⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-25 更新
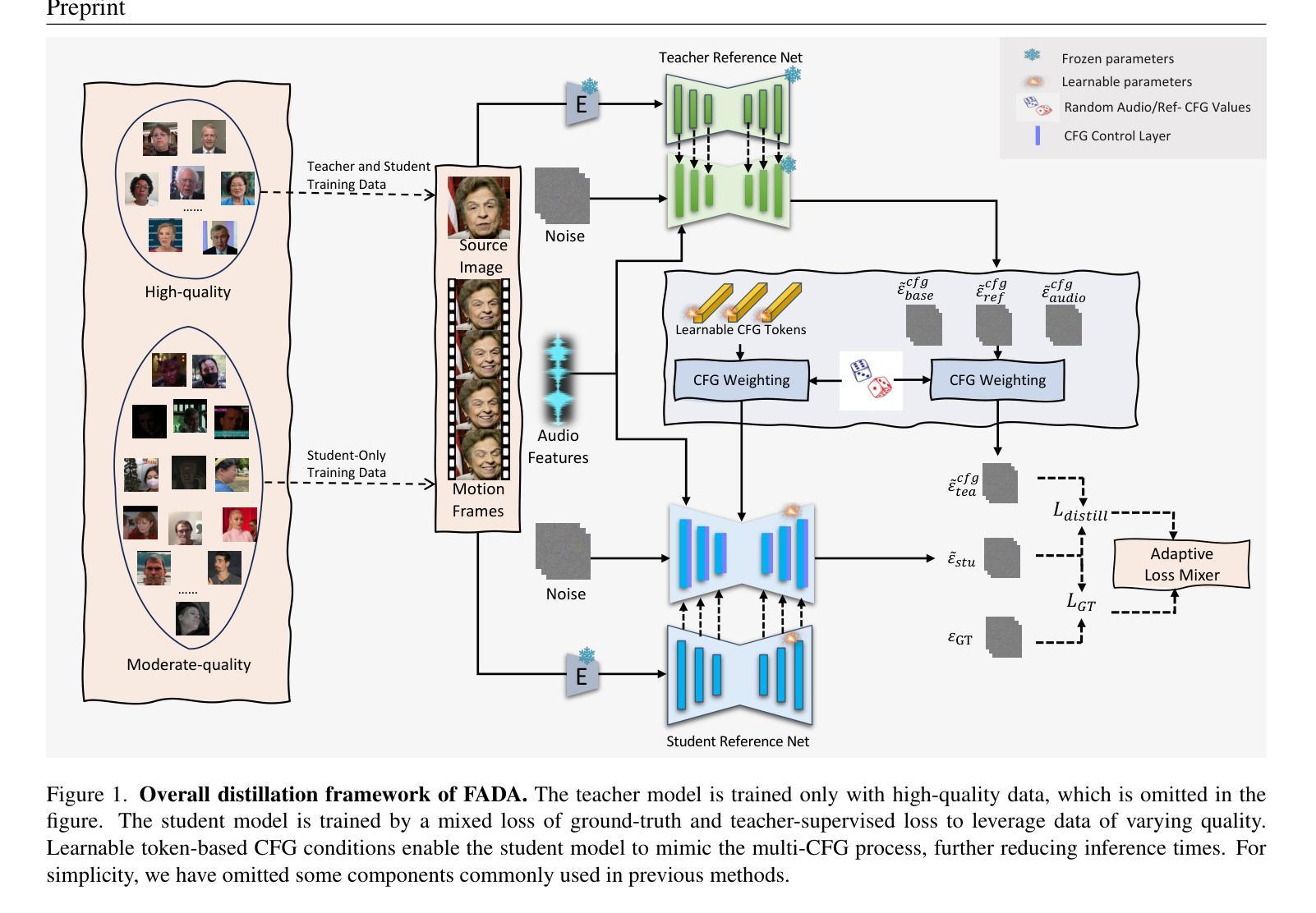
FADA: Fast Diffusion Avatar Synthesis with Mixed-Supervised Multi-CFG Distillation
Authors:Tianyun Zhong, Chao Liang, Jianwen Jiang, Gaojie Lin, Jiaqi Yang, Zhou Zhao
Diffusion-based audio-driven talking avatar methods have recently gained attention for their high-fidelity, vivid, and expressive results. However, their slow inference speed limits practical applications. Despite the development of various distillation techniques for diffusion models, we found that naive diffusion distillation methods do not yield satisfactory results. Distilled models exhibit reduced robustness with open-set input images and a decreased correlation between audio and video compared to teacher models, undermining the advantages of diffusion models. To address this, we propose FADA (Fast Diffusion Avatar Synthesis with Mixed-Supervised Multi-CFG Distillation). We first designed a mixed-supervised loss to leverage data of varying quality and enhance the overall model capability as well as robustness. Additionally, we propose a multi-CFG distillation with learnable tokens to utilize the correlation between audio and reference image conditions, reducing the threefold inference runs caused by multi-CFG with acceptable quality degradation. Extensive experiments across multiple datasets show that FADA generates vivid videos comparable to recent diffusion model-based methods while achieving an NFE speedup of 4.17-12.5 times. Demos are available at our webpage http://fadavatar.github.io.
基于扩散的音频驱动对话式化身方法因其高保真、生动、表达丰富而备受关注。然而,其较慢的推理速度限制了实际应用。尽管针对扩散模型开发了各种蒸馏技术,但我们发现简单的扩散蒸馏方法并不能产生令人满意的结果。与教师模型相比,蒸馏模型对开放集输入图像的稳健性降低,音频和视频的关联性也减弱,这削弱了扩散模型的优势。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了FADA(基于混合监督多CFG蒸馏的快速扩散化身合成)。首先,我们设计了一种混合监督损失,以利用不同质量的数据,提高模型的整体能力和稳健性。此外,我们提出了一种带有可学习标记的多CFG蒸馏方法,利用音频和参考图像条件之间的相关性,通过多CFG减少三倍推理运行次数,同时可接受质量降级。在多个数据集上的广泛实验表明,FADA生成的视频生动,与最近的扩散模型方法相比,实现了NFE加速4.17-12.5倍。演示可在我们的网页上查看:http://fadavatar.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
扩散模型驱动的音频说话人偶方法以其高保真、生动和表现力强的结果而受到关注。然而,其较慢的推理速度限制了实际应用。尽管有各种蒸馏技术用于扩散模型,但我们发现简单的扩散蒸馏方法并不能产生令人满意的结果。蒸馏模型对开放集输入图像的稳健性降低,音频和视频的关联性下降,削弱了扩散模型的优势。为解决这一问题,我们提出了FADA(混合监督多CFG蒸馏的快速扩散人偶合成)。我们设计了混合监督损失,以利用不同质量的数据,提高模型的整体能力和稳健性。此外,我们提出了带有可学习标记的多CFG蒸馏,利用音频和参考图像条件之间的相关性,减少了因多CFG导致推理次数增加三倍的同时,实现了质量上的可接受退化。在多个数据集上的实验表明,FADA生成的视频生动逼真,与最新的扩散模型方法相当,同时实现了4.17至12.5倍的NFE加速。演示视频可在我们的网页上查看:http://fadavatar.github.io。
关键见解
- 扩散模型驱动的音频说话人偶方法具有高清效果但推理速度慢。
- 简单的扩散模型蒸馏方法效果不佳,会降低模型的稳健性和音频视频关联性。
- 提出FADA方法,结合混合监督损失和多CFG蒸馏技术,提高模型稳健性并加速推理。
- FADA利用不同质量的数据,通过混合监督损失提高模型整体性能。
- 多CFG蒸馏减少了推理次数,同时保证了可接受的质量退化。
点此查看论文截图

SilVar: Speech Driven Multimodal Model for Reasoning Visual Question Answering and Object Localization
Authors:Tan-Hanh Pham, Hoang-Nam Le, Phu-Vinh Nguyen, Chris Ngo, Truong-Son Hy
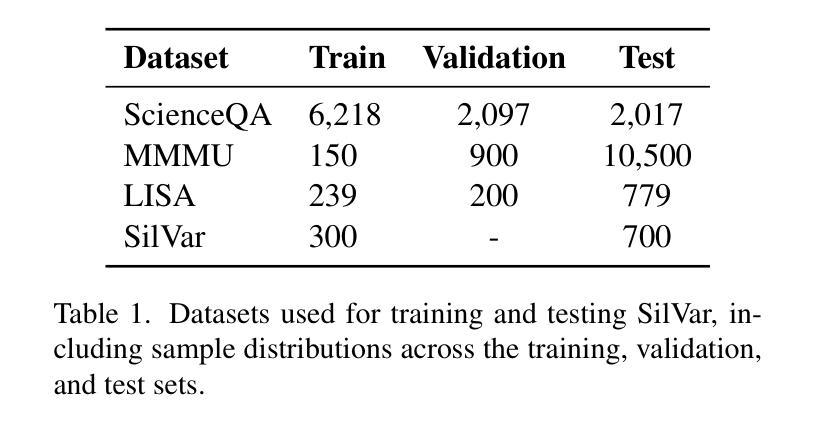
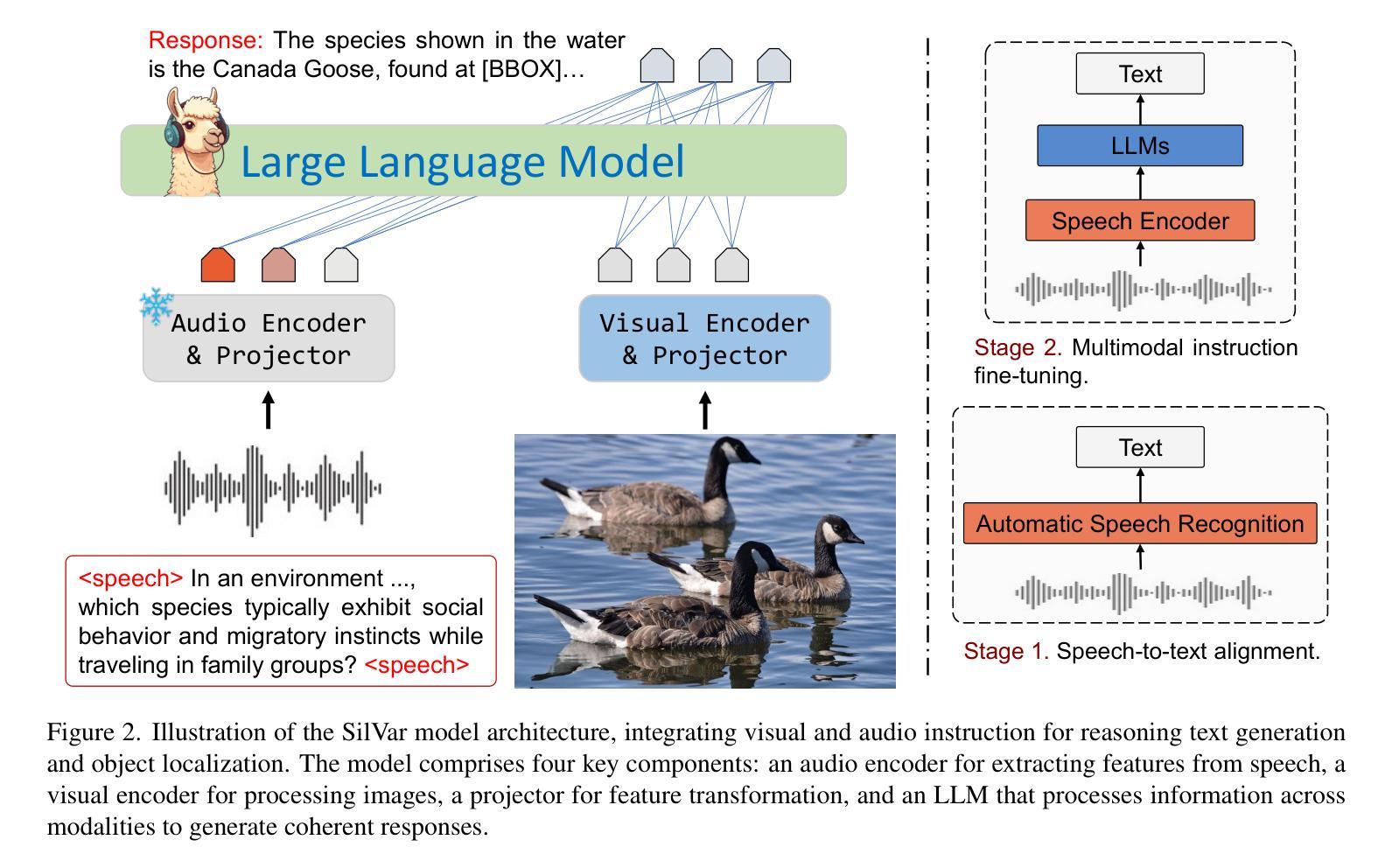
Visual Language Models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across tasks, including visual question answering and image captioning. However, most models rely on text-based instructions, limiting their effectiveness in human-machine interactions. Moreover, the quality of language models depends on reasoning and prompting techniques, such as COT, which remain underexplored when using speech instructions. To address these challenges, we propose SilVar, a novel end-to-end multimodal model that uses speech instructions for reasoning in visual question answering. In addition, we investigate reasoning techniques with levels including conversational, simple, and complex speech instruction. SilVar is built upon CLIP, Whisper, and LLaMA 3.1-8B, enabling intuitive interactions by allowing users to provide verbal or text instructions. To this end, we introduce a dataset designed to challenge models with speech-based reasoning tasks for object localization. This dataset enhances the model ability to process and explain visual scenes from spoken input, moving beyond object recognition to reasoning-based interactions. The experiments show that SilVar achieves SOTA performance on the MMMU and ScienceQA benchmarks despite the challenge of speech-based instructions. We believe SilVar will inspire next-generation multimodal reasoning models, toward expert artificial general intelligence. Our code and dataset are available here.
视觉语言模型在视觉问答和图像描述等多个任务中展现出卓越的能力。然而,大多数模型依赖于文本指令,这在人机交互中限制了其有效性。此外,语言模型的质量依赖于推理和提示技术,如上下文线索(COT),在使用语音指令时这项技术仍被忽视。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了SilVar,这是一种新型端到端的跨模态模型,它使用语音指令进行视觉问答的推理。此外,我们还研究了包括对话、简单和复杂语音指令在内的推理技术。SilVar建立在CLIP、Whisper和LLaMA 3.1-8B的基础上,允许用户提供口头或文本指令,从而实现直观交互。为此,我们引入了一个数据集,旨在通过基于语音的推理任务来挑战模型进行物体定位。该数据集提高了模型处理并解释来自口头输入的视觉场景的能力,超越了物体识别走向基于推理的交互。实验表明,尽管存在基于语音的指令的挑战,SilVar在MMMU和ScienceQA基准测试中仍达到了最先进的性能。我们相信SilVar将启发下一代跨模态推理模型,朝着专家通用人工智能的方向发展。我们的代码和数据集可在此处获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages
Summary
多模态模型SilVar解决了视觉语言模型在人机交互中的局限性问题。SilVar通过采用语音指令进行视觉问答中的推理,实现了利用简单或复杂的语音指令完成任务的目标。同时建立了包含多模态指令的语言推理数据集,使模型能够根据语音输入解释和处理视觉场景。实验证明,SilVar在多模态模型和科学问答基准测试中表现优秀。我们认为它将激发下一代专家人工智能模型的生成与发展。其源代码及数据集均已开放。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态模型SilVar解决了视觉语言模型在接收语音指令方面的不足,推动了多模态任务交互的深入发展。
- 模型支持三种类型的语音指令层次,从简单的到复杂的满足不同难度的需求。
- 模型基于CLIP、Whisper和LLaMA技术构建,可实现用户通过口头或文本指令进行直观交互。
- 数据集建立,该数据集为基于语音推理的任务设计,用以挑战模型对象定位能力并推动其向更高层次发展。
- 实验表明,尽管面临语音指令的挑战,SilVar在多个基准测试中实现了最佳性能。
- 模型代码和数据集公开供大众使用,促进了研究者的交流和技术的进一步发展。
点此查看论文截图


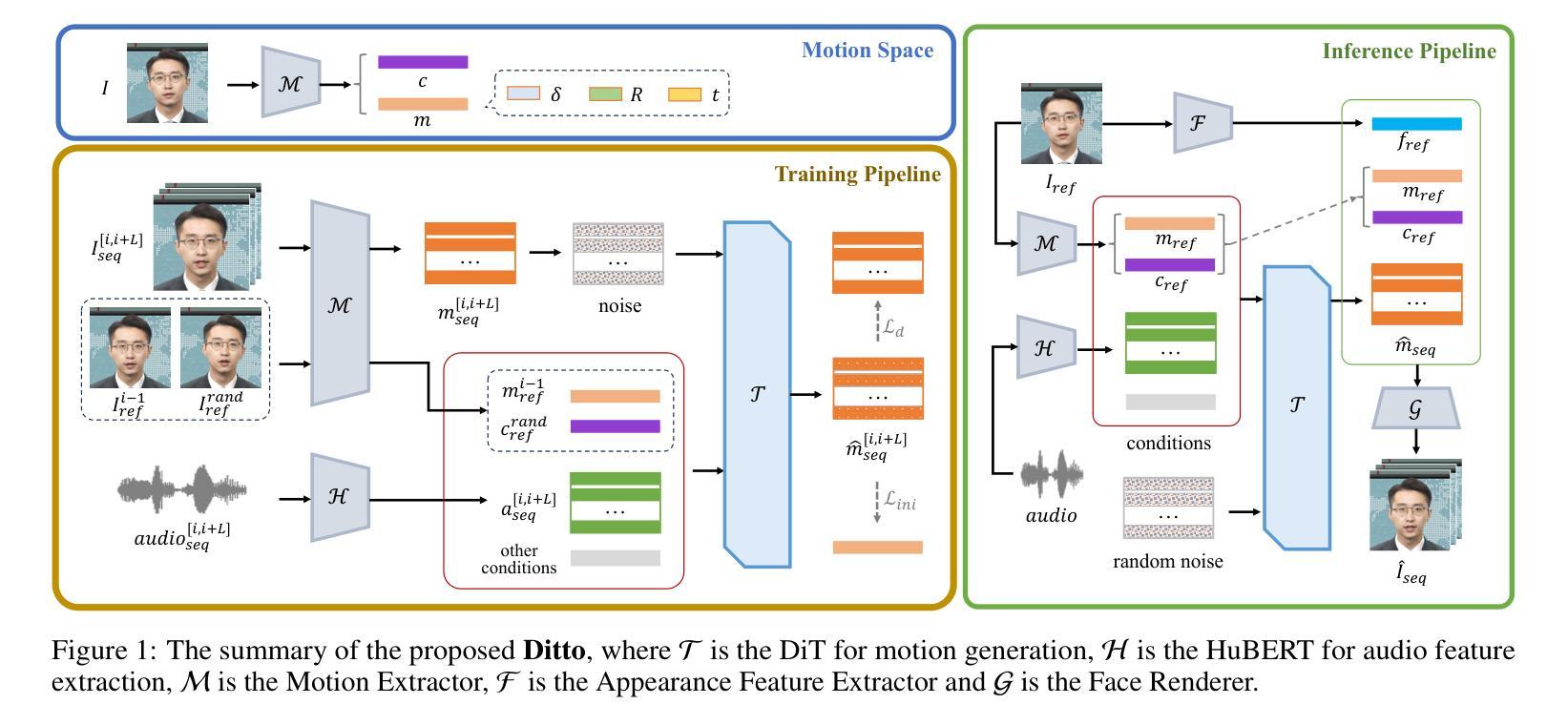
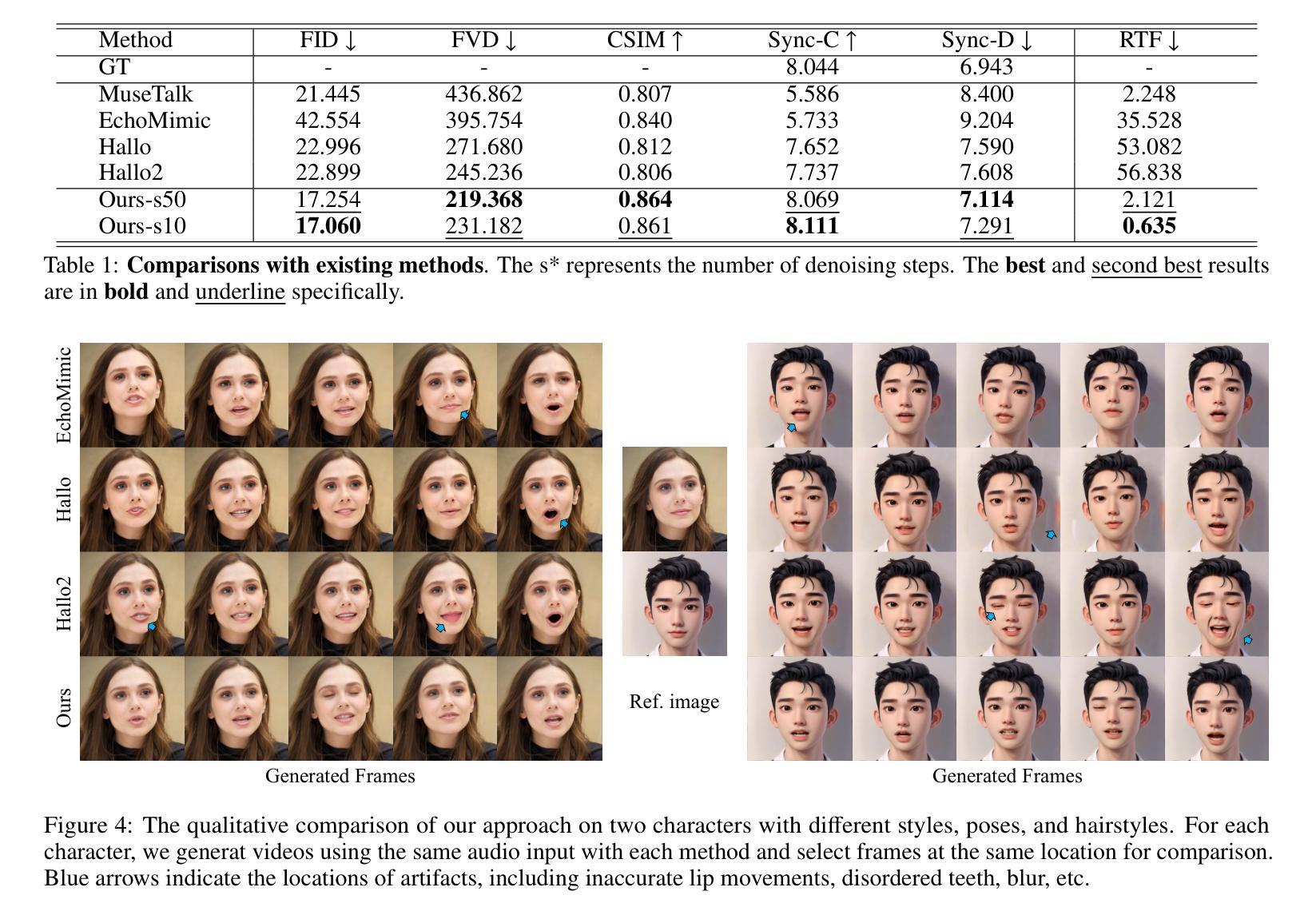
Ditto: Motion-Space Diffusion for Controllable Realtime Talking Head Synthesis
Authors:Tianqi Li, Ruobing Zheng, Minghui Yang, Jingdong Chen, Ming Yang
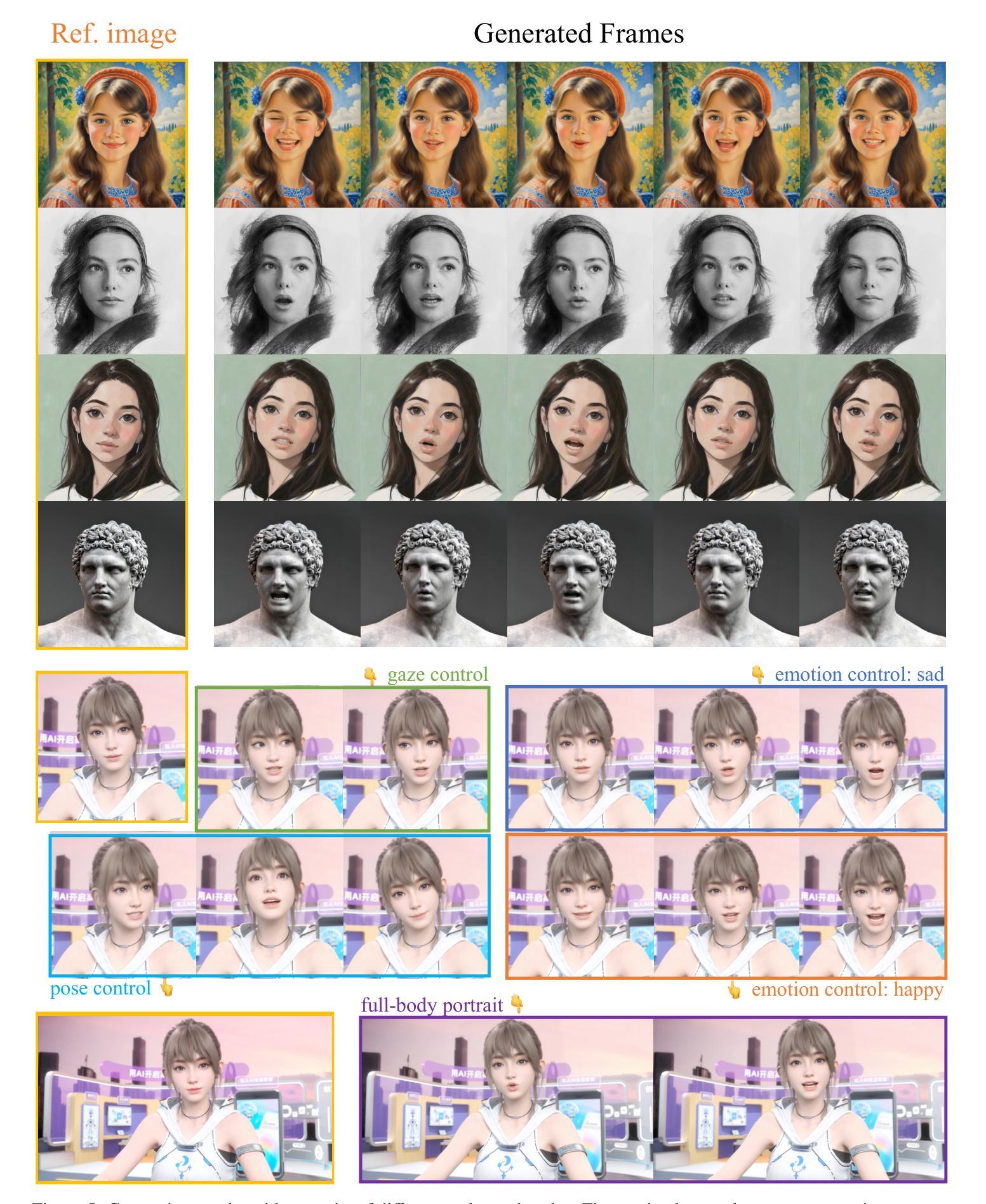
Recent advances in diffusion models have revolutionized audio-driven talking head synthesis. Beyond precise lip synchronization, diffusion-based methods excel in generating subtle expressions and natural head movements that are well-aligned with the audio signal. However, these methods are confronted by slow inference speed, insufficient fine-grained control over facial motions, and occasional visual artifacts largely due to an implicit latent space derived from Variational Auto-Encoders (VAE), which prevent their adoption in realtime interaction applications. To address these issues, we introduce Ditto, a diffusion-based framework that enables controllable realtime talking head synthesis. Our key innovation lies in bridging motion generation and photorealistic neural rendering through an explicit identity-agnostic motion space, replacing conventional VAE representations. This design substantially reduces the complexity of diffusion learning while enabling precise control over the synthesized talking heads. We further propose an inference strategy that jointly optimizes three key components: audio feature extraction, motion generation, and video synthesis. This optimization enables streaming processing, realtime inference, and low first-frame delay, which are the functionalities crucial for interactive applications such as AI assistants. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that Ditto generates compelling talking head videos and substantially outperforms existing methods in both motion control and realtime performance.
最新的扩散模型进展已经彻底改变了音频驱动的说话人头部合成技术。除了精确的唇部同步外,基于扩散的方法还擅长生成与音频信号对齐的微妙表情和自然头部运动。然而,这些方法面临着推理速度慢、对面部运动的精细控制不足以及偶尔出现的视觉伪影等问题,这主要是因为源于变分自动编码器(VAE)的隐性潜在空间所导致的,阻碍了它们在实时交互应用中的采用。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了Ditto,这是一个基于扩散的框架,能够实现可控的实时说话人头部合成。我们的关键创新之处在于通过明确的身份无关运动空间,将运动生成和逼真的神经渲染联系起来,取代了传统的VAE表示。这种设计大大简化了扩散学习的复杂性,同时实现对合成说话头部的精确控制。我们还提出了一种联合优化三个关键组件的推理策略:音频特征提取、运动生成和视频合成。这种优化实现了流式处理、实时推理和低首帧延迟等功能,这对于人工智能助手等交互式应用至关重要。大量的实验结果表明,Ditto生成的说话人头部视频非常吸引人,在运动控制和实时性能方面都大大优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://digital-avatar.github.io/ai/Ditto/
Summary
最新的扩散模型技术革新了音频驱动下的说话人头部合成。这种技术能实现精细的唇部同步,并能生成与音频信号相吻合的细微表情和自然头部运动。然而,扩散模型面临着推理速度慢、对面部运动控制不足以及偶尔的视觉伪影等问题,这主要是由于采用变分自编码器(VAE)的隐性潜在空间所致,限制了其在实时交互应用中的采用。为解决这些问题,我们推出Ditto,这是一个基于扩散模型的框架,可实现可控的实时说话人头部合成。我们的关键创新之处在于通过明确的身份无关运动空间,建立运动生成和逼真的神经渲染之间的桥梁,替代传统的VAE表示。这种设计大大简化了扩散学习,同时实现对合成说话头部的精确控制。我们还提出了一种推理策略,联合优化音频特征提取、运动生成和视频合成三个关键组件。这种优化实现了流式处理、实时推理和低首帧延迟等功能,对于人工智能助手等交互式应用至关重要。实验结果证明,Ditto生成的说话人头部视频令人信服,在运动控制和实时性能上大大优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在音频驱动的说话头部合成领域具有显著优势,能够生成与音频信号同步的细微表情和头部运动。
- 当前扩散模型面临推理速度慢、对面部运动控制不足和视觉伪影等问题,主要源于变分自编码器的隐性潜在空间。
- Ditto框架通过明确的身份无关运动空间实现实时可控的说话头部合成,提高了运动生成和神经渲染之间的桥梁。
- Ditto设计简化了扩散学习,并实现了对面部运动的精确控制。
- 联合优化音频特征提取、运动生成和视频合成的推理策略,实现了流式处理、实时推理和低首帧延迟等功能。
- Ditto在说话头部视频生成方面表现出优异性能,显著优于现有方法。
- Ditto的技术对于交互式应用如人工智能助手等具有重要价值。
点此查看论文截图