⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-26 更新
PartGen: Part-level 3D Generation and Reconstruction with Multi-View Diffusion Models
Authors:Minghao Chen, Roman Shapovalov, Iro Laina, Tom Monnier, Jianyuan Wang, David Novotny, Andrea Vedaldi
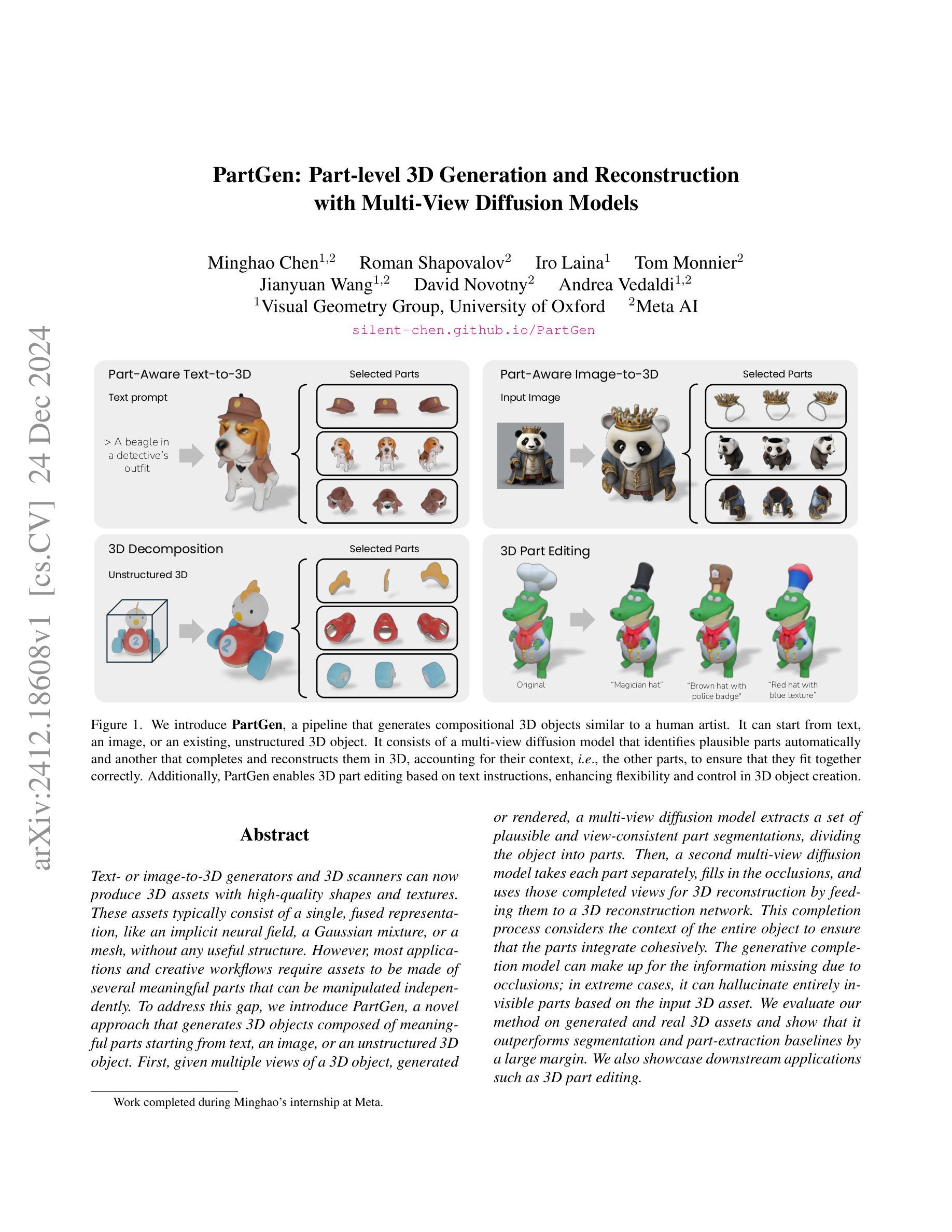
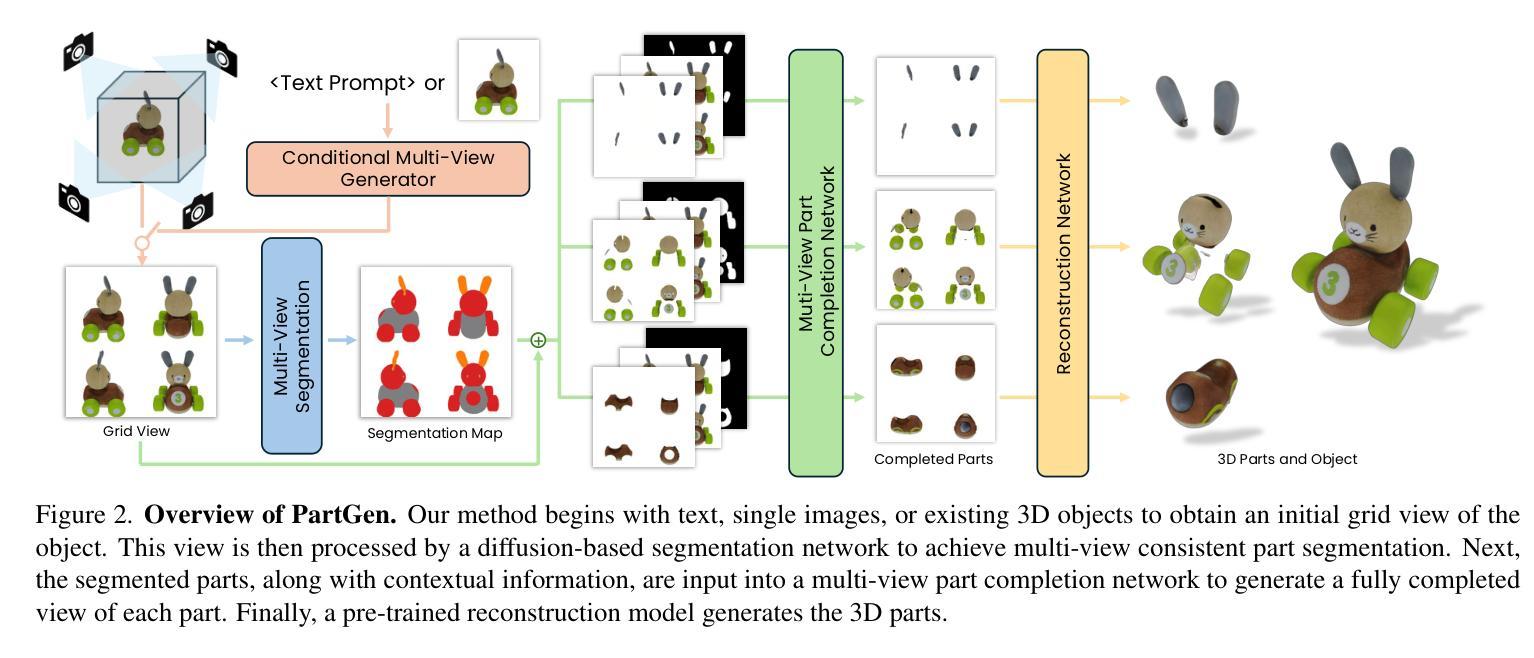
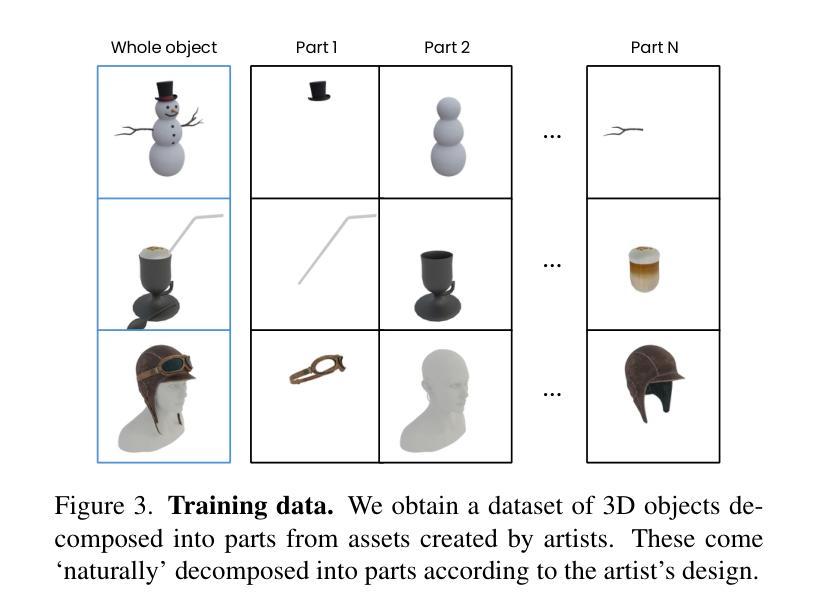
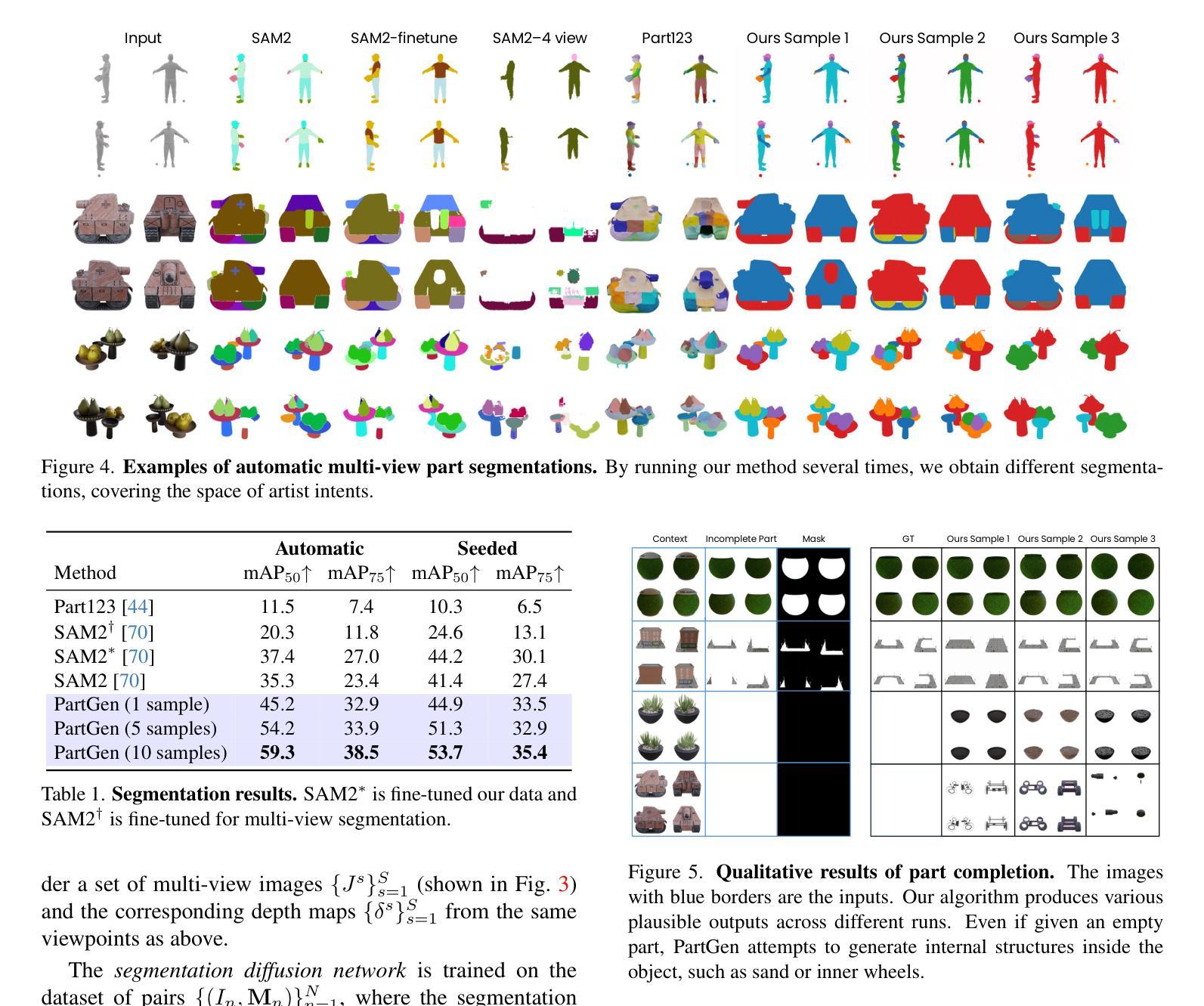
Text- or image-to-3D generators and 3D scanners can now produce 3D assets with high-quality shapes and textures. These assets typically consist of a single, fused representation, like an implicit neural field, a Gaussian mixture, or a mesh, without any useful structure. However, most applications and creative workflows require assets to be made of several meaningful parts that can be manipulated independently. To address this gap, we introduce PartGen, a novel approach that generates 3D objects composed of meaningful parts starting from text, an image, or an unstructured 3D object. First, given multiple views of a 3D object, generated or rendered, a multi-view diffusion model extracts a set of plausible and view-consistent part segmentations, dividing the object into parts. Then, a second multi-view diffusion model takes each part separately, fills in the occlusions, and uses those completed views for 3D reconstruction by feeding them to a 3D reconstruction network. This completion process considers the context of the entire object to ensure that the parts integrate cohesively. The generative completion model can make up for the information missing due to occlusions; in extreme cases, it can hallucinate entirely invisible parts based on the input 3D asset. We evaluate our method on generated and real 3D assets and show that it outperforms segmentation and part-extraction baselines by a large margin. We also showcase downstream applications such as 3D part editing.
文本或图像到3D生成器和3D扫描仪现在可以生成具有高质量形状和纹理的3D资产。这些资产通常由单一融合表示组成,如隐式神经网络、高斯混合或网格,而没有有用的结构。然而,大多数应用程序和创意工作流程要求资产由可以独立操作的多个有意义的部分组成。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了PartGen,这是一种从文本、图像或无序的3D对象开始生成由有意义的部件组成的3D对象的新方法。首先,给定一个3D对象的多个视图,无论是生成的还是渲染的,多视图扩散模型会提取一组合理且视图一致的部分分割,将对象分割成各个部分。然后,第二个多视图扩散模型单独处理每个部分,填充遮挡物,并使用这些完成的视图进行3D重建,方法是将其输入到3D重建网络中。此完成过程会考虑整个对象的上下文,以确保各部分能够紧密集成。生成完成模型可以弥补因遮挡而缺失的信息;在极端情况下,它可以根据输入的3D资产完全虚构出不可见的部分。我们在生成的和真实的3D资产上评估了我们的方法,并显示出它大大优于分割和部分提取的基线。我们还展示了下游应用,如3D零件编辑。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://silent-chen.github.io/PartGen/
Summary
该文介绍了一种名为PartGen的新方法,该方法能够从文本、图像或无序的3D对象开始,生成由有意义的部件组成的3D物体。PartGen通过多视角扩散模型提取出可能的、视角一致的部件分割,然后对每一个部件进行填充和完善,最后通过3D重建网络进行三维重建。此方法能够弥补因遮挡而缺失的信息,甚至在极端情况下,可以基于输入的3D资产凭空生成完全不可见的部件。PartGen在生成和真实的3D资产上的表现均优于现有的分割和部件提取方法,并在3D部件编辑等下游应用展示了其潜力。
Key Takeaways
- PartGen能够生成由有意义部件组成的3D资产,从文本、图像或无序的3D对象开始。
- PartGen使用多视角扩散模型提取3D物体的部件分割。
- 扩散模型能够填充和完善部件,并考虑整个物体的上下文来确保部件的整合。
- PartGen能够弥补因遮挡而缺失的信息,甚至生成完全不可见的部件。
- PartGen在生成和真实的3D资产上的表现均优于现有的方法。
- PartGen具有广泛的应用潜力,如3D部件编辑等下游应用。
- PartGen为创建和操作复杂的3D场景提供了一个有效的工具,有助于推动3D生成和编辑技术的发展。
点此查看论文截图
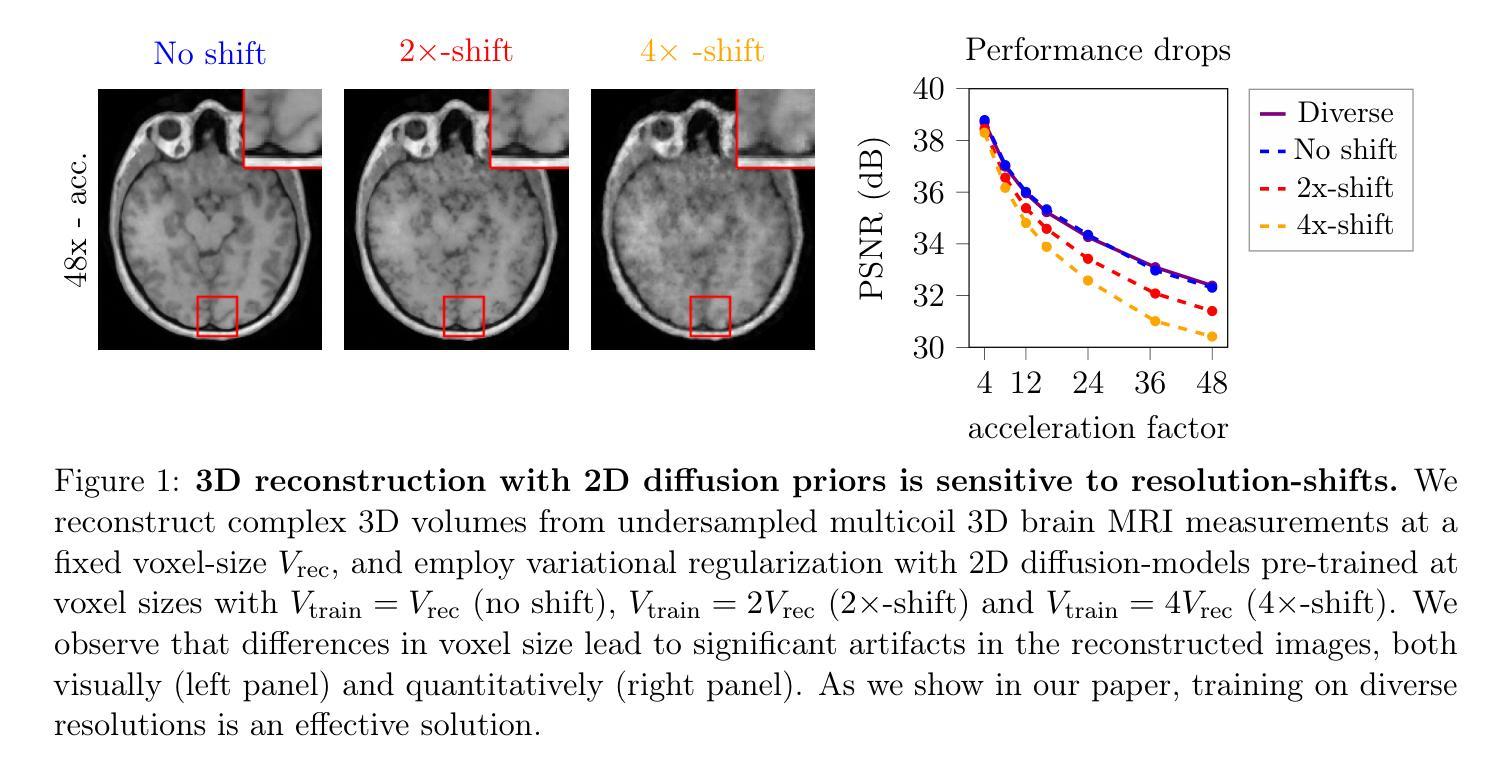
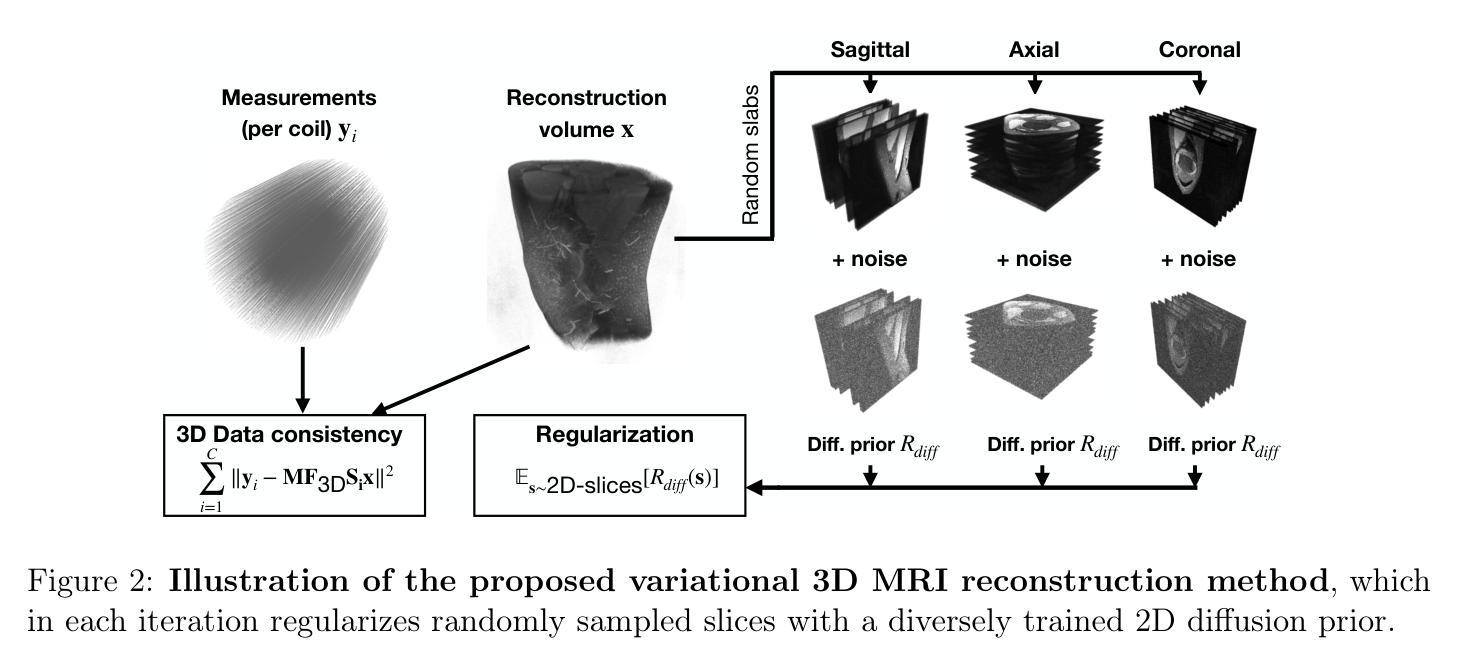
Resolution-Robust 3D MRI Reconstruction with 2D Diffusion Priors: Diverse-Resolution Training Outperforms Interpolation
Authors:Anselm Krainovic, Stefan Ruschke, Reinhard Heckel
Deep learning-based 3D imaging, in particular magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), is challenging because of limited availability of 3D training data. Therefore, 2D diffusion models trained on 2D slices are starting to be leveraged for 3D MRI reconstruction. However, as we show in this paper, existing methods pertain to a fixed voxel size, and performance degrades when the voxel size is varied, as it is often the case in clinical practice. In this paper, we propose and study several approaches for resolution-robust 3D MRI reconstruction with 2D diffusion priors. As a result of this investigation, we obtain a simple resolution-robust variational 3D reconstruction approach based on diffusion-guided regularization of randomly sampled 2D slices. This method provides competitive reconstruction quality compared to posterior sampling baselines. Towards resolving the sensitivity to resolution-shifts, we investigate state-of-the-art model-based approaches including Gaussian splatting, neural representations, and infinite-dimensional diffusion models, as well as a simple data-centric approach of training the diffusion model on several resolutions. Our experiments demonstrate that the model-based approaches fail to close the performance gap in 3D MRI. In contrast, the data-centric approach of training the diffusion model on various resolutions effectively provides a resolution-robust method without compromising accuracy.
基于深度学习的3D成像,特别是磁共振成像(MRI),由于3D训练数据的有限可用性而具有挑战性。因此,开始利用在2D切片上训练的2D扩散模型进行3D MRI重建。然而,我们在本文中展示,现有方法涉及固定的体素大小,当体素大小发生变化时,性能会下降,这在临床实践中是常见的情况。在本文中,我们针对具有2D扩散先验的分辨率稳健的3D MRI重建提出了几种方法并进行了研究。通过这项研究,我们获得了一种基于随机采样2D切片的扩散引导正则化的简单分辨率稳健变分3D重建方法。该方法与后采样基线相比,提供了具有竞争力的重建质量。为了解决对分辨率变化的敏感性,我们调查了基于模型的最新方法,包括高斯喷射、神经表示和无限维扩散模型,以及一种在多种分辨率上训练扩散模型的简单以数据为中心的方法。我们的实验表明,基于模型的方法未能缩小在3D MRI中的性能差距。相反,以数据为中心的在多种分辨率上训练扩散模型的方法有效地提供了一种分辨率稳健的方法,而不会牺牲准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了基于深度学习的三维成像技术(尤其是磁共振成像)所面临的挑战。因三维训练数据的局限性,开始利用二维扩散模型进行三维MRI重建。然而,现有方法受限于固定的体素大小,在临床实践中体素大小变化时性能会下降。本文提出并研究了几种具有二维扩散先验的分辨率鲁棒三维MRI重建方法。经过调查,得出一种基于扩散引导正则化的简单分辨率鲁棒三维重建方法,对随机采样的二维切片进行处理。与后采样基线相比,该方法具有竞争力的重建质量。为解决对分辨率变化的敏感性,本文研究了基于模型的方法,包括高斯溅射、神经表征和无限维扩散模型等,以及一种简单的以数据为中心的训练扩散模型的方法,即在多种分辨率上进行训练。实验表明,基于模型的方法在3D MRI中未能弥补性能差距。相反,以数据为中心的训练扩散模型的方法在各种分辨率上提供有效的分辨率鲁棒方法,且不损失准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在三维成像(尤其是MRI)中的应用面临缺乏足够的三维训练数据的挑战。
- 当前的方法受限于固定的体素大小,使得在临床实践中体素大小变化时性能下降。
- 提出了一种基于扩散引导正则化的分辨率鲁棒的三维MRI重建方法,该方法处理随机采样的二维切片。
- 与后采样基线相比,该方法具有竞争力的重建质量。
- 尝试多种模型方法以解决分辨率变化的问题,包括高斯溅射、神经表征和无限维扩散模型等,但效果并不理想。
- 一种以数据为中心的训练扩散模型的方法在各种分辨率上表现有效,提供分辨率鲁棒性且不损失准确性。
点此查看论文截图

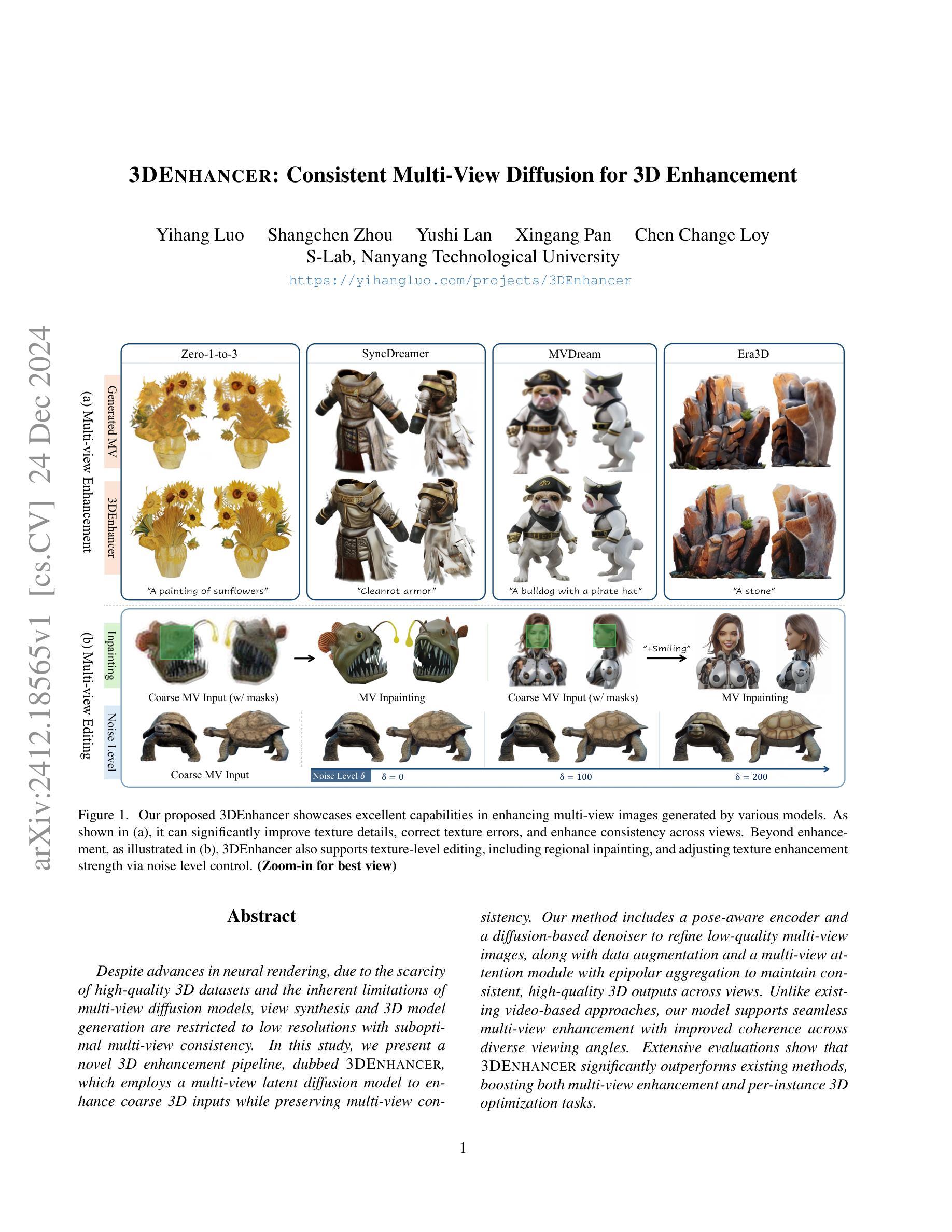
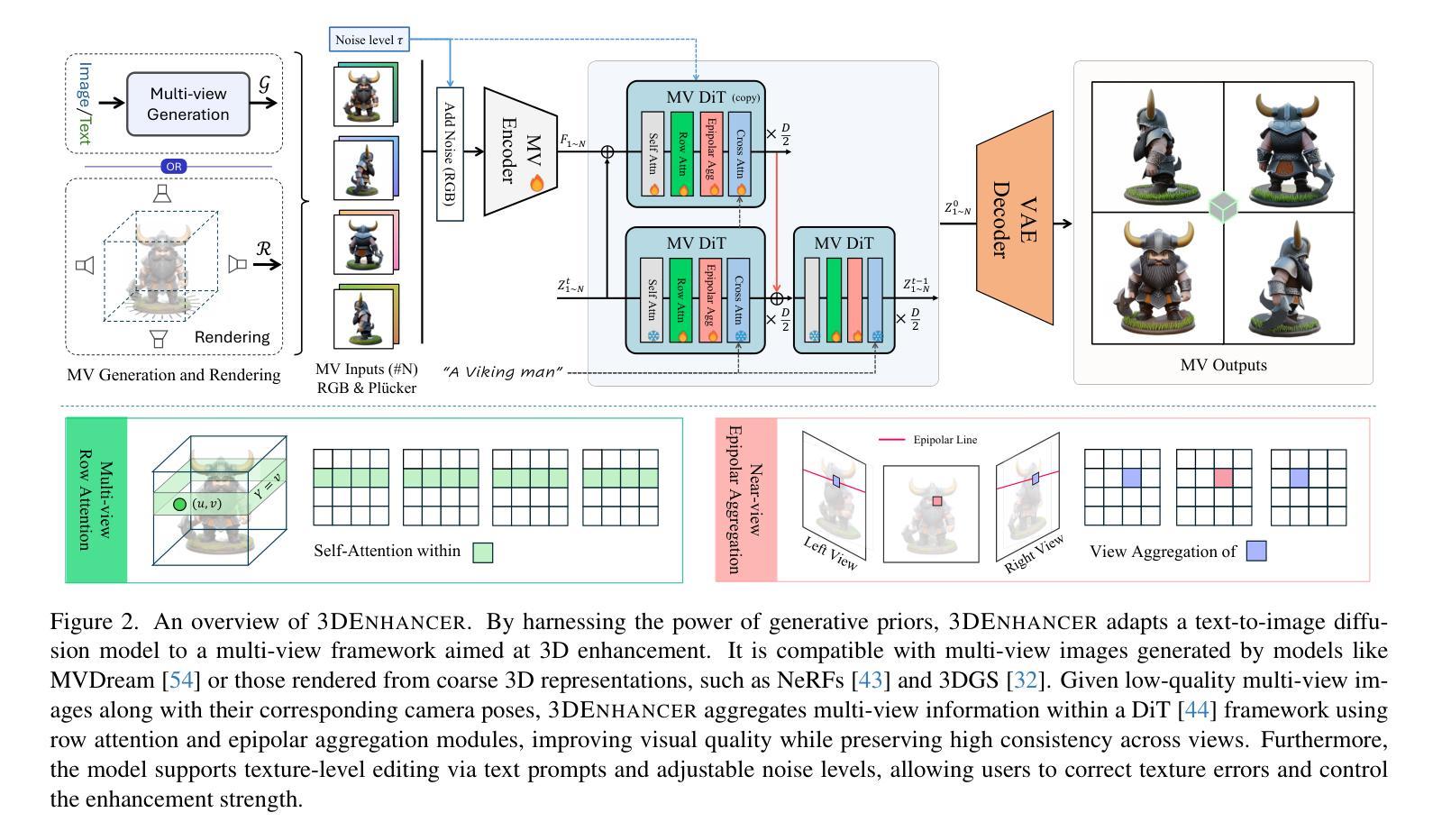
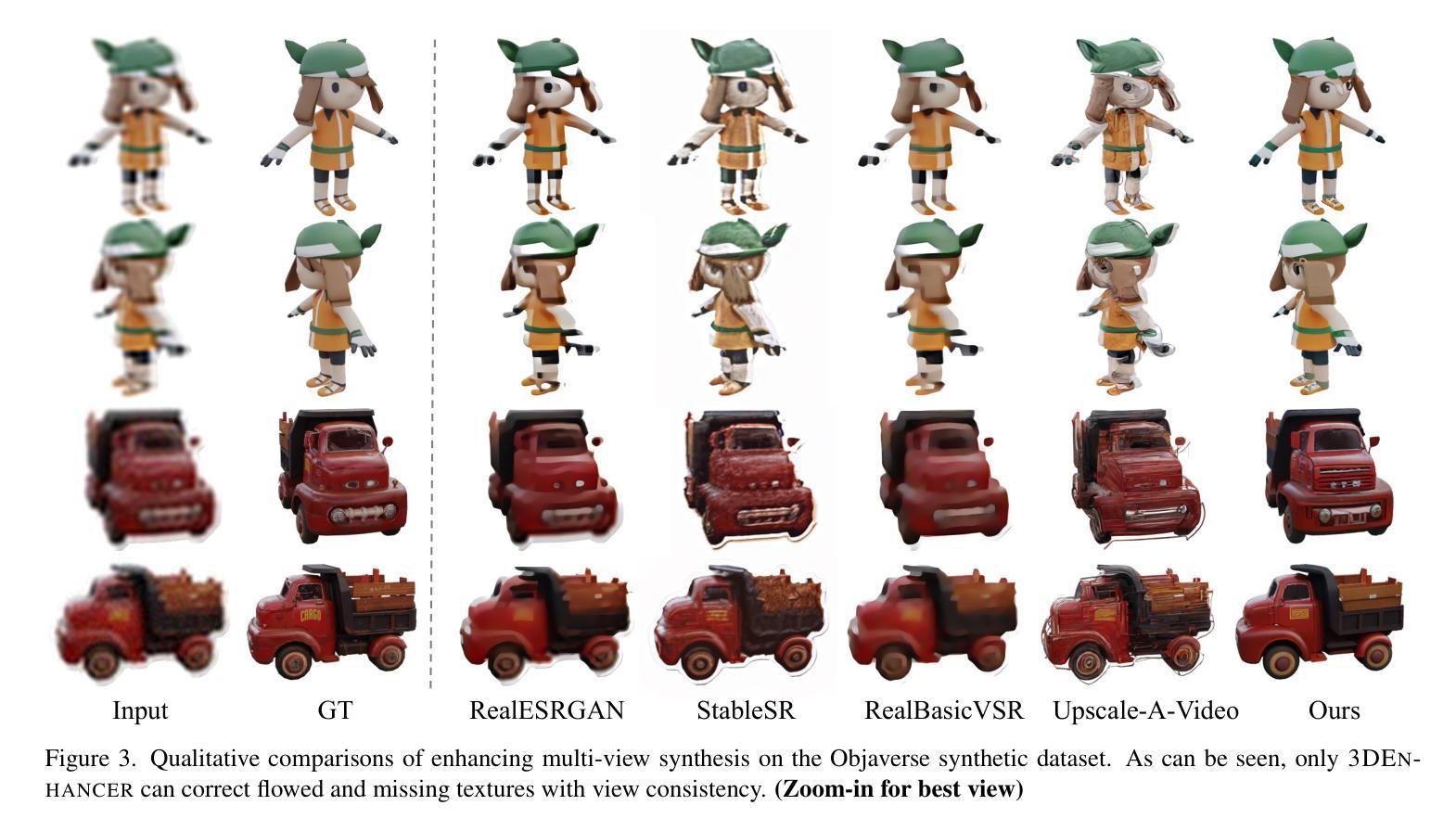
3DEnhancer: Consistent Multi-View Diffusion for 3D Enhancement
Authors:Yihang Luo, Shangchen Zhou, Yushi Lan, Xingang Pan, Chen Change Loy
Despite advances in neural rendering, due to the scarcity of high-quality 3D datasets and the inherent limitations of multi-view diffusion models, view synthesis and 3D model generation are restricted to low resolutions with suboptimal multi-view consistency. In this study, we present a novel 3D enhancement pipeline, dubbed 3DEnhancer, which employs a multi-view latent diffusion model to enhance coarse 3D inputs while preserving multi-view consistency. Our method includes a pose-aware encoder and a diffusion-based denoiser to refine low-quality multi-view images, along with data augmentation and a multi-view attention module with epipolar aggregation to maintain consistent, high-quality 3D outputs across views. Unlike existing video-based approaches, our model supports seamless multi-view enhancement with improved coherence across diverse viewing angles. Extensive evaluations show that 3DEnhancer significantly outperforms existing methods, boosting both multi-view enhancement and per-instance 3D optimization tasks.
尽管神经网络渲染有所进展,但由于高质量3D数据集稀缺以及多视角扩散模型本身的局限性,视图合成和3D模型生成仍然受限于低分辨率,并且多视角一致性不佳。在本研究中,我们提出了一种新型3D增强流程,名为“3DEnhancer”,它采用多视角潜在扩散模型,能够在保持多视角一致性的同时,增强粗糙的3D输入。我们的方法包括一个姿态感知编码器和一个基于扩散的去噪器,用于细化低质量的多视角图像,还包括数据增强和带有极线聚合的多视角注意力模块,以在多种视角之间保持一致、高质量输出。与现有的视频方法不同,我们的模型支持无缝的多视角增强,并且在不同的观看角度上都具备更强的连贯性。广泛评估表明,相较于现有方法,3DEnhancer在多视角增强和每个实例的3D优化任务上都表现出显著优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://yihangluo.com/projects/3DEnhancer
Summary
本文提出了一种名为3DEnhancer的新型3D增强管道,采用多视角潜在扩散模型,对粗糙的3D输入进行增强,同时保持多视角的一致性。通过姿态感知编码器、基于扩散的去噪器、数据增强和多视角注意力模块等多种技术,实现了低质量多视角图像的精细处理,并维持了跨视角的高品质3D输出一致性。与现有视频方法不同,该模型支持无缝多视角增强,在不同观看角度间具有更好的连贯性。评估表明,3DEnhancer显著优于现有方法,同时提升了多视角增强和每个实例的3D优化任务的效果。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了新型的3D增强管道——3DEnhancer。
- 采用多视角潜在扩散模型进行低质量3D输入的增强。
- 通过姿态感知编码器和基于扩散的去噪器对低质量的多视角图像进行精细处理。
- 利用数据增强和多视角注意力模块维持跨视角的高品质输出一致性。
- 与现有视频方法不同,支持无缝多视角增强,提高不同观看角度间的连贯性。
- 评估结果显示,3DEnhancer在多项任务上显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图
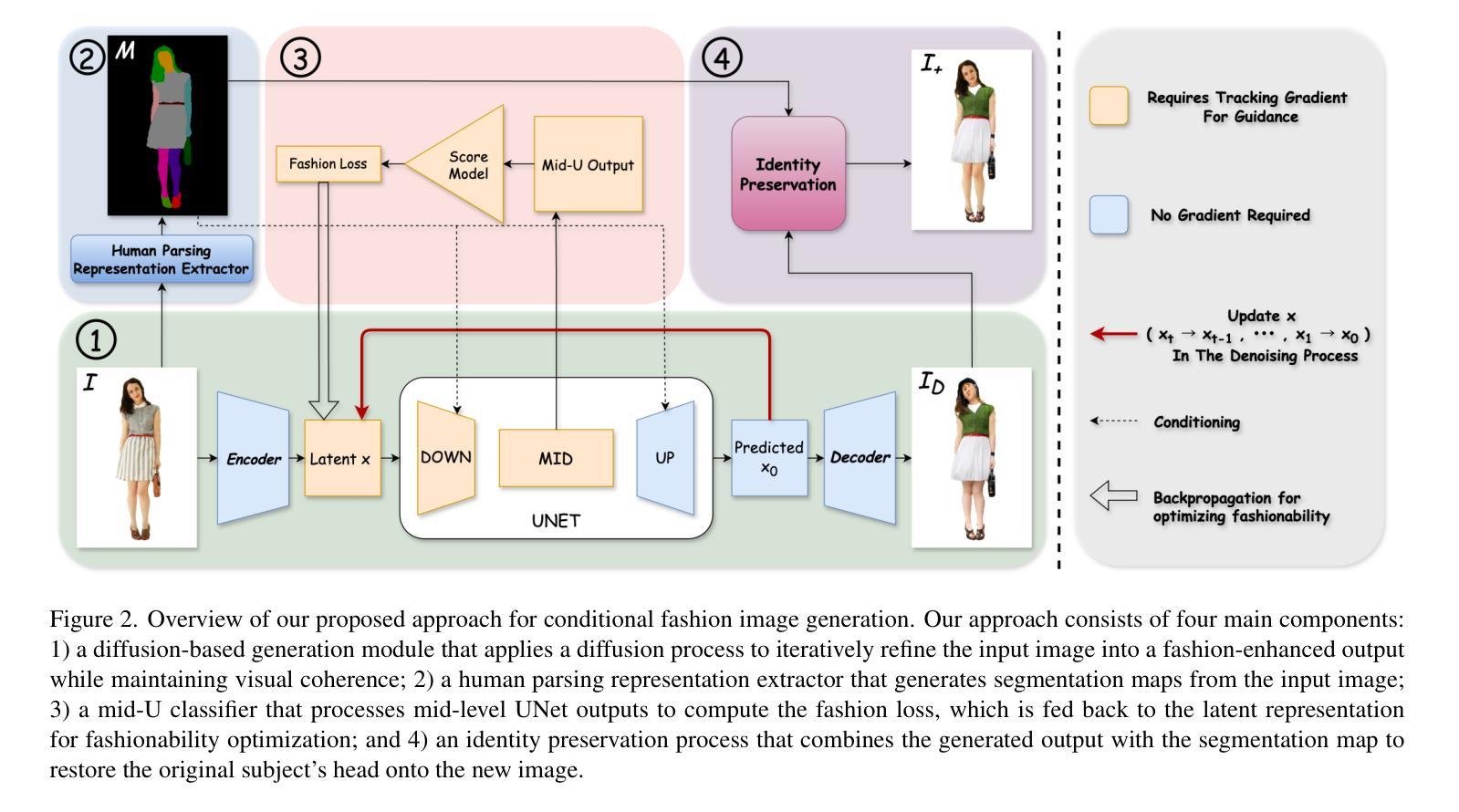
Fashionability-Enhancing Outfit Image Editing with Conditional Diffusion Models
Authors:Qice Qin, Yuki Hirakawa, Ryotaro Shimizu, Takuya Furusawa, Edgar Simo-Serra
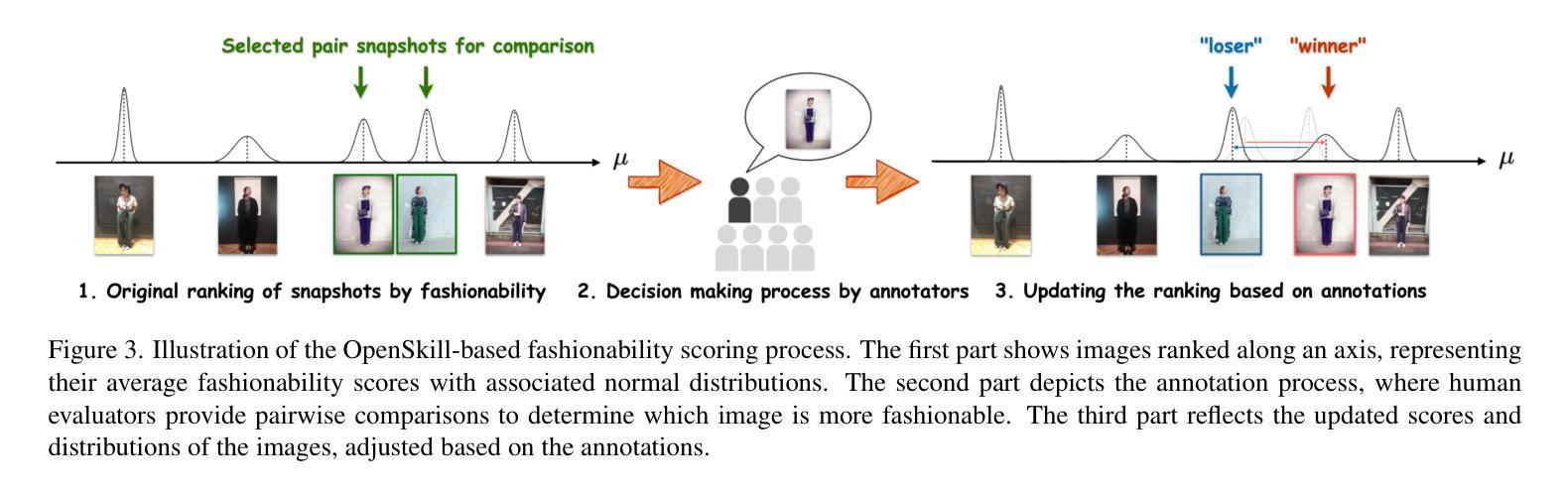
Image generation in the fashion domain has predominantly focused on preserving body characteristics or following input prompts, but little attention has been paid to improving the inherent fashionability of the output images. This paper presents a novel diffusion model-based approach that generates fashion images with improved fashionability while maintaining control over key attributes. Key components of our method include: 1) fashionability enhancement, which ensures that the generated images are more fashionable than the input; 2) preservation of body characteristics, encouraging the generated images to maintain the original shape and proportions of the input; and 3) automatic fashion optimization, which does not rely on manual input or external prompts. We also employ two methods to collect training data for guidance while generating and evaluating the images. In particular, we rate outfit images using fashionability scores annotated by multiple fashion experts through OpenSkill-based and five critical aspect-based pairwise comparisons. These methods provide complementary perspectives for assessing and improving the fashionability of the generated images. The experimental results show that our approach outperforms the baseline Fashion++ in generating images with superior fashionability, demonstrating its effectiveness in producing more stylish and appealing fashion images.
时尚领域的图像生成主要聚焦于保留人体特征或遵循输入提示,但对提高输出图像的内在时尚性关注较少。本文提出了一种基于扩散模型的新方法,在保持关键属性控制的同时,生成具有改进时尚性的时尚图像。我们的方法的关键组成部分包括:1)时尚性增强,确保生成的图像比输入图像更时尚;2)保留人体特征,鼓励生成的图像保持输入的原始形状和比例;3)自动时尚优化,不依赖手动输入或外部提示。我们还采用两种方法收集训练数据,用于在生成和评估图像时进行指导。特别是,我们通过基于OpenSkill和五个关键方面的成对比较,由多名时尚专家对服装图像进行时尚度评分注释。这些方法为评估和提高生成图像的时尚性提供了互补的视角。实验结果表明,我们的方法在生成具有优越时尚性的图像方面优于基线Fashion++,证明其在生成更时尚和吸引人的时尚图像方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 6 figures
Summary
本文提出了一种基于扩散模型的新方法,用于生成时尚图像。该方法可改善生成图像的时尚性,同时保持对关键属性的控制。该研究采用多种方法收集训练数据,并利用时尚专家标注的时尚评分来评估和改进生成图像的时尚性。实验结果表明,该方法在生成具有更高时尚性的图像方面优于基线Fashion++。
Key Takeaways
- 时尚领域的图像生成主要关注保留身体特征或遵循输入提示,但很少有人关注提高输出图像的内在时尚性。
- 本文提出了一种基于扩散模型的方法,能够生成具有改进时尚性的时尚图像,同时保持对关键属性的控制。
- 方法的关键组成部分包括:提高时尚性、保留身体特征以及自动时尚优化。
- 采用两种方法来收集训练数据,用于在生成和评估图像时提供指导。
- 通过基于时尚的评分和五个关键方面的成对比较,由多位时尚专家对服装图像进行评估。
- 这些方法提供了评估和改进生成图像时尚性的互补视角。
点此查看论文截图

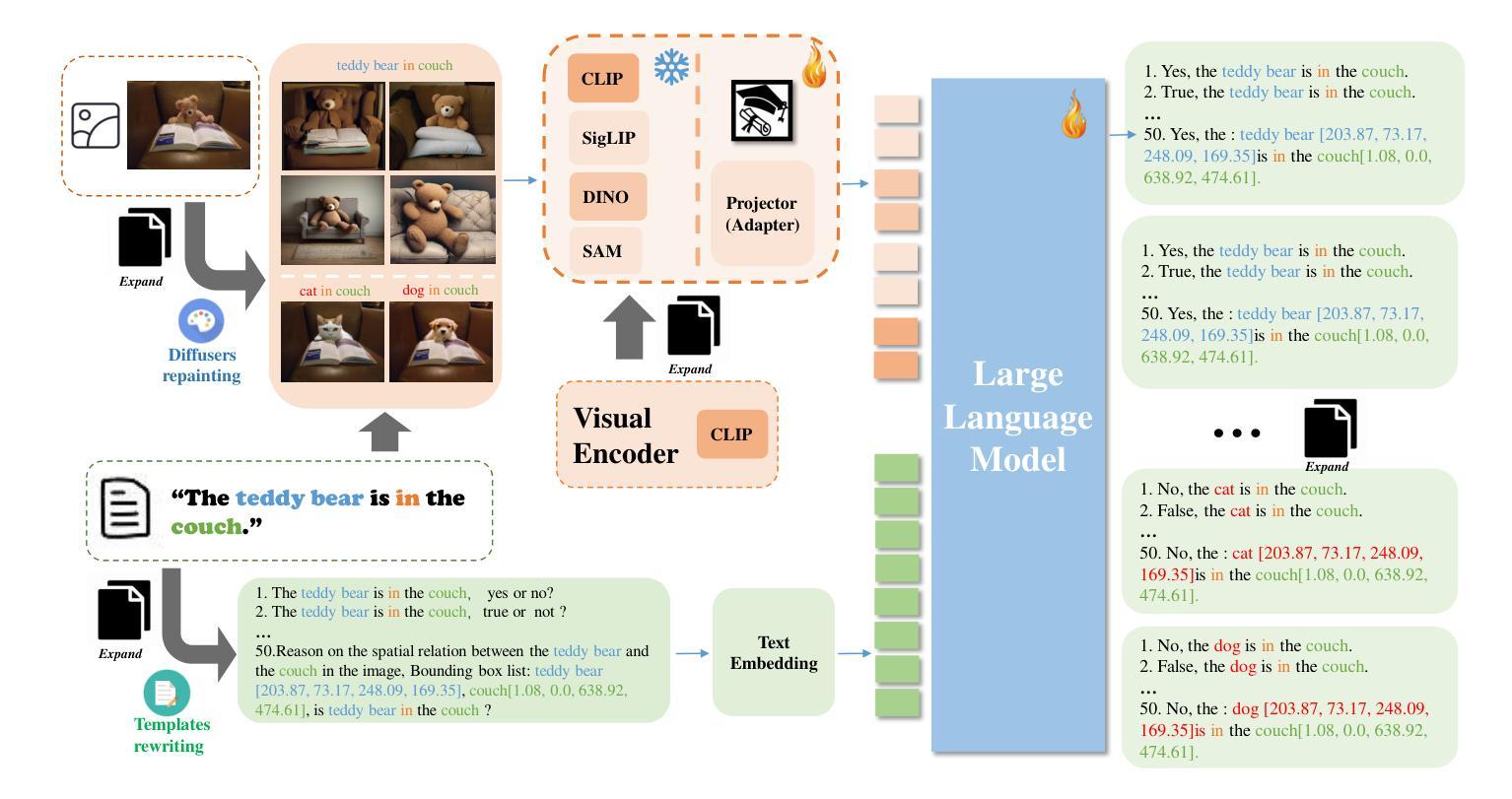
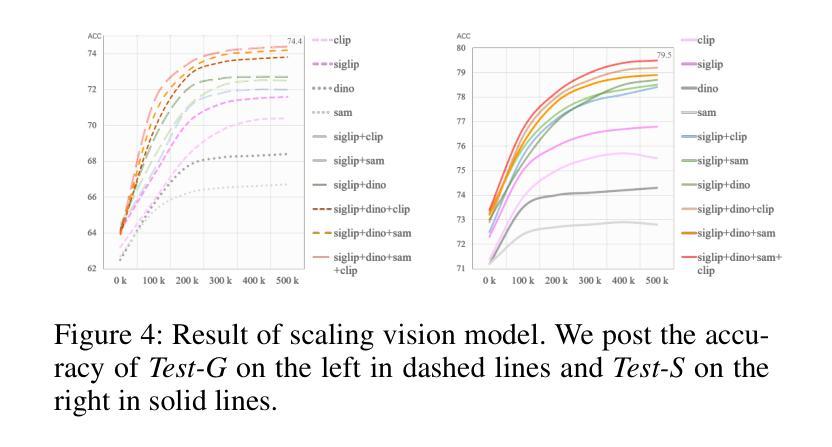
Expand VSR Benchmark for VLLM to Expertize in Spatial Rules
Authors:Peijin Xie, Lin Sun, Bingquan Liu, Dexin Wang, Xiangzheng Zhang, Chengjie Sun, Jiajia Zhang
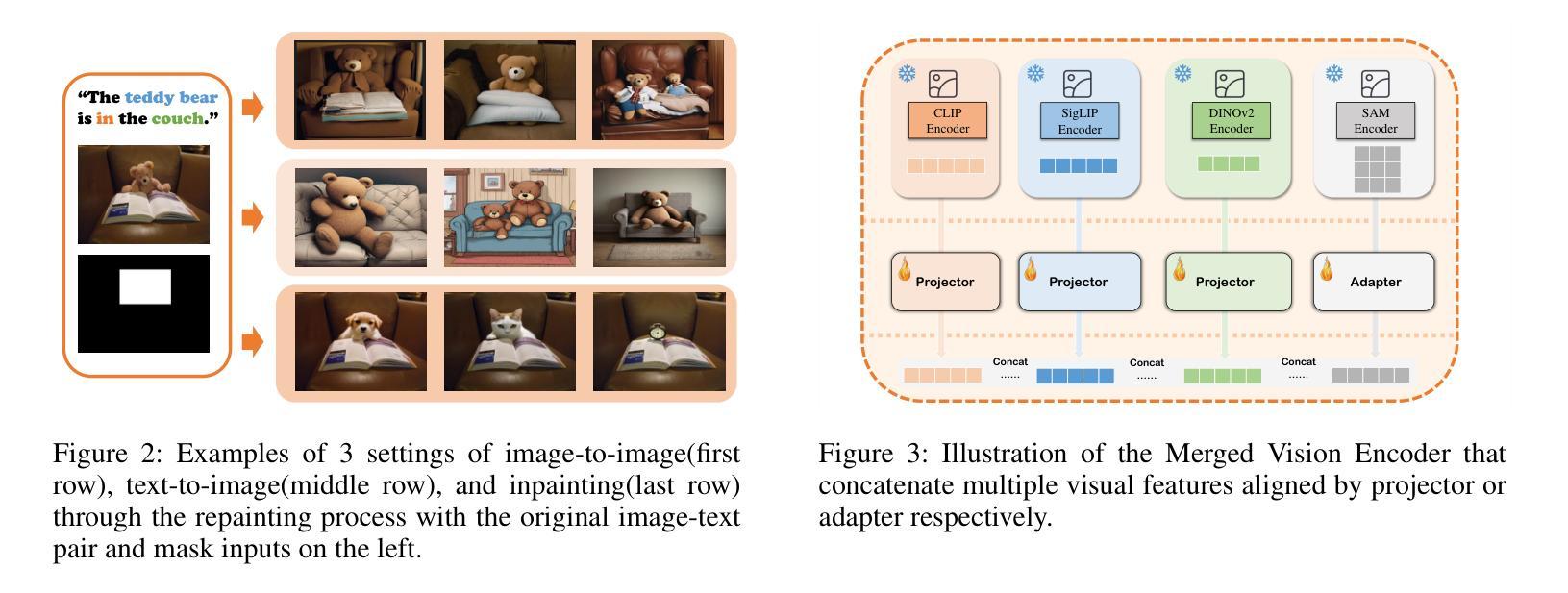
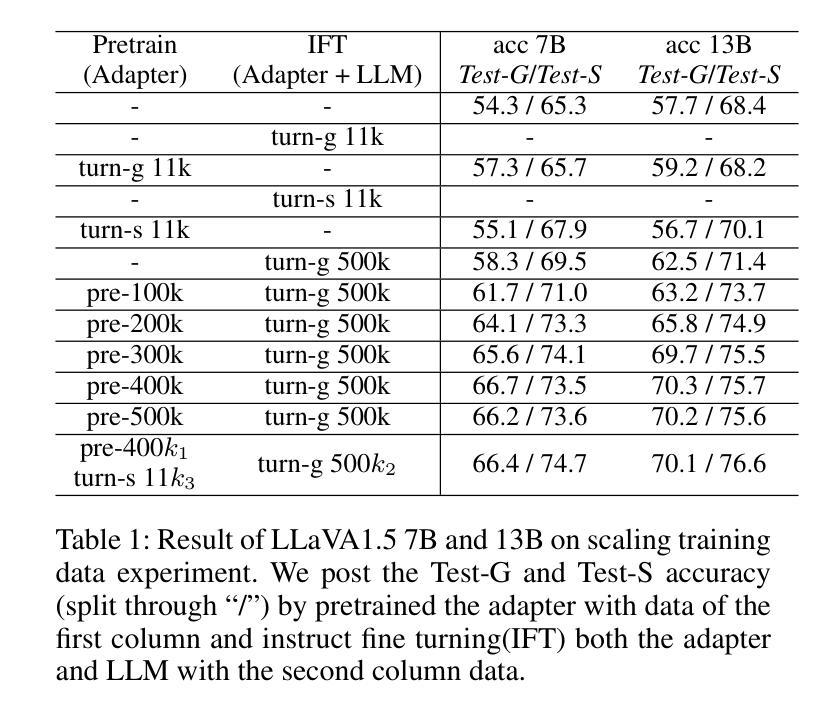
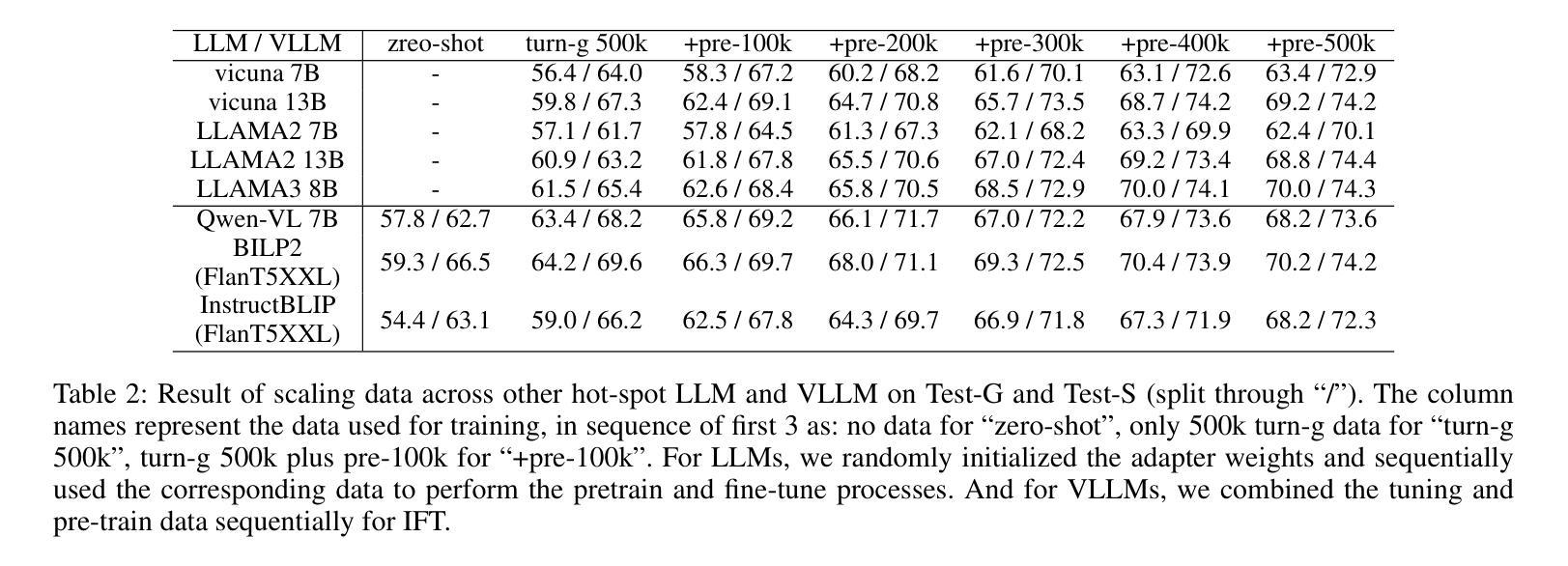
Distinguishing spatial relations is a basic part of human cognition which requires fine-grained perception on cross-instance. Although benchmarks like MME, MMBench and SEED comprehensively have evaluated various capabilities which already include visual spatial reasoning(VSR). There is still a lack of sufficient quantity and quality evaluation and optimization datasets for Vision Large Language Models(VLLMs) specifically targeting visual positional reasoning. To handle this, we first diagnosed current VLLMs with the VSR dataset and proposed a unified test set. We found current VLLMs to exhibit a contradiction of over-sensitivity to language instructions and under-sensitivity to visual positional information. By expanding the original benchmark from two aspects of tunning data and model structure, we mitigated this phenomenon. To our knowledge, we expanded spatially positioned image data controllably using diffusion models for the first time and integrated original visual encoding(CLIP) with other 3 powerful visual encoders(SigLIP, SAM and DINO). After conducting combination experiments on scaling data and models, we obtained a VLLM VSR Expert(VSRE) that not only generalizes better to different instructions but also accurately distinguishes differences in visual positional information. VSRE achieved over a 27% increase in accuracy on the VSR test set. It becomes a performant VLLM on the position reasoning of both the VSR dataset and relevant subsets of other evaluation benchmarks. We open-sourced the expanded model with data and Appendix at \url{https://github.com/peijin360/vsre} and hope it will accelerate advancements in VLLM on VSR learning.
区分空间关系是人类认知的基本组成部分,这需要跨实例的精细感知。虽然MME、MMBench和SEED等基准测试已经全面评估了各种能力,其中包括视觉空间推理(VSR)。然而,针对视觉大语言模型(VLLMs)专门用于视觉位置推理的充足数量和质量评价和优化的数据集仍然缺乏。为了解决这个问题,我们首先使用VSR数据集对当前的VLLMs进行了诊断,并提出了一个统一的测试集。我们发现当前的VLLMs表现出对语言指令过于敏感和对视觉位置信息不够敏感的矛盾。我们通过从调整数据和模型结构两个方面扩展基准测试,缓解了这一现象。据我们所知,我们首次使用扩散模型可控地扩展了空间定位图像数据,并将原始的视觉编码(CLIP)与其他三种强大的视觉编码器(SigLIP、SAM和DINO)进行了集成。在扩大数据和模型规模的组合实验后,我们获得了一个VLLM VSR专家(VSRE),它不仅能更好地适应不同的指令,还能准确区分视觉位置信息的差异。VSRE在VSR测试集上的准确率提高了27%以上。它成为在VSR数据集和其他相关子集的定位推理方面的性能良好的VLLM。我们已在https://github.com/peijin360/vsre开源扩展的模型和附录数据,希望它能加速VLLM在VSR学习方面的进展。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
该文研究了人类认知中的空间关系区分能力,并指出当前针对视觉大语言模型(VLLMs)在视觉位置推理方面的数据集缺乏足够的数量和质量。文章通过诊断当前VLLMs与VSR数据集的问题,提出了一种统一的测试集,并发现当前模型对语言指令过于敏感而对视觉位置信息不够敏感的问题。通过从数据和模型结构两方面进行扩展,缓解了这一问题。此外,文章首次使用扩散模型可控地扩展了空间定位图像数据,并将原始视觉编码CLIP与其他三种强大的视觉编码器SigLIP、SAM和DINO相结合。通过数据和模型的规模扩展组合实验,获得了VLLM VSR Expert(VSRE),该模型不仅对不同指令的泛化能力更强,而且能准确区分视觉位置信息的差异。VSRE在VSR测试集上的准确率提高了超过27%,成为在VSR数据集和其他相关子集的位置推理方面的优秀VLLM。研究团队已公开扩展的模型和附录数据,以加速VLLM在VSR学习方面的进展。
关键见解
- 当前针对视觉大语言模型(VLLMs)在视觉位置推理方面的数据集缺乏足够的数量和质量评价和优化。
- 对当前VLLMs进行诊断,发现它们对语言指令过于敏感,对视觉位置信息不够敏感。
- 通过扩展数据和模型结构,提出了一种缓解上述现象的方法。
- 首次使用扩散模型可控地扩展空间定位图像数据,并将CLIP与其他三种视觉编码器结合。
- 通过组合实验,获得了名为VSRE的VLLM VSR Expert,该模型在VSR数据集上的准确率显著提高。
- VSRE模型已在不同指令中表现出良好的泛化能力,并能准确区分视觉位置信息的差异。
- 研究团队已公开模型和附录数据,以加速VLLM在VSR学习方面的进展。
点此查看论文截图

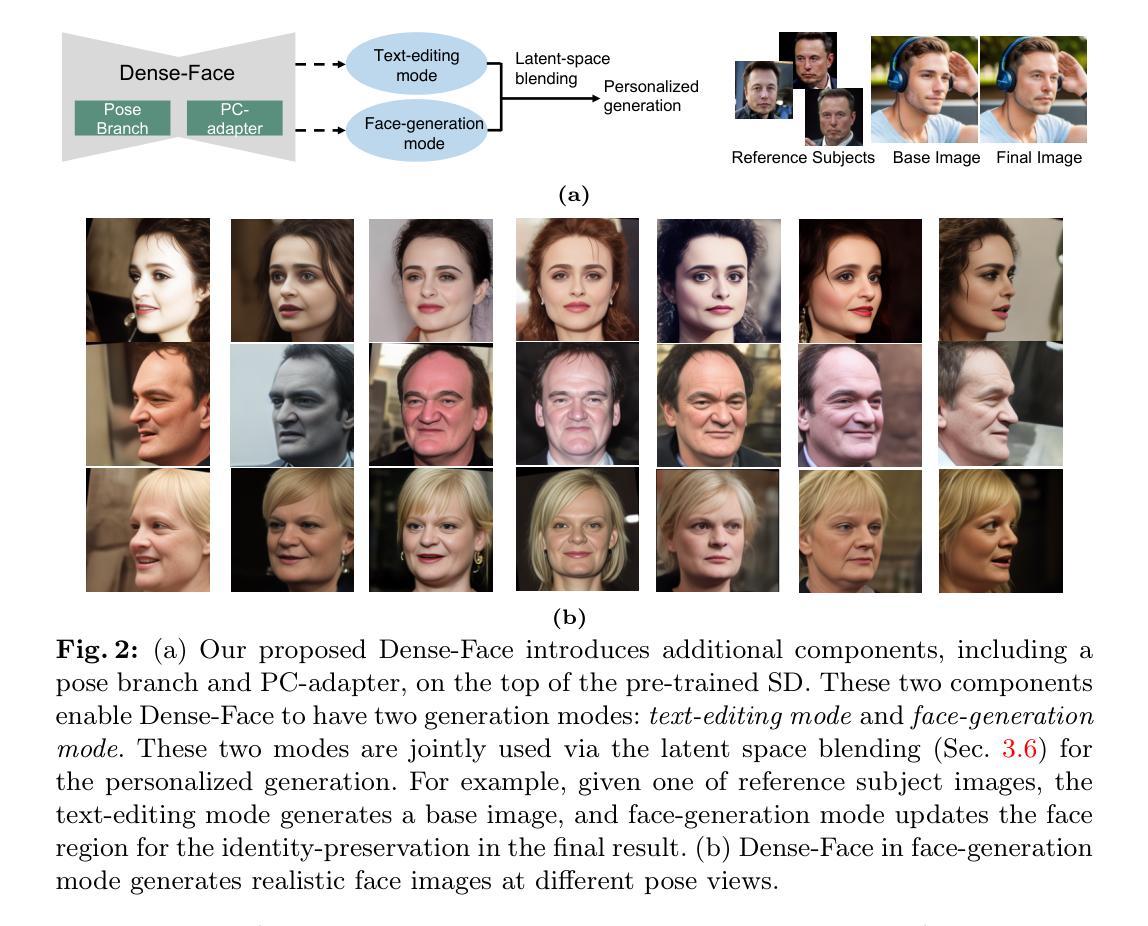
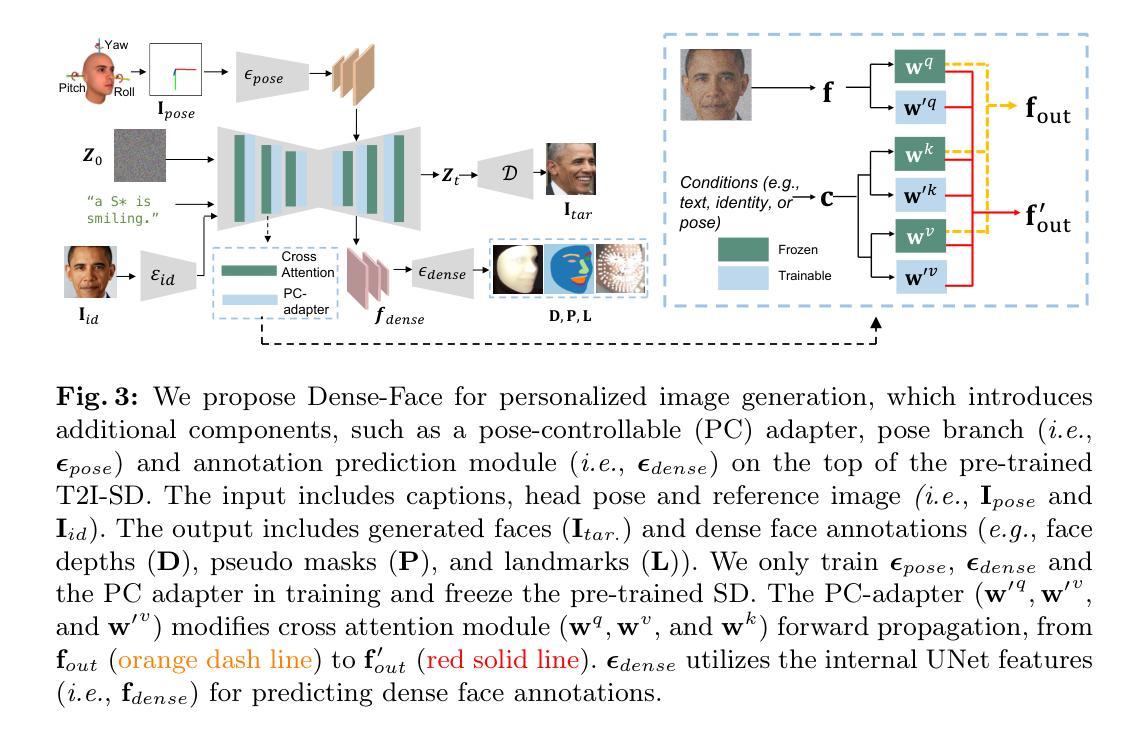
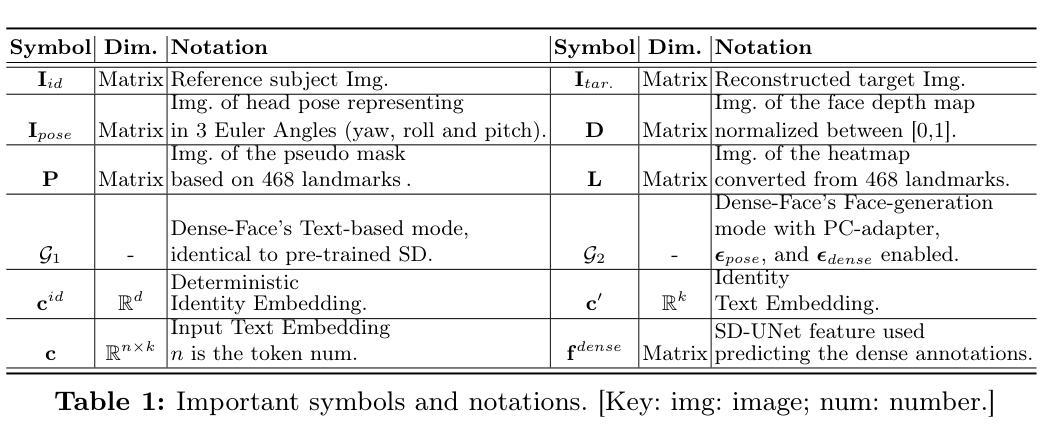
Dense-Face: Personalized Face Generation Model via Dense Annotation Prediction
Authors:Xiao Guo, Manh Tran, Jiaxin Cheng, Xiaoming Liu
The text-to-image (T2I) personalization diffusion model can generate images of the novel concept based on the user input text caption. However, existing T2I personalized methods either require test-time fine-tuning or fail to generate images that align well with the given text caption. In this work, we propose a new T2I personalization diffusion model, Dense-Face, which can generate face images with a consistent identity as the given reference subject and align well with the text caption. Specifically, we introduce a pose-controllable adapter for the high-fidelity image generation while maintaining the text-based editing ability of the pre-trained stable diffusion (SD). Additionally, we use internal features of the SD UNet to predict dense face annotations, enabling the proposed method to gain domain knowledge in face generation. Empirically, our method achieves state-of-the-art or competitive generation performance in image-text alignment, identity preservation, and pose control.
文本转图像(T2I)个性化扩散模型可以根据用户输入的文本描述生成新型概念的图像。然而,现有的T2I个性化方法要么需要测试时的微调,要么无法生成与给定文本描述相符的图像。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新的T2I个性化扩散模型——Dense-Face,该模型能够生成与给定参考主体身份一致的面部图像,并与文本描述良好对齐。具体来说,我们在保持预训练稳定扩散(SD)的文本编辑能力的同时,引入了一个姿态可控的适配器,用于高保真图像生成。此外,我们还使用SD UNet的内部特征来预测密集面部注释,使所提出的方法能够获取面部生成的领域知识。从经验上看,我们的方法在图像文本对齐、身份保留和姿态控制方面达到了最先进的或具有竞争力的生成性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 figures, 5 tables
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型文本转图像个性化扩散模型——Dense-Face。该模型能够根据用户输入的文本描述生成新颖概念的图像,并且能生成与给定参考主体身份一致的人脸图像,同时与文本描述高度对齐。模型引入了姿态可控适配器,以在保持基于文本的编辑能力的同时,实现高保真图像生成。此外,通过使用预训练稳定扩散的内部特征来预测密集人脸注释,使该方法获得人脸生成领域的专业知识。实验表明,该方法在图像文本对齐、身份保留和姿态控制方面达到了领先水平或具有竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- Dense-Face模型能够根据用户输入的文本描述生成新颖概念的图像。
- 该模型能够生成与给定参考主体身份一致的人脸图像。
- Dense-Face模型引入了姿态可控适配器以实现高保真图像生成。
- 模型结合了预训练稳定扩散的内部特征进行密集人脸注释预测。
- Dense-Face模型在图像文本对齐方面达到了领先水平或具有竞争力。
- 该模型在身份保留和姿态控制方面表现出色。
点此查看论文截图

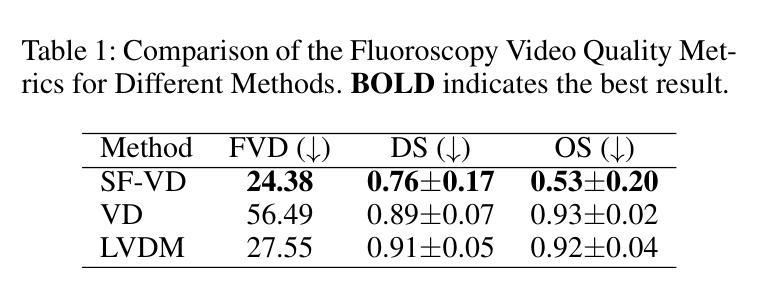
Label-Efficient Data Augmentation with Video Diffusion Models for Guidewire Segmentation in Cardiac Fluoroscopy
Authors:Shaoyan Pan, Yikang Liu, Lin Zhao, Eric Z. Chen, Xiao Chen, Terrence Chen, Shanhui Sun
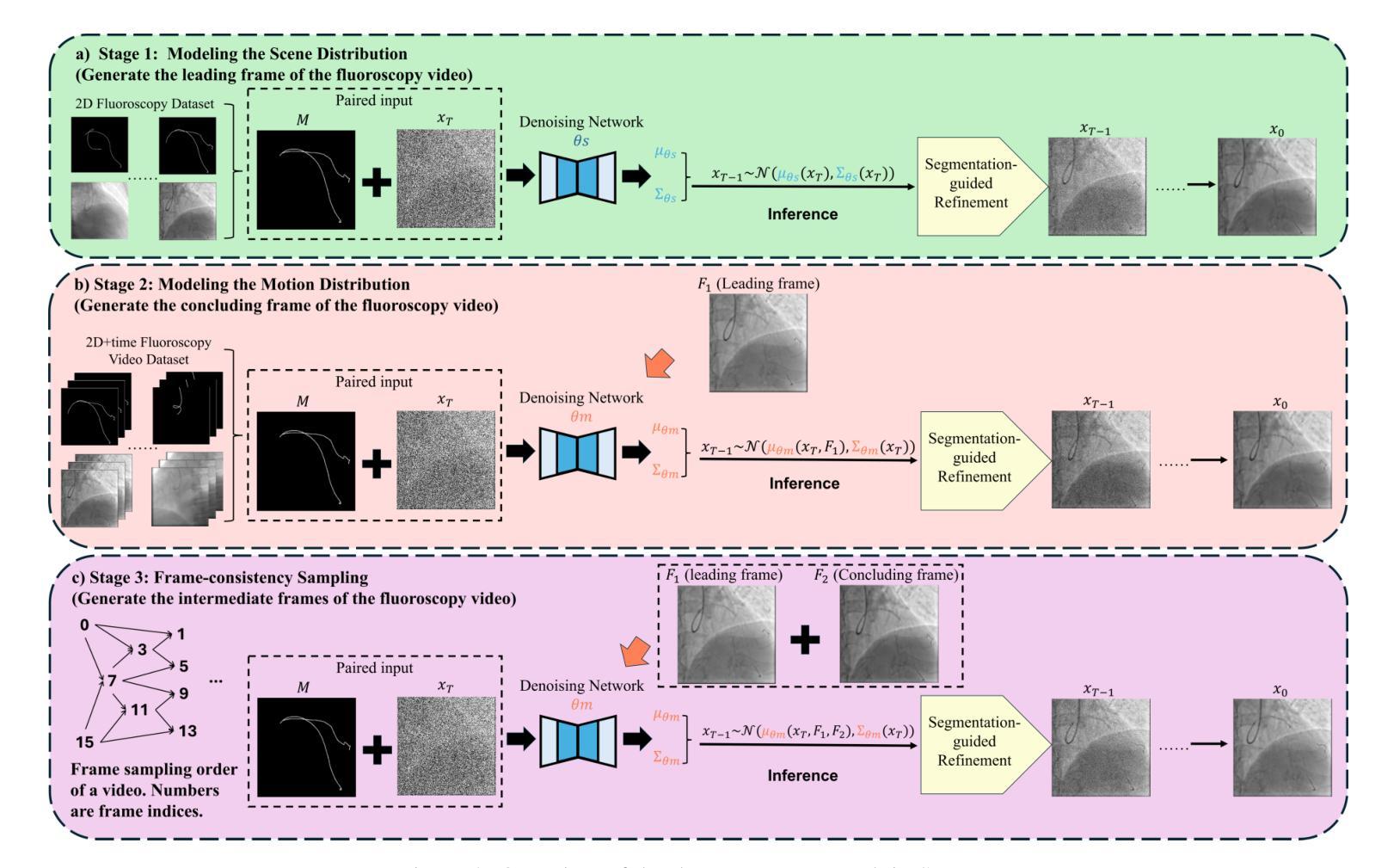
The accurate segmentation of guidewires in interventional cardiac fluoroscopy videos is crucial for computer-aided navigation tasks. Although deep learning methods have demonstrated high accuracy and robustness in wire segmentation, they require substantial annotated datasets for generalizability, underscoring the need for extensive labeled data to enhance model performance. To address this challenge, we propose the Segmentation-guided Frame-consistency Video Diffusion Model (SF-VD) to generate large collections of labeled fluoroscopy videos, augmenting the training data for wire segmentation networks. SF-VD leverages videos with limited annotations by independently modeling scene distribution and motion distribution. It first samples the scene distribution by generating 2D fluoroscopy images with wires positioned according to a specified input mask, and then samples the motion distribution by progressively generating subsequent frames, ensuring frame-to-frame coherence through a frame-consistency strategy. A segmentation-guided mechanism further refines the process by adjusting wire contrast, ensuring a diverse range of visibility in the synthesized image. Evaluation on a fluoroscopy dataset confirms the superior quality of the generated videos and shows significant improvements in guidewire segmentation.
在心脏介入手术的荧视视频中对导线的精确分割对于计算机辅助导航任务至关重要。虽然深度学习的方法已经在导线分割中显示出较高的准确性和稳健性,但它们需要大规模的标注数据集来实现泛化,这突显了对大量标注数据的需要以提高模型性能。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了基于分割引导的帧一致性视频扩散模型(SF-VD),用于生成大量标注的荧视视频,增强导线分割网络的训练数据。SF-VD通过独立建模场景分布和运动分布来利用标注不足的视频。它首先通过根据指定的输入掩膜生成带有导线的二维荧视图像来采样场景分布,然后通过逐步生成后续帧来采样运动分布,并通过帧一致性策略确保帧与帧之间的连贯性。分割引导机制进一步调整了导线的对比度,确保合成图像的可见性范围多样化。在荧视数据集上的评估证实了所生成视频的高质量,并显示出在导线分割方面的显著改善。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI 2025
Summary
在心脏介入手术荧光透视视频中准确分割导丝对于计算机辅助导航任务至关重要。为解决深度学习模型在导丝分割中对大量标注数据的依赖问题,我们提出了基于分割引导的帧一致性视频扩散模型(SF-VD)。该模型能生成大量标注的荧光透视视频,增强导丝分割网络的训练数据。SF-VD通过独立建模场景分布和运动分布,利用有限标注的视频样本进行训练。它首先根据指定的输入掩膜生成二维荧光透视图像来采样场景分布,然后通过逐步生成后续帧来采样运动分布,确保帧间一致性。分割引导机制进一步调整导丝对比度,确保合成图像的可见性多样性。在荧光数据集上的评估证明,生成视频的质量上乘,导丝分割的改进显著。
Key Takeaways
- 导丝在心脏介入手术荧光透视视频中的准确分割对计算机辅助导航至关重要。
- 深度学习在导丝分割中虽表现出高准确性与稳健性,但需大量标注数据来提升模型性能。
- 提出SF-VD模型以生成大量标注的荧光透视视频,增强导丝分割网络的训练数据。
- SF-VD通过独立建模场景分布和运动分布来处理有限标注视频样本。
- 模型通过生成二维荧光透视图像采样场景分布,并逐步生成后续帧来采样运动分布。
- 分割引导机制调整导丝对比度,确保合成图像的可见性多样性。
点此查看论文截图


Adversarial Score identity Distillation: Rapidly Surpassing the Teacher in One Step
Authors:Mingyuan Zhou, Huangjie Zheng, Yi Gu, Zhendong Wang, Hai Huang
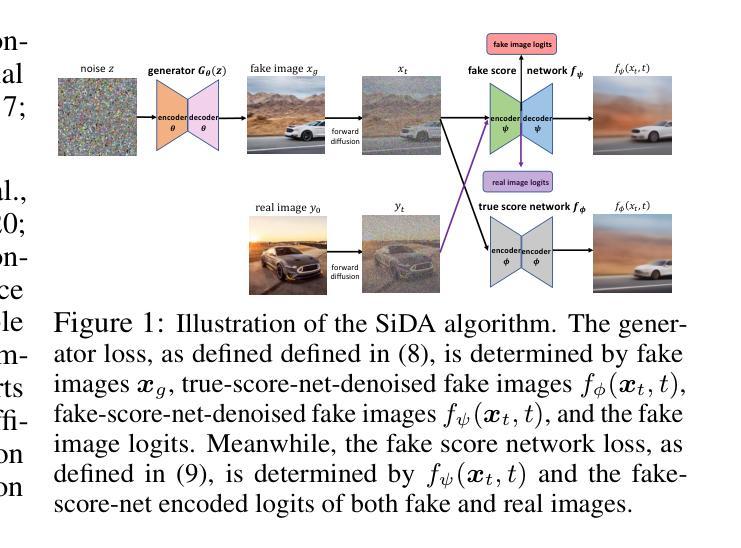
Score identity Distillation (SiD) is a data-free method that has achieved SOTA performance in image generation by leveraging only a pretrained diffusion model, without requiring any training data. However, its ultimate performance is constrained by how accurate the pretrained model captures the true data scores at different stages of the diffusion process. In this paper, we introduce SiDA (SiD with Adversarial Loss), which not only enhances generation quality but also improves distillation efficiency by incorporating real images and adversarial loss. SiDA utilizes the encoder from the generator’s score network as a discriminator, allowing it to distinguish between real images and those generated by SiD. The adversarial loss is batch-normalized within each GPU and then combined with the original SiD loss. This integration effectively incorporates the average “fakeness” per GPU batch into the pixel-based SiD loss, enabling SiDA to distill a single-step generator. SiDA converges significantly faster than its predecessor when distilled from scratch, and swiftly improves upon the original model’s performance during fine-tuning from a pre-distilled SiD generator. This one-step adversarial distillation method establishes new benchmarks in generation performance when distilling EDM diffusion models, achieving FID scores of 1.110 on ImageNet 64x64. When distilling EDM2 models trained on ImageNet 512x512, our SiDA method surpasses even the largest teacher model, EDM2-XXL, which achieved an FID of 1.81 using classifier-free guidance (CFG) and 63 generation steps. In contrast, SiDA achieves FID scores of 2.156 for size XS, 1.669 for S, 1.488 for M, 1.413 for L, 1.379 for XL, and 1.366 for XXL, all without CFG and in a single generation step. These results highlight substantial improvements across all model sizes. Our code is available at https://github.com/mingyuanzhou/SiD/tree/sida.
Score identity Distillation(SiD)是一种无需数据的方法,仅利用预训练的扩散模型,无需任何训练数据,在图像生成方面达到了 state-of-the-art(SOTA)的性能。然而,其最终性能受限于预训练模型在扩散过程的不同阶段捕捉真实数据准确度的程度。在本文中,我们引入了带有对抗性损失(Adversarial Loss)的SiD(SiDA)。SiDA不仅提高了生成质量,而且通过结合真实图像和对抗性损失提高了蒸馏效率。SiDA使用生成器评分网络中的编码器作为鉴别器,能够区分真实图像和SiD生成的图像。对抗性损失在每个GPU内进行批量归一化,然后与原始SiD损失相结合。这种结合有效地将每个GPU批次的平均“虚假性”纳入基于像素的SiD损失,使SiDA能够蒸馏单步生成器。当从零开始蒸馏时,SiDA比其前身收敛得更快,并且在预蒸馏的SiD生成器上进行微调时,能迅速提高原始模型的性能。这种一步对抗性蒸馏方法在为EDM扩散模型进行蒸馏时,在ImageNet 64x64上实现了FID分数为1.110的新基准。当对ImageNet 512x512训练的EDM2模型进行蒸馏时,我们的SiDA方法甚至超越了最大的教师模型EDM2-XXL,该模型使用无分类器引导(CFG)和63个生成步骤实现了FID分数为1.81。相比之下,SiDA实现了FID分数为2.156(XS大小)、1.669(S大小)、1.488(M大小)、1.413(L大小)、1.379(XL大小)和1.366(XXL大小),所有这些都没有使用CFG且仅在一个生成步骤中完成。这些结果突显了所有模型尺寸的显著改进。我们的代码位于 https://github.com/mingyuanzhou/SiD/tree/sida。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages (main text), 34 figures, and 10 tables
摘要
SiDA(带有对抗损失的分数身份蒸馏法)是一种结合真实图像与对抗损失的技术,提高了图像生成的品质与蒸馏效率。它通过引入对抗损失并融入原有SiD(分数身份蒸馏法)损失,有效结合平均“假度”与像素级SiD损失,实现了单步生成器的蒸馏。SiDA相较于前代技术,从空白状态开始蒸馏时收敛速度更快,并且在预蒸馏SiD生成器上进行微调时迅速提升性能。这一单步对抗蒸馏方法打破了蒸馏扩散模型的生成性能记录,如在ImageNet 64x64上实现FID得分1.110。在蒸馏训练于ImageNet 512x512的EDM2模型时,SiDA方法甚至超越了使用无分类指导(CFG)和63步生成的最大的教师模型EDM2-XXL(FID 1.81)。相反,SiDA在所有模型尺寸上都实现了显著改进,无需CFG即可在单一生成步骤中达到FID得分:XS为2.156、S为1.669、M为1.488、L为1.413、XL为1.379以及XXL为1.366。
关键见解
- SiDA是首个结合真实图像和对抗损失以提高图像生成质量和蒸馏效率的方法。
- SiDA利用生成器分数网络中的编码器作为判别器,能够区分真实图像和由SiD生成的图像。
- 对抗损失与SiD损失的融合,有效融入了GPU批处理中的平均“假度”,实现了单步生成器的蒸馏。
- SiDA在多种模型尺寸上实现了显著的性能提升,无需复杂的分类指导(CFG)和多个生成步骤。
- SiDA在ImageNet 64x64上达到了FID得分1.110的新性能基准。
- 对于更大尺寸的ImageNet 512x512模型,SiDA超越了最先进模型的性能表现。
- SiDA方法已经开源,并且具有广泛的应用前景,尤其是在提高图像生成质量和效率方面。
点此查看论文截图

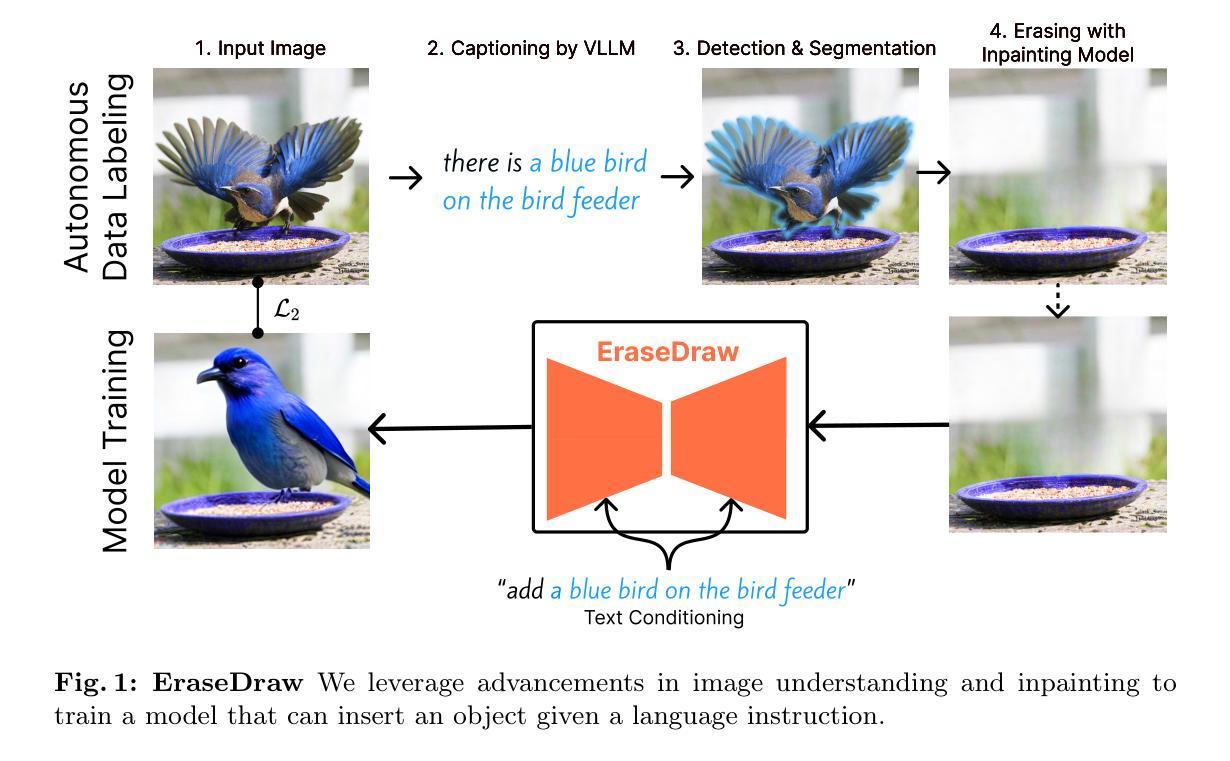
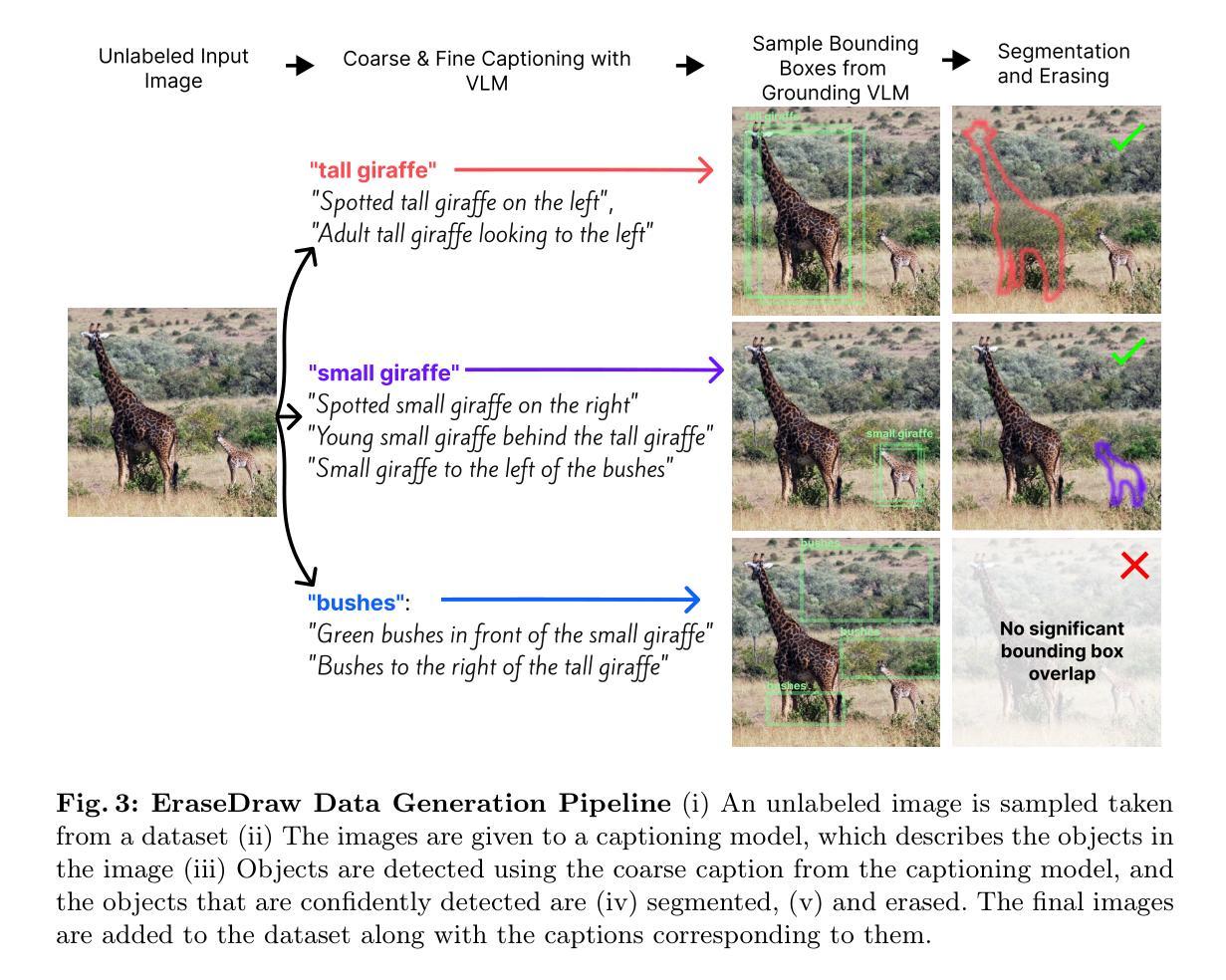
EraseDraw: Learning to Draw Step-by-Step via Erasing Objects from Images
Authors:Alper Canberk, Maksym Bondarenko, Ege Ozguroglu, Ruoshi Liu, Carl Vondrick
Creative processes such as painting often involve creating different components of an image one by one. Can we build a computational model to perform this task? Prior works often fail by making global changes to the image, inserting objects in unrealistic spatial locations, and generating inaccurate lighting details. We observe that while state-of-the-art models perform poorly on object insertion, they can remove objects and erase the background in natural images very well. Inverting the direction of object removal, we obtain high-quality data for learning to insert objects that are spatially, physically, and optically consistent with the surroundings. With this scalable automatic data generation pipeline, we can create a dataset for learning object insertion, which is used to train our proposed text conditioned diffusion model. Qualitative and quantitative experiments have shown that our model achieves state-of-the-art results in object insertion, particularly for in-the-wild images. We show compelling results on diverse insertion prompts and images across various domains.In addition, we automate iterative insertion by combining our insertion model with beam search guided by CLIP.
绘画等创造性过程通常涉及逐个创建图像的不同组成部分。我们可以建立一个计算模型来完成这项任务吗?先前的工作往往通过在图像上进行全局更改、在不现实的空间位置插入对象以及生成不准确的光照细节而失败。我们发现,虽然最先进的模型在对象插入方面表现不佳,但它们可以很好地从自然图像中移除对象和背景。通过反转对象移除的方向,我们可以获得高质量的数据来学习插入与周围环境在空间、物理和光学上一致的物体。通过这种可扩展的自动数据生成管道,我们可以创建一个用于学习对象插入的数据集,该数据集用于训练我们提出的文本条件扩散模型。定性和定量实验表明,我们的模型在对象插入方面达到了最新水平,特别是在野外图像方面。我们在各种插入提示和跨域图像上展示了令人信服的结果。此外,我们将插入模型与CLIP引导的束搜索相结合,实现了自动迭代插入。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
创作过程如绘画需逐个构建图像的不同组成部分。能否建立计算模型完成此任务?先前的工作常因全局更改图像、插入不现实的物体位置及生成不准确的光照细节而失败。我们发现虽然最新模型在物体插入方面表现不佳,但在自然图像的背景去除方面非常出色。通过反转物体移除的方向,我们获得了高质量数据,学习插入与周围环境在空间、物理和光学上一致的物体。利用这一可扩展的自动数据生成管道,我们创建了用于训练文本条件扩散模型的数据集。实验证明,我们的模型在物体插入方面达到最新水平,特别是在野外图像方面。我们展示了各种插入提示和跨域图像的令人信服的结果。此外,我们将插入模型与CLIP引导的束搜索相结合,实现了自动迭代插入。
Key Takeaways
- 计算模型可模拟创作过程如绘画中的物体逐个构建。
- 先前模型在插入物体时表现欠佳,存在空间位置不真实、光照细节不准确等问题。
- 最新模型在去除背景方面表现优秀,通过反转这一方向获得高质量数据用于学习物体插入。
- 建立了自动数据生成管道以训练文本条件扩散模型。
- 模型在物体插入方面达到最新水平,特别是在处理野外图像时效果显著。
- 模型可处理多种插入提示和跨域图像。
点此查看论文截图