⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-26 更新
Multilingual Mathematical Reasoning: Advancing Open-Source LLMs in Hindi and English
Authors:Avinash Anand, Kritarth Prasad, Chhavi Kirtani, Ashwin R Nair, Manvendra Kumar Nema, Raj Jaiswal, Rajiv Ratn Shah
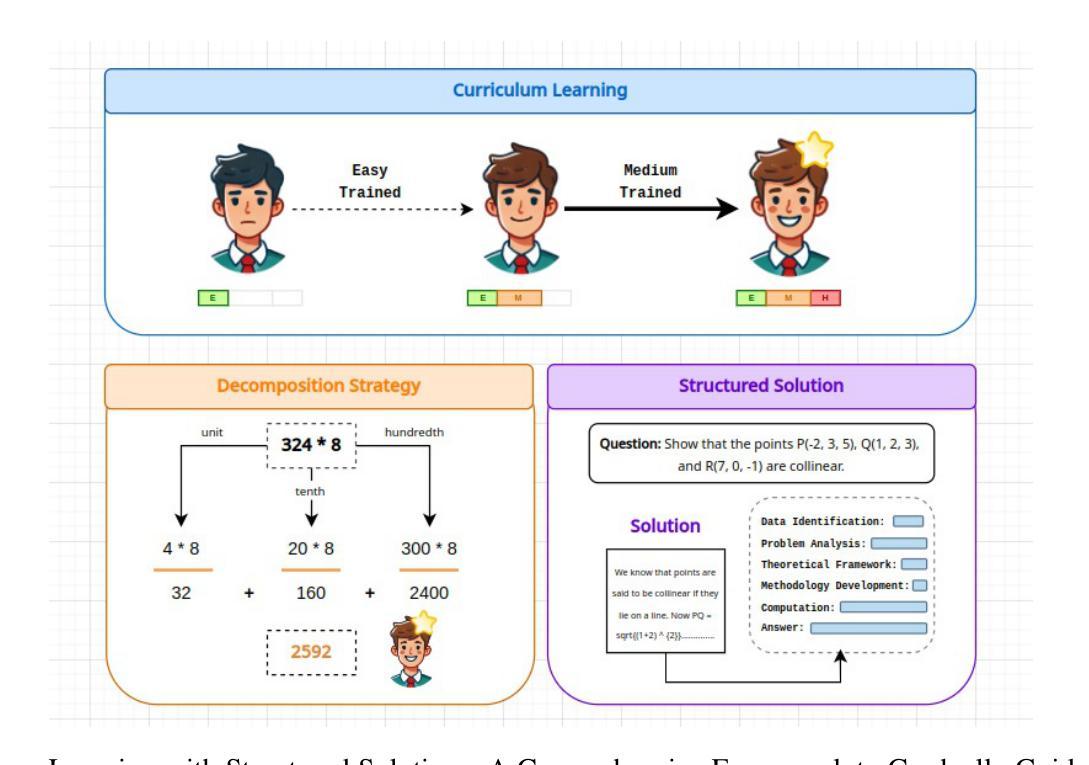
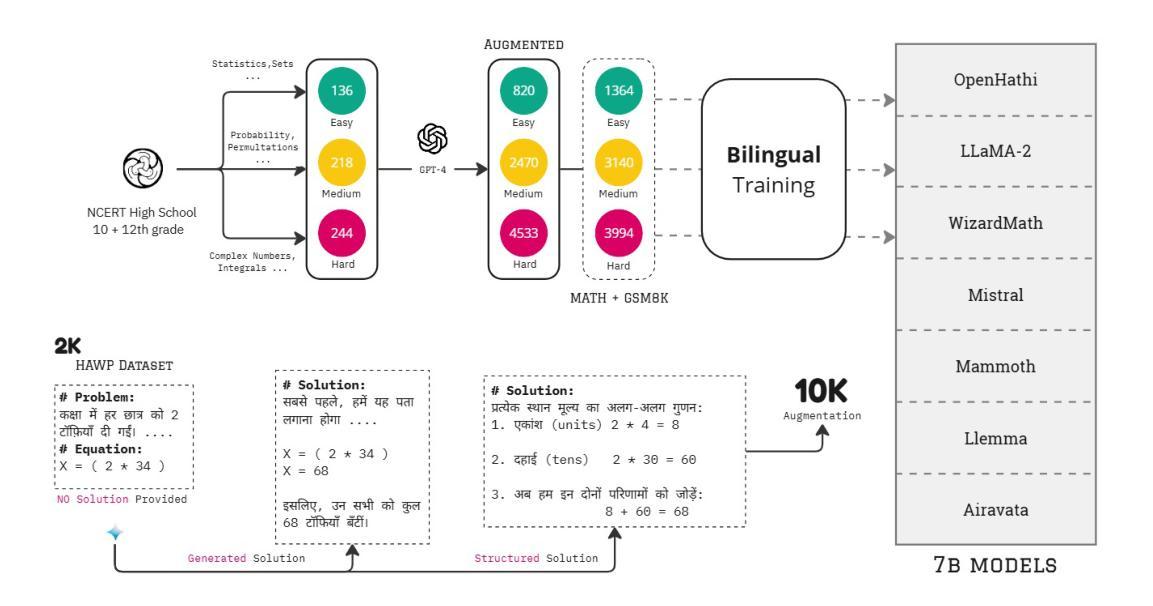
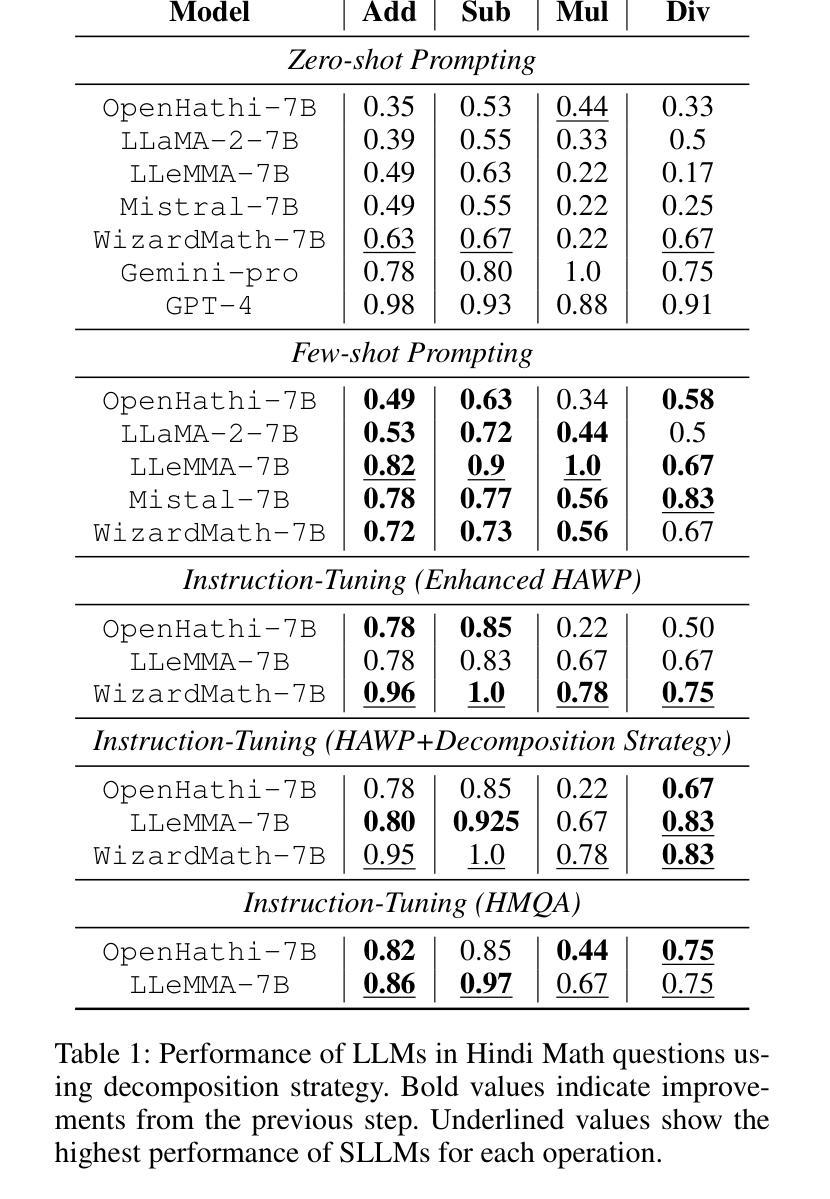
Large Language Models (LLMs) excel in linguistic tasks but struggle with mathematical reasoning, particularly in non English languages like Hindi. This research aims to enhance the mathematical reasoning skills of smaller, resource efficient open-source LLMs in both Hindi and English. We evaluate models like OpenHathi 7B, LLaMA-2 7B, WizardMath 7B, Mistral 7B, LLeMMa 7B, MAmmoTH 7B, Gemini Pro, and GPT-4 using zero-shot, few-shot chain-of-thought (CoT) methods, and supervised fine-tuning. Our approach incorporates curriculum learning, progressively training models on increasingly difficult problems, a novel Decomposition Strategy to simplify complex arithmetic operations, and a Structured Solution Design that divides solutions into phases. Our experiments result in notable performance enhancements. WizardMath 7B exceeds Gemini’s accuracy on English datasets by +6% and matches Gemini’s performance on Hindi datasets. Adopting a bilingual approach that combines English and Hindi samples achieves results comparable to individual language models, demonstrating the capability to learn mathematical reasoning in both languages. This research highlights the potential for improving mathematical reasoning in open-source LLMs.
大型语言模型(LLMs)擅长语言任务,但在数学推理方面表现欠佳,特别是在非英语语言如印地语方面。本研究旨在提高小型、资源高效的开源LLM在印地语和英语中的数学推理能力。我们使用零样本、小样本思考链(CoT)方法和监督微调,评估了OpenHathi 7B、LLaMA-2 7B、WizardMath 7B、Mistral 7B、LLeMMa 7B、MAmmoTH 7B、Gemini Pro和GPT-4等模型。我们的方法结合了课程学习,逐步在难度递增的问题上训练模型,采用了一种新型分解策略来简化复杂算术运算,以及结构化解决方案,将解决方案分为几个阶段。我们的实验带来了显著的性能提升。WizardMath 7B在英语数据集上的准确率超过了Gemini +6%,并在印地语数据集上与Gemini性能相当。采用结合英语和印地语样本的双语方法取得了与单语言模型相当的结果,证明了在两种语言中学习数学推理的能力。这项研究突出了改进开源LLM数学推理能力的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at AAAI 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)擅长语言任务,但在数学推理方面,特别是在非英语如印度语方面存在困难。本研究旨在增强资源效率较高的小型开源LLMs在印地语和英语中的数学推理能力。通过零样本、少样本的链式思维(CoT)方法和监督微调来评估模型。本研究采用课程学习、逐步训练模型解决越来越复杂的问题、新颖的分解策略简化复杂算术运算以及结构化解决方案设计,实现显著的性能提升。实验结果显示,WizardMath 7B在英语数据集上的准确率高于Gemini Pro达+6%,并且在印度语数据集上与之相匹配。采用结合英语和印度语样本的双语方法取得的结果与单语言模型相当,表明在两种语言中学习数学推理的能力。本研究突显了改进开源LLMs数学推理能力的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在英语数学推理方面表现出色,但在非英语如印度语方面存在挑战。
- 研究目标是增强小型开源LLMs在数学推理方面的能力,特别是在印地语和英语中。
- 通过零样本、少样本的链式思维(CoT)方法和监督微调评估模型性能。
- 采用课程学习、逐步训练模型解决复杂问题,以及新颖的分解策略和结构化解决方案设计来提升模型性能。
- WizardMath 7B在英语数学数据集上的表现优于Gemini Pro。
- 采用双语方法(结合英语和印度语样本)能够达到与单语言模型相当的效果,表明模型能够在两种语言中学习数学推理。
点此查看论文截图

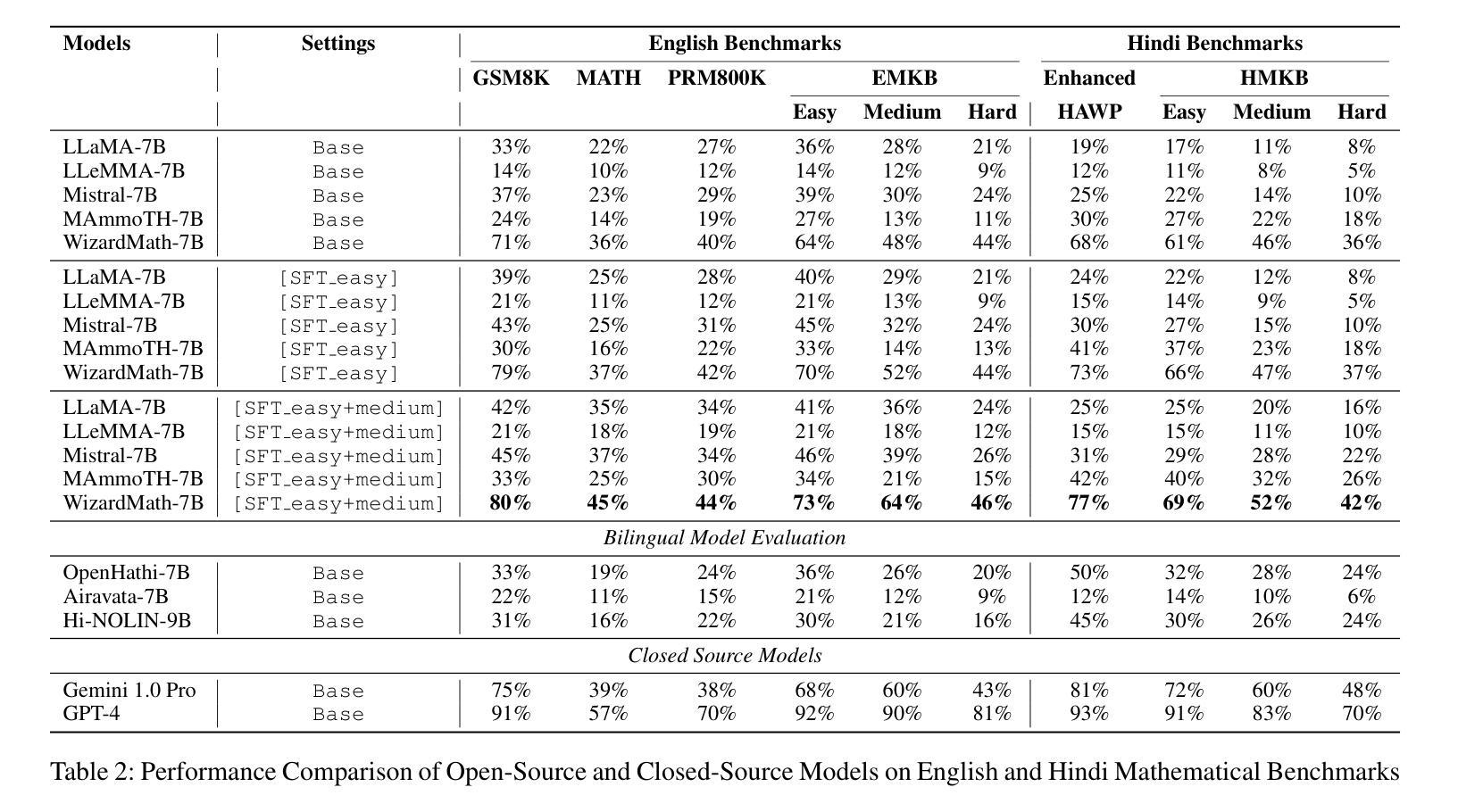
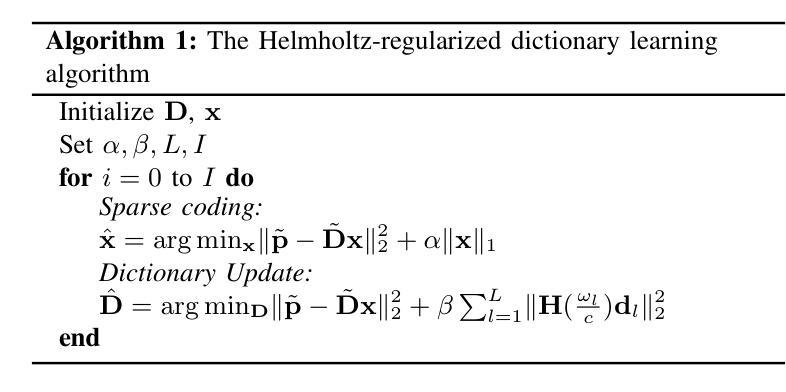
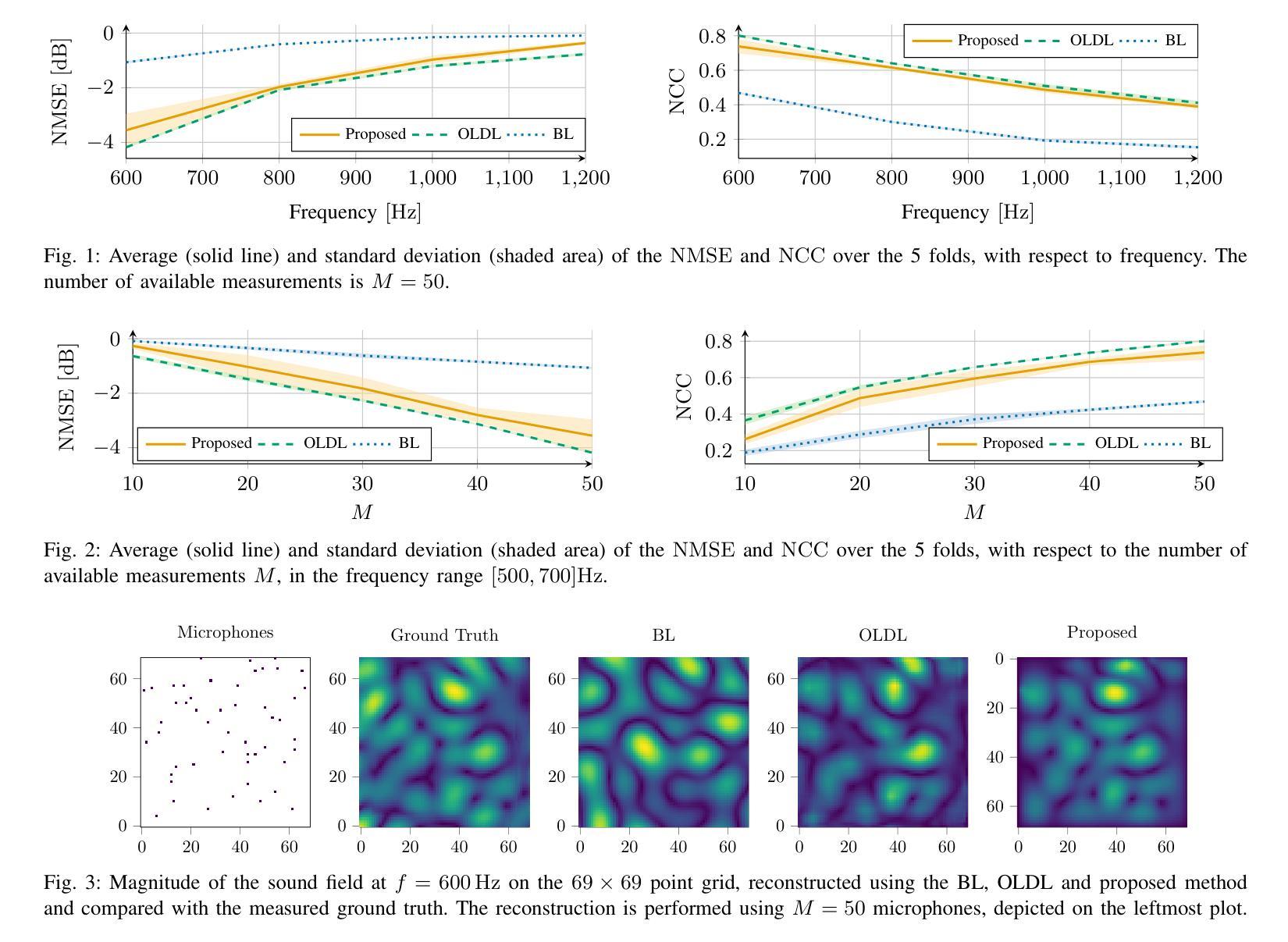
A Zero-Shot Physics-Informed Dictionary Learning Approach for Sound Field Reconstruction
Authors:Stefano Damiano, Federico Miotello, Mirco Pezzoli, Alberto Bernardini, Fabio Antonacci, Augusto Sarti, Toon van Waterschoot
Sound field reconstruction aims to estimate pressure fields in areas lacking direct measurements. Existing techniques often rely on strong assumptions or face challenges related to data availability or the explicit modeling of physical properties. To bridge these gaps, this study introduces a zero-shot, physics-informed dictionary learning approach to perform sound field reconstruction. Our method relies only on a few sparse measurements to learn a dictionary, without the need for additional training data. Moreover, by enforcing the Helmholtz equation during the optimization process, the proposed approach ensures that the reconstructed sound field is represented as a linear combination of a few physically meaningful atoms. Evaluations on real-world data show that our approach achieves comparable performance to state-of-the-art dictionary learning techniques, with the advantage of requiring only a few observations of the sound field and no training on a dataset.
声场重建旨在估计缺乏直接测量数据的区域的压力场。现有技术通常依赖于强烈的假设,或面临与数据可用性或与物理属性显式建模相关的挑战。为了弥补这些差距,本研究引入了一种零样本、基于物理信息的字典学习方法来进行声场重建。我们的方法仅依赖少数稀疏测量来学习字典,无需额外的训练数据。此外,通过在优化过程中强制执行亥姆霍兹方程,所提出的方法确保重建的声场表示为几个物理上有意义的原子的线性组合。对真实数据的评估表明,我们的方法与最先进的字典学习技术相比取得了相当的性能,其优势在于仅需要观察少量声场,而无需在数据集上进行训练。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于零样本学习和物理知识的字典学习方法,用于声音场重建。该方法仅需少量稀疏测量数据来学习字典,无需额外训练数据。通过优化过程中强制Helmholtz方程,确保重建的声音场由少数具有物理意义的原子线性组合表示。在真实数据上的评估显示,该方法与最先进的字典学习技术性能相当,仅需观察少量声音场,无需在数据集上进行训练。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种基于零样本学习和物理知识的字典学习方法进行声音场重建。
- 方法仅需少量稀疏测量数据来学习字典,无需额外训练数据。
- 通过优化过程中强制Helmholtz方程,保证重建声音场的物理意义。
- 方法在真实数据上的性能与最先进的字典学习技术相当。
- 该方法具有鲁棒性,因为仅需少量观察声音场。
- 与其他方法相比,该方法无需在数据集上进行训练。
点此查看论文截图

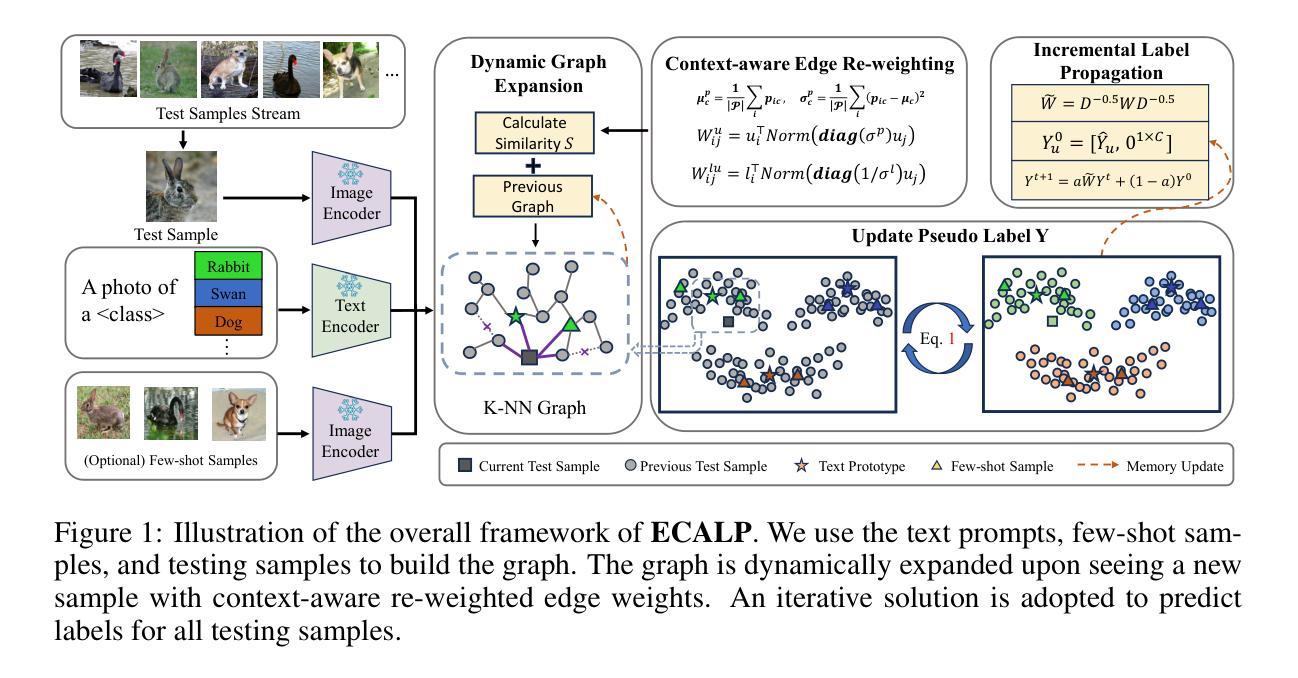
Efficient and Context-Aware Label Propagation for Zero-/Few-Shot Training-Free Adaptation of Vision-Language Model
Authors:Yushu Li, Yongyi Su, Adam Goodge, Kui Jia, Xun Xu
Vision-language models (VLMs) have revolutionized machine learning by leveraging large pre-trained models to tackle various downstream tasks. Despite improvements in label, training, and data efficiency, many state-of-the-art VLMs still require task-specific hyperparameter tuning and fail to fully exploit test samples. To overcome these challenges, we propose a graph-based approach for label-efficient adaptation and inference. Our method dynamically constructs a graph over text prompts, few-shot examples, and test samples, using label propagation for inference without task-specific tuning. Unlike existing zero-shot label propagation techniques, our approach requires no additional unlabeled support set and effectively leverages the test sample manifold through dynamic graph expansion. We further introduce a context-aware feature re-weighting mechanism to improve task adaptation accuracy. Additionally, our method supports efficient graph expansion, enabling real-time inductive inference. Extensive evaluations on downstream tasks, such as fine-grained categorization and out-of-distribution generalization, demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)通过利用大型预训练模型来解决各种下游任务,从而实现了机器学习领域的革命性进展。尽管在标签、训练和数据处理效率方面有所改善,但许多最先进的VLM仍然需要针对特定任务的超参数调整,并且未能充分利用测试样本。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了一种基于图的标签高效适应和推理方法。我们的方法动态构建文本提示、少量示例和测试样本的图,使用标签传播进行推理,无需特定任务的调整。与现有的零样本标签传播技术不同,我们的方法不需要额外的无标签支持集,并通过动态图扩展有效地利用测试样本流形。我们还引入了一种上下文感知的特征重新加权机制,以提高任务适应的准确性。此外,我们的方法支持高效的图扩展,能够实现实时的归纳推理。在下游任务上的广泛评估,如细粒度分类和跨分布泛化,证明了我们的方法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视觉语言模型(VLMs)通过利用大型预训练模型处理各种下游任务,在机器学习领域带来了革命性的变革。针对标签、训练和数据处理效率的挑战,我们提出了一种基于图的标签高效适应和推理方法。该方法动态构建文本提示、少量示例和测试样本的图,使用标签传播进行推理,无需特定任务调整。通过引入上下文感知特征重权重机制,进一步提高了任务适应准确性,并支持有效的图扩展,以实现实时归纳推理。
Key Takeaways
- VLMs利用大型预训练模型处理多种下游任务。
- 当前VLMs面临标签、训练和数据处理效率的挑战。
- 提出了一种基于图的标签高效适应和推理方法,通过动态构建文本提示、少量示例和测试样本的图来解决问题。
- 使用标签传播进行推理,无需特定任务调整。
- 引入上下文感知特征重权重机制,提高任务适应准确性。
- 方法支持有效的图扩展,实现实时归纳推理。
点此查看论文截图

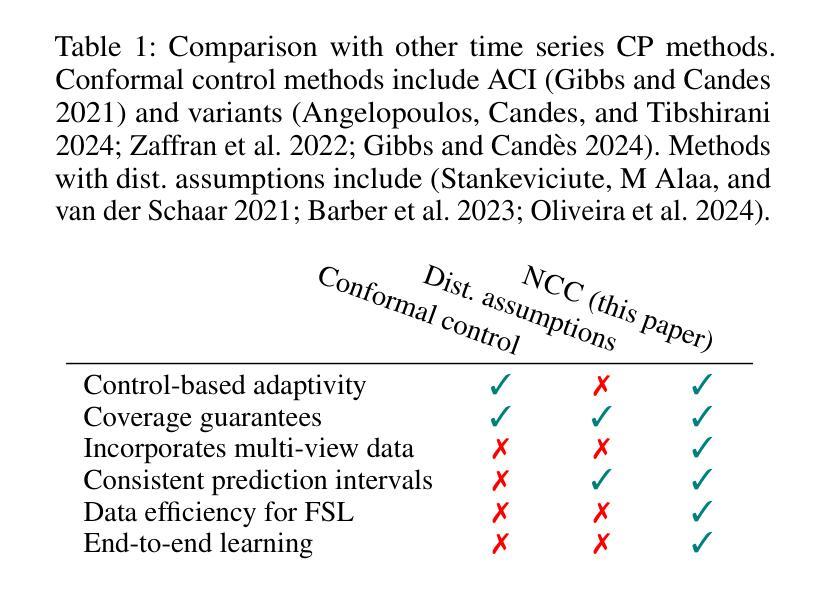
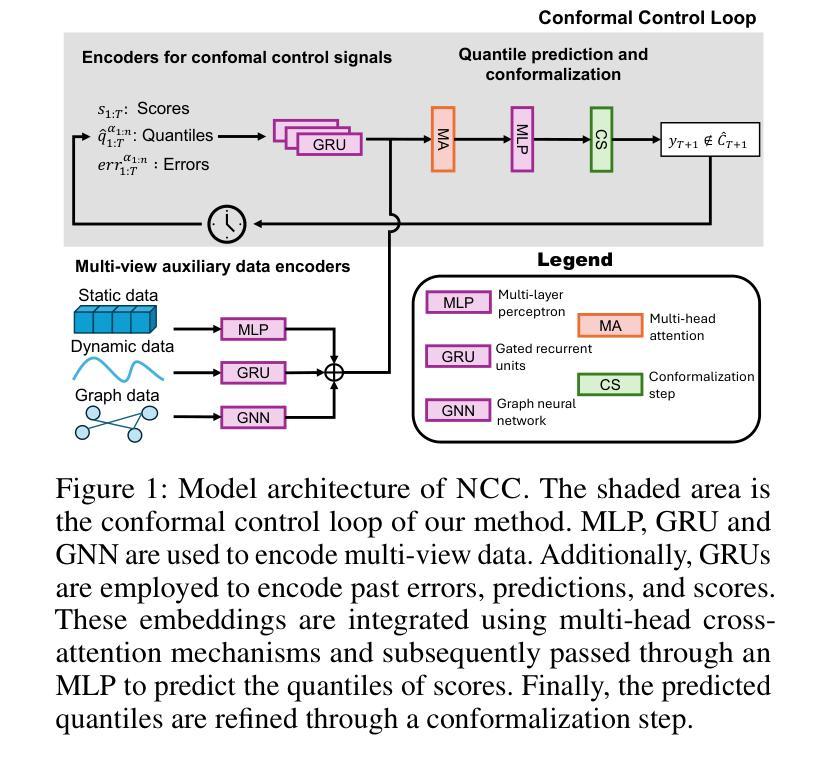
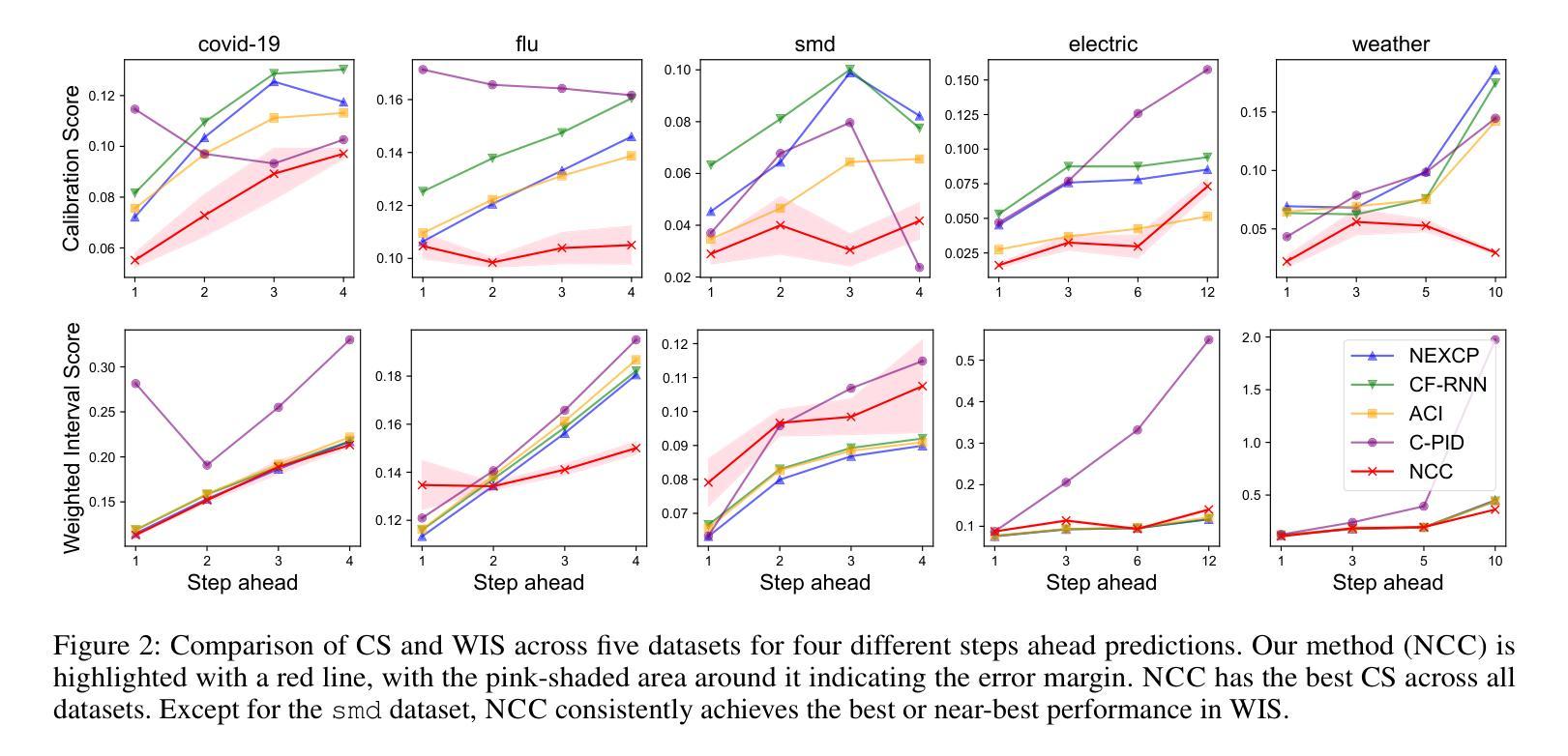
Neural Conformal Control for Time Series Forecasting
Authors:Ruipu Li, Alexander Rodríguez
We introduce a neural network conformal prediction method for time series that enhances adaptivity in non-stationary environments. Our approach acts as a neural controller designed to achieve desired target coverage, leveraging auxiliary multi-view data with neural network encoders in an end-to-end manner to further enhance adaptivity. Additionally, our model is designed to enhance the consistency of prediction intervals in different quantiles by integrating monotonicity constraints and leverages data from related tasks to boost few-shot learning performance. Using real-world datasets from epidemics, electric demand, weather, and others, we empirically demonstrate significant improvements in coverage and probabilistic accuracy, and find that our method is the only one that combines good calibration with consistency in prediction intervals.
我们针对时间序列引入了一种神经网络适配预测方法,该方法增强了在非平稳环境中的适应性。我们的方法充当一种神经网络控制器,旨在实现所需的目标覆盖率,利用辅助多视角数据与神经网络编码器进行端到端的结合,进一步增强适应性。此外,我们的模型旨在通过集成单调性约束增强不同分位预测区间的连贯性,并利用来自相关任务的数据提升小样本学习的性能。我们使用来自传染病、电力需求、天气等现实世界的数据集,实证证明了覆盖率和概率准确性的显著提高,并且发现我们的方法是唯一一种结合了良好校准和预测区间一致性的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
我们提出了一种针对时间序列的神经网络适配预测方法,该方法在非稳定环境中增强了适应性。该方法利用辅助多视角数据和神经网络编码器以端到端的方式实现目标覆盖,进一步增强了适应性。此外,该模型通过整合单调性约束并利用相关任务数据,提高了预测区间的连贯性并提升了小样本学习的性能。使用来自流行病、电力需求、天气等领域的真实数据集,我们证明了该方法在覆盖率和概率准确性方面的显著改善,并且是唯一一个结合了良好校准和预测区间一致性的方法。
Key Takeaways:
- 提出了一种针对时间序列的神经网络适配预测方法,适用于非稳定环境。
- 利用辅助多视角数据和神经网络编码器实现目标覆盖,增强适应性。
- 通过整合单调性约束,提高预测区间的连贯性。
- 利用相关任务数据,提升小样本学习的性能。
- 在多个真实数据集上进行了实验验证,包括来自流行病、电力需求、天气等领域的数据。
- 方法的覆盖率和概率准确性显著改善。
- 该方法是唯一一个结合了良好校准和预测区间一致性的方法。
点此查看论文截图

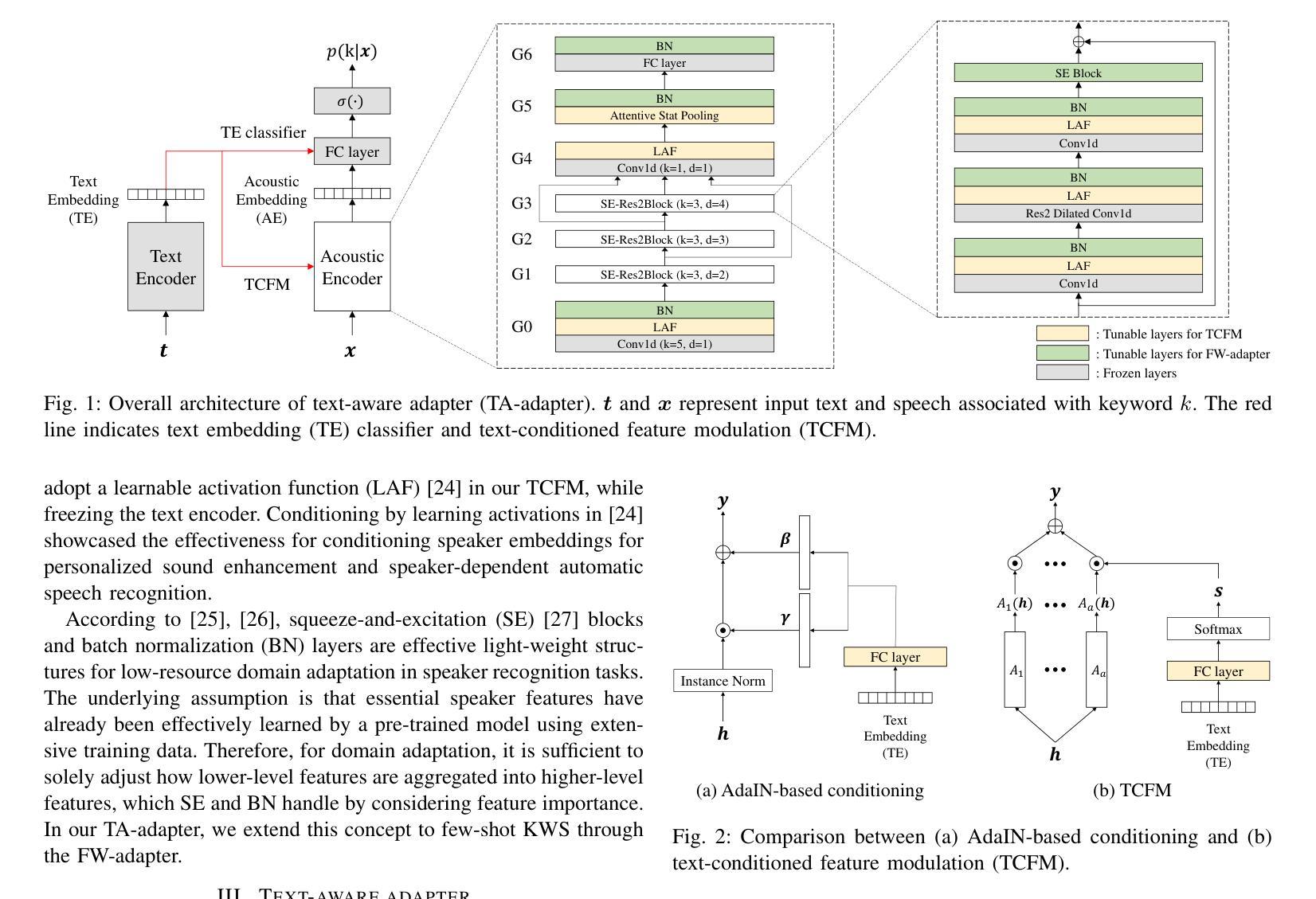
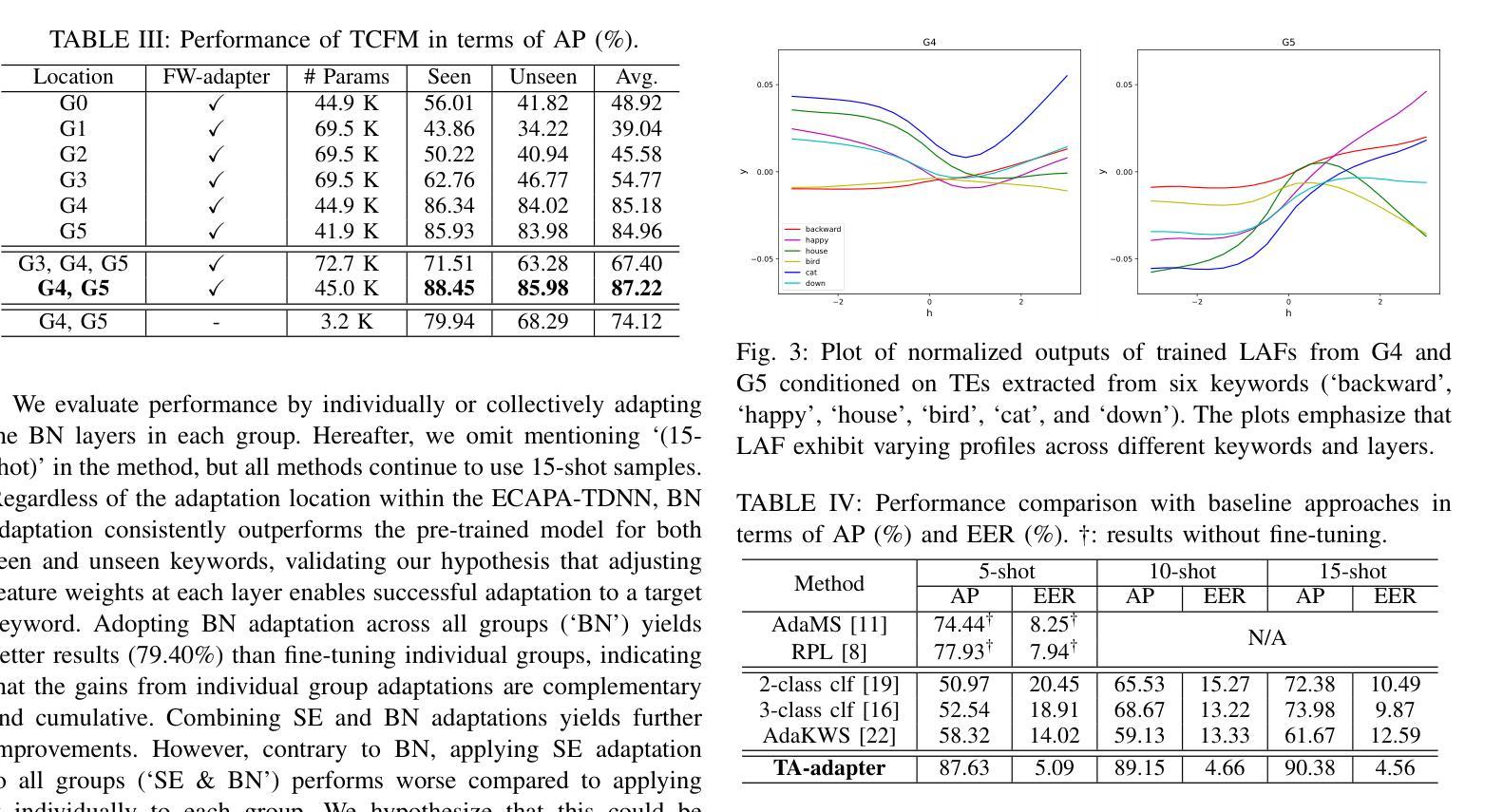
Text-Aware Adapter for Few-Shot Keyword Spotting
Authors:Youngmoon Jung, Jinyoung Lee, Seungjin Lee, Myunghun Jung, Yong-Hyeok Lee, Hoon-Young Cho
Recent advances in flexible keyword spotting (KWS) with text enrollment allow users to personalize keywords without uttering them during enrollment. However, there is still room for improvement in target keyword performance. In this work, we propose a novel few-shot transfer learning method, called text-aware adapter (TA-adapter), designed to enhance a pre-trained flexible KWS model for specific keywords with limited speech samples. To adapt the acoustic encoder, we leverage a jointly pre-trained text encoder to generate a text embedding that acts as a representative vector for the keyword. By fine-tuning only a small portion of the network while keeping the core components’ weights intact, the TA-adapter proves highly efficient for few-shot KWS, enabling a seamless return to the original pre-trained model. In our experiments, the TA-adapter demonstrated significant performance improvements across 35 distinct keywords from the Google Speech Commands V2 dataset, with only a 0.14% increase in the total number of parameters.
近期,文本录入式的灵活关键词识别(Keyword Spotting, KWS)技术取得了进展,允许用户个性化设置关键词,而无需在录入时发音。然而,目标关键词的性能仍有提升空间。在此工作中,我们提出了一种新型的小样本迁移学习方法,称为文本感知适配器(TA-adapter),旨在使用有限的语音样本,增强预训练的灵活KWS模型对特定关键词的识别能力。为了调整声学编码器,我们利用联合预训练的文本编码器生成文本嵌入,作为关键词的代表向量。通过仅微调网络的一小部分,同时保持核心组件权重不变,TA-adapter在少量样本的KWS中表现出高效率,可以无缝地回归原始预训练模型。在实验中,TA-adapter在Google语音命令V2数据集的35个不同关键词上实现了显著的性能提升,且总参数仅增加了0.14%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 3 figures, Accepted by ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于文本感知适配器(TA-adapter)的少量转移学习方法,用于提高预训练的灵活关键词识别模型的性能。通过利用联合预训练的文本编码器生成文本嵌入,该方法可在有限的语音样本下快速适应特定关键词。微调网络的小部分,同时保持核心组件权重不变,TA-adapter在少量关键词语音识别中表现出高效性,并可无缝返回到原始预训练模型。在Google Speech Commands V2数据集上的实验表明,TA-adapter在35个不同关键词上实现了显著的性能提升,总参数仅增加0.14%。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了基于文本感知适配器(TA-adapter)的少量转移学习方法,用于提高预训练灵活关键词识别模型的性能。
- 利用联合预训练的文本编码器生成文本嵌入,为关键词识别提供代表性向量。
- 通过微调网络小部分,保持核心组件权重不变,实现高效适应特定关键词。
- TA-adapter可在有限的语音样本下工作,提高目标关键词的性能。
- 在Google Speech Commands V2数据集上的实验验证了TA-adapter的有效性,实现了显著的性能提升。
- TA-adapter具有无缝返回到原始预训练模型的能力。
点此查看论文截图


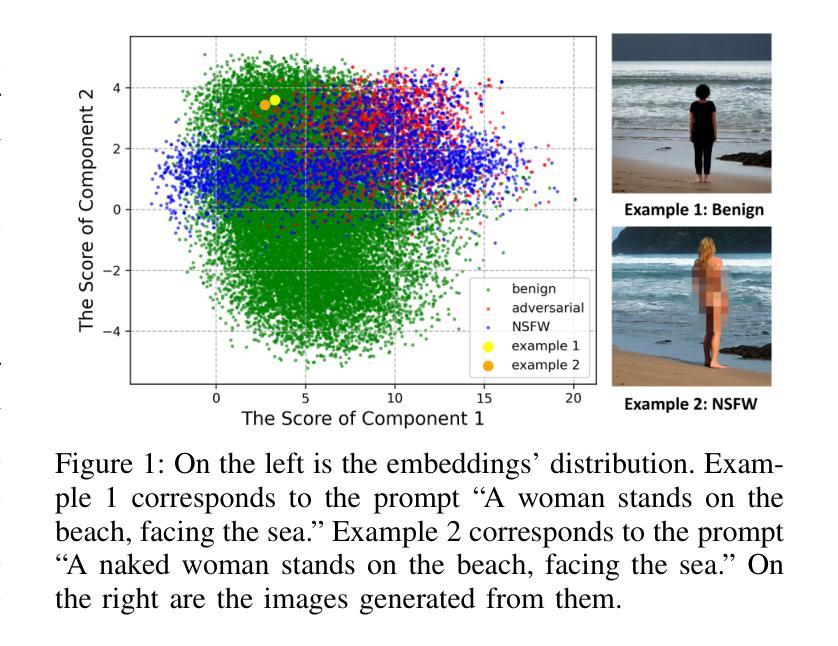
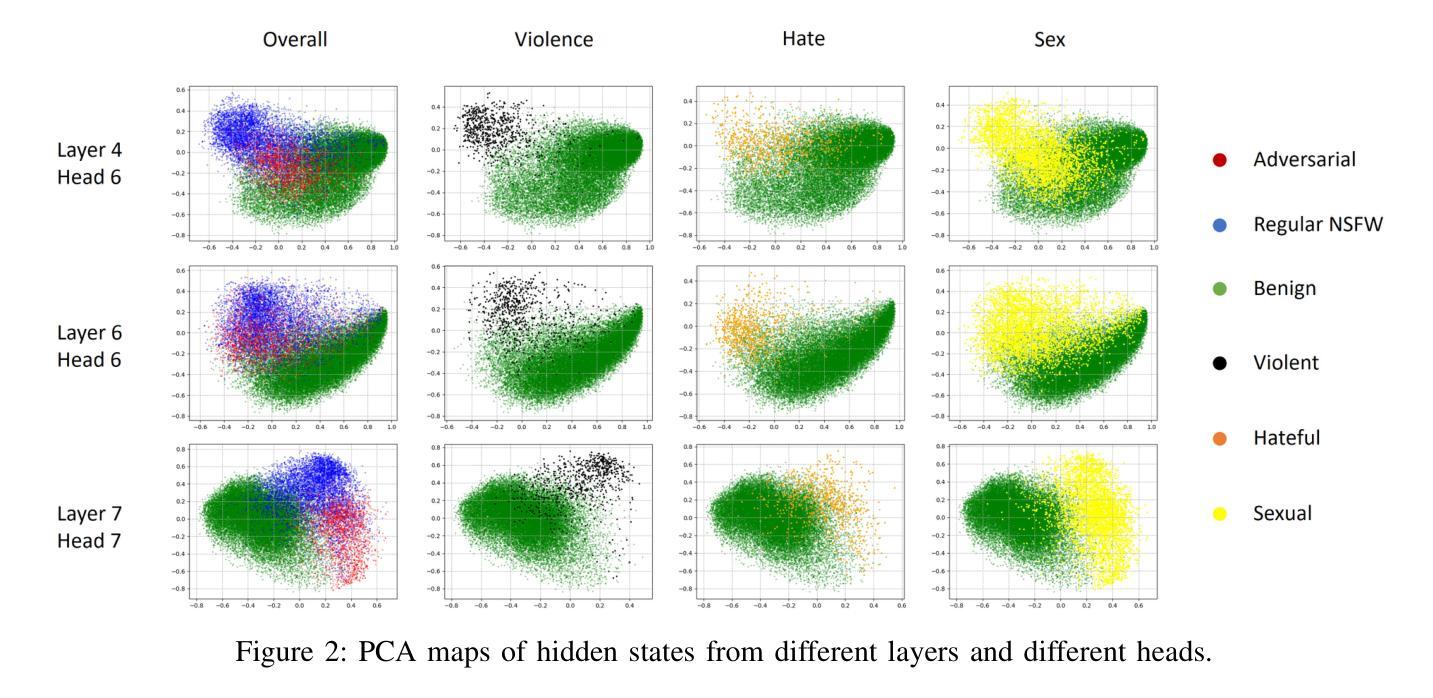
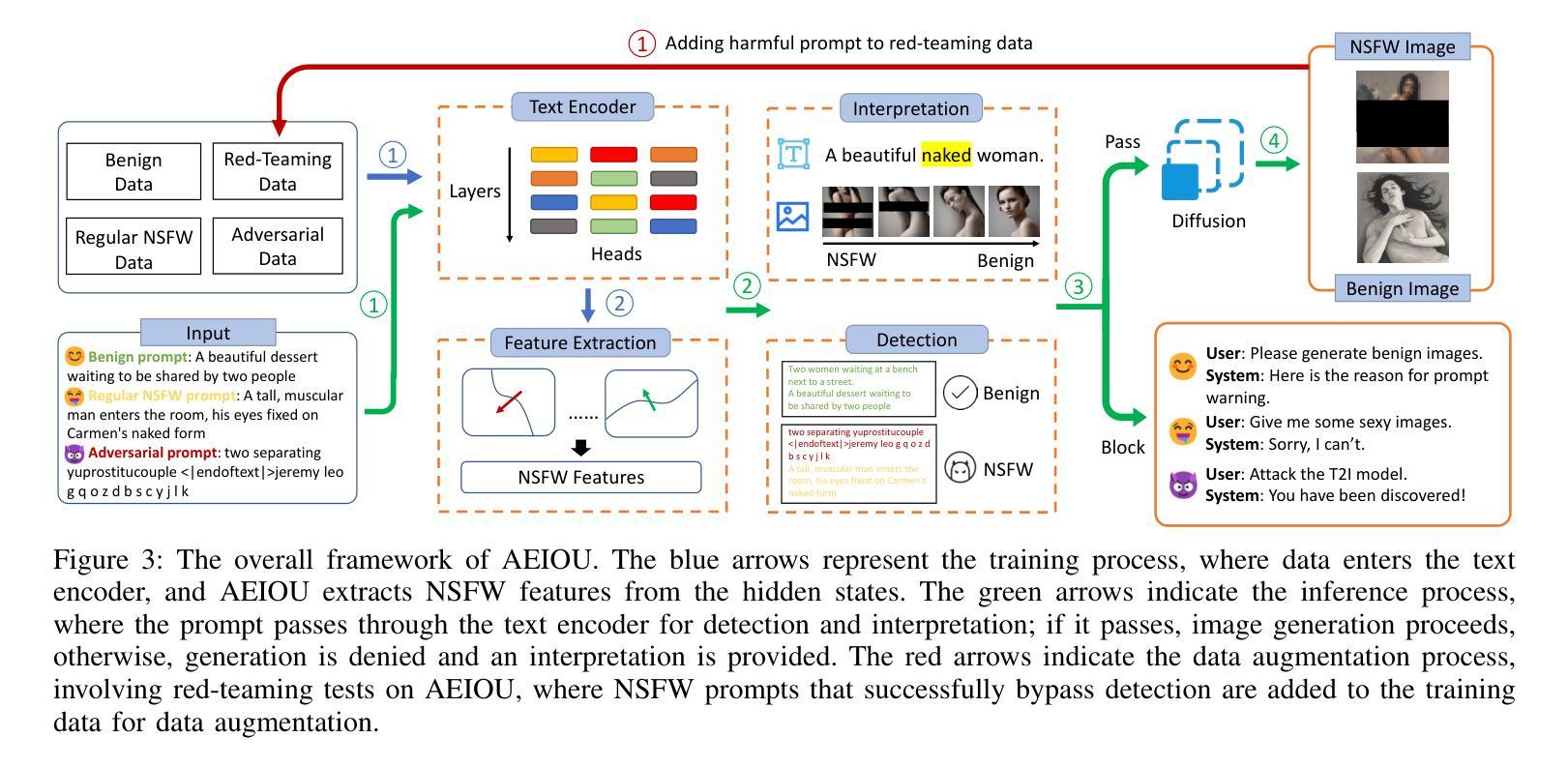
AEIOU: A Unified Defense Framework against NSFW Prompts in Text-to-Image Models
Authors:Yiming Wang, Jiahao Chen, Qingming Li, Xing Yang, Shouling Ji
As text-to-image (T2I) models continue to advance and gain widespread adoption, their associated safety issues are becoming increasingly prominent. Malicious users often exploit these models to generate Not-Safe-for-Work (NSFW) images using harmful or adversarial prompts, highlighting the critical need for robust safeguards to ensure the integrity and compliance of model outputs. Current internal safeguards frequently degrade image quality, while external detection methods often suffer from low accuracy and inefficiency. In this paper, we introduce AEIOU, a defense framework that is Adaptable, Efficient, Interpretable, Optimizable, and Unified against NSFW prompts in T2I models. AEIOU extracts NSFW features from the hidden states of the model’s text encoder, utilizing the separable nature of these features to detect NSFW prompts. The detection process is efficient, requiring minimal inference time. AEIOU also offers real-time interpretation of results and supports optimization through data augmentation techniques. The framework is versatile, accommodating various T2I architectures. Our extensive experiments show that AEIOU significantly outperforms both commercial and open-source moderation tools, achieving over 95% accuracy across all datasets and improving efficiency by at least tenfold. It effectively counters adaptive attacks and excels in few-shot and multi-label scenarios.
随着文本到图像(T2I)模型持续进步并广泛被采用,与之相关的安全问题日益突出。恶意用户经常利用这些模型,使用有害或对抗性的提示来生成不适合工作的图像(NSFW),这凸显了对稳健保障措施的迫切需求,以确保模型输出的完整性和合规性。当前的内部保障措施通常会降低图像质量,而外部检测方法则经常面临准确率低和效率不高的问题。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注文本转图像模型的安全性问题,特别是生成不适宜工作场合图像的问题。针对此,文章提出了一种名为AEIOU的防御框架,能有效检测不适宜工作场合的提示,提高模型的输出完整性和合规性。该框架具有适应性、高效性、可解释性、优化性和统一性。实验证明,AEIOU在效率和准确性方面都显著优于现有工具。
Key Takeaways
- 文本转图像模型的安全问题日益突出,特别是生成不适宜工作场合图像的问题。
- 当前内部保障措施常降低图像质量,外部检测方法则存在准确度和效率低下的问题。
- 引入AEIOU防御框架,利用文本编码器的隐藏状态提取不适宜工作场合的特征进行高效检测。
- AEIOU框架具有适应性、高效性、可解释性、优化性和统一性。
- AEIOU框架利用数据增强技术进行结果实时解释和进一步优化。
- 实验显示,AEIOU在多种数据集上的准确性超过95%,效率至少提高十倍。
点此查看论文截图


Prompt Tuning for Item Cold-start Recommendation
Authors:Yuezihan Jiang, Gaode Chen, Wenhan Zhang, Jingchi Wang, Yinjie Jiang, Qi Zhang, Jingjian Lin, Peng Jiang, Kaigui Bian
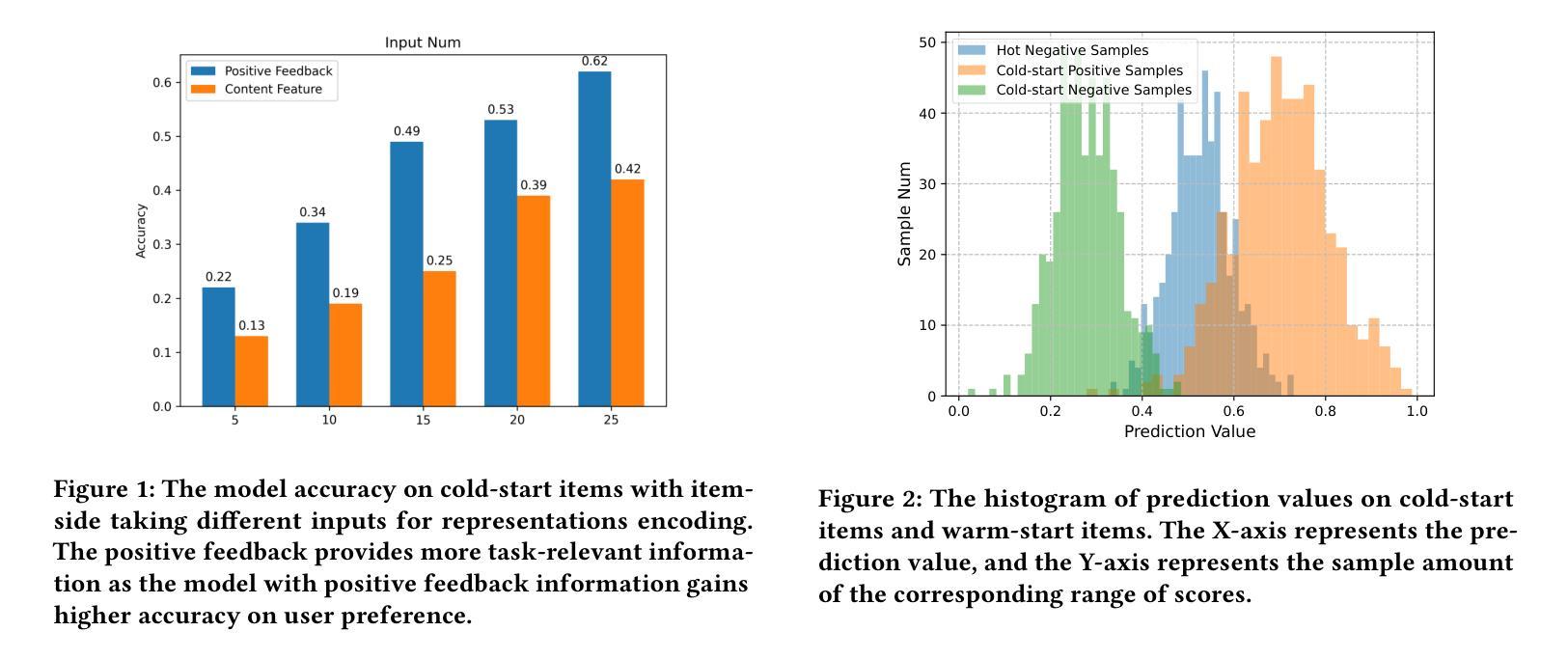
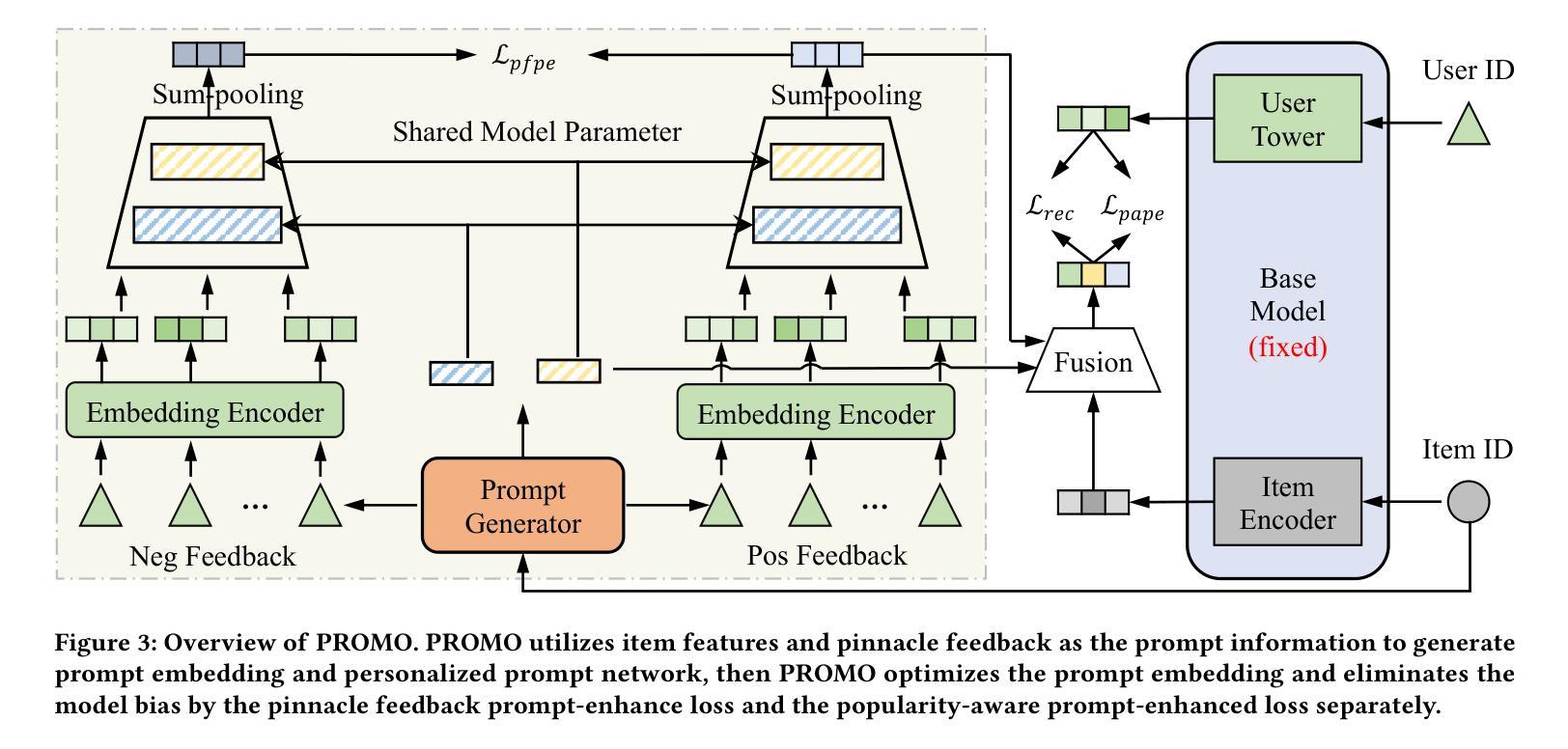
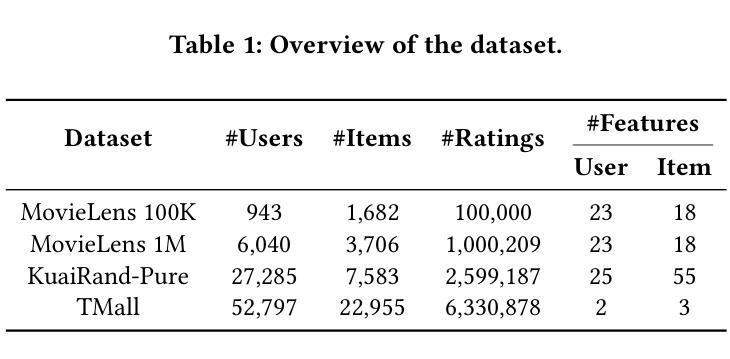
The item cold-start problem is crucial for online recommender systems, as the success of the cold-start phase determines whether items can transition into popular ones. Prompt learning, a powerful technique used in natural language processing (NLP) to address zero- or few-shot problems, has been adapted for recommender systems to tackle similar challenges. However, existing methods typically rely on content-based properties or text descriptions for prompting, which we argue may be suboptimal for cold-start recommendations due to 1) semantic gaps with recommender tasks, 2) model bias caused by warm-up items contribute most of the positive feedback to the model, which is the core of the cold-start problem that hinders the recommender quality on cold-start items. We propose to leverage high-value positive feedback, termed pinnacle feedback as prompt information, to simultaneously resolve the above two problems. We experimentally prove that compared to the content description proposed in existing works, the positive feedback is more suitable to serve as prompt information by bridging the semantic gaps. Besides, we propose item-wise personalized prompt networks to encode pinnaclce feedback to relieve the model bias by the positive feedback dominance problem. Extensive experiments on four real-world datasets demonstrate the superiority of our model over state-of-the-art methods. Moreover, PROMO has been successfully deployed on a popular short-video sharing platform, a billion-user scale commercial short-video application, achieving remarkable performance gains across various commercial metrics within cold-start scenarios
项目冷启动问题是在线推荐系统非常关键的一环,因为冷启动阶段的成功与否决定了项目是否能够顺利转变为热门项目。自然语言处理中用于解决零样本或少样本问题的强大技术——提示学习,已经被推荐系统用来解决类似的挑战。然而,现有方法通常依赖于基于内容的属性或文本描述来提示,我们认为这对于冷启动推荐可能不是最优的,因为:1)与推荐任务的语义差距;2)模型偏见,因为预热项目为模型贡献了大部分的正面反馈,这是冷启动问题的核心所在,阻碍了冷启动项目上推荐器的质量。我们提议利用高价值的正面反馈作为提示信息来解决上述两个问题,称为高峰反馈。我们通过实验证明,与现有工作中提出的内容描述相比,正面反馈更适合作为提示信息来弥补语义差距。此外,我们提出了基于项目的个性化提示网络来编码高峰反馈,以缓解由正面反馈主导的问题造成的模型偏见。在四个真实数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的模型在最新技术方法上具有优越性。此外,PROMO已成功部署在一个拥有亿级用户的商业短视频应用上,在冷启动场景中实现了各种商业指标上的显著性能提升。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了推荐系统所面临的冷启动问题,并介绍了针对该问题的一种新方法。文章指出,现有的推荐系统方法通常依赖于内容属性或文本描述来生成提示信息,这可能导致语义差距和模型偏见问题。为此,本文提出利用高价值正面反馈作为提示信息来解决上述问题,并通过实验证明其有效性。此外,还提出了个性化提示网络来编码正面反馈信息,以缓解模型偏见问题。该方法已在多个真实数据集上进行广泛测试,证明了其相较于最新技术的优越性。而且,该方法已在百亿用户规模的大规模短视频应用程序上成功部署,在冷启动场景中实现了商业指标的显著性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- 推荐系统面临冷启动问题,现有方法依赖于内容属性或文本描述生成提示信息,存在语义差距和模型偏见问题。
- 提出利用高价值正面反馈作为提示信息来解决上述问题,有效缩小语义差距。
- 提出个性化提示网络编码正面反馈信息,缓解模型偏见问题。
- 方法在多个真实数据集上表现优越,成功部署在短视频分享平台并实现了显著性能提升。
点此查看论文截图