⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-02 更新
Prometheus: 3D-Aware Latent Diffusion Models for Feed-Forward Text-to-3D Scene Generation
Authors:Yuanbo Yang, Jiahao Shao, Xinyang Li, Yujun Shen, Andreas Geiger, Yiyi Liao
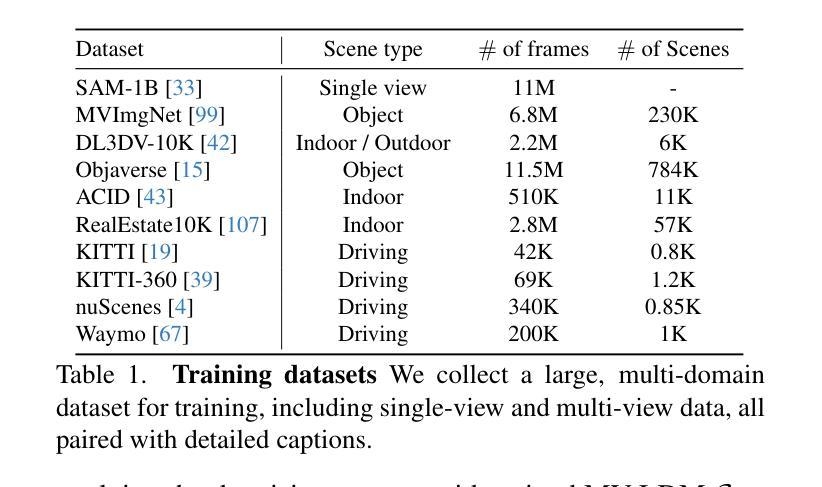
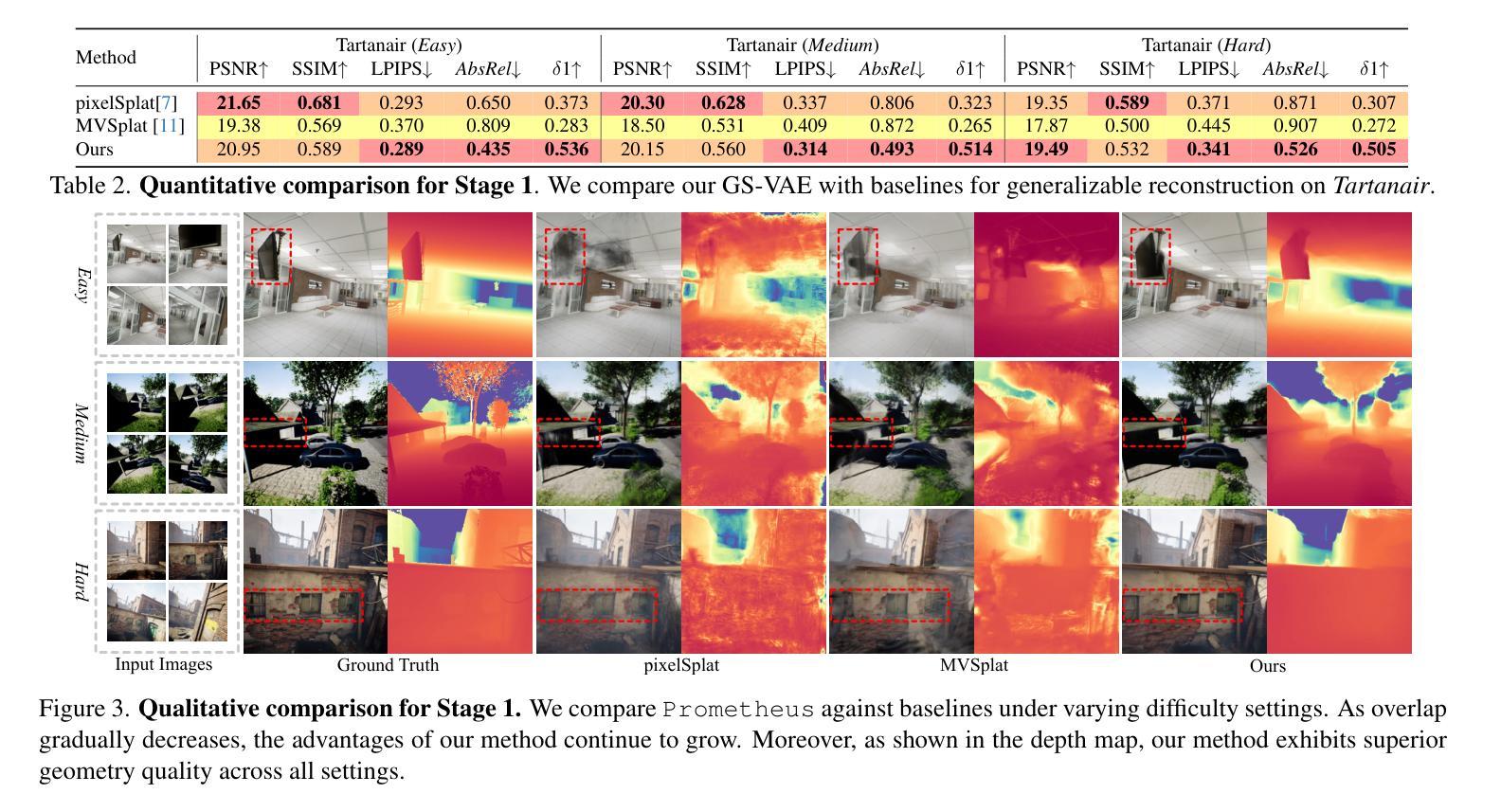
In this work, we introduce Prometheus, a 3D-aware latent diffusion model for text-to-3D generation at both object and scene levels in seconds. We formulate 3D scene generation as multi-view, feed-forward, pixel-aligned 3D Gaussian generation within the latent diffusion paradigm. To ensure generalizability, we build our model upon pre-trained text-to-image generation model with only minimal adjustments, and further train it using a large number of images from both single-view and multi-view datasets. Furthermore, we introduce an RGB-D latent space into 3D Gaussian generation to disentangle appearance and geometry information, enabling efficient feed-forward generation of 3D Gaussians with better fidelity and geometry. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in both feed-forward 3D Gaussian reconstruction and text-to-3D generation. Project page: https://freemty.github.io/project-prometheus/
在这项工作中,我们介绍了Prometheus,这是一个3D感知潜在扩散模型,可在对象和场景级别进行文本到3D的即时生成。我们将3D场景生成公式化为潜在扩散范式内的多视图、前馈、像素对齐的3D高斯生成。为了确保通用性,我们的模型建立在预训练的文本到图像生成模型之上,只需进行最小的调整,并使用大量来自单视图和多视图数据集的图片进行进一步训练。此外,我们将RGB-D潜在空间引入到3D高斯生成中,以分离外观和几何信息,实现高效的前馈3D高斯生成,具有更高的保真度和几何性。大量的实验结果证明了我们的方法在前馈3D高斯重建和文本到3D生成中的有效性。项目页面:https://freemty.github.io/project-prometheus/
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究提出了Prometheus,这是一款基于文本到三维场景的生成模型,能在几秒内完成物体和场景级别的三维感知潜在扩散模型构建。模型在已有的文本到图像生成模型的基础上稍作调整进行训练和优化,用于处理单视角和多视角数据集的庞大图像库。我们还将RGB-D潜在空间引入到三维高斯生成过程中以区分表面纹理信息和几何信息,从而实现在三维高斯模型中的高效正向生成,具有更高的保真度和几何特性。实验证明,该方法在正向三维高斯重建和文本到三维生成方面均具有良好的效果。
Key Takeaways
- Prometheus是一个基于文本到三维场景的生成模型,可以在几秒内完成物体和场景级别的构建。
- 该模型适用于单视角和多视角数据集的庞大图像库处理。
- RGB-D潜在空间被引入以区分表面纹理信息和几何信息,有助于在三维高斯模型中更高效正向生成高质量场景。
- 该方法能提高正向三维高斯重建的精度和效率。
- 该方法能有效利用已有的文本到图像生成模型,具有良好的可扩展性和兼容性。
- 模型展示了广泛的适用性,能够有效处理多种类型的文本到三维生成任务。
点此查看论文截图

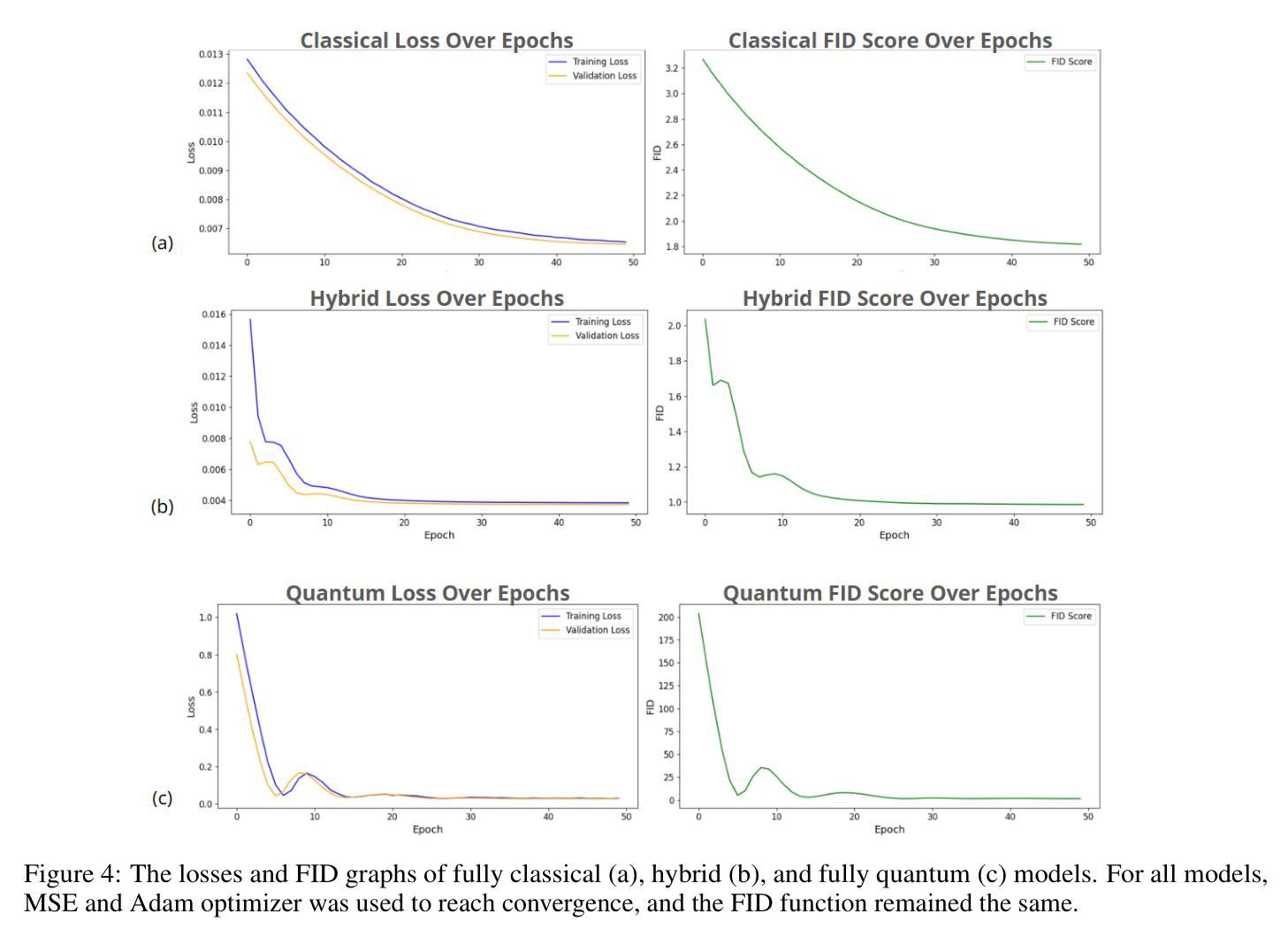
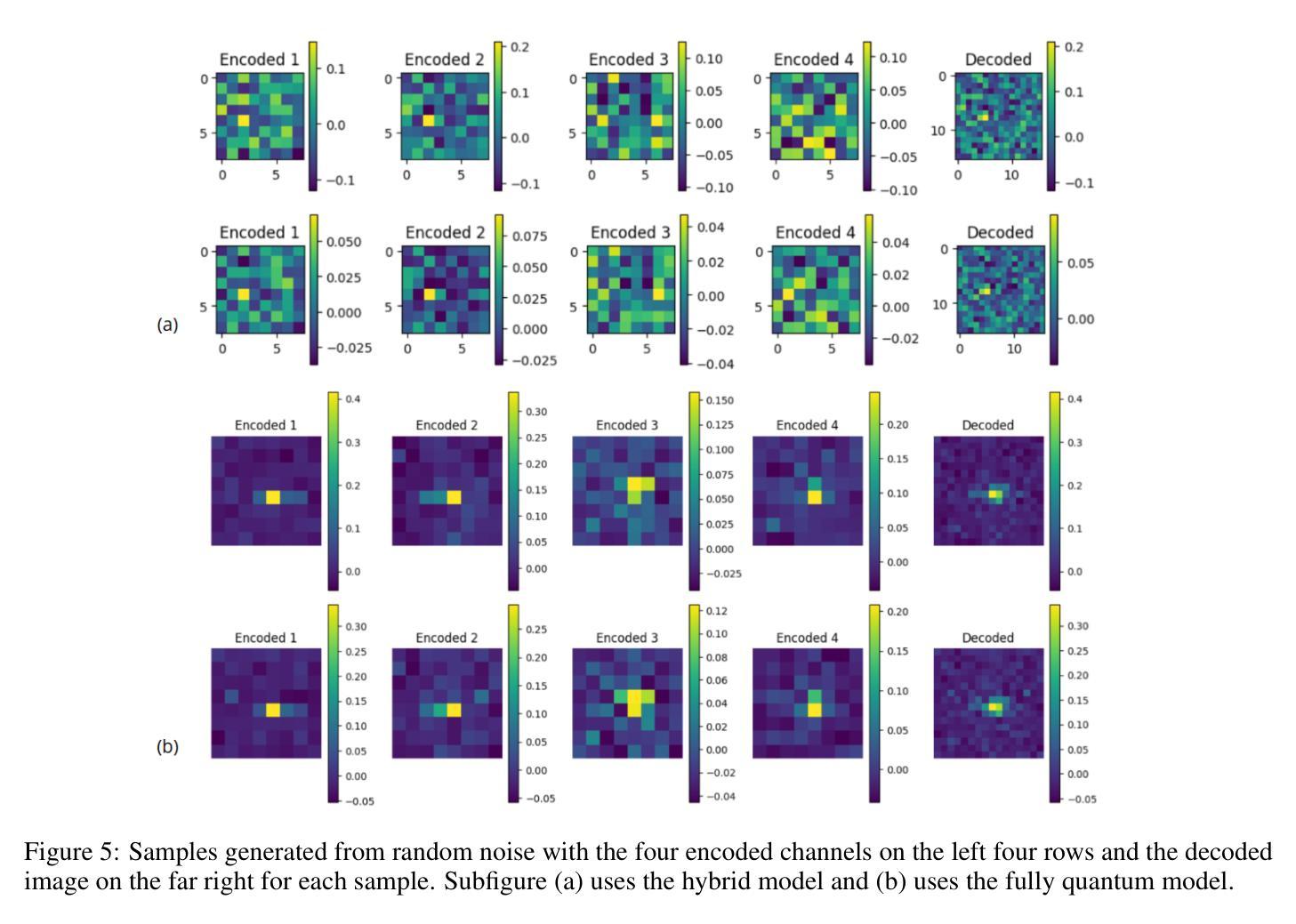
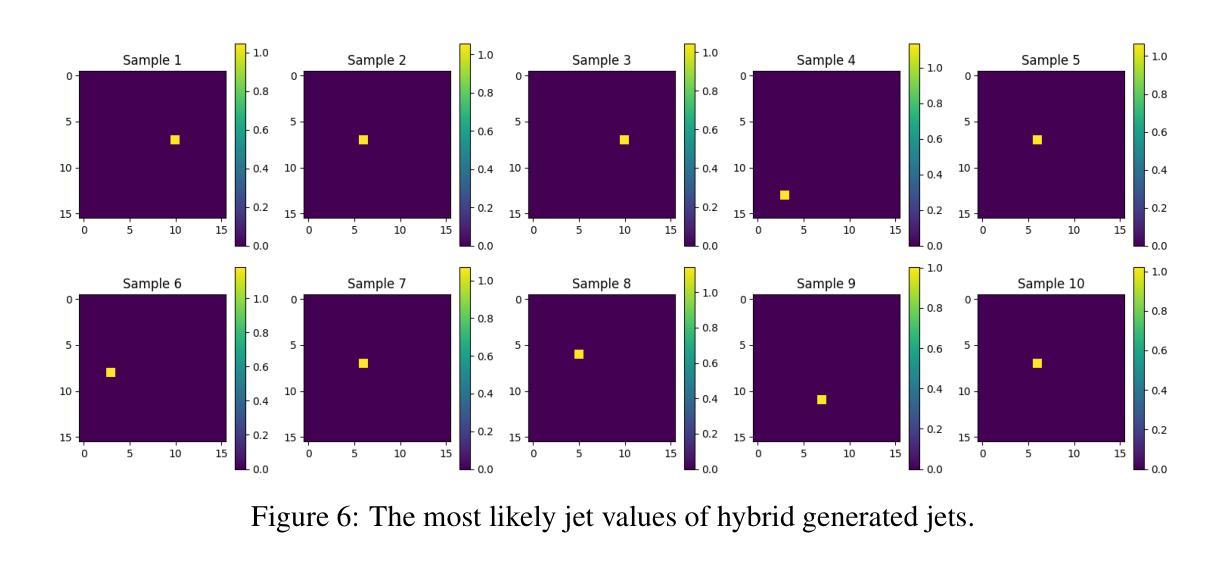
Quantum Diffusion Model for Quark and Gluon Jet Generation
Authors:Mariia Baidachna, Rey Guadarrama, Gopal Ramesh Dahale, Tom Magorsch, Isabel Pedraza, Konstantin T. Matchev, Katia Matcheva, Kyoungchul Kong, Sergei Gleyzer
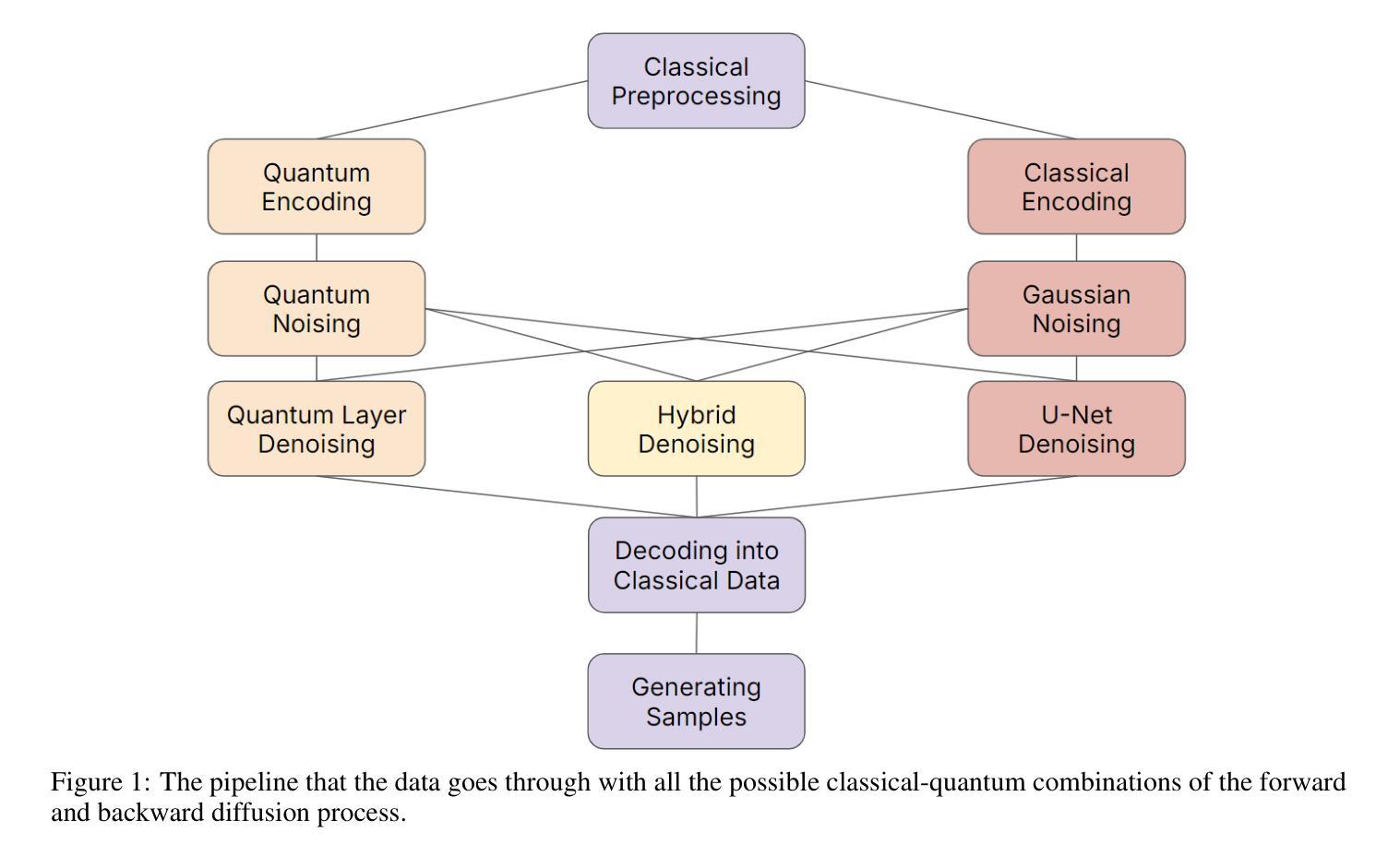
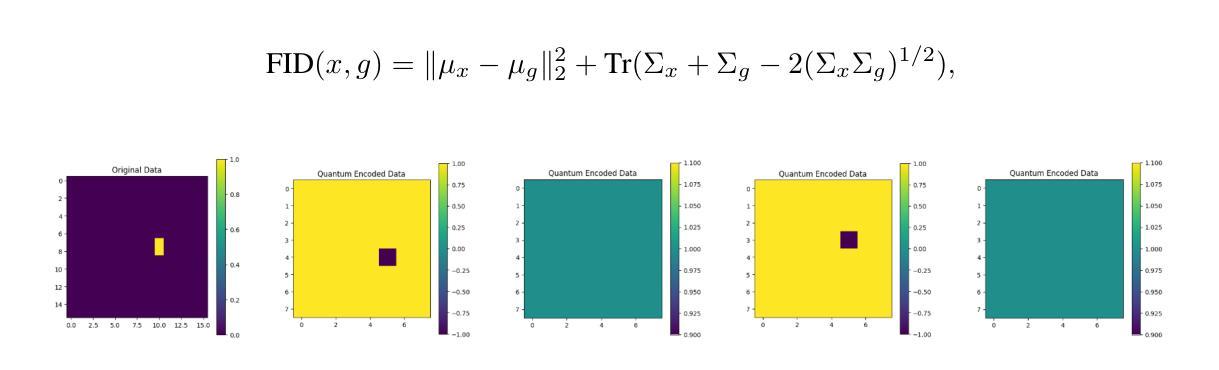
Diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable success in image generation, but they are computationally intensive and time-consuming to train. In this paper, we introduce a novel diffusion model that benefits from quantum computing techniques in order to mitigate computational challenges and enhance generative performance within high energy physics data. The fully quantum diffusion model replaces Gaussian noise with random unitary matrices in the forward process and incorporates a variational quantum circuit within the U-Net in the denoising architecture. We run evaluations on the structurally complex quark and gluon jets dataset from the Large Hadron Collider. The results demonstrate that the fully quantum and hybrid models are competitive with a similar classical model for jet generation, highlighting the potential of using quantum techniques for machine learning problems.
扩散模型在图像生成方面取得了显著的成功,但在计算方面密集且训练耗时较长。在本文中,我们引入了一种新型扩散模型,受益于量子计算技术来缓解计算挑战,提高高能物理数据中的生成性能。全量子扩散模型用随机酉矩阵替换正向过程中的高斯噪声,并在降噪架构中的U-Net中融入变分量子电路。我们在大型强子对撞机结构复杂的夸克和胶子喷射数据集上进行了评估。结果表明,全量子模型和混合模型在与喷射生成的类似经典模型的竞争中表现良好,突显了使用量子技术解决机器学习问题的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for the NeurIPS 2024 MLNCP workshop
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型扩散模型,该模型利用量子计算技术来缓解计算挑战,并提高高能物理数据的生成性能。通过随机单位矩阵替换高斯噪声进行正向过程,并在去噪架构的U-Net中引入变分量子电路。在大型强子对撞机结构复杂的夸克和胶子射流数据集上进行评估的结果表明,完全量子模型和混合模型在射流生成方面与类似的经典模型具有竞争力,突显了量子技术在机器学习问题中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 新型扩散模型结合量子计算技术以提高生成性能。
- 用随机单位矩阵替换高斯噪声来进行正向过程。
- 在去噪架构U-Net中引入变分量子电路。
- 模型在大型强子对撞机的复杂数据集上表现良好。
- 完全量子模型和混合模型在射流生成方面表现出竞争力。
- 量子技术在解决机器学习问题中具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图

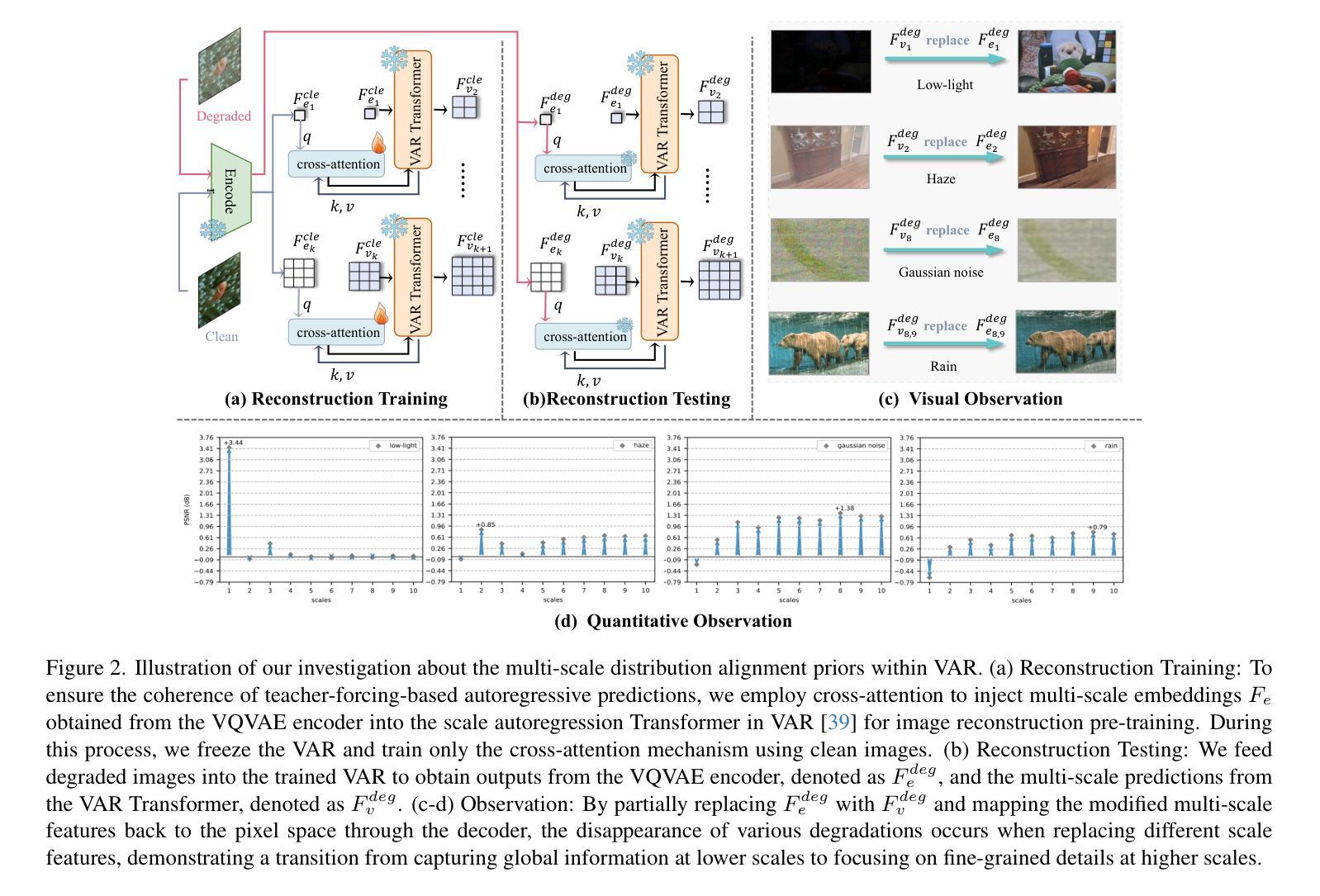
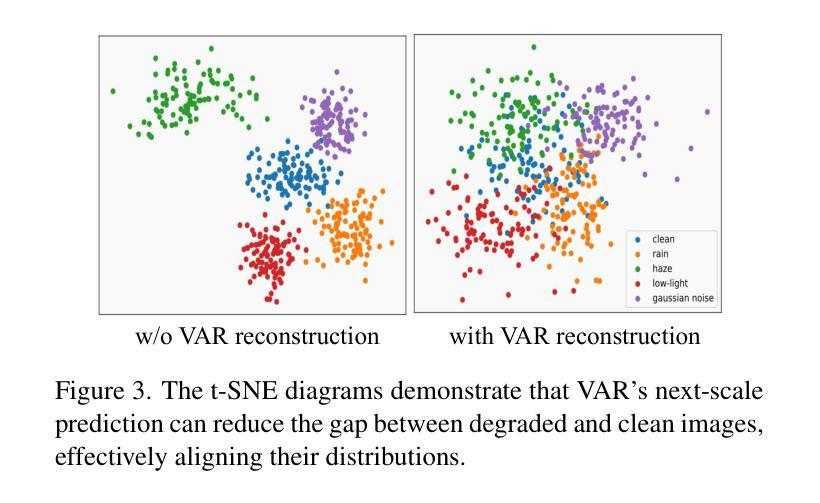
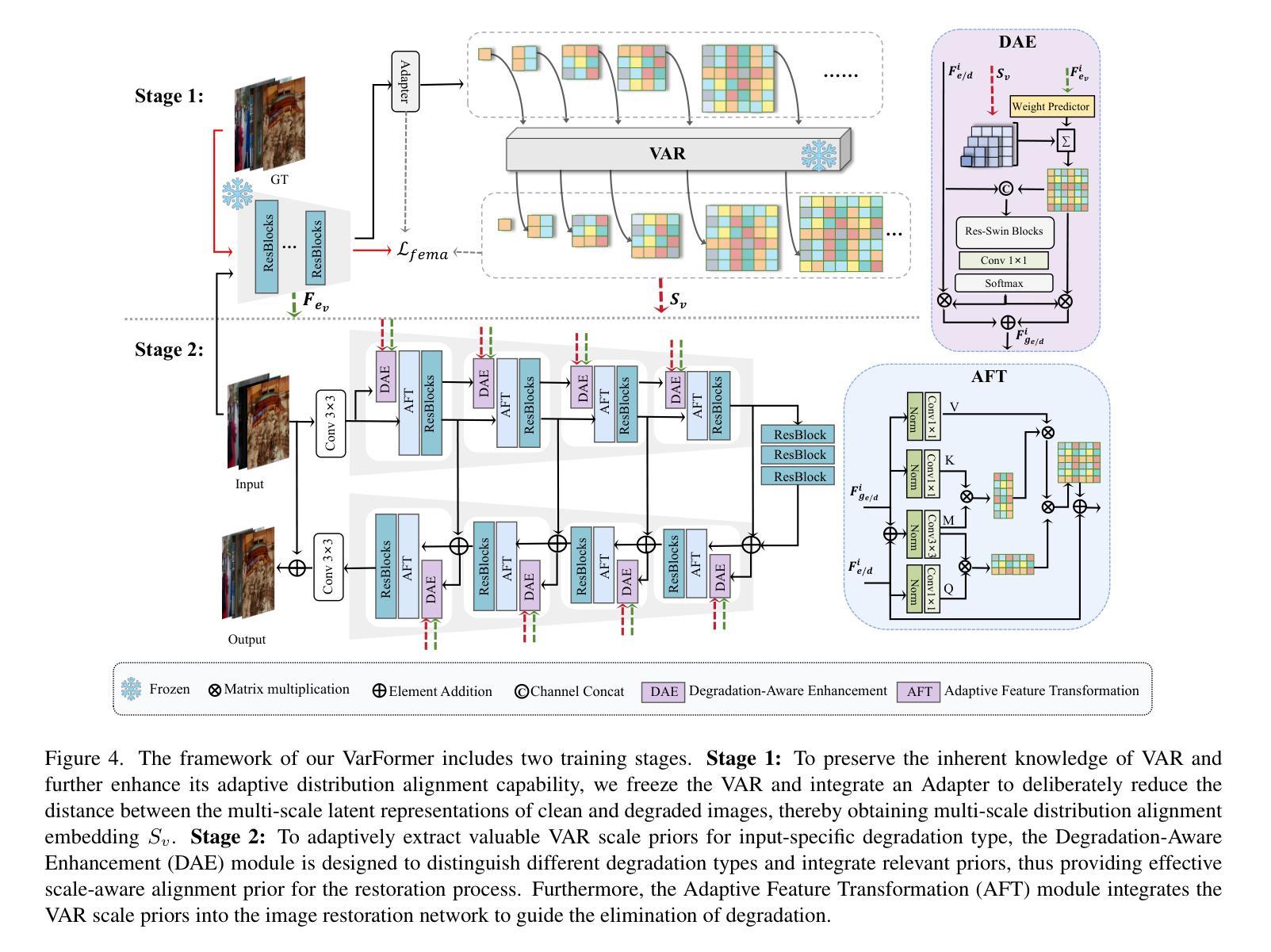
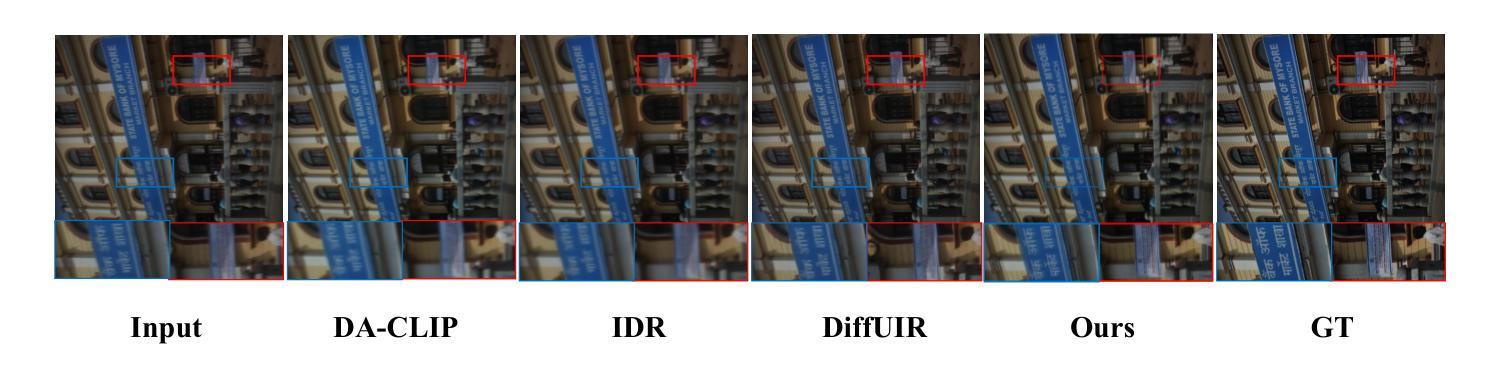
Varformer: Adapting VAR’s Generative Prior for Image Restoration
Authors:Siyang Wang, Feng Zhao
Generative models trained on extensive high-quality datasets effectively capture the structural and statistical properties of clean images, rendering them powerful priors for transforming degraded features into clean ones in image restoration. VAR, a novel image generative paradigm, surpasses diffusion models in generation quality by applying a next-scale prediction approach. It progressively captures both global structures and fine-grained details through the autoregressive process, consistent with the multi-scale restoration principle widely acknowledged in the restoration community. Furthermore, we observe that during the image reconstruction process utilizing VAR, scale predictions automatically modulate the input, facilitating the alignment of representations at subsequent scales with the distribution of clean images. To harness VAR’s adaptive distribution alignment capability in image restoration tasks, we formulate the multi-scale latent representations within VAR as the restoration prior, thus advancing our delicately designed VarFormer framework. The strategic application of these priors enables our VarFormer to achieve remarkable generalization on unseen tasks while also reducing training computational costs. Extensive experiments underscores that our VarFormer outperforms existing multi-task image restoration methods across various restoration tasks.
生成模型在大量高质量数据集上进行训练,能够有效地捕捉清洁图像的结构和统计特性,使其成为将退化特征转换为清洁特征进行图像修复的强大先验。VAR作为一种新的图像生成范式,通过应用下一尺度预测方法,在生成质量上超越了扩散模型。它通过自回归过程逐步捕捉全局结构和精细细节,这与修复社区广泛认可的多尺度修复原则相一致。此外,我们在使用VAR进行图像重建过程中观察到,尺度预测会自动调整输入,便于后续尺度上的表示与清洁图像分布的对齐。为了利用VAR在图像修复任务中的自适应分布对齐能力,我们将VAR内的多尺度潜在表示作为修复先验,从而推进了我们精心设计的VarFormer框架。这些先验的战略应用使我们的VarFormer在未见任务上实现了显著泛化,同时降低了训练计算成本。大量实验证明,我们的VarFormer在多种修复任务上优于现有的多任务图像修复方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:新型图像生成范式VAR通过应用多尺度预测方法,有效捕捉图像的全局结构和精细细节,超越了扩散模型在生成质量上的表现。VAR在图像重建过程中自动调整尺度预测,实现后续尺度的表示与干净图像分布的对齐。基于VAR的多尺度潜在表示作为恢复先验,提出的VarFormer框架在多项图像恢复任务上表现出卓越的性能和较低的培训计算成本。
Key Takeaways:
- 生成模型在高质量数据集上的训练,能有效捕捉干净图像的结构和统计属性,为图像恢复中退化特征转化为干净特征提供强大先验。
- VAR作为一种新型图像生成范式,通过下一尺度预测方法,在生成质量上超越了扩散模型。
- VAR能够渐进捕捉图像的全局结构和精细细节,符合恢复社区广泛认可的多尺度恢复原则。
- 在使用VAR的图像重建过程中,尺度预测能自动调整输入,促进后续尺度的表示与干净图像分布的对齐。
- VarFormer框架利用VAR的自适应分布对齐能力,在图像恢复任务中表现出优异性能。
- VarFormer通过精心设计的多尺度潜在表示作为恢复先验,实现了在未见任务上的卓越泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

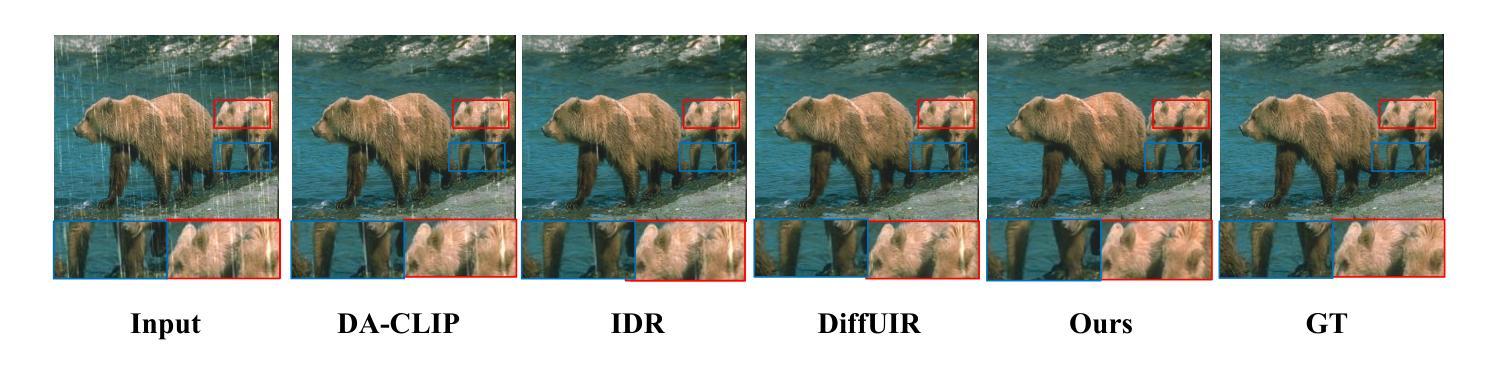
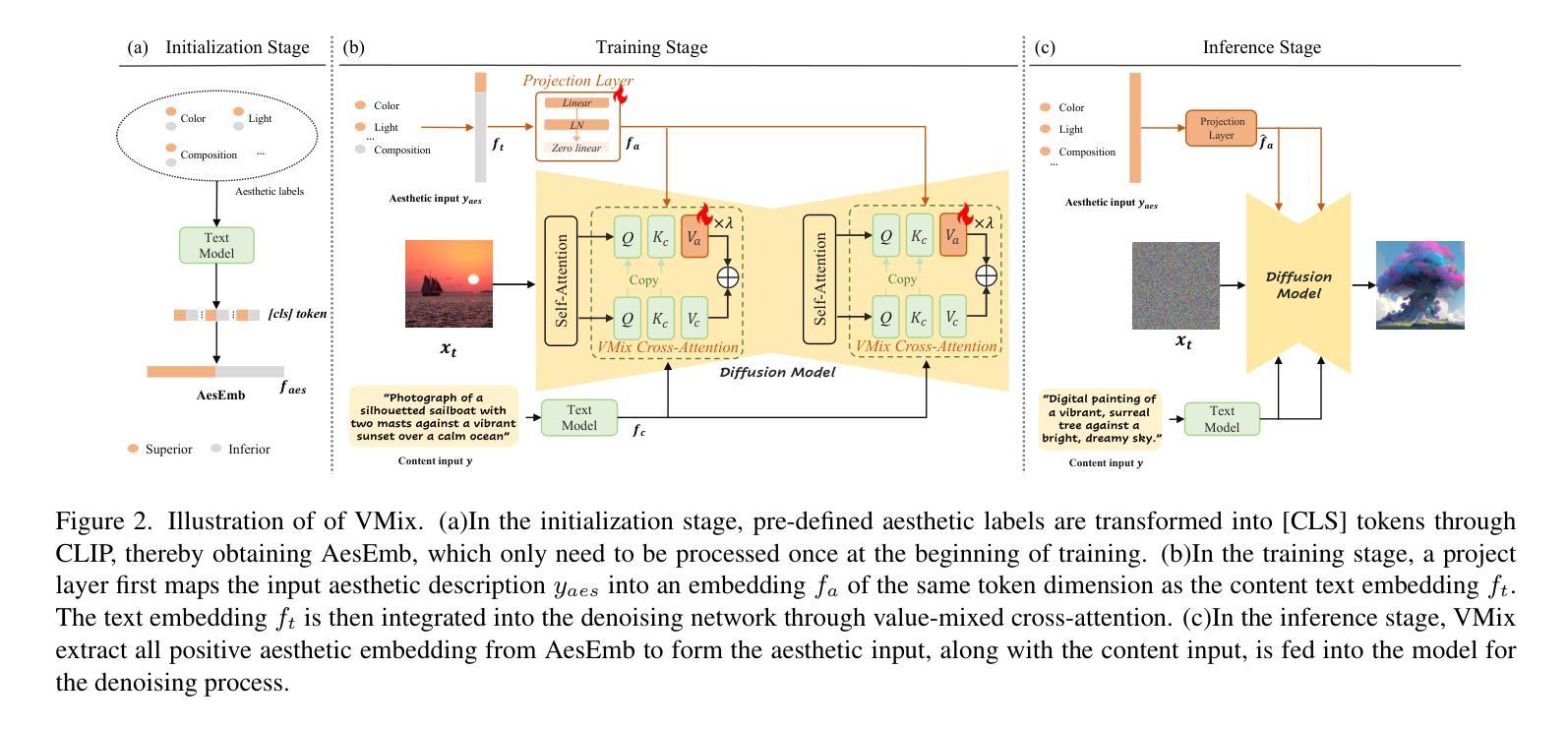
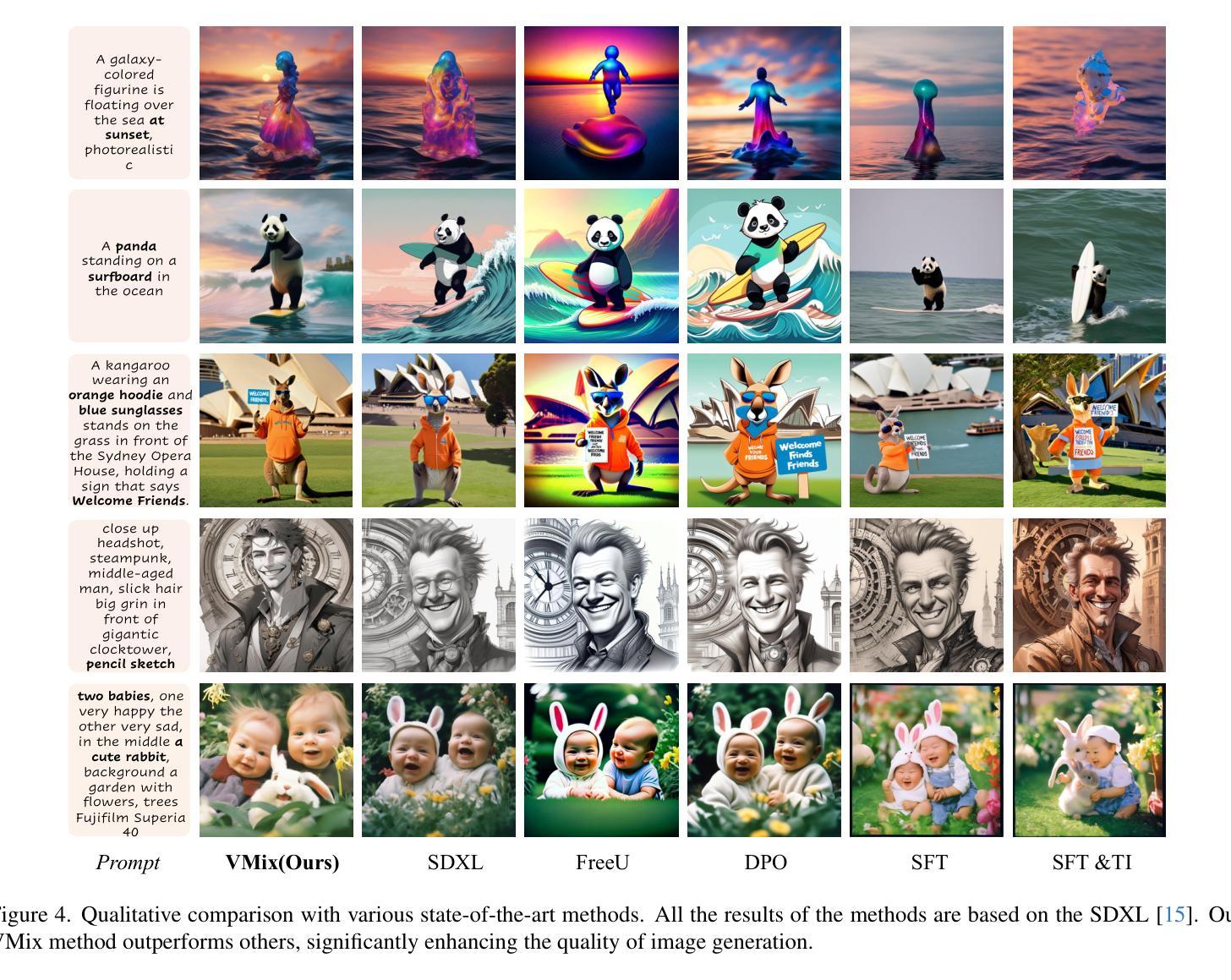
VMix: Improving Text-to-Image Diffusion Model with Cross-Attention Mixing Control
Authors:Shaojin Wu, Fei Ding, Mengqi Huang, Wei Liu, Qian He
While diffusion models show extraordinary talents in text-to-image generation, they may still fail to generate highly aesthetic images. More specifically, there is still a gap between the generated images and the real-world aesthetic images in finer-grained dimensions including color, lighting, composition, etc. In this paper, we propose Cross-Attention Value Mixing Control (VMix) Adapter, a plug-and-play aesthetics adapter, to upgrade the quality of generated images while maintaining generality across visual concepts by (1) disentangling the input text prompt into the content description and aesthetic description by the initialization of aesthetic embedding, and (2) integrating aesthetic conditions into the denoising process through value-mixed cross-attention, with the network connected by zero-initialized linear layers. Our key insight is to enhance the aesthetic presentation of existing diffusion models by designing a superior condition control method, all while preserving the image-text alignment. Through our meticulous design, VMix is flexible enough to be applied to community models for better visual performance without retraining. To validate the effectiveness of our method, we conducted extensive experiments, showing that VMix outperforms other state-of-the-art methods and is compatible with other community modules (e.g., LoRA, ControlNet, and IPAdapter) for image generation. The project page is https://vmix-diffusion.github.io/VMix/.
尽管扩散模型在文本到图像生成方面表现出卓越的天赋,但它们仍然可能无法生成具有高度审美感的图像。更具体地说,在更精细的维度(包括颜色、光线、构图等)上,生成的图像与真实世界的审美图像之间仍然存在差距。在本文中,我们提出了Cross-Attention Value Mixing Control(VMix)适配器,这是一种即插即用的美学适配器,旨在通过(1)通过初始化美学嵌入将输入文本提示解耦为内容描述和美学描述,(2)通过值混合交叉注意力将美学条件集成到去噪过程中,通过网络与零初始化线性层连接,来升级生成的图像质量,同时保持视觉概念的普遍性。我们的关键见解是通过设计一种优越的条件控制方法来提高现有扩散模型的美学表现,同时保留图像文本的对齐。通过我们的精心设计,VMix足够灵活,可应用于社区模型以获得更好的视觉性能而无需重新训练。为了验证我们方法的有效性,我们进行了大量实验,结果表明VMix优于其他最先进的方法,并且与用于图像生成的其他社区模块(例如LoRA、ControlNet和IPAdapter)兼容。项目页面是https://vmix-diffusion.github.io/VMix/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Codes and models are available at https://github.com/fenfenfenfan/VMix
Summary
本文提出一种名为Cross-Attention Value Mixing Control(VMix)Adapter的美学适配器,旨在提高扩散模型生成图像的质量,同时保持对视觉概念的普遍性。它通过初始化美学嵌入来将输入文本提示分解为内容描述和美学描述,并通过值混合交叉注意力将美学条件融入去噪过程。VMix设计了一种优越的条件控制方法,提高了现有扩散模型的美学表现,同时保持了图像与文本的对应性。此外,VMix灵活适用于社区模型,无需重新训练即可提高视觉性能。实验证明,VMix在图像生成方面优于其他最先进的方法,并与其他社区模块(如LoRA、ControlNet和IPAdapter)兼容。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在文本到图像生成方面表现出卓越的能力,但在生成具有高度美学价值的图像方面仍存在不足。
- 提出了一种新的美学适配器Cross-Attention Value Mixing Control(VMix)Adapter,旨在提高扩散模型生成图像的质量。
- VMix通过初始化美学嵌入来分解输入文本提示,并进一步通过值混合交叉注意力将美学条件融入去噪过程。
- VMix设计了一种优越的条件控制方法,提高了现有扩散模型的美学表现,同时保持图像与文本的对应性。
- VMix可灵活应用于社区模型,无需重新训练即可提升视觉性能。
- 实验证明VMix在图像生成方面优于其他先进方法。
- VMix与其他社区模块兼容,如LoRA、ControlNet和IPAdapter。
点此查看论文截图


HFI: A unified framework for training-free detection and implicit watermarking of latent diffusion model generated images
Authors:Sungik Choi, Sungwoo Park, Jaehoon Lee, Seunghyun Kim, Stanley Jungkyu Choi, Moontae Lee
Dramatic advances in the quality of the latent diffusion models (LDMs) also led to the malicious use of AI-generated images. While current AI-generated image detection methods assume the availability of real/AI-generated images for training, this is practically limited given the vast expressibility of LDMs. This motivates the training-free detection setup where no related data are available in advance. The existing LDM-generated image detection method assumes that images generated by LDM are easier to reconstruct using an autoencoder than real images. However, we observe that this reconstruction distance is overfitted to background information, leading the current method to underperform in detecting images with simple backgrounds. To address this, we propose a novel method called HFI. Specifically, by viewing the autoencoder of LDM as a downsampling-upsampling kernel, HFI measures the extent of aliasing, a distortion of high-frequency information that appears in the reconstructed image. HFI is training-free, efficient, and consistently outperforms other training-free methods in detecting challenging images generated by various generative models. We also show that HFI can successfully detect the images generated from the specified LDM as a means of implicit watermarking. HFI outperforms the best baseline method while achieving magnitudes of
潜在扩散模型(LDM)质量的显著进步也导致了AI生成图像被恶意使用。当前AI生成的图像检测方法假设有真实/AI生成的图像可用于训练,但考虑到LDM的巨大表达能力,这在实践中是有限的。这促使了无需训练的检测设置的出现,即提前没有相关数据可用。现有的LDM生成的图像检测方法假设使用自编码器重建LDM生成的图像比重建真实图像更容易。然而,我们观察到这种重建距离是过度拟合背景信息的,导致当前方法在检测具有简单背景的图像时表现不佳。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种名为HFI的新方法。具体来说,通过将LDM的自编码器视为下采样-上采样内核,HFI测量重建图像中出现的混叠程度,即高频信息的失真。HFI无需训练,效率高,并且在检测由各种生成模型生成的具有挑战性的图像时始终优于其他无需训练的方法。我们还展示了HFI可以成功检测从特定LDM生成的图像,作为一种隐式水印手段。HFI在无需训练的基线方法中表现出优越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了潜在扩散模型(LDM)的进展及其被恶意利用生成图像的问题。现有AI生成图像的检测方法受限于训练数据,而LDM生成的图像检测依赖于图像重构距离来判断。然而,这种方法容易忽略简单背景图像的检测。为此,本文提出了一种新的检测方法——HFI。它通过测量重建图像中的混叠程度来衡量高频信息的失真程度,无需训练即可高效检测各种生成模型生成的挑战图像。此外,HFI还可用于检测特定LDM生成的图像作为隐性水印。
Key Takeaways
- LDM的进展导致AI生成图像的恶意使用问题。
- 现有AI生成图像检测方法受限于训练数据,且难以检测简单背景图像。
- 本文提出了一种新的检测方法HFI,基于高频信息的失真程度来衡量混叠程度。
- HFI无需训练即可高效检测各种生成模型生成的挑战图像。
- HFI可成功检测特定LDM生成的图像作为隐性水印。
- HFI相较于最佳基线方法表现更优。
点此查看论文截图
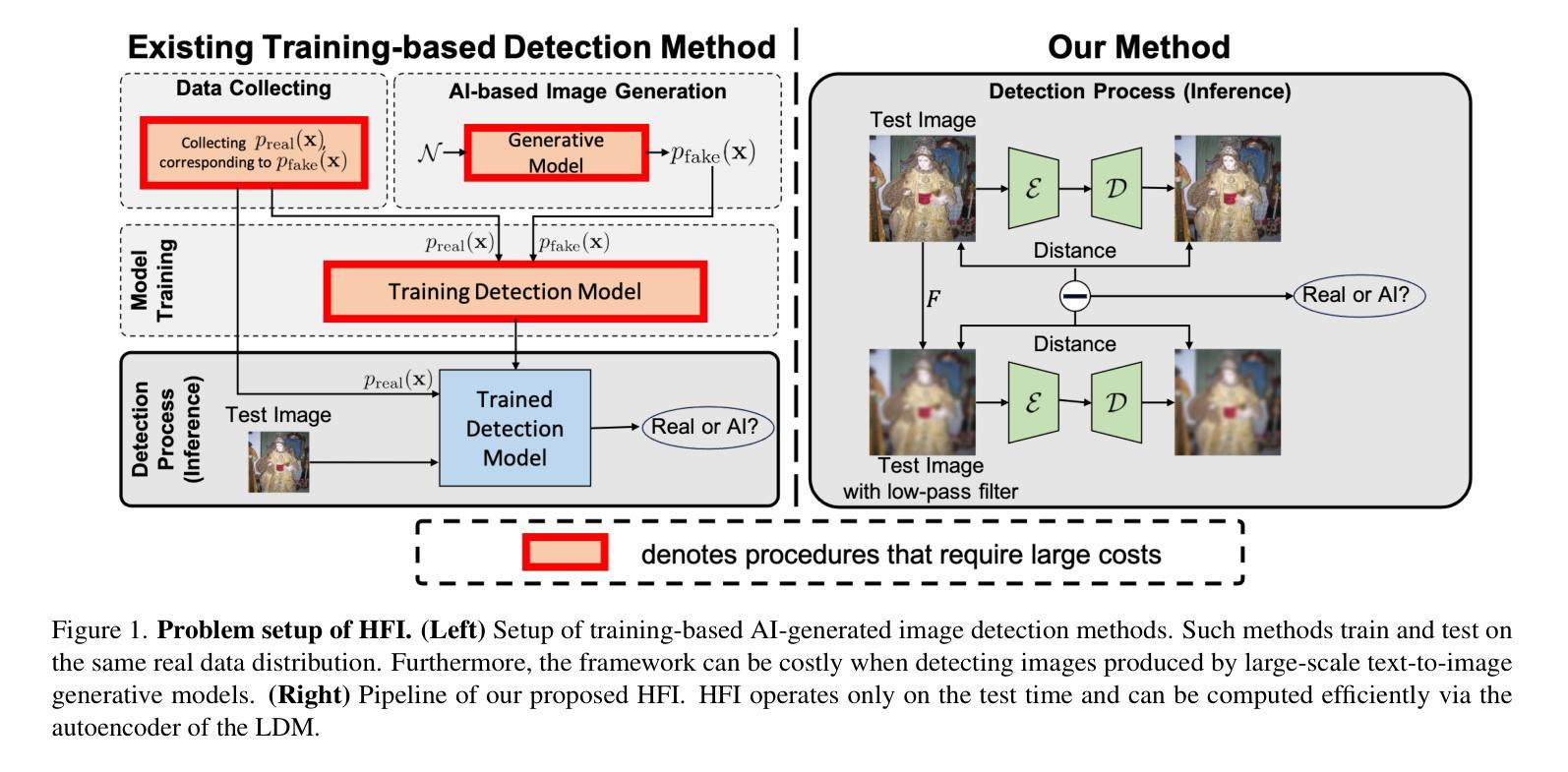
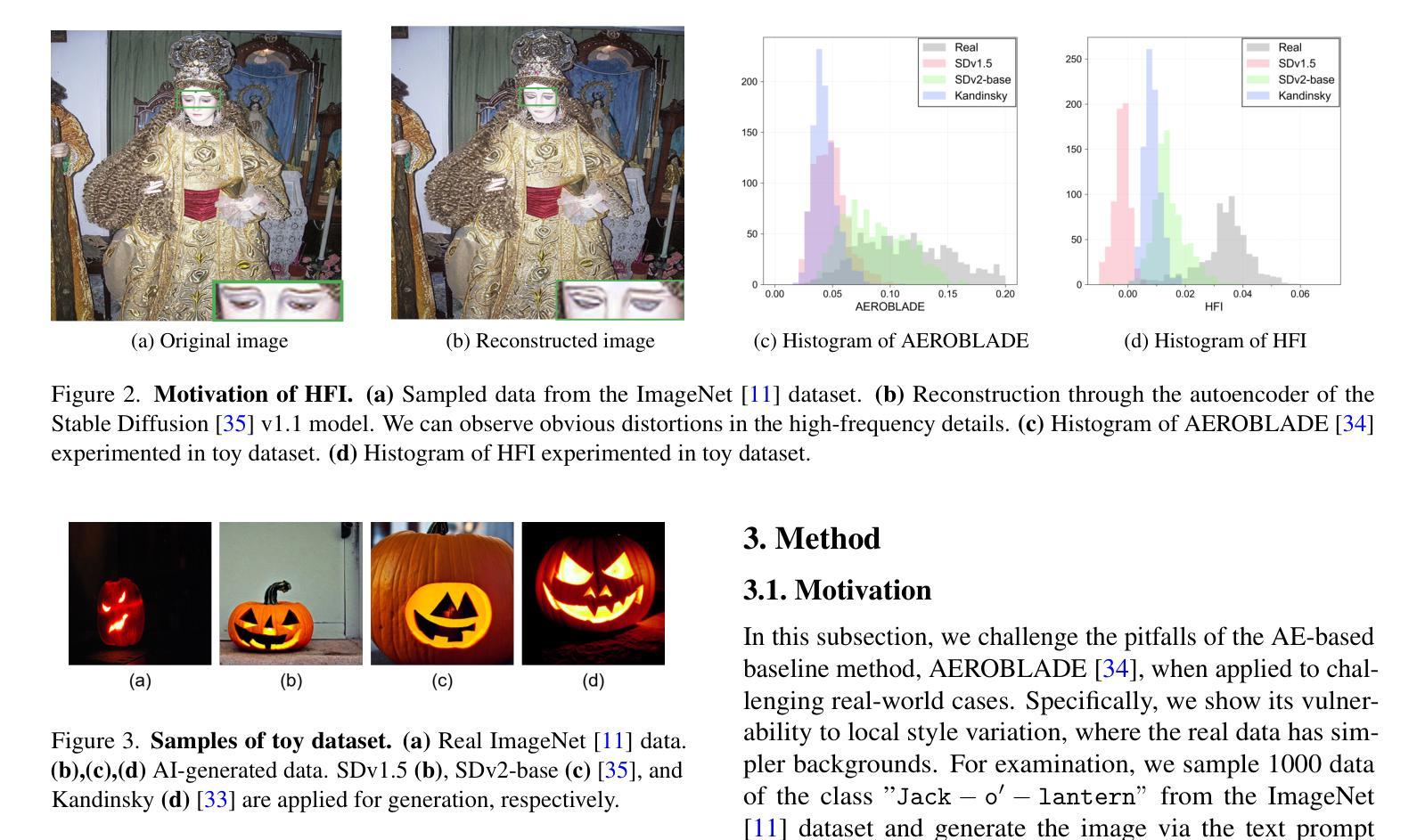
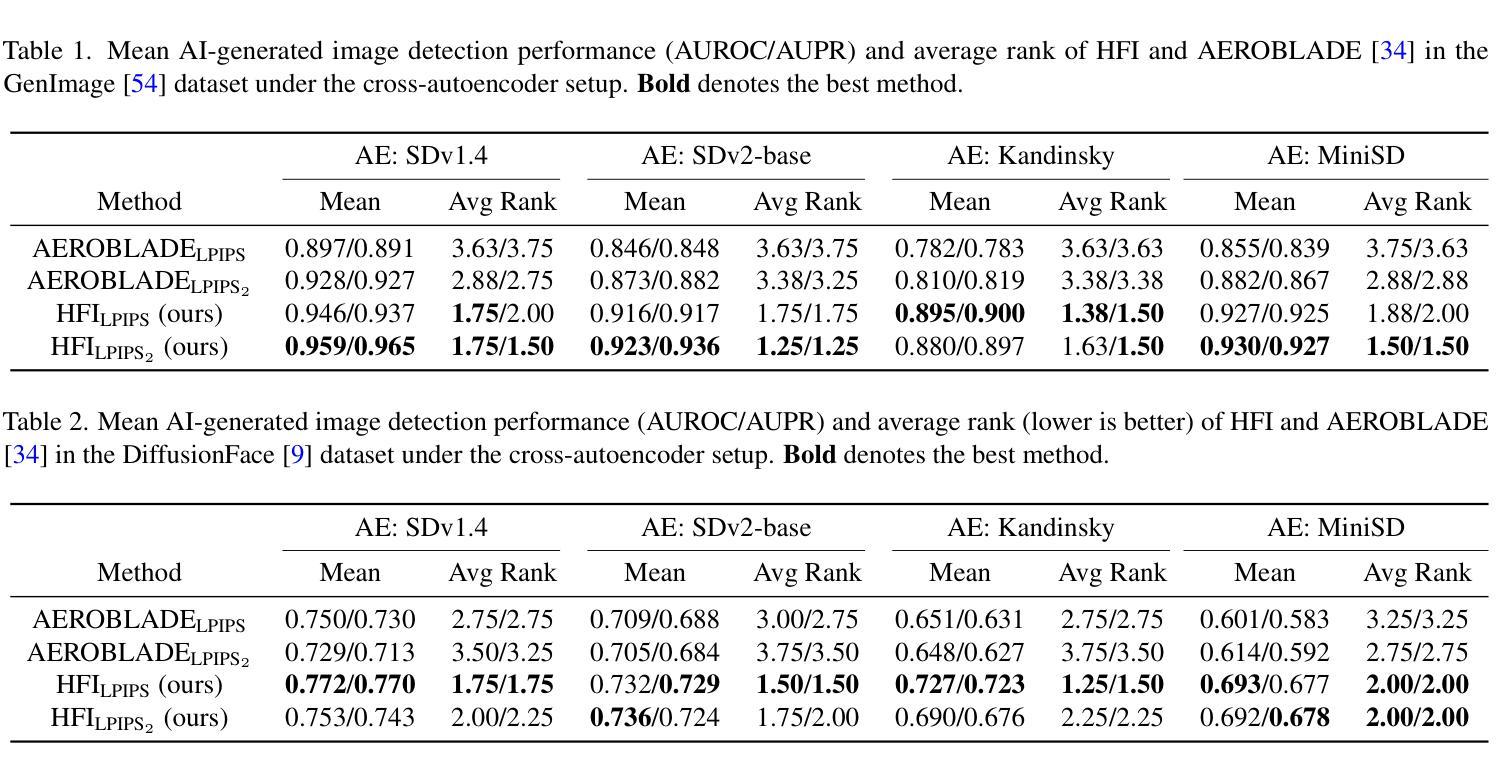
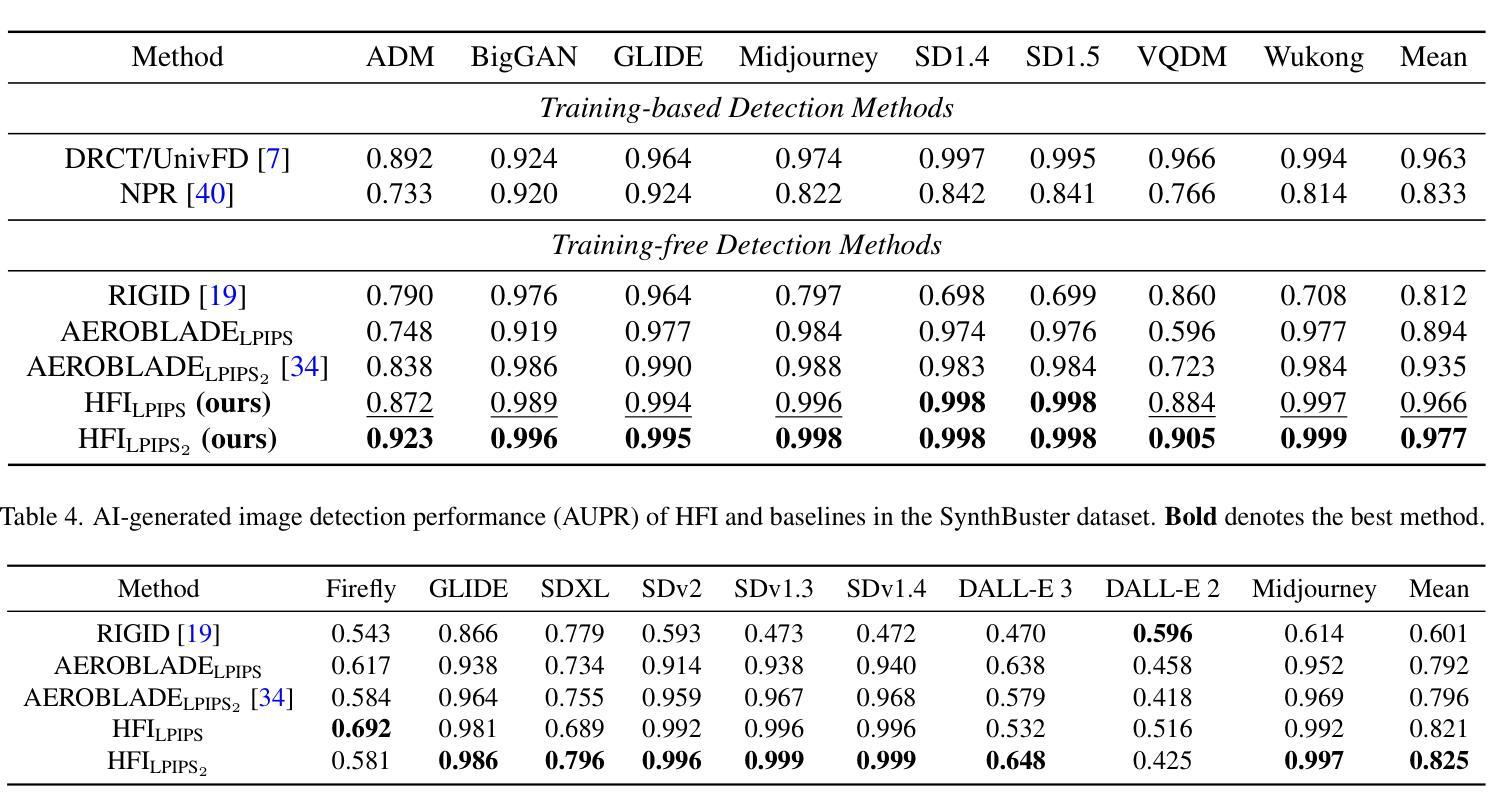
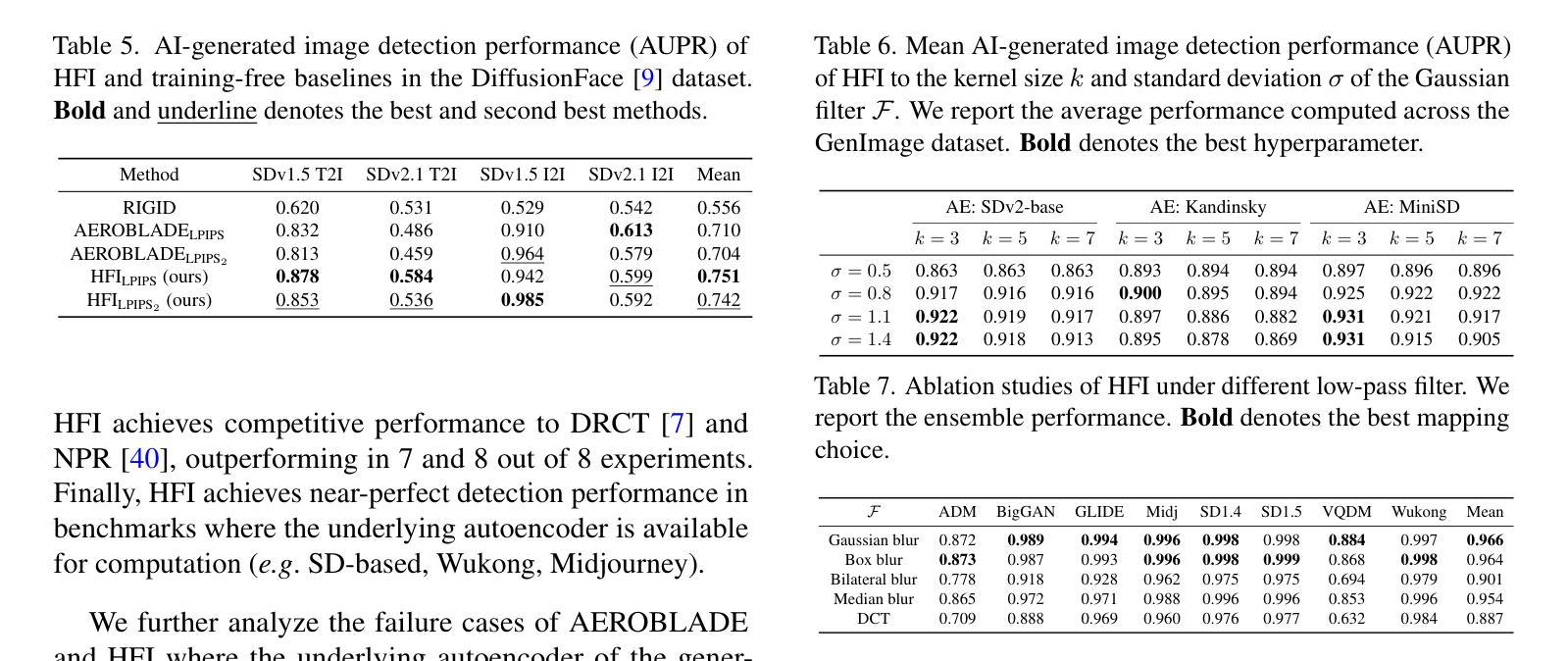
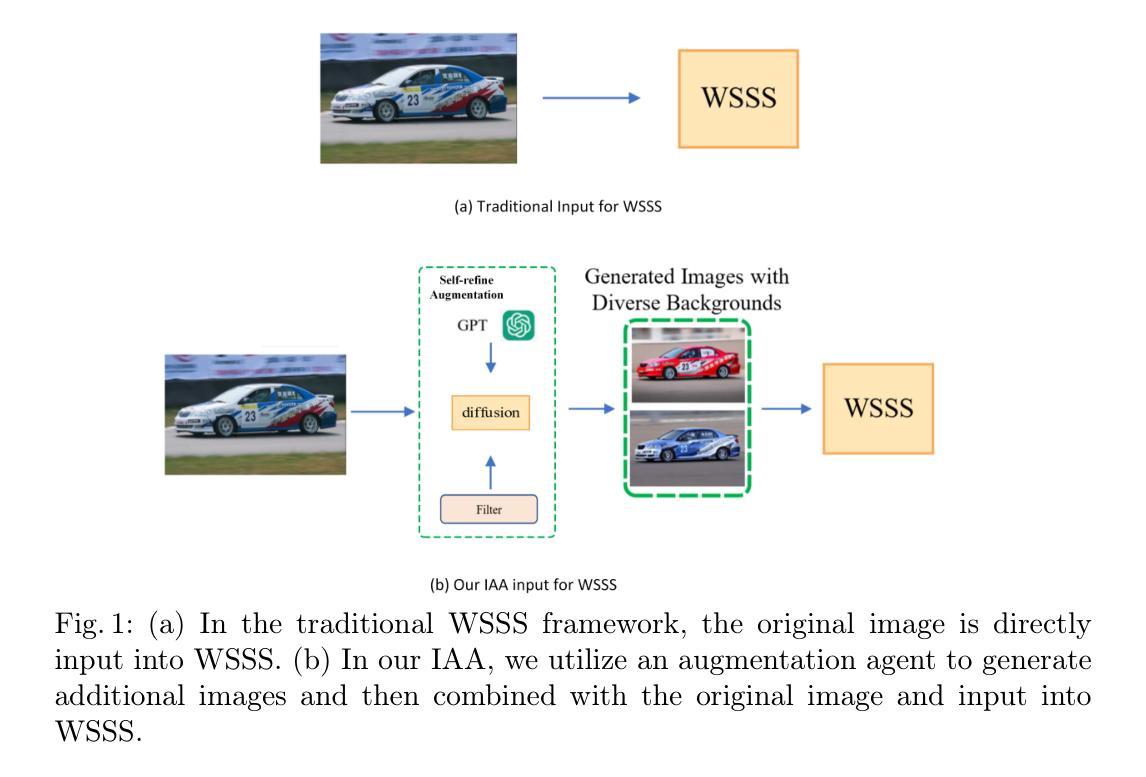
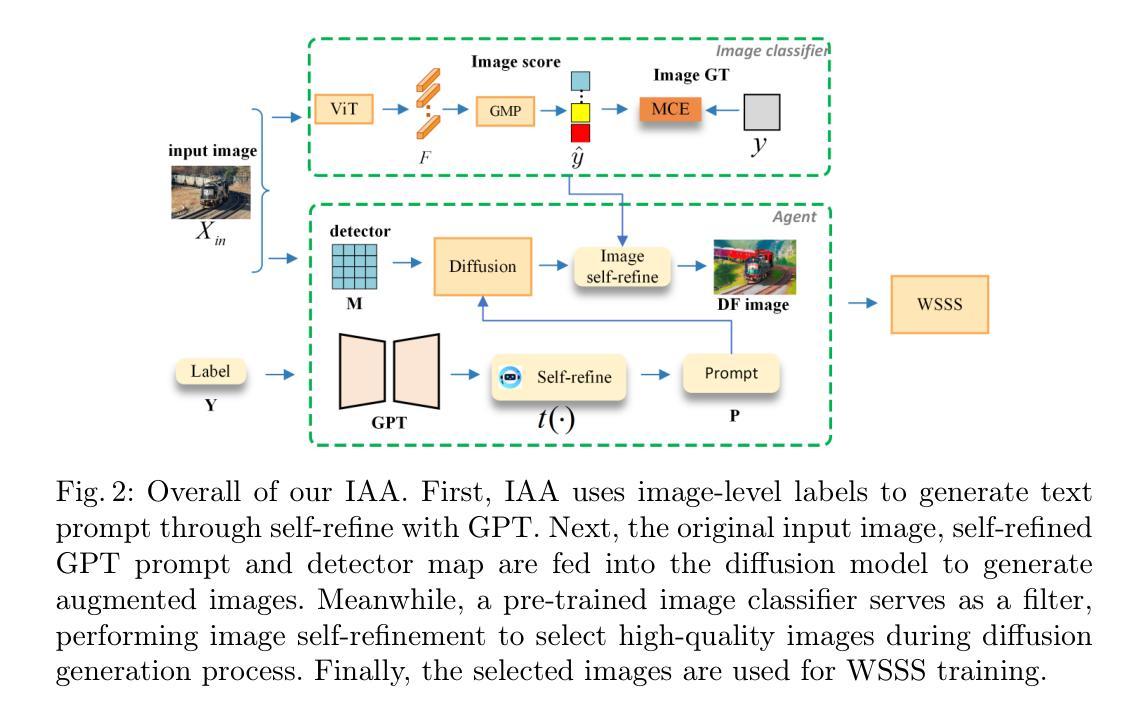
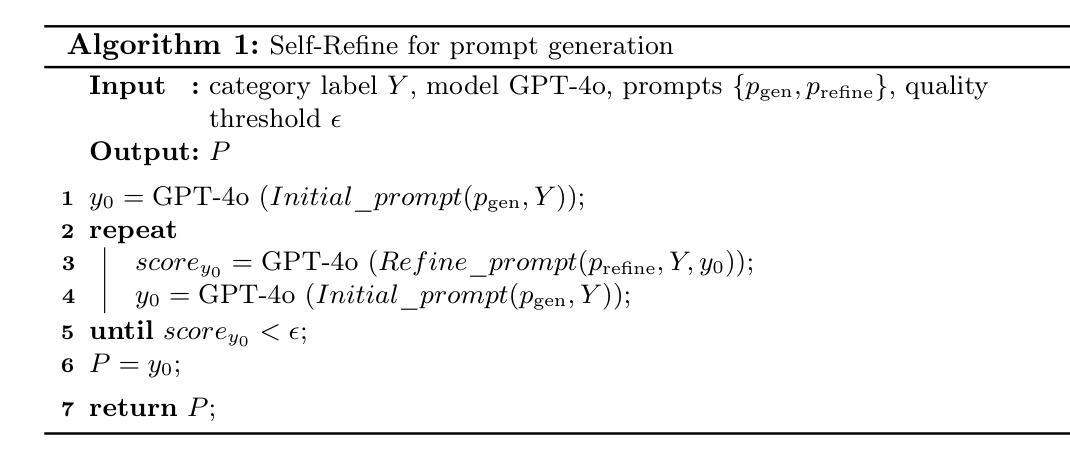
Image Augmentation Agent for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Wangyu Wu, Xianglin Qiu, Siqi Song, Zhenhong Chen, Xiaowei Huang, Fei Ma, Jimin Xiao
Weakly-supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) has achieved remarkable progress using only image-level labels. However, most existing WSSS methods focus on designing new network structures and loss functions to generate more accurate dense labels, overlooking the limitations imposed by fixed datasets, which can constrain performance improvements. We argue that more diverse trainable images provides WSSS richer information and help model understand more comprehensive semantic pattern. Therefore in this paper, we introduce a novel approach called Image Augmentation Agent (IAA) which shows that it is possible to enhance WSSS from data generation perspective. IAA mainly design an augmentation agent that leverages large language models (LLMs) and diffusion models to automatically generate additional images for WSSS. In practice, to address the instability in prompt generation by LLMs, we develop a prompt self-refinement mechanism. It allow LLMs to re-evaluate the rationality of generated prompts to produce more coherent prompts. Additionally, we insert an online filter into diffusion generation process to dynamically ensure the quality and balance of generated images. Experimental results show that our method significantly surpasses state-of-the-art WSSS approaches on the PASCAL VOC 2012 and MS COCO 2014 datasets.
弱监督语义分割(WSSS)仅使用图像级标签取得了显著的进步。然而,大多数现有的WSSS方法主要集中在设计新的网络结构和损失函数来生成更准确的密集标签,而忽略了固定数据集所带来的限制,这可能会限制性能的提升。我们认为,提供更多可训练的图像可以为WSSS提供更丰富的信息,并帮助模型理解更全面的语义模式。因此,在本文中,我们介绍了一种新方法,称为图像增强代理(IAA),它表明从数据生成的角度增强WSSS是可能的。IAA主要设计了一个增强代理,利用大型语言模型(LLM)和扩散模型自动为WSSS生成额外的图像。在实践中,为了解决LLM提示生成中的不稳定问题,我们开发了一种提示自我完善机制。它允许LLM重新评估生成提示的合理性,以产生更连贯的提示。此外,我们在扩散生成过程中插入了一个在线过滤器,以动态确保生成图像的质量和平衡。实验结果表明,我们的方法在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上显著超越了最先进的WSSS方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为Image Augmentation Agent(IAA)的方法,从数据生成的角度提升弱监督语义分割(WSSS)性能。通过利用大型语言模型(LLMs)和扩散模型自动为WSSS生成额外图像,并设计了一种提示自我完善机制和在线过滤器,解决了语言模型提示生成的不稳定性和图像生成质量的问题。在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上的实验结果优于现有WSSS方法。
Key Takeaways
- 利用大型语言模型(LLMs)和扩散模型提出一种新颖方法Image Augmentation Agent(IAA),从数据生成角度提升弱监督语义分割(WSSS)性能。
- IAA设计了一个提示自我完善机制,使LLMs能够重新评估生成的提示的合理性,产生更连贯的提示。
- 为了保证图像的质量与平衡,在扩散生成过程中插入了在线过滤器。
- 方法专注于解决固定数据集带来的局限性,通过提供更多多样化的训练图像,使WSSS获得更丰富信息和更全面的语义模式理解。
- 实验结果显示,在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上,该方法显著超越了现有的WSSS方法。
- 该方法强调了数据多样性和生成图像质量在提升WSSS性能中的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

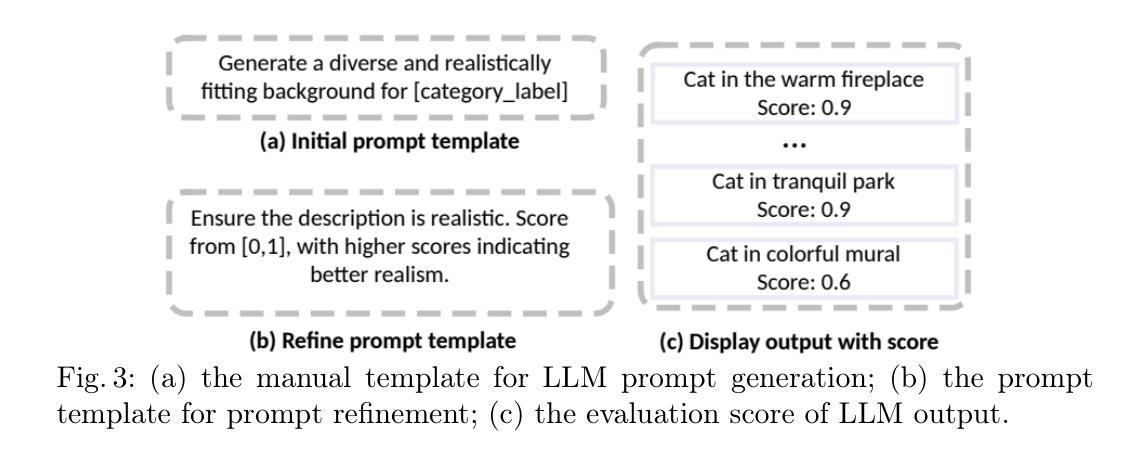
Bringing Objects to Life: 4D generation from 3D objects
Authors:Ohad Rahamim, Ori Malca, Dvir Samuel, Gal Chechik
Recent advancements in generative modeling now enable the creation of 4D content (moving 3D objects) controlled with text prompts. 4D generation has large potential in applications like virtual worlds, media, and gaming, but existing methods provide limited control over the appearance and geometry of generated content. In this work, we introduce a method for animating user-provided 3D objects by conditioning on textual prompts to guide 4D generation, enabling custom animations while maintaining the identity of the original object. We first convert a 3D mesh into a ``static” 4D Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) that preserves the visual attributes of the input object. Then, we animate the object using an Image-to-Video diffusion model driven by text. To improve motion realism, we introduce an incremental viewpoint selection protocol for sampling perspectives to promote lifelike movement and a masked Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) loss, which leverages attention maps to focus optimization on relevant regions. We evaluate our model in terms of temporal coherence, prompt adherence, and visual fidelity and find that our method outperforms baselines that are based on other approaches, achieving up to threefold improvements in identity preservation measured using LPIPS scores, and effectively balancing visual quality with dynamic content.
近期生成模型的进步使得通过文本提示创建4D内容(动态3D物体)成为可能。4D生成在虚拟世界、媒体和游戏等领域具有巨大潜力,但现有方法在控制生成内容的外观和几何形状方面存在局限性。在这项工作中,我们介绍了一种通过文本提示来引导动画的4D生成方法,使用户提供的3D物体动画化,同时保持原始物体的身份。首先,我们将一个三维网格转换成一个保留输入物体视觉属性的“静态”四维神经辐射场(NeRF)。然后,我们使用文本驱动的图像到视频扩散模型来制作动画。为了提高运动逼真度,我们引入了一种增量视点选择协议,用于采样视角以促进逼真的运动,以及带有屏蔽的分数蒸馏采样(SDS)损失,利用注意力图来专注于优化相关区域。我们根据时间一致性、提示符合度和视觉保真度来评估我们的模型,发现我们的方法在身份保留方面优于其他方法的三倍左右,并在保持视觉质量的同时有效地平衡了动态内容。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种通过文本提示驱动动画用户提供的3D对象的方法,实现了4D内容生成。该方法将3D网格转换为静态的4D神经辐射场(NeRF),然后使用图像到视频的扩散模型进行动画化。为提高运动真实感,引入了增量视角选择协议和掩模得分蒸馏采样(SDS)损失。该方法在保持物体身份、时间连贯性和视觉保真度方面优于其他方法。
Key Takeaways
- 生成建模技术已发展到可以创建受文本提示控制的4D内容(动态3D对象)。
- 4D生成在虚拟世界、媒体和游戏等领域具有巨大潜力。
- 本文介绍了一种通过文本提示驱动动画用户提供的3D对象的方法。
- 方法包括将3D网格转换为静态的4D神经辐射场(NeRF),然后使用图像到视频的扩散模型进行动画化。
- 为提高运动真实感,引入了增量视角选择协议和掩模得分蒸馏采样(SDS)损失。
- 该方法在保持物体身份、时间连贯性和视觉保真度方面进行了评估,并表现出优于其他方法的性能。
点此查看论文截图

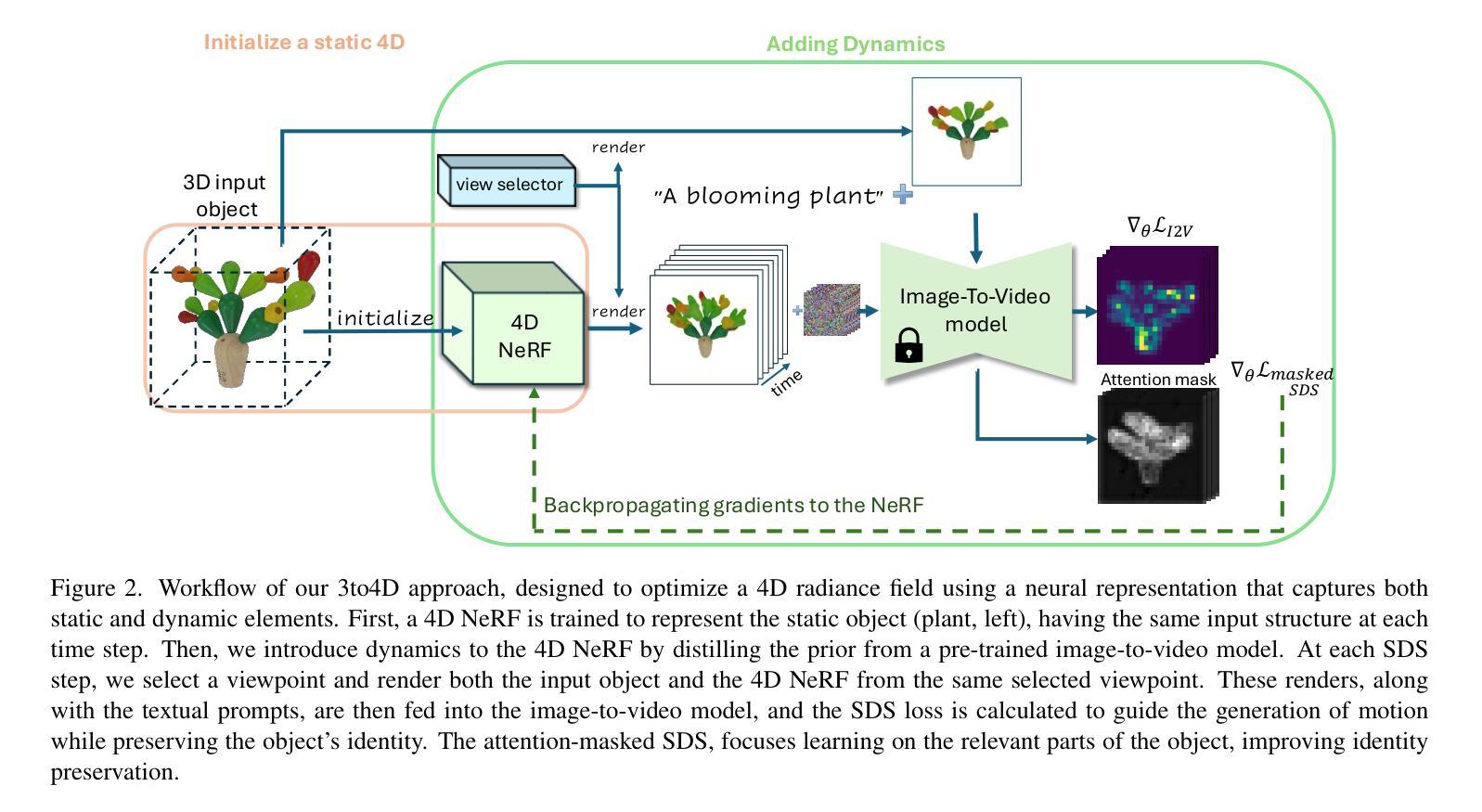
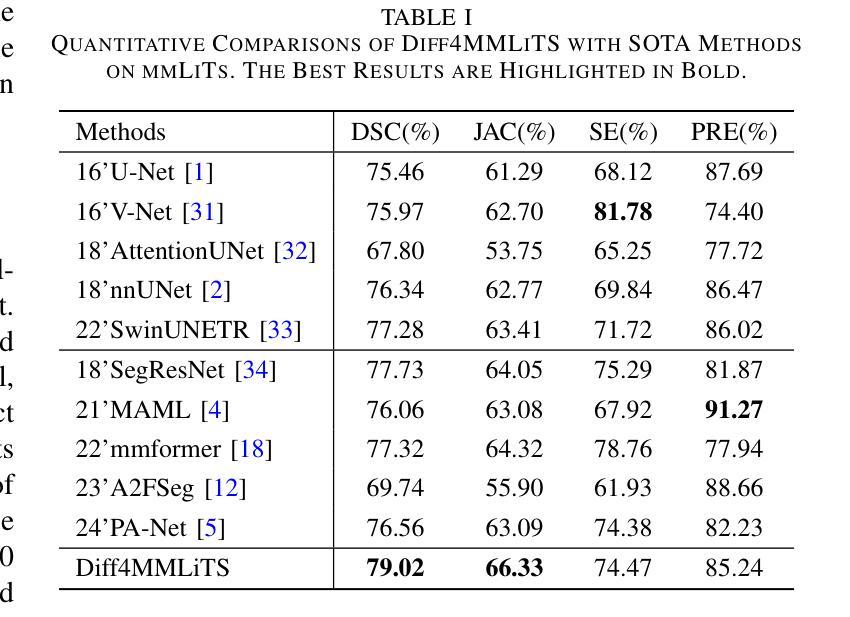
Diff4MMLiTS: Advanced Multimodal Liver Tumor Segmentation via Diffusion-Based Image Synthesis and Alignment
Authors:Shiyun Chen, Li Lin, Pujin Cheng, ZhiCheng Jin, JianJian Chen, HaiDong Zhu, Kenneth K. Y. Wong, Xiaoying Tang
Multimodal learning has been demonstrated to enhance performance across various clinical tasks, owing to the diverse perspectives offered by different modalities of data. However, existing multimodal segmentation methods rely on well-registered multimodal data, which is unrealistic for real-world clinical images, particularly for indistinct and diffuse regions such as liver tumors. In this paper, we introduce Diff4MMLiTS, a four-stage multimodal liver tumor segmentation pipeline: pre-registration of the target organs in multimodal CTs; dilation of the annotated modality’s mask and followed by its use in inpainting to obtain multimodal normal CTs without tumors; synthesis of strictly aligned multimodal CTs with tumors using the latent diffusion model based on multimodal CT features and randomly generated tumor masks; and finally, training the segmentation model, thus eliminating the need for strictly aligned multimodal data. Extensive experiments on public and internal datasets demonstrate the superiority of Diff4MMLiTS over other state-of-the-art multimodal segmentation methods.
多模态学习已证明可以增强各种临床任务的表现,这是由于不同模态的数据提供了不同的视角。然而,现有的多模态分割方法依赖于已注册的多模态数据,这对于现实世界中的临床图像来说并不现实,特别是对于模糊和散漫的区域(如肝脏肿瘤)。在本文中,我们介绍了Diff4MMLiTS,这是一个四阶段的多模态肝脏肿瘤分割流程:多模态CT中目标器官的预注册;对注释模态的掩膜进行膨胀,然后用于修复以获得不含肿瘤的多模态正常CT;使用基于多模态CT特征和随机生成的肿瘤掩膜进行潜在扩散模型的合成,生成含有肿瘤的多模态CT;最后,训练分割模型,从而消除了对严格对齐的多模态数据的需求。在公共和内部数据集上的大量实验表明,Diff4MMLiTS优于其他最先进的多模态分割方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Diff4MMLiTS,一种四阶段的多模态肝脏肿瘤分割管道,旨在解决真实世界临床图像中多模态数据分割的问题。该方法通过预注册目标器官、膨胀标注模态的掩膜并进行补全操作,获得不含肿瘤的多模态正常CT图像。随后,基于多模态CT特征和随机生成的肿瘤掩膜,利用潜在扩散模型合成严格对齐的多模态CT图像。最后,训练分割模型,无需严格对齐的多模态数据。在公共和内部数据集上的实验表明,Diff4MMLiTS优于其他最先进的多模态分割方法。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态学习可以提升各种临床任务的性能,因为不同模态的数据提供了不同的视角。
- 现有多模态分割方法依赖于良好注册的多模态数据,这在真实世界的临床图像中是不现实的。
- Diff4MMLiTS是一种四阶段的多模态肝脏肿瘤分割管道,包括预注册、掩膜膨胀与补全、合成严格对齐的多模态CT图像和训练分割模型。
- Diff4MMLiTS解决了对严格对齐的多模态数据的需要。
- 该方法在公共和内部数据集上的实验表现优于其他先进的多模态分割方法。
- 利用潜在扩散模型合成严格对齐的多模态CT图像是此方法的一大亮点。
点此查看论文截图

EraseAnything: Enabling Concept Erasure in Rectified Flow Transformers
Authors:Daiheng Gao, Shilin Lu, Shaw Walters, Wenbo Zhou, Jiaming Chu, Jie Zhang, Bang Zhang, Mengxi Jia, Jian Zhao, Zhaoxin Fan, Weiming Zhang
Removing unwanted concepts from large-scale text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models while maintaining their overall generative quality remains an open challenge. This difficulty is especially pronounced in emerging paradigms, such as Stable Diffusion (SD) v3 and Flux, which incorporate flow matching and transformer-based architectures. These advancements limit the transferability of existing concept-erasure techniques that were originally designed for the previous T2I paradigm (\textit{e.g.}, SD v1.4). In this work, we introduce \logopic \textbf{EraseAnything}, the first method specifically developed to address concept erasure within the latest flow-based T2I framework. We formulate concept erasure as a bi-level optimization problem, employing LoRA-based parameter tuning and an attention map regularizer to selectively suppress undesirable activations. Furthermore, we propose a self-contrastive learning strategy to ensure that removing unwanted concepts does not inadvertently harm performance on unrelated ones. Experimental results demonstrate that EraseAnything successfully fills the research gap left by earlier methods in this new T2I paradigm, achieving state-of-the-art performance across a wide range of concept erasure tasks.
从大规模文本到图像(T2I)的扩散模型中移除不需要的概念,同时保持其整体的生成质量,仍然是一个待解决的难题。特别是在新兴的模式中,如稳定扩散(SD)v3和Flux,这些模式融入了流匹配和基于transformer的架构,这一难题变得更加突出。这些进展限制了原先为旧T2I模式(例如SD v1.4)设计的概念擦除技术的可转移性。在这项工作中,我们引入了专门为最新流式T2I框架中的概念擦除而开发的方法——LoPic EraseAnything。我们将概念擦除公式化为一个两级优化问题,采用基于LoRA的参数调整和注意力图正则化来选择性抑制不需要的激活。此外,我们提出了一种自我对比学习策略,以确保移除不需要的概念不会无意中损害其他不相关概念的性能。实验结果表明,EraseAnything成功填补了早期方法在新T2I模式中的研究空白,在广泛的概念擦除任务中实现了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 18 figures
Summary
大规模文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型的概念移除技术是一个挑战性问题,特别是在新的模型如Stable Diffusion v3和Flux中。本研究提出了针对最新流T2I框架的概念移除方法——EraseAnything。通过采用基于LoRA的参数调优和注意力图正则化,实现选择性抑制不需要的激活,同时通过自我对比学习策略确保不影响无关概念的性能。实验结果表明,EraseAnything填补了当前T2I模型移除技术的空白,并在概念移除任务上达到了最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型的概念移除是一项重要挑战。特别是在新兴模型中,如Stable Diffusion v3和Flux中面临更多挑战。这些模型融入了新的特性如流匹配和基于Transformer的架构。
- EraseAnything是首个针对最新流式T2I框架设计的概念移除方法。解决了之前为旧T2I范式设计的概念移除技术在最新模型中的不适用问题。
- EraseAnything通过将概念移除建模为双层优化问题,并采用LoRA技术进行参数调整来选择性抑制不需要的激活。
- 该方法采用注意力图正则化,确保不需要的概念在模型中受到有效抑制。
- EraseAnything引入了一种自我对比学习策略,以确保移除不需要的概念时不会损害模型在其他概念上的性能。
- 实验结果表明,EraseAnything在多种概念移除任务上实现了最佳性能,填补了当前研究的空白。
点此查看论文截图


FairDiffusion: Enhancing Equity in Latent Diffusion Models via Fair Bayesian Perturbation
Authors:Yan Luo, Muhammad Osama Khan, Congcong Wen, Muhammad Muneeb Afzal, Titus Fidelis Wuermeling, Min Shi, Yu Tian, Yi Fang, Mengyu Wang
Recent progress in generative AI, especially diffusion models, has demonstrated significant utility in text-to-image synthesis. Particularly in healthcare, these models offer immense potential in generating synthetic datasets and training medical students. However, despite these strong performances, it remains uncertain if the image generation quality is consistent across different demographic subgroups. To address this critical concern, we present the first comprehensive study on the fairness of medical text-to-image diffusion models. Our extensive evaluations of the popular Stable Diffusion model reveal significant disparities across gender, race, and ethnicity. To mitigate these biases, we introduce FairDiffusion, an equity-aware latent diffusion model that enhances fairness in both image generation quality as well as the semantic correlation of clinical features. In addition, we also design and curate FairGenMed, the first dataset for studying the fairness of medical generative models. Complementing this effort, we further evaluate FairDiffusion on two widely-used external medical datasets: HAM10000 (dermatoscopic images) and CheXpert (chest X-rays) to demonstrate FairDiffusion’s effectiveness in addressing fairness concerns across diverse medical imaging modalities. Together, FairDiffusion and FairGenMed significantly advance research in fair generative learning, promoting equitable benefits of generative AI in healthcare.
最近生成人工智能,尤其是扩散模型在文本到图像合成方面的进展,已经显示出巨大的实用价值。特别是在医疗保健领域,这些模型在生成合成数据集和培训医学生方面拥有巨大潜力。然而,尽管这些表现强劲,但不同人口亚组之间的图像生成质量是否一致仍然不确定。为了解决这一关键担忧,我们首次对医疗文本到图像扩散模型的公平性进行了全面研究。我们对流行的Stable Diffusion模型的广泛评估表明,其在性别、种族和民族方面存在显著差异。为了缓解这些偏见,我们引入了FairDiffusion,这是一个注重公平性的潜在扩散模型,它提高了图像生成质量和临床特征语义相关性的公平性。此外,我们还设计和整理了FairGenMed,这是首个用于研究医疗生成模型公平性的数据集。作为补充,我们进一步在两个广泛使用的外部医疗数据集上对FairDiffusion进行了评估:HAM10000(皮肤科图像)和CheXpert(胸部X射线),以证明FairDiffusion在不同医疗成像模式解决公平性问题的有效性。总之,FairDiffusion和FairGenMed的相结合,显著推动了公平生成学习的研究,促进了生成人工智能在医疗保健领域的公平受益。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The data and code are made publicly available at https://github.com/Harvard-Ophthalmology-AI-Lab/FairDiffusion
Summary
文本介绍了生成式人工智能在医疗领域的应用,特别是扩散模型在生成合成数据集和培训医学生方面的潜力。文章还提出了对医疗文本到图像扩散模型公平性的首次全面研究,揭示了性别、种族和民族之间的显著差异,并介绍了旨在提高图像生成质量和临床特征语义相关性的公平扩散模型(FairDiffusion)。此外,还设计和整理了用于研究医疗生成模型公平性的FairGenMed数据集,并在两个常用的外部医疗数据集上评估了FairDiffusion的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在生成合成数据集和培训医学生方面表现出巨大的潜力。
- 医疗文本到图像扩散模型的公平性存在不确定性,需要进一步研究。
- 对流行的Stable Diffusion模型的评估显示,其在不同人群之间存在显著差异。
- 引入FairDiffusion模型,旨在提高图像生成质量和临床特征的语义相关性。
- 设计和整理了用于研究医疗生成模型公平性的FairGenMed数据集。
- FairDiffusion在两个常用的外部医疗数据集上的评估证明了其有效性。
点此查看论文截图

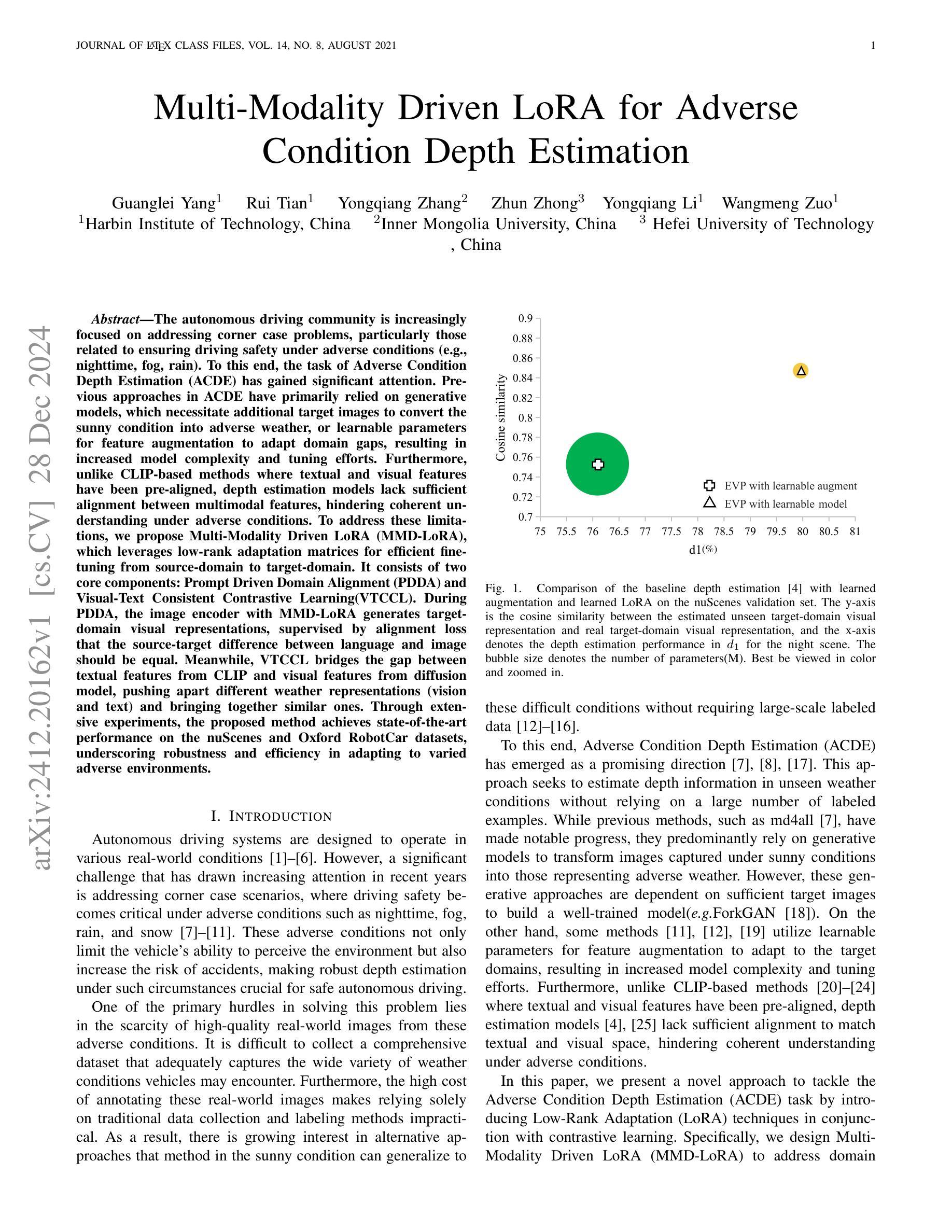
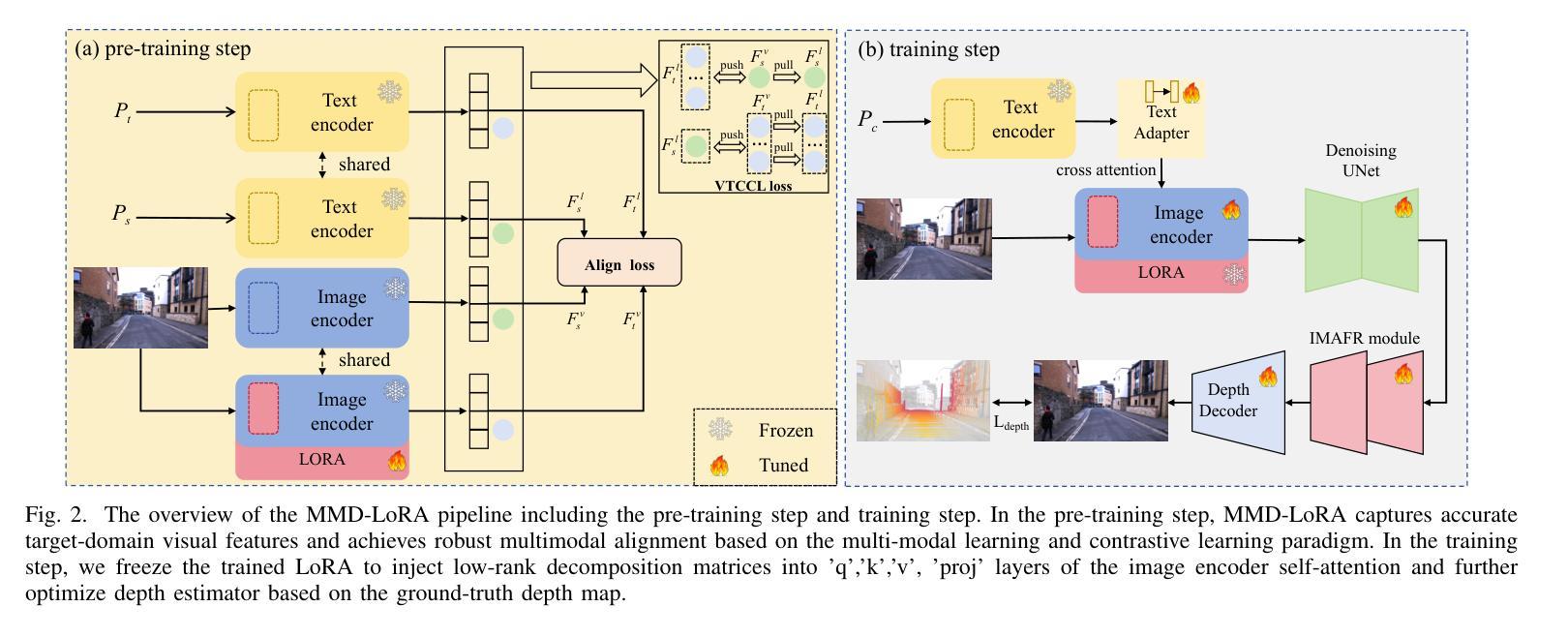
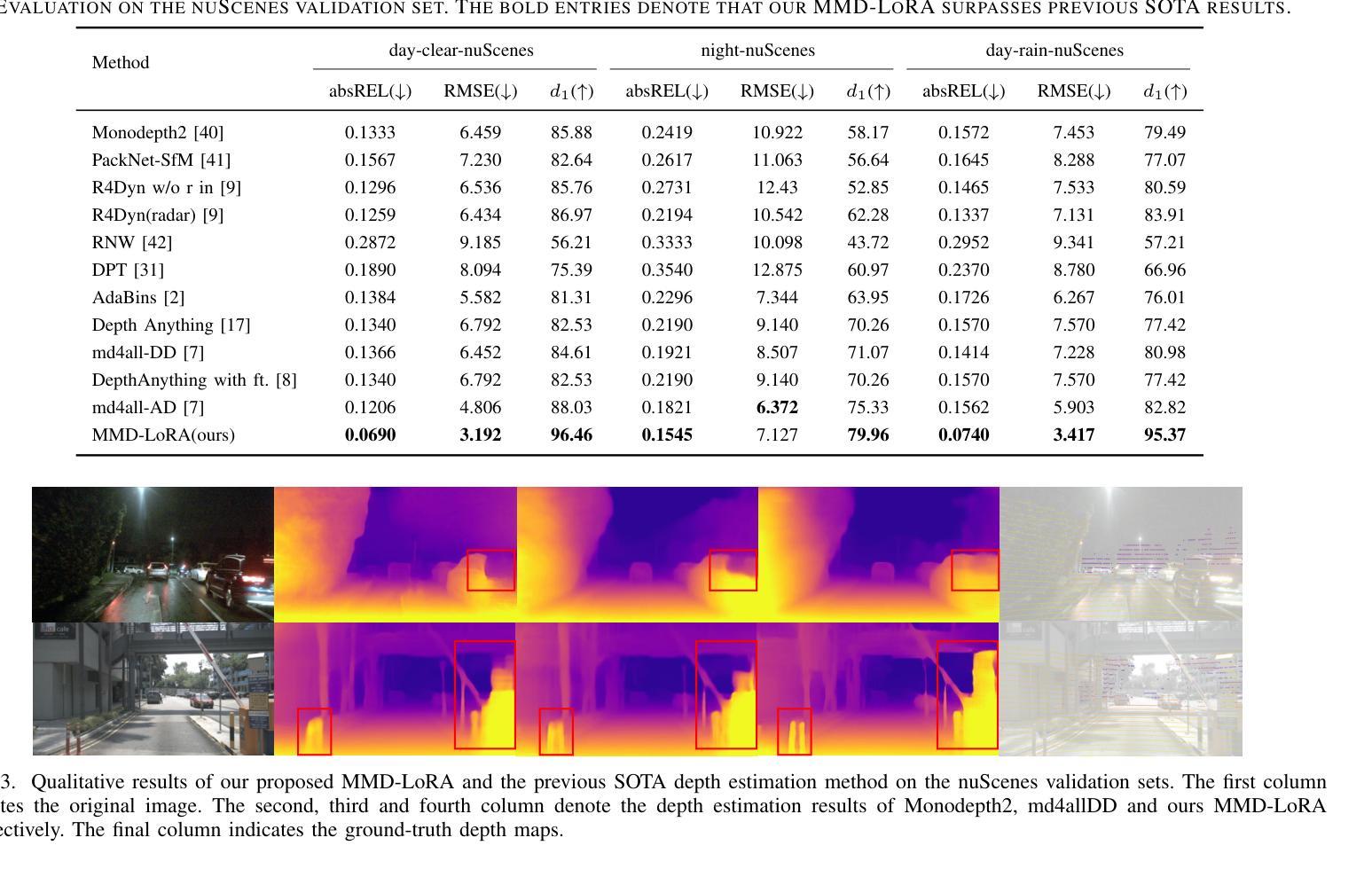
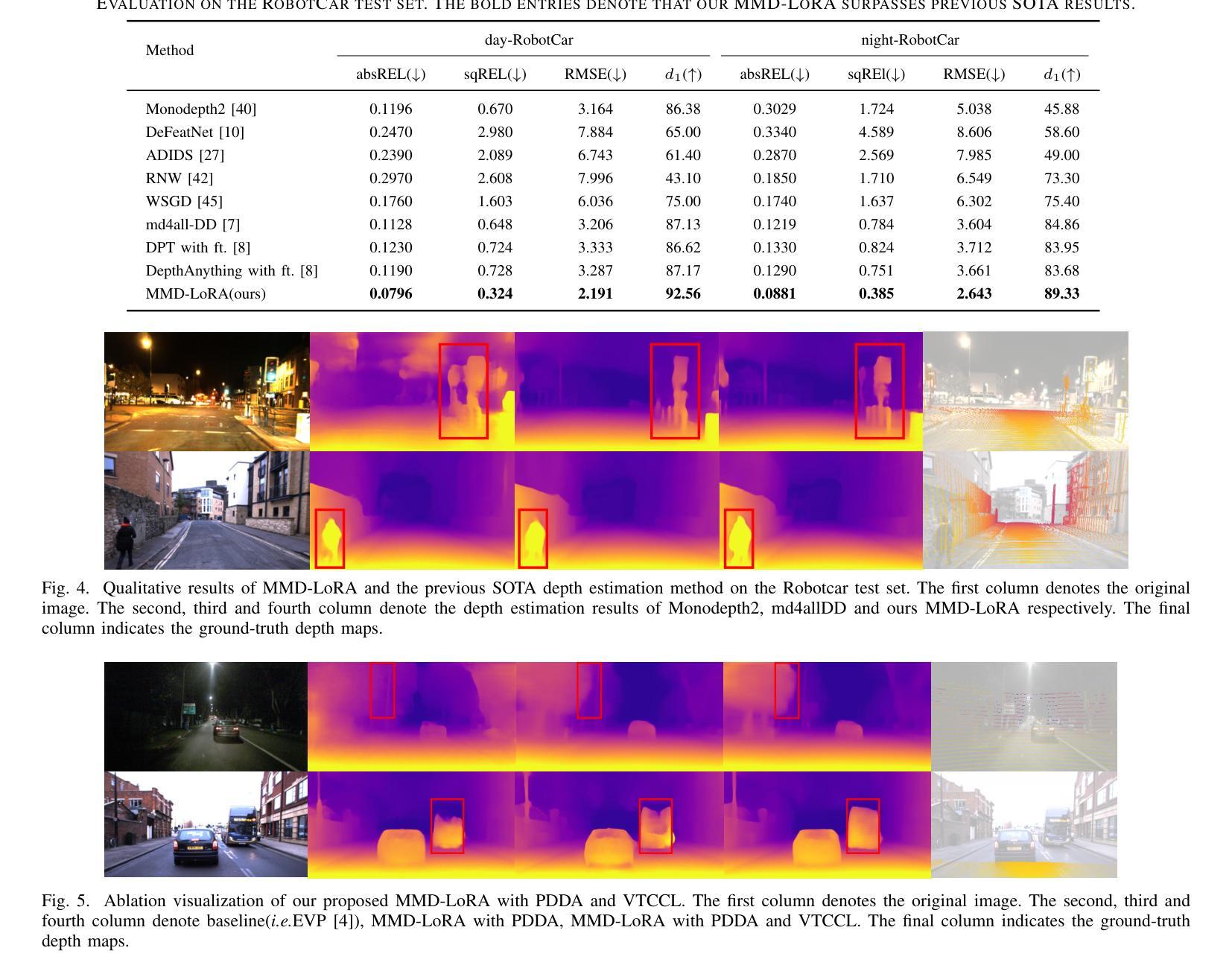
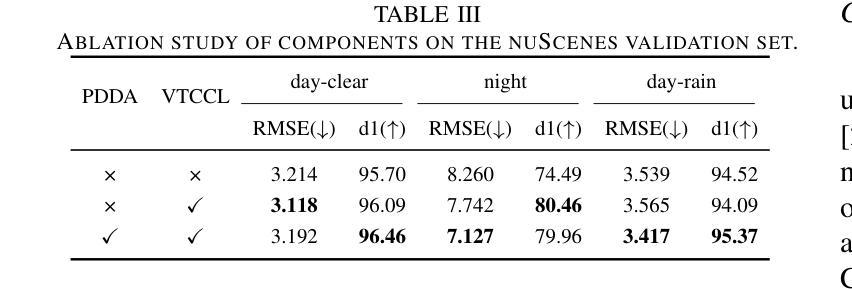
Multi-Modality Driven LoRA for Adverse Condition Depth Estimation
Authors:Guanglei Yang, Rui Tian, Yongqiang Zhang, Zhun Zhong, Yongqiang Li, Wangmeng Zuo
The autonomous driving community is increasingly focused on addressing corner case problems, particularly those related to ensuring driving safety under adverse conditions (e.g., nighttime, fog, rain). To this end, the task of Adverse Condition Depth Estimation (ACDE) has gained significant attention. Previous approaches in ACDE have primarily relied on generative models, which necessitate additional target images to convert the sunny condition into adverse weather, or learnable parameters for feature augmentation to adapt domain gaps, resulting in increased model complexity and tuning efforts. Furthermore, unlike CLIP-based methods where textual and visual features have been pre-aligned, depth estimation models lack sufficient alignment between multimodal features, hindering coherent understanding under adverse conditions. To address these limitations, we propose Multi-Modality Driven LoRA (MMD-LoRA), which leverages low-rank adaptation matrices for efficient fine-tuning from source-domain to target-domain. It consists of two core components: Prompt Driven Domain Alignment (PDDA) and Visual-Text Consistent Contrastive Learning(VTCCL). During PDDA, the image encoder with MMD-LoRA generates target-domain visual representations, supervised by alignment loss that the source-target difference between language and image should be equal. Meanwhile, VTCCL bridges the gap between textual features from CLIP and visual features from diffusion model, pushing apart different weather representations (vision and text) and bringing together similar ones. Through extensive experiments, the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance on the nuScenes and Oxford RobotCar datasets, underscoring robustness and efficiency in adapting to varied adverse environments.
自动驾驶社区越来越关注边缘情况问题的处理,尤其是那些与恶劣条件下的驾驶安全有关的情境(例如夜间、雾天和雨天)。为此,恶劣条件下的深度估计(ACDE)任务受到了广泛关注。以前的ACDE方法主要依赖于生成模型,需要额外的目标图像将晴朗条件转换为恶劣天气,或者使用可学习的参数进行特征增强以适应领域差异,这增加了模型复杂性和调整工作量。此外,与基于CLIP的方法不同,其中文本和视觉特征已经预先对齐,深度估计模型在多种模态特征之间缺乏足够的对齐,阻碍了恶劣条件下的连贯理解。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了多模态驱动的LoRA(MMD-LoRA),它利用低秩适应矩阵进行高效的源域到目标域的微调。它包含两个核心组件:提示驱动的域对齐(PDDA)和视觉文本一致对比学习(VTCCL)。在PDDA期间,带有MMD-LoRA的图像编码器生成目标域的视觉表示,由对齐损失进行监督,该损失使源语言和目标图像之间的差异相等。同时,VTCCL桥接了CLIP的文本特征和扩散模型的视觉特征之间的差距,将不同的天气表示(视觉和文本)区分开来并将相似的表示聚集在一起。通过广泛的实验,所提出的方法在nuScenes和Oxford RobotCar数据集上达到了最先进的性能,突显了在适应各种恶劣环境中的稳健性和效率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注自动驾驶领域中的极端情况问题处理,特别是在恶劣条件下的驾驶安全问题。为此,研究提出Adverse Condition Depth Estimation(ACDE)任务并介绍了一种新的解决方案:Multi-Modality Driven LoRA(MMD-LoRA)。该方法使用低秩适配矩阵,优化了源域到目标域的精细调整,主要包含两个核心组件:Prompt Driven Domain Alignment(PDDA)和Visual-Text Consistent Contrastive Learning(VTCCL)。通过广泛的实验验证,该方法在nuScenes和Oxford RobotCar数据集上实现了最佳性能,突显其在适应不同恶劣环境中的稳健性和效率。
Key Takeaways
- 自动驾驶领域日益关注极端情况问题处理,特别是恶劣条件下的驾驶安全。
- Adverse Condition Depth Estimation (ACDE) 任务旨在解决这一问题。
- 现有方法主要依赖生成模型,需要额外的目标图像或学习参数进行特征增强以适应领域差异,导致模型复杂和调试工作量大。
- Multi-Modality Driven LoRA (MMD-LoRA) 被提出以解决上述问题,它使用低秩适配矩阵进行高效的源域到目标域的微调。
- MMD-LoRA 包含两个核心组件:PDDA 和 VTCCL。PDDA 负责生成目标域视觉表示,而 VTCCL 则弥合了文本特征和视觉特征之间的差距。
点此查看论文截图
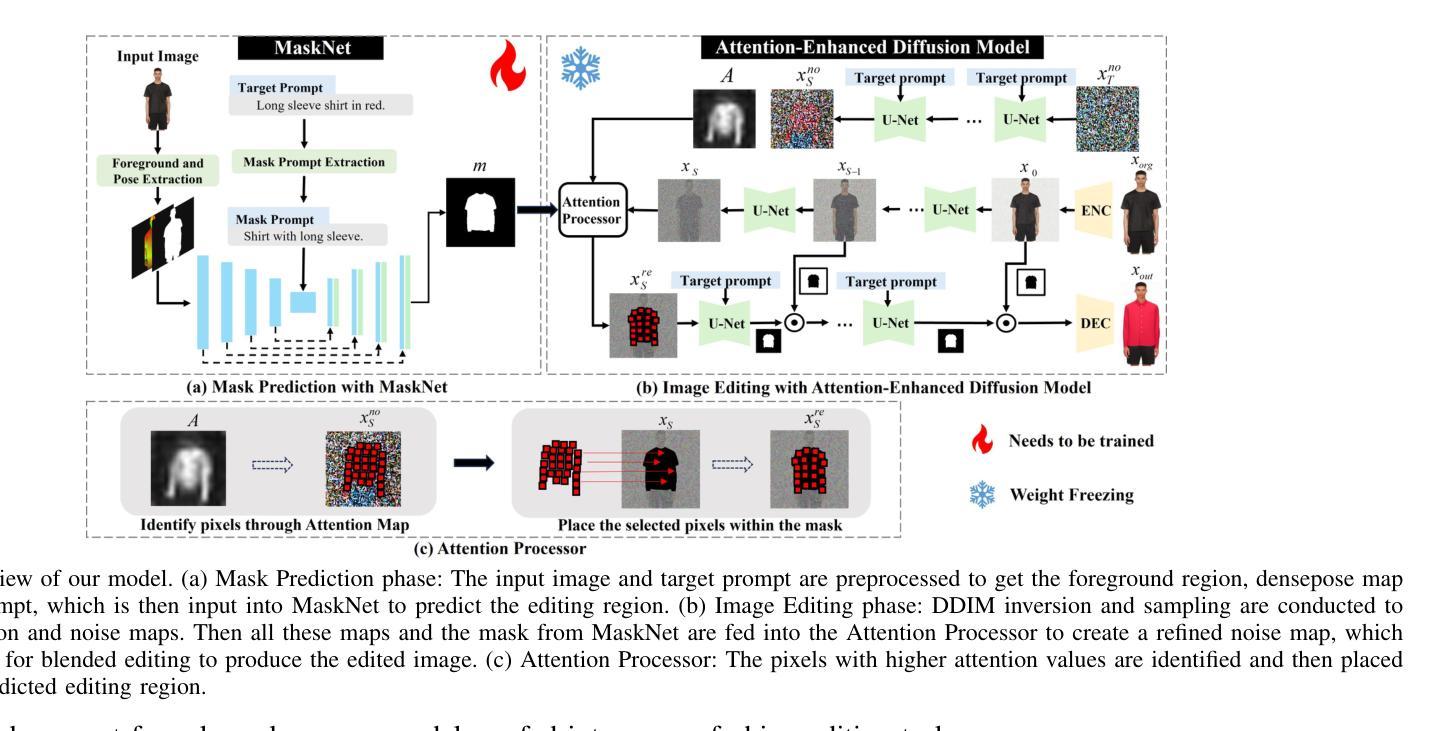
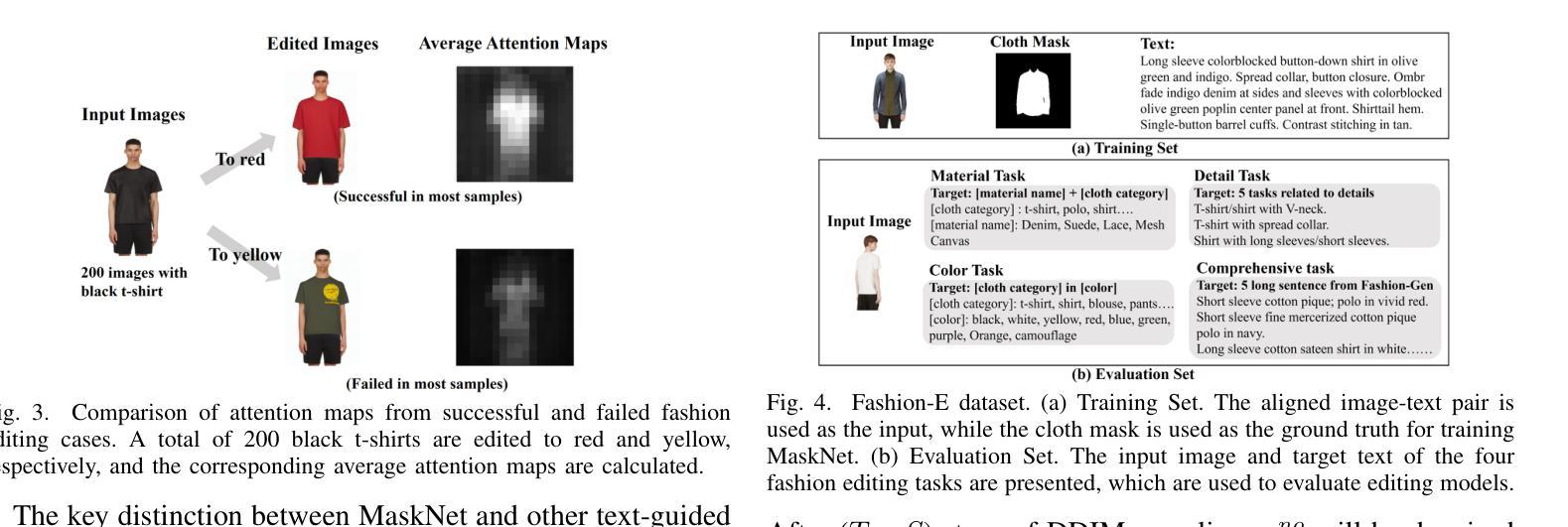
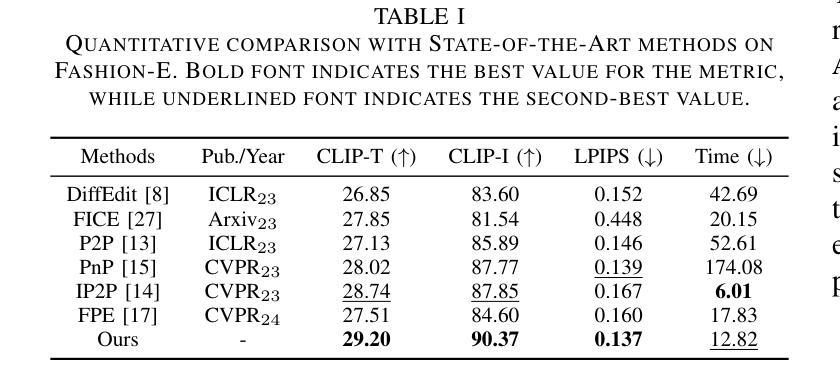
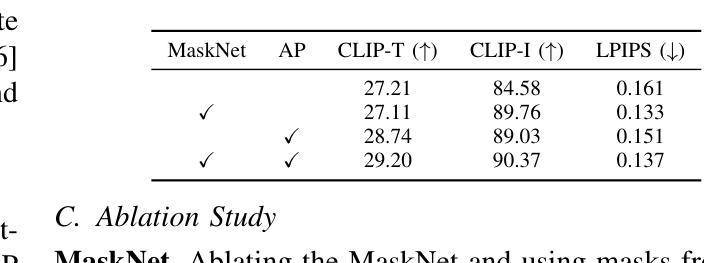
MADiff: Text-Guided Fashion Image Editing with Mask Prediction and Attention-Enhanced Diffusion
Authors:Zechao Zhan, Dehong Gao, Jinxia Zhang, Jiale Huang, Yang Hu, Xin Wang
Text-guided image editing model has achieved great success in general domain. However, directly applying these models to the fashion domain may encounter two issues: (1) Inaccurate localization of editing region; (2) Weak editing magnitude. To address these issues, the MADiff model is proposed. Specifically, to more accurately identify editing region, the MaskNet is proposed, in which the foreground region, densepose and mask prompts from large language model are fed into a lightweight UNet to predict the mask for editing region. To strengthen the editing magnitude, the Attention-Enhanced Diffusion Model is proposed, where the noise map, attention map, and the mask from MaskNet are fed into the proposed Attention Processor to produce a refined noise map. By integrating the refined noise map into the diffusion model, the edited image can better align with the target prompt. Given the absence of benchmarks in fashion image editing, we constructed a dataset named Fashion-E, comprising 28390 image-text pairs in the training set, and 2639 image-text pairs for four types of fashion tasks in the evaluation set. Extensive experiments on Fashion-E demonstrate that our proposed method can accurately predict the mask of editing region and significantly enhance editing magnitude in fashion image editing compared to the state-of-the-art methods.
文本引导的图像编辑模型在通用领域已经取得了巨大的成功。然而,直接将这些模型应用于时尚领域可能会遇到两个问题:(1)编辑区域定位不准确;(2)编辑幅度较弱。为了解决这些问题,提出了MADiff模型。具体来说,为了更准确地识别编辑区域,提出了MaskNet,其中将前景区域、densepose和大语言模型的掩码提示输入到轻量级的UNet中,以预测编辑区域的掩码。为了增强编辑幅度,提出了注意力增强扩散模型,其中将噪声图、注意力图和MaskNet的掩码输入到提出的注意力处理器中,以产生精细的噪声图。通过将精细的噪声图集成到扩散模型中,编辑后的图像可以更好地与目标提示对齐。鉴于时尚图像编辑缺乏基准测试集,我们构建了一个名为Fashion-E的数据集,其中包括训练集中的28390个图像-文本对,以及评估集中的2639个图像-文本对,用于四种时尚任务。在Fashion-E上的广泛实验表明,我们提出的方法能够准确预测编辑区域的掩码,并在时尚图像编辑中显著增强编辑幅度,与最先进的方法相比具有优势。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本指导的图像编辑模型在通用领域取得了巨大成功,但在时尚领域应用时面临区域定位不准确和编辑强度弱的问题。为解决这个问题,提出了MADiff模型,包括MaskNet和Attention-Enhanced Diffusion Model。MaskNet通过前景区域、densepose和大型语言模型的掩膜提示来预测编辑区域掩膜,提高区域定位准确性。Attention-Enhanced Diffusion Model则通过噪声图、注意力图和MaskNet的掩膜来产生精细的噪声图,增强编辑强度。因时尚图像编辑缺乏基准测试集,故构建了Fashion-E数据集。实验表明,该方法能准确预测编辑区域掩膜,显著提高时尚图像编辑的编辑强度。
Key Takeaways
- 文本指导的图像编辑模型在通用领域成功,但在时尚领域面临区域定位不准确和编辑强度弱的问题。
- MADiff模型包括MaskNet和Attention-Enhanced Diffusion Model,分别解决区域定位和编辑强度问题。
- MaskNet使用前景区域、densepose和大型语言模型的掩膜提示来预测编辑区域掩膜。
- Attention-Enhanced Diffusion Model通过噪声图、注意力图和MaskNet的掩膜产生精细的噪声图,增强编辑强度。
- 时尚图像编辑领域缺乏基准测试集,因此构建了Fashion-E数据集。
- 实验表明,MADiff模型能准确预测编辑区域掩膜。
点此查看论文截图


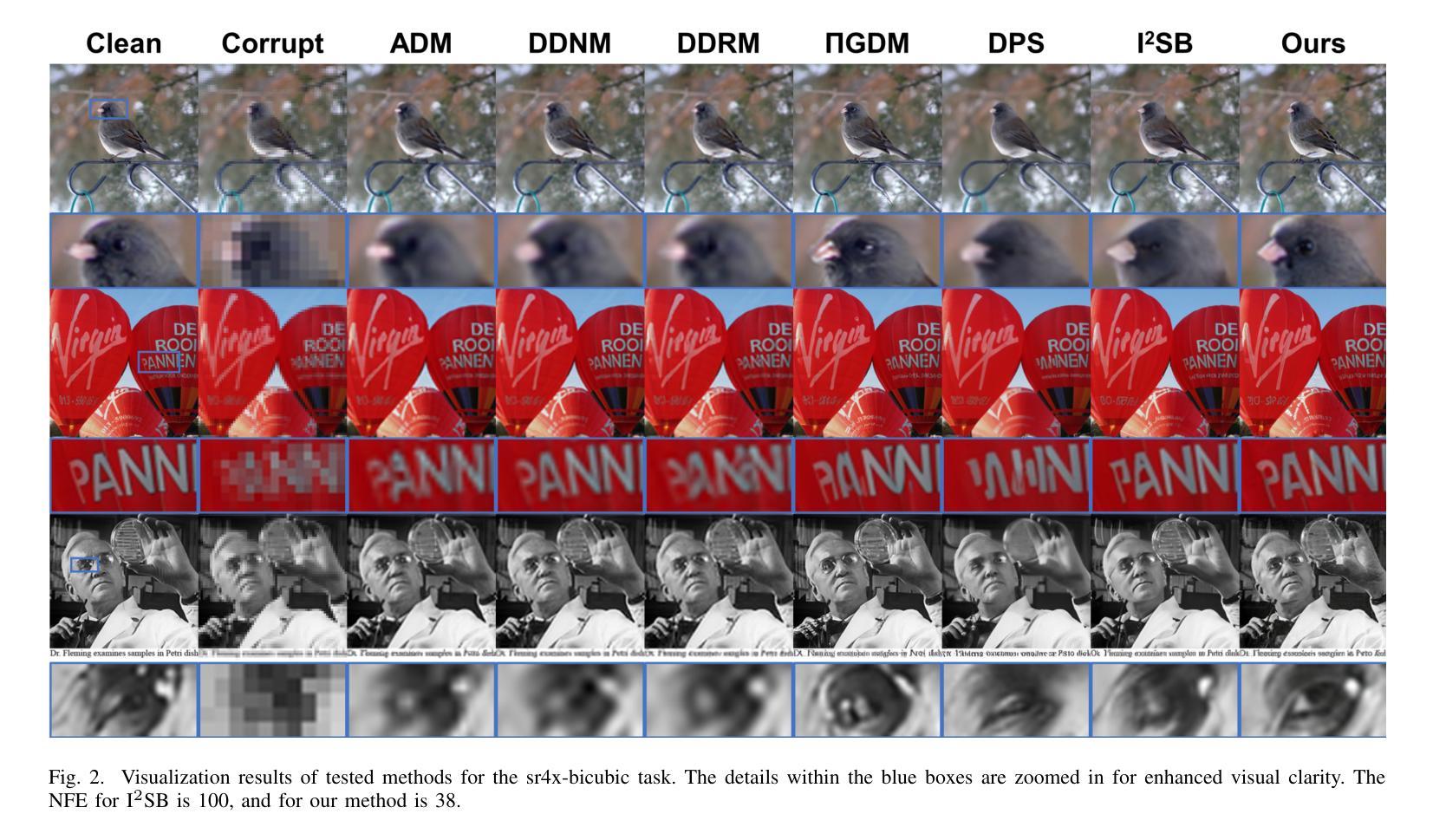
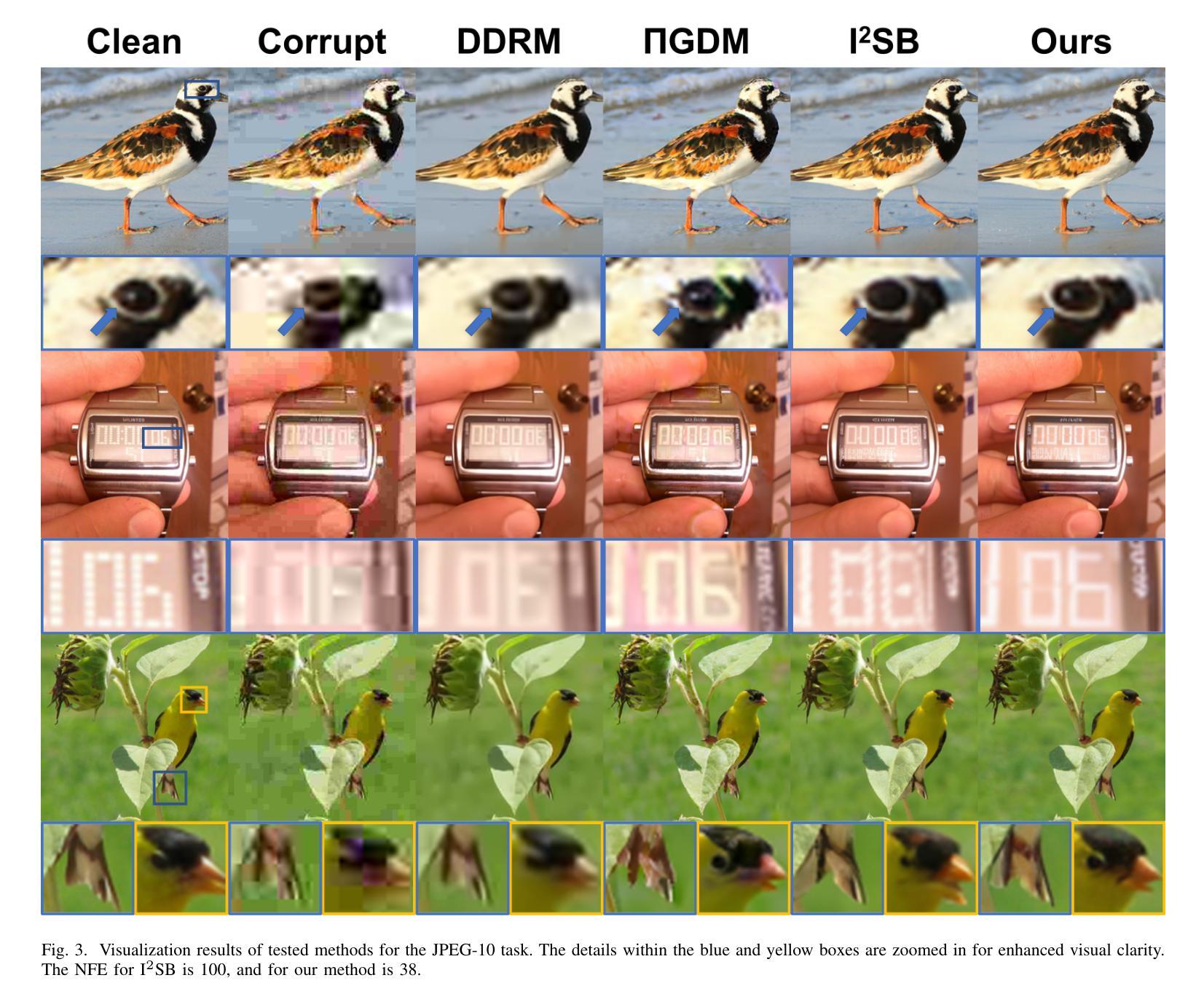
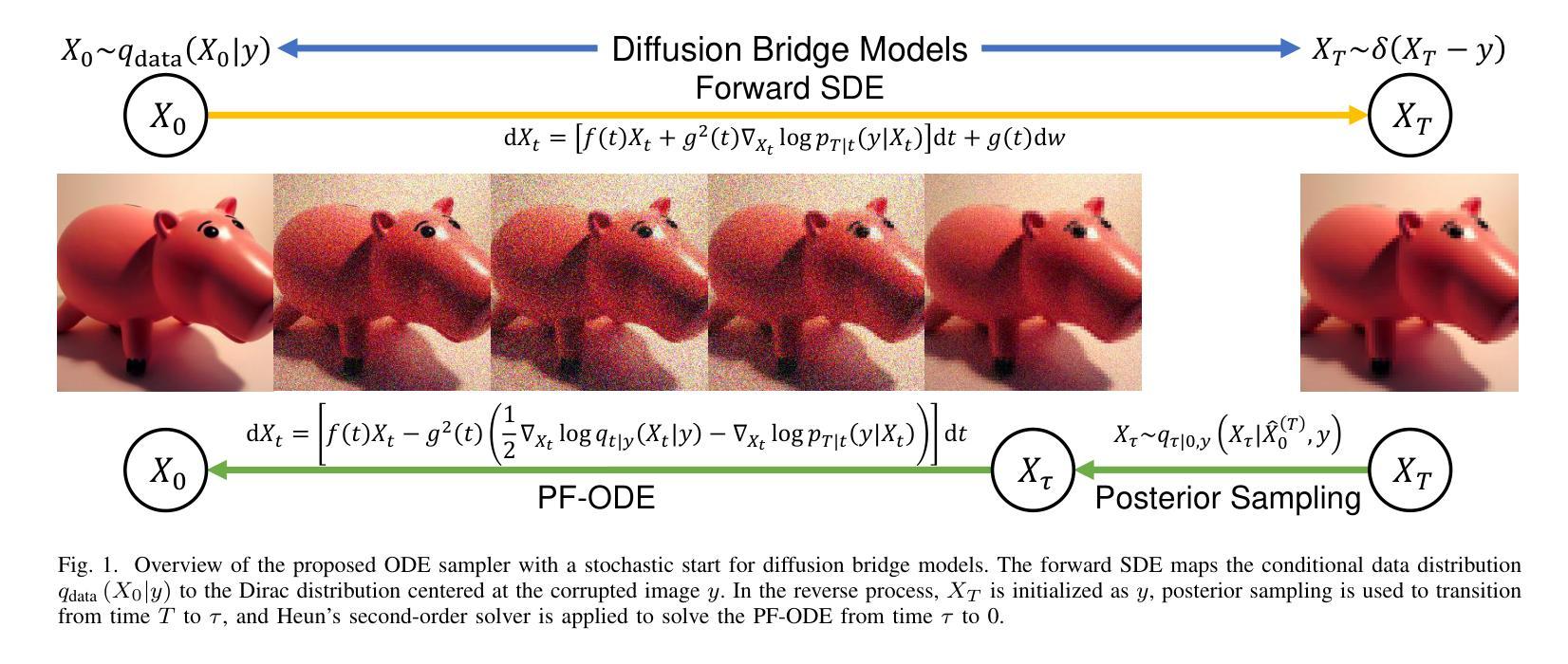
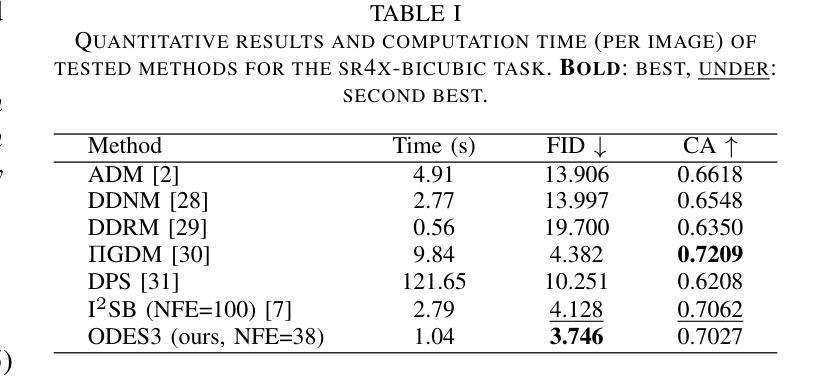
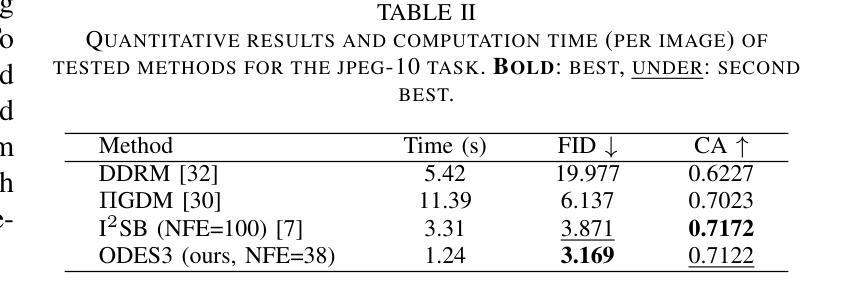
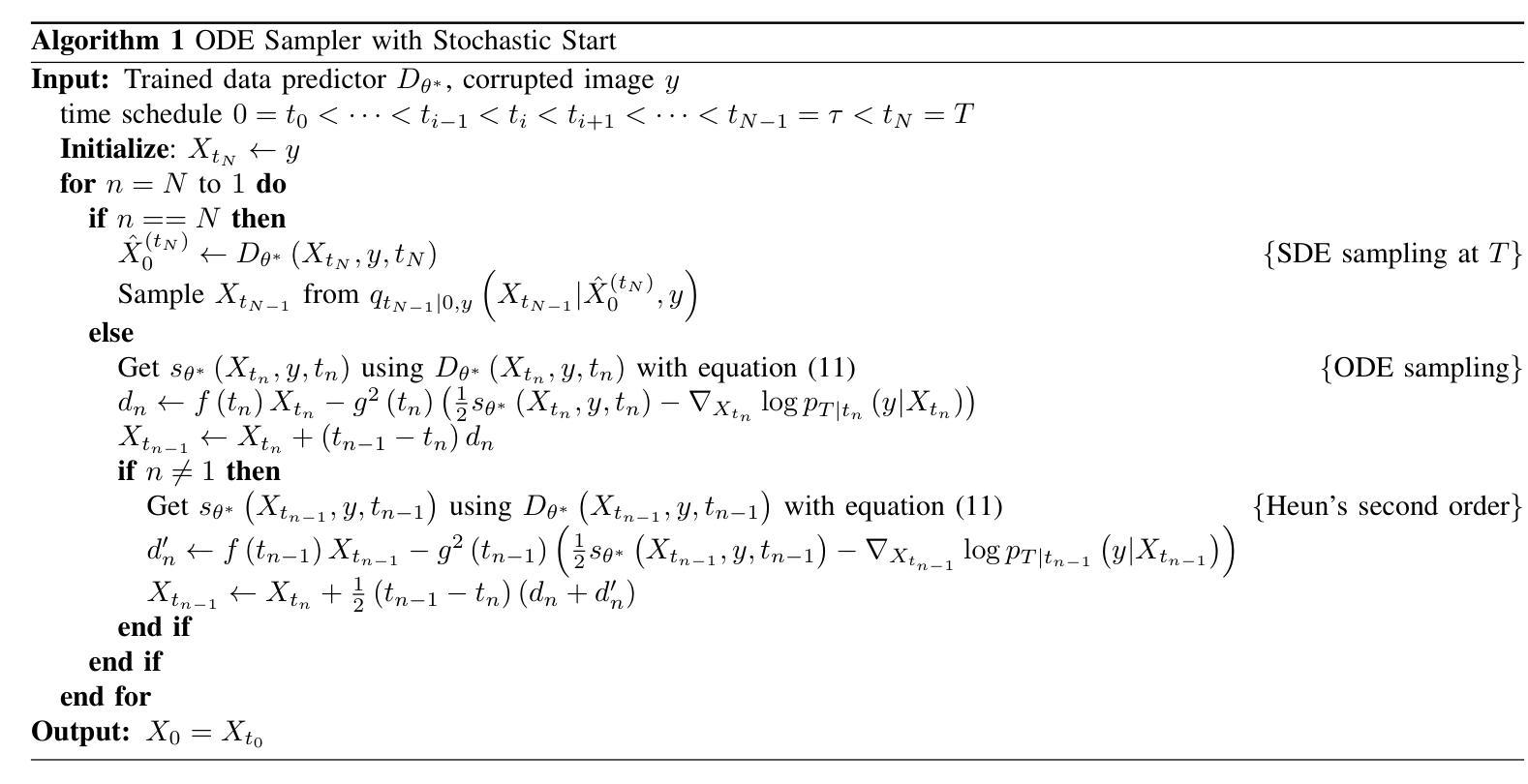
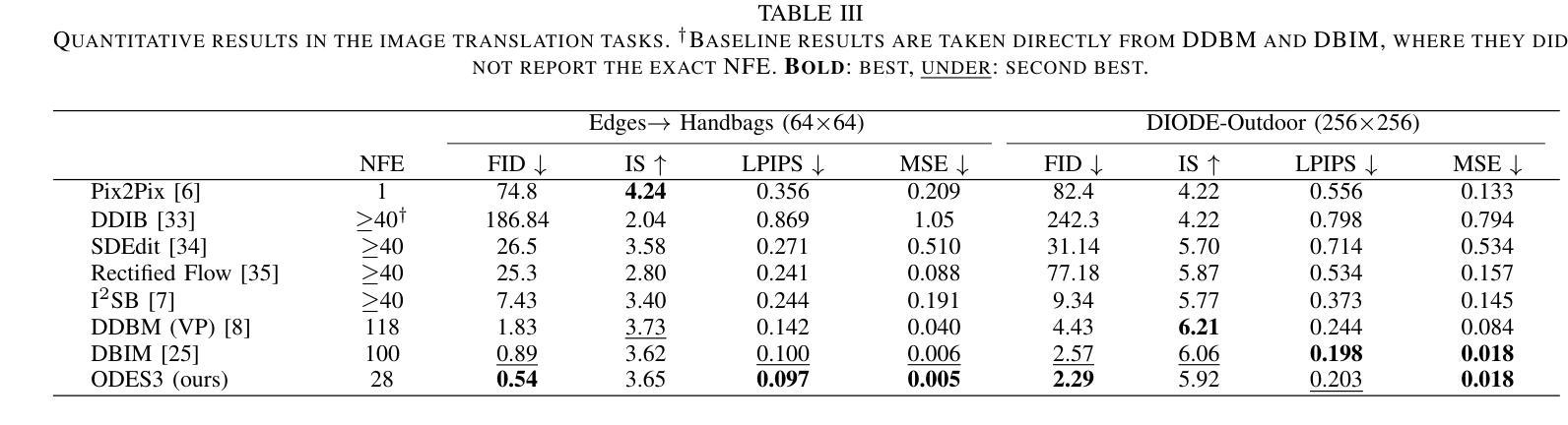
An Ordinary Differential Equation Sampler with Stochastic Start for Diffusion Bridge Models
Authors:Yuang Wang, Pengfei Jin, Li Zhang, Quanzheng Li, Zhiqiang Chen, Dufan Wu
Diffusion bridge models have demonstrated promising performance in conditional image generation tasks, such as image restoration and translation, by initializing the generative process from corrupted images instead of pure Gaussian noise. However, existing diffusion bridge models often rely on Stochastic Differential Equation (SDE) samplers, which result in slower inference speed compared to diffusion models that employ high-order Ordinary Differential Equation (ODE) solvers for acceleration. To mitigate this gap, we propose a high-order ODE sampler with a stochastic start for diffusion bridge models. To overcome the singular behavior of the probability flow ODE (PF-ODE) at the beginning of the reverse process, a posterior sampling approach was introduced at the first reverse step. The sampling was designed to ensure a smooth transition from corrupted images to the generative trajectory while reducing discretization errors. Following this stochastic start, Heun’s second-order solver is applied to solve the PF-ODE, achieving high perceptual quality with significantly reduced neural function evaluations (NFEs). Our method is fully compatible with pretrained diffusion bridge models and requires no additional training. Extensive experiments on image restoration and translation tasks, including super-resolution, JPEG restoration, Edges-to-Handbags, and DIODE-Outdoor, demonstrated that our sampler outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both visual quality and Frechet Inception Distance (FID).
扩散桥模型在条件图像生成任务中表现优异,如图像恢复和翻译,它通过从受损图像而不是纯高斯噪声开始生成过程。然而,现有的扩散桥模型通常依赖于随机微分方程(SDE)采样器,与采用高阶常微分方程(ODE)求解器进行加速的扩散模型相比,推理速度较慢。为了弥补这一差距,我们为扩散桥模型提出了一种具有随机起始的高阶ODE采样器。为了解决反向过程中概率流ODE(PF-ODE)在起始时的奇异行为,我们在第一次反向步骤中引入了后采样方法。采样的设计是为了确保从受损图像到生成轨迹的平稳过渡,同时减少离散化误差。随后采用Heun的二阶求解器解决PF-ODE,在保证感知质量高的同时,大大降低了神经功能评估次数(NFEs)。我们的方法与预训练的扩散桥模型完全兼容,无需额外训练。在图像恢复和翻译任务的大量实验,包括超分辨率、JPEG恢复、Edges-to-Handbags和DIODE-Outdoor等实验表明,我们的采样器在视觉质量和Frechet Inception Distance(FID)方面都优于现有最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 5 figures, This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
Summary
扩散桥模型在条件图像生成任务中展现出良好的性能,如图像恢复和翻译。它通过从损坏的图像开始生成过程,而不是使用纯高斯噪声,实现性能提升。然而,现有扩散桥模型通常依赖随机微分方程(SDE)采样器,导致推理速度较慢。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种结合随机起始的高阶常微分方程(ODE)采样器。在反向过程开始时,引入概率流ODE(PF-ODE)的后采样方法,确保从损坏图像到生成轨迹的平稳过渡,同时减少离散化误差。随后使用Heun的二阶求解器解决PF-ODE问题,实现了感知质量的提升和神经函数评估(NFEs)的显著降低。该方法与预训练的扩散桥模型完全兼容,无需额外训练。实验证明,我们的采样器在视觉质量和Frechet Inception Distance(FID)方面都优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散桥模型通过从损坏图像开始生成过程实现条件图像生成任务性能的提升。
- 现有扩散桥模型依赖SDE采样器导致推理速度较慢。
- 提出一种结合随机起始的高阶ODE采样器来加快推理速度并提升生成质量。
- 通过引入概率流ODE的后采样方法确保从损坏图像到生成轨迹的平稳过渡。
- 使用Heun的二阶求解器解决PF-ODE问题,提高感知质量并降低神经函数评估。
- 方法与预训练的扩散桥模型兼容,无需额外训练。
点此查看论文截图



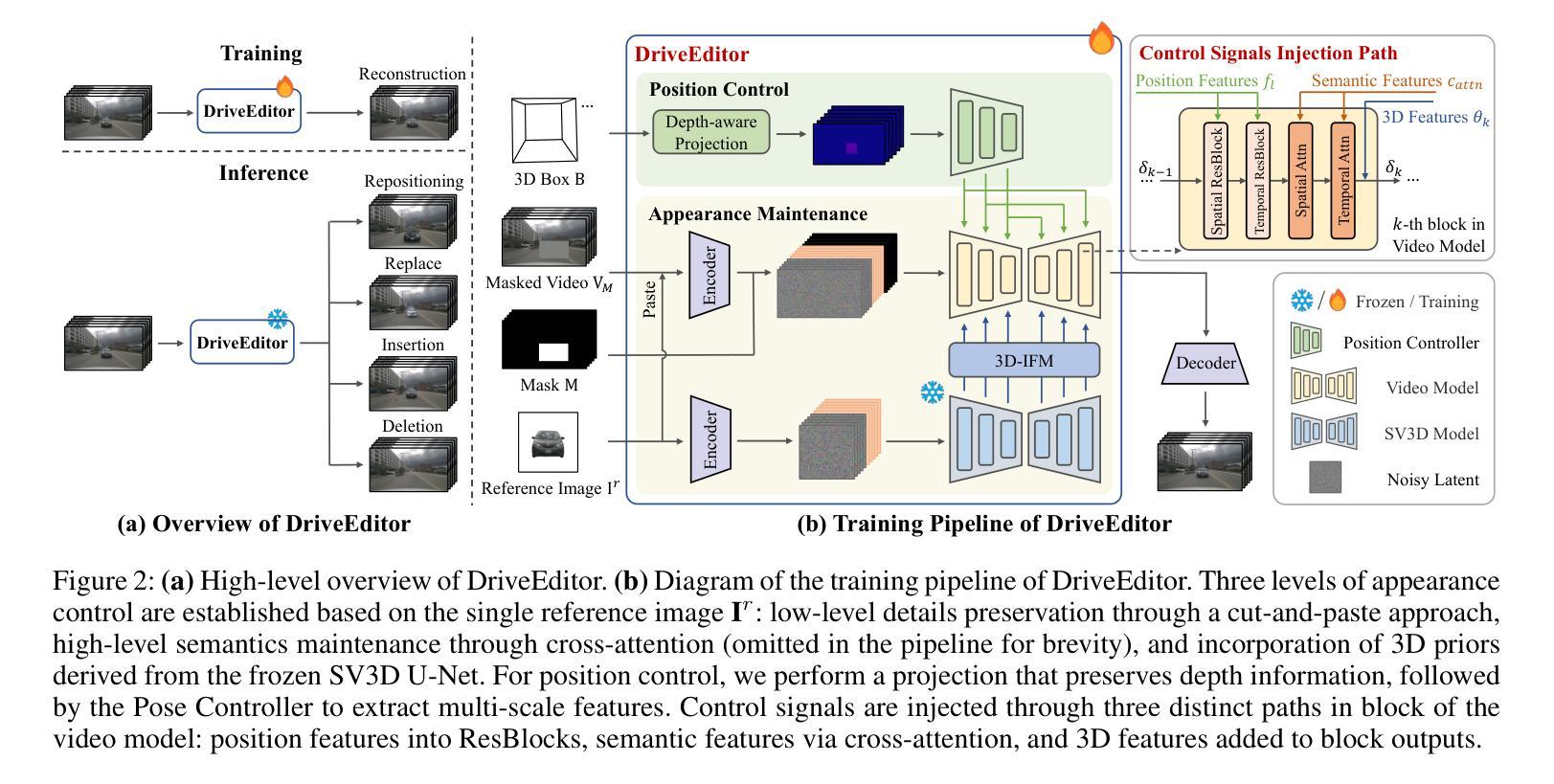
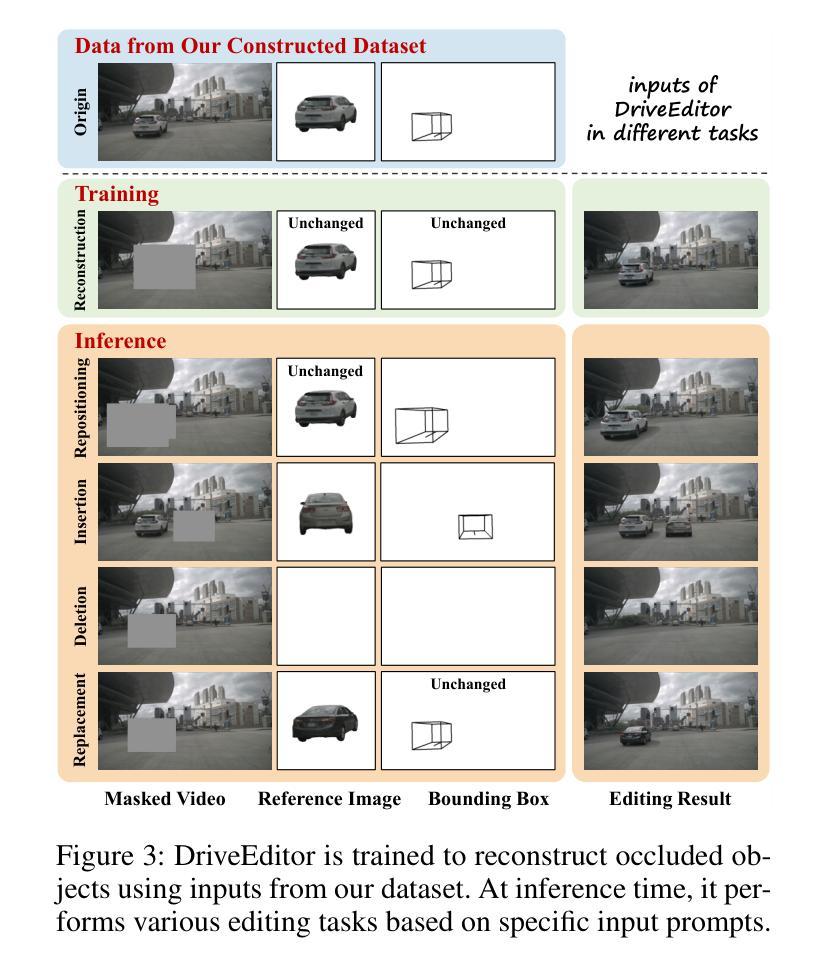
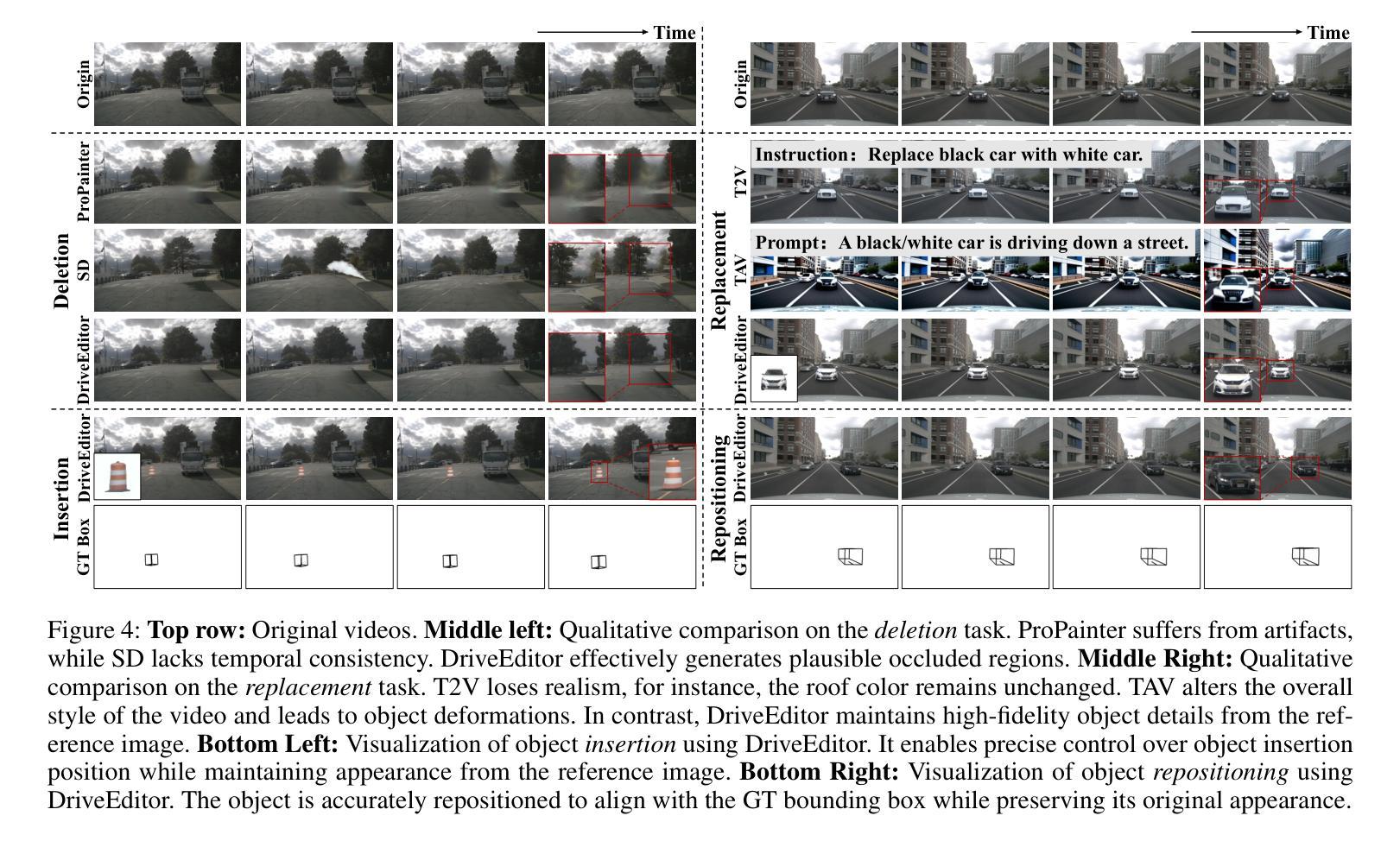
DriveEditor: A Unified 3D Information-Guided Framework for Controllable Object Editing in Driving Scenes
Authors:Yiyuan Liang, Zhiying Yan, Liqun Chen, Jiahuan Zhou, Luxin Yan, Sheng Zhong, Xu Zou
Vision-centric autonomous driving systems require diverse data for robust training and evaluation, which can be augmented by manipulating object positions and appearances within existing scene captures. While recent advancements in diffusion models have shown promise in video editing, their application to object manipulation in driving scenarios remains challenging due to imprecise positional control and difficulties in preserving high-fidelity object appearances. To address these challenges in position and appearance control, we introduce DriveEditor, a diffusion-based framework for object editing in driving videos. DriveEditor offers a unified framework for comprehensive object editing operations, including repositioning, replacement, deletion, and insertion. These diverse manipulations are all achieved through a shared set of varying inputs, processed by identical position control and appearance maintenance modules. The position control module projects the given 3D bounding box while preserving depth information and hierarchically injects it into the diffusion process, enabling precise control over object position and orientation. The appearance maintenance module preserves consistent attributes with a single reference image by employing a three-tiered approach: low-level detail preservation, high-level semantic maintenance, and the integration of 3D priors from a novel view synthesis model. Extensive qualitative and quantitative evaluations on the nuScenes dataset demonstrate DriveEditor’s exceptional fidelity and controllability in generating diverse driving scene edits, as well as its remarkable ability to facilitate downstream tasks. Project page: https://yvanliang.github.io/DriveEditor.
视觉为中心的自驾系统需要多样化的数据进行稳健的训练和评估,这些数据可以通过操作现有场景捕捉中的物体位置和外观来扩充。虽然扩散模型领域的最新进展在视频编辑方面显示出潜力,但它们在驾驶场景中的物体操作应用仍然具有挑战性,主要是由于位置控制不精确以及保持高保真物体外观的困难。为了解决这些位置和外观控制的挑战,我们引入了DriveEditor,这是一个基于扩散模型的驾驶视频物体编辑框架。DriveEditor提供了一个统一的框架,用于全面的物体编辑操作,包括重新定位、替换、删除和插入。这些不同的操作都是通过一组可变的输入实现的,这些输入由相同的定位控制和外观维护模块处理。定位控制模块投影给定的3D边界框,同时保留深度信息并按层次结构注入扩散过程,实现对物体位置和方向的精确控制。外观维护模块通过采用三级方法:保留低级别细节、保持高级语义以及从新型视图合成模型中整合3D先验知识,从而以单一参考图像保持一致的属性。在nuScenes数据集上进行的大量定性和定量评估表明,DriveEditor在生成各种驾驶场景编辑方面具有出色的保真度和可控性,并且在促进下游任务方面具有显著的能力。项目页面:https://yvanliang.github.io/DriveEditor。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了基于扩散模型的驾驶视频对象编辑框架DriveEditor。该框架可实现驾驶视频中对象的全面编辑操作,包括重新定位、替换、删除和插入等。通过精准的位置控制模块和外观维护模块,DriveEditor能够在编辑对象时保持高精度和高保真度。其在nuScenes数据集上的评估结果表明,DriveEditor在生成多样化的驾驶场景编辑方面具有出色的保真度和可控性,并能有效促进下游任务。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在驾驶视频对象编辑中具有潜力。
- DriveEditor框架支持多种驾驶视频中的对象编辑操作。
- 位置控制模块能够实现对象位置的精确控制,同时保留深度信息。
- 外观维护模块采用三层方法,保持与参考图像一致的属性。
- DriveEditor在nuScenes数据集上的表现优异,具有高的保真度和可控性。
- DriveEditor有助于生成多样化的驾驶场景编辑,对下游任务有促进作用。
点此查看论文截图


PartGen: Part-level 3D Generation and Reconstruction with Multi-View Diffusion Models
Authors:Minghao Chen, Roman Shapovalov, Iro Laina, Tom Monnier, Jianyuan Wang, David Novotny, Andrea Vedaldi
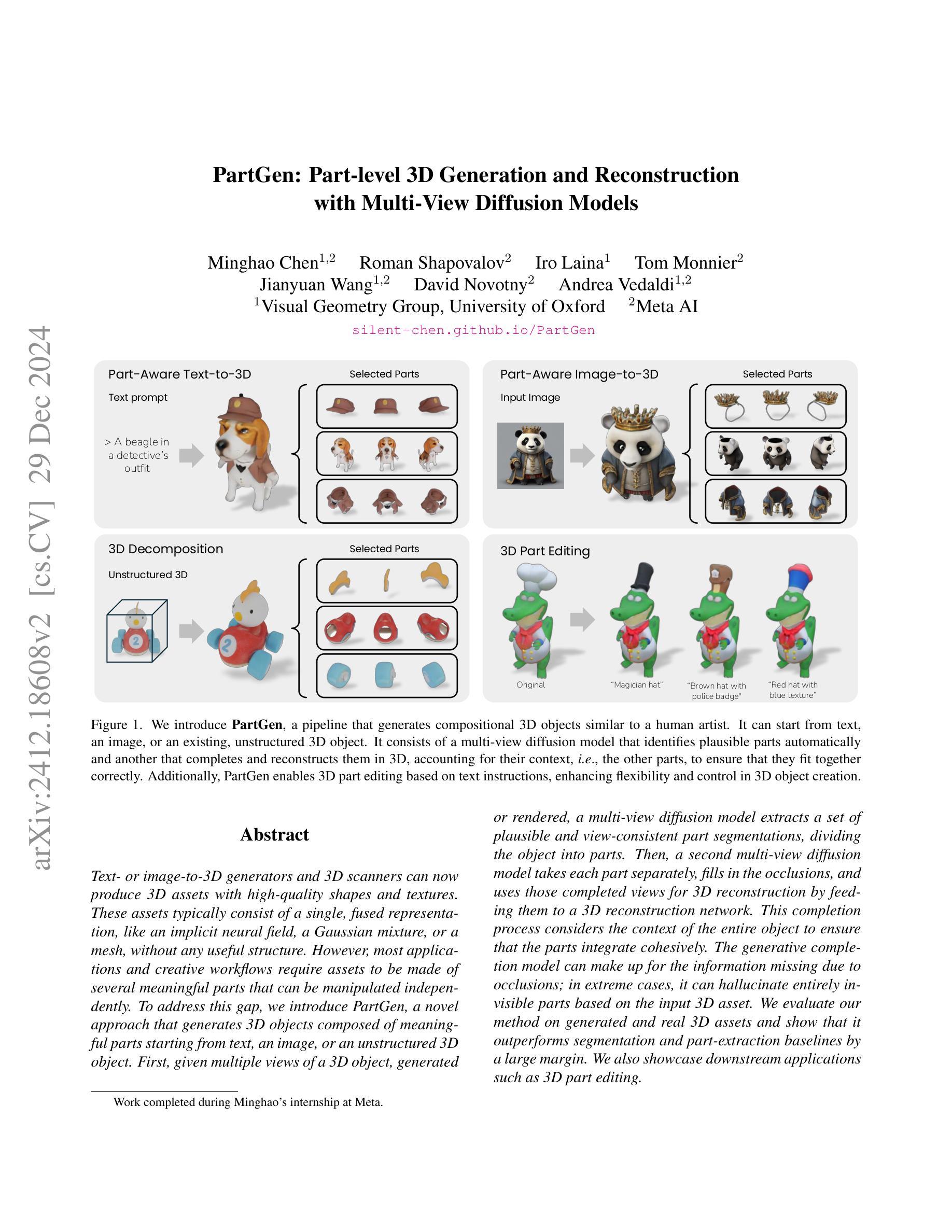
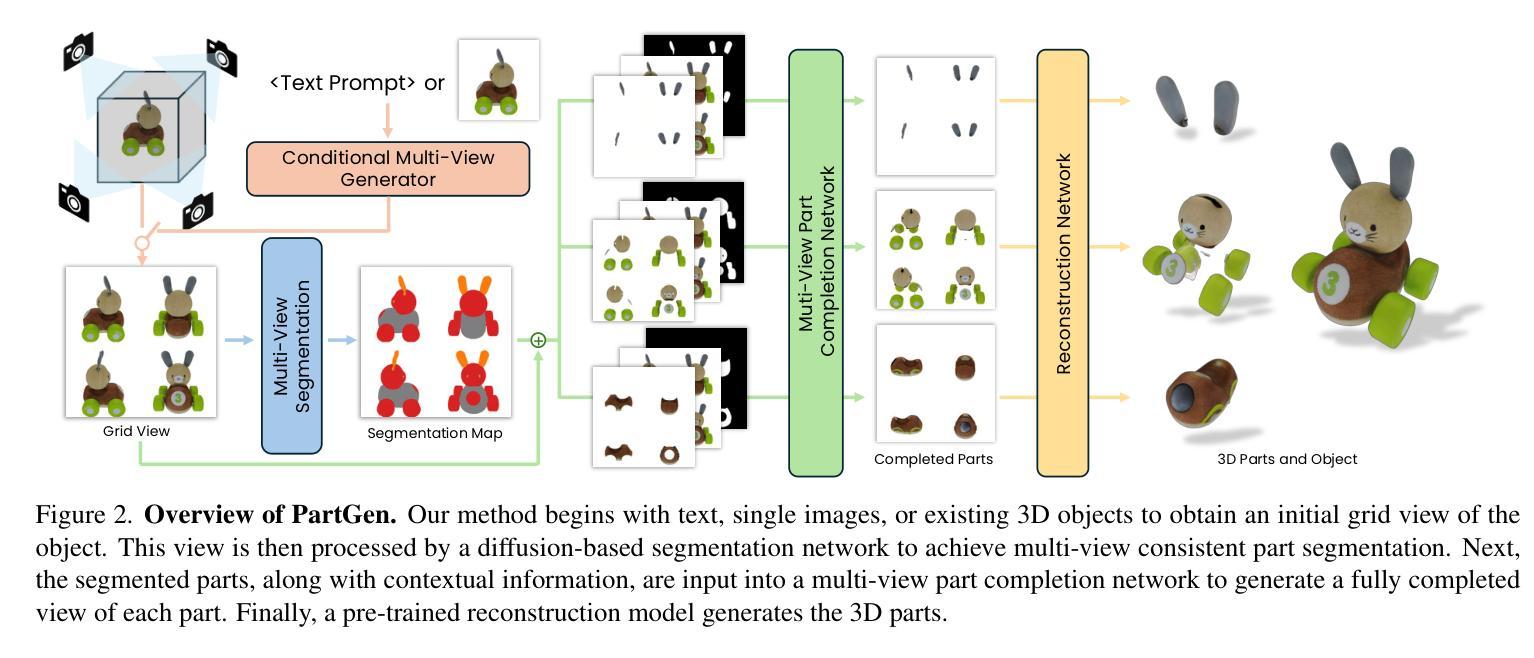
Text- or image-to-3D generators and 3D scanners can now produce 3D assets with high-quality shapes and textures. These assets typically consist of a single, fused representation, like an implicit neural field, a Gaussian mixture, or a mesh, without any useful structure. However, most applications and creative workflows require assets to be made of several meaningful parts that can be manipulated independently. To address this gap, we introduce PartGen, a novel approach that generates 3D objects composed of meaningful parts starting from text, an image, or an unstructured 3D object. First, given multiple views of a 3D object, generated or rendered, a multi-view diffusion model extracts a set of plausible and view-consistent part segmentations, dividing the object into parts. Then, a second multi-view diffusion model takes each part separately, fills in the occlusions, and uses those completed views for 3D reconstruction by feeding them to a 3D reconstruction network. This completion process considers the context of the entire object to ensure that the parts integrate cohesively. The generative completion model can make up for the information missing due to occlusions; in extreme cases, it can hallucinate entirely invisible parts based on the input 3D asset. We evaluate our method on generated and real 3D assets and show that it outperforms segmentation and part-extraction baselines by a large margin. We also showcase downstream applications such as 3D part editing.
文本或图像到3D生成器和3D扫描仪现在可以生成具有高质量形状和纹理的3D资产。这些资产通常由单一融合表示组成,如隐式神经网络、高斯混合或网格,但没有有用的结构。然而,大多数应用程序和创意工作流程要求资产由可以独立操作的多个有意义的部分组成。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了PartGen,这是一种从文本、图像或无序的3D对象开始生成由有意义的部分组成的3D物体的新方法。首先,给定一个3D物体的多个视图(无论是生成的还是渲染的),多视图扩散模型会从这些视图中提取一套合理且视角一致的部分分割,将物体分割成各个部分。然后,第二个多视图扩散模型会分别处理每个部分,填充遮挡物,并使用这些完成的视图进行3D重建,方法是将其输入到3D重建网络中。这个完成过程会考虑整个物体的上下文,以确保各部分能够紧密集成。生成完成模型可以弥补因遮挡而缺失的信息;在极端情况下,它可以根据输入的3D资产完全虚构出不可见的部分。我们在生成的和真实的3D资产上评估了我们的方法,并显示出它大大超越了分割和部件提取的基线。我们还展示了下游应用,如3D部件编辑。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://silent-chen.github.io/PartGen/
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为PartGen的新方法,该方法能够从文本、图像或无序的3D对象中生成由有意义的部件组成的3D物体。它采用多视角扩散模型进行部件分割,并填充遮挡部分,然后通过3D重建网络进行重建。此方法能够弥补因遮挡造成的信息缺失,甚至在极端情况下可以基于输入的3D资产生成完全不可见的部件。PartGen在生成和真实的3D资产上的表现优于传统的分割和部件提取方法,并展示了在3D部件编辑等下游应用中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- PartGen是一种能够从文本、图像或无序的3D对象生成由有意义部件组成的3D物体的新方法。
- PartGen采用多视角扩散模型进行部件分割,能够将物体分成多个可独立操作的部件。
- 方法中的遮挡填充和3D重建过程能够基于整个物体的上下文进行,确保部件的整合性。
- 生成完成模型可以弥补因遮挡造成的信息缺失,甚至能够基于输入的3D资产生成完全不可见的部件。
- PartGen在生成和真实3D资产上的表现优于传统的分割和部件提取方法。
- PartGen具有广泛的应用前景,例如在3D编辑、游戏开发、虚拟现实等领域。
点此查看论文截图
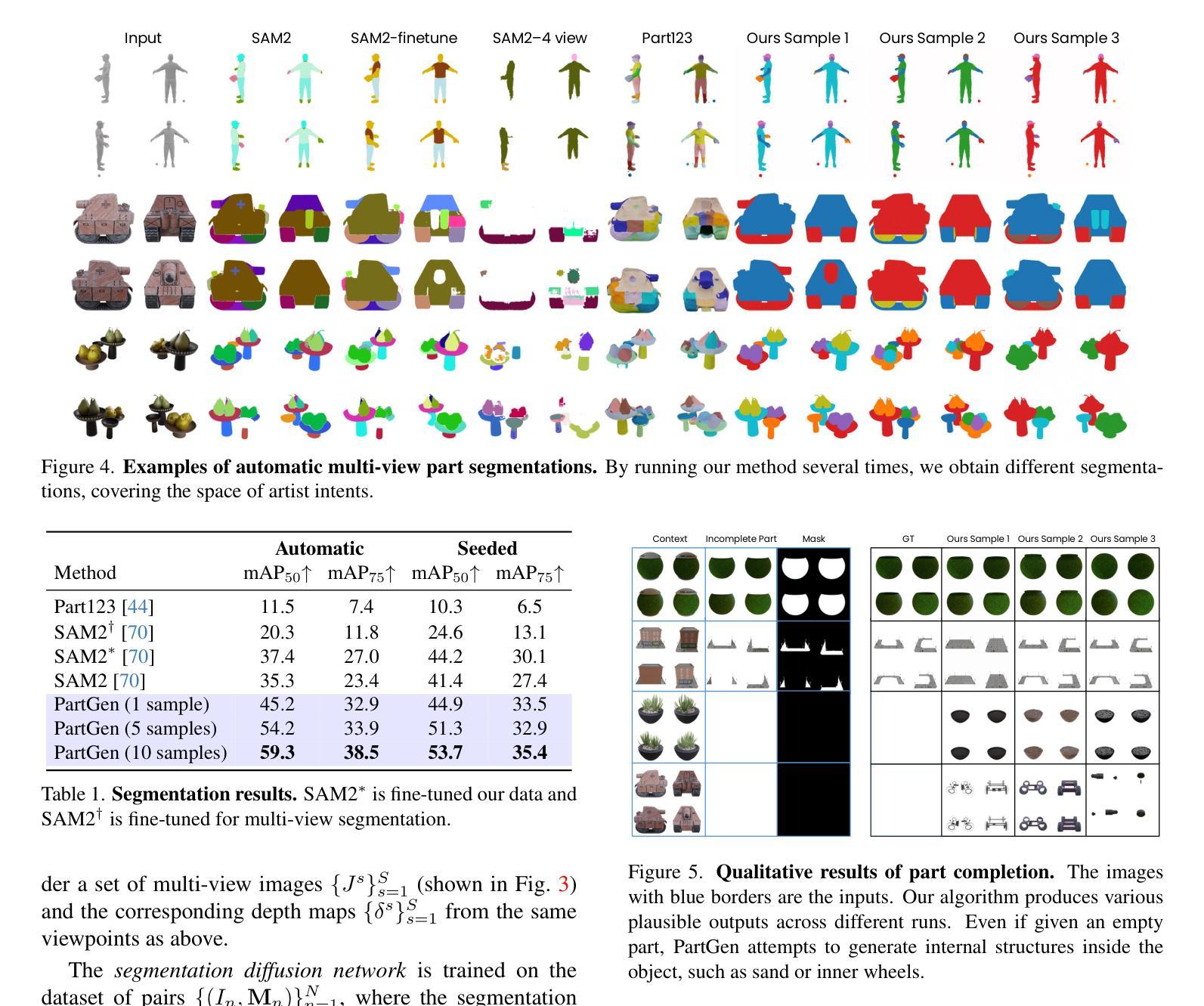
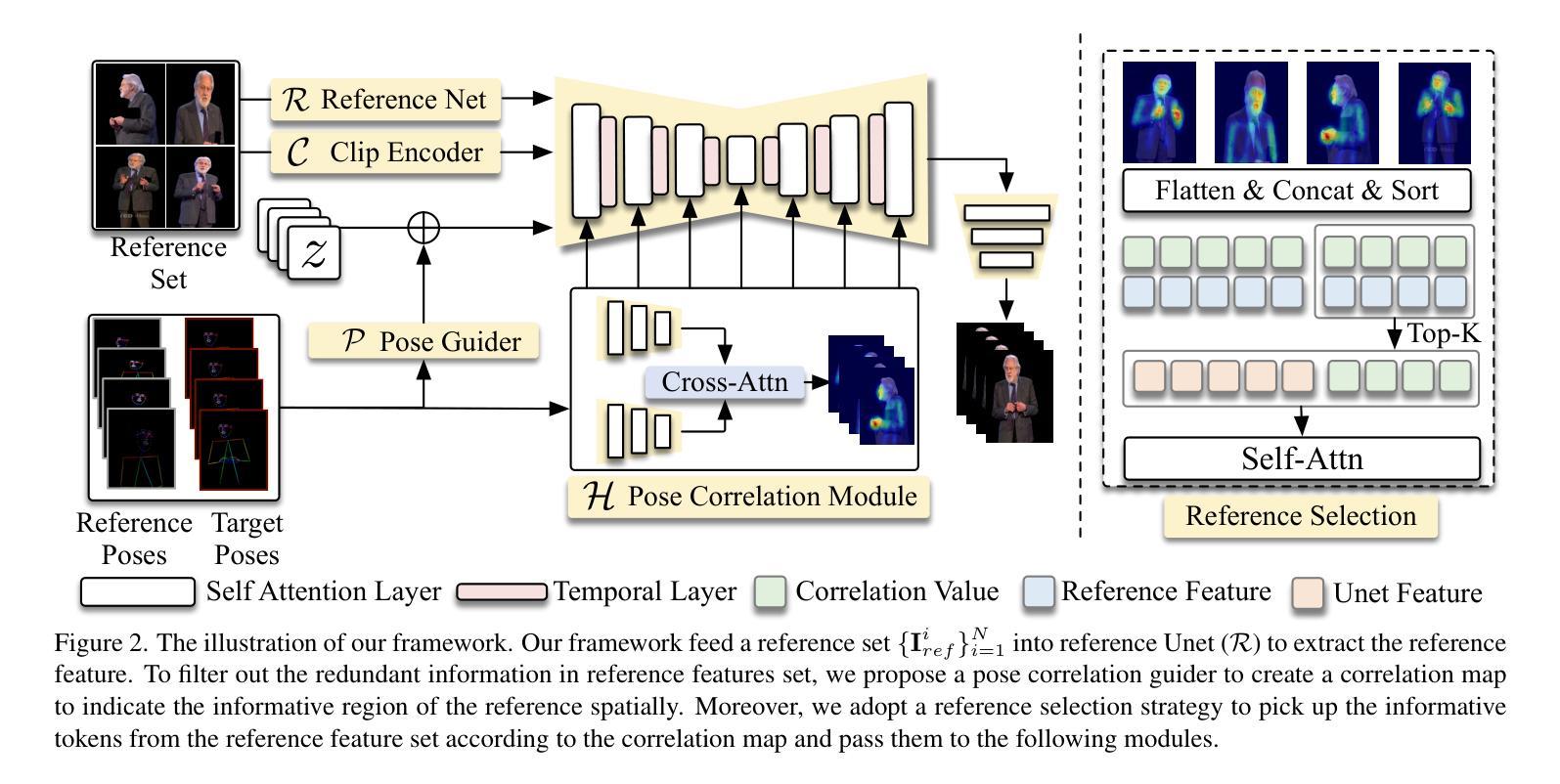
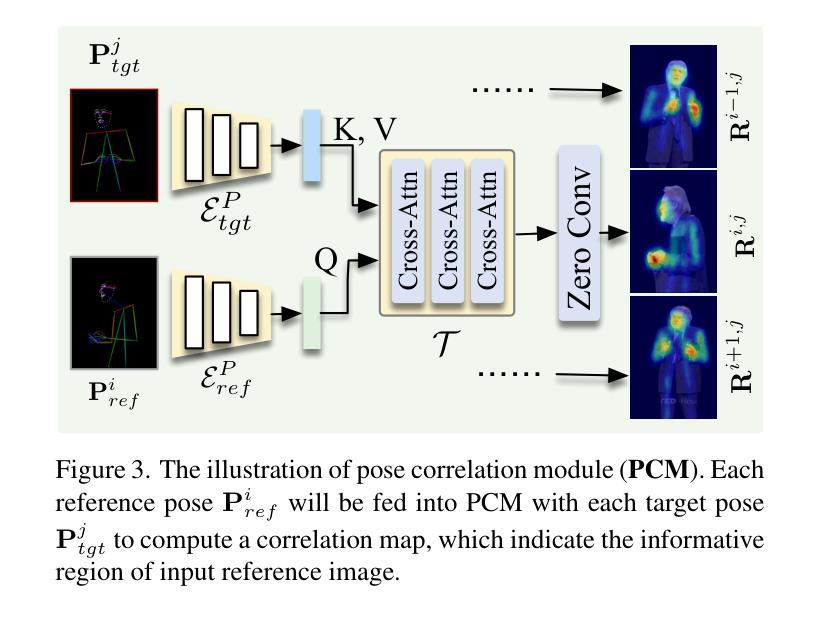
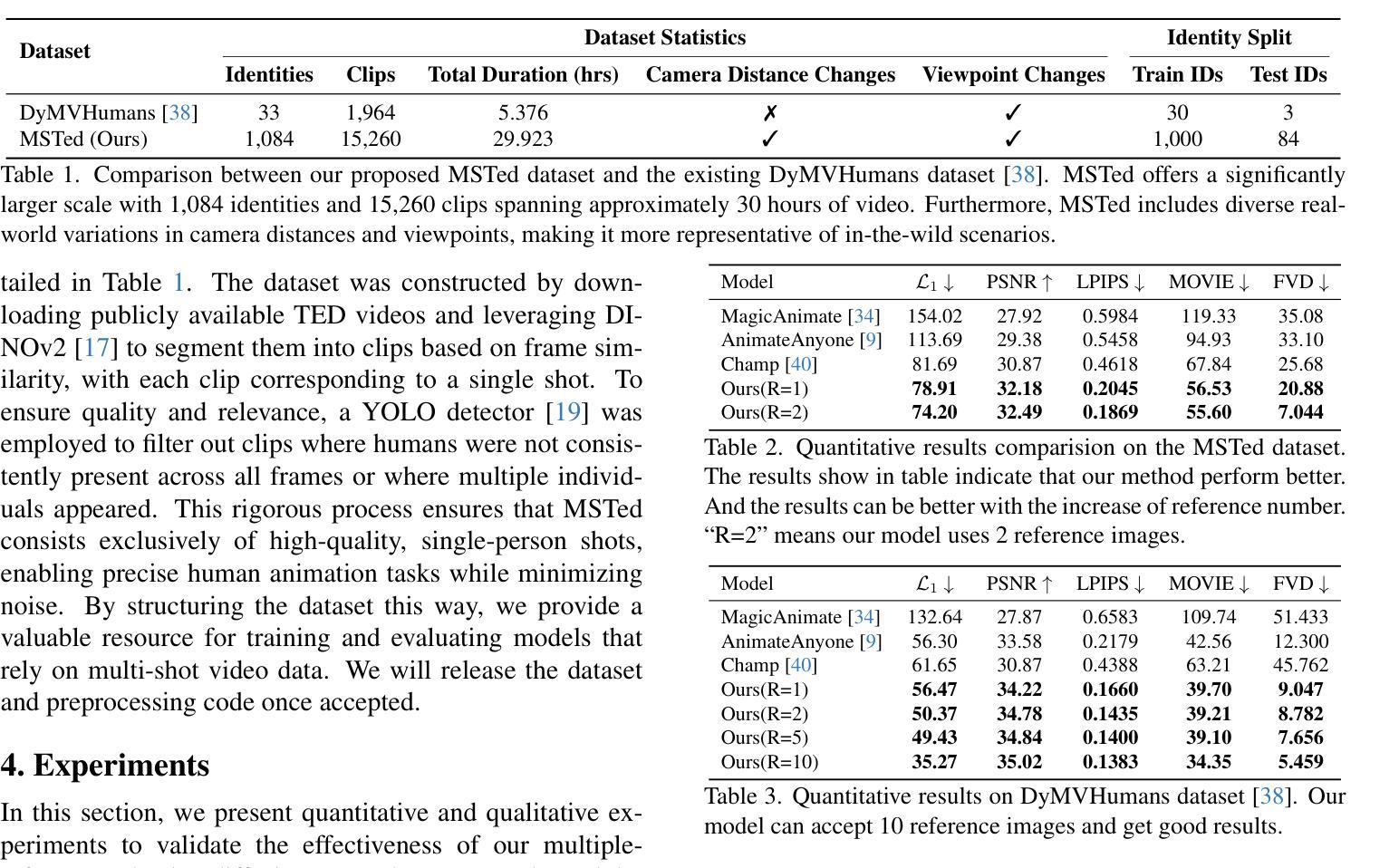
Free-viewpoint Human Animation with Pose-correlated Reference Selection
Authors:Fa-Ting Hong, Zhan Xu, Haiyang Liu, Qinjie Lin, Luchuan Song, Zhixin Shu, Yang Zhou, Duygu Ceylan, Dan Xu
Diffusion-based human animation aims to animate a human character based on a source human image as well as driving signals such as a sequence of poses. Leveraging the generative capacity of diffusion model, existing approaches are able to generate high-fidelity poses, but struggle with significant viewpoint changes, especially in zoom-in/zoom-out scenarios where camera-character distance varies. This limits the applications such as cinematic shot type plan or camera control. We propose a pose-correlated reference selection diffusion network, supporting substantial viewpoint variations in human animation. Our key idea is to enable the network to utilize multiple reference images as input, since significant viewpoint changes often lead to missing appearance details on the human body. To eliminate the computational cost, we first introduce a novel pose correlation module to compute similarities between non-aligned target and source poses, and then propose an adaptive reference selection strategy, utilizing the attention map to identify key regions for animation generation. To train our model, we curated a large dataset from public TED talks featuring varied shots of the same character, helping the model learn synthesis for different perspectives. Our experimental results show that with the same number of reference images, our model performs favorably compared to the current SOTA methods under large viewpoint change. We further show that the adaptive reference selection is able to choose the most relevant reference regions to generate humans under free viewpoints.
基于扩散的人体动画旨在根据源人体图像以及驱动信号(如一系列姿势)来使人物角色动画化。利用扩散模型的生成能力,现有方法能够生成高保真度的姿势,但在视点变化较大时面临挑战,特别是在缩放场景(如摄像机与角色的距离变化)中尤为如此。这限制了其在电影拍摄计划或相机控制等方面的应用。我们提出了一种姿态相关参考选择扩散网络,支持人体动画中的大幅视点变化。我们的核心思想是让网络使用多个参考图像作为输入,因为视点的大幅变化通常会导致人体外观细节缺失。为了降低计算成本,我们首先引入了一种新型的姿态相关性模块,用于计算未对齐的目标和源姿态之间的相似性,然后提出了一种自适应参考选择策略,利用注意力图来识别动画生成的关键区域。为了训练我们的模型,我们从公共TED演讲中整理了一个大型数据集,展示了同一角色的不同镜头,帮助模型学习不同视角的合成。实验结果表明,在相同数量的参考图像下,我们的模型在大视点变化方面与当前最佳方法相比表现良好。我们进一步表明,自适应参考选择能够选择最相关的参考区域来在自由视角下生成人体。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review; Project page: https://harlanhong.github.io/publications/fvhuman/index.html
Summary
基于扩散模型的人体动画技术能通过源人体图像和驱动信号(如一系列姿势)来动画化人物角色。现有方法虽能生成高保真姿势,但在视角变化较大的情况下,特别是在镜头推拉(zoom-in/zoom-out)场景中,由于相机与角色的距离变化导致的视角变化较大,应用受限,如电影拍摄计划或相机控制等。本文提出了一种姿态相关的参考选择扩散网络,支持人体动画中的大幅视角变化。我们的核心思想是让网络能够使用多个参考图像作为输入,因为视角的重大变化通常会导致人体外观细节缺失。我们引入了一个新颖的姿态关联模块来计算非对齐目标姿态和源姿态之间的相似性,并提出了一种自适应参考选择策略,利用注意力图来识别动画生成的关键区域。在大型数据集上的实验表明,与当前最佳方法相比,我们的模型在相同数量的参考图像下,在大视角变化的情况下表现良好。进一步展示了自适应参考选择能够选择最相关的参考区域,在自由视角下生成人体。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型用于基于源图像和驱动信号的人体动画。
- 现有方法在面对视角变化时面临挑战,特别是在镜头推拉场景中。
- 提出了一种姿态相关的参考选择扩散网络,以处理大幅视角变化。
- 引入姿态关联模块计算目标姿态和源姿态的相似性。
- 提出自适应参考选择策略,利用注意力图识别动画生成的关键区域。
- 使用公共TED讲座的大型数据集进行模型训练,学习不同视角的合成。
点此查看论文截图

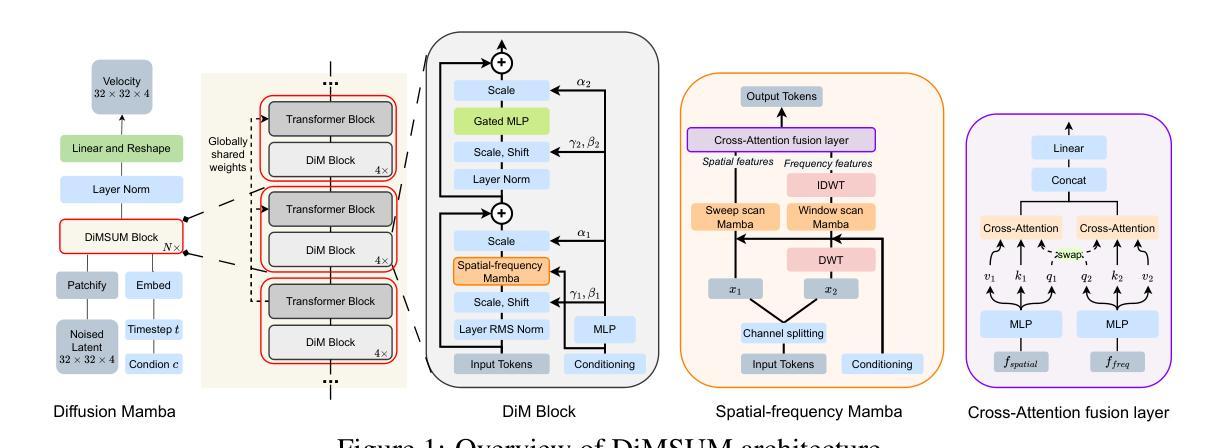
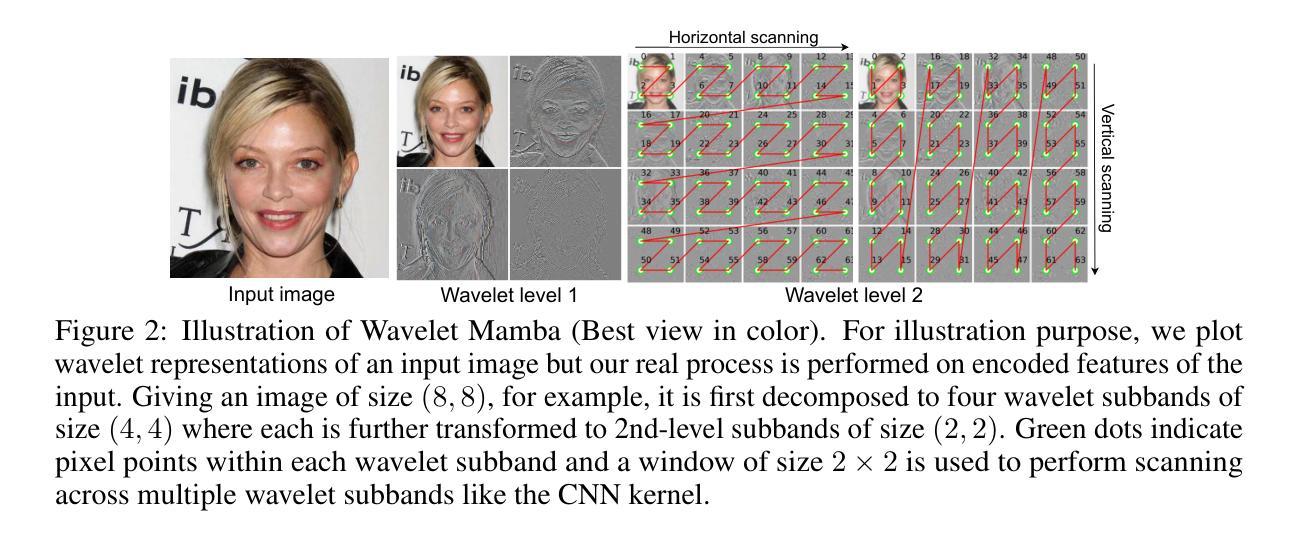
DiMSUM: Diffusion Mamba – A Scalable and Unified Spatial-Frequency Method for Image Generation
Authors:Hao Phung, Quan Dao, Trung Dao, Hoang Phan, Dimitris Metaxas, Anh Tran
We introduce a novel state-space architecture for diffusion models, effectively harnessing spatial and frequency information to enhance the inductive bias towards local features in input images for image generation tasks. While state-space networks, including Mamba, a revolutionary advancement in recurrent neural networks, typically scan input sequences from left to right, they face difficulties in designing effective scanning strategies, especially in the processing of image data. Our method demonstrates that integrating wavelet transformation into Mamba enhances the local structure awareness of visual inputs and better captures long-range relations of frequencies by disentangling them into wavelet subbands, representing both low- and high-frequency components. These wavelet-based outputs are then processed and seamlessly fused with the original Mamba outputs through a cross-attention fusion layer, combining both spatial and frequency information to optimize the order awareness of state-space models which is essential for the details and overall quality of image generation. Besides, we introduce a globally-shared transformer to supercharge the performance of Mamba, harnessing its exceptional power to capture global relationships. Through extensive experiments on standard benchmarks, our method demonstrates superior results compared to DiT and DIFFUSSM, achieving faster training convergence and delivering high-quality outputs. The codes and pretrained models are released at https://github.com/VinAIResearch/DiMSUM.git.
我们为扩散模型引入了一种新型状态空间架构,有效利用空间和频率信息,增强对输入图像局部特征的归纳偏见,以用于图像生成任务。状态空间网络(包括革命性的循环神经网络Mamba)通常从左到右扫描输入序列,但在设计有效的扫描策略时面临困难,特别是在处理图像数据时。我们的方法证明,通过将小波变换整合到Mamba中,可以增强对视觉输入的局部结构感知能力,并通过将频率分解为小波子带更好地捕获长期频率关系,这些子带代表低频和高频成分。这些基于小波的输出经过处理,并通过交叉注意融合层无缝融合到原始Mamba输出中,结合空间和频率信息优化状态空间模型的顺序感知能力,这对于图像生成的细节和整体质量至关重要。此外,我们引入了一个全局共享变压器来提升Mamba的性能,利用其捕捉全局关系的出色能力。在标准基准测试上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法相较于DiT和DIFFUSSM展现出优越的结果,实现更快的训练收敛速度并产生高质量输出。代码和预训练模型已发布在https://github.com/VinAIResearch/DiMSUM.git上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to NeurIPS 2024. Project page: https://vinairesearch.github.io/DiMSUM/
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型状态空间架构的扩散模型,该模型通过利用小波变换强化局部特征感知,并结合Mamba网络,有效结合空间与频率信息,提升图像生成任务的性能。通过引入全局共享变压器,进一步提升了Mamba的性能。实验表明,该模型在标准基准测试上表现优异,与DiT和DIFFUSSM相比,训练收敛更快,输出质量更高。
Key Takeaways
- 新型状态空间架构扩散模型结合了空间与频率信息,以增强图像生成任务的性能。
- 通过引入小波变换,提升模型对局部结构的感知能力,并更好地捕捉频率的长期关系。
- 结合小波输出和Mamba输出,通过交叉注意融合层优化状态空间模型的顺序感知能力。
- 引入全局共享变压器以进一步提升Mamba性能。
- 该模型在标准基准测试上表现优越,与现有方法相比,训练收敛更快,输出质量更高。
- 模型代码和预训练模型已发布在https://github.com/VinAIResearch/DiMSUM.git。
点此查看论文截图


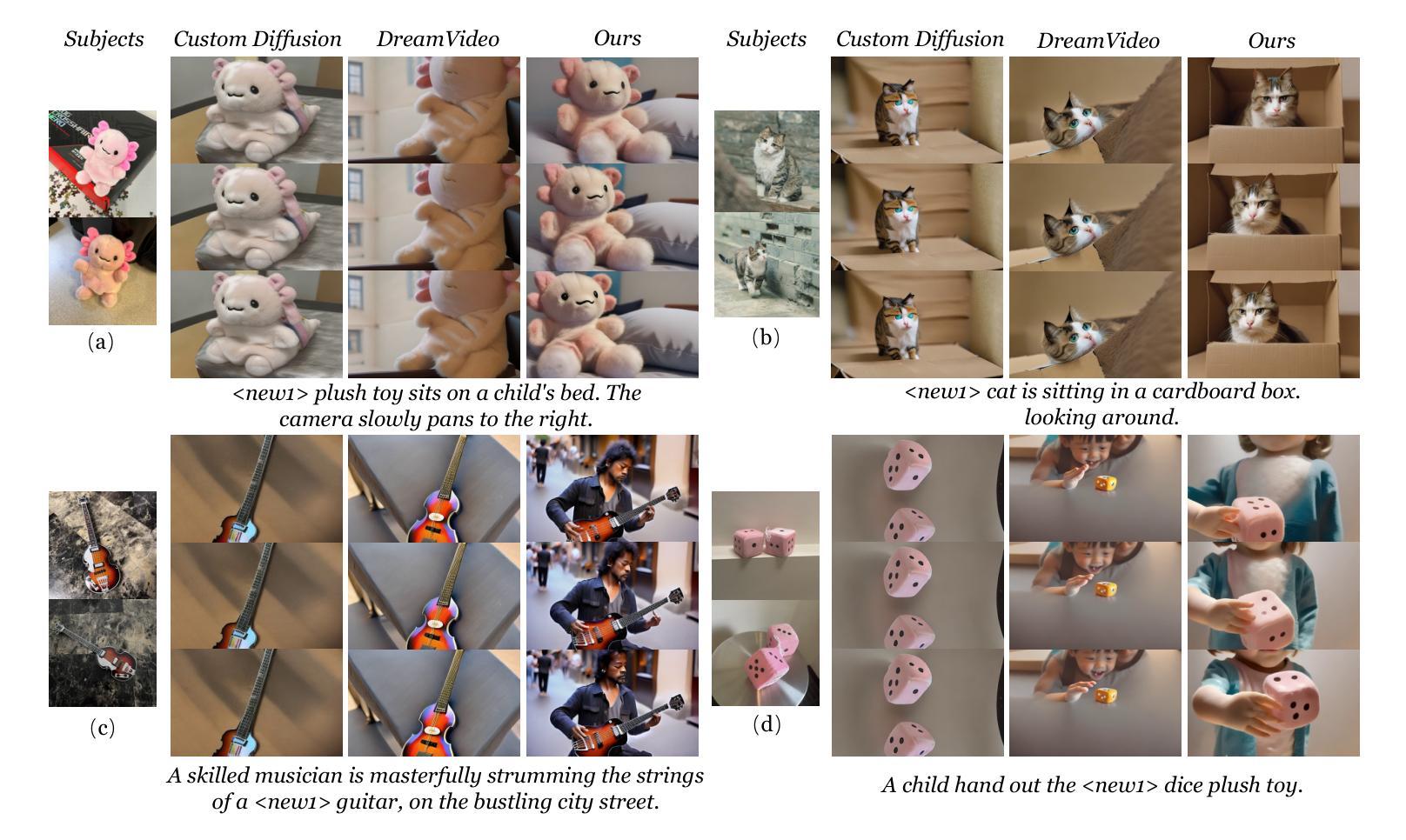
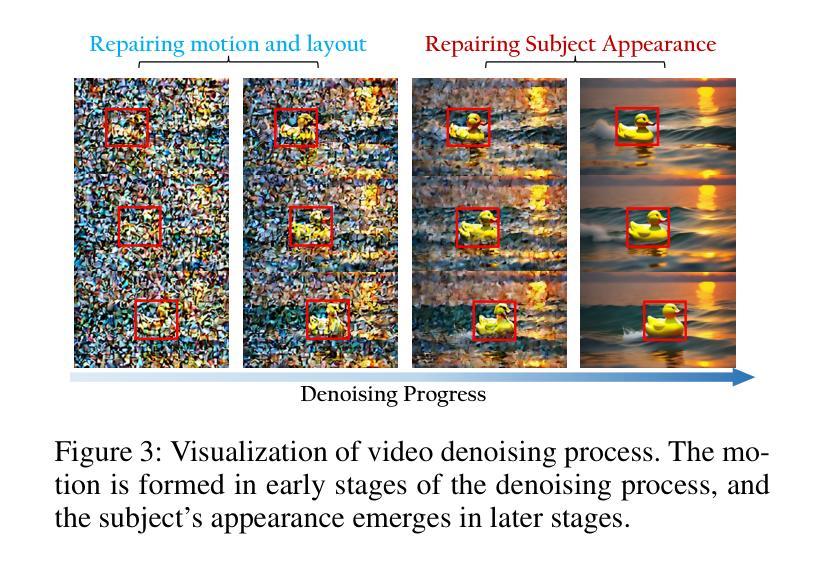
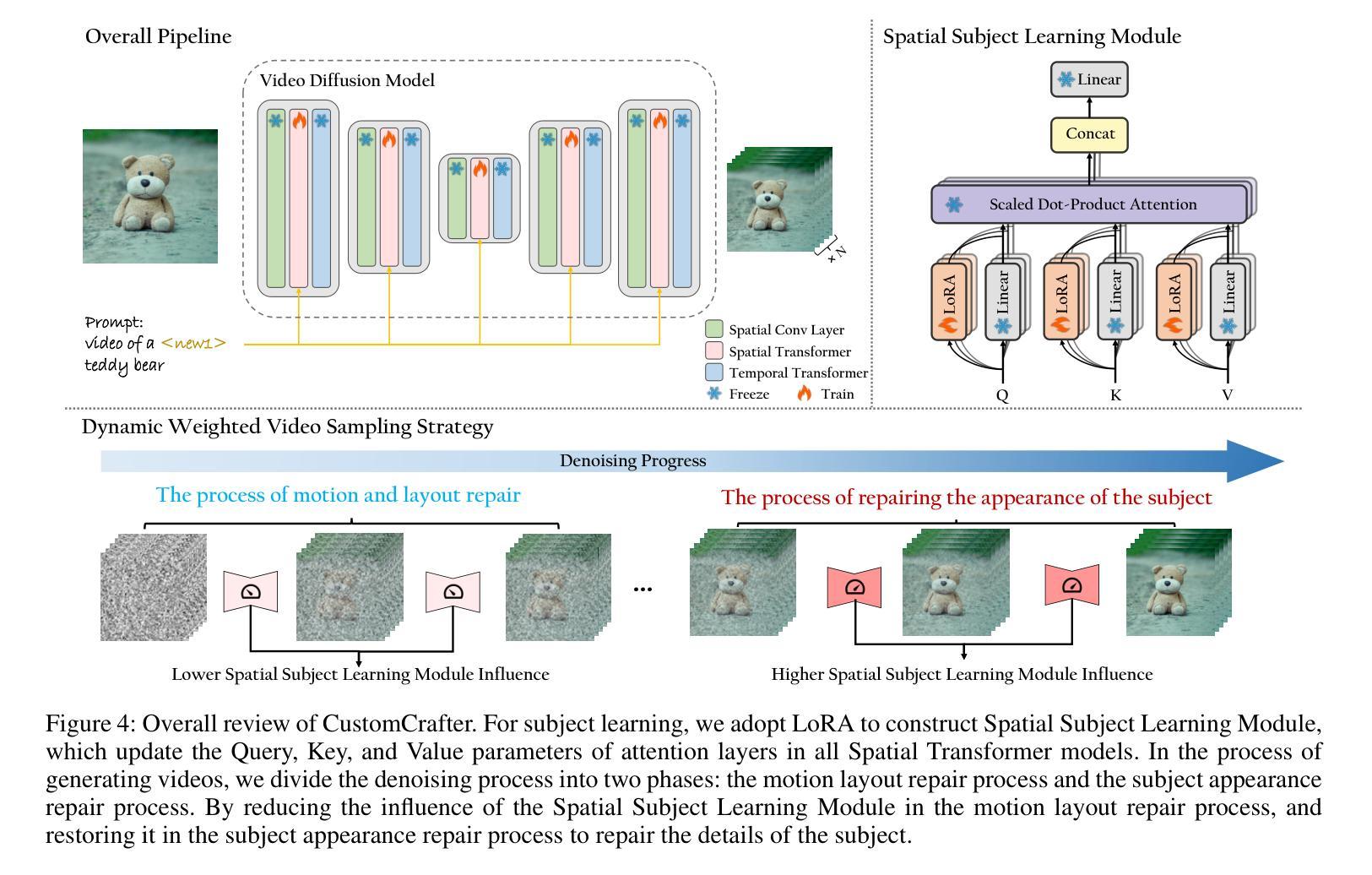
CustomCrafter: Customized Video Generation with Preserving Motion and Concept Composition Abilities
Authors:Tao Wu, Yong Zhang, Xintao Wang, Xianpan Zhou, Guangcong Zheng, Zhongang Qi, Ying Shan, Xi Li
Customized video generation aims to generate high-quality videos guided by text prompts and subject’s reference images. However, since it is only trained on static images, the fine-tuning process of subject learning disrupts abilities of video diffusion models (VDMs) to combine concepts and generate motions. To restore these abilities, some methods use additional video similar to the prompt to fine-tune or guide the model. This requires frequent changes of guiding videos and even re-tuning of the model when generating different motions, which is very inconvenient for users. In this paper, we propose CustomCrafter, a novel framework that preserves the model’s motion generation and conceptual combination abilities without additional video and fine-tuning to recovery. For preserving conceptual combination ability, we design a plug-and-play module to update few parameters in VDMs, enhancing the model’s ability to capture the appearance details and the ability of concept combinations for new subjects. For motion generation, we observed that VDMs tend to restore the motion of video in the early stage of denoising, while focusing on the recovery of subject details in the later stage. Therefore, we propose Dynamic Weighted Video Sampling Strategy. Using the pluggability of our subject learning modules, we reduce the impact of this module on motion generation in the early stage of denoising, preserving the ability to generate motion of VDMs. In the later stage of denoising, we restore this module to repair the appearance details of the specified subject, thereby ensuring the fidelity of the subject’s appearance. Experimental results show that our method has a significant improvement compared to previous methods. Code is available at https://github.com/WuTao-CS/CustomCrafter
定制化视频生成旨在通过文本提示和参考图像生成高质量视频。然而,由于其仅对静态图像进行训练,主体学习的微调过程会破坏视频扩散模型(VDMs)结合概念和生成运动的能力。为了恢复这些能力,一些方法使用与提示相似的额外视频来微调或指导模型。这需要在生成不同运动时频繁更换指导视频,甚至重新调整模型,非常不方便用户。在本文中,我们提出了CustomCrafter,这是一个新型框架,无需额外的视频和微调即可保留模型的运动生成和概念结合能力。为了保留概念结合能力,我们设计了一个即插即用模块来更新VDM中的少数参数,增强模型捕捉外观细节和结合新概念的能力。对于运动生成,我们观察到VDM倾向于在降噪的早期阶段恢复视频的运动,同时专注于后期恢复主体的细节。因此,我们提出了动态加权视频采样策略。利用我们主体学习模块的即插即用特性,我们在降噪的早期阶段减少该模块对运动生成的影响,保留VDMs生成运动的能力。在降噪的后期阶段,我们恢复此模块以修复指定主体的外观细节,从而确保主体外观的保真度。实验结果表明,我们的方法与之前的方法相比具有显著改进。代码可访问:https://github.com/WuTao-CS/CustomCrafter
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025. Project page: https://customcrafter.github.io/
Summary
该文提出一个名为CustomCrafter的新框架,旨在解决视频扩散模型(VDMs)在定制化视频生成时面临的问题。该框架能够在无需额外视频和指导调整的情况下,保持模型的运动生成和概念组合能力。通过设计即插即用模块更新VDMs中的少数参数,提升模型对新主题的外观细节捕捉和概念组合能力。同时,采用动态加权视频采样策略,在降噪的早期阶段减少模块对运动生成的影响,确保VDMs的运动生成能力,并在后期修复指定主题的外观细节。实验结果显新框架相比以往方法有明显改进。
Key Takeaways
- CustomCrafter框架解决了视频扩散模型(VDMs)在定制化视频生成时面临的概念组合和运动生成能力受损的问题。
- 无需额外视频和指导调整,就能保持VDMs的运动生成和概念组合能力。
- 设计了即插即用模块,通过更新少数参数提升模型对新主题的外观细节捕捉和概念组合能力。
- 采用动态加权视频采样策略,确保VDMs在降噪过程中既能生成流畅运动,又能修复主题的外观细节。
- 在实验环节,CustomCrafter相比以往方法表现出显著改进。
- CustomCrafter框架的代码已公开可访问。
- 该方法对于提高视频生成的质量和效率具有潜在的重要意义。
点此查看论文截图


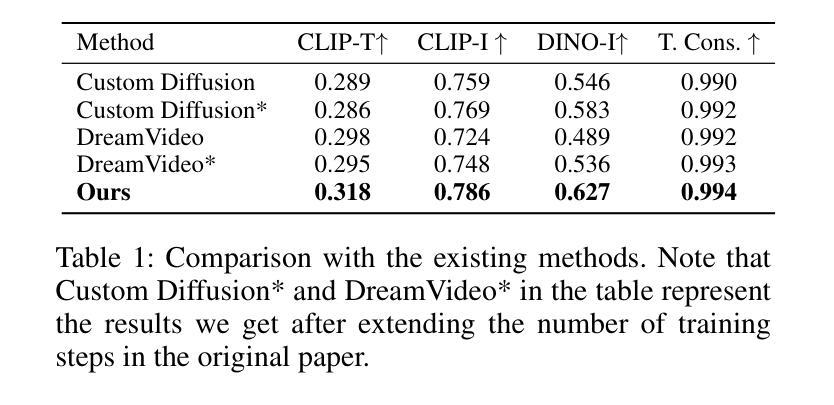

ssProp: Energy-Efficient Training for Convolutional Neural Networks with Scheduled Sparse Back Propagation
Authors:Lujia Zhong, Shuo Huang, Yonggang Shi
Recently, deep learning has made remarkable strides, especially with generative modeling, such as large language models and probabilistic diffusion models. However, training these models often involves significant computational resources, requiring billions of petaFLOPs. This high resource consumption results in substantial energy usage and a large carbon footprint, raising critical environmental concerns. Back-propagation (BP) is a major source of computational expense during training deep learning models. To advance research on energy-efficient training and allow for sparse learning on any machine and device, we propose a general, energy-efficient convolution module that can be seamlessly integrated into any deep learning architecture. Specifically, we introduce channel-wise sparsity with additional gradient selection schedulers during backward based on the assumption that BP is often dense and inefficient, which can lead to over-fitting and high computational consumption. Our experiments demonstrate that our approach reduces 40% computations while potentially improving model performance, validated on image classification and generation tasks. This reduction can lead to significant energy savings and a lower carbon footprint during the research and development phases of large-scale AI systems. Additionally, our method mitigates over-fitting in a manner distinct from Dropout, allowing it to be combined with Dropout to further enhance model performance and reduce computational resource usage. Extensive experiments validate that our method generalizes to a variety of datasets and tasks and is compatible with a wide range of deep learning architectures and modules. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/lujiazho/ssProp.
最近,深度学习领域取得了显著的进步,特别是在生成模型方面,如大型语言模型和概率扩散模型。然而,训练这些模型通常需要大量的计算资源,需要数以亿计的petaFLOPs。这种高资源消耗导致大量能源消耗和较大的碳足迹,引发了关键的环境问题。反向传播(BP)是训练深度学习模型时计算成本的主要来源。为了推进节能训练的研究,并实现在任何机器和设备上进行稀疏学习,我们提出了一种通用的节能卷积模块,它可以无缝地集成到任何深度学习架构中。具体来说,我们引入了通道稀疏性和基于反向传播中常用的梯度选择调度器,假设反向传播通常是密集且低效的,这可能导致过拟合和高计算消耗。我们的实验表明,我们的方法减少了40%的计算量,同时可能提高模型的性能,这在图像分类和生成任务中得到了验证。这种减少可以节省大量能源并降低大型人工智能系统在研发阶段的碳足迹。此外,我们的方法以与Dropout不同的方式减轻过拟合问题,允许其与Dropout结合使用,以进一步提高模型性能和降低计算资源的使用。广泛的实验验证了我们的方法可以推广到各种数据集和任务,并且与各种深度学习架构和模块兼容。代码可在https://github.com/lujiazho/ssProp公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI24 Workshop: Scalable and Efficient Artificial Intelligence Systems
Summary
本文提出一种通用的、节能的卷积模块,可无缝集成到任何深度学习架构中,以提高能源效率并实现在任何机器和设备上的稀疏学习。通过引入基于通道稀疏性和附加梯度选择调度器的后向传播方法,该模块能够在图像分类和生成任务上减少计算量并提高模型性能。该方法可显著降低大型AI系统在研发阶段的能耗和碳排放,并以不同于Dropout的方式缓解过拟合问题,可与Dropout结合使用,进一步提高模型性能和降低计算资源使用量。实验证明,该方法可广泛应用于各种数据集和任务,兼容多种深度学习架构和模块。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习中的生成建模如大型语言模型和概率扩散模型取得了显著进展,但训练这些模型需要大量的计算资源和能源。
- 反向传播(BP)是训练深度学习模型中的主要计算成本来源。
- 提出了一种通用的、节能的卷积模块,该模块可以提高能源效率并实现在任何机器和设备上的稀疏学习。
- 通过引入基于通道稀疏性和附加梯度选择调度器的技术,该模块在图像分类和生成任务上实现了计算量的减少和模型性能的潜在提高。
- 该方法能够减少大型AI系统在研发阶段的能耗和碳排放。
- 与Dropout不同,该方法以独特的方式缓解过拟合问题,并与Dropout结合使用以进一步提高模型性能和降低计算资源使用量。
点此查看论文截图

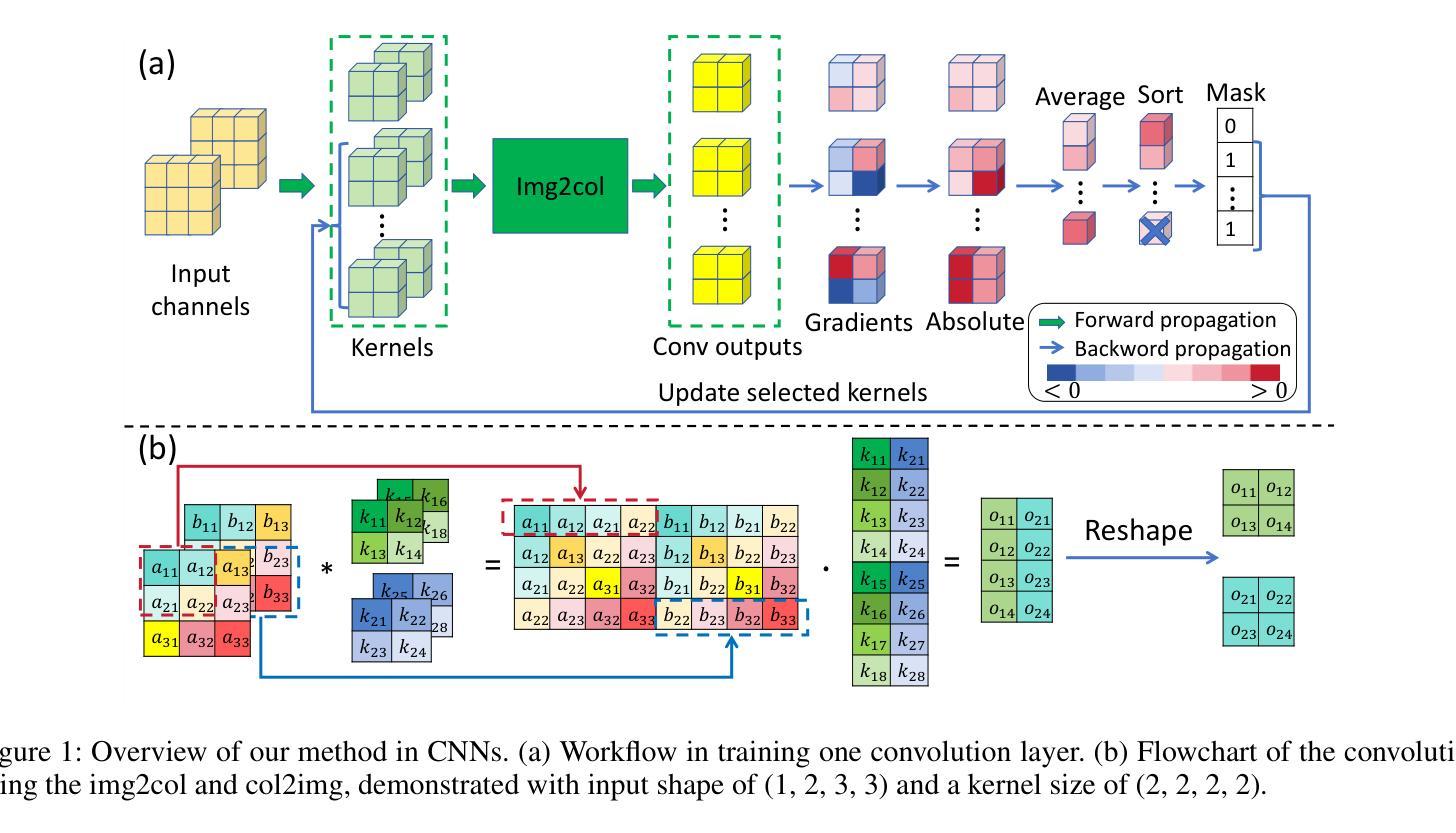
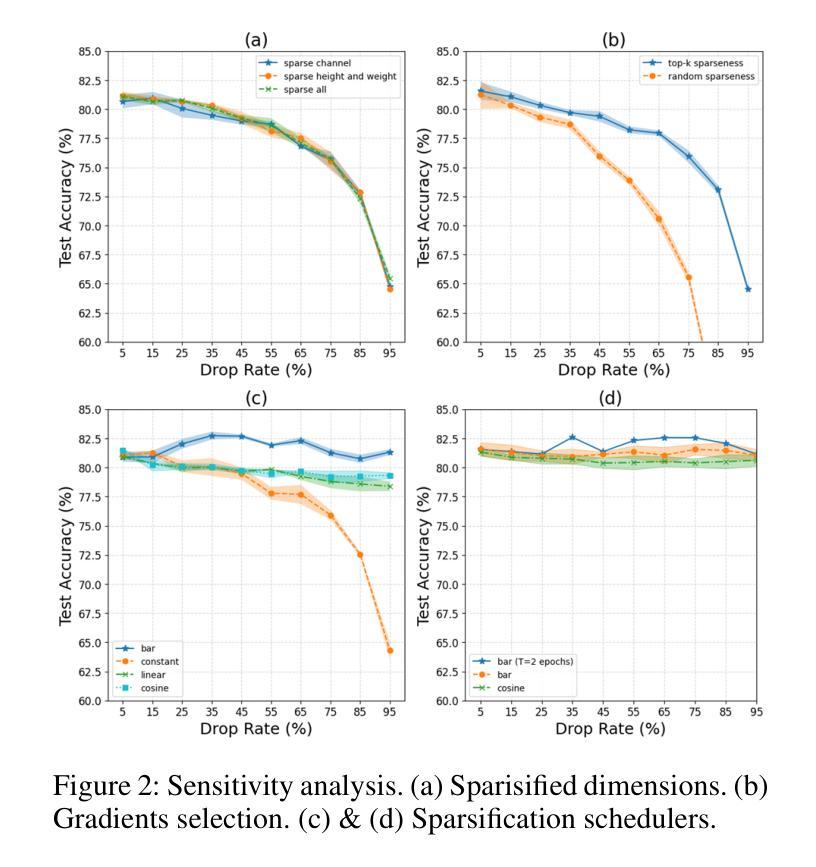
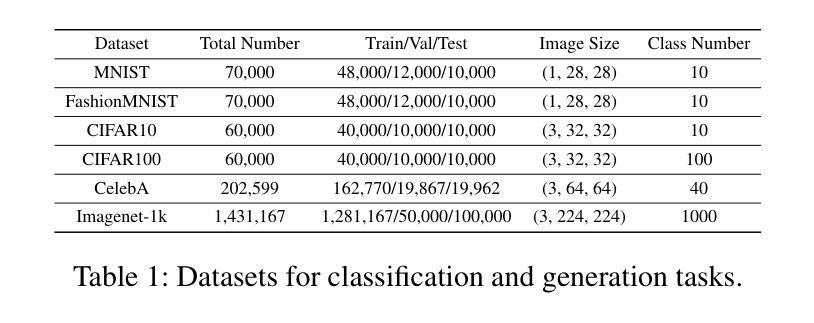

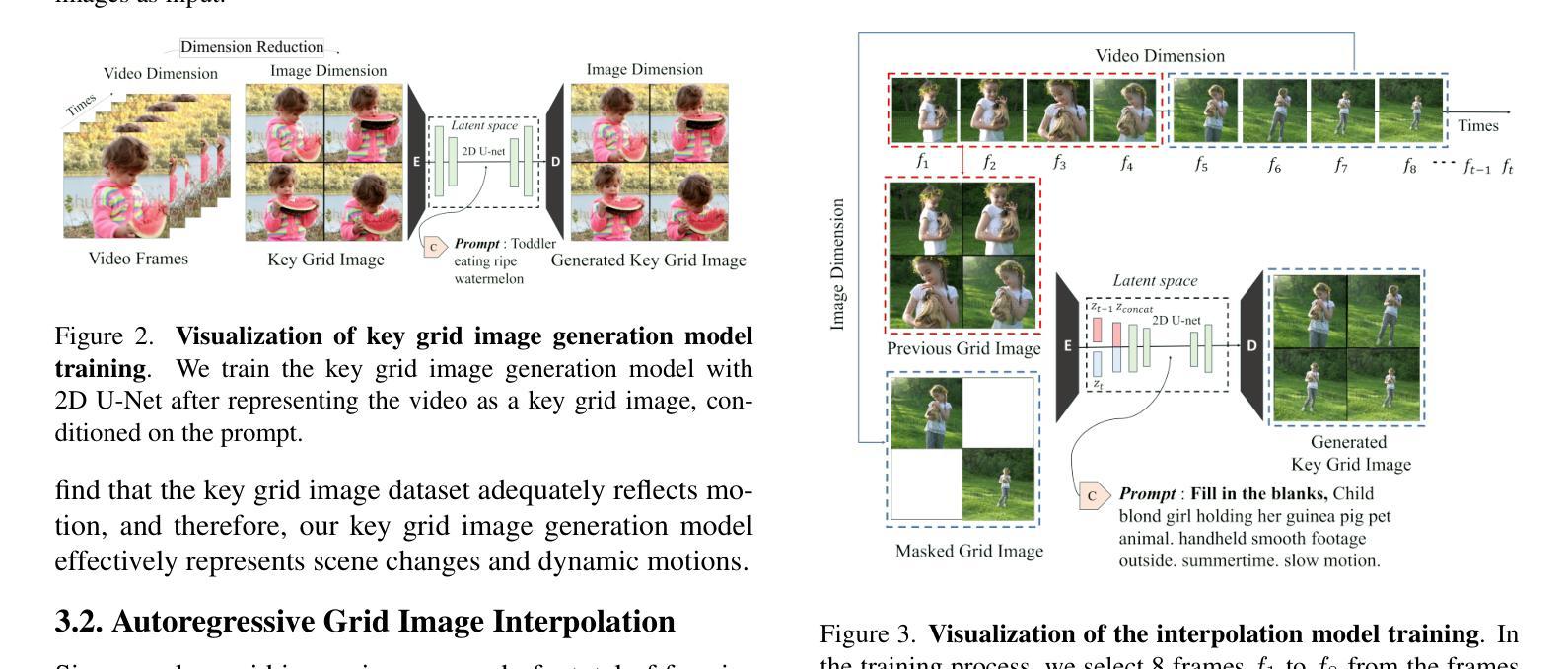
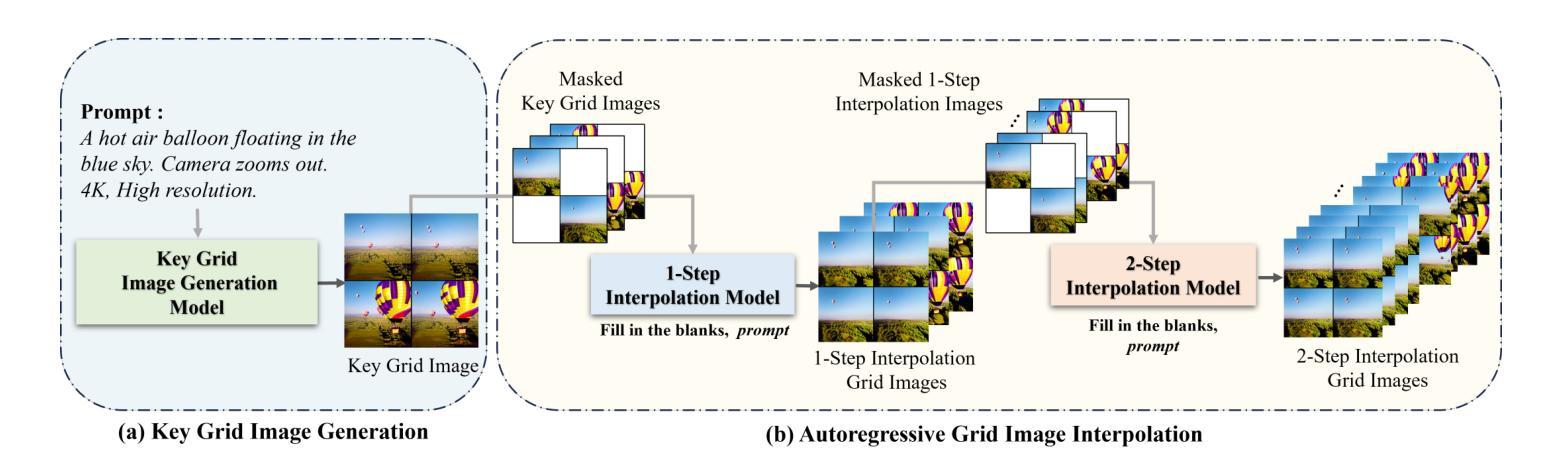
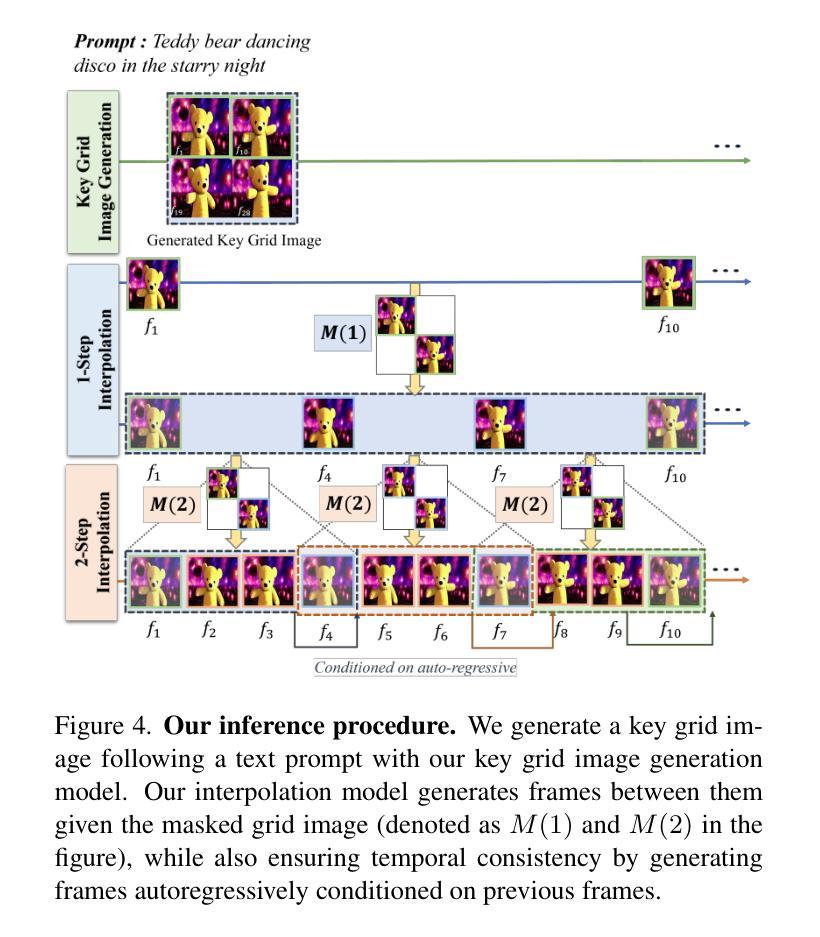
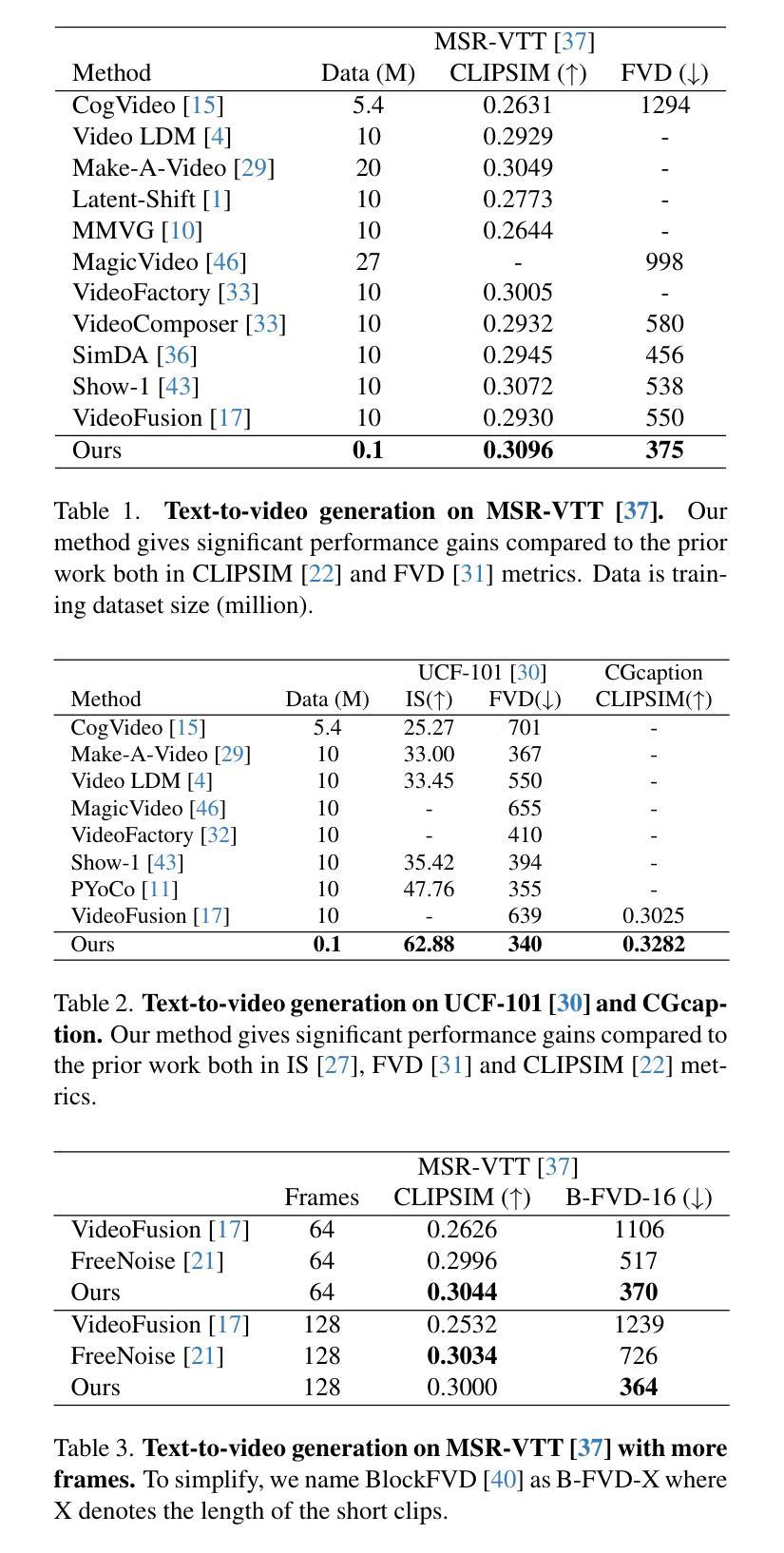
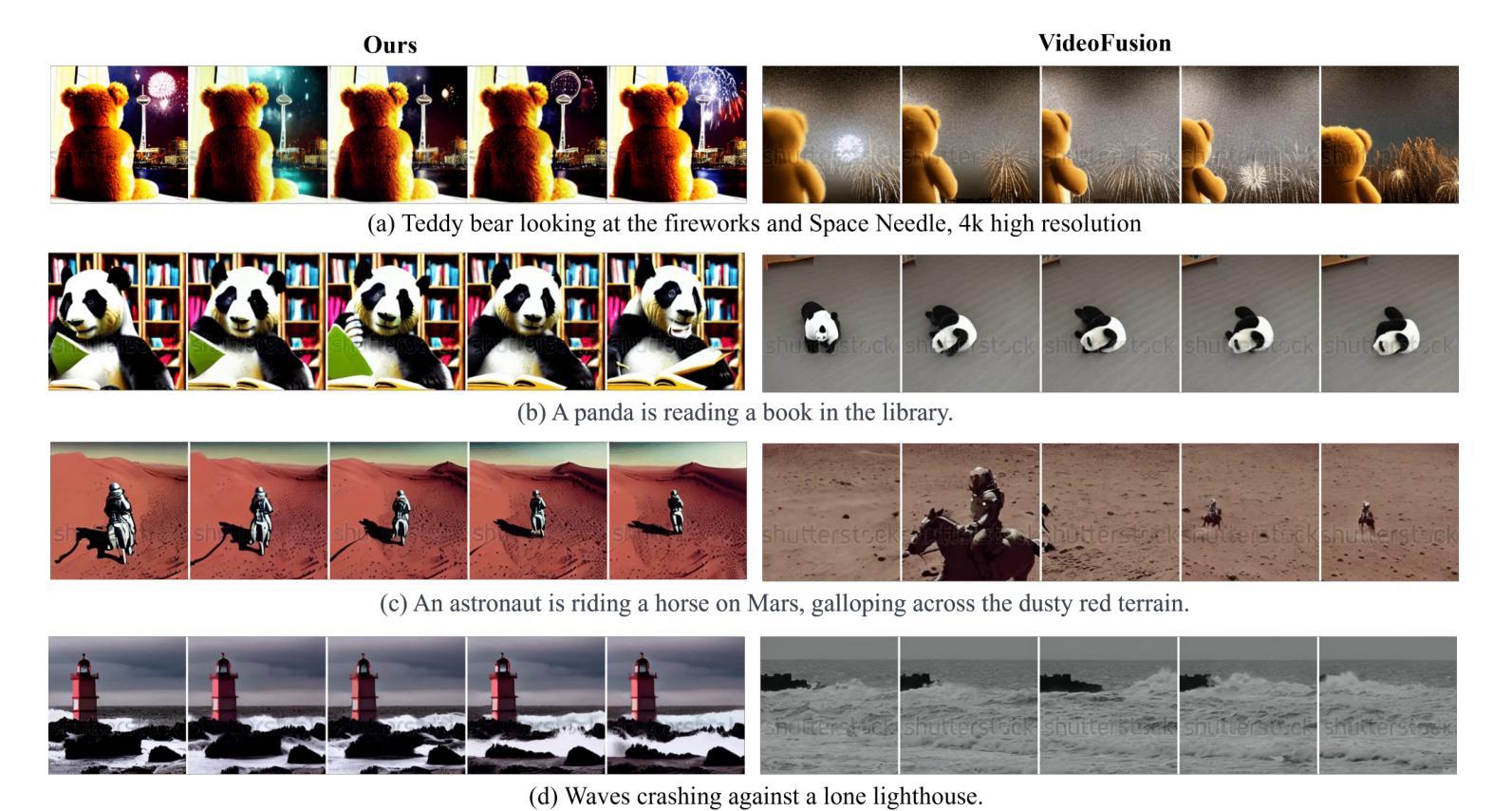
Grid Diffusion Models for Text-to-Video Generation
Authors:Taegyeong Lee, Soyeong Kwon, Taehwan Kim
Recent advances in the diffusion models have significantly improved text-to-image generation. However, generating videos from text is a more challenging task than generating images from text, due to the much larger dataset and higher computational cost required. Most existing video generation methods use either a 3D U-Net architecture that considers the temporal dimension or autoregressive generation. These methods require large datasets and are limited in terms of computational costs compared to text-to-image generation. To tackle these challenges, we propose a simple but effective novel grid diffusion for text-to-video generation without temporal dimension in architecture and a large text-video paired dataset. We can generate a high-quality video using a fixed amount of GPU memory regardless of the number of frames by representing the video as a grid image. Additionally, since our method reduces the dimensions of the video to the dimensions of the image, various image-based methods can be applied to videos, such as text-guided video manipulation from image manipulation. Our proposed method outperforms the existing methods in both quantitative and qualitative evaluations, demonstrating the suitability of our model for real-world video generation.
近期扩散模型的新进展在文本到图像生成方面取得了显著的提升。然而,从文本生成视频是一项比从文本生成图像更具挑战性的任务,这主要是由于所需的数据集更大和计算成本更高。目前大多数视频生成方法使用考虑时间维度的3D U-Net架构或自回归生成。这些方法需要大量数据集,并且在计算成本方面与文本到图像生成相比存在局限。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种简单有效的新型网格扩散方法,用于文本到视频生成,无需考虑架构中的时间维度和大型文本-视频配对数据集。通过将视频表示为网格图像,我们可以使用固定量的GPU内存生成高质量视频,无论帧数如何。此外,由于我们的方法将视频的维度减少到图像的维度,因此各种基于图像的方法可以应用于视频,例如基于文本引导的图像操作进行视频操作。所提出的方法在定量和定性评估中都优于现有方法,证明了我们模型在现实世界视频生成中的适用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper is being withdrawn due to issues of misconduct in the experiments presented in Table 1 and 5. We recognize this as an ethical concern and sincerely apologize to the research community for any inconvenience it may have caused
摘要
最新扩散模型进展显著提升了文本到图像生成能力。然而,文本生成视频的任务比文本生成图像更具挑战性,涉及更大的数据集和更高的计算成本。现有视频生成方法多采用考虑时间维度的3D U-Net架构或自回归生成。这些方法需要大量数据集,与文本到图像生成相比,计算成本方面存在局限。为应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种简单有效的网格扩散新方法,用于文本到视频生成,无需考虑时间维度和大型文本视频配对数据集。通过把视频表示为网格图像,我们能以固定GPU内存生成高质量视频,无论帧数多少。此外,由于我们的方法将视频维度降至图像维度,各种基于图像的方法可应用于视频,如文本引导的视频操作来自图像操作。我们的方法在定量和定性评估上均优于现有方法,证明了我们模型在真实视频生成中的适用性。
关键见解
- 扩散模型的最新进展已经显著提高了文本到图像的生成能力。
- 文本生成视频任务由于需要更大的数据集和更高的计算成本而更具挑战性。
- 现有视频生成方法主要采用3D U-Net架构或自回归生成,存在计算成本高的局限。
- 提出了一种新的网格扩散方法,无需考虑时间维度和大型文本视频配对数据集,用于文本到视频生成。
- 通过将视频表示为网格图像,能在固定GPU内存下生成高质量视频,无论帧数多少。
- 方法降低了视频维度至图像维度,使得图像处理方法可应用于视频操作。
点此查看论文截图