⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-02 更新
Defending Multimodal Backdoored Models by Repulsive Visual Prompt Tuning
Authors:Zhifang Zhang, Shuo He, Bingquan Shen, Lei Feng
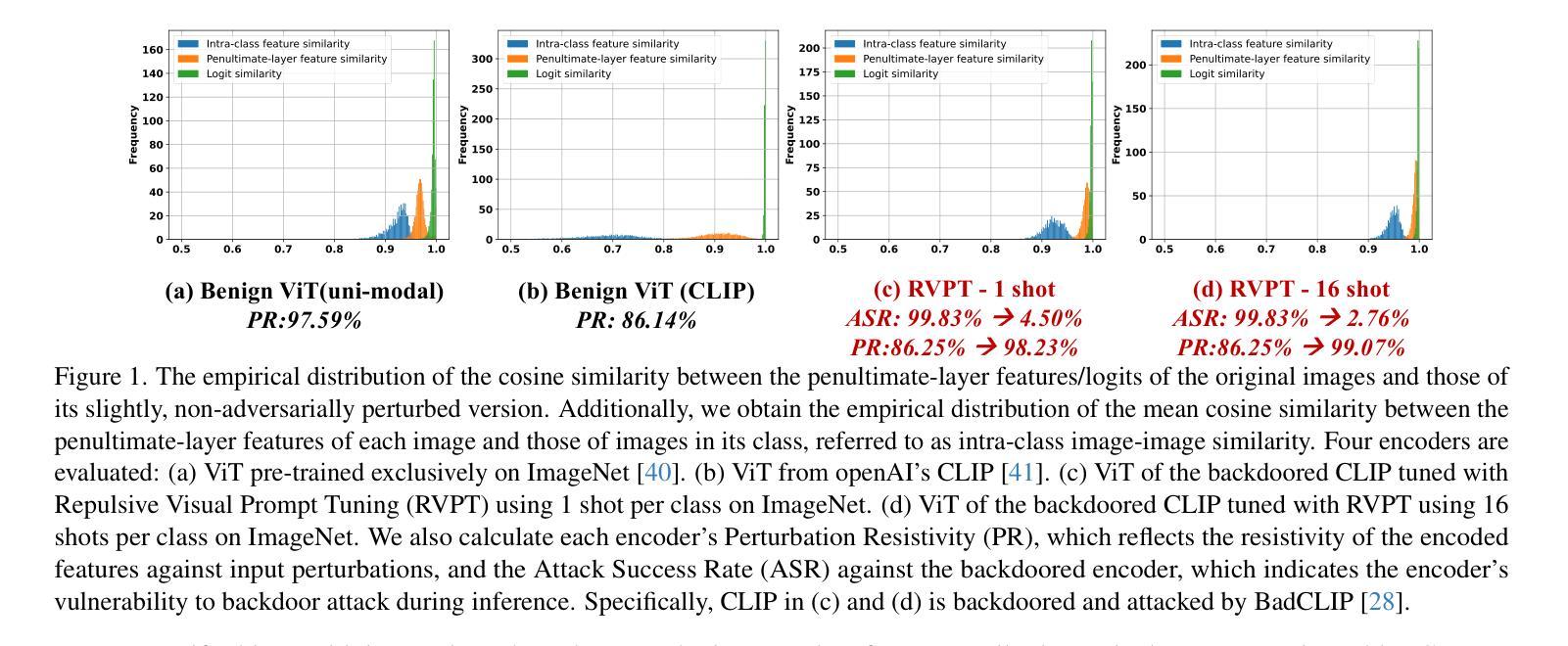
Multimodal contrastive learning models (e.g., CLIP) can learn high-quality representations from large-scale image-text datasets, yet they exhibit significant vulnerabilities to backdoor attacks, raising serious safety concerns. In this paper, we disclose that CLIP’s vulnerabilities primarily stem from its excessive encoding of class-irrelevant features, which can compromise the model’s visual feature resistivity to input perturbations, making it more susceptible to capturing the trigger patterns inserted by backdoor attacks. Inspired by this finding, we propose Repulsive Visual Prompt Tuning (RVPT), a novel defense approach that employs specially designed deep visual prompt tuning and feature-repelling loss to eliminate excessive class-irrelevant features while simultaneously optimizing cross-entropy loss to maintain clean accuracy. Unlike existing multimodal backdoor defense methods that typically require the availability of poisoned data or involve fine-tuning the entire model, RVPT leverages few-shot downstream clean samples and only tunes a small number of parameters. Empirical results demonstrate that RVPT tunes only 0.27% of the parameters relative to CLIP, yet it significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, reducing the attack success rate from 67.53% to 2.76% against SoTA attacks and effectively generalizing its defensive capabilities across multiple datasets.
多模态对比学习模型(例如CLIP)可以从大规模图像文本数据集中学习高质量表示,但它们对后门攻击表现出显著脆弱性,这引发了严重的安全担忧。在本文中,我们披露CLIP的脆弱性主要源于其对与类别无关特征的过度编码,这可能会损害模型对输入扰动的视觉特征电阻,使其更容易捕获由后门攻击插入的触发模式。受这一发现的启发,我们提出了名为“排斥视觉提示调整”(RVPT)的新型防御方法,该方法采用专门设计的深度视觉提示调整和特征排斥损失,以消除过多的与类别无关的特征,同时优化交叉熵损失以保持清洁准确性。与通常需要中毒数据或涉及对整个模型进行微调的传统多模态后门防御方法不同,RVPT利用少量下游清洁样本,并且只调整少量参数。经验结果表明,RVPT仅调整CLIP的0.27%参数,却显著优于最新基线技术,将攻击成功率从67.53%降低到2.76%,有效抵御了最先进的攻击,并在多个数据集上实现了防御能力的有效泛化。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于CLIP等多模态对比学习模型的图像文本数据集能学习高质量表示,但其存在易受后门攻击影响的脆弱性,引起严重的安全问题。研究发现,CLIP的脆弱性主要源于其对非类别特征的过度编码,削弱了模型对输入扰动的视觉特征抗性,易于捕获后门攻击插入的触发模式。为此,本文提出采用深度视觉提示调整和特征排斥损失的防御方法——RVPT。RVPT在不要求中毒数据可用性或涉及整个模型微调的前提下,通过优化少量参数实现了良好的防御效果。实验结果证明,RVPT仅调整CLIP的0.27%参数,即可显著超越现有技术基线,攻击成功率从原来的67.53%降低到仅存的2.76%,并且在多个数据集上实现了有效的防御能力推广。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态对比学习模型如CLIP面临后门攻击的风险,存在安全隐患。
- CLIP的脆弱性源于其对非类别特征的过度编码,使其易受触发模式插入攻击影响。
- 新提出的防御方法RVPT,旨在消除多余的类别无关特征。通过深度视觉提示调整和特征排斥损失实现优化。
- RVPT仅调整少量参数即可实现高效防御,与现有方法相比有显著优势。实验证明其在不同数据集上防御效果广泛适用。
- RVPT针对后门攻击的防御能力强大,攻击成功率显著降低。
- RVPT方法具有强大的泛化能力,能在多个数据集上有效抵御攻击。
点此查看论文截图

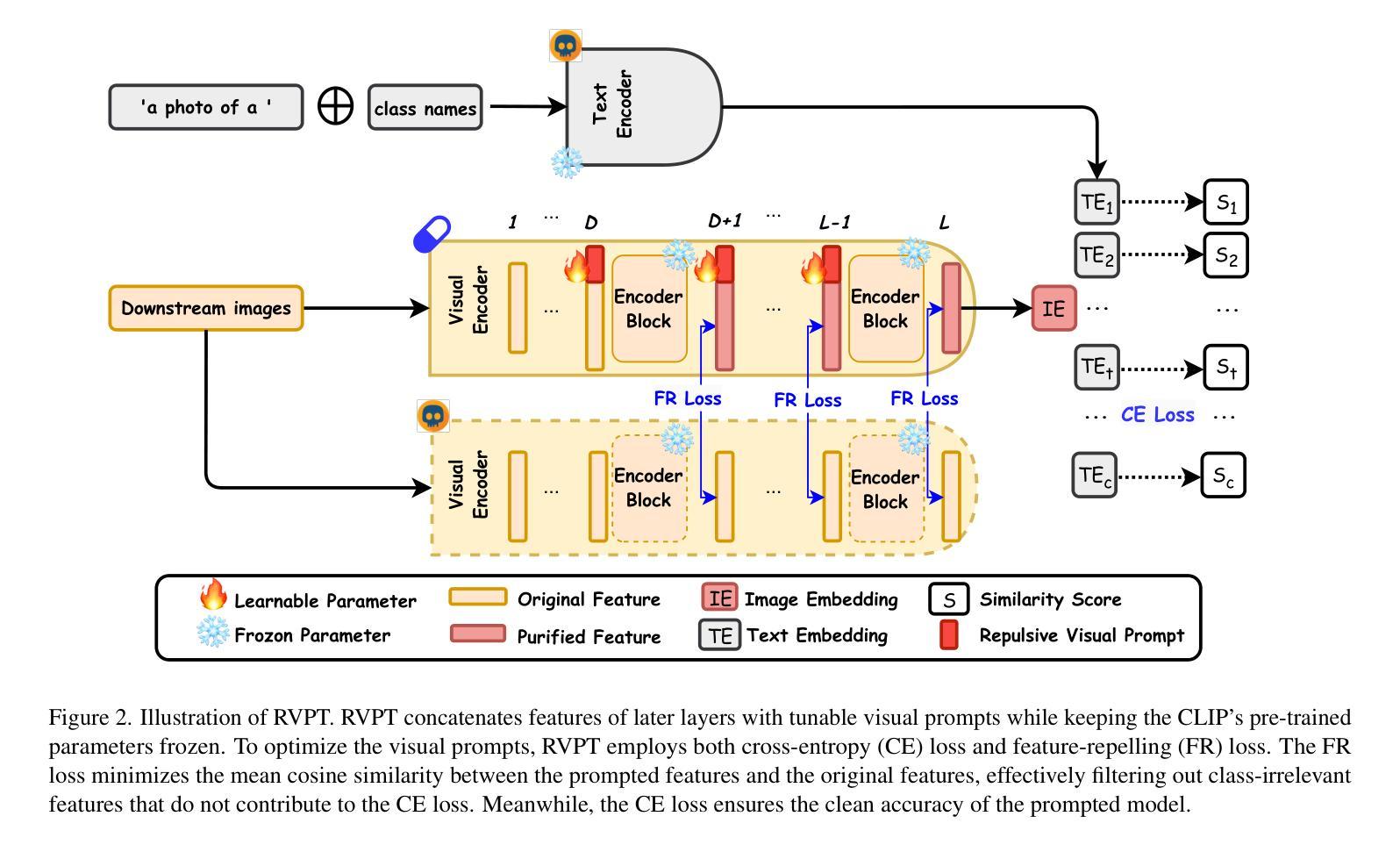
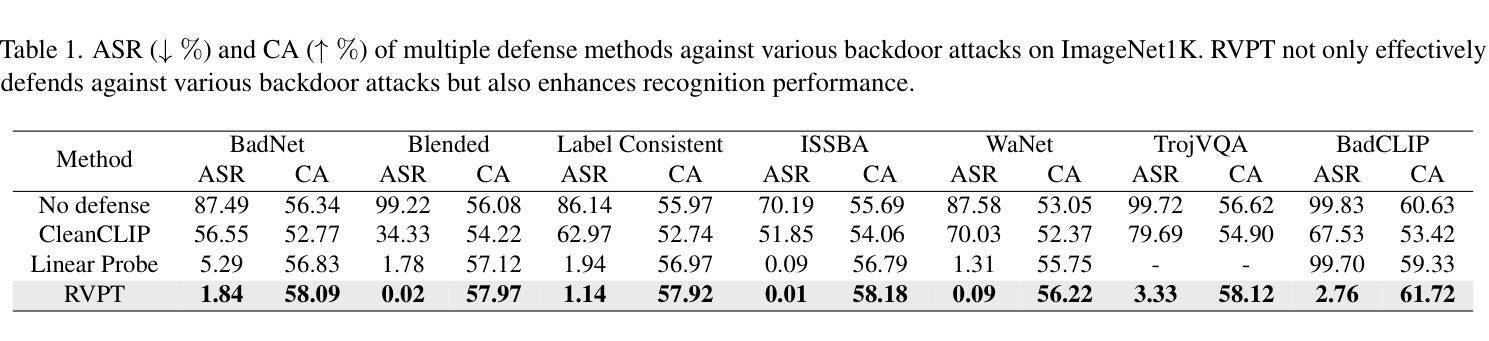
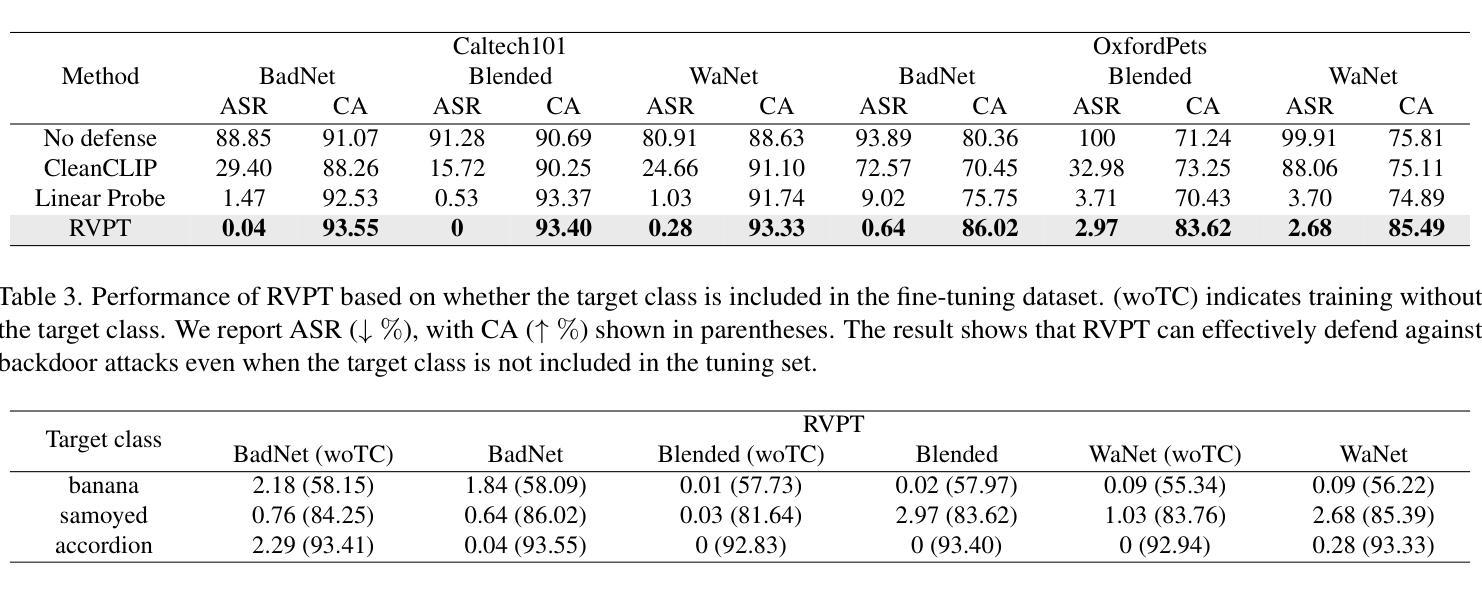
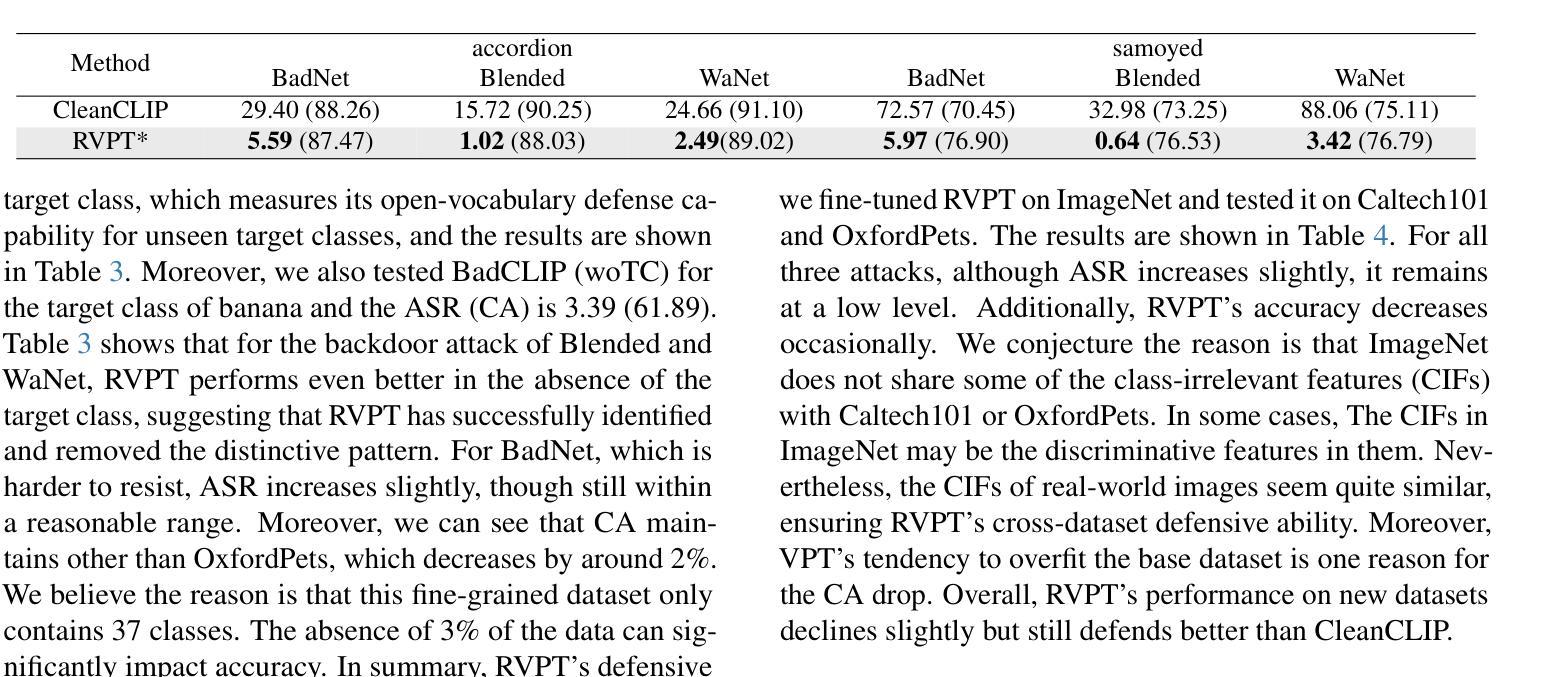
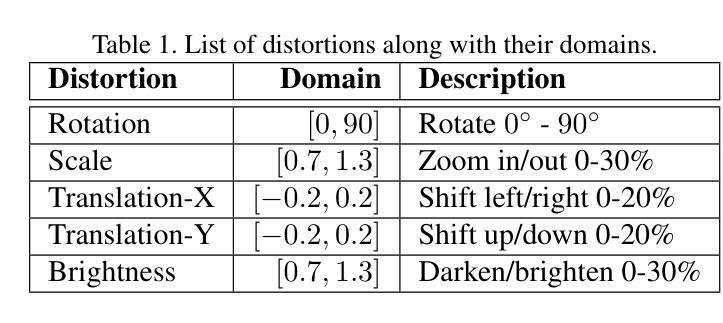
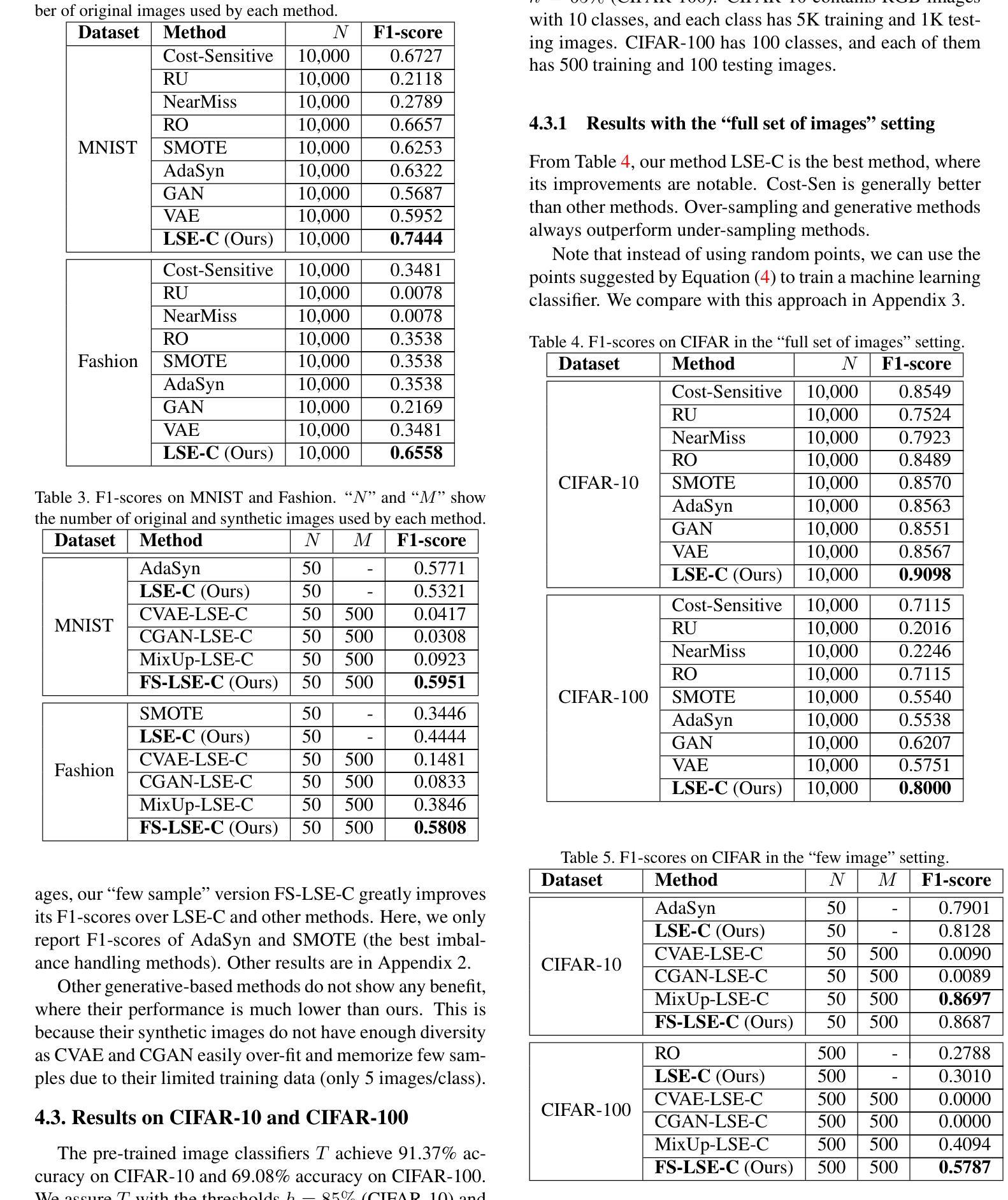
Few-shot Algorithm Assurance
Authors:Dang Nguyen, Sunil Gupta
In image classification tasks, deep learning models are vulnerable to image distortion. For successful deployment, it is important to identify distortion levels under which the model is usable i.e. its accuracy stays above a stipulated threshold. We refer to this problem as Model Assurance under Image Distortion, and formulate it as a classification task. Given a distortion level, our goal is to predict if the model’s accuracy on the set of distorted images is greater than a threshold. We propose a novel classifier based on a Level Set Estimation (LSE) algorithm, which uses the LSE’s mean and variance functions to form the classification rule. We further extend our method to a “few sample” setting where we can only acquire few real images to perform the model assurance process. Our idea is to generate extra synthetic images using a novel Conditional Variational Autoencoder model with two new loss functions. We conduct extensive experiments to show that our classification method significantly outperforms strong baselines on five benchmark image datasets.
在图像分类任务中,深度学习模型容易受到图像失真的影响。为了确保成功部署,重要的是要确定模型在何种失真水平下是可用的,即其准确性保持在规定的阈值之上。我们将这个问题称为图像失真下的模型保证,并将其制定为一个分类任务。给定失真水平,我们的目标是预测模型在失真图像集上的准确性是否高于阈值。我们提出了一种基于水平集估计(LSE)算法的新型分类器,该分类器使用LSE的均值和方差函数来形成分类规则。我们将该方法进一步扩展到“少量样本”设置,其中我们只能获取少量真实图像来执行模型保证过程。我们的想法是利用新型条件变分自动编码器模型生成额外的合成图像,该模型具有两个新的损失函数。我们进行了大量实验,结果表明我们的分类方法在五个基准图像数据集上显著优于强大的基线。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出模型在图像分类任务中对图像失真的脆弱性问题,并定义此为模型在失真图像上的准确率高于规定阈值的问题,称为模型保证下的图像失真问题。文章建议使用基于水平集估计(LSE)算法的全新分类器来解决这一问题,并通过实验证明该方法在五个基准图像数据集上的表现显著优于其他方法。当面临真实图像样本有限的情况时,通过采用新型的条件变分自动编码器模型及两个新损失函数生成额外合成图像来应对。
Key Takeaways
- 模型在图像分类任务中面临图像失真的脆弱性挑战。
- 引入模型保证下的图像失真问题,定义为模型在失真图像上的准确率高于某一阈值。
- 提出基于水平集估计(LSE)算法的新型分类器来解决此问题。
- LSE算法利用均值和方差函数形成分类规则。
- 当真实图像样本有限时,通过新型的条件变分自动编码器模型及两个新损失函数生成合成图像以应对挑战。
- 方法在五个基准图像数据集上的表现显著优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

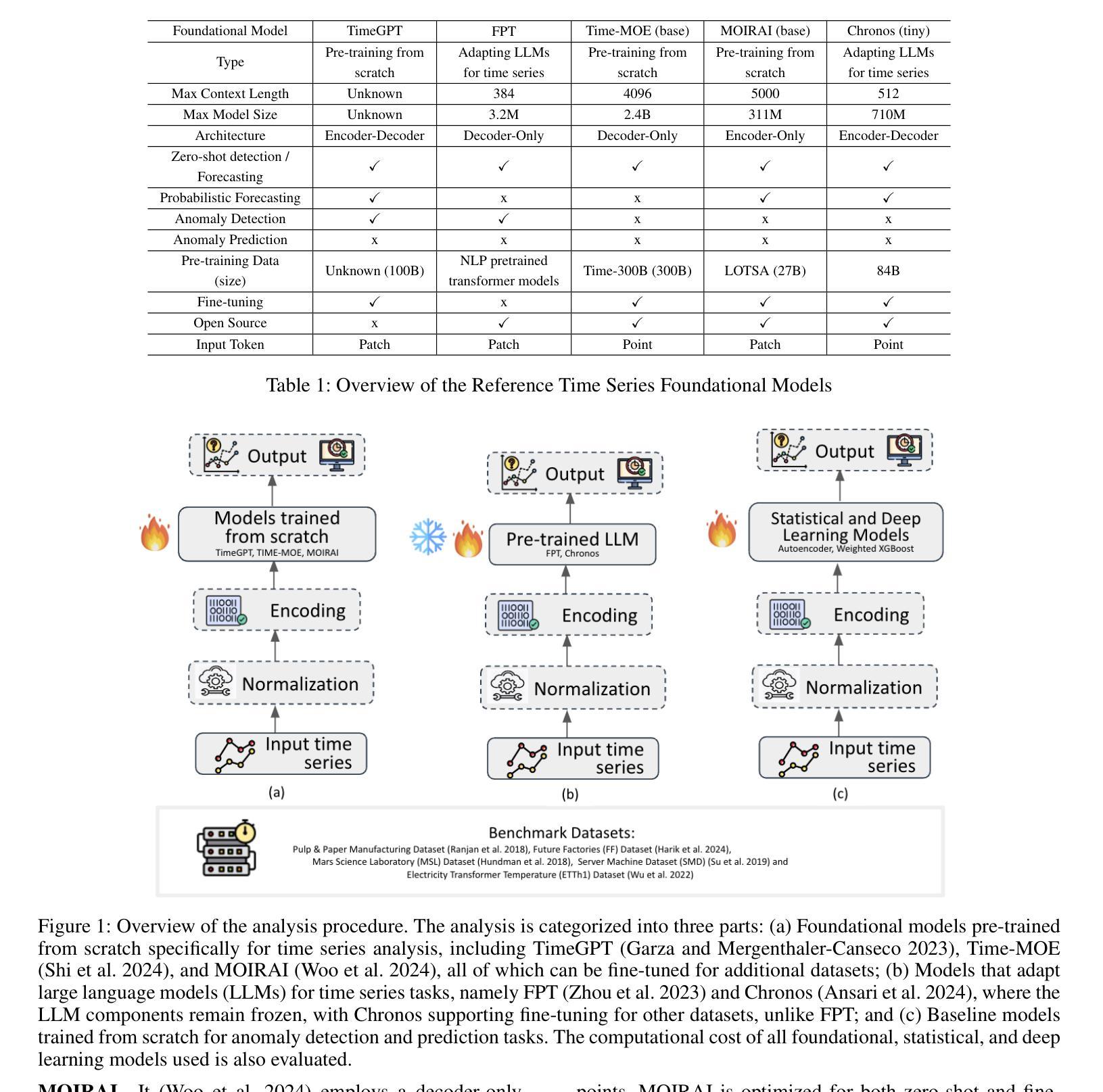
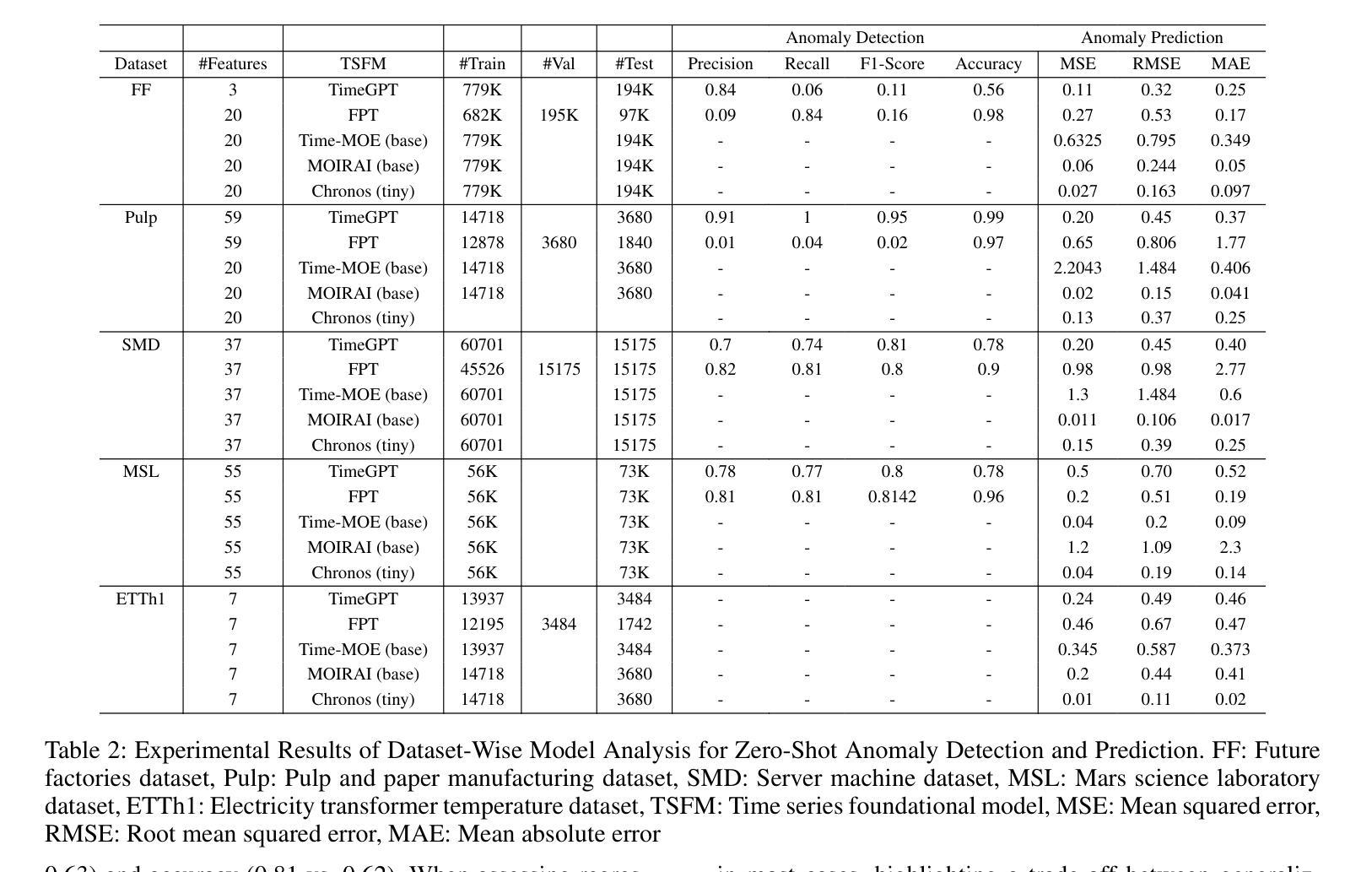
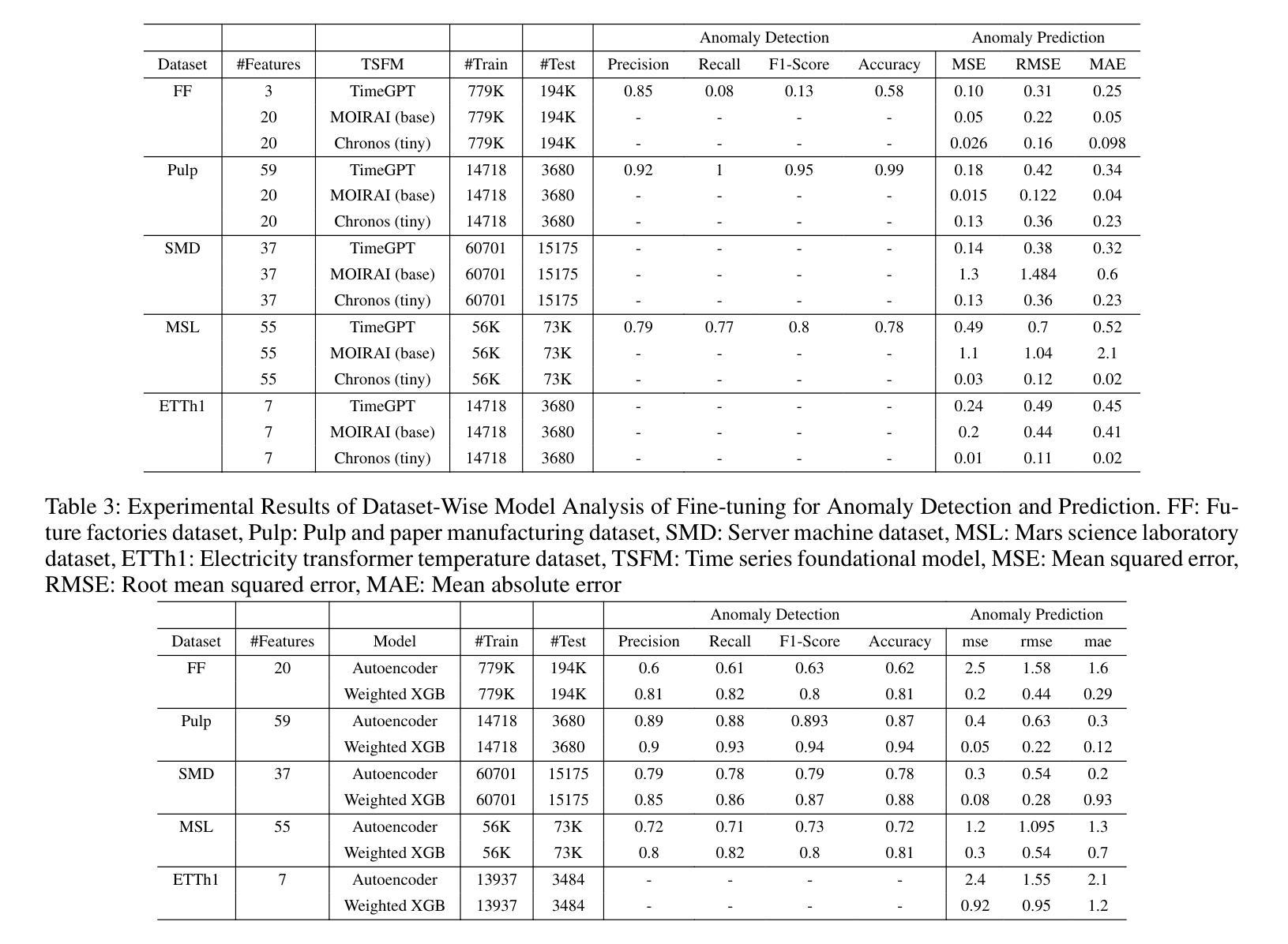
Time Series Foundational Models: Their Role in Anomaly Detection and Prediction
Authors:Chathurangi Shyalika, Harleen Kaur Bagga, Ahan Bhatt, Renjith Prasad, Alaa Al Ghazo, Amit Sheth
Time series foundational models (TSFM) have gained prominence in time series forecasting, promising state-of-the-art performance across various applications. However, their application in anomaly detection and prediction remains underexplored, with growing concerns regarding their black-box nature, lack of interpretability and applicability. This paper critically evaluates the efficacy of TSFM in anomaly detection and prediction tasks. We systematically analyze TSFM across multiple datasets, including those characterized by the absence of discernible patterns, trends and seasonality. Our analysis shows that while TSFMs can be extended for anomaly detection and prediction, traditional statistical and deep learning models often match or outperform TSFM in these tasks. Additionally, TSFMs require high computational resources but fail to capture sequential dependencies effectively or improve performance in few-shot or zero-shot scenarios. \noindent The preprocessed datasets, codes to reproduce the results and supplementary materials are available at https://github.com/smtmnfg/TSFM.
时间序列基础模型(TSFM)在时间序列预测领域已经崭露头角,并在各种应用中展现出卓越的性能。然而,其在异常检测和预测方面的应用仍然被较少探索,并且由于它们黑箱性质、缺乏可解释性和适用性的担忧日益增加。本文对TSFM在异常检测和预测任务中的有效性进行了深入评估。我们系统地分析了多个数据集上的TSFM,包括那些以缺乏可辨识的模式、趋势和季节性为特征的数据集。我们的分析表明,虽然可以将TSFM扩展到异常检测和预测任务中,但传统的统计模型和深度学习模型在这些任务中往往与TSFM相匹配或表现更好。此外,TSFM需要较高的计算资源,但在小样本或零样本场景中未能有效地捕捉序列依赖性或提高性能。预处理过的数据集、用于重现结果的代码和补充材料可通过https://github.com/smtmnfg/TSFM获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 6 figures, 5 tables. Accepted at AAAI2025 Anomaly Detection in Scientific Domains Workshop
Summary
时间序列基础模型(TSFM)在时间序列预测中受到广泛关注,但在异常检测和预测方面的应用仍然探索不足。本文对TSFM在异常检测和预测任务中的有效性进行了评估,发现虽然TSFM可以扩展到异常检测和预测任务中,但在这些任务中,传统的统计模型和深度学习模型往往与TSFM相匹配或表现更好。此外,TSFM需要较高的计算资源,但在少样本或零样本场景中无法有效捕捉序列依赖性或提高性能。
Key Takeaways
- 时间序列基础模型(TSFM)在时间序列预测领域受到广泛关注。
- TSFM在异常检测和预测方面的应用仍然探索不足。
- TSFM可以扩展到异常检测和预测任务中。
- 在异常检测和预测任务中,传统的统计模型和深度学习模型往往与TSFM相匹配或表现更好。
- TSFM需要较高的计算资源。
- 在少样本或零样本场景中,TSFM无法有效捕捉序列依赖性或提高性能。
点此查看论文截图

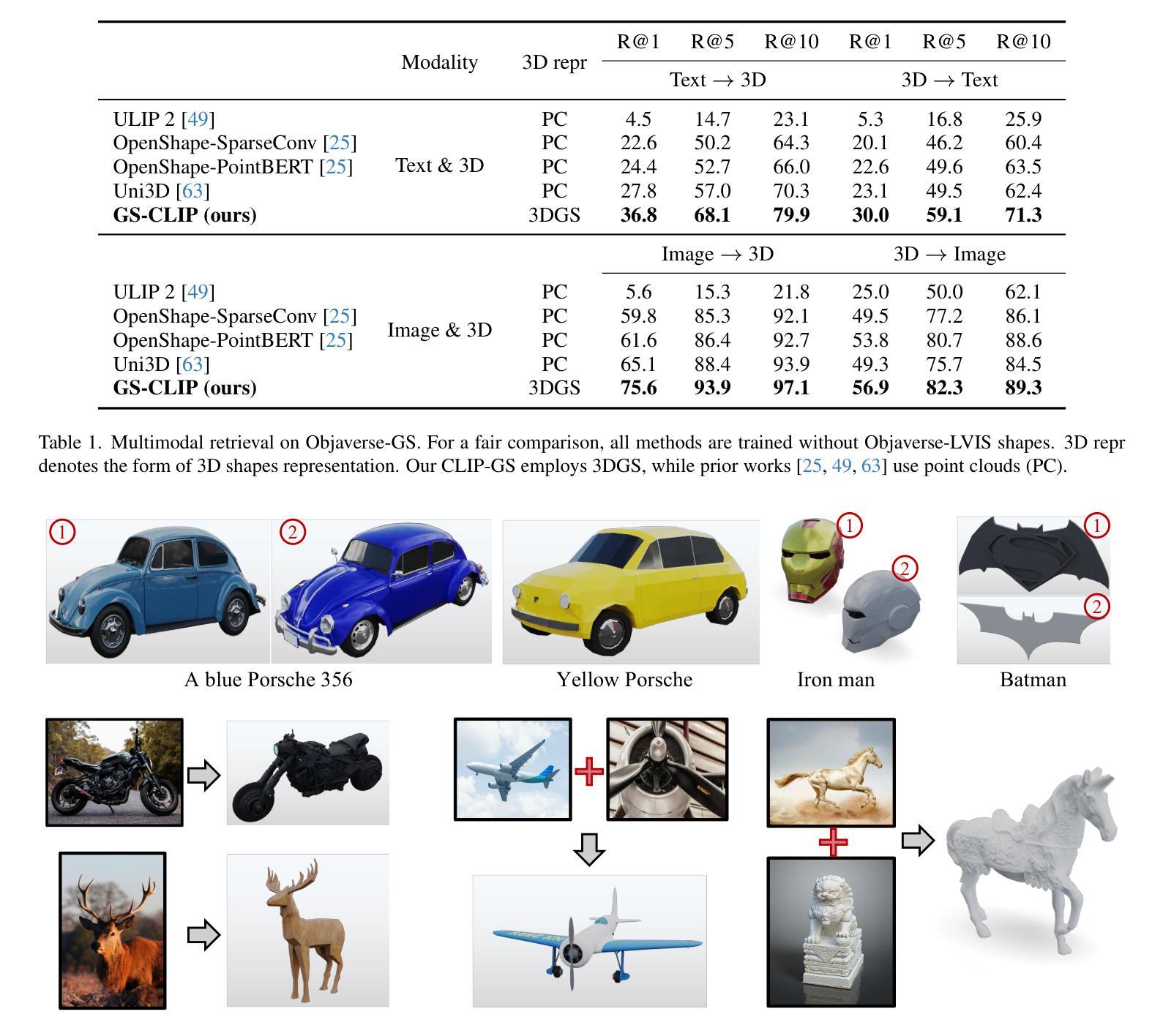
CLIP-GS: Unifying Vision-Language Representation with 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Siyu Jiao, Haoye Dong, Yuyang Yin, Zequn Jie, Yinlong Qian, Yao Zhao, Humphrey Shi, Yunchao Wei
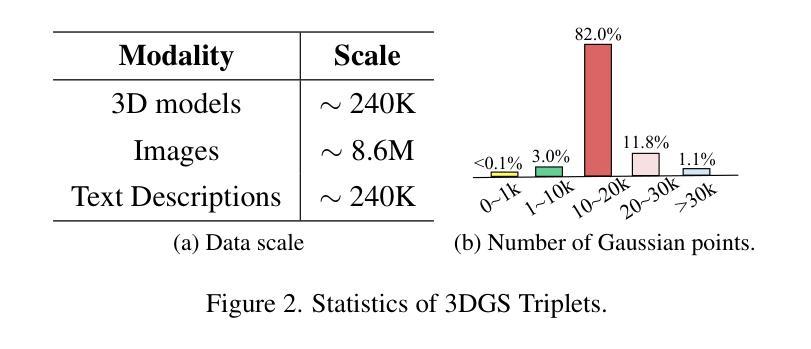
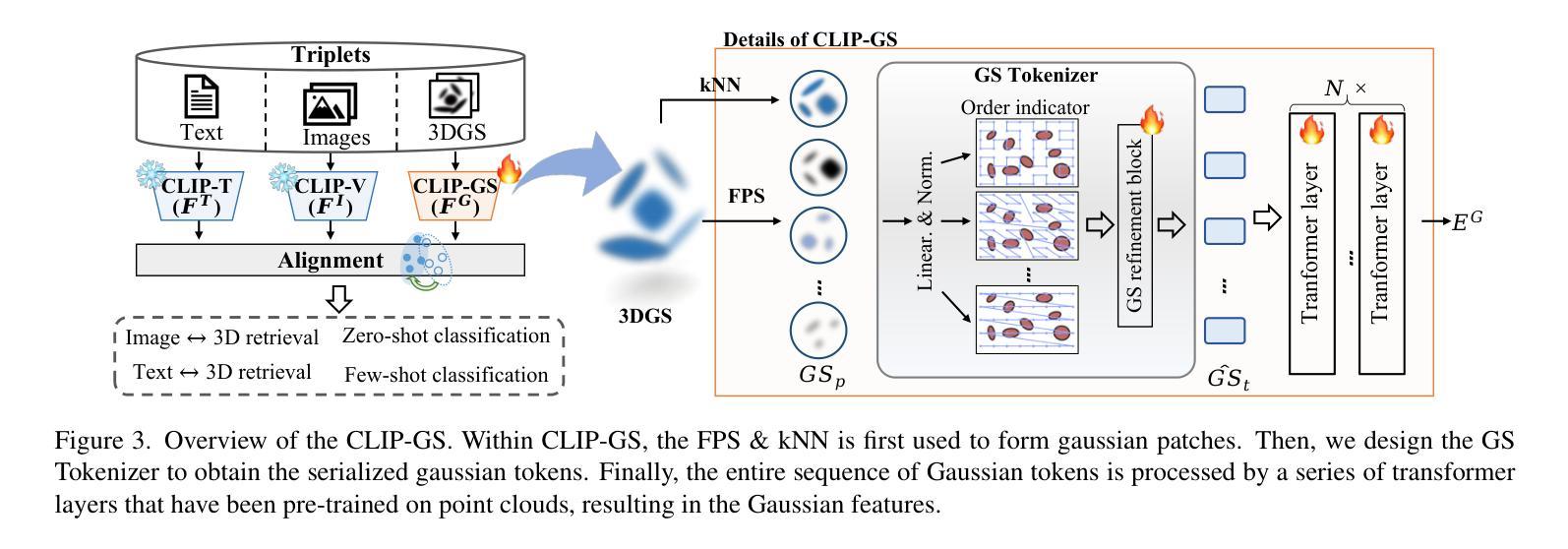
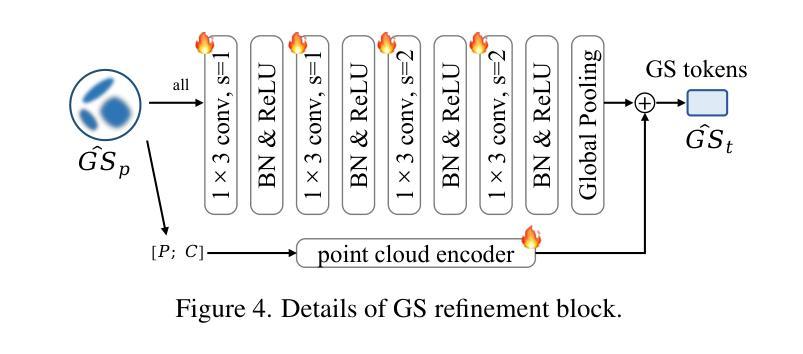
Recent works in 3D multimodal learning have made remarkable progress. However, typically 3D multimodal models are only capable of handling point clouds. Compared to the emerging 3D representation technique, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), the spatially sparse point cloud cannot depict the texture information of 3D objects, resulting in inferior reconstruction capabilities. This limitation constrains the potential of point cloud-based 3D multimodal representation learning. In this paper, we present CLIP-GS, a novel multimodal representation learning framework grounded in 3DGS. We introduce the GS Tokenizer to generate serialized gaussian tokens, which are then processed through transformer layers pre-initialized with weights from point cloud models, resulting in the 3DGS embeddings. CLIP-GS leverages contrastive loss between 3DGS and the visual-text embeddings of CLIP, and we introduce an image voting loss to guide the directionality and convergence of gradient optimization. Furthermore, we develop an efficient way to generate triplets of 3DGS, images, and text, facilitating CLIP-GS in learning unified multimodal representations. Leveraging the well-aligned multimodal representations, CLIP-GS demonstrates versatility and outperforms point cloud-based models on various 3D tasks, including multimodal retrieval, zero-shot, and few-shot classification.
近期,在三维多模态学习领域取得了显著进展。然而,典型的三维多模态模型通常只能处理点云数据。与新兴的三维表示技术相比,三维高斯展开(3DGS)在表达三维物体的纹理信息方面,稀疏的点云无法很好地描述纹理信息,导致重建能力受限。这一局限性制约了基于点云的三维多模态表示学习的潜力。在本文中,我们提出了基于三维高斯展开(CLIP-GS)的新型多模态表示学习框架。我们引入了GS分词器生成序列化高斯令牌,这些令牌经过使用点云模型的权重进行预初始化的变压器层处理,生成三维高斯嵌入。CLIP-GS利用三维高斯嵌入与CLIP的视觉文本嵌入之间的对比损失,并引入了图像投票损失来指导梯度优化的方向性和收敛性。此外,我们开发了一种有效的方法来生成三维高斯嵌入、图像和文本的三元组,促进了CLIP-GS在学习统一的多模态表示时的应用。利用对齐良好的多模态表示,CLIP-GS表现出多功能性并在多种三维任务上超越了基于点云的模型,包括多模态检索、零样本学习和小样本文本分类等。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于3DGS的多模态表示学习框架CLIP-GS的研究。针对点云在描述纹理信息方面的不足,提出了GS Tokenizer生成高斯令牌,通过预训练的点云模型与Transformer层生成3DGS嵌入。通过对比CLIP的视觉文本嵌入和图像投票损失实现优化。能够生成统一的跨模态三元组表示,有助于在多种任务上表现超越点云模型。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS技术相较于传统的点云技术能更好地描述纹理信息,提升重建能力。
- CLIP-GS是一个基于3DGS的多模态表示学习框架,旨在解决点云处理模型的问题。
- GS Tokenizer可以生成序列化高斯令牌并处理以得到更有效的3DGS嵌入。
- CLIP-GS使用对比损失和图像投票损失进行梯度优化方向指导。
- CLIP-GS能够生成跨模态的三元组表示,包括图像、文本和3DGS数据。
- CLIP-GS在多种任务上表现超越点云模型,包括多模态检索、零样本和少样本分类等。
点此查看论文截图

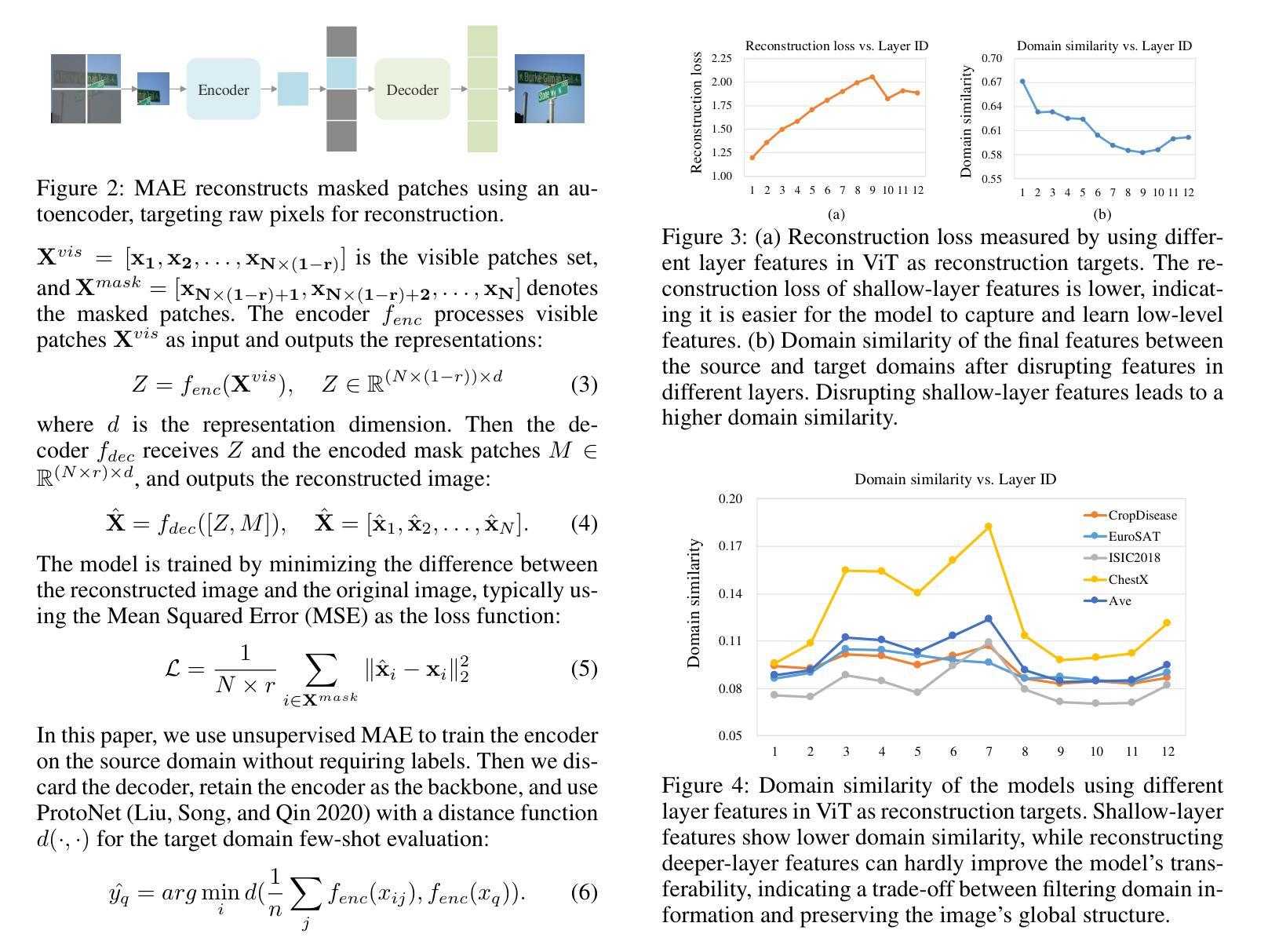
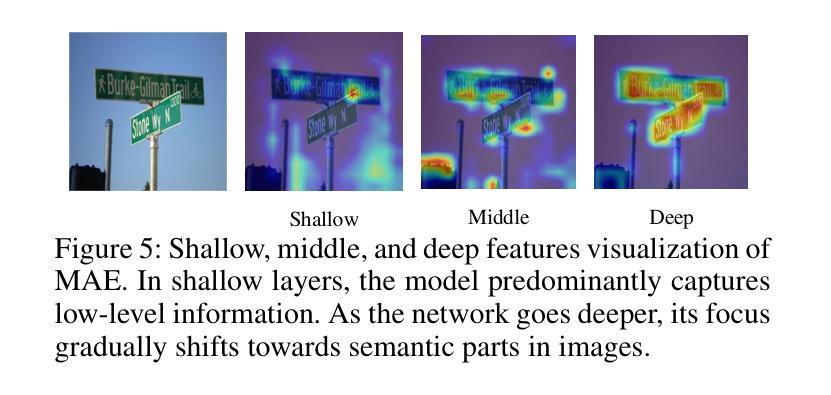
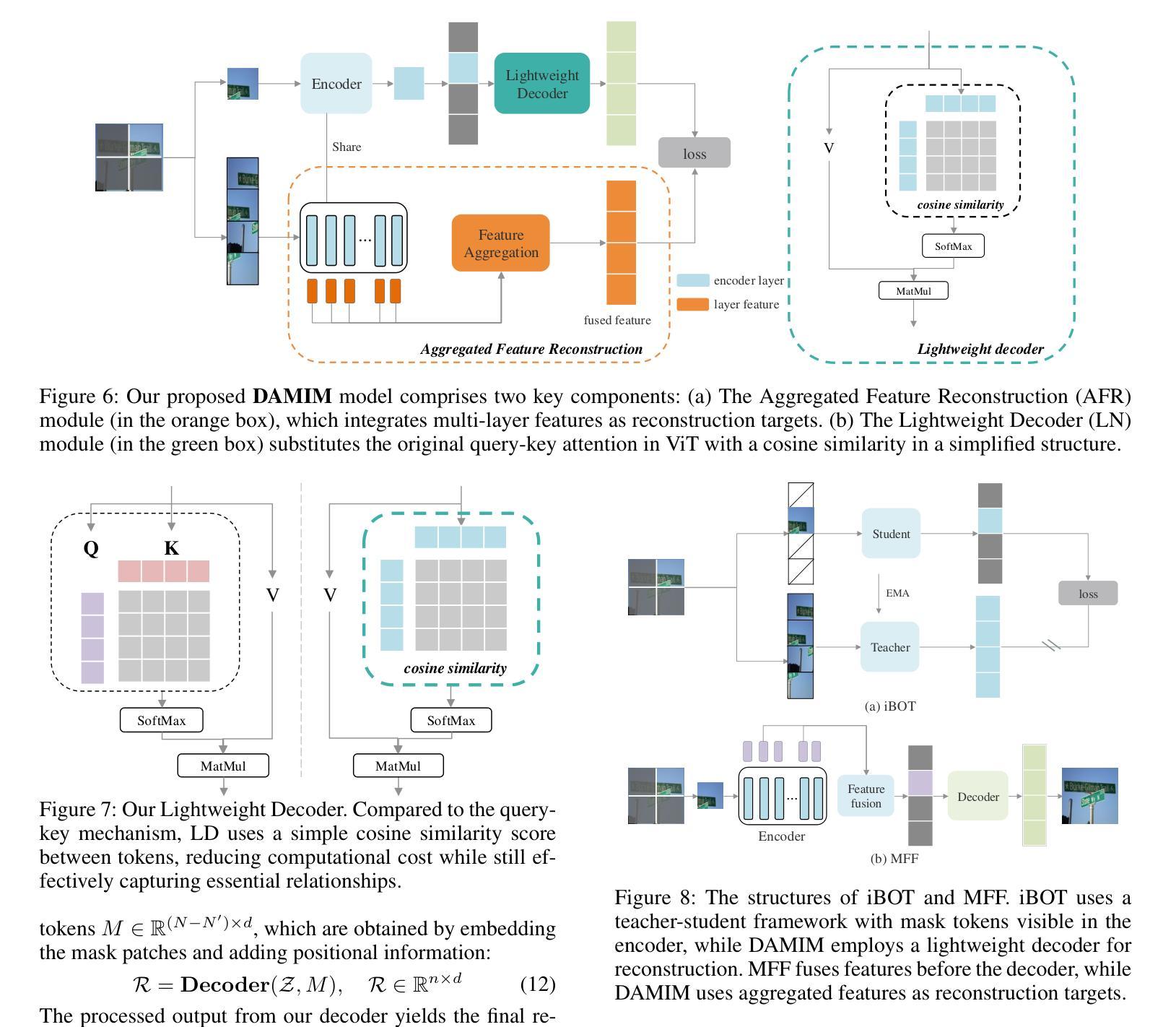
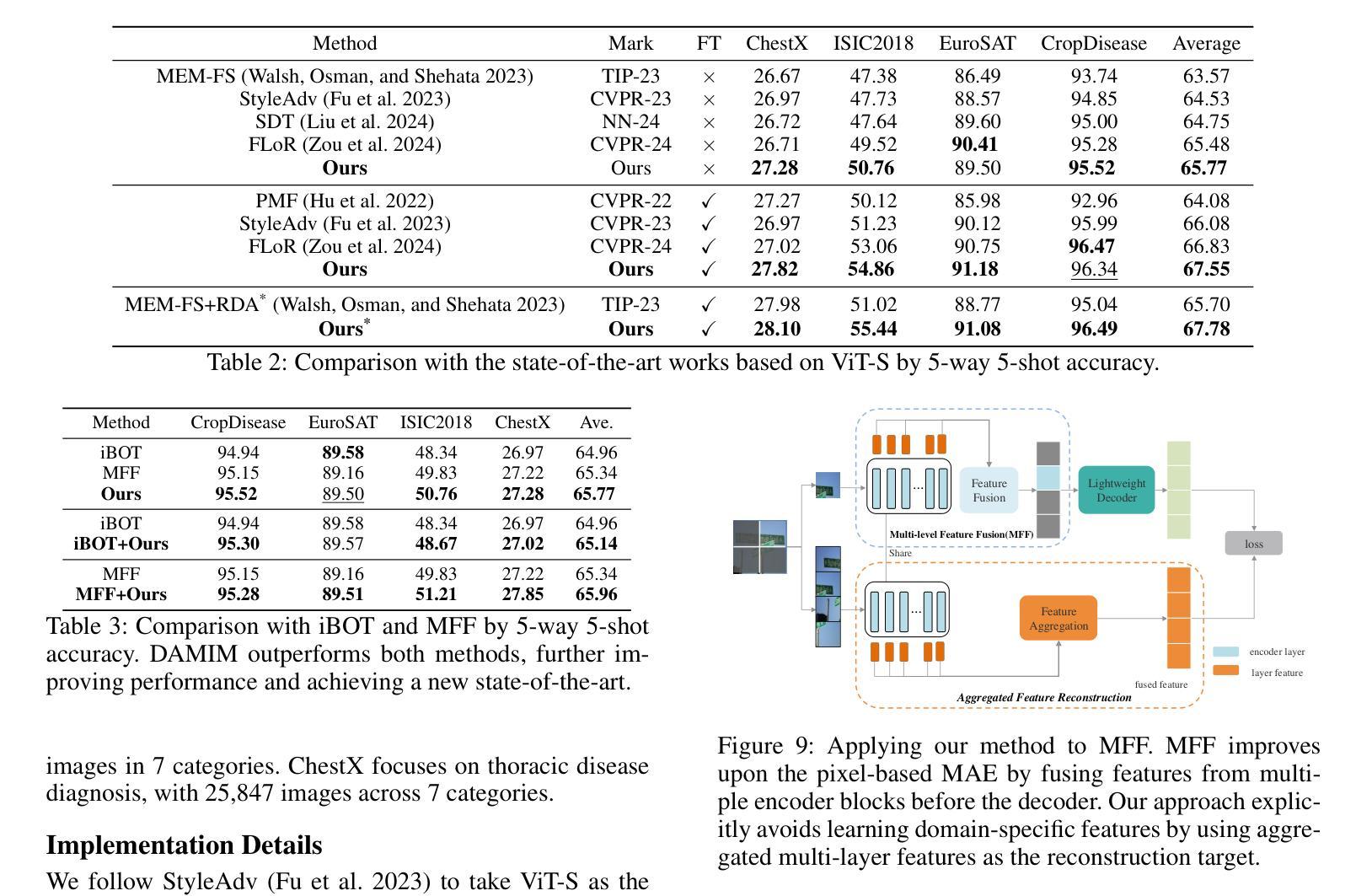
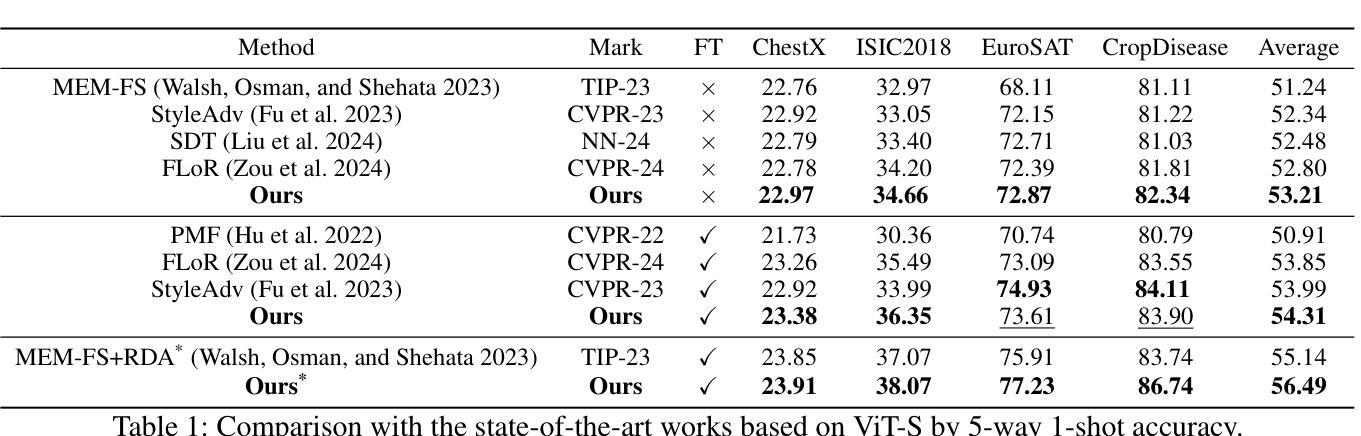
Reconstruction Target Matters in Masked Image Modeling for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Learning
Authors:Ran Ma, Yixiong Zou, Yuhua Li, Ruixuan Li
Cross-Domain Few-Shot Learning (CDFSL) requires the model to transfer knowledge from the data-abundant source domain to data-scarce target domains for fast adaptation, where the large domain gap makes CDFSL a challenging problem. Masked Autoencoder (MAE) excels in effectively using unlabeled data and learning image’s global structures, enhancing model generalization and robustness. However, in the CDFSL task with significant domain shifts, we find MAE even shows lower performance than the baseline supervised models. In this paper, we first delve into this phenomenon for an interpretation. We find that MAE tends to focus on low-level domain information during reconstructing pixels while changing the reconstruction target to token features could mitigate this problem. However, not all features are beneficial, as we then find reconstructing high-level features can hardly improve the model’s transferability, indicating a trade-off between filtering domain information and preserving the image’s global structure. In all, the reconstruction target matters for the CDFSL task. Based on the above findings and interpretations, we further propose Domain-Agnostic Masked Image Modeling (DAMIM) for the CDFSL task. DAMIM includes an Aggregated Feature Reconstruction module to automatically aggregate features for reconstruction, with balanced learning of domain-agnostic information and images’ global structure, and a Lightweight Decoder module to further benefit the encoder’s generalizability. Experiments on four CDFSL datasets demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance.
跨域小样本学习(CDFSL)要求模型从数据丰富的源域转移知识到数据稀缺的目标域,以实现快速适应,而较大的域差距使得CDFSL成为一个具有挑战性的问题。掩码自动编码器(MAE)擅长有效地使用无标签数据并学习图像的全局结构,增强了模型的通用性和稳健性。然而,在具有显著域转移特性的CDFSL任务中,我们发现MAE的性能甚至低于基线监督模型。在本文中,我们首先深入研究这一现象进行解释。我们发现MAE在重建像素时倾向于关注低级别的域信息,而将重建目标改为令牌特征可以缓解这个问题。然而,并非所有特性都是有益的,因为我们还发现重建高级特性几乎不能提高模型的迁移能力,这表明在过滤域信息和保留图像全局结构之间存在权衡。总之,重建目标对于CDFSL任务很重要。基于上述发现和解释,我们进一步为CDFSL任务提出了领域无关掩码图像建模(DAMIM)。DAMIM包括一个聚合特征重建模块,该模块可自动聚合特征进行重建,平衡领域无关信息的学习与图像全局结构的平衡学习,以及一个轻量级解码器模块,进一步促进编码器的泛化能力。在四个CDFSL数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法达到了最新技术水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了跨域小样本学习(CDFSL)中的挑战,发现Masked Autoencoder(MAE)在处理显著域转移的CDFSL任务时性能下降。通过对现象的分析,本文发现MAE在重建像素时过于关注低级域信息,而改变重建目标为令牌特征可以缓解此问题。然而,并非所有特征都有益,重建高级特征对模型可迁移性的提升有限,这显示出在过滤域信息和保留图像全局结构之间存在权衡。基于此,本文提出了面向CDFSL任务的Domain-Agnostic Masked Image Modeling(DAMIM)。DAMIM包括一个聚合特征重建模块,用于自动聚合特征进行重建,并平衡学习领域无关信息和图像全局结构的学习;还包括一个轻量级解码器模块,以进一步促进编码器的泛化能力。实验证明,该方法在四个CDFSL数据集上取得了最新性能。
Key Takeaways
- 跨域小样本学习(CDFSL)面临从数据丰富的源域转移到数据稀缺的目标域的挑战,其中显著的域差距使得任务更具挑战性。
- Masked Autoencoder(MAE)在处理CDFSL任务时性能下降,尤其是在显著域转移的情况下。
- MAE在重建像素时过于关注低级别域信息,改变重建目标至令牌特征能够缓解该问题。
- 在过滤域信息和保留图像全局结构之间存在权衡,高级特征的重建对模型可迁移性的提升有限。
- 论文提出了Domain-Agnostic Masked Image Modeling(DAMIM)方法,用于CDFSL任务。
- DAMIM包括一个聚合特征重建模块,能自动聚合特征并平衡学习领域无关信息和图像全局结构。
点此查看论文截图

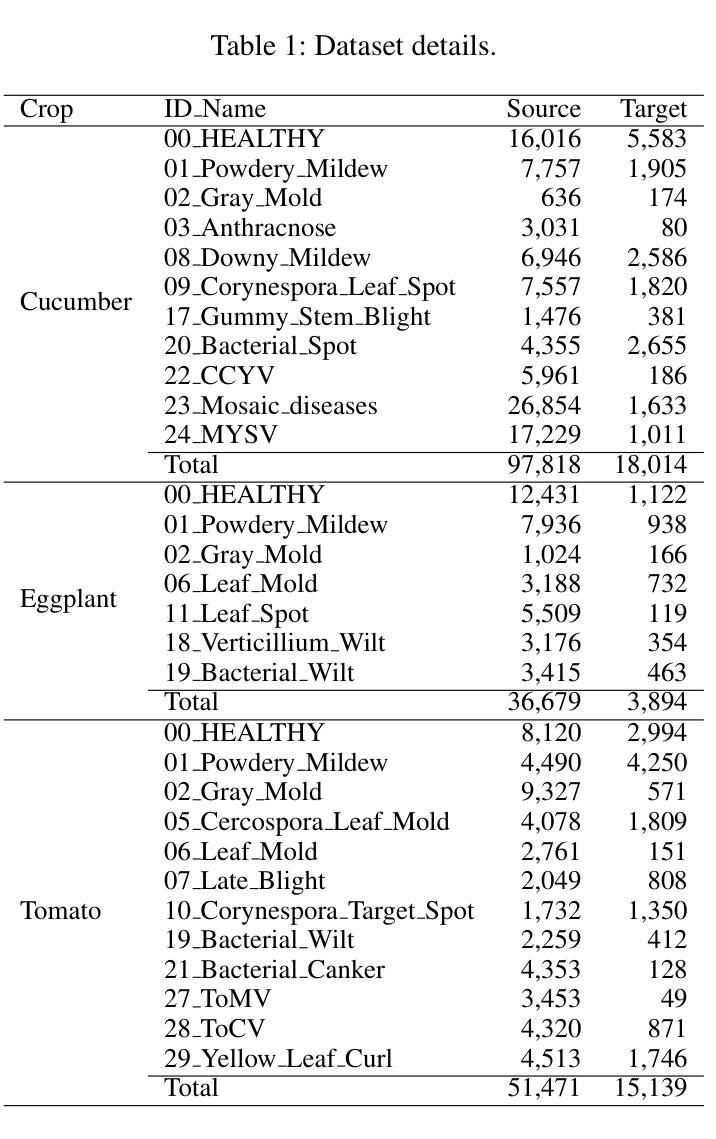
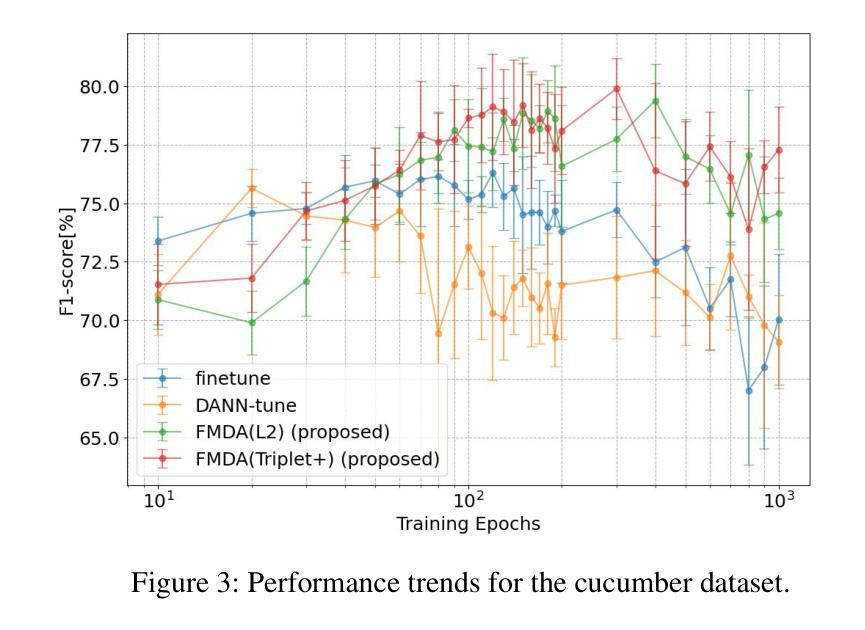
Few-shot Metric Domain Adaptation: Practical Learning Strategies for an Automated Plant Disease Diagnosis
Authors:Shoma Kudo, Satoshi Kagiwada, Hitoshi Iyatomi
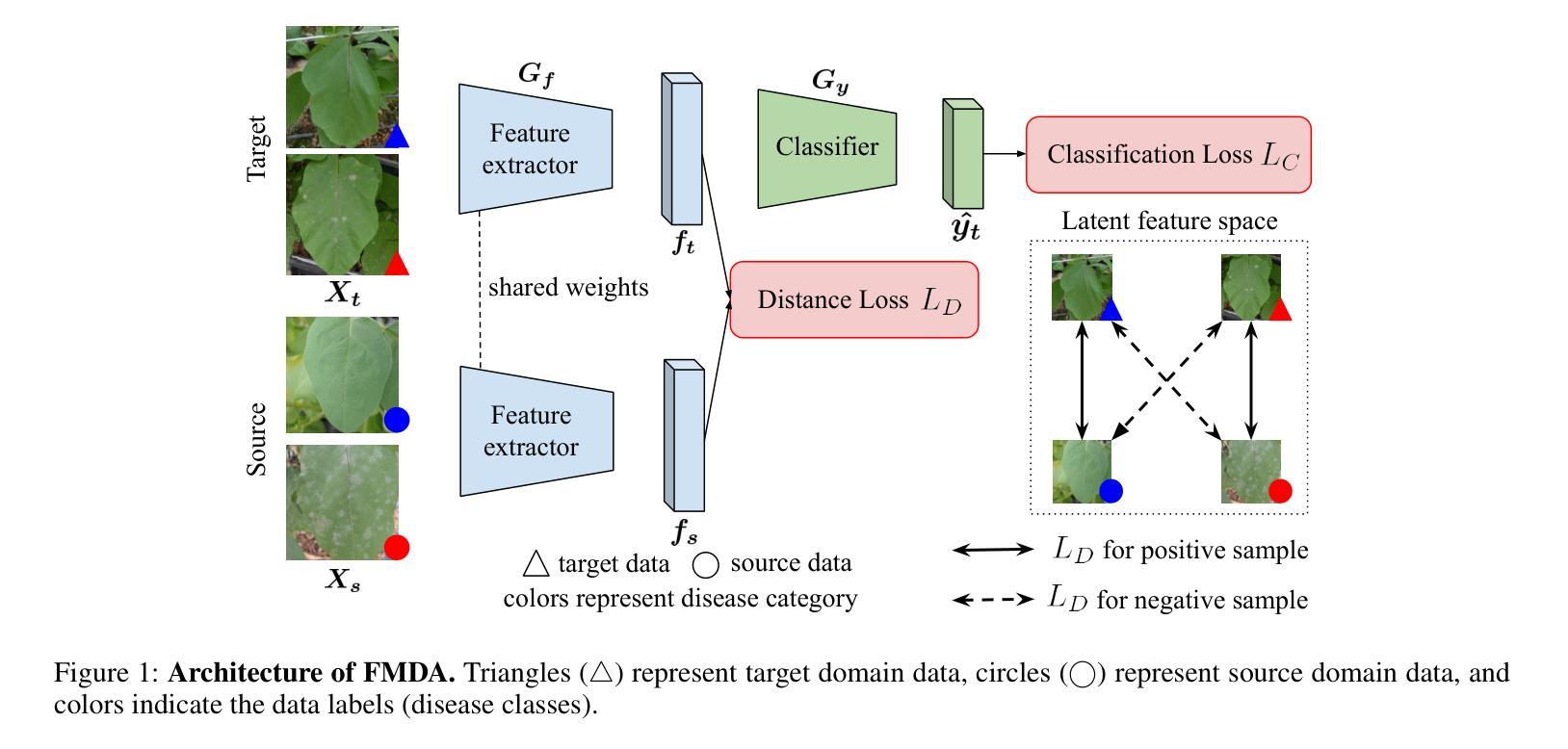
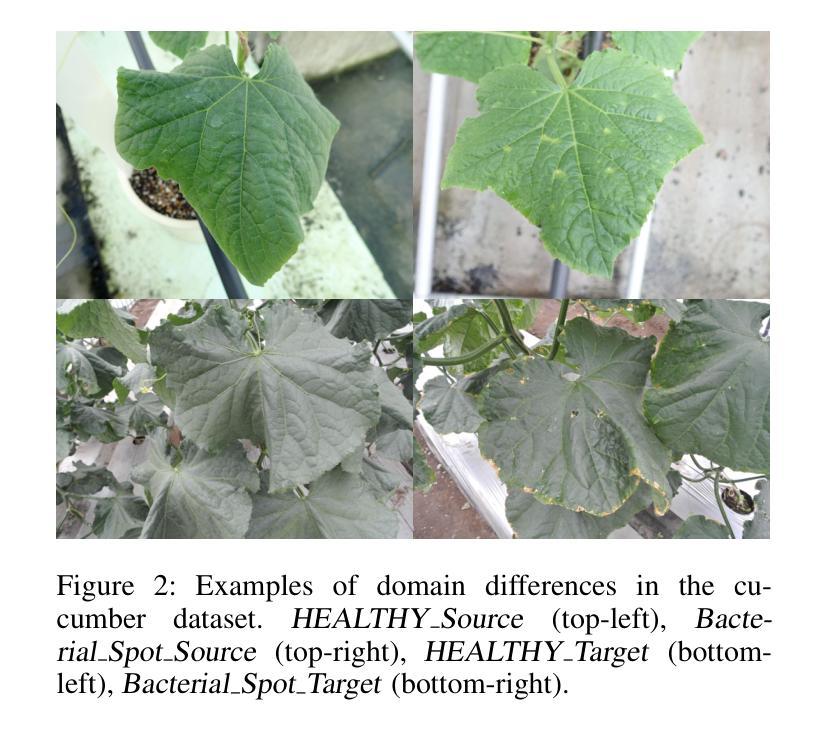
Numerous studies have explored image-based automated systems for plant disease diagnosis, demonstrating impressive diagnostic capabilities. However, recent large-scale analyses have revealed a critical limitation: that the diagnostic capability suffers significantly when validated on images captured in environments (domains) differing from those used during training. This shortfall stems from the inherently limited dataset size and the diverse manifestation of disease symptoms, combined with substantial variations in cultivation environments and imaging conditions, such as equipment and composition. These factors lead to insufficient variety in training data, ultimately constraining the system’s robustness and generalization. To address these challenges, we propose Few-shot Metric Domain Adaptation (FMDA), a flexible and effective approach for enhancing diagnostic accuracy in practical systems, even when only limited target data is available. FMDA reduces domain discrepancies by introducing a constraint to the diagnostic model that minimizes the “distance” between feature spaces of source (training) data and target data with limited samples. FMDA is computationally efficient, requiring only basic feature distance calculations and backpropagation, and can be seamlessly integrated into any machine learning (ML) pipeline. In large-scale experiments, involving 223,015 leaf images across 20 fields and 3 crop species, FMDA achieved F1 score improvements of 11.1 to 29.3 points compared to cases without target data, using only 10 images per disease from the target domain. Moreover, FMDA consistently outperformed fine-tuning methods utilizing the same data, with an average improvement of 8.5 points.
许多研究已经探讨了基于图像的植物疾病诊断自动化系统,并展示了令人印象深刻的诊断能力。然而,最近的大规模分析揭示了一个关键的局限性:当在不同于训练阶段使用的环境(领域)中捕获的图像上进行验证时,诊断能力会受到显著影响。这一缺陷源于数据集大小本身的限制、疾病症状表现的多样性,以及栽培环境、成像条件(如设备和组成)的显著差异。这些因素导致训练数据缺乏足够的多样性,最终限制系统的稳健性和泛化能力。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了 Few-shot Metric Domain Adaptation(FMDA)方法,这是一种灵活有效的方法,即使在只有有限的目标数据可用的情况下,也可以提高实际系统中的诊断准确性。FMDA 通过在诊断模型中引入一个约束来减少领域差异,该约束最小化了源(训练)数据目标数据特征空间之间的“距离”,而目标数据仅包含有限样本。FMDA 计算效率高,只需进行基本特征距离计算和反向传播,可以无缝集成到任何机器学习(ML)管道中。在大规模实验中,涉及 20 个领域和 3 个作物种类的 223,015 张叶片图像,FMDA 在仅使用目标域每疾病 10 张图像的情况下,与无目标数据的情况相比,F1 分数的改进范围为 11.1 至 29.3 点。此外,FMDA 始终优于使用相同数据的微调方法,平均提高了 8.5 点。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 4 figures, 3 tables. Accepted at 4th Annual AAAI Workshop on AI to Accelerate Science and Engineering (AI2ASE)
Summary
本文探讨了基于图像的植物疾病诊断自动化系统在环境差异下的诊断能力受限问题。为此,提出了Few-shot Metric Domain Adaptation(FMDA)方法,通过最小化源(训练)数据特征空间与目标数据特征空间的“距离”,提高诊断模型的鲁棒性和泛化能力。FMDA方法计算效率高,可无缝融入任何机器学习管道。在大型实验中,FMDA使用仅来自目标域的少量图像(每疾病仅10张)实现了相较于无目标数据情况的F1分数提高11.1至29.3点,且优于使用相同数据的微调方法,平均提高8.5点。
Key Takeaways
- 图像自动化植物疾病诊断系统在环境差异下存在诊断能力受限的问题。
- 问题的根源在于数据集大小有限、疾病症状表现多样以及栽培环境和成像条件的变化。
- 引入Few-shot Metric Domain Adaptation(FMDA)方法,通过最小化源(训练)数据特征空间与目标数据特征空间的“距离”,提高诊断模型的鲁棒性和泛化能力。
- FMDA方法计算效率高,可融入任何机器学习管道。
- 在大型实验中,FMDA在仅使用目标域的少量图像情况下,实现了显著的诊断准确性提高。
- FMDA相较于传统方法有明显优势,尤其在缺乏大量目标数据的情况下。
点此查看论文截图

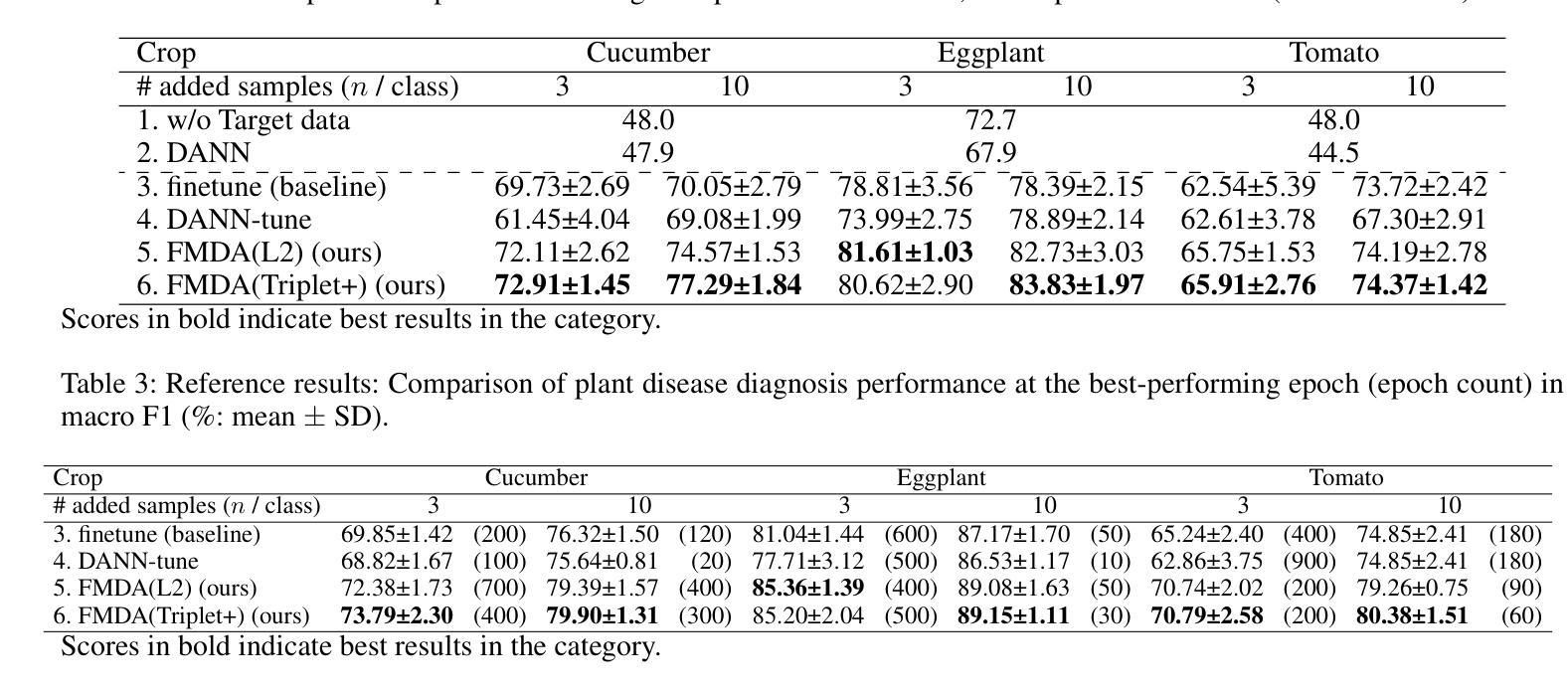
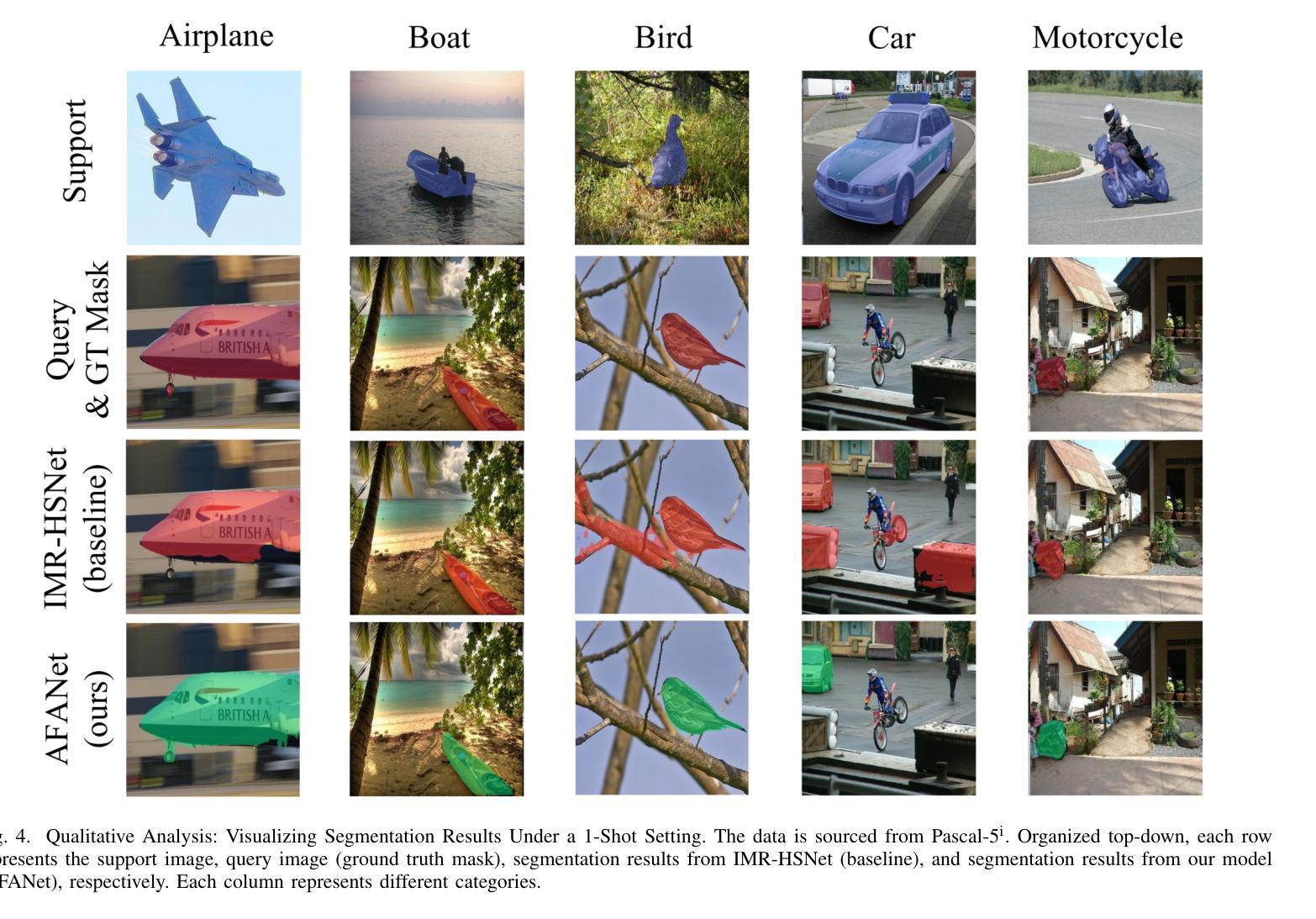
AFANet: Adaptive Frequency-Aware Network for Weakly-Supervised Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Jiaqi Ma, Guo-Sen Xie, Fang Zhao, Zechao Li
Few-shot learning aims to recognize novel concepts by leveraging prior knowledge learned from a few samples. However, for visually intensive tasks such as few-shot semantic segmentation, pixel-level annotations are time-consuming and costly. Therefore, in this paper, we utilize the more challenging image-level annotations and propose an adaptive frequency-aware network (AFANet) for weakly-supervised few-shot semantic segmentation (WFSS). Specifically, we first propose a cross-granularity frequency-aware module (CFM) that decouples RGB images into high-frequency and low-frequency distributions and further optimizes semantic structural information by realigning them. Unlike most existing WFSS methods using the textual information from the multi-modal language-vision model, e.g., CLIP, in an offline learning manner, we further propose a CLIP-guided spatial-adapter module (CSM), which performs spatial domain adaptive transformation on textual information through online learning, thus providing enriched cross-modal semantic information for CFM. Extensive experiments on the Pascal-5\textsuperscript{i} and COCO-20\textsuperscript{i} datasets demonstrate that AFANet has achieved state-of-the-art performance. The code is available at https://github.com/jarch-ma/AFANet.
少量学习旨在通过从少量样本中学习到的先验知识来识别新概念。然而,对于视觉密集型任务,如少量语义分割,像素级注释既耗时又成本高昂。因此,本文利用更具挑战性的图像级注释,并提出了一种自适应频率感知网络(AFANet)用于弱监督少量语义分割(WFSS)。具体来说,我们首先提出了跨粒度频率感知模块(CFM),它将RGB图像分解为高频和低频分布,并通过重新对齐进一步优化语义结构信息。与大多数现有WFSS方法不同,这些方法以离线学习方式使用多模态语言视觉模型的文本信息(例如CLIP),我们进一步提出了CLIP引导的空间适配器模块(CSM),该模块通过在线学习对文本信息进行空间域自适应转换,从而为CFM提供丰富的跨模态语义信息。在Pascal-5i和COCO-20i数据集上的大量实验表明,AFANet已达到最新性能水平。代码可在https://github.com/jarch-ma/AFANet找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by TMM 2024
Summary
本文提出了一种基于自适应频率感知网络(AFANet)的弱监督少样本语义分割(WFSS)方法。该方法利用图像级标注,通过跨粒度频率感知模块(CFM)解耦图像的高频和低频分布,并通过CLIP引导的空间适配器模块(CSM)进行在线学习,实现空间域自适应转换,提高了跨模态语义信息。在Pascal-5i和COCO-20i数据集上的实验表明,AFANet达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 少样本学习旨在通过从少量样本中学习到的先验知识来识别新概念。
- 针对视觉密集型任务如少样本语义分割,像素级标注是耗时且昂贵的。
- 本文使用更具挑战性的图像级标注,并提出自适应频率感知网络(AFANet)进行弱监督少样本语义分割(WFSS)。
- AFANet包括跨粒度频率感知模块(CFM),将图像解耦为高频和低频分布,并通过对齐语义结构信息来进一步优化。
- 与大多数使用多模态语言视觉模型的离线学习方式不同,本文提出了CLIP引导的空间适配器模块(CSM),通过在线学习对文本信息进行空间域自适应转换。
- 实验结果表明,AFANet在Pascal-5i和COCO-20i数据集上达到了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

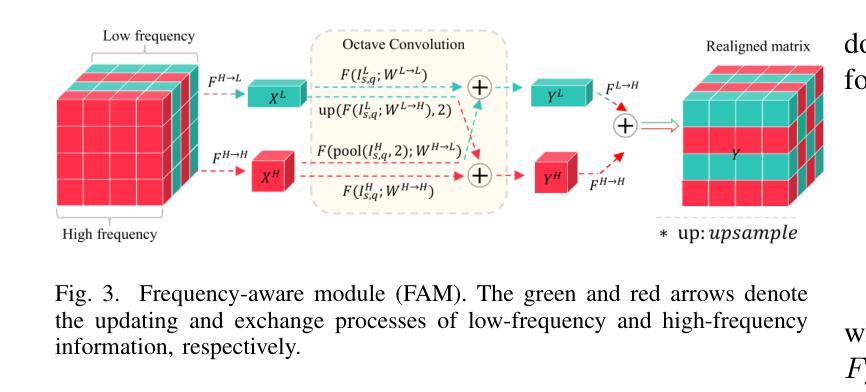
FAMNet: Frequency-aware Matching Network for Cross-domain Few-shot Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Yuntian Bo, Yazhou Zhu, Lunbo Li, Haofeng Zhang
Existing few-shot medical image segmentation (FSMIS) models fail to address a practical issue in medical imaging: the domain shift caused by different imaging techniques, which limits the applicability to current FSMIS tasks. To overcome this limitation, we focus on the cross-domain few-shot medical image segmentation (CD-FSMIS) task, aiming to develop a generalized model capable of adapting to a broader range of medical image segmentation scenarios with limited labeled data from the novel target domain. Inspired by the characteristics of frequency domain similarity across different domains, we propose a Frequency-aware Matching Network (FAMNet), which includes two key components: a Frequency-aware Matching (FAM) module and a Multi-Spectral Fusion (MSF) module. The FAM module tackles two problems during the meta-learning phase: 1) intra-domain variance caused by the inherent support-query bias, due to the different appearances of organs and lesions, and 2) inter-domain variance caused by different medical imaging techniques. Additionally, we design an MSF module to integrate the different frequency features decoupled by the FAM module, and further mitigate the impact of inter-domain variance on the model’s segmentation performance. Combining these two modules, our FAMNet surpasses existing FSMIS models and Cross-domain Few-shot Semantic Segmentation models on three cross-domain datasets, achieving state-of-the-art performance in the CD-FSMIS task.
现有的少样本医学图像分割(FSMIS)模型无法解决医学成像中的一个实际问题:由不同成像技术引起的域偏移,这限制了其在当前FSMIS任务中的应用。为了克服这一局限性,我们专注于跨域少样本医学图像分割(CD-FSMIS)任务,旨在开发一种通用模型,该模型能够在新的目标域中有限标记数据的情况下,适应更广泛的医学图像分割场景。我们受到不同领域频率域相似性特征的启发,提出了一种频率感知匹配网络(FAMNet),它包括两个关键组件:频率感知匹配(FAM)模块和多光谱融合(MSF)模块。FAM模块解决了元学习阶段的两个问题:1)由于器官和病变的不同外观引起的域内方差导致的固有支持查询偏见;以及2)由于不同的医学成像技术引起的域间方差。此外,我们设计了一个MSF模块,以整合FAM模块解耦的不同频率特征,并进一步减轻域间方差对模型分割性能的影响。结合这两个模块,我们的FAMNet在三个跨域数据集上的表现超越了现有的FSMIS模型和跨域少样本语义分割模型,在CD-FSMIS任务中达到了最新技术水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by the 39th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-25)
Summary
本文关注跨域少样本医疗图像分割(CD-FSMIS)任务,旨在开发一个通用模型,能够在有限的新目标域标记数据的情况下,适应更广泛的医疗图像分割场景。为此,提出频率感知匹配网络(FAMNet),包括频率感知匹配(FAM)和多光谱融合(MSF)两个关键组件。该网络解决了元学习阶段的域内和域间方差问题,并在三个跨域数据集上超越了现有的FSMIS模型和跨域少样本语义分割模型,在CD-FSMIS任务中取得了最新性能。
Key Takeaways
- 现有少样本医疗图像分割(FSMIS)模型面临因不同成像技术导致的域偏移问题,限制了其在现实任务中的应用。
- 提出跨域少样本医疗图像分割(CD-FSMIS)任务,旨在开发一个能适应更广泛医疗图像分割场景的通用模型,在有限的新目标域标记数据的情况下。
- 提出频率感知匹配网络(FAMNet),包含频率感知匹配(FAM)和多光谱融合(MSF)两个关键组件,以解决元学习阶段的域内和域间方差问题。
- FAM模块解决了因不同器官和病变的外观造成的域内方差以及因不同医疗成像技术造成的域间方差问题。
- MSF模块用于整合由FAM模块解耦的不同频率特征,进一步减轻域间方差对模型分割性能的影响。
- FAMNet在三个跨域数据集上超越了现有的FSMIS模型和跨域少样本语义分割模型。
点此查看论文截图

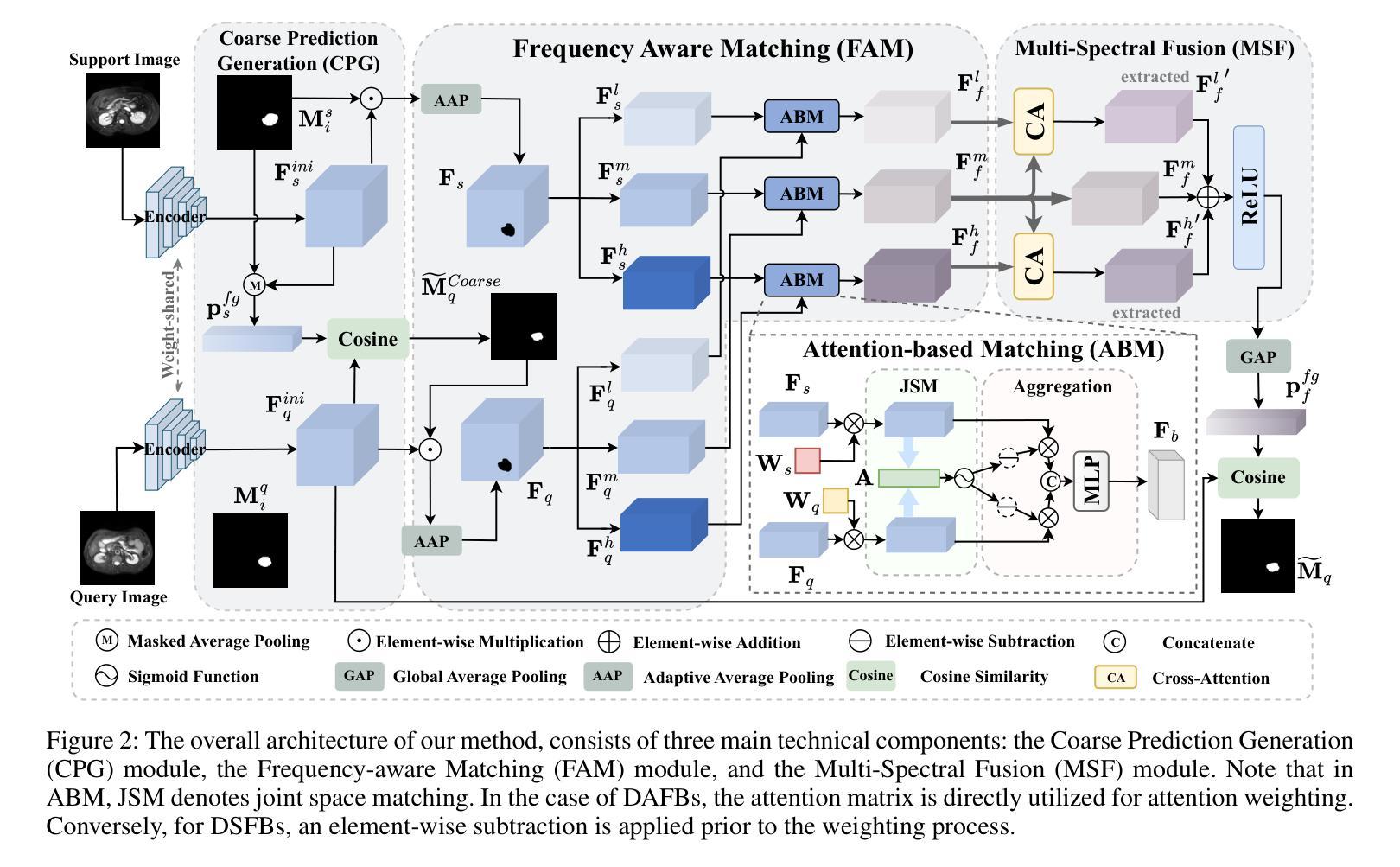
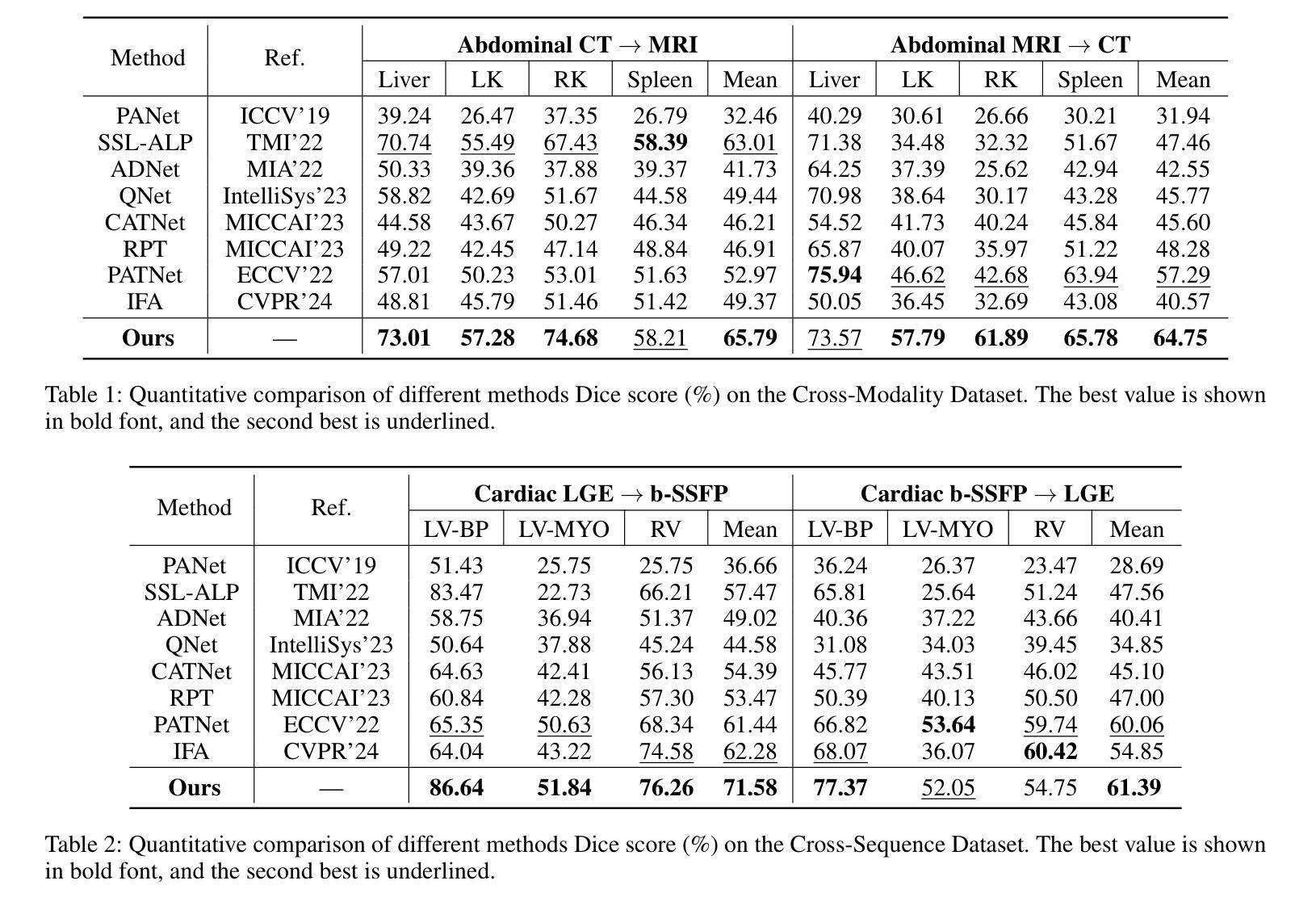
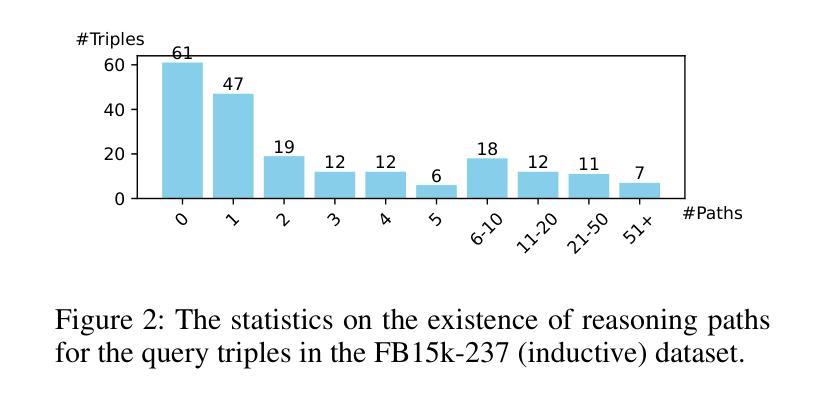
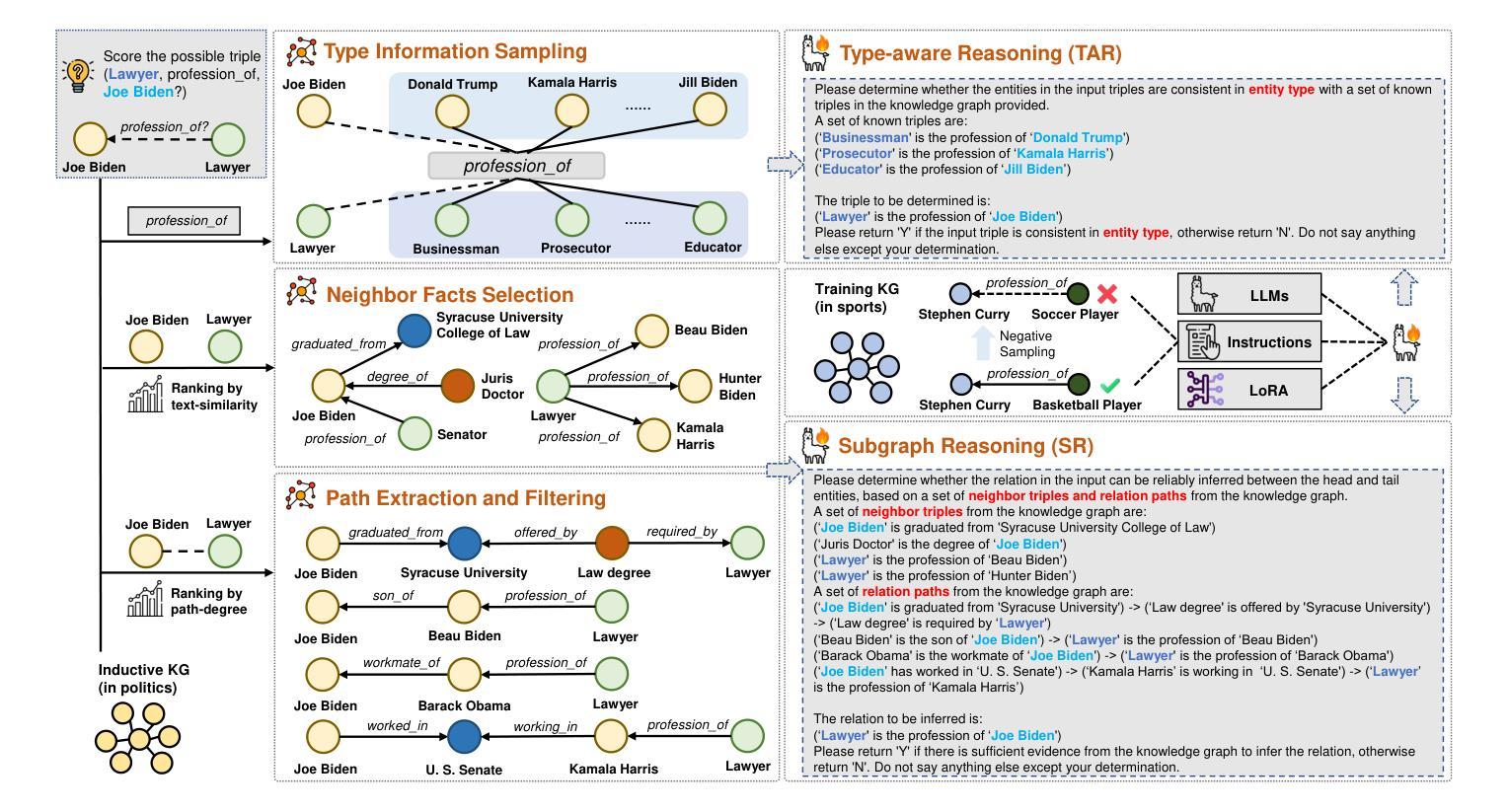
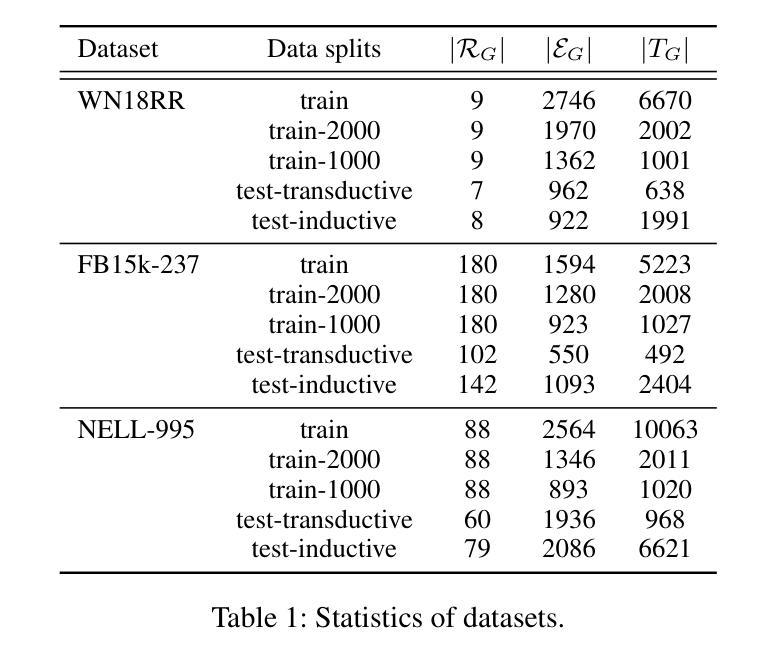
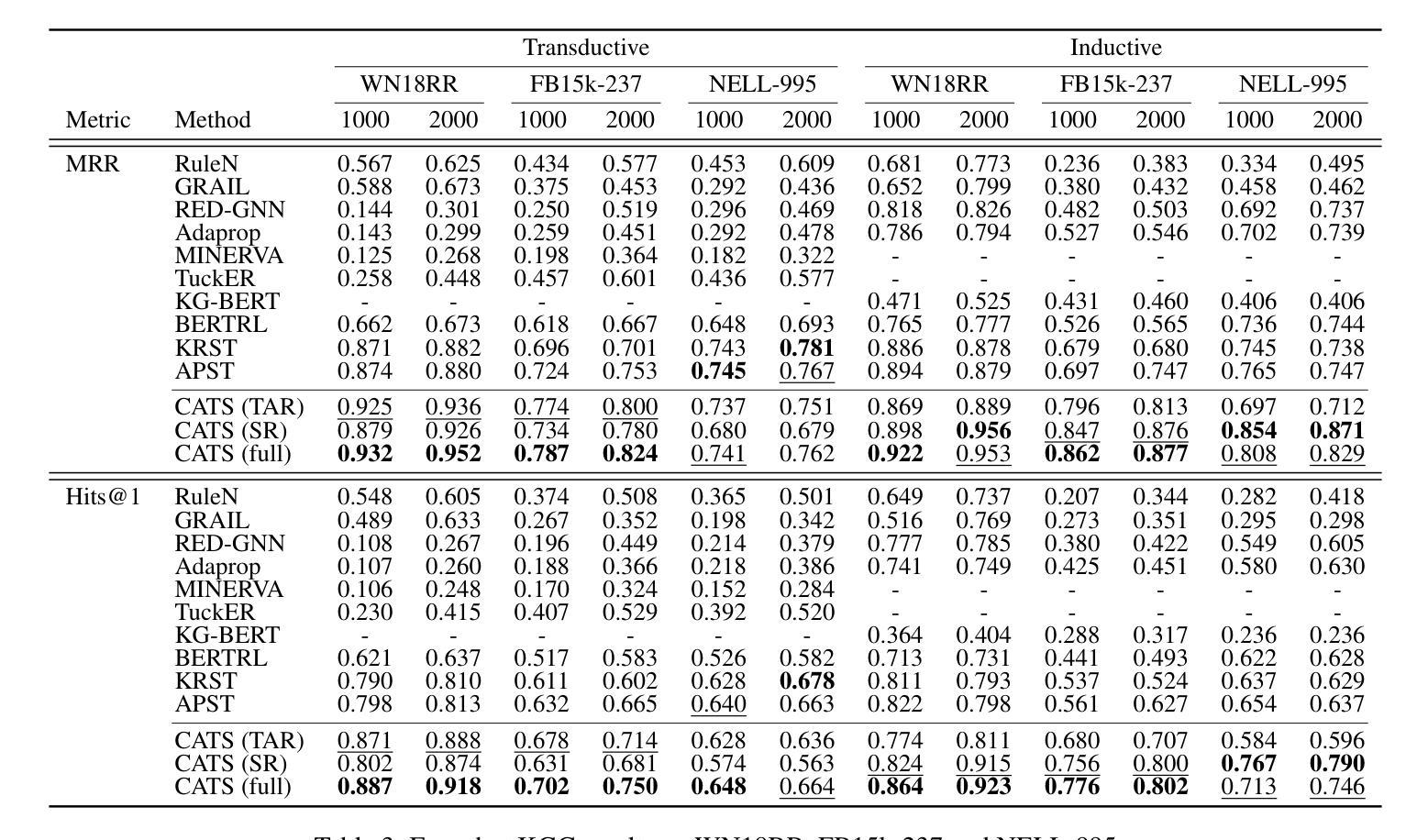
Context-aware Inductive Knowledge Graph Completion with Latent Type Constraints and Subgraph Reasoning
Authors:Muzhi Li, Cehao Yang, Chengjin Xu, Zixing Song, Xuhui Jiang, Jian Guo, Ho-fung Leung, Irwin King
Inductive knowledge graph completion (KGC) aims to predict missing triples with unseen entities. Recent works focus on modeling reasoning paths between the head and tail entity as direct supporting evidence. However, these methods depend heavily on the existence and quality of reasoning paths, which limits their general applicability in different scenarios. In addition, we observe that latent type constraints and neighboring facts inherent in KGs are also vital in inferring missing triples. To effectively utilize all useful information in KGs, we introduce CATS, a novel context-aware inductive KGC solution. With sufficient guidance from proper prompts and supervised fine-tuning, CATS activates the strong semantic understanding and reasoning capabilities of large language models to assess the existence of query triples, which consist of two modules. First, the type-aware reasoning module evaluates whether the candidate entity matches the latent entity type as required by the query relation. Then, the subgraph reasoning module selects relevant reasoning paths and neighboring facts, and evaluates their correlation to the query triple. Experiment results on three widely used datasets demonstrate that CATS significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in 16 out of 18 transductive, inductive, and few-shot settings with an average absolute MRR improvement of 7.2%.
归纳式知识图谱补全(KGC)旨在预测缺失的三元组与未见过的实体。近期的研究工作集中在将头实体和尾实体之间的推理路径建模为直接支持证据。然而,这些方法严重依赖于推理路径的存在和品质,这限制了它们在不同场景中的通用性。此外,我们观察到知识图谱中隐含的类型约束和邻近事实在推断缺失三元组中也是至关重要的。为了有效地利用知识图谱中的所有有用信息,我们引入了CATS,这是一种新型上下文感知归纳KGC解决方案。在适当的提示和经过监督精细调整的充足指导下,CATS激活了大型语言模型的强大语义理解和推理能力来评估查询三元组的存在与否,其由两个模块组成。首先,类型感知推理模块评估候选实体是否符合查询关系所需的潜在实体类型。然后,子图推理模块选择相关的推理路径和邻近事实,并评估它们与查询三元组的关联度。在三个广泛使用的数据集上的实验结果表明,CATS在18种转换、归纳和小样本设置中显著优于最先进的方法,平均绝对MRR值提高了7.2%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于归纳知识图谱补全(KGC)的目标是对缺失的三元组进行预测,尤其是针对未见过的实体。当前方法主要聚焦于对头实体和尾实体之间的推理路径进行建模,作为直接的支持证据。然而,这些方法严重依赖于推理路径的存在和质量,限制了其在不同场景中的通用性。此外,知识图谱中隐性的类型约束和邻近事实对于推断缺失三元组也是至关重要的。为了有效利用知识图谱中的所有有用信息,我们提出了CATS这一新型上下文感知归纳KGC解决方案。通过适当的提示和精细监督微调,CATS能够激发大型语言模型的强大语义理解和推理能力,以评估查询三元组的存在性。该方案包含两个模块:类型感知推理模块评估候选实体是否符合查询关系所需的潜在实体类型;子图推理模块选择相关的推理路径和邻近事实,并评估其与查询三元组的关联度。在三个广泛使用的数据集上的实验结果表明,CATS在转导性、归纳性和少样本设置的16种场景下显著优于最先进的方法,平均绝对MRR值提高了7.2%。
Key Takeaways
- 归纳知识图谱补全旨在预测缺失的三元组,尤其是涉及未见实体的情形。
- 当前方法主要依赖推理路径进行建模,限制了其在不同场景中的通用性。
- 隐性类型约束和邻近事实在知识图谱中同样重要,对于推断缺失三元组至关重要。
- CATS是一种新型上下文感知归纳KGC解决方案,旨在有效利用知识图谱中的所有信息。
- CATS包含两个模块:类型感知推理模块和子图推理模块。
- CATS通过适当的提示和精细监督微调,利用大型语言模型的语义理解和推理能力。
点此查看论文截图

Federated Learning with MMD-based Early Stopping for Adaptive GNSS Interference Classification
Authors:Nishant S. Gaikwad, Lucas Heublein, Nisha L. Raichur, Tobias Feigl, Christopher Mutschler, Felix Ott
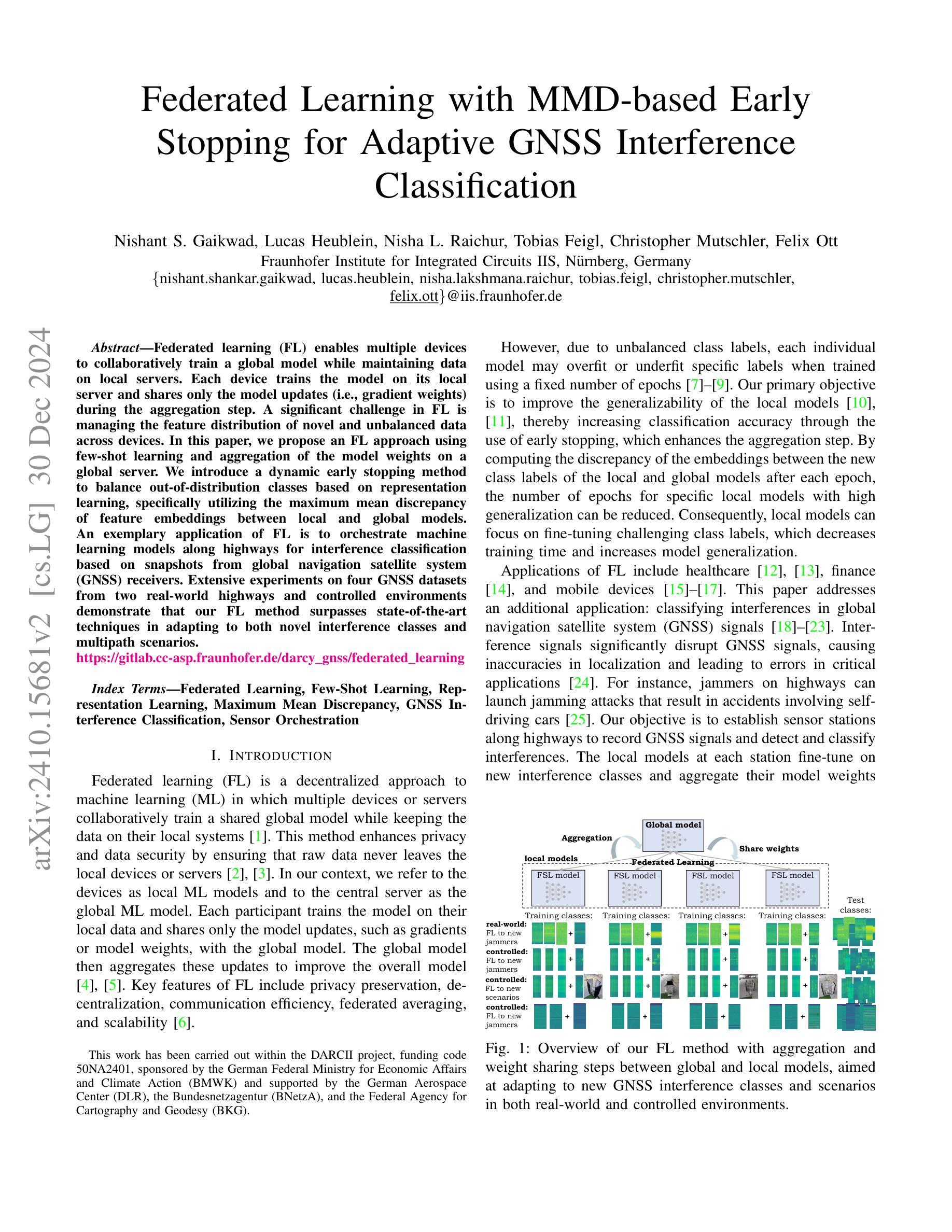
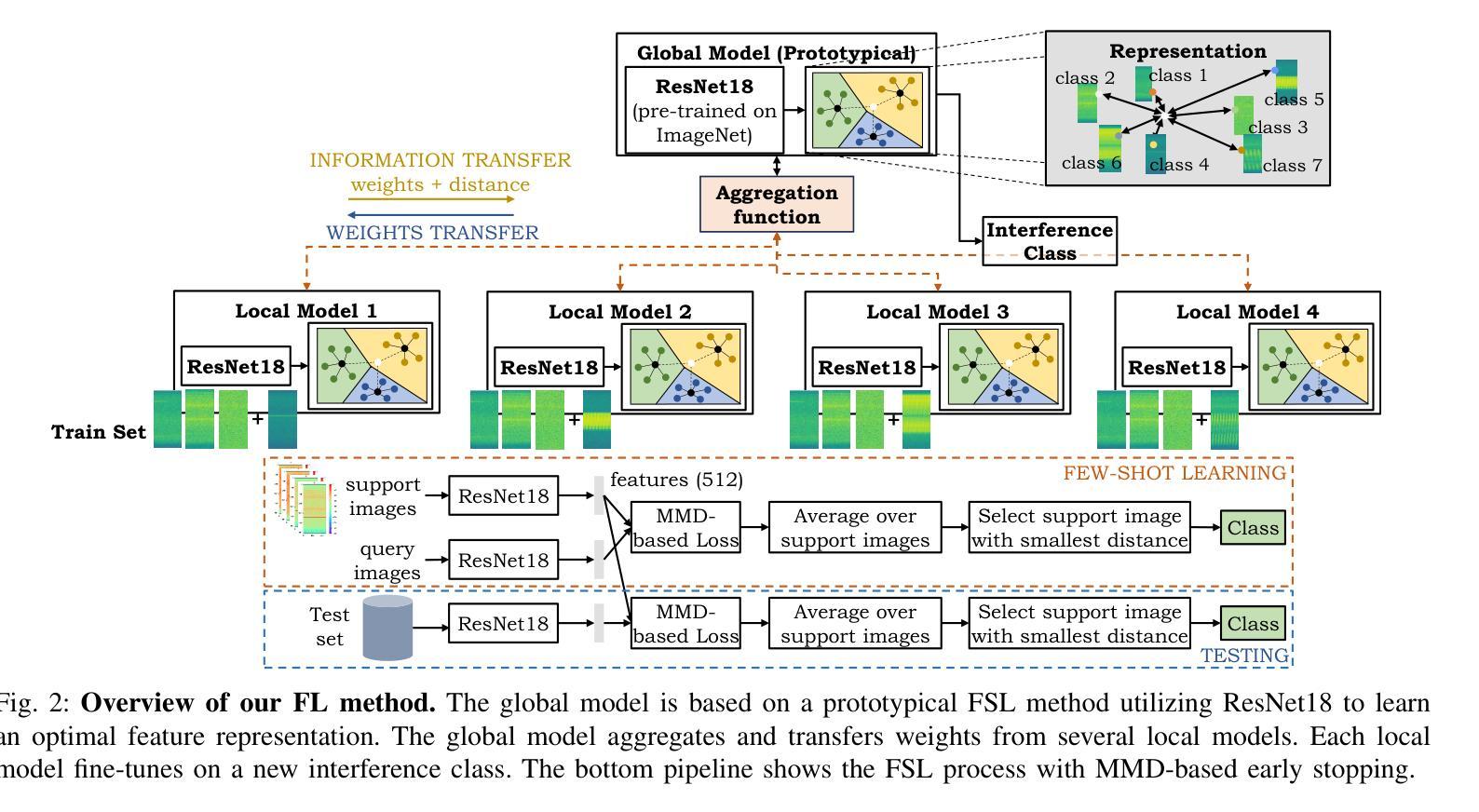
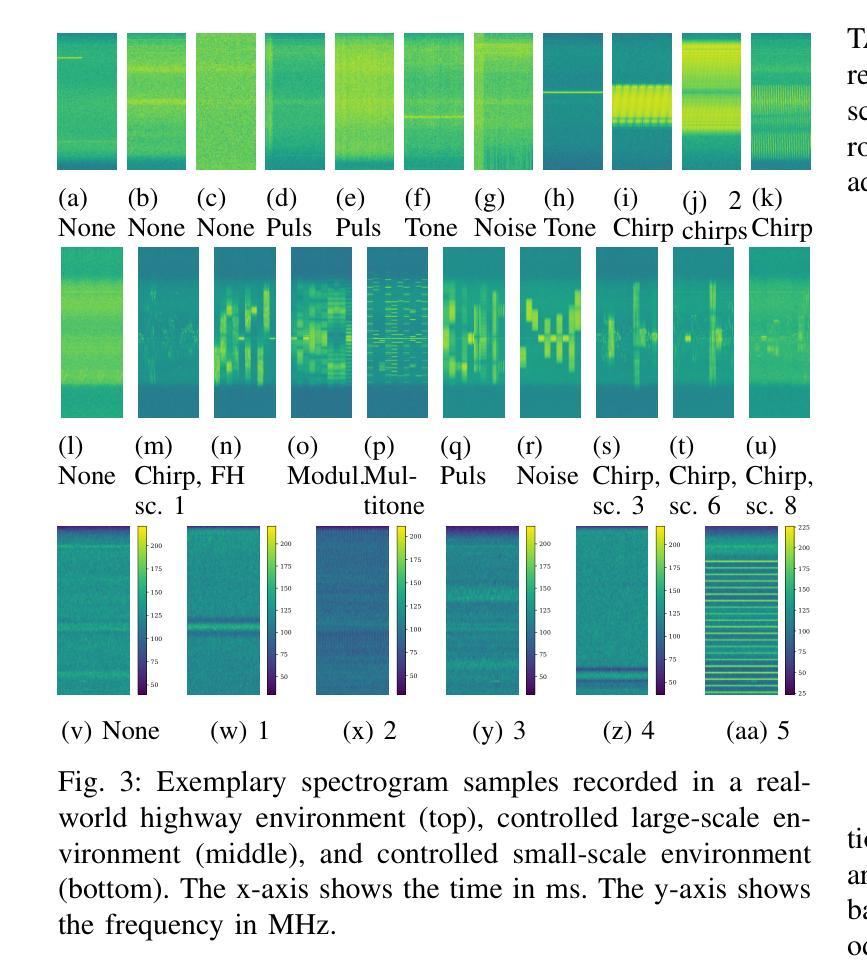
Federated learning (FL) enables multiple devices to collaboratively train a global model while maintaining data on local servers. Each device trains the model on its local server and shares only the model updates (i.e., gradient weights) during the aggregation step. A significant challenge in FL is managing the feature distribution of novel and unbalanced data across devices. In this paper, we propose an FL approach using few-shot learning and aggregation of the model weights on a global server. We introduce a dynamic early stopping method to balance out-of-distribution classes based on representation learning, specifically utilizing the maximum mean discrepancy of feature embeddings between local and global models. An exemplary application of FL is to orchestrate machine learning models along highways for interference classification based on snapshots from global navigation satellite system (GNSS) receivers. Extensive experiments on four GNSS datasets from two real-world highways and controlled environments demonstrate that our FL method surpasses state-of-the-art techniques in adapting to both novel interference classes and multipath scenarios.
联邦学习(FL)允许多个设备协同训练全局模型,同时保持数据存储在本地服务器上。每个设备都在其本地服务器上训练模型,仅在聚合步骤中共享模型更新(即梯度权重)。联邦学习面临的一个主要挑战是管理跨设备的新颖且不平衡数据的特征分布。在本文中,我们提出了一种使用少量样本学习和全局服务器上的模型权重聚合的联邦学习方法。我们引入了一种动态早期停止方法来平衡超出分布类别的表示学习,特别是通过利用本地和全局模型之间的特征嵌入的最大平均差异值来实现这一点。联邦学习的一个典型应用是在高速公路上协同组织机器学习模型,基于全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)接收器的快照进行干扰分类。在两条实际高速公路和控制环境中的四个GNSS数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的联邦学习方法在适应新颖干扰类别和多路径场景方面超越了最先进的技术手段。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Git repository: https://gitlab.cc-asp.fraunhofer.de/darcy_gnss/federated_learning
Summary
联邦学习(FL)允许多个设备在本地服务器上协作训练全局模型的同时保持本地数据的安全。模型在本地服务器上训练,仅在聚合阶段共享模型更新(即梯度权重)。在FL中,管理新型和不平衡数据在设备间的特征分布是一大挑战。本文提出了一种基于联邦学习和少样本学习的模型权重聚合方法,引入了一种动态早期停止方法以平衡异常类特征分布。具体采用代表学习,基于局部和全局模型特征嵌入的最大均值差异来区分。此外,以全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)接收机的高速公路干扰分类为例展示了联邦学习的应用。实验证明,该联邦学习方法在适应新型干扰类和多径场景方面优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 联邦学习允许设备在本地训练模型并共享模型更新,以保护本地数据的安全。
- 管理新型和不平衡数据在设备间的特征分布是联邦学习的一个关键挑战。
- 提出了一种基于联邦学习和少样本学习的模型权重聚合方法。
- 动态早期停止方法被用来平衡异常类特征分布。该方法通过基于代表学习的最大均值差异来区分局部和全局模型的特征嵌入。
- 全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)接收机的干扰分类是联邦学习的一个典型应用示例。
点此查看论文截图

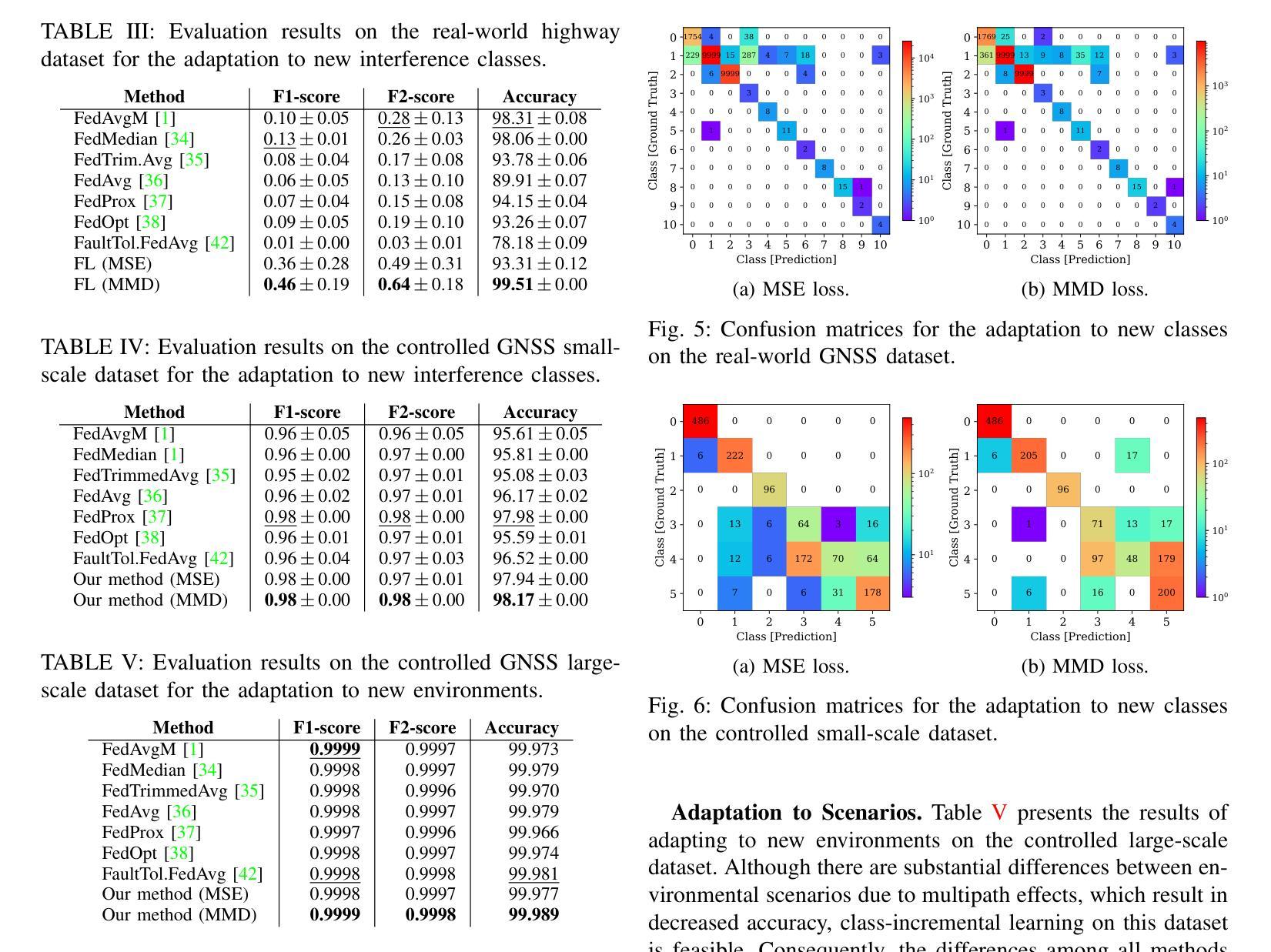
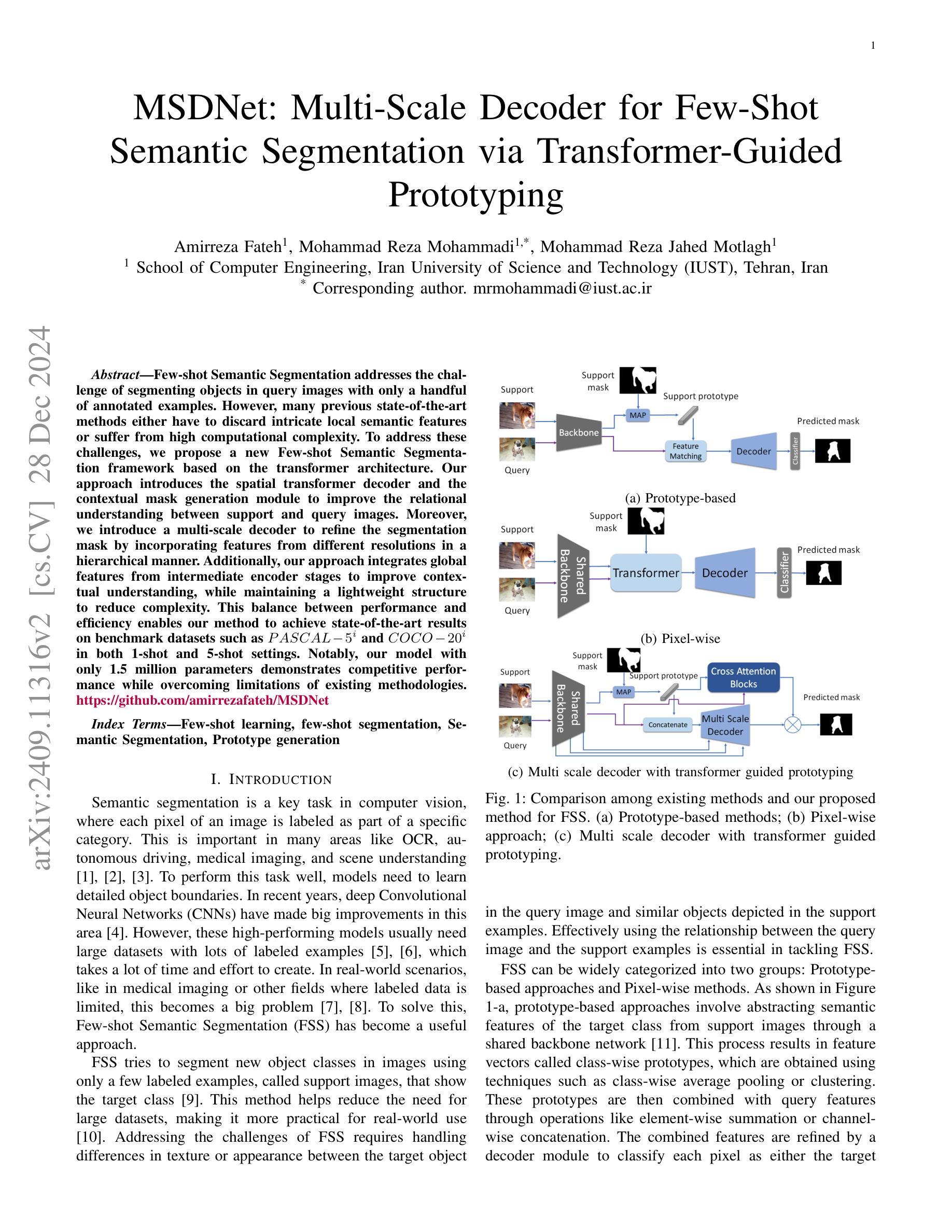
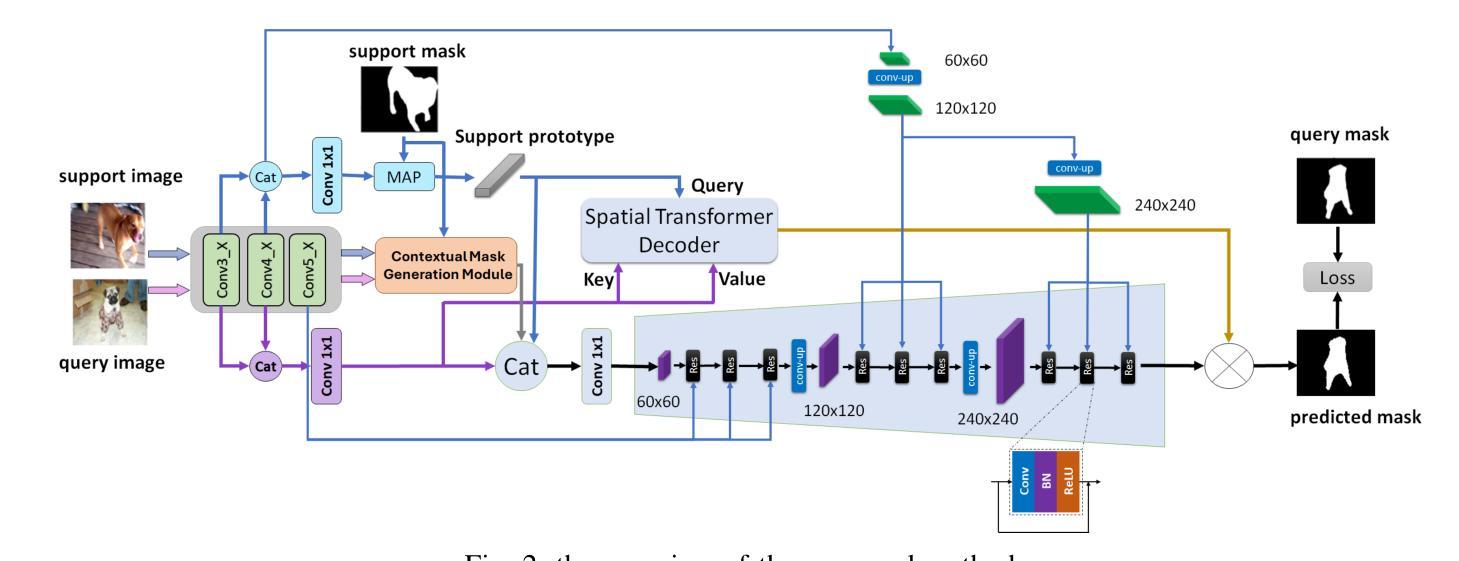
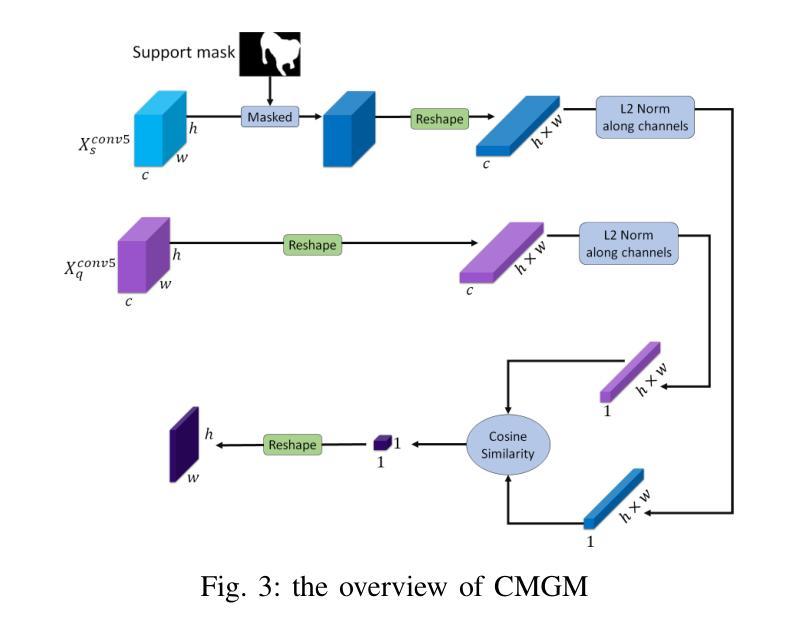
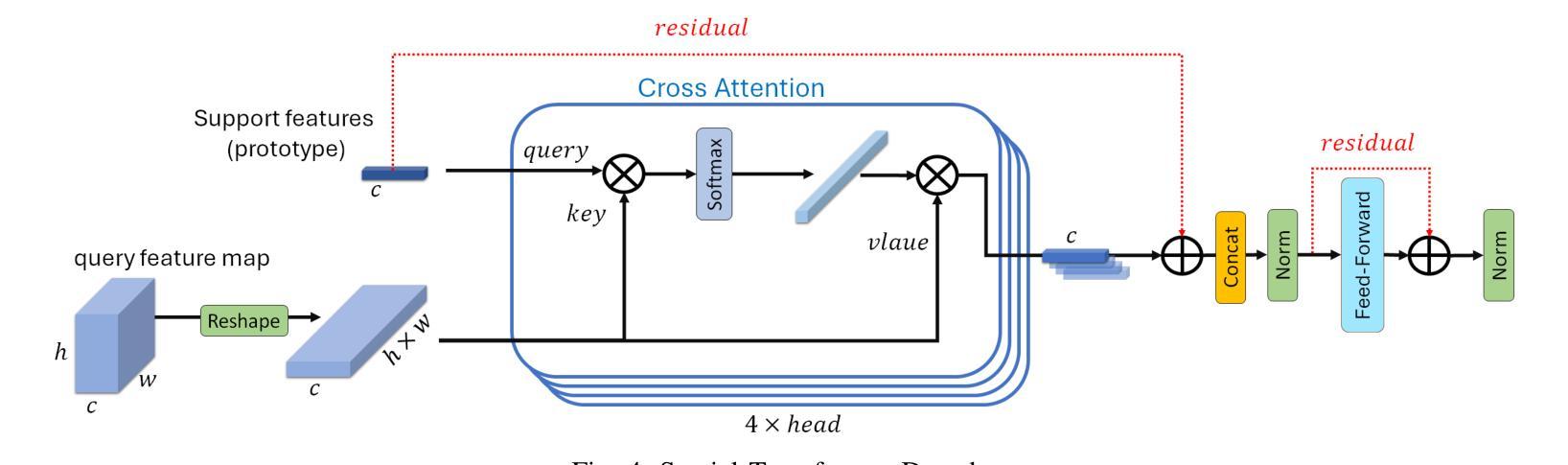
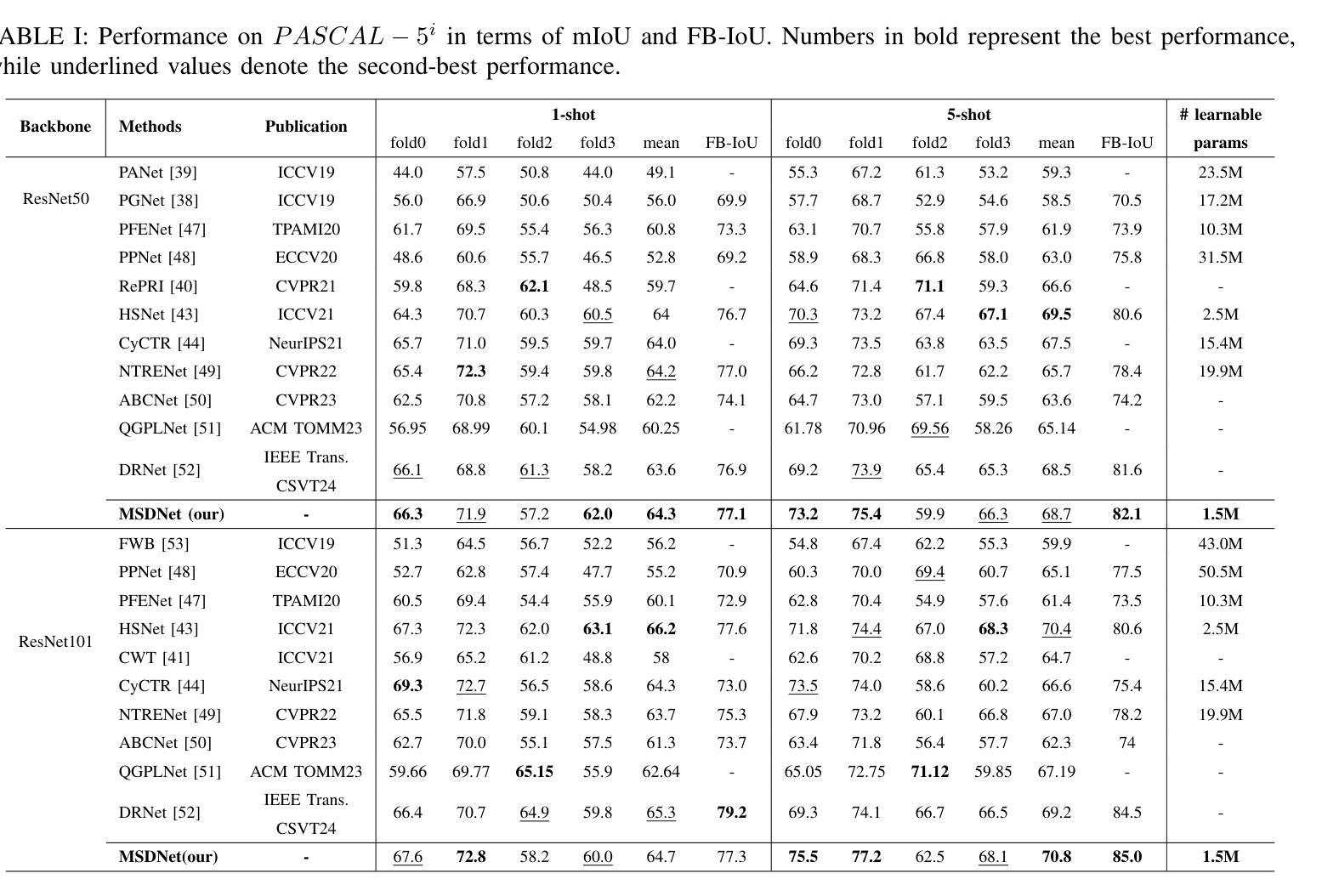
MSDNet: Multi-Scale Decoder for Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation via Transformer-Guided Prototyping
Authors:Amirreza Fateh, Mohammad Reza Mohammadi, Mohammad Reza Jahed Motlagh
Few-shot Semantic Segmentation addresses the challenge of segmenting objects in query images with only a handful of annotated examples. However, many previous state-of-the-art methods either have to discard intricate local semantic features or suffer from high computational complexity. To address these challenges, we propose a new Few-shot Semantic Segmentation framework based on the transformer architecture. Our approach introduces the spatial transformer decoder and the contextual mask generation module to improve the relational understanding between support and query images. Moreover, we introduce a multi-scale decoder to refine the segmentation mask by incorporating features from different resolutions in a hierarchical manner. Additionally, our approach integrates global features from intermediate encoder stages to improve contextual understanding, while maintaining a lightweight structure to reduce complexity. This balance between performance and efficiency enables our method to achieve state-of-the-art results on benchmark datasets such as $PASCAL-5^i$ and $COCO-20^i$ in both 1-shot and 5-shot settings. Notably, our model with only 1.5 million parameters demonstrates competitive performance while overcoming limitations of existing methodologies. https://github.com/amirrezafateh/MSDNet
少样本语义分割旨在解决仅使用少量标注样本对查询图像中的对象进行分割的挑战。然而,许多之前的最先进的方法要么不得不放弃复杂的局部语义特征,要么面临高计算复杂度的问题。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种基于transformer架构的少样本语义分割新框架。我们的方法引入了空间变换解码器和上下文掩码生成模块,以提高支持图像和查询图像之间的关系理解。此外,我们引入了多尺度解码器,以分层的方式融入不同分辨率的特征来优化分割掩码。同时,我们的方法融合了中间编码器阶段的全局特征,以提高上下文理解,同时保持轻量级结构以降低复杂度。性能与效率之间的这种平衡使我们的方法在PASCAL-5i和COCO-20i等基准数据集上实现了最先进的1-shot和5-shot结果。值得注意的是,我们的模型仅有150万个参数,展示了具有竞争力的性能,同时克服了现有方法的局限性。可通过https://github.com/amirrezafateh/MSDNet了解详情。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Transformer架构的Few-shot语义分割框架,通过引入空间变换解码器、上下文掩膜生成模块和多尺度解码器,提高了对支持图像和查询图像之间关系的理解,实现了精细的语义分割,在PASCAL-5i和COCO-20i等基准数据集上取得了最先进的成果。该方法在保持高效的同时,实现了出色的性能。
Key Takeaways
- Few-shot语义分割面临挑战,需要仅使用少量标注样本对查询图像进行对象分割。
- 提出的基于Transformer架构的Few-shot语义分割框架,通过引入空间变换解码器、上下文掩膜生成模块改善关系理解。
- 多尺度解码器用于通过分层方式融入不同分辨率的特征,以优化分割掩膜。
- 集成中间编码器阶段的全球特征,以提高上下文理解,同时保持轻量级结构以降低复杂性。
- 该方法在基准数据集上实现最先进的成果,如PASCAL-5i和COCO-20i,在1-shot和5-shot设置下均表现优异。
- 与现有方法相比,该模型仅1.5百万参数,在保持竞争力的同时,克服了现有方法的局限性。
点此查看论文截图
TAVP: Task-Adaptive Visual Prompt for Cross-domain Few-shot Segmentation
Authors:Jiaqi Yang, Yaning Zhang, Jingxi Hu, Xiangjian He, Linlin Shen, Guoping Qiu
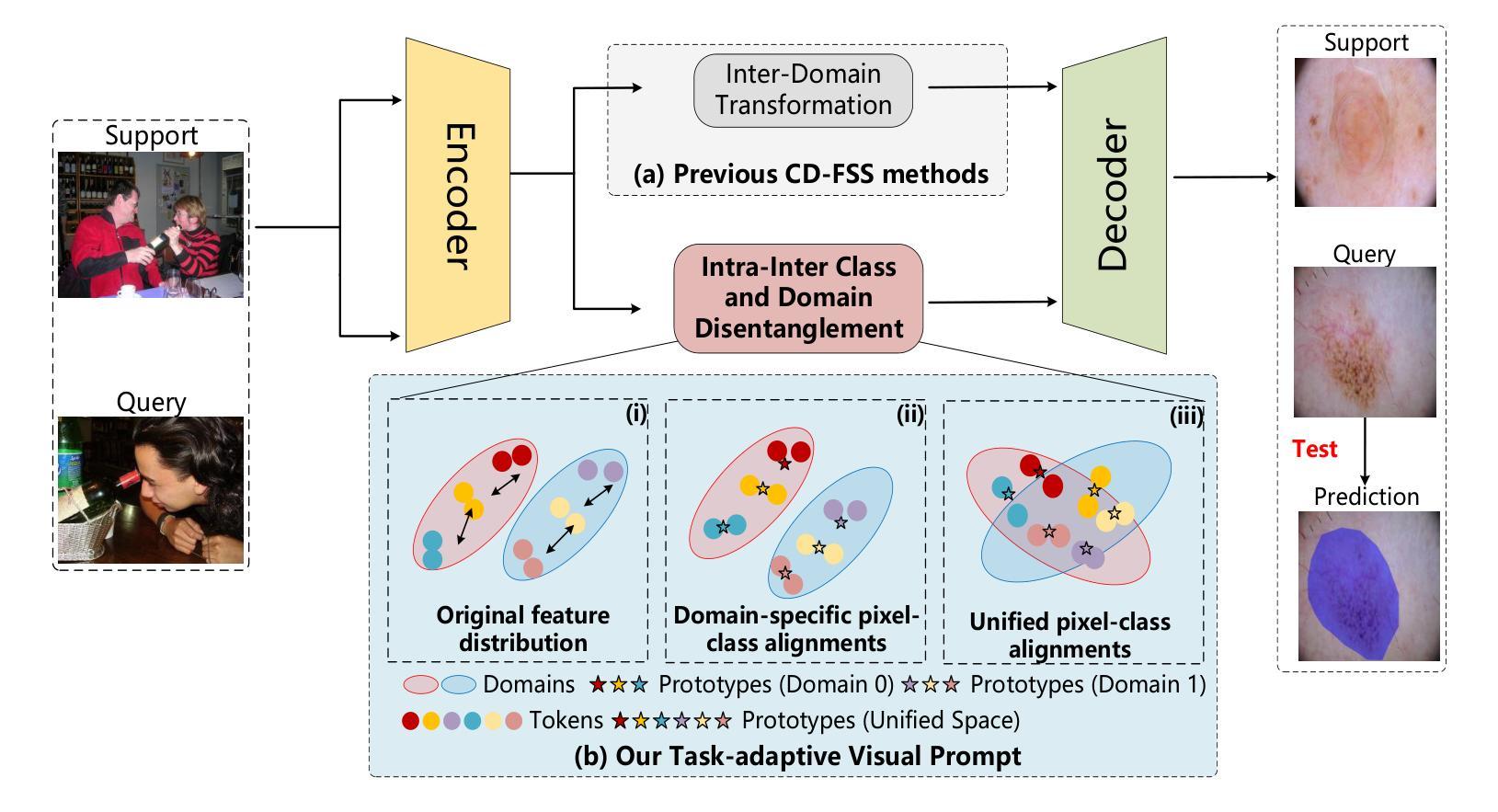
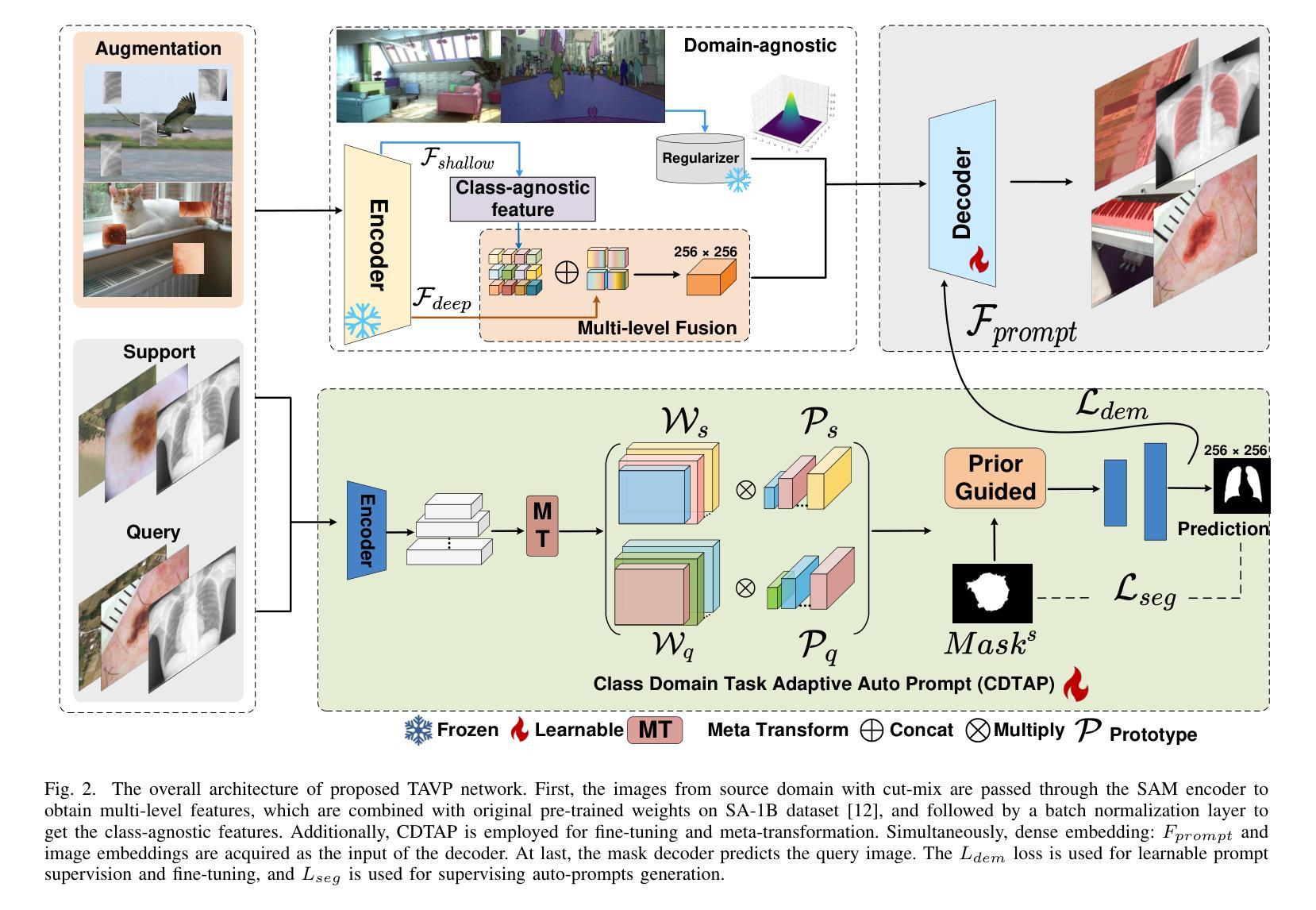
While large visual models (LVM) demonstrated significant potential in image understanding, due to the application of large-scale pre-training, the Segment Anything Model (SAM) has also achieved great success in the field of image segmentation, supporting flexible interactive cues and strong learning capabilities. However, SAM’s performance often falls short in cross-domain and few-shot applications. Previous work has performed poorly in transferring prior knowledge from base models to new applications. To tackle this issue, we propose a task-adaptive auto-visual prompt framework, a new paradigm for Cross-dominan Few-shot segmentation (CD-FSS). First, a Multi-level Feature Fusion (MFF) was used for integrated feature extraction as prior knowledge. Besides, we incorporate a Class Domain Task-Adaptive Auto-Prompt (CDTAP) module to enable class-domain agnostic feature extraction and generate high-quality, learnable visual prompts. This significant advancement uses a unique generative approach to prompts alongside a comprehensive model structure and specialized prototype computation. While ensuring that the prior knowledge of SAM is not discarded, the new branch disentangles category and domain information through prototypes, guiding it in adapting the CD-FSS. Comprehensive experiments across four cross-domain datasets demonstrate that our model outperforms the state-of-the-art CD-FSS approach, achieving an average accuracy improvement of 1.3% in the 1-shot setting and 11.76% in the 5-shot setting.
虽然大型视觉模型(LVM)在图像理解方面表现出了巨大的潜力,并得益于大规模预训练的应用,但在图像分割领域,Segment Anything Model(SAM)也取得了巨大的成功,它支持灵活的交互提示和强大的学习能力。然而,SAM在跨域和少样本应用中的表现往往不尽如人意。以前的工作在将先验知识从基础模型转移到新应用上的效果很差。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种任务自适应自动视觉提示框架,这是一种用于跨域少样本分割(CD-FSS)的新范式。首先,我们使用多级特征融合(MFF)进行集成特征提取作为先验知识。此外,我们结合了类域任务自适应自动提示(CDTAP)模块,以实现类域无关的特征提取,并生成高质量、可学习的视觉提示。这项重大进展采用了一种独特的生成提示方法,并配备了全面的模型结构和专门的原型计算。在保留SAM的先验知识的同时,新分支通过原型解纠缠类别和域信息,引导其适应CD-FSS。在四个跨域数据集上的综合实验表明,我们的模型优于最先进的CD-FSS方法,在1次拍摄的情况下平均准确率提高1.3%,在5次拍摄的情况下平均准确率提高11.76%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型视觉模型(LVM)在图像理解方面展现出巨大潜力,而Segment Anything Model(SAM)在图像分割领域也取得了成功,具有灵活交互提示和强大学习能力。但在跨域和少镜头应用中,SAM表现欠佳。为解决这个问题,我们提出了任务自适应自动视觉提示框架,这是一种新的跨域少镜头分割(CD-FSS)范式。我们使用多级别特征融合(MFF)进行特征提取,并结合类域任务自适应自动提示(CDTAP)模块,生成高质量、可学习的视觉提示。实验表明,我们的模型在四个跨域数据集上优于最先进CD-FSS方法,在单镜头设置下平均精度提高1.3%,在五镜头设置下提高11.76%。
Key Takeaways
- 大型视觉模型(LVM)在图像理解方面表现出显著潜力。
- Segment Anything Model(SAM)在图像分割领域取得成功,但其在跨域和少镜头应用中表现不足。
- 提出的任务自适应自动视觉提示框架是一种新的跨域少镜头分割(CD-FSS)方法。
- 多级别特征融合(MFF)用于集成特征提取作为先验知识。
- 类域任务自适应自动提示(CDTAP)模块可生成高质量、可学习的视觉提示。
- 模型在四个跨域数据集上的表现优于现有CD-FSS方法。
点此查看论文截图

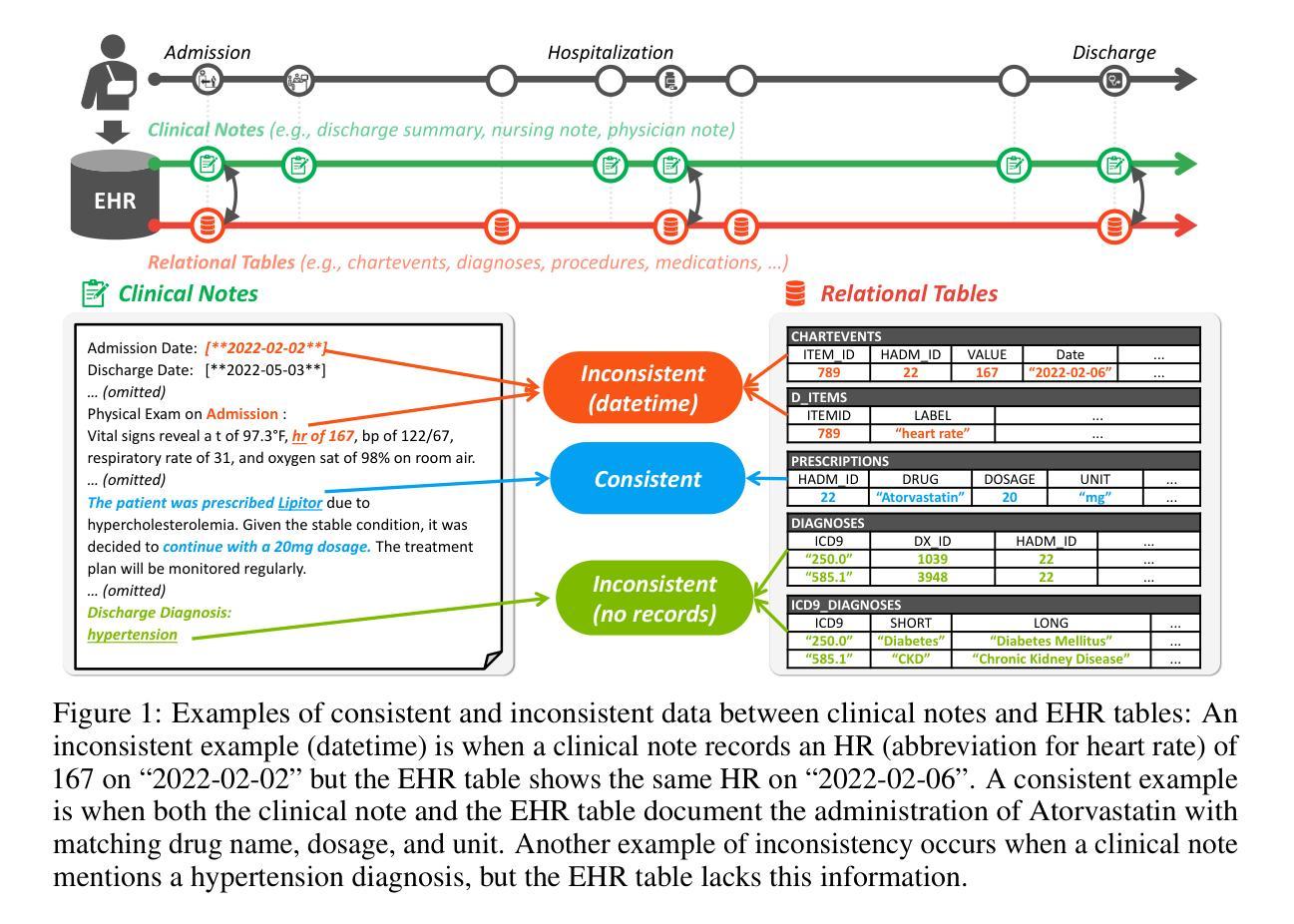
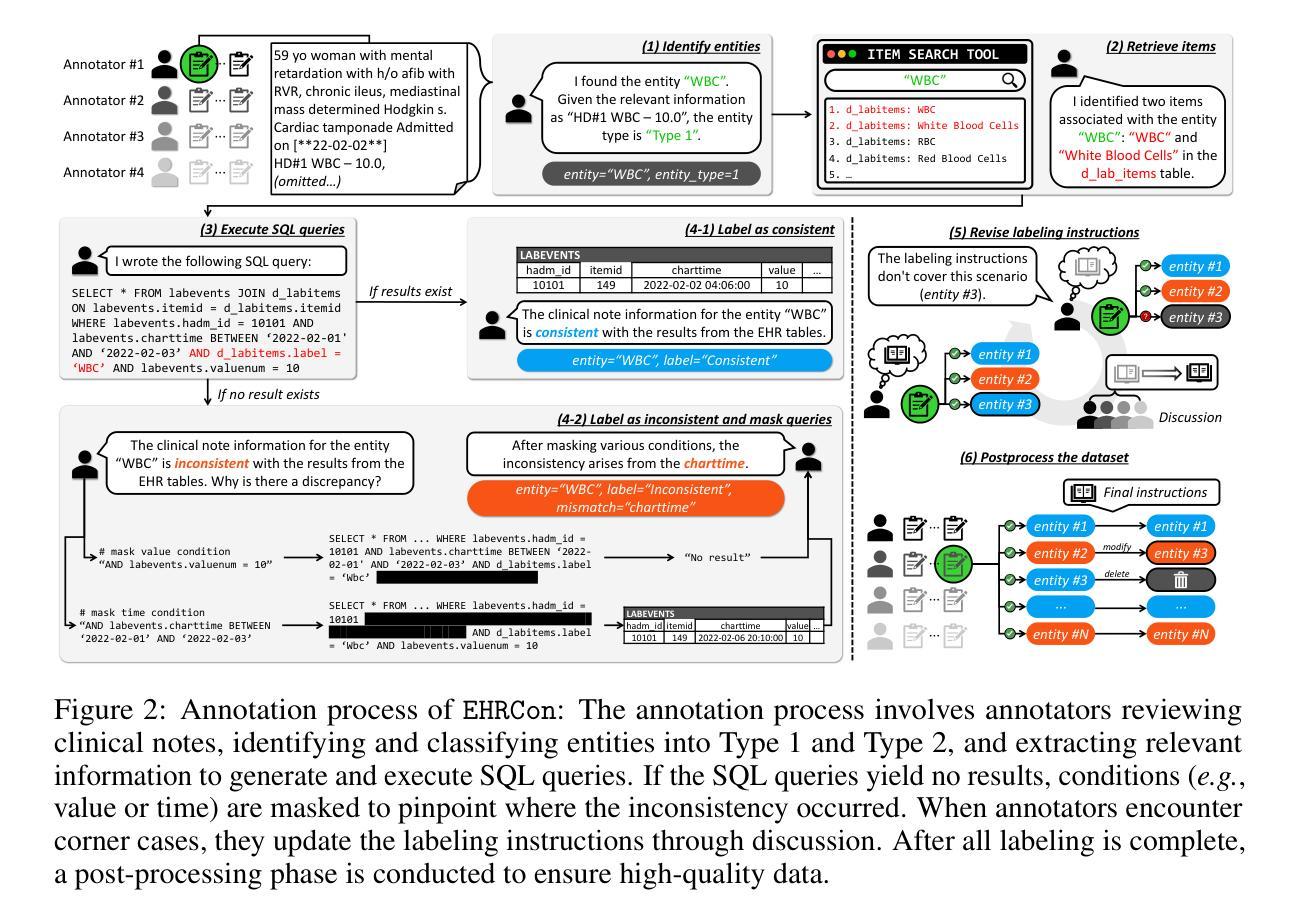
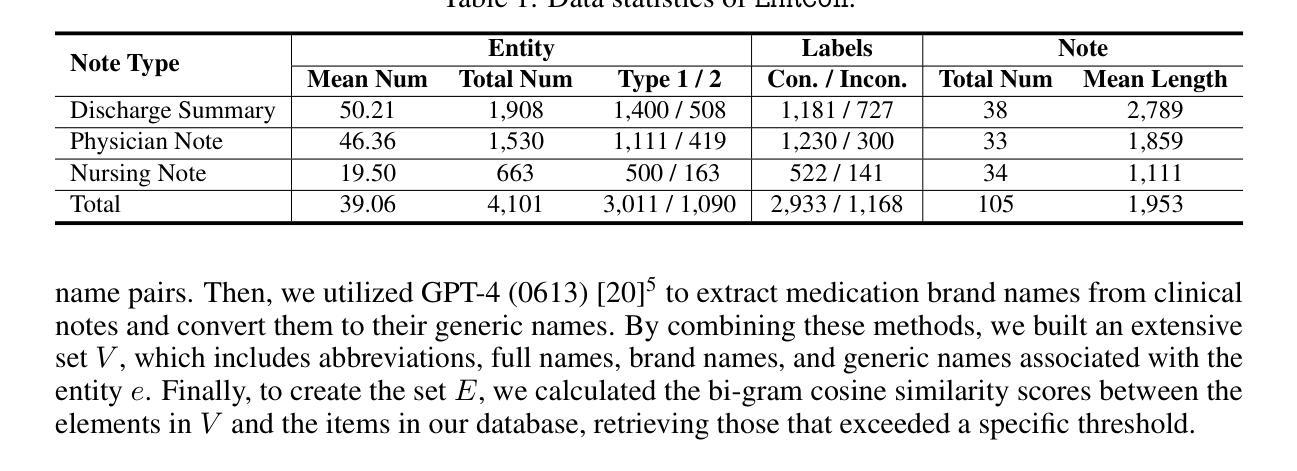
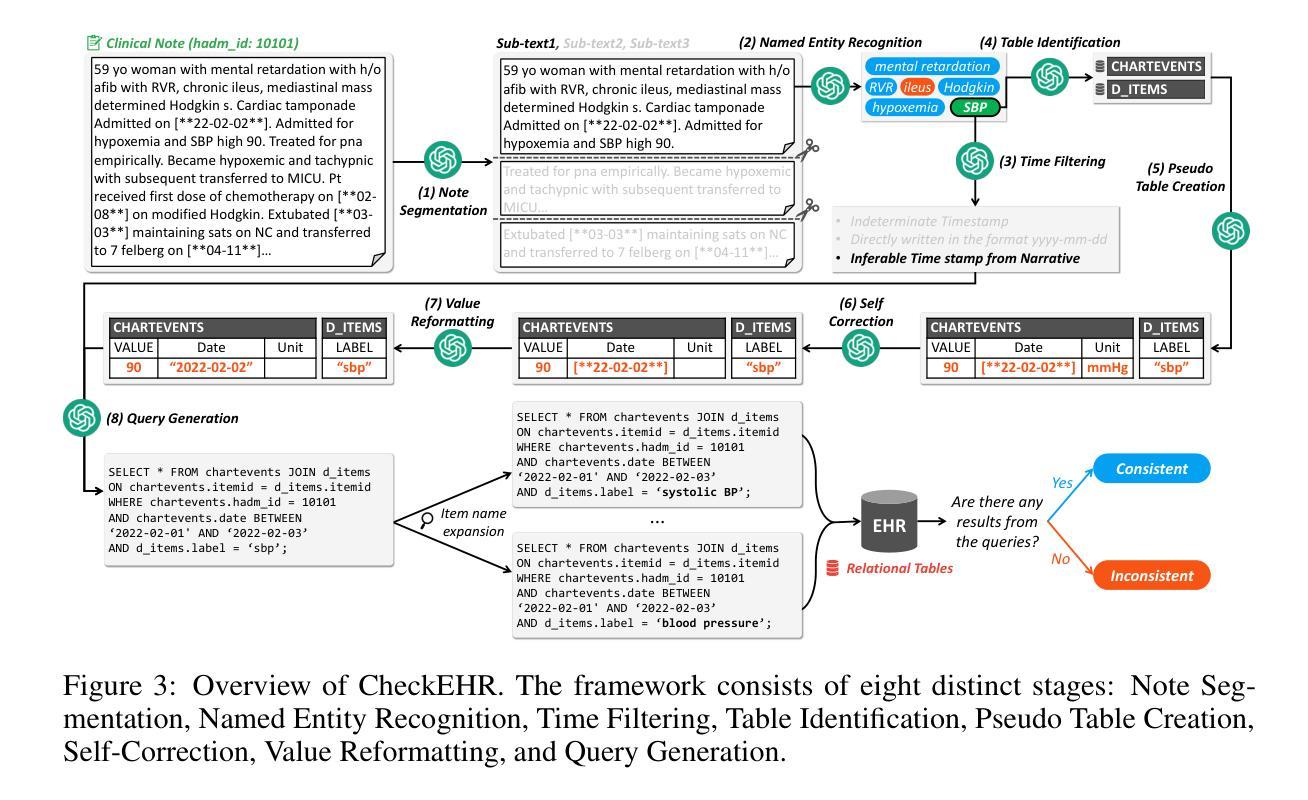
EHRCon: Dataset for Checking Consistency between Unstructured Notes and Structured Tables in Electronic Health Records
Authors:Yeonsu Kwon, Jiho Kim, Gyubok Lee, Seongsu Bae, Daeun Kyung, Wonchul Cha, Tom Pollard, Alistair Johnson, Edward Choi
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) are integral for storing comprehensive patient medical records, combining structured data (e.g., medications) with detailed clinical notes (e.g., physician notes). These elements are essential for straightforward data retrieval and provide deep, contextual insights into patient care. However, they often suffer from discrepancies due to unintuitive EHR system designs and human errors, posing serious risks to patient safety. To address this, we developed EHRCon, a new dataset and task specifically designed to ensure data consistency between structured tables and unstructured notes in EHRs. EHRCon was crafted in collaboration with healthcare professionals using the MIMIC-III EHR dataset, and includes manual annotations of 4,101 entities across 105 clinical notes checked against database entries for consistency. EHRCon has two versions, one using the original MIMIC-III schema, and another using the OMOP CDM schema, in order to increase its applicability and generalizability. Furthermore, leveraging the capabilities of large language models, we introduce CheckEHR, a novel framework for verifying the consistency between clinical notes and database tables. CheckEHR utilizes an eight-stage process and shows promising results in both few-shot and zero-shot settings. The code is available at https://github.com/dustn1259/EHRCon.
电子健康记录(EHRs)对于存储全面的患者医疗记录至关重要,它结合了结构化数据(例如药物信息)和详细的临床笔记(例如医生笔记)。这些要素对于直接的数据检索至关重要,并为患者护理提供了深入、具体的见解。然而,由于电子健康记录系统的不直观设计和人为错误,它们常常会出现差异,给患者的安全带来严重风险。为了解决这个问题,我们开发了EHRCon,这是一个专门设计的新数据集和任务,旨在确保电子健康记录中结构化表格和未结构化笔记之间的数据一致性。EHRCon是与医疗保健专业人员合作,利用MIMIC-III电子健康记录数据集制作的,其中包括对数据库条目的一致性检查的105个临床笔记中的4,101个实体的手动注释。EHRCon有两个版本,一个使用原始的MIMIC-III模式,另一个使用OMOP CDM模式,以增加其适用性和通用性。此外,利用大型语言模型的能力,我们推出了CheckEHR,这是一个验证临床笔记和数据库表格之间一致性的新框架。CheckEHR采用一个八阶段的流程,并在小样和零样本环境中都显示出有希望的结果。相关代码可在https://github.com/dustn1259/EHRCon找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
电子健康记录(EHRs)融合了结构化数据和非结构化临床笔记,是患者医疗记录的关键存储工具。然而,由于EHR系统设计的非直观性和人为错误,数据一致性存在风险。为解决这一问题,我们开发了EHRCon数据集和任务,确保EHR中结构化表格与未结构化笔记之间的数据一致性。EHRCon与医疗保健专业人士合作创建,包括在数据库条目中手动注释的4,101个实体的一致性检查。此外,我们利用大型语言模型的能力,推出了CheckEHR框架,用于验证临床笔记和数据库表格之间的一致性。CheckEHR展示出在少量甚至无样本的情况下具有应用前景。其代码已公开。
Key Takeaways:
- 电子健康记录(EHRs)结合了结构化数据和非结构化临床笔记,为患者医疗记录提供了全面存储方案。
- EHRs因系统设计的非直观性和人为错误常常出现数据不一致的问题,给患者安全带来风险。
- 开发EHRCon数据集和任务是为了确保EHR中数据的一致性。该数据集由医疗保健专业人士合作创建,并包括在数据库条目中手动注释的实体一致性检查。
- EHRCon有两个版本,分别使用原始的MIMIC-III模式和OMOP CDM模式,以提高其适用性和通用性。
- CheckEHR框架被用于验证临床笔记和数据库表格之间的一致性,它通过利用大型语言模型的能力实现了这一目标。
- CheckEHR在少量样本甚至无样本的情况下表现出良好的应用前景。
点此查看论文截图

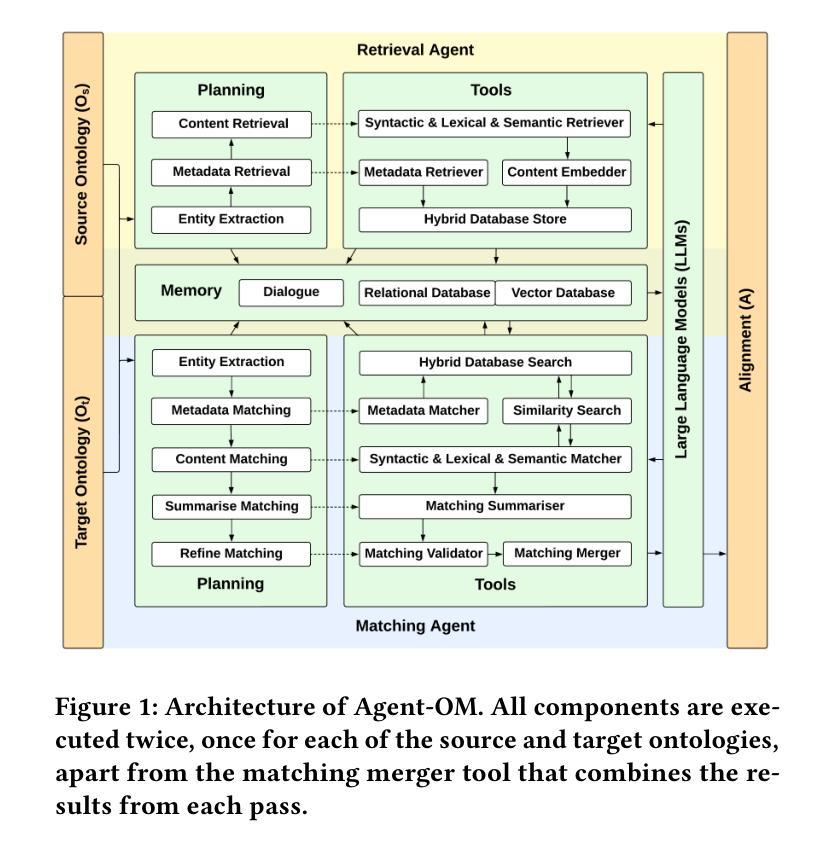
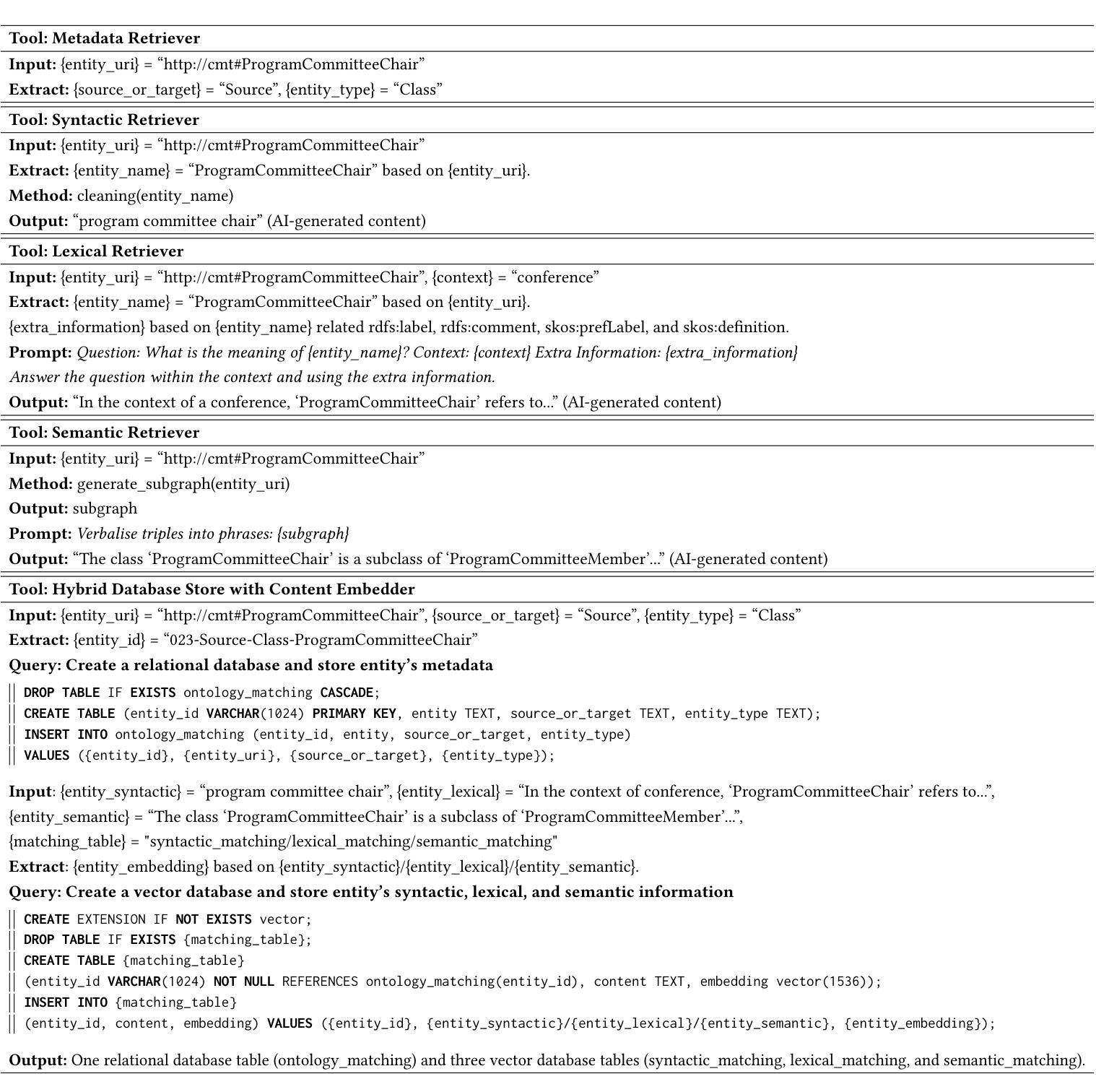
Agent-OM: Leveraging LLM Agents for Ontology Matching
Authors:Zhangcheng Qiang, Weiqing Wang, Kerry Taylor
Ontology matching (OM) enables semantic interoperability between different ontologies and resolves their conceptual heterogeneity by aligning related entities. OM systems currently have two prevailing design paradigms: conventional knowledge-based expert systems and newer machine learning-based predictive systems. While large language models (LLMs) and LLM agents have revolutionised data engineering and have been applied creatively in many domains, their potential for OM remains underexplored. This study introduces a novel agent-powered LLM-based design paradigm for OM systems. With consideration of several specific challenges in leveraging LLM agents for OM, we propose a generic framework, namely Agent-OM (Agent for Ontology Matching), consisting of two Siamese agents for retrieval and matching, with a set of OM tools. Our framework is implemented in a proof-of-concept system. Evaluations of three Ontology Alignment Evaluation Initiative (OAEI) tracks over state-of-the-art OM systems show that our system can achieve results very close to the long-standing best performance on simple OM tasks and can significantly improve the performance on complex and few-shot OM tasks.
本体匹配(OM)通过使不同本体之间实现语义互操作性,并通过对齐相关实体解决其概念上的异质性。目前,OM系统主要有两种流行的设计范式:传统的基于知识的专家系统和较新的基于机器学习的预测系统。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)和LLM代理已经彻底改变了数据工程,并在许多领域得到了创造性的应用,但它们在OM中的潜力尚未得到充分探索。本研究介绍了一种基于代理的LLM设计范式的OM系统。考虑到利用LLM代理进行OM面临的若干特定挑战,我们提出了一个通用框架,即Agent-OM(用于本体匹配的代理),该框架包含两个用于检索和匹配的Siamese代理以及一组OM工具。我们的框架在一个概念验证系统中实现。对三个本体对齐评估倡议(OAEI)赛道上的最新OM系统的评估表明,我们的系统在简单OM任务上的结果非常接近长期以来的最佳性能,并在复杂和少样本OM任务上可以显著提高性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 12 figures, 3 tables
总结
本研究介绍了一种新型基于LLM代理的OM系统设计范式。针对利用LLM代理进行OM的特定挑战,提出了一个通用的Agent-OM框架,包含两个用于检索和匹配的Siamese代理和一组OM工具。在证明概念的系统上实现该框架,并通过与先进的OM系统的评价对比,结果表明该系统在简单OM任务上表现接近最佳水平,并在复杂和少样本OM任务上显著提高性能。
关键见解
- 本研究提出了一种新的基于LLM代理的OM系统设计范式。
- 介绍了针对利用LLM代理进行OM的特定挑战而设计的通用Agent-OM框架。
- Agent-OM框架包含两个用于检索和匹配的Siamese代理和一组OM工具。
- 该框架在证明概念的系统上进行了实现。
- 与先进的OM系统的评价对比显示,该系统在简单OM任务上表现接近最佳水平。
- 在复杂和少样本OM任务上,该系统显著提高性能。
点此查看论文截图

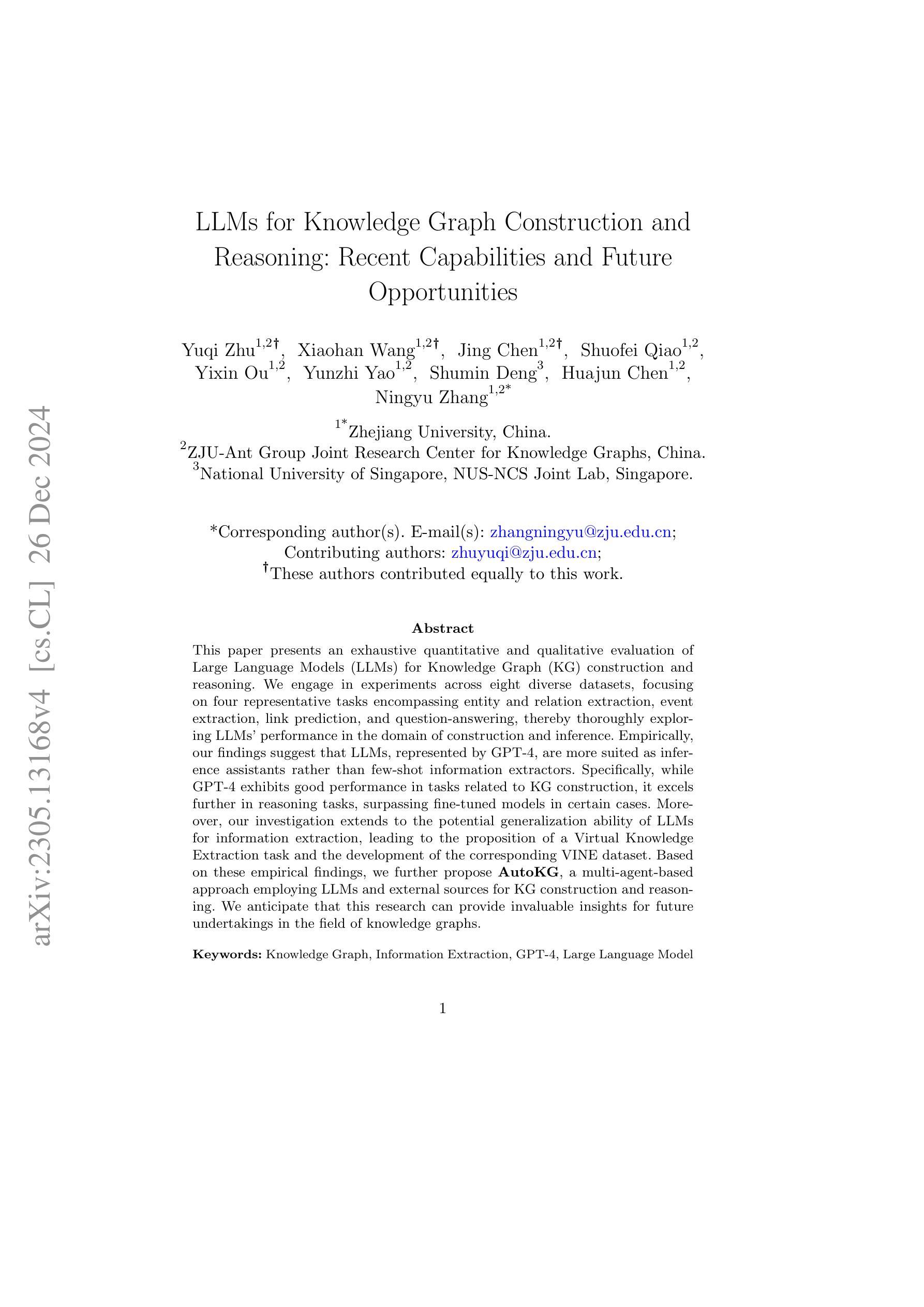
LLMs for Knowledge Graph Construction and Reasoning: Recent Capabilities and Future Opportunities
Authors:Yuqi Zhu, Xiaohan Wang, Jing Chen, Shuofei Qiao, Yixin Ou, Yunzhi Yao, Shumin Deng, Huajun Chen, Ningyu Zhang
This paper presents an exhaustive quantitative and qualitative evaluation of Large Language Models (LLMs) for Knowledge Graph (KG) construction and reasoning. We engage in experiments across eight diverse datasets, focusing on four representative tasks encompassing entity and relation extraction, event extraction, link prediction, and question-answering, thereby thoroughly exploring LLMs’ performance in the domain of construction and inference. Empirically, our findings suggest that LLMs, represented by GPT-4, are more suited as inference assistants rather than few-shot information extractors. Specifically, while GPT-4 exhibits good performance in tasks related to KG construction, it excels further in reasoning tasks, surpassing fine-tuned models in certain cases. Moreover, our investigation extends to the potential generalization ability of LLMs for information extraction, leading to the proposition of a Virtual Knowledge Extraction task and the development of the corresponding VINE dataset. Based on these empirical findings, we further propose AutoKG, a multi-agent-based approach employing LLMs and external sources for KG construction and reasoning. We anticipate that this research can provide invaluable insights for future undertakings in the field of knowledge graphs. The code and datasets are in https://github.com/zjunlp/AutoKG.
本文全面定量和定性地评估了大型语言模型(LLM)在知识图谱(KG)构建和推理中的应用。我们在八个不同的数据集上进行了实验,重点研究四个代表性任务,包括实体和关系抽取、事件抽取、链接预测和问答,从而全面探索LLM在构建和推理领域的性能。实证研究结果表明,以GPT-4为代表的大型语言模型更适合作为推理助手,而非少数情况下的信息提取器。具体而言,GPT-4在知识图谱构建相关任务上表现良好,在推理任务上更是表现出卓越的性能,在某些情况下甚至超过了微调模型。此外,我们的调查还扩展到大型语言模型在信息提取方面的潜在泛化能力,从而提出了虚拟知识提取任务并开发了相应的VINE数据集。基于这些实证发现,我们进一步提出了AutoKG,这是一种基于多代理的方法,利用大型语言模型和外部资源来进行知识图谱的构建和推理。我们预期这项研究能为未来知识图谱领域的研究提供宝贵的见解。代码和数据集位于https://github.com/zjunlp 可以在这里找到代码和数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF World Wide Web Journal
Summary
本文全面评估了大型语言模型(LLMs)在知识图谱(KG)构建和推理方面的表现。实验涉及八个不同数据集,涵盖实体和关系抽取、事件抽取、链接预测和问答等四个代表性任务,深入探讨了LLMs在构建和推理领域的性能。研究发现,GPT-4等LLMs更适合作为推理助手而非少样本信息提取器。在KG构建相关任务中表现良好,在推理任务中更是表现出超越微调模型的实力。此外,研究还扩展了LLMs在信息提取方面的潜在泛化能力,提出了虚拟知识提取任务及相应的VINE数据集。基于这些发现,本文进一步提出了AutoKG,一种基于多代理的方法,利用LLMs和外部资源用于KG构建和推理。
Key Takeaways
- 论文对大型语言模型在知识图谱构建和推理方面进行了全面评估。
- 实验涉及多个数据集和代表性任务,包括实体和关系抽取、事件抽取、链接预测和问答。
- GPT-4等LLMs更适合作为推理助手,而非少样本信息提取器。
- 在知识图谱构建任务中,GPT-4表现良好,尤其在推理任务中表现卓越,有时超越微调模型。
- 研究扩展了LLMs在信息提取方面的潜在泛化能力。
- 论文提出了虚拟知识提取任务及相应的VINE数据集。
- 基于实证发现,论文进一步提出了AutoKG,一种基于多代理的方法,利用LLMs和外部资源进行KG构建和推理。
点此查看论文截图