⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-26 更新
Decentralized Intelligence in GameFi: Embodied AI Agents and the Convergence of DeFi and Virtual Ecosystems
Authors:Fernando Jia, Jade Zheng, Florence Li
In the rapidly evolving landscape of GameFi, a fusion of gaming and decentralized finance (DeFi), there exists a critical need to enhance player engagement and economic interaction within gaming ecosystems. Our GameFi ecosystem aims to fundamentally transform this landscape by integrating advanced embodied AI agents into GameFi platforms. These AI agents, developed using cutting-edge large language models (LLMs), such as GPT-4 and Claude AI, are capable of proactive, adaptive, and contextually rich interactions with players. By going beyond traditional scripted responses, these agents become integral participants in the game’s narrative and economic systems, directly influencing player strategies and in-game economies. We address the limitations of current GameFi platforms, which often lack immersive AI interactions and mechanisms for community engagement or creator monetization. Through the deep integration of AI agents with blockchain technology, we establish a consensus-driven, decentralized GameFi ecosystem. This ecosystem empowers creators to monetize their contributions and fosters democratic collaboration among players and creators. Furthermore, by embedding DeFi mechanisms into the gaming experience, we enhance economic participation and provide new opportunities for financial interactions within the game. Our approach enhances player immersion and retention and advances the GameFi ecosystem by bridging traditional gaming with Web3 technologies. By integrating sophisticated AI and DeFi elements, we contribute to the development of more engaging, economically robust, and community-centric gaming environments. This project represents a significant advancement in the state-of-the-art in GameFi, offering insights and methodologies that can be applied throughout the gaming industry.
在游戏与去中心化金融(DeFi)的融合体GameFi迅速发展的背景下,增强玩家在游戏生态系统中的参与度和经济互动显得尤为重要。我们的GameFi生态系统旨在通过把先进的嵌入式AI代理整合到GameFi平台,从根本上改变这一现状。这些使用最前沿的大型语言模型(如GPT-4和Claude AI)开发的AI代理,具备与玩家进行积极主动、自适应和语境丰富的交互能力。这些代理超越了传统的脚本响应,成为游戏叙事和经济系统的不可或缺的一部分,直接影响玩家的策略和游戏内经济。我们解决了当前GameFi平台的局限性,这些平台通常缺乏沉浸式的AI交互和社区参与或创作者盈利的机制。通过AI代理与区块链技术的深度整合,我们建立了一个去中心化的GameFi生态系统,以共识驱动。这个生态系统让创作者能够盈利,并促进玩家和创作者之间的民主合作。此外,通过将DeFi机制嵌入到游戏体验中,我们增强了经济参与度,并为游戏内的金融互动提供了新的机会。我们的方法提高了玩家的沉浸感和留存率,并通过桥接传统游戏和Web3技术,推动了GameFi生态系统的发展。通过整合先进的AI和DeFi元素,我们致力于开发更具吸引力、经济稳健和以社区为中心的游戏环境。这个项目代表了GameFi领域的最新进展,提供了可应用于整个游戏行业的见解和方法论。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 4 figures
Summary
游戏金融(GameFi)领域正经历快速演化,融合游戏与去中心化金融(DeFi)的需求愈发迫切。该项目通过整合先进的智能体AI技术到GameFi平台来实现根本性的变革。AI智能体不仅能进行主动、自适应的丰富互动,还能融入游戏叙事和经济系统,直接影响玩家策略与游戏经济。项目解决了当前GameFi平台缺乏沉浸式AI交互和社区参与机制的痛点。通过深度整合AI智能体与区块链技术,我们构建了一个共识驱动的去中心化GameFi生态系统,让创作者能从中获利并促进玩家与创作者之间的民主合作。此项目为GameFi领域的最前沿技术提供了见解和方法论,对整个游戏产业具有广泛的应用价值。
Key Takeaways
- GameFi领域正经历快速演化,需要增强玩家参与和与游戏经济系统的互动。
- 通过集成先进的智能体AI技术,我们的GameFi生态系统可实现更丰富的玩家互动体验。
- AI智能体能融入游戏叙事和经济系统,直接影响玩家策略和游戏经济。
- 项目解决了当前GameFi平台的局限性,包括缺乏沉浸式AI交互和社区参与机制。
- 通过整合AI智能体与区块链技术,建立了一个共识驱动的去中心化GameFi生态系统。
- 该生态系统促进创作者从中获利并加强玩家与创作者之间的民主合作。
点此查看论文截图

GeAR: Graph-enhanced Agent for Retrieval-augmented Generation
Authors:Zhili Shen, Chenxin Diao, Pavlos Vougiouklis, Pascual Merita, Shriram Piramanayagam, Damien Graux, Dandan Tu, Zeren Jiang, Ruofei Lai, Yang Ren, Jeff Z. Pan
Retrieval-augmented generation systems rely on effective document retrieval capabilities. By design, conventional sparse or dense retrievers face challenges in multi-hop retrieval scenarios. In this paper, we present GeAR, which advances RAG performance through two key innovations: (i) graph expansion, which enhances any conventional base retriever, such as BM25, and (ii) an agent framework that incorporates graph expansion. Our evaluation demonstrates GeAR’s superior retrieval performance on three multi-hop question answering datasets. Additionally, our system achieves state-of-the-art results with improvements exceeding 10% on the challenging MuSiQue dataset, while requiring fewer tokens and iterations compared to other multi-step retrieval systems.
检索增强生成系统依赖于有效的文档检索能力。传统稀疏或密集检索器在设计上在多跳检索场景中面临挑战。在本文中,我们提出了GeAR,它通过两个关键创新提高了RAG的性能:(i)图扩展,它可以增强任何传统的基本检索器,如BM25;(ii)一个结合了图扩展的代理框架。我们的评估表明,GeAR在三个多跳问答数据集上的检索性能优越。此外,我们的系统在具有挑战性的MuSiQue数据集上的改进超过了10%,与其他多步检索系统相比,需要的令牌和迭代次数更少。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了GeAR系统,它通过两个关键创新点提高了检索增强生成系统(RAG)的性能:一是图扩展技术,可增强传统基础检索器(如BM25)的能力;二是引入图扩展的代理框架。评估结果表明,GeAR在三个多跳问答数据集上的检索性能卓越,并在具有挑战性的MuSiQue数据集上实现了超过其他多步检索系统10%的改进,同时减少了令牌和迭代次数。
Key Takeaways
- GeAR系统通过图扩展技术增强了检索增强生成系统(RAG)的性能。
- GeAR可以增强的传统基础检索器如BM25。
- GeAR引入了一个代理框架来应用图扩展技术。
- 在三个多跳问答数据集上,GeAR的检索性能表现卓越。
- GeAR在MuSiQue数据集上的性能超过了其他多步检索系统,改进超过10%。
- GeAR系统相比其他多步检索系统使用的令牌和迭代次数更少。
点此查看论文截图


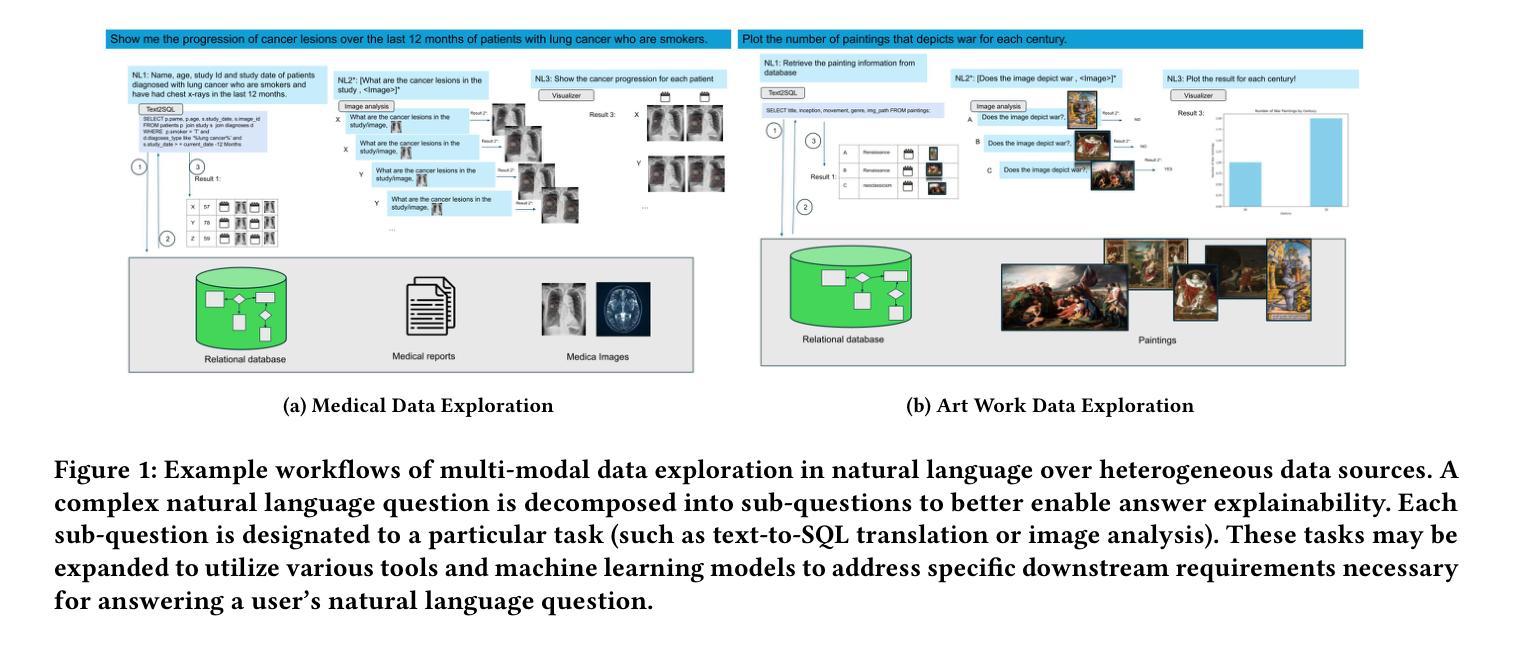
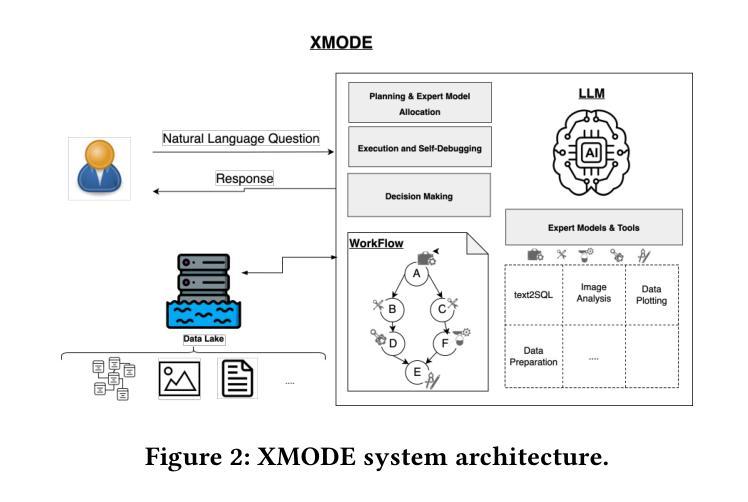
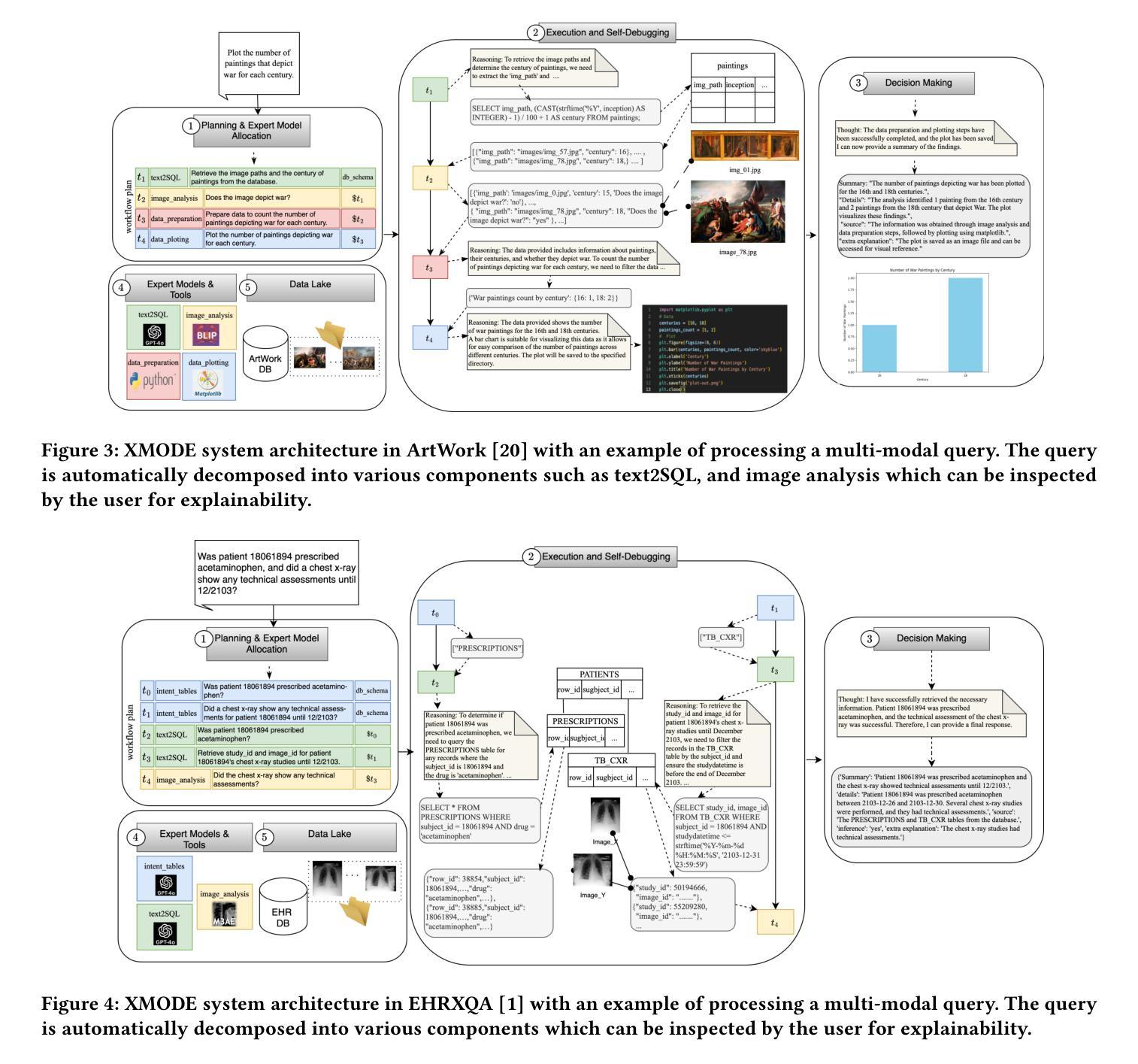
Explainable Multi-Modal Data Exploration in Natural Language via LLM Agent
Authors:Farhad Nooralahzadeh, Yi Zhang, Jonathan Furst, Kurt Stockinger
International enterprises, organizations, or hospitals collect large amounts of multi-modal data stored in databases, text documents, images, and videos. While there has been recent progress in the separate fields of multi-modal data exploration as well as in database systems that automatically translate natural language questions to database query languages, the research challenge of querying database systems combined with other unstructured modalities such as images in natural language is widely unexplored. In this paper, we propose XMODE - a system that enables explainable, multi-modal data exploration in natural language. Our approach is based on the following research contributions: (1) Our system is inspired by a real-world use case that enables users to explore multi-modal information systems. (2) XMODE leverages a LLM-based agentic AI framework to decompose a natural language question into subtasks such as text-to-SQL generation and image analysis. (3) Experimental results on multi-modal datasets over relational data and images demonstrate that our system outperforms state-of-the-art multi-modal exploration systems, excelling not only in accuracy but also in various performance metrics such as query latency, API costs, planning efficiency, and explanation quality, thanks to the more effective utilization of the reasoning capabilities of LLMs.
国际企业、组织或医院收集大量多模式数据,存储在数据库、文本文档、图像和视频中。虽然最近在多模式数据探索领域以及能够自动将自然语言问题翻译成数据库查询语言的数据库系统领域已经取得了进展,但将数据库系统与图像等其它非结构化模态结合,以自然语言进行查询的研究挑战仍然鲜有人探索。在本文中,我们提出了XMODE系统,该系统可实现可解释的多模式数据自然语言探索。我们的方法基于以下研究贡献:(1)我们的系统受到真实世界用例的启发,使用户能够探索多模式信息系统。(2)XMODE利用基于大型语言模型(LLM)的智能代理框架,将自然语言问题分解为文本到SQL生成和图像分析等子任务。(3)在关系数据和图像上的多模式数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的系统优于最新的多模式探索系统,不仅在准确性上表现出色,而且在查询延迟、API成本、规划效率和解释质量等各种性能指标上也表现出色,这得益于大型语言模型推理能力的有效利用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多模态数据查询的挑战在于如何结合数据库系统和自然语言进行查询。本文提出了一种名为XMODE的系统,该系统可解释多模态数据探索的自然语言。该系统利用基于大型语言模型的代理人工智能框架分解自然语言问题,如文本到SQL的生成和图像分析等子任务。实验结果表明,该系统在关系数据和图像的多模态数据集上的性能优于最新的多模态探索系统,不仅在准确性上表现出色,而且在查询延迟、API成本、规划效率和解释质量等性能指标上也有显著提高。
Key Takeaways
- 国际企业或组织大量收集多模态数据存储在数据库、文本文档、图像和视频中。
- 多模态数据查询结合数据库系统和自然语言的查询挑战尚未得到充分研究。
- 本文提出了XMODE系统,一个可解释的多模态数据探索的自然语言系统。
- XMODE系统受到实际使用案例的启发,使用户能够探索多模态信息系统。
- XMODE利用基于大型语言模型的代理人工智能框架来分解自然语言问题。
- 实验结果表明,XMODE系统在多模态数据集上的性能优于其他系统,在准确性、查询延迟、API成本、规划效率和解释质量等方面都有显著提高。
点此查看论文截图

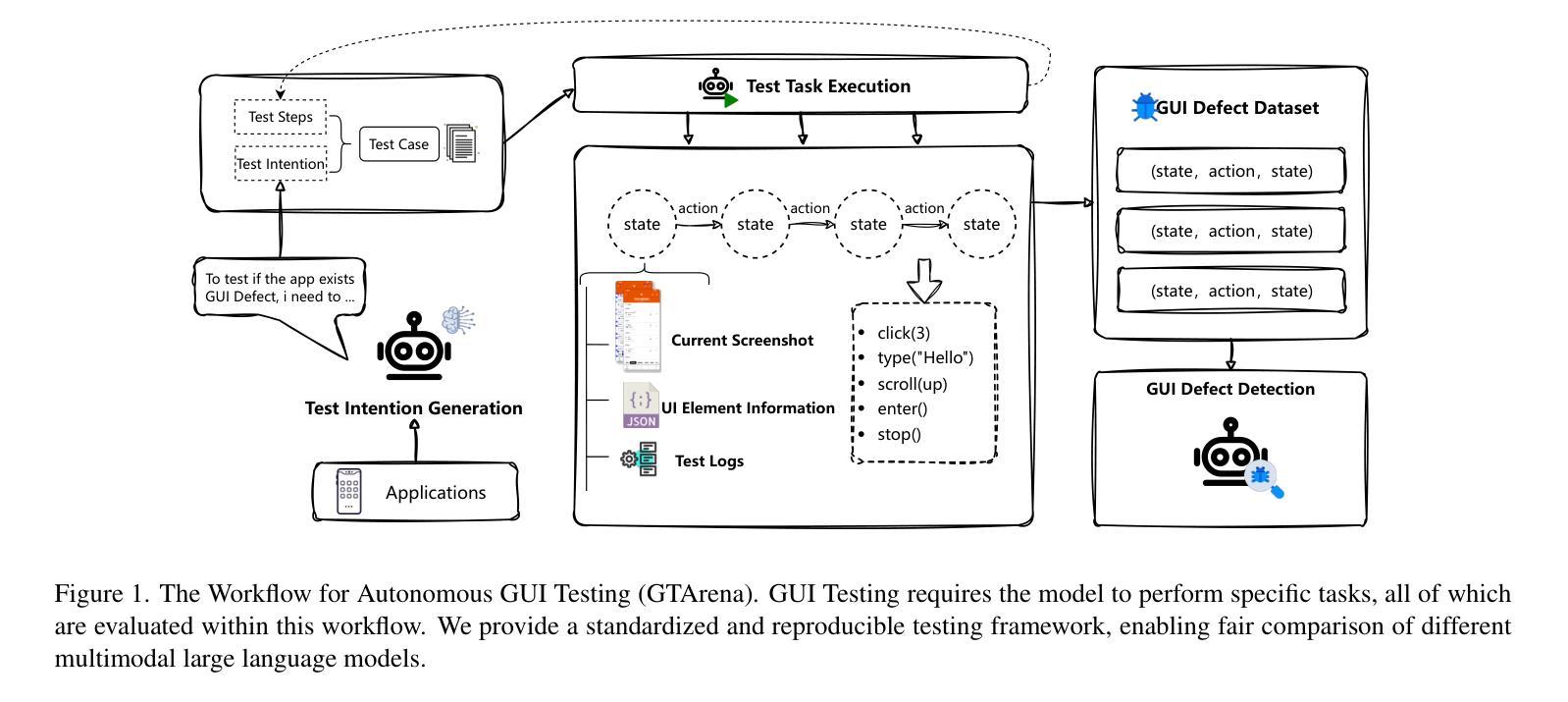
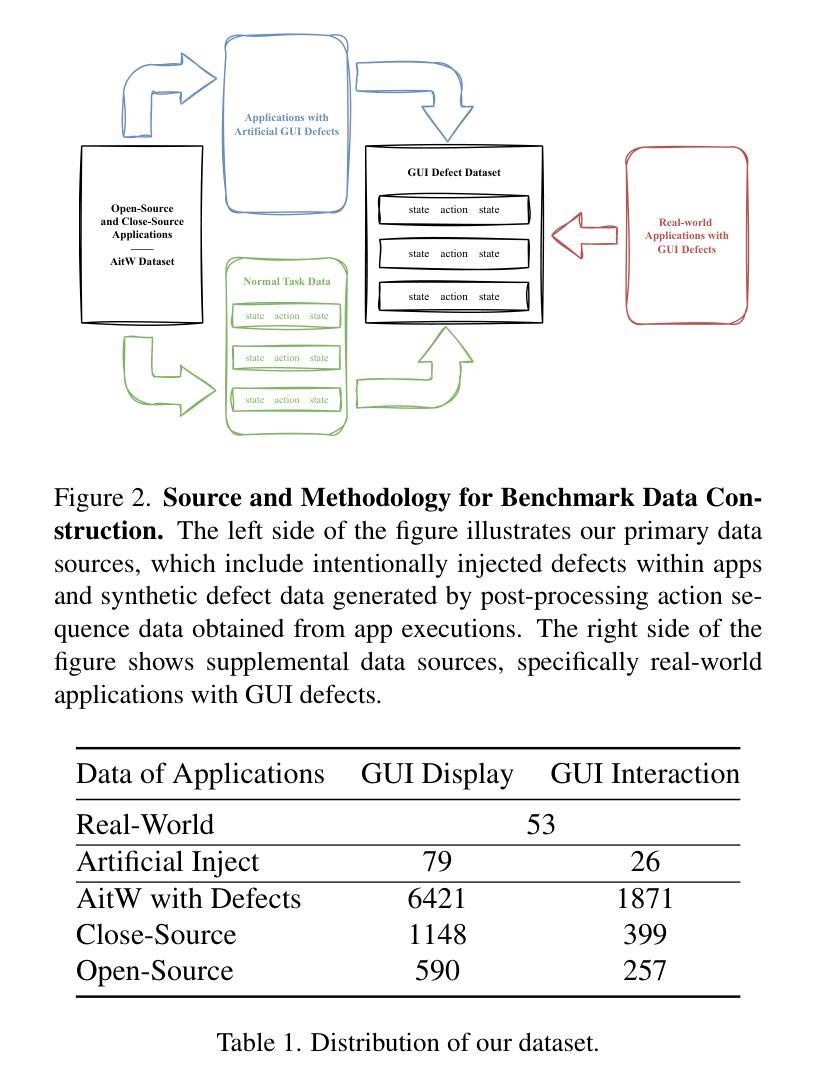
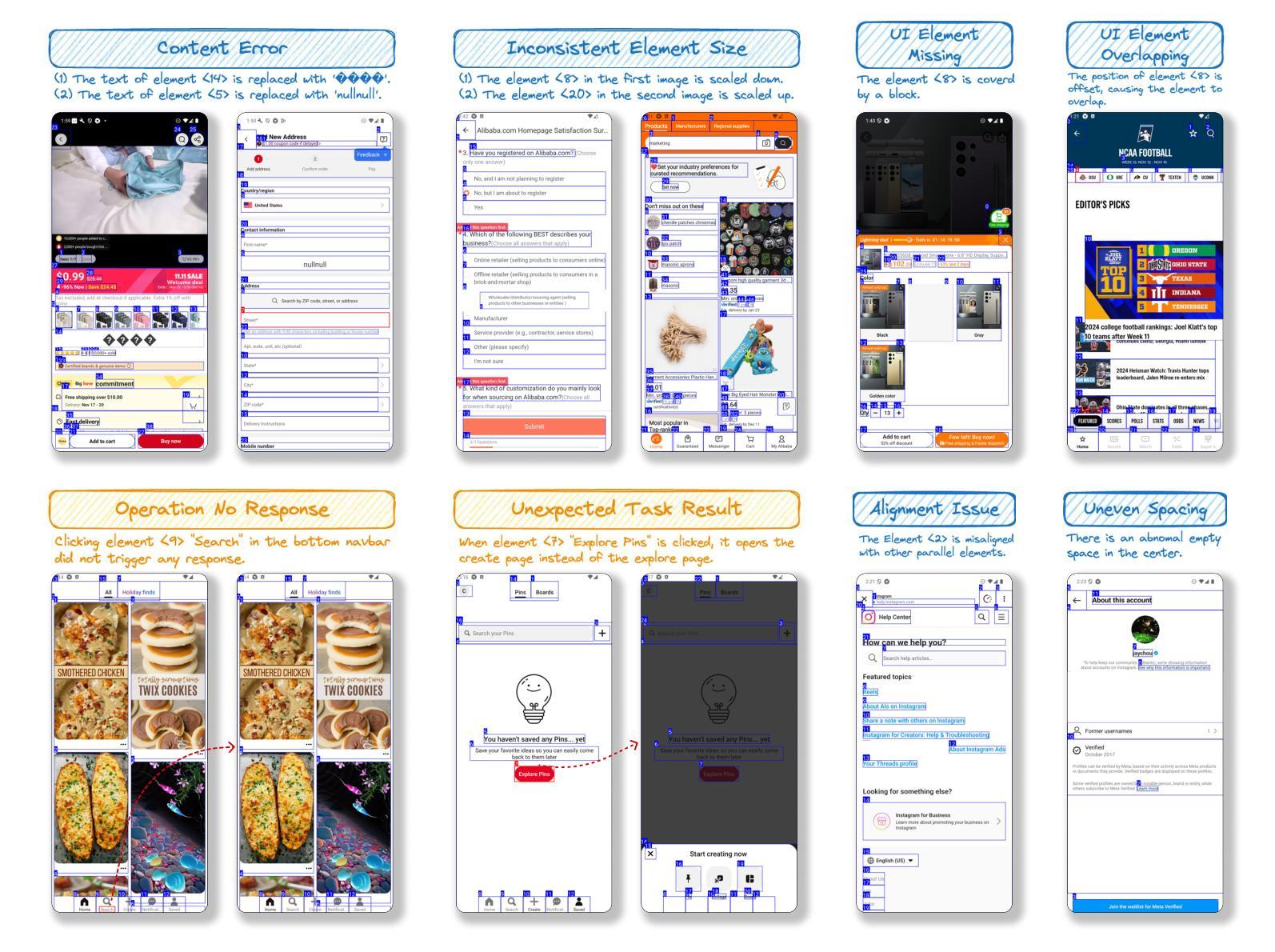
GUI Testing Arena: A Unified Benchmark for Advancing Autonomous GUI Testing Agent
Authors:Kangjia Zhao, Jiahui Song, Leigang Sha, Haozhan Shen, Zhi Chen, Tiancheng Zhao, Xiubo Liang, Jianwei Yin
Nowadays, research on GUI agents is a hot topic in the AI community. However, current research focuses on GUI task automation, limiting the scope of applications in various GUI scenarios. In this paper, we propose a formalized and comprehensive environment to evaluate the entire process of automated GUI Testing (GTArena), offering a fair, standardized environment for consistent operation of diverse multimodal large language models. We divide the testing process into three key subtasks: test intention generation, test task execution, and GUI defect detection, and construct a benchmark dataset based on these to conduct a comprehensive evaluation. It evaluates the performance of different models using three data types: real mobile applications, mobile applications with artificially injected defects, and synthetic data, thoroughly assessing their capabilities in this relevant task. Additionally, we propose a method that helps researchers explore the correlation between the performance of multimodal language large models in specific scenarios and their general capabilities in standard benchmark tests. Experimental results indicate that even the most advanced models struggle to perform well across all sub-tasks of automated GUI Testing, highlighting a significant gap between the current capabilities of Autonomous GUI Testing and its practical, real-world applicability. This gap provides guidance for the future direction of GUI Agent development. Our code is available at https://github.com/ZJU-ACES-ISE/ChatUITest.
如今,对GUI代理的研究是人工智能社区中的热门话题。然而,当前的研究主要集中在GUI任务自动化上,这限制了其在各种GUI场景中的应用范围。在本文中,我们提出了一个形式化且全面的环境,以评估自动化GUI测试(GTArena)的整个流程,为多种模态大型语言模型的持续操作提供了一个公平、标准化的环境。我们将测试过程分为三大关键子任务:测试意图生成、测试任务执行和GUI缺陷检测,并基于这些构建了基准数据集来进行全面评估。它使用三种数据类型评估不同模型的表现:真实移动应用程序、人工注入缺陷的移动应用程序和合成数据,彻底评估了它们在相关任务中的能力。此外,我们提出了一种方法,帮助研究人员探索特定场景中多模态语言大型模型的表现与其在标准基准测试中的通用能力之间的相关性。实验结果表明,即使在最先进的模型中,也很难在所有自动化GUI测试的子任务中表现出色,这突显了当前自主GUI测试的能力与其实际现实世界应用之间的显著差距。这一差距为GUI代理未来的发展方向提供了指导。我们的代码可在https://github.com/ZJU-ACES-ISE/ChatUITest上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
自动化图形用户界面(GUI)测试是当前人工智能社区的研究热点。然而,当前的研究主要集中在GUI任务自动化上,限制了在不同GUI场景中的应用范围。本文提出了一种形式化、全面的环境来评估自动化GUI测试的全过程(GTArena),为各种多模态大型语言模型的持续运行提供了一个公平、标准化的环境。我们将测试过程分为测试意图生成、测试任务执行和GUI缺陷检测三个关键子任务,并基于这些构建了基准数据集进行综合评估。评估使用了真实移动应用程序、人工注入缺陷的移动应用程序和合成数据三种数据类型,全面评估了不同模型在此任务中的性能。本文还提出了一种方法,帮助研究人员探索特定场景中多模态语言大型模型性能与其在标准基准测试中的通用能力之间的相关性。实验结果表明,最先进的模型在自动化GUI测试的所有子任务中都表现得不够出色,突显出自主GUI测试的当前能力与实际应用之间的巨大差距,这为GUI代理的未来发展方向提供了指导。
Key Takeaways
- 当前研究集中在GUI任务自动化上,限制了其在不同GUI场景中的应用范围。
- 提出了一种新的自动化GUI测试环境(GTArena),包含测试意图生成、测试任务执行和GUI缺陷检测三个关键子任务。
- 构建了一个基准数据集,用于全面评估不同模型在自动化GUI测试中的性能。
- 评估使用了真实移动应用程序、人工注入缺陷的移动应用程序和合成数据三种数据类型。
- 提出了一种方法,探索多模态语言大型模型在特定场景中的性能与其在标准基准测试中的通用能力之间的相关性。
- 实验结果表明,最先进的模型在自动化GUI测试的所有子任务中都存在不足,突显出现有技术与实际应用之间的巨大差距。
点此查看论文截图


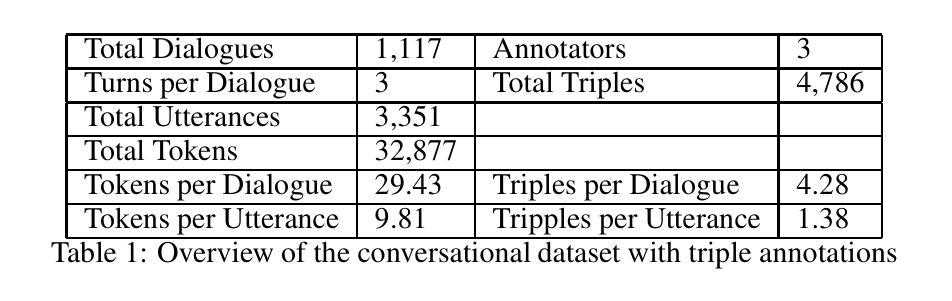
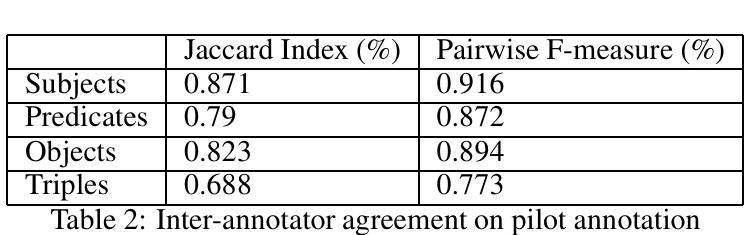
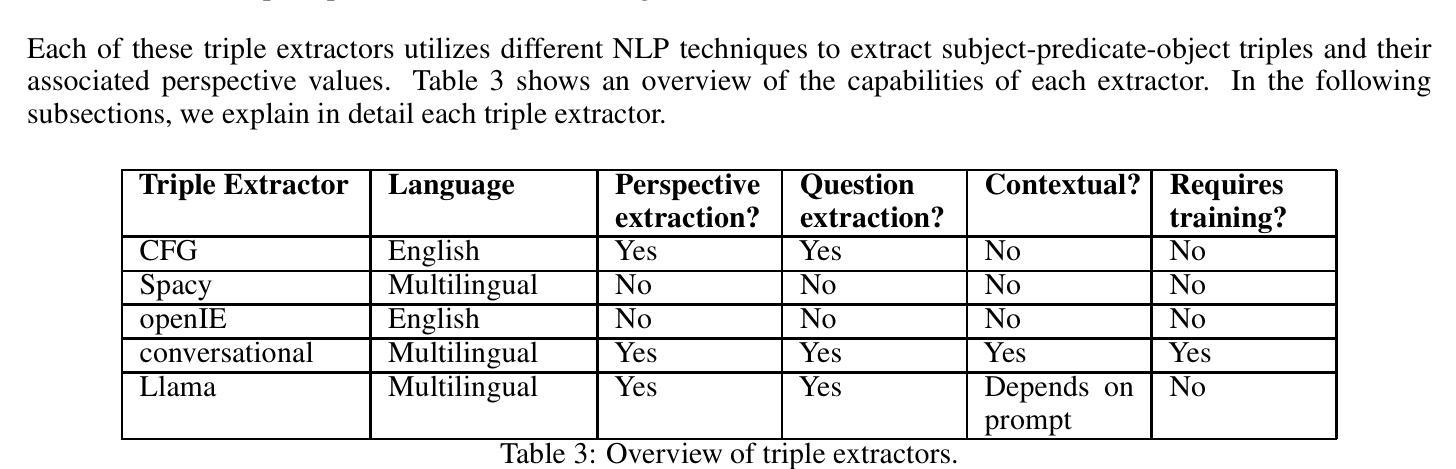
Extracting triples from dialogues for conversational social agents
Authors:Piek Vossen, Selene Báez Santamaría, Lenka Bajčetić, Thomas Belluci
Obtaining an explicit understanding of communication within a Hybrid Intelligence collaboration is essential to create controllable and transparent agents. In this paper, we describe a number of Natural Language Understanding models that extract explicit symbolic triples from social conversation. Triple extraction has mostly been developed and tested for Knowledge Base Completion using Wikipedia text and data for training and testing. However, social conversation is very different as a genre in which interlocutors exchange information in sequences of utterances that involve statements, questions, and answers. Phenomena such as co-reference, ellipsis, coordination, and implicit and explicit negation or confirmation are more prominent in conversation than in Wikipedia text. We therefore describe an attempt to fill this gap by releasing data sets for training and testing triple extraction from social conversation. We also created five triple extraction models and tested them in our evaluation data. The highest precision is 51.14 for complete triples and 69.32 for triple elements when tested on single utterances. However, scores for conversational triples that span multiple turns are much lower, showing that extracting knowledge from true conversational data is much more challenging.
在混合智能协作中明确理解通信对于创建可控和透明的智能体至关重要。在本文中,我们描述了多个自然语言理解模型,这些模型可以从社会对话中提取明确的符号三元组。三元组提取主要被开发和测试用于知识库补全,使用维基百科文本和数据进行训练和测试。然而,社会对话作为一种类型是非常不同的,对话者在连续的语句中交流信息,这些语句涉及陈述、问题和答案。诸如共指、省略、协调以及隐性和显性否定或确认等语言现象在对话中比在维基百科文本中更为突出。因此,我们试图通过发布用于从社会对话中训练和测试三元组提取的数据集来填补这一空白。我们还创建了五个三元组提取模型并在我们的评估数据中对它们进行了测试。在单个话语中进行测试时,完整三元组的最高精度为51.14,三元组元素的最高精度为69.32。但是,跨越多个回合的对话三元组的分数要低得多,这表明从真正的对话数据中提取知识更具挑战性。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
在Hybrid Intelligence协作中获取明确沟通理解对于创建可控和透明的智能体至关重要。本文介绍了多种自然语言理解模型,这些模型可从社会对话中提取明确的符号三元组。虽然三元组提取主要被开发并测试用于知识库补全,使用维基百科文本和数据进行训练和测试,但社会对话作为一种体裁,在对话过程中涉及声明、提问和回答等一系列言语交流方式有很大不同。因此在对话中更常见某些现象,如共指、省略、协调以及隐式和显式否定或确认等。本文尝试填补这一空白,通过发布用于训练和测试从社会对话中提取三元组的数据集。同时创建了五个三元组提取模型并在评估数据中进行测试。在单轮对话测试中,完整三元组的最高精度为51.14%,三元组元素的精度为69.32%,但跨多轮对话的三元组分数要低得多,表明从真正的对话数据中提取知识更具挑战性。
关键见解
- 理解和分析Hybrid Intelligence协作中的沟通对于创建可控和透明的智能体至关重要。
- 三元组提取模型在社会对话中的应用仍存在挑战,需要针对对话的特性进行优化。
- 社会对话与维基百科文本在语言和结构上存在显著差异,这对三元组提取提出了更高的挑战。
- 共指、省略、协调以及隐式和显式否定或确认等语言现象在社会对话中更为常见。
- 数据集的发布对于训练和测试从社会对话中提取三元组的模型至关重要。
- 在单轮对话测试中,三元组提取模型的精度有待提高,特别是在跨多轮对话的情境中。
- 从真正的对话数据中提取知识比从静态文本中提取更具挑战性。
点此查看论文截图

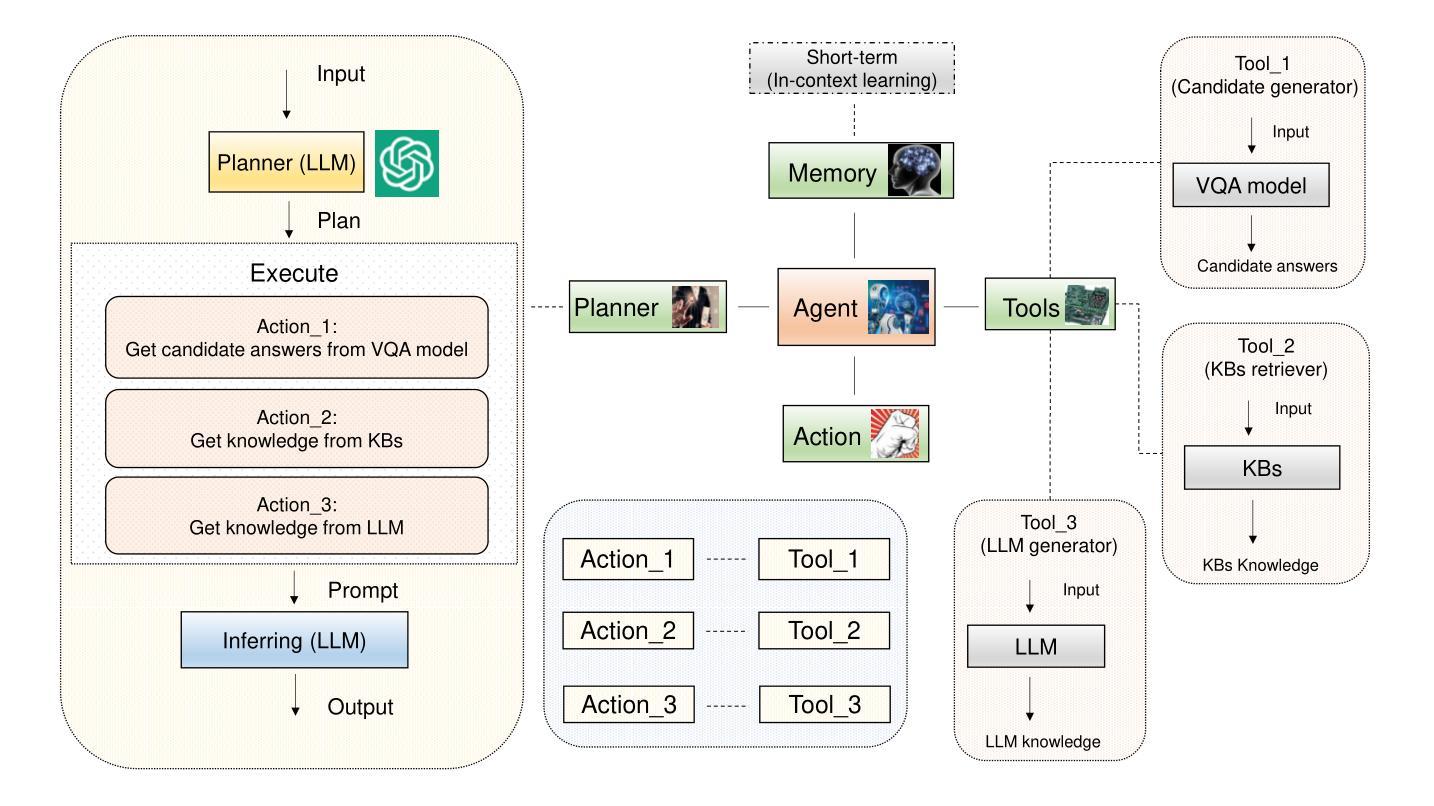
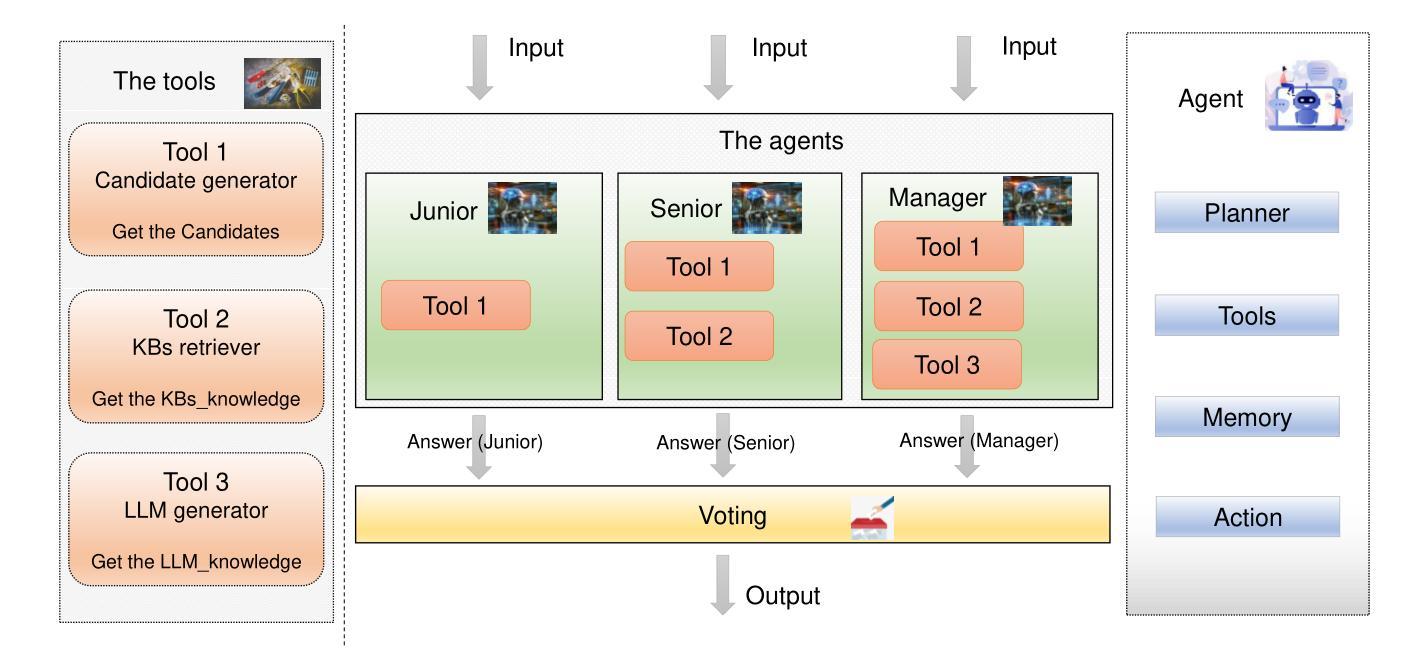
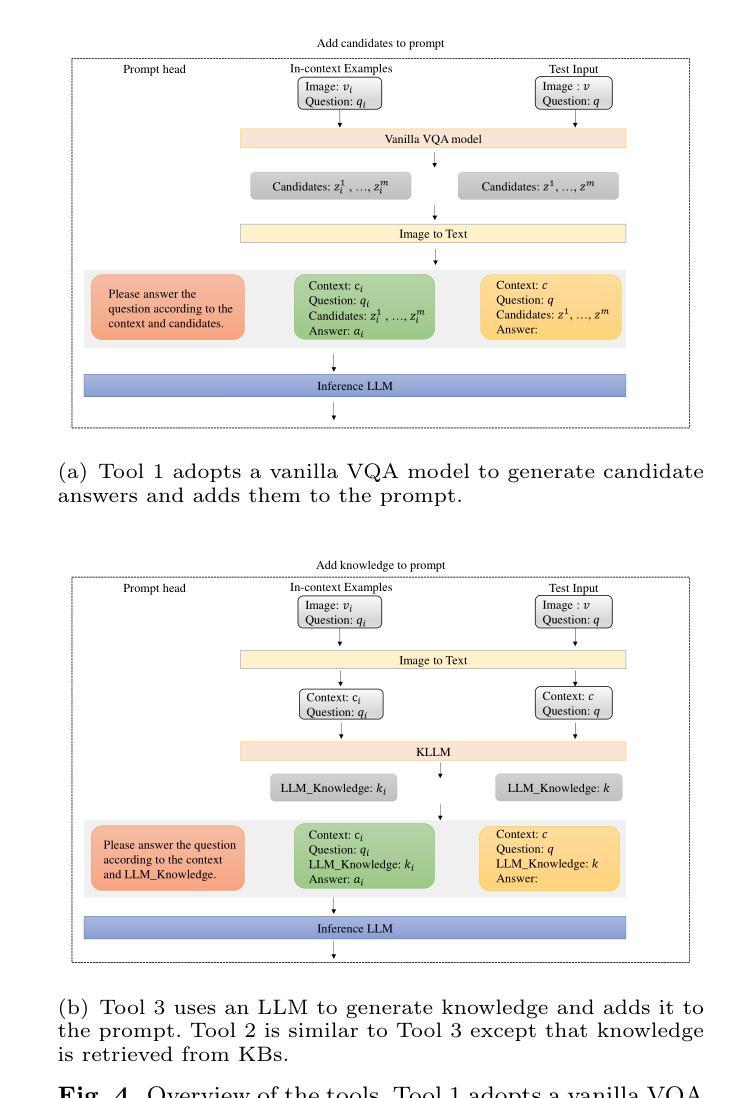
Multi-Agents Based on Large Language Models for Knowledge-based Visual Question Answering
Authors:Zhongjian Hu, Peng Yang, Bing Li, Zhenqi Wang
Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved impressive results in knowledge-based Visual Question Answering (VQA). However existing methods still have challenges: the inability to use external tools autonomously, and the inability to work in teams. Humans tend to know whether they need to use external tools when they encounter a new question, e.g., they tend to be able to give a direct answer to a familiar question, whereas they tend to use tools such as search engines when they encounter an unfamiliar question. In addition, humans also tend to collaborate and discuss with others to get better answers. Inspired by this, we propose the multi-agent voting framework. We design three LLM-based agents that simulate different levels of staff in a team, and assign the available tools according to the levels. Each agent provides the corresponding answer, and finally all the answers provided by the agents are voted to get the final answer. Experiments on OK-VQA and A-OKVQA show that our approach outperforms other baselines by 2.2 and 1.0, respectively.
大型语言模型(LLMs)在知识型视觉问答(VQA)中取得了令人印象深刻的结果。然而,现有方法仍面临挑战:无法自主使用外部工具,且无法团队合作。人类在遇到新问题时,往往知道是否需要借助外部工具,例如,对于熟悉的问题,他们往往能直接给出答案,而对于不熟悉的问题,则会使用搜索引擎等工具。此外,人类还倾向于与他人协作和讨论以得到更好的答案。受此启发,我们提出了多智能体投票框架。我们设计了三个基于LLM的智能体,模拟团队中不同级别的员工,并根据级别分配可用工具。每个智能体提供相应的答案,最后对所有智能体提供的答案进行投票以得到最终答案。在OK-VQA和A-OKVQA上的实验表明,我们的方法分别比其他基线方法高出2.2和1.0。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
大型语言模型在知识型视觉问答(VQA)中取得了令人印象深刻的结果,但现有方法仍面临挑战,如无法自主使用外部工具且无法团队协作。人类遇到新问题时知道是否需要借助外部工具,如对于熟悉问题可直接回答,对于不熟悉问题则使用搜索引擎。此外,人类还会与他人协作和讨论以获取更好的答案。受此启发,我们提出了多智能体投票框架。我们设计了三个基于大型语言模型的智能体,模拟团队中不同级别的员工,并根据级别分配可用工具。每个智能体提供相应的答案,最终对智能体提供的所有答案进行投票以得出最终答案。在OK-VQA和A-OKVQA上的实验表明,我们的方法分别比其他基线方法高出2.2和1.0。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型在知识型视觉问答中表现优异,但仍面临自主使用外部工具和团队协作的挑战。
- 人类遇到新问题时,知道是否需要借助外部工具,这一能力可借鉴到LLM模型中。
- 人类会与他人协作和讨论以获取更好的答案,受此启发,提出了多智能体投票框架。
- 设计了三个基于大型语言模型的智能体,模拟团队中不同级别的员工,并根据级别分配工具。
- 每个智能体提供的答案都会进行投票,以得出最终答案。
- 在OK-VQA和A-OKVQA上的实验表明,该多智能体投票框架的方法优于其他基线方法。
- 该方法通过模拟团队协作和工具使用,提高了大型语言模型在视觉问答任务中的性能。
点此查看论文截图


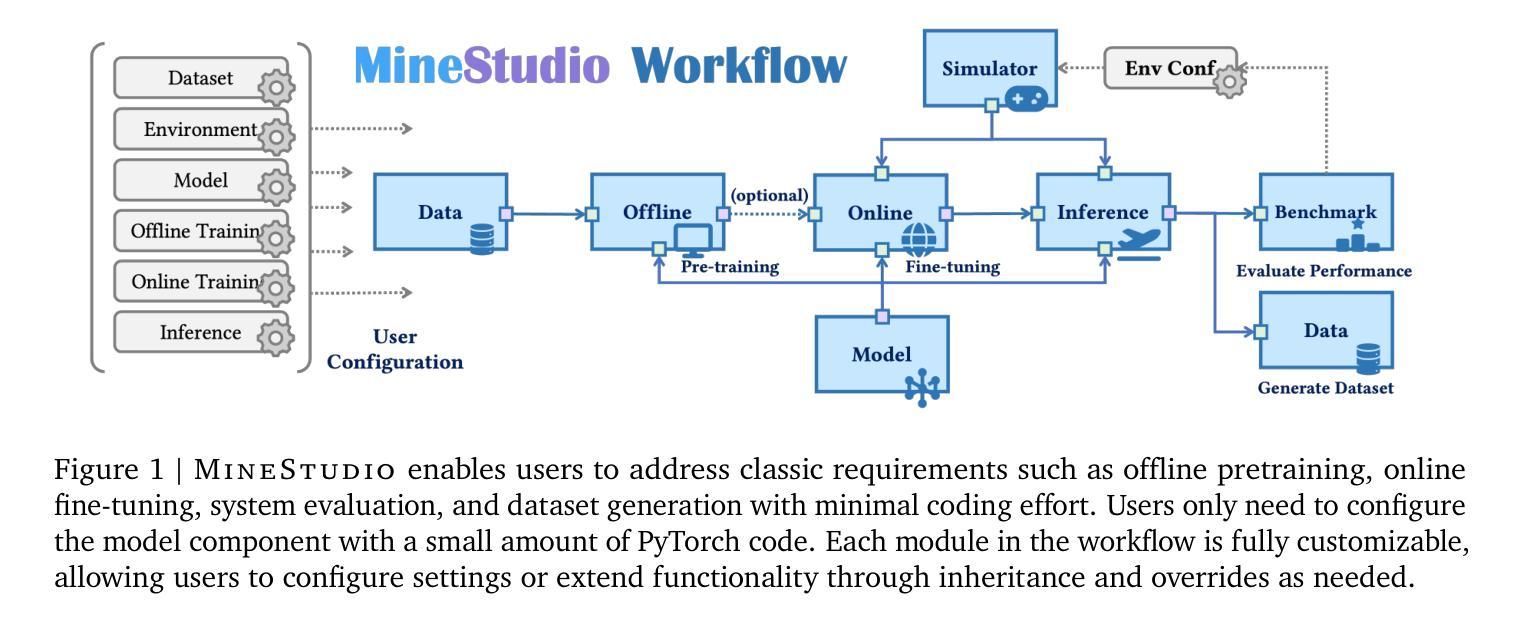
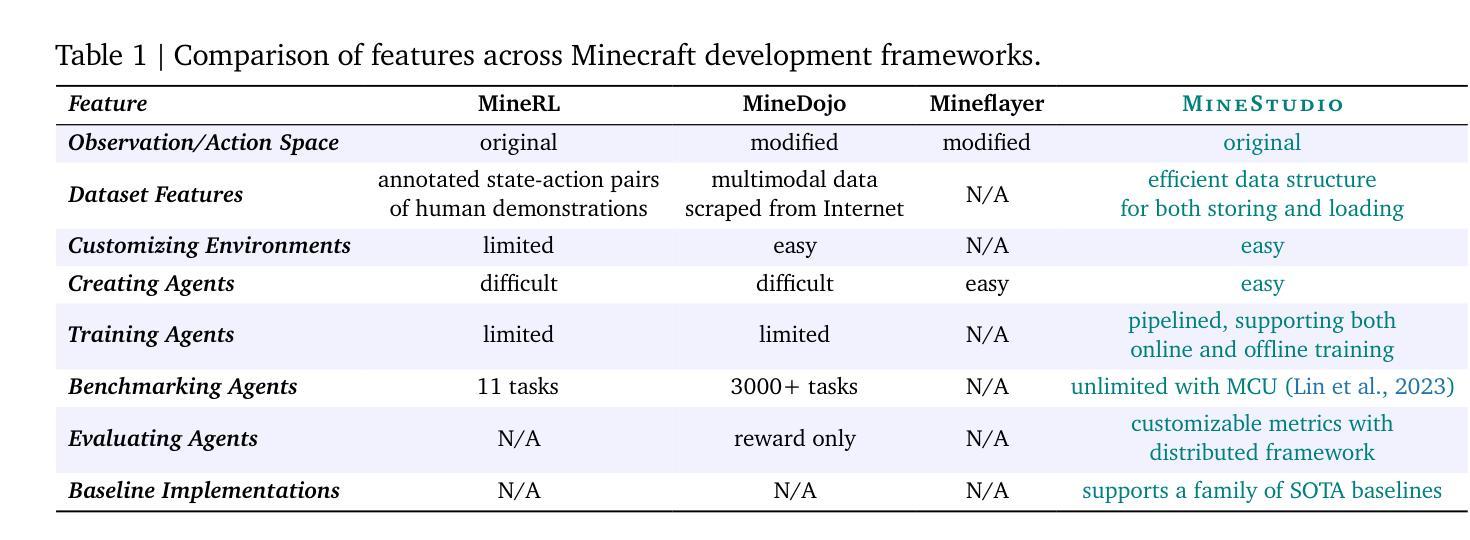
MinsStudio: A Streamlined Package for Minecraft AI Agent Development
Authors:Shaofei Cai, Zhancun Mu, Kaichen He, Bowei Zhang, Xinyue Zheng, Anji Liu, Yitao Liang
Minecraft has emerged as a valuable testbed for embodied intelligence and sequential decision-making research, yet the development and validation of novel agents remains hindered by significant engineering challenges. This paper presents MineStudio, an open-source software package designed to streamline embodied policy development in Minecraft. MineStudio represents the first comprehensive integration of seven critical engineering components: simulator, data, model, offline pretraining, online finetuning, inference, and benchmark, thereby allowing users to concentrate their efforts on algorithm innovation. We provide a user-friendly API design accompanied by comprehensive documentation and tutorials. The complete codebase is publicly available at https://github.com/CraftJarvis/MineStudio.
《我的世界》已经成为对实体智能和序列决策研究的重要试验场,但新型代理的开发和验证仍然受到重大工程挑战的阻碍。本文介绍了MineStudio,这是一款开源软件包,旨在简化《我的世界》中的实体策略开发。MineStudio首次全面集成了七个关键工程组件:模拟器、数据、模型、离线预训练、在线微调、推理和基准测试,从而让用户能够专注于算法创新。我们提供了用户友好的API设计,并配有全面的文档和教程。完整的代码库可在https://github.com/CraftJarvis/MineStudio中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Minecraft已成为体智能和序列决策研究的重要测试平台,但新型智能体的开发与验证仍面临重大工程挑战。本文介绍了一款名为MineStudio的开源软件包,旨在简化Minecraft中的智能体策略开发。MineStudio首次全面整合了七个关键工程组件:模拟器、数据、模型、离线预训练、在线微调、推理和基准测试,使用户能够专注于算法创新。我们提供了用户友好的API设计和全面的文档及教程。完整的代码库可在https://github.com/CraftJarvis/MineStudio找到。
Key Takeaways
- Minecraft已成为体智能和序列决策研究的测试平台。
- 开发新型智能体面临重大工程挑战。
- MineStudio是一个开源软件包,旨在简化Minecraft中的智能体策略开发。
- MineStudio整合了七个关键工程组件:模拟器、数据、模型等。
- MineStudio提供用户友好的API设计和全面的文档及教程。
- MineStudio可帮助用户专注于算法创新。
点此查看论文截图

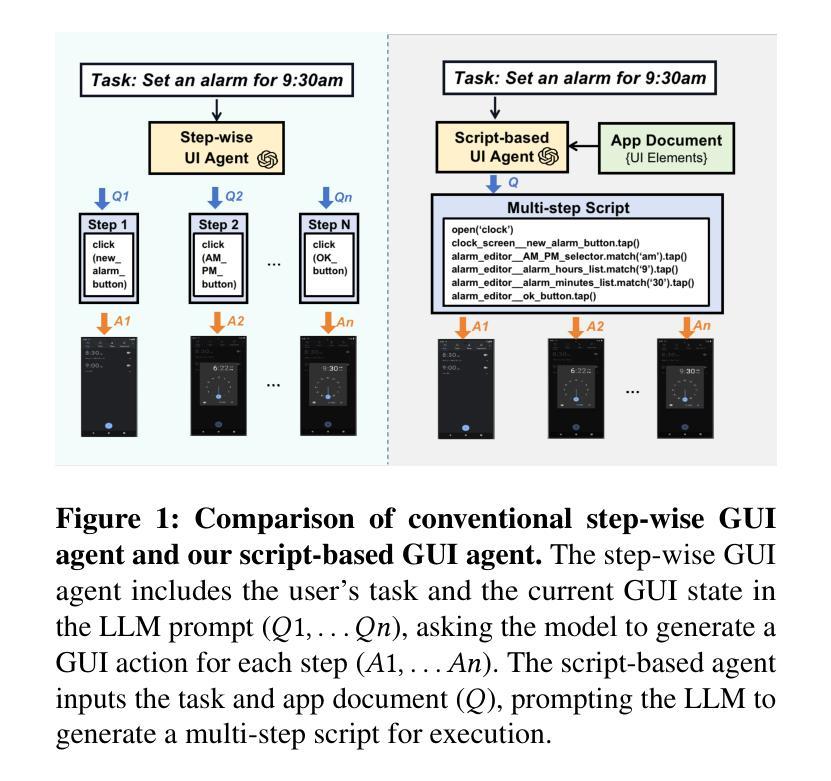
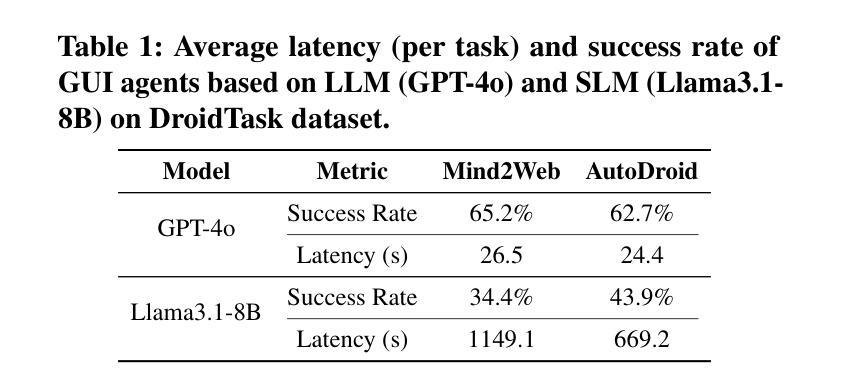
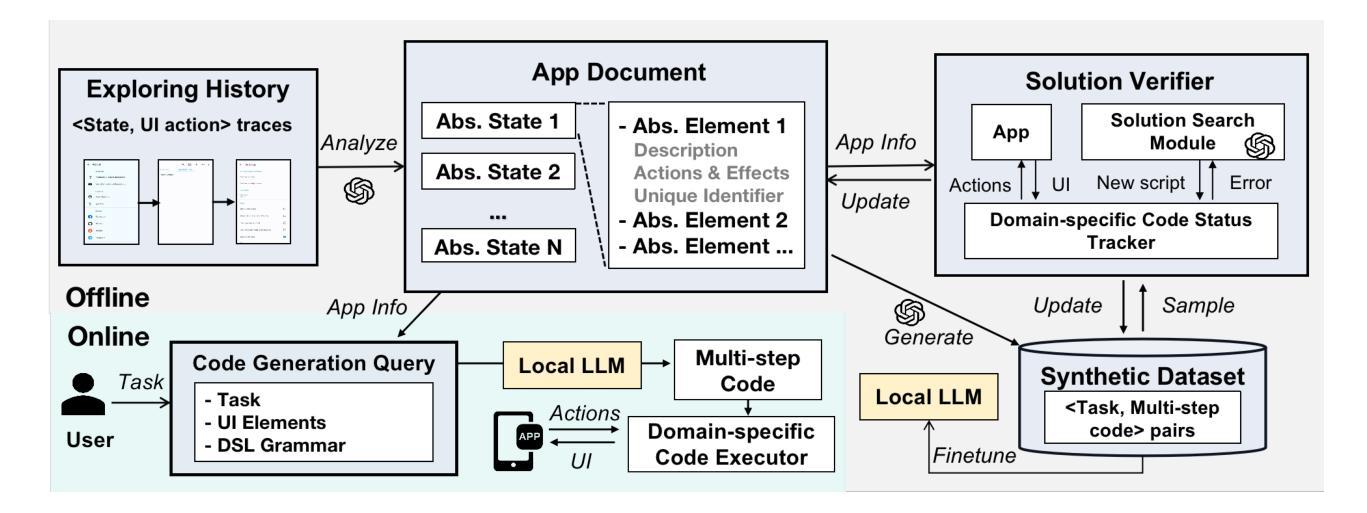
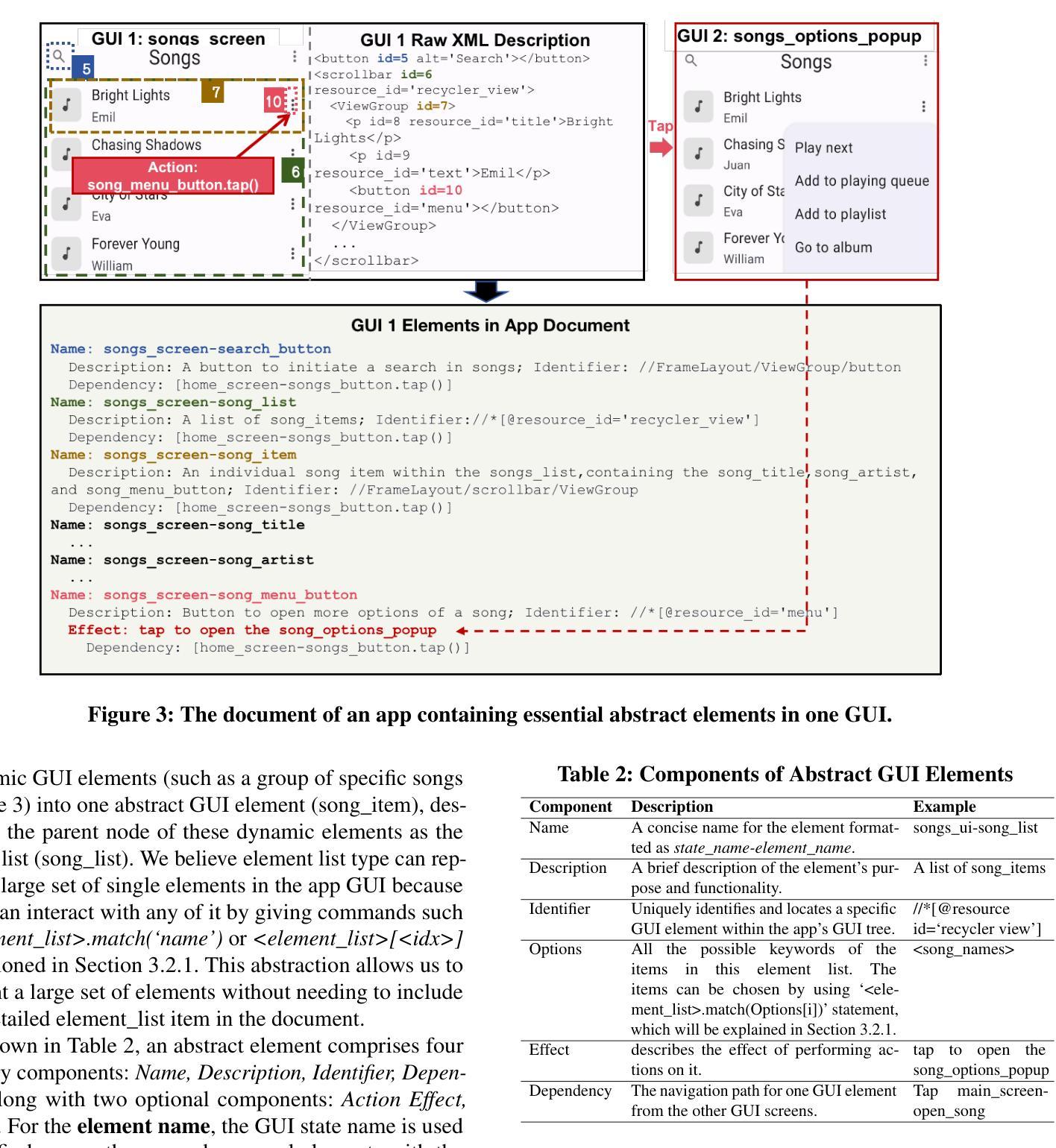
AutoDroid-V2: Boosting SLM-based GUI Agents via Code Generation
Authors:Hao Wen, Shizuo Tian, Borislav Pavlov, Wenjie Du, Yixuan Li, Ge Chang, Shanhui Zhao, Jiacheng Liu, Yunxin Liu, Ya-Qin Zhang, Yuanchun Li
Large language models (LLMs) have brought exciting new advances to mobile UI agents, a long-standing research field that aims to complete arbitrary natural language tasks through mobile UI interactions. However, existing UI agents usually demand high reasoning capabilities of powerful large models that are difficult to be deployed locally on end-users’ devices, which raises huge concerns about user privacy and centralized serving cost. One way to reduce the required model size is to customize a smaller domain-specific model with high-quality training data, e.g. large-scale human demonstrations of diverse types of apps and tasks, while such datasets are extremely difficult to obtain. Inspired by the remarkable coding abilities of recent small language models (SLMs), we propose to convert the UI task automation problem to a code generation problem, which can be effectively solved by an on-device SLM and efficiently executed with an on-device code interpreter. Unlike normal coding tasks that can be extensively pretrained with public datasets, generating UI automation code is challenging due to the diversity, complexity, and variability of target apps. Therefore, we adopt a document-centered approach that automatically builds fine-grained API documentation for each app and generates diverse task samples based on this documentation. By guiding the agent with the synthetic documents and task samples, it learns to generate precise and efficient scripts to complete unseen tasks. Based on detailed comparisons with state-of-the-art mobile UI agents, our approach effectively improves the mobile task automation with significantly higher success rates and lower latency/token consumption. Code will be open-sourced.
大型语言模型(LLM)为移动用户界面代理(UI agents)带来了激动人心的全新进展。这是一个长期的研究领域,旨在通过移动UI交互完成任意的自然语言任务。然而,现有的UI代理通常需要强大的大型模型的高度推理能力,这些模型很难在最终用户的设备上本地部署,这引发了人们对用户隐私和集中式服务成本的巨大担忧。减少所需模型大小的一种方法是使用高质量的训练数据定制较小的特定领域模型,例如各种应用程序和任务的大规模人类演示,然而这样的数据集极难获得。受近期小型语言模型(SLM)出色编码能力的启发,我们提出将UI任务自动化问题转换为代码生成问题,该问题可以通过设备上的SLM有效解决并通过设备上的代码解释器高效执行。与可以用公共数据集进行大量预训练的正常编码任务不同,生成UI自动化代码具有挑战性,因为目标应用程序的多样性、复杂性和可变性。因此,我们采用以文档为中心的方法,该方法自动为每个应用程序构建精细的API文档,并基于此文档生成多样化的任务样本。通过用合成文档和任务样本指导代理,它学会了生成精确高效的脚本来完成看不见的任务。与最新的移动UI代理的详细比较表明,我们的方法有效地提高了移动任务自动化水平,成功率显著提高,延迟和令牌消耗大大降低。代码将开源。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 5 figures
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)为移动UI代理带来了先进的研究进展,旨在通过移动UI交互完成任意自然语言任务。然而,现有UI代理通常需要强大的大型模型的高度推理能力,难以在最终用户设备上本地部署,引发了关于用户隐私和集中服务成本的担忧。研究提出了一种将UI任务自动化问题转化为代码生成问题的方法,可以通过设备上的小型语言模型(SLM)有效解决并高效执行。研究采用以文档为中心的方法,自动生成针对每个应用程序的精细API文档,并基于此文档生成多样化的任务样本。通过引导代理使用合成文档和任务样本,学习生成精确高效的脚本以完成未见过的任务。与最先进的移动UI代理的详细比较表明,该方法有效提高移动任务自动化成功率并降低延迟和令牌消耗。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)推动了移动UI代理的研究进展。
- 现有UI代理对强大模型的推理能力要求高,难以在最终用户设备上部署,引发隐私和成本问题。
- 提出将UI任务自动化转化为代码生成问题的方法,利用小型语言模型(SLM)解决并在设备上执行。
- 采用以文档为中心的方法,自动生成针对每个应用程序的精细API文档及多样化任务样本。
- 合成文档和任务样本引导代理生成精确高效的脚本以完成未知任务。
- 与现有技术相比,该方法提高了移动任务自动化的成功率并降低了延迟和令牌消耗。
点此查看论文截图

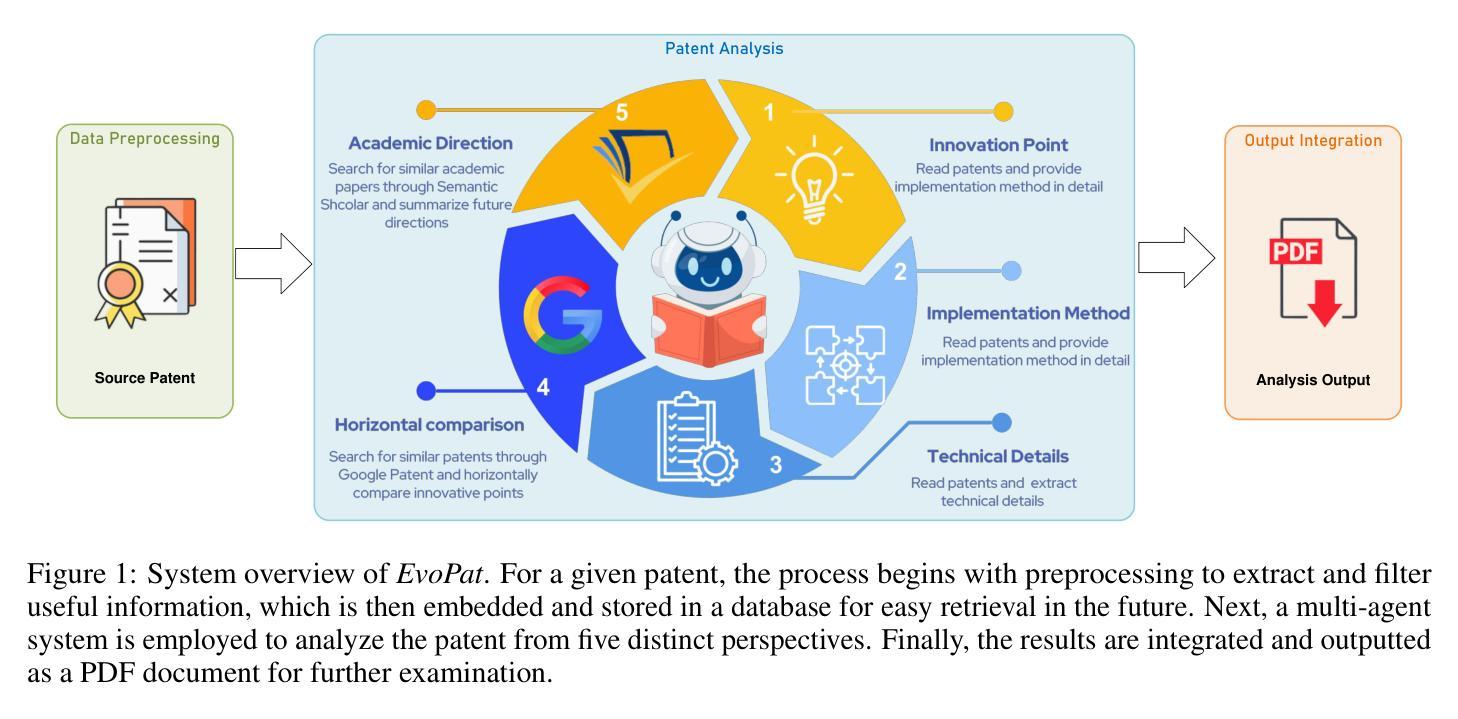
EvoPat: A Multi-LLM-based Patents Summarization and Analysis Agent
Authors:Suyuan Wang, Xueqian Yin, Menghao Wang, Ruofeng Guo, Kai Nan
The rapid growth of scientific techniques and knowledge is reflected in the exponential increase in new patents filed annually. While these patents drive innovation, they also present significant burden for researchers and engineers, especially newcomers. To avoid the tedious work of navigating a vast and complex landscape to identify trends and breakthroughs, researchers urgently need efficient tools to summarize, evaluate, and contextualize patents, revealing their innovative contributions and underlying scientific principles.To address this need, we present EvoPat, a multi-LLM-based patent agent designed to assist users in analyzing patents through Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and advanced search strategies. EvoPat leverages multiple Large Language Models (LLMs), each performing specialized roles such as planning, identifying innovations, and conducting comparative evaluations. The system integrates data from local databases, including patents, literature, product catalogous, and company repositories, and online searches to provide up-to-date insights. The ability to collect information not included in original database automatically is also implemented. Through extensive testing in the natural language processing (NLP) domain, we demonstrate that EvoPat outperforms GPT-4 in tasks such as patent summarization, comparative analysis, and technical evaluation. EvoPat represents a significant step toward creating AI-powered tools that empower researchers and engineers to efficiently navigate the complexities of the patent landscape.
科学技术的快速发展反映在每年新申请专利的指数级增长上。虽然这些专利推动了创新,但它们也给研究人员和工程师,尤其是新手带来了巨大的负担。为了避免在庞大而复杂的领域中寻找趋势和突破而进行的乏味工作,研究人员急需有效的工具来总结、评估和解释专利,揭示其创新贡献和潜在的科学原理。为了解决这一需求,我们推出了EvoPat,这是一个基于多语言模型(LLM)的专利代理,旨在通过检索增强生成(RAG)和高级搜索策略来帮助用户分析专利。EvoPat利用多个大型语言模型(LLM),每个模型都扮演着专业角色,如规划、识别创新和进行比较评估等。该系统整合了本地数据库(包括专利、文献、产品目录和公司存储库)和在线搜索数据,以提供最新的见解。系统还实现了自动收集原始数据库中未包含信息的功能。在自然语言处理(NLP)领域的广泛测试中,我们证明EvoPat在专利总结、比较分析和技术评估等任务上的表现优于GPT-4。EvoPat朝着创建赋能研究人员和工程师高效浏览专利复杂领域的AI工具迈出了重要一步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages,2 figures,8 tables
Summary
专利数量逐年增长,对研究者和工程师来说是一项重大挑战。EvoPat专利代理应运而生,它利用多种大型语言模型(LLM),通过检索增强生成(RAG)和高级搜索策略,协助用户分析专利。系统集成了本地数据库和在线搜索数据,提供最新的见解,并在自然语言处理(NLP)领域测试中表现出出色的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 专利数量增长迅速,对研究者和工程师带来挑战。
- EvoPat是一个基于多LLM的专利代理,旨在协助用户分析专利。
- EvoPat通过检索增强生成(RAG)和高级搜索策略进行专利分析。
- EvoPat整合了本地数据库和在线搜索数据,提供最新的见解。
- EvoPat能够自动收集未包含在原始数据库中的信息。
- 在自然语言处理(NLP)领域测试中,EvoPat表现出出色的性能。
点此查看论文截图


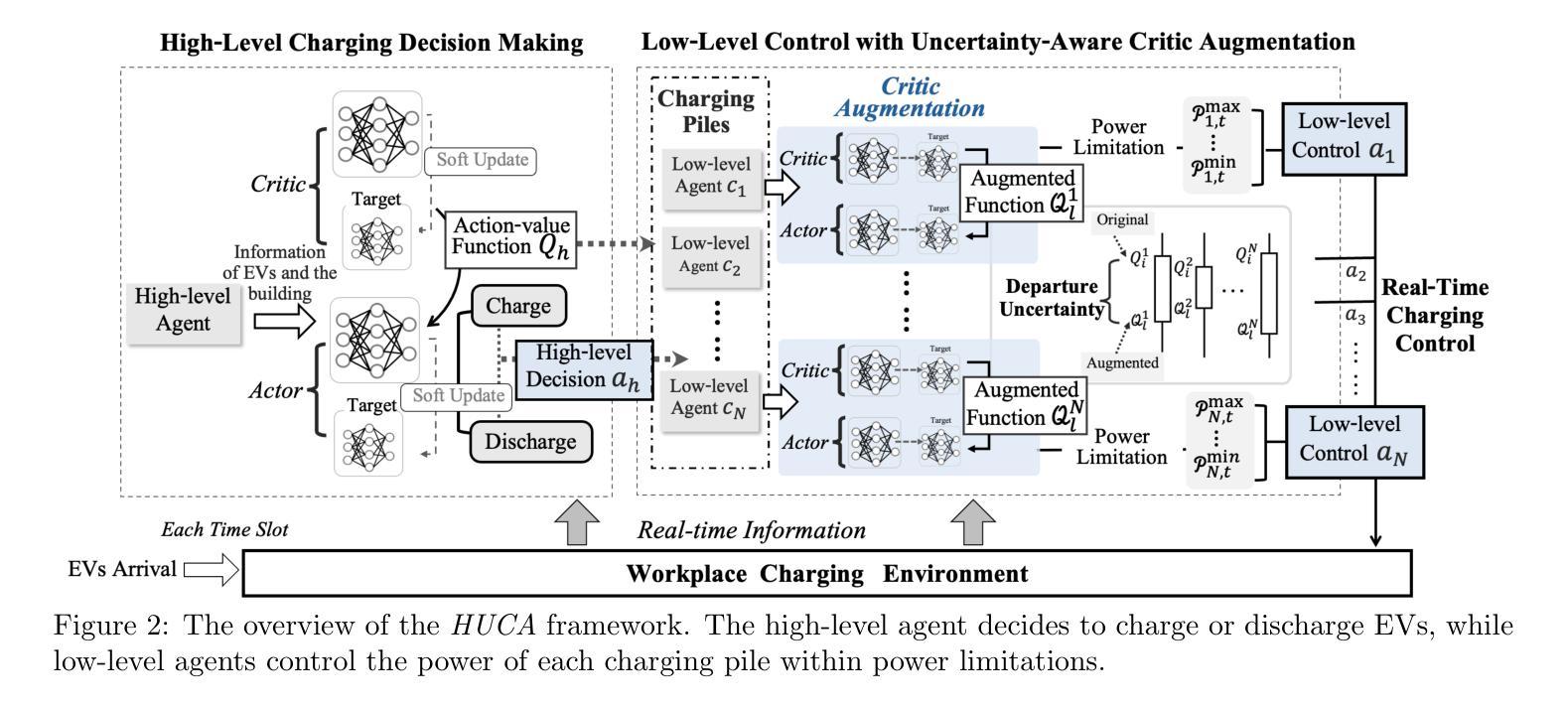
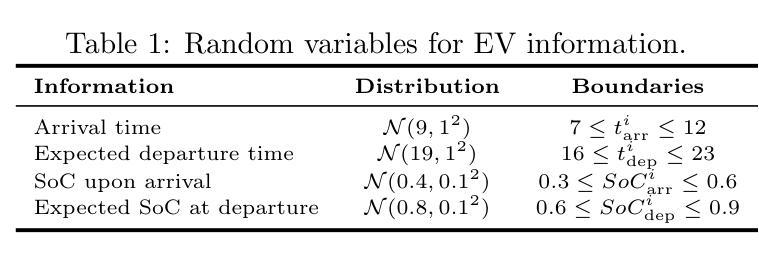
Uncertainty-Aware Critic Augmentation for Hierarchical Multi-Agent EV Charging Control
Authors:Lo Pang-Yun Ting, Ali Şenol, Huan-Yang Wang, Hsu-Chao Lai, Kun-Ta Chuang, Huan Liu
The advanced bidirectional EV charging and discharging technology, aimed at supporting grid stability and emergency operations, has driven a growing interest in workplace applications. It not only effectively reduces electricity expenses but also enhances the resilience of handling practical issues, such as peak power limitation, fluctuating energy prices, and unpredictable EV departures. However, existing EV charging strategies have yet to fully consider these factors in a way that benefits both office buildings and EV users simultaneously. To address these issues, we propose HUCA, a novel real-time charging control for regulating energy demands for both the building and electric vehicles. HUCA employs hierarchical actor-critic networks to dynamically reduce electricity costs in buildings, accounting for the needs of EV charging in the dynamic pricing scenario. To tackle the uncertain EV departures, a new critic augmentation is introduced to account for departure uncertainties in evaluating the charging decisions, while maintaining the robustness of the charging control. Experiments on real-world electricity datasets under both simulated certain and uncertain departure scenarios demonstrate that HUCA outperforms baselines in terms of total electricity costs while maintaining competitive performance in fulfilling EV charging requirements. A case study also manifests that HUCA effectively balances energy supply between the building and EVs based on real-time information.
先进的双向电动汽车充电和放电技术,旨在支持电网稳定性和紧急操作,已经引起了在工作场所应用方面的浓厚兴趣。该技术不仅有效地降低了电费,还提高了应对实际问题的能力,例如功率峰值限制、能源价格波动和不可预测的电动汽车离开。然而,现有的电动汽车充电策略还没有以一种可以同时惠及办公大楼和电动汽车用户的方式来充分考虑这些因素。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了HUCA,这是一种新型的实时充电控制,用于调节建筑物和电动汽车的能源需求。HUCA采用分层演员评论家网络,动态降低建筑物内的电力成本,并考虑电动汽车充电在动态定价场景中的需求。为了解决电动汽车不确定的离开时间问题,引入了一个新的评论家扩充,以考虑离开时间的不确定性在评估充电决策的同时,保持充电控制的稳健性。在模拟的确定性和不确定性离开场景下的真实世界电力数据集上的实验表明,HUCA在总电力成本方面优于基线,同时在满足电动汽车充电要求方面表现具有竞争力。一个案例研究还表明,HUCA基于实时信息有效地平衡了建筑物和电动汽车之间的能源供应。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
先进的双向电动汽车充电与放电技术对于支持电网稳定和应急操作产生了极大的兴趣,特别是在工作场所的应用。该技术不仅能有效降低电力成本,还能增强应对实际问题的能力,如峰值功率限制、能源价格浮动和不可预测的电动汽车离开等。为解决这些问题,提出了一种新型实时充电控制HUCA,用于调节建筑物和电动汽车的能源需求。HUCA采用分层actor-critic网络,在动态定价场景中动态降低建筑电力成本,同时考虑电动汽车充电的需求。实验结果表明,HUCA在总电力成本方面优于基线,同时在满足电动汽车充电要求方面表现具有竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 先进的双向电动汽车充电放电技术已引起对工作场所应用的兴趣,支持电网稳定和应急操作。
- 该技术有助于降低电力成本并增强应对峰值功率限制、能源价格浮动和不可预测的电动汽车离开等实际问题的能力。
- HUCA是一种新型实时充电控制,用于调节建筑物和电动汽车的能源需求。
- HUCA采用分层actor-critic网络,在动态定价场景中平衡电力成本与电动汽车充电需求。
- 为应对不可预测的电动汽车离开,HUCA引入了新的评价增强机制。
- 实验结果表明,HUCA在降低总电力成本方面表现优越,同时满足电动汽车的充电要求。
点此查看论文截图

Dynamic Multi-Agent Orchestration and Retrieval for Multi-Source Question-Answer Systems using Large Language Models
Authors:Antony Seabra, Claudio Cavalcante, Joao Nepomuceno, Lucas Lago, Nicolaas Ruberg, Sergio Lifschitz
We propose a methodology that combines several advanced techniques in Large Language Model (LLM) retrieval to support the development of robust, multi-source question-answer systems. This methodology is designed to integrate information from diverse data sources, including unstructured documents (PDFs) and structured databases, through a coordinated multi-agent orchestration and dynamic retrieval approach. Our methodology leverages specialized agents-such as SQL agents, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) agents, and router agents - that dynamically select the most appropriate retrieval strategy based on the nature of each query. To further improve accuracy and contextual relevance, we employ dynamic prompt engineering, which adapts in real time to query-specific contexts. The methodology’s effectiveness is demonstrated within the domain of Contract Management, where complex queries often require seamless interaction between unstructured and structured data. Our results indicate that this approach enhances response accuracy and relevance, offering a versatile and scalable framework for developing question-answer systems that can operate across various domains and data sources.
我们提出了一种结合大型语言模型(LLM)检索中的多种先进技术的方法论,以支持开发稳健的、多源问答系统。该方法论旨在通过协同的多智能体编排和动态检索方法,整合来自各种数据源的信息,包括非结构化文档(PDF)和结构化数据库。我们的方法利用专门的智能体,如SQL智能体、检索增强生成(RAG)智能体和路由智能体,根据每种查询的性质动态选择最合适的检索策略。为了进一步提高准确性和上下文相关性,我们采用了动态提示工程,它能实时适应特定查询的上下文。该方法论在合同管理领域得到了验证,复杂的查询通常需要非结构化数据和结构化数据之间的无缝交互。我们的结果表明,这种方法提高了响应的准确性和相关性,为能够在各个领域和数据源中运行的问答系统的开发提供了一个通用且可扩展的框架。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF International Conference on NLP, AI, Computer Science & Engineering (NLAICSE 2024)
Summary
该文章提出了一种结合多种先进技术的方法,支持开发稳健的多源问答系统。该方法通过协同多代理编排和动态检索方法,整合来自不同数据源的信息,包括非结构化文档(如PDF)和结构化数据库。通过利用专门的代理,如SQL代理、检索增强生成(RAG)代理和路由代理等,根据每个查询的性质动态选择最合适的检索策略。为了进一步提高准确性和上下文相关性,文章还采用了动态提示工程,该工程能够实时适应查询特定的上下文。该方法在合同管理等领域的复杂查询中表现出了强大的效果,通过无缝交互非结构化数据和结构化数据提高了应答的准确性和相关性。总体来说,这为开发跨不同领域和数据源的问答系统提供了一个通用且可扩展的框架。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种结合多种先进技术的方法,旨在支持开发多源问答系统。
- 通过协同多代理编排和动态检索方法整合不同数据源的信息。
- 利用专门的代理(如SQL代理、RAG代理和路由代理)根据查询的性质动态选择检索策略。
- 采用动态提示工程,提高准确性和上下文相关性。
- 在合同管理等领域的复杂查询中表现出强大的效果。
- 通过无缝交互非结构化数据和结构化数据提高了应答的准确性和相关性。
点此查看论文截图

Tacit Learning with Adaptive Information Selection for Cooperative Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Lunjun Liu, Weilai Jiang, Yaonan Wang
In multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL), the centralized training with decentralized execution (CTDE) framework has gained widespread adoption due to its strong performance. However, the further development of CTDE faces two key challenges. First, agents struggle to autonomously assess the relevance of input information for cooperative tasks, impairing their decision-making abilities. Second, in communication-limited scenarios with partial observability, agents are unable to access global information, restricting their ability to collaborate effectively from a global perspective. To address these challenges, we introduce a novel cooperative MARL framework based on information selection and tacit learning. In this framework, agents gradually develop implicit coordination during training, enabling them to infer the cooperative behavior of others in a discrete space without communication, relying solely on local information. Moreover, we integrate gating and selection mechanisms, allowing agents to adaptively filter information based on environmental changes, thereby enhancing their decision-making capabilities. Experiments on popular MARL benchmarks show that our framework can be seamlessly integrated with state-of-the-art algorithms, leading to significant performance improvements.
在多智能体强化学习(MARL)中,由于强大的性能表现,采用集中训练与分散执行(CTDE)框架的方法已经得到了广泛应用。然而,CTDE的进一步发展面临两大挑战。首先,智能体难以自主评估输入信息对于合作任务的相关性,从而影响了其决策能力。其次,在通信受限且部分可观察的场景中,智能体无法访问全局信息,限制了它们从全局角度进行有效协作的能力。为了应对这些挑战,我们基于信息选择和隐性学习,引入了一种新型的合作MARL框架。在此框架中,智能体在训练过程中逐渐发展出隐性协调,使它们能够在离散空间中依靠本地信息,无需通信就能推断出他人的合作行为。此外,我们整合了门控和选择机制,使智能体能根据环境变化自适应地过滤信息,从而提升其决策能力。在流行的MARL基准测试上的实验表明,我们的框架可以无缝地融入最新算法,带来显著的性能提升。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAMAS 2025 (Extended Abstract)
Summary
在强化学习多智能体(MARL)领域,中心化训练分布式执行(CTDE)框架由于表现出良好的性能而受到广泛采用。然而,该框架面临两大挑战:智能体难以自主评估输入信息对合作任务的重要性;以及在通信受限和具有部分可观察性的场景中,智能体无法获取全局信息,限制了它们从全局角度进行有效协作的能力。为解决这些挑战,提出了一种基于信息选择和默识学习的新型合作式MARL框架。在此框架中,智能体在训练过程中逐渐发展出隐性协调,仅依靠局部信息即可在不通信的情况下推断出离散空间中他人的合作行为。此外,集成了门控和选择机制,使智能体能根据环境变化自适应过滤信息,从而提高决策能力。实验表明,该框架可无缝融入最新算法,带来显著性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- CTDE框架在多智能体强化学习(MARL)中广泛应用,但面临自主评估信息相关性和通信受限的挑战。
- 提出了一种新型合作式MARL框架,该框架基于信息选择和默识学习。
- 智能体在训练过程中逐渐发展隐性协调,能在离散空间中推断他人行为。
- 通过整合门控和选择机制,智能体能自适应过滤信息,提高决策能力。
- 该框架可无缝融入当前先进的算法。
- 实验表明该框架能显著提升性能。
- 该框架有助于增强智能体在复杂环境中的适应性和协作能力。
点此查看论文截图

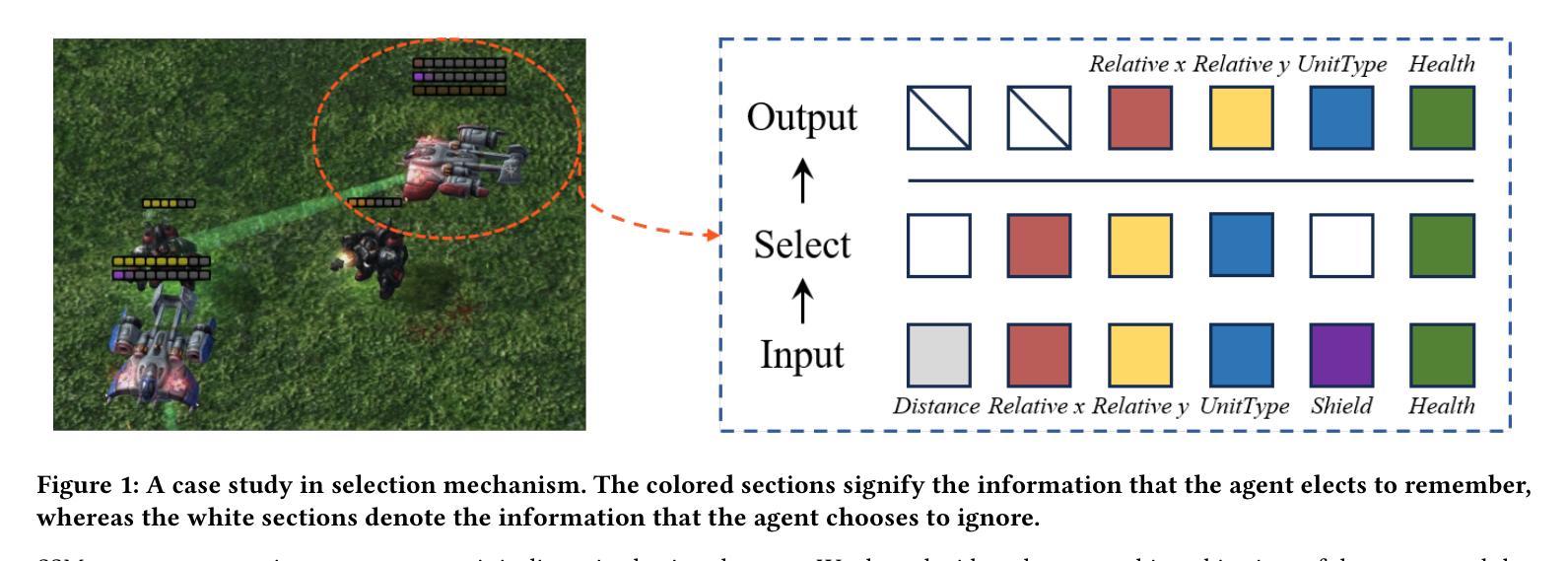
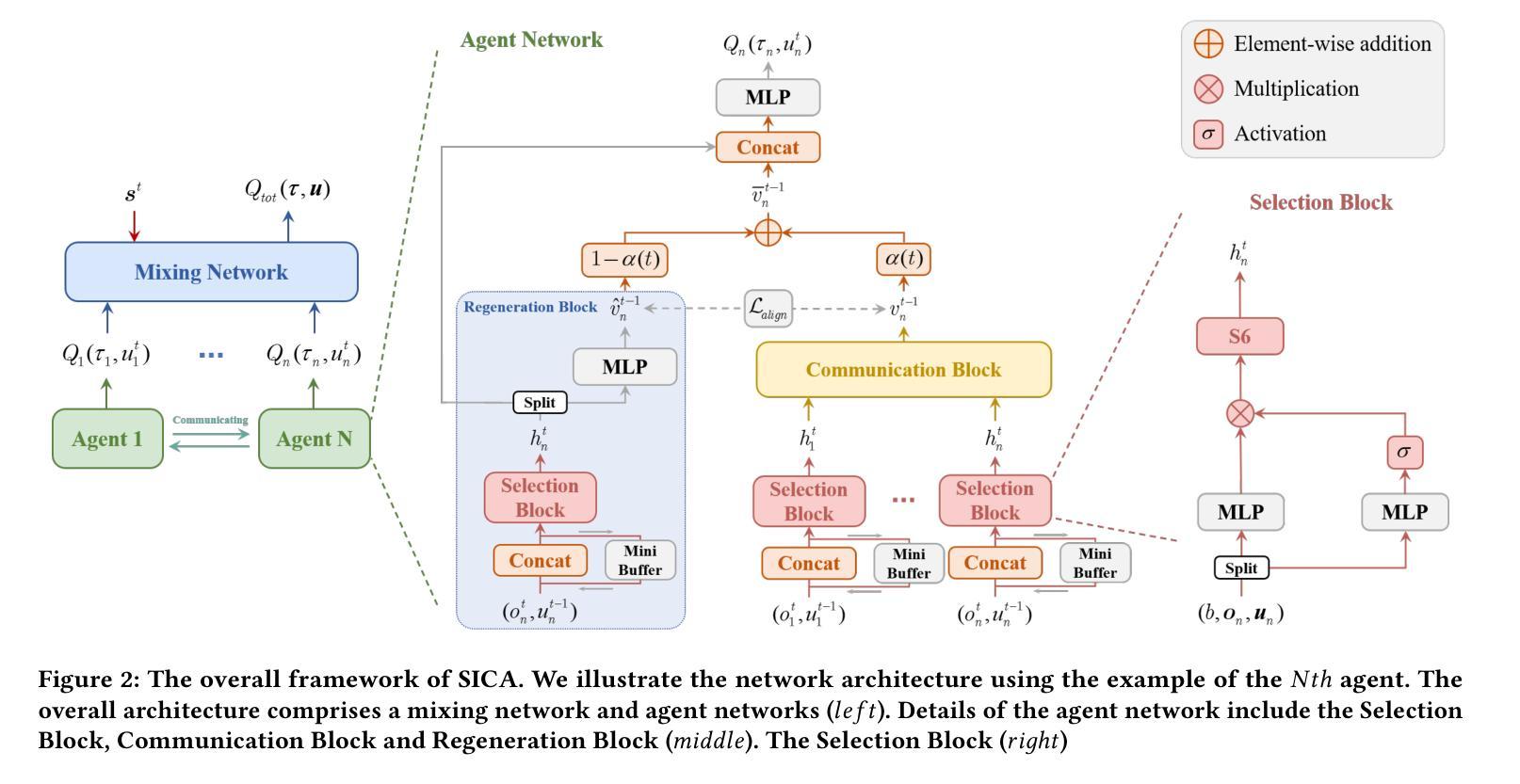
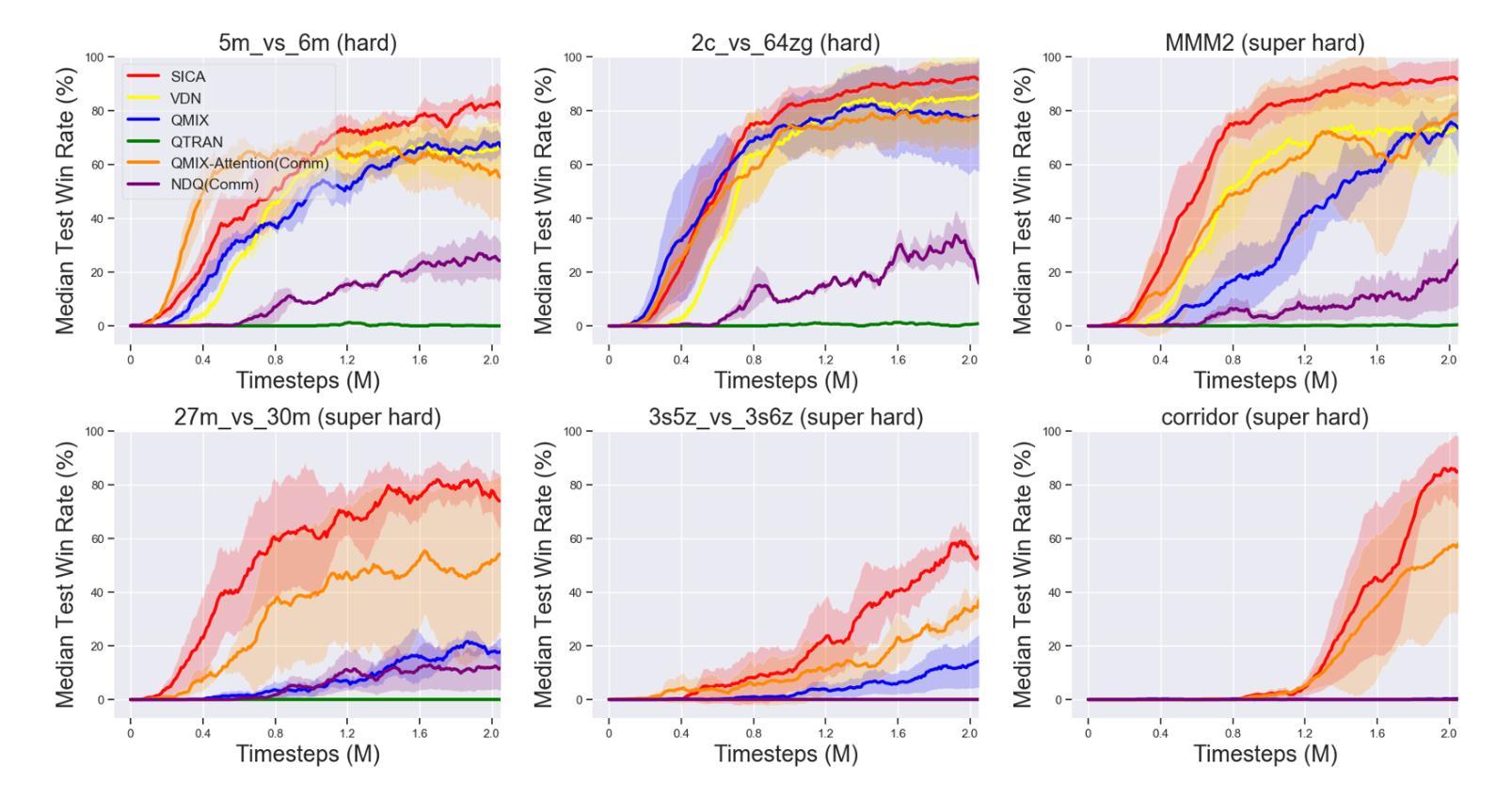
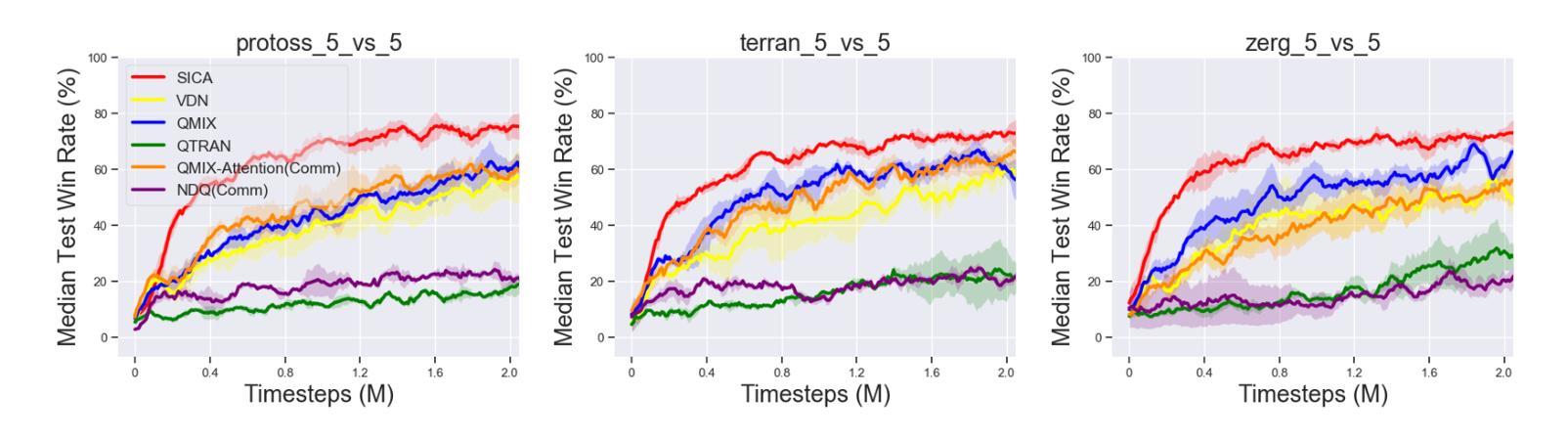
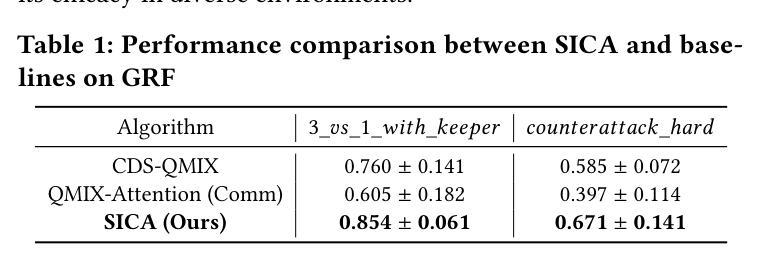
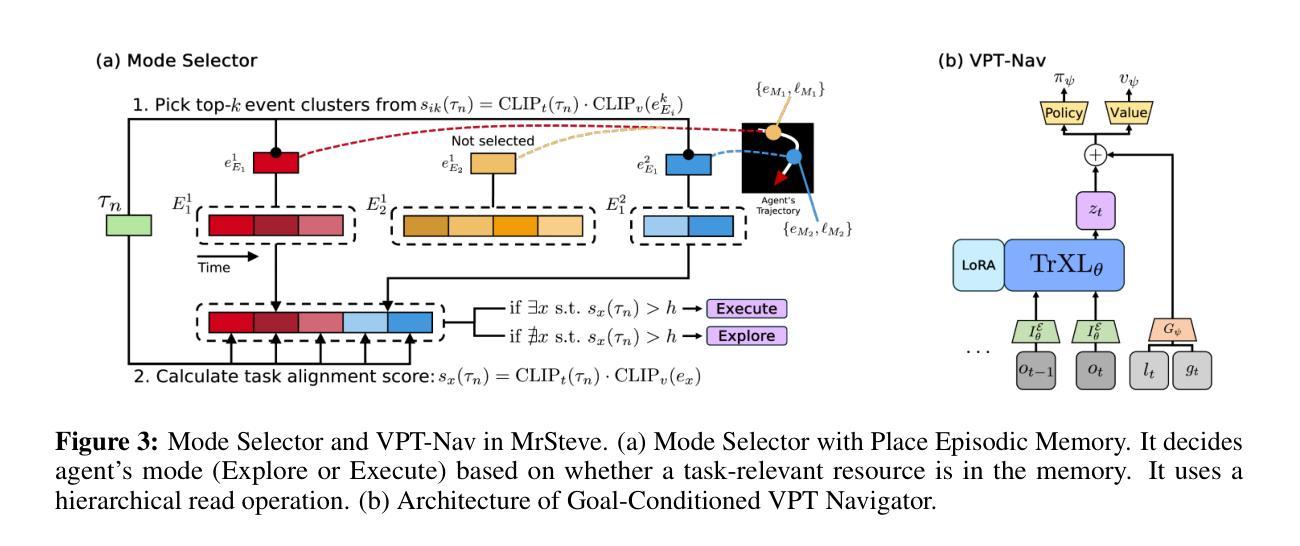
MrSteve: Instruction-Following Agents in Minecraft with What-Where-When Memory
Authors:Junyeong Park, Junmo Cho, Sungjin Ahn
Significant advances have been made in developing general-purpose embodied AI in environments like Minecraft through the adoption of LLM-augmented hierarchical approaches. While these approaches, which combine high-level planners with low-level controllers, show promise, low-level controllers frequently become performance bottlenecks due to repeated failures. In this paper, we argue that the primary cause of failure in many low-level controllers is the absence of an episodic memory system. To address this, we introduce MrSteve (Memory Recall Steve-1), a novel low-level controller equipped with Place Event Memory (PEM), a form of episodic memory that captures what, where, and when information from episodes. This directly addresses the main limitation of the popular low-level controller, Steve-1. Unlike previous models that rely on short-term memory, PEM organizes spatial and event-based data, enabling efficient recall and navigation in long-horizon tasks. Additionally, we propose an Exploration Strategy and a Memory-Augmented Task Solving Framework, allowing agents to alternate between exploration and task-solving based on recalled events. Our approach significantly improves task-solving and exploration efficiency compared to existing methods. We will release our code and demos on the project page: https://sites.google.com/view/mr-steve.
在Minecraft等环境中,通过采用LLM增强分层方法,通用实体人工智能的发展取得了重大进展。虽然这些结合高级规划器和低级控制器的方法显示出潜力,但由于反复失败,低级控制器往往成为性能瓶颈。在本文中,我们认为许多低级控制器失败的主要原因是缺乏情境记忆系统。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了MrSteve(记忆召回史蒂夫-1),这是一种新型低级控制器,配备了Place Event Memory(PEM),这是一种情境记忆,可以捕捉事件中的“什么、哪里和何时”信息。这直接解决了流行的低级控制器史蒂夫-1的主要局限性。与以往依赖短期记忆力的模型不同,PEM能够组织基于空间和事件的数据,从而在长期任务中实现高效回忆和导航。此外,我们提出了一种探索策略和任务解决框架Memory-Augmented Task Solving Framework,使智能体能够根据回忆的事件在探索和任务解决之间交替。与现有方法相比,我们的方法显著提高了任务解决和探索效率。我们会在项目页面发布我们的代码和演示:https://sites.google.com/view/mr-steve。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在Minecraft等环境中,通用实体人工智能的发展已取得了重大进展,采用了LLM增强层次结构的方法,结合了高级规划器和低级控制器。然而,由于重复失败,低级控制器往往成为性能瓶颈。本文认为,许多低级控制器失败的主要原因是缺乏情景记忆系统。为解决这一问题,我们推出了MrSteve(记忆召回Steve-1),这是一种新型低级控制器,配备了Place Event Memory(PEM),一种情景记忆,可以捕捉事件中的“什么、哪里、何时”信息。这直接解决了流行的低级控制器Steve-1的主要局限性。与依赖短期记忆的先前模型不同,PEM能够组织空间和时间事件数据,在长周期任务中实现高效回忆和导航。此外,我们还提出了探索策略和记忆增强任务解决框架,使智能体能够根据回忆的事件在探索和解决问题之间交替。我们的方法显著提高了与现有方法相比的任务解决和探索效率。相关代码和演示将在项目页面发布:https://sites.google.com/view/mr-steve。
Key Takeaways
- 通用实体AI在Minecraft等环境中取得显著进展,采用LLM增强层次结构方法。
- 低级控制器成为性能瓶颈,主要由于重复失败。
- 低级控制器失败的主要原因是缺乏情景记忆系统。
- 引入新型低级控制器MrSteve,配备Place Event Memory(PEM)。
- PEM能捕捉事件的“什么、哪里、何时”信息,提高长周期任务中的效率。
- 提出了探索策略和记忆增强任务解决框架。
点此查看论文截图

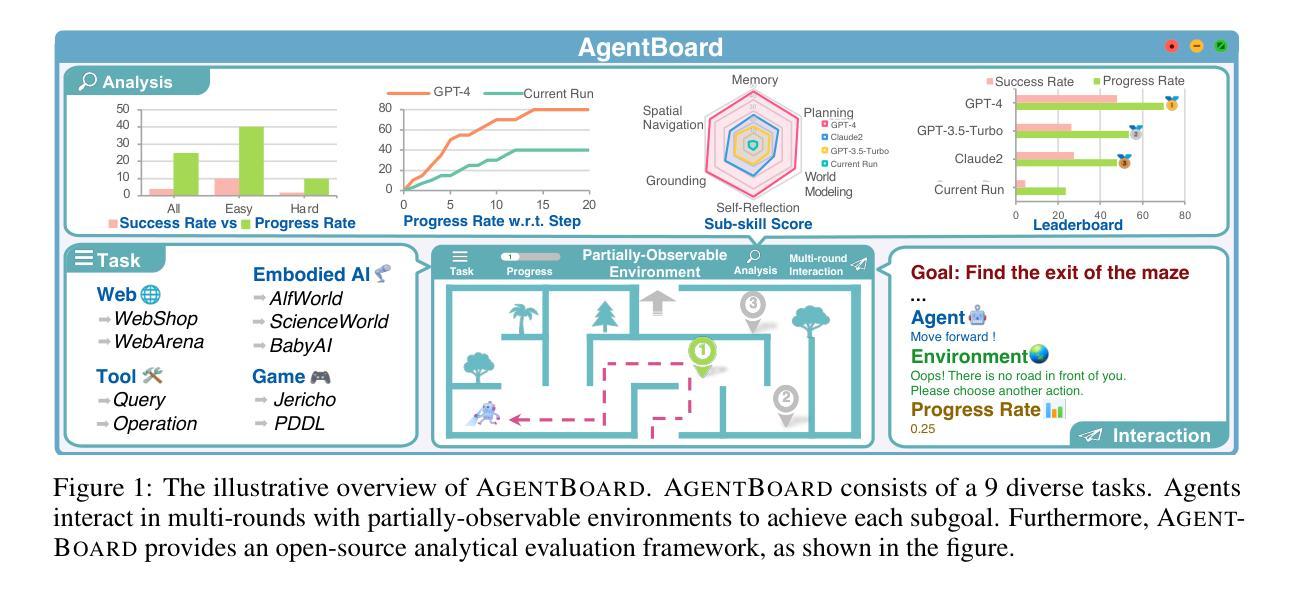
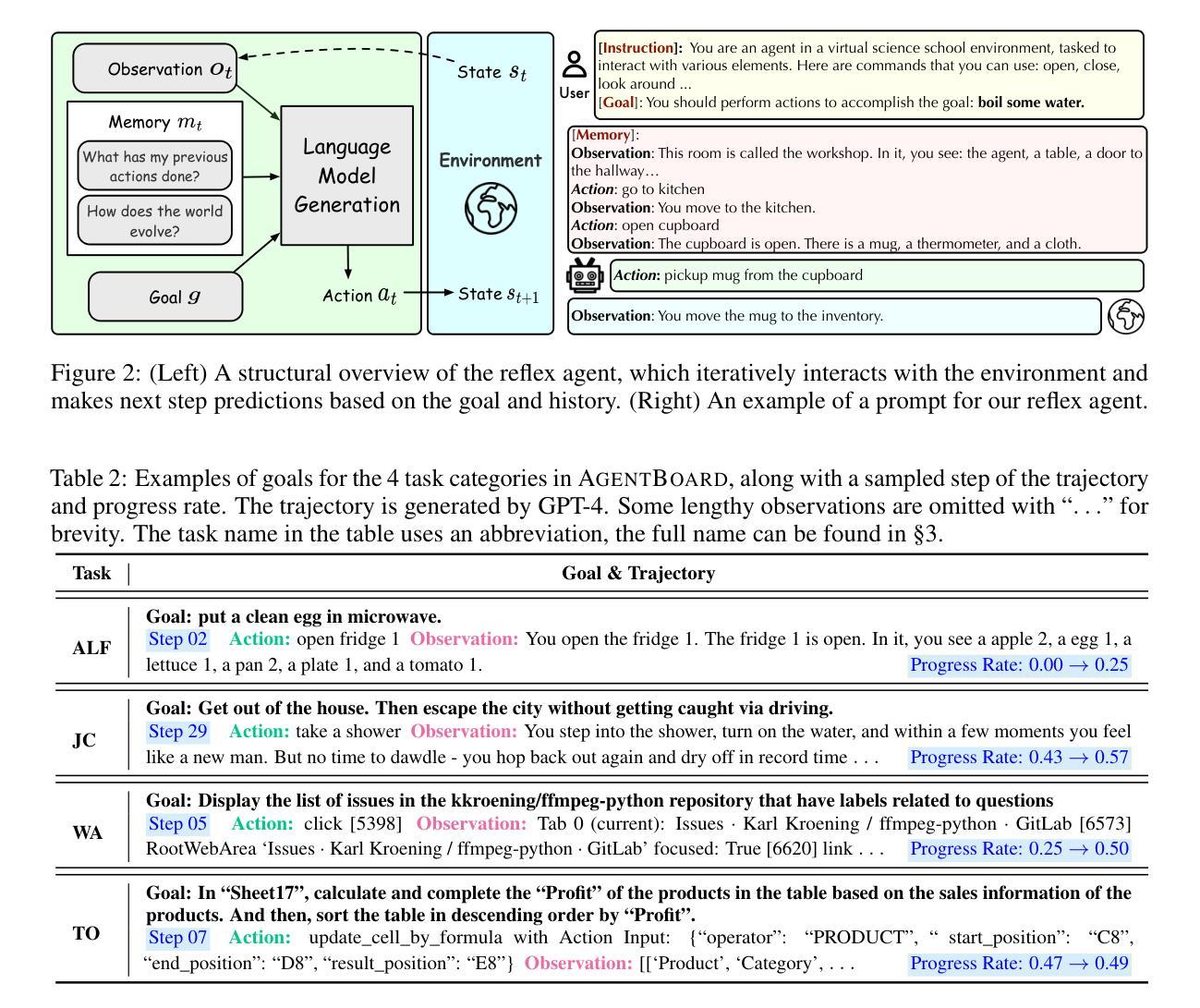
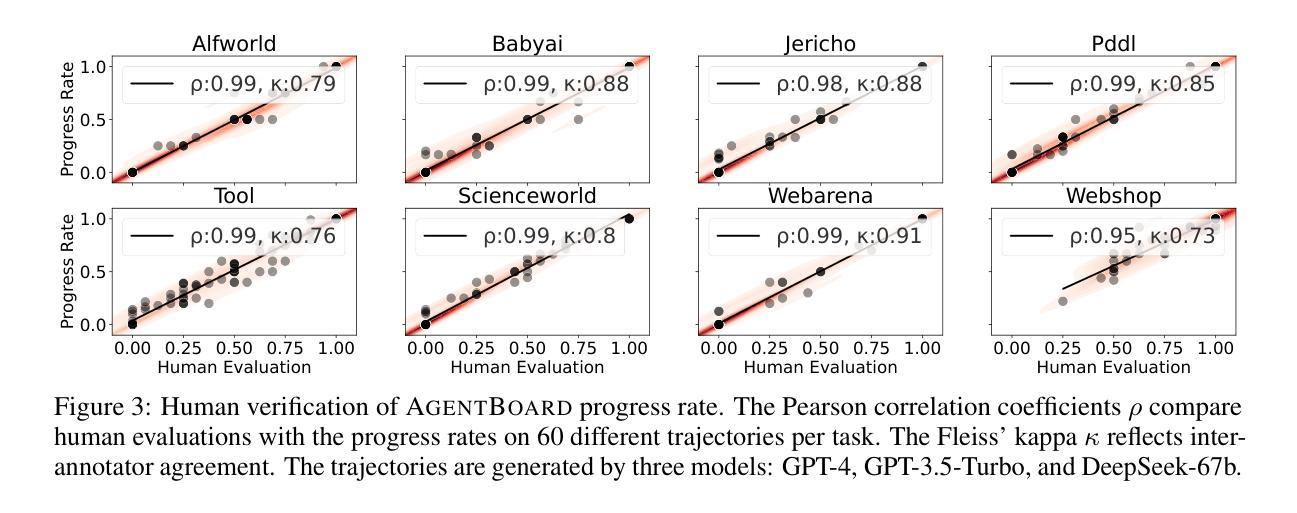
AgentBoard: An Analytical Evaluation Board of Multi-turn LLM Agents
Authors:Chang Ma, Junlei Zhang, Zhihao Zhu, Cheng Yang, Yujiu Yang, Yaohui Jin, Zhenzhong Lan, Lingpeng Kong, Junxian He
Evaluating Large Language Models (LLMs) as general-purpose agents is essential for understanding their capabilities and facilitating their integration into practical applications. However, the evaluation process presents substantial challenges. A primary obstacle is the benchmarking of agent performance across diverse scenarios within a unified framework, especially in maintaining partially-observable environments and ensuring multi-round interactions. Moreover, current evaluation frameworks mostly focus on the final success rate, revealing few insights during the process and failing to provide a deep understanding of the model abilities. To address these challenges, we introduce AgentBoard, a pioneering comprehensive benchmark and accompanied open-source evaluation framework tailored to analytical evaluation of LLM agents. AgentBoard offers a fine-grained progress rate metric that captures incremental advancements as well as a comprehensive evaluation toolkit that features easy assessment of agents for multi-faceted analysis. This not only sheds light on the capabilities and limitations of LLM agents but also propels the interpretability of their performance to the forefront. Ultimately, AgentBoard serves as a step towards demystifying agent behaviors and accelerating the development of stronger LLM agents.
评估大型语言模型(LLM)作为通用代理人的能力对于理解其功能和促进其在实践中的应用至关重要。然而,评估过程存在相当大的挑战。主要的障碍是在统一框架下对不同场景中的代理性能进行基准测试,尤其是在维持部分可观察的环境和确保多轮交互方面。此外,当前的评估框架主要关注最终的成功率,很少揭示过程中的见解,也无法深入了解模型的能力。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了AgentBoard,这是一个开创性的全面基准测试,并伴随着专为LLM代理分析评估量身定制的开源评估框架。AgentBoard提供了一个精细的进度率指标,可以捕捉增量进展,以及一个综合评估工具包,可以轻松对代理进行多方面评估。这不仅揭示了LLM代理的能力和局限性,还将对其性能的解读推向了前沿。最终,AgentBoard是朝着揭示代理行为、加速开发更强大的LLM代理方向迈出的一步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2024 (Oral)
Summary:
评估大型语言模型(LLM)作为通用代理人的能力对于理解其功能和促进其在实践中的应用至关重要。然而,评估过程面临巨大挑战,如在一个统一框架下对代理人在不同场景中的表现进行基准测试,特别是在保持部分可观察环境和确保多轮交互方面的挑战。现有的评估框架主要关注最终的成功率,忽视了过程性的洞察,无法深入了解模型的能力。为解决这些挑战,我们推出AgentBoard,这是一个开创性的全面基准伴随开源评估框架,专为LLM代理人的分析评估而设计。AgentBoard提供精细的进度率指标,捕捉增量进展,并配备全面的评估工具包,轻松对代理人进行多方面分析。这不仅揭示了LLM代理人的能力和局限性,还将对其性能的解释性推向了前沿。最终,AgentBoard是朝着揭示代理行为、加速更强LLM代理人的开发迈出的一步。
Key Takeaways:
- 评估大型语言模型(LLM)作为通用代理人的能力至关重要。
- 评估过程面临诸多挑战,如统一框架下的多场景基准测试。
- 现有评估框架主要关注最终成功率,忽视过程洞察。
- AgentBoard是一个全面的基准伴随开源评估框架,专为LLM代理人的分析评估而设计。
- AgentBoard提供精细的进度率指标和全面的评估工具包。
- AgentBoard有助于揭示LLM代理人的能力和局限性,并推动对其性能的解释性。
点此查看论文截图

CoMIX: A Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning Training Architecture for Efficient Decentralized Coordination and Independent Decision-Making
Authors:Giovanni Minelli, Mirco Musolesi
Robust coordination skills enable agents to operate cohesively in shared environments, together towards a common goal and, ideally, individually without hindering each other’s progress. To this end, this paper presents Coordinated QMIX (CoMIX), a novel training framework for decentralized agents that enables emergent coordination through flexible policies, allowing at the same time independent decision-making at individual level. CoMIX models selfish and collaborative behavior as incremental steps in each agent’s decision process. This allows agents to dynamically adapt their behavior to different situations balancing independence and collaboration. Experiments using a variety of simulation environments demonstrate that CoMIX outperforms baselines on collaborative tasks. The results validate our incremental approach as effective technique for improving coordination in multi-agent systems.
具有稳健协调技能的智能体能够在共享环境中协同操作,共同朝着一个共同目标前进,理想情况下,个体之间不会相互阻碍彼此的进步。为此,本文提出了协调QMIX(CoMIX)这一新型去中心化智能体训练框架。它通过灵活的策略实现智能体之间的协调出现,同时允许个体层面进行独立决策。CoMIX将自私和协作行为建模为智能体决策过程中的增量步骤。这使得智能体能够根据不同的情境动态调整其行为,在独立性和协作性之间取得平衡。在各种仿真环境中进行的实验表明,在协作任务方面,CoMIX优于基准线。结果验证了我们的增量方法作为提高多智能体系统协调性的有效技术。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
复杂环境下多智能体协作问题可通过新型训练框架Coordinated QMIX(CoMIX)解决。该框架支持灵活策略,促进智能体间协调同时维持个体独立决策能力。CoMIX将自私与协作行为建模为智能体决策过程中的逐步增长步骤,实现行为动态适应不同情况,平衡独立与协作。实验表明,CoMIX在协作任务上优于基准方法,验证了增量方法在改善多智能体系统协调中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- Coordinated QMIX(CoMIX)是一种用于训练去中心化智能体的新型框架。
- CoMIX通过灵活的策略促进智能体间的协调。
- CoMIX允许个体智能体在决策过程中保持独立。
- CoMIX将自私和协作行为建模为决策过程中的逐步增长步骤。
- 智能体能通过CoMIX动态适应不同情境,平衡独立与协作。
- 实验证明,在协作任务上,CoMIX表现优于基准方法。
点此查看论文截图