⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-26 更新
Explainable Multi-Modal Data Exploration in Natural Language via LLM Agent
Authors:Farhad Nooralahzadeh, Yi Zhang, Jonathan Furst, Kurt Stockinger
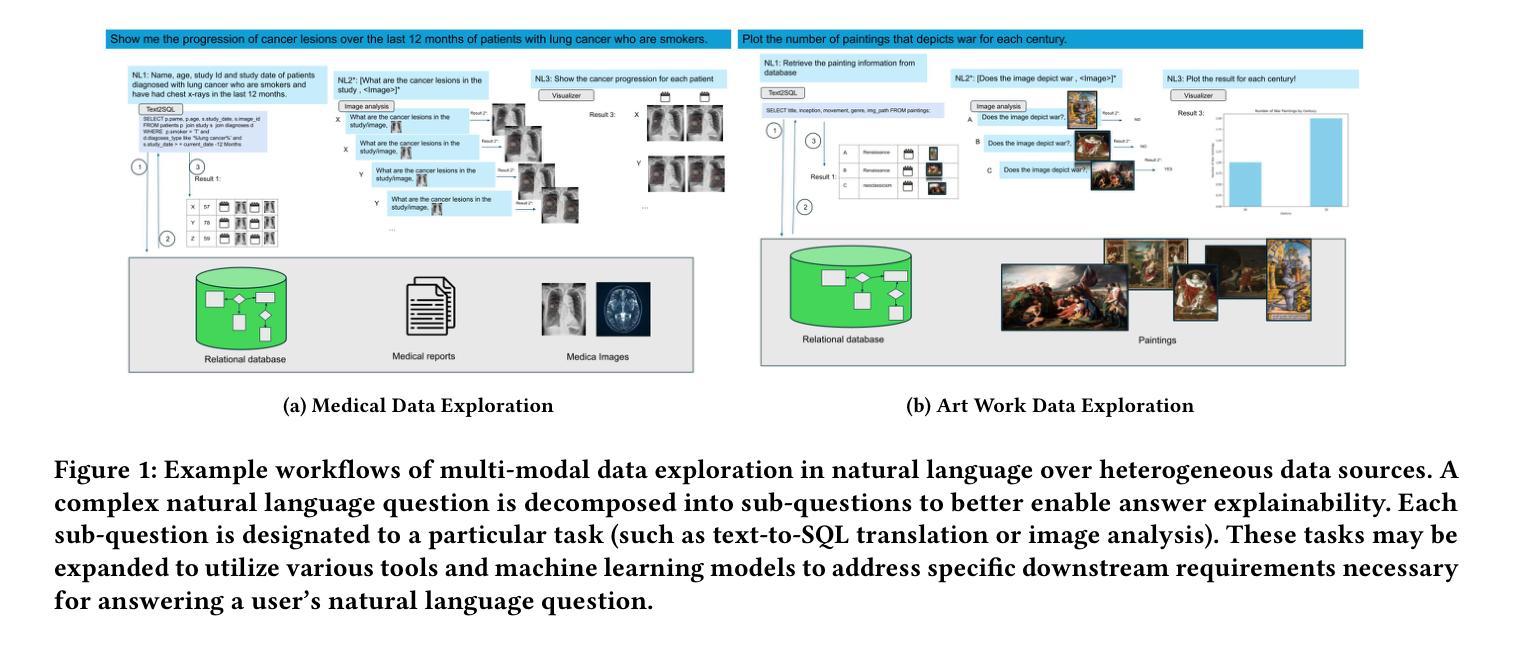
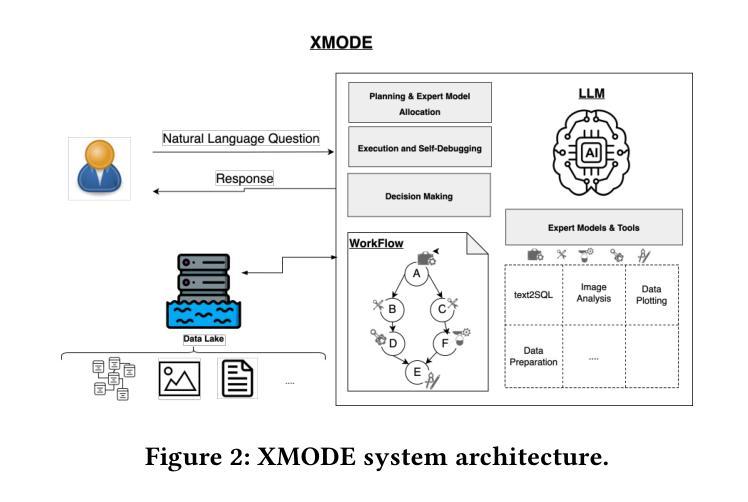
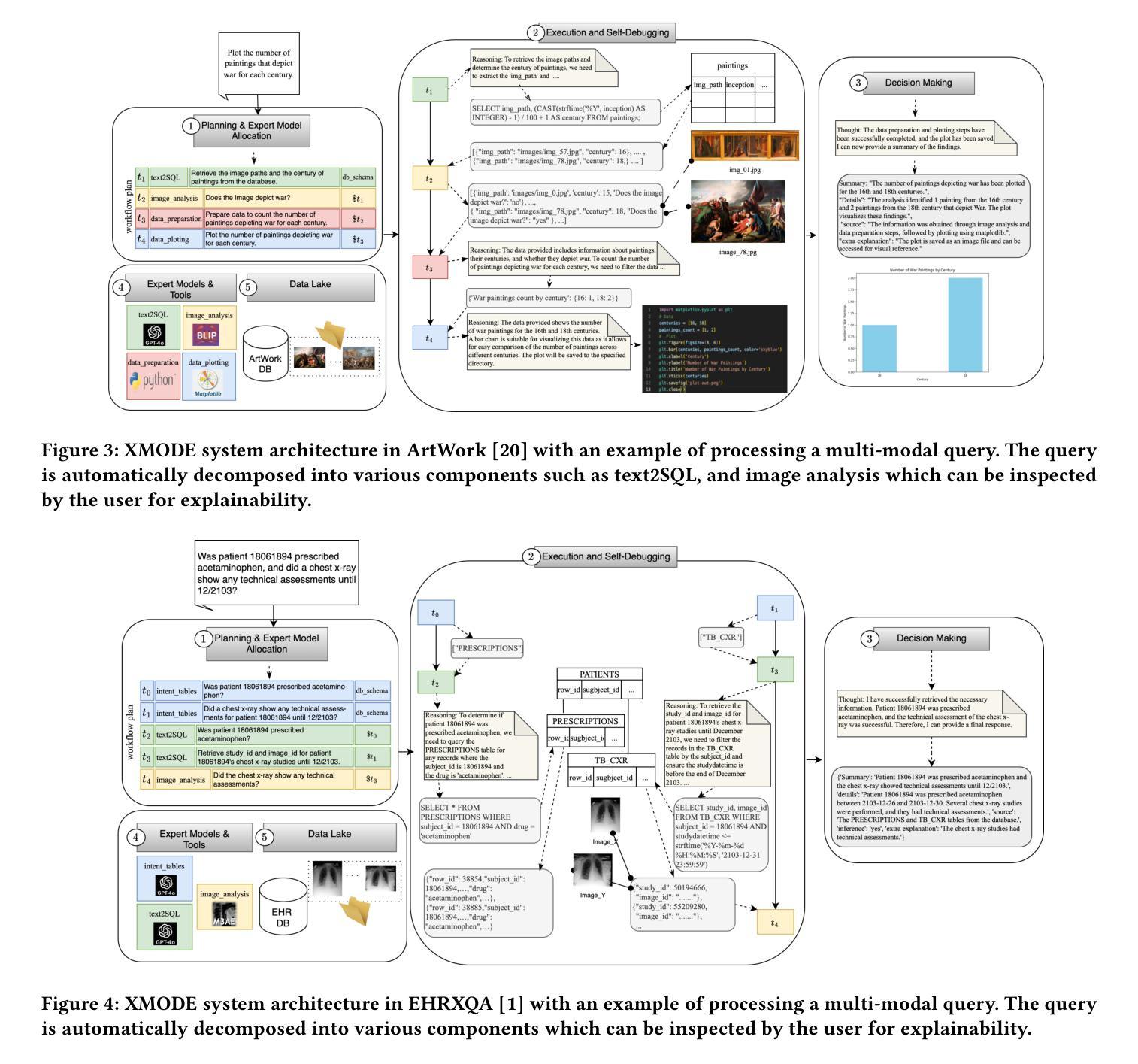
International enterprises, organizations, or hospitals collect large amounts of multi-modal data stored in databases, text documents, images, and videos. While there has been recent progress in the separate fields of multi-modal data exploration as well as in database systems that automatically translate natural language questions to database query languages, the research challenge of querying database systems combined with other unstructured modalities such as images in natural language is widely unexplored. In this paper, we propose XMODE - a system that enables explainable, multi-modal data exploration in natural language. Our approach is based on the following research contributions: (1) Our system is inspired by a real-world use case that enables users to explore multi-modal information systems. (2) XMODE leverages a LLM-based agentic AI framework to decompose a natural language question into subtasks such as text-to-SQL generation and image analysis. (3) Experimental results on multi-modal datasets over relational data and images demonstrate that our system outperforms state-of-the-art multi-modal exploration systems, excelling not only in accuracy but also in various performance metrics such as query latency, API costs, planning efficiency, and explanation quality, thanks to the more effective utilization of the reasoning capabilities of LLMs.
国际企业、组织或医院收集大量存储在数据库、文本文档、图像和视频中的多模式数据。虽然最近在多模式数据探索领域以及能够自动将自然语言问题翻译成数据库查询语言的数据库系统方面取得了进展,但将数据库系统与图像等无结构模式结合使用自然语言进行查询的研究挑战仍然鲜有探索。在本文中,我们提出了XMODE系统,该系统支持以自然语言进行可解释的多模式数据探索。我们的方法基于以下研究贡献:(1)我们的系统受到真实世界用例的启发,使用户能够探索多模式信息系统。(2)XMODE利用基于大型语言模型的代理人工智能框架,将自然语言问题分解为文本到SQL生成和图像分析等子任务。(3)在关系数据和图像上的多模式数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的系统优于最先进的多模式探索系统,不仅在准确性上表现优异,而且在查询延迟、API成本、规划效率和解释质量等各种性能指标上也表现出色,这得益于对大型语言模型推理能力的更有效利用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多模态数据探索是当前的挑战之一。本文提出了XMODE系统,该系统结合了自然语言处理与多模态数据探索技术,能够实现可解释的多模态数据探索。它通过将自然语言问题分解为多个子任务并借助于大型语言模型进行分析和推理,以提高查询的效率和准确性。实验结果表明,XMODE系统在多模态数据集上的性能优于现有系统,具有更高的准确性、更快的查询延迟、更低的API成本、更高的规划效率和更好的解释质量。
Key Takeaways
- 国际企业或组织在处理大量多模态数据时面临挑战,这些多模态数据包括数据库、文本文档、图像和视频等。
- 当前研究中,多模态数据探索与数据库系统的自然语言查询翻译结合的研究尚未得到充分探索。
- XMODE系统能够实现可解释的多模态数据探索,通过自然语言处理技术结合大型语言模型进行问题分解和任务分析。
- XMODE系统的核心功能包括将自然语言问题分解为多个子任务并进行处理,如文本到SQL的生成和图像分析等。
- XMODE系统通过利用大型语言模型的推理能力,提高了查询的准确性和性能指标,如查询延迟、API成本、规划效率和解释质量等。
- 实验结果表明,XMODE系统在多模态数据集上的性能优于现有系统。
点此查看论文截图

Go With the Flow: Fast Diffusion for Gaussian Mixture Models
Authors:George Rapakoulias, Ali Reza Pedram, Panagiotis Tsiotras
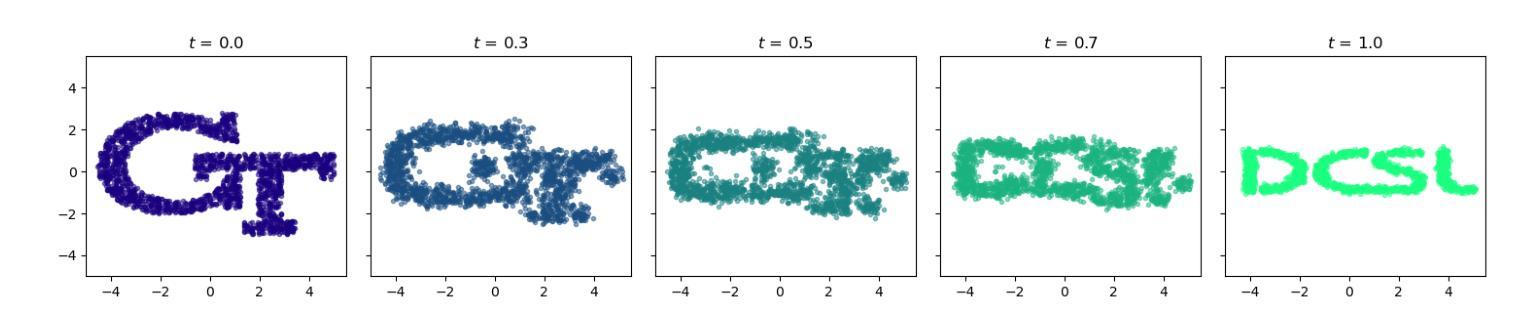
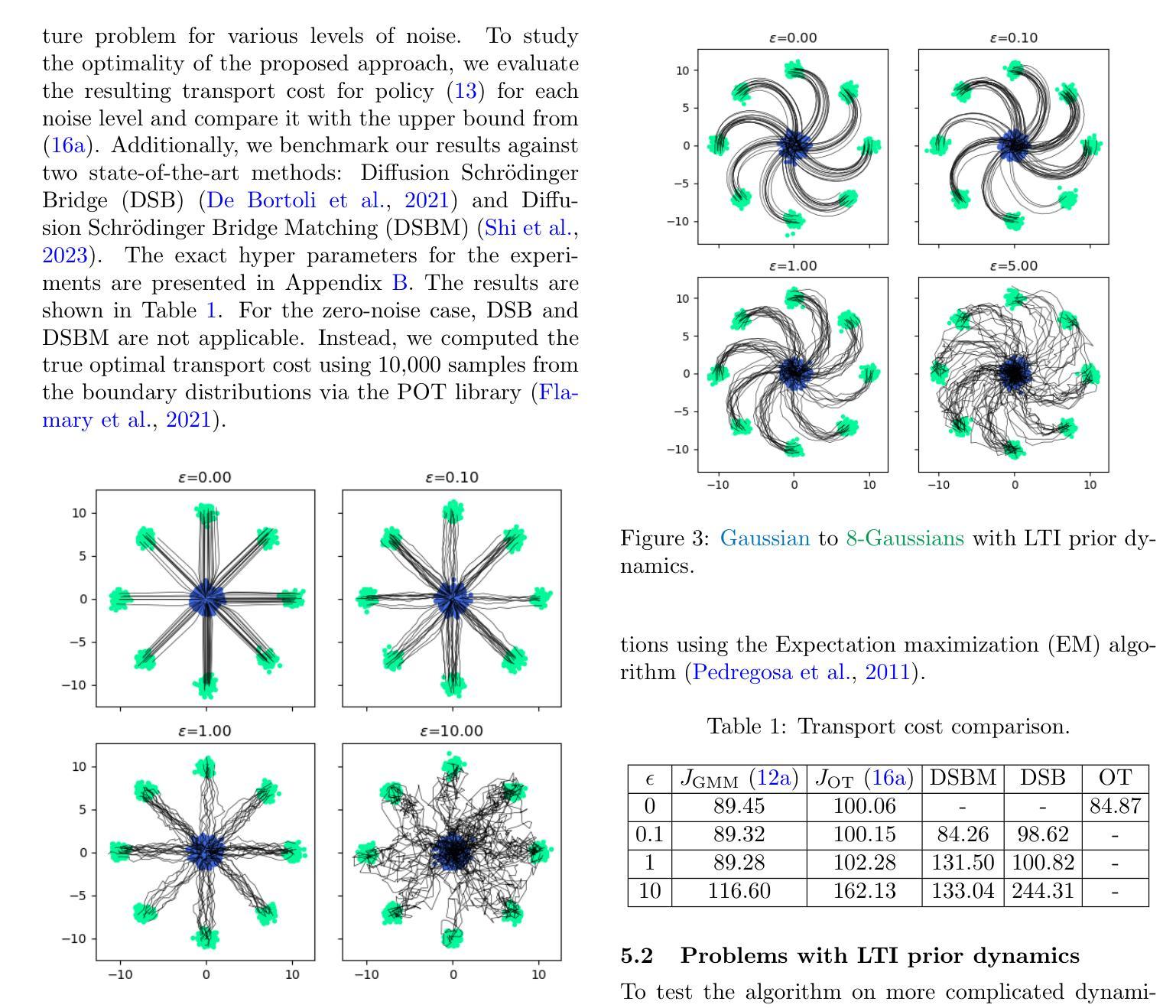
Schr"{o}dinger Bridges (SB) are diffusion processes that steer, in finite time, a given initial distribution to another final one while minimizing a suitable cost functional. Although various methods for computing SBs have recently been proposed in the literature, most of these approaches require computationally expensive training schemes, even for solving low-dimensional problems. In this work, we propose an analytic parametrization of a set of feasible policies for steering the distribution of a dynamical system from one Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) to another. Instead of relying on standard non-convex optimization techniques, the optimal policy within the set can be approximated as the solution of a low-dimensional linear program whose dimension scales linearly with the number of components in each mixture. Furthermore, our method generalizes naturally to more general classes of dynamical systems such as controllable Linear Time-Varying systems that cannot currently be solved using traditional neural SB approaches. We showcase the potential of this approach in low-to-moderate dimensional problems such as image-to-image translation in the latent space of an autoencoder, and various other examples. We also benchmark our approach on an Entropic Optimal Transport (EOT) problem and show that it outperforms state-of-the-art methods in cases where the boundary distributions are mixture models while requiring virtually no training.
薛定谔桥(Schrödinger Bridges,简称SB)是一种扩散过程,能够在有限时间内将给定的初始分布引导到另一个最终分布,同时最小化适当的成本函数。尽管最近在文献中提出了多种计算SB的方法,但大多数这些方法都需要计算量昂贵的训练方案,即使对于解决低维问题也是如此。在这项工作中,我们为引导动态系统从一个高斯混合模型(Gaussian Mixture Model,简称GMM)到另一个GMM的分布,提出了一组可行策略的解析参数化方法。我们不再依赖标准的非凸优化技术,而是将集合中的最佳策略近似为低维线性程序的解,其维度与每个混合中的组件数量呈线性关系。此外,我们的方法可以自然地推广到更一般的动态系统类别,如目前无法使用传统神经SB方法解决的可控线性时变系统。我们在低至中度维度的问题中展示了该方法的潜力,例如在自动编码器的潜在空间中的图像到图像翻译以及其他各种示例。我们还针对熵最优传输(EOT)问题对我们的方法进行了基准测试,并表明它在边界分布为混合模型的情况下优于最新方法,几乎不需要进行训练。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Schrödinger Bridges(SB)的概念,这是一种扩散过程,能在有限时间内将给定的初始分布引导至另一个最终分布,同时最小化适当的成本函数。针对SB的计算方法,本文提出了一种对可行策略集的分析参数化方法,用于从高斯混合模型(GMM)的一个分布引导到另一个分布。该方法通过低维线性规划来近似最优策略,其维度与每个混合中的组件数量呈线性关系。此外,该方法自然地推广到更一般的动力系统,如可控的线性时变系统,而传统的神经SB方法则无法解决。该方法在图像域翻译等低维到中等维度问题以及熵最优传输问题上表现出了潜力。
Key Takeaways
- Schrödinger Bridges (SB) 是一种扩散过程,能在有限时间内将给定的初始分布引导至目标分布,同时最小化成本函数。
- 当前大多数计算SB的方法需要昂贵的训练方案,即使是解决低维问题。
- 提出了一种对SB的可行策略集的分析参数化方法,适用于高斯混合模型(GMM)的分布引导。
- 通过低维线性规划来近似最优策略,其维度与混合中的组件数量线性相关。
- 该方法自然适用于更一般的动力系统,如可控的线性时变系统。
- 该方法在图像域翻译等低维到中等维度问题上有潜在应用。
点此查看论文截图