-8B的基础上,允许用户提供口头或文本指令,从而实现直观交互。为此,我们引入了一个数据集,旨在通过基于语音的推理任务来挑战模型进行目标定位。该数据集提高了模型从口语输入处理并解释视觉场景的能力,超越了目标识别,实现了基于推理的交互。实验表明,尽管面临基于语音的指令挑战,SilVar在MMMU和ScienceQA基准测试中仍达到最佳性能。我们相信SilVar将启发下一代跨模态推理模型,朝着专家通用人工智能的方向发展。我们的代码和数据集可在此处访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages
Summary
视觉语言模型在视觉问答和图像描述等任务中展现出卓越的能力。然而,大多数模型依赖文本指令,在人机交互中效果有限。针对这一问题,我们提出SilVar,一种使用语音指令进行视觉问答推理的新型端到端多模态模型。SilVar结合CLIP、Whisper和LLaMA 3.1-8B构建,允许用户通过口头或文本指令进行直观交互。我们引入了一个数据集,旨在通过语音推理任务挑战模型在物体定位方面的能力。实验表明,尽管存在语音指令的挑战,SilVar在MMMU和ScienceQA基准测试中取得了卓越表现。我们相信SilVar将启发下一代多模态推理模型,推动人工智能向专家级通用智能发展。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉语言模型在视觉问答和图像描述等任务中表现出强大的能力。
- 大多数视觉语言模型依赖文本指令,限制了其在人机交互中的有效性。
- 语音指令为视觉问答推理提供了新途径,有助于提高模型的交互性和实用性。
- SilVar是一种新型的多模态模型,结合了CLIP、Whisper和LLaMA技术,支持口头或文本指令。
- 引入了一个新的数据集,用于挑战模型在语音推理任务中的物体定位能力。
- 实验表明,SilVar在MMMU和ScienceQA基准测试中表现优异,尽管面临语音指令的挑战。
点此查看论文截图


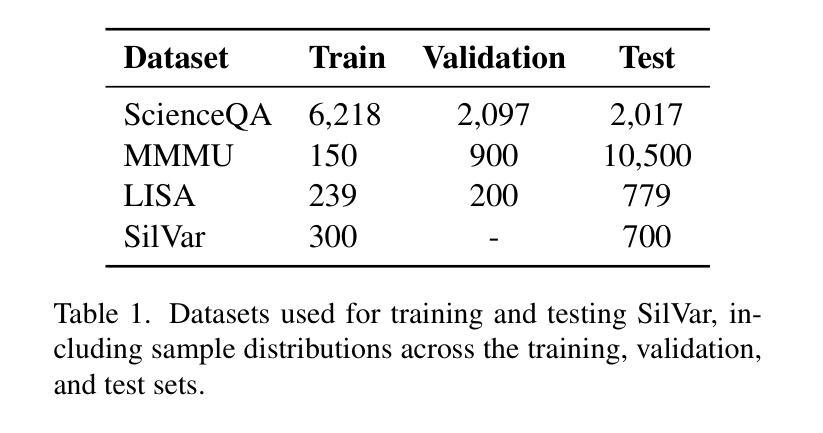
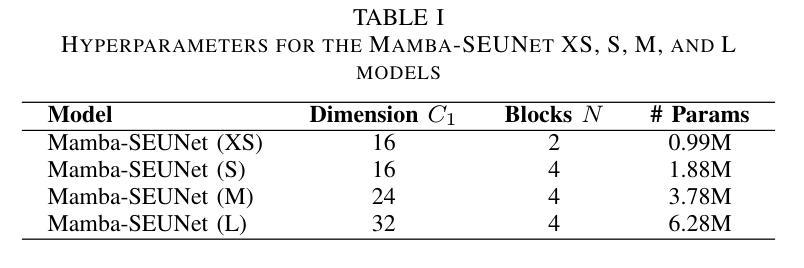
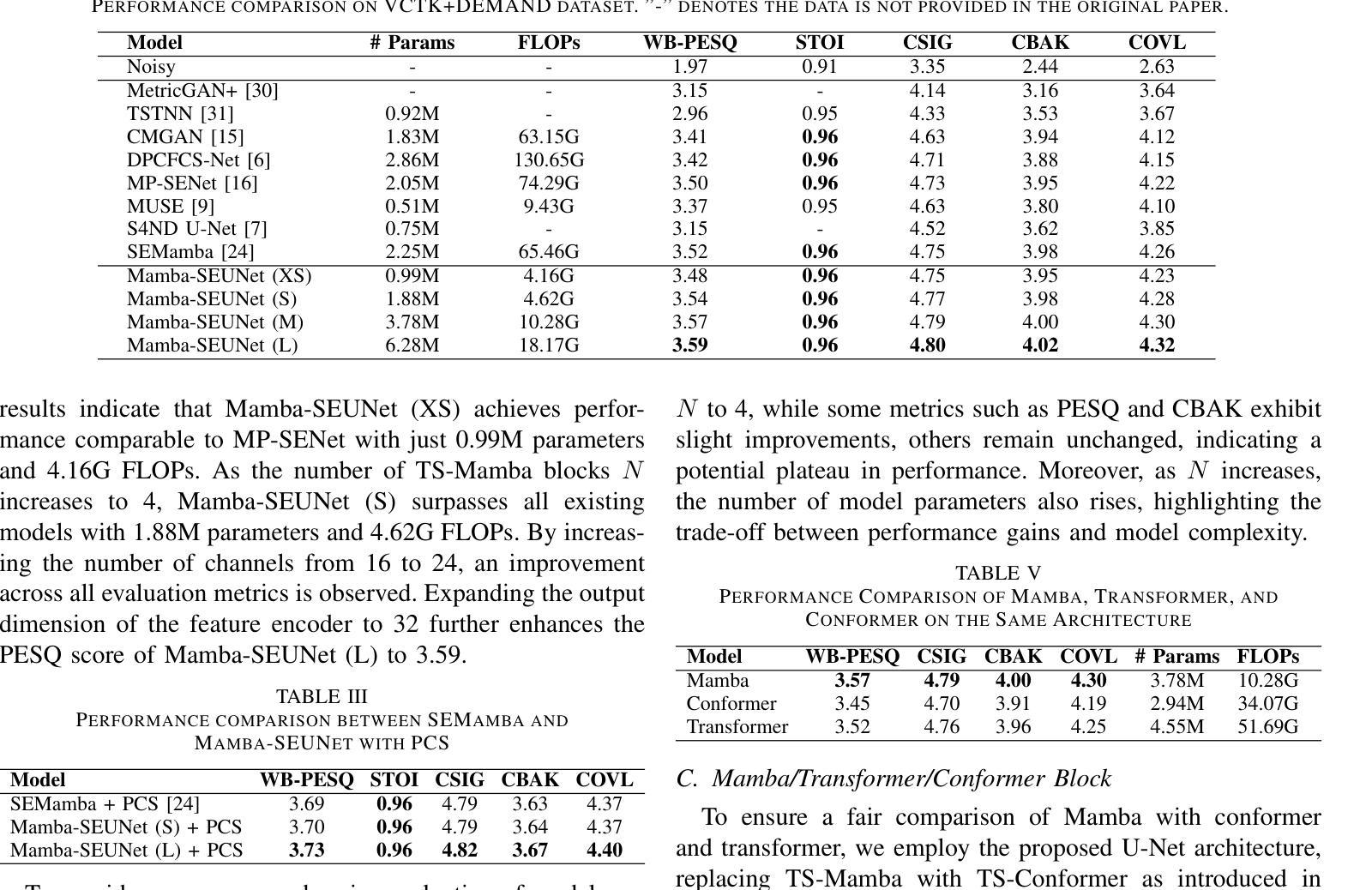
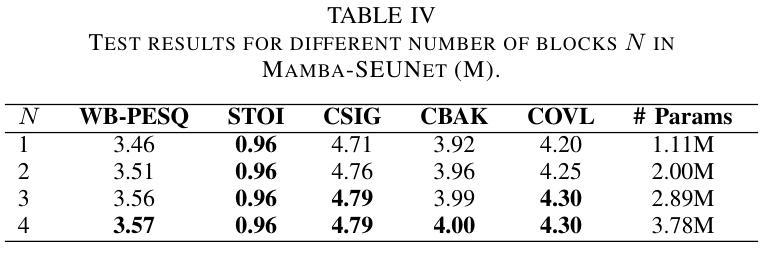
Mamba-SEUNet: Mamba UNet for Monaural Speech Enhancement
Authors:Junyu Wang, Zizhen Lin, Tianrui Wang, Meng Ge, Longbiao Wang, Jianwu Dang
In recent speech enhancement (SE) research, transformer and its variants have emerged as the predominant methodologies. However, the quadratic complexity of the self-attention mechanism imposes certain limitations on practical deployment. Mamba, as a novel state-space model (SSM), has gained widespread application in natural language processing and computer vision due to its strong capabilities in modeling long sequences and relatively low computational complexity. In this work, we introduce Mamba-SEUNet, an innovative architecture that integrates Mamba with U-Net for SE tasks. By leveraging bidirectional Mamba to model forward and backward dependencies of speech signals at different resolutions, and incorporating skip connections to capture multi-scale information, our approach achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance. Experimental results on the VCTK+DEMAND dataset indicate that Mamba-SEUNet attains a PESQ score of 3.59, while maintaining low computational complexity. When combined with the Perceptual Contrast Stretching technique, Mamba-SEUNet further improves the PESQ score to 3.73.
在最近的语音增强(SE)研究中,Transformer及其变体已经成为主要的方法论。然而,自注意力机制的二次复杂性对实际部署施加了一定的限制。Mamba作为一种新型的状态空间模型(SSM),由于其强大的长序列建模能力和相对较低的计算复杂性,在自然语言处理和计算机视觉中得到了广泛应用。在这项工作中,我们介绍了Mamba-SEUNet,这是一种将Mamba与U-Net结合用于SE任务的创新架构。通过利用双向Mamba来建模语音信号在不同分辨率上的前向和后向依赖关系,并结合跳过连接来捕获多尺度信息,我们的方法达到了最新(SOTA)的性能。在VCTK+DEMAND数据集上的实验结果表明,Mamba-SEUNet的PESQ得分为3.59,同时保持较低的计算复杂性。当与感知对比度拉伸技术相结合时,Mamba-SEUNet的PESQ得分进一步提高到3.73。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Mamba-SEUNet结合Mamba和U-Net,利用双向Mamba对语音信号的前向和后向依赖进行建模,实现语音增强任务的高性能。实验结果表明,Mamba-SEUNet在VCTK+DEMAND数据集上取得了较高的PESQ评分,且计算复杂度较低。与感知对比度拉伸技术结合后,性能进一步提升。
Key Takeaways
- 近期语音增强研究中,Transformer及其变体是主要的方法论。
- Mamba作为一种新型的状态空间模型(SSM),在天然语言处理和计算机视觉中得到了广泛应用。
- Mamba-SEUNet结合了Mamba和U-Net,用于语音增强任务。
- Mamba-SEUNet利用双向Mamba对语音信号的不同分辨率进行建模,并加入跳跃连接来捕捉多尺度信息。
- 实验结果表明,Mamba-SEUNet在VCTK+DEMAND数据集上取得了先进性能,PESQ评分为3.59。
- Mamba-SEUNet计算复杂度较低。
点此查看论文截图

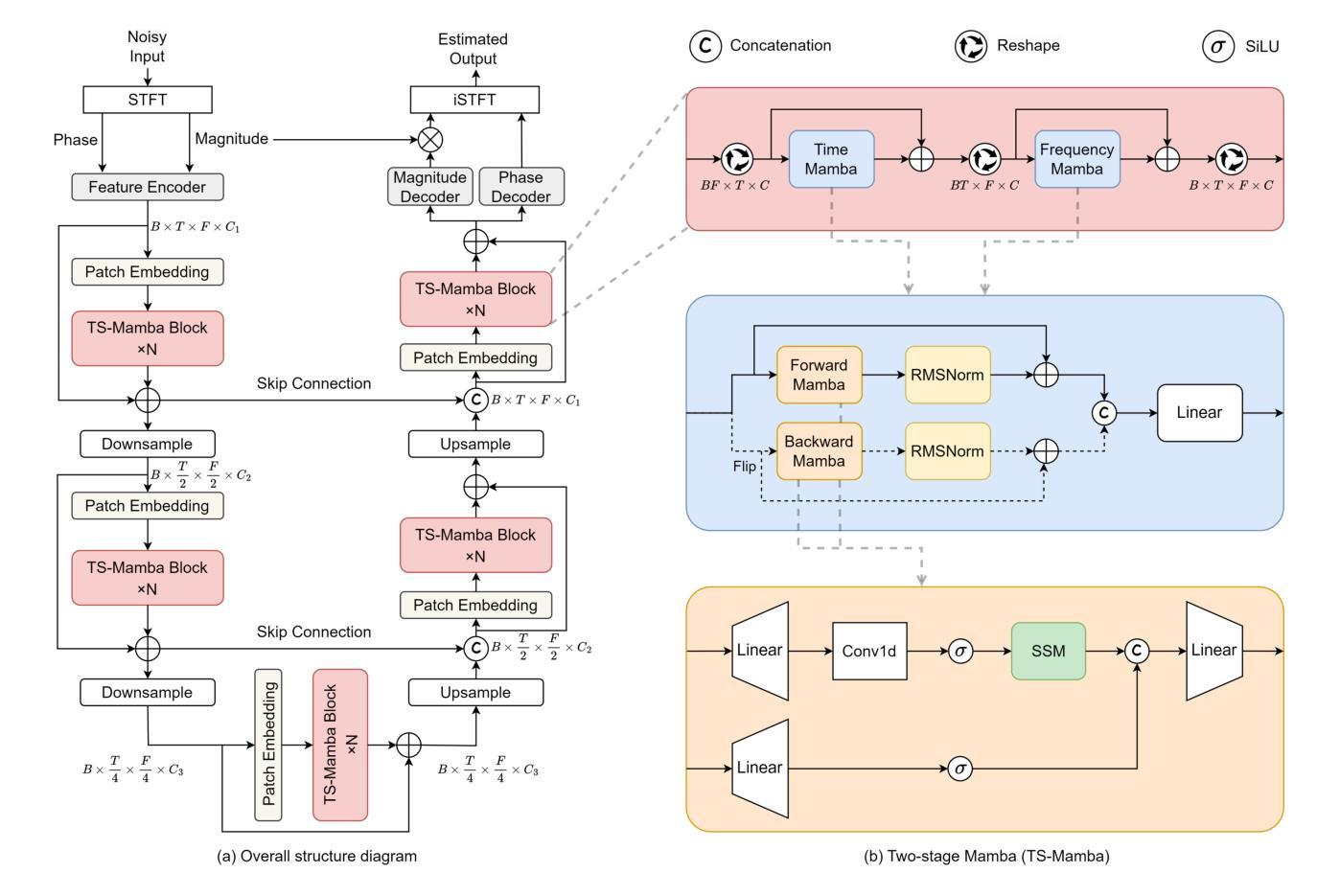
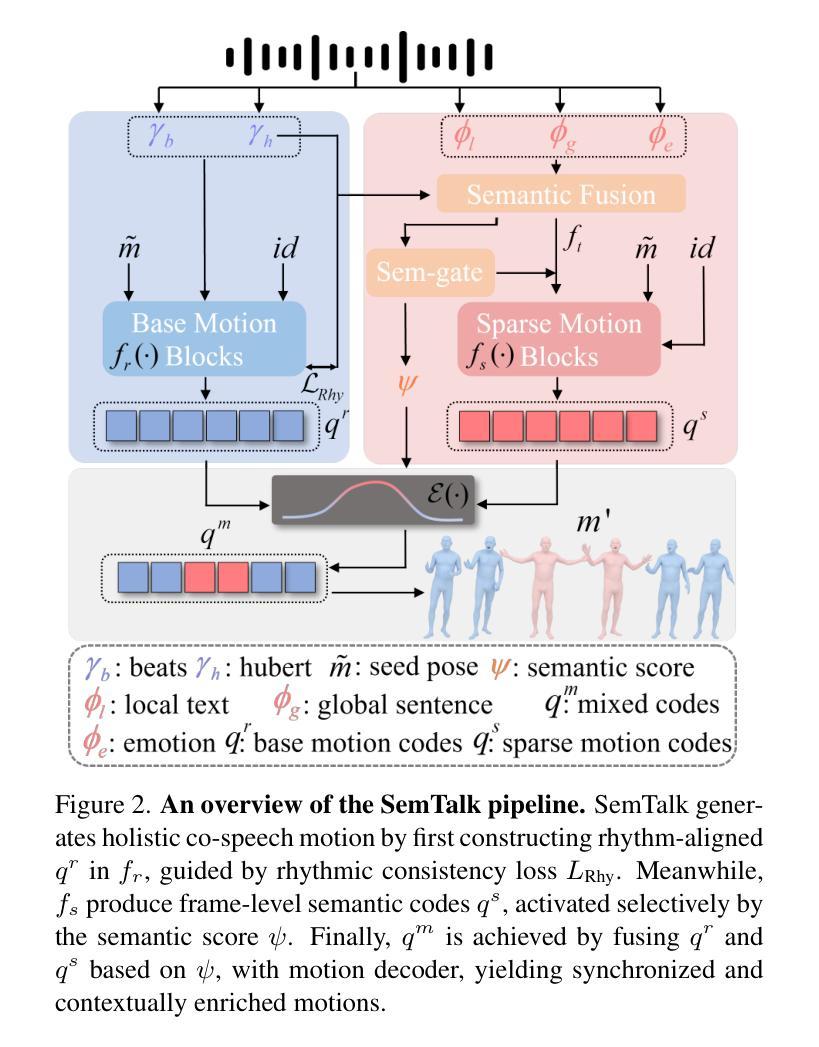
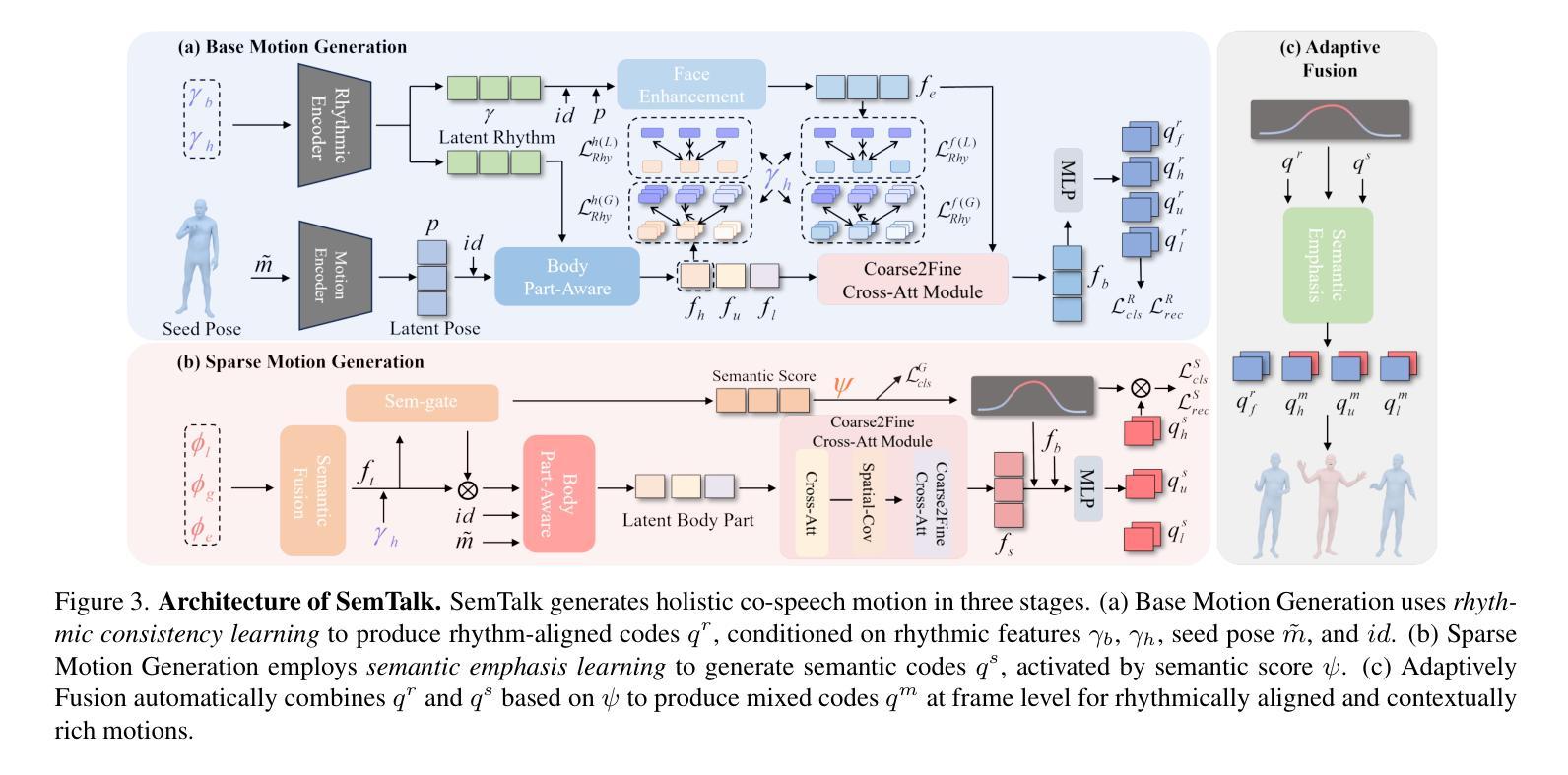
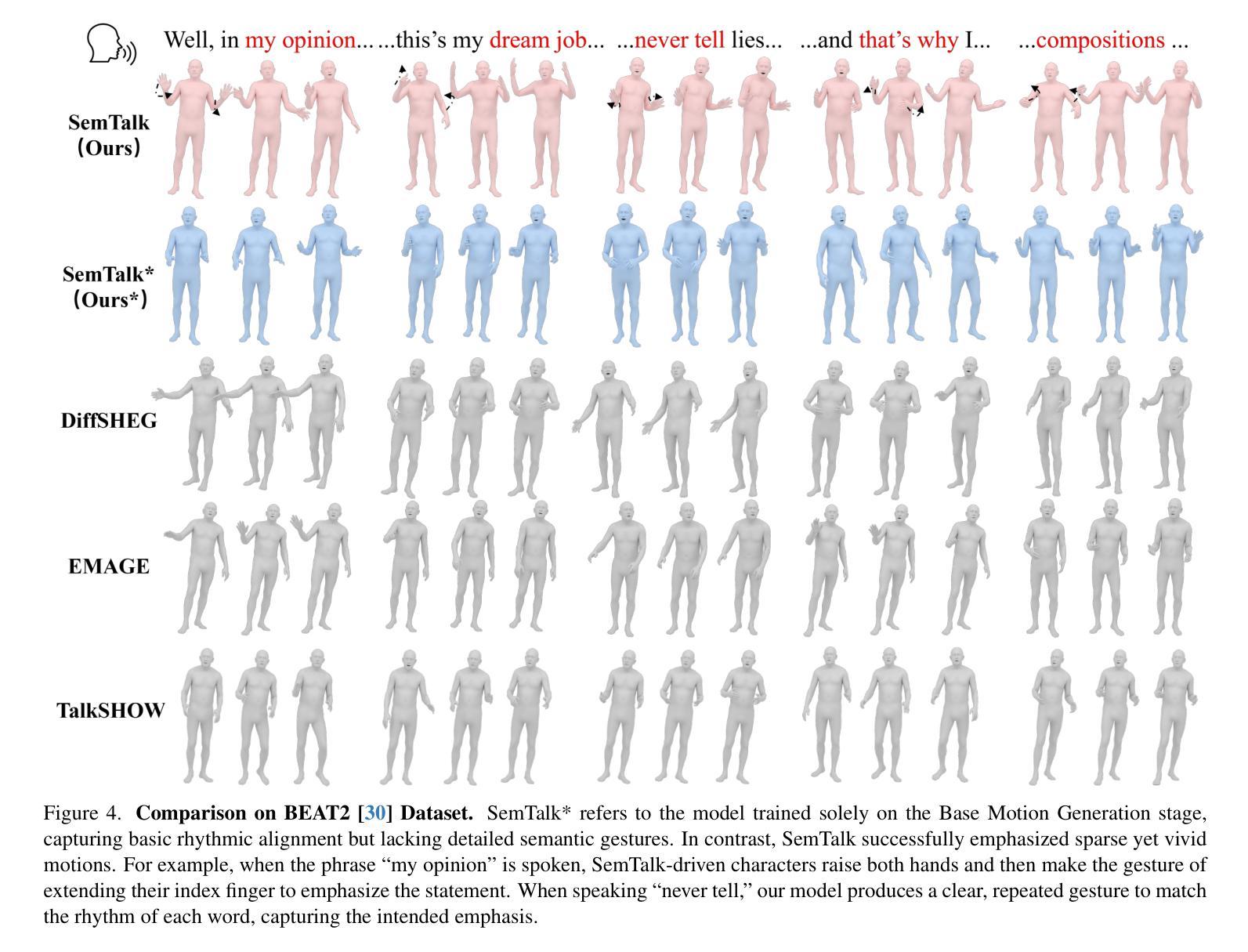
SemTalk: Holistic Co-speech Motion Generation with Frame-level Semantic Emphasis
Authors:Xiangyue Zhang, Jiangfang Li, Jiaxu Zhang, Ziqiang Dang, Jianqiang Ren, Liefeng Bo, Zhigang Tu
A good co-speech motion generation cannot be achieved without a careful integration of common rhythmic motion and rare yet essential semantic motion. In this work, we propose SemTalk for holistic co-speech motion generation with frame-level semantic emphasis. Our key insight is to separately learn general motions and sparse motions, and then adaptively fuse them. In particular, rhythmic consistency learning is explored to establish rhythm-related base motion, ensuring a coherent foundation that synchronizes gestures with the speech rhythm. Subsequently, textit{semantic emphasis learning is designed to generate semantic-aware sparse motion, focusing on frame-level semantic cues. Finally, to integrate sparse motion into the base motion and generate semantic-emphasized co-speech gestures, we further leverage a learned semantic score for adaptive synthesis. Qualitative and quantitative comparisons on two public datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art, delivering high-quality co-speech motion with enhanced semantic richness over a stable base motion.
在共同语言运动生成中,如果不仔细融合常见的节奏运动和罕见但至关重要的语义运动,就无法实现良好的共同语言运动生成。在这项工作中,我们提出了用于整体共同语言运动生成的SemTalk方法,具有帧级语义强调。我们的关键见解是分别学习常规运动和稀疏运动,然后自适应地融合它们。特别是,探索了节奏一致性学习以建立与节奏相关的基本运动,确保手势与语音节奏的同步协调基础。随后,设计了语义重点学习以生成具有语义感知的稀疏运动,侧重于帧级语义线索。最后,为了将稀疏运动融入基本运动并生成具有语义强调的共同语言手势,我们进一步利用学习到的语义分数进行自适应合成。在两项公共数据集上的定性和定量比较表明,我们的方法优于现有技术,提供高质量的共同语言运动,在稳定的基本运动上增加了语义丰富性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 8 figures
Summary
本文提出一种基于语义强调的协同语音动作生成方法SemTalk,通过分离学习通用动作和稀疏动作,并自适应融合。通过节奏一致性学习建立与节奏相关的基本动作,确保动作与语音节奏的同步。语义强调学习用于生成语义感知的稀疏动作,专注于帧级语义线索。最后,利用学习的语义分数将稀疏动作集成到基本动作中,生成具有语义强调的协同语音动作。此方法在公共数据集上的表现优于现有技术,能生成高质量、语义丰富的协同语音动作。
Key Takeaways
- 协同语音动作生成需结合通用节奏动作和关键语义动作。
- 提出SemTalk方法,通过分离学习通用动作和稀疏动作,实现全息协同语音动作生成。
- 节奏一致性学习确保动作与语音节奏的同步。
- 语义强调学习关注帧级语义线索,生成语义感知的稀疏动作。
- 利用学习的语义分数自适应合成协同语音动作。
- 在公共数据集上表现出优于现有技术的效果。
点此查看论文截图

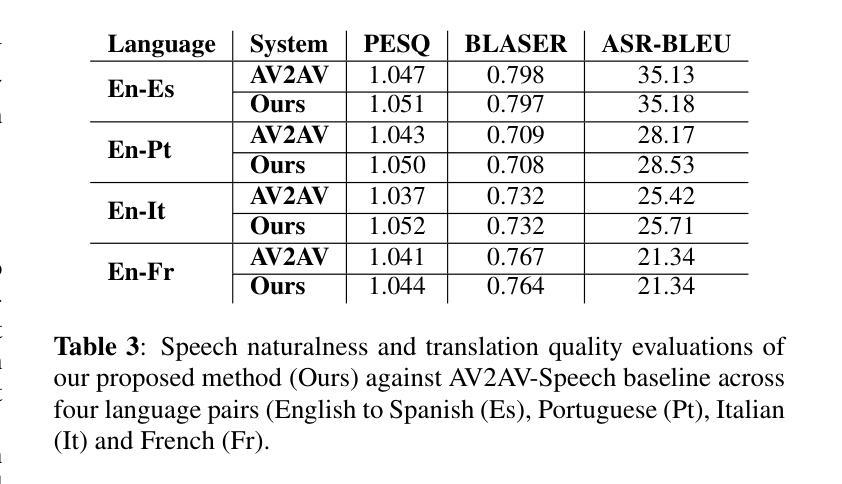
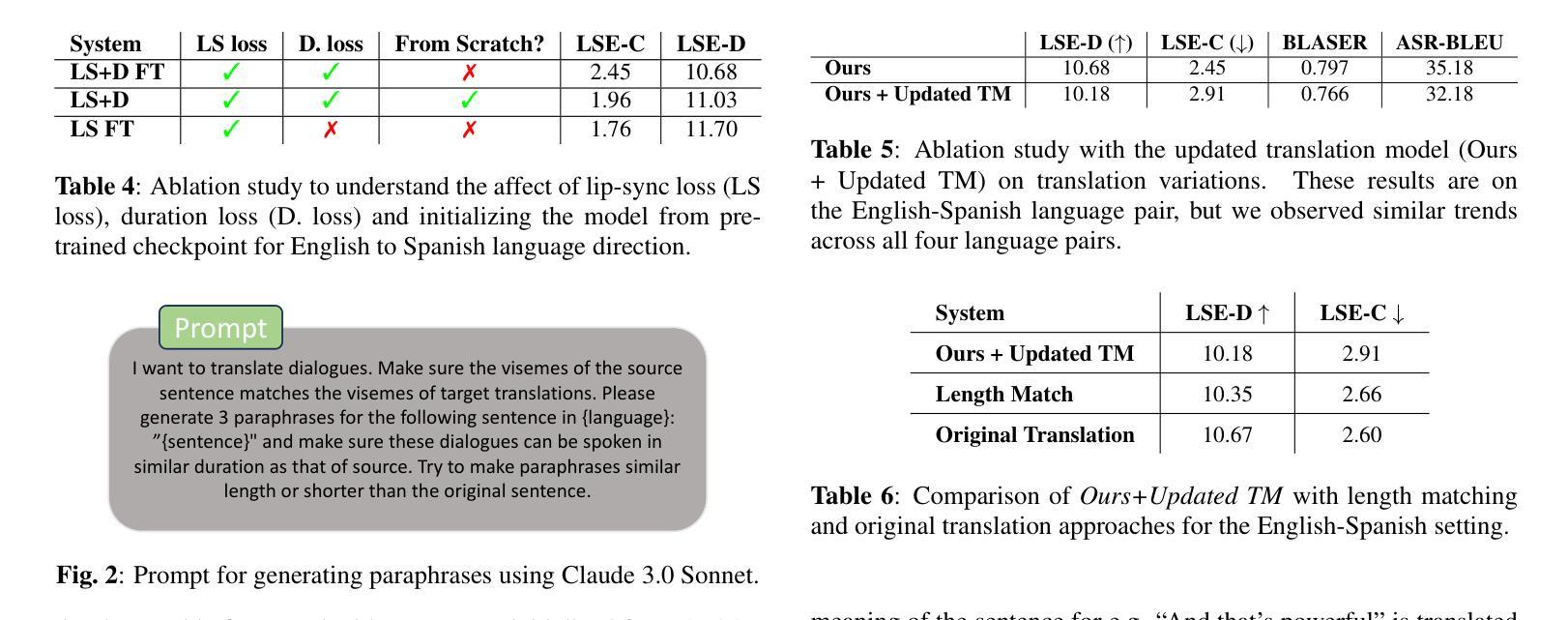
Improving Lip-synchrony in Direct Audio-Visual Speech-to-Speech Translation
Authors:Lucas Goncalves, Prashant Mathur, Xing Niu, Brady Houston, Chandrashekhar Lavania, Srikanth Vishnubhotla, Lijia Sun, Anthony Ferritto
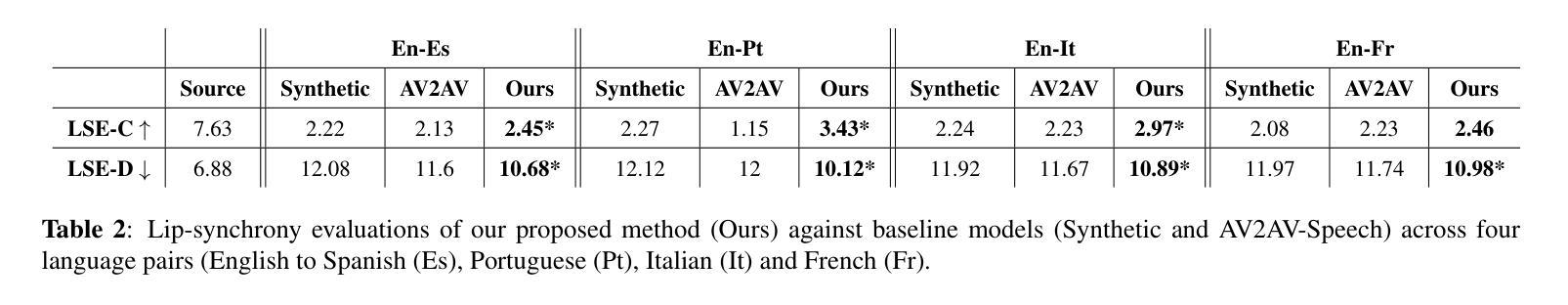
Audio-Visual Speech-to-Speech Translation typically prioritizes improving translation quality and naturalness. However, an equally critical aspect in audio-visual content is lip-synchrony-ensuring that the movements of the lips match the spoken content-essential for maintaining realism in dubbed videos. Despite its importance, the inclusion of lip-synchrony constraints in AVS2S models has been largely overlooked. This study addresses this gap by integrating a lip-synchrony loss into the training process of AVS2S models. Our proposed method significantly enhances lip-synchrony in direct audio-visual speech-to-speech translation, achieving an average LSE-D score of 10.67, representing a 9.2% reduction in LSE-D over a strong baseline across four language pairs. Additionally, it maintains the naturalness and high quality of the translated speech when overlaid onto the original video, without any degradation in translation quality.
视听语音到语音翻译通常优先考虑提高翻译质量和自然度。然而,在视听内容中,同样关键的一个方面是唇同步问题——确保嘴唇的动作与所说话的内容相匹配,这对于保持配音视频的真实性至关重要。尽管其重要性不容忽视,但在AVS2S模型中融入唇同步约束却被大大忽视了。本研究通过向AVS2S模型的训练过程引入唇同步损失来填补这一空白。所提出的方法显著提高了直接视听语音到语音翻译中的唇同步效果,平均LSE-D得分为10.67,在四种语言对上相对于强大的基线模型,LSE-D降低了9.2%。此外,该方法在保持翻译语音的自然性和高质量的同时,将其覆盖在原始视频上,没有降低翻译质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICASSP, 4 pages
Summary
本文研究了音频视觉语音到语音的翻译问题,强调了唇同步的重要性,即在音频视觉内容中确保嘴唇动作与口语内容相匹配,对于保持视频配音的真实性至关重要。该研究通过将唇同步损失纳入AVS2S模型的训练过程中,填补了这一空白。所提出的方法在直接音频视觉语音到语音的翻译中显著提高了唇同步性,在四种语言对上平均LSE-D得分为10.67,相较于强基线降低了9.2%。同时,该方法在保持翻译语音的自然性和高质量时,不会降低翻译质量。
Key Takeaways
- 音频视觉语音到语音的翻译中,唇同步的重要性被强调,它对于保持视频配音的真实性至关重要。
- 现有研究中,将唇同步约束纳入AVS2S模型的做法被忽视。
- 研究通过整合唇同步损失到AVS2S模型的训练过程中,提高了唇同步性。
- 所提出的方法在四种语言对上平均LSE-D得分为10.67,相较于强基线降低了9.2%。
- 方法在改善唇同步性的同时,不影响翻译语音的自然性和高质量。
- 该方法能够为直接音频视觉语音到语音的翻译带来显著的提升。
点此查看论文截图


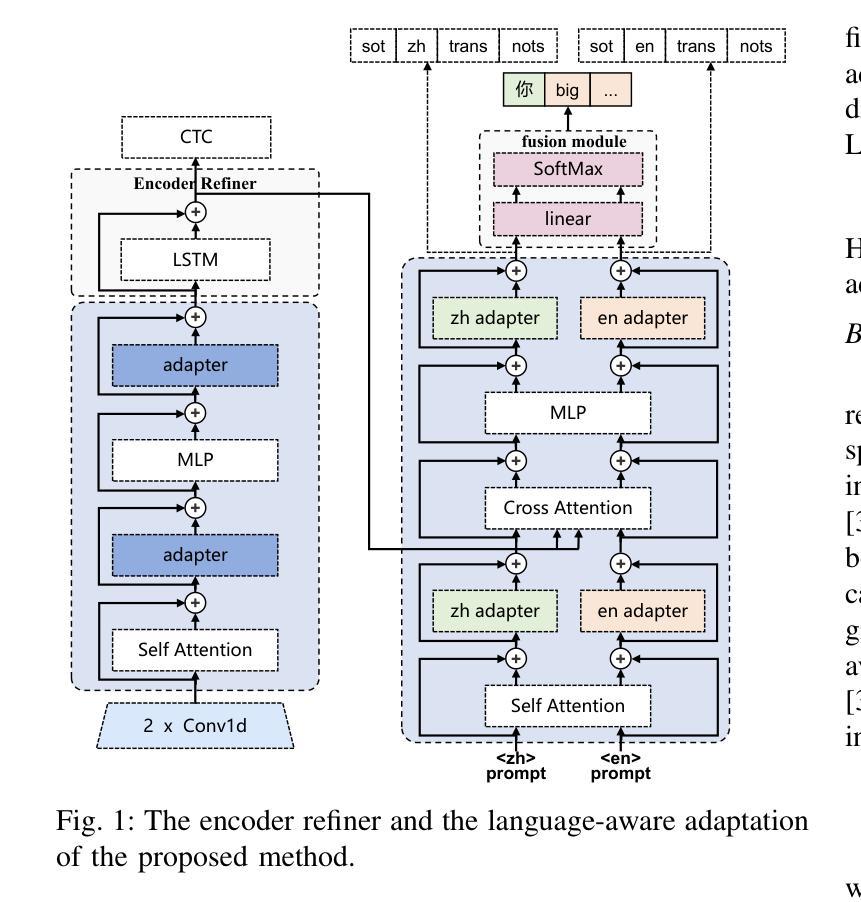
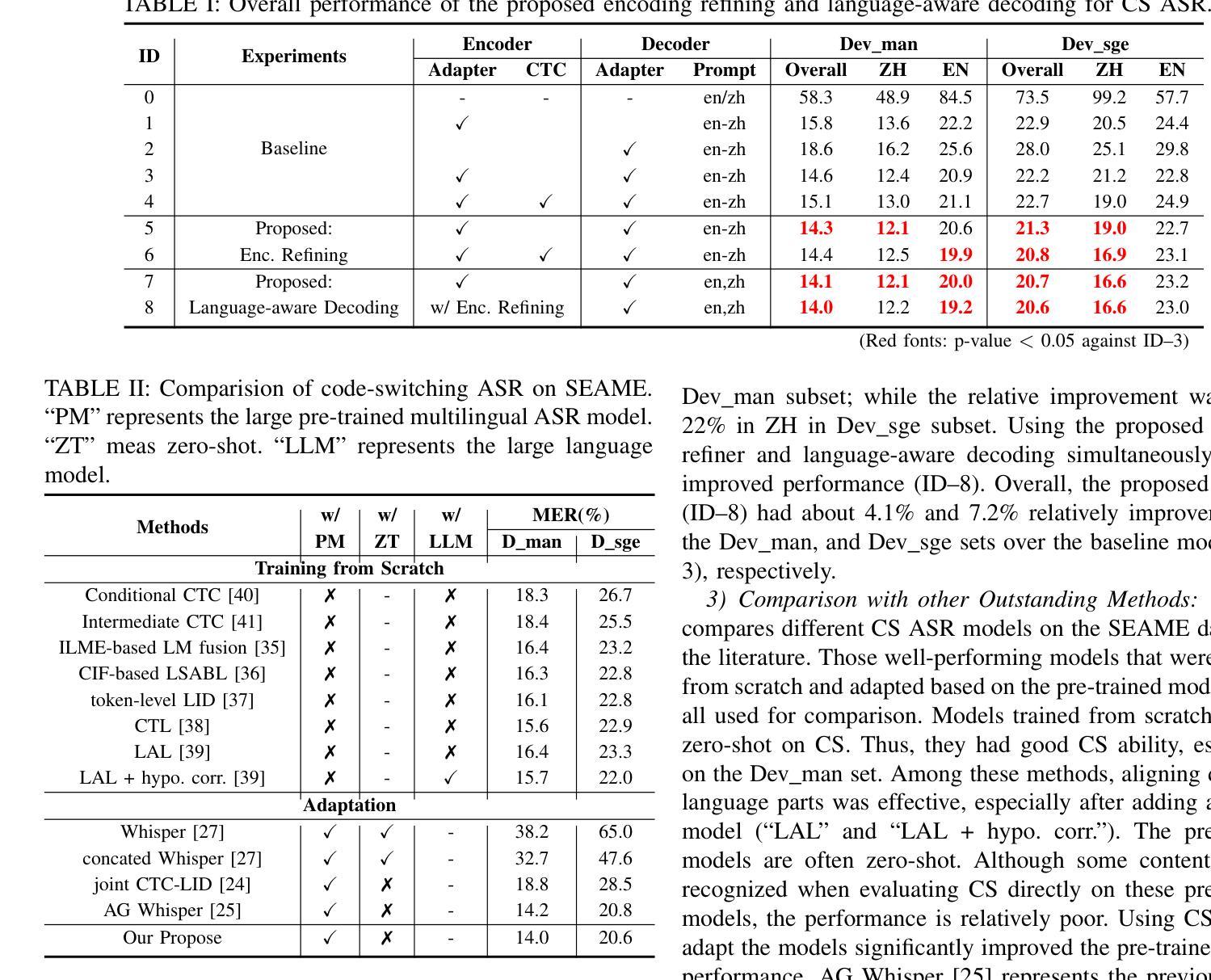
Adapting Whisper for Code-Switching through Encoding Refining and Language-Aware Decoding
Authors:Jiahui Zhao, Hao Shi, Chenrui Cui, Tianrui Wang, Hexin Liu, Zhaoheng Ni, Lingxuan Ye, Longbiao Wang
Code-switching (CS) automatic speech recognition (ASR) faces challenges due to the language confusion resulting from accents, auditory similarity, and seamless language switches. Adaptation on the pre-trained multi-lingual model has shown promising performance for CS-ASR. In this paper, we adapt Whisper, which is a large-scale multilingual pre-trained speech recognition model, to CS from both encoder and decoder parts. First, we propose an encoder refiner to enhance the encoder’s capacity of intra-sentence swithching. Second, we propose using two sets of language-aware adapters with different language prompt embeddings to achieve language-specific decoding information in each decoder layer. Then, a fusion module is added to fuse the language-aware decoding. The experimental results using the SEAME dataset show that, compared with the baseline model, the proposed approach achieves a relative MER reduction of 4.1% and 7.2% on the dev_man and dev_sge test sets, respectively, surpassing state-of-the-art methods. Through experiments, we found that the proposed method significantly improves the performance on non-native language in CS speech, indicating that our approach enables Whisper to better distinguish between the two languages.
代码切换(CS)自动语音识别(ASR)面临着由于口音、听觉相似性和无缝语言切换导致的语言混淆所带来的挑战。预训练的多元语言模型的调整对CS-ASR表现出了有前景的性能。在本文中,我们适应了大规模的多元语言预训练语音识别模型Whisper,既适应于编码器部分也适应于解码器部分。首先,我们提出了一个编码器精炼器,以提高编码器在句子内切换的能力。其次,我们建议使用两组带有不同语言提示嵌入的语言感知适配器来实现每个解码器层中的语言特定解码信息。然后,添加一个融合模块来融合语言感知解码。使用SEAME数据集的实验结果表明,与基线模型相比,所提出的方法在dev_man和dev_sge测试集上相对MER分别降低了4.1%和7.2%,超过了最先进的方法。通过实验,我们发现该方法在非母语在CS语音上的表现显著提高,这表明我们的方法使Whisper能够更好地区分两种语言。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了自动语音识别系统在处理代码切换(CS)时的挑战,并通过对大型预训练的多语言语音模型Whisper进行适应取得了进展。论文通过增强编码器内的句子切换能力并引入语言感知解码器来提高CS语音识别的性能。实验结果表明,该方法相较于基线模型在相对词错误率上有所降低,且在处理非母语语言时表现更优。
Key Takeaways
- 代码切换(CS)自动语音识别(ASR)面临由口音、听觉相似性和无缝语言切换引起的语言混淆挑战。
- 适应预训练的多语言模型对于CS-ASR具有前景。
- 对Whisper模型的编码器进行改进,增强其句子内切换能力。
- 引入语言感知适配器与语言提示嵌入,实现解码器的语言特异性。
- 通过融合模块融合语言感知解码结果。
- 实验结果表明,该方法相较于基线模型在SEAME数据集上的性能有所提升。
点此查看论文截图

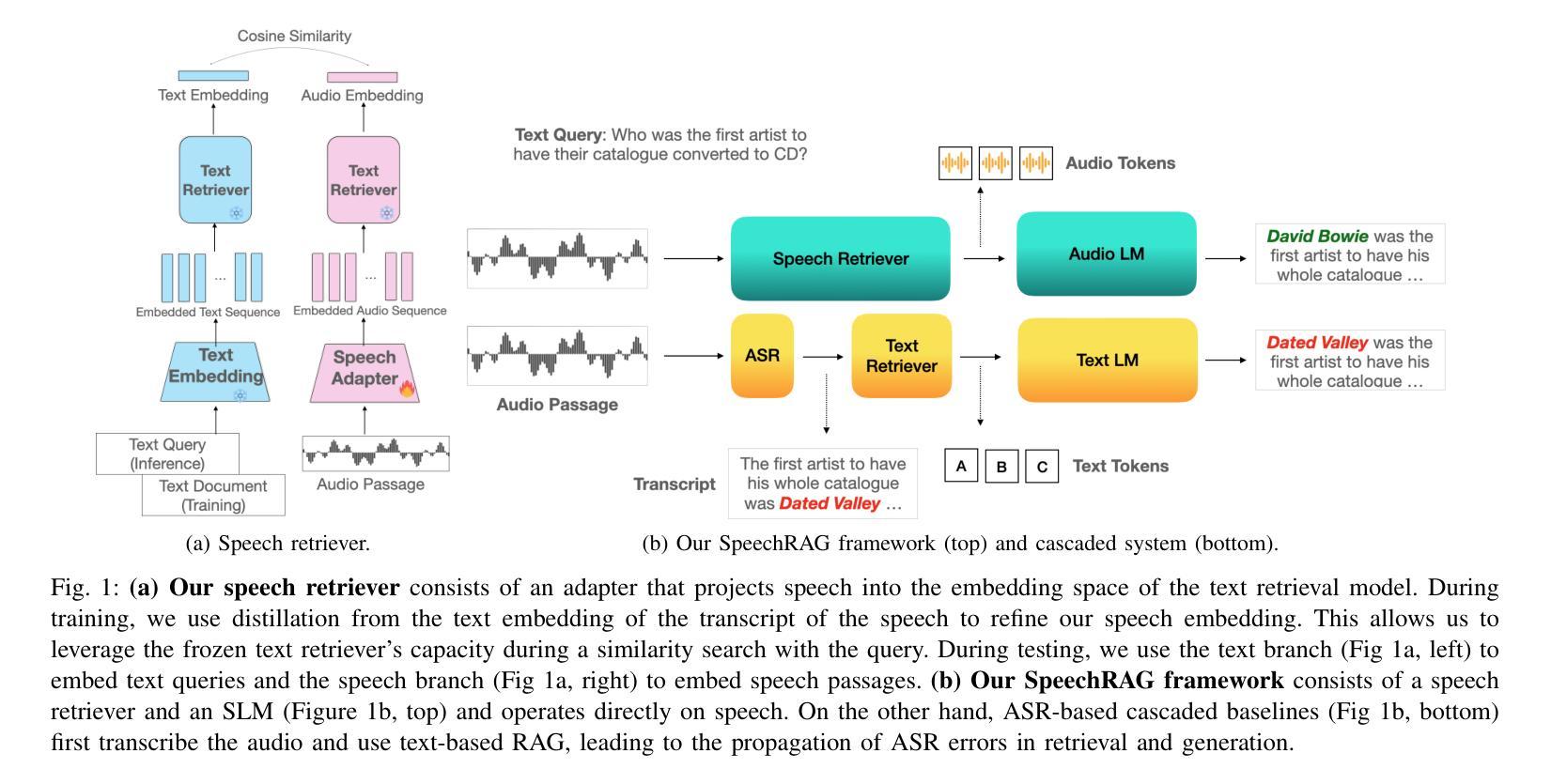
Speech Retrieval-Augmented Generation without Automatic Speech Recognition
Authors:Do June Min, Karel Mundnich, Andy Lapastora, Erfan Soltanmohammadi, Srikanth Ronanki, Kyu Han
One common approach for question answering over speech data is to first transcribe speech using automatic speech recognition (ASR) and then employ text-based retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) on the transcriptions. While this cascaded pipeline has proven effective in many practical settings, ASR errors can propagate to the retrieval and generation steps. To overcome this limitation, we introduce SpeechRAG, a novel framework designed for open-question answering over spoken data. Our proposed approach fine-tunes a pre-trained speech encoder into a speech adapter fed into a frozen large language model (LLM)–based retrieval model. By aligning the embedding spaces of text and speech, our speech retriever directly retrieves audio passages from text-based queries, leveraging the retrieval capacity of the frozen text retriever. Our retrieval experiments on spoken question answering datasets show that direct speech retrieval does not degrade over the text-based baseline, and outperforms the cascaded systems using ASR. For generation, we use a speech language model (SLM) as a generator, conditioned on audio passages rather than transcripts. Without fine-tuning of the SLM, this approach outperforms cascaded text-based models when there is high WER in the transcripts.
针对语音数据的问答的一个常见方法是首先使用自动语音识别(ASR)进行语音转录,然后在转录上应用基于文本的检索增强生成(RAG)。虽然这种级联管道已在许多实际场景中证明是有效的,但ASR错误可能会传播到检索和生成步骤。为了克服这一局限性,我们引入了SpeechRAG,这是一个专为开放式问题回答设计的全新框架,用于处理口语数据。我们提出的方法是对预训练的语音编码器进行微调,使其适应于基于冻结的大型语言模型(LLM)的检索模型的语音适配器。通过对文本和语音的嵌入空间进行对齐,我们的语音检索器可以直接从基于文本的查询中检索音频片段,利用冻结的文本检索器的检索能力。我们在口语问答数据集上的检索实验表明,直接语音检索并不亚于基于文本的基线,并且表现优于使用ASR的级联系统。对于生成,我们使用语音语言模型(SLM)作为生成器,以音频片段为条件,而不是文本。在不微调SLM的情况下,当转录中的字词错误率(WER)较高时,此方法的表现优于级联的基于文本模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:为提高语音识别(ASR)错误在问答系统中的影响,引入SpeechRAG框架,该框架通过微调预训练语音编码器并将其输入到基于大型语言模型(LLM)的检索模型中,实现直接语音检索。通过文本和语音嵌入空间的对齐,该语音检索器可直接从基于文本的查询中检索音频片段。实验表明,直接语音检索在口语问答数据集上的表现不亚于基于文本的基线系统,且优于级联系统。生成部分则采用语音语言模型(SLM)作为生成器,以音频片段为条件,无需对SLM进行微调,当字幕错误率较高时,表现优于级联的基于文本模型。
Key Takeaways:
- SpeechRAG是一个为口语问答设计的全新框架,它通过微调预训练语音编码器以进行语音适配。
- 该框架利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行检索,实现直接语音检索。
- 通过文本和语音嵌入空间的对齐,SpeechRAG能够从基于文本的查询中直接检索音频片段。
- 实验显示,直接语音检索在口语问答数据集上的表现与基于文本的基线系统相当。
- 与级联系统相比,SpeechRAG具有更好的性能。
- 在生成阶段,采用语音语言模型(SLM)作为生成器,以音频片段为条件,无需对SLM进行微调。
点此查看论文截图




Enhancing Multilingual ASR for Unseen Languages via Language Embedding Modeling
Authors:Shao-Syuan Huang, Kuan-Po Huang, Andy T. Liu, Hung-yi Lee
Multilingual Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) aims to recognize and transcribe speech from multiple languages within a single system. Whisper, one of the most advanced ASR models, excels in this domain by handling 99 languages effectively, leveraging a vast amount of data and incorporating language tags as prefixes to guide the recognition process. However, despite its success, Whisper struggles with unseen languages, those not included in its pre-training. Motivated by the observation that many languages share linguistic characteristics, we propose methods that exploit these relationships to enhance ASR performance on unseen languages. Specifically, we introduce a weighted sum method, which computes a weighted sum of the embeddings of language tags, using Whisper’s predicted language probabilities. In addition, we develop a predictor-based approach that refines the weighted sum embedding to more closely approximate the true embedding for unseen languages. Experimental results demonstrate substantial improvements in ASR performance, both in zero-shot and fine-tuning settings. Our proposed methods outperform baseline approaches, providing an effective solution for addressing unseen languages in multilingual ASR.
多语言自动语音识别(ASR)旨在在一个系统中识别和转录多种语言的语音。whisper是最先进的ASR模型之一,通过处理99种语言,利用大量数据并融入语言标签作为前缀来引导识别过程,在该领域表现出色。然而,尽管取得了成功,whisper仍面临着未见过的语言的挑战,这些语言并未包含在预训练之中。受多种语言具有共同语言特性的观察结果的启发,我们提出了利用这些关系提高未见语言的ASR性能的方法。具体来说,我们引入了一种加权和的方法,该方法计算语言标签嵌入的加权和,使用whisper预测的语音概率。此外,我们开发了一种基于预测的方法,对加权和嵌入进行微调,以更精确地逼近未见语言的真实嵌入。实验结果表明,在零样本和微调设置中,ASR性能均有显著提高。我们提出的方法优于基线方法,为解决多语种ASR中的未见语言问题提供了有效的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICASSP 2025
Summary
多语种自动语音识别(ASR)旨在在一个系统中识别和转录多种语言的语音。最先进的ASR模型之一Whisper能够有效处理99种语言,利用大量数据和引入语言标签前缀来引导识别过程。然而,Whisper在未见语言(即预训练阶段未包含的语言)方面存在挑战。受多种语言具有共享语言特性的启发,本文提出利用这些关系提高未见语言的ASR性能的方法。具体提出了加权和方法和基于预测器的方法,前者计算语言标签嵌入的加权和,使用Whisper预测的语言概率;后者对加权和嵌入进行精细化,以更接近于未见语言的真实嵌入。实验结果证明,在零样本和微调设置中,本文提出的方法在ASR性能上取得了显著提高,并优于基准方法,为处理多语种ASR中的未见语言提供了有效解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 多语种自动语音识别(ASR)能在一个系统中识别和转录多种语言的语音。
- Whisper是处理多种语言的有效ASR模型,但面临未见语言的挑战。
- 多种语言具有共享语言特性,可以利用这些关系提高ASR性能。
- 提出了加权和方法和基于预测器的方法来提高ASR对未见语言的性能。
- 加权和方法通过计算语言标签嵌入的加权和来工作,利用预测的语言概率。
- 基于预测器的方法对加权和嵌入进行精细化,以更接近未见语言的真实嵌入。
点此查看论文截图



Transducer-Llama: Integrating LLMs into Streamable Transducer-based Speech Recognition
Authors:Keqi Deng, Jinxi Guo, Yingyi Ma, Niko Moritz, Philip C. Woodland, Ozlem Kalinli, Mike Seltzer
While large language models (LLMs) have been applied to automatic speech recognition (ASR), the task of making the model streamable remains a challenge. This paper proposes a novel model architecture, Transducer-Llama, that integrates LLMs into a Factorized Transducer (FT) model, naturally enabling streaming capabilities. Furthermore, given that the large vocabulary of LLMs can cause data sparsity issue and increased training costs for spoken language systems, this paper introduces an efficient vocabulary adaptation technique to align LLMs with speech system vocabularies. The results show that directly optimizing the FT model with a strong pre-trained LLM-based predictor using the RNN-T loss yields some but limited improvements over a smaller pre-trained LM predictor. Therefore, this paper proposes a weak-to-strong LM swap strategy, using a weak LM predictor during RNN-T loss training and then replacing it with a strong LLM. After LM replacement, the minimum word error rate (MWER) loss is employed to finetune the integration of the LLM predictor with the Transducer-Llama model. Experiments on the LibriSpeech and large-scale multi-lingual LibriSpeech corpora show that the proposed streaming Transducer-Llama approach gave a 17% relative WER reduction (WERR) over a strong FT baseline and a 32% WERR over an RNN-T baseline.
在大型语言模型(LLM)已应用于自动语音识别(ASR)的情况下,实现模型的流式传输任务仍然是一个挑战。本文提出了一种新型模型架构Transducer-Llama,该架构将LLM集成到分解式转换器(FT)模型中,自然地实现了流式传输功能。此外,鉴于LLM的大量词汇可能导致数据稀疏问题以及增加口语系统的训练成本,本文介绍了一种有效的词汇适应技术,以使LLM与语音系统词汇对齐。结果表明,使用强大的预训练LLM预测器直接优化FT模型,并使用RNN-T损失进行训练,相较于较小的预训练LM预测器虽然有一定改进,但改进有限。因此,本文提出了从弱到强的LM替换策略,即在RNN-T损失训练期间使用弱LM预测器,然后将其替换为强大的LLM。在LM替换之后,采用最小单词错误率(MWER)损失对LLM预测器与Transducer-Llama模型的集成进行微调。在LibriSpeech和大规模多语种LibriSpeech语料库上的实验表明,所提出的流式传输Transducer-Llama方法相较于强大的FT基准线和RNN-T基准线分别实现了17%和32%的相对字词错误率减少(WERR)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICASSP 2025
Summary
该文提出一种结合大型语言模型(LLMs)的流式自动语音识别模型Transducer-Llama。针对LLMs词汇量大导致的训练和识别问题,引入了一种有效的词汇表适应技术。通过对基于强预训练LLM预测器的流式转导器模型进行优化,采用替换策略以提高识别性能。实验结果显示,该方法相较于基准模型显著提高了识别性能。
Key Takeaways
- Transducer-Llama模型结合了大型语言模型(LLMs),实现流式自动语音识别(ASR)。
- 针对LLMs词汇量大带来的数据稀疏和训练成本问题,提出了有效的词汇表适应技术。
- 直接优化基于强预训练LLM预测器的流式转导器模型有所提升,但效果有限。
- 采用弱到强的LM替换策略,先用弱LM预测器进行训练,再替换为强LLM预测器。
- 引入最小词错误率(MWER)损失来微调LLM预测器与Transducer-Llama模型的集成。
- 在LibriSpeech数据集上的实验表明,Transducer-Llama方法相较于强基线模型和RNN-T基线模型,显著降低了词错误率(WER)。
点此查看论文截图






LAMA-UT: Language Agnostic Multilingual ASR through Orthography Unification and Language-Specific Transliteration
Authors:Sangmin Lee, Woo-Jin Chung, Hong-Goo Kang
Building a universal multilingual automatic speech recognition (ASR) model that performs equitably across languages has long been a challenge due to its inherent difficulties. To address this task we introduce a Language-Agnostic Multilingual ASR pipeline through orthography Unification and language-specific Transliteration (LAMA-UT). LAMA-UT operates without any language-specific modules while matching the performance of state-of-the-art models trained on a minimal amount of data. Our pipeline consists of two key steps. First, we utilize a universal transcription generator to unify orthographic features into Romanized form and capture common phonetic characteristics across diverse languages. Second, we utilize a universal converter to transform these universal transcriptions into language-specific ones. In experiments, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method leveraging universal transcriptions for massively multilingual ASR. Our pipeline achieves a relative error reduction rate of 45% when compared to Whisper and performs comparably to MMS, despite being trained on only 0.1% of Whisper’s training data. Furthermore, our pipeline does not rely on any language-specific modules. However, it performs on par with zero-shot ASR approaches which utilize additional language-specific lexicons and language models. We expect this framework to serve as a cornerstone for flexible multilingual ASR systems that are generalizable even to unseen languages.
构建一个适用于多种语言的自动语音识别(ASR)模型,能够在各种语言之间实现公平表现,长期以来一直是一个挑战,因为其固有的困难。为了解决这一任务,我们通过正字法统一和针对特定语言的转写(LAMA-UT),引入了语言无关的多语言ASR管道。LAMA-UT在没有任何针对特定语言的模块的情况下运行,同时匹配在少量数据上训练的最新模型的性能。我们的管道包括两个关键步骤。首先,我们利用通用转录生成器将正字特征统一为罗马化形式,并捕捉不同语言的共同语音特征。其次,我们利用通用转换器将这些通用转录转换为特定语言的转录。在实验中,我们展示了利用通用转录进行大规模多语言ASR的方法的有效性。与whisper相比,我们的管道在相对误差减少率方面实现了45%的降低,尽管它只接受了whisper 0.1%的训练数据。此外,我们的管道不依赖于任何针对特定语言的模块,但其性能与零镜头ASR方法相当,后者利用额外的针对特定语言的词汇和语言模型。我们希望这个框架能成为灵活的多语言ASR系统的基石,即使对于未见过的语言,它也具有通用性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种跨语言的自动语音识别(ASR)模型,即语言无关的多语言ASR管道,通过正字法统一和语言特定转写(LAMA-UT)来解决在不同语言中表现均衡的挑战。该管道无需任何特定语言的模块,即可匹配在少量数据上训练的先进模型性能。实验证明,该方法利用通用转录来实现大规模多语言ASR的有效性,相较于Whisper,相对误差减少率达到45%,并在训练数据量仅为其十分之一的情况下表现出优异性能。虽然该管道不依赖任何特定语言的模块,但其性能与零样本ASR方法相当,后者使用额外的特定语言词典和语言模型。该框架有望成为灵活的多语言ASR系统的基石,能够推广到未见过的语言。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的跨语言ASR模型——语言无关的多语言ASR管道(LAMA-UT)。
- 通过正字法统一和语言特定转写两个关键步骤实现该模型。
- 无需特定语言的模块,即能匹配在少量数据上训练的先进模型性能。
- 实验证明,该方法在相对误差减少率方面表现优异,相较于Whisper达到45%。
- 在训练数据量仅为其十分之一的情况下表现优异。
- 该管道性能与零样本ASR方法相当。
点此查看论文截图







BEST-STD: Bidirectional Mamba-Enhanced Speech Tokenization for Spoken Term Detection
Authors:Anup Singh, Kris Demuynck, Vipul Arora
Spoken term detection (STD) is often hindered by reliance on frame-level features and the computationally intensive DTW-based template matching, limiting its practicality. To address these challenges, we propose a novel approach that encodes speech into discrete, speaker-agnostic semantic tokens. This facilitates fast retrieval using text-based search algorithms and effectively handles out-of-vocabulary terms. Our approach focuses on generating consistent token sequences across varying utterances of the same term. We also propose a bidirectional state space modeling within the Mamba encoder, trained in a self-supervised learning framework, to learn contextual frame-level features that are further encoded into discrete tokens. Our analysis shows that our speech tokens exhibit greater speaker invariance than those from existing tokenizers, making them more suitable for STD tasks. Empirical evaluation on LibriSpeech and TIMIT databases indicates that our method outperforms existing STD baselines while being more efficient.
语音术语检测(STD)通常受到依赖于帧级特征和计算密集型的基于DTW的模板匹配的阻碍,这限制了其实用性。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种将语音编码为离散、独立于说话人的语义令牌的新方法。这有助于使用基于文本的搜索算法进行快速检索,并有效地处理词汇表之外的术语。我们的方法侧重于生成同一术语不同表达之间一致的令牌序列。我们还提出了一种在Mamba编码器内部的双向状态空间建模,在自我监督的学习框架中进行训练,以学习上下文帧级特征,这些特征进一步被编码成离散令牌。我们的分析表明,我们的语音令牌表现出比现有分词器更高的说话人不变性,使其更适合于STD任务。在LibriSpeech和TIMIT数据库上的经验评估表明,我们的方法优于现有的STD基线方法,同时效率更高。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICASSP 2025
Summary:
针对当前语音术语检测(STD)面临的挑战,如依赖帧级特征和基于DTW的模板匹配导致的计算量大,我们提出了一种新的解决方案。该方法将语音编码为离散、独立于说话者的语义令牌,促进使用文本搜索算法进行快速检索,并有效处理词汇表外的术语。该方法专注于生成同一术语不同表达形式的一致令牌序列,并提出在Mamba编码器内使用双向状态空间建模,以在自我监督学习框架中学习环境级别的特征。此外,生成的语音令牌表现出更高的说话人无关性,使得它们更适合用于STD任务。在LibriSpeech和TIMIT数据库上的实证评估表明,我们的方法不仅优于现有的STD基线,而且更高效。
Key Takeaways:
- 语音术语检测(STD)面临依赖帧级特征和计算密集型DTW模板匹配的挑战。
- 提出了一种新的方法来解决上述问题,通过将语音编码为独立于说话者的语义令牌来促进快速检索和处理词汇表外的术语。
- 方法注重生成同一术语不同表达形式的一致令牌序列。
- 引入了双向状态空间建模,在自我监督学习框架中学习环境级别的特征。
- 生成的语音令牌展现出较高的说话人无关性,提高了其在STD任务中的适用性。
- 在LibriSpeech和TIMIT数据库上的实证评估表明该方法优于现有的STD基线。
点此查看论文截图





Multi-Source Spatial Knowledge Understanding for Immersive Visual Text-to-Speech
Authors:Shuwei He, Rui Liu
Visual Text-to-Speech (VTTS) aims to take the environmental image as the prompt to synthesize reverberant speech for the spoken content. Previous works focus on the RGB modality for global environmental modeling, overlooking the potential of multi-source spatial knowledge like depth, speaker position, and environmental semantics. To address these issues, we propose a novel multi-source spatial knowledge understanding scheme for immersive VTTS, termed MS2KU-VTTS. Specifically, we first prioritize RGB image as the dominant source and consider depth image, speaker position knowledge from object detection, and Gemini-generated semantic captions as supplementary sources. Afterwards, we propose a serial interaction mechanism to effectively integrate both dominant and supplementary sources. The resulting multi-source knowledge is dynamically integrated based on the respective contributions of each source.This enriched interaction and integration of multi-source spatial knowledge guides the speech generation model, enhancing the immersive speech experience. Experimental results demonstrate that the MS$^2$KU-VTTS surpasses existing baselines in generating immersive speech. Demos and code are available at: https://github.com/AI-S2-Lab/MS2KU-VTTS.
视觉文本到语音(VTTS)旨在以环境图像为提示,合成响亮的内容语音。以前的研究工作主要集中在RGB模态进行全局环境建模,忽略了深度、说话者位置和环境语义等多源空间知识的潜力。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种用于沉浸式VTTS的多源空间知识理解方案,称为MS2KU-VTTS。具体来说,我们首先以RGB图像作为主要来源,并将深度图像、来自对象检测的说话者位置知识以及Gemini生成的语义字幕作为辅助来源。然后,我们提出了一种串行交互机制,以有效地整合主要来源和辅助来源。所得的多源知识是动态整合的,基于每个来源的相对贡献。这种丰富的多源空间知识的交互和整合引导语音生成模型,增强了沉浸式语音体验。实验结果表明,MS$^2$KU-VTTS在生成沉浸式语音方面超过了现有基线。相关演示和代码可在:https://github.com/AI-S2-Lab/MS2KU-VTTS 获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 1 figure, Accepted by ICASSP’2025
Summary
本文介绍了视觉文本语音转换(VTTS)的目标是利用环境图像合成语音内容。针对以往研究仅关注RGB模态进行全局环境建模,忽视了深度、说话者位置和语义等多源空间知识的问题,提出了一种名为MS^2KU-VTTS的多源空间知识理解方案。该方案以RGB图像为主要来源,考虑深度图像、从对象检测中获得的说话者位置知识以及Gemini生成的语义字幕作为辅助来源。通过串行交互机制有效地整合了主要和辅助来源的知识,并根据各来源的贡献动态集成多源知识。这丰富了多源空间知识的交互和整合,指导语音生成模型,提高了沉浸式语音体验。实验结果表明,MS^2KU-VTTS在生成沉浸式语音方面超过了现有基线。
Key Takeaways
- VTTS旨在利用环境图像合成语音内容。
- 以往研究主要关注RGB模态进行全局环境建模,忽视了多源空间知识。
- MS^2KU-VTTS方案提出以RGB图像为主要来源,同时考虑深度图像、说话者位置知识和语义字幕作为辅助来源。
- 通过串行交互机制整合了主要和辅助来源的知识。
- 多源知识根据各来源的贡献动态集成。
- 丰富的多源空间知识交互和整合提高了沉浸式语音体验。
- MS^2KU-VTTS在生成沉浸式语音方面超越了现有基线。
点此查看论文截图