⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-25 更新
Kernel-Aware Graph Prompt Learning for Few-Shot Anomaly Detection
Authors:Fenfang Tao, Guo-Sen Xie, Fang Zhao, Xiangbo Shu
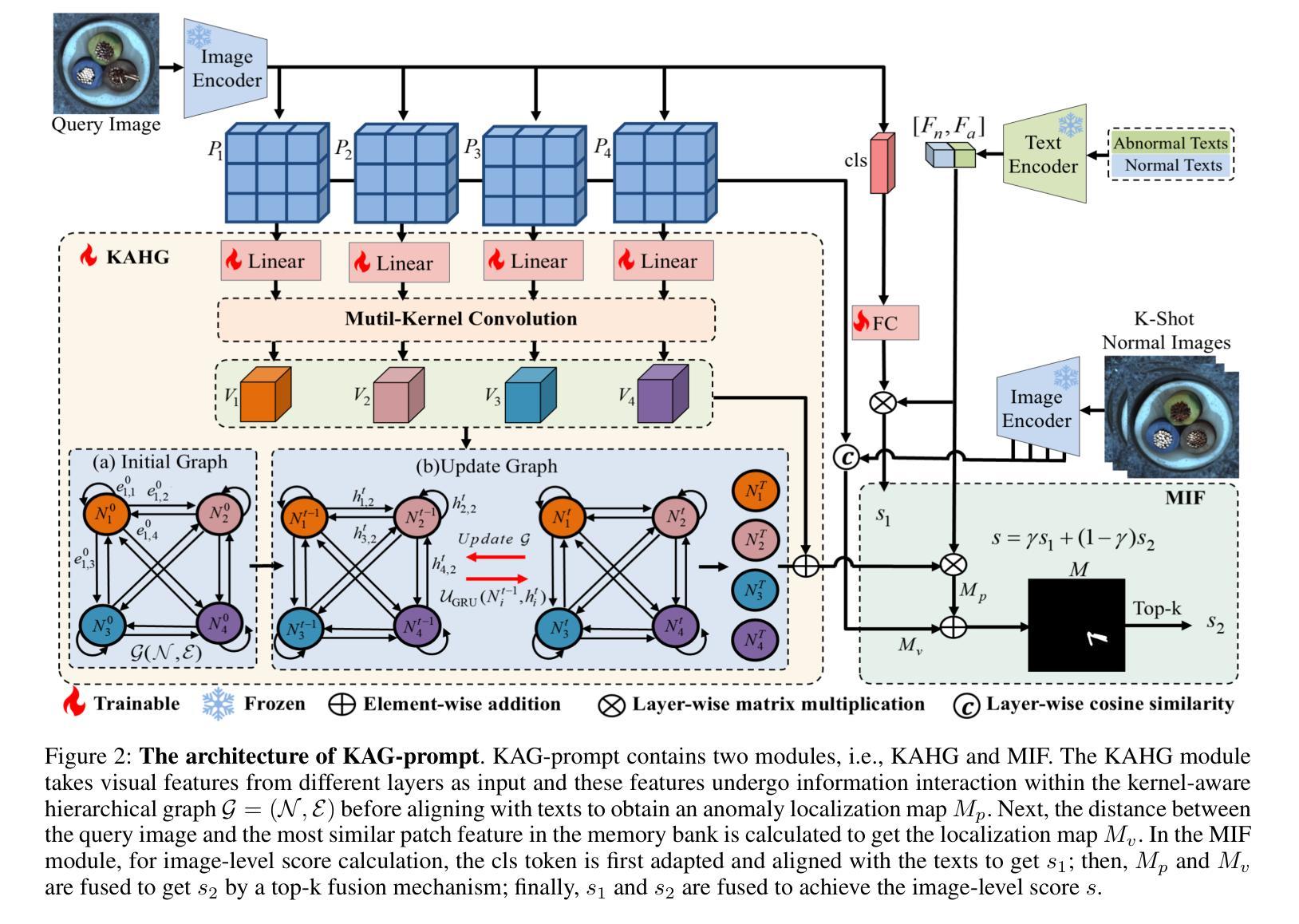
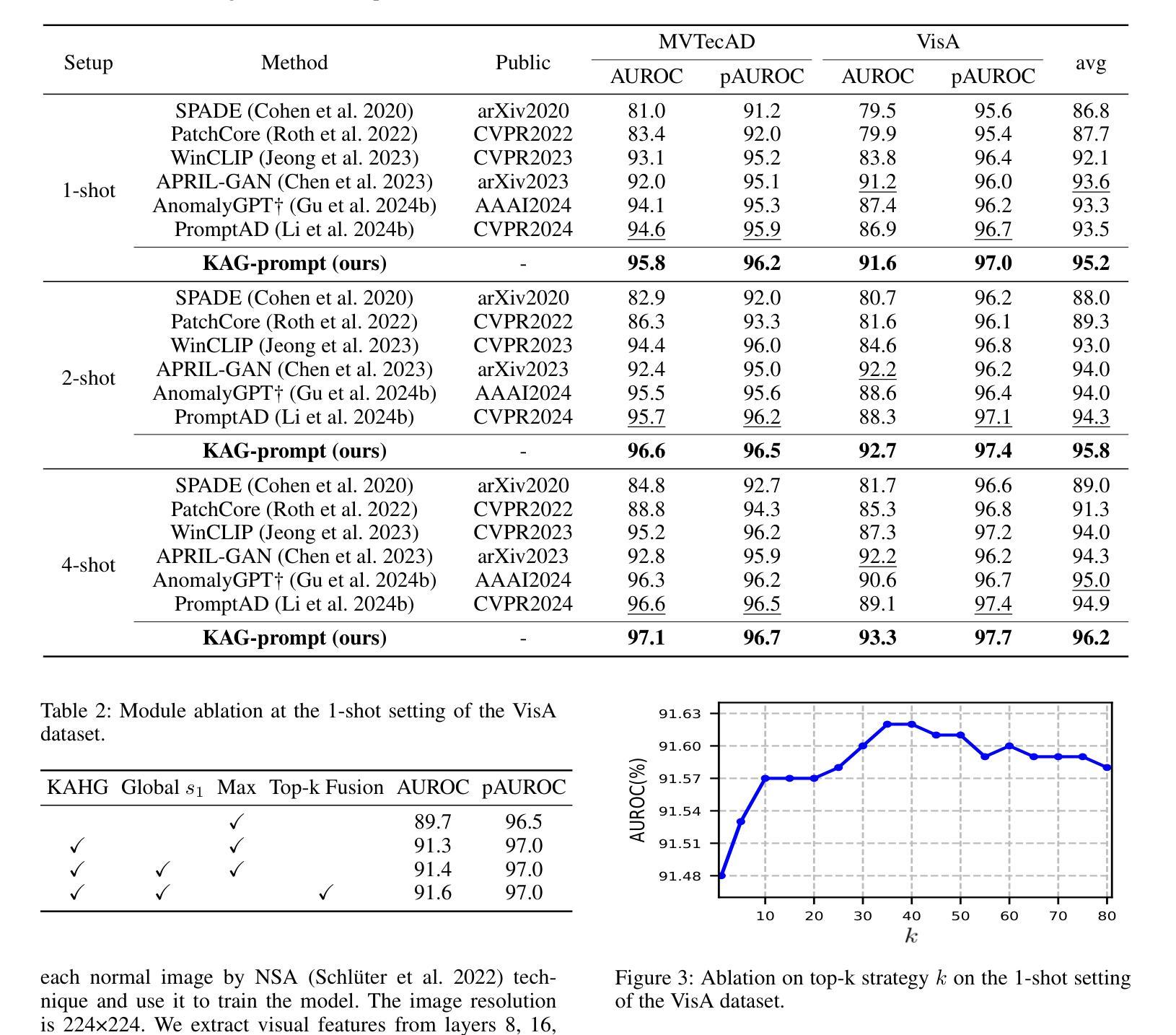
Few-shot anomaly detection (FSAD) aims to detect unseen anomaly regions with the guidance of very few normal support images from the same class. Existing FSAD methods usually find anomalies by directly designing complex text prompts to align them with visual features under the prevailing large vision-language model paradigm. However, these methods, almost always, neglect intrinsic contextual information in visual features, e.g., the interaction relationships between different vision layers, which is an important clue for detecting anomalies comprehensively. To this end, we propose a kernel-aware graph prompt learning framework, termed as KAG-prompt, by reasoning the cross-layer relations among visual features for FSAD. Specifically, a kernel-aware hierarchical graph is built by taking the different layer features focusing on anomalous regions of different sizes as nodes, meanwhile, the relationships between arbitrary pairs of nodes stand for the edges of the graph. By message passing over this graph, KAG-prompt can capture cross-layer contextual information, thus leading to more accurate anomaly prediction. Moreover, to integrate the information of multiple important anomaly signals in the prediction map, we propose a novel image-level scoring method based on multi-level information fusion. Extensive experiments on MVTecAD and VisA datasets show that KAG-prompt achieves state-of-the-art FSAD results for image-level/pixel-level anomaly detection. Code is available at https://github.com/CVL-hub/KAG-prompt.git.
少数镜头异常检测(FSAD)旨在通过同一类别中非常少的正常支持图像来检测未见过的异常区域。现有的FSAD方法通常通过设计复杂的文本提示来与流行的大型视觉语言模型范式下的视觉特征对齐来发现异常值。然而,这些方法几乎总是忽略了视觉特征中的内在上下文信息,例如不同视觉层之间的交互关系,这是全面检测异常的重要线索。为此,我们提出了一个内核感知图提示学习框架,称为KAG-prompt,通过推理FSAD中视觉特征的跨层关系。具体来说,以关注不同大小异常区域的不同层特征作为节点,构建了一个内核感知分层图,同时,任意节点对之间的关系代表图的边。通过在此图上进行消息传递,KAG-prompt可以捕获跨层上下文信息,从而实现更准确的异常预测。此外,为了整合预测图中多个重要异常信号的信息,我们提出了一种基于多层次信息融合的新型图像级评分方法。在MVTecAD和VisA数据集上的大量实验表明,KAG-prompt在图像级/像素级的异常检测中达到了最先进的FSAD结果。代码可在https://github.com/CVL-hub/KAG-prompt.git找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to AAAI 2025
摘要
本文提出了一种基于核心感知图提示学习(KAG-prompt)的少量异常检测框架。该框架旨在解决现有方法中忽视视觉特征内层间关系的问题,这对于全面检测异常至关重要。通过建立以不同层级特征为核心感知的层次图,捕捉跨层上下文信息,从而提高异常检测的准确性。此外,本文还提出了一种基于多层级信息融合的新颖图像级评分方法,以整合预测图中多个重要的异常信号。在MVTecAD和VisA数据集上的实验表明,KAG-prompt在图像级和像素级的异常检测中取得了最新的成果。
关键见解
- 现有FSAD方法通常在大规模视觉语言模型框架下,通过设计复杂的文本提示来识别异常,但忽略了视觉特征的内在上下文信息。
- KAG-prompt框架通过推理视觉特征的跨层关系来解决这一问题。
- 核心感知层次图的建立,将不同层级的特征(特别是关注不同大小的异常区域)作为节点,任意节点之间的关系作为图的边。
- 通过在图上传递消息,KAG-prompt能够捕捉跨层上下文信息,从而进行更准确的异常预测。
- 提出了一种新的图像级评分方法,基于多层级信息融合,整合预测图中多个重要的异常信号。
- 在MVTecAD和VisA数据集上的实验表明,KAG-prompt框架在FSAD中实现了最佳结果。
点此查看论文截图

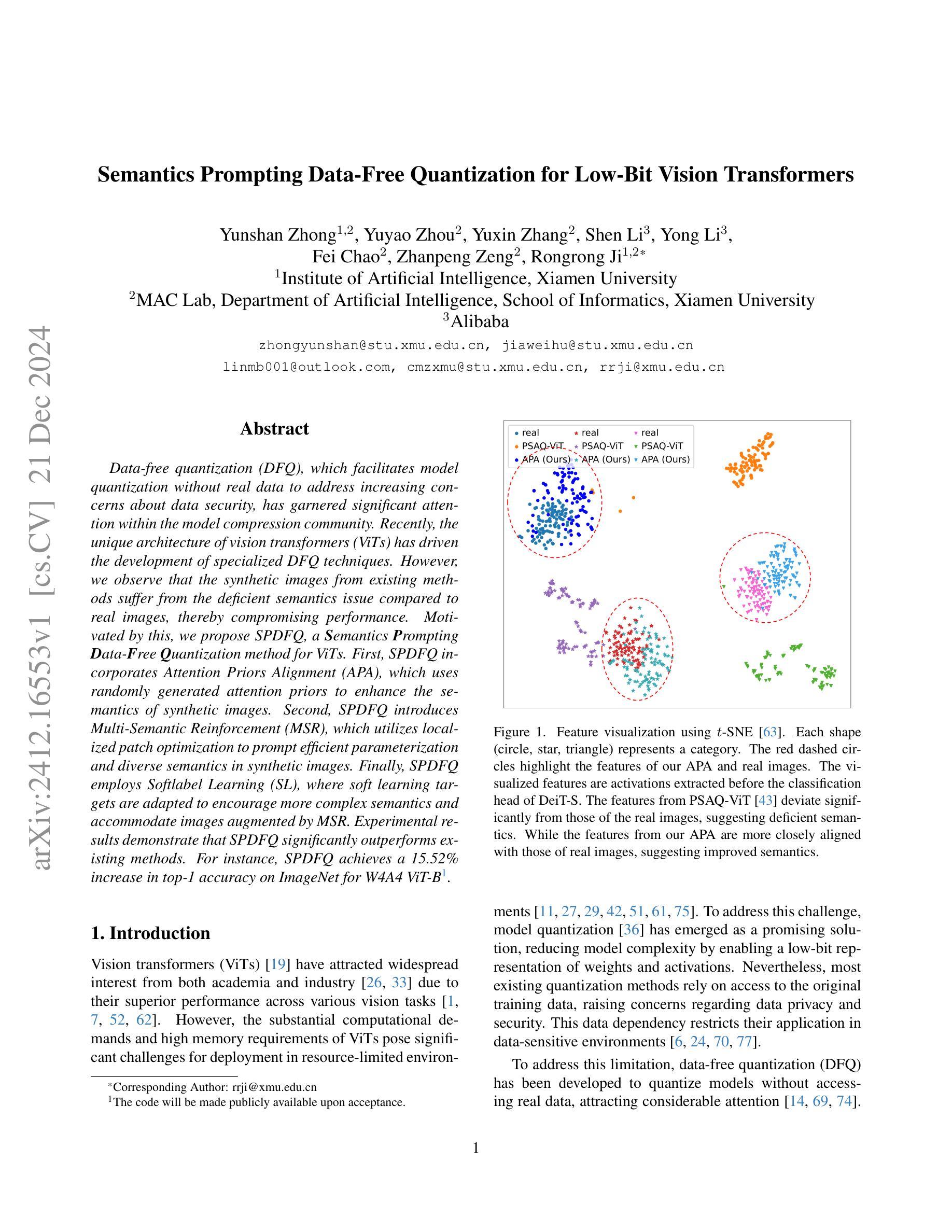
Semantics Prompting Data-Free Quantization for Low-Bit Vision Transformers
Authors:Yunshan Zhong, Yuyao Zhou, Yuxin Zhang, Shen Li, Yong Li, Fei Chao, Zhanpeng Zeng, Rongrong Ji
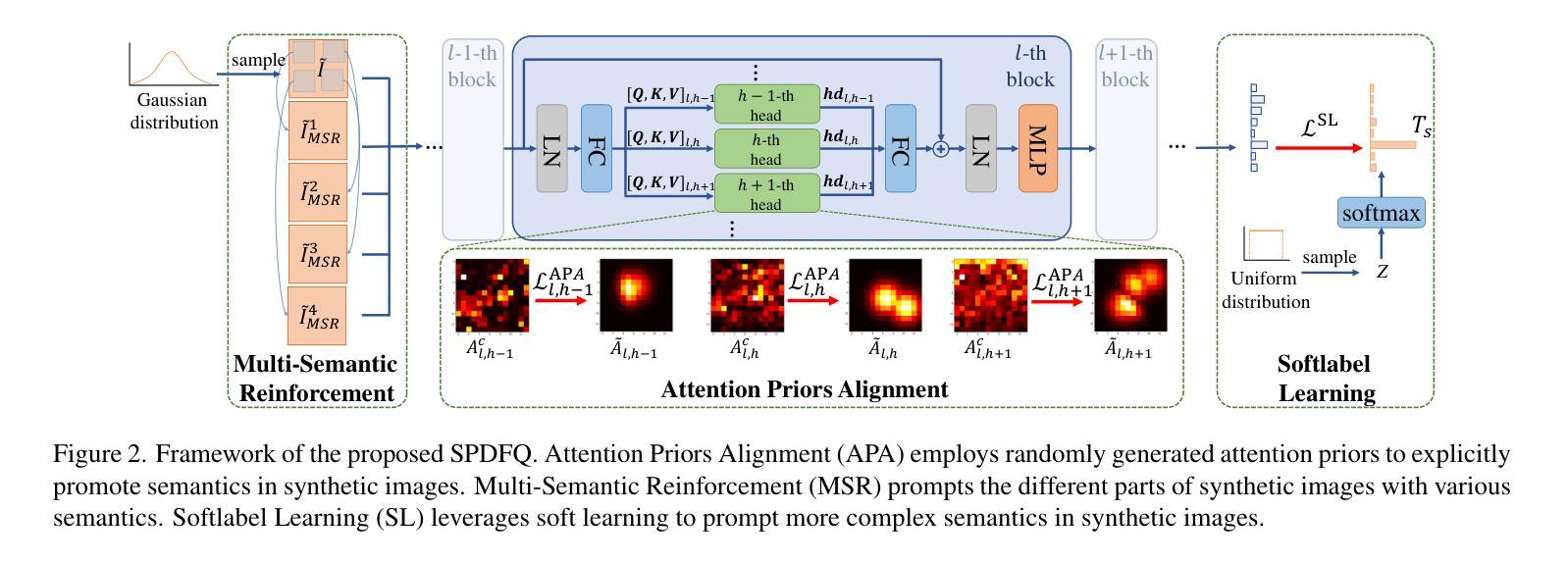
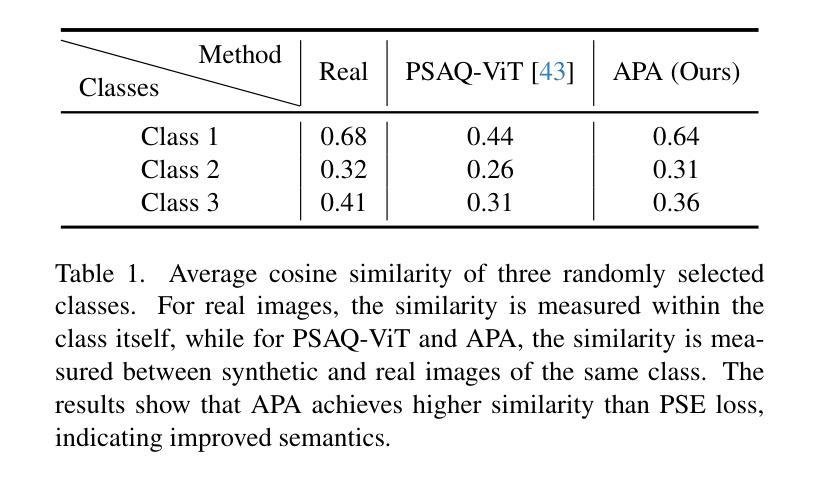
Data-free quantization (DFQ), which facilitates model quantization without real data to address increasing concerns about data security, has garnered significant attention within the model compression community. Recently, the unique architecture of vision transformers (ViTs) has driven the development of specialized DFQ techniques. However, we observe that the synthetic images from existing methods suffer from the deficient semantics issue compared to real images, thereby compromising performance. Motivated by this, we propose SPDFQ, a Semantics Prompting Data-Free Quantization method for ViTs. First, SPDFQ incorporates Attention Priors Alignment (APA), which uses randomly generated attention priors to enhance the semantics of synthetic images. Second, SPDFQ introduces Multi-Semantic Reinforcement (MSR), which utilizes localized patch optimization to prompt efficient parameterization and diverse semantics in synthetic images. Finally, SPDFQ employs Softlabel Learning (SL), where soft learning targets are adapted to encourage more complex semantics and accommodate images augmented by MSR. Experimental results demonstrate that SPDFQ significantly outperforms existing methods. For instance, SPDFQ achieves a 15.52% increase in top-1 accuracy on ImageNet for W4A4 ViT-B
无数据量化(DFQ)技术无需真实数据即可实现模型量化,这有助于解决日益突出的数据安全担忧,因此在模型压缩领域引起了广泛关注。最近,视觉变压器(ViT)的独特架构推动了专用DFQ技术的发展。然而,我们观察到与真实图像相比,现有方法生成的合成图像存在语义缺陷问题,从而影响了性能。鉴于此,我们提出了SPDFQ,一种用于ViT的语义提示无数据量化方法。首先,SPDFQ结合了注意力先验对齐(APA),使用随机生成的注意力先验来增强合成图像的语义。其次,SPDFQ引入了多语义增强(MSR),利用局部斑块优化来提示合成图像中的高效参数化和多样语义。最后,SPDFQ采用软标签学习(SL),其中软学习目标是适应和鼓励更复杂的语义,并适应由MSR增强的图像。实验结果表明,SPDFQ显著优于现有方法。例如,在ImageNet上,SPDFQ的top-1准确率提高了15.52%,适用于W4A4 ViT-B模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对视觉变压器(ViTs)的语义提示数据免费量化(SPDFQ)方法。该方法通过引入注意力先验对齐(APA)、多语义增强(MSR)和软标签学习(SL)等技术,解决了现有数据免费量化方法中合成图像语义不足的问题。实验结果表明,SPDFQ在ImageNet上的top-1准确率较现有方法提高了15.52%。
Key Takeaways
- 数据免费量化(DFQ)方法无需真实数据即可进行模型量化,解决了数据安全问题。
- 现有DFQ方法在合成图像方面存在语义不足的问题。
- SPDFQ方法针对视觉变压器(ViTs)架构进行开发,通过引入APA、MSR和SL技术来解决合成图像语义不足的问题。
- APA使用随机生成的注意力先验来增强合成图像的语义。
- MSR通过局部补丁优化来提示高效的参数化和合成图像的多样语义。
- SL采用软学习目标来鼓励更复杂的语义,并适应由MSR增强的图像。
点此查看论文截图
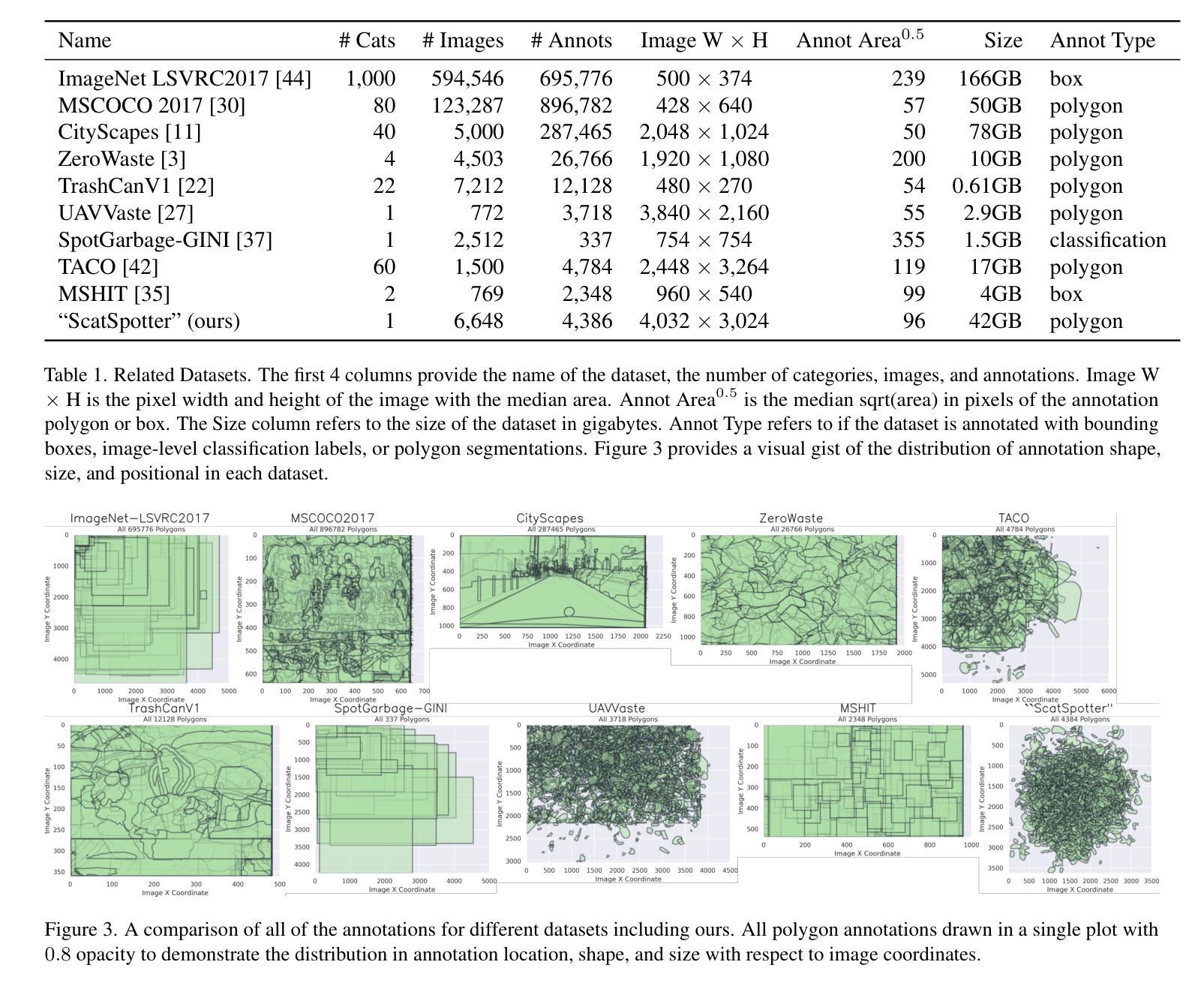
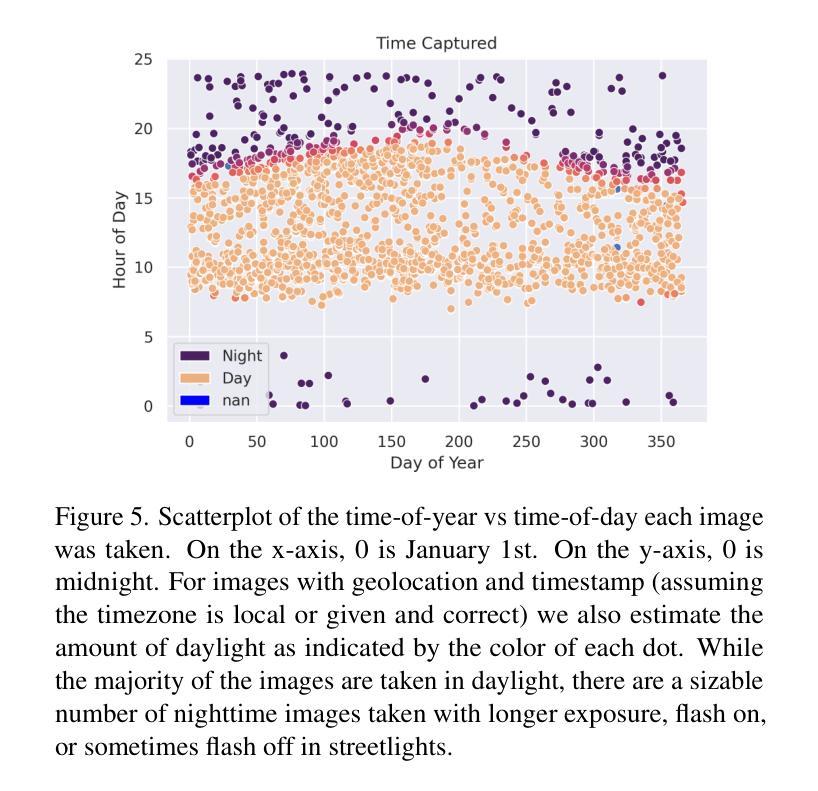
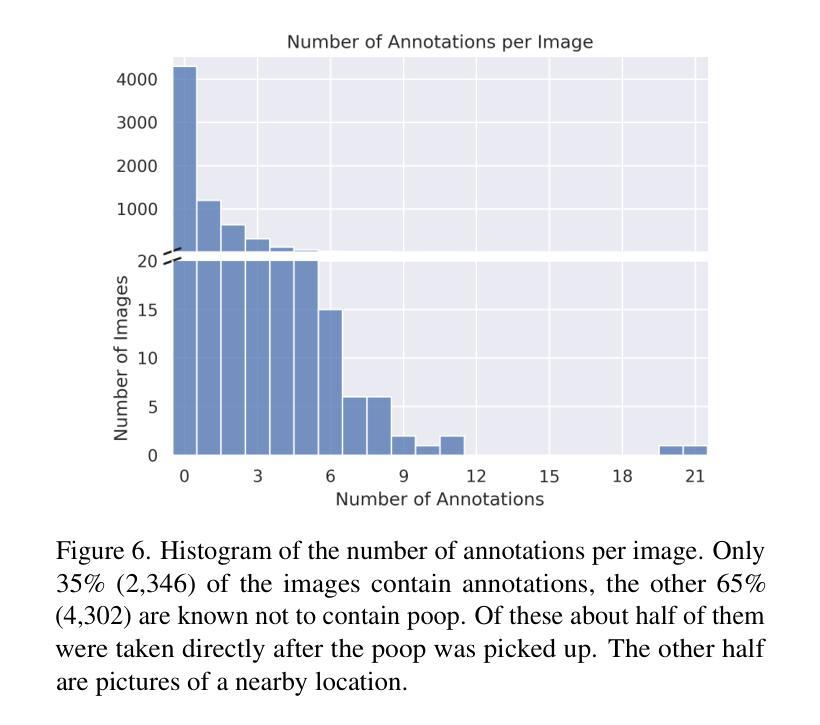
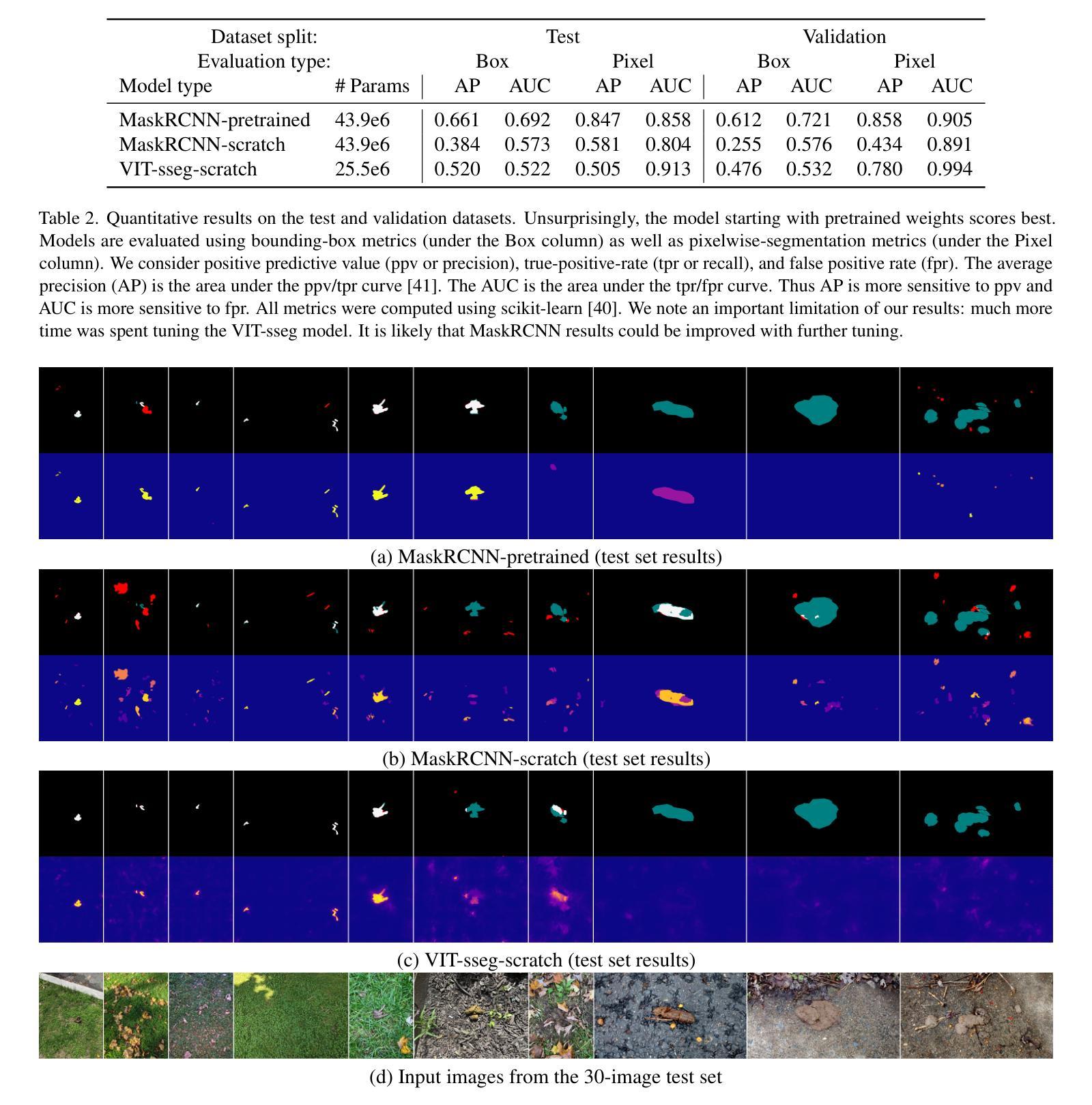
“ScatSpotter” 2024 – A Distributed Dog Poop Detection Dataset
Authors:Jon Crall
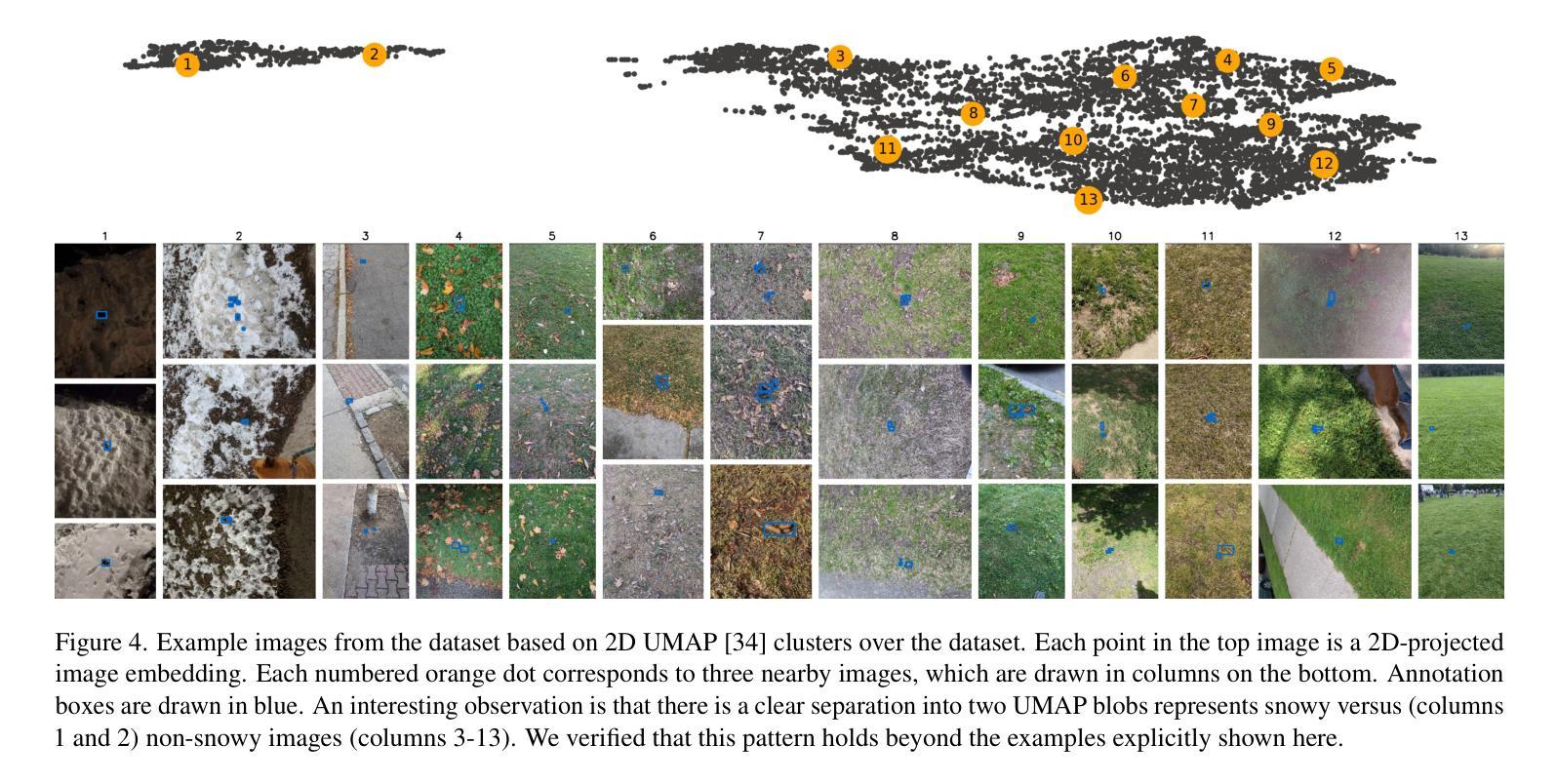
We introduce a new – currently 42 gigabyte – ``living’’ dataset of phone images of dog feces, annotated with manually drawn or AI-assisted polygon labels. There are 6k full resolution images and 4k detailed polygon annotations. The collection and annotation of images started in late 2020 and the dataset grows by roughly 1GB a month. We train VIT and MaskRCNN baseline models to explore the difficulty of the dataset. The best model achieves a pixelwise average precision of 0.858 on a 691-image validation set and 0.847 on a small independently captured 30-image contributor test set. The most recent snapshot of dataset is made publicly available through three different distribution methods: one centralized (Girder) and two decentralized (IPFS and BitTorrent). We study of the trade-offs between distribution methods and discuss the feasibility of each with respect to reliably sharing open scientific data. The code to reproduce the experiments is hosted on GitHub, and the data is published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license. Model weights are made publicly available with the dataset. Experimental hardware, time, energy, and emissions are quantified.
我们引入了一个新数据集——目前为42GB的犬类粪便手机图片“活跃”数据集,该数据集通过手绘或AI辅助多边形标签进行标注。其中包含6000张全分辨率图像和4000个详细多边形标注。数据集的收集和标注工作始于2020年底,目前每月增长大约1GB。为了探索该数据集的难度,我们使用VIT和MaskRCNN基准模型进行训练。最好的模型在包含691张图像的验证集上实现了像素平均精确度为0.858,在独立捕获的包含30张图像的小贡献者测试集上为0.847。数据集的最新快照通过三种不同的分发方法进行公开提供:一种集中式(Girder)和两种去中心化方法(IPFS和BitTorrent)。我们研究了不同分发方法之间的权衡,并讨论了它们在可靠共享开放科学数据方面的可行性。重现实验的代码托管在GitHub上,数据以创意共享署名4.0国际许可证发布。模型的权重与数据集一同公开提供。实验硬件、时间、能量和排放都已量化评估。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF dataset paper, unreviewed
Summary
本文介绍了一个新型“动态”狗狗粪便图像数据集,包含6千张高分辨率图像和4千个详细多边形标注。采用VIT和MaskRCNN基线模型进行训练,探索数据集的难度。最佳模型在验证集和独立测试集上达到较高的像素级平均精度。数据集通过三种分发方法公开提供,包括集中式方法和两种分散式方法。同时,探讨了不同分发方法的权衡,以及公开共享科学数据的可靠性。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一个新型狗狗粪便图像数据集,大小为42GB,包含6k高分辨率图像和4k多边形标注。
- 数据集是“动态”的,自2020年末开始收集和标注,每月增长约1GB。
- 使用VIT和MaskRCNN基线模型进行训练,探索数据集的难度。
- 最佳模型在验证集和独立测试集上表现出较高的像素级平均精度。
- 数据集通过Girder的集中分发方法和IPFS、BitTorrent的分散分发方法公开提供。
- 探讨了不同分发方法的权衡,并讨论了公开共享科学数据的可靠性。
点此查看论文截图


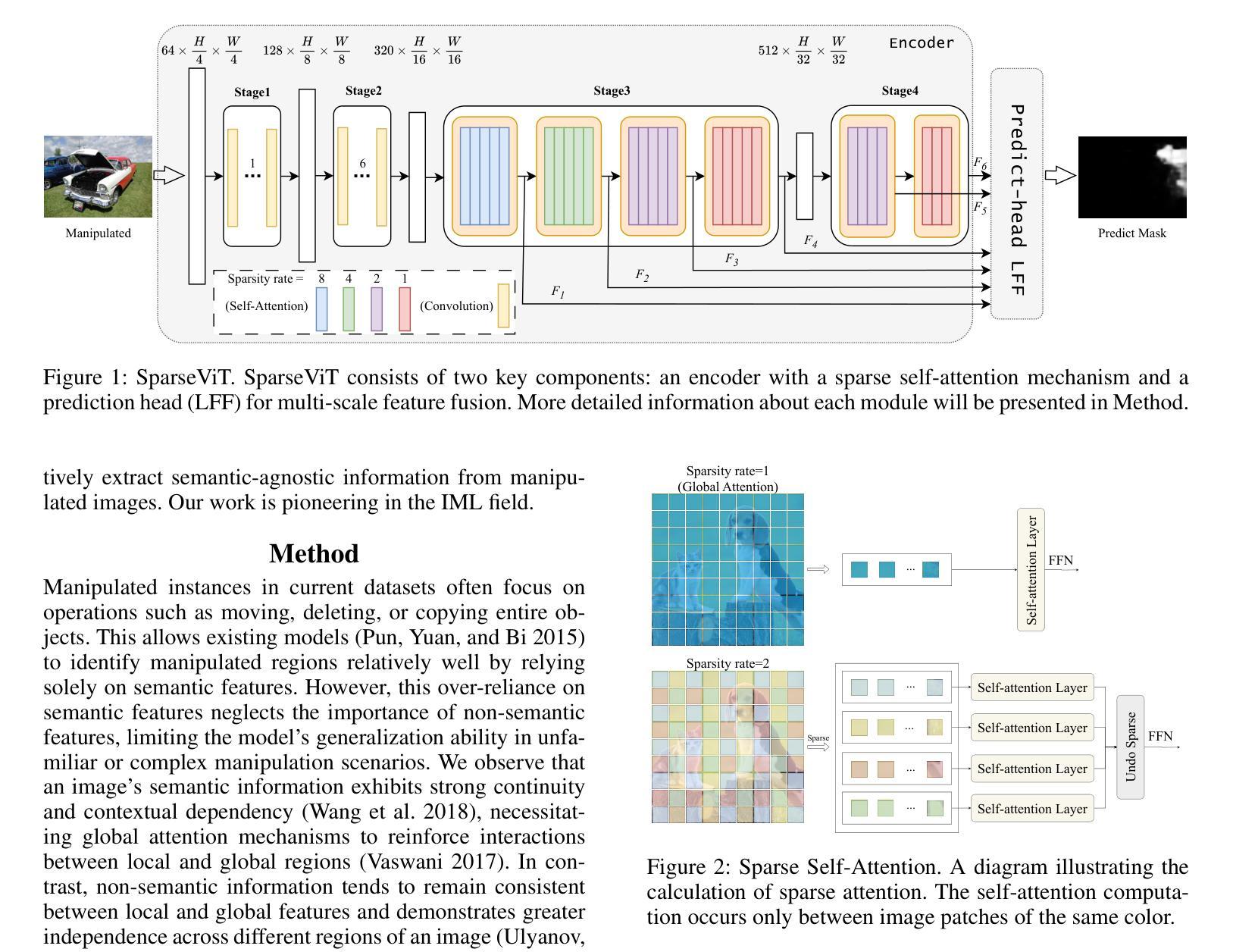
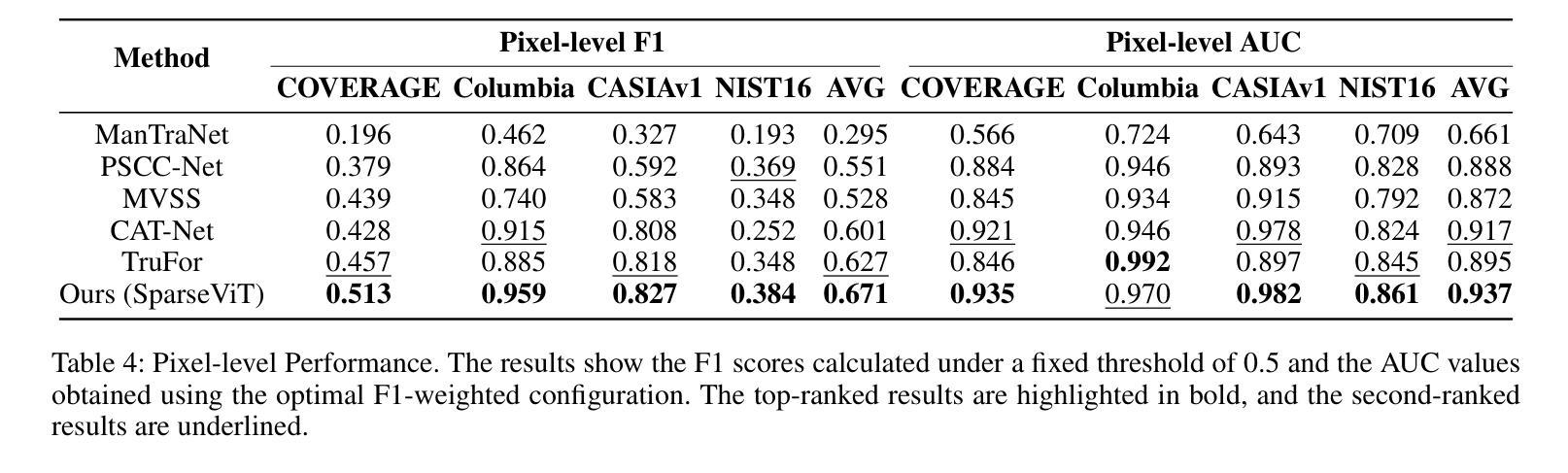
Can We Get Rid of Handcrafted Feature Extractors? SparseViT: Nonsemantics-Centered, Parameter-Efficient Image Manipulation Localization through Spare-Coding Transformer
Authors:Lei Su, Xiaochen Ma, Xuekang Zhu, Chaoqun Niu, Zeyu Lei, Ji-Zhe Zhou
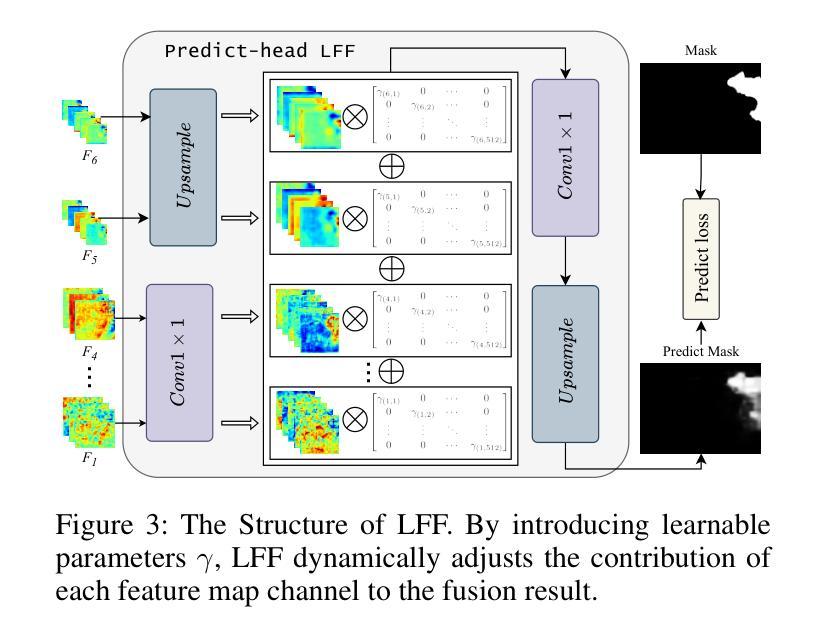
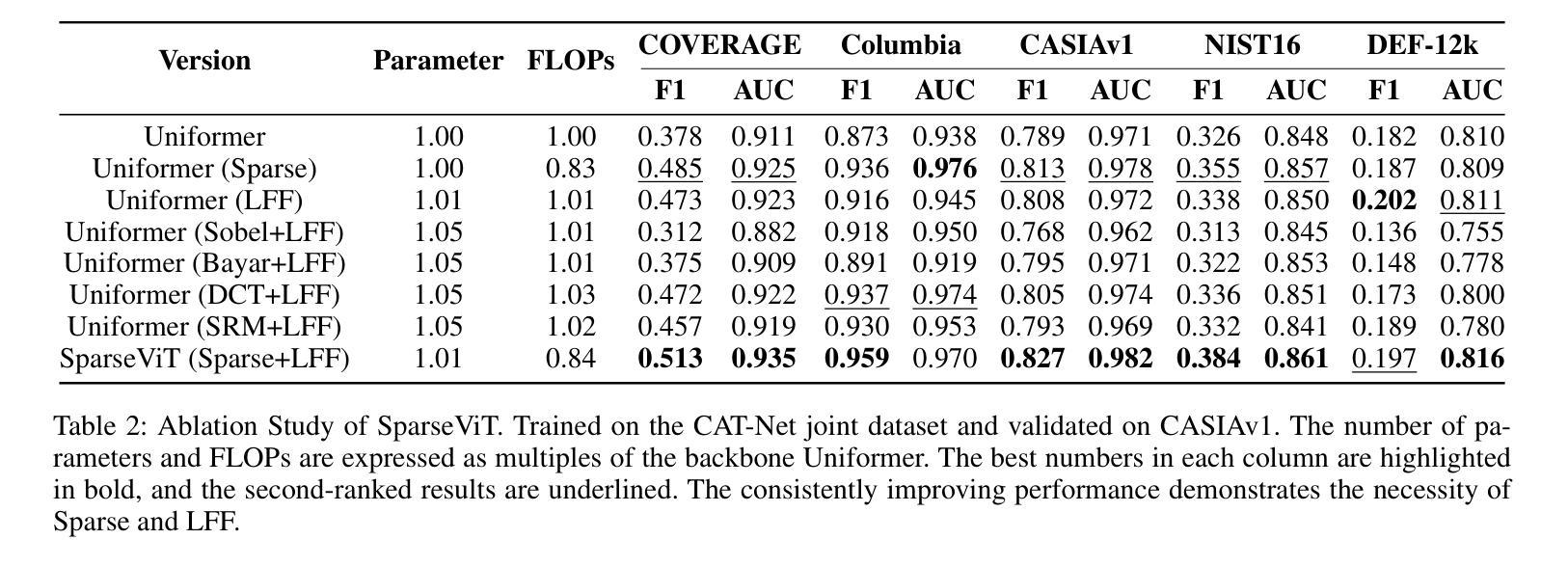
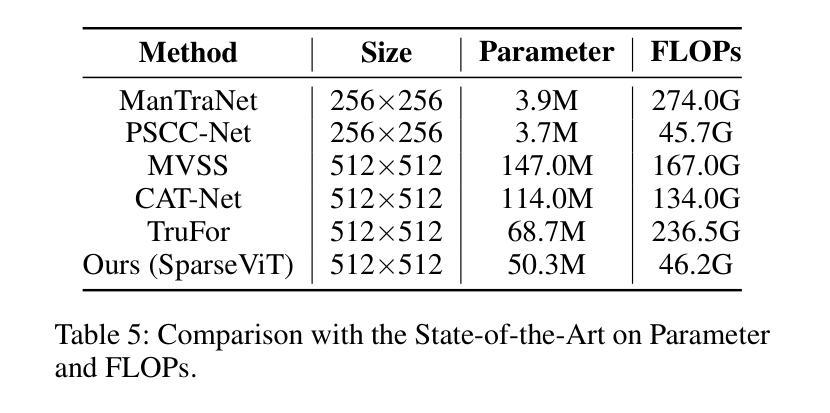
Non-semantic features or semantic-agnostic features, which are irrelevant to image context but sensitive to image manipulations, are recognized as evidential to Image Manipulation Localization (IML). Since manual labels are impossible, existing works rely on handcrafted methods to extract non-semantic features. Handcrafted non-semantic features jeopardize IML model’s generalization ability in unseen or complex scenarios. Therefore, for IML, the elephant in the room is: How to adaptively extract non-semantic features? Non-semantic features are context-irrelevant and manipulation-sensitive. That is, within an image, they are consistent across patches unless manipulation occurs. Then, spare and discrete interactions among image patches are sufficient for extracting non-semantic features. However, image semantics vary drastically on different patches, requiring dense and continuous interactions among image patches for learning semantic representations. Hence, in this paper, we propose a Sparse Vision Transformer (SparseViT), which reformulates the dense, global self-attention in ViT into a sparse, discrete manner. Such sparse self-attention breaks image semantics and forces SparseViT to adaptively extract non-semantic features for images. Besides, compared with existing IML models, the sparse self-attention mechanism largely reduced the model size (max 80% in FLOPs), achieving stunning parameter efficiency and computation reduction. Extensive experiments demonstrate that, without any handcrafted feature extractors, SparseViT is superior in both generalization and efficiency across benchmark datasets.
非语义特征或语义无关特征是指与图像上下文无关但对图像操作敏感的特征,被认为是图像操作定位(IML)的有力证据。由于手动标签不可能,现有工作依赖于手工方法提取非语义特征。手工非语义特征会损害IML模型在未见或复杂场景中的泛化能力。因此,对于IML来说,关键问题是:如何自适应地提取非语义特征?非语义特征是上下文无关且对操作敏感的。也就是说,在一张图像内,除非发生操作,否则它们在各个补丁中是一致的。然后,图像补丁之间的稀疏离散交互足以提取非语义特征。然而,不同补丁上的图像语义差异很大,需要密集的连续交互来学习语义表示。因此,本文提出了Sparse Vision Transformer(SparseViT),它将ViT中的密集全局自注意力重新制定为稀疏离散方式。这种稀疏自注意力打破了图像语义,并迫使SparseViT自适应地提取图像的非语义特征。此外,与现有的IML模型相比,稀疏自注意力机制极大地减少了模型大小(最多减少80%的浮点运算),实现了惊人的参数效率和计算减少。大量实验表明,无需任何手工特征提取器,SparseViT在基准数据集上在泛化和效率方面都表现出卓越性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF published to AAAI2025
Summary
非语义特征对图像上下文无关但对图像操作敏感,被视为图像操作定位(IML)的证据。现有工作依赖手工制作方法提取非语义特征,这削弱了IML模型的未见场景和复杂场景的泛化能力。本文提出了Sparse Vision Transformer(SparseViT),通过稀疏、离散的方式重新制定ViT中的密集全局自注意力,以适应性地提取图像的非语义特征。此外,与现有的IML模型相比,SparseViT的稀疏自注意力机制大大减少了模型规模(最多减少80%的FLOPs),实现了惊人的参数效率和计算减少。实验表明,SparseViT在基准数据集上在泛化和效率方面都优于其他模型。
Key Takeaways
- 非语义特征对于图像操作定位(IML)很重要,但现有手工制作方法提取的非语义特征限制了模型的泛化能力。
- Sparse Vision Transformer(SparseViT)通过稀疏、离散的自注意力机制改革,以适应性地提取非语义特征。
- SparseViT的稀疏自注意力机制能大幅度减少模型规模,提高参数效率和计算效率。
- 非语义特征是上下文无关的,只在图像操作时出现变化。
- 在图像内,非语义特征是跨补丁一致的,而图像语义则在不同的补丁上差异很大。
- SparseViT能实现出色的泛化能力和效率,并且不需要任何手工制作的特征提取器。
点此查看论文截图