⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-26 更新
Extracting triples from dialogues for conversational social agents
Authors:Piek Vossen, Selene Báez Santamaría, Lenka Bajčetić, Thomas Belluci
Obtaining an explicit understanding of communication within a Hybrid Intelligence collaboration is essential to create controllable and transparent agents. In this paper, we describe a number of Natural Language Understanding models that extract explicit symbolic triples from social conversation. Triple extraction has mostly been developed and tested for Knowledge Base Completion using Wikipedia text and data for training and testing. However, social conversation is very different as a genre in which interlocutors exchange information in sequences of utterances that involve statements, questions, and answers. Phenomena such as co-reference, ellipsis, coordination, and implicit and explicit negation or confirmation are more prominent in conversation than in Wikipedia text. We therefore describe an attempt to fill this gap by releasing data sets for training and testing triple extraction from social conversation. We also created five triple extraction models and tested them in our evaluation data. The highest precision is 51.14 for complete triples and 69.32 for triple elements when tested on single utterances. However, scores for conversational triples that span multiple turns are much lower, showing that extracting knowledge from true conversational data is much more challenging.
在混合智能协作中获得明确的沟通理解对于创建可控且透明的智能体至关重要。在本文中,我们描述了一些自然语言理解模型,这些模型可以从社会对话中提取明确的符号三元组。三元组提取主要已开发并测试用于使用维基百科文本和数据训练和测试的知识库完成。然而,社交对话作为交流类型大不相同,交际者在一系列的话语中交换信息,涉及陈述、问题和答案。对话中的现象如共指、省略、协调以及隐性和显性否定或确认比在维基百科文本中更为突出。因此,我们试图通过发布用于训练和测试从社交对话中提取三元组的数据集来填补这一空白。我们还创建了五个三元组提取模型并在我们的评估数据中进行测试。当在单个话语上进行测试时,最高准确率为完整三元组的51.14%和三元素的三元组的69.32%。但是,跨多轮会话的三元组得分要低得多,这表明从真实对话数据中提取知识更具挑战性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文着重介绍了在混合智能协作中,理解沟通的重要性,并描述了一系列自然语言理解模型,这些模型能够从社会对话中提取明确的象征性三元组。针对对话的三元组提取面临诸多挑战,如对话的连贯性、言外之意等,因此作者尝试发布数据集以供训练和测试。最高精确度测试结果展示在单轮对话中提取的三元组精度为51.14%,元素精度为69.32%,但在多轮对话中的表现则较差,说明从真实对话中提取知识更具挑战性。
Key Takeaways
- 混合智能协作中理解沟通的重要性。
- 自然语言理解模型能够从社会对话中提取明确象征性三元组。
- 三元组提取在对话中的应用面临挑战,如对话连贯性、言外之意等。
- 数据集发布以供训练和测试三元组提取。
- 单轮对话中的三元组提取最高精度为51.14%,元素精度为69.32%。
- 多轮对话中的三元组提取难度更大。
点此查看论文截图

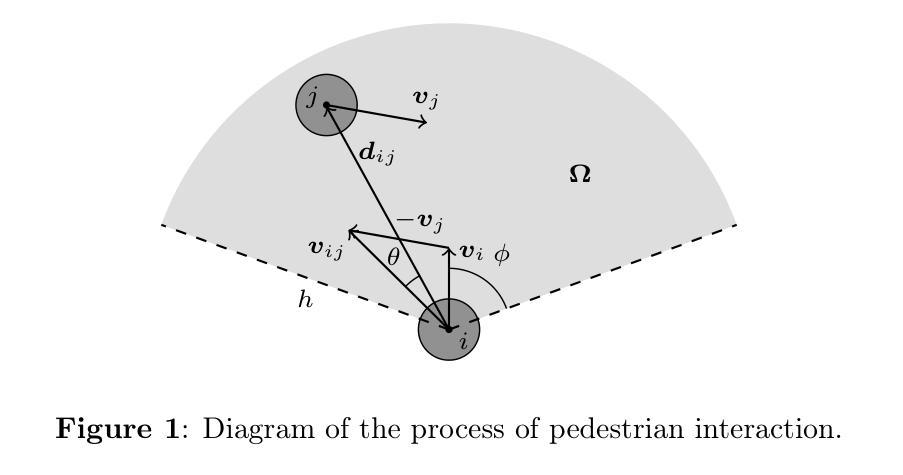
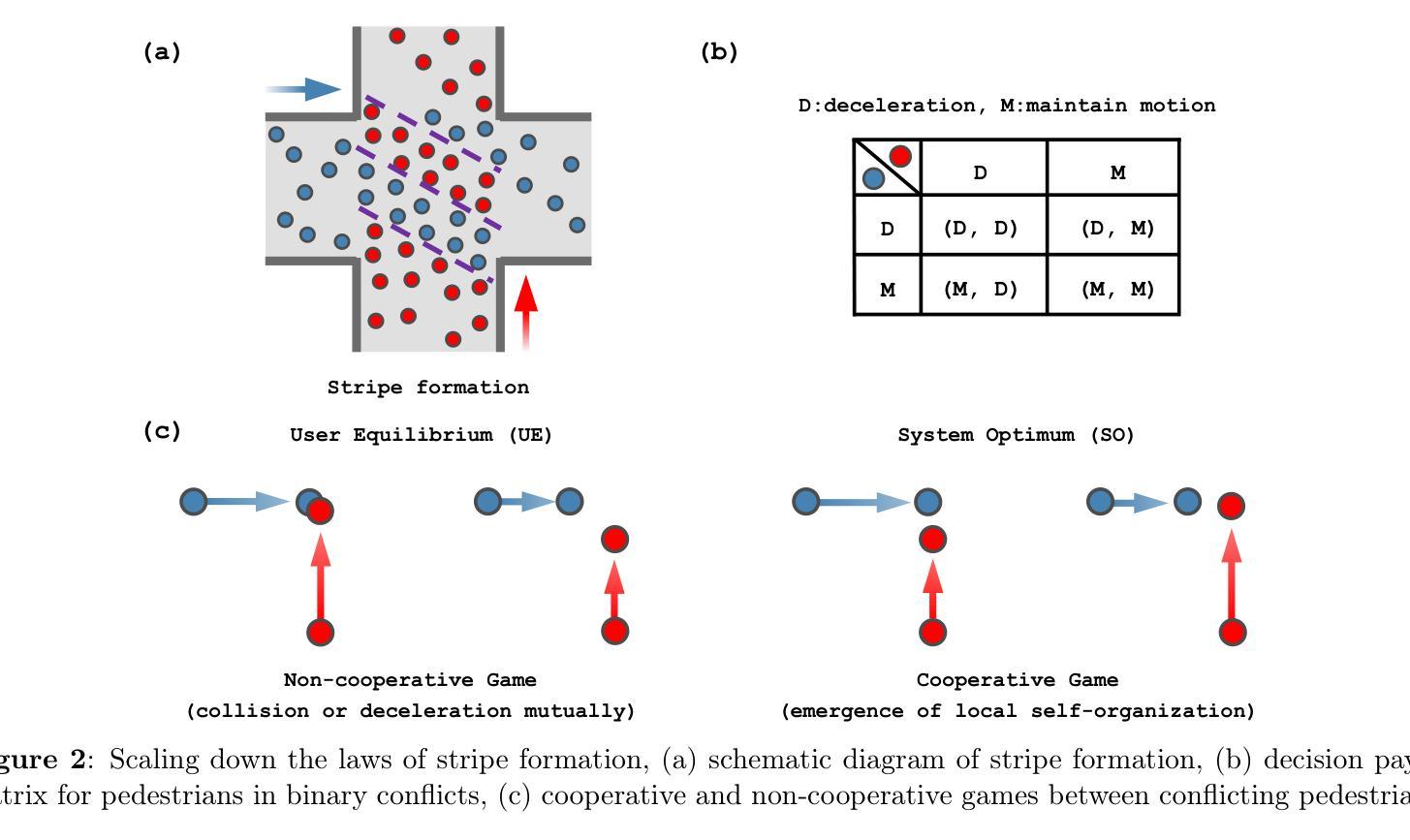
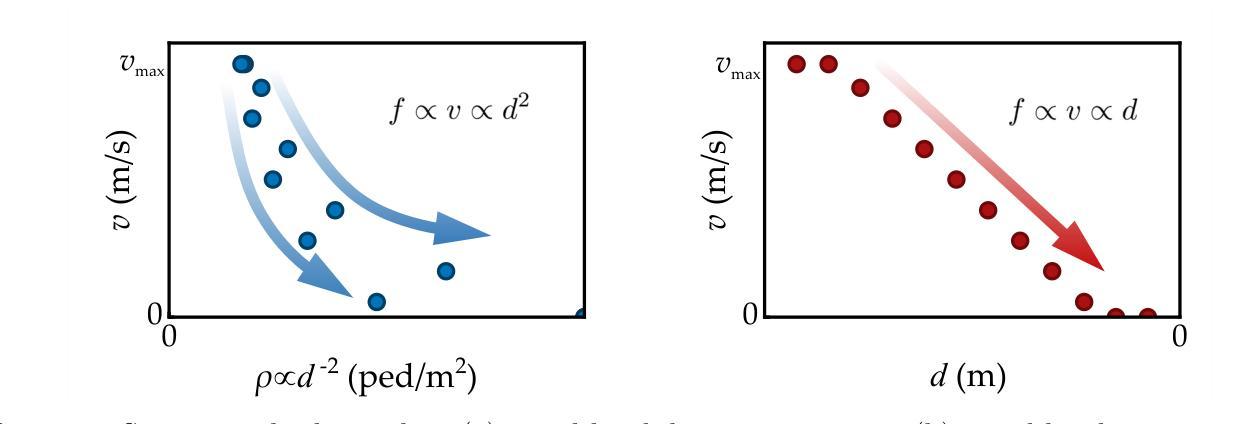
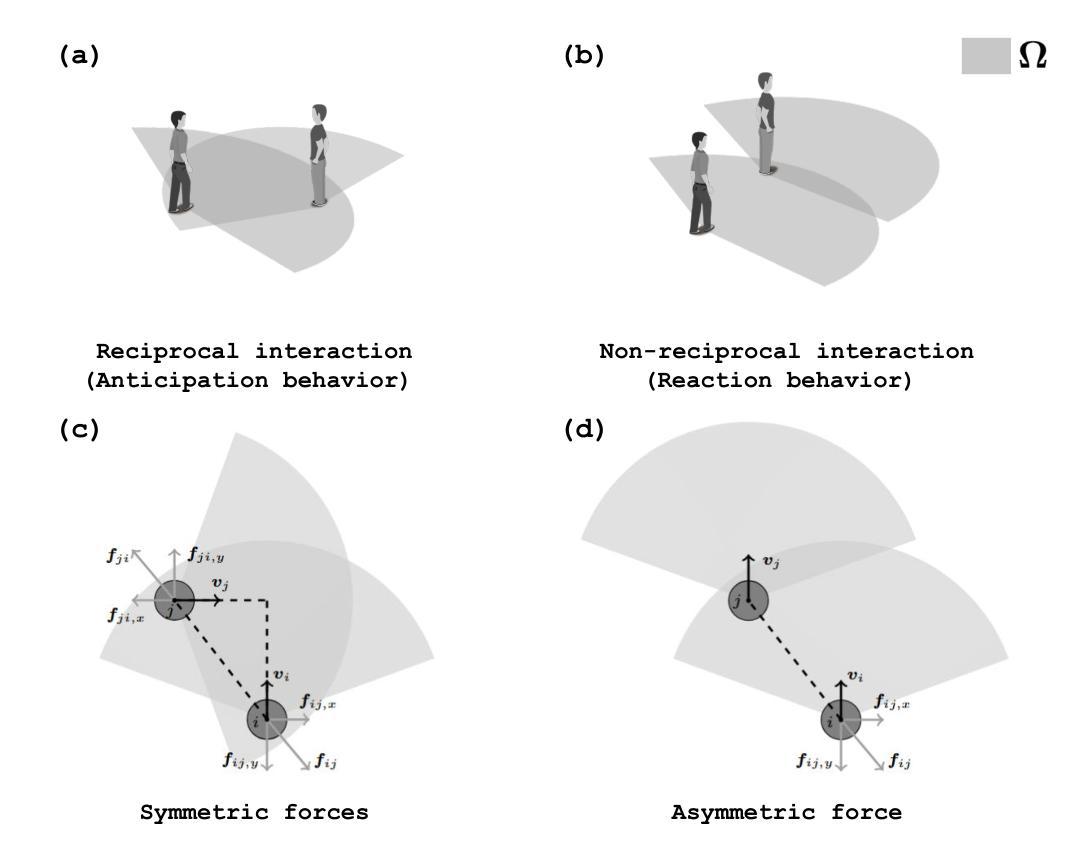
CosForce: A Force-Based General Model Considering Pedestrian Anticipation and Reaction Mechanisms
Authors:Jinghui Wang, Wei Lv
In this study, a force-based general model, named the CosForce model, has been developed. To the best of our knowledge, this may represent the most simplified version of the force-based model. Considering the anisotropic interplay of pedestrians, the model focuses on binary interactions rather than metric-based interactions. Specifically, cosine functions are employed to describe the asymmetric interactions between the focal pedestrian and their nearest neighbor, implicitly simulating anticipation and reaction mechanisms. In addition to numerical calibration in basic scenarios, the simulation primarily focuses on two intriguing crowd phenomena: “phase separation” and the “catfish effect”. Speed related metrics are introduced to quantitatively analyze self-organizing phenomena, and the “catfish effect” is examined from the perspective of momentum assessment. Many of the results require further exploration, particularly with support from empirical data. This study provides a new perspective on pedestrian modeling: the dynamics among pedestrians can be simplified as binary interactions.
在这项研究中,已经开发了一种基于力的一般模型,名为CosForce模型。据我们所知,这可能代表了基于力的模型中最简化的版本。考虑到行人的各向异性相互作用,该模型侧重于二元交互,而非基于度量的交互。具体来说,采用余弦函数来描述目标行人与其最近邻居之间的不对称交互,从而隐式地模拟预期和反应机制。除基本场景中的数值校准外,模拟主要集中于两个有趣的群体现象:“相分离”和“鲶鱼效应”。引入速度相关指标来定量分析自组织现象,并从动量评估的角度研究“鲶鱼效应”。许多结果需要进一步探索,特别是需要实证数据的支持。这项研究为行人建模提供了一个新的视角:行人之间的动态可以简化为二元交互。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 14 figures
Summary
本研究开发了一种基于力量的通用模型,名为CosForce模型。此模型可能是迄今为止最简化的力量模型之一,主要关注行人之间的二元交互作用,而非基于度量的交互作用。利用余弦函数描述目标行人与最近邻行人之间的不对称交互,并模拟其预期和反应机制。仿真研究聚焦于“相分离”和“鲶鱼效应”两种有趣的群体现象,并从动量评估的角度探讨了“鲶鱼效应”。本研究为行人建模提供了新的视角:行人之间的动态可以简化为二元交互。
Key Takeaways
- 研究开发了名为CosForce模型的基于力量的通用模型。
- 此模型是迄今为止最简化的力量模型之一。
- 模型主要关注行人之间的二元交互作用,而非基于度量的交互。
- 利用余弦函数描述目标行人与最近邻行人之间的不对称交互。
- 仿真研究聚焦于“相分离”和“鲶鱼效应”两种群体现象。
- 从动量评估的角度探讨了“鲶鱼效应”。
点此查看论文截图

Flow Matching for Optimal Reaction Coordinates of Biomolecular System
Authors:Mingyuan Zhang, Zhicheng Zhang, Hao Wu, Yong Wang
We present flow matching for reaction coordinates (FMRC), a novel deep learning algorithm designed to identify optimal reaction coordinates (RC) in biomolecular reversible dynamics. FMRC is based on the mathematical principles of lumpability and decomposability, which we reformulate into a conditional probability framework for efficient data-driven optimization using deep generative models. While FMRC does not explicitly learn the well-established transfer operator or its eigenfunctions, it can effectively encode the dynamics of leading eigenfunctions of the system transfer operator into its low-dimensional RC space. We further quantitatively compare its performance with several state-of-the-art algorithms by evaluating the quality of Markov state models (MSM) constructed in their respective RC spaces, demonstrating the superiority of FMRC in three increasingly complex biomolecular systems. In addition, we successfully demonstrated the efficacy of FMRC for bias deposition in the enhanced sampling of a simple model system. Finally, we discuss its potential applications in downstream applications such as enhanced sampling methods and MSM construction.
我们提出了反应坐标流匹配(FMRC)这一新型深度学习算法,旨在识别生物分子可逆动力学中的最佳反应坐标(RC)。FMRC基于聚集性和可分性的数学原理,我们将其重新制定为条件概率框架,以便使用深度生成模型进行有效的数据驱动优化。虽然FMRC没有显式地学习已经建立的转移算子或其特征函数,但它可以有效地将系统转移算子前导特征函数的动态编码到其低维RC空间中。我们通过评估在各自RC空间中构建的马尔可夫状态模型(MSM)的质量,定量比较了其与其他几种最新算法的性能,在三个日益复杂的生物分子系统中证明了FMRC的优越性。此外,我们还成功证明了FMRC在简单模型系统的增强采样中的偏见沉积的有效性。最后,我们讨论了其在下游应用(如增强采样方法和MSM构建)中的潜在应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF For Supporting Information, please see https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acs.jctc.4c01139
Summary
基于流匹配反应坐标(FMRC)的深度学习算法,旨在识别生物分子可逆动力学中的最佳反应坐标(RC)。FMRC基于集合性和可分性的数学原理,被重新构建为条件概率框架,用于高效的数据驱动优化。其虽不直接学习已知的系统转移算子或其特征函数,但能编码系统转移算子主导特征函数的动态信息到低维的反应坐标空间中。通过与多种前沿算法的定量比较,证实FMRC在三个复杂的生物分子系统中的优越性。此外,还成功展示了其在简单模型系统的增强采样中的偏差沉积的有效性,并探讨了其在下游应用中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- FMRC是一种用于识别生物分子可逆动力学中的最佳反应坐标(RC)的深度学习算法。
- FMRC基于集合性和可分性的数学原理,构建了一个条件概率框架。
- FMRC能有效编码系统转移算子的主导特征函数的动态信息到低维的反应坐标空间中。
- 通过与多种算法的定量比较,证实了FMRC在复杂生物分子系统中的优越性。
- FMRC在简单模型系统的增强采样中实现了有效的偏差沉积。
- FMRC在下游应用如增强采样方法和马尔可夫状态模型构建中具有潜在应用价值。
点此查看论文截图