⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-26 更新
Property Enhanced Instruction Tuning for Multi-task Molecule Generation with Large Language Models
Authors:Xuan Lin, Long Chen, Yile Wang, Xiangxiang Zeng, Philip S. Yu
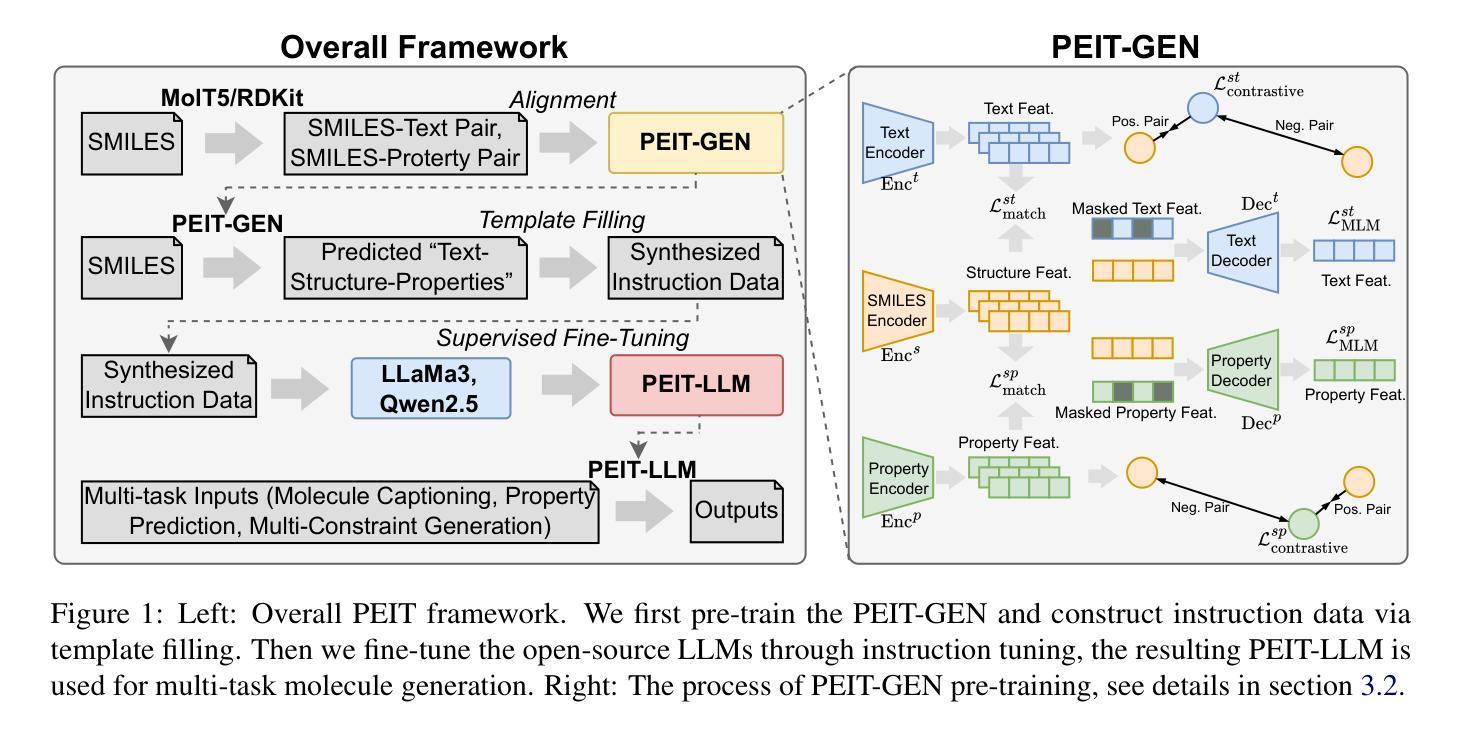
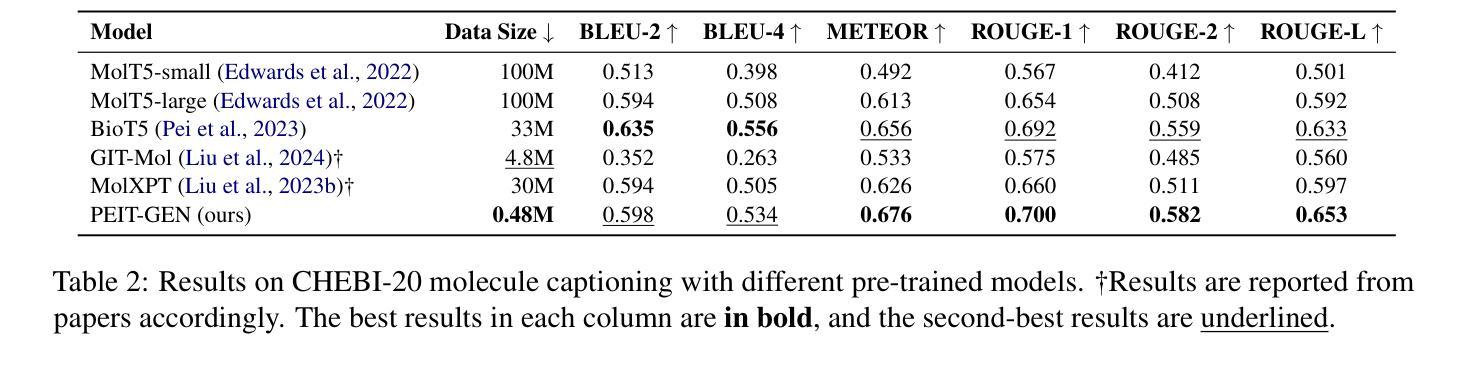
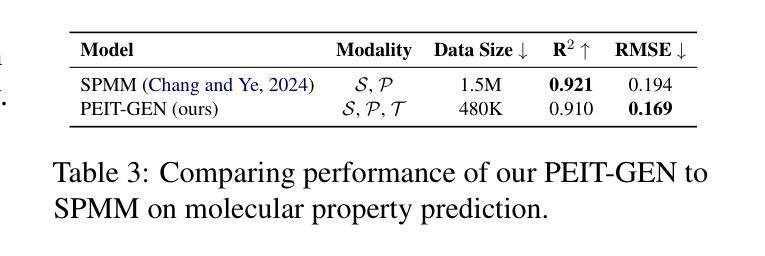
Large language models (LLMs) are widely applied in various natural language processing tasks such as question answering and machine translation. However, due to the lack of labeled data and the difficulty of manual annotation for biochemical properties, the performance for molecule generation tasks is still limited, especially for tasks involving multi-properties constraints. In this work, we present a two-step framework PEIT (Property Enhanced Instruction Tuning) to improve LLMs for molecular-related tasks. In the first step, we use textual descriptions, SMILES, and biochemical properties as multimodal inputs to pre-train a model called PEIT-GEN, by aligning multi-modal representations to synthesize instruction data. In the second step, we fine-tune existing open-source LLMs with the synthesized data, the resulting PEIT-LLM can handle molecule captioning, text-based molecule generation, molecular property prediction, and our newly proposed multi-constraint molecule generation tasks. Experimental results show that our pre-trained PEIT-GEN outperforms MolT5 and BioT5 in molecule captioning, demonstrating modalities align well between textual descriptions, structures, and biochemical properties. Furthermore, PEIT-LLM shows promising improvements in multi-task molecule generation, proving the scalability of the PEIT framework for various molecular tasks. We release the code, constructed instruction data, and model checkpoints in https://github.com/chenlong164/PEIT.
大型语言模型(LLM)广泛应用于问答、机器翻译等各种自然语言处理任务。然而,由于缺乏标签数据和生化属性手动标注的困难,分子生成任务的性能仍然有限,特别是涉及多属性约束的任务。在这项工作中,我们提出了一个两阶段的PEIT(属性增强指令调整)框架,以改进分子相关任务的LLM。在第一步中,我们使用文本描述、SMILES和生物化学属性作为多模式输入,通过对齐多模式表示来合成指令数据,从而预训练一个名为PEIT-GEN的模型。在第二步中,我们使用合成数据对现有的开源LLM进行微调,得到的PEIT-LLM可以处理分子描述、文本基础的分子生成、分子属性预测以及我们新提出的多约束分子生成任务。实验结果表明,我们预训练的PEIT-GEN在分子描述方面优于MolT5和BioT5,证明了文本描述、结构和生物化学属性之间的模态对齐良好。此外,PEIT-LLM在多任务分子生成方面显示出有希望的改进,证明了PEIT框架对各种分子任务的可扩展性。我们在https://github.com/chenlong164/PEIT发布了代码、构建指令数据和模型检查点。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在自然语言处理任务中广泛应用,但在分子生成任务上的表现因缺乏标签数据和手动标注的困难而受到限制。本研究提出了一种两步框架PEIT,以提高LLMs在分子相关任务上的性能。首先,使用文本描述、SMILES和生物化学属性等多模式输入预训练模型PEIT-GEN;其次,用合成数据微调现有开源LLMs,得到的PEIT-LLM可以处理分子描述、文本基础的分子生成、分子属性预测以及新提出的多约束分子生成任务。实验结果表明,预训练的PEIT-GEN在分子描述上优于MolT5和BioT5,证明文本描述、结构和生物化学属性之间的模态对齐良好。此外,PEIT-LLM在多任务分子生成方面显示出可喜的改进,证明了PEIT框架在各种分子任务中的可扩展性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在分子生成任务上的表现受限,主要由于缺乏标签数据和手动标注的困难。
- 提出一种两步框架PEIT,旨在提高LLMs在分子相关任务上的性能。
- PEIT框架包括两个步骤:使用多模式输入预训练模型PEIT-GEN,然后用合成数据微调现有开源LLMs。
- PEIT-GEN通过模态对齐,合成指令数据,可处理分子描述、文本基础的分子生成等任务。
- 实验结果表明,PEIT-GEN在分子描述任务上表现优异,验证了文本描述、结构和生物化学属性之间的良好模态对齐。
- PEIT-LLM在多任务分子生成方面有明显改进,证明了PEIT框架的扩展性。
点此查看论文截图