⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-02 更新
Unified dimensionality reduction techniques in chronic liver disease detection
Authors:Anand Karna, Naina Khan, Rahul Rauniyar, Prashant Giridhar Shambharkar
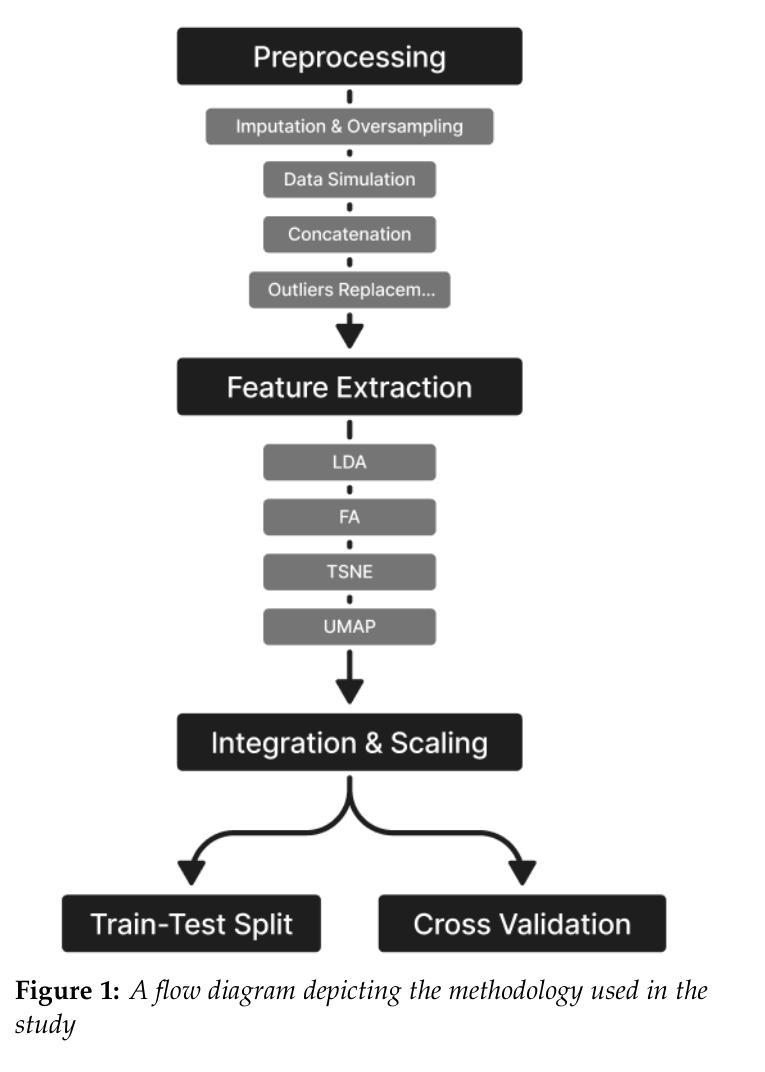
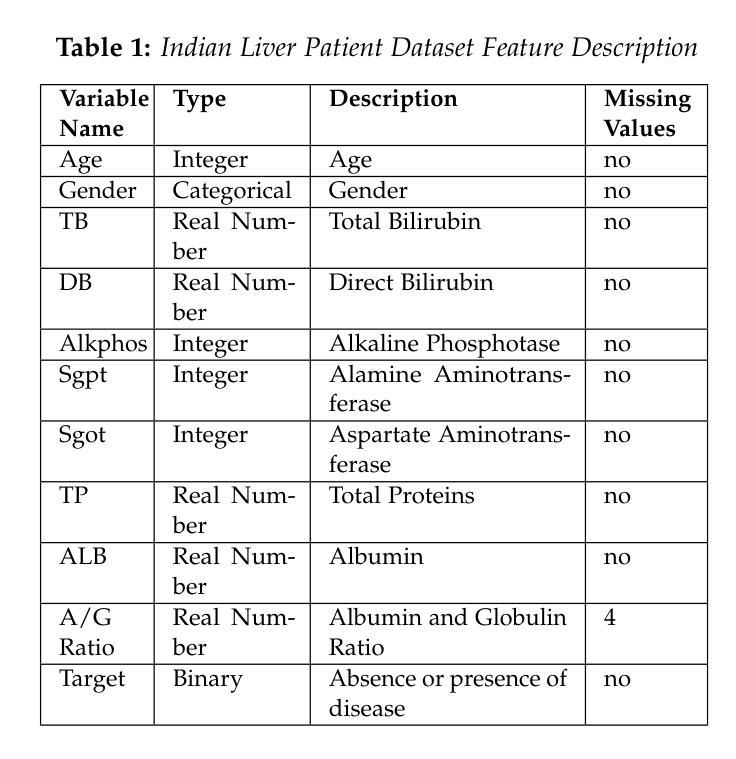
Globally, chronic liver disease continues to be a major health concern that requires precise predictive models for prompt detection and treatment. Using the Indian Liver Patient Dataset (ILPD) from the University of California at Irvine’s UCI Machine Learning Repository, a number of machine learning algorithms are investigated in this study. The main focus of our research is this dataset, which includes the medical records of 583 patients, 416 of whom have been diagnosed with liver disease and 167 of whom have not. There are several aspects to this work, including feature extraction and dimensionality reduction methods like Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA), Factor Analysis (FA), t-distributed Stochastic Neighbour Embedding (t-SNE), and Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP). The purpose of the study is to investigate how well these approaches work for converting high-dimensional datasets and improving prediction accuracy. To assess the prediction ability of the improved models, a number of classification methods were used, such as Multi-layer Perceptron, Random Forest, K-nearest neighbours, and Logistic Regression. Remarkably, the improved models performed admirably, with Random Forest having the highest accuracy of 98.31% in 10-fold cross-validation and 95.79% in train-test split evaluation. Findings offer important new perspectives on the choice and use of customized feature extraction and dimensionality reduction methods, which improve predictive models for patients with chronic liver disease.
在全球范围,慢性肝病仍然是一个重要的健康问题,需要精确的预测模型来进行及时的检测和医治。本研究使用来自加州大学欧文分校UCI机器学习存储库的印度肝病数据集(ILPD),并探索了多种机器学习算法。我们的研究主要集中在这个数据集上,其中包括583名患者的医疗记录,其中416人被诊断为肝病,而167人未被诊断出肝病。这项工作包括特征提取和降维方法,如线性判别分析(LDA)、因子分析(FA)、t分布随机邻域嵌入(t-SNE)和统一流形逼近与投影(UMAP)。研究的目的是调查这些方法在高维数据集转换和预测精度改进方面的表现如何。为了评估改进模型的预测能力,采用了多层感知器、随机森林、K近邻和逻辑回归等分类方法。值得注意的是,改进后的模型表现良好,其中随机森林在10倍交叉验证中的准确率最高,达到98.31%,在训练测试分割评估中的准确率为95.79%。研究结果提供了关于选择和使用针对慢性肝病患者定制的特征提取和降维方法的重要新视角,有助于改进预测模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文利用印度肝脏病人数据集(ILPD),调查了多种机器学习方法在慢性肝病预测模型中的应用。研究包括特征提取和降维方法,以及分类方法,如多层感知器、随机森林、K近邻和逻辑回归。结果显示,改进后的模型表现优异,其中随机森林在10倍交叉验证和训练-测试集分割评估中的准确率分别高达98.31%和95.79%。这为慢性肝病预测模型的选择和使用提供了重要的新视角。
Key Takeaways
- 慢性肝病是全球性的主要健康问题,需要精确的预测模型进行及时检测和治疗的支持。
- 研究使用了印度肝脏病人数据集(ILPD),该数据集包含了583名患者的医疗记录,其中416名被诊断为肝病。
- 研究涉及特征提取和降维方法,如线性判别分析(LDA)、因子分析(FA)、t分布随机邻嵌入(t-SNE)和统一流形逼近和投影(UMAP)。
- 使用了多种分类方法,包括多层感知器、随机森林、K近邻和逻辑回归来评估改进后的模型的预测能力。
- 随机森林在10倍交叉验证和训练-测试集分割评估中表现出最高的准确性,分别为98.31%和95.79%。
- 研究结果提供了关于特征提取和降维方法选择和使用的重要新视角,这些方法可改善慢性肝病的预测模型。
点此查看论文截图

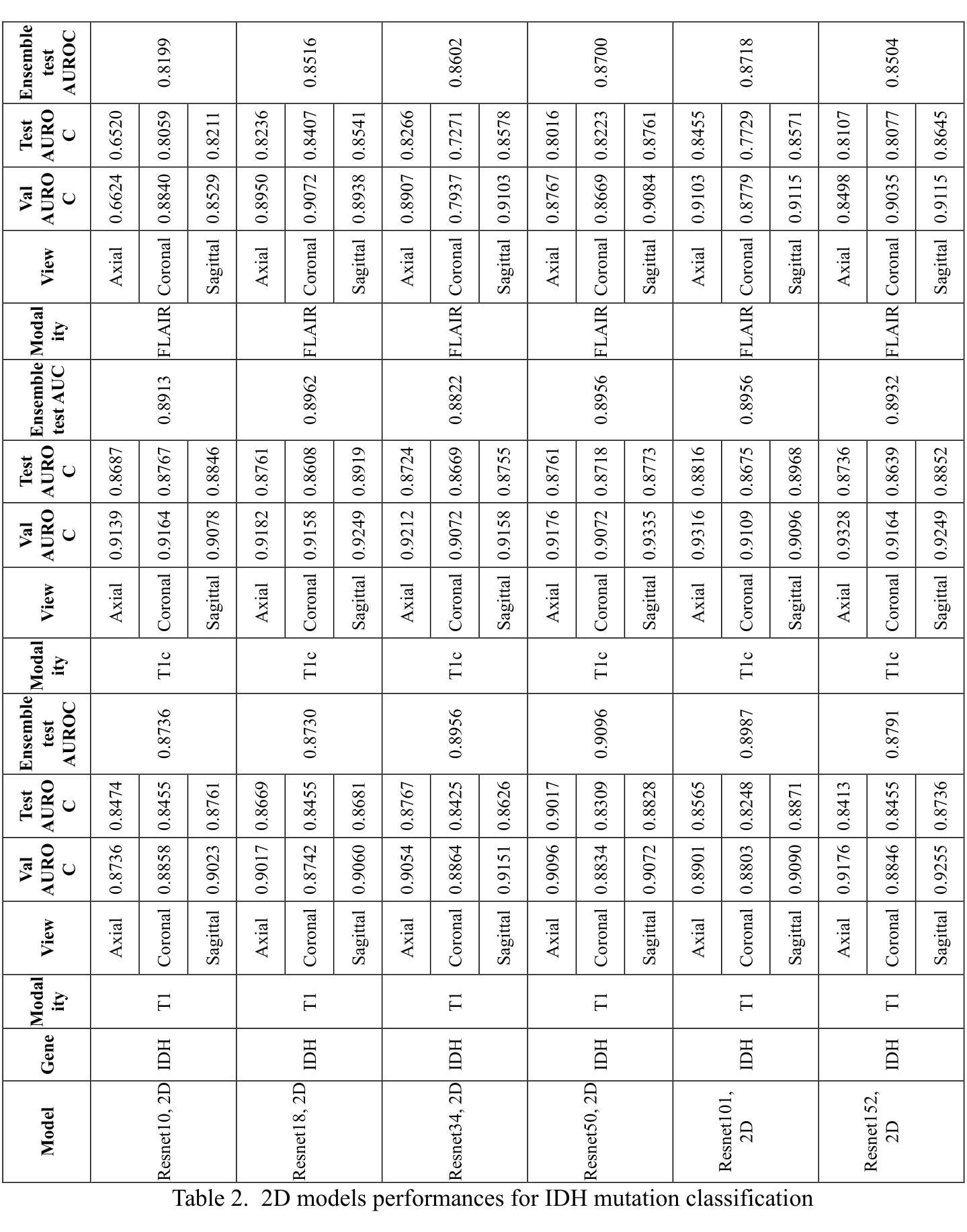
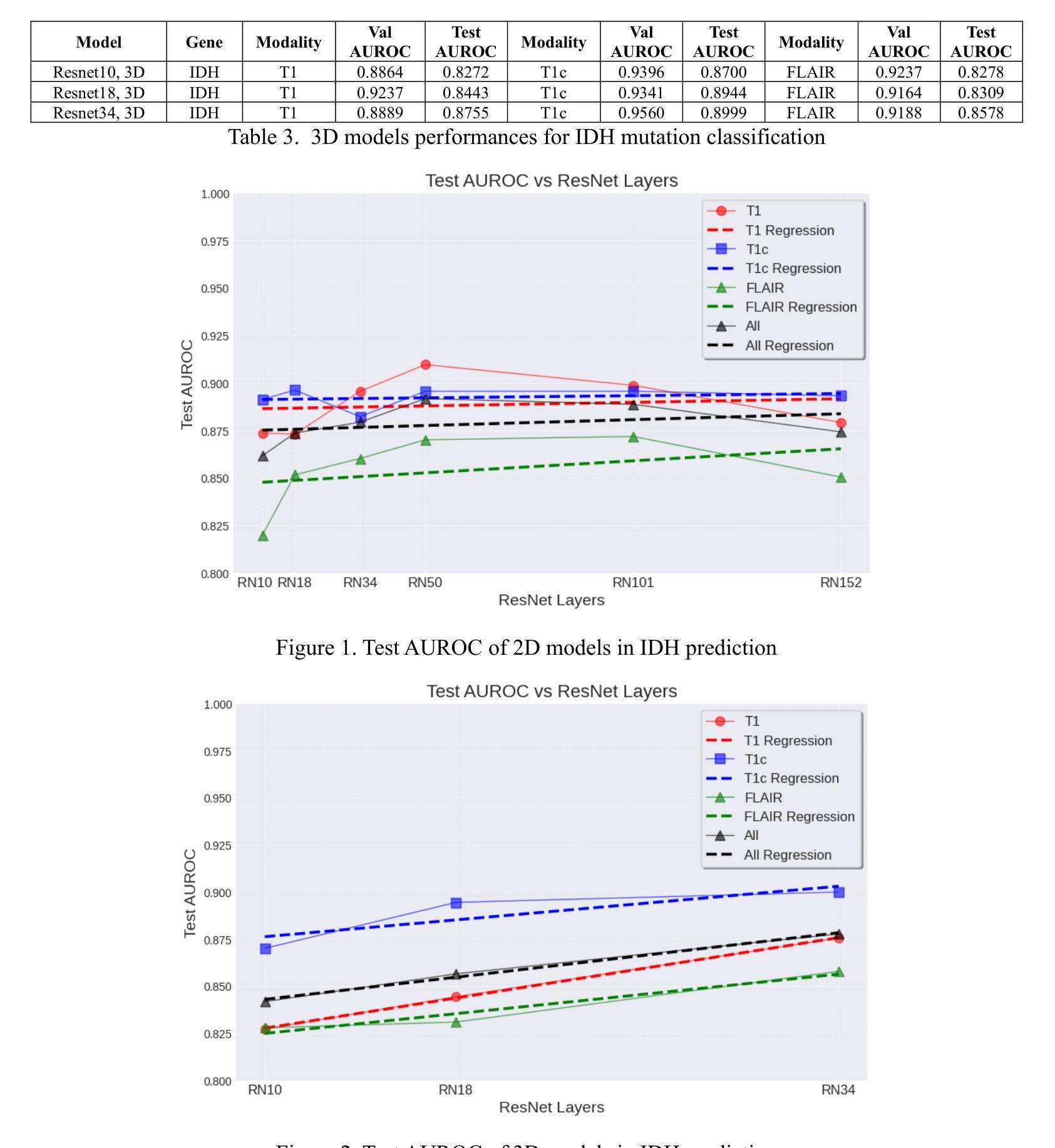
Comparative Analysis of 2D and 3D ResNet Architectures for IDH and MGMT Mutation Detection in Glioma Patients
Authors:Danial Elyassirad, Benyamin Gheiji, Mahsa Vatanparast, Amir Mahmoud Ahmadzadeh, Neda Kamandi, Amirmohammad Soleimanian, Sara Salehi, Shahriar Faghani
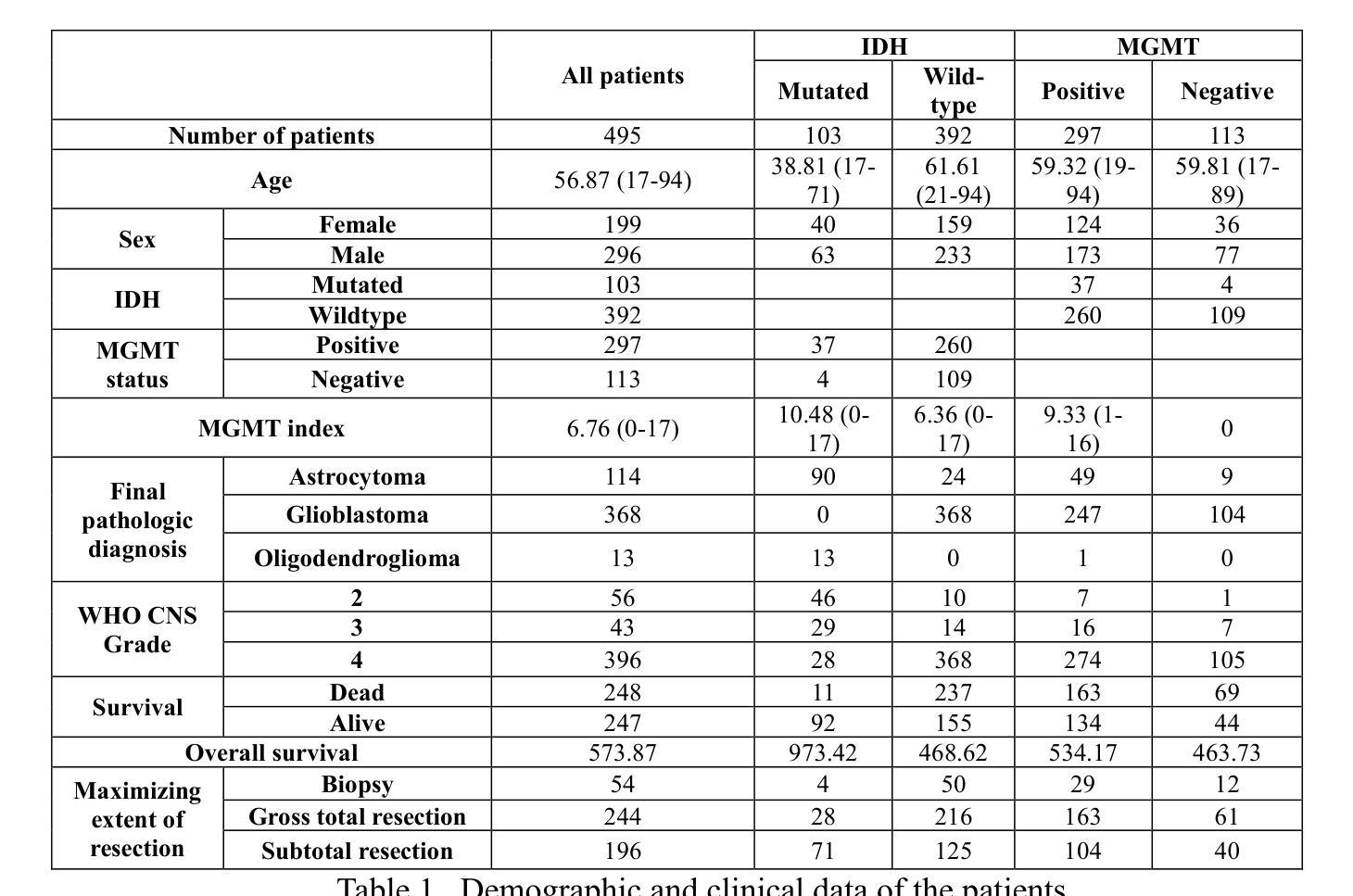
Gliomas are the most common cause of mortality among primary brain tumors. Molecular markers, including Isocitrate Dehydrogenase (IDH) and O[6]-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) influence treatment responses and prognosis. Deep learning (DL) models may provide a non-invasive method for predicting the status of these molecular markers. To achieve non-invasive determination of gene mutations in glioma patients, we compare 2D and 3D ResNet models to predict IDH and MGMT status, using T1, post-contrast T1, and FLAIR MRI sequences. USCF glioma dataset was used, which contains 495 patients with known IDH and 410 patients with known MGMT status. The dataset was divided into training (60%), tuning (20%), and test (20%) subsets at the patient level. The 2D models take axial, coronal, and sagittal tumor slices as three separate models. To ensemble the 2D predictions the three different views were combined using logistic regression. Various ResNet architectures (ResNet10, 18, 34, 50, 101, 152) were trained. For the 3D approach, we incorporated the entire brain tumor volume in the ResNet10, 18, and 34 models. After optimizing each model, the models with the lowest tuning loss were selected for further evaluation on the separate test sets. The best-performing models in IDH prediction were the 2D ResNet50, achieving a test area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) of 0.9096, and the 3D ResNet34, which reached a test AUROC of 0.8999. For MGMT status prediction, the 2D ResNet152 achieved a test AUROC of 0.6168; however, all 3D models yielded AUROCs less than 0.5. Overall, the study indicated that both 2D and 3D models showed high predictive value for IDH prediction, with slightly better performance in 2D models.
胶质瘤是原发性脑肿瘤中导致死亡最常见的原因。分子标记物,包括异柠檬酸脱氢酶(IDH)和O[6]-甲基鸟嘌呤-DNA甲基转移酶(MGMT)影响治疗效果和预后。深度学习(DL)模型可能提供一种非侵入性方法来预测这些分子标记物的状态。为了实现胶质瘤患者基因突变的非侵入性测定,我们比较了用于预测IDH和MGMT状态的2D和3D ResNet模型,使用T1、增强T1和FLAIR MRI序列。USCF胶质瘤数据集包含495例已知IDH状态和410例已知MGMT状态的患者。数据集按患者水平分为训练(60%)、调整(20%)和测试(20%)子集。2D模型将轴向、冠状向和矢状面的肿瘤切片作为三个单独模型。为了集成2D预测,使用逻辑回归将三个不同视图结合起来。对各种ResNet架构(ResNet10、18、34、50、101、152)进行了训练。对于3D方法,我们将整个脑肿瘤体积纳入ResNet10、18和34模型中。在优化每个模型后,选择调整损失最低的模型在单独的测试集上进行进一步评估。在IDH预测中表现最好的模型是2D ResNet50,测试曲线下面积(AUROC)为0.9096,3D ResNet34的测试AUROC为0.8999。在MGMT状态预测方面,2D ResNet152的测试AUROC为0.6168;然而,所有3D模型的AUROC均低于0.5。总体而言,研究结果表明,2D和3D模型在IDH预测中都表现出较高的预测价值,2D模型的性能略好。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 PAGES, 2 Figures, 3 Tables
Summary
本文研究了使用深度学习模型非侵入性地预测脑胶质瘤患者IDH和MGMT分子标记状态的方法。通过对比2D和3D ResNet模型,发现2D模型在IDH预测方面表现稍优,而3D模型在MGMT预测方面效果欠佳。研究为脑胶质瘤的个性化治疗提供了潜在的非侵入性预测工具。
Key Takeaways
- Gliomas是主要导致原发性脑肿瘤死亡的原因。
- 分子标记如IDH和MGMT影响治疗反应和预后。
- 深度学习模型提供了一种非侵入性预测这些分子标记状态的方法。
- 对比了2D和3D ResNet模型,在预测IDH状态方面都有较高的准确性。
- 2D模型在IDH预测方面表现稍优于3D模型。
- MGMT状态预测方面,2D模型表现较好,而所有3D模型的预测效果均不理想。
点此查看论文截图

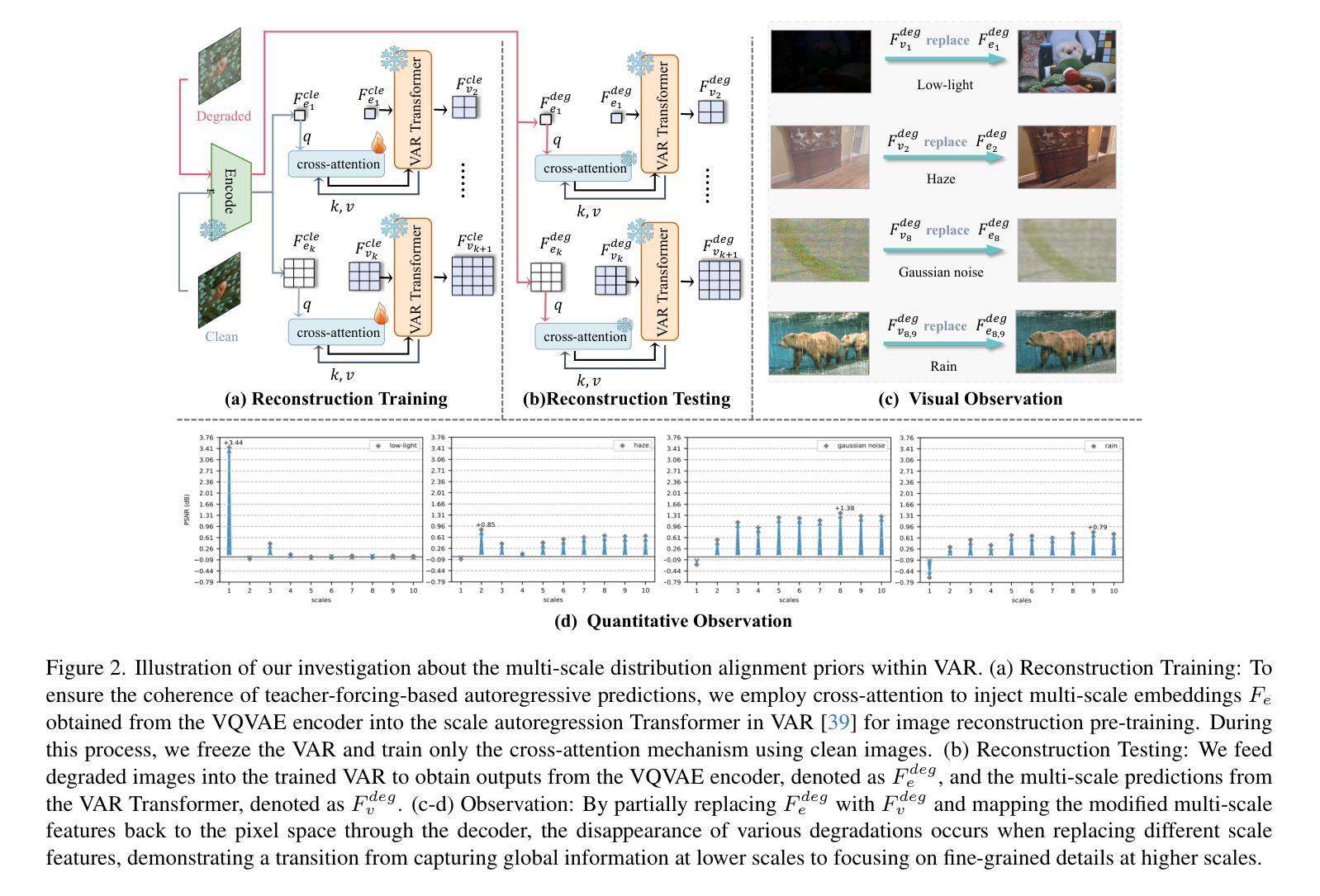
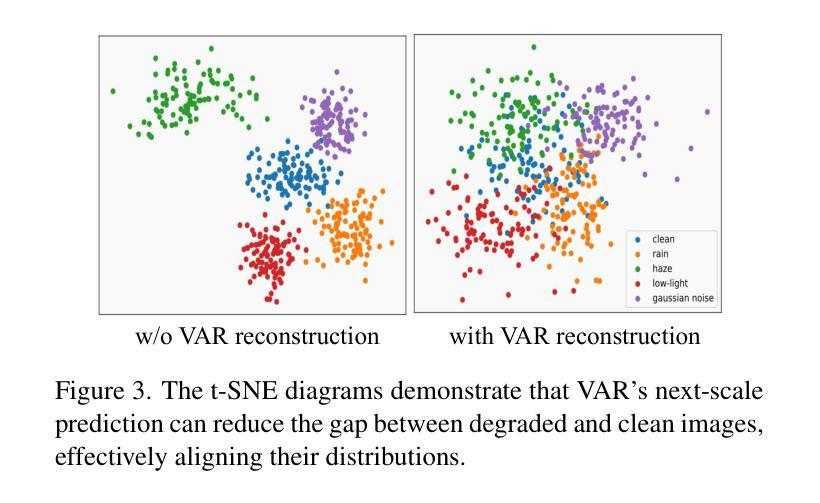
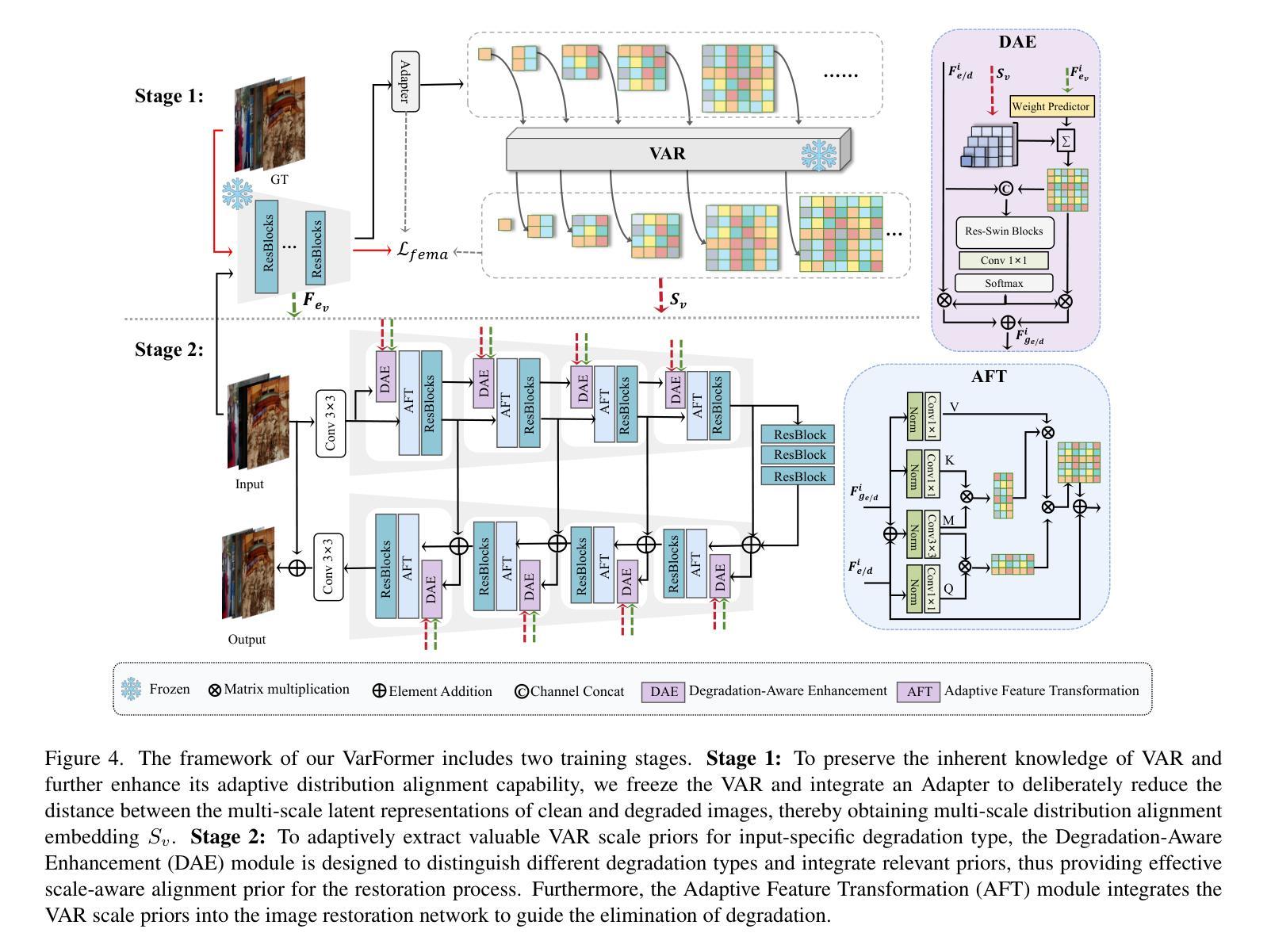
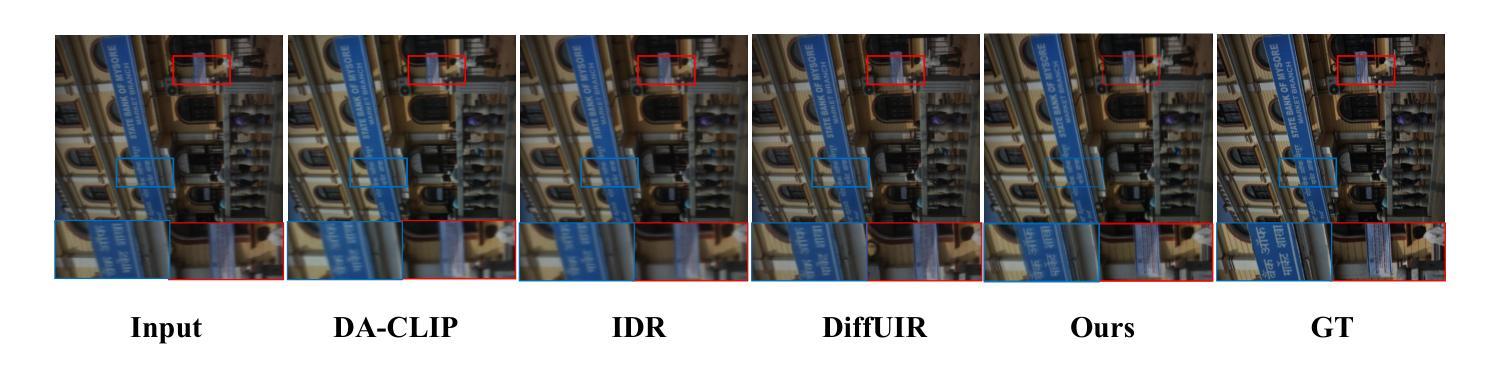
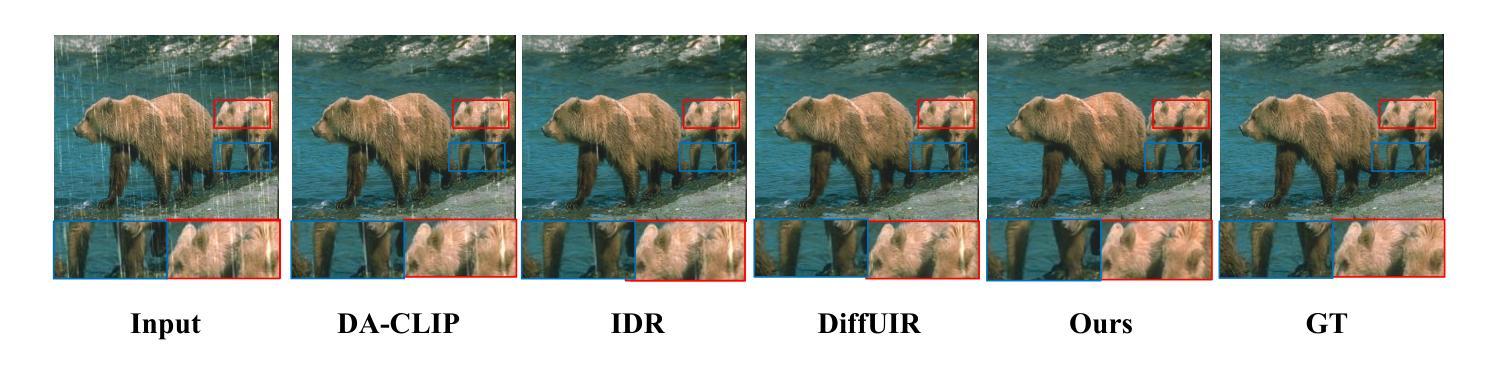
Varformer: Adapting VAR’s Generative Prior for Image Restoration
Authors:Siyang Wang, Feng Zhao
Generative models trained on extensive high-quality datasets effectively capture the structural and statistical properties of clean images, rendering them powerful priors for transforming degraded features into clean ones in image restoration. VAR, a novel image generative paradigm, surpasses diffusion models in generation quality by applying a next-scale prediction approach. It progressively captures both global structures and fine-grained details through the autoregressive process, consistent with the multi-scale restoration principle widely acknowledged in the restoration community. Furthermore, we observe that during the image reconstruction process utilizing VAR, scale predictions automatically modulate the input, facilitating the alignment of representations at subsequent scales with the distribution of clean images. To harness VAR’s adaptive distribution alignment capability in image restoration tasks, we formulate the multi-scale latent representations within VAR as the restoration prior, thus advancing our delicately designed VarFormer framework. The strategic application of these priors enables our VarFormer to achieve remarkable generalization on unseen tasks while also reducing training computational costs. Extensive experiments underscores that our VarFormer outperforms existing multi-task image restoration methods across various restoration tasks.
生成模型经过在大量高质量数据集上的训练,能够有效捕捉清洁图像的结构和统计特性,使其成为将退化特征转换为清洁图像的强大先验知识,用于图像修复。VAR作为一种新的图像生成范式,通过应用下一尺度预测方法,在生成质量上超越了扩散模型。它通过自回归过程逐步捕捉全局结构和精细细节,这与修复界广泛认可的多尺度修复原则相一致。此外,我们观察到,在利用VAR进行图像重建的过程中,尺度预测会自动调整输入,促进后续尺度的表示与清洁图像分布的对齐。为了利用VAR在图像修复任务中的自适应分布对齐能力,我们将VAR内的多尺度潜在表示定义为修复先验,从而推进了我们精心设计的VarFormer框架。这些先验知识的战略应用使我们的VarFormer在未见任务上实现了卓越的泛化能力,同时降低了训练计算成本。大量实验证明,我们的VarFormer在多种修复任务上优于现有的多任务图像修复方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
生成模型经大规模高质量数据集训练后,能有效捕捉清晰图像的结构和统计特性,在图像修复中将退化特征转化为清晰特征时表现出强大的先验能力。新型图像生成范式VAR,通过应用下一尺度预测方法,在生成质量上超越了扩散模型。VAR遵循多尺度修复原则,渐进捕捉全局结构和精细细节。在利用VAR进行图像重建时,尺度预测可自动调整输入,有助于后续尺度表示与清晰图像分布的对齐。我们将VAR中的多尺度潜在表示作为修复先验,构建了精巧的VarFormer框架,该框架可自适应分布对齐能力,在图像修复任务中表现出卓越性能。VarFormer在多种修复任务上优于现有多任务图像修复方法。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型经高质量数据集训练后能有效捕捉图像结构和统计特性。
- VAR采用下一尺度预测方法,生成质量超越扩散模型。
- VAR遵循多尺度修复原则,渐进捕捉全局结构和精细细节。
- VAR在图像重建过程中自动调整尺度预测。
- VarFormer利用VAR中的多尺度潜在表示作为修复先验。
- VarFormer具有自适应分布对齐能力,在图像修复任务中表现卓越。
- VarFormer在多种修复任务上优于现有多任务图像修复方法。
点此查看论文截图

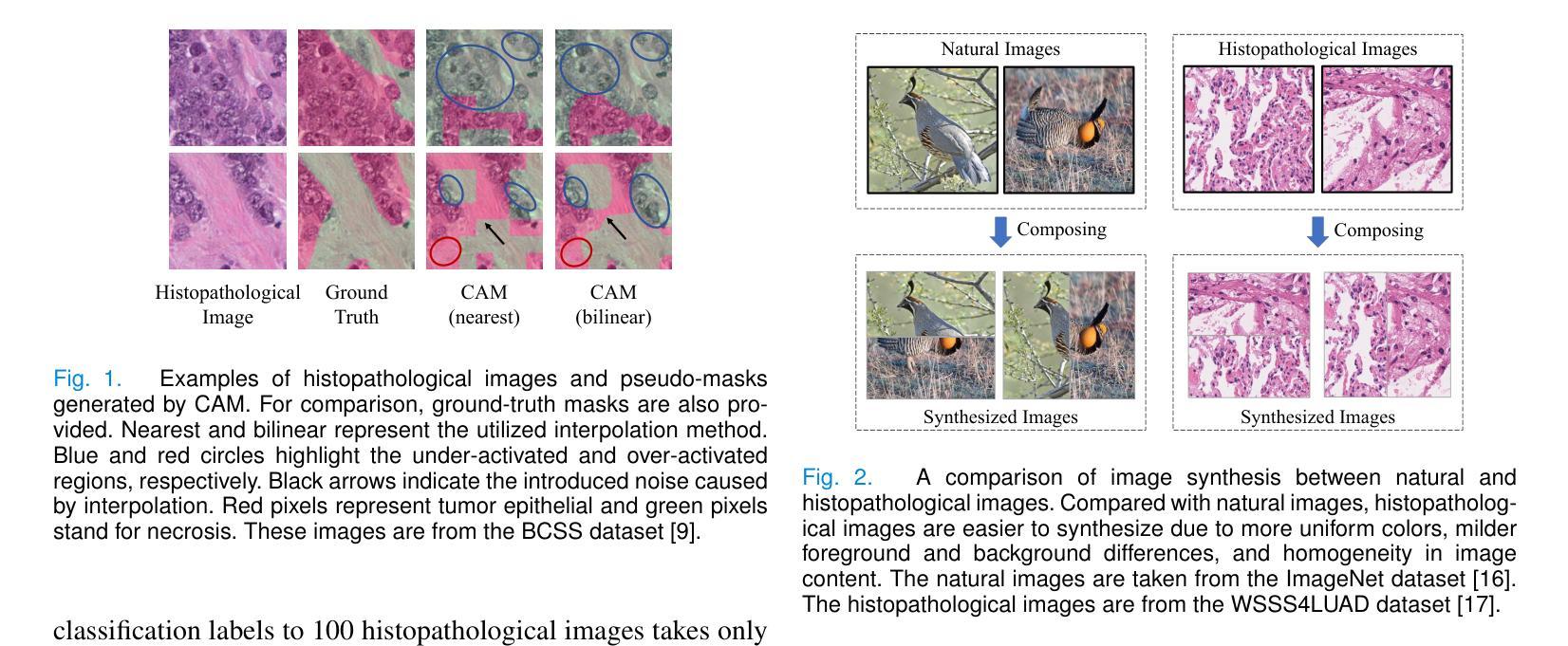
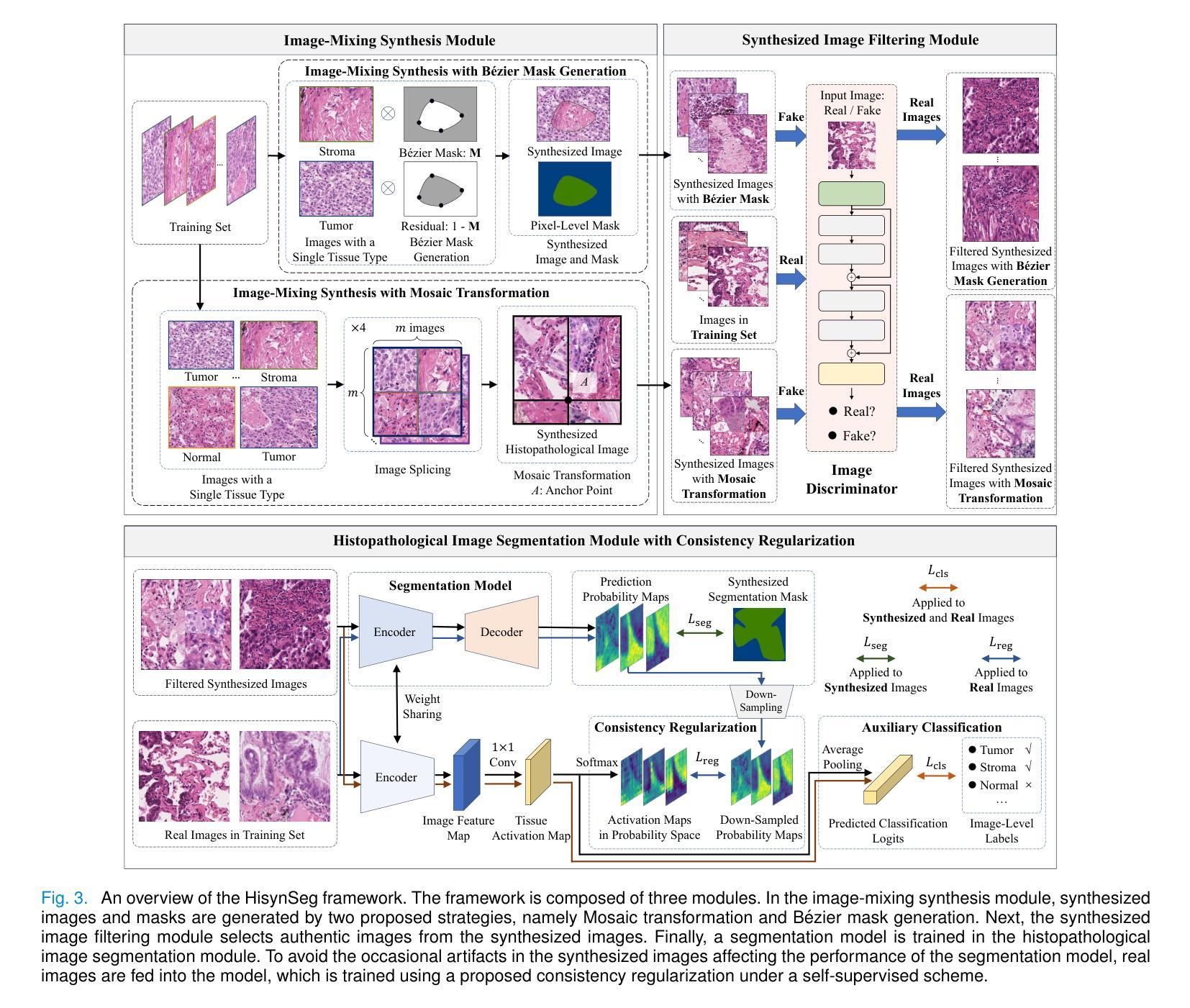
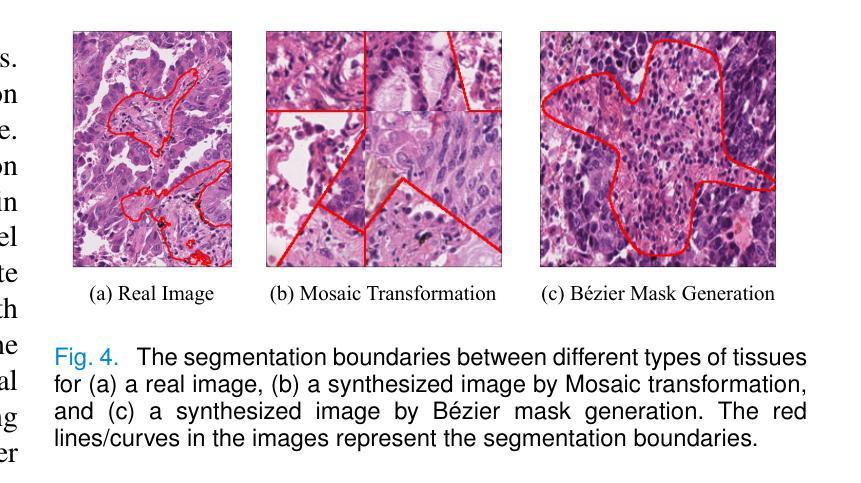
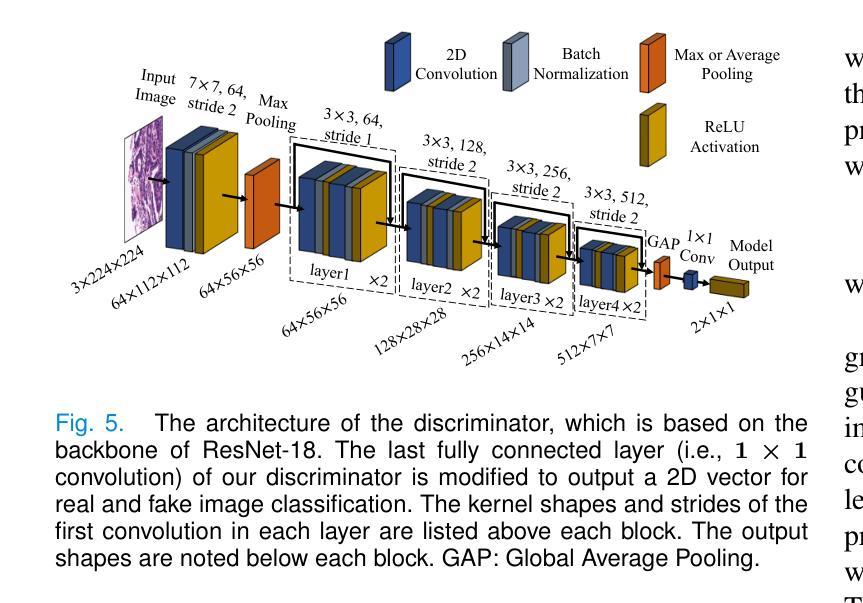
HisynSeg: Weakly-Supervised Histopathological Image Segmentation via Image-Mixing Synthesis and Consistency Regularization
Authors:Zijie Fang, Yifeng Wang, Peizhang Xie, Zhi Wang, Yongbing Zhang
Tissue semantic segmentation is one of the key tasks in computational pathology. To avoid the expensive and laborious acquisition of pixel-level annotations, a wide range of studies attempt to adopt the class activation map (CAM), a weakly-supervised learning scheme, to achieve pixel-level tissue segmentation. However, CAM-based methods are prone to suffer from under-activation and over-activation issues, leading to poor segmentation performance. To address this problem, we propose a novel weakly-supervised semantic segmentation framework for histopathological images based on image-mixing synthesis and consistency regularization, dubbed HisynSeg. Specifically, synthesized histopathological images with pixel-level masks are generated for fully-supervised model training, where two synthesis strategies are proposed based on Mosaic transformation and B'ezier mask generation. Besides, an image filtering module is developed to guarantee the authenticity of the synthesized images. In order to further avoid the model overfitting to the occasional synthesis artifacts, we additionally propose a novel self-supervised consistency regularization, which enables the real images without segmentation masks to supervise the training of the segmentation model. By integrating the proposed techniques, the HisynSeg framework successfully transforms the weakly-supervised semantic segmentation problem into a fully-supervised one, greatly improving the segmentation accuracy. Experimental results on three datasets prove that the proposed method achieves a state-of-the-art performance. Code is available at https://github.com/Vison307/HisynSeg.
组织语义分割是计算病理学中的一项关键任务。为了避免昂贵且费力的像素级注释采集,大量研究尝试采用类激活图(CAM)这种弱监督学习方案,以实现像素级组织分割。然而,基于CAM的方法容易遭受欠激活和过度激活的问题,导致分割性能不佳。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于图像混合合成和一致性正则化的弱监督语义分割框架,用于病理图像分析,称为HisynSeg。具体而言,我们生成带有像素级掩膜的合成病理图像,用于全监督模型训练,其中提出了两种基于马赛克变换和贝塞尔掩膜生成的合成策略。此外,还开发了一个图像过滤模块,以保证合成图像的真实性。为了进一步避免模型对偶尔的合成伪影过度适应,我们还提出了一种新型的自监督一致性正则化,这使得没有分割掩膜的真实图像能够监督分割模型的训练。通过整合所提出的技术,HisynSeg框架成功将弱监督语义分割问题转化为全监督问题,大大提高了分割精度。在三个数据集上的实验结果证明,该方法达到了最先进的表现。相关代码可通过https://github.com/Vison307/HisynSeg获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging
Summary
本文介绍了针对计算病理学中的组织语义分割任务,提出了一种基于图像混合合成和一致性正则化的弱监督语义分割框架HisynSeg。该框架通过生成合成病理图像和像素级掩膜进行全监督模型训练,并采用了两种合成策略:基于马赛克变换和贝塞尔掩膜生成。同时,开发了一个图像过滤模块以保证合成图像的真实性。为避免模型对合成工件的过度拟合,引入了自我监督的一致性正则化,使得无需分割掩膜的真实图像能够监督分割模型的训练。通过整合这些技术,HisynSeg框架成功将弱监督语义分割问题转化为全监督问题,大大提高了分割精度。在三个数据集上的实验结果证明了该方法达到了先进水平。
Key Takeaways
- HisynSeg框架解决了计算病理学中的组织语义分割问题,采用弱监督学习方法。
- 利用图像混合合成进行全监督模型训练,包括马赛克变换和贝塞尔掩膜生成的两种合成策略。
- 图像过滤模块确保合成图像的真实性。
- 引入自我监督的一致性正则化,避免模型对合成工件的过度拟合。
- HisynSeg框架成功提高分割精度,并在三个数据集上达到先进水平。
- 该方法的代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

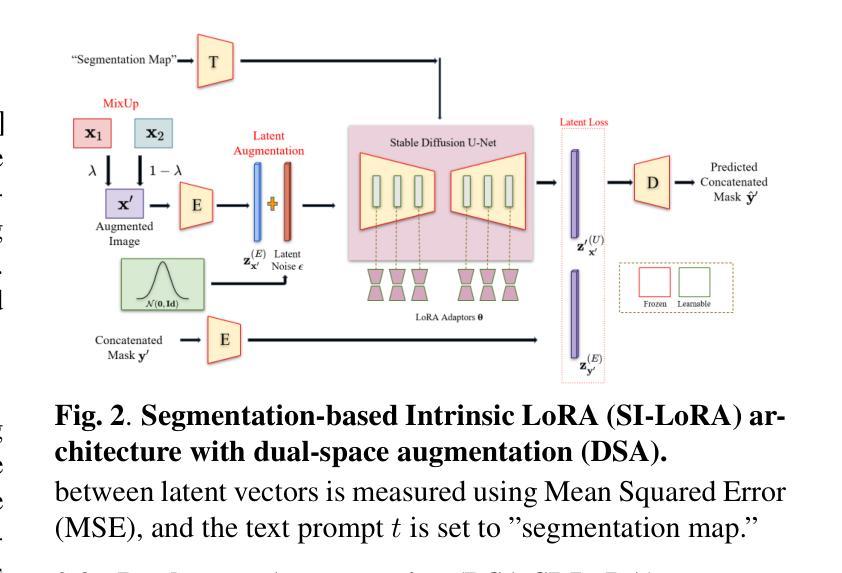
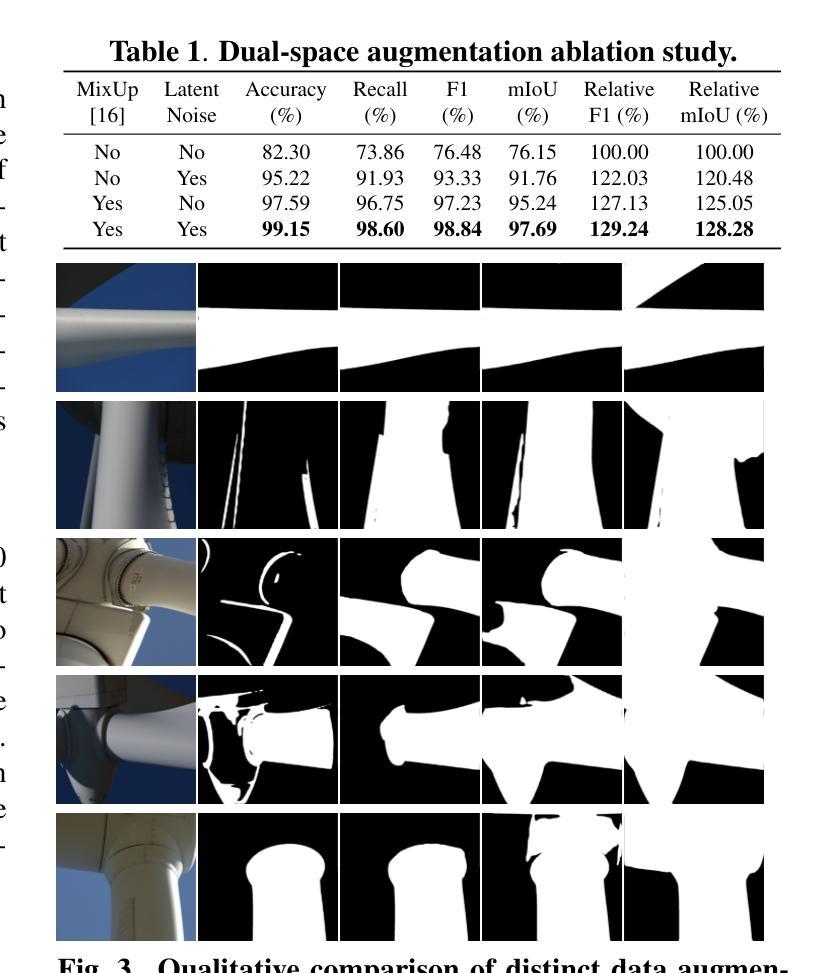
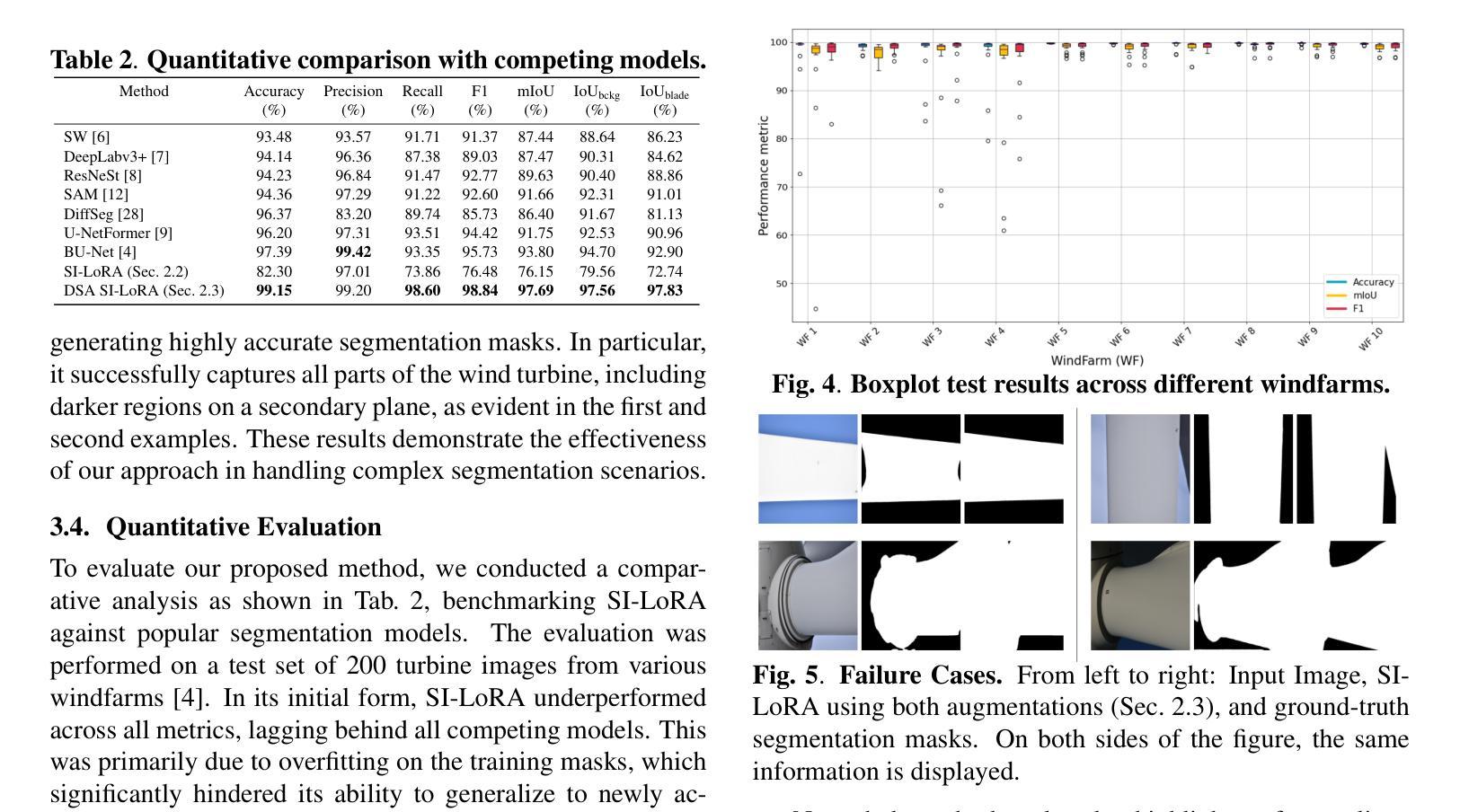
Dual-Space Augmented Intrinsic-LoRA for Wind Turbine Segmentation
Authors:Shubh Singhal, Raül Pérez-Gonzalo, Andreas Espersen, Antonio Agudo
Accurate segmentation of wind turbine blade (WTB) images is critical for effective assessments, as it directly influences the performance of automated damage detection systems. Despite advancements in large universal vision models, these models often underperform in domain-specific tasks like WTB segmentation. To address this, we extend Intrinsic LoRA for image segmentation, and propose a novel dual-space augmentation strategy that integrates both image-level and latent-space augmentations. The image-space augmentation is achieved through linear interpolation between image pairs, while the latent-space augmentation is accomplished by introducing a noise-based latent probabilistic model. Our approach significantly boosts segmentation accuracy, surpassing current state-of-the-art methods in WTB image segmentation.
风力发电机叶片(WTB)图像的精确分割对于有效评估至关重要,因为它直接影响自动化损伤检测系统的性能。尽管通用视觉模型取得了进展,但这些模型在特定领域的任务(如WTB分割)中往往表现不佳。为了解决这一问题,我们扩展了用于图像分割的内在LoRA方法,并提出了一种新的双空间增强策略,该策略结合了图像级和潜在空间级的增强。图像空间的增强是通过图像对之间的线性插值来实现的,而潜在空间的增强则是通过引入基于噪声的潜在概率模型来实现的。我们的方法显著提高了分割精度,在WTB图像分割中超越了当前最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Authors Shubh Singhal and Ra"ul P'erez-Gonzalo contributed equally to this work. Accepted to ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文介绍了风力发电机叶片(WTB)图像精准分割的重要性及其对自动化损伤检测系统性能的影响。针对通用大型视觉模型在特定领域任务中表现不佳的问题,本文扩展了Intrinsic LoRA图像分割方法,并提出了一种新的双空间增强策略,该策略结合了图像级和潜在空间级的增强。通过图像对之间的线性插值实现图像空间增强,而通过引入基于噪声的潜在概率模型实现潜在空间增强。该方法显著提高了分割精度,超越了当前风力发电机叶片图像分割领域最先进的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 风力发电机叶片(WTB)图像分割对于评估至关重要,影响自动化损伤检测系统的性能。
- 通用大型视觉模型在特定任务(如WTB分割)中表现不佳。
- 扩展了Intrinsic LoRA方法用于图像分割。
- 提出了一种新的双空间增强策略,结合图像级和潜在空间级的增强。
- 图像空间增强通过图像对之间的线性插值实现。
- 潜在空间增强通过引入基于噪声的潜在概率模型实现。
点此查看论文截图

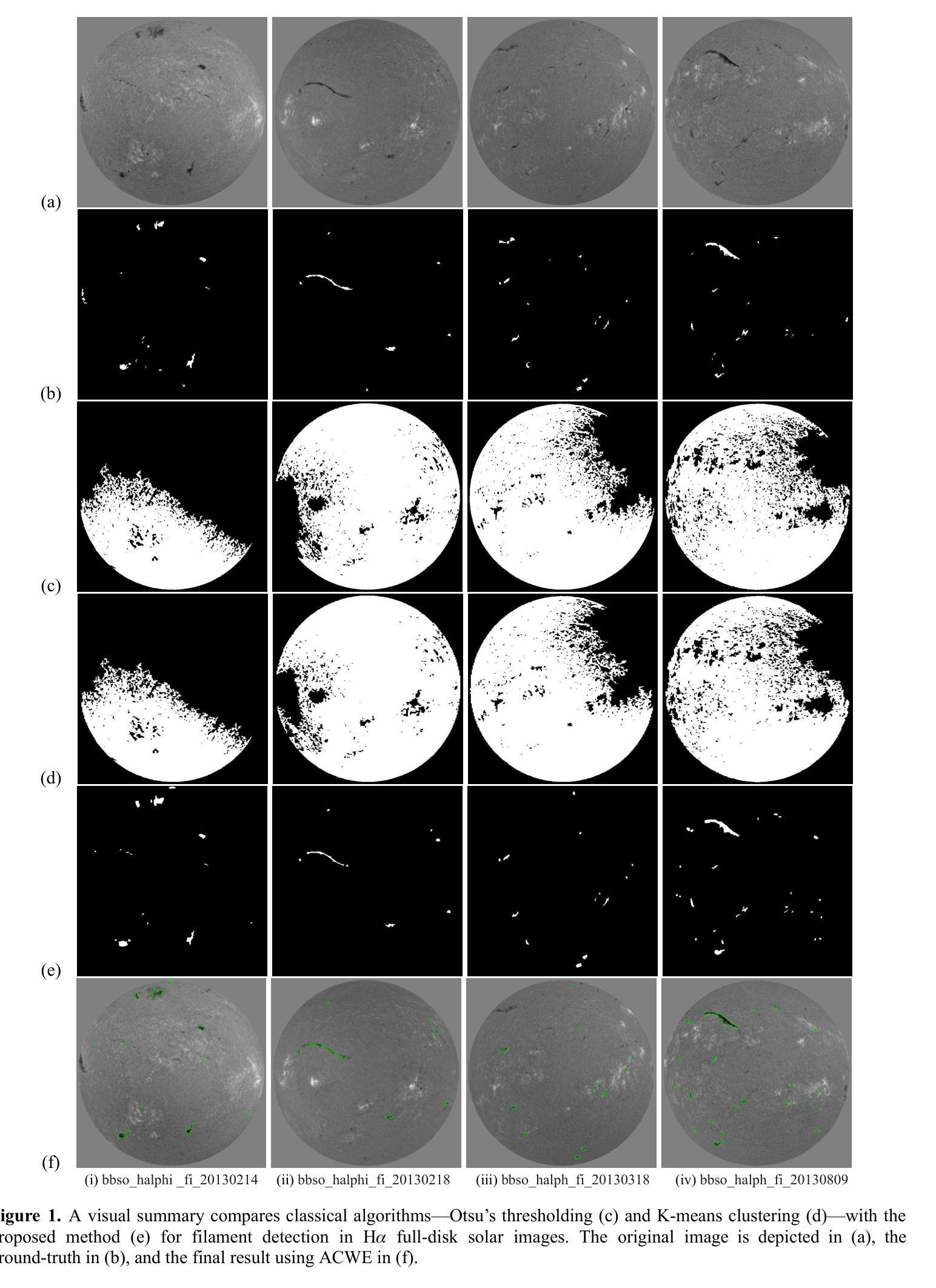
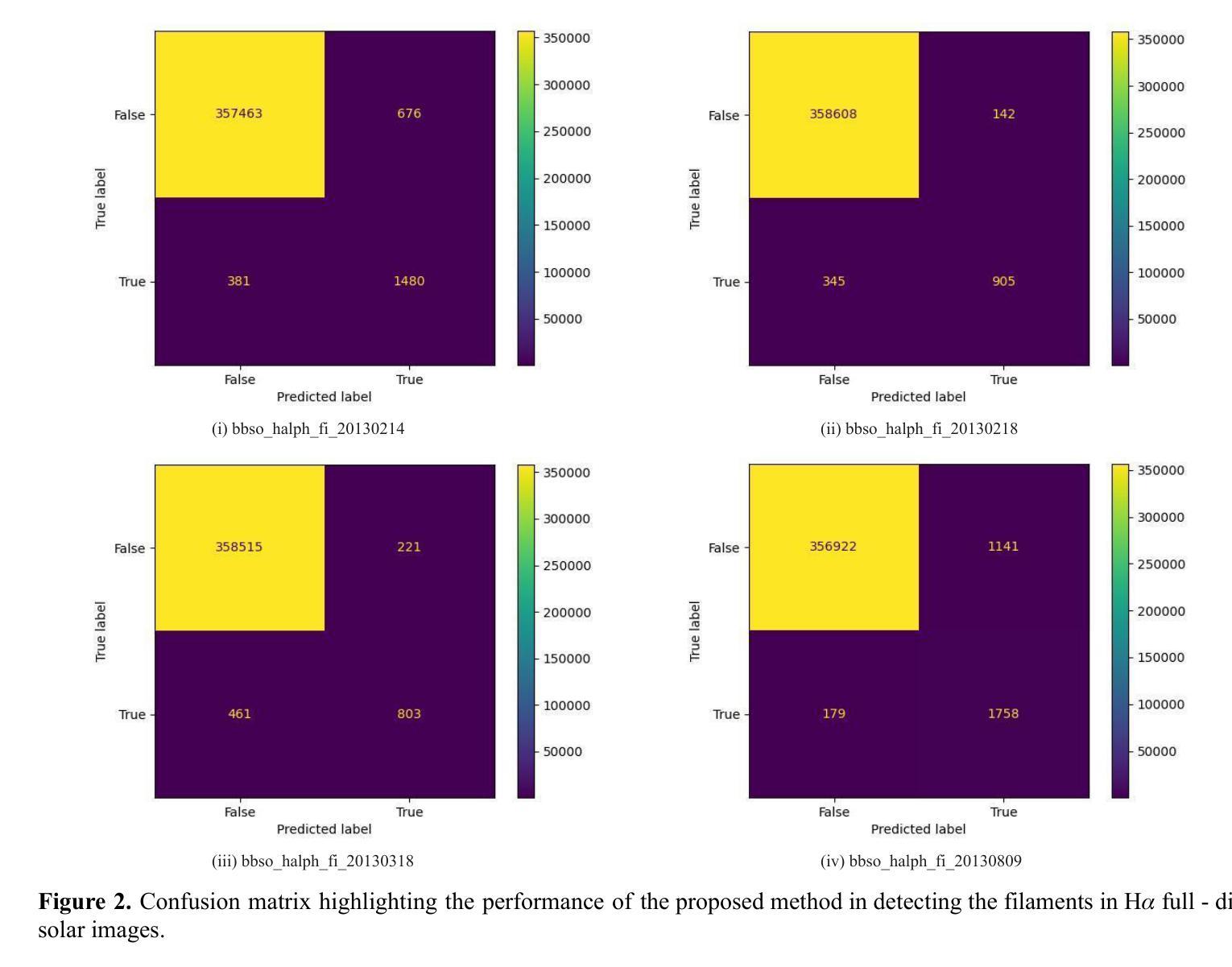
Solar Filaments Detection using Active Contours Without Edges
Authors:Sanmoy Bandyopadhyay, Vaibhav Pant
In this article, an active contours without edges (ACWE)-based algorithm has been proposed for the detection of solar filaments in H-alpha full-disk solar images. The overall algorithm consists of three main steps of image processing. These are image pre-processing, image segmentation, and image post-processing. Here in the work, contours are initialized on the solar image and allowed to deform based on the energy function. As soon as the contour reaches the boundary of the desired object, the energy function gets reduced, and the contour stops evolving. The proposed algorithm has been applied to few benchmark datasets and has been compared with the classical technique of object detection. The results analysis indicates that the proposed algorithm outperforms the results obtained using the existing classical algorithm of object detection.
本文提出了一种基于无边缘活动轮廓(ACWE)的算法,用于检测H-alpha全日面太阳图像中的太阳丝。该算法总体包括三个主要的图像处理步骤:图像预处理、图像分割和图像后处理。在此工作中,轮廓在太阳图像上进行初始化,并允许其根据能量函数进行变形。一旦轮廓达到目标对象的边界,能量函数就会减小,轮廓就会停止演化。该算法已应用于一些基准数据集,并与经典的目标检测技术进行了比较。结果分析表明,该算法的性能优于现有经典目标检测算法所获得的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 2 figures
Summary
本文提出一种基于无边缘活动轮廓(ACWE)的算法,用于在H-alpha全日面图像中检测太阳纤维。算法主要包括图像预处理、图像分割和图像后处理三个步骤。通过初始化太阳图像上的轮廓,并允许其根据能量函数变形,当轮廓达到目标对象边界时,能量函数减少,轮廓停止演化。该算法已应用于多个基准数据集,并与经典的目标检测技术进行和对,结果表明该算法优于现有的经典目标检测算法。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了基于无边缘活动轮廓(ACWE)的算法用于检测太阳纤维。
- 算法包含图像预处理、图像分割和图像后处理三个主要步骤。
- 轮廓在太阳图像上初始化,并基于能量函数进行变形。
- 当轮廓达到目标对象边界时,能量函数减少,轮廓停止演化。
- 该算法已应用于多个基准数据集。
- 该算法与经典的目标检测技术进行了比较。
点此查看论文截图

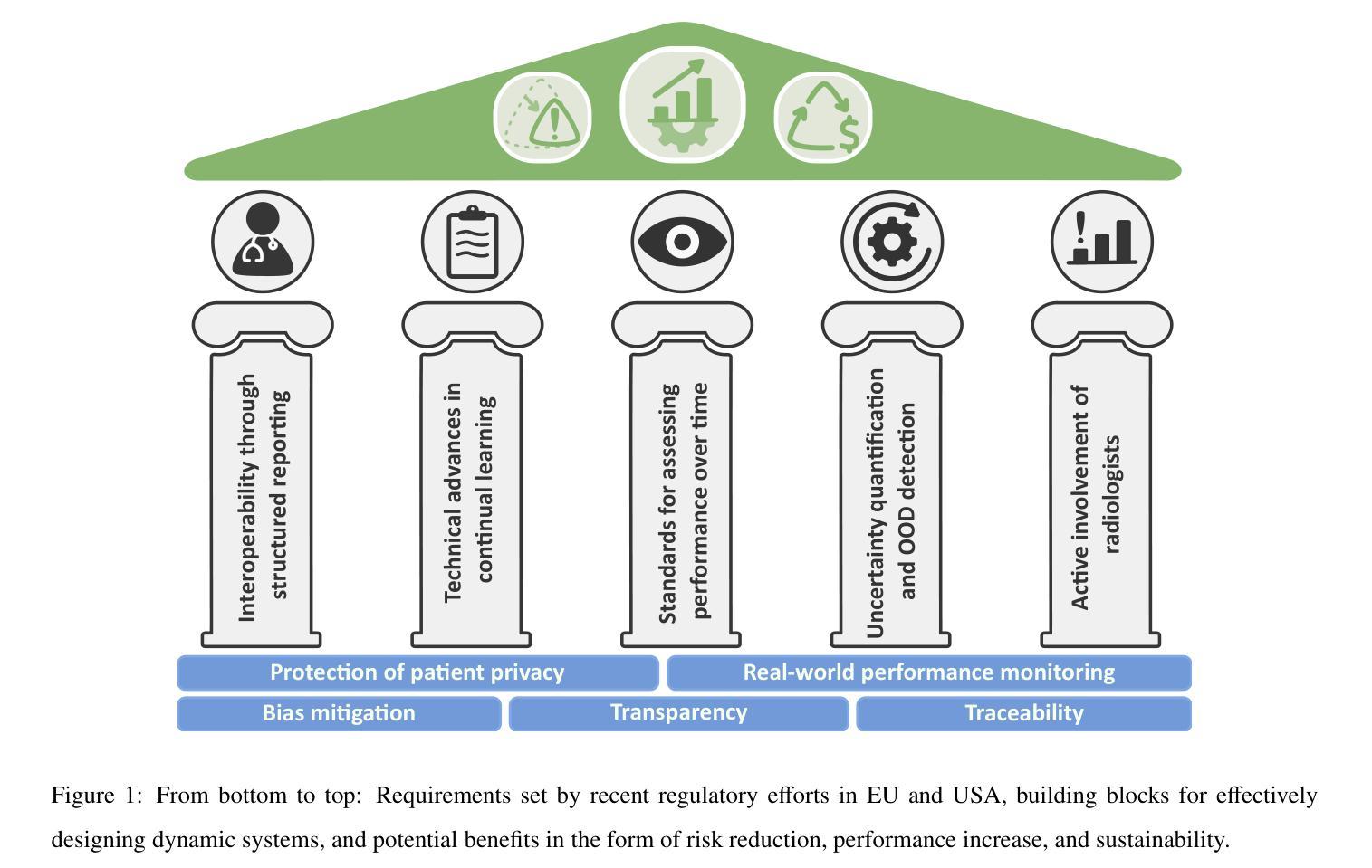
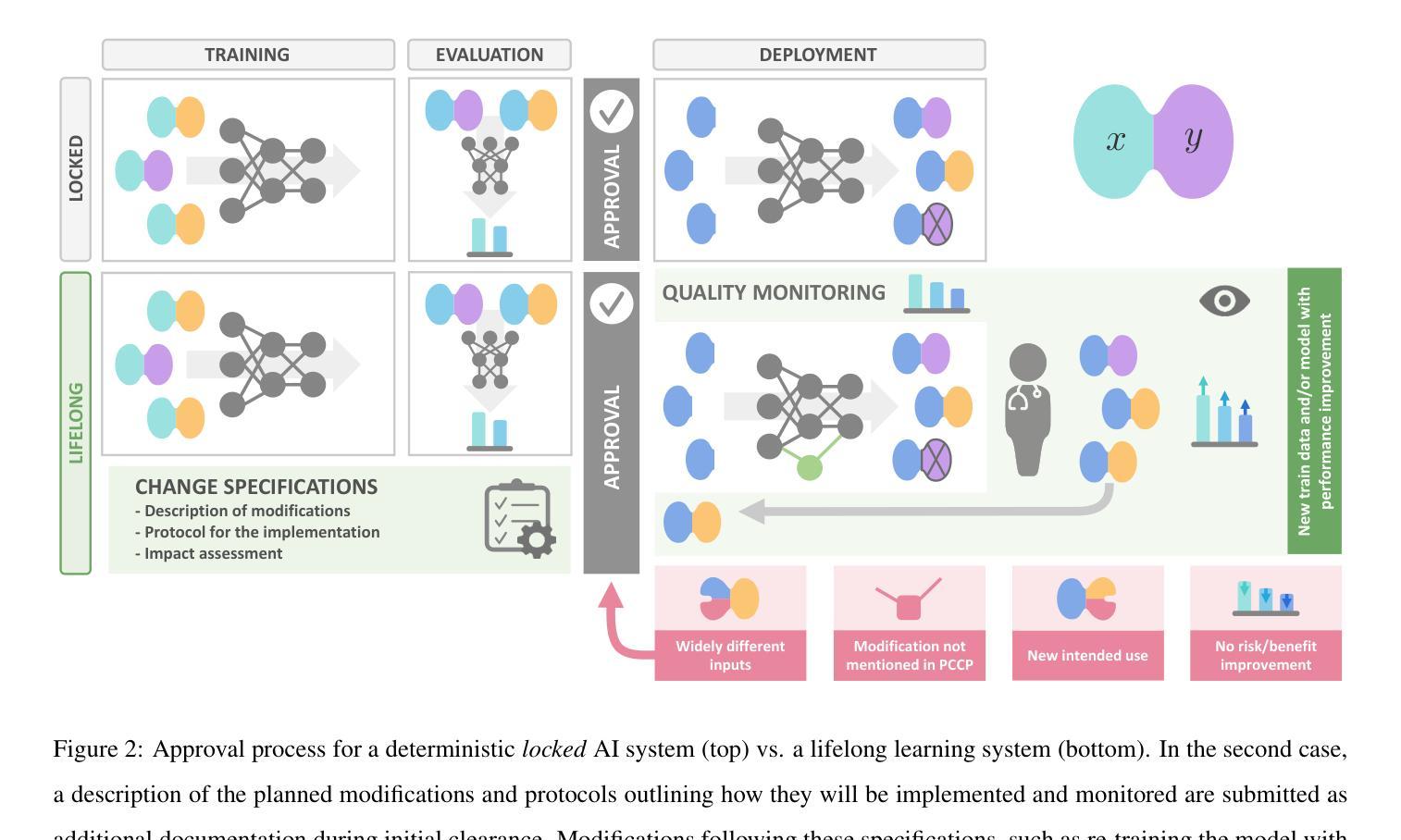
Regulating radiology AI medical devices that evolve in their lifecycle
Authors:Camila González, Moritz Fuchs, Daniel Pinto dos Santos, Philipp Matthies, Manuel Trenz, Maximilian Grüning, Akshay Chaudhari, David B. Larson, Ahmed Othman, Moon Kim, Felix Nensa, Anirban Mukhopadhyay
Over time, the distribution of medical image data drifts due to multiple factors, including shifts in patient demographics, acquisition devices, and disease manifestation. While human radiologists can extrapolate their knowledge to such changes, AI systems cannot. In fact, deep learning models are highly susceptible to even slight variations in image characteristics. Therefore, manufacturers must update their models with new data to ensure that they remain safe and effective. Until recently, conducting such model updates in the USA and European Union meant applying for re-approval. Given the time and monetary costs associated with these processes, updates were infrequent, and obsolete systems continued functioning for too long. During 2024, several developments in the regulatory frameworks of these regions have taken place that promise to streamline the process of rolling out model updates safely: The European Artificial Intelligence Act came into effect last August, and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) released the final marketing submission recommendations for a Predetermined Change Control Plan (PCCP) in December. We give an overview of the requirements and objectives of recent regulatory efforts and summarize the building blocks needed for successfully deploying dynamic systems. At the center of these pieces of regulation - and as prerequisites for manufacturers to conduct model updates without re-approval - are the need to describe the data collection and re-training processes and to establish real-world quality monitoring mechanisms.
随着时间的推移,由于患者人口统计学变化、采集设备和疾病表现的变化等多个因素,医学图像数据的分布会发生变化。虽然人类放射科医生可以推断出他们的知识能够应对这些变化,但人工智能系统却无法做到。事实上,深度学习模型甚至对图像特性中的轻微变化也高度敏感。因此,制造商必须使用新数据更新他们的模型,以确保其安全性和有效性。直到最近,在美国和欧盟进行此类模型更新意味着需要重新获得批准。由于这些流程涉及的时间和金钱成本,更新并不频繁,且过时的系统继续运行了太长时间。在2024年期间,这些地区监管框架的若干发展有望简化安全推出模型更新的流程:欧洲《人工智能法案》已于去年八月生效,美国食品和药物管理局(FDA)在十二月发布了预定的变更控制计划(PCCP)的最终市场营销提交建议。我们概述了最近的监管工作的要求和目标,并总结了成功部署动态系统所需的构建模块。这些法规的核心——以及制造商进行模型更新而不需重新获得批准的先决条件——是需要描述数据收集和再训练过程,并建立现实世界的质量监控机制。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医疗图像数据的分布因患者人口结构、采集设备和疾病表现等多个因素而随时间漂移。人工智能系统难以应对这种变化,深度学习模型对图像特性甚至细微变化都非常敏感。制造商必须更新模型以确保其安全和有效性。近期,美国和欧盟的监管框架发展简化了模型更新的流程:欧洲人工智能法案生效,FDA发布预定变更控制计划的最终市场提交建议。本文概述了最新监管要求的目标和要点,并总结了成功部署动态系统所需的构建模块。核心在于描述数据收集和再训练流程,并建立真实世界质量监测机制,作为制造商进行无需重新审批的模型更新的先决条件。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗图像数据的分布会随时间漂移,这对AI系统来说是个挑战。
- 深度学习模型对图像特性的变化非常敏感。
- 制造商需要更新医疗图像数据模型以确保其安全和有效性。
- 美国和欧盟的监管框架发展简化了模型更新的流程。
- 欧洲人工智能法案和FDA的预定变更控制计划对模型更新有重要指导意义。
- 描述数据收集和再训练流程是模型更新的关键。
点此查看论文截图

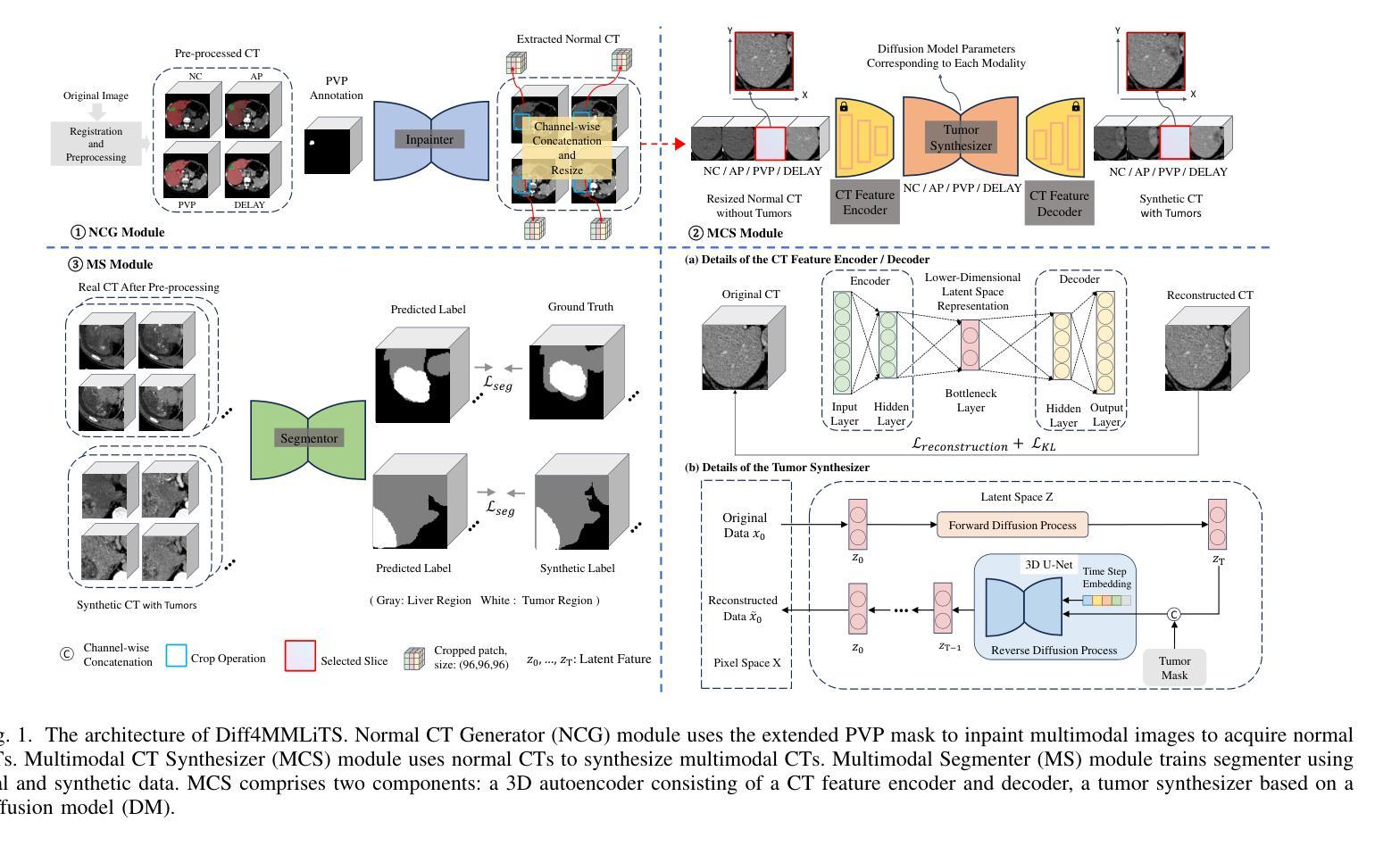
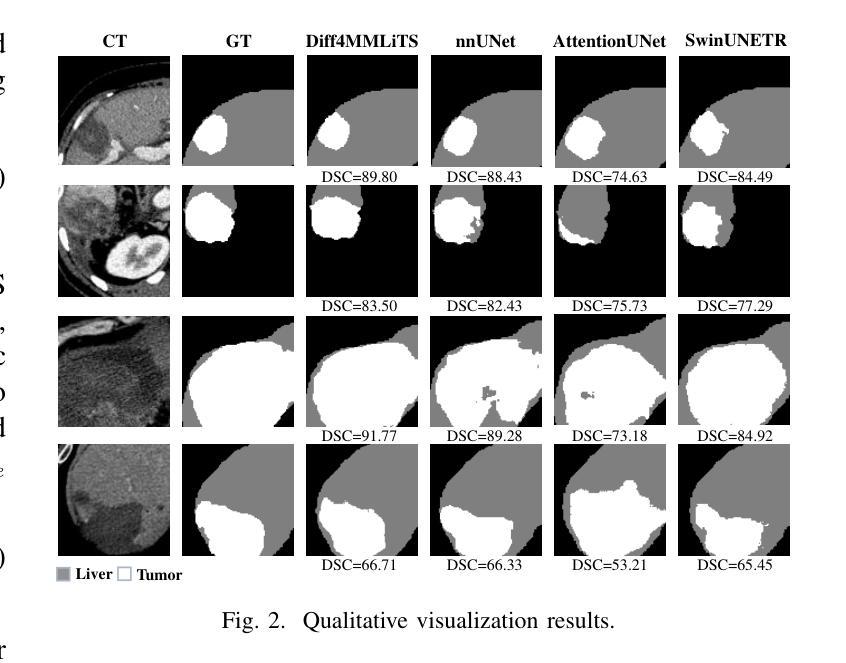
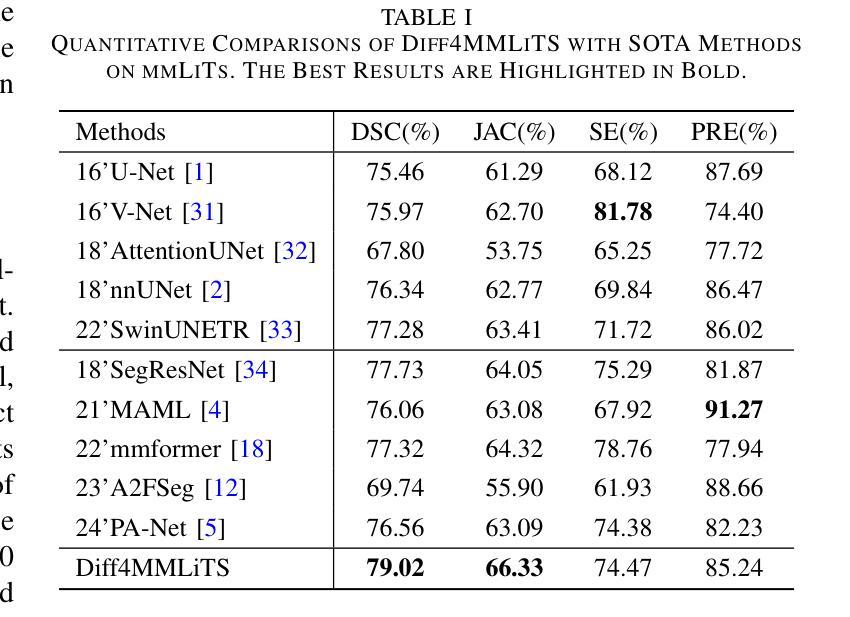
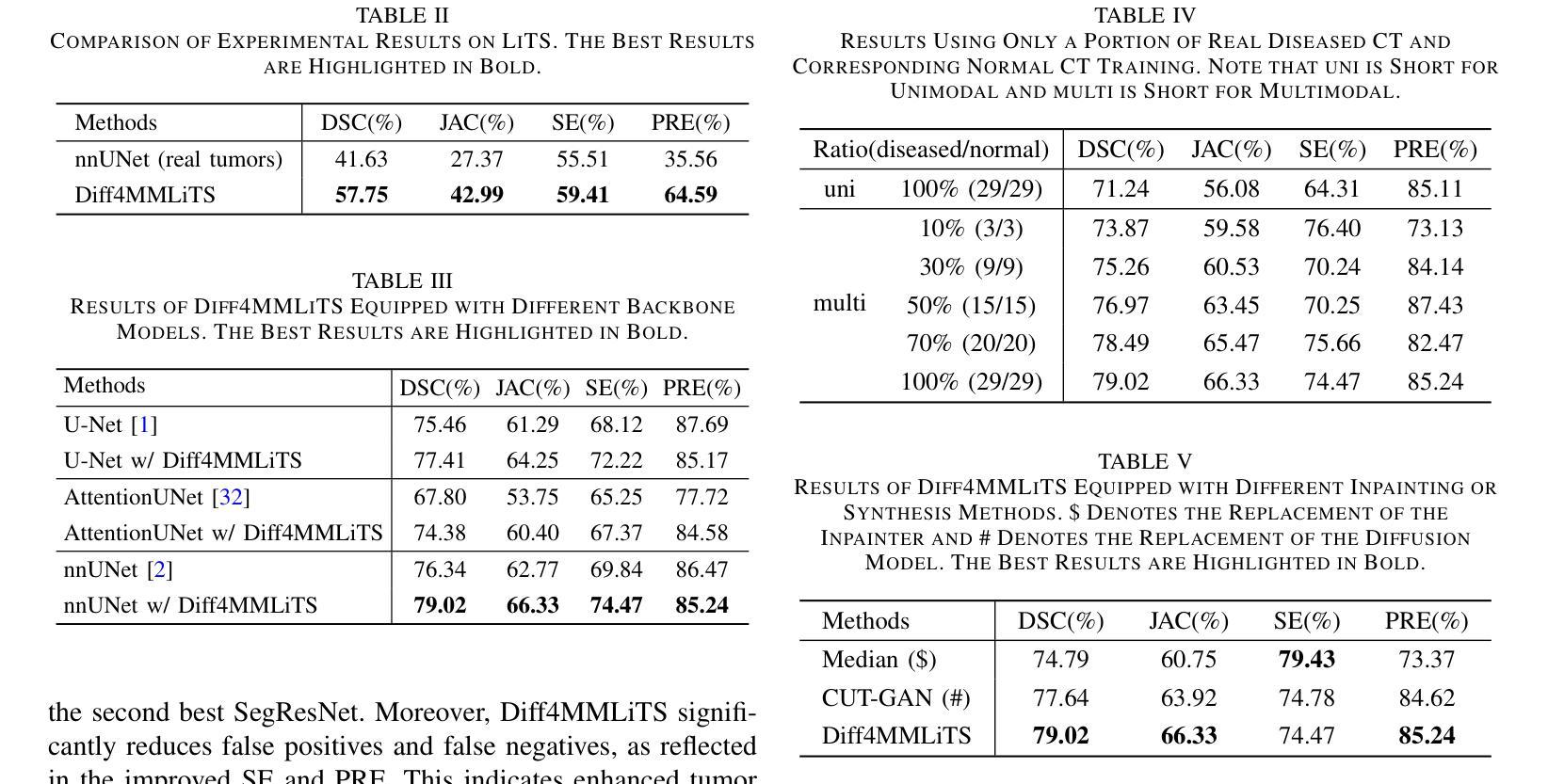
Diff4MMLiTS: Advanced Multimodal Liver Tumor Segmentation via Diffusion-Based Image Synthesis and Alignment
Authors:Shiyun Chen, Li Lin, Pujin Cheng, ZhiCheng Jin, JianJian Chen, HaiDong Zhu, Kenneth K. Y. Wong, Xiaoying Tang
Multimodal learning has been demonstrated to enhance performance across various clinical tasks, owing to the diverse perspectives offered by different modalities of data. However, existing multimodal segmentation methods rely on well-registered multimodal data, which is unrealistic for real-world clinical images, particularly for indistinct and diffuse regions such as liver tumors. In this paper, we introduce Diff4MMLiTS, a four-stage multimodal liver tumor segmentation pipeline: pre-registration of the target organs in multimodal CTs; dilation of the annotated modality’s mask and followed by its use in inpainting to obtain multimodal normal CTs without tumors; synthesis of strictly aligned multimodal CTs with tumors using the latent diffusion model based on multimodal CT features and randomly generated tumor masks; and finally, training the segmentation model, thus eliminating the need for strictly aligned multimodal data. Extensive experiments on public and internal datasets demonstrate the superiority of Diff4MMLiTS over other state-of-the-art multimodal segmentation methods.
多模态学习已证明可以通过不同模态数据提供的不同视角来提升各种临床任务的表现。然而,现有的多模态分割方法依赖于良好配准的多模态数据,这对于真实世界的临床图像来说并不现实,特别是对于模糊和散漫的区域(如肝脏肿瘤)。在本文中,我们介绍了Diff4MMLiTS,这是一个四阶段的多模态肝脏肿瘤分割流程:在多模态CT中对目标器官进行预注册;扩大标注模态的掩膜,然后用于图像修复,以获得不含肿瘤的多模态正常CT;使用基于多模态CT特征和随机生成的肿瘤掩膜进行潜在扩散模型的严格对齐多模态CT肿瘤合成;最后,训练分割模型,从而消除了对严格对齐的多模态数据的需求。在公共和内部数据集上的大量实验表明,Diff4MMLiTS优于其他最先进的多模态分割方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Diff4MMLiTS,这是一种四阶段的多模态肝脏肿瘤分割方法,包括目标器官在多种CT中的预注册、对标注模态的掩膜进行膨胀并用于填充以获得不含肿瘤的多种CT、合成严格对齐的含肿瘤的多模态CT图像以及训练分割模型,从而消除了对严格对齐的多模态数据的需求。实验证明,与其他最先进的模态分割方法相比,Diff4MMLiTS具有优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态学习可以提高在各种临床任务中的性能,因为它提供了不同数据模式的多样化视角。
- 现有的多模态分割方法依赖于良好注册的多模态数据,这在现实世界的临床图像中是不切实际的。
- Diff4MMLiTS是一种新型的四阶段多模态肝脏肿瘤分割方法,包括预注册、掩膜膨胀与填充、合成严格对齐的含肿瘤CT图像以及训练分割模型。
- Diff4MMLiTS通过消除对严格对齐的多模态数据的需求,改进了多模态分割。
- 公共和内部数据集的实验证明了Diff4MMLiTS相较于其他先进的多模态分割方法的优越性。
- Diff4MMLiTS在处理模糊和扩散区域(如肝脏肿瘤)时具有优势。
点此查看论文截图

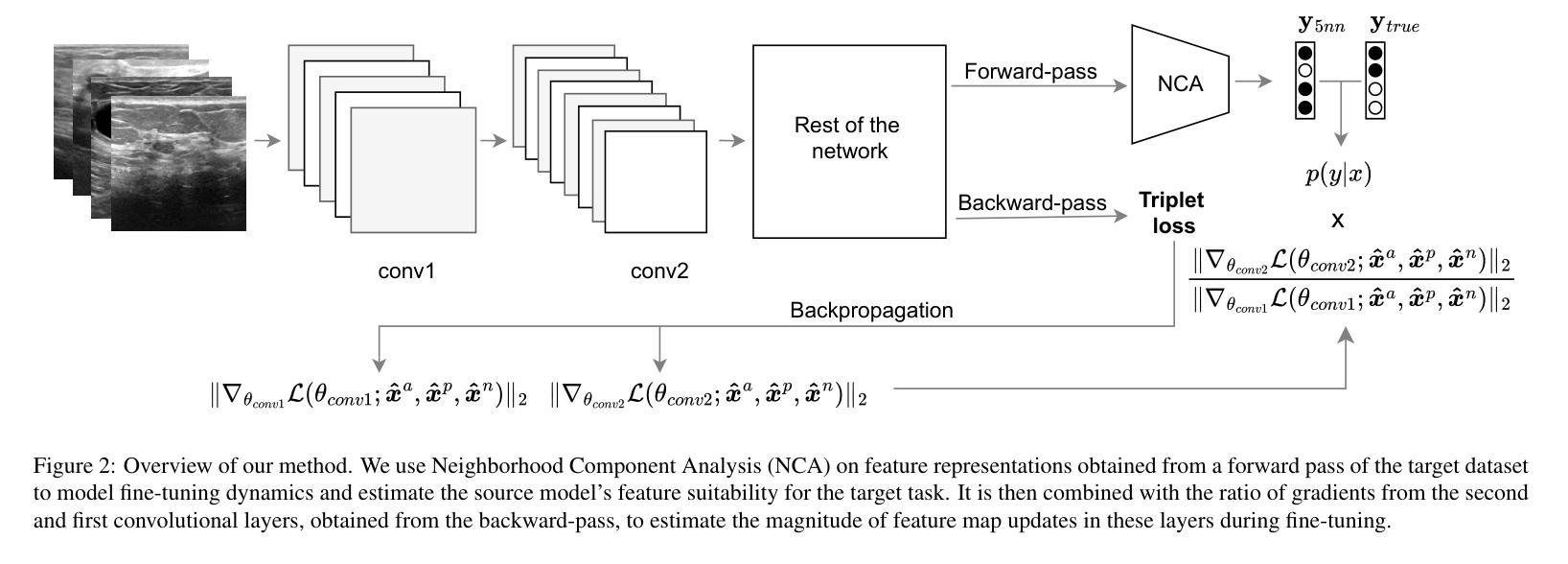
On dataset transferability in medical image classification
Authors:Dovile Juodelyte, Enzo Ferrante, Yucheng Lu, Prabhant Singh, Joaquin Vanschoren, Veronika Cheplygina
Current transferability estimation methods designed for natural image datasets are often suboptimal in medical image classification. These methods primarily focus on estimating the suitability of pre-trained source model features for a target dataset, which can lead to unrealistic predictions, such as suggesting that the target dataset is the best source for itself. To address this, we propose a novel transferability metric that combines feature quality with gradients to evaluate both the suitability and adaptability of source model features for target tasks. We evaluate our approach in two new scenarios: source dataset transferability for medical image classification and cross-domain transferability. Our results show that our method outperforms existing transferability metrics in both settings. We also provide insight into the factors influencing transfer performance in medical image classification, as well as the dynamics of cross-domain transfer from natural to medical images. Additionally, we provide ground-truth transfer performance benchmarking results to encourage further research into transferability estimation for medical image classification. Our code and experiments are available at https://github.com/DovileDo/transferability-in-medical-imaging.
针对自然图像数据集设计的现有可迁移性估计方法在医学图像分类中通常表现不佳。这些方法主要关注估计预训练源模型特征对目标数据集的适用性,这可能导致不现实的预测,例如认为目标数据集本身是最佳的来源。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种新的可迁移性度量方法,该方法结合了特征质量和梯度,以评估源模型特征对目标任务的适用性和适应性。我们在两种新场景中评估了我们的方法:医学图像分类的源数据集可迁移性和跨域可迁移性。我们的结果表明,我们的方法在两种设置中都优于现有的可迁移性度量方法。我们还深入了解了影响医学图像分类中迁移性能的因素,以及从自然图像到医学图像的跨域迁移的动力学。此外,我们提供了真实的迁移性能基准测试结果,以鼓励对医学图像分类的可迁移性估计进行进一步研究。我们的代码和实验可在https://github.com/DovileDo/transferability-in-medical-imaging找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像分类中,现有迁移能力评估方法存在不足。现有方法主要关注预训练源模型特征对目标数据集的适用性评估,可能导致不合理预测。为此,本文提出一种结合特征质量与梯度的新迁移能力评估指标,评估源模型特征对目标任务的适应性和可调整性。在医学图像分类的源数据集迁移性和跨域迁移性两个场景中验证了该方法的有效性。本文还深入探讨了影响医学图像分类迁移性能的因素以及从自然图像到医学图像的跨域迁移动态。本文提供真实迁移性能基准测试结果,以推动医学图像分类的迁移能力评估研究。
Key Takeaways
- 当前为自然图像数据集设计的迁移能力评估方法在医学图像分类中表现不佳。
- 现有方法主要关注预训练源模型特征对目标数据集的适用性,可能导致不合理预测。
- 本文提出了结合特征质量与梯度的迁移能力评估新方法,更全面地评价源模型特征的适应性和可调整性。
- 验证了该方法在医学图像分类的源数据集迁移性和跨域迁移性两个场景中的有效性。
- 探讨了影响医学图像分类迁移性能的关键因素。
- 提供了从自然图像到医学图像的跨域迁移动态的分析。
点此查看论文截图

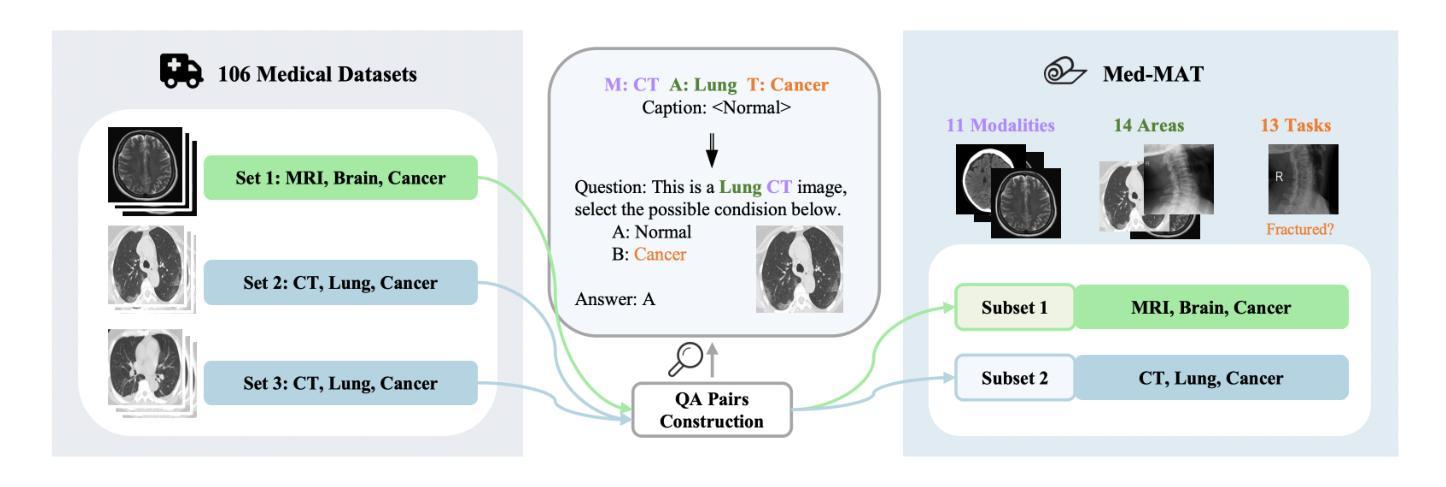
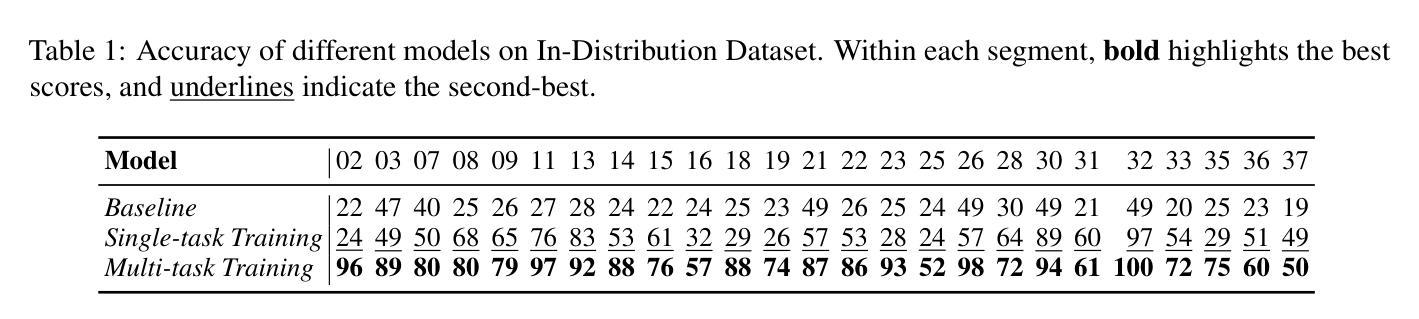
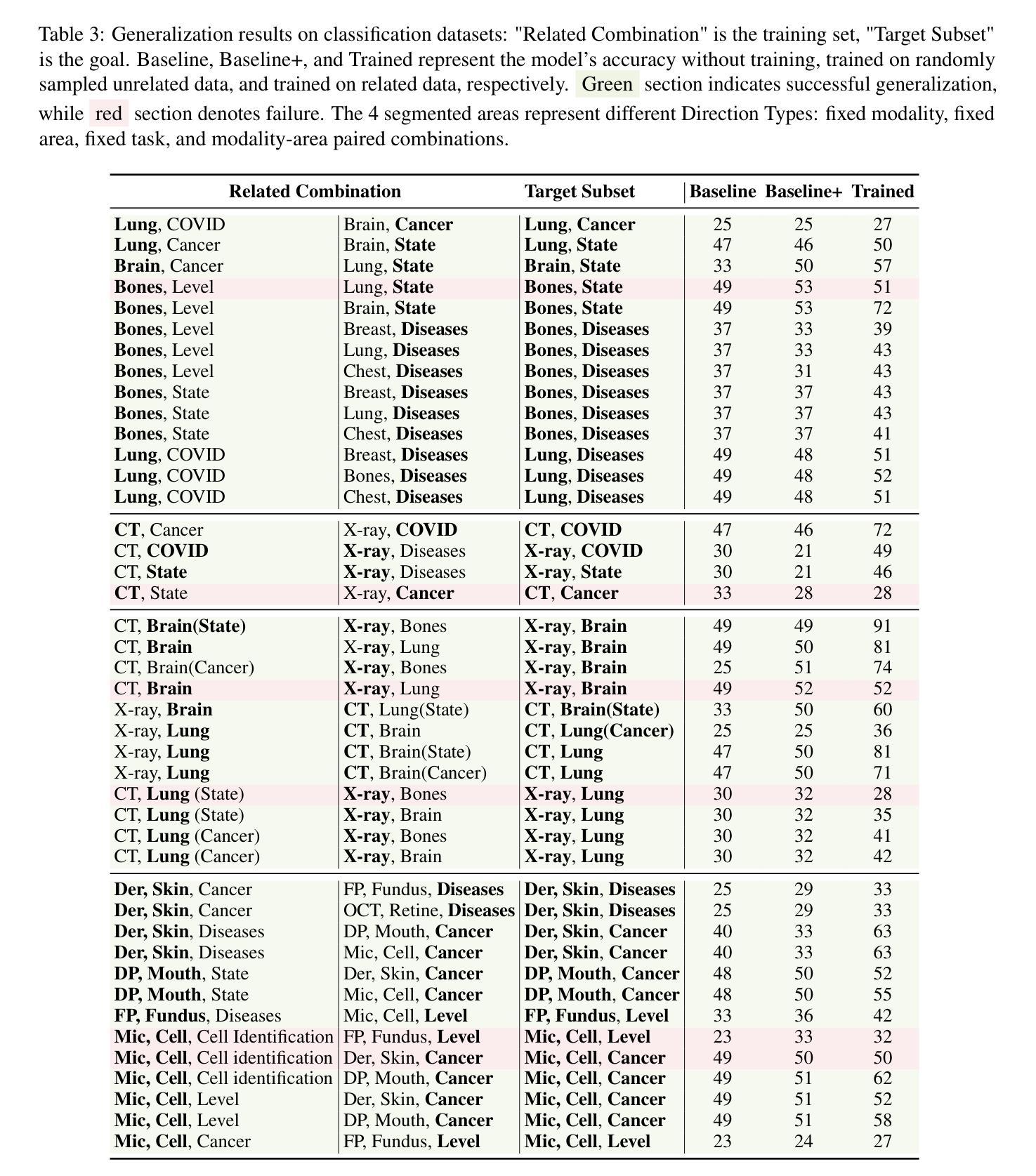
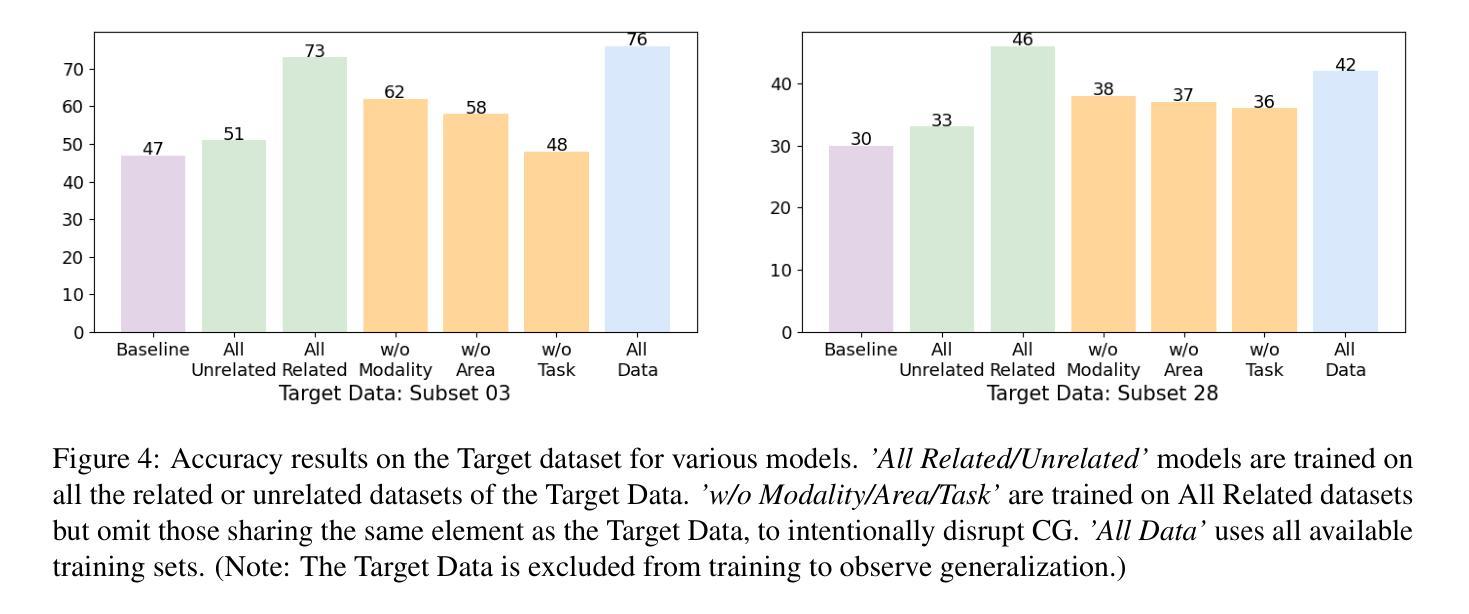
On the Compositional Generalization of Multimodal LLMs for Medical Imaging
Authors:Zhenyang Cai, Junying Chen, Rongsheng Wang, Weihong Wang, Yonglin Deng, Dingjie Song, Yize Chen, Zixu Zhang, Benyou Wang
Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) hold significant potential in the medical field, but their capabilities are often limited by insufficient data in certain medical domains, highlighting the need for understanding what kinds of images can be used by MLLMs for generalization. Current research suggests that multi-task training outperforms single-task as different tasks can benefit each other, but they often overlook the internal relationships within these tasks, providing limited guidance on selecting datasets to enhance specific tasks. To analyze this phenomenon, we attempted to employ compositional generalization (CG)-the ability of models to understand novel combinations by recombining learned elements-as a guiding framework. Since medical images can be precisely defined by Modality, Anatomical area, and Task, naturally providing an environment for exploring CG. Therefore, we assembled 106 medical datasets to create Med-MAT for comprehensive experiments. The experiments confirmed that MLLMs can use CG to understand unseen medical images and identified CG as one of the main drivers of the generalization observed in multi-task training. Additionally, further studies demonstrated that CG effectively supports datasets with limited data and delivers consistent performance across different backbones, highlighting its versatility and broad applicability. Med-MAT is publicly available at https://github.com/FreedomIntelligence/Med-MAT.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在医学领域具有巨大潜力,但其能力往往因某些医学领域数据不足而受到限制,这强调了对MLLMs可用于泛化的图像类型理解的重要性。当前的研究表明,多任务训练优于单任务训练,因为不同的任务可以相互受益,但它们往往忽略了这些任务之间的内部关系,在如何选择数据集以增强特定任务方面提供有限的指导。为了分析这一现象,我们尝试采用组合泛化(CG)作为指导框架,即模型通过重新组合已学习的元素来理解新型组合的能力。由于医学图像可以通过模态、解剖部位和任务进行精确定义,因此自然为探索CG提供了环境。因此,我们收集了1—0个医学数据集来创建Med-MAT进行综合实验。实验证实,MLLMs可以使用CG来理解未见过的医学图像,并确定CG是多任务训练中观察到的泛化的主要驱动力之一。此外,进一步研究证明CG可有效支持有限数据集,并在不同主干网络上实现一致性能,凸显了其通用性和广泛适用性。Med-MAT可在https://github.com/FreedomIntelligence/Med-MAT上公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在医学领域具有巨大潜力,但其能力往往受限于特定医学领域的数据不足。研究表明,多任务训练优于单任务训练,但常常忽视任务间的内在关系,对于如何选择数据集以增强特定任务的指导有限。本研究尝试采用组合泛化(CG)作为指导框架,分析这一现象。由于医学图像可通过模态、解剖区域和任务进行精确定义,自然为探索CG提供了环境。因此,我们创建了Med-MAT进行综合性实验。实验证实,MLLMs可利用CG理解未见医学图像,并确定为多任务训练中所见泛化的主要驱动力之一。CG可支持数据集有限的情况,并在不同主干网络上表现一致,凸显其通用性和广泛应用性。Med-MAT已在公开平台上发布。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在医学领域有巨大潜力,但数据不足限制其发展。
- 多任务训练优于单任务训练,但缺乏对任务间内在关系的关注。
- 组合泛化(CG)作为指导框架,有助于理解MLLMs如何处理未见医学图像。
- 医学图像可通过模态、解剖区域和任务进行精确定义,适合探索CG。
- Med-MAT实验证实MLLMs可利用CG进行泛化,并确定其为多任务训练中的主要驱动力。
- CG在数据集有限的情况下表现出支持能力。
点此查看论文截图


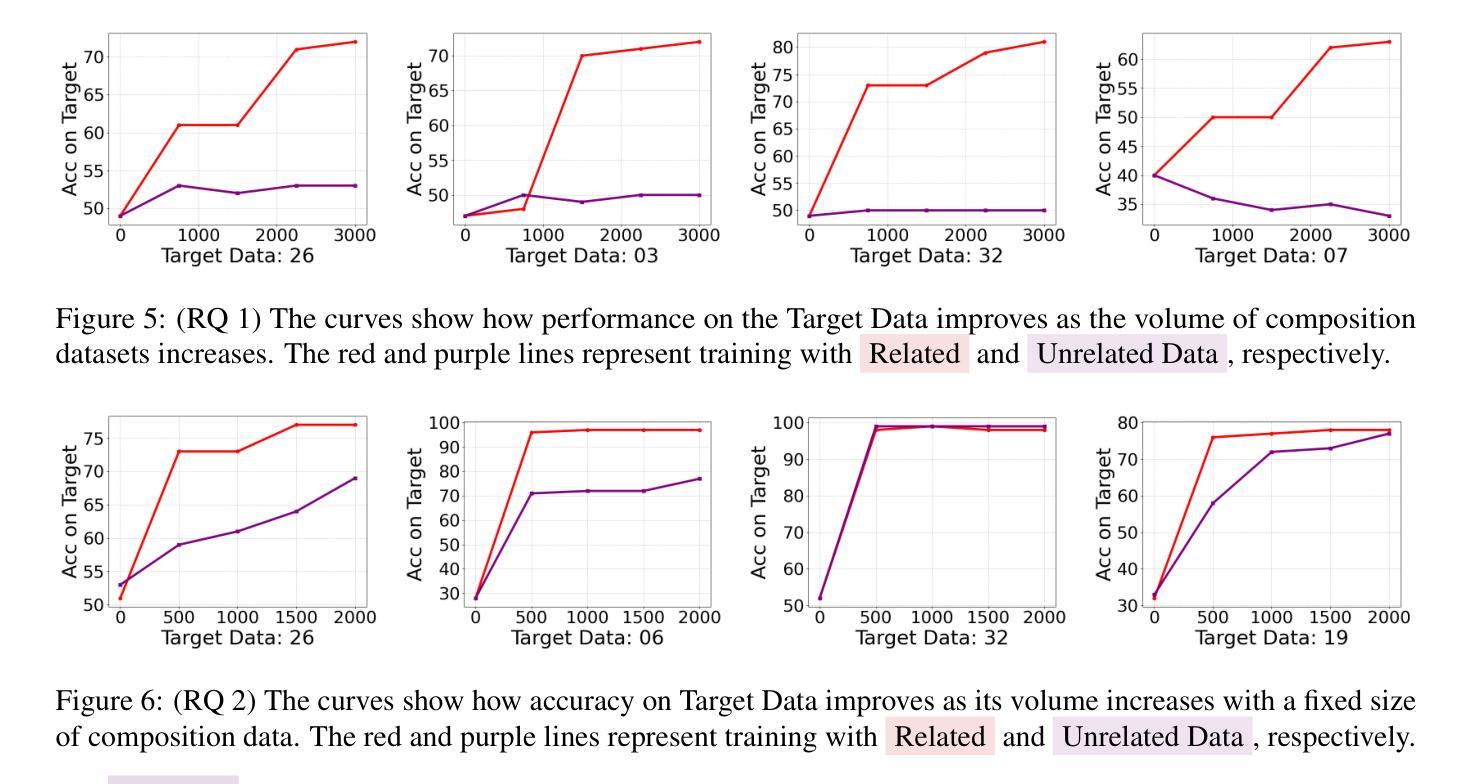
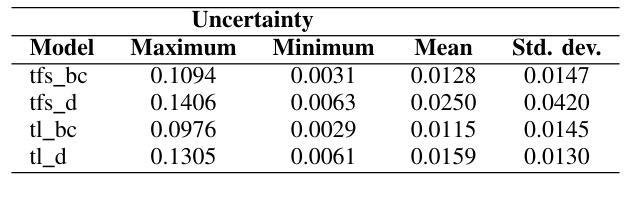
Uncertainty Quantified Deep Learning and Regression Analysis Framework for Image Segmentation of Skin Cancer Lesions
Authors:Elhoucine Elfatimi, Pratik Shah
Deep learning models (DLMs) frequently achieve accurate segmentation and classification of tumors from medical images. However, DLMs lacking feedback on their image segmentation mechanisms, such as Dice coefficients and confidence in their performance, face challenges when processing previously unseen images in real-world clinical settings. Uncertainty estimates to identify DLM predictions at the cellular or single-pixel level that require clinician review can enhance trust. However, their deployment requires significant computational resources. This study reports two DLMs, one trained from scratch and another based on transfer learning, with Monte Carlo dropout or Bayes-by-backprop uncertainty estimations to segment lesions from the publicly available The International Skin Imaging Collaboration-19 dermoscopy image database with cancerous lesions. A novel approach to compute pixel-by-pixel uncertainty estimations of DLM segmentation performance in multiple clinical regions from a single dermoscopy image with corresponding Dice scores is reported for the first time. Image-level uncertainty maps demonstrated correspondence between imperfect DLM segmentation and high uncertainty levels in specific skin tissue regions, with or without lesions. Four new linear regression models that can predict the Dice performance of DLM segmentation using constants and uncertainty measures, either individually or in combination from lesions, tissue structures, and non-tissue pixel regions critical for clinical diagnosis and prognostication in skin images (Spearman’s correlation, p < 0.05), are reported for the first time for low-compute uncertainty estimation workflows.
深度学习模型(DLMs)通常能准确地从医学图像中分割和识别肿瘤。然而,对于缺乏关于图像分割机制反馈的DLMs,如在dice系数和表现置信度等方面的反馈,在处理现实世界临床环境中的先前未见过的图像时面临挑战。不确定性估计有助于识别DLM预测在细胞或单个像素级别的问题,需要进行医师审核以增强信任。然而,其部署需要大量的计算资源。本研究报告了两个深度学习模型,一个从头开始训练,另一个基于迁移学习,采用蒙特卡洛dropout或贝叶斯反向传播不确定性估计来从国际皮肤成像协作组织(International Skin Imaging Collaboration)公开的19个皮肤镜图像数据库中分割病变部位。本研究首次报道了一种计算单个皮肤镜图像中多个临床区域的像素级不确定性估计的新方法,并给出了相应的Dice评分。图像级别的不确定性地图显示了深度学习模型分割的不完美与高不确定性的特定皮肤组织区域之间的对应关系,无论这些区域是否有病变。本研究首次报道了四个新的线性回归模型,能够利用常数和不确定性度量来预测深度学习模型的Dice分割性能,这些度量可单独或组合使用,针对病变、组织结构和皮肤图像中用于临床诊断和预后评估的非组织像素区域(Spearman相关性,p < 0.05),用于低计算不确定性估计工作流程。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Presented at the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), accepted for publication and in press by IEEE
Summary
深度学习模型在医学图像肿瘤分割和分类中表现准确。然而,缺乏反馈机制的深度学习模型在处理未见过的图像时面临挑战。不确定性估计有助于识别细胞或单像素级别的预测,但需要临床医生审核。本研究报告了两个深度学习模型,一个从头开始训练,另一个基于迁移学习,使用蒙特卡洛dropout或贝叶斯反向传播不确定性估计来分割来自公开可用国际皮肤成像协作组织的皮肤镜图像库中的病变。报告了一种新型方法,该方法可在单个皮肤镜图像中计算多个临床区域像素级的不确定性估计,并首次报道了相应的Dice得分。图像级别的不确定性映射显示了深度学习模型分割不完美与特定皮肤组织区域的高不确定性水平之间的对应关系,这些区域可能有病变也可能没有。此外,还首次报告了四个新的线性回归模型,这些模型可以使用常数和不确定性度量来预测深度学习模型分割的Dice性能,适用于病变、组织结构和非组织像素区域,对临床诊断和预后预测具有重要意义(斯皮尔曼相关性,p < 0.05)。报告的这些方法主要针对低计算不确定性估计工作流程。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习模型在医学图像肿瘤分割和分类中具有高精度。
- 缺乏反馈机制的深度学习模型在处理未见过的图像时可能面临挑战。
- 不确定性估计有助于提高深度学习模型预测的可信度和可解释性。
- 本研究通过使用蒙特卡洛dropout或贝叶斯反向传播方法进行不确定性估计,实现了对皮肤病变的准确分割。
- 报告了一种新型方法,可以在单个皮肤镜图像中计算多个临床区域的像素级不确定性估计。
- 图像级别的不确定性映射显示了深度学习模型分割与特定皮肤组织区域的高不确定性水平之间的关联。
点此查看论文截图

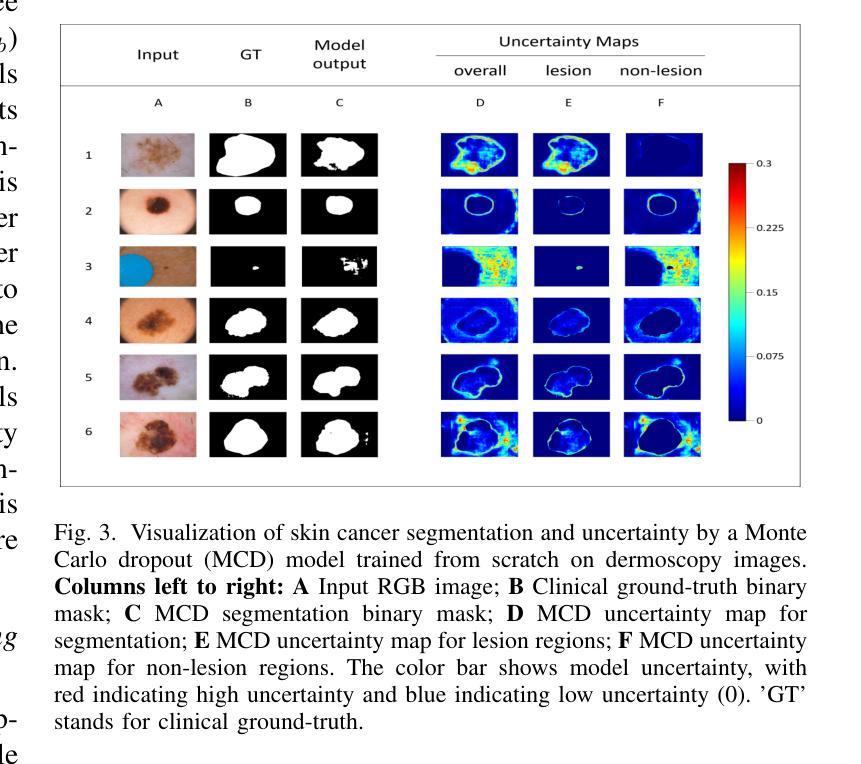
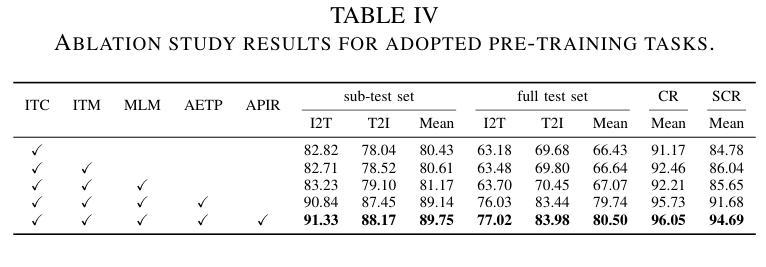
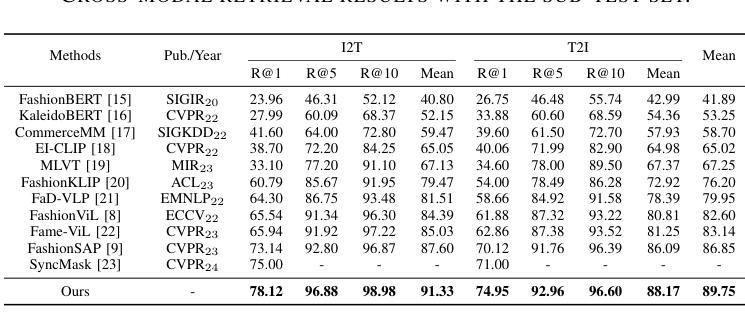
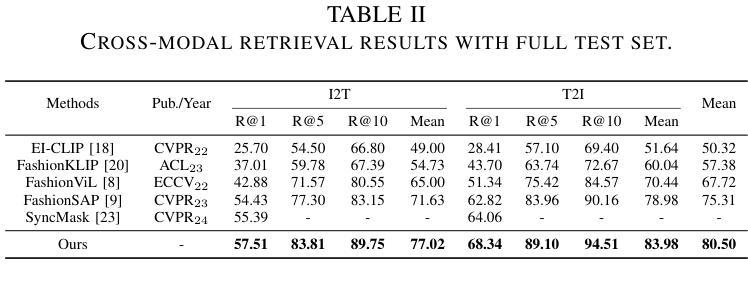
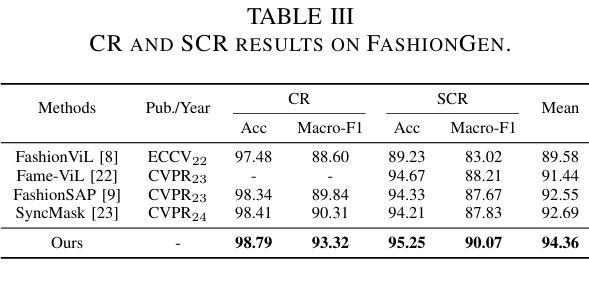
FashionFAE: Fine-grained Attributes Enhanced Fashion Vision-Language Pre-training
Authors:Jiale Huang, Dehong Gao, Jinxia Zhang, Zechao Zhan, Yang Hu, Xin Wang
Large-scale Vision-Language Pre-training (VLP) has demonstrated remarkable success in the general domain. However, in the fashion domain, items are distinguished by fine-grained attributes like texture and material, which are crucial for tasks such as retrieval. Existing models often fail to leverage these fine-grained attributes from both text and image modalities. To address the above issues, we propose a novel approach for the fashion domain, Fine-grained Attributes Enhanced VLP (FashionFAE), which focuses on the detailed characteristics of fashion data. An attribute-emphasized text prediction task is proposed to predict fine-grained attributes of the items. This forces the model to focus on the salient attributes from the text modality. Additionally, a novel attribute-promoted image reconstruction task is proposed, which further enhances the fine-grained ability of the model by leveraging the representative attributes from the image modality. Extensive experiments show that FashionFAE significantly outperforms State-Of-The-Art (SOTA) methods, achieving 2.9% and 5.2% improvements in retrieval on sub-test and full test sets, respectively, and a 1.6% average improvement in recognition tasks.
大规模视觉语言预训练(VLP)在通用领域已经取得了显著的成功。然而,在时尚领域,物品是通过诸如质地和材料等细微特征来区分的,这对于检索等任务至关重要。现有模型往往无法从文本和图像模式两方面利用这些细微特征。为了解决上述问题,我们针对时尚领域提出了一种新的方法,即精细特征属性增强VLP(FashionFAE),它专注于时尚数据的详细特征。提出了一种以属性为重点的文本预测任务,用于预测物品的细微属性。这迫使模型关注文本模式的显著属性。此外,还提出了一种新的属性促进图像重建任务,通过利用图像模式的代表性属性,进一步提高了模型的精细特征能力。大量实验表明,FashionFAE显著优于最新方法,在子测试集和全集测试集的检索任务中分别提高了2.9%和5.2%,在识别任务中平均提高了1.6%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大规模视觉语言预训练(VLP)在通用领域取得了显著的成功,但在时尚领域,由于时尚产品之间的细微差别如纹理和材质等对于检索等任务至关重要,现有模型往往无法充分利用这些细微特征。为解决这一问题,本文提出了一种针对时尚领域的新型方法——精细属性增强视觉语言预训练(FashionFAE),通过强调属性预测任务,使模型关注文本模态中的关键属性。同时,引入了一种新的属性促进图像重建任务,利用图像模态中的代表性属性进一步提升模型的精细识别能力。实验表明,FashionFAE在子测试集和全集测试集上的检索任务分别提高了2.9%和5.2%,识别任务平均提高了1.6%,显著优于现有技术前沿。
Key Takeaways
- 大规模视觉语言预训练(VLP)在时尚领域的表现存在提升空间。
- 现有模型在时尚领域未能充分利用文本和图像模态中的细微特征(如纹理和材质)。
- 提出了一种针对时尚领域的新型方法——FashionFAE,通过强调属性预测任务和引入属性促进图像重建任务来解决上述问题。
- FashionFAE能够关注文本模态中的关键属性,并进一步提升模型的精细识别能力。
- 实验结果表明,FashionFAE在检索任务上显著优于现有技术前沿,在子测试集和全集测试集上的改进分别为2.9%和5.2%。
- 在识别任务上,FashionFAE也表现出优越性能,平均提高了1.6%。
- FashionFAE的方法为时尚领域的视觉语言预训练提供了新的思路和方法论。
点此查看论文截图

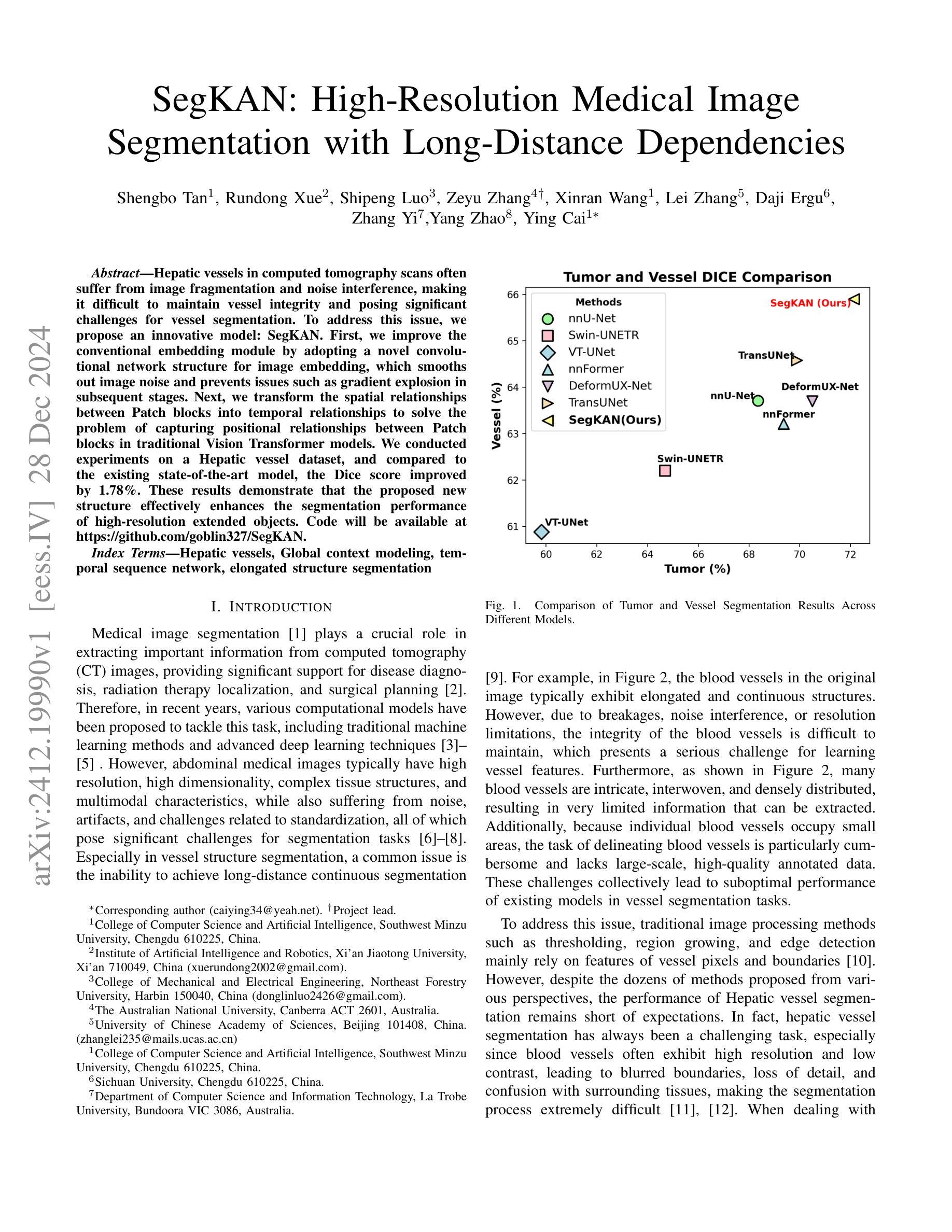
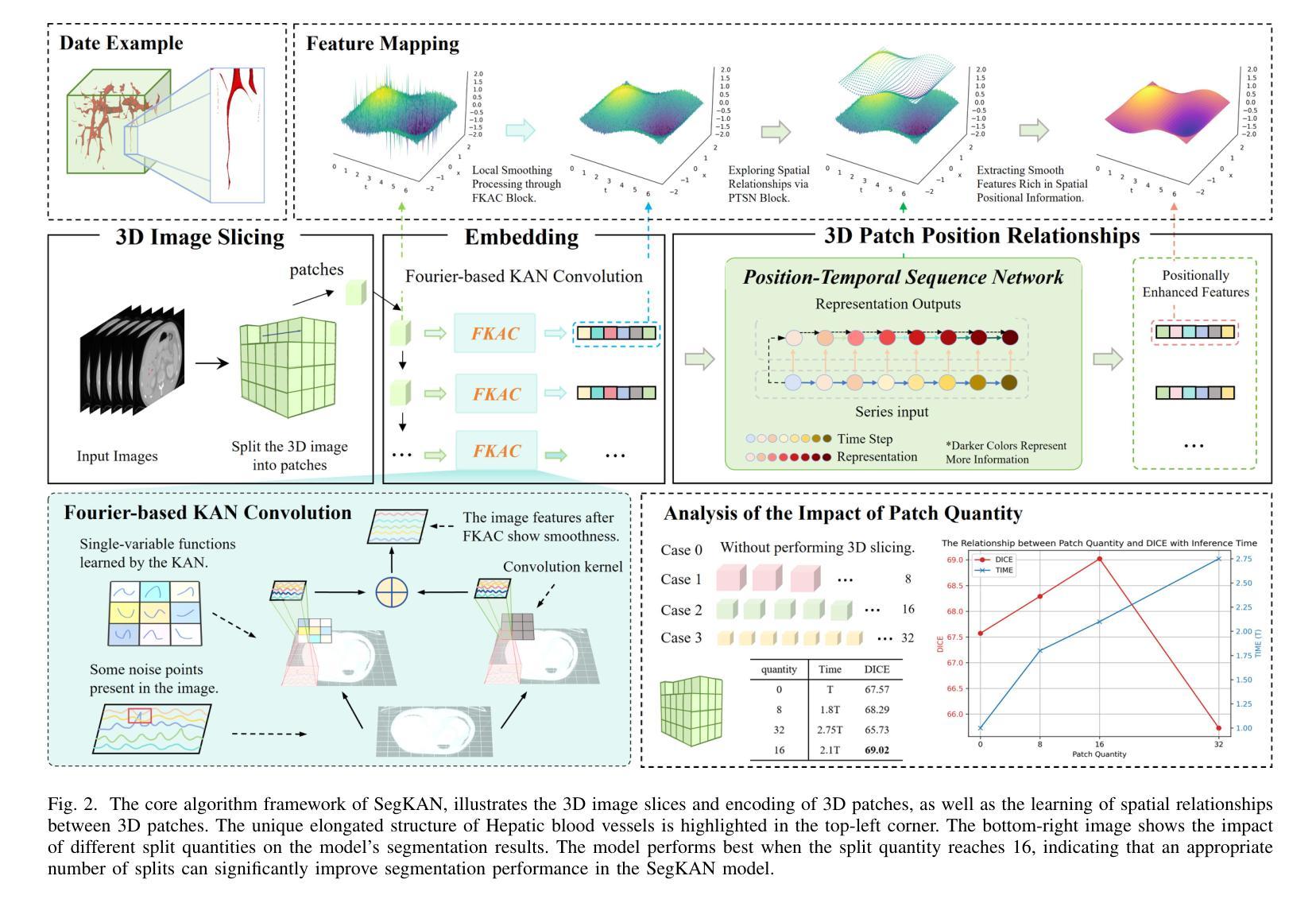
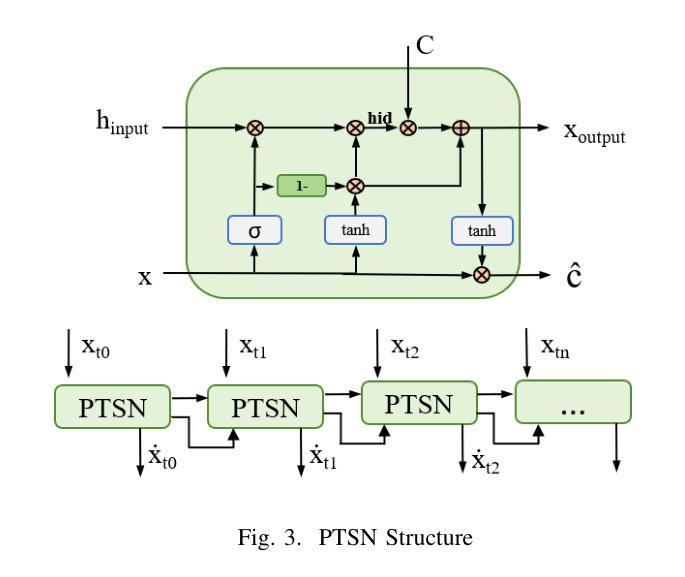
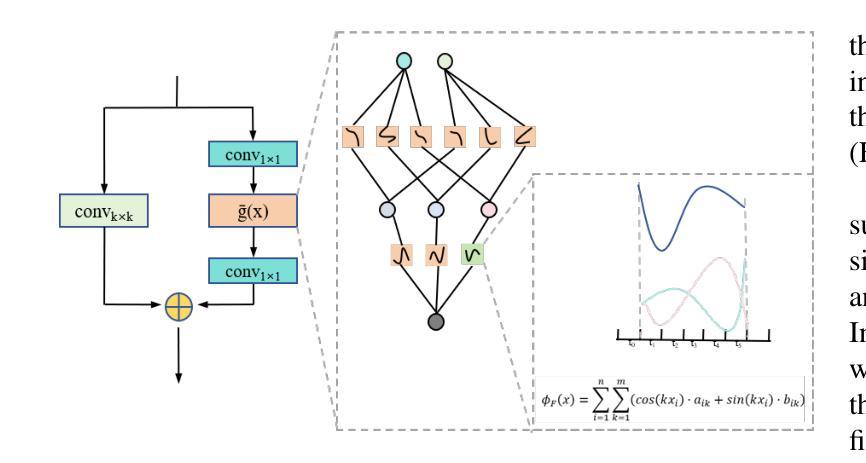
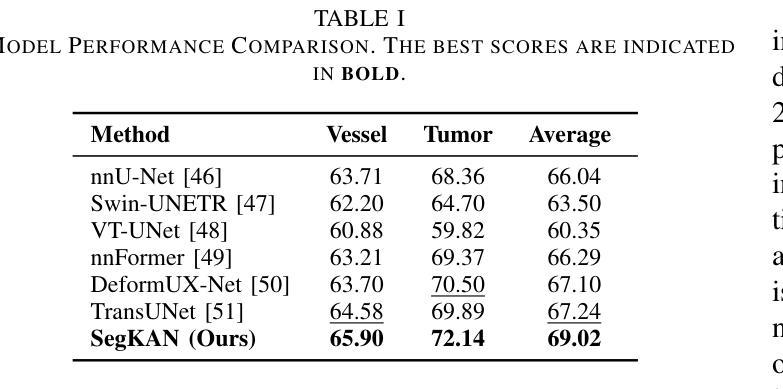
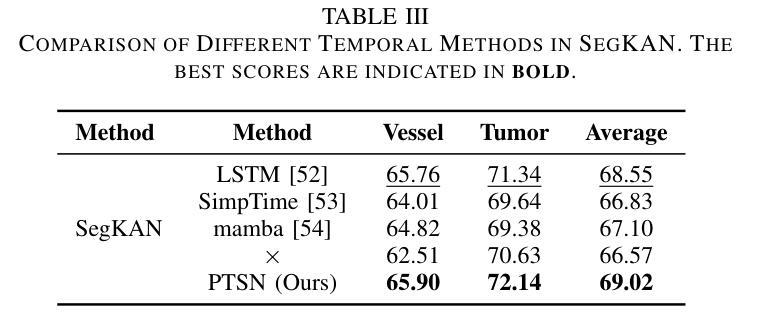
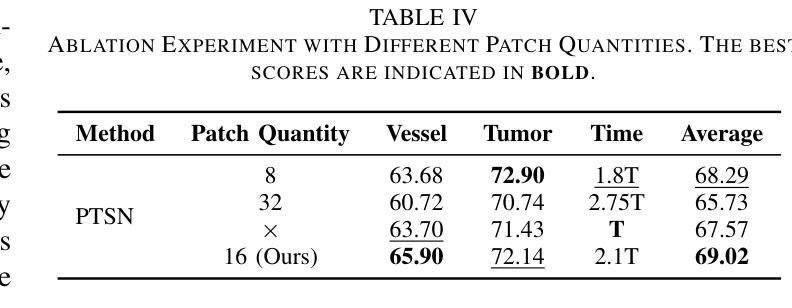
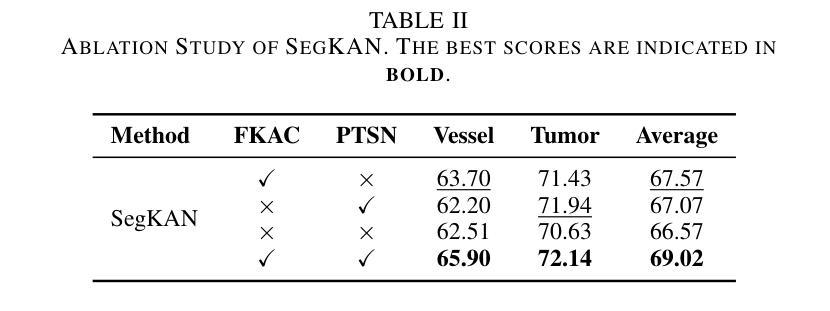
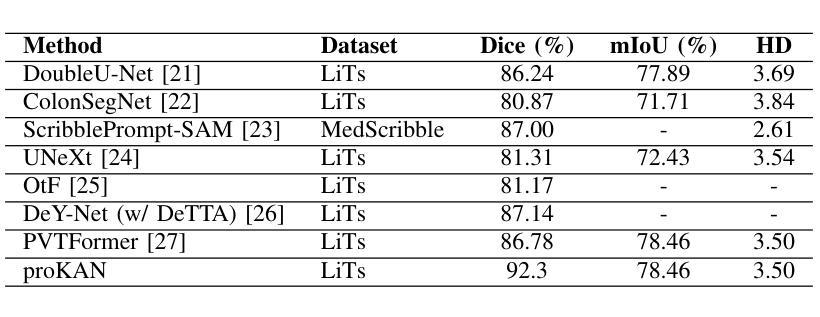
SegKAN: High-Resolution Medical Image Segmentation with Long-Distance Dependencies
Authors:Shengbo Tan, Rundong Xue, Shipeng Luo, Zeyu Zhang, Xinran Wang, Lei Zhang, Daji Ergu, Zhang Yi, Yang Zhao, Ying Cai
Hepatic vessels in computed tomography scans often suffer from image fragmentation and noise interference, making it difficult to maintain vessel integrity and posing significant challenges for vessel segmentation. To address this issue, we propose an innovative model: SegKAN. First, we improve the conventional embedding module by adopting a novel convolutional network structure for image embedding, which smooths out image noise and prevents issues such as gradient explosion in subsequent stages. Next, we transform the spatial relationships between Patch blocks into temporal relationships to solve the problem of capturing positional relationships between Patch blocks in traditional Vision Transformer models. We conducted experiments on a Hepatic vessel dataset, and compared to the existing state-of-the-art model, the Dice score improved by 1.78%. These results demonstrate that the proposed new structure effectively enhances the segmentation performance of high-resolution extended objects. Code will be available at https://github.com/goblin327/SegKAN
在计算机断层扫描中,肝脏血管经常受到图像碎片和噪声干扰的影响,这使得保持血管的完整性变得困难,并为血管分割带来了重大挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新型模型:SegKAN。首先,我们通过采用新型卷积网络结构对图像进行嵌入,改进了传统的嵌入模块,该结构能够平滑图像噪声,并在后续阶段防止梯度爆炸等问题。接着,我们将Patch块之间的空间关系转换为时间关系,解决了传统视觉转换器模型中捕获Patch块之间位置关系的问题。我们在肝脏血管数据集上进行了实验,与现有最先进的模型相比,Dice得分提高了1.7t%。结果表明,所提出的新结构有效地提高了高分辨率扩展对象的分割性能。代码将在https://github.com/goblin327/SegKAN上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为SegKAN的新模型,用于解决肝脏血管在计算机断层扫描中的图像碎片化与噪声干扰问题。该模型改进了传统的嵌入模块,采用新型卷积网络结构进行图像嵌入,平滑图像噪声,并解决了后续阶段的梯度爆炸问题。此外,模型将Patch块之间的空间关系转换为时间关系,解决了传统视觉转换器模型中捕获Patch块之间位置关系的问题。实验结果显示,与现有最先进的模型相比,SegKAN在肝脏血管数据集上的Dice得分提高了1.78%,表明该新结构有效提高了高分辨率扩展对象的分割性能。
Key Takeaways
- SegKAN模型被提出以解决肝脏血管在计算机断层扫描中的图像碎片化及噪声问题。
- 改进了传统的嵌入模块,采用新型卷积网络结构进行图像嵌入。
- 模型能够平滑图像噪声,并防止后续阶段的梯度爆炸问题。
- 通过将Patch块之间的空间关系转换为时间关系,解决了传统视觉转换器模型的缺陷。
- 实验结果对比显示,SegKAN模型在肝脏血管数据集上的性能优于现有最先进的模型。
- SegKAN模型的Dice得分提高了1.78%,表明其有效提高了高分辨率扩展对象的分割性能。
点此查看论文截图
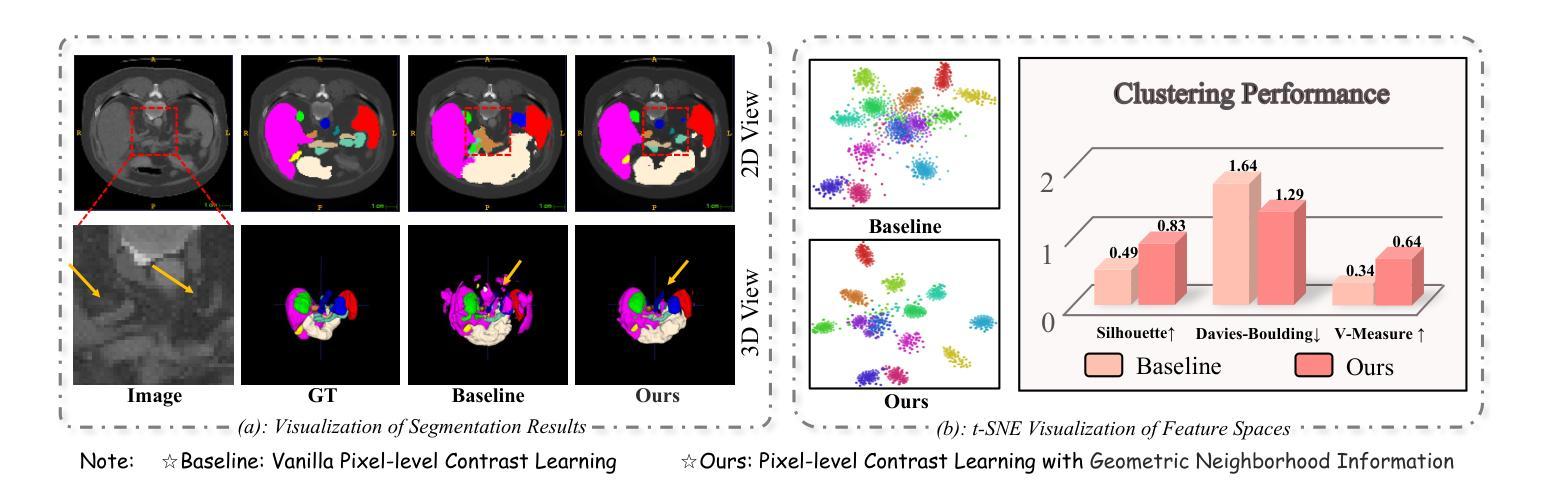
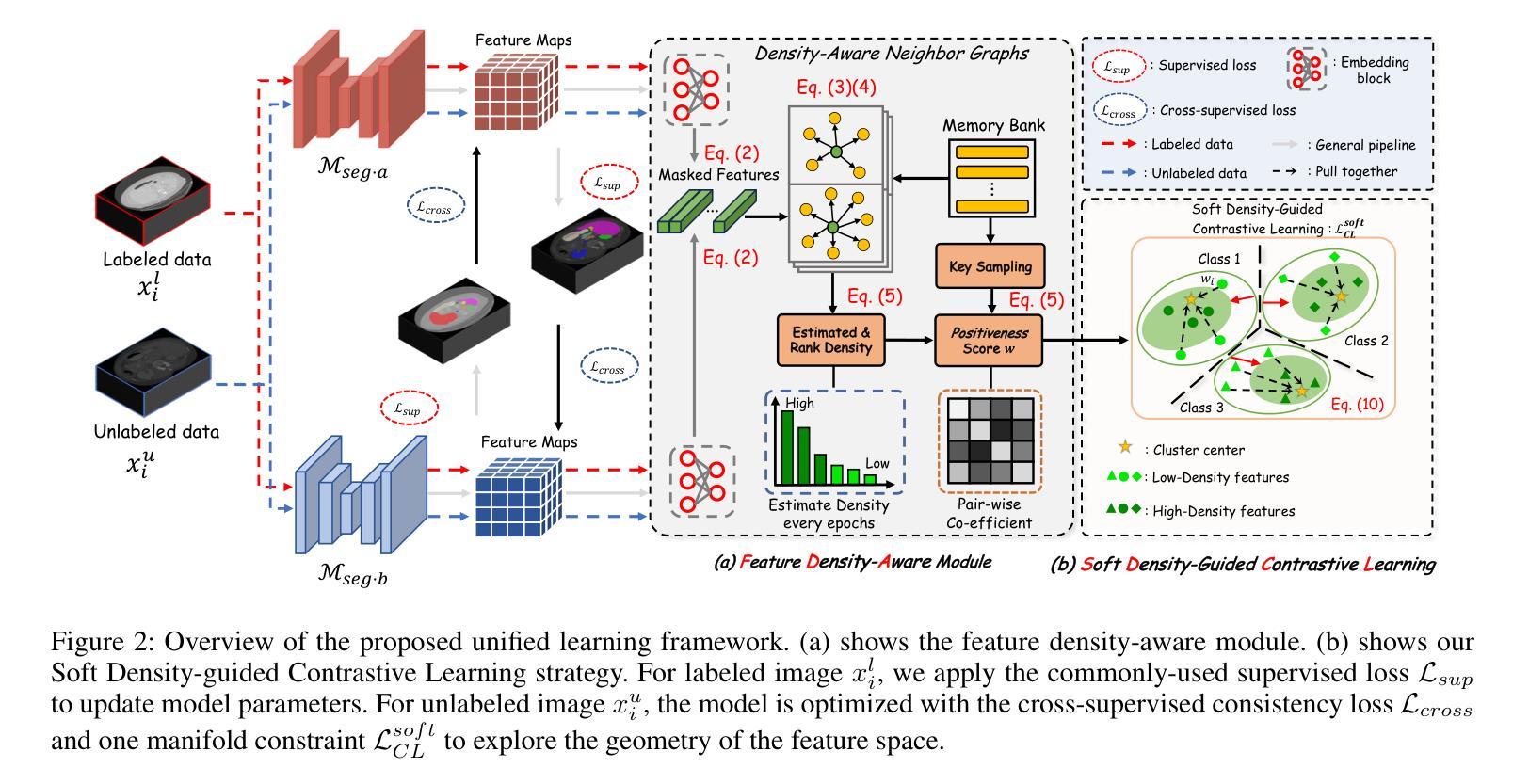
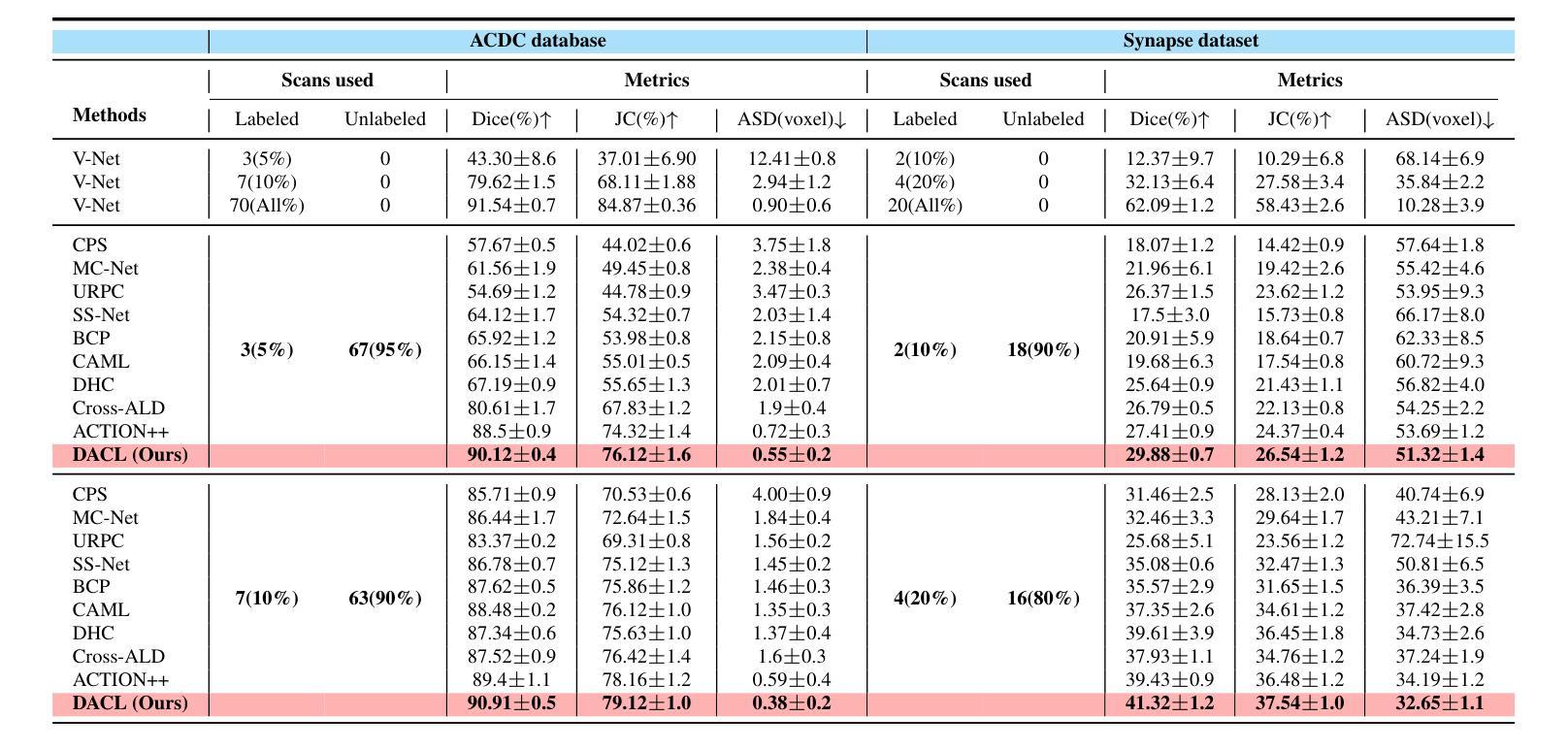
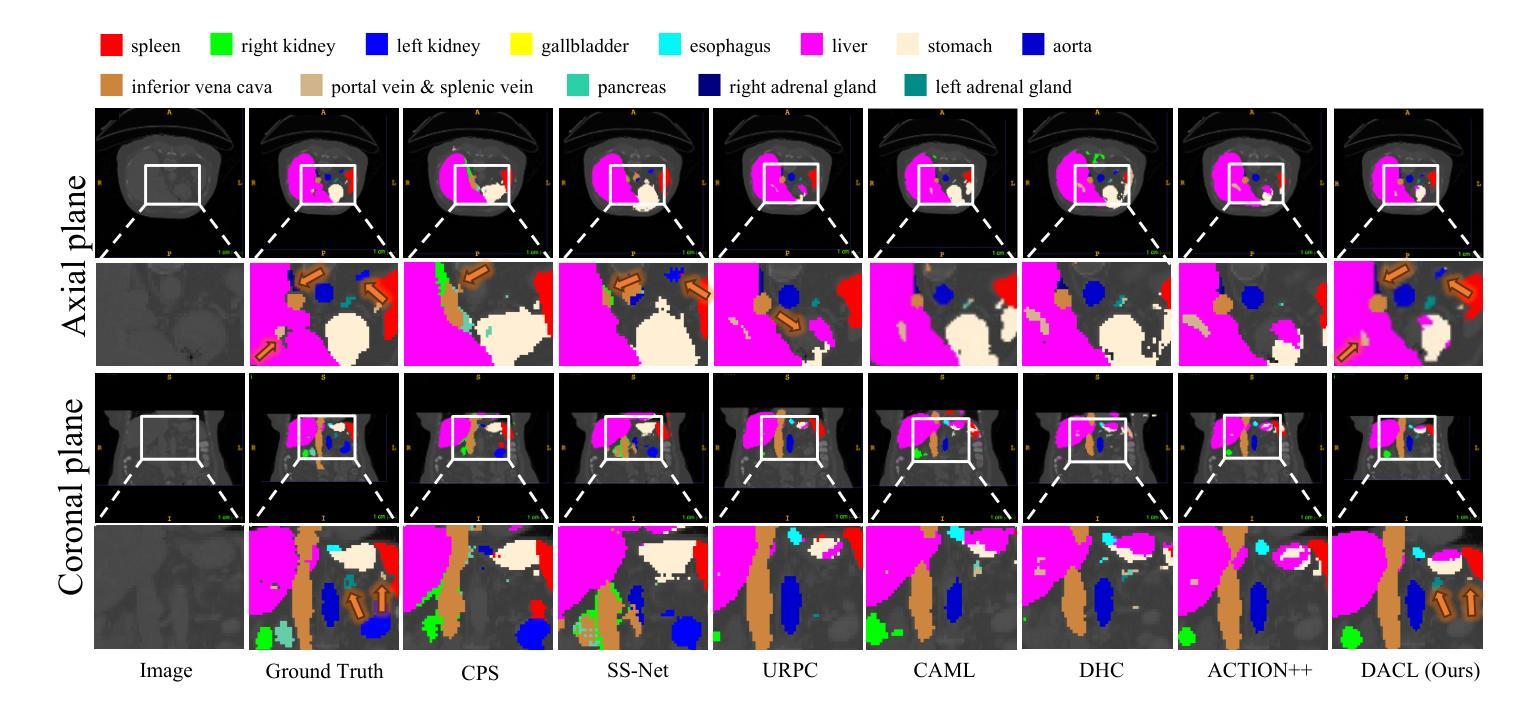
Neighbor Does Matter: Density-Aware Contrastive Learning for Medical Semi-supervised Segmentation
Authors:Feilong Tang, Zhongxing Xu, Ming Hu, Wenxue Li, Peng Xia, Yiheng Zhong, Hanjun Wu, Jionglong Su, Zongyuan Ge
In medical image analysis, multi-organ semi-supervised segmentation faces challenges such as insufficient labels and low contrast in soft tissues. To address these issues, existing studies typically employ semi-supervised segmentation techniques using pseudo-labeling and consistency regularization. However, these methods mainly rely on individual data samples for training, ignoring the rich neighborhood information present in the feature space. In this work, we argue that supervisory information can be directly extracted from the geometry of the feature space. Inspired by the density-based clustering hypothesis, we propose using feature density to locate sparse regions within feature clusters. Our goal is to increase intra-class compactness by addressing sparsity issues. To achieve this, we propose a Density-Aware Contrastive Learning (DACL) strategy, pushing anchored features in sparse regions towards cluster centers approximated by high-density positive samples, resulting in more compact clusters. Specifically, our method constructs density-aware neighbor graphs using labeled and unlabeled data samples to estimate feature density and locate sparse regions. We also combine label-guided co-training with density-guided geometric regularization to form complementary supervision for unlabeled data. Experiments on the Multi-Organ Segmentation Challenge dataset demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art methods, highlighting its efficacy in medical image segmentation tasks.
在医学图像分析领域,多器官半监督分割面临着标签不足和软组织对比度低等挑战。为了解决这个问题,现有研究通常采用基于伪标签和一致性正则化的半监督分割技术。然而,这些方法主要依赖于个别数据样本进行训练,忽略了特征空间中丰富的邻近信息。在这项工作中,我们认为监督信息可以直接从特征空间的几何形状中提取。受基于密度的聚类假设的启发,我们提出使用特征密度来定位特征聚类中的稀疏区域。我们的目标是通过解决稀疏性问题来增加类内紧凑性。为了实现这一目标,我们提出了一种密度感知对比学习(DACL)策略,将锚点特征推向由高密度正样本近似的聚类中心,从而形成更紧凑的聚类。具体来说,我们的方法使用有标签和无标签的数据样本构建密度感知邻近图,以估计特征密度并定位稀疏区域。我们还结合了标签引导的协同训练和密度引导的几何正则化,为无标签数据形成互补监督。在Multi-Organ Segmentation Challenge数据集上的实验表明,我们提出的方法优于最新方法,突显其在医学图像分割任务中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于特征密度的对比学习(DACL)策略,用于解决医学图像多器官分割中的半监督问题。针对稀疏区域,通过利用特征空间的几何结构提取监督信息,提高类内紧凑性。在Multi-Organ Segmentation Challenge数据集上的实验表明,该方法优于现有技术,有效应用于医学图像分割任务。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像多器官分割中的半监督问题面临挑战,如标签不足和软组织对比度低。
- 现有研究通常使用伪标签和一致性正则化等半监督分割技术。
- 本研究利用特征空间的几何结构直接提取监督信息,解决稀疏区域问题,提高类内紧凑性。
- 提出密度感知对比学习(DACL)策略,将锚点特征推向由高密度正样本近似表示的簇中心,形成更紧凑的簇。
- 通过构建密度感知的邻居图来估计特征密度并定位稀疏区域,使用有标签和无标签数据样本。
- 结合标签引导的协同训练和密度引导几何正则化,为无标签数据形成互补监督。
点此查看论文截图

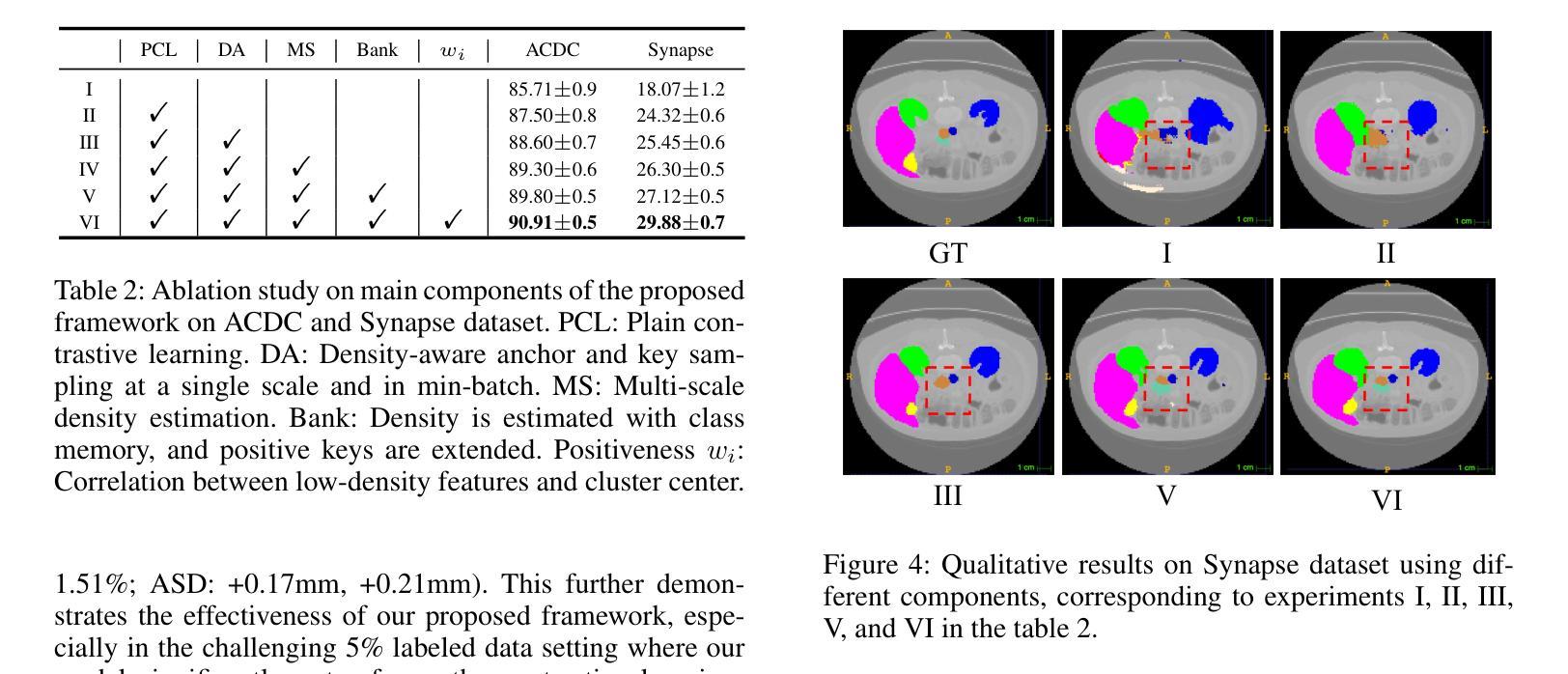
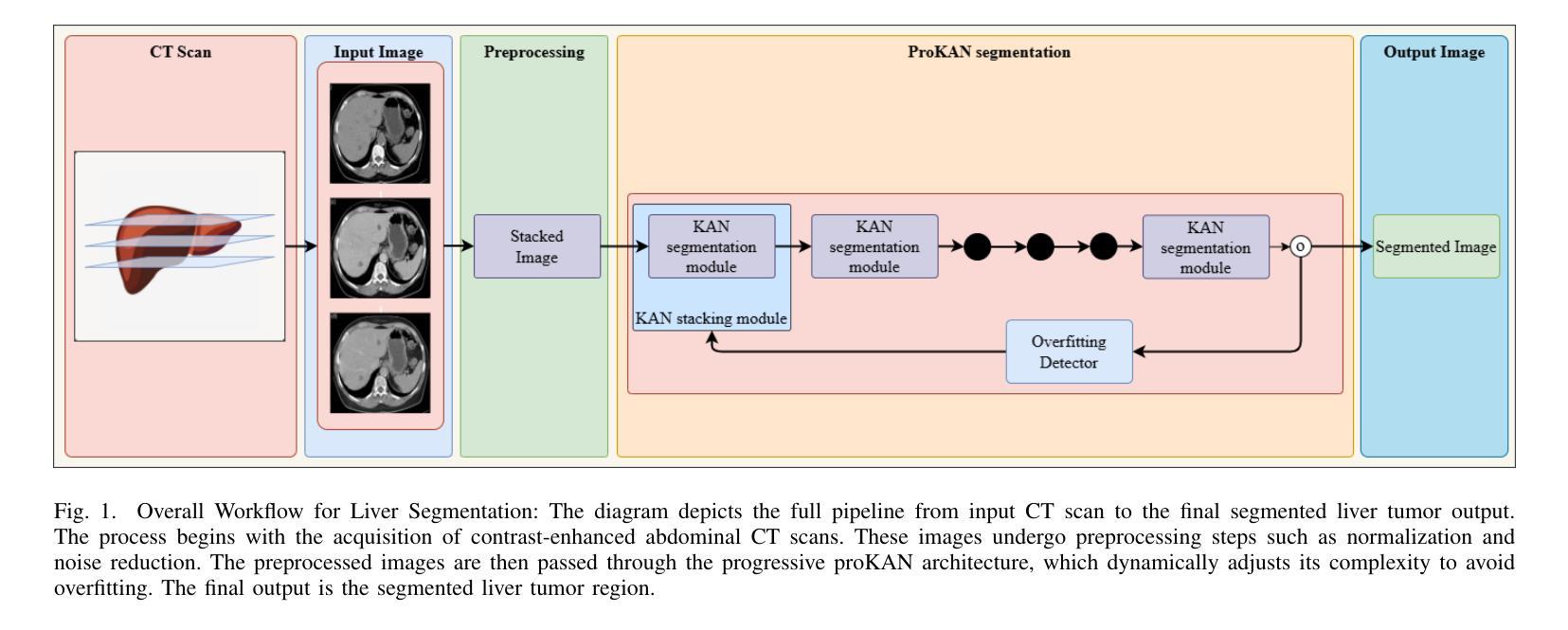
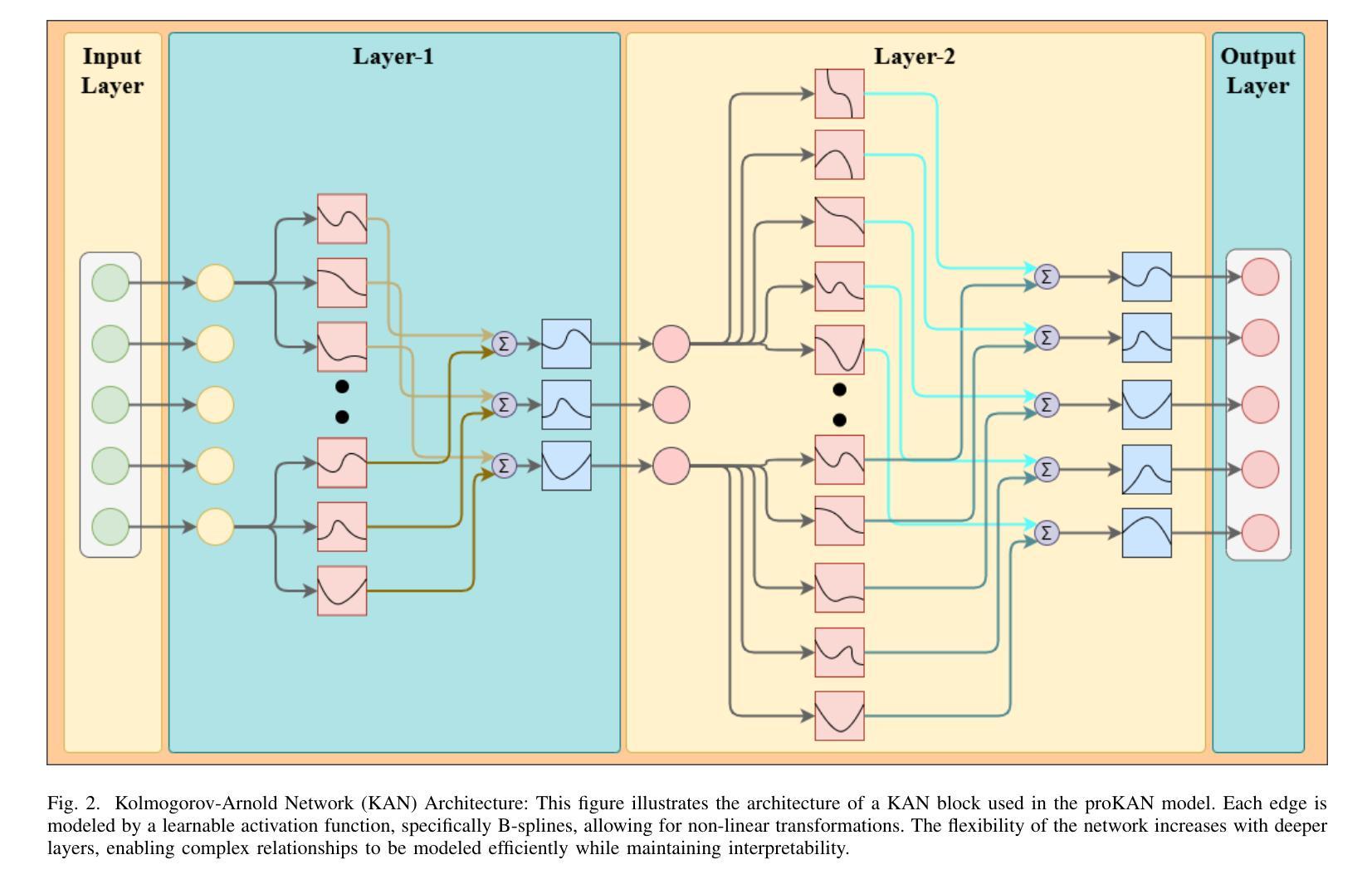
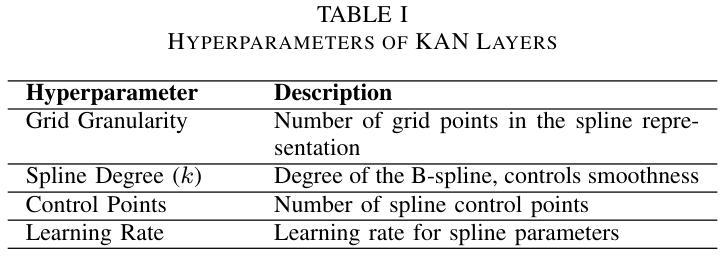
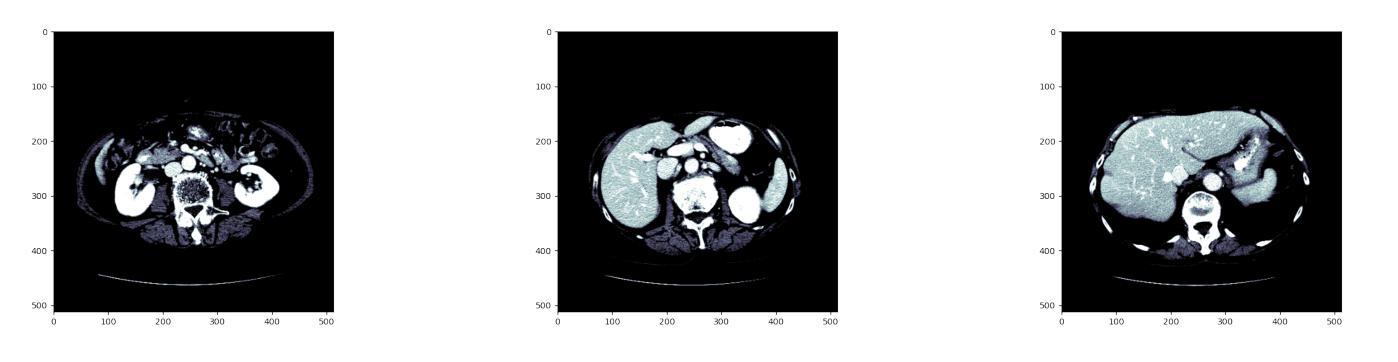
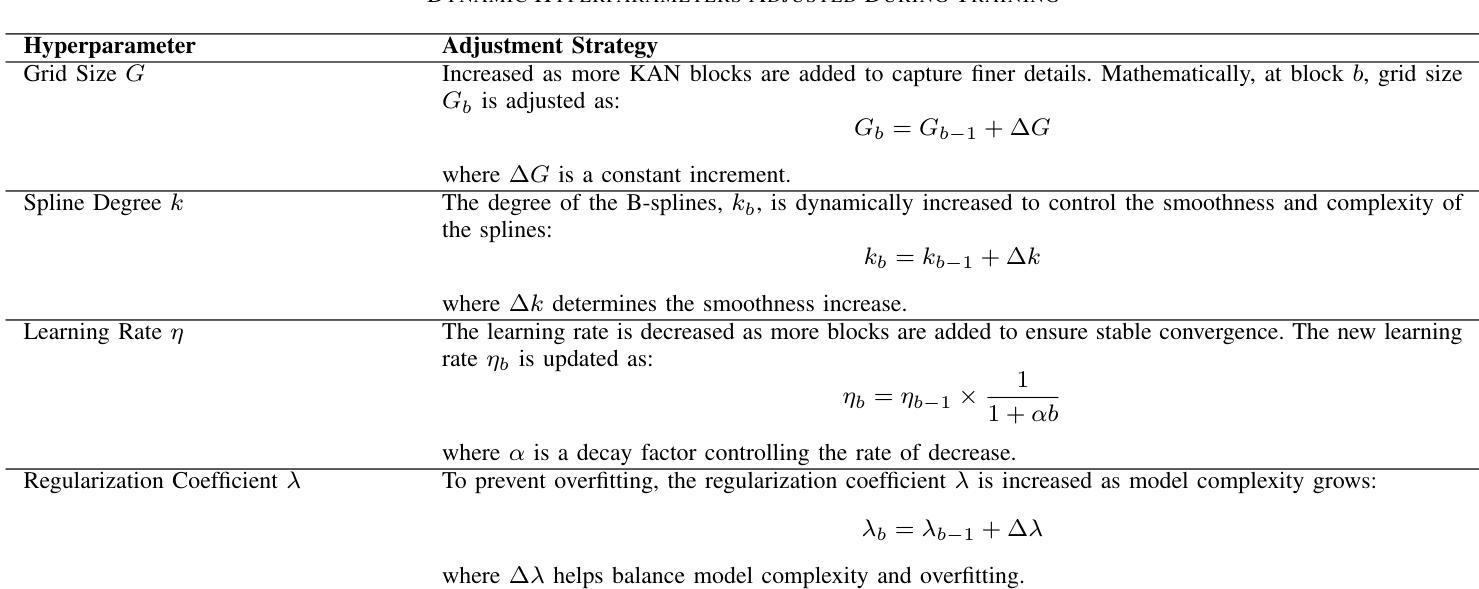
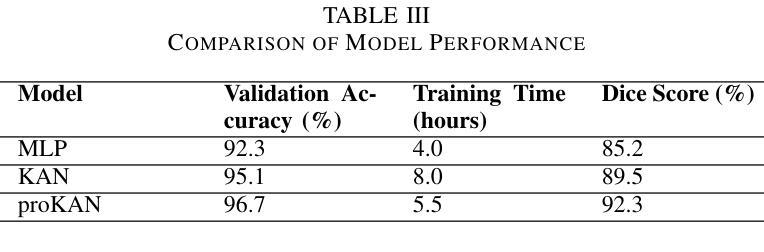
ProKAN: Progressive Stacking of Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks for Efficient Liver Segmentation
Authors:Bhavesh Gyanchandani, Aditya Oza, Abhinav Roy
The growing need for accurate and efficient 3D identification of tumors, particularly in liver segmentation, has spurred considerable research into deep learning models. While many existing architectures offer strong performance, they often face challenges such as overfitting and excessive computational costs. An adjustable and flexible architecture that strikes a balance between time efficiency and model complexity remains an unmet requirement. In this paper, we introduce proKAN, a progressive stacking methodology for Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) designed to address these challenges. Unlike traditional architectures, proKAN dynamically adjusts its complexity by progressively adding KAN blocks during training, based on overfitting behavior. This approach allows the network to stop growing when overfitting is detected, preventing unnecessary computational overhead while maintaining high accuracy. Additionally, proKAN utilizes KAN’s learnable activation functions modeled through B-splines, which provide enhanced flexibility in learning complex relationships in 3D medical data. Our proposed architecture achieves state-of-the-art performance in liver segmentation tasks, outperforming standard Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs) and fixed KAN architectures. The dynamic nature of proKAN ensures efficient training times and high accuracy without the risk of overfitting. Furthermore, proKAN provides better interpretability by allowing insight into the decision-making process through its learnable coefficients. The experimental results demonstrate a significant improvement in accuracy, Dice score, and time efficiency, making proKAN a compelling solution for 3D medical image segmentation tasks.
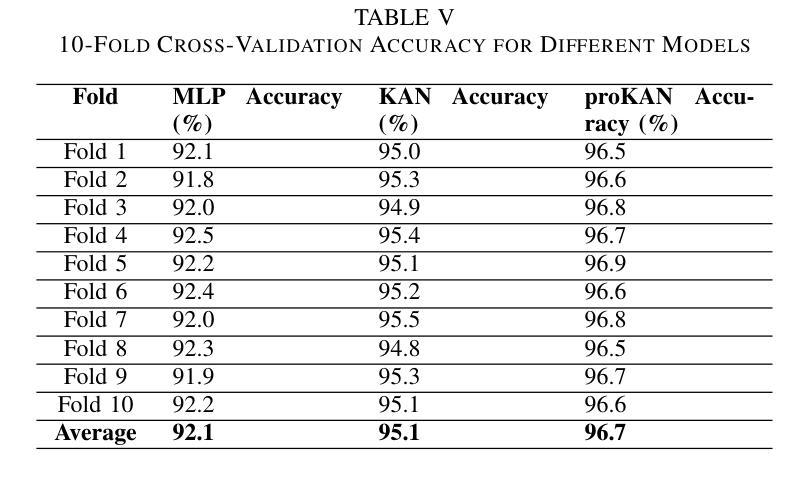
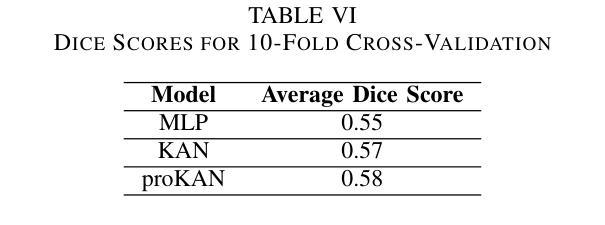
对于准确且高效的3D肿瘤识别,特别是在肝脏分割中的需求日益增长,已经激发了深度学习模型的深入研究。尽管现有的许多架构都表现出强大的性能,但它们常常面临过拟合和计算成本过高的挑战。一种能在时间效率和模型复杂度之间取得平衡的可调整和灵活架构仍然是一个未满足的需求。在本文中,我们介绍了proKAN,这是一种针对Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KANs)的渐进堆叠方法,旨在解决这些挑战。与传统的架构不同,proKAN根据过拟合行为在训练过程中动态地添加KAN块来调整其复杂性。这种方法允许网络在检测到过拟合时停止增长,既防止了不必要的计算开销,又保持了较高的准确性。此外,proKAN利用通过B样条建模的KAN的可学习激活函数,提供了在3D医学数据中学习复杂关系的增强灵活性。我们提出的架构在肝脏分割任务中实现了最先进的性能,优于标准的多层感知器(MLPs)和固定的KAN架构。proKAN的动态特性确保了高效的训练时间和高准确性,且没有过拟合的风险。此外,proKAN通过其可学习系数提供了更好的可解释性,可以深入了解决策过程。实验结果表明,在准确性、Dice分数和时间效率方面都有显著提高,使proKAN成为3D医学图像分割任务的理想解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对肝脏分割任务中的三维肿瘤识别需求,提出一种名为proKAN的新型深度学习模型架构。该架构采用渐进堆叠Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KANs)的方法,可动态调整模型复杂度,通过检测过拟合现象来停止网络增长,实现高效的时间利用和高精度。同时,proKAN利用通过B样条曲线建模的可学习激活函数,增强了在三维医学数据中学习复杂关系的能力。实验结果表明,proKAN在肝脏分割任务中实现了卓越的性能,显著提高了准确性、Dice评分和时间效率,成为解决三维医学图像分割任务的有力解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- proKAN是一种针对深度学习模型的新的架构方法,专门用于解决肝脏分割中的三维肿瘤识别问题。
- proKAN采用渐进堆叠Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KANs),可动态调整模型复杂度以平衡时间和效率。
- 过拟合检测机制允许网络在检测到过拟合时停止增长,避免不必要的计算开销。
- proKAN使用通过B样条曲线建模的可学习激活函数,增强了在三维医学数据中的学习能力。
- 实验结果显示proKAN在肝脏分割任务中实现了最佳性能,优于多层感知器(MLPs)和固定KAN架构。
- proKAN不仅提高了准确性和Dice评分,还提高了时间效率。
点此查看论文截图

CAD-GPT: Synthesising CAD Construction Sequence with Spatial Reasoning-Enhanced Multimodal LLMs
Authors:Siyu Wang, Cailian Chen, Xinyi Le, Qimin Xu, Lei Xu, Yanzhou Zhang, Jie Yang
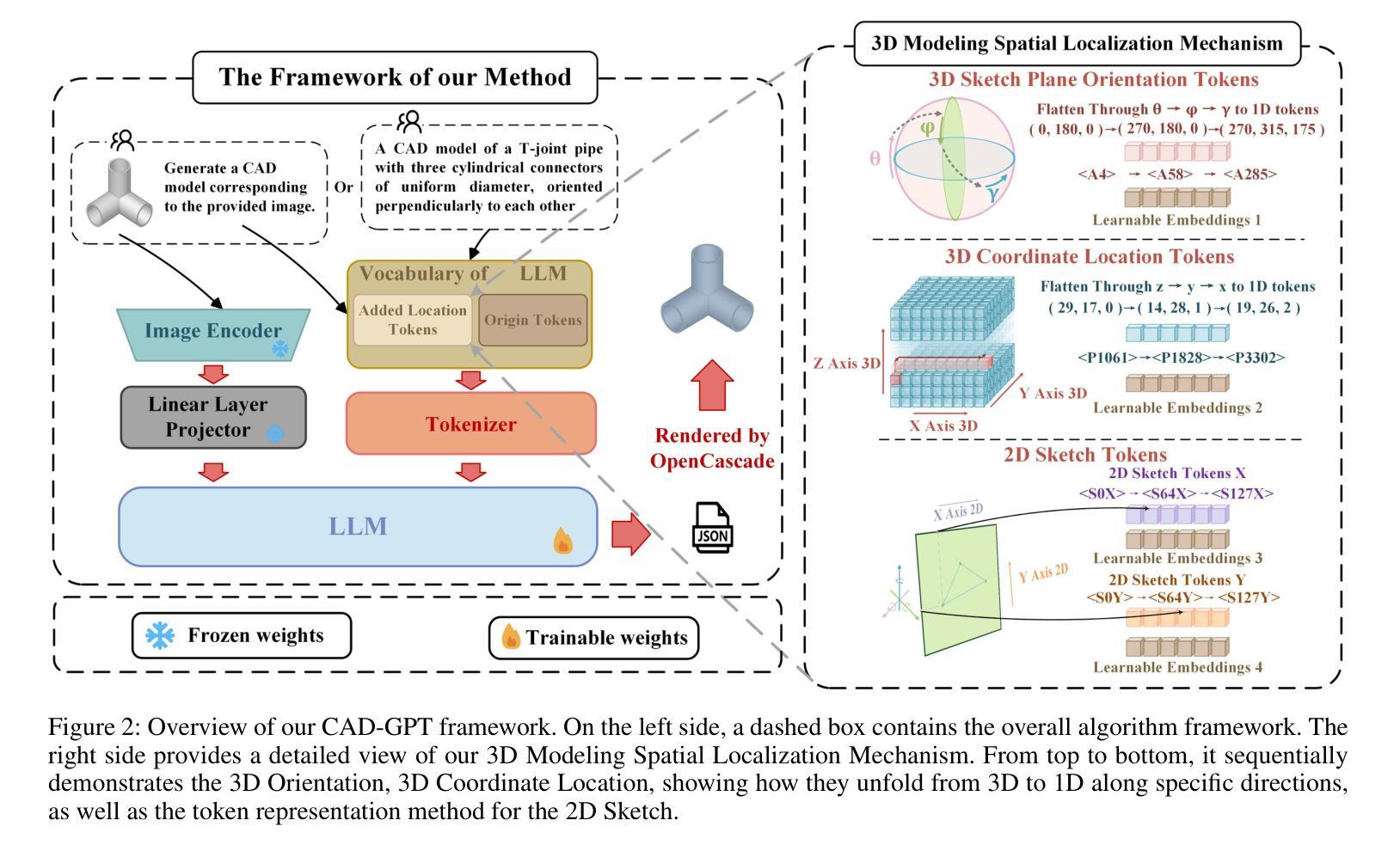
Computer-aided design (CAD) significantly enhances the efficiency, accuracy, and innovation of design processes by enabling precise 2D and 3D modeling, extensive analysis, and optimization. Existing methods for creating CAD models rely on latent vectors or point clouds, which are difficult to obtain and costly to store. Recent advances in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have inspired researchers to use natural language instructions and images for CAD model construction. However, these models still struggle with inferring accurate 3D spatial location and orientation, leading to inaccuracies in determining the spatial 3D starting points and extrusion directions for constructing geometries. This work introduces CAD-GPT, a CAD synthesis method with spatial reasoning-enhanced MLLM that takes either a single image or a textual description as input. To achieve precise spatial inference, our approach introduces a 3D Modeling Spatial Mechanism. This method maps 3D spatial positions and 3D sketch plane rotation angles into a 1D linguistic feature space using a specialized spatial unfolding mechanism, while discretizing 2D sketch coordinates into an appropriate planar space to enable precise determination of spatial starting position, sketch orientation, and 2D sketch coordinate translations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CAD-GPT consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in CAD model synthesis, both quantitatively and qualitatively.
计算机辅助设计(CAD)通过实现精确的2D和3D建模、深入的分析和优化,显著提高了设计过程的效率、准确性和创新性。现有的创建CAD模型的方法依赖于潜在向量或点云,这些难以获取且成本高昂。最近的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)的进步激发了研究人员使用自然语言指令和图像进行CAD模型构建。然而,这些模型在推断准确的3D空间位置和方向时仍存在问题,导致在确定构建几何体的空间3D起始点和挤压方向时产生不精确结果。这项工作引入了CAD-GPT,这是一种带有空间推理增强型MLLM的CAD合成方法,它接受单张图像或文本描述作为输入。为了精确的空间推断,我们的方法引入了一种3D建模空间机制。这种方法使用专门的展开机制将3D空间位置和3D草图平面旋转角度映射到一维语言特征空间中,同时将二维草图坐标离散化到适当的平面空间中,以实现精确的空间起始位置、草图方向和二维草图坐标转换的确定。大量实验表明,无论是在数量上还是在质量上,CAD-GPT在CAD模型合成方面均持续优于现有最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
CAD-GPT方法利用空间推理增强型多模态大型语言模型,通过单张图像或文本描述输入,实现计算机辅助设计(CAD)合成。该方法引入3D建模空间机制,将3D空间位置和3D草图平面旋转角度映射到1D语言特征空间,同时离散化2D草图坐标,以实现空间起始位置、草图方向和2D草图坐标翻译的精确确定。实验表明,CAD-GPT在CAD模型合成方面,无论是定量还是定性,都一致优于现有最先进的方法。
Key Takeaways
- CAD-GPT利用多模态大型语言模型进行计算机辅助设计合成,接受图像或文本描述作为输入。
- 现有CAD模型创建方法主要依赖潜在向量或点云,但获取和存储成本较高。
- CAD-GPT面临的主要挑战是推断准确的3D空间位置和方向,影响几何构造的空间3D起点和挤压方向。
- CAD-GPT引入的3D建模空间机制将3D空间位置和旋转角度映射到1D语言特征空间。
- 该方法离散化2D草图坐标,以实现空间位置的精确确定。
- 实验证明,CAD-GPT在CAD模型合成方面的性能优于现有方法。
- CAD-GPT的引入有望提高设计效率、准确性和创新性。
点此查看论文截图


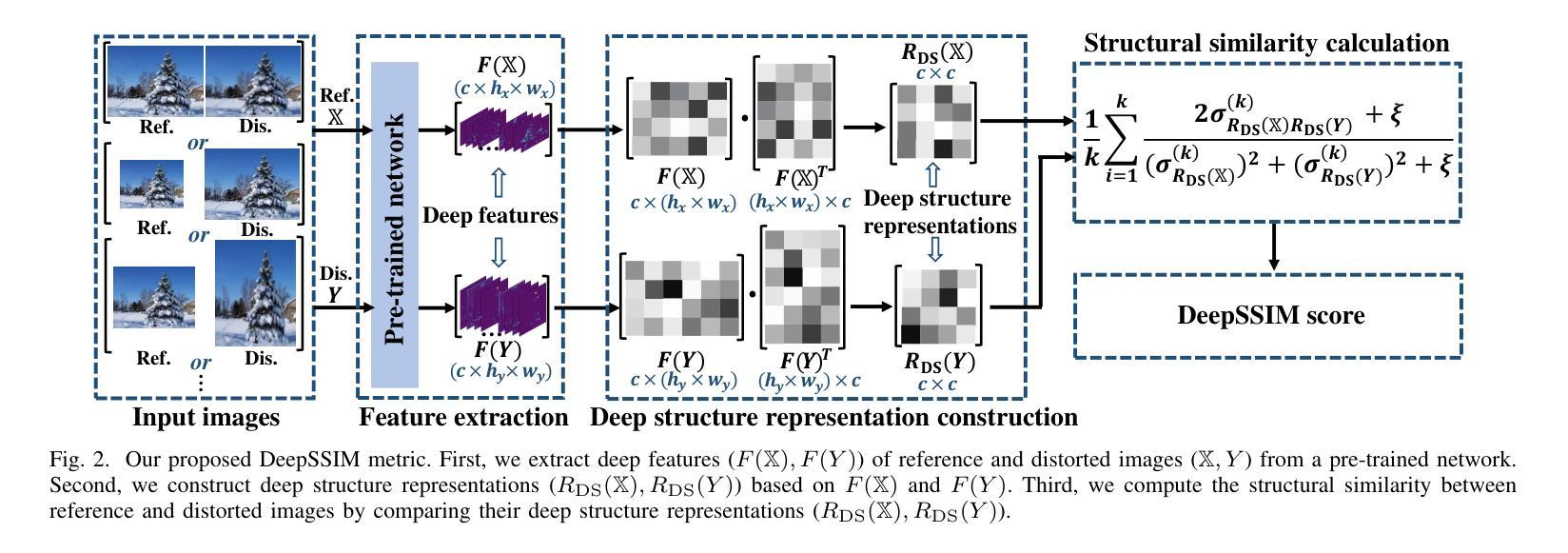
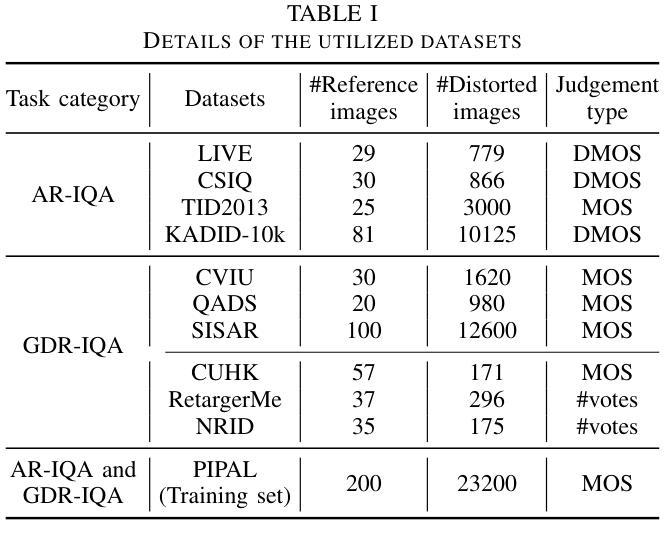
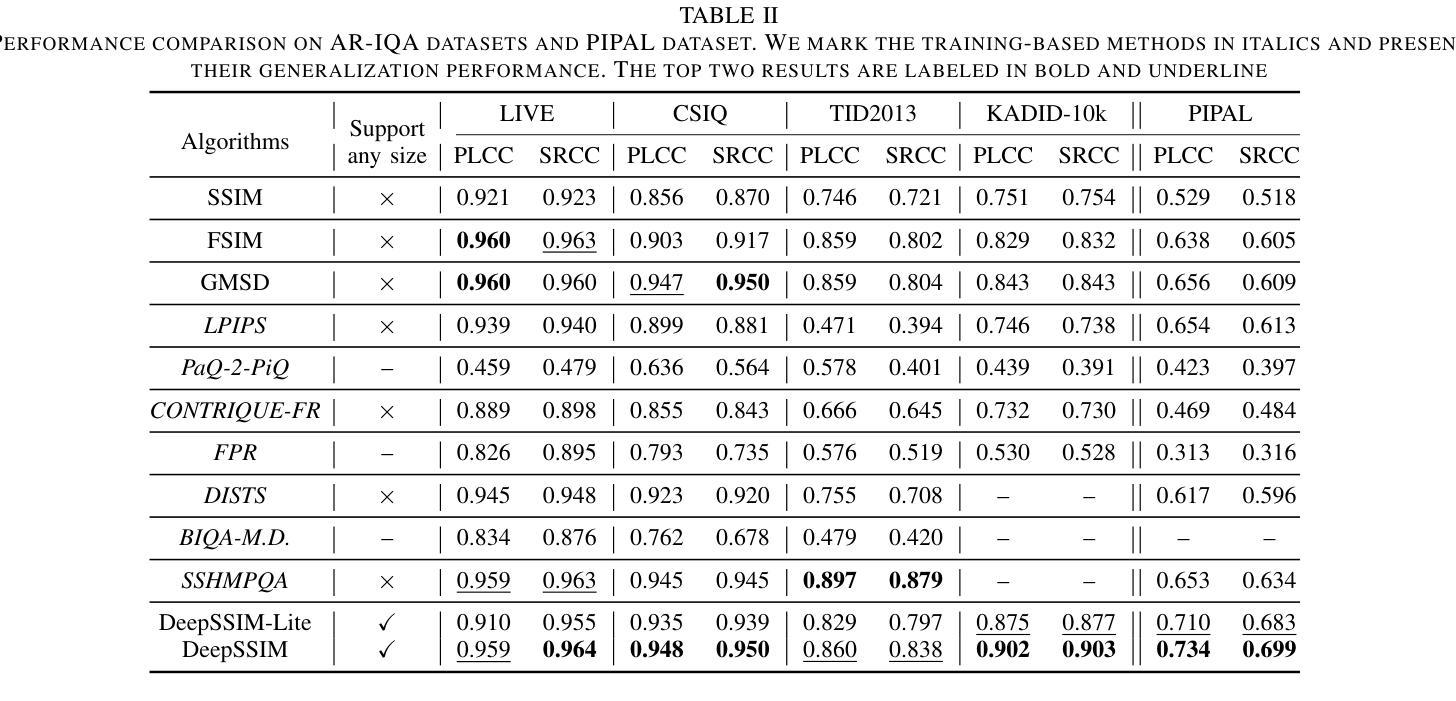
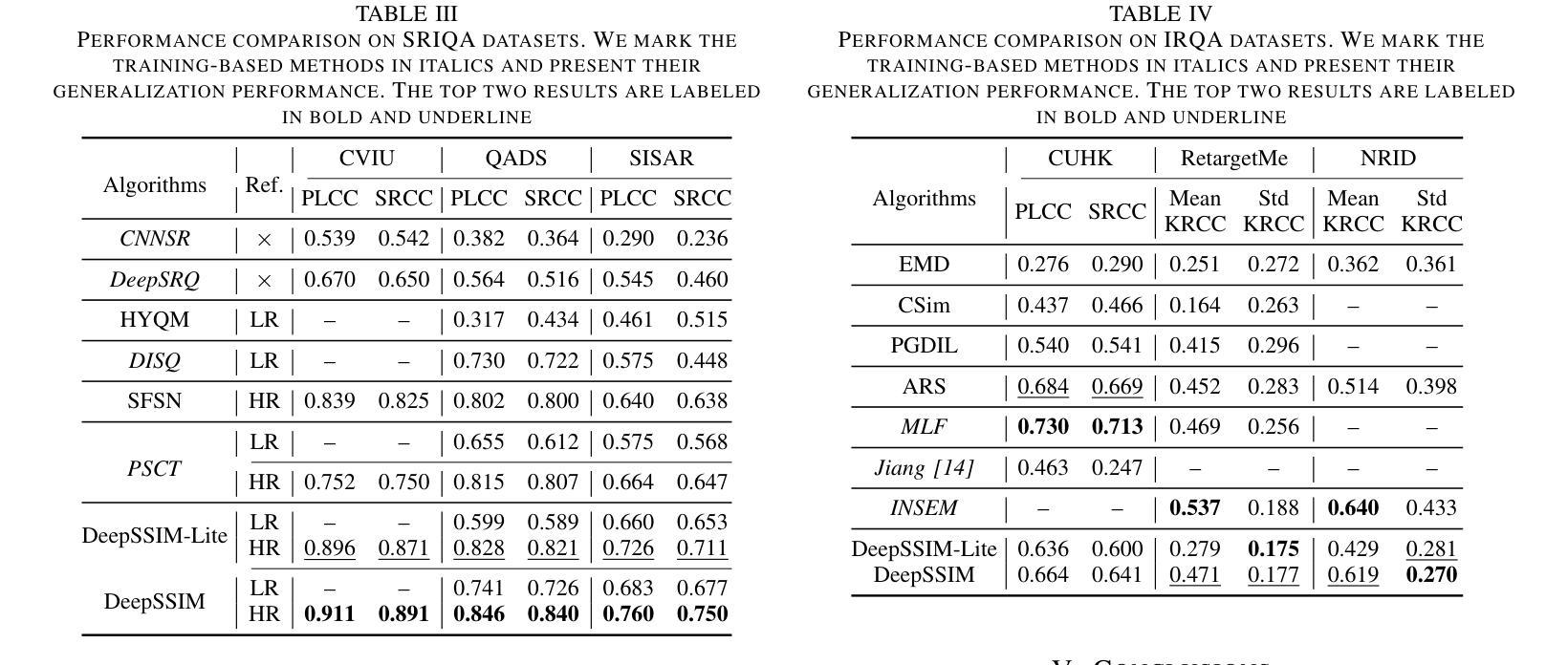
Structural Similarity in Deep Features: Image Quality Assessment Robust to Geometrically Disparate Reference
Authors:Keke Zhang, Weiling Chen, Tiesong Zhao, Zhou Wang
Image Quality Assessment (IQA) with references plays an important role in optimizing and evaluating computer vision tasks. Traditional methods assume that all pixels of the reference and test images are fully aligned. Such Aligned-Reference IQA (AR-IQA) approaches fail to address many real-world problems with various geometric deformations between the two images. Although significant effort has been made to attack Geometrically-Disparate-Reference IQA (GDR-IQA) problem, it has been addressed in a task-dependent fashion, for example, by dedicated designs for image super-resolution and retargeting, or by assuming the geometric distortions to be small that can be countered by translation-robust filters or by explicit image registrations. Here we rethink this problem and propose a unified, non-training-based Deep Structural Similarity (DeepSSIM) approach to address the above problems in a single framework, which assesses structural similarity of deep features in a simple but efficient way and uses an attention calibration strategy to alleviate attention deviation. The proposed method, without application-specific design, achieves state-of-the-art performance on AR-IQA datasets and meanwhile shows strong robustness to various GDR-IQA test cases. Interestingly, our test also shows the effectiveness of DeepSSIM as an optimization tool for training image super-resolution, enhancement and restoration, implying an even wider generalizability. \footnote{Source code will be made public after the review is completed.
图像质量评估(IQA)在优化和评估计算机视觉任务中起着重要作用。传统的方法假设参考图像和测试图像的所有像素完全对齐。这种对齐参考IQA(AR-IQA)方法无法解决两个图像之间存在各种几何变形等真实世界问题。尽管人们已经为解决几何离散参考IQA(GDR-IQA)问题付出了巨大努力,但它仍然是以任务依赖的方式解决,例如通过为图像超分辨率和重定向设计的专用设备,或者假设几何畸变足够小可以通过平移稳健滤波器或显式图像注册来克服。在这里我们对这个问题进行了重新思考,并提出了一个统一的、非基于训练深度结构相似性(DeepSSIM)方法来解决上述问题,它以一种简单高效的方式评估深度特征的结构相似性,并使用注意力校准策略来缓解注意力偏差。该方法无需针对特定应用进行设计,在AR-IQA数据集上实现了最先进的性能,同时在各种GDR-IQA测试用例中表现出强大的稳健性。有趣的是,我们的测试还显示了DeepSSIM作为图像超分辨率、增强和修复训练优化工具的有效性,这表明其更广泛的通用性。\footnote{源代码将在审查完成后公开。}
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于深度结构相似性(DeepSSIM)的统一非训练方法来解决图像质量评估(IQA)中的问题。该方法无需针对特定任务进行设计,即可在单一框架内解决对齐参考图像质量评估(AR-IQA)和几何离散参考图像质量评估(GDR-IQA)问题。它通过评估深度特征的结构相似性,并使用注意力校准策略来减轻注意力偏差,实现了对多种情况下的鲁棒性。此外,DeepSSIM还被证明是一种有效的优化工具,可用于训练图像超分辨率、增强和修复任务,显示出其更广泛的通用性。
Key Takeaways
- 传统图像质量评估方法假设参考和测试图像的所有像素完全对齐,不适用于具有几何变形的真实世界问题。
- 一种新的非训练基于深度结构相似性(DeepSSIM)的方法被提出,用于解决对齐和几何离散参考图像质量评估(AR-IQA和GDR-IQA)问题。
- 该方法通过评估深度特征的结构相似性,实现简单而有效的图像质量评估。
- 使用了注意力校准策略来减轻注意力偏差,增强了方法的鲁棒性。
- 该方法无需针对特定任务进行设计,且在AR-IQA数据集上实现了最佳性能。
- DeepSSIM对于解决图像超分辨率、增强和恢复等任务具有优化作用,显示出其广泛的通用性。
点此查看论文截图

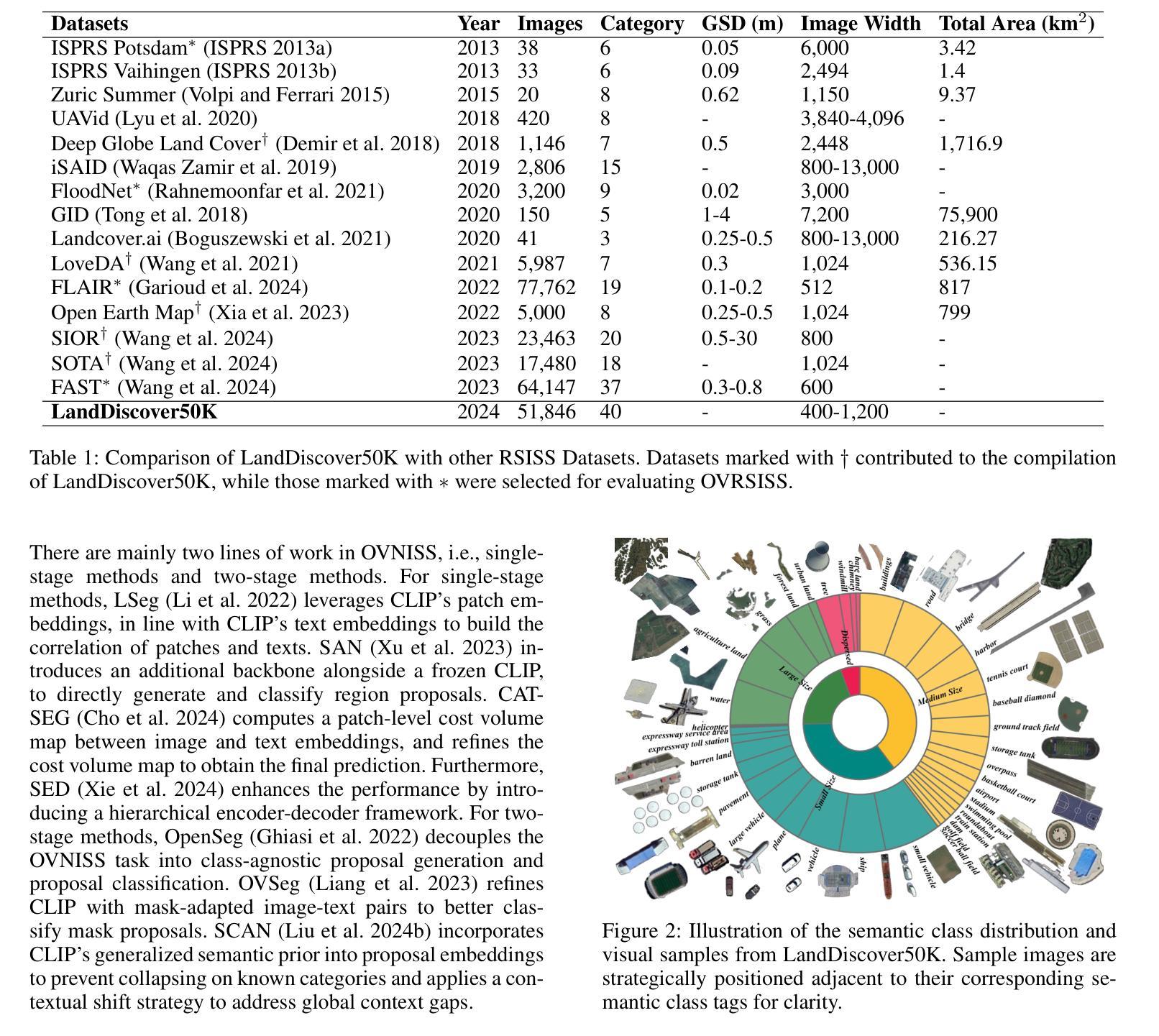
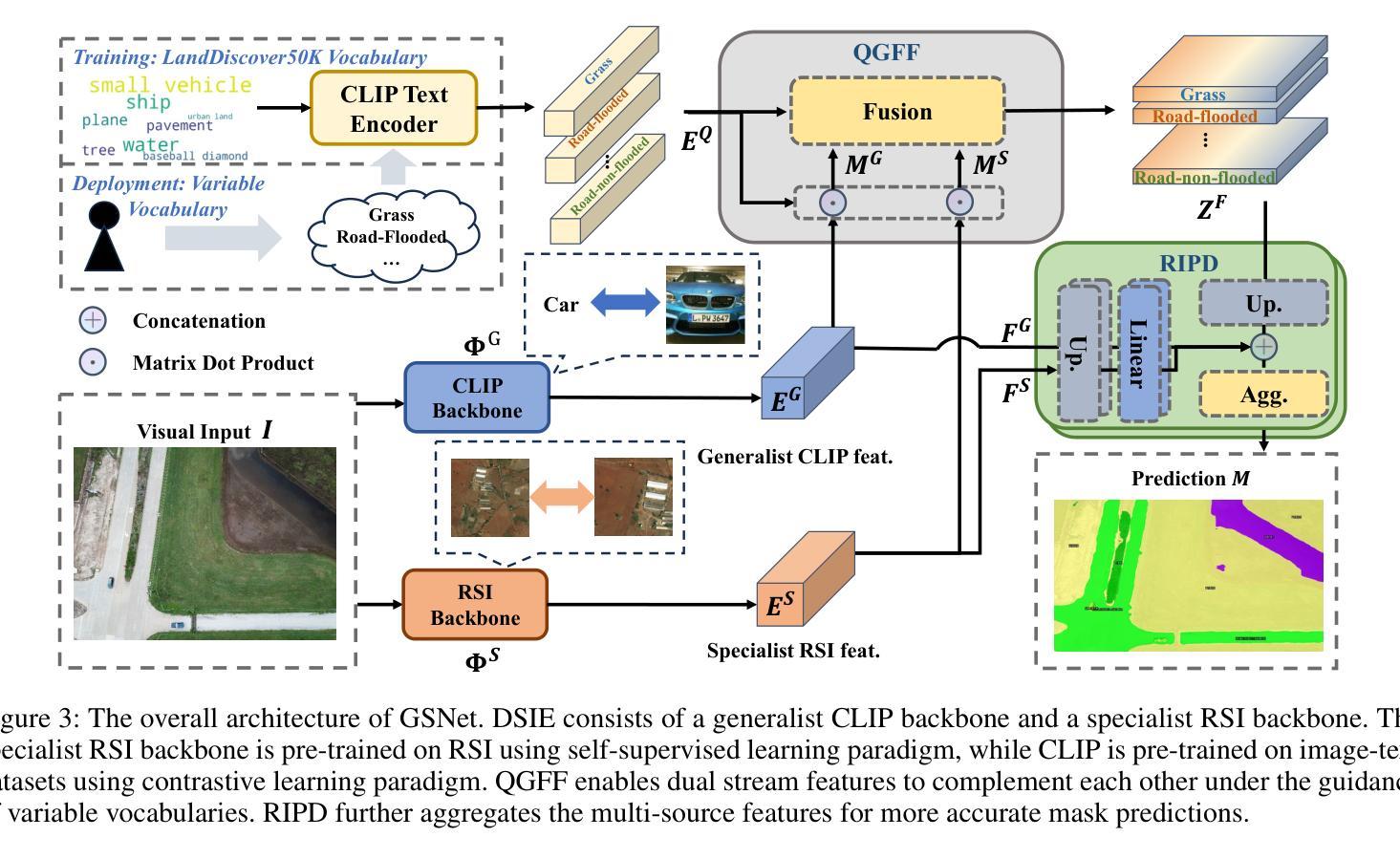
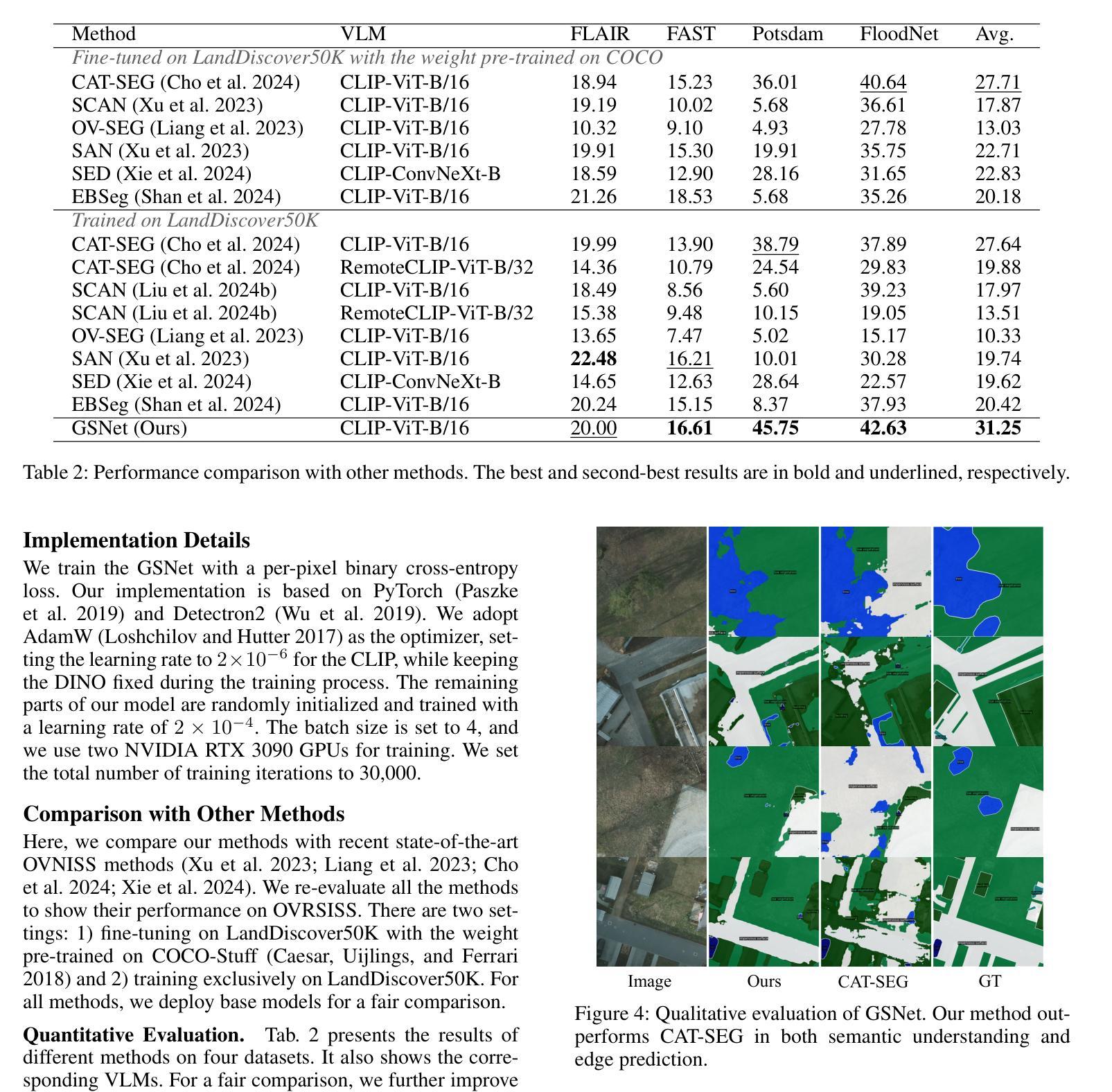
Towards Open-Vocabulary Remote Sensing Image Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Chengyang Ye, Yunzhi Zhuge, Pingping Zhang
Recently, deep learning based methods have revolutionized remote sensing image segmentation. However, these methods usually rely on a pre-defined semantic class set, thus needing additional image annotation and model training when adapting to new classes. More importantly, they are unable to segment arbitrary semantic classes. In this work, we introduce Open-Vocabulary Remote Sensing Image Semantic Segmentation (OVRSISS), which aims to segment arbitrary semantic classes in remote sensing images. To address the lack of OVRSISS datasets, we develop LandDiscover50K, a comprehensive dataset of 51,846 images covering 40 diverse semantic classes. In addition, we propose a novel framework named GSNet that integrates domain priors from special remote sensing models and versatile capabilities of general vision-language models. Technically, GSNet consists of a Dual-Stream Image Encoder (DSIE), a Query-Guided Feature Fusion (QGFF), and a Residual Information Preservation Decoder (RIPD). DSIE first captures comprehensive features from both special models and general models in dual streams. Then, with the guidance of variable vocabularies, QGFF integrates specialist and generalist features, enabling them to complement each other. Finally, RIPD is proposed to aggregate multi-source features for more accurate mask predictions. Experiments show that our method outperforms other methods by a large margin, and our proposed LandDiscover50K improves the performance of OVRSISS methods. The proposed dataset and method will be made publicly available at https://github.com/yecy749/GSNet.
最近,基于深度学习的方法在遥感图像分割领域掀起了革命性的变革。然而,这些方法通常依赖于预先定义的语义类别集,因此在适应新类别时需要额外的图像标注和模型训练。更重要的是,它们无法对任意语义类别进行分割。在这项工作中,我们引入了开放词汇遥感图像语义分割(OVRSISS),旨在实现对遥感图像中任意语义类别的分割。为了解决OVRSISS数据集缺乏的问题,我们开发了LandDiscover50K,这是一个包含51,846张图像的综合数据集,涵盖40个多样化的语义类别。此外,我们提出了一种名为GSNet的新型框架,它整合了特殊遥感模型的领域先验知识和通用视觉语言模型的通用能力。在技术上,GSNet由双流图像编码器(DSIE)、查询引导特征融合(QGFF)和残差信息保留解码器(RIPD)组成。DSIE首先从特殊模型和通用模型的双流中提取全面特征。然后,在可变词汇表的指导下,QGFF整合专业和普通特征,使它们能够相互补充。最后,RIPD被提出来聚合多源特征,以进行更准确的掩膜预测。实验表明,我们的方法在其他方法上具有较大优势,我们提出的LandDiscover50K提高了OVRSISS方法的性能。所提出的数据集和方法将在https://github.com/yecy749/GSNet上公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI2025
Summary
基于深度学习的方法在遥感图像分割领域引发了一场革命。然而,这些方法通常需要预设的语义类别集,当适应新类别时需要额外的图像注释和模型训练。为解决此问题,本文提出了开放词汇遥感图像语义分割(OVRSISS),旨在实现对遥感图像中的任意语义类别进行分割。为应对缺乏OVRSISS数据集的问题,本文开发了LandDiscover50K数据集,包含51,846张图像,涵盖40个多样化的语义类别。此外,本文提出了一种名为GSNet的新型框架,该框架融合了特殊遥感模型的领域先验知识和通用视觉语言模型的通用能力。实验表明,该方法与其他方法相比具有显著优势,LandDiscover50K数据集提高了OVRSISS方法的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在遥感图像分割中的应用已经引发了一场革命。
- 当前方法依赖于预设的语义类别集,难以适应新类别。
- 本文提出了开放词汇遥感图像语义分割(OVRSISS),旨在解决这一问题。
- LandDiscover50K数据集被开发出来以支持OVRSISS,包含多样化的语义类别。
- GSNet框架被提出,融合了特殊遥感模型和通用视觉语言模型的优点。
- GSNet包括双流图像编码器、查询引导特征融合和残差信息保留解码器。
点此查看论文截图

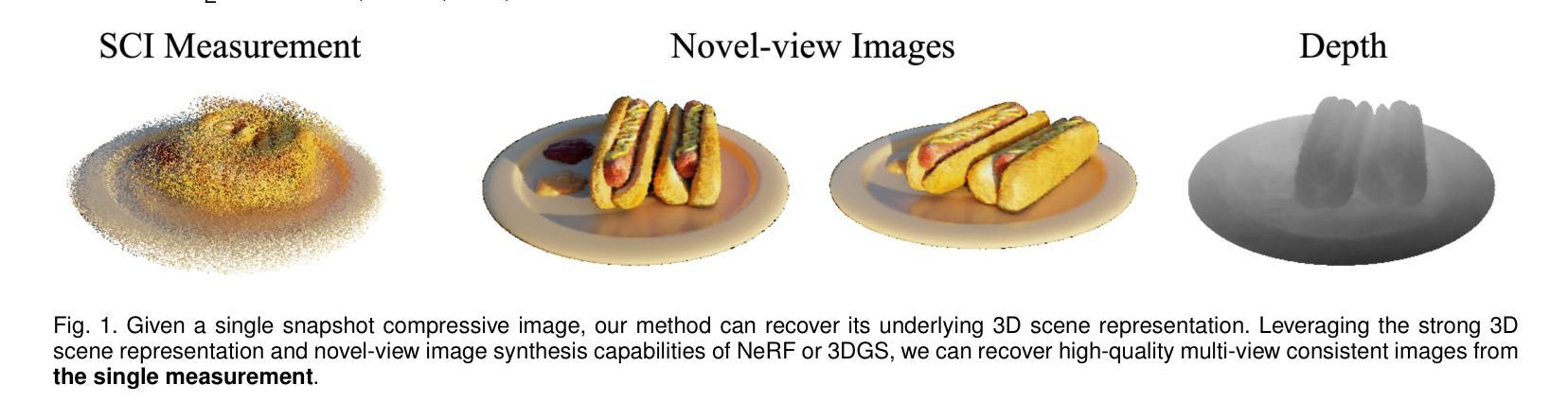
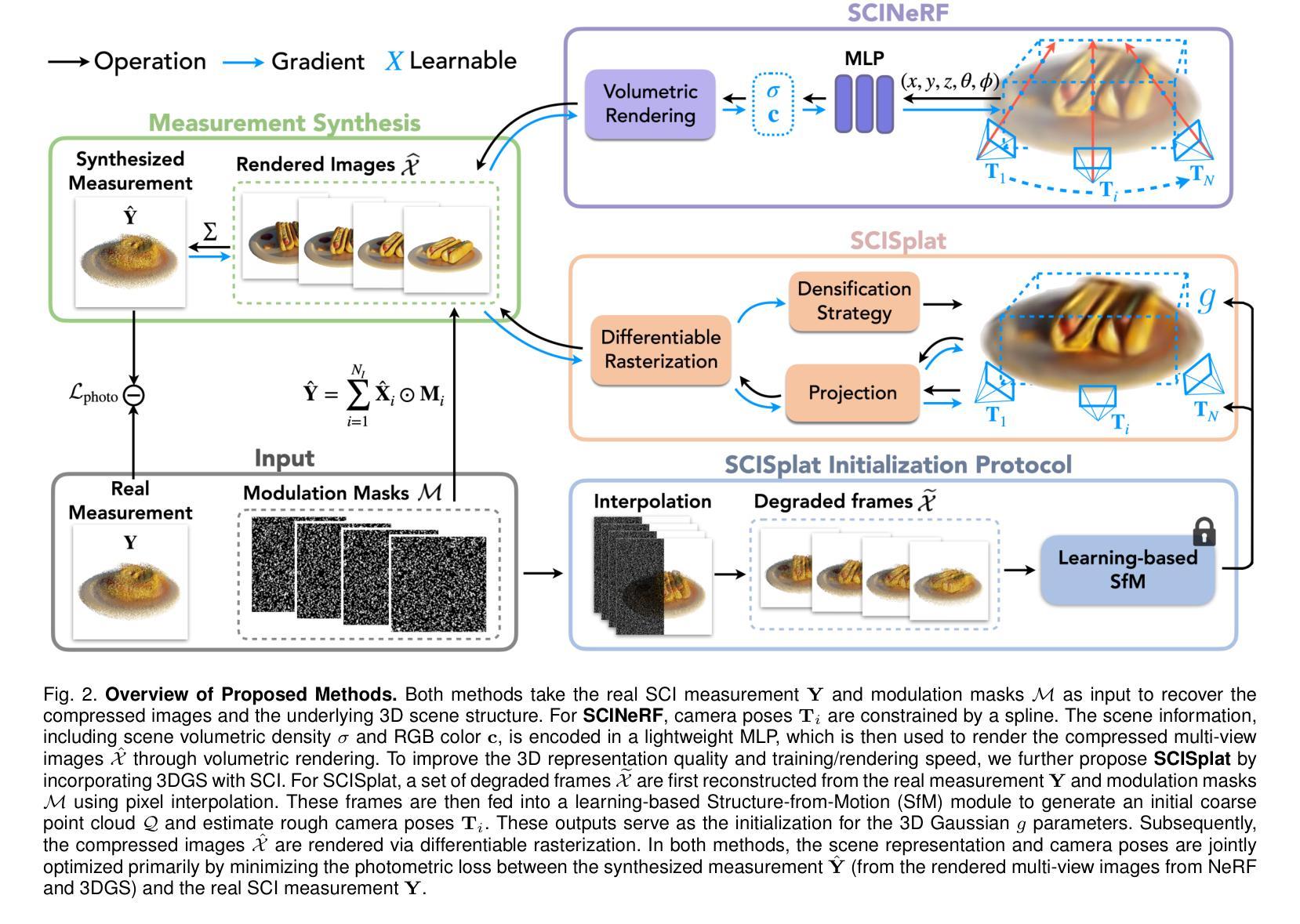
Learning Radiance Fields from a Single Snapshot Compressive Image
Authors:Yunhao Li, Xiang Liu, Xiaodong Wang, Xin Yuan, Peidong Liu
In this paper, we explore the potential of Snapshot Compressive Imaging (SCI) technique for recovering the underlying 3D scene structure from a single temporal compressed image. SCI is a cost-effective method that enables the recording of high-dimensional data, such as hyperspectral or temporal information, into a single image using low-cost 2D imaging sensors. To achieve this, a series of specially designed 2D masks are usually employed, reducing storage and transmission requirements and offering potential privacy protection. Inspired by this, we take one step further to recover the encoded 3D scene information leveraging powerful 3D scene representation capabilities of neural radiance fields (NeRF). Specifically, we propose SCINeRF, in which we formulate the physical imaging process of SCI as part of the training of NeRF, allowing us to exploit its impressive performance in capturing complex scene structures. In addition, we further integrate the popular 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) framework and propose SCISplat to improve 3D scene reconstruction quality and training/rendering speed by explicitly optimizing point clouds into 3D Gaussian representations. To assess the effectiveness of our method, we conduct extensive evaluations using both synthetic data and real data captured by our SCI system. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed approach surpasses the state-of-the-art methods in terms of image reconstruction and novel view synthesis. Moreover, our method also exhibits the ability to render high frame-rate multi-view consistent images in real time by leveraging SCI and the rendering capabilities of 3DGS. Codes will be available at: https://github.com/WU- CVGL/SCISplat.
本文探讨了Snapshot Compressive Imaging(SCI)技术在从单个时间压缩图像中恢复潜在的3D场景结构方面的潜力。SCI是一种经济高效的方法,能够将高维数据(如超光谱或时间信息)使用低成本2D成像传感器记录为单个图像。为实现这一点,通常使用一系列专门设计的2D掩膜,以降低存储和传输要求,并提供潜在的隐私保护。在此基础上,我们进一步利用神经辐射场(NeRF)强大的3D场景表示能力,恢复编码的3D场景信息。具体来说,我们提出了SCINeRF,将SCI的物理成像过程作为NeRF训练的一部分,从而充分利用其在捕捉复杂场景结构方面的卓越性能。此外,我们进一步集成了流行的3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)框架,并提出了SCISplat,通过显式优化点云到3D高斯表示,提高3D场景重建质量以及训练和渲染速度。为了评估我们方法的有效性,我们使用合成数据和由我们的SCI系统捕获的真实数据进行了广泛评估。实验结果表明,我们提出的方法在图像重建和新颖视图合成方面超越了最先进的方法。而且,我们的方法还展示了利用SCI和3DGS的渲染能力实时呈现高帧率多视角一致图像的能力。代码将在以下网址提供:https://github.com/WU-CVGL/SCISplat。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探索了快照压缩成像(SCI)技术在从单个时间压缩图像中恢复潜在的三维场景结构方面的潜力。SCI是一种具有成本效益的方法,能够将高维数据(如光谱或时间信息)使用低成本的二维成像传感器记录为单个图像。为达到此目的,通常使用一系列专门设计的二维掩膜,以降低存储和传输要求,并提供潜在的隐私保护。受启发于此,本文进一步利用神经辐射场(NeRF)的强大三维场景表示能力来恢复编码的三维场景信息。本文提出了SCINeRF和SCISplat方法,将SCI的物理成像过程纳入NeRF的训练中,并通过显式优化点云到三维高斯表示来提高三维场景重建质量、训练和渲染速度。实验结果表明,本文提出的方法在图像重建和新颖视图合成方面超越了现有技术。此外,该方法还展示了利用SCI和3DGS的渲染能力实时呈现高帧率、多视角一致图像的能力。
Key Takeaways
- SCI技术能够从低成本2D成像传感器记录高维数据,如光谱或时间信息,为存储和传输提供了高效解决方案。
- 使用一系列专门设计的二维掩膜可以增强隐私保护。
- SCINeRF方法通过将SCI的物理成像过程纳入NeRF的训练中,提高了对复杂场景结构的捕捉能力。
- SCISplat方法通过整合3D高斯Splatting框架提高了三维场景重建质量、训练和渲染速度。
- 该方法在图像重建和新颖视图合成方面超越了现有技术。
- SCISplat能够实现高帧率、多视角一致图像的实时渲染。
点此查看论文截图