⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-26 更新
Resolution-Robust 3D MRI Reconstruction with 2D Diffusion Priors: Diverse-Resolution Training Outperforms Interpolation
Authors:Anselm Krainovic, Stefan Ruschke, Reinhard Heckel
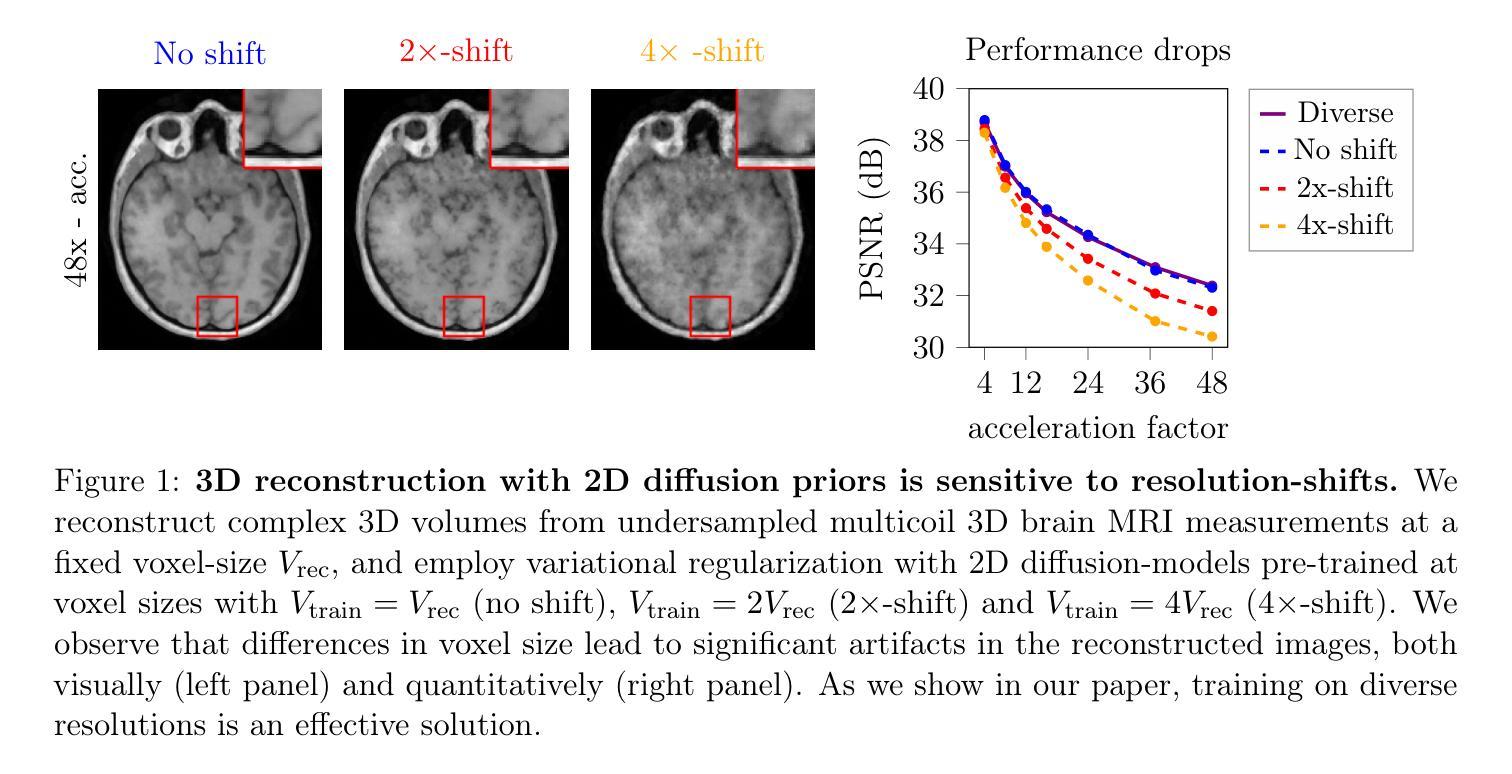
Deep learning-based 3D imaging, in particular magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), is challenging because of limited availability of 3D training data. Therefore, 2D diffusion models trained on 2D slices are starting to be leveraged for 3D MRI reconstruction. However, as we show in this paper, existing methods pertain to a fixed voxel size, and performance degrades when the voxel size is varied, as it is often the case in clinical practice. In this paper, we propose and study several approaches for resolution-robust 3D MRI reconstruction with 2D diffusion priors. As a result of this investigation, we obtain a simple resolution-robust variational 3D reconstruction approach based on diffusion-guided regularization of randomly sampled 2D slices. This method provides competitive reconstruction quality compared to posterior sampling baselines. Towards resolving the sensitivity to resolution-shifts, we investigate state-of-the-art model-based approaches including Gaussian splatting, neural representations, and infinite-dimensional diffusion models, as well as a simple data-centric approach of training the diffusion model on several resolutions. Our experiments demonstrate that the model-based approaches fail to close the performance gap in 3D MRI. In contrast, the data-centric approach of training the diffusion model on various resolutions effectively provides a resolution-robust method without compromising accuracy.
基于深度学习的3D成像,特别是磁共振成像(MRI)面临挑战,因为高质量的三维训练数据有限。因此,人们开始利用二维扩散模型对二维切片进行训练,用于三维MRI重建。然而,我们在本文中展示,现有方法涉及固定体素大小,当体素大小发生变化时,性能会下降,这在临床实践中是常见的情况。在本文中,我们针对具有二维扩散先验的分辨率鲁棒三维MRI重建提出了几种方法并进行研究。通过这项研究,我们获得了一种基于随机采样二维切片的扩散引导正则化的简单分辨率鲁棒三维重建方法。该方法与后采样基线相比,可提供具有竞争力的重建质量。为了解决对分辨率变化的敏感性,我们调查了基于模型的最新方法,包括高斯展片法、神经表示和无限维扩散模型等,以及一种以数据为中心的简单方法,即在多种分辨率上训练扩散模型。我们的实验表明,基于模型的最新方法未能缩小三维MRI的性能差距。相比之下,以数据为中心的直接在多种分辨率上训练扩散模型的方法有效地提供了一种分辨率鲁棒的方法,不会损害准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习在三维成像,特别是磁共振成像(MRI)中面临挑战,因为高质量的三维训练数据有限。研究者开始利用二维扩散模型对三维MRI进行重建。然而,现有方法受限于固定体素大小,在临床实践中体素大小变化时性能下降。本文提出并研究了几种分辨率稳健的三维MRI重建方法,基于二维扩散先验。经过研究,提出了一种基于扩散引导正则化的随机采样二维切片分辨率稳健的三维重建方法。此外,本文对基于模型的最新方法如高斯涂抹、神经表示和无限维扩散模型以及一种简单的以数据为中心的训练扩散模型的方法进行了实验对比。实验表明,基于模型的方法在3D MRI上无法缩小性能差距。相反,以数据为中心的训练扩散模型在各种分辨率上的方法有效地提供了分辨率稳健且准确的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在三维磁共振成像(MRI)中面临高质量训练数据有限的挑战。
- 二维扩散模型被用于三维MRI重建。
- 现有方法受限于固定体素大小,体素大小变化时性能下降。
- 提出了几种分辨率稳健的三维MRI重建方法,基于二维扩散先验。
- 一种基于扩散引导正则化的随机采样二维切片方法提供竞争力。
- 基于模型的方法在解决分辨率变化问题上效果有限。
点此查看论文截图

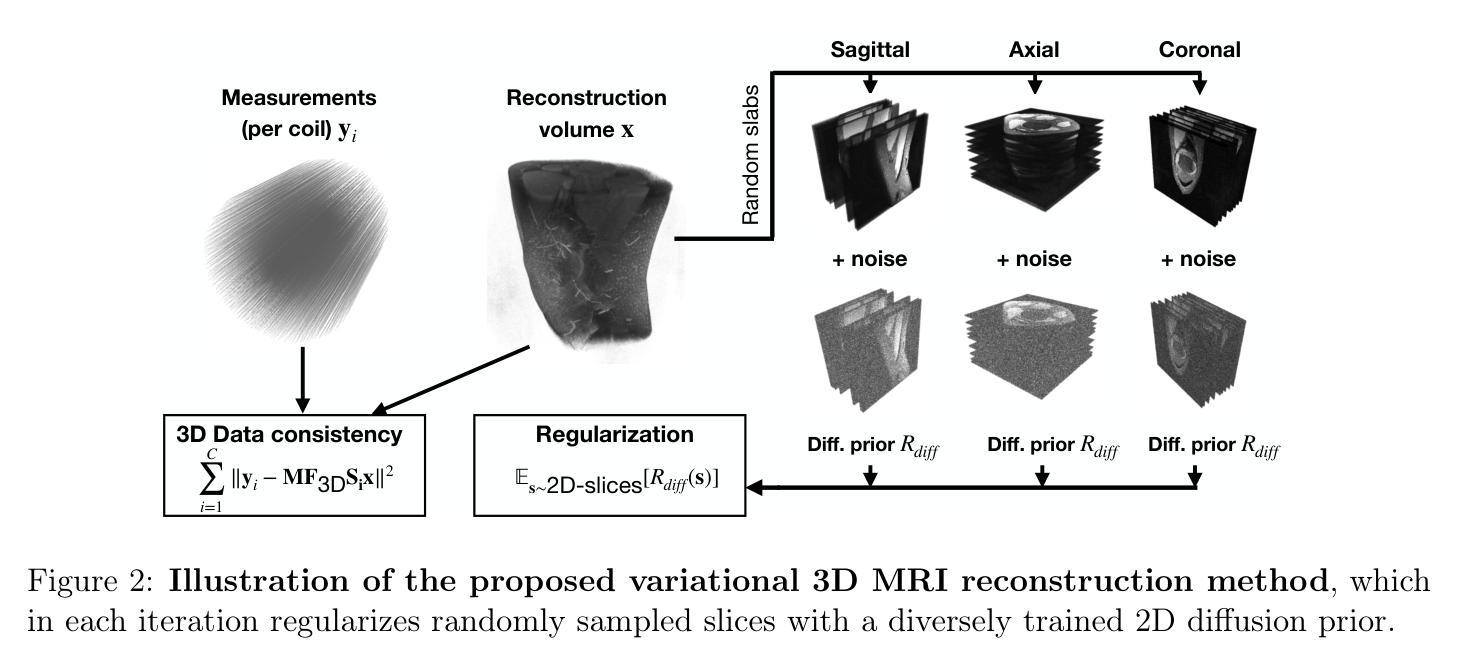
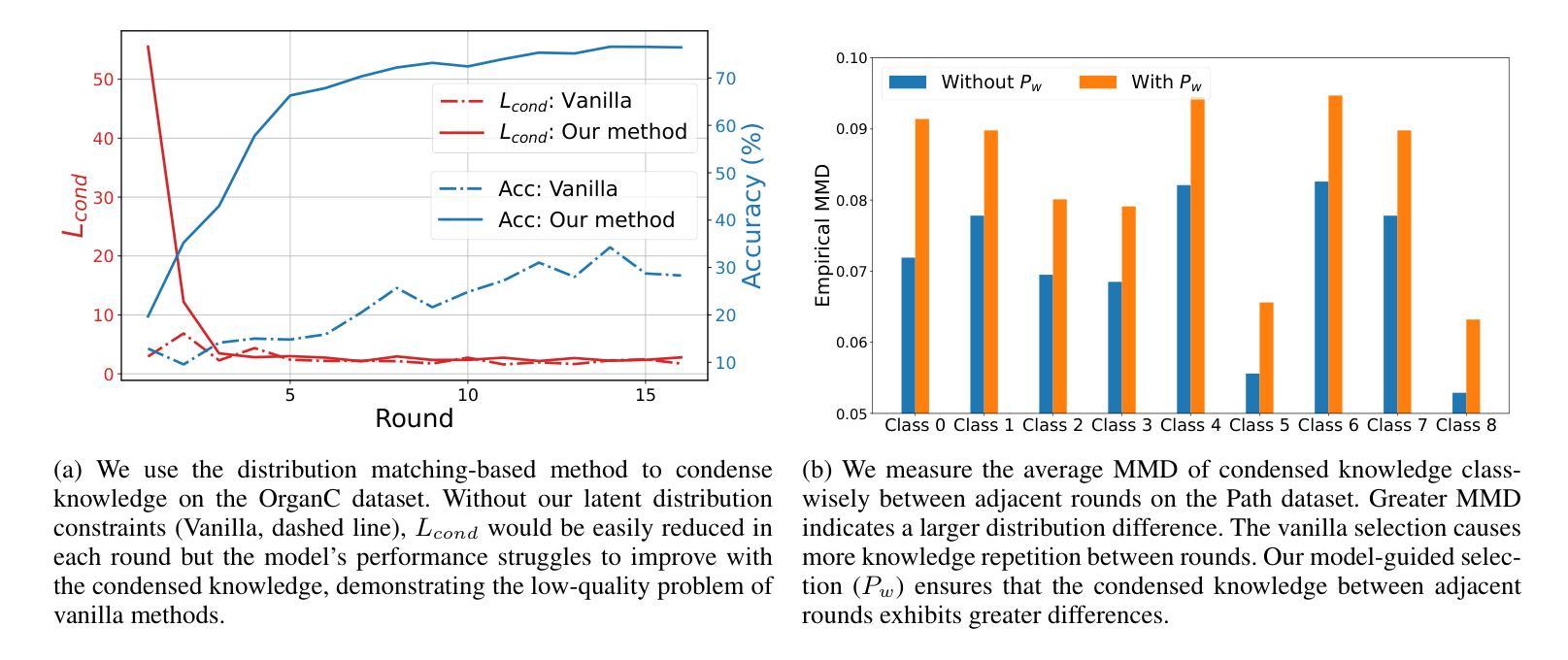
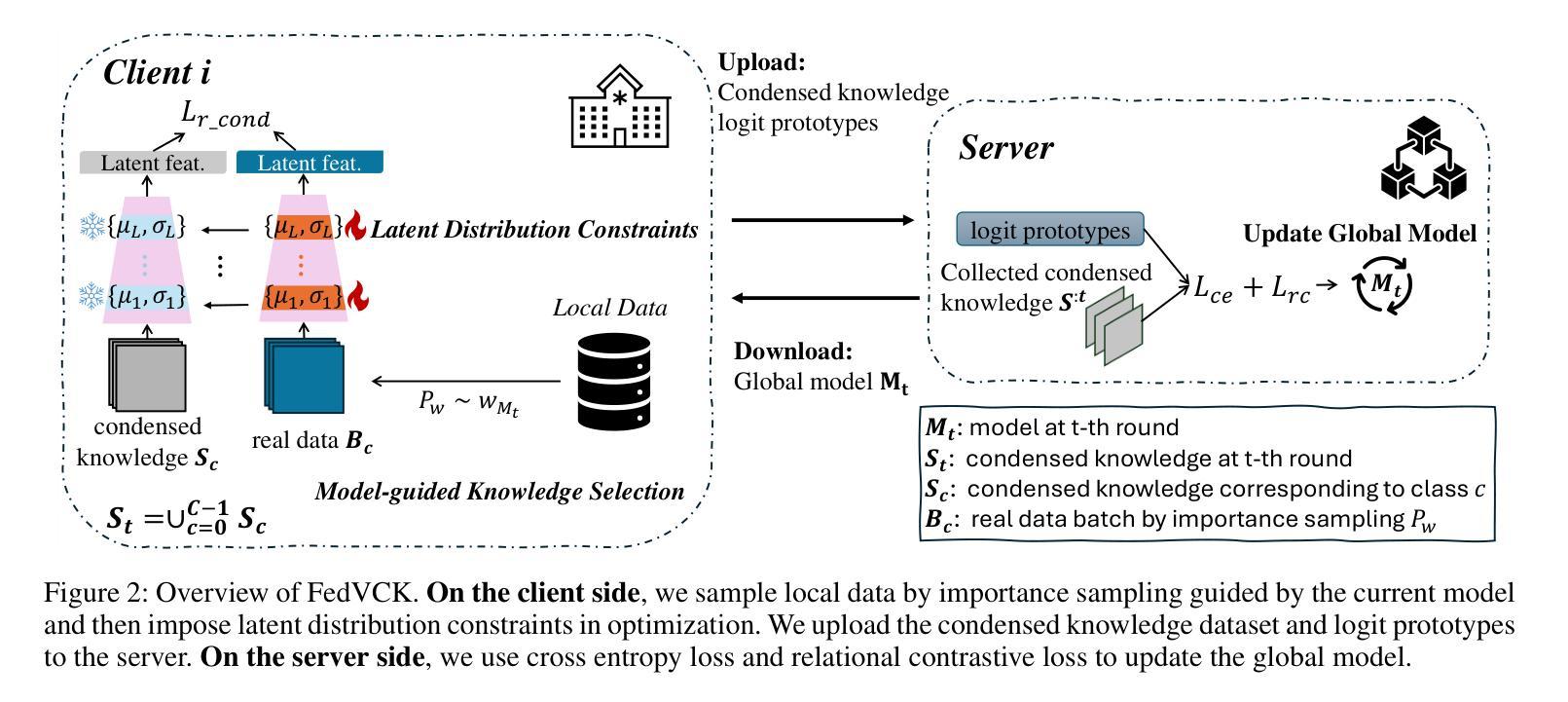
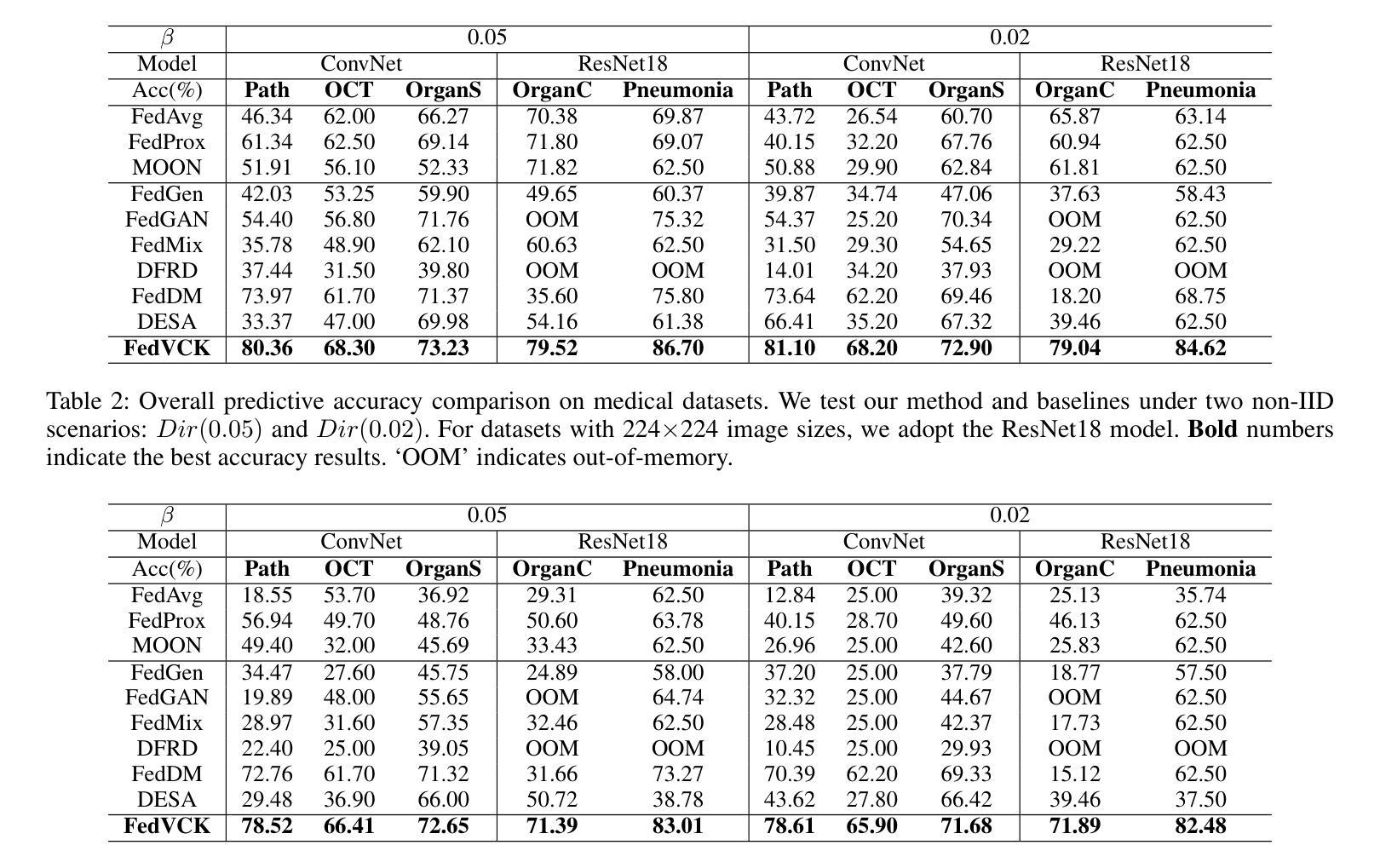
FedVCK: Non-IID Robust and Communication-Efficient Federated Learning via Valuable Condensed Knowledge for Medical Image Analysis
Authors:Guochen Yan, Luyuan Xie, Xinyi Gao, Wentao Zhang, Qingni Shen, Yuejian Fang, Zhonghai Wu
Federated learning has become a promising solution for collaboration among medical institutions. However, data owned by each institution would be highly heterogeneous and the distribution is always non-independent and identical distribution (non-IID), resulting in client drift and unsatisfactory performance. Despite existing federated learning methods attempting to solve the non-IID problems, they still show marginal advantages but rely on frequent communication which would incur high costs and privacy concerns. In this paper, we propose a novel federated learning method: \textbf{Fed}erated learning via \textbf{V}aluable \textbf{C}ondensed \textbf{K}nowledge (FedVCK). We enhance the quality of condensed knowledge and select the most necessary knowledge guided by models, to tackle the non-IID problem within limited communication budgets effectively. Specifically, on the client side, we condense the knowledge of each client into a small dataset and further enhance the condensation procedure with latent distribution constraints, facilitating the effective capture of high-quality knowledge. During each round, we specifically target and condense knowledge that has not been assimilated by the current model, thereby preventing unnecessary repetition of homogeneous knowledge and minimizing the frequency of communications required. On the server side, we propose relational supervised contrastive learning to provide more supervision signals to aid the global model updating. Comprehensive experiments across various medical tasks show that FedVCK can outperform state-of-the-art methods, demonstrating that it’s non-IID robust and communication-efficient.
联邦学习已成为医疗机构间协作的具有前景的解决方案。然而,每个机构拥有的数据将是高度异构的,且分布通常是非独立同分布的(non-IID),导致客户端偏移和性能不佳。尽管现有的联邦学习方法试图解决非IID问题,但它们仍显示出有限的优势,并且依赖于频繁的通信,这会产生高昂的成本和隐私担忧。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的联邦学习方法:通过有价值的浓缩知识(FedVCK)进行联邦学习。我们提高了浓缩知识的质量,并在模型的指导下选择最必要的知识,以在有限的通信预算内有效解决非IID问题。具体来说,在客户端,我们将每个客户端的知识浓缩成一个小数据集,并进一步通过潜在分布约束增强浓缩过程,从而有效地捕获高质量的知识。在每一轮中,我们特别针对当前模型尚未吸收的知识进行浓缩,从而防止不必要地重复同质知识并最小化所需的通信频率。在服务器端,我们提出了关系监督对比学习,为全局模型更新提供更多的监督信号。在多种医学任务上的综合实验表明,FedVCK可以超越最新方法,表明其在非IID情况下的稳健性和通信效率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种新型的联邦学习方法——FedVCK,通过凝结有价值的知识来解决医疗机构间数据高度异构和非独立同分布(non-IID)的问题,提高模型性能。该方法在客户端通过凝结知识并施加潜在分布约束来捕获高质量知识,减少通信频率;在服务器端采用关系监督对比学习,为全局模型更新提供更多监督信号。实验表明,FedVCK在医疗任务上表现出优异性能,具有non-IID鲁棒性和通信效率。
Key Takeaways
- 联邦学习已成为医疗协作领域的一种有前途的解决方案。
- 医疗机构数据存在高度异构性和非独立同分布(non-IID)问题,导致模型性能不佳。
- 现有联邦学习方法虽能解决non-IID问题,但通信成本高昂并存在隐私担忧。
- FedVCK方法通过凝结和选择必要的知识来解决non-IID问题,并在有限通信预算内有效应对。
- FedVCK在客户端实施知识凝结,并施加潜在分布约束以捕获高质量知识。
- 在服务器端,FedVCK采用关系监督对比学习,为全局模型更新提供更多监督信号。
点此查看论文截图

Advancing Deformable Medical Image Registration with Multi-axis Cross-covariance Attention
Authors:Mingyuan Meng, Michael Fulham, Lei Bi, Jinman Kim
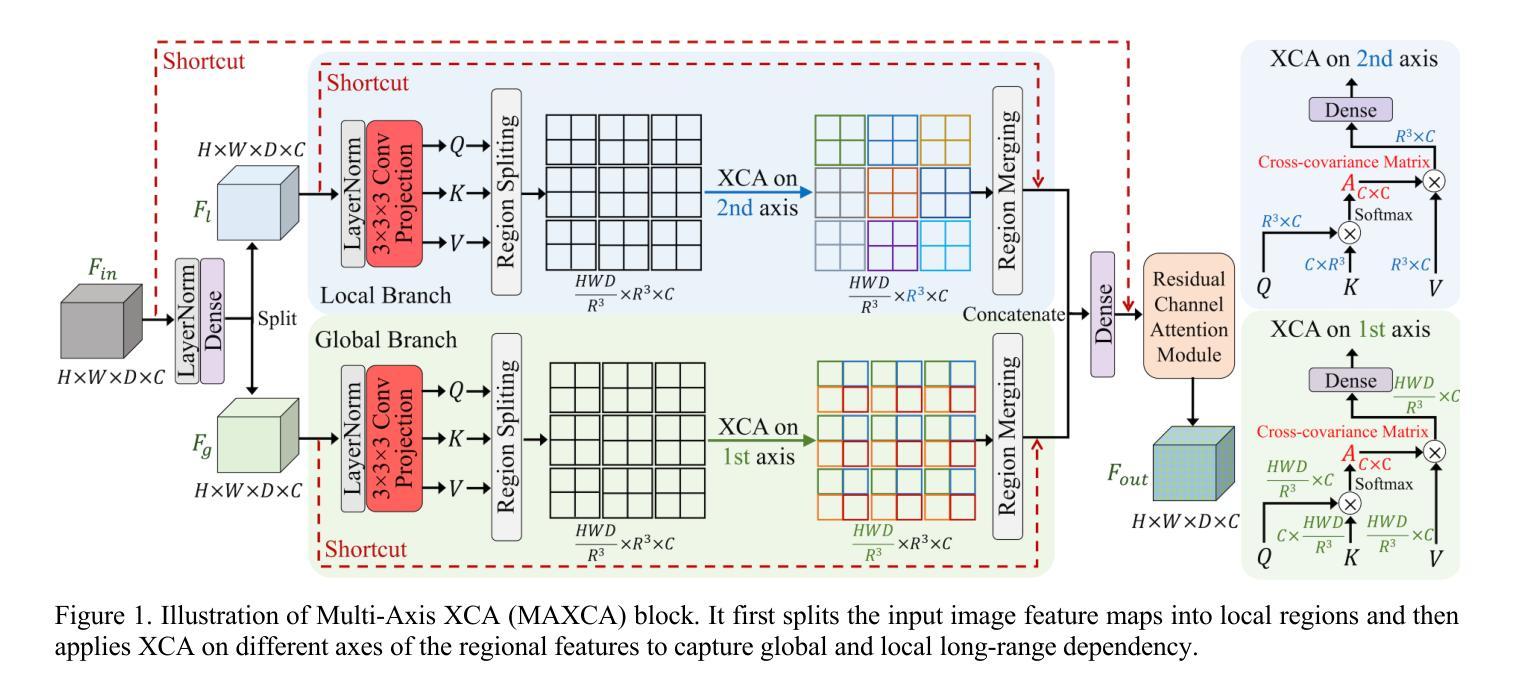
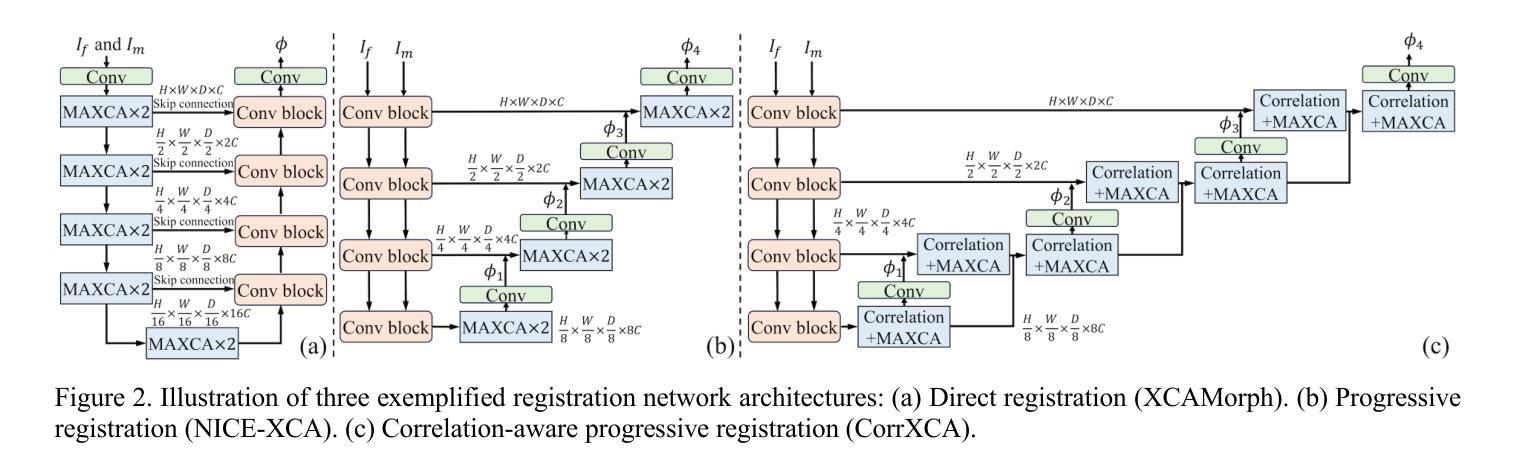
Deformable image registration is a fundamental requirement for medical image analysis. Recently, transformers have been widely used in deep learning-based registration methods for their ability to capture long-range dependency via self-attention (SA). However, the high computation and memory loads of SA (growing quadratically with the spatial resolution) hinder transformers from processing subtle textural information in high-resolution image features, e.g., at the full and half image resolutions. This limits deformable registration as the high-resolution textural information is crucial for finding precise pixel-wise correspondence between subtle anatomical structures. Cross-covariance Attention (XCA), as a “transposed” version of SA that operates across feature channels, has complexity growing linearly with the spatial resolution, providing the feasibility of capturing long-range dependency among high-resolution image features. However, existing XCA-based transformers merely capture coarse global long-range dependency, which are unsuitable for deformable image registration relying primarily on fine-grained local correspondence. In this study, we propose to improve existing deep learning-based registration methods by embedding a new XCA mechanism. To this end, we design an XCA-based transformer block optimized for deformable medical image registration, named Multi-Axis XCA (MAXCA). Our MAXCA serves as a general network block that can be embedded into various registration network architectures. It can capture both global and local long-range dependency among high-resolution image features by applying regional and dilated XCA in parallel via a multi-axis design. Extensive experiments on two well-benchmarked inter-/intra-patient registration tasks with seven public medical datasets demonstrate that our MAXCA block enables state-of-the-art registration performance.
可变图像配准(Deformable Image Registration)是医学图像分析的基本需求。近期,由于其通过自注意力(Self-Attention, SA)捕捉长距离依赖关系的能力,transformer在各种基于深度学习的配准方法中得到了广泛应用。然而,自注意力的计算与内存负载较高(随着空间分辨率的二次方增长),这限制了其在处理高清晰度图像特征中的微妙纹理信息方面的能力,比如在全图和半图分辨率时。这对于可变配准是一个限制,因为高清晰度的纹理信息对于在微妙的解剖结构之间找到精确的像素对应至关重要。作为在特征通道之间进行操作的跨协方差注意力(Cross-covariance Attention, XCA)是一种自注意力的“转置”版本,其复杂性随空间分辨率线性增长,为捕捉高清晰度图像特征之间的长距离依赖关系提供了可行性。然而,现有的基于XCA的transformer仅捕捉粗糙的全局长距离依赖关系,对于主要依赖于精细局部对应关系的可变图像配准来说并不适用。本研究旨在通过嵌入新的XCA机制改进现有的基于深度学习的配准方法。为此,我们设计了一个基于XCA的优化块用于可变医学图像配准,称为多轴XCA(MAXCA)。我们的MAXCA作为一个通用网络块,可以嵌入到各种配准网络架构中。它通过并行应用区域和膨胀XCA的多轴设计来捕捉高分辨率图像特征之间的全局和局部长距离依赖关系。在两个广泛认可的患者间和患者内配准任务上的七个公开医学数据集的大量实验表明,我们的MAXCA块可实现最先进的配准性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under Review
摘要
本研究针对医学图像分析中的可变形图像配准问题,提出了基于交叉协方差注意力(XCA)机制的改进深度学习方法。通过设计一种名为Multi-Axis XCA(MAXCA)的XCA基础transformer块,能捕获高分辨图像特征中的全局和局部远程依赖关系,实现了对现有深度学习配准方法的改进。该MAXCA块可作为通用网络块嵌入各种配准网络架构中。在跨患者和同一患者的配准任务以及七个公开医学数据集上的广泛实验表明,MAXCA块实现了最先进的配准性能。
关键见解
- 可变形图像配准在医学图像分析中具有重要意义。
- 变压器因自我注意力(SA)机制而广泛应用于深度学习中,但其在处理高分辨图像特征时的计算和内存负载较高。
- 交叉协方差注意力(XCA)作为一种“转置”的自注意力机制,能在高分辨图像特征上捕获远程依赖性,复杂度随空间分辨率呈线性增长。
- 现有基于XCA的变压器仅捕获粗糙的全局长程依赖性,不适用于依赖精细局部对应的可变形图像配准。
- 研究中提出了Multi-Axis XCA(MAXCA)块,这是一种针对可变形医学图像配准的XCA基础变压器块。
- MAXCA块通过并行应用区域和膨胀XCA的多轴设计,能够捕获高分辨图像特征中的全局和局部远程依赖性。
点此查看论文截图

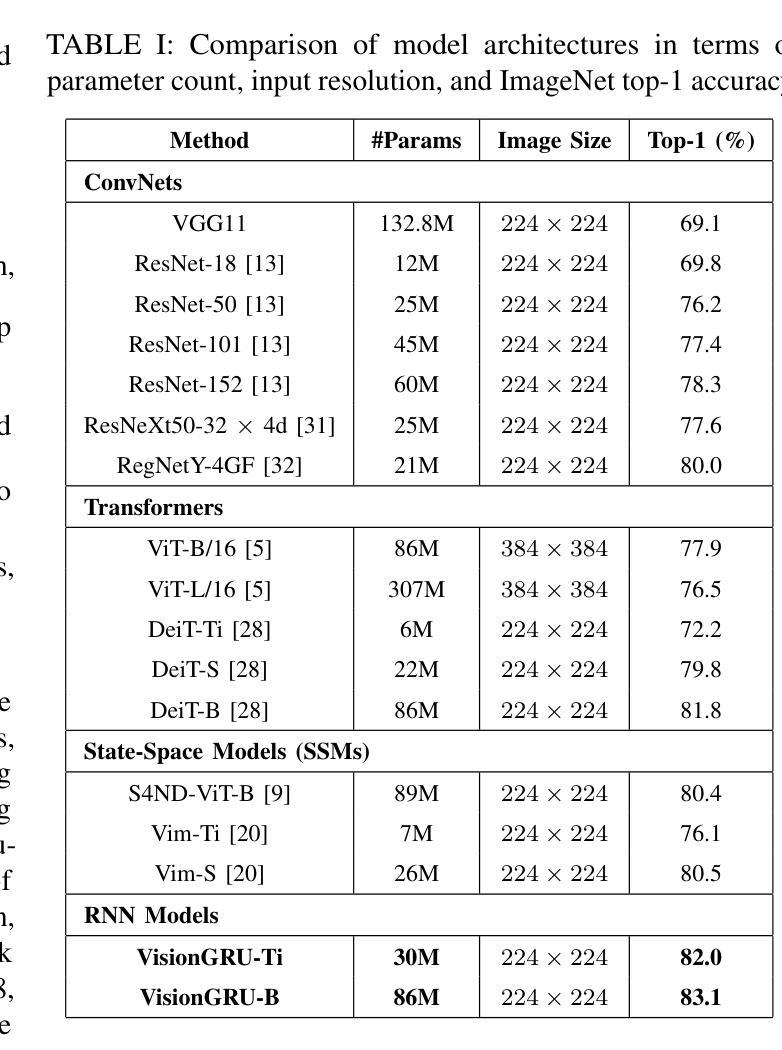
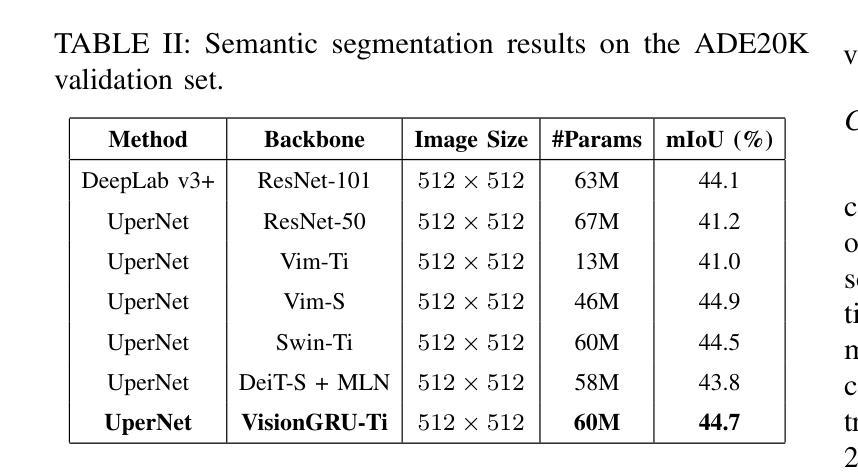
VisionGRU: A Linear-Complexity RNN Model for Efficient Image Analysis
Authors:Shicheng Yin, Kaixuan Yin, Weixing Chen, Enbo Huang, Yang Liu
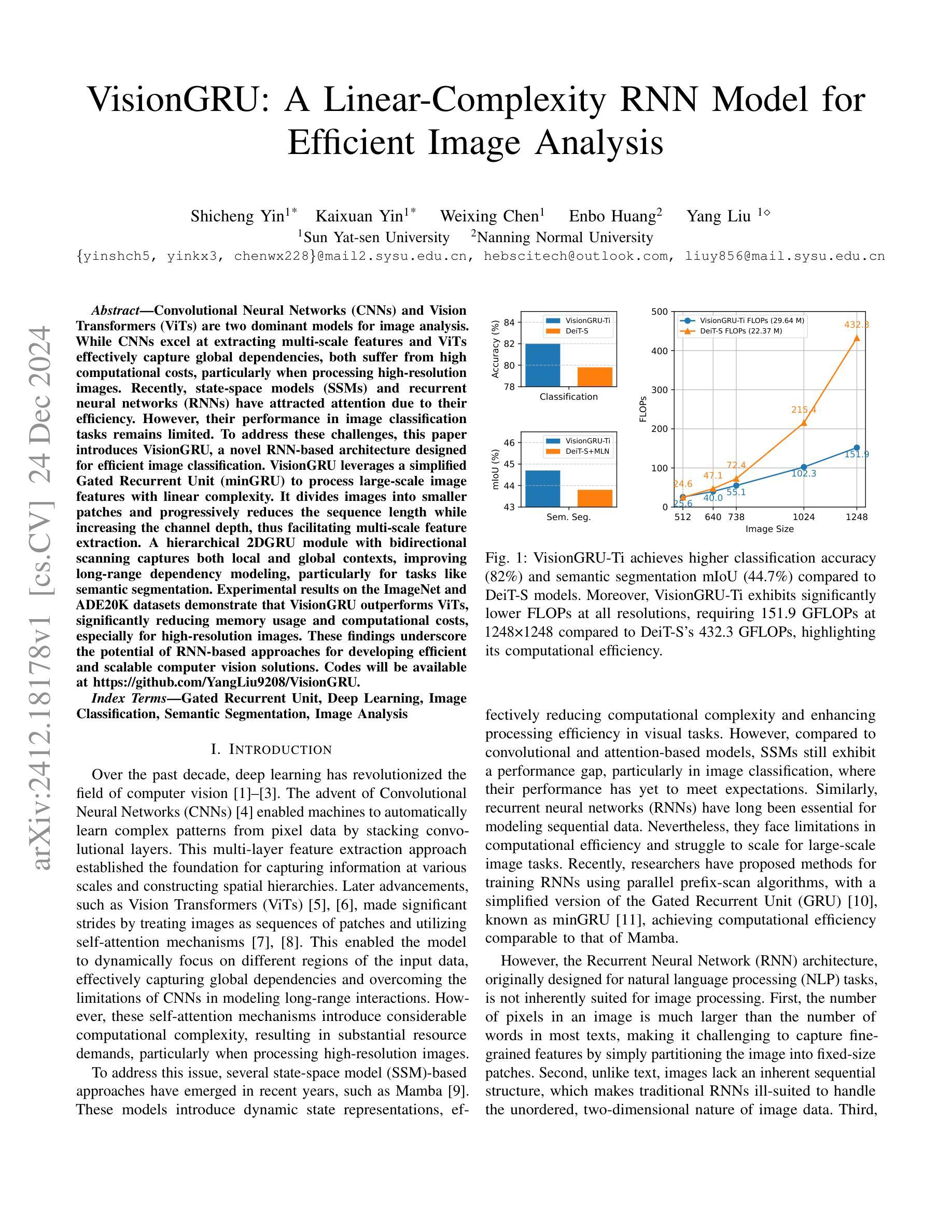
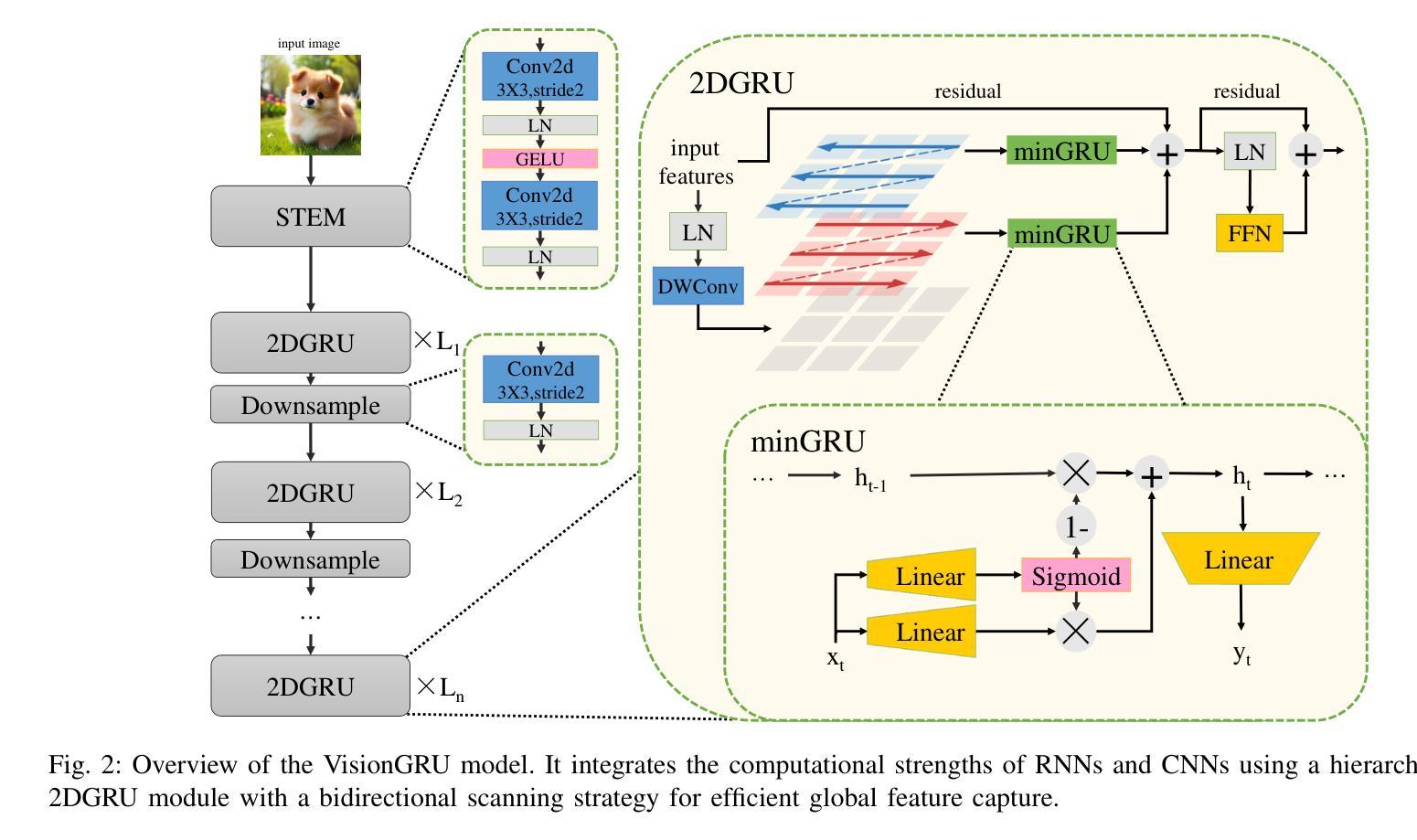
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Vision Transformers (ViTs) are two dominant models for image analysis. While CNNs excel at extracting multi-scale features and ViTs effectively capture global dependencies, both suffer from high computational costs, particularly when processing high-resolution images. Recently, state-space models (SSMs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) have attracted attention due to their efficiency. However, their performance in image classification tasks remains limited. To address these challenges, this paper introduces VisionGRU, a novel RNN-based architecture designed for efficient image classification. VisionGRU leverages a simplified Gated Recurrent Unit (minGRU) to process large-scale image features with linear complexity. It divides images into smaller patches and progressively reduces the sequence length while increasing the channel depth, thus facilitating multi-scale feature extraction. A hierarchical 2DGRU module with bidirectional scanning captures both local and global contexts, improving long-range dependency modeling, particularly for tasks like semantic segmentation. Experimental results on the ImageNet and ADE20K datasets demonstrate that VisionGRU outperforms ViTs, significantly reducing memory usage and computational costs, especially for high-resolution images. These findings underscore the potential of RNN-based approaches for developing efficient and scalable computer vision solutions. Codes will be available at https://github.com/YangLiu9208/VisionGRU.
卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT)是图像分析的两种主导模型。虽然CNN擅长提取多尺度特征,而ViT能有效地捕捉全局依赖性,但它们都存在计算成本高昂的问题,特别是在处理高分辨率图像时。近年来,由于效率较高,状态空间模型(SSM)和循环神经网络(RNN)备受关注。然而,它们在图像分类任务中的表现仍然有限。为了解决这些挑战,本文提出了一种新型的基于RNN的图像分类架构——VisionGRU。VisionGRU利用简化的门控循环单元(minGRU)以线性复杂度处理大规模图像特征。它将图像分成较小的斑块,逐步减少序列长度,同时增加通道深度,从而便于多尺度特征提取。具有双向扫描的分层2DGRU模块能够捕获局部和全局上下文,改进了长距离依赖建模,尤其在语义分割等任务中表现优异。在ImageNet和ADE20K数据集上的实验结果证明,VisionGRU的性能优于ViT,显著减少了内存使用和计算成本,尤其适用于高分辨率图像。这些发现突显了基于RNN的方法在开发高效且可扩展的计算机视觉解决方案方面的潜力。相关代码将在https://github.com/YangLiu9208/VisionGRU上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Codes will be available at https://github.com/YangLiu9208/VisionGRU
Summary
本论文提出一种基于RNN的新型图像分类架构——VisionGRU,它利用简化的门控循环单元(minGRU)处理大规模图像特征,具有线性复杂度。VisionGRU将图像分成较小的斑块,在增加通道深度的同时逐步减少序列长度,促进多尺度特征提取。其层次化的2DGRU模块具有双向扫描功能,能捕捉局部和全局上下文,特别是在语义分割等任务中,长期依赖建模表现优异。在ImageNet和ADE20K数据集上的实验结果表明,VisionGRU在降低内存使用和计算成本的同时,优于ViTs,特别是在处理高分辨率图像时表现更出色。
Key Takeaways
- VisionGRU是一种基于RNN的新型图像分类架构。
- VisionGRU利用简化的Gated Recurrent Unit(minGRU)处理图像特征,具有线性复杂度。
- VisionGRU将图像分成较小的斑块,逐步处理,促进多尺度特征提取。
- 层次化的2DGRU模块具有双向扫描,能捕捉局部和全局上下文。
- VisionGRU在语义分割等任务中,长期依赖建模表现优异。
- 在ImageNet和ADE20K数据集上,VisionGRU表现优于ViTs,尤其是处理高分辨率图像时。
点此查看论文截图

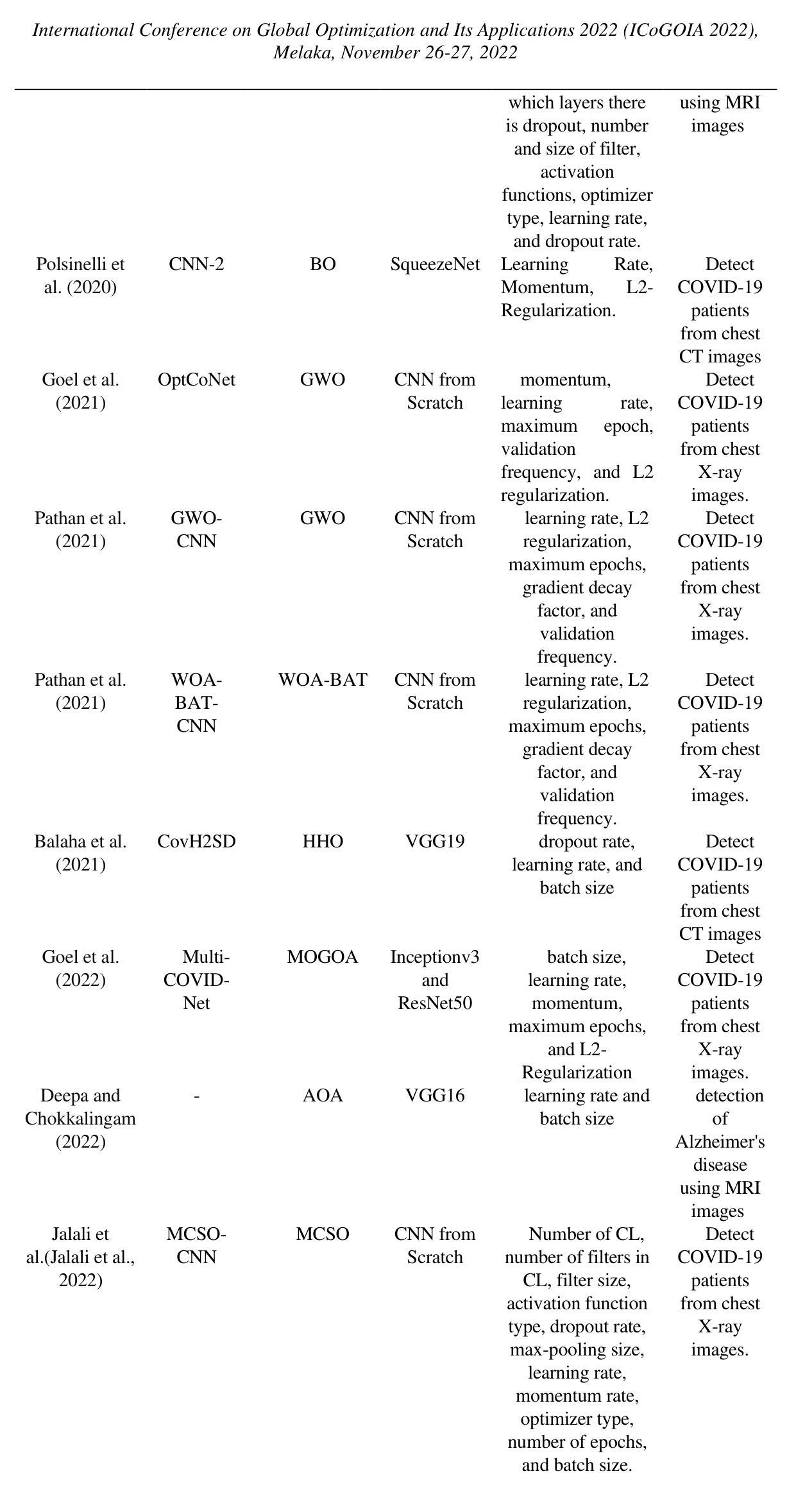
Optimization of Convolutional Neural Network Hyperparameter for Medical Image Diagnosis using Metaheuristic Algorithms: A short Recent Review (2019-2022)
Authors:Qusay Shihab Hamad, Hussein Samma, Shahrel Azmin Suandi
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have been successfully utilized in the medical diagnosis of many illnesses. Nevertheless, identifying the optimal architecture and hyperparameters among the available possibilities might be a substantial challenge. Typically, CNN hyperparameter selection is performed manually. Nonetheless, this is a computationally costly procedure, as numerous rounds of hyperparameter settings must be evaluated to determine which produces the best results. Choosing the proper hyperparameter settings has always been a crucial and challenging task, as it depends on the researcher’s knowledge and experience. This study will present work done in recent years on the usage of metaheuristic optimization algorithms in the CNN optimization process. It looks at a number of recent studies that focus on the use of optimization methods to optimize hyperparameters in order to find high-performing CNNs. This helps researchers figure out how to set hyperparameters efficiently.
卷积神经网络(CNNs)已在多种疾病的医学诊断中成功应用。然而,在众多的可能架构和超参数中识别出最优的架构和超参数可能是一个巨大的挑战。通常,CNN超参数的选择是手动完成的。然而,这是一个计算成本高昂的过程,因为必须评估多轮超参数设置,以确定哪种设置能产生最佳结果。选择合适的超参数设置一直是一项至关重要且具挑战性的任务,因为它取决于研究人员的知识和经验。本研究将介绍近年来在卷积神经网络优化过程中使用元启发式优化算法的工作。它关注了一些近期的研究,这些研究专注于使用优化方法来优化超参数,以找到高性能的卷积神经网络。这有助于研究人员有效地设置超参数。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF its a conference paper; the full proceeding is available online at https://icogoia.utem.edu.my/proceedings.html
Summary
卷积神经网络(CNN)在医学诊断中已得到广泛应用。然而,在众多的网络架构与超参数中,如何选择最优的架构与超参数是一个巨大的挑战。手动选择CNN超参数是一个计算成本高昂的过程,需要评估多种超参数设置以找出最佳结果。本研究将介绍近年来使用元启发式优化算法在CNN优化过程中的研究。该研究关注使用优化方法来优化超参数,以找到性能高的CNN,有助于研究人员高效设置超参数。
Key Takeaways
- CNN已成功应用于医学诊断。
- 选择CNN的最优架构和超参数是一个挑战。
- 手动选择CNN超参数是一个计算成本高昂的过程。
- 元启发式优化算法被用于CNN的优化过程中。
- 使用优化方法来优化超参数,以找到高性能的CNN。
- 这些方法有助于研究人员更有效地设置CNN的超参数。
点此查看论文截图


Hyperbolic Chamfer Distance for Point Cloud Completion and Beyond
Authors:Fangzhou Lin, Songlin Hou, Haotian Liu, Shang Gao, Kazunori D Yamada, Haichong K. Zhang, Ziming Zhang
Chamfer Distance (CD) is widely used as a metric to quantify difference between two point clouds. In point cloud completion, Chamfer Distance (CD) is typically used as a loss function in deep learning frameworks. However, it is generally acknowledged within the field that Chamfer Distance (CD) is vulnerable to the presence of outliers, which can consequently lead to the convergence on suboptimal models. In divergence from the existing literature, which largely concentrates on resolving such concerns in the realm of Euclidean space, we put forth a notably uncomplicated yet potent metric specifically designed for point cloud completion tasks: {Hyperbolic Chamfer Distance (HyperCD)}. This metric conducts Chamfer Distance computations within the parameters of hyperbolic space. During the backpropagation process, HyperCD systematically allocates greater weight to matched point pairs exhibiting reduced Euclidean distances. This mechanism facilitates the preservation of accurate point pair matches while permitting the incremental adjustment of suboptimal matches, thereby contributing to enhanced point cloud completion outcomes. Moreover, measure the shape dissimilarity is not solely work for point cloud completion task, we further explore its applications in other generative related tasks, including single image reconstruction from point cloud, and upsampling. We demonstrate state-of-the-art performance on the point cloud completion benchmark datasets, PCN, ShapeNet-55, and ShapeNet-34, and show from visualization that HyperCD can significantly improve the surface smoothness, we also provide the provide experimental results beyond completion task.
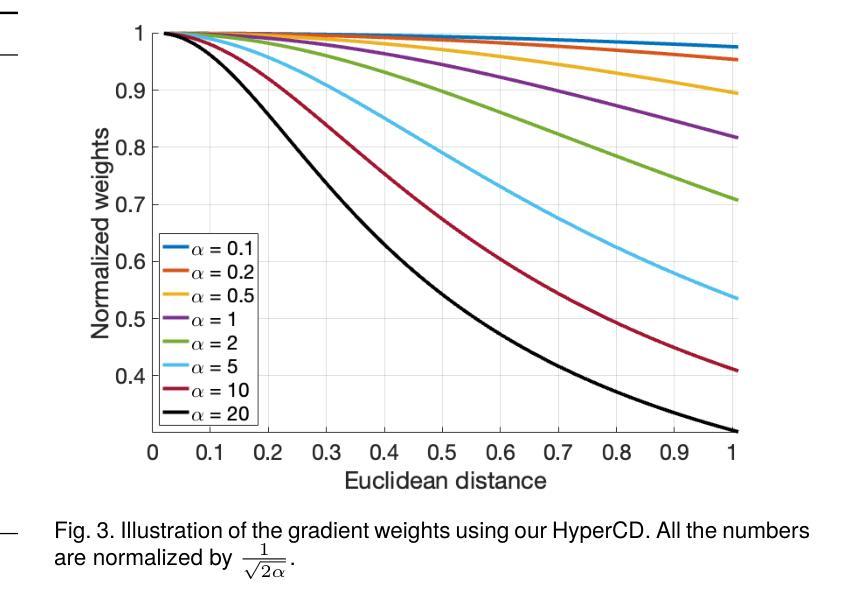
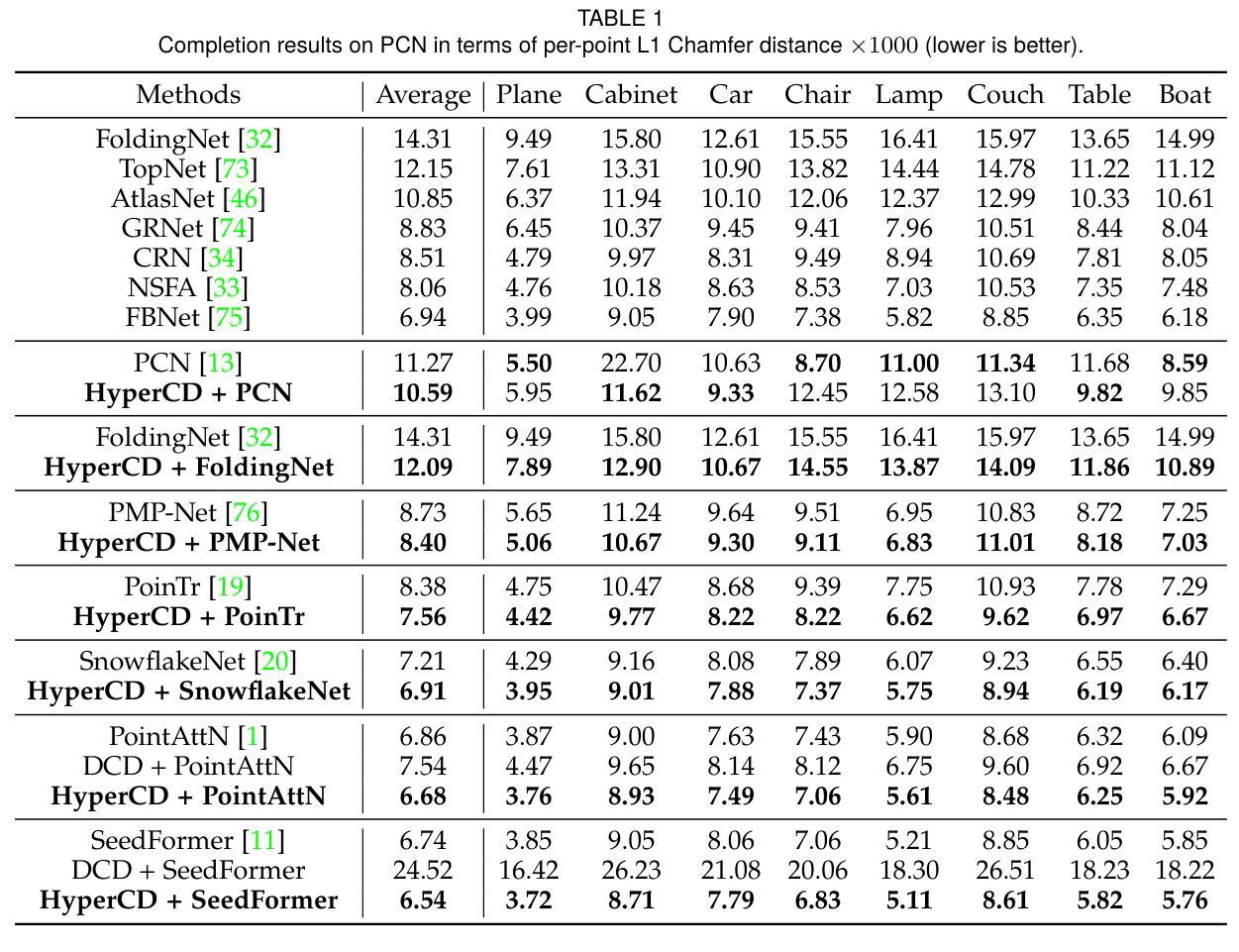
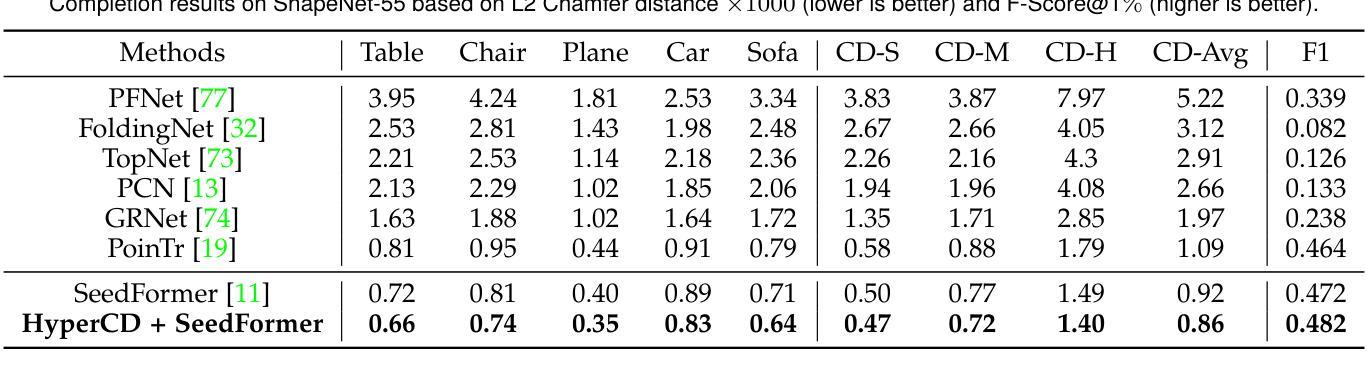
Chamfer Distance(CD)被广泛用作衡量两个点云之间差异的指标。在点云补全中,Chamfer Distance(CD)通常作为深度学习框架中的损失函数。然而,业内普遍认为Chamfer Distance(CD)容易受到异常值的影响,这可能导致收敛到非最优模型。与现有文献大多集中在解决欧几里得空间领域的此类问题不同,我们提出了一种专门为点云补全任务设计的简洁而强大的指标:Hyperbolic Chamfer Distance(HyperCD)。该指标在双曲空间参数内进行Chamfer Distance计算。在反向传播过程中,HyperCD系统地给表现出较小欧几里得距离的匹配点分配更大的权重。这种机制有助于保留准确的点对匹配,同时允许对次优匹配进行增量调整,从而提高了点云补全的效果。此外,测量形状差异不仅仅适用于点云补全任务,我们还进一步探索了其在其他生成相关任务中的应用,包括从点云重建单张图像和上采样。我们在点云补全基准数据集PCN、ShapeNet-55和ShapeNet-34上展示了最先进的性能,并通过可视化展示HyperCD可以显著提高表面平滑度。我们还提供了超出补全任务实验的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 6 figures
摘要
提出一种针对点云完成任务的新型度量标准——Hyperbolic Chamfer Distance (HyperCD)。该度量在双曲空间中进行Chamfer Distance计算,为匹配点分配更大的权重,有助于保留准确的点匹配并调整次优匹配,从而提高点云完成结果。除了点云完成任务外,还探索了其在其他生成相关任务中的应用,包括点云到单图像的重建和采样等。在PCN、ShapeNet-55和ShapeNet-34等点云完成基准数据集上表现出卓越性能。
关键见解
- 提出了一种新的点云完成度量标准——Hyperbolic Chamfer Distance (HyperCD)。
- HyperCD在双曲空间中进行Chamfer Distance计算,提高了点匹配的准确性并允许调整次优匹配。
- HyperCD能显著改善点云完成的表面平滑度。
- 除了点云完成任务外,HyperCD还应用于其他生成相关任务,如点云到单图像的重建和采样等。
- 在多个点云完成基准数据集上,HyperCD实现了卓越的性能。
- HyperCD不仅有助于解决由于存在离群值而导致的Chamfer Distance的局限性,还为提高点云完成质量提供了新的思路。
点此查看论文截图
Parkinson Disease Detection Based on In-air Dynamics Feature Extraction and Selection Using Machine Learning
Authors:Jungpil Shin, Abu Saleh Musa Miah, Koki Hirooka, Md. Al Mehedi Hasan, Md. Maniruzzaman
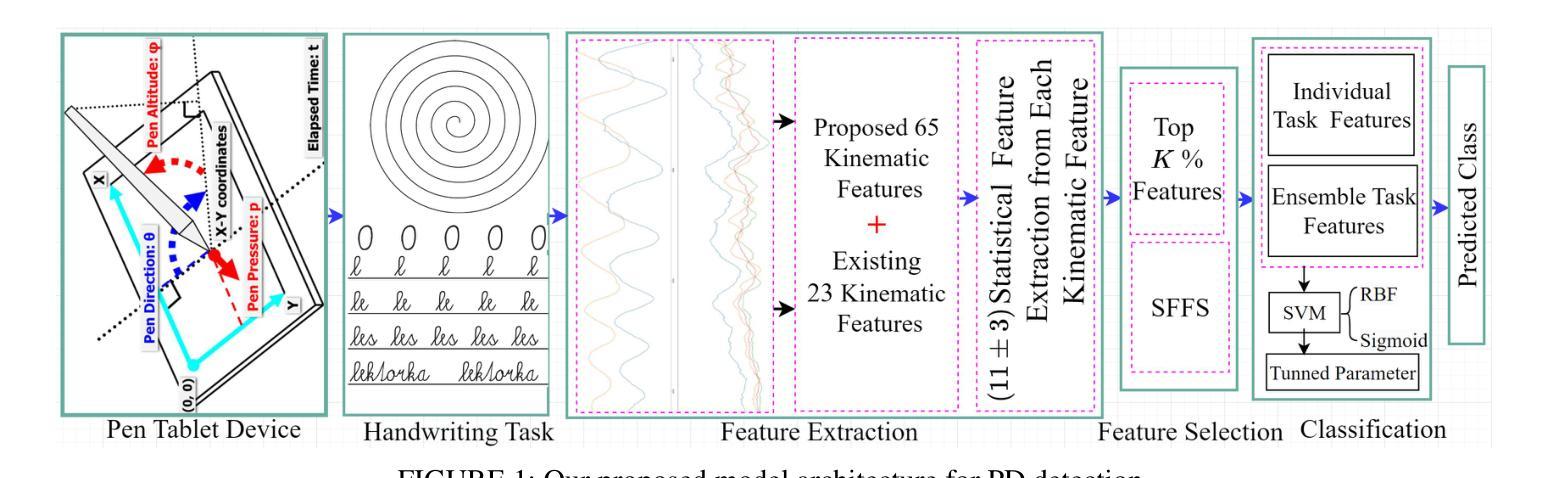
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurological disorder that impairs movement control, leading to symptoms such as tremors, stiffness, and bradykinesia. Many researchers analyzing handwriting data for PD detection typically rely on computing statistical features over the entirety of the handwriting task. While this method can capture broad patterns, it has several limitations, including a lack of focus on dynamic change, oversimplified feature representation, lack of directional information, and missing micro-movements or subtle variations. Consequently, these systems face challenges in achieving good performance accuracy, robustness, and sensitivity. To overcome this problem, we proposed an optimized PD detection methodology that incorporates newly developed dynamic kinematic features and machine learning (ML)-based techniques to capture movement dynamics during handwriting tasks. In the procedure, we first extracted 65 newly developed kinematic features from the first and last 10% phases of the handwriting task rather than using the entire task. Alongside this, we also reused 23 existing kinematic features, resulting in a comprehensive new feature set. Next, we enhanced the kinematic features by applying statistical formulas to compute hierarchical features from the handwriting data. This approach allows us to capture subtle movement variations that distinguish PD patients from healthy controls. To further optimize the feature set, we applied the Sequential Forward Floating Selection method to select the most relevant features, reducing dimensionality and computational complexity. Finally, we employed an ML-based approach based on ensemble voting across top-performing tasks, achieving an impressive 96.99% accuracy on task-wise classification and 99.98% accuracy on task ensembles, surpassing the existing state-of-the-art model by 2% for the PaHaW dataset.
帕金森病(PD)是一种进行性神经疾病,会损害运动控制,导致震颤、僵硬和行动迟缓等症状。许多研究人员在分析帕金森病的手写数据检测时,通常依赖于对整个手写任务进行统计特征的计算。虽然这种方法可以捕捉大致的模式,但它存在一些局限性,包括缺乏动态变化的关注、特征表示过于简化、缺乏方向信息和缺失的微动作或细微变化。因此,这些系统在实现性能准确性、稳健性和敏感性方面面临挑战。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种优化的帕金森病检测方法论,该方法结合了新开发的动态运动特征以及基于机器学习(ML)的技术,以捕捉手写任务过程中的运动动态。在该过程中,我们从手写任务的开始和结束10%的阶段中提取了65个新开发的运动特征,而不是使用整个任务。同时,我们还重用了23个现有的运动特征,形成了一个全面的新特征集。接下来,我们通过应用统计公式来计算手写数据的分层特征来增强运动特征。这种方法允许我们捕捉到细微的运动变化,以区分帕金森病患者和健康对照者。为了进一步优化特征集,我们采用了序贯前向浮动选择方法,以选择最相关的特征,降低维度和计算复杂性。最后,我们基于任务性能最佳的集合投票方法采用了一种基于机器学习的策略,在任务级分类上取得了令人印象深刻的96.99%的准确率,在任务集合上达到了惊人的99.98%的准确率,超过了PaHaW数据集上的现有最先进的模型2%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
帕金森病(PD)是一种影响运动控制的神经性疾病。传统的手写数据分析方法存在局限性,如忽视动态变化、特征表示过于简化等。本研究提出了一种优化的PD检测法,结合新的动态运动特征和机器学习技术,以捕捉手写过程中的运动动态。该研究从书写任务的开始和结束阶段提取特征,同时利用统计公式计算层次特征,以区分PD患者和健康人。通过特征选择方法优化特征集,并采用基于集成投票的机器学习法,取得了高准确率。
Key Takeaways
- 帕金森病是一种影响运动控制的神经性疾病,具有手抖、僵硬和迟缓等症状。
- 传统的手写数据分析方法在PD检测中存在局限性,缺乏动态变化关注及细微运动捕捉。
- 本研究提出了一种结合新的动态运动特征和机器学习技术的优化PD检测方法。
- 研究从手写任务的特定阶段提取特征,并计算层次特征以区分PD患者和健康人。
点此查看论文截图

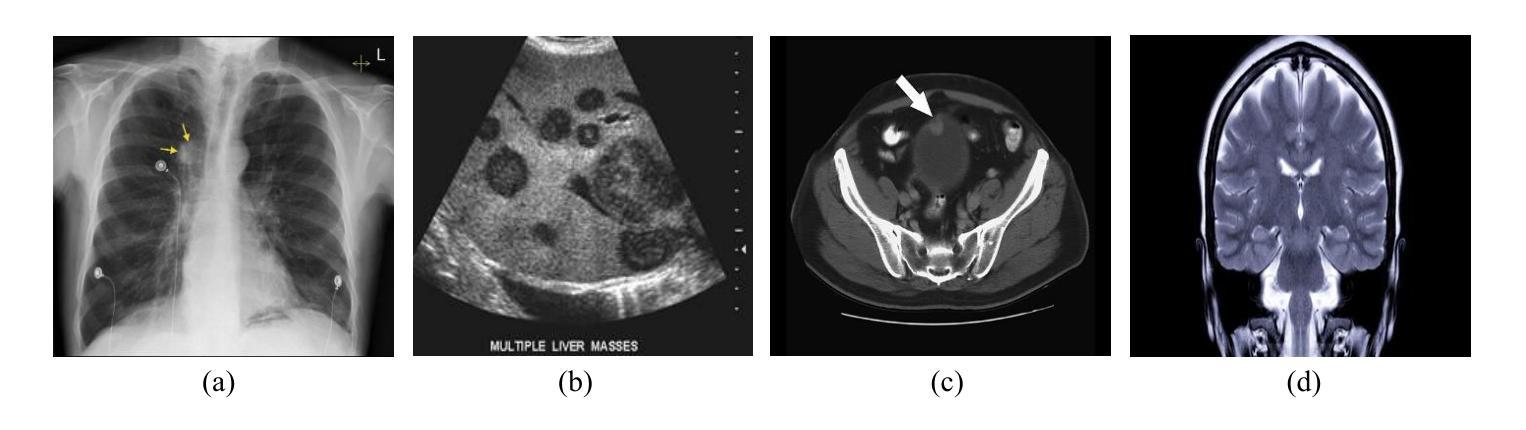
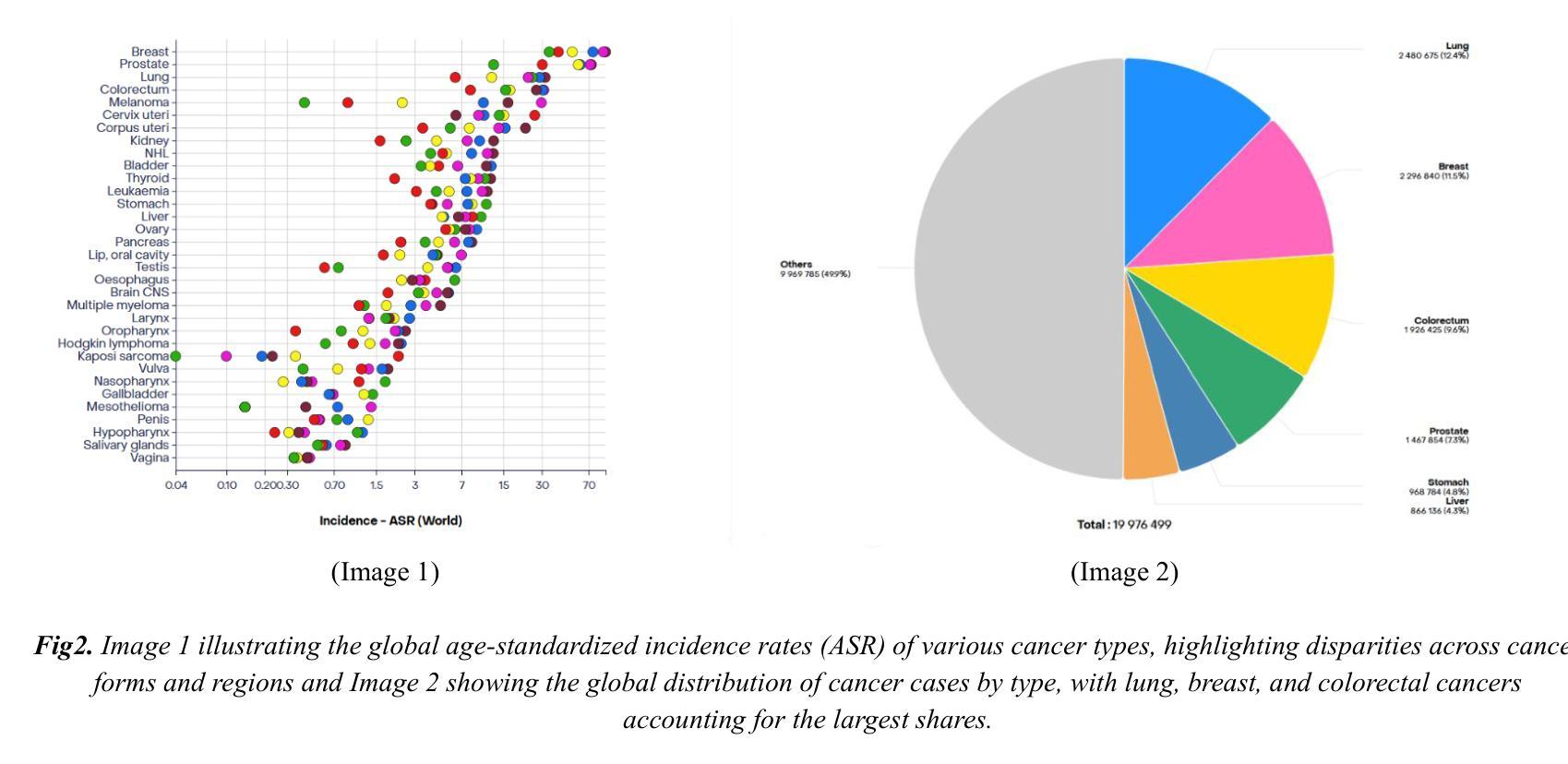
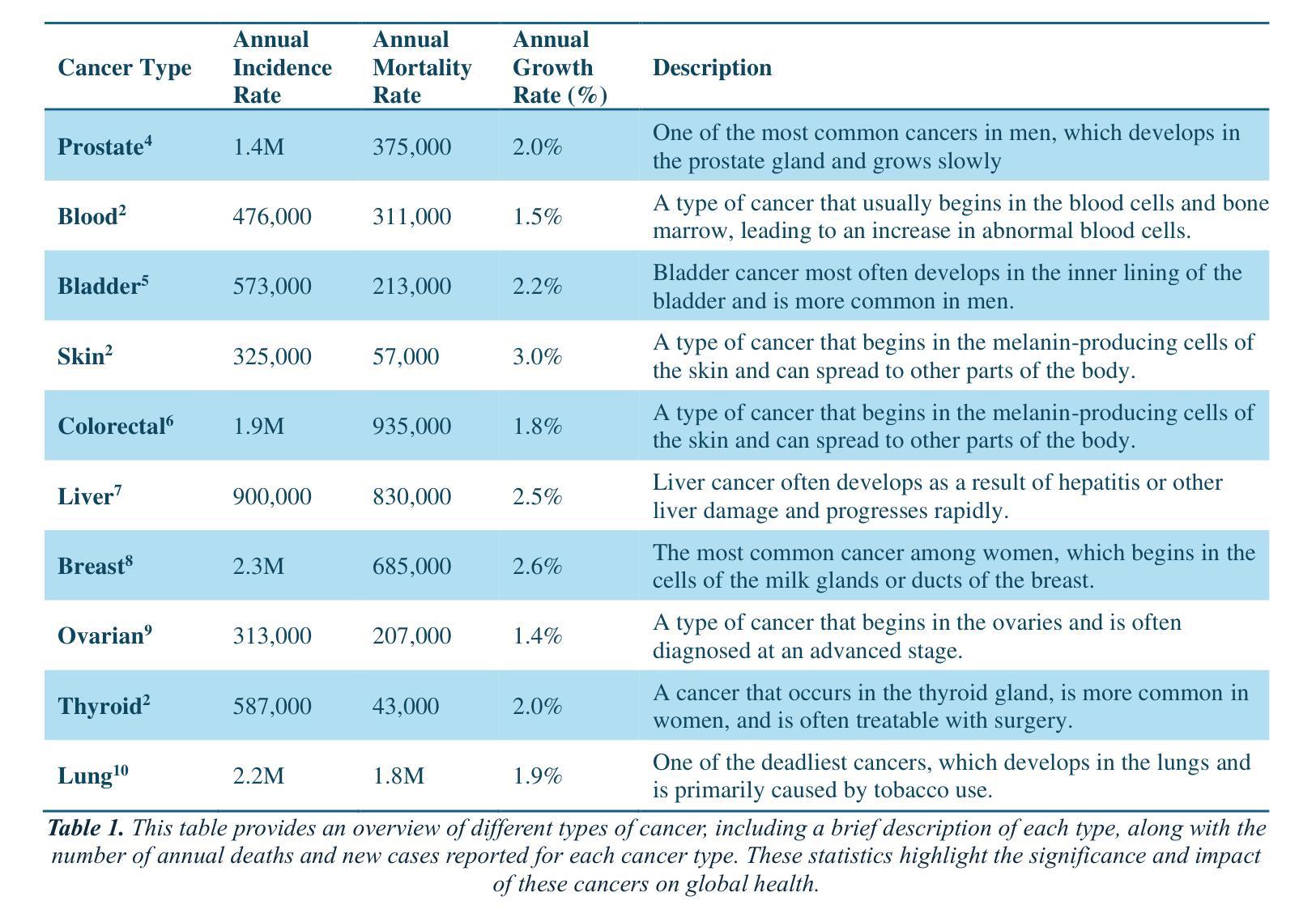
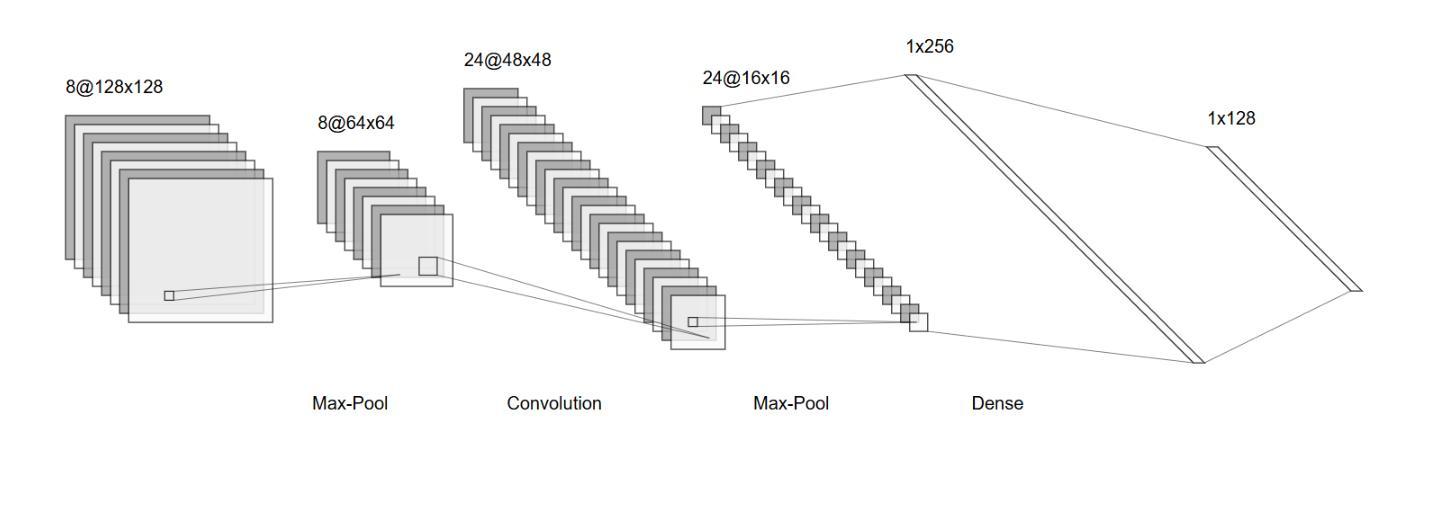
The Potential of Convolutional Neural Networks for Cancer Detection
Authors:Hossein Molaeian, Kaveh Karamjani, Sina Teimouri, Saeed Roshani, Sobhan Roshani
Early detection of cancer is critical in improving treatment outcomes and increasing survival rates, particularly for common cancers such as lung, breast, and prostate which collectively contribute to a significant global mortality burden. With advancements in imaging technologies and data processing, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have emerged as a powerful tool for analyzing and classifying medical images, enabling more precise cancer detection. This paper provides a comprehensive review of recent studies leveraging CNN models for detecting ten different types of cancer. Each study employs distinct CNN architectures to identify patterns associated with these cancers, utilizing diverse datasets. Key differences and strengths of these architectures are meticulously compared and analyzed, highlighting their efficacy in improving early detection. Beyond reviewing the performance and limitations of CNN-based cancer detection methods, this study explores the feasibility of integrating CNNs into clinical settings as an early detection tool, potentially complementing or replacing traditional methods. Despite significant progress, challenges remain, including data diversity, result interpretation, and ethical considerations. By identifying the best-performing CNN architectures and providing a comparative analysis, this study aims to contribute a comprehensive perspective on the application of CNNs in cancer detection and their role in advancing diagnostic capabilities in healthcare.
癌症的早期发现对于提高治疗效果和增加存活率至关重要,特别是对于肺癌、乳腺癌和前列腺癌等常见癌症,它们共同造成了全球大量的死亡负担。随着成像技术和数据处理的发展,卷积神经网络(CNN)已成为分析和分类医学图像的强大工具,能够实现更精确的癌症检测。本文全面回顾了最近利用CNN模型检测十种不同类型癌症的研究。每项研究都采用不同的CNN架构来识别与这些癌症相关的模式,并利用各种数据集。本文精心比较和分析了这些架构的主要差异和优点,突出了它们在提高早期检测率方面的有效性。除了回顾基于CNN的癌症检测方法的性能和局限性外,本研究还探讨了将CNN集成到临床环境中作为早期检测工具的可行性,可能补充或替代传统方法。尽管取得了重大进展,但仍存在挑战,包括数据多样性、结果解释和伦理考量。通过确定表现最佳的CNN架构并提供比较分析,本研究旨在为CNN在癌症检测中的应用及其在提高医疗诊断能力方面的作用提供全面视角。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文综述了近期利用卷积神经网络(CNN)模型检测十种不同类型癌症的研究。这些研究采用不同的CNN架构识别与癌症相关的模式,并利用多样数据集进行验证。文章比较分析了这些架构的关键差异和优势,强调了它们在提高癌症早期检测方面的效能。此外,文章还探讨了将CNN集成到临床环境中作为早期检测工具的可行性,并指出了当前面临的挑战和未来的研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- 早期癌症检测对改善治疗结果和提高存活率至关重要,特别是对于肺癌、乳腺癌和前列腺癌等常见癌症。
- 卷积神经网络(CNN)在分析和分类医疗图像方面表现出强大的能力,能更精确地检测癌症。
- 综述了利用CNN模型检测十种不同类型癌症的最近研究,这些研究采用不同的CNN架构并利用多样数据集进行验证。
- CNN架构在癌症检测中的效能得到了比较和分析,强调了它们对提高早期检测率的重要性。
- 探讨了将CNN集成到临床环境中作为癌症早期检测工具的可行性,这可能会补充或替代传统方法。
- 当前面临的挑战包括数据多样性、结果解读和伦理考虑等因素。
点此查看论文截图

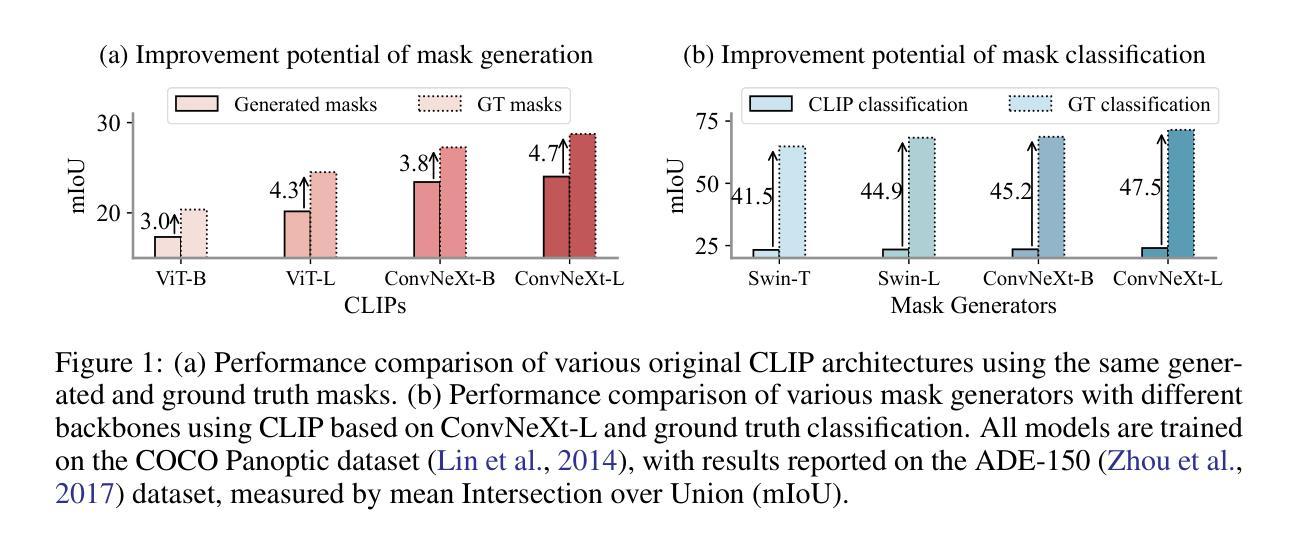
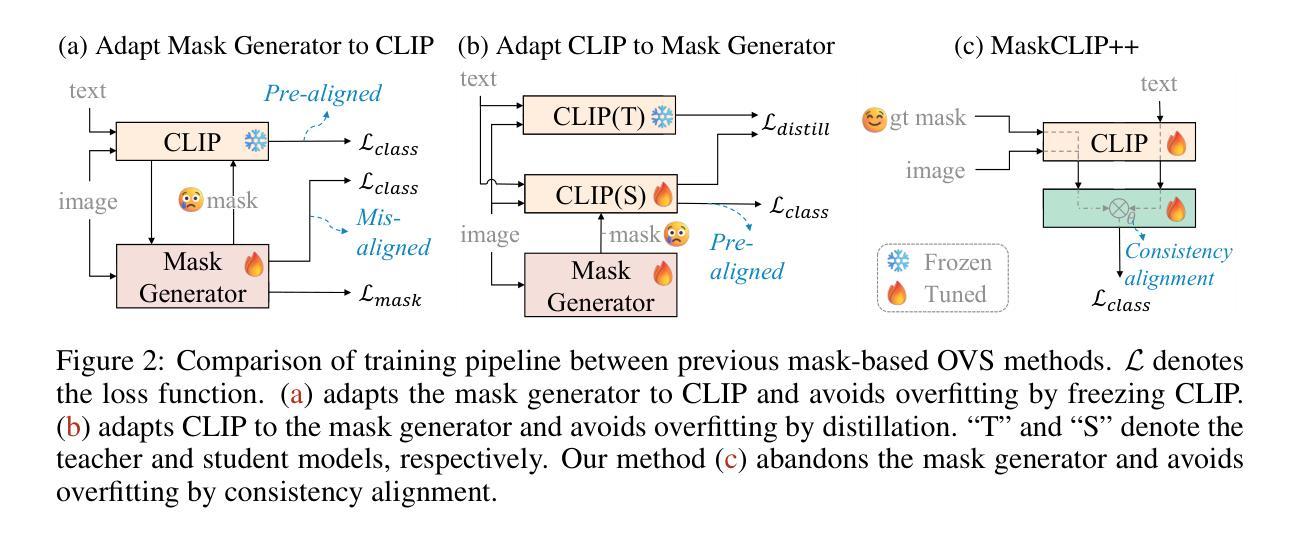
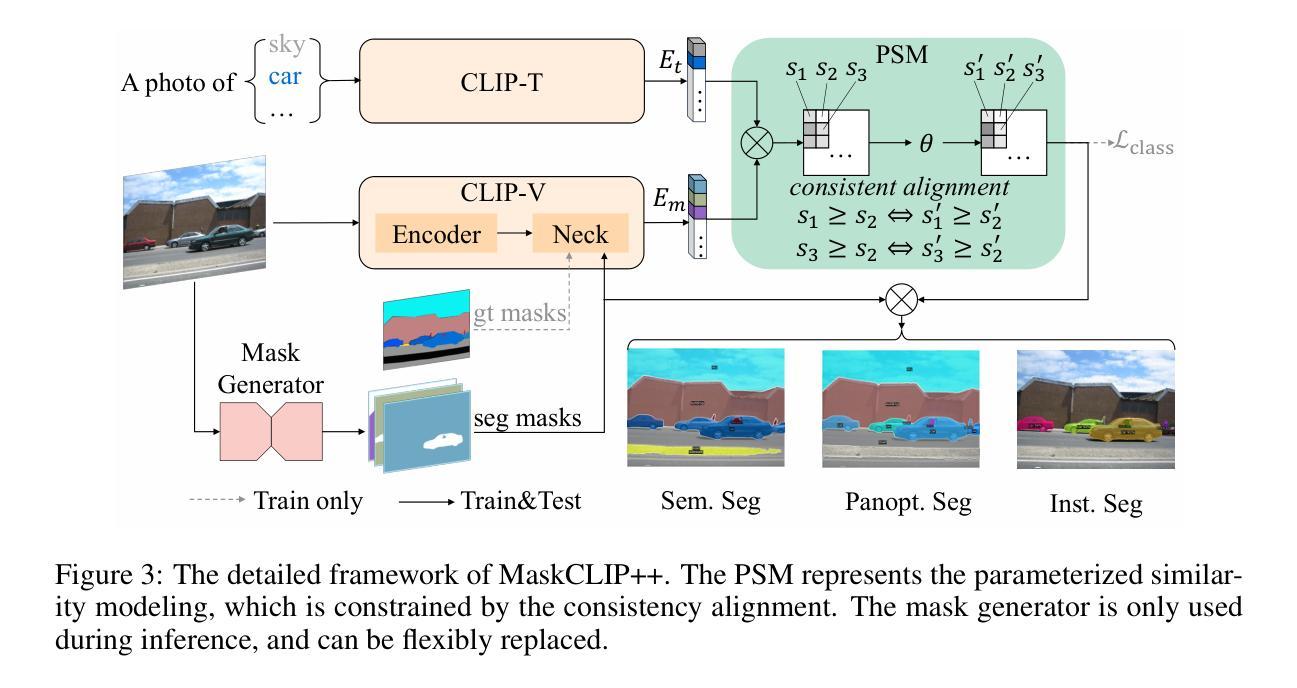
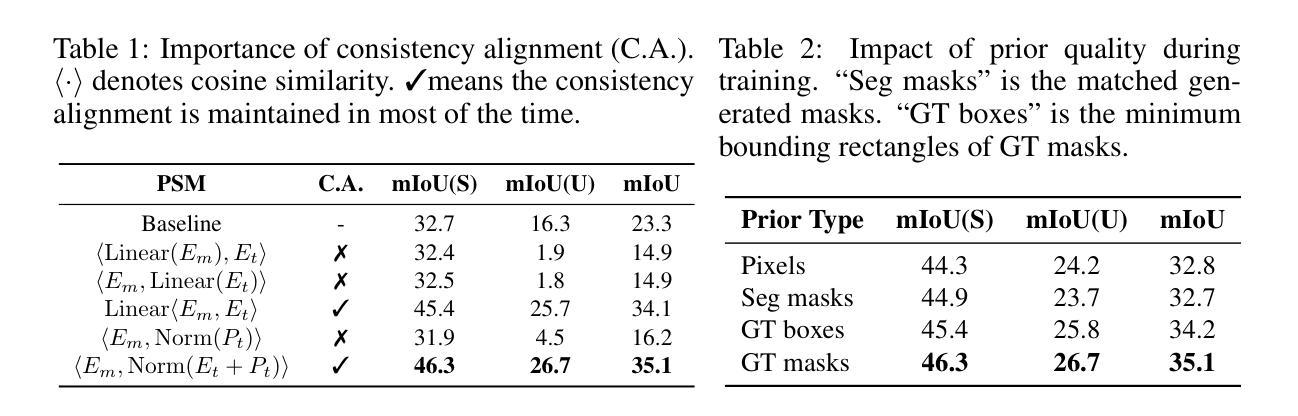
MaskCLIP++: A Mask-Based CLIP Fine-tuning Framework for Open-Vocabulary Image Segmentation
Authors:Quan-Sheng Zeng, Yunheng Li, Daquan Zhou, Guanbin Li, Qibin Hou, Ming-Ming Cheng
Open-vocabulary image segmentation has been advanced through the synergy between mask generators and vision-language models like Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP). Previous approaches focus on generating masks while aligning mask features with text embeddings during training. In this paper, we observe that relying on generated low-quality masks can weaken the alignment of vision and language in regional representations. This motivates us to present a new fine-tuning framework, named MaskCLIP++, which uses ground-truth masks instead of generated masks to enhance the mask classification capability of CLIP. Due to the limited diversity of image segmentation datasets with mask annotations, we propose incorporating a consistency alignment constraint during fine-tuning, which alleviates categorical bias toward the fine-tuning dataset. After low-cost fine-tuning, combining with the mask generator in previous state-of-the-art mask-based open vocabulary segmentation methods, we achieve performance improvements of +1.7, +2.3, +2.1, +3.1, and +0.3 mIoU on the A-847, PC-459, A-150, PC-59, and PAS-20 datasets, respectively. Code is released at https://github.com/HVision-NKU/MaskCLIPpp .
基于掩膜生成器和对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)等视觉语言模型之间的协同作用,开放词汇图像分割技术已经得到了发展。早期的方法侧重于生成掩膜,并在训练过程中将掩膜特征与文本嵌入进行对齐。在本文中,我们观察到依赖生成的低质量掩膜会削弱区域表示中的视觉和语言对齐。这促使我们提出一个新的微调框架,名为MaskCLIP++,它使用真实掩膜代替生成的掩膜,以提高CLIP的掩膜分类能力。由于带有掩膜标注的图像分割数据集多样性有限,我们提出了在微调过程中引入一致性对齐约束,这减轻了对微调数据集的类别偏见。经过低成本微调后,与之前最先进的基于掩膜开放词汇分割方法中的掩膜生成器相结合,我们在A-847、PC-459、A-150、PC-59和PAS-20数据集上分别实现了+1.7、+2.3、+2.1、+3.1和+0.3的mIoU性能提升。代码已发布在https://github.com/HVision-NKU/MaskCLIPpp上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 8 figures. Add code link
Summary
本文提出了一种名为MaskCLIP++的新微调框架,使用真实掩膜替代生成的掩膜提升CLIP的掩膜分类能力。为提高图像分割数据集掩膜标注的多样性,提出了一致性对齐约束。结合之前的先进掩膜生成器进行微调后,在多个数据集上的性能有所提升。
Key Takeaways
- MaskCLIP++使用真实掩膜替代生成掩膜,以增强CLIP的掩膜分类能力。
- 生成的低质量掩膜可能导致视觉和语言区域表示的对齐减弱。
- 为提高图像分割数据集的多样性,提出了在微调过程中加入一致性对齐约束。
- MaskCLIP++通过对Mask generator的融入和微调提升性能。
- 在不同数据集上进行实验验证,实现了mIoU性能的提升。
- 项目的代码已经公开发布在GitHub上。
点此查看论文截图

AgriBench: A Hierarchical Agriculture Benchmark for Multimodal Large Language Models
Authors:Yutong Zhou, Masahiro Ryo
We introduce AgriBench, the first agriculture benchmark designed to evaluate MultiModal Large Language Models (MM-LLMs) for agriculture applications. To further address the agriculture knowledge-based dataset limitation problem, we propose MM-LUCAS, a multimodal agriculture dataset, that includes 1,784 landscape images, segmentation masks, depth maps, and detailed annotations (geographical location, country, date, land cover and land use taxonomic details, quality scores, aesthetic scores, etc), based on the Land Use/Cover Area Frame Survey (LUCAS) dataset, which contains comparable statistics on land use and land cover for the European Union (EU) territory. This work presents a groundbreaking perspective in advancing agriculture MM-LLMs and is still in progress, offering valuable insights for future developments and innovations in specific expert knowledge-based MM-LLMs.
我们介绍了Agribench,这是第一个针对农业应用的多模态大型语言模型(MM-LLM)设计的农业基准测试。为了进一步解决基于农业的数据库限制问题,我们提出了多模态农业数据集MM-LUCAS。该数据集基于土地利用/覆盖面积框架调查(LUCAS)数据集,包含了1784张景观图像、分割掩膜、深度图以及详细的注释(包括地理位置、国家、日期、土地覆盖和土地利用分类详情、质量分数、美学分数等)。LUCAS数据集包含欧盟领土内土地利用和土地覆盖的可比统计数据。这项工作为推进农业MM-LLM提供了全新的视角,并且仍在进行中,为未来在特定专业知识为基础的MM-LLM领域的发展和创新提供了宝贵的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPPA @ECCV2024. Dataset: https://github.com/Yutong-Zhou-cv/AgriBench
Summary
推出农业基准测试AgriBench,评估多模态大型语言模型在农业应用的表现。为解决农业知识数据集限制问题,基于土地利用/覆盖面积框架调查(LUCAS)数据集提出多模态农业数据集MM-LUCAS,包含景观图像、分割掩膜、深度图及详细注解,推动农业MM-LLM的发展。
Key Takeaways
- AgriBench是首个用于评估多模态大型语言模型在农业应用方面的基准测试。
- MM-LUCAS是一个多模态农业数据集,基于LUCAS数据集构建,包含丰富的农业相关数据和详细注解。
- MM-LUCAS数据集旨在解决农业知识数据集限制的问题。
- 数据集包含景观图像、分割掩膜、深度图等多媒体数据。
- 数据集包含地理位置、国家、日期、土地覆盖和利用分类详情、质量评分、美学评分等详细注解。
- AgriBench和MM-LUCAS的推出为农业MM-LLM的发展提供了有价值的见解和洞察力。
点此查看论文截图

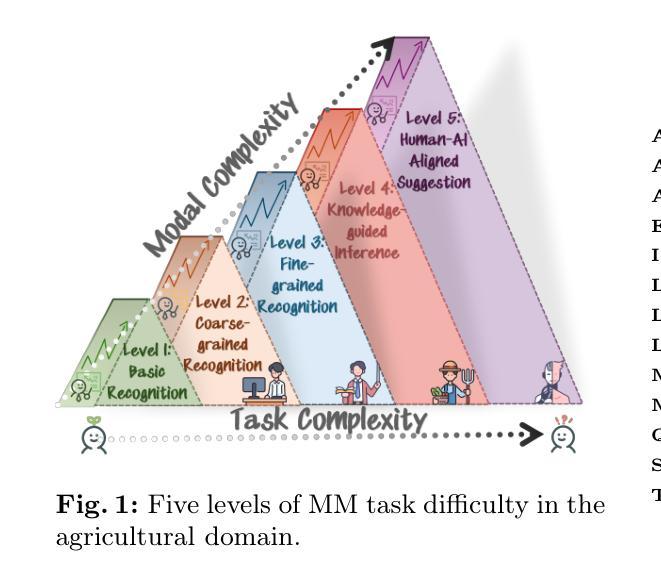
Concept Complement Bottleneck Model for Interpretable Medical Image Diagnosis
Authors:Hongmei Wang, Junlin Hou, Hao Chen
Models based on human-understandable concepts have received extensive attention to improve model interpretability for trustworthy artificial intelligence in the field of medical image analysis. These methods can provide convincing explanations for model decisions but heavily rely on the detailed annotation of pre-defined concepts. Consequently, they may not be effective in cases where concepts or annotations are incomplete or low-quality. Although some methods automatically discover effective and new visual concepts rather than using pre-defined concepts or could find some human-understandable concepts via large Language models, they are prone to veering away from medical diagnostic evidence and are challenging to understand. In this paper, we propose a concept complement bottleneck model for interpretable medical image diagnosis with the aim of complementing the existing concept set and finding new concepts bridging the gap between explainable models. Specifically, we propose to use concept adapters for specific concepts to mine the concept differences and score concepts in their own attention channels to support almost fairly concept learning. Then, we devise a concept complement strategy to learn new concepts while jointly using known concepts to improve model performance. Comprehensive experiments on medical datasets demonstrate that our model outperforms the state-of-the-art competitors in concept detection and disease diagnosis tasks while providing diverse explanations to ensure model interpretability effectively.
基于人类可理解概念的模型在医学图像分析领域受到了广泛关注,以提高人工智能模型的解释性,从而实现可信赖的人工智能。这些方法可以为模型决策提供令人信服的解释,但它们严重依赖于预先定义概念的详细注释。因此,在概念或注释不完整或质量低的情况下,它们可能无法有效发挥作用。尽管一些方法能够自动发现有效的新视觉概念,而不是使用预先定义的概念,或者可以通过大型语言模型发现一些人类可理解的概念,但它们容易偏离医学诊断证据,且难以理解。在本文中,我们提出了一种概念补充瓶颈模型,旨在用于解释医学图像诊断,目标是补充现有概念集,并找到填补解释性模型之间差距的新概念。具体来说,我们建议使用特定概念的概念适配器来挖掘概念差异,并在各自的注意力通道中对概念进行评分,以支持几乎公平的概念学习。然后,我们设计了一种概念补充策略,在学习新概念的同时,结合已知概念来提高模型性能。在医学数据集上的综合实验表明,我们的模型在概念检测和疾病诊断任务上优于最新竞争对手,同时提供多样化的解释,以确保模型的有效解释性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 5 figures,
Summary
医学图像分析领域,基于人类可理解概念的模型受到广泛关注以提高模型的可解释性。该方法可为模型决策提供有力解释,但依赖于预定义概念的详细标注,若概念或标注不完整或质量低下则效果不佳。本文提出概念补充瓶颈模型,旨在补充现有概念集并发现新概念以缩小解释性模型的差距。通过概念适配器挖掘概念差异,并在各自注意力通道评分新概念以支持几乎公平的概念学习。实验证明该模型在医学数据集上超越最新竞争对手,在概念检测和疾病诊断任务上表现优异,同时提供多样的解释以确保模型的有效可解释性。
Key Takeaways
1. 基于人类可理解概念的模型在医学图像分析领域备受关注,以提高模型的可解释性。
2. 这些方法需要预定义概念的详细标注,若标注不完整或质量低下可能会影响效果。
3. 本文提出了一个新的概念补充瓶颈模型,旨在补充现有概念集并发现新概念。
4. 使用概念适配器挖掘概念差异,并在各自的注意力通道评分新概念。
5. 提出了一种概念补充策略,以学习新概念的同时利用已知概念来提高模型性能。
6. 在医学数据集上的实验证明该模型在概念检测和疾病诊断任务上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图
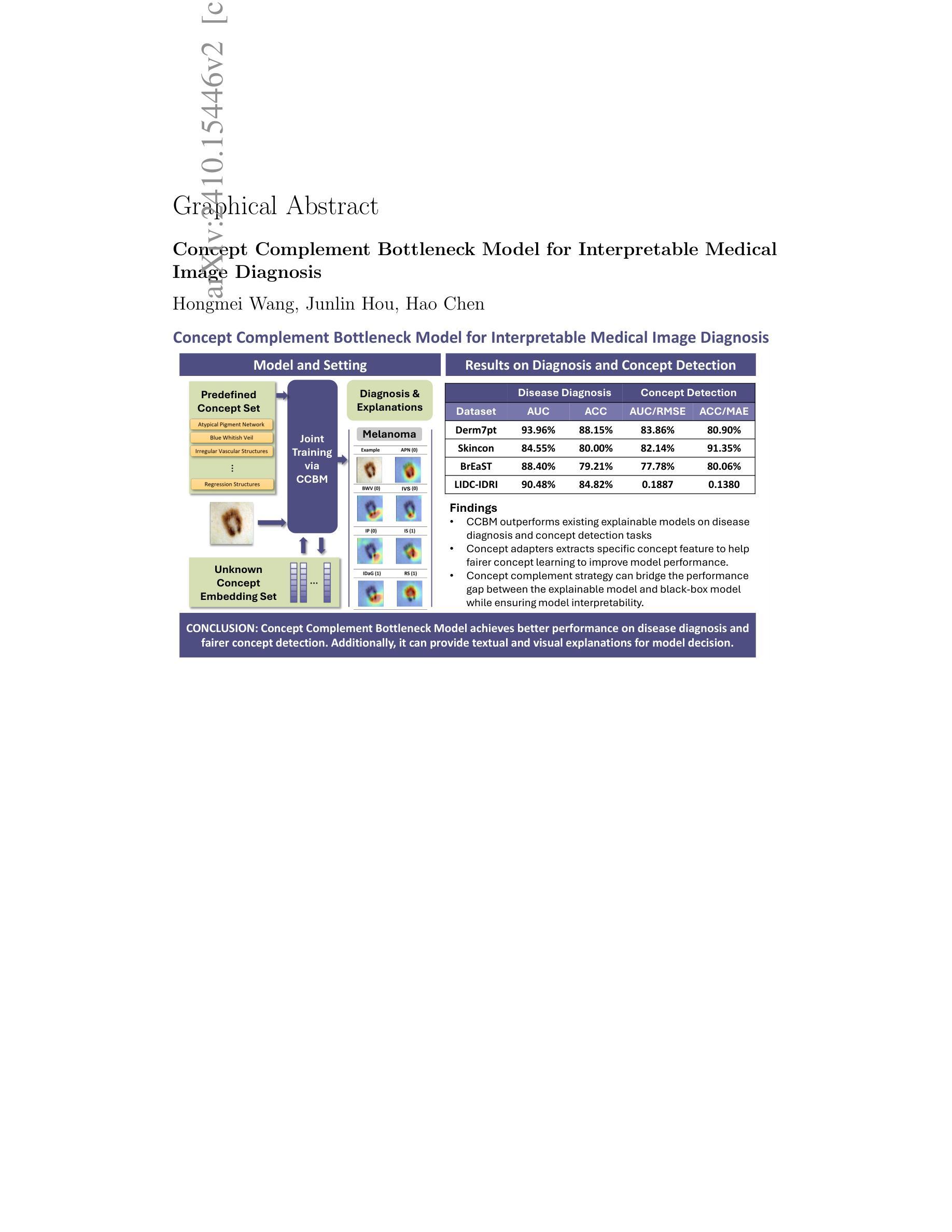
Rate-Adaptive Generative Semantic Communication Using Conditional Diffusion Models
Authors:Pujing Yang, Guangyi Zhang, Yunlong Cai
Recent advances in deep learning-based joint source-channel coding (DJSCC) have shown promise for end-to-end semantic image transmission. However, most existing schemes primarily focus on optimizing pixel-wise metrics, which often fail to align with human perception, leading to lower perceptual quality. In this letter, we propose a novel generative DJSCC approach using conditional diffusion models to enhance the perceptual quality of transmitted images. Specifically, by utilizing entropy models, we effectively manage transmission bandwidth based on the estimated entropy of transmitted sym-bols. These symbols are then used at the receiver as conditional information to guide a conditional diffusion decoder in image reconstruction. Our model is built upon the emerging advanced mamba-like linear attention (MLLA) skeleton, which excels in image processing tasks while also offering fast inference speed. Besides, we introduce a multi-stage training strategy to ensure the stability and improve the overall performance of the model. Simulation results demonstrate that our proposed method significantly outperforms existing approaches in terms of perceptual quality.
近年来,基于深度学习的联合源信道编码(DJSCC)的最新进展为端到端的语义图像传输展现了前景。然而,大多数现有方案主要关注优化像素级的指标,这些指标通常与人类感知不匹配,导致感知质量较低。在这篇文章中,我们提出了一种利用条件扩散模型的新型生成式DJSCC方法,以提高传输图像的感知质量。具体来说,我们利用熵模型,根据传输符号的估计熵有效地管理传输带宽。这些符号然后在接收器端作为条件信息,用于指导图像重建中的条件扩散解码器。我们的模型建立在新兴的马姆巴式线性注意力(MLLA)骨架之上,该骨架在图像处理任务中表现出色,同时提供了快速推理速度。此外,我们引入了一种多阶段训练策略,以确保模型的稳定性并提高其整体性能。仿真结果表明,我们提出的方法在感知质量方面显著优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于深度学习的联合源信道编码(DJSCC)最新进展为端到端的语义图像传输展现了潜力。然而,大多数现有方案主要关注像素级的优化指标,这些指标往往不符合人类感知,导致感知质量较低。本研究提出了一种基于条件扩散模型的新型生成式DJSCC方法,以提高传输图像的感知质量。具体来说,我们利用��on模型有效管理传输带宽,根据传输符号的估计熵进行传输。这些符号随后被用作接收器的条件信息,以指导图像重建中的条件扩散解码器。我们的模型建立在新兴的马姆巴式线性注意力(MLLA)骨架之上,该骨架在图像处理任务上表现出色,同时提供快速推理速度。此外,我们引入了一种多阶段训练策略,以确保模型的稳定性并提高其整体性能。仿真结果表明,我们提出的方法在感知质量方面显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习的联合源信道编码(DJSCC)在语义图像传输中具有潜力。
- 现有方案主要关注像素级优化指标,这往往不符合人类感知。
- 提出一种新型生成式DJSCC方法,基于条件扩散模型提高传输图像的感知质量。
- 利用熵模型有效管理传输带宽,根据传输符号的估计熵进行数据传输。
- 模型采用马姆巴式线性注意力(MLLA)骨架,适用于图像处理并具备快速推理能力。
- 引入多阶段训练策略,提高模型稳定性和整体性能。
点此查看论文截图

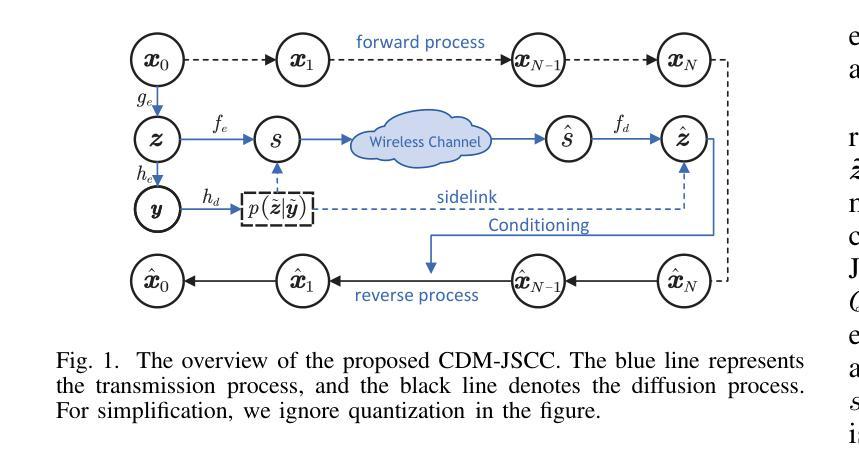
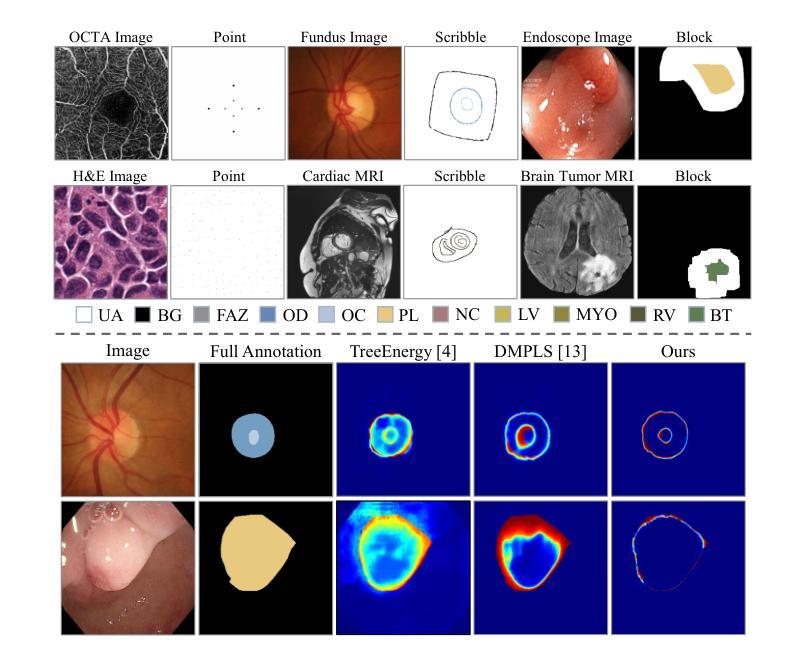
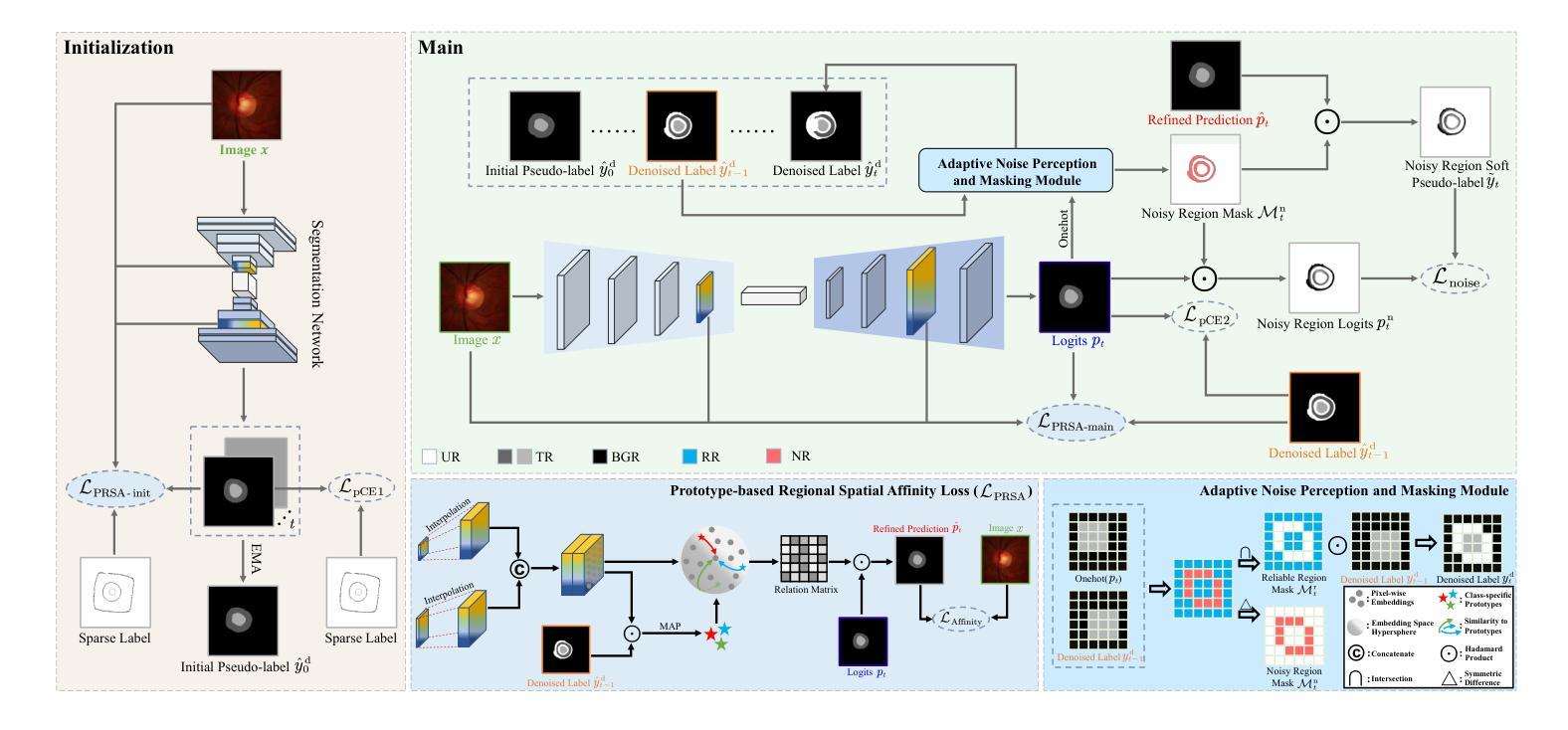
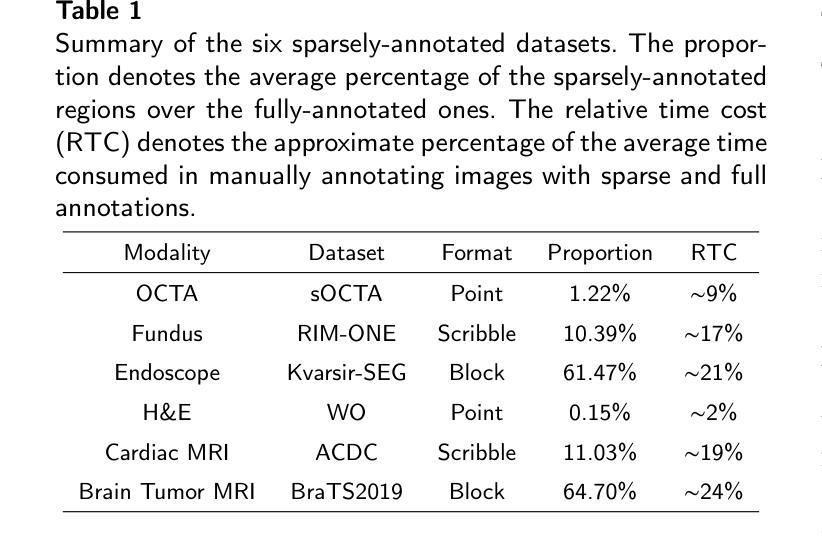
ProCNS: Progressive Prototype Calibration and Noise Suppression for Weakly-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Y. Liu, L. Lin, K. K. Y. Wong, X. Tang
Weakly-supervised segmentation (WSS) has emerged as a solution to mitigate the conflict between annotation cost and model performance by adopting sparse annotation formats (e.g., point, scribble, block, etc.). Typical approaches attempt to exploit anatomy and topology priors to directly expand sparse annotations into pseudo-labels. However, due to a lack of attention to the ambiguous edges in medical images and insufficient exploration of sparse supervision, existing approaches tend to generate erroneous and overconfident pseudo proposals in noisy regions, leading to cumulative model error and performance degradation. In this work, we propose a novel WSS approach, named ProCNS, encompassing two synergistic modules devised with the principles of progressive prototype calibration and noise suppression. Specifically, we design a Prototype-based Regional Spatial Affinity (PRSA) loss to maximize the pair-wise affinities between spatial and semantic elements, providing our model of interest with more reliable guidance. The affinities are derived from the input images and the prototype-refined predictions. Meanwhile, we propose an Adaptive Noise Perception and Masking (ANPM) module to obtain more enriched and representative prototype representations, which adaptively identifies and masks noisy regions within the pseudo proposals, reducing potential erroneous interference during prototype computation. Furthermore, we generate specialized soft pseudo-labels for the noisy regions identified by ANPM, providing supplementary supervision. Extensive experiments on six medical image segmentation tasks involving different modalities demonstrate that the proposed framework significantly outperforms representative state-of-the-art methods.
弱监督分割(WSS)作为一种解决方案,通过采用稀疏注释格式(如点、涂鸦、块等)来缓解注释成本与模型性能之间的冲突。典型的方法试图利用解剖学和拓扑学先验知识来直接将稀疏注释扩展为伪标签。然而,由于医学图像中模糊边缘的忽视以及稀疏监督的不足,现有方法往往会在噪声区域生成错误且过于自信的伪提案,从而导致模型的累积误差和性能下降。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型的WSS方法,名为ProCNS,包含两个协同工作的模块,以渐进原型校准和噪声抑制的原则设计。具体来说,我们设计了一种基于原型的区域空间亲和力(PRSA)损失,以最大化空间元素和语义元素之间的成对亲和力,为我们的目标模型提供更可靠的指导。亲和力来源于输入图像和经过原型优化的预测结果。同时,我们提出了自适应噪声感知和掩蔽(ANPM)模块,以获得更丰富和具有代表性的原型表示,该模块能够自适应地识别和掩蔽伪提案中的噪声区域,减少在原型计算过程中潜在的错误干扰。此外,我们为ANPM识别的噪声区域生成专门的软伪标签,以提供额外的监督。在六个涉及不同模态的医疗图像分割任务上的大量实验表明,所提出的框架显著优于具有代表性的最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像分割中的弱监督学习(WSS)方法存在误差累积和性能下降的问题。为解决此问题,本文提出了一种名为ProCNS的新型WSS方法,包含两个协同模块,基于渐进原型校准和噪声抑制原则。设计了一种基于区域空间亲和力的损失函数PRSA,提高模型可靠性。并提出自适应噪声感知和掩蔽模块ANPM,用于更丰富和代表性的原型表示,减少伪提案中的噪声干扰。在六种医学图像分割任务上的实验表明,该方法显著优于现有先进技术。
Key Takeaways
- 弱监督分割(WSS)是解决标注成本与模型性能冲突的一种解决方案,采用稀疏标注格式(如点、涂鸦、块等)。
- 现有方法倾向于在噪声区域产生错误和过于自信的伪提案,导致模型误差累积和性能下降。
- 本文提出了一种新型WSS方法ProCNS,包含两个协同模块:基于渐进原型校准和噪声抑制。
- 设计了PRSA损失函数,通过最大化空间元素和语义元素之间的配对亲和力,为模型提供更可靠的指导。
- ANPM模块能够自适应地识别和掩盖伪提案中的噪声区域,减少潜在错误干扰。
- ProCNS生成针对ANPM识别的噪声区域的特殊软伪标签,提供额外的监督。
点此查看论文截图