⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-02 更新
SM3Det: A Unified Model for Multi-Modal Remote Sensing Object Detection
Authors:Yuxuan Li, Xiang Li, Yunheng Li, Yicheng Zhang, Yimian Dai, Qibin Hou, Ming-Ming Cheng, Jian Yang
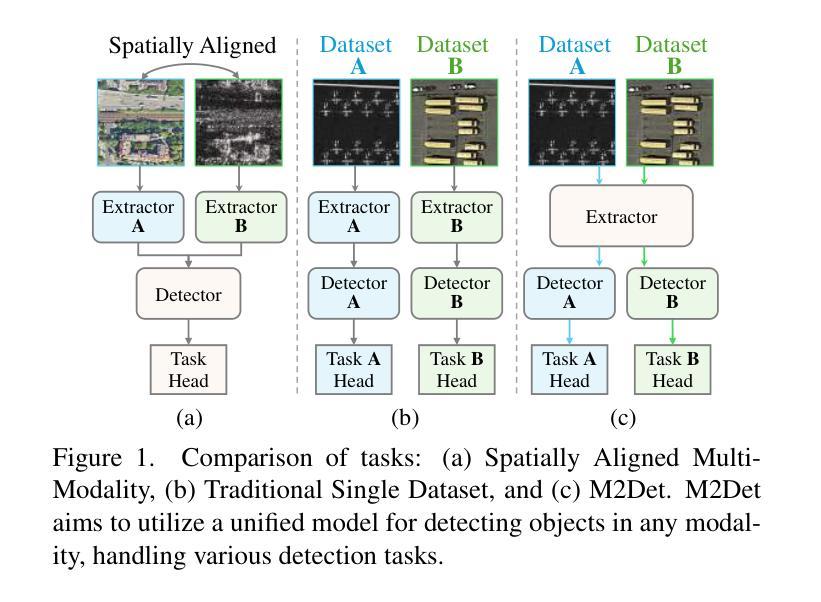
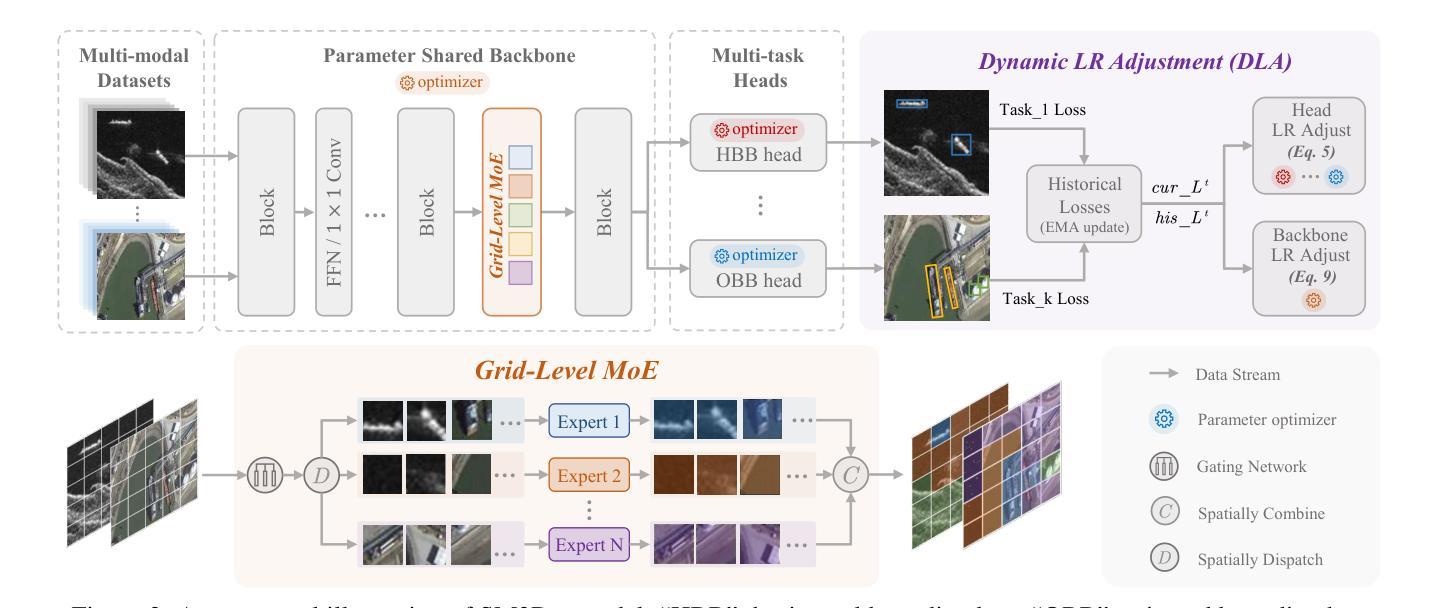
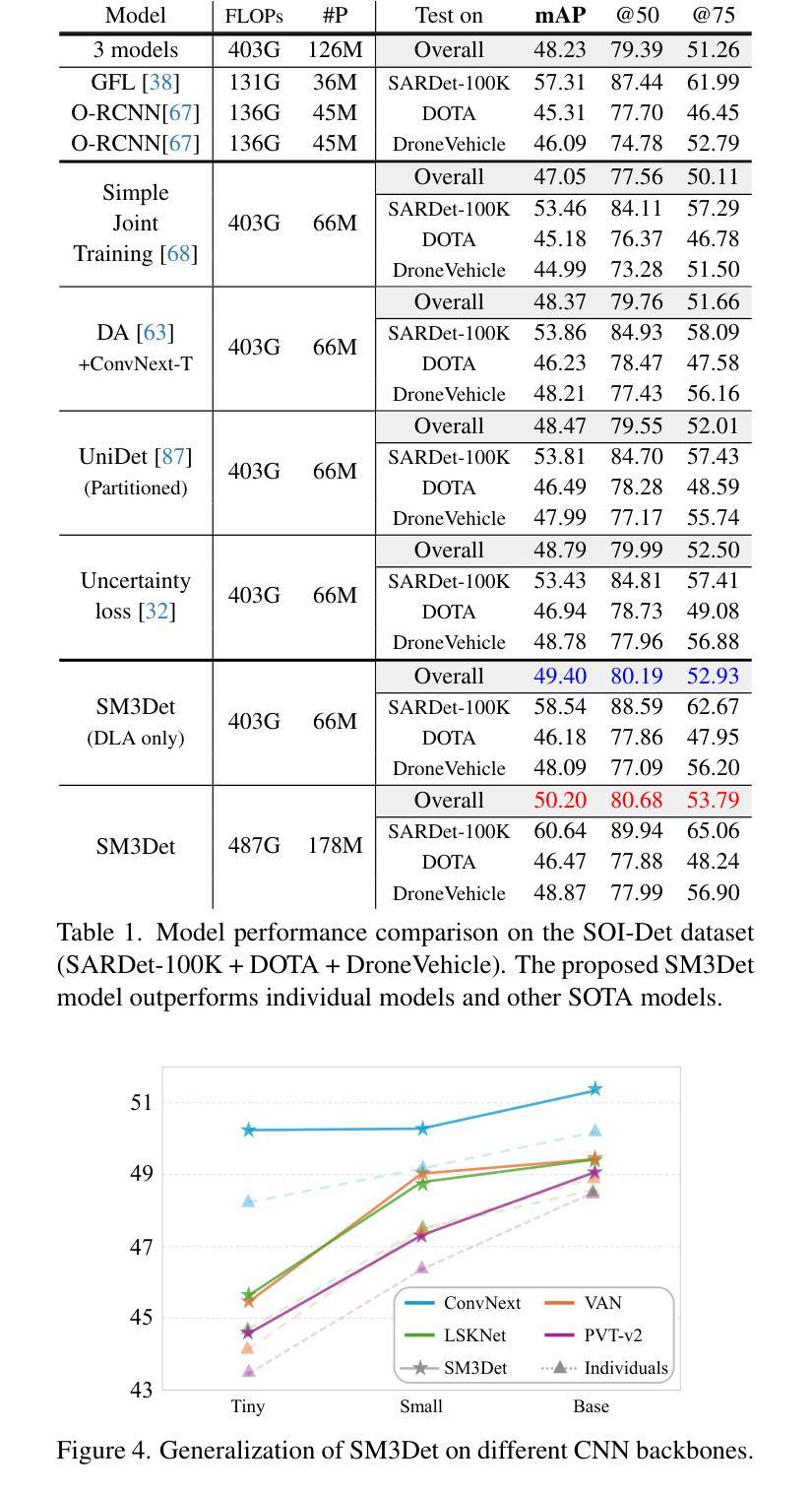
With the rapid advancement of remote sensing technology, high-resolution multi-modal imagery is now more widely accessible. Conventional Object detection models are trained on a single dataset, often restricted to a specific imaging modality and annotation format. However, such an approach overlooks the valuable shared knowledge across multi-modalities and limits the model’s applicability in more versatile scenarios. This paper introduces a new task called Multi-Modal Datasets and Multi-Task Object Detection (M2Det) for remote sensing, designed to accurately detect horizontal or oriented objects from any sensor modality. This task poses challenges due to 1) the trade-offs involved in managing multi-modal modelling and 2) the complexities of multi-task optimization. To address these, we establish a benchmark dataset and propose a unified model, SM3Det (Single Model for Multi-Modal datasets and Multi-Task object Detection). SM3Det leverages a grid-level sparse MoE backbone to enable joint knowledge learning while preserving distinct feature representations for different modalities. Furthermore, it integrates a consistency and synchronization optimization strategy using dynamic learning rate adjustment, allowing it to effectively handle varying levels of learning difficulty across modalities and tasks. Extensive experiments demonstrate SM3Det’s effectiveness and generalizability, consistently outperforming specialized models on individual datasets. The code is available at https://github.com/zcablii/SM3Det.
随着遥感技术的快速发展,高分辨率多模态图像现在更加普及。传统的目标检测模型是在单一数据集上进行训练的,通常局限于特定的成像方式和注释格式。然而,这种方法忽略了多模态之间宝贵的共享知识,并限制了模型在更通用场景中的应用。本文介绍了一个针对遥感的新任务,称为多模态数据集和多任务目标检测(M2Det)。此任务旨在准确检测来自任何传感器模态的水平或定向目标。此任务面临着两个挑战:1)涉及多模态建模的权衡问题;2 2)多任务优化的复杂性。为了应对这些挑战,我们建立了一个基准数据集并提出了一种统一模型SM3Det(多模态数据集和多任务目标检测的单模型)。SM3Det利用网格级稀疏MoE骨干网实现联合知识学习,同时保留不同模态的不同特征表示。此外,它采用动态学习率调整的一致性同步优化策略,能够有效处理不同模态和任务之间不同等级的学习难度。大量实验证明了SM3Det的有效性和通用性,在单个数据集上的表现均优于专业模型。相关代码可通过以下网址获取:https://github.com/zcablii/SM3Det。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着遥感技术的快速发展,高分辨率多模态图像现在更加易于获取。常规目标检测模型通常仅在单一数据集上进行训练,受限于特定的成像方式和注释格式。然而,这种方法忽略了多模态之间的共享知识,并限制了模型在更通用场景中的应用。本文介绍了遥感中的多模态数据集多任务目标检测(M2Det)新任务,旨在从任何传感器模态准确检测水平或定向目标。该任务面临管理多模态建模和多任务优化的权衡问题。为应对这些挑战,我们建立了一个基准数据集并提出了一种统一模型SM3Det。SM3Det利用网格级稀疏MoE主干实现联合知识学习,同时保留不同模态的独特特征表示。此外,它采用一致性同步优化策略及动态学习率调整,有效处理不同模态和任务的学习难度差异。实验证明SM3Det的有效性和通用性,在个别数据集上表现优于专业模型。相关代码可在链接找到。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感技术快速发展,高分辨率多模态图像广泛可获取。
- 常规目标检测模型通常在单一数据集上训练,限制其在多模态和更通用场景中的应用。
- 引入新的任务——多模态数据集多任务目标检测(M2Det),旨在从任何传感器模态准确检测目标。
- M2Det面临管理多模态建模和多任务优化的挑战。
- 提出SM3Det模型,利用网格级稀疏MoE主干实现联合知识学习,同时保留不同模态的独特特征表示。
- SM3Det采用一致性同步优化策略及动态学习率调整,以处理不同模态和任务的学习难度差异。
点此查看论文截图

YOLO-UniOW: Efficient Universal Open-World Object Detection
Authors:Lihao Liu, Juexiao Feng, Hui Chen, Ao Wang, Lin Song, Jungong Han, Guiguang Ding
Traditional object detection models are constrained by the limitations of closed-set datasets, detecting only categories encountered during training. While multimodal models have extended category recognition by aligning text and image modalities, they introduce significant inference overhead due to cross-modality fusion and still remain restricted by predefined vocabulary, leaving them ineffective at handling unknown objects in open-world scenarios. In this work, we introduce Universal Open-World Object Detection (Uni-OWD), a new paradigm that unifies open-vocabulary and open-world object detection tasks. To address the challenges of this setting, we propose YOLO-UniOW, a novel model that advances the boundaries of efficiency, versatility, and performance. YOLO-UniOW incorporates Adaptive Decision Learning to replace computationally expensive cross-modality fusion with lightweight alignment in the CLIP latent space, achieving efficient detection without compromising generalization. Additionally, we design a Wildcard Learning strategy that detects out-of-distribution objects as “unknown” while enabling dynamic vocabulary expansion without the need for incremental learning. This design empowers YOLO-UniOW to seamlessly adapt to new categories in open-world environments. Extensive experiments validate the superiority of YOLO-UniOW, achieving achieving 34.6 AP and 30.0 APr on LVIS with an inference speed of 69.6 FPS. The model also sets benchmarks on M-OWODB, S-OWODB, and nuScenes datasets, showcasing its unmatched performance in open-world object detection. Code and models are available at https://github.com/THU-MIG/YOLO-UniOW.
传统目标检测模型受限于封闭数据集,只能检测训练时遇到的目标类别。虽然多模态模型通过文本和图像模态的对齐扩展了类别识别能力,但由于跨模态融合而引入了显著的推理开销,并且仍然受到预设词汇表的限制,无法处理开放世界场景中的未知对象。在这项工作中,我们引入了统一开放世界目标检测(Uni-OWD)这一新范式,将开放词汇表和开放世界目标检测任务统一起来。为了应对这一设置中的挑战,我们提出了YOLO-UniOW这一新型模型,在效率、通用性和性能上推进了边界。YOLO-UniOW结合了自适应决策学习,用轻量级的对齐替换计算昂贵的跨模态融合,在CLIP潜在空间中实现高效检测而不损害泛化能力。此外,我们还设计了Wildcard学习策略,能够检测分布外的对象并将其标记为“未知”,同时实现动态词汇扩展而无需增量学习。这一设计使YOLO-UniOW能够轻松适应开放世界环境中的新类别。大量实验验证了YOLO-UniOW的优越性,在LVIS上实现了34.6的AP和30.0的APr,推理速度为每秒69.6帧。该模型还在M-OWODB、S-OWODB和nuScenes数据集上设定了基准测试,展示了其在开放世界目标检测中的卓越性能。相关代码和模型可通过https://github.com/THU-MIG/YOLO-UniOW获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
传统目标检测模型受限于封闭数据集,只能检测训练时遇到的目标类别。多模态模型通过文本和图像模态的对齐扩展了类别识别能力,但引入了由于跨模态融合造成的推理开销,并且仍然受限于预设词汇表,无法处理开放世界场景中的未知对象。本文提出统一开放词汇和开放世界目标检测任务的新范式——通用开放世界目标检测(Uni-OWD)。针对此设置,我们提出了YOLO-UniOW模型,该模型在效率、通用性和性能方面取得了突破。YOLO-UniOW采用自适应决策学习,以轻量级对齐替换计算昂贵的跨模态融合,在CLIP潜在空间中实现高效检测而不影响泛化。此外,我们设计了Wildcard学习策略,能够检测异常对象并将其标记为“未知”,同时实现无需增量学习的动态词汇扩展。这使得YOLO-UniOW能够轻松适应开放环境中的新类别。经过广泛实验验证,YOLO-UniOW在LVIS数据集上取得了34.6的AP和30.0的APr,推理速度为69.6 FPS。该模型还在M-OWODB、S-OWODB和nuScenes数据集上设定了基准,展示了其在开放世界目标检测中的卓越性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 传统目标检测模型受限于封闭数据集,难以应对开放世界中的未知对象。
- YOLO-UniOW模型通过结合自适应决策学习和Wildcard学习策略,实现了开放词汇和开放世界目标检测的统一。
- YOLO-UniOW采用轻量级对齐方式,在CLIP潜在空间中实现高效检测。
- Wildcard学习策略能检测异常对象并标记为“未知”,同时实现动态词汇扩展。
- YOLO-UniOW在多个数据集上实现了卓越性能,包括LVIS、M-OWODB、S-OWODB和nuScenes。
- YOLO-UniOW模型具有高效的推理速度,达到69.6 FPS。
点此查看论文截图
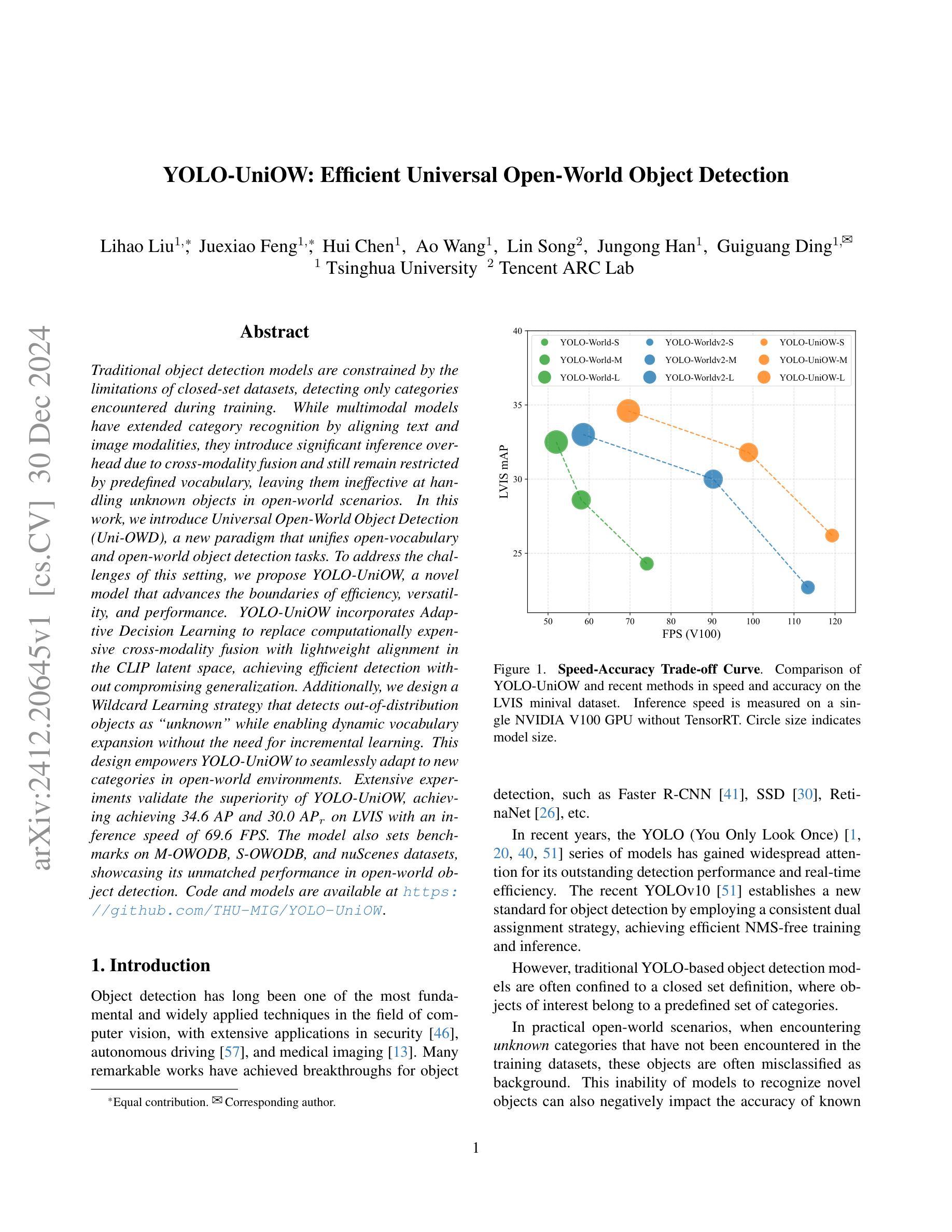
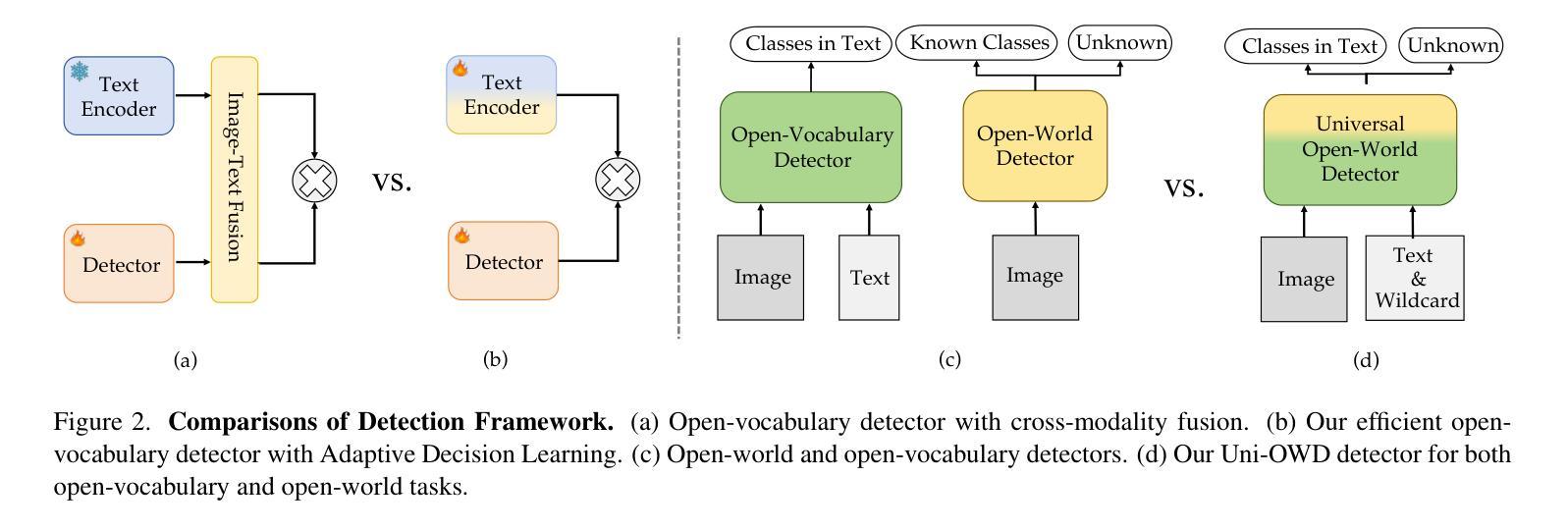
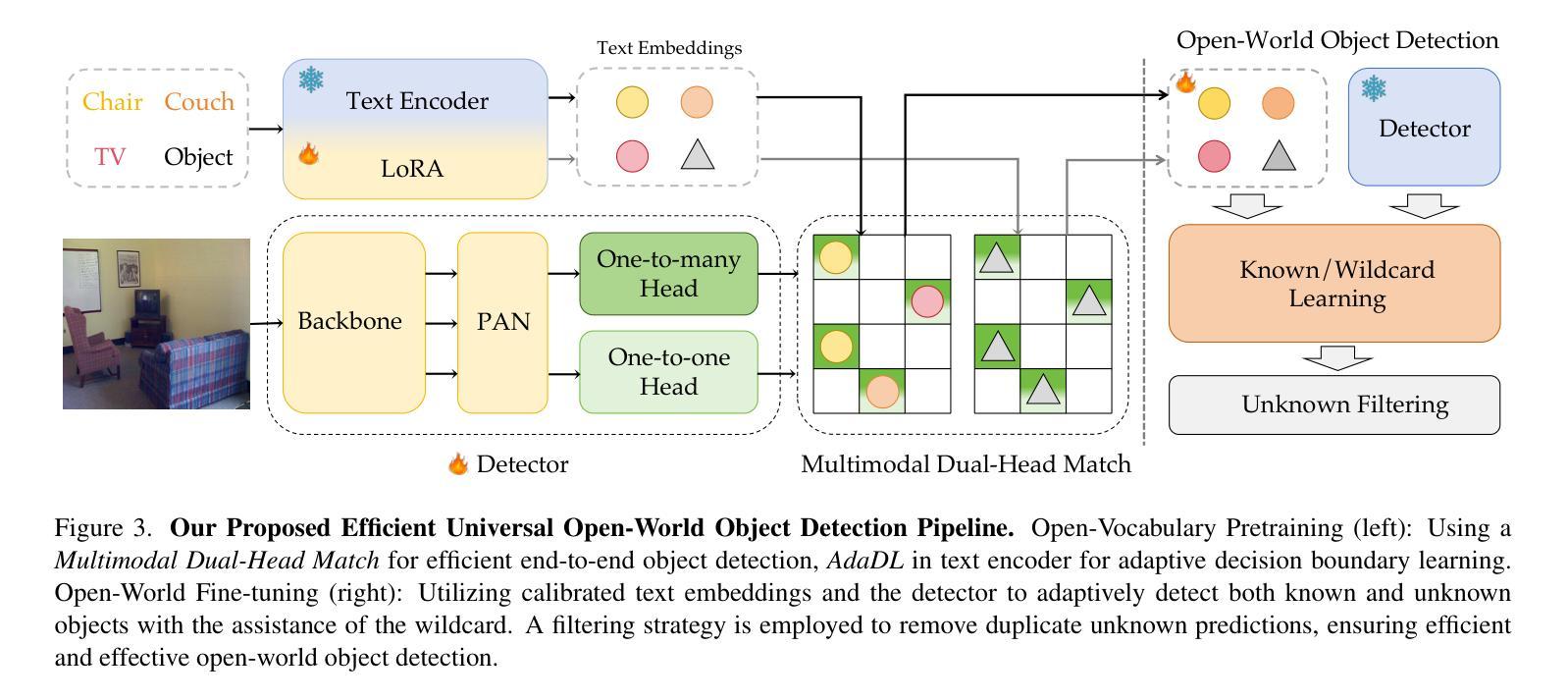
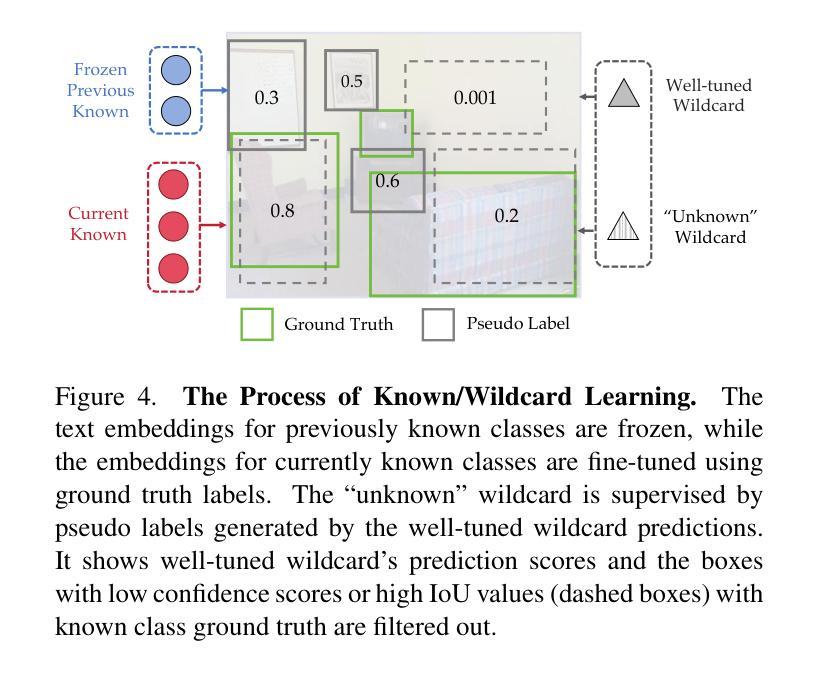
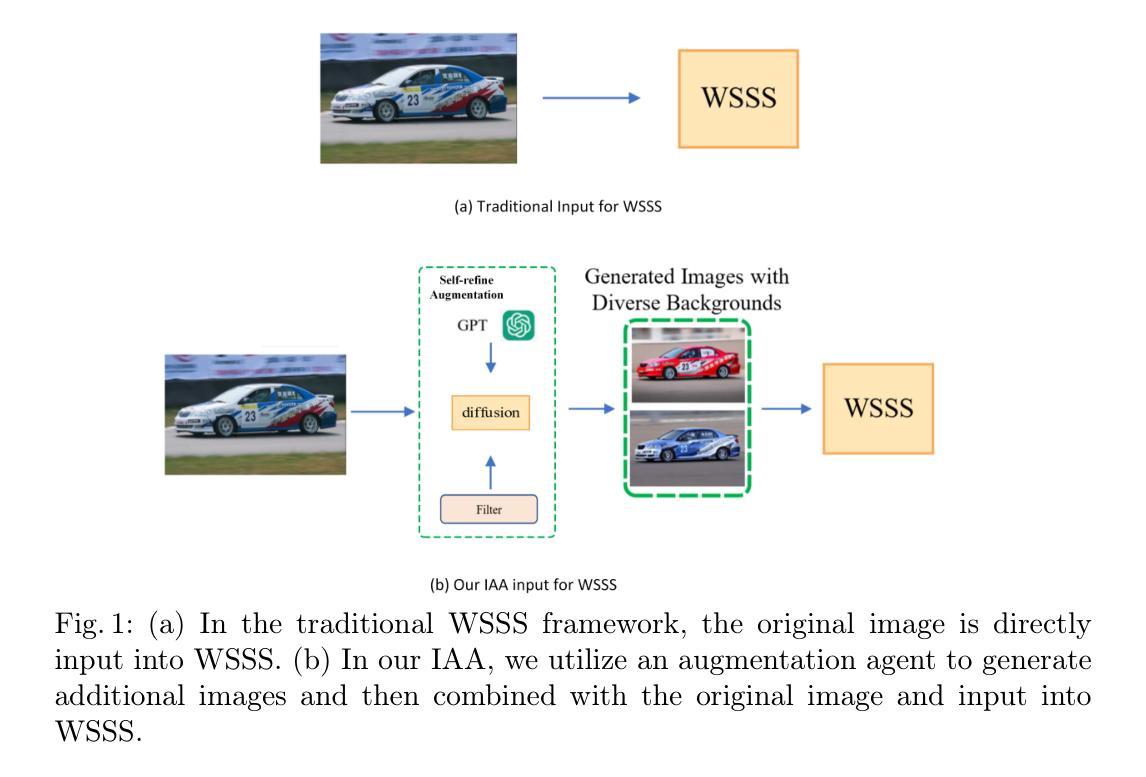
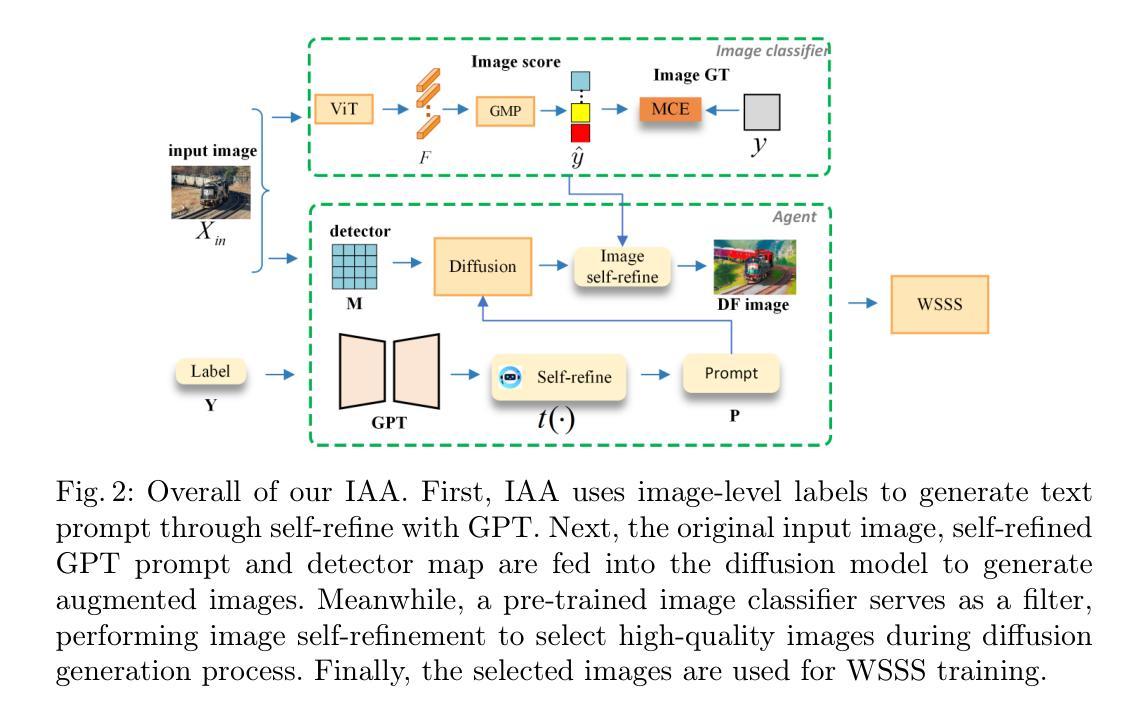
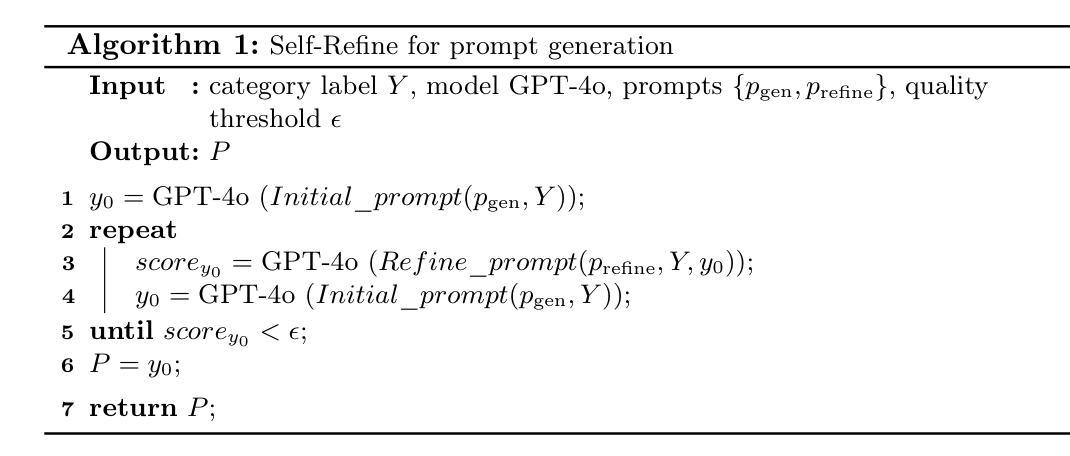
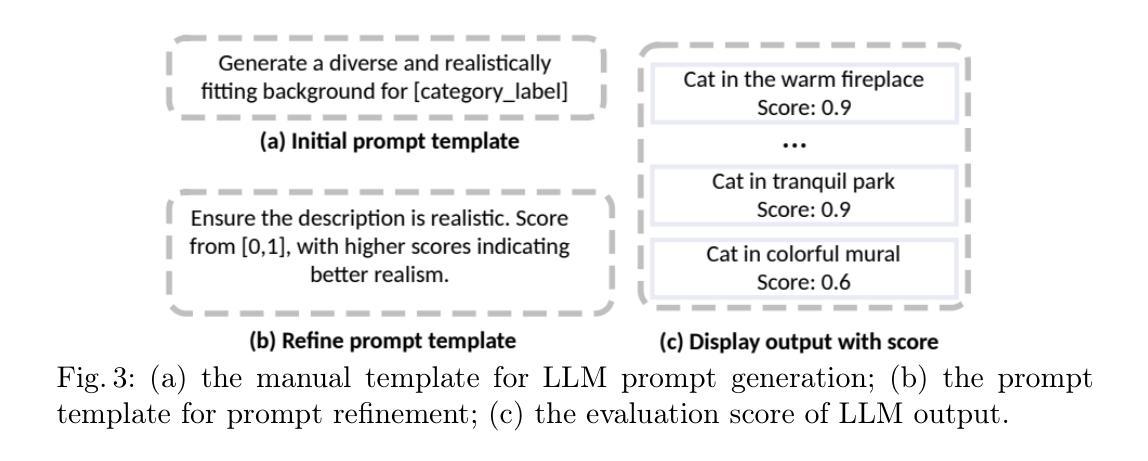
Image Augmentation Agent for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Wangyu Wu, Xianglin Qiu, Siqi Song, Zhenhong Chen, Xiaowei Huang, Fei Ma, Jimin Xiao
Weakly-supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) has achieved remarkable progress using only image-level labels. However, most existing WSSS methods focus on designing new network structures and loss functions to generate more accurate dense labels, overlooking the limitations imposed by fixed datasets, which can constrain performance improvements. We argue that more diverse trainable images provides WSSS richer information and help model understand more comprehensive semantic pattern. Therefore in this paper, we introduce a novel approach called Image Augmentation Agent (IAA) which shows that it is possible to enhance WSSS from data generation perspective. IAA mainly design an augmentation agent that leverages large language models (LLMs) and diffusion models to automatically generate additional images for WSSS. In practice, to address the instability in prompt generation by LLMs, we develop a prompt self-refinement mechanism. It allow LLMs to re-evaluate the rationality of generated prompts to produce more coherent prompts. Additionally, we insert an online filter into diffusion generation process to dynamically ensure the quality and balance of generated images. Experimental results show that our method significantly surpasses state-of-the-art WSSS approaches on the PASCAL VOC 2012 and MS COCO 2014 datasets.
弱监督语义分割(WSSS)仅使用图像级标签取得了显著的进步。然而,大多数现有的WSSS方法主要关注设计新的网络结构和损失函数来生成更精确的密集标签,而忽视了固定数据集所带来的限制,这些限制可能会限制性能的提升。我们认为,提供更多可训练图像的多样性可以为WSSS提供更丰富的信息,并帮助模型理解更全面的语义模式。因此,在本文中,我们介绍了一种新方法,称为图像增强代理(IAA),它表明从数据生成的角度增强WSSS是可能的。IAA主要设计了一个增强代理,它利用大型语言模型(LLM)和扩散模型来自动为WSSS生成额外的图像。在实践中,为了解决LLM在提示生成中的不稳定性问题,我们开发了一种提示自我优化机制。它允许LLM重新评估生成的提示的合理性,以产生更连贯的提示。此外,我们在扩散生成过程中插入了一个在线过滤器,以动态确保生成图像的质量和平衡。实验结果表明,我们的方法在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上显著超越了最先进的WSSS方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为Image Augmentation Agent(IAA)的方法,从数据生成的角度提升弱监督语义分割(WSSS)性能。通过利用大型语言模型(LLMs)和扩散模型自动生成额外图像,增强WSSS的训练图像多样性。提出一种提示自我完善机制,确保生成的提示更加合理和连贯。在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法显著超越了现有WSSS方法。
Key Takeaways
- IAA方法从数据生成角度提升弱监督语义分割性能。
- 利用大型语言模型(LLMs)和扩散模型自动生成额外图像,增加训练图像多样性。
- 提出一种提示自我完善机制,解决语言模型提示生成的不稳定问题。
- 在在线过滤中确保生成图像的质量和平衡。
- 方法在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上表现优异。
- 突破现有WSSS方法的局限,不仅仅关注网络结构和损失函数设计。
点此查看论文截图

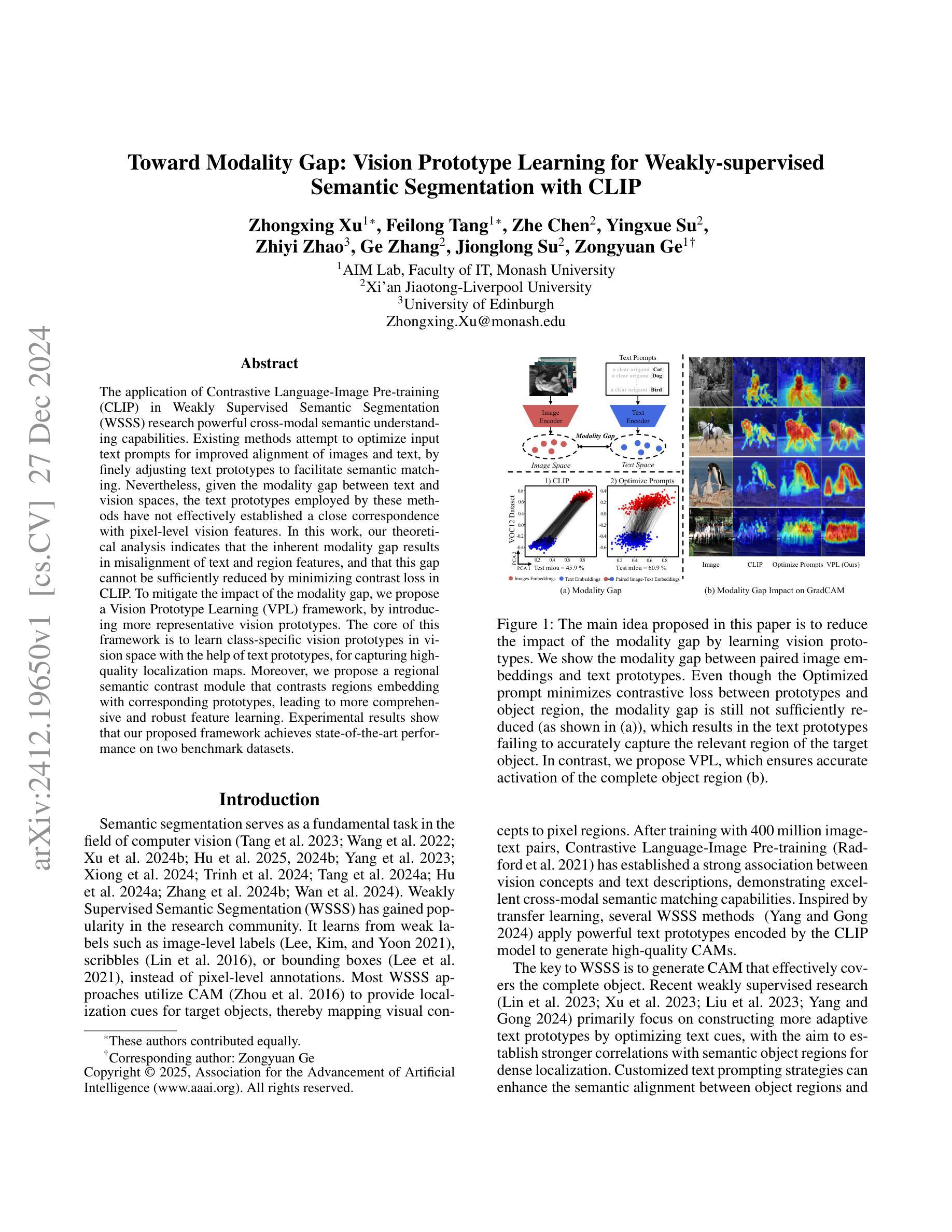
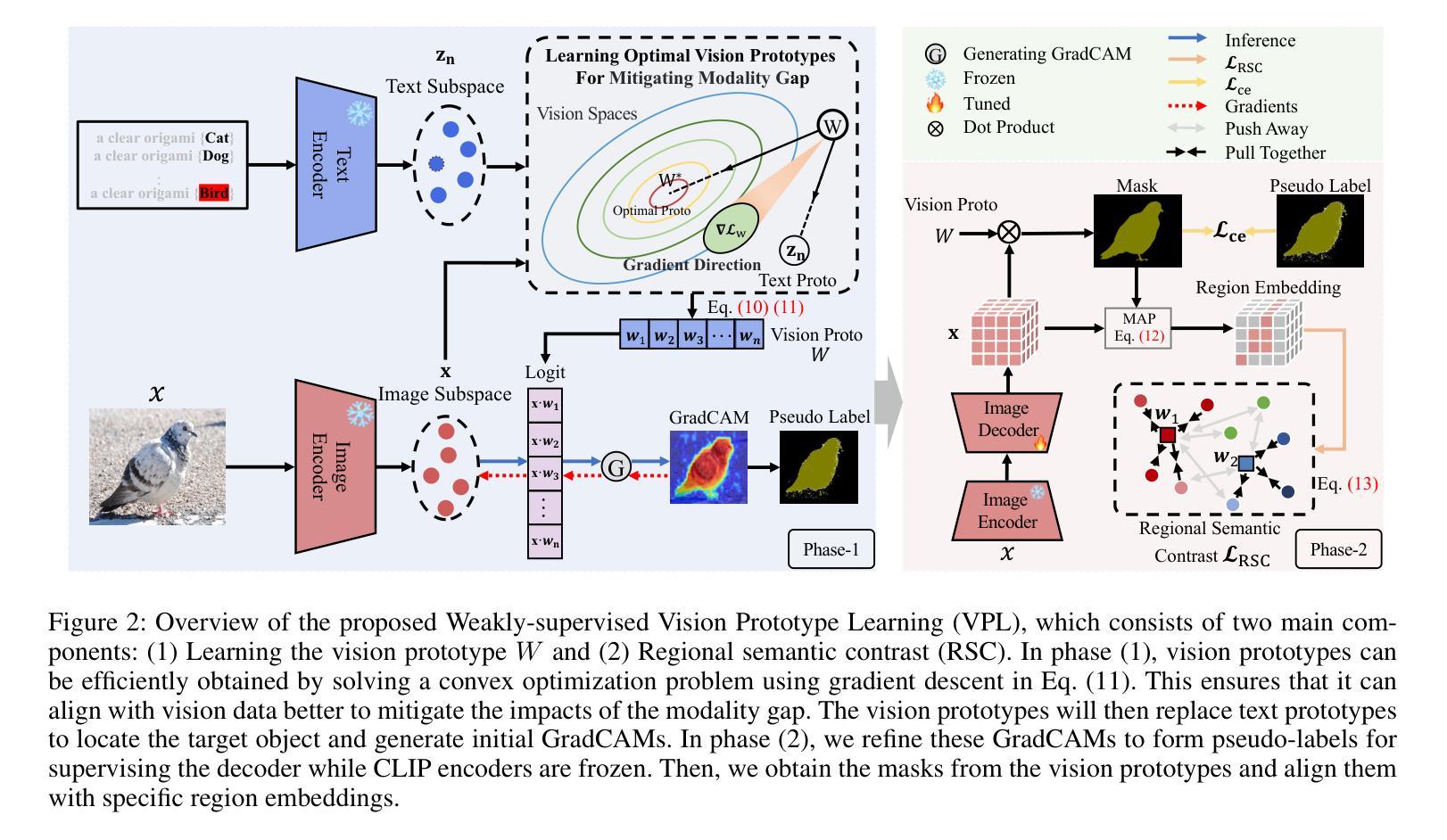
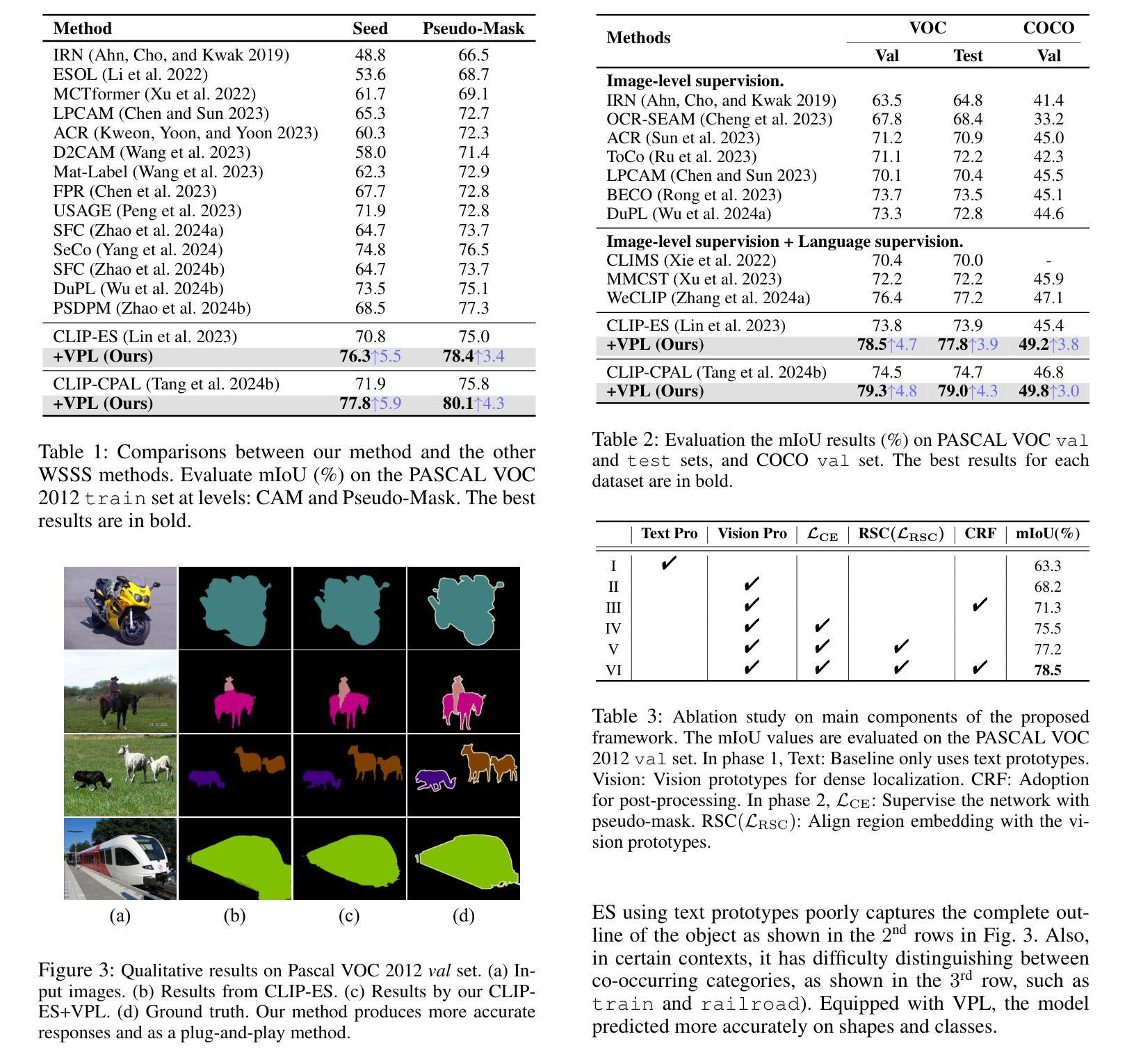
Toward Modality Gap: Vision Prototype Learning for Weakly-supervised Semantic Segmentation with CLIP
Authors:Zhongxing Xu, Feilong Tang, Zhe Chen, Yingxue Su, Zhiyi Zhao, Ge Zhang, Jionglong Su, Zongyuan Ge
The application of Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) in Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation (WSSS) research powerful cross-modal semantic understanding capabilities. Existing methods attempt to optimize input text prompts for improved alignment of images and text, by finely adjusting text prototypes to facilitate semantic matching. Nevertheless, given the modality gap between text and vision spaces, the text prototypes employed by these methods have not effectively established a close correspondence with pixel-level vision features. In this work, our theoretical analysis indicates that the inherent modality gap results in misalignment of text and region features, and that this gap cannot be sufficiently reduced by minimizing contrast loss in CLIP. To mitigate the impact of the modality gap, we propose a Vision Prototype Learning (VPL) framework, by introducing more representative vision prototypes. The core of this framework is to learn class-specific vision prototypes in vision space with the help of text prototypes, for capturing high-quality localization maps. Moreover, we propose a regional semantic contrast module that contrasts regions embedding with corresponding prototypes, leading to more comprehensive and robust feature learning. Experimental results show that our proposed framework achieves state-of-the-art performance on two benchmark datasets.
对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)在弱监督语义分割(WSSS)研究中的应用展现了强大的跨模态语义理解功能。现有方法试图优化输入文本提示,以改进图像和文本的对齐方式,通过微调文本原型来促进语义匹配。然而,鉴于文本和视觉空间之间的模态差距,这些方法所采用的文本原型并未有效地与像素级视觉特征建立紧密对应关系。在我们的理论分析中,固有的模态差距会导致文本和区域特征的错位,并且仅仅通过最小化CLIP中的对比损失不足以缩小这一差距。为了减轻模态差距的影响,我们提出了视觉原型学习(VPL)框架,通过引入更具代表性的视觉原型。该框架的核心是在视觉空间的帮助下,学习特定类别的视觉原型,以捕获高质量的定位图。此外,我们提出了区域语义对比模块,该模块将区域嵌入与相应的原型进行对比,从而实现更全面和稳健的特征学习。实验结果表明,我们提出的框架在两个基准数据集上达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究应用Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training(CLIP)于Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation(WSSS)中,实现跨模态语义理解。现有方法通过微调文本提示优化图像与文本的匹配度,但模态间的差距导致文本原型未能与像素级视觉特征建立紧密对应关系。本研究提出Vision Prototype Learning(VPL)框架,引入更具代表性的视觉原型,以学习特定类别的视觉特征。同时,本研究设计了一种区域语义对比模块,该模块对比区域嵌入与对应原型的特征,实现更全面和鲁棒的特征学习。实验结果表明,该框架在两项基准测试中达到领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP在WSSS研究中的应用展示了强大的跨模态语义理解功能。
- 现有方法试图通过微调文本提示来优化图像和文本的匹配度。
- 模态差距导致文本原型未能有效地与像素级视觉特征相对应。
- 引入VPL框架以学习更具代表性的视觉原型。
- VPL框架借助文本原型在视觉空间内学习特定类别的视觉特征。
- 设计了区域语义对比模块,实现更全面和鲁棒的特征学习。
点此查看论文截图
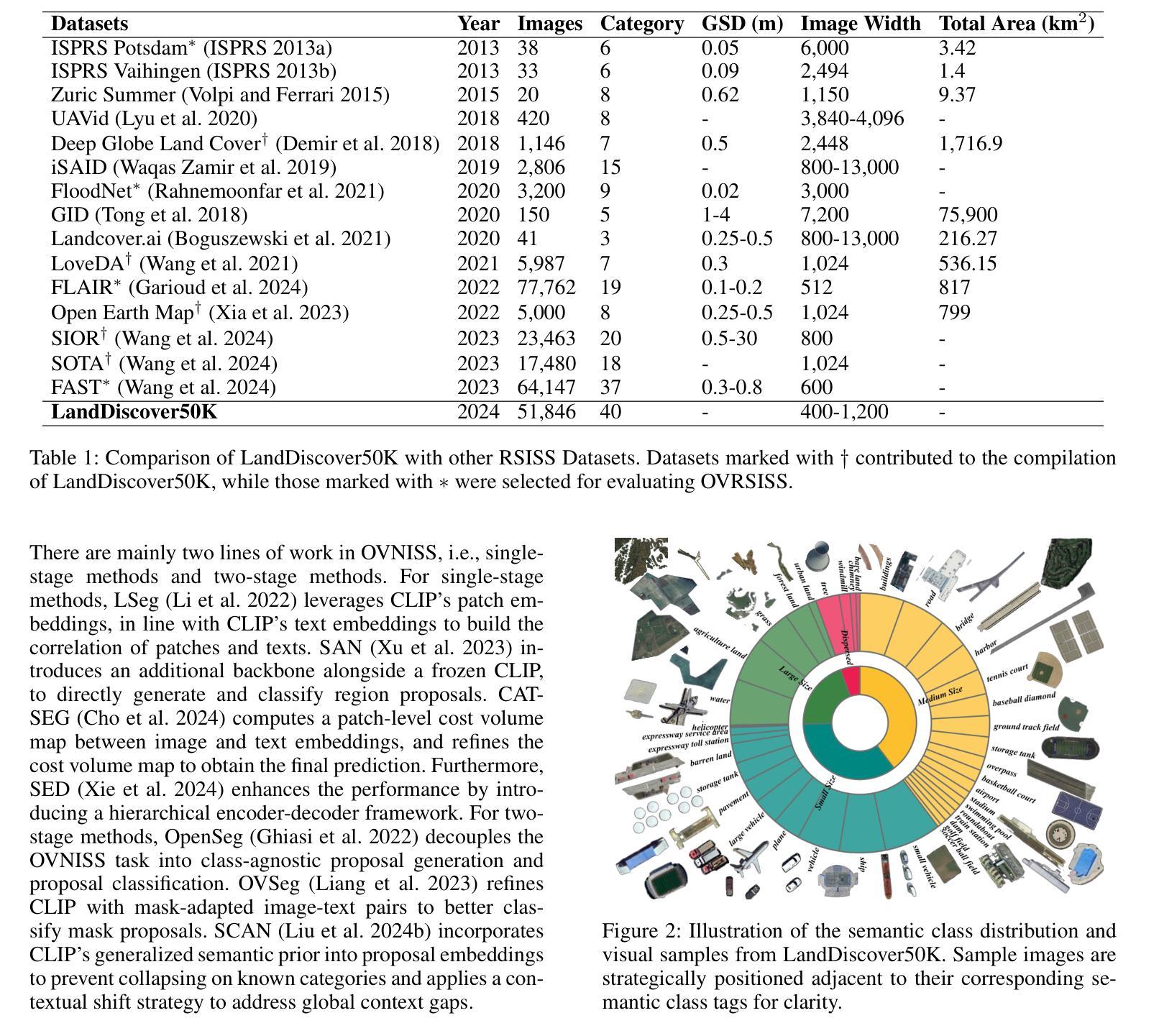
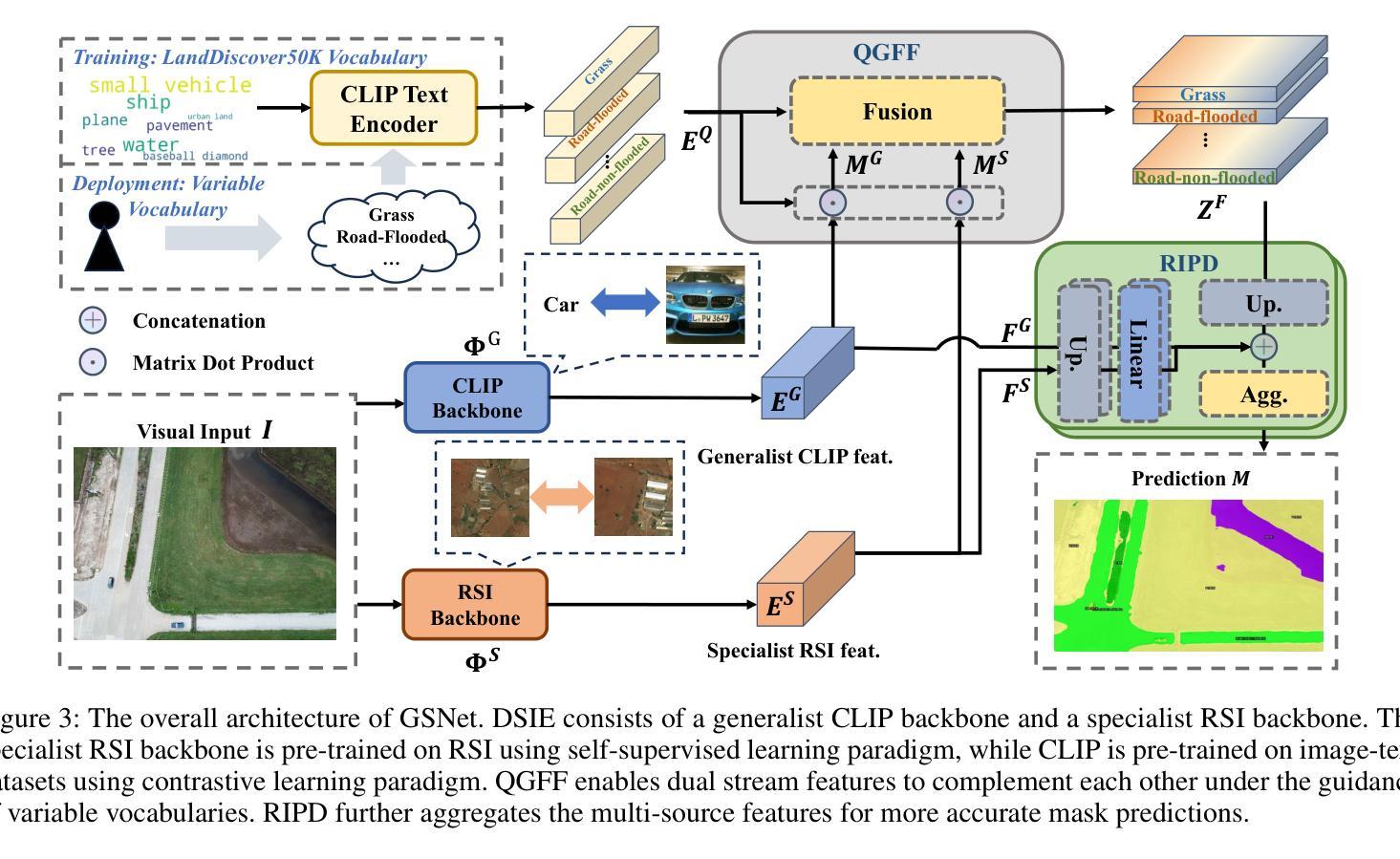
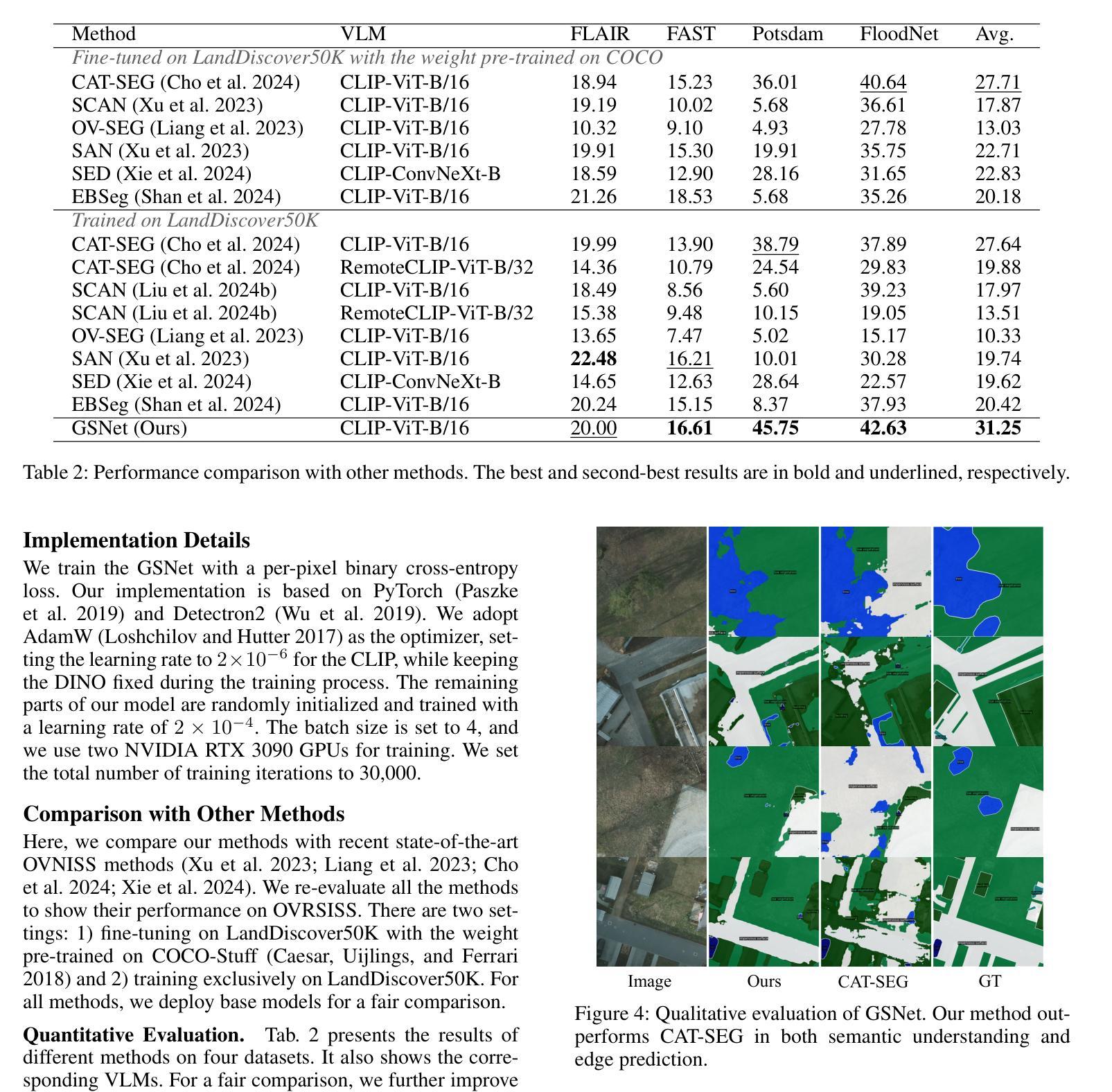
Towards Open-Vocabulary Remote Sensing Image Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Chengyang Ye, Yunzhi Zhuge, Pingping Zhang
Recently, deep learning based methods have revolutionized remote sensing image segmentation. However, these methods usually rely on a pre-defined semantic class set, thus needing additional image annotation and model training when adapting to new classes. More importantly, they are unable to segment arbitrary semantic classes. In this work, we introduce Open-Vocabulary Remote Sensing Image Semantic Segmentation (OVRSISS), which aims to segment arbitrary semantic classes in remote sensing images. To address the lack of OVRSISS datasets, we develop LandDiscover50K, a comprehensive dataset of 51,846 images covering 40 diverse semantic classes. In addition, we propose a novel framework named GSNet that integrates domain priors from special remote sensing models and versatile capabilities of general vision-language models. Technically, GSNet consists of a Dual-Stream Image Encoder (DSIE), a Query-Guided Feature Fusion (QGFF), and a Residual Information Preservation Decoder (RIPD). DSIE first captures comprehensive features from both special models and general models in dual streams. Then, with the guidance of variable vocabularies, QGFF integrates specialist and generalist features, enabling them to complement each other. Finally, RIPD is proposed to aggregate multi-source features for more accurate mask predictions. Experiments show that our method outperforms other methods by a large margin, and our proposed LandDiscover50K improves the performance of OVRSISS methods. The proposed dataset and method will be made publicly available at https://github.com/yecy749/GSNet.
最近,基于深度学习的方法在遥感图像分割领域掀起了革命性的变革。然而,这些方法通常依赖于预先定义的语义类别集,因此在适应新类别时需要额外的图像标注和模型训练。更重要的是,它们无法对任意语义类别进行分割。在这项工作中,我们引入了开放词汇遥感图像语义分割(OVRSISS),旨在实现对遥感图像中任意语义类别的分割。为了解决OVRSISS数据集缺乏的问题,我们开发了LandDiscover50K,这是一个包含51,846张图像的综合数据集,涵盖了40个多样化的语义类别。此外,我们提出了一种新的框架GSNet,它融合了特殊遥感模型的领域先验知识和通用视觉语言模型的通用能力。技术上,GSNet包括双流图像编码器(DSIE)、查询引导特征融合(QGFF)和残差信息保留解码器(RIPD)。首先,DSIE从特殊模型和一般模型的双流中捕获全面的特征。然后,在可变词汇表的指导下,QGFF融合了专业特征和通用特征,使它们能够相互补充。最后,RIPD被提出来聚合多源特征,以进行更准确的掩膜预测。实验表明,我们的方法在其他方法的基础上取得了很大的优势,我们提出的LandDiscover50K也提高了OVRSISS方法的性能。该数据集和方法将在https://github.com/yecy749/GSNet上公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI2025
Summary:近期深度学习在遥感图像分割领域引发革命。然而,现有方法受限于预定义语义类别集,难以适应新类别。本文提出开放词汇遥感图像语义分割(OVRSISS),旨在实现对遥感图像中的任意语义类别进行分割。为应对OVRSISS数据集缺乏的问题,本文开发了LandDiscover50K数据集。此外,提出了一种名为GSNet的新框架,融合了特殊遥感模型的领域先验知识和通用视觉语言模型的通用能力。实验表明,该方法大幅优于其他方法,LandDiscover50K数据集提高了OVRSISS方法的性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 深度学习在遥感图像分割中取得显著进展。
- 现有方法受限于预定义语义类别,需额外图像标注和模型训练以适应新类别。
- 提出开放词汇遥感图像语义分割(OVRSISS)以分割任意语义类别。
- 开发LandDiscover50K数据集,包含51,846张图像,覆盖40个多样语义类别。
- 提出GSNet框架,融合特殊遥感模型和通用视觉语言模型的优点。
- GSNet包括双流图像编码器(DSIE)、查询引导特征融合(QGFF)和残差信息保留解码器(RIPD)。
点此查看论文截图

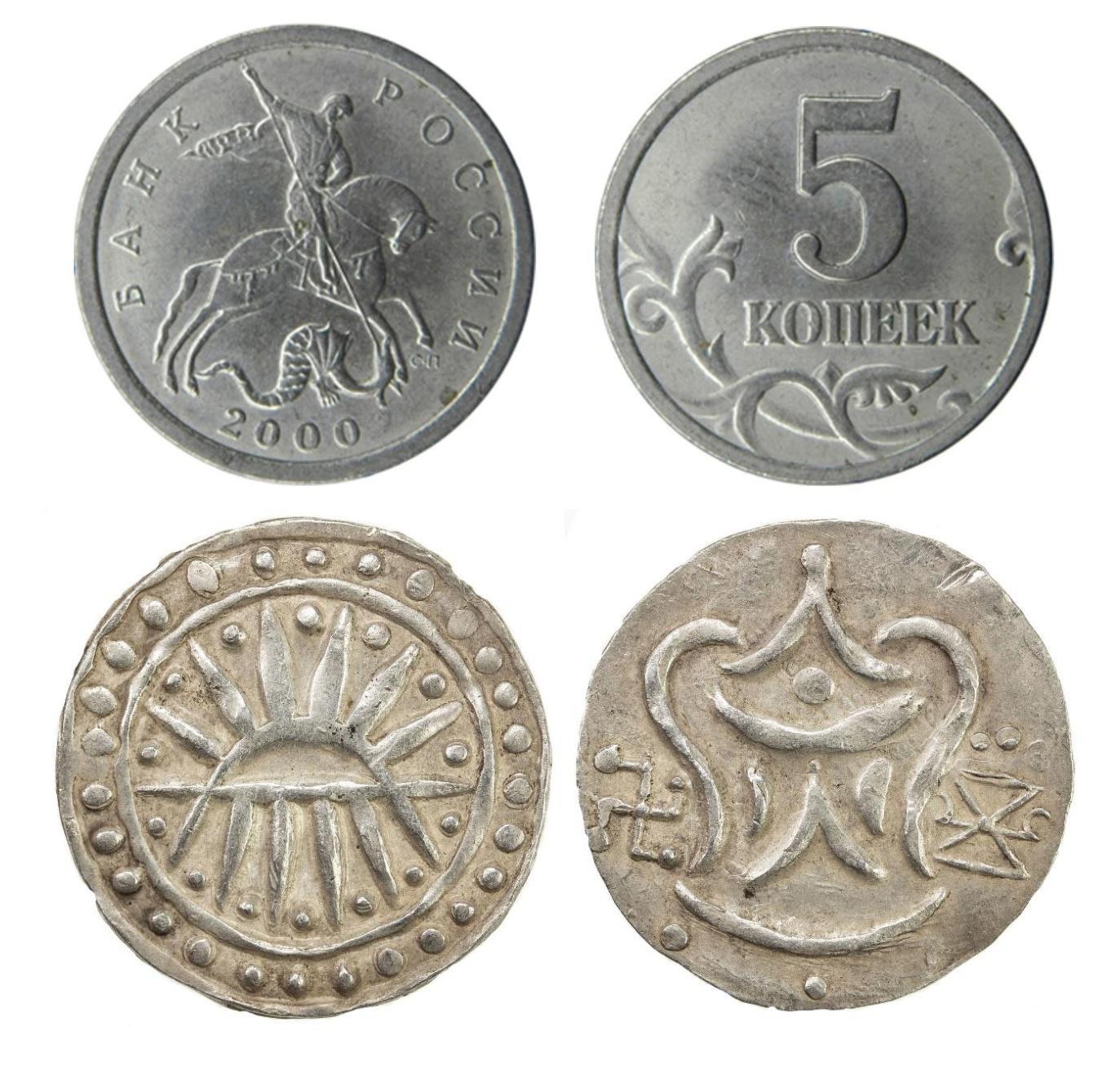
From Coin to Data: The Impact of Object Detection on Digital Numismatics
Authors:Rafael Cabral, Maria De Iorio, Andrew Harris
In this work we investigate the application of advanced object detection techniques to digital numismatics, focussing on the analysis of historical coins. Leveraging models such as Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP), we develop a flexible framework for identifying and classifying specific coin features using both image and textual descriptions. By examining two distinct datasets, modern Russian coins featuring intricate “Saint George and the Dragon” designs and degraded 1st millennium AD Southeast Asian coins bearing Hindu-Buddhist symbols, we evaluate the efficacy of different detection algorithms in search and classification tasks. Our results demonstrate the superior performance of larger CLIP models in detecting complex imagery, while traditional methods excel in identifying simple geometric patterns. Additionally, we propose a statistical calibration mechanism to enhance the reliability of similarity scores in low-quality datasets. This work highlights the transformative potential of integrating state-of-the-art object detection into digital numismatics, enabling more scalable, precise, and efficient analysis of historical artifacts. These advancements pave the way for new methodologies in cultural heritage research, artefact provenance studies, and the detection of forgeries.
在这项工作中,我们研究了先进的目标检测技术在数字钱币学中的应用,重点分析了历史硬币。我们利用诸如对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)的模型,开发了一个灵活的框架,该框架可以使用图像和文本描述来识别和分类特定的硬币特征。通过检查两个独特的数据集——具有复杂“圣乔治和龙”设计的现代俄罗斯硬币和退化的一千年前的东南亚带有印度教佛教符号的硬币,我们评估了不同检测算法在搜索和分类任务中的有效性。我们的结果表明,在检测复杂图像方面,较大的CLIP模型表现出卓越的性能,而传统方法在识别简单几何模式方面表现出色。此外,我们提出了一种统计校准机制,以提高低质量数据集中相似性评分的可靠性。这项工作强调了将最新目标检测技术集成到数字钱币学中所带来的变革性潜力,能够实现更大规模、更精确、更高效的历史文物分析。这些进步为文化遗产研究、文物原产地研究和伪造检测等领域开辟了新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了先进的目标检测技术在数字钱币学中的应用,重点分析了对历史硬币的分析。研究团队利用对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)模型,开发了一个灵活框架,能够通过图像和文本描述来识别和分类硬币特征。通过对带有复杂“圣乔治与龙”设计的现代俄罗斯硬币和带有印度教佛教符号的1世纪东南亚硬币两个数据集的研究,评估了不同检测算法在搜索和分类任务中的有效性。结果显示大型CLIP模型在检测复杂图像方面表现优异,而传统方法在识别简单几何图案方面更出色。此外,研究还提出了一种统计校准机制,以提高低质量数据集中相似度评分的可靠性。该研究突显了将最新目标检测技术融入数字钱币学的潜力,为更规模化、精确和高效的历史文物分析打开了新途径,并为文化遗产研究、文物溯源研究和伪造检测提供了新的方法论。
Key Takeaways
- 研究将先进的目标检测技术应用于数字钱币学,专注于历史硬币的分析。
- 利用CLIP模型开发了一个灵活框架,可通过图像和文本描述进行硬币特征识别和分类。
- 通过两个不同数据集的研究,评估了不同检测算法在硬币识别和分类任务中的效能。
- 大型CLIP模型在检测复杂图像方面表现优异,而传统方法更擅长识别简单几何图案。
- 提出了一种统计校准机制,以提高低质量数据集中相似度评分的可靠性。
- 研究突显了将最新目标检测技术融入数字钱币学的潜力。
点此查看论文截图


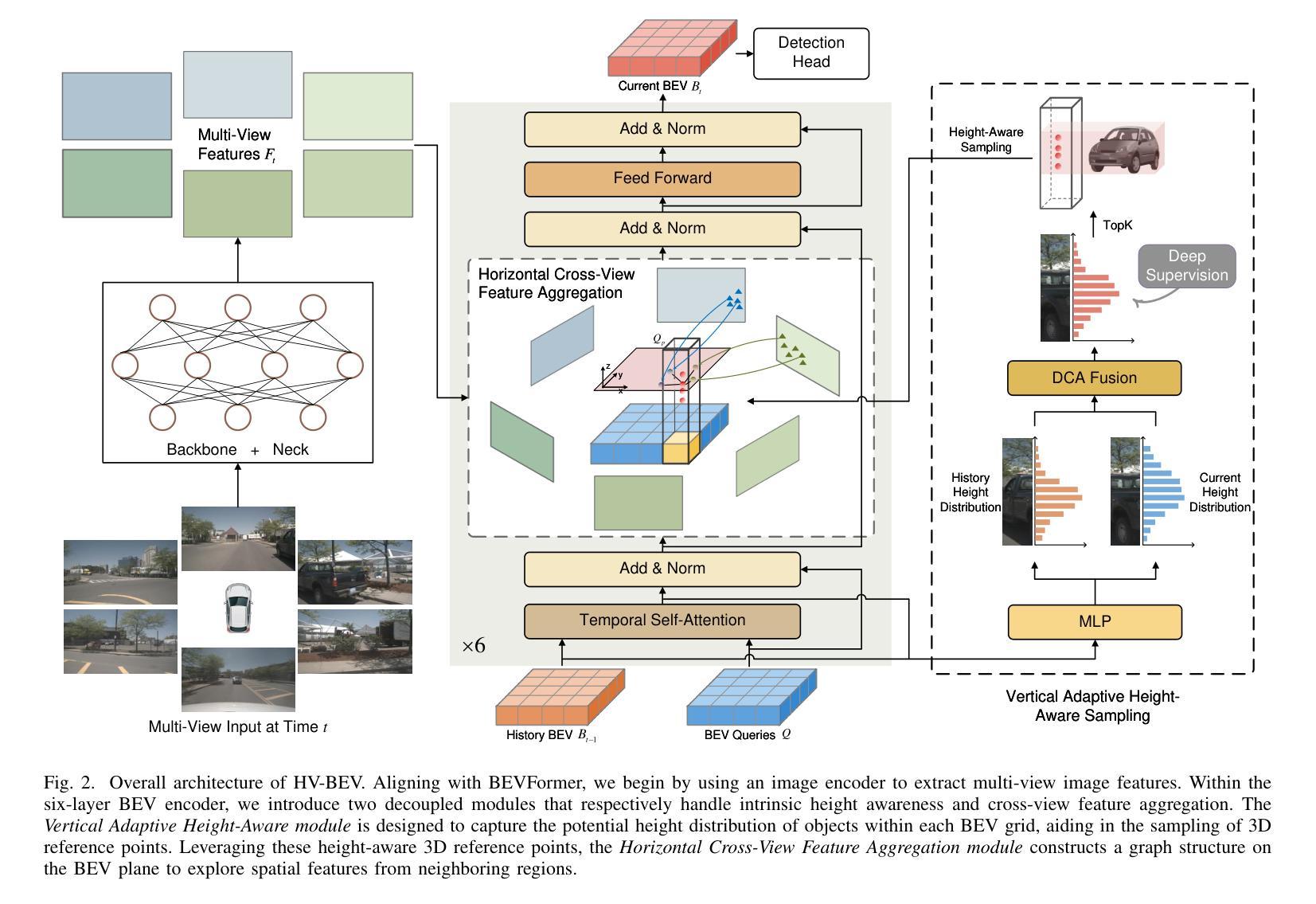
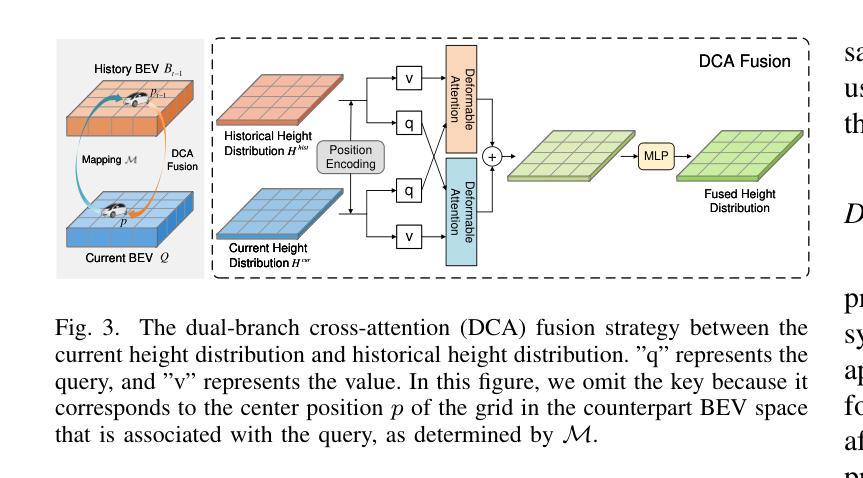
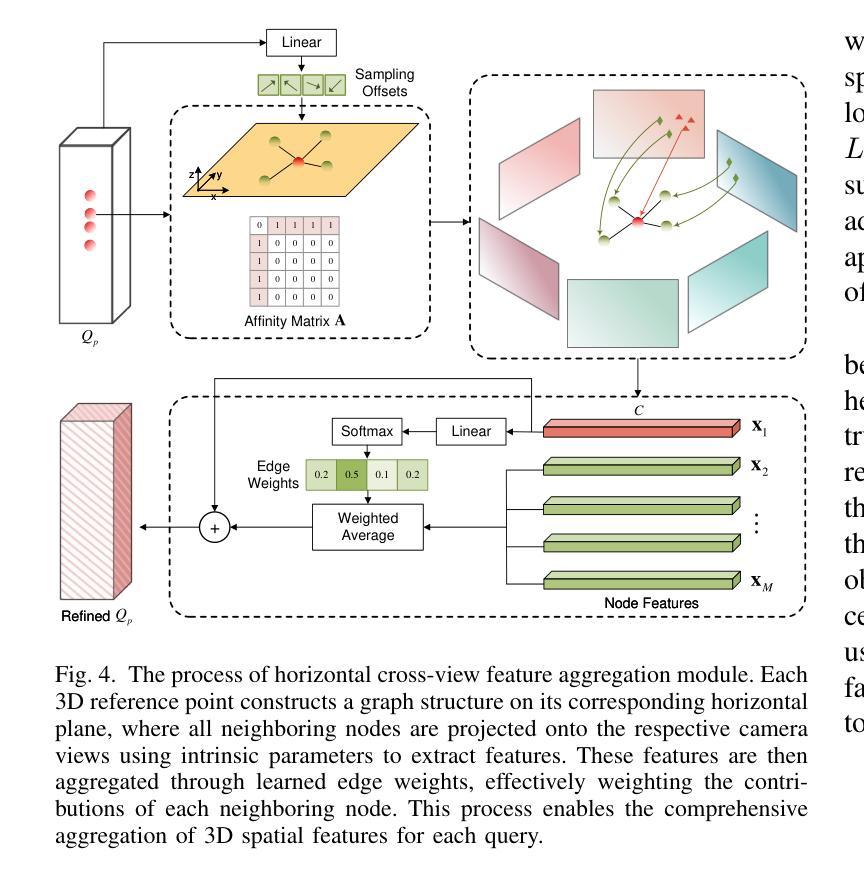
HV-BEV: Decoupling Horizontal and Vertical Feature Sampling for Multi-View 3D Object Detection
Authors:Di Wu, Feng Yang, Benlian Xu, Pan Liao, Wenhui Zhao, Dingwen Zhang
The application of vision-based multi-view environmental perception system has been increasingly recognized in autonomous driving technology, especially the BEV-based models. Current state-of-the-art solutions primarily encode image features from each camera view into the BEV space through explicit or implicit depth prediction. However, these methods often focus on improving the accuracy of projecting 2D features into corresponding depth regions, while overlooking the highly structured information of real-world objects and the varying height distributions of objects across different scenes. In this work, we propose HV-BEV, a novel approach that decouples feature sampling in the BEV grid queries paradigm into horizontal feature aggregation and vertical adaptive height-aware reference point sampling, aiming to improve both the aggregation of objects’ complete information and generalization to diverse road environments. Specifically, we construct a learnable graph structure in the horizontal plane aligned with the ground for 3D reference points, reinforcing the association of the same instance across different BEV grids, especially when the instance spans multiple image views around the vehicle. Additionally, instead of relying on uniform sampling within a fixed height range, we introduce a height-aware module that incorporates historical information, enabling the reference points to adaptively focus on the varying heights at which objects appear in different scenes. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our proposed method, demonstrating its superior performance over the baseline across the nuScenes dataset. Moreover, our best-performing model achieves a remarkable 50.5% mAP and 59.8% NDS on the nuScenes testing set.
基于视觉的多视图环境感知系统在自动驾驶技术中的应用,特别是基于鸟瞰视图(BEV)的模型,已经得到了越来越多的认可。当前先进解决方案主要通过显式或隐式的深度预测,将每个相机视图的图像特征编码到鸟瞰视图空间中。然而,这些方法往往侧重于提高将二维特征投影到相应深度区域的准确性,而忽略了现实世界物体的高度结构化信息和不同场景中物体高度分布的多样性。
针对这一问题,我们提出了HV-BEV这一新方法,它将鸟瞰视图网格查询范式中的特征采样解耦为水平特征聚合和垂直自适应高度感知参考点采样,旨在提高物体完整信息的聚合能力以及对不同道路环境的泛化能力。具体而言,我们在与地面对齐的水平面上构建了可学习的图结构,用于三维参考点,加强了不同鸟瞰视图网格中同一实例的关联,特别是当实例跨越车辆周围多个视图时。此外,我们引入了高度感知模块,该模块利用历史信息,而不是在固定高度范围内进行均匀采样,使参考点能够自适应地关注不同场景中物体出现的高度变化。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 7 figures, submitted to T-ITS
Summary
本文介绍了在自动驾驶技术中,基于视觉的多视角环境感知系统的应用,特别是基于BEV(鸟瞰视图)的模型。针对现有方法忽略真实世界物体的结构化信息和场景中的物体高度分布的问题,提出了一种新的方法HV-BEV。该方法将BEV网格查询范式中的特征采样解耦为水平特征聚合和垂直自适应高度感知参考点采样,旨在改进物体的完整信息聚合和多样化道路环境的泛化能力。通过构建与地面对齐的可学习图结构,强化不同BEV网格中同一实例的关联。同时,引入高度感知模块,结合历史信息,使参考点能自适应关注不同场景中物体的不同高度。实验验证了该方法的有效性,在nuScenes数据集上优于基线方法,最佳模型在nuScenes测试集上达到了50.5%的mAP和59.8%的NDS。
Key Takeaways
- 自动驾驶技术中,基于视觉的多视角环境感知系统的重要性日益凸显,特别是BEV模型。
- 当前方法主要通过对图像特征进行编码并映射到BEV空间,但忽视了物体的结构化信息和高度分布。
- HV-BEV方法旨在改进物体的完整信息聚合和泛化能力,通过水平特征聚合和垂直自适应高度感知参考点采样解耦特征采样。
- HV-BEV构建了一个与地面对齐的可学习图结构,强化不同BEV网格中同一实例的关联。
- 引入高度感知模块,结合历史信息,使参考点能自适应关注不同场景中物体的不同高度。
- 实验验证了HV-BEV方法的有效性,在nuScenes数据集上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

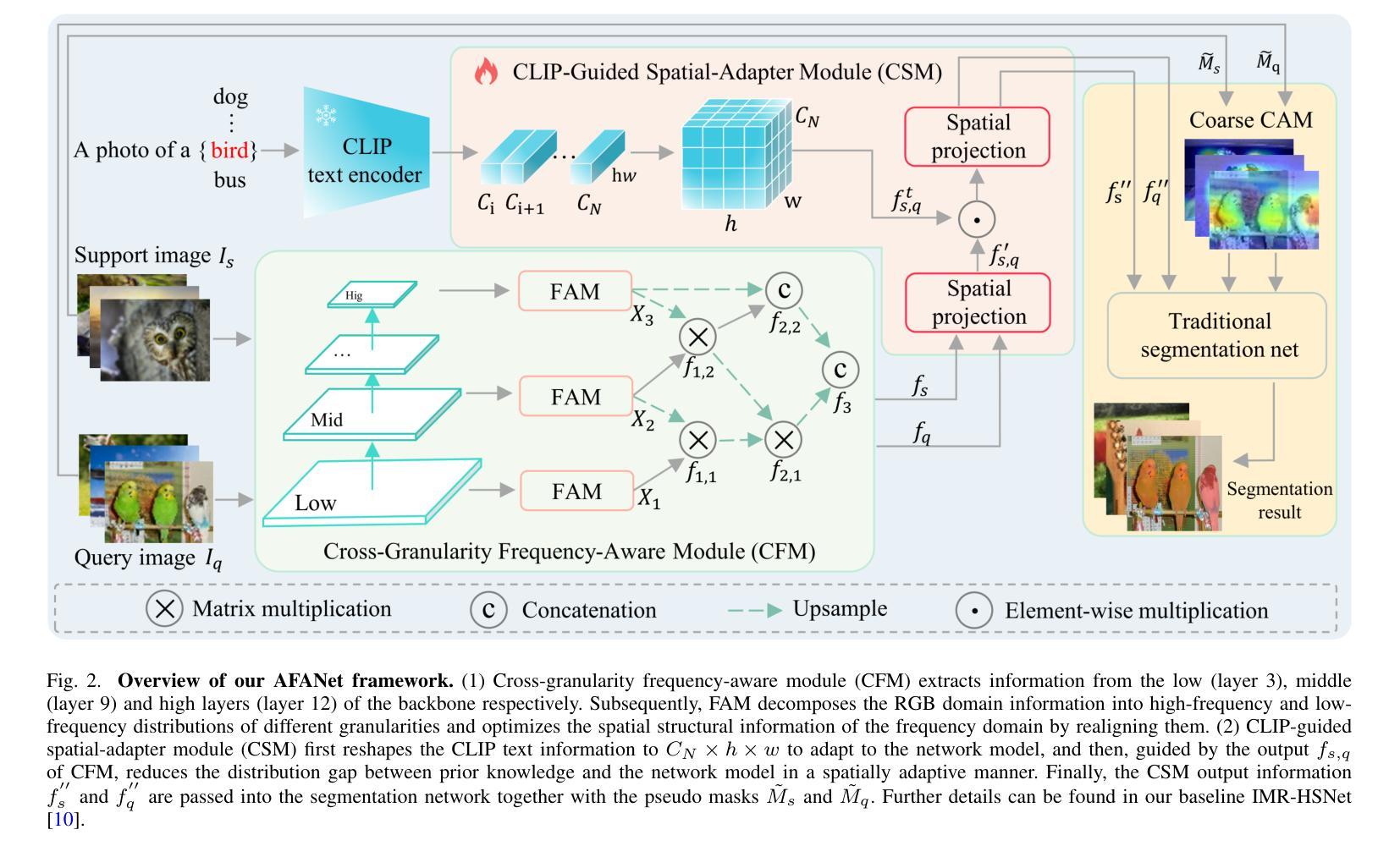
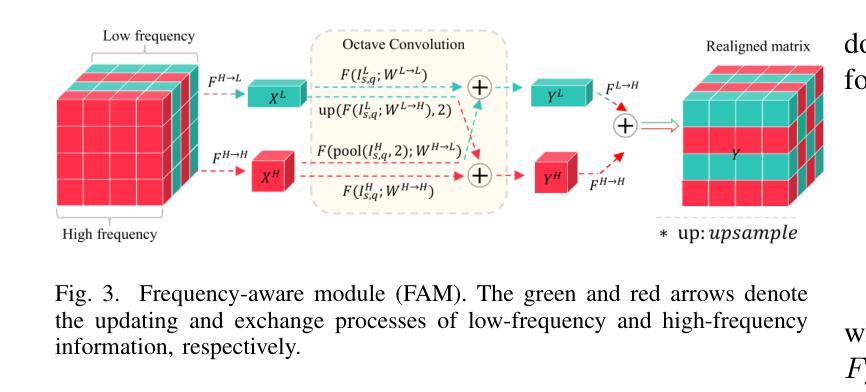
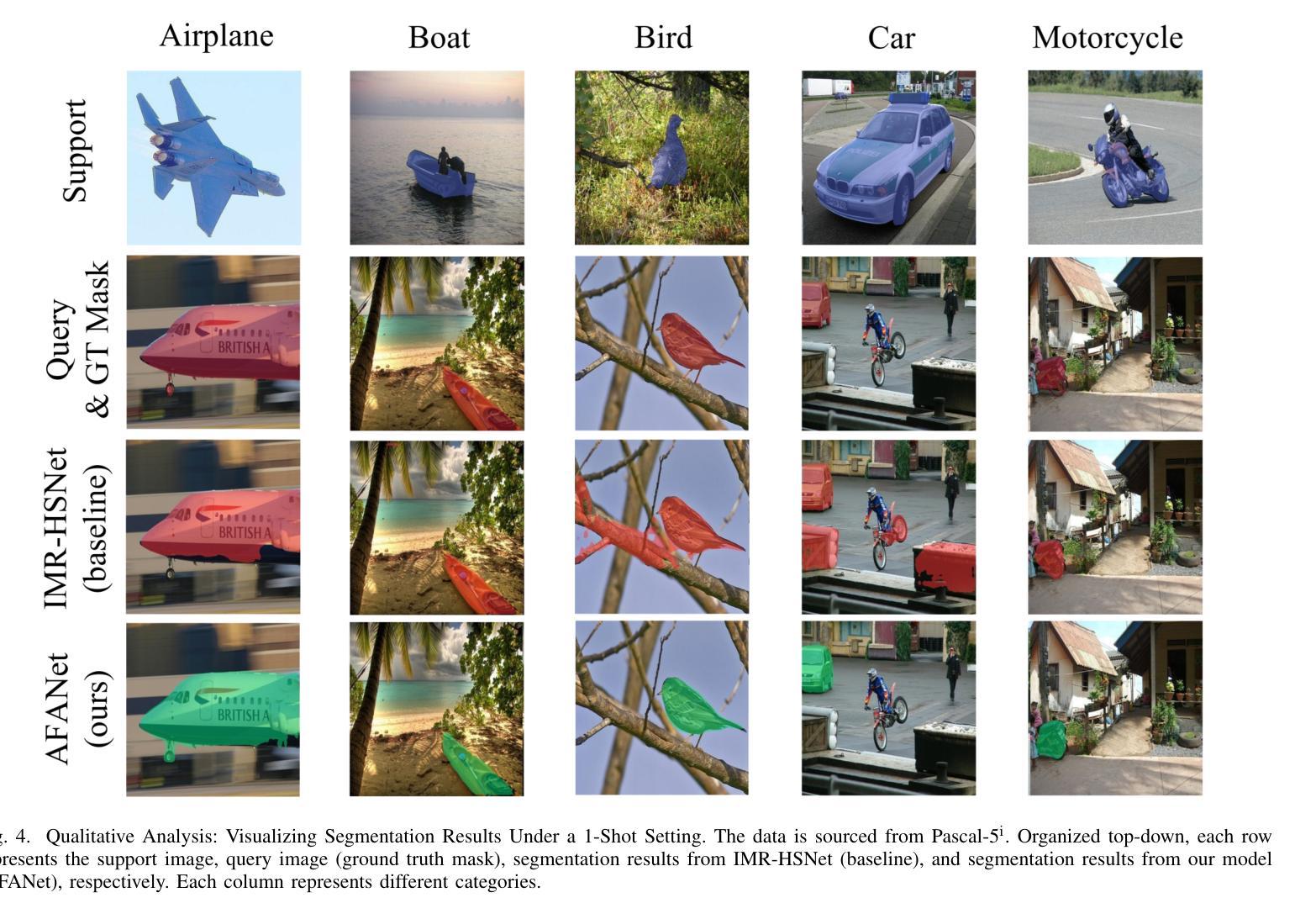
AFANet: Adaptive Frequency-Aware Network for Weakly-Supervised Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Jiaqi Ma, Guo-Sen Xie, Fang Zhao, Zechao Li
Few-shot learning aims to recognize novel concepts by leveraging prior knowledge learned from a few samples. However, for visually intensive tasks such as few-shot semantic segmentation, pixel-level annotations are time-consuming and costly. Therefore, in this paper, we utilize the more challenging image-level annotations and propose an adaptive frequency-aware network (AFANet) for weakly-supervised few-shot semantic segmentation (WFSS). Specifically, we first propose a cross-granularity frequency-aware module (CFM) that decouples RGB images into high-frequency and low-frequency distributions and further optimizes semantic structural information by realigning them. Unlike most existing WFSS methods using the textual information from the multi-modal language-vision model, e.g., CLIP, in an offline learning manner, we further propose a CLIP-guided spatial-adapter module (CSM), which performs spatial domain adaptive transformation on textual information through online learning, thus providing enriched cross-modal semantic information for CFM. Extensive experiments on the Pascal-5\textsuperscript{i} and COCO-20\textsuperscript{i} datasets demonstrate that AFANet has achieved state-of-the-art performance. The code is available at https://github.com/jarch-ma/AFANet.
少量学习旨在通过从少量样本中学习到的先验知识来识别新概念。然而,对于视觉密集型任务(如少量语义分割)而言,像素级注释既耗时又成本高昂。因此,本文利用更具挑战性的图像级注释,并提出自适应频率感知网络(AFANet)进行弱监督下的少量语义分割(WFSS)。具体来说,我们首先提出了跨粒度频率感知模块(CFM),它将RGB图像分解成高频和低频分布,并通过重新对齐进一步优化语义结构信息。与大多数现有的WFSS方法不同,这些方法采用离线学习的多模态语言视觉模型的文本信息(例如CLIP),我们还提出了CLIP引导的空间适配器模块(CSM),该模块通过在线学习对文本信息进行空间域自适应转换,从而为CFM提供丰富的跨模态语义信息。在Pascal-5i和COCO-20i数据集上的大量实验表明,AFANet已经达到了最先进的性能。代码可在https://github.com/jarch-ma/AFANet找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by TMM 2024
Summary
该论文探讨了小样本学习在弱监督下的语义分割应用。针对图像级别的标注挑战,提出了自适应频率感知网络(AFANet)。通过交叉粒度频率感知模块(CFM)处理图像,并结合CLIP指导的空间适配器模块(CSM),实现了在线学习的跨模态语义信息,优化分割性能并达到了先进水平。相关代码已发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文关注小样本学习在弱监督下的语义分割问题,旨在解决像素级标注耗时耗资的问题。
- 引入自适应频率感知网络(AFANet),采用图像级标注进行训练。
- 提出交叉粒度频率感知模块(CFM),能够分离图像的高频和低频分布,并优化语义结构信息。
- 与大多数使用离线学习方式的弱监督语义分割方法不同,该论文采用在线学习的方式处理文本信息。
- 引入CLIP指导的空间适配器模块(CSM),对文本信息进行空间域自适应转换,提供丰富的跨模态语义信息。
- 在Pascal-5i和COCO-20i数据集上进行了广泛实验,验证了AFANet的有效性,并达到了领先水平。
点此查看论文截图

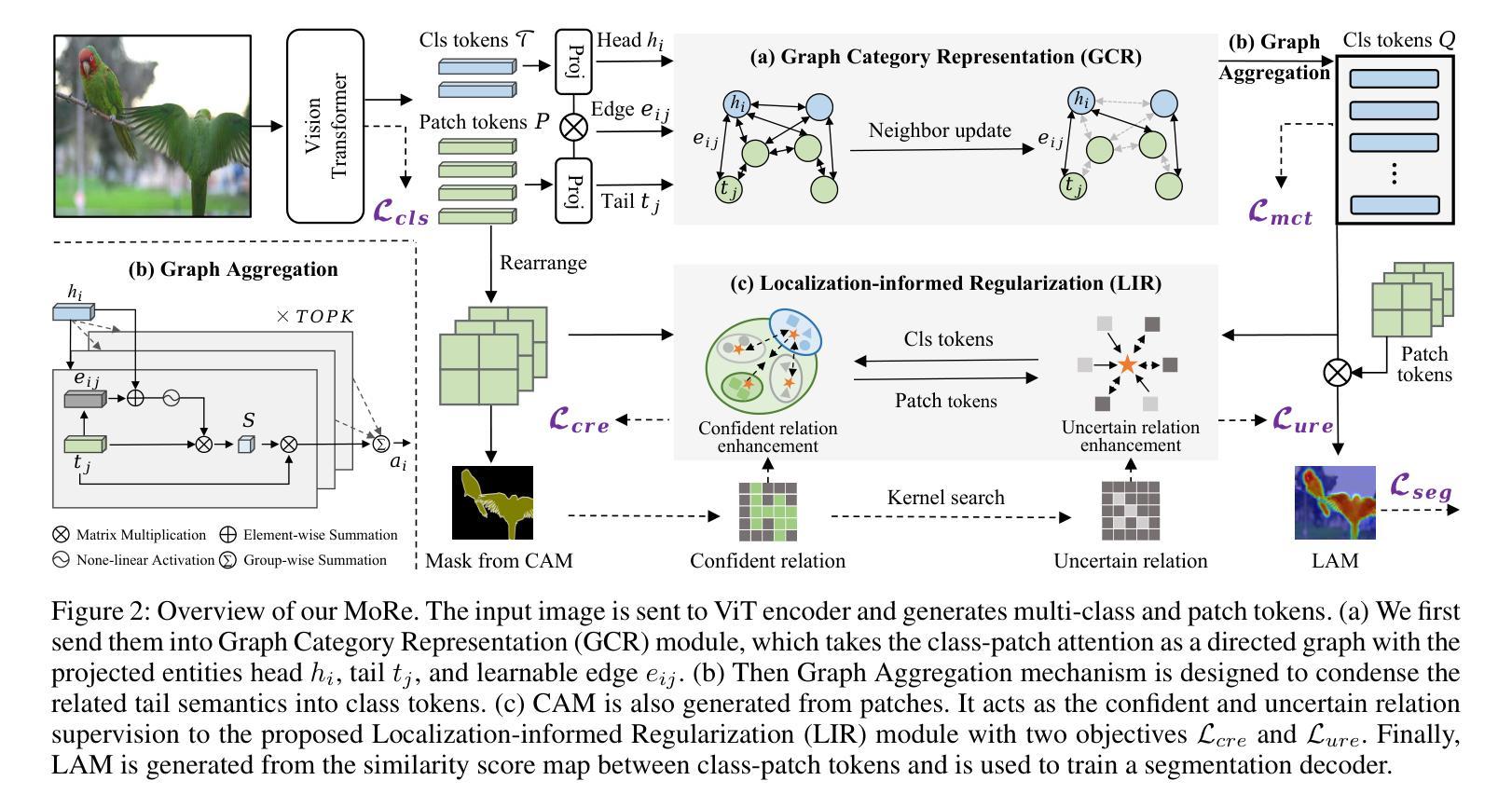
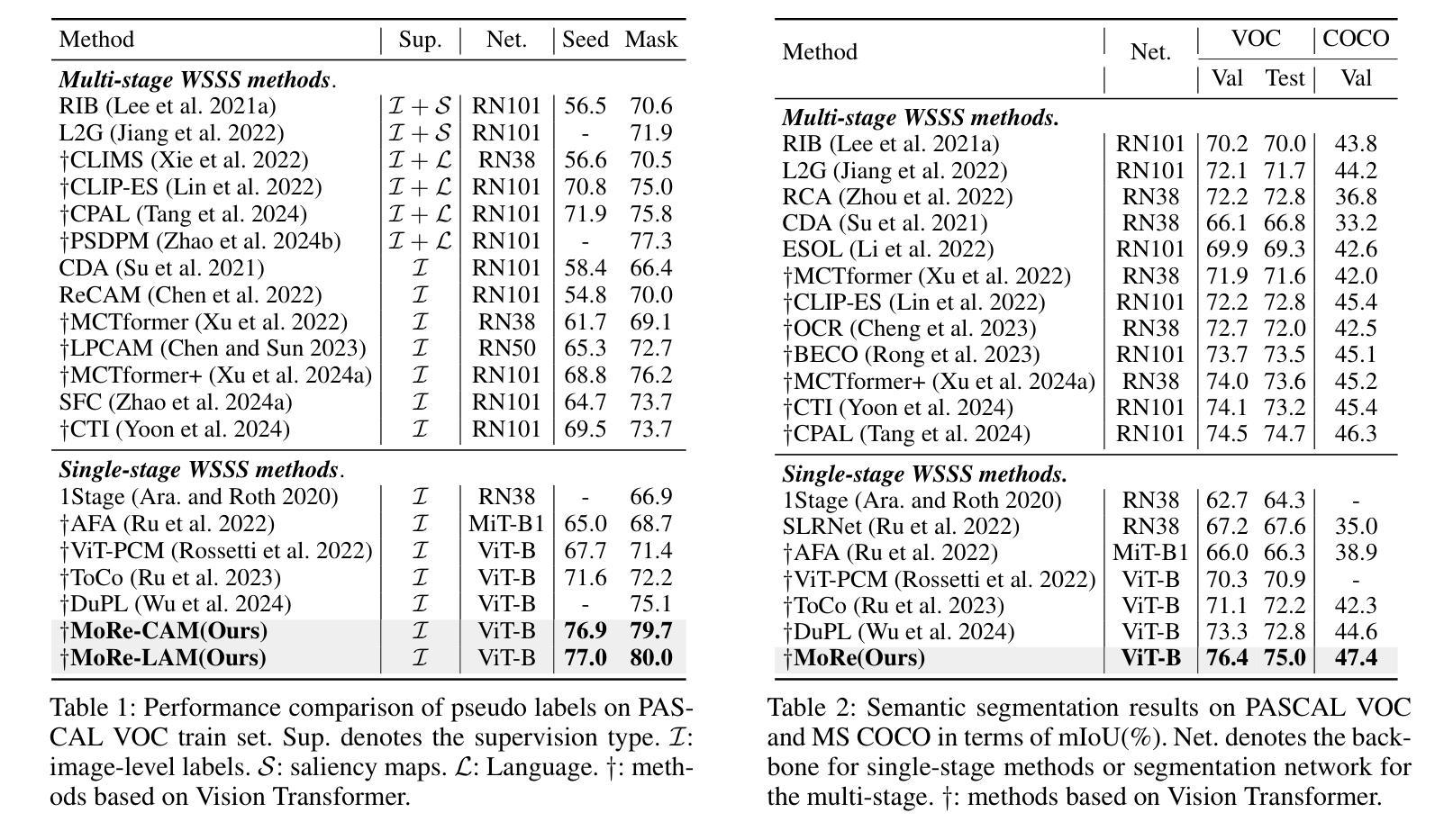
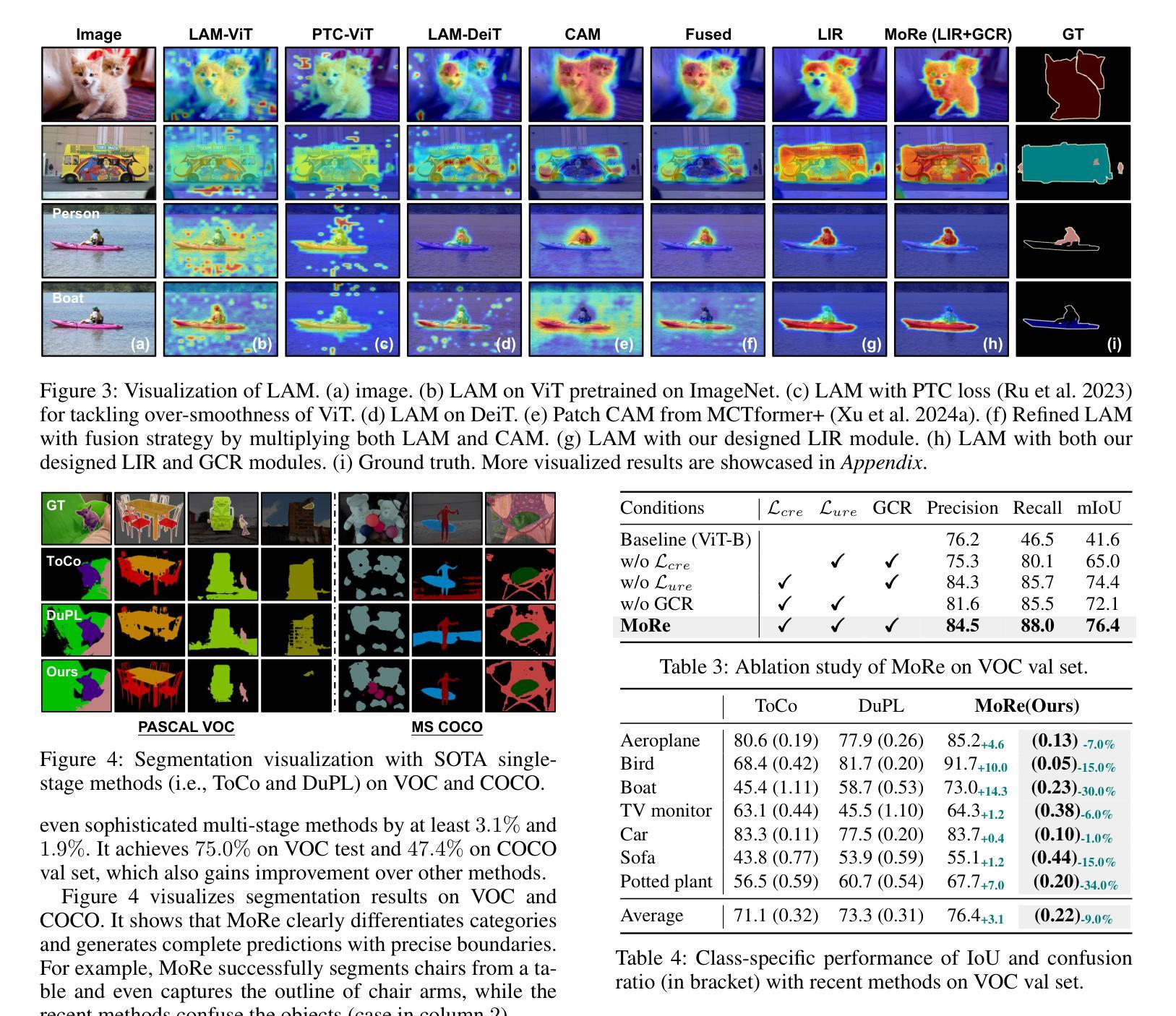
MoRe: Class Patch Attention Needs Regularization for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Zhiwei Yang, Yucong Meng, Kexue Fu, Shuo Wang, Zhijian Song
Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation (WSSS) with image-level labels typically uses Class Activation Maps (CAM) to achieve dense predictions. Recently, Vision Transformer (ViT) has provided an alternative to generate localization maps from class-patch attention. However, due to insufficient constraints on modeling such attention, we observe that the Localization Attention Maps (LAM) often struggle with the artifact issue, i.e., patch regions with minimal semantic relevance are falsely activated by class tokens. In this work, we propose MoRe to address this issue and further explore the potential of LAM. Our findings suggest that imposing additional regularization on class-patch attention is necessary. To this end, we first view the attention as a novel directed graph and propose the Graph Category Representation module to implicitly regularize the interaction among class-patch entities. It ensures that class tokens dynamically condense the related patch information and suppress unrelated artifacts at a graph level. Second, motivated by the observation that CAM from classification weights maintains smooth localization of objects, we devise the Localization-informed Regularization module to explicitly regularize the class-patch attention. It directly mines the token relations from CAM and further supervises the consistency between class and patch tokens in a learnable manner. Extensive experiments are conducted on PASCAL VOC and MS COCO, validating that MoRe effectively addresses the artifact issue and achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing recent single-stage and even multi-stage methods. Code is available at https://github.com/zwyang6/MoRe.
使用图像级标签的弱监督语义分割(WSSS)通常使用类激活图(CAM)来实现密集预测。最近,视觉转换器(ViT)提供了一种从类补丁注意力生成定位图的替代方案。然而,由于对这类注意力的建模约束不足,我们观察到定位注意力图(LAM)经常面临伪影问题,即语义相关性极小的补丁区域会被类令牌错误激活。在这项工作中,我们提出MoRe来解决这个问题,并进一步研究LAM的潜力。我们的研究结果表明,对类补丁注意力施加额外的正则化是必要的。为此,我们首先将注意力视为一种新型的有向图,并提出图类别表示模块,以隐含地正则化类补丁实体之间的交互。它确保类令牌能够动态地凝聚相关的补丁信息,并在图级别抑制不相关的伪影。其次,受分类权重CAM能够保持对象定位平滑性的观察启发,我们设计了定位信息正则化模块,以显式地正则化类补丁注意力。它直接从CAM挖掘令牌关系,并以可学习的方式监督类令牌和补丁令牌之间的一致性。在PASCAL VOC和MS COCO上进行了大量实验,验证了MoRe有效地解决了伪影问题,并实现了最先进的性能,超越了最近的单阶段甚至多阶段方法。代码可用在https://github.com/zwyang6/MoRe。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI 2025
Summary
本文探讨了基于图像级别标签的弱监督语义分割(WSSS)问题。文章指出,使用Vision Transformer(ViT)生成的Localization Attention Maps(LAM)常常受到伪影问题的影响。为解决这一问题,本文提出了MoRe方法,通过额外的正则化对类补丁注意力进行约束。MoRe包括两个模块:Graph Category Representation模块和Localization-informed Regularization模块,前者通过构建类补丁实体的有向图来隐式地约束类补丁之间的交互,后者则从分类权重的CAM中提取token关系,以显式地监督类补丁注意力的一致性。实验证明,MoRe有效地解决了伪影问题,并在PASCAL VOC和MS COCO数据集上实现了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- WSSS中使用Class Activation Maps (CAM) 实现密集预测。
- Vision Transformer (ViT) 可生成Localization Attention Maps (LAM)。
- LAM存在伪影问题,即不相关的补丁区域会被类标记错误激活。
- MoRe方法通过额外的正则化解决LAM的伪影问题。
- MoRe包括Graph Category Representation模块和Localization-informed Regularization模块。
- MoRe在PASCAL VOC和MS COCO数据集上实现了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

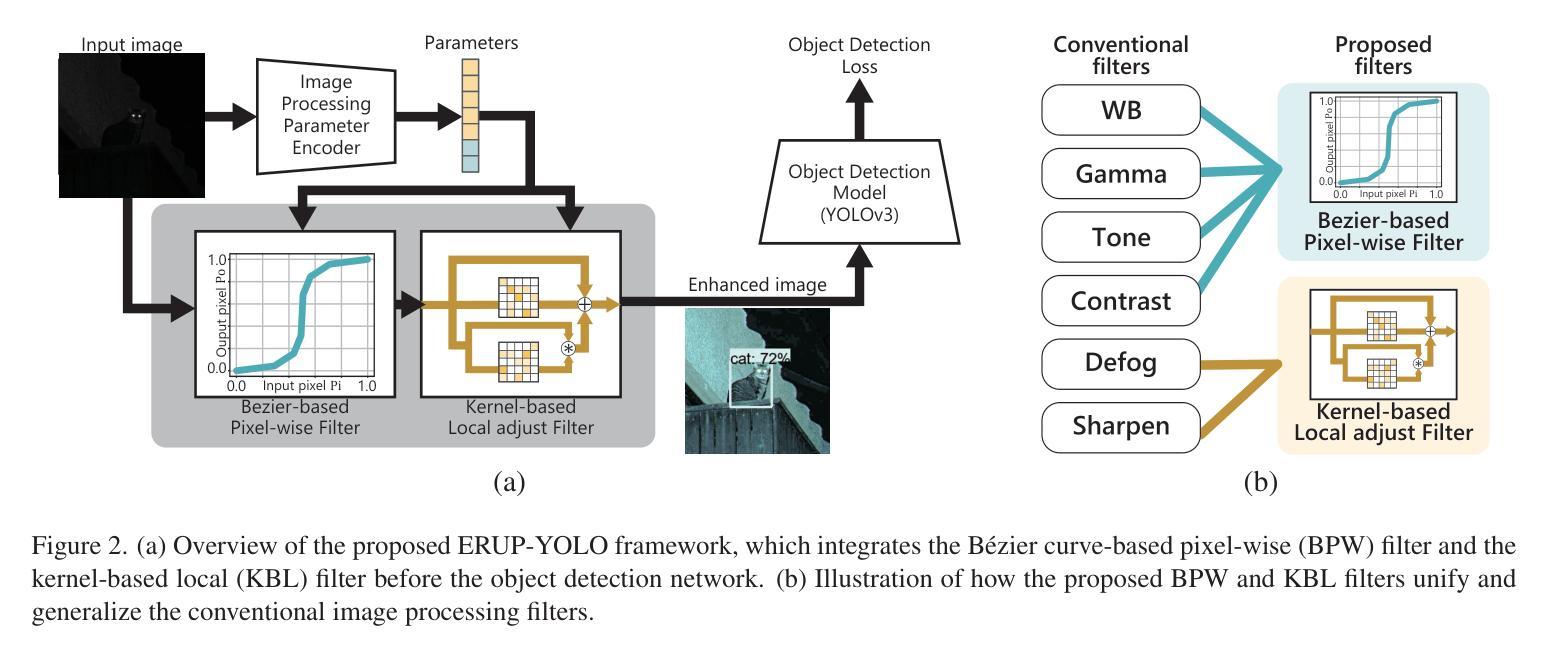
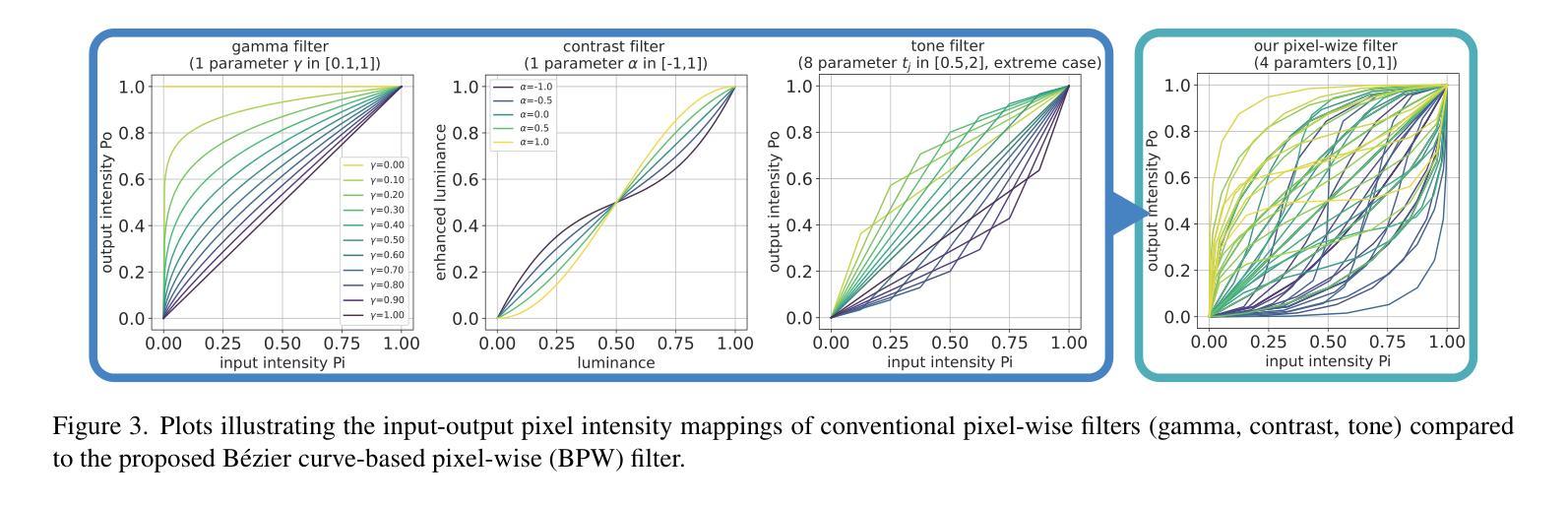
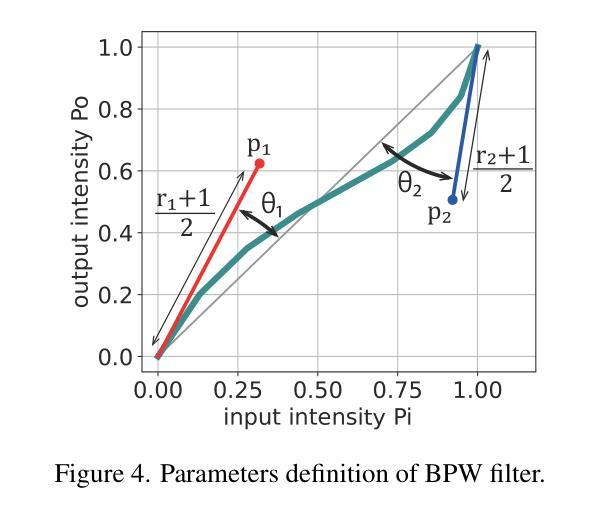
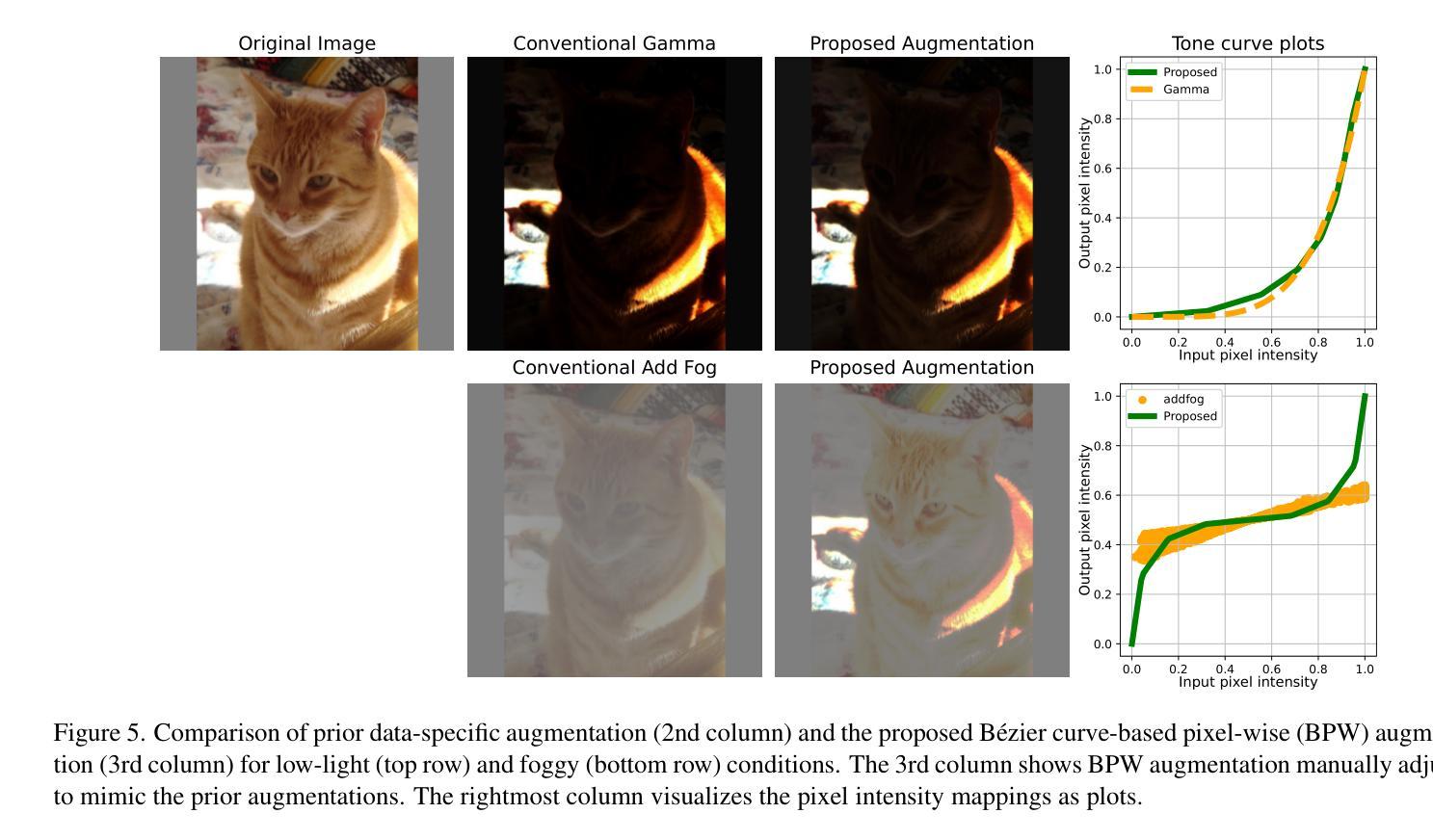
ERUP-YOLO: Enhancing Object Detection Robustness for Adverse Weather Condition by Unified Image-Adaptive Processing
Authors:Yuka Ogino, Yuho Shoji, Takahiro Toizumi, Atsushi Ito
We propose an image-adaptive object detection method for adverse weather conditions such as fog and low-light. Our framework employs differentiable preprocessing filters to perform image enhancement suitable for later-stage object detections. Our framework introduces two differentiable filters: a B'ezier curve-based pixel-wise (BPW) filter and a kernel-based local (KBL) filter. These filters unify the functions of classical image processing filters and improve performance of object detection. We also propose a domain-agnostic data augmentation strategy using the BPW filter. Our method does not require data-specific customization of the filter combinations, parameter ranges, and data augmentation. We evaluate our proposed approach, called Enhanced Robustness by Unified Image Processing (ERUP)-YOLO, by applying it to the YOLOv3 detector. Experiments on adverse weather datasets demonstrate that our proposed filters match or exceed the expressiveness of conventional methods and our ERUP-YOLO achieved superior performance in a wide range of adverse weather conditions, including fog and low-light conditions.
我们提出了一种针对恶劣天气条件(如雾和低光)的自适应图像目标检测方法。我们的框架采用可微分的预处理滤波器,执行适用于后期目标检测的图像增强。我们的框架引入两种可微分滤波器:基于贝塞尔曲线的像素级(BPW)滤波器和基于核的局部(KBL)滤波器。这些滤波器结合了传统图像处理滤波器的功能,提高了目标检测的性能。我们还提出了一种基于BPW滤波器的领域无关数据增强策略。我们的方法不需要针对特定数据集定制滤波器组合、参数范围和数据增强。我们将所提方法称为统一图像处理增强稳健性(ERUP)-YOLO,并将其应用于YOLOv3检测器。在恶劣天气数据集上的实验表明,我们所提出的滤波器与常规方法的表达能力相匹配,甚至更高,并且我们的ERUP-YOLO在包括雾和低光条件在内的各种恶劣天气条件下均取得了卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to WACV 2025
Summary:
针对恶劣天气条件(如雾和低光环境),我们提出了一种自适应图像的目标检测方法。该方法采用可微分预处理滤波器进行图像增强,为后期目标检测提供有力支持。研究中引入了两种可微分滤波器:基于Bézier曲线的像素级(BPW)滤波器和基于核的局部(KBL)滤波器。它们融合了传统图像处理滤波器的功能,提高了目标检测性能。同时,我们提出了一种基于BPW滤波器的通用数据增强策略。该方法无需针对特定数据定制滤波器组合、参数范围和数据增强方式。将该方法应用于YOLOv3检测器,实验表明,所提滤波器在恶劣天气数据集中的表现与常规方法相当或更优,ERUP-YOLO在雾和低光条件下的性能卓越。
Key Takeaways:
- 提出了一种自适应图像的目标检测方法,适用于恶劣天气条件。
- 引入两种可微分预处理滤波器:BPW滤波器和KBL滤波器,融合传统图像处理功能。
- 采用BPW滤波器设计了一种通用数据增强策略,提高了模型在恶劣天气下的鲁棒性。
- 方法无需针对特定数据集定制滤波器组合、参数范围和数据增强方式。
- 实验表明,所提滤波器在恶劣天气数据集中的表现良好。
- ERUP-YOLO在雾和低光条件下的性能卓越。
点此查看论文截图

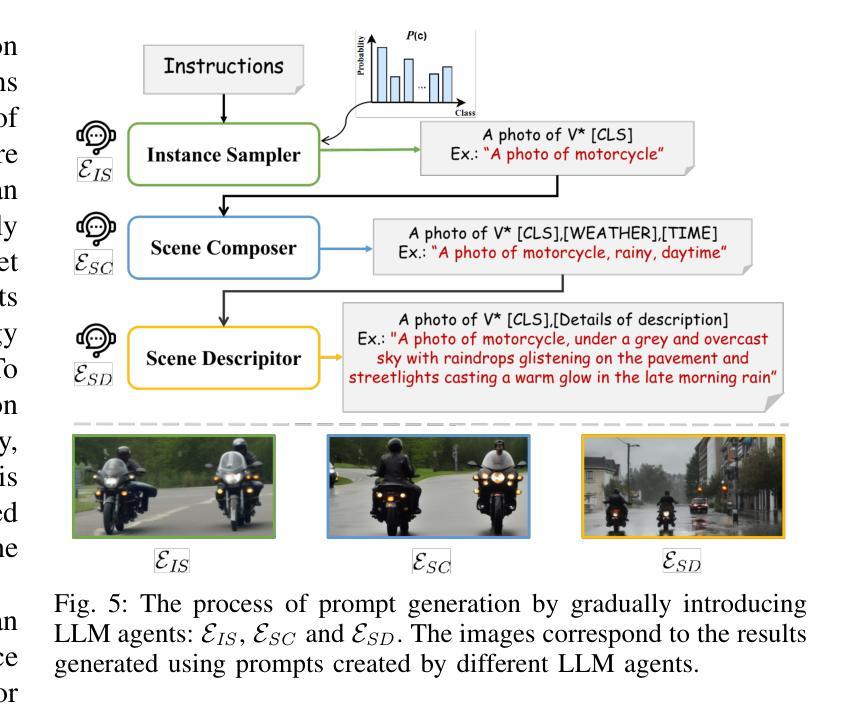
WeatherDG: LLM-assisted Diffusion Model for Procedural Weather Generation in Domain-Generalized Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Chenghao Qian, Yuhu Guo, Yuhong Mo, Wenjing Li
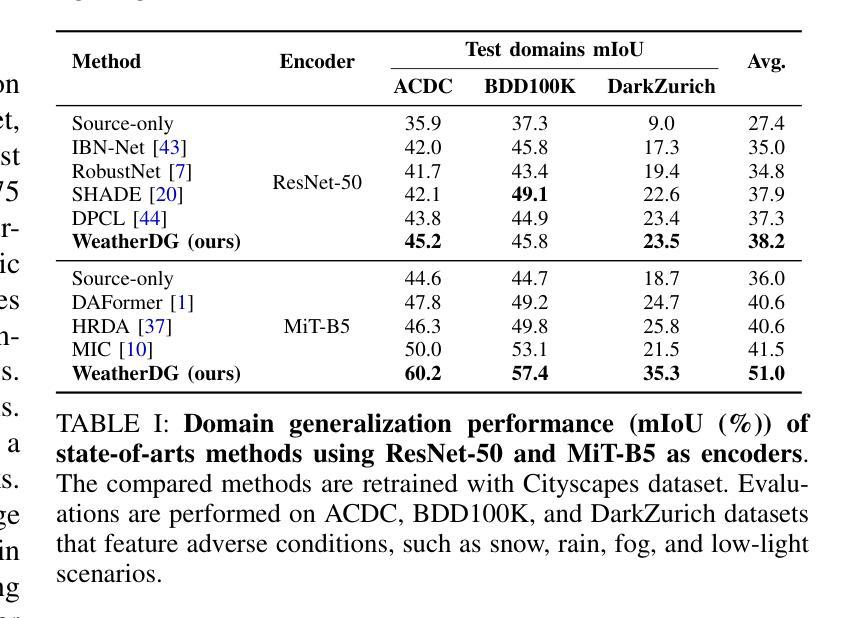
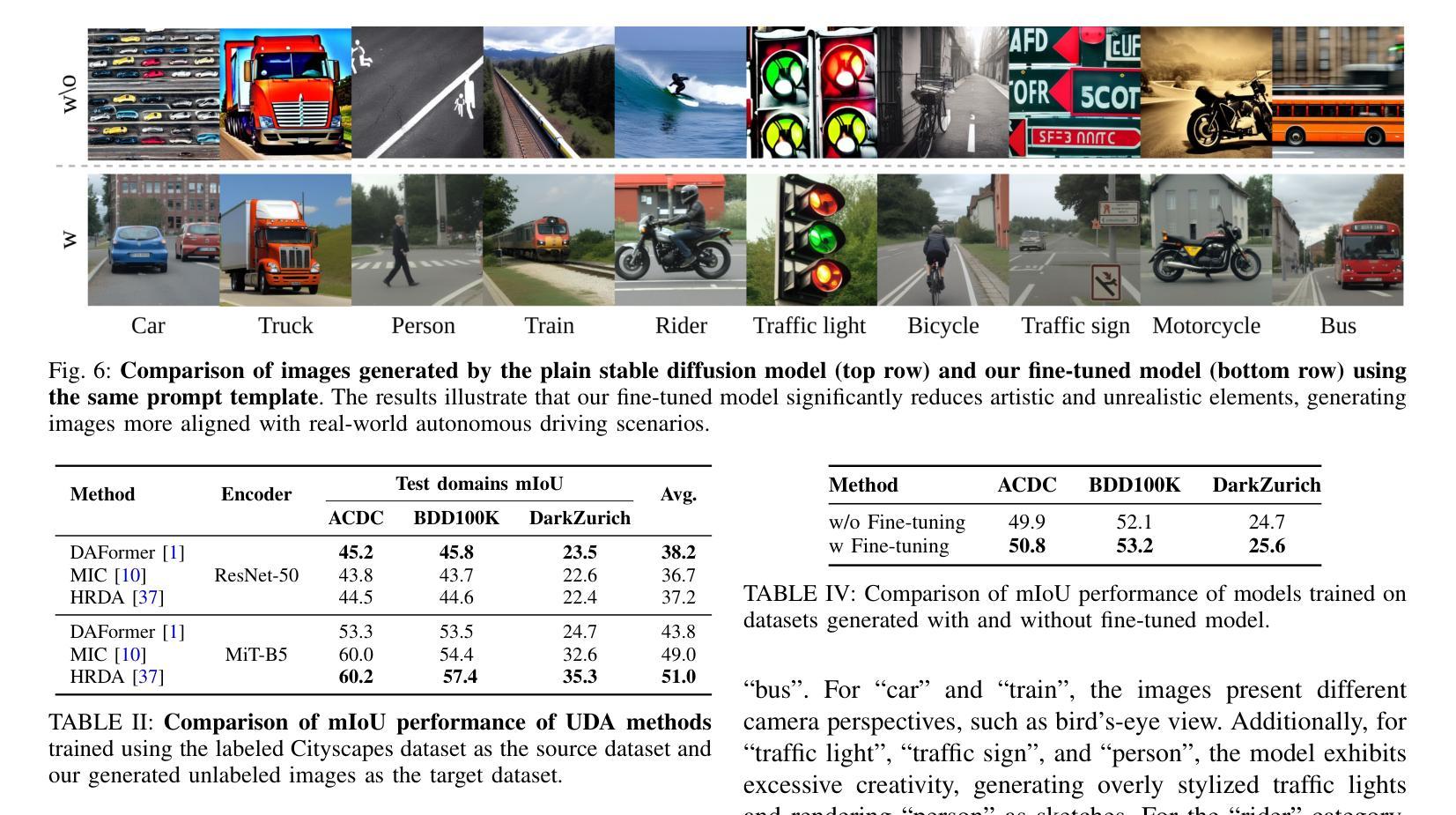
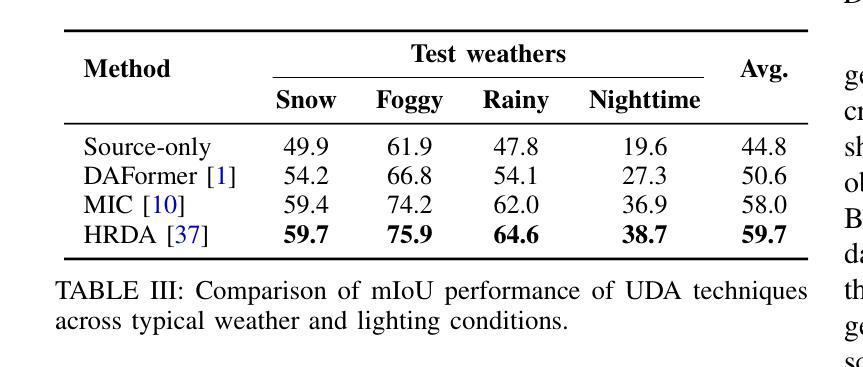
In this work, we propose a novel approach, namely WeatherDG, that can generate realistic, weather-diverse, and driving-screen images based on the cooperation of two foundation models, i.e, Stable Diffusion (SD) and Large Language Model (LLM). Specifically, we first fine-tune the SD with source data, aligning the content and layout of generated samples with real-world driving scenarios. Then, we propose a procedural prompt generation method based on LLM, which can enrich scenario descriptions and help SD automatically generate more diverse, detailed images. In addition, we introduce a balanced generation strategy, which encourages the SD to generate high-quality objects of tailed classes under various weather conditions, such as riders and motorcycles. This segmentation-model-agnostic method can improve the generalization ability of existing models by additionally adapting them with the generated synthetic data. Experiments on three challenging datasets show that our method can significantly improve the segmentation performance of different state-of-the-art models on target domains. Notably, in the setting of ‘’Cityscapes to ACDC’’, our method improves the baseline HRDA by 13.9% in mIoU.
在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新的方法,名为WeatherDG,它可以通过两个基础模型的合作,即Stable Diffusion(SD)和大型语言模型(LLM),生成现实、天气多样、驾驶屏图像。具体来说,我们首先使用源数据对SD进行微调,使生成样本的内容和布局与真实世界的驾驶场景对齐。然后,我们提出了一种基于LLM的程序化提示生成方法,可以丰富场景描述,帮助SD自动生成更多样化、更详细的图像。此外,我们引入了一种平衡生成策略,鼓励SD在各种天气条件下为长尾类生成高质量对象,如骑行者和摩托车。这种与分割模型无关的方法可以通过使用生成的合成数据额外适应现有模型,从而提高其泛化能力。在三个具有挑战性的数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法可以显著提高目标域上不同最新模型的分割性能。值得注意的是,在“城市景观到ACDC”的设置中,我们的方法将基线HRDA的mIoU提高了13.9%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于Stable Diffusion(SD)和Large Language Model(LLM)协同工作的新型图像生成方法WeatherDG。该方法能够生成逼真的、天气多变的驾驶场景图像。通过微调SD模型以匹配真实驾驶场景的内容和布局,并结合LLM生成丰富的场景描述,实现自动生成更多样化、更详细的图像。此外,引入了一种平衡生成策略,鼓励SD在多种天气条件下生成高质量的目标长尾类图像,如骑行者和摩托车。该方法对现有的模型具有良好的通用性,通过适应生成的合成数据,可在三个具有挑战性的数据集上的实验证明,能显著提高不同最先进模型的分割性能。特别是在“Cityscapes到ACDC”的设置中,该方法将基线HRDA提高了13.9%的mIoU。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了名为WeatherDG的新型图像生成方法,基于Stable Diffusion和Large Language Model。
- 通过微调SD模型,使生成的图像内容与真实驾驶场景布局相匹配。
- 利用LLM生成丰富的场景描述,使SD能够自动生成更多样化、详细的图像。
- 引入平衡生成策略,鼓励生成高质量的长尾类目标图像,如骑行者和摩托车。
- 方法具有良好的通用性,适用于多种模型。
- 实验表明,该方法在三个数据集上显著提高模型的分割性能。
点此查看论文截图


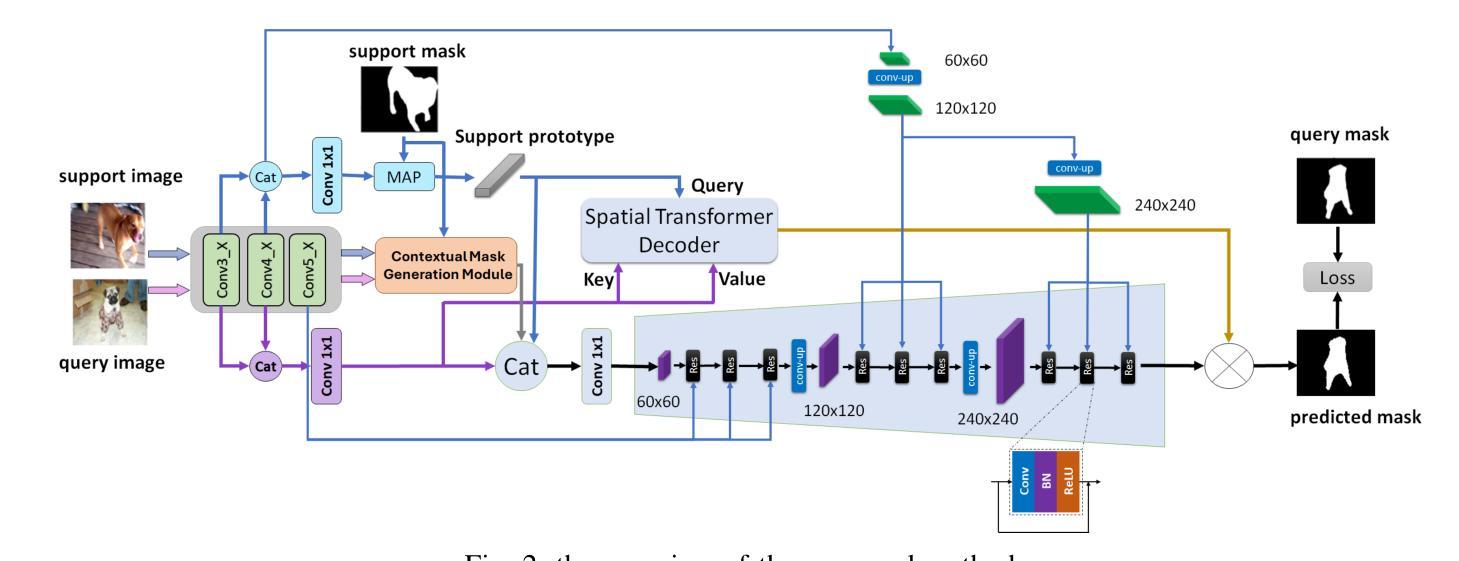
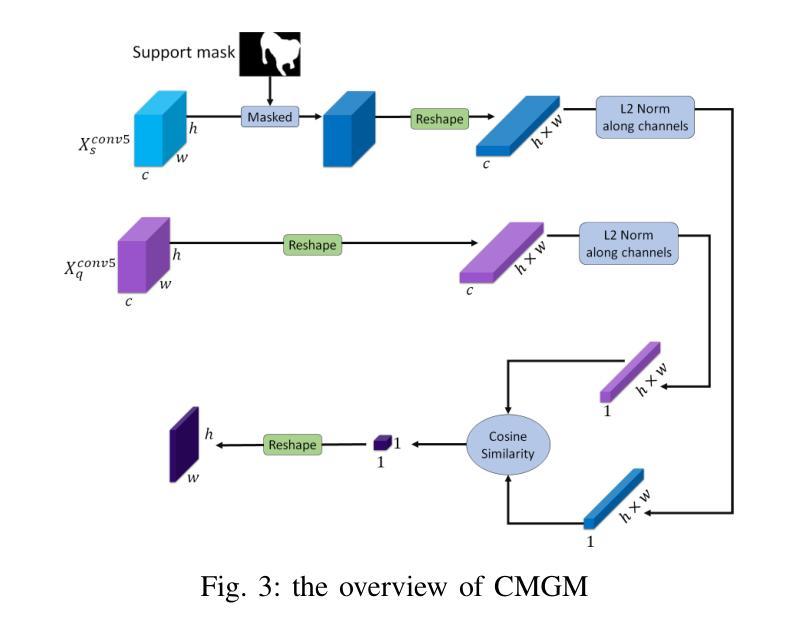
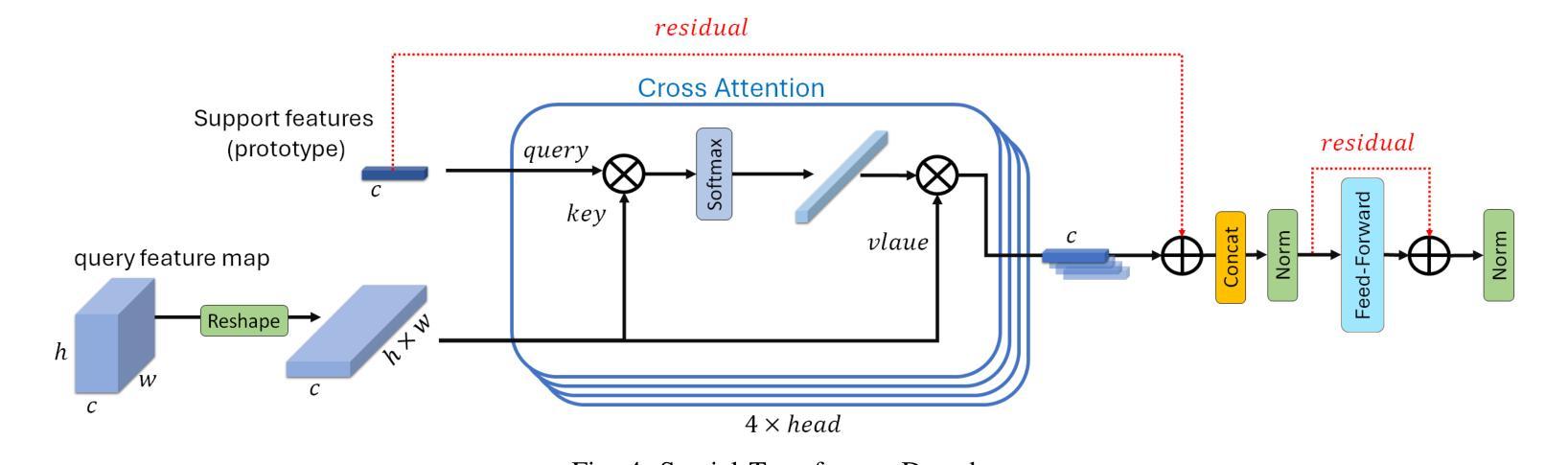
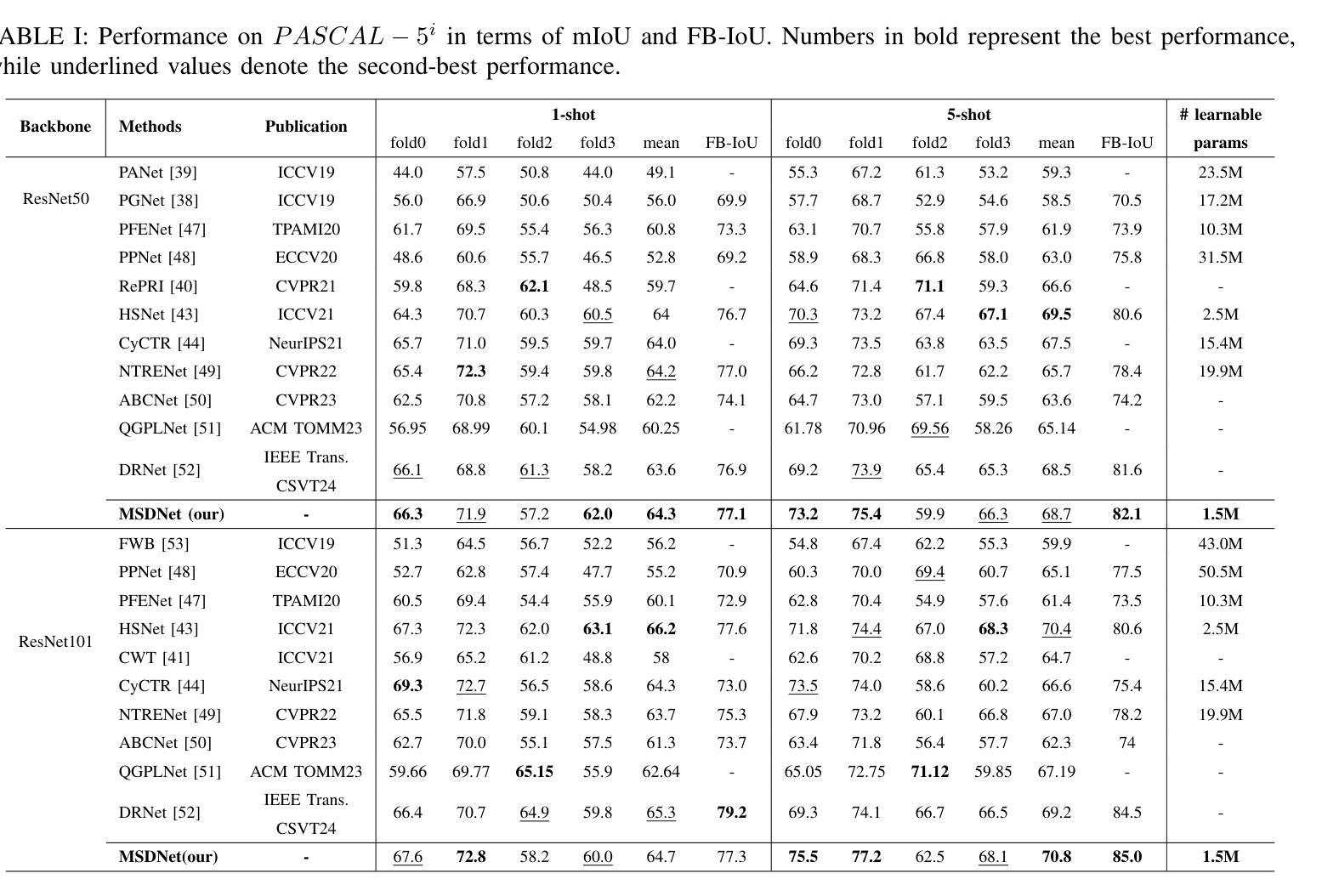
MSDNet: Multi-Scale Decoder for Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation via Transformer-Guided Prototyping
Authors:Amirreza Fateh, Mohammad Reza Mohammadi, Mohammad Reza Jahed Motlagh
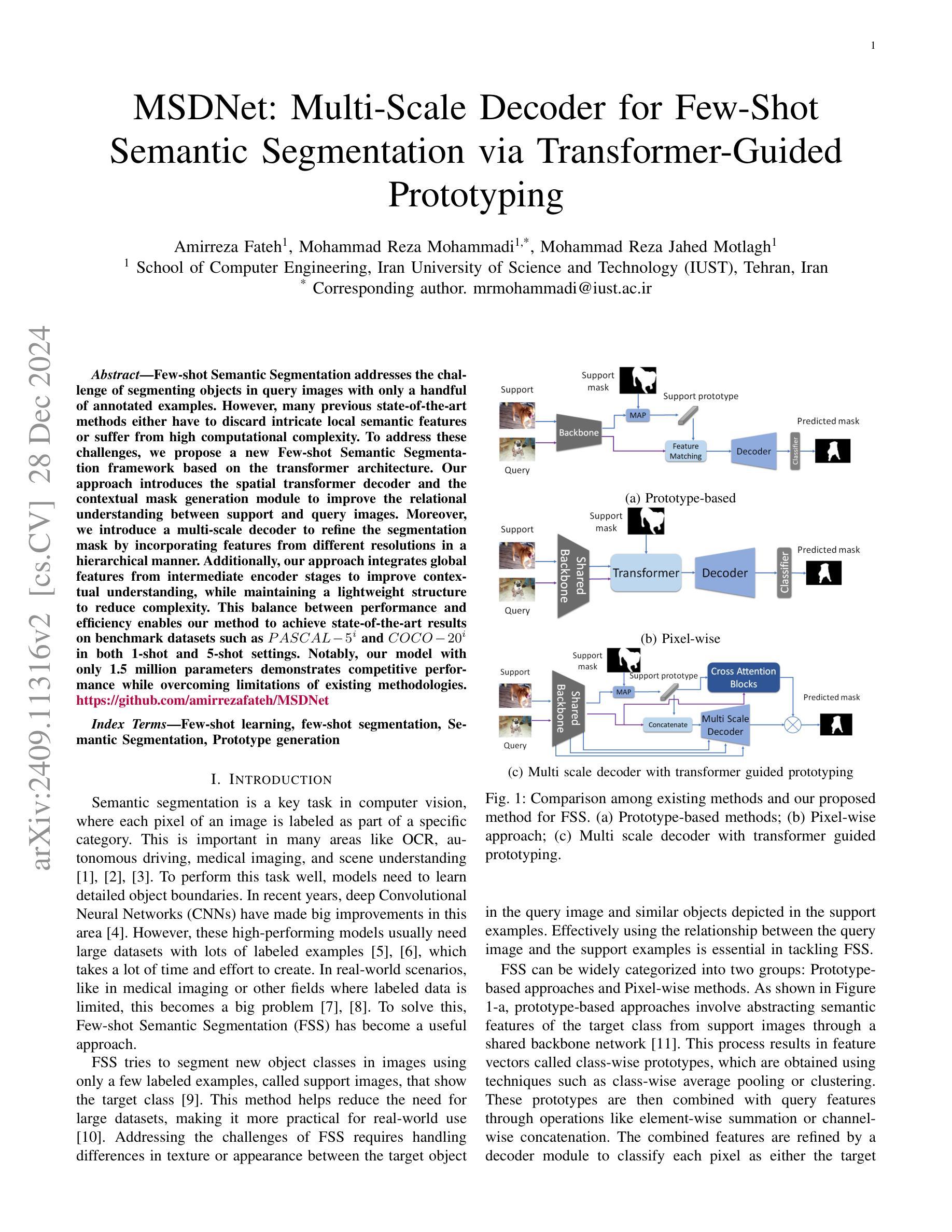
Few-shot Semantic Segmentation addresses the challenge of segmenting objects in query images with only a handful of annotated examples. However, many previous state-of-the-art methods either have to discard intricate local semantic features or suffer from high computational complexity. To address these challenges, we propose a new Few-shot Semantic Segmentation framework based on the transformer architecture. Our approach introduces the spatial transformer decoder and the contextual mask generation module to improve the relational understanding between support and query images. Moreover, we introduce a multi-scale decoder to refine the segmentation mask by incorporating features from different resolutions in a hierarchical manner. Additionally, our approach integrates global features from intermediate encoder stages to improve contextual understanding, while maintaining a lightweight structure to reduce complexity. This balance between performance and efficiency enables our method to achieve state-of-the-art results on benchmark datasets such as $PASCAL-5^i$ and $COCO-20^i$ in both 1-shot and 5-shot settings. Notably, our model with only 1.5 million parameters demonstrates competitive performance while overcoming limitations of existing methodologies. https://github.com/amirrezafateh/MSDNet
少数语义分割(Few-shot Semantic Segmentation)旨在解决仅使用少量标注样本对查询图像进行对象分割的挑战。然而,许多之前的最先进方法要么需要丢弃复杂的局部语义特征,要么面临高计算复杂度的问题。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种基于Transformer架构的少数语义分割新框架。我们的方法引入了空间变换解码器和上下文掩膜生成模块,以提高支持图像和查询图像之间的关系理解。此外,我们引入了多尺度解码器,以分层方式融入不同分辨率的特征来优化分割掩膜。同时,我们的方法融合了中间编码器阶段的全局特征以提高上下文理解,同时保持轻量级结构以降低复杂度。性能和效率之间的这种平衡使我们的方法在PASCAL-5i和COCO-20i等基准数据集上实现了最先进的成果,无论是在一次性拍摄(1-shot)还是五次拍摄(5-shot)的设置中都是如此。值得注意的是,我们的模型仅有150万参数,在克服现有方法局限性的同时表现出了竞争力。详情请访问:https://github.com/amirrezafateh/MSDNet。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Transformer架构,提出新的少样本语义分割框架,通过空间变换解码器、上下文掩膜生成模块和多尺度解码器,改善支持图像和查询图像之间的关系理解,实现精细的分割掩膜。在PASCAL-5^i和COCO-20^i等基准数据集上实现了一阶和五阶情况下的业界领先结果,展现出高效且具备竞争力的性能。更多详情访问:https://github.com/amirrezafateh/MSDNet。
Key Takeaways
- 针对少样本语义分割的挑战,提出新的基于Transformer架构的框架。
- 引入空间变换解码器和上下文掩膜生成模块,改善支持图像和查询图像的关系理解。
- 通过多尺度解码器结合不同分辨率的特征,实现分割掩膜的精细化。
- 整合中间编码器阶段的全球特征,提升上下文理解。
- 保持轻量级结构以降低复杂性,在基准数据集上实现业界领先结果。
- 仅用150万参数便展现出竞争力的性能。
点此查看论文截图
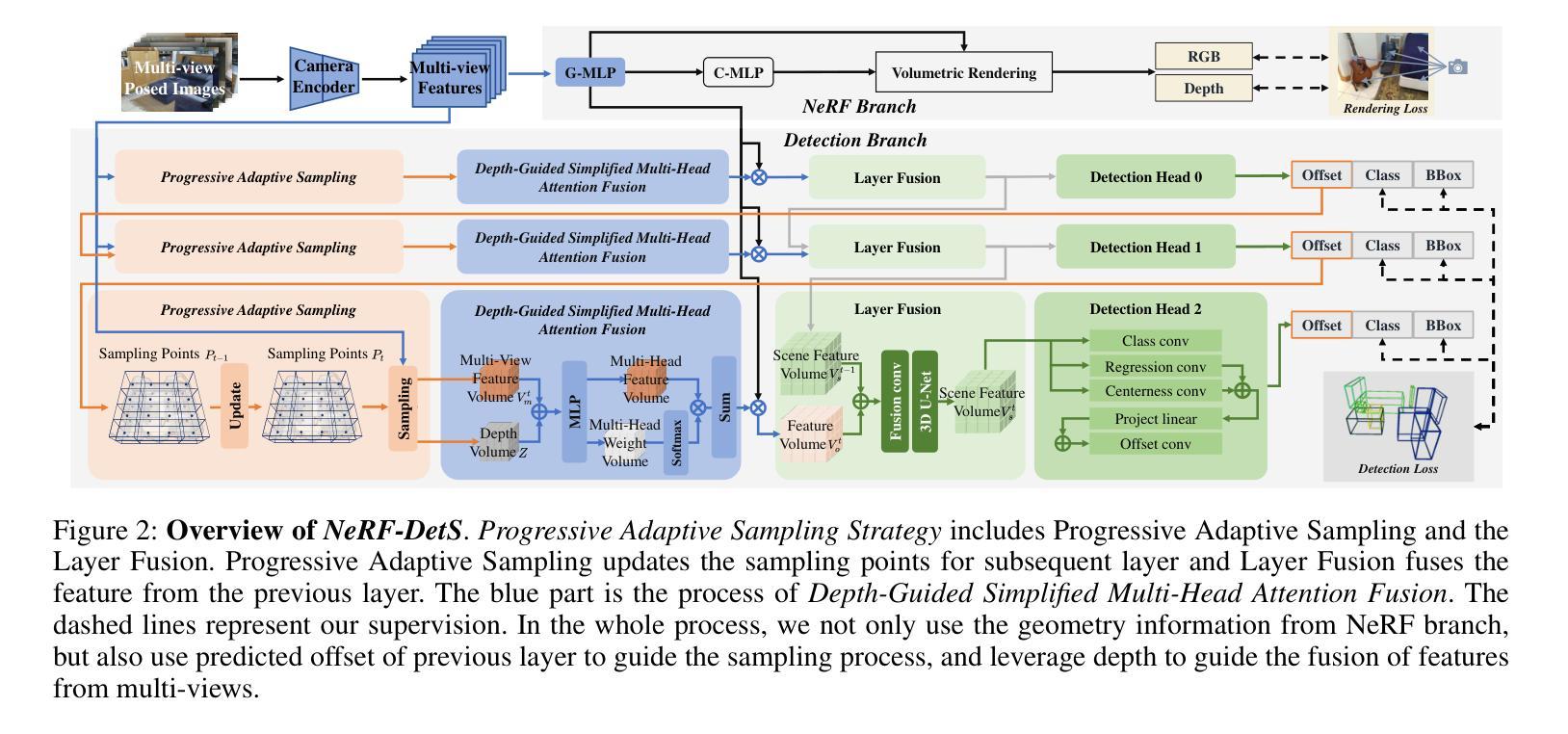
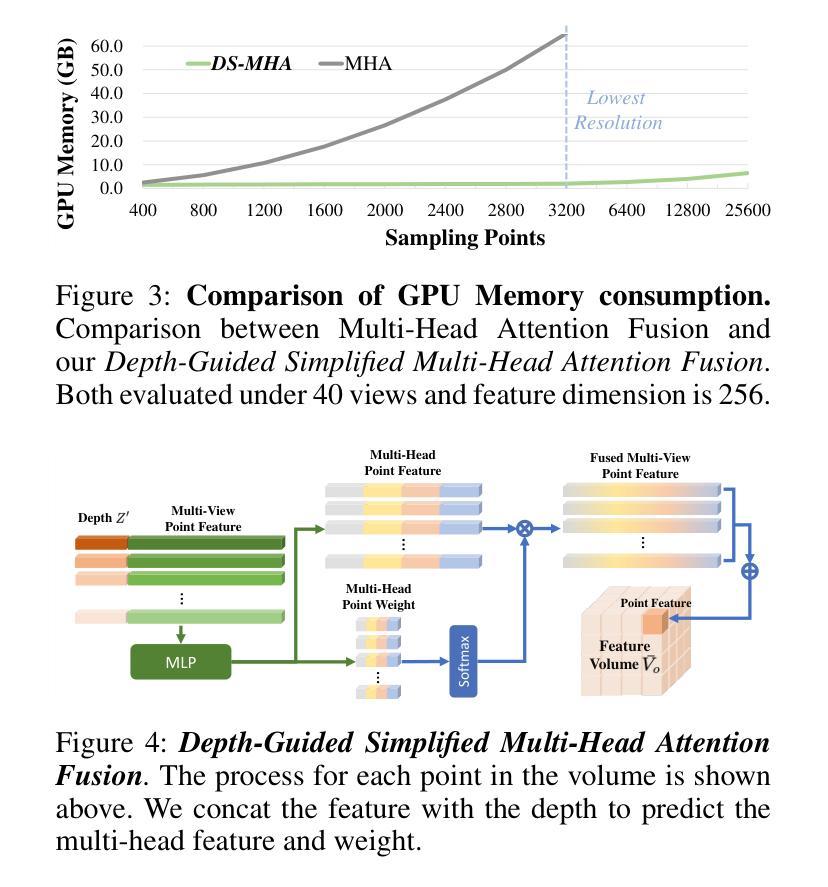
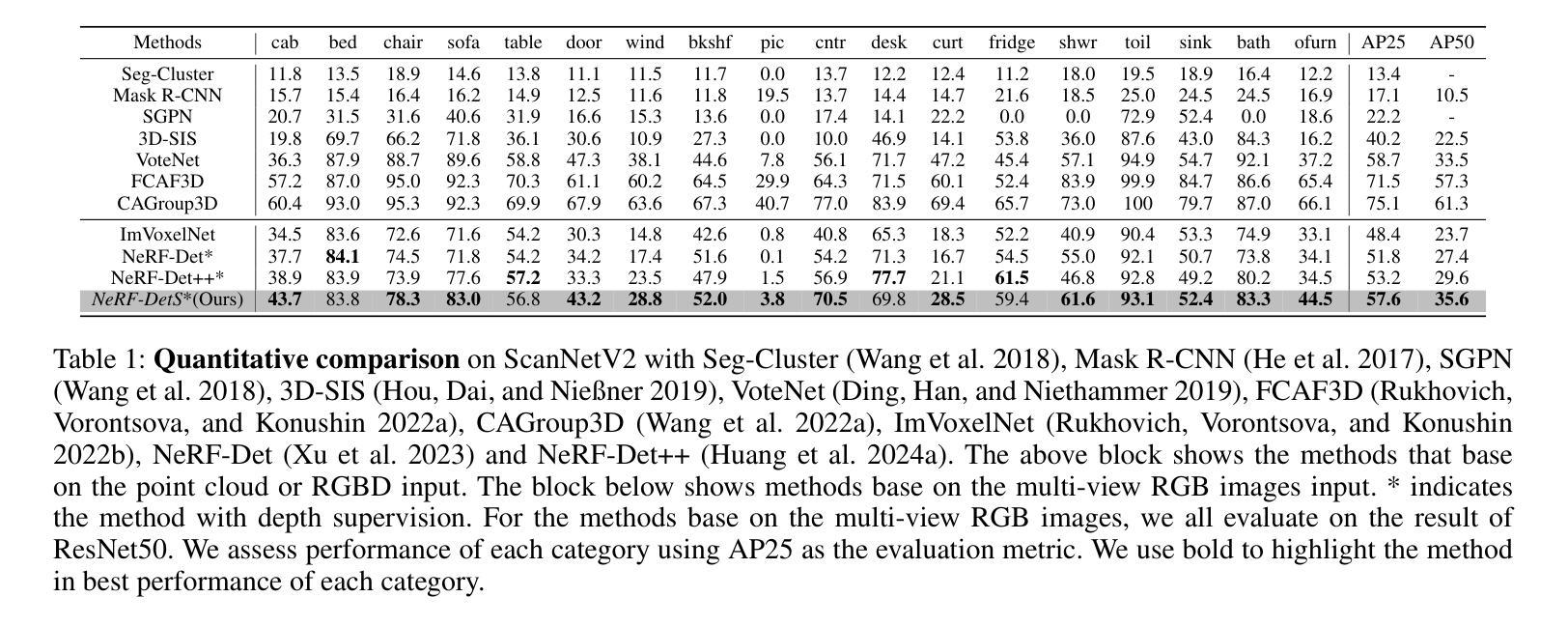
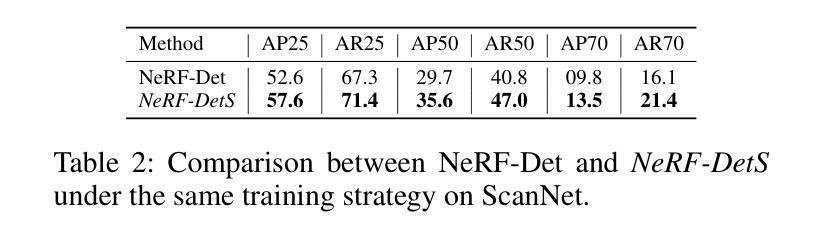
NeRF-DetS: Enhanced Adaptive Spatial-wise Sampling and View-wise Fusion Strategies for NeRF-based Indoor Multi-view 3D Object Detection
Authors:Chi Huang, Xinyang Li, Yansong Qu, Changli Wu, Xiaofan Li, Shengchuan Zhang, Liujuan Cao
In indoor scenes, the diverse distribution of object locations and scales makes the visual 3D perception task a big challenge. Previous works (e.g, NeRF-Det) have demonstrated that implicit representation has the capacity to benefit the visual 3D perception task in indoor scenes with high amount of overlap between input images. However, previous works cannot fully utilize the advancement of implicit representation because of fixed sampling and simple multi-view feature fusion. In this paper, inspired by sparse fashion method (e.g, DETR3D), we propose a simple yet effective method, NeRF-DetS, to address above issues. NeRF-DetS includes two modules: Progressive Adaptive Sampling Strategy (PASS) and Depth-Guided Simplified Multi-Head Attention Fusion (DS-MHA). Specifically, (1)PASS can automatically sample features of each layer within a dense 3D detector, using offsets predicted by the previous layer. (2)DS-MHA can not only efficiently fuse multi-view features with strong occlusion awareness but also reduce computational cost. Extensive experiments on ScanNetV2 dataset demonstrate our NeRF-DetS outperforms NeRF-Det, by achieving +5.02% and +5.92% improvement in mAP under IoU25 and IoU50, respectively. Also, NeRF-DetS shows consistent improvements on ARKITScenes.
在室内场景中,物体位置和尺度的多样分布使得视觉3D感知任务面临巨大挑战。先前的工作(例如NeRF-Det)已经证明,隐式表示有助于室内场景的视觉3D感知任务,尤其是在输入图像之间存在大量重叠的情况下。然而,由于固定的采样和简单的多视图特征融合,先前的工作无法充分利用隐式表示的进步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了室内场景中视觉3D感知的挑战,包括对象位置和尺度的多样性。受稀疏方法(如DETR3D)的启发,提出了一种简单有效的方法NeRF-DetS,包括渐进自适应采样策略(PASS)和深度引导简化多头注意力融合(DS-MHA)。实验表明,NeRF-DetS在ScanNetV2数据集上的性能优于NeRF-Det,在IoU25和IoU50下的mAP分别提高了+5.02%和+5.92%,并且在ARKITScenes上也表现出一致的提升。
Key Takeaways
- 室内场景中,对象位置和尺度的多样性使得视觉3D感知任务充满挑战。
- 之前的作品(如NeRF-Det)已经证明了隐式表示对室内场景视觉3D感知任务的潜力。
- NeRF-DetS方法通过结合渐进自适应采样策略和深度引导简化多头注意力融合来解决先前方法的问题。
- PASS能够自动在密集3D检测器中的每一层采样特征。
- DS-MHA能够高效地融合多视图特征,具有强大的遮挡意识,并降低计算成本。
- 在ScanNetV2数据集上的实验表明,NeRF-DetS的性能优于NeRF-Det,并且在ARKITScenes上也有一致的提升。
点此查看论文截图

Language-Guided Instance-Aware Domain-Adaptive Panoptic Segmentation
Authors:Elham Amin Mansour, Ozan Unal, Suman Saha, Benjamin Bejar, Luc Van Gool
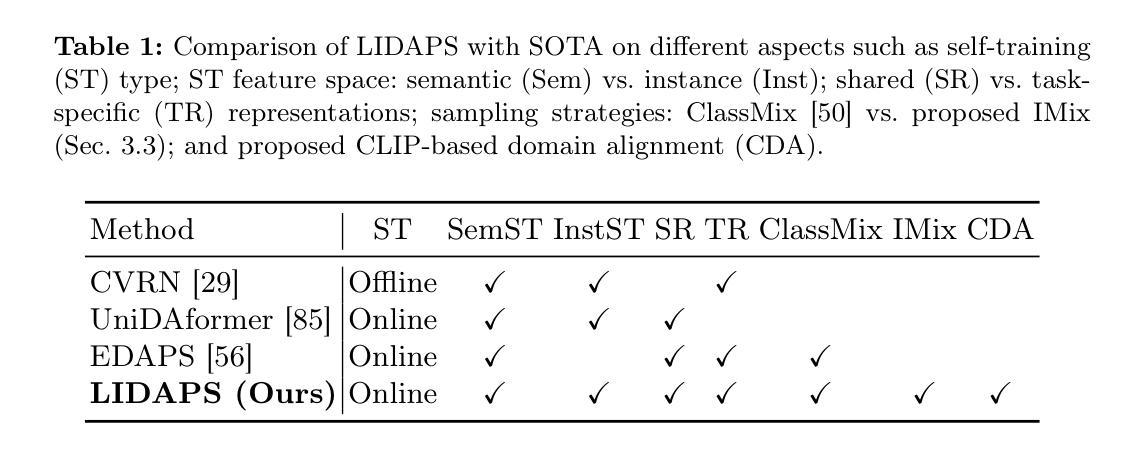
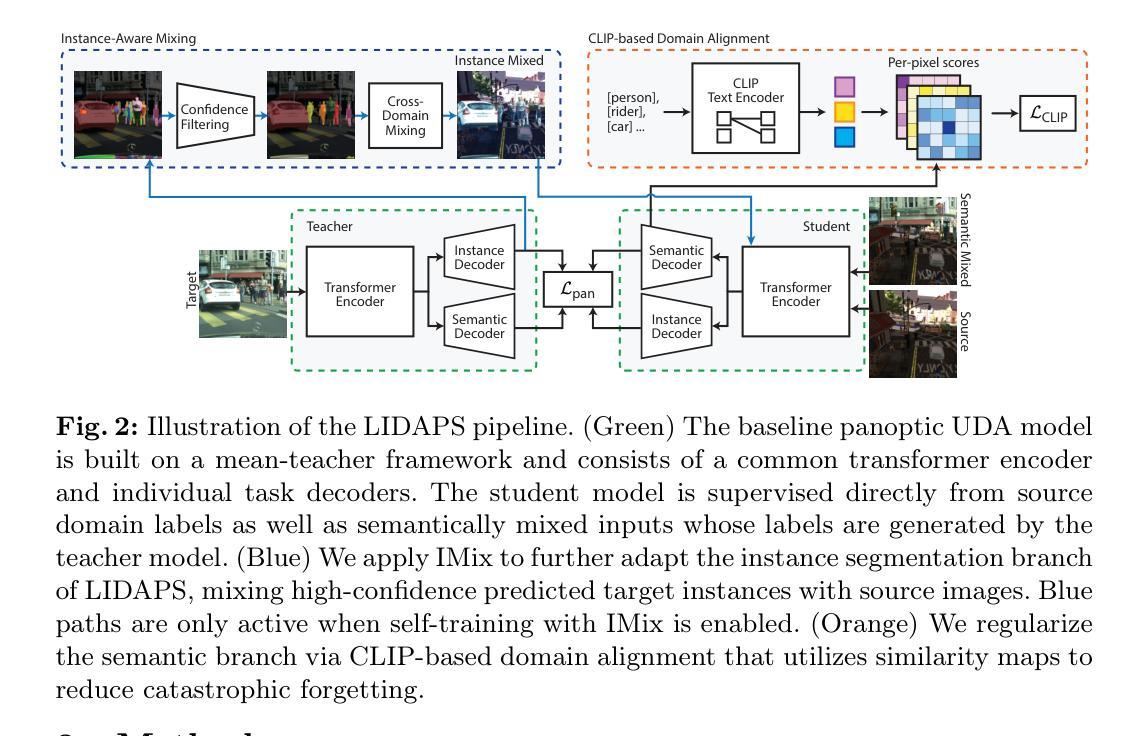
The increasing relevance of panoptic segmentation is tied to the advancements in autonomous driving and AR/VR applications. However, the deployment of such models has been limited due to the expensive nature of dense data annotation, giving rise to unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA). A key challenge in panoptic UDA is reducing the domain gap between a labeled source and an unlabeled target domain while harmonizing the subtasks of semantic and instance segmentation to limit catastrophic interference. While considerable progress has been achieved, existing approaches mainly focus on the adaptation of semantic segmentation. In this work, we focus on incorporating instance-level adaptation via a novel instance-aware cross-domain mixing strategy IMix. IMix significantly enhances the panoptic quality by improving instance segmentation performance. Specifically, we propose inserting high-confidence predicted instances from the target domain onto source images, retaining the exhaustiveness of the resulting pseudo-labels while reducing the injected confirmation bias. Nevertheless, such an enhancement comes at the cost of degraded semantic performance, attributed to catastrophic forgetting. To mitigate this issue, we regularize our semantic branch by employing CLIP-based domain alignment (CDA), exploiting the domain-robustness of natural language prompts. Finally, we present an end-to-end model incorporating these two mechanisms called LIDAPS, achieving state-of-the-art results on all popular panoptic UDA benchmarks.
全景分割的日益重要性是与自动驾驶和AR/VR应用的进步相联系的。然而,由于密集数据标注的高昂成本,此类模型的部署受到限制,催生了无监督域自适应(UDA)的出现。全景UDA的关键挑战在于缩小有标签源域和无标签目标域之间的域差距,同时协调语义分割和实例分割的子任务,以避免灾难性干扰。虽然已取得了相当大的进展,但现有方法主要集中在语义分割的适应上。在这项工作中,我们专注于通过一种新型实例感知跨域混合策略IMix,融入实例级适应。IMix通过提高实例分割性能,显著提高了全景质量。具体来说,我们提出了一种将目标域的高置信度预测实例插入源图像的方法,保留了所得伪标签的详尽性,同时减少了注入的确认偏见。然而,这种增强是以语义性能下降为代价的,这是由于灾难性遗忘造成的。为了缓解这个问题,我们通过采用基于CLIP的域对齐(CDA)来规范我们的语义分支,利用自然语言提示的域稳健性。最后,我们提出了一种端到端的模型,该模型融合了这两种机制,称为LIDAPS,在所有人气旺盛的全景UDA基准测试上均达到最新水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the 2025 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV)
Summary:随着自动驾驶和AR/VR应用的不断发展,全景分割的重要性日益凸显。然而,由于密集数据标注的高成本,全景分割模型的部署受到限制,这推动了无监督域自适应(UDA)的研究。本文关注无监督域自适应中的全景分割问题,提出了一种结合实例级自适应的新方法IMix,通过插入目标域的高置信度预测实例到源图像中,提高了全景分割的质量。然而,这可能导致语义性能下降,出现灾难性遗忘问题。为解决这一问题,本文采用基于CLIP的域对齐(CDA)方法,利用自然语言提示的域稳健性进行语义分支正则化。最终,本文提出了一种结合这两种机制的端到端模型LIDAPS,在主流全景UDA基准测试上实现最佳结果。
Key Takeaways:
- 全景分割在自动驾驶和AR/VR应用中越来越重要,但密集数据标注的高成本限制了其模型部署。
- 无监督域自适应(UDA)是解决全景分割中跨域问题的一种有效方法。
- IMix方法通过实例级自适应提高全景分割质量,通过将目标域的高置信度预测实例插入源图像中实现。
- IMix方法可能导致语义性能下降和灾难性遗忘问题。
- 为解决语义性能下降问题,采用基于CLIP的域对齐(CDA)方法进行语义分支正则化。
- LIDAPS模型结合IMix和CDA机制,实现了在主流全景UDA基准测试上的最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图