⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-26 更新
Resolution-Robust 3D MRI Reconstruction with 2D Diffusion Priors: Diverse-Resolution Training Outperforms Interpolation
Authors:Anselm Krainovic, Stefan Ruschke, Reinhard Heckel
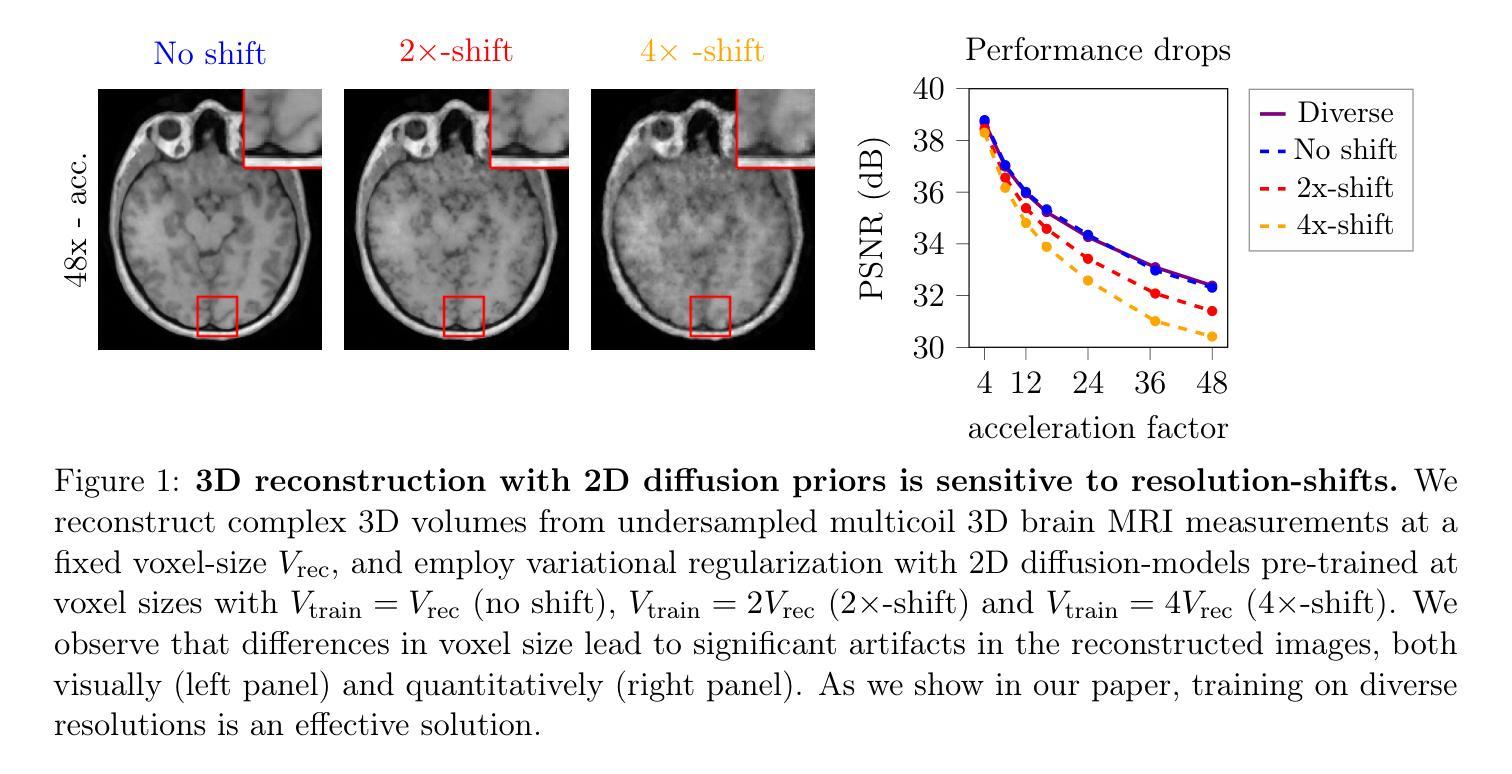
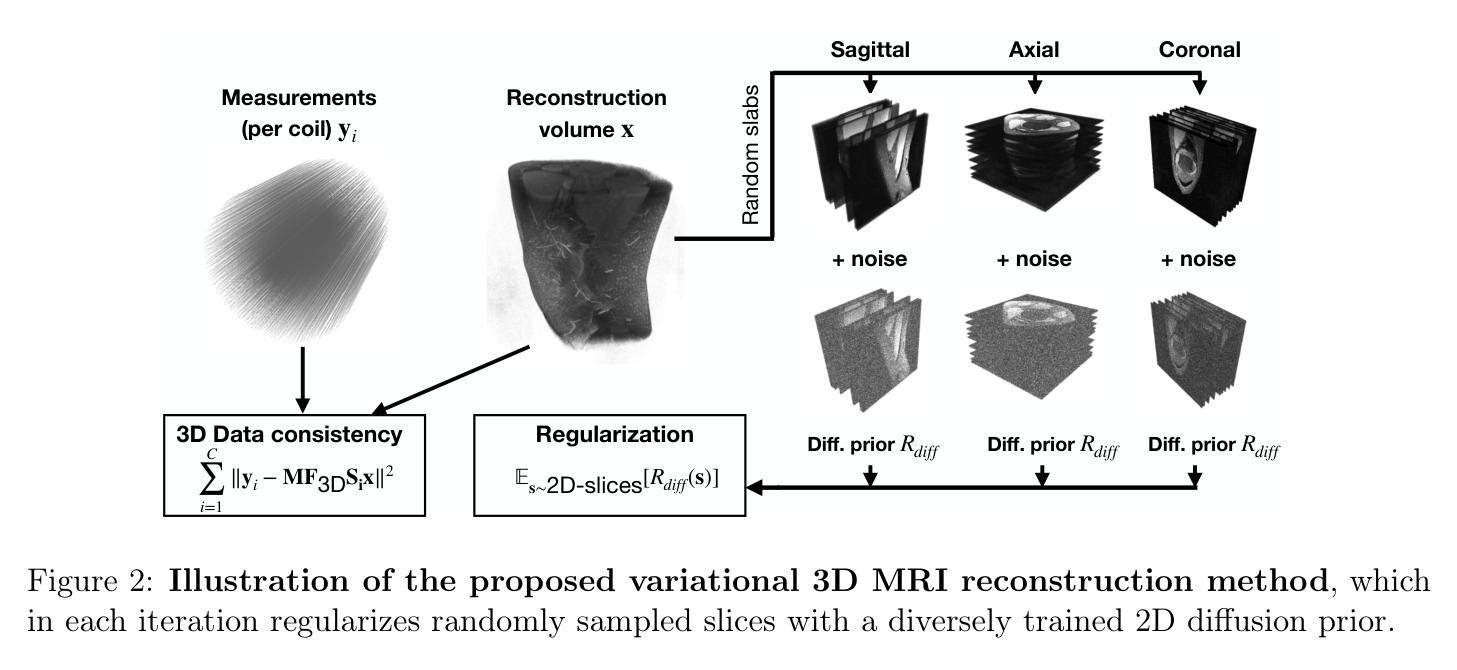
Deep learning-based 3D imaging, in particular magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), is challenging because of limited availability of 3D training data. Therefore, 2D diffusion models trained on 2D slices are starting to be leveraged for 3D MRI reconstruction. However, as we show in this paper, existing methods pertain to a fixed voxel size, and performance degrades when the voxel size is varied, as it is often the case in clinical practice. In this paper, we propose and study several approaches for resolution-robust 3D MRI reconstruction with 2D diffusion priors. As a result of this investigation, we obtain a simple resolution-robust variational 3D reconstruction approach based on diffusion-guided regularization of randomly sampled 2D slices. This method provides competitive reconstruction quality compared to posterior sampling baselines. Towards resolving the sensitivity to resolution-shifts, we investigate state-of-the-art model-based approaches including Gaussian splatting, neural representations, and infinite-dimensional diffusion models, as well as a simple data-centric approach of training the diffusion model on several resolutions. Our experiments demonstrate that the model-based approaches fail to close the performance gap in 3D MRI. In contrast, the data-centric approach of training the diffusion model on various resolutions effectively provides a resolution-robust method without compromising accuracy.
基于深度学习的3D成像,特别是磁共振成像(MRI),由于3D训练数据的有限可用性而面临挑战。因此,开始在2D切片上训练的2D扩散模型被用于3D MRI重建。然而,我们在本文中展示,现有方法涉及固定的体素大小,当体素大小发生变化时,性能会下降,这在临床实践中经常发生。在本文中,我们针对具有2D扩散先验的分辨率鲁棒性3D MRI重建提出了几种方法并进行了研究。通过这项研究,我们获得了一种基于随机采样2D切片的扩散引导正则化的简单分辨率鲁棒性3D重建方法。该方法与后采样基线相比,提供了具有竞争力的重建质量。为了解决对分辨率变化的敏感性,我们调查了最新的基于模型的方法,包括高斯涂抹、神经表征和无限维扩散模型,以及一种简单的以数据为中心的方法,即对扩散模型进行多种分辨率的训练。我们的实验表明,基于模型的方法未能缩小3D MRI的性能差距。相比之下,以数据为中心的训练扩散模型在各种分辨率上的方法有效地提供了一种分辨率鲁棒的方法,而不损害准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习在三维成像,特别是磁共振成像(MRI)中面临3D训练数据有限的问题。因此,人们开始利用二维扩散模型对二维切片进行训练,用于三维MRI重建。然而,本文展示的方法受限于固定的体素大小,当体素大小变化时性能会下降,这在临床实践中是常见的情况。本文提出并研究了几种具有二维扩散先验的分辨率鲁棒三维MRI重建方法。通过调查,我们得到了一种基于扩散引导正则化的简单分辨率鲁棒变分三维重建方法,对随机采样的二维切片进行处理。该方法与采样基线相比具有竞争力。为解决对分辨率变化的敏感性,我们调查了基于模型的方法,包括高斯喷涂、神经表征和无限维扩散模型等,以及一种简单的以数据为中心的训练扩散模型的方法,使用多种分辨率。实验表明,基于模型的方法在3D MRI上未能缩小性能差距。相反,以数据为中心的训练扩散模型的方法在各种分辨率下有效提供了一种分辨率鲁棒的方法,且不损失准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在3D MRI成像中面临训练数据有限的挑战,因此研究者开始使用基于二维扩散模型的三维重建方法。
- 当前方法受限于固定的体素大小,当体素大小变化时性能会下降。
- 本文提出了一种基于扩散引导正则化的分辨率鲁棒的三维MRI重建方法,该方法处理随机采样的二维切片。
- 与采样基线相比,该方法具有竞争力的重建质量。
- 调查了多种模型方法,包括高斯喷涂、神经表征和无限维扩散模型等,但它们在3D MRI上的性能未能达到期望。
- 一种以数据为中心的训练扩散模型的方法在各种分辨率下表现出色,提供了分辨率鲁棒的方法。
点此查看论文截图

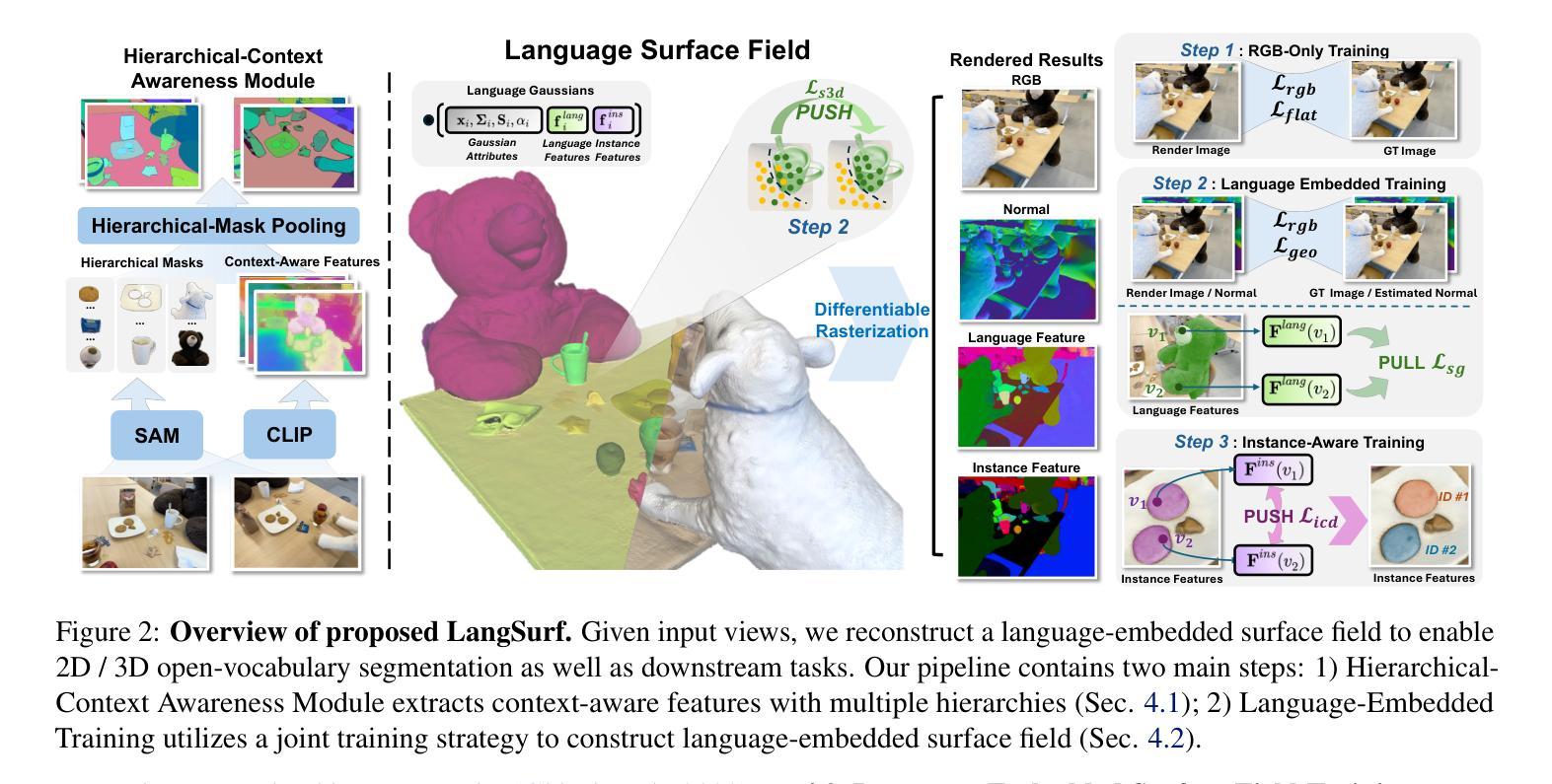
LangSurf: Language-Embedded Surface Gaussians for 3D Scene Understanding
Authors:Hao Li, Roy Qin, Zhengyu Zou, Diqi He, Bohan Li, Bingquan Dai, Dingewn Zhang, Junwei Han
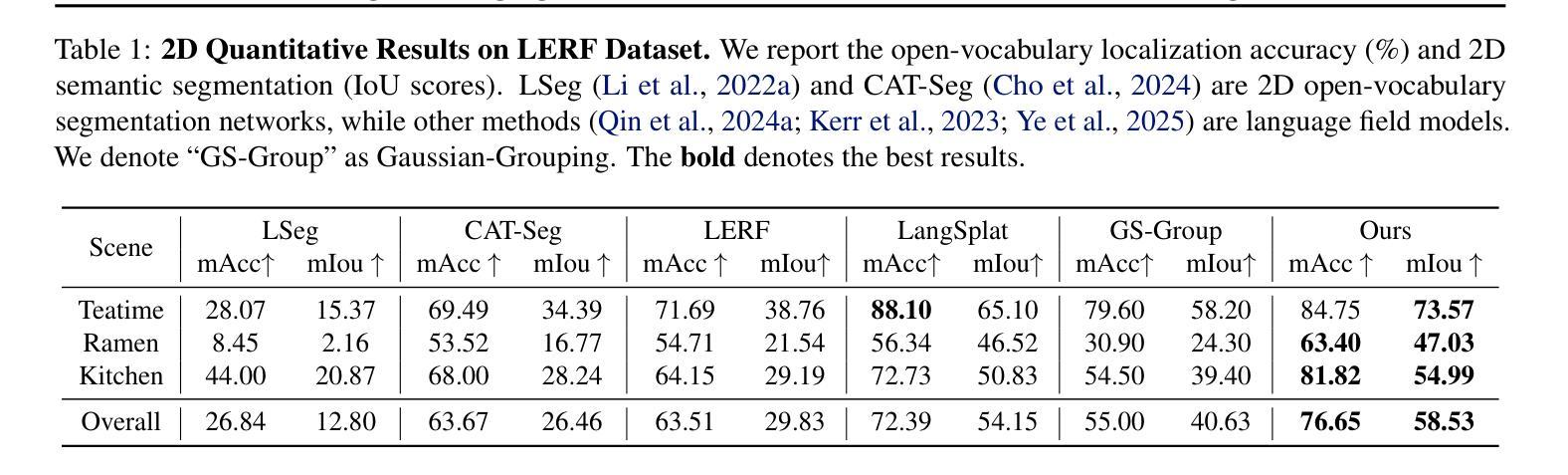
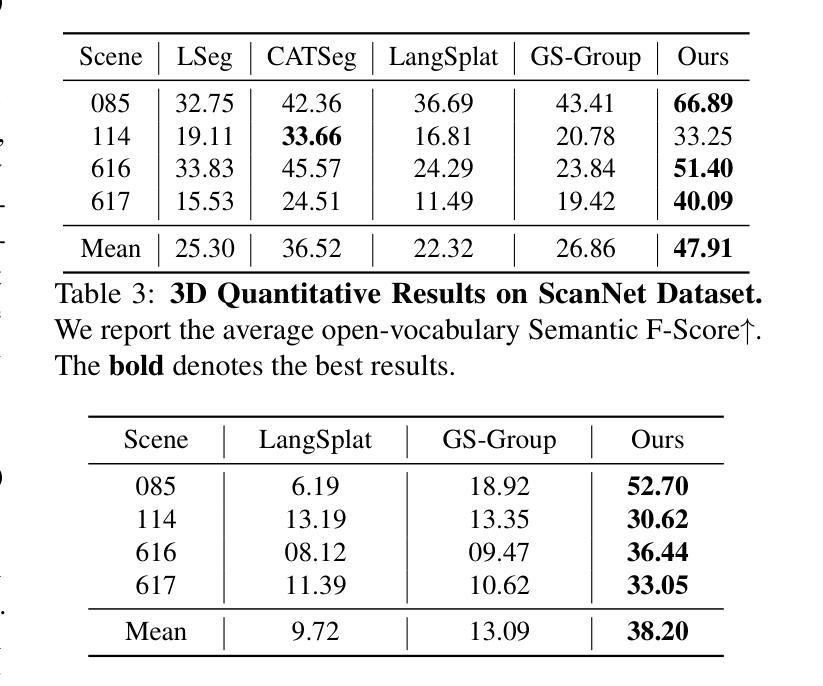
Applying Gaussian Splatting to perception tasks for 3D scene understanding is becoming increasingly popular. Most existing works primarily focus on rendering 2D feature maps from novel viewpoints, which leads to an imprecise 3D language field with outlier languages, ultimately failing to align objects in 3D space. By utilizing masked images for feature extraction, these approaches also lack essential contextual information, leading to inaccurate feature representation. To this end, we propose a Language-Embedded Surface Field (LangSurf), which accurately aligns the 3D language fields with the surface of objects, facilitating precise 2D and 3D segmentation with text query, widely expanding the downstream tasks such as removal and editing. The core of LangSurf is a joint training strategy that flattens the language Gaussian on the object surfaces using geometry supervision and contrastive losses to assign accurate language features to the Gaussians of objects. In addition, we also introduce the Hierarchical-Context Awareness Module to extract features at the image level for contextual information then perform hierarchical mask pooling using masks segmented by SAM to obtain fine-grained language features in different hierarchies. Extensive experiments on open-vocabulary 2D and 3D semantic segmentation demonstrate that LangSurf outperforms the previous state-of-the-art method LangSplat by a large margin. As shown in Fig. 1, our method is capable of segmenting objects in 3D space, thus boosting the effectiveness of our approach in instance recognition, removal, and editing, which is also supported by comprehensive experiments. \url{https://langsurf.github.io}.
将高斯平铺应用于3D场景理解的感知任务越来越受欢迎。现有的大多数工作主要集中在从新的视角渲染2D特征图,这导致了不精确的3D语言字段出现离群值语言,最终无法在3D空间中实现对齐对象。通过利用掩码图像进行特征提取,这些方法还缺乏必要的上下文信息,导致特征表示不准确。为此,我们提出了语言嵌入表面场(LangSurf),它准确地将对齐的3D语言字段与对象的表面相对应,实现了精确的二维和三维分割文本查询,并大大扩展了下流任务,如移除和编辑。LangSurf的核心是一种联合训练策略,它通过几何监督和对比损失将语言高斯平铺在对象表面上,为对象的高斯分配准确的语言特征。此外,我们还引入了层次上下文感知模块,以在图像级别提取特征以获得上下文信息,然后使用SAM分割的掩码进行分层掩码池以获得不同层次上的精细语言特征。在开放词汇二维和三维语义分割方面的广泛实验表明,LangSurf大大超越了以前的最先进方法LangSplat。如图1所示,我们的方法能够在三维空间中分割对象,从而提高了在实例识别、删除和编辑方面的方法的有效性,这也是由综合实验所支持的。网站链接。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF \url{https://langsurf.github.io}
Summary
本文提出一种名为Language-Embedded Surface Field(LangSurf)的方法,用于解决现有方法在三维场景理解中的不足。该方法通过联合训练策略将语言高斯映射在物体表面,并利用几何监督和对比损失来分配准确的语言特征给物体高斯。同时引入层次上下文感知模块,提取图像级别的特征并获取层次化的掩膜池化,以获取不同层次的精细语言特征。实验证明,LangSurf在开放词汇的二维和三维语义分割任务上大幅超越了现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- LangSurf解决了现有方法在3D场景理解中的语言场不准确问题,通过对物体表面的语言高斯映射实现精确对齐。
- 核心的联合训练策略利用几何监督和对比损失为物体高斯分配准确的语言特征。
- 引入层次上下文感知模块,提取图像级别的特征并获取层次化的掩膜池化,以获取不同层次的精细语言特征。
- LangSurf在二维和三维语义分割任务上表现出卓越性能,支持实例识别、移除和编辑等下游任务。
点此查看论文截图


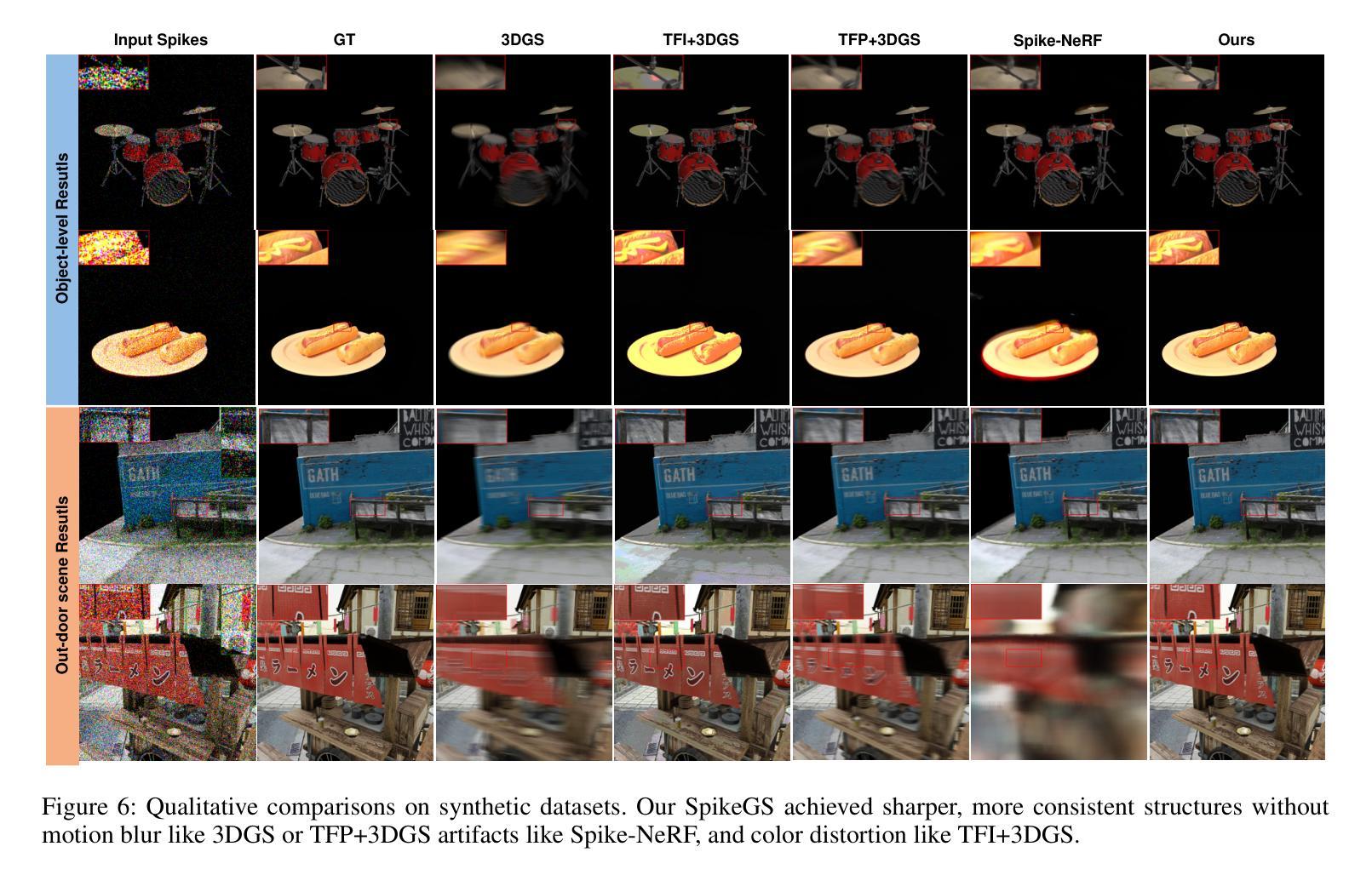
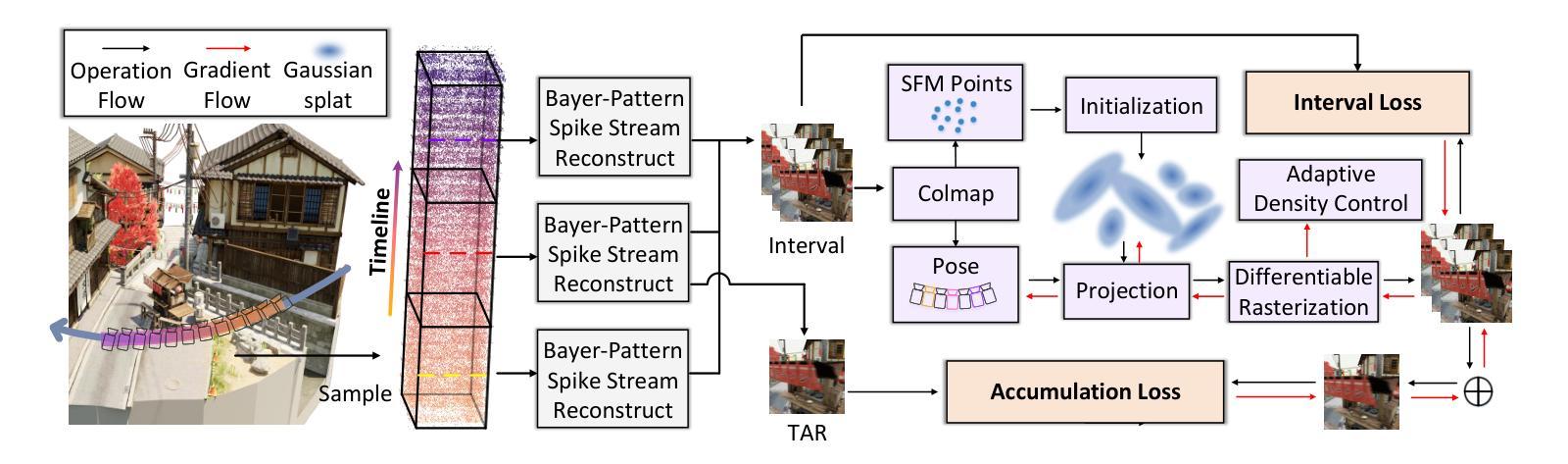
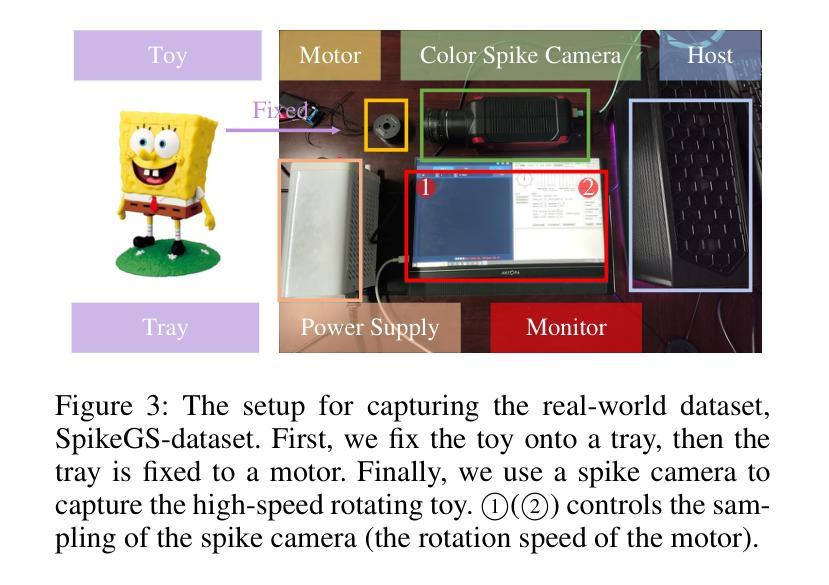
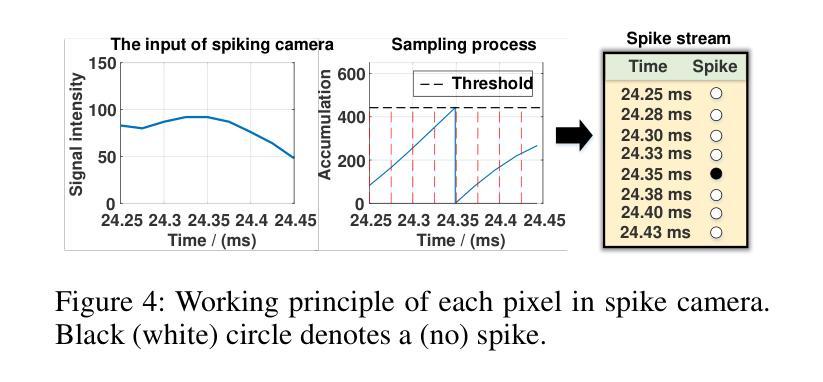
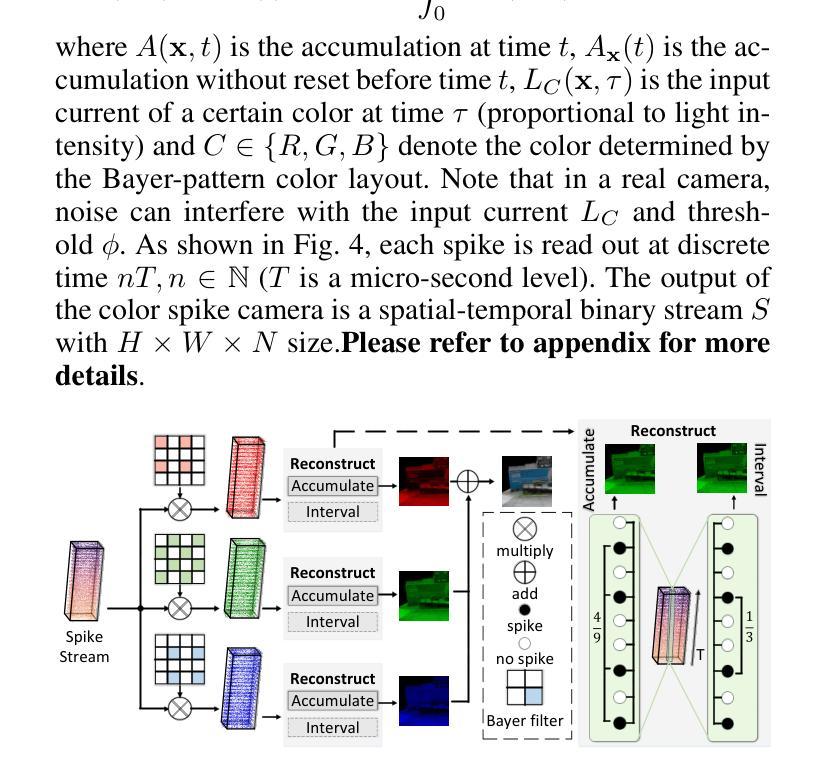
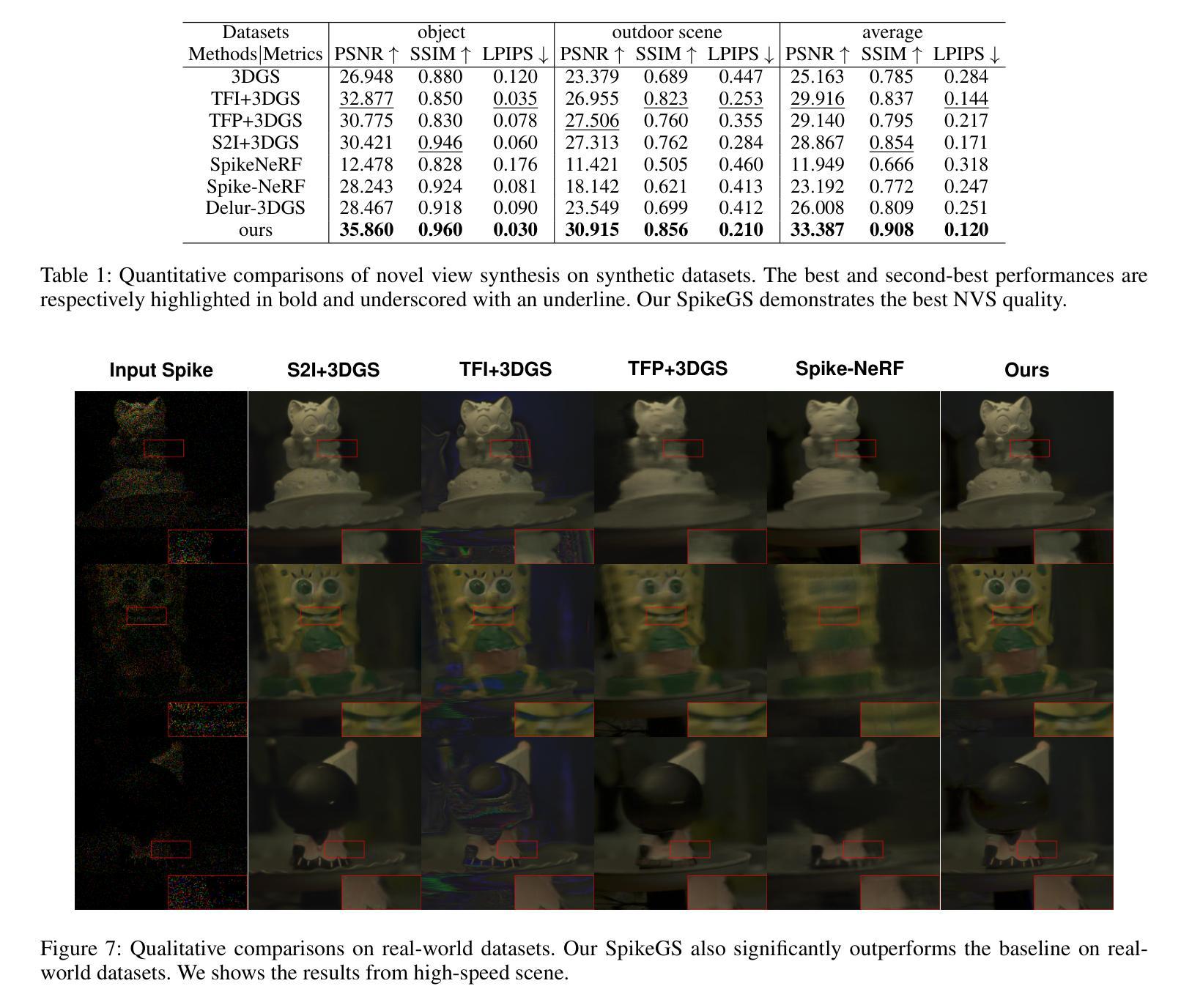
SpikeGS: Reconstruct 3D scene via fast-moving bio-inspired sensors
Authors:Yijia Guo, Liwen Hu, Yuanxi Bai, Jiawei Yao, Lei Ma, Tiejun Huang
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) demonstrates unparalleled superior performance in 3D scene reconstruction. However, 3DGS heavily relies on the sharp images. Fulfilling this requirement can be challenging in real-world scenarios especially when the camera moves fast, which severely limits the application of 3DGS. To address these challenges, we proposed Spike Gausian Splatting (SpikeGS), the first framework that integrates the spike streams into 3DGS pipeline to reconstruct 3D scenes via a fast-moving bio-inspired camera. With accumulation rasterization, interval supervision, and a specially designed pipeline, SpikeGS extracts detailed geometry and texture from high temporal resolution but texture lacking spike stream, reconstructs 3D scenes captured in 1 second. Extensive experiments on multiple synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate the superiority of SpikeGS compared with existing spike-based and deblur 3D scene reconstruction methods. Codes and data will be released soon.
3D高斯融合(3DGS)在3D场景重建中表现出无与伦比的优势性能。然而,3DGS严重依赖于清晰图像。在现实世界场景中,尤其是在相机快速移动时,满足这一要求可能会具有挑战性,从而严重限制了3DGS的应用。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了Spike高斯融合(SpikeGS),这是第一个将脉冲流集成到3DGS管道中的框架,通过快速移动的生物启发相机重建3D场景。通过累积光栅化、间隔监督以及专门设计的管道,SpikeGS从高时间分辨率但纹理缺失的脉冲流中提取详细的几何和纹理信息,可以在1秒内重建捕获的3D场景。在多个合成和真实数据集上的大量实验表明,与现有的基于脉冲和去模糊的3D场景重建方法相比,SpikeGS具有优越性。代码和数据将很快发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI2025
Summary
在复杂的3D重建中,针对由于高速运动导致的成像质量不佳问题,提出了一种名为Spike Gaussian Splatting(SpikeGS)的新框架。SpikeGS结合了脉冲流技术,通过积累渲染、间隔监督以及特殊设计的管道,能够从高时间分辨率但纹理不足的脉冲流中提取详细的几何和纹理信息,并快速重建三维场景。经过大量的实验验证,SpikeGS在各种合成和实际数据集上的表现优于其他基于脉冲的去模糊和三维重建方法。此技术的推出将对相关应用产生重大影响。代码和数据集将很快发布。
Key Takeaways
- Spike Gaussian Splatting(SpikeGS)框架解决了传统3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)在高速运动相机拍摄时面临的挑战。
- SpikeGS结合了脉冲流技术,提高了从高时间分辨率但纹理不足的图像中提取详细几何和纹理信息的能力。
- SpikeGS利用积累渲染和间隔监督技术,能够从短暂的图像中获取足够的细节来重建三维场景。
- SpikeGS的特殊设计管道能够应对快速拍摄下的三维重建任务,展现出优越的性能。
点此查看论文截图