⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-02 更新
Dialogue Director: Bridging the Gap in Dialogue Visualization for Multimodal Storytelling
Authors:Min Zhang, Zilin Wang, Liyan Chen, Kunhong Liu, Juncong Lin
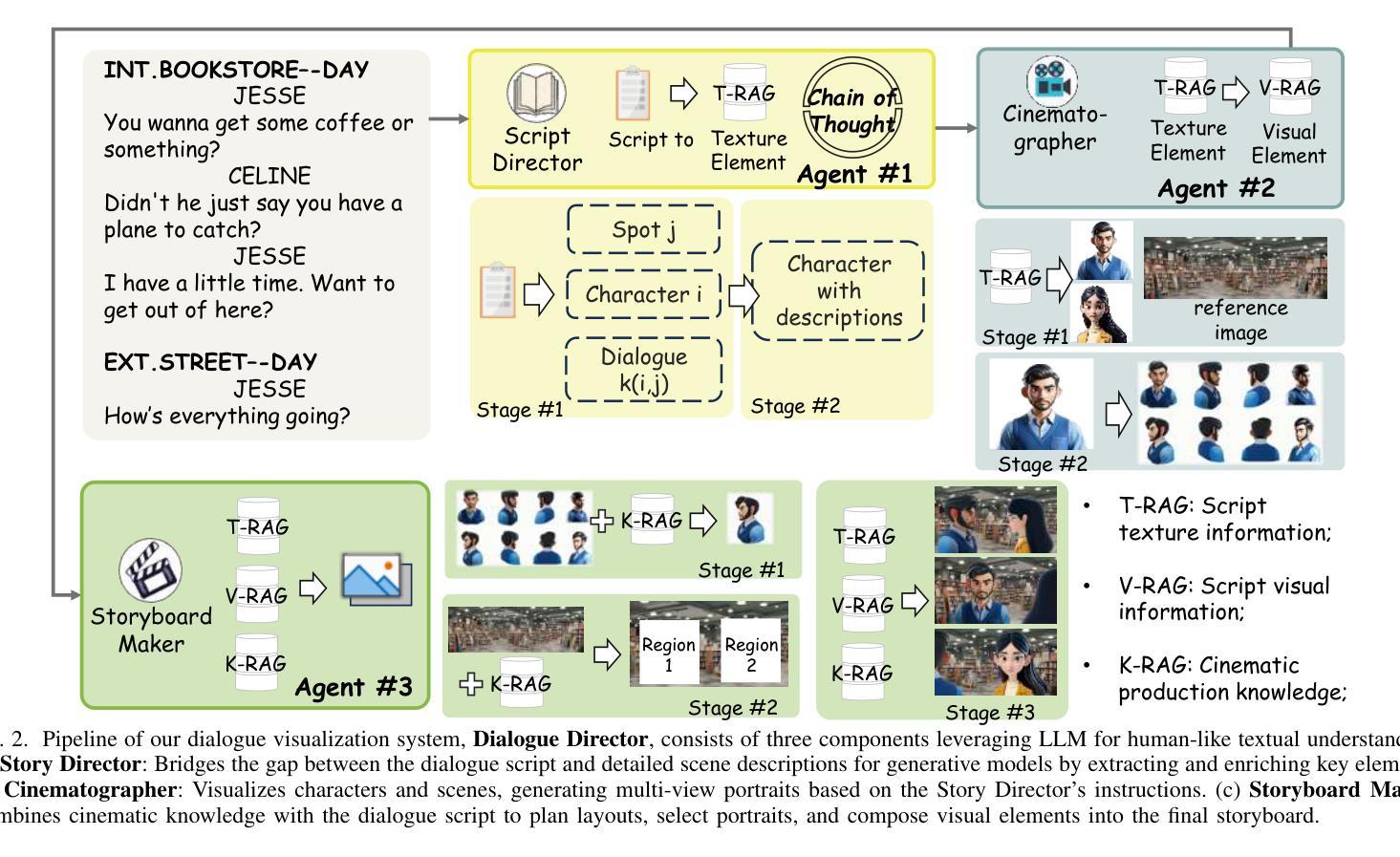
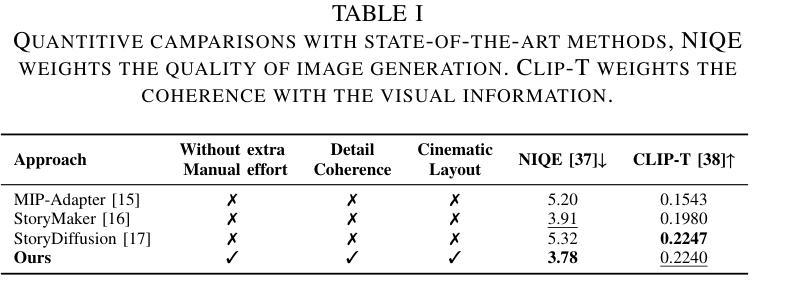
Recent advances in AI-driven storytelling have enhanced video generation and story visualization. However, translating dialogue-centric scripts into coherent storyboards remains a significant challenge due to limited script detail, inadequate physical context understanding, and the complexity of integrating cinematic principles. To address these challenges, we propose Dialogue Visualization, a novel task that transforms dialogue scripts into dynamic, multi-view storyboards. We introduce Dialogue Director, a training-free multimodal framework comprising a Script Director, Cinematographer, and Storyboard Maker. This framework leverages large multimodal models and diffusion-based architectures, employing techniques such as Chain-of-Thought reasoning, Retrieval-Augmented Generation, and multi-view synthesis to improve script understanding, physical context comprehension, and cinematic knowledge integration. Experimental results demonstrate that Dialogue Director outperforms state-of-the-art methods in script interpretation, physical world understanding, and cinematic principle application, significantly advancing the quality and controllability of dialogue-based story visualization.
近年来,人工智能驱动的故事创作技术取得了进展,提升了视频生成和故事可视化。然而,将对话为中心的剧本转化为连贯的故事板仍然是一个巨大的挑战,这主要是由于剧本细节有限、对物理上下文理解不足以及整合电影原则复杂性较高。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了对话可视化这一新任务,它将对话剧本转化为动态、多视角的故事板。我们介绍了无训练对话导演这一多媒体框架,包括剧本导演、摄影师和故事板制作。该框架利用大型多媒体模型和基于扩散的架构,采用思维链推理、增强检索生成和多视角合成等技术,提高了剧本理解、物理上下文理解和电影知识整合。实验结果表明,对话导演在剧本解读、物理世界理解和电影原则应用方面优于现有技术,显著提高了基于对话的故事可视化的质量和可控性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
AI驱动的故事讲述的最新进展已经提升了视频生成和故事可视化。然而,将对话为中心的脚本转化为连贯的故事板仍是一个挑战,因为脚本细节有限、对物理上下文理解不足以及整合电影原则复杂性高。为解决这些挑战,我们提出了对话可视化这一新任务,能将对话脚本转化为动态、多视角的故事板。我们引入了无训练的多模态框架Dialogue Director,包含Script Director、Cinematographer和Storyboard Maker。该框架利用大型多模态模型和扩散架构,采用Chain-of-Thought推理、增强检索生成和多视角合成等技术,提高脚本理解、物理上下文理解和电影知识整合。实验结果表明,Dialogue Director在脚本解读、物理世界理解和电影原则应用方面超越了现有方法,显著提高了基于对话的故事可视化的质量和可控性。
Key Takeaways
- AI驱动的故事讲述增强了视频生成和故事可视化。
- 将对话脚本转化为故事板存在挑战,如脚本细节有限、物理上下文理解不足以及电影原则整合复杂。
- 提出了对话可视化新任务,能转化对话脚本为动态、多视角故事板。
- 引入了无训练的多模态框架Dialogue Director,包含Script Director、Cinematographer和Storyboard Maker。
- Dialogue Director利用大型多模态模型和扩散架构。
- Dialogue Director采用多种技术提高脚本理解、物理上下文理解和电影知识整合。
点此查看论文截图


Scoring with Large Language Models: A Study on Measuring Empathy of Responses in Dialogues
Authors:Henry J. Xie, Jinghan Zhang, Xinhao Zhang, Kunpeng Liu
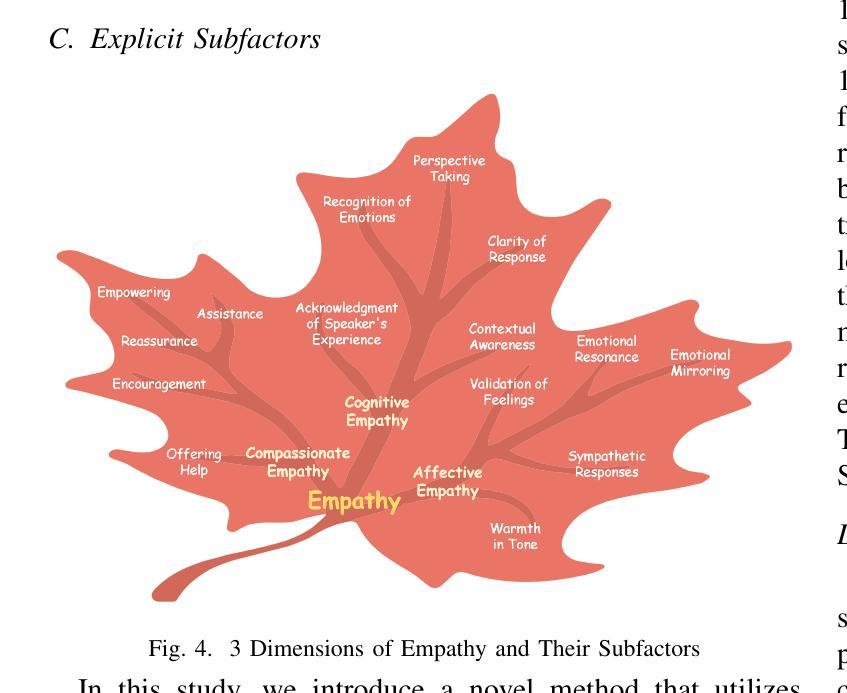
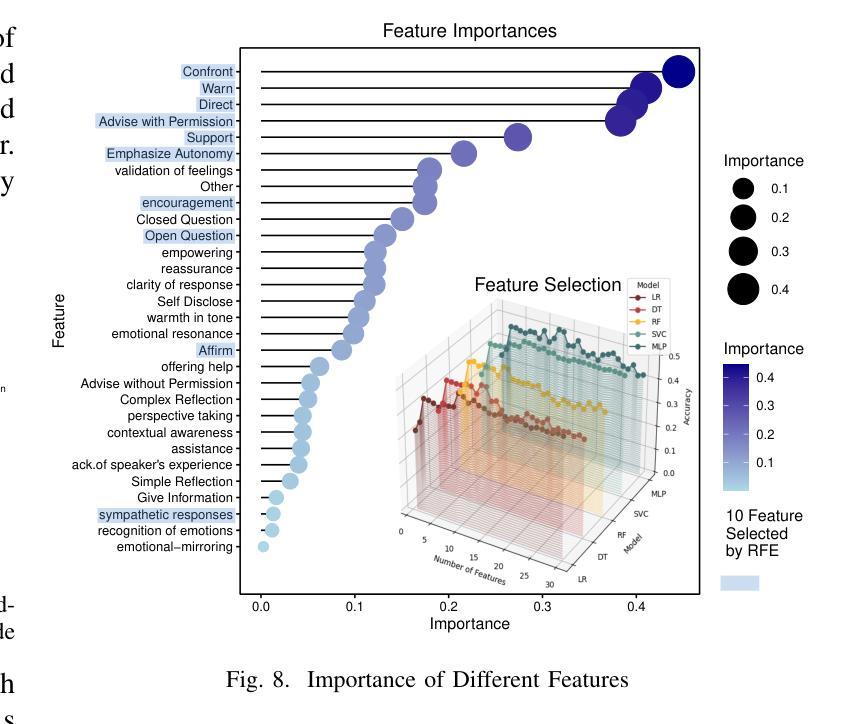
In recent years, Large Language Models (LLMs) have become increasingly more powerful in their ability to complete complex tasks. One such task in which LLMs are often employed is scoring, i.e., assigning a numerical value from a certain scale to a subject. In this paper, we strive to understand how LLMs score, specifically in the context of empathy scoring. We develop a novel and comprehensive framework for investigating how effective LLMs are at measuring and scoring empathy of responses in dialogues, and what methods can be employed to deepen our understanding of LLM scoring. Our strategy is to approximate the performance of state-of-the-art and fine-tuned LLMs with explicit and explainable features. We train classifiers using various features of dialogues including embeddings, the Motivational Interviewing Treatment Integrity (MITI) Code, a set of explicit subfactors of empathy as proposed by LLMs, and a combination of the MITI Code and the explicit subfactors. Our results show that when only using embeddings, it is possible to achieve performance close to that of generic LLMs, and when utilizing the MITI Code and explicit subfactors scored by an LLM, the trained classifiers can closely match the performance of fine-tuned LLMs. We employ feature selection methods to derive the most crucial features in the process of empathy scoring. Our work provides a new perspective toward understanding LLM empathy scoring and helps the LLM community explore the potential of LLM scoring in social science studies.
近年来,大型语言模型(LLMs)在完成复杂任务方面的能力越来越强。LLMs经常用于评分任务,即给某个主题分配一个数值。在本文中,我们致力于了解LLMs如何进行评分,特别是在共情评分方面的情境。我们开发了一个新颖而全面的框架,旨在研究LLMs在对话中衡量和评估回应的共情能力,以及可以采取哪些方法来深化我们对LLM评分的理解。我们的策略是通过具有明确和可解释特征的最新和最精细调整的LLMs来近似其性能。我们使用各种对话特征来训练分类器,包括嵌入、动机访谈治疗完整性(MITI)代码、LLM提出的明确子因素集合以及MITI代码和明确子因素的组合。我们的结果表明,仅使用嵌入时,可以达到接近通用LLMs的性能;当利用MITI代码和LLM评分的明确子因素时,训练的分类器可以紧密匹配精细调整的LLMs的性能。我们采用特征选择方法来推导共情评分过程中最重要的特征。我们的工作提供了一个新的视角来理解LLM共情评分,并帮助LLM社区探索LLM评分在社会科学研究中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE BigData 2024
摘要
近年来,大型语言模型(LLMs)在完成复杂任务方面的能力越来越强。其中一个常见的任务是评分,即为某个主题分配数值值。本文旨在了解LLMs如何评分,特别是在共情评分方面的上下文。我们开发了一个全面且新颖的框架,用于研究LLMs在对话中衡量和评分共情的有效性以及深入了解LLM评分的方法。我们的策略是通过具有明确和可解释特征的最新和最精细的LLMs来评估其性能。我们使用对话的各种特征训练分类器,包括嵌入、动机访谈治疗完整性(MITI)代码、LLM提出的明确子因素的集合以及MITI代码和明确子因素的组合。结果表明,仅使用嵌入时,性能接近通用LLMs;而当利用MITI代码和LLM评分的明确子因素时,训练的分类器可以接近精细调整的LLMs的性能。我们采用特征选择方法来推导共情评分过程中最重要的特征。我们的工作提供了一个理解LLM共情评分的新视角,并帮助LLM社区探索LLM评分在社会科学研究中的潜力。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在共情评分方面表现出强大的能力,能够通过数值化方式评估对话中的共情程度。
- 开发了一个全面框架来研究和理解LLMs在共情评分方面的性能,包括使用多种特征训练分类器。
- 仅使用嵌入可以达到接近通用LLMs的性能,而结合MITI代码和LLM评分的明确子因素能接近精细调整的LLMs的性能。
- LLMs在共情评分方面的潜力巨大,可以为社会科学研究提供新的视角和工具。
- 特征选择方法有助于确定共情评分过程中最重要的特征,这可以为进一步改进LLMs提供方向。
- 该研究为理解LLMs如何处理复杂任务如共情评分提供了深入见解,有助于推动LLM技术的进一步发展。
点此查看论文截图

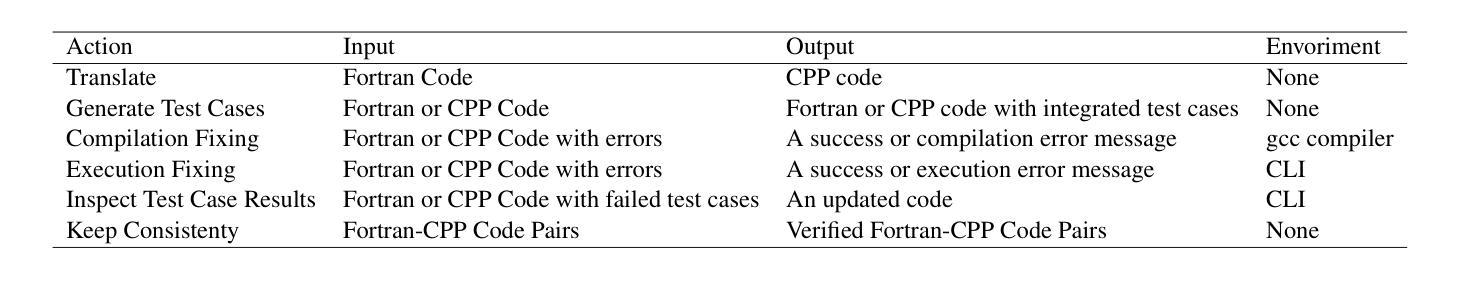
Fortran2CPP: Automating Fortran-to-C++ Migration using LLMs via Multi-Turn Dialogue and Dual-Agent Integration
Authors:Le Chen, Bin Lei, Dunzhi Zhou, Pei-Hung Lin, Chunhua Liao, Caiwen Ding, Ali Jannesari
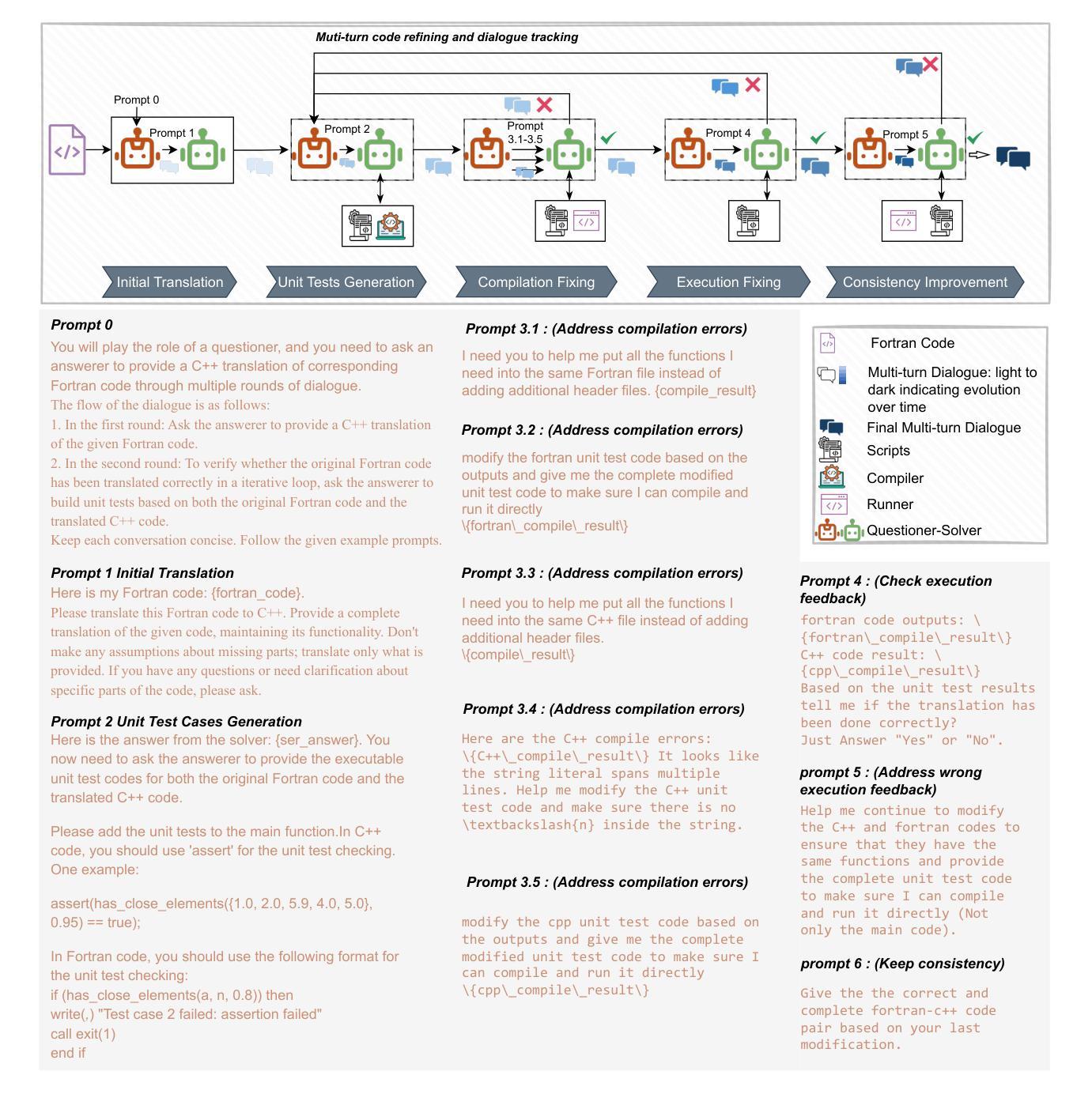
Migrating Fortran code to C++ is a common task for many scientific computing teams, driven by the need to leverage modern programming paradigms, enhance cross-platform compatibility, and improve maintainability. Automating this translation process using large language models (LLMs) has shown promise, but the lack of high-quality, specialized datasets has hindered their effectiveness. In this paper, we address this challenge by introducing a novel multi-turn dialogue dataset, Fortran2CPP, specifically designed for Fortran-to-C++ code migration. Our dataset, significantly larger than existing alternatives, is generated using a unique LLM-driven, dual-agent pipeline incorporating iterative compilation, execution, and code repair to ensure high quality and functional correctness. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our dataset, we fine-tuned several open-weight LLMs on Fortran2CPP and evaluated their performance on two independent benchmarks. Fine-tuning on our dataset led to remarkable gains, with models achieving up to a 3.31x increase in CodeBLEU score and a 92% improvement in compilation success rate. This highlights the dataset’s ability to enhance both the syntactic accuracy and compilability of the translated C++ code. Our dataset and model have been open-sourced and are available on our public GitHub repository\footnote{\url{https://github.com/HPC-Fortran2CPP/Fortran2Cpp}}.
将Fortran代码迁移到C++是许多科学计算团队常见的任务,其驱动力在于需要利用现代编程范式,提高跨平台兼容性,并改善可维护性。使用大型语言模型(LLM)自动化此翻译过程已显示出前景,但缺乏高质量的专业数据集阻碍了其有效性。在本文中,我们通过引入一种新型的多轮对话数据集Fortran2CPP,专门用于Fortran到C++的代码迁移,来解决这一挑战。我们的数据集比现有替代方案大得多,是使用独特的LLM驱动双代理管道生成的,该管道结合了迭代编译、执行和代码修复,以确保高质量和功能正确性。为了证明我们数据集的有效性,我们在Fortran2CPP上对几个开源LLM进行了微调,并在两个独立基准测试上评估了它们的性能。在我们数据集上进行微调带来了显著的提升,模型在CodeBLEU分数上最高提升了3.31倍,编译成功率提高了92%。这突显了数据集在提高翻译后的C++代码语法准确性和可编译性方面的能力。我们的数据集和模型已开源,可在我们的公共GitHub仓库中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了将Fortran代码迁移到C++的自动化过程。通过使用大型语言模型(LLMs),研究人员创建了一个新型的多轮对话数据集Fortran2CPP,用于解决迁移问题。此数据集是专为Fortran到C++的代码迁移设计,它通过一种基于LLM的双重代理管道生成数据,并展现出出色的表现能力。对几种开源的大型语言模型进行了调优实验,结果令人印象深刻,验证了数据集的可靠性和高效性。模型在CodeBLEU得分上提高了三倍以上,编译成功率提高了百分之九十二。数据集已开源,可在GitHub上获取。
Key Takeaways
- Fortran代码迁移到C++的需求迫切,大型语言模型(LLMs)在自动化翻译过程中具有潜力。
- Fortran2CPP数据集专为Fortran到C++的代码迁移设计,显著大于现有数据集。
- Fortran2CPP数据集通过LLM驱动的双重代理管道生成,确保高质量和功能性正确性。
- 数据集在编译成功率和语法准确性方面表现出卓越性能,对几个开源大型语言模型的微调实验证明了其有效性。
- Fortran2CPP数据集的公开源码已经在GitHub上发布。
点此查看论文截图

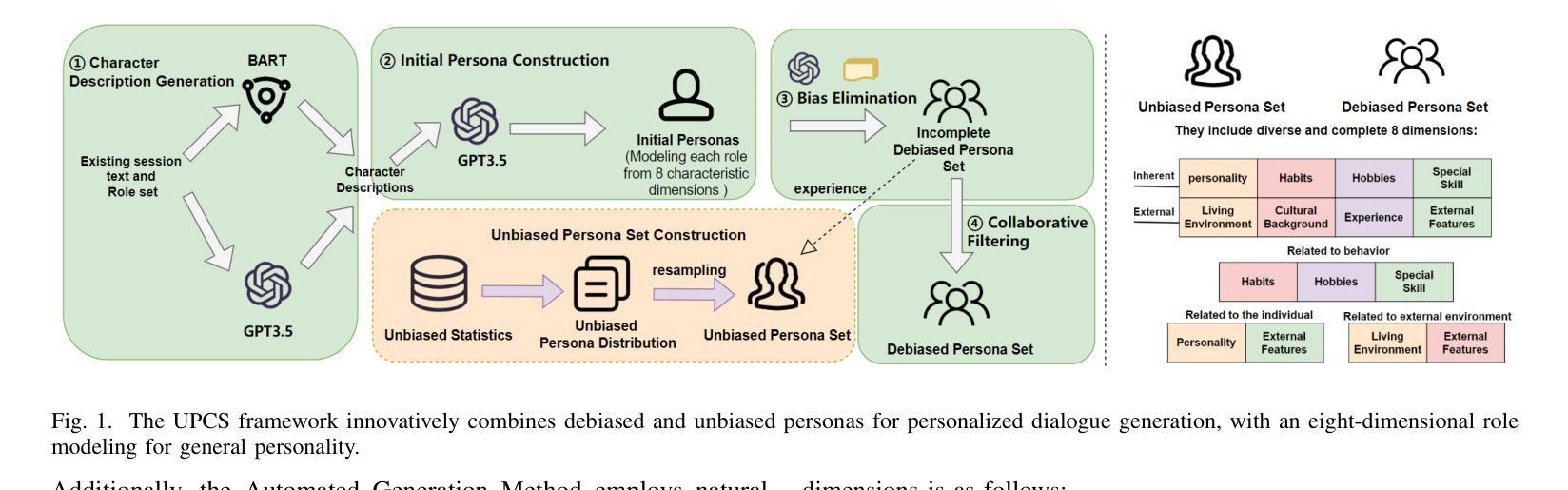
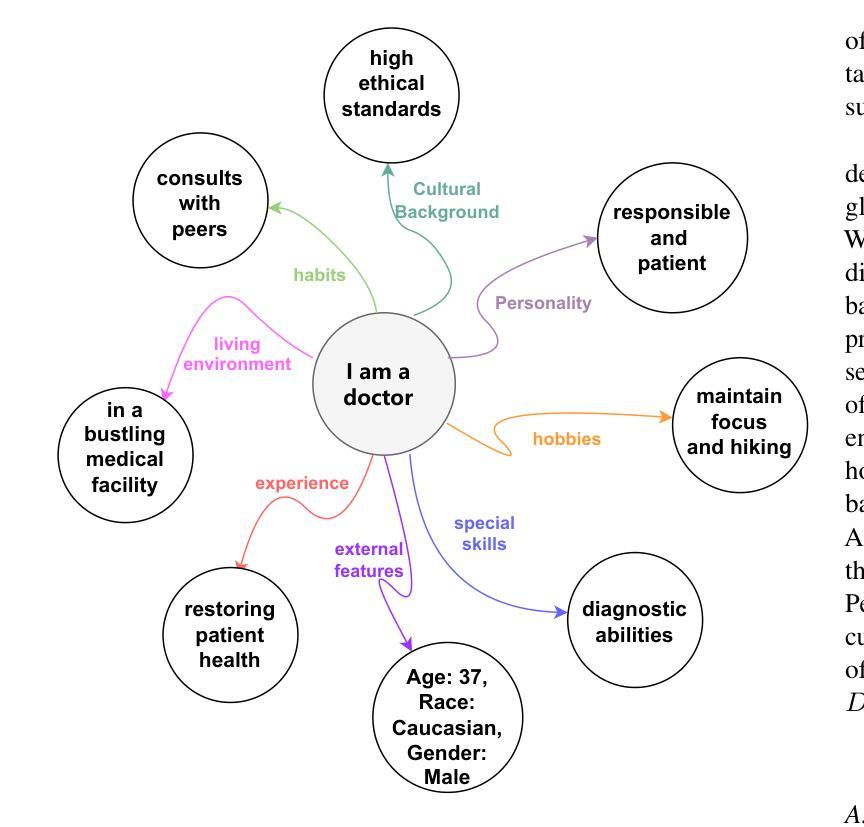
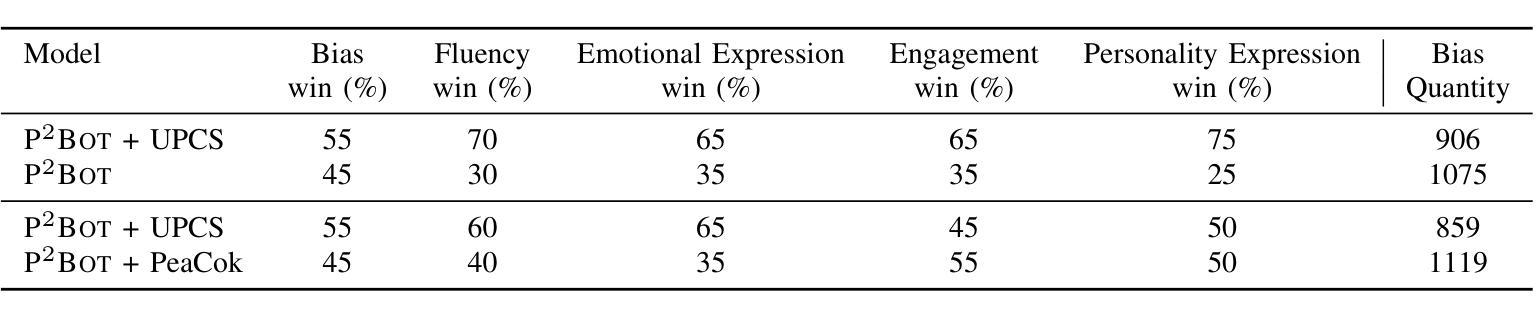
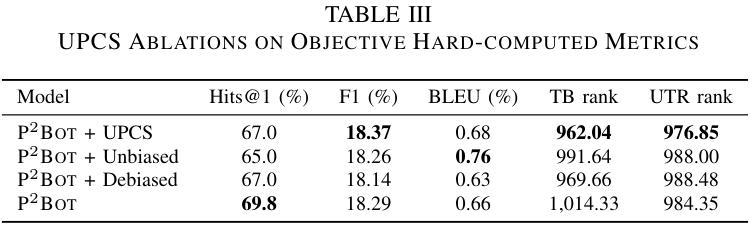
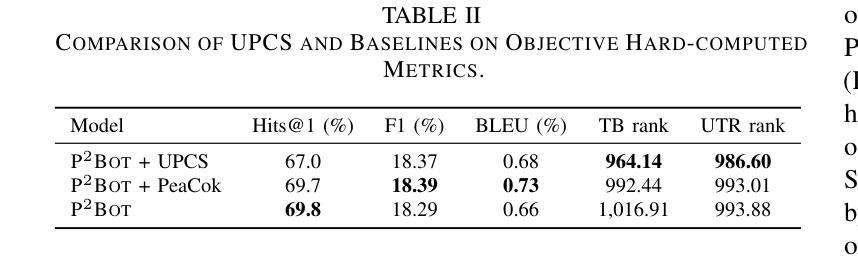
UPCS: Unbiased Persona Construction for Dialogue Generation
Authors:Kuiyun Chen, Yanbin Wei
Narrative systems, such as dialogue and storytelling systems, often utilize persona profiles to enhance personalized interactions. Existing persona profiles frequently exhibit biases, posing risks to system integrity and fairness. To address this, we introduce the UPCS framework, which categorizes character descriptions into eight dimensions, including bias mitigation strategies. Experimental results demonstrate UPCS’s superiority in accuracy, diversity, bias elimination, and user satisfaction, marking a significant advancement in persona construction for reliable narrative systems.
对话和叙事系统等叙事系统常常利用人物角色简介增强个性化交互。现有的人物角色简介通常会表现出偏见,对系统完整性和公平性构成风险。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了UPCS框架,该框架将人物描述分为八个维度,包括偏见缓解策略。实验结果表明,UPCS在准确性、多样性、偏见消除和用户满意度方面表现出卓越的优势,为可靠叙事系统中的人物构建树立了重要里程碑。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
叙述系统如对话和故事叙述系统常利用人物角色描述增强个性化互动。现有的人物角色描述常带有偏见,对系统完整性和公平性构成风险。为解决此问题,我们引入了UPCS框架,该框架将人物角色描述分为八个维度,包括偏见缓解策略。实验结果表明,UPCS在准确性、多样性、偏见消除和用户满意度方面表现优越,为可靠叙述系统的人物角色构建带来了重大进步。
Key Takeaways:
- 叙述系统利用人物角色描述增强互动。
- 现有的人物角色描述存在偏见问题,影响系统公平性和完整性。
- UPCS框架用于人物角色描述,分为八个维度。
- UPCS框架包括偏见缓解策略。
- 实验证明UPCS在准确性、多样性、偏见消除方面表现优越。
- UPCS提高了用户满意度。
点此查看论文截图

Population of tetraneutron continuum in reactions of $^{8}$He on deuterium
Authors:I. A. Muzalevskii, N. B. Shulgina, A. A. Bezbakh, V. Chudoba, S. A. Krupko, S. G. Belogurov, D. Biare, I. A. Egorova, A. S. Fomichev, E. M. Gazeeva, A. V. Gorshkov, L. V. Grigorenko, G. Kaminski, M. Khirk, O. Kiselev, D. A. Kostyleva, M. Yu. Kozlov, B. Mauyey, I. Mukha, E. Yu. Nikolskii, Yu. L. Parfenova, W. Piatek, A. M. Quynh, A. Serikov, S. I. Sidorchuk, P. G. Sharov, R. S. Slepnev, S. V. Stepantsov, A. Swiercz, P. Szymkiewicz, G. M. Ter-Akopian, B. Zalewski
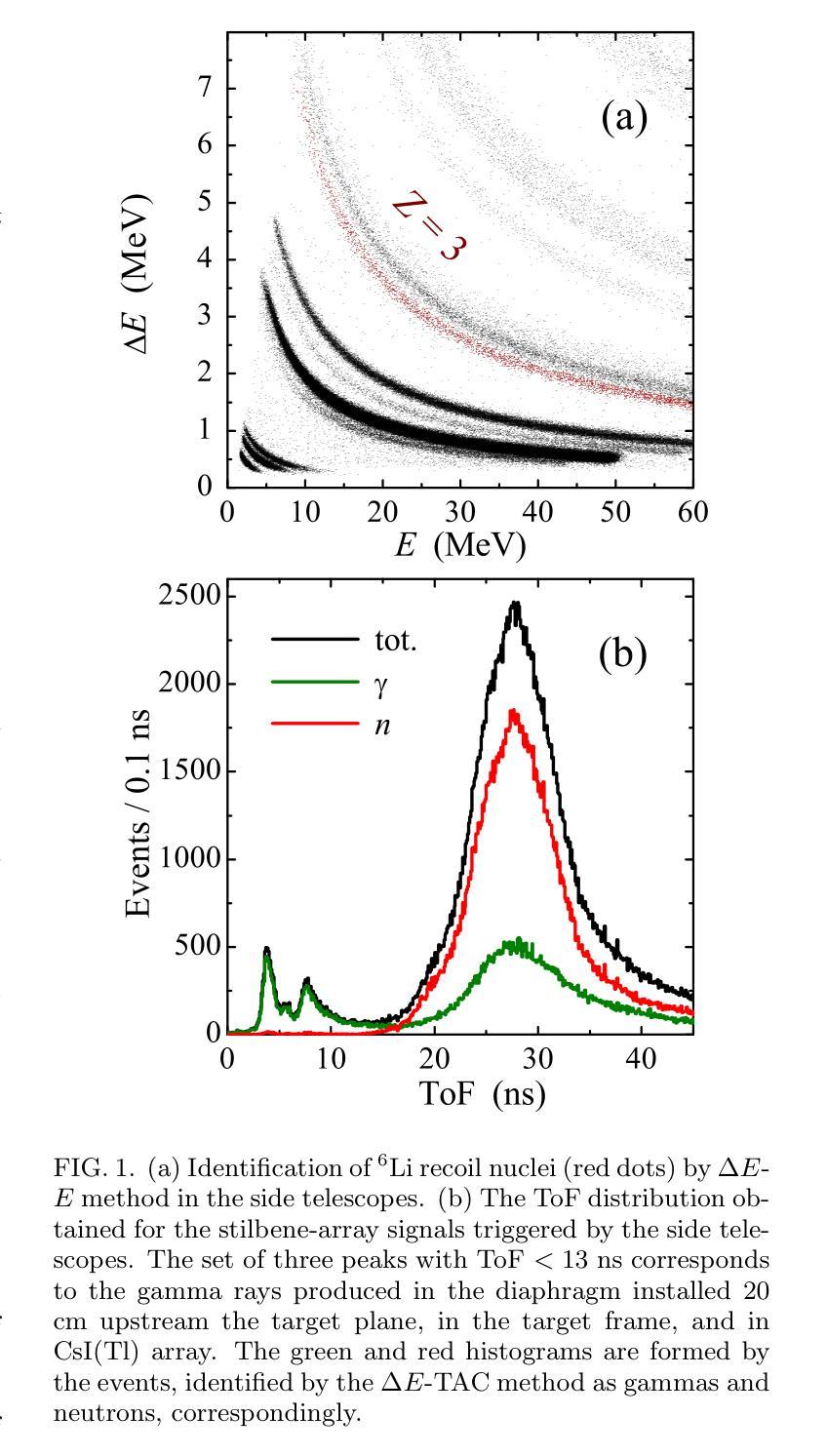
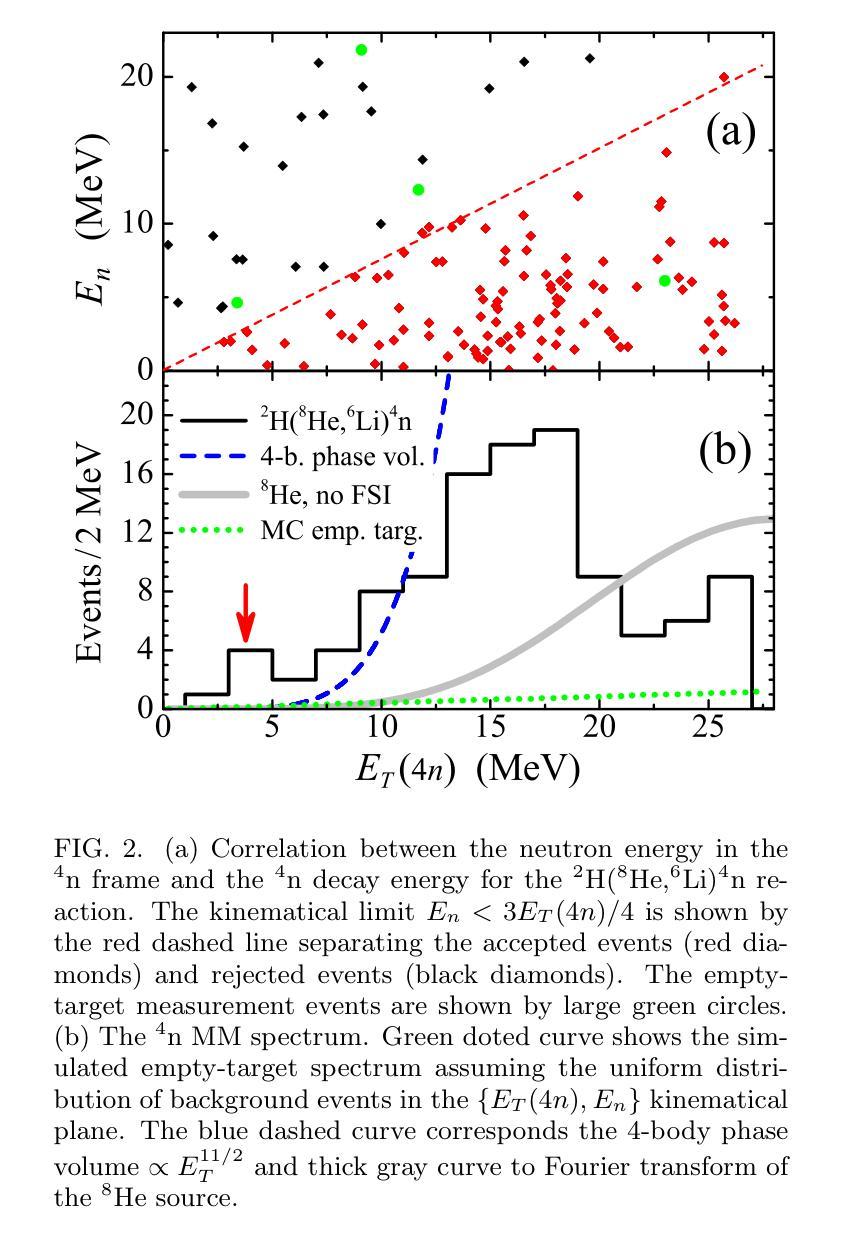
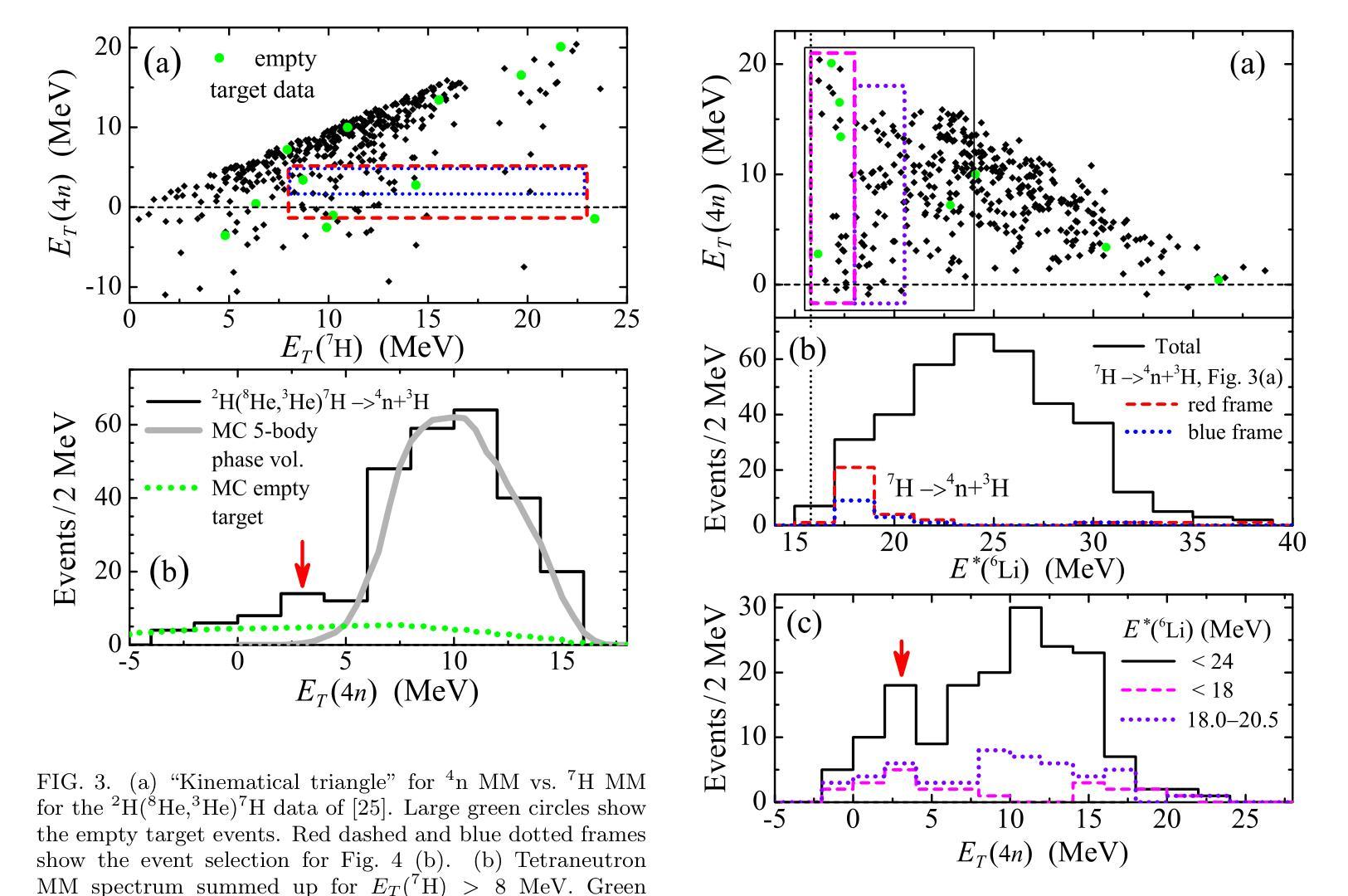
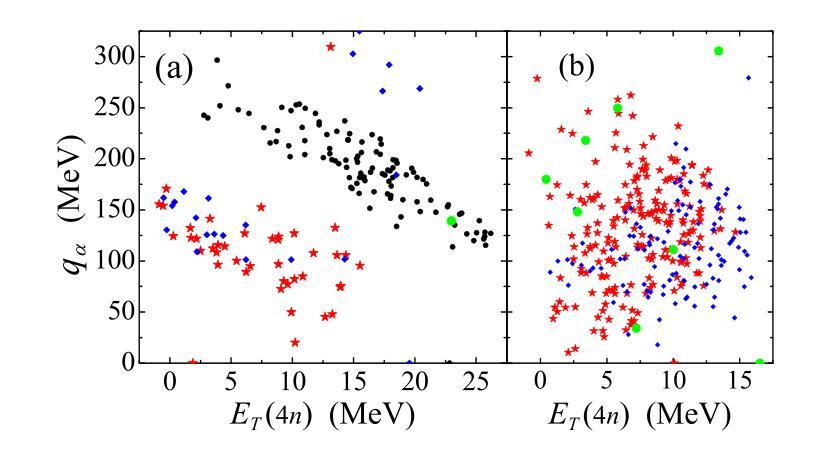
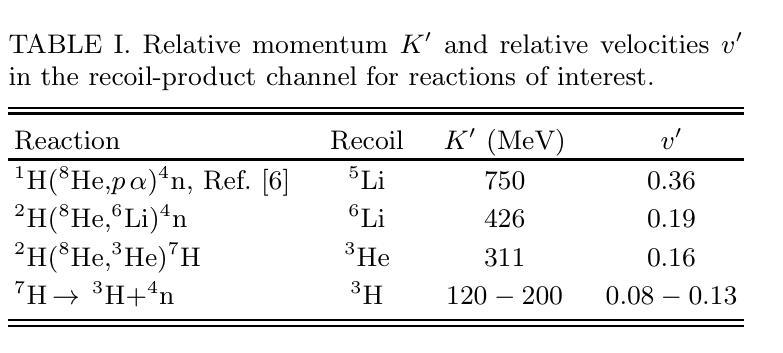
Search for the population of the low-energy continuum of a tetraneutron system was performed for reactions of the $^{8}$He beam on a deuterium target. These studies are based on the data [I.A. Muzalevskii \textit{et al.}, Phys.\ Rev.\ C \textbf{103}, 044313 (2021)], previously used for the studies of $^{7}$H and $^{6}$H in the $^2\text{H}(^8\text{He},{^3\text{He}})^{7}$H and $^2\text{H}(^8\text{He},{^4\text{He}})^{6}$H reactions. Evidence for a hump in the $^4$n continuum at $3.5 \pm 0.7$ and $3.2 \pm 0.8$ MeV was observed in the $^2$H($^8$He,$^6$Li)$^4$n and $^2$H($^8$He,$^3$He)$^7$H$\rightarrow ^3$H+$^4$n reactions, respectively. The observed statistics is quite low (6 events and up to 40 events) corresponding to very low cross sections of few microbarns or tens of microbarns. The background conditions for the $^2$H($^8$He,$^6$Li)$^4$n reaction are shown to be good, favoring the physical nature of the observed events. The $^2$H($^8$He,$^3$He)$^7$H$\rightarrow ^3$H+$^4$n process transforms to the $^2$H($^8$He,$^6$Li$^{\ast})^4n$ reaction in the limit of the highest $^7$H decay energies. The population of the low-energy region in the $^{4}$n spectrum is found to be perfectly correlated with the population of the lowest $^{6}$Li state in the $^{3}$He+$^{3}$H continuum with $E^*=18$ MeV. Theoretical calculations of $^{8}$He in a five-body $\alpha$+$4n$ and of $^{4}$n in a four-body hyperspherical models are presented. The $^{8}$He wave function is shown to contain strong specific correlations, which may give rise to very low-energy structures in tetraneutron continuum in extreme-peripheral reaction scenarios.
对四中子系统低能连续谱的人口搜索,是通过对$^{8}$He束与氘靶的反应进行的。这些研究基于[I.A. Muzalevskii等人,物理评论C(Phys. Rev. C)\textbf{103},044313(2021年)]的数据,之前曾用于研究$^{7}$H和$^{6}$H在$^2\text{H}(^8\text{He},{^3\text{He}})^{7}$H和$^2\text{H}(^8\text{He},{^4\text{He}})^{6}$H的反应。在$^2$H($^8$He,$^6$Li)$^4$n和$^2$H($^8$He,$^3$He)$^7$H$\rightarrow ^3$H+$^4$n的反应中,观察到$^4$n连续谱在$3.5 \pm 0.7$和$3.2 \pm 0.8$MeV处存在凸起。所观察到的统计数字相当低(6个事件和最多40个事件),对应于少数微巴或数十微巴的截面。对于$^2$H($^8$He,$^6$Li)$^4$n反应的背景条件表明情况良好,有利于观察到的事件的物理性质。在最高$^7$H衰变能的极限条件下,$^2$H($^8$He,$^3$He)$^7$H$\rightarrow ^3$H+$^4$n过程转化为$^2$H($^8$He,$^6$Li$^{\ast})^4n$反应。发现$^{4}$n光谱的低能区的种群与$^{3}$He+$^{3}$H连续体中最低$^{6}$Li态(E*=18MeV)的种群密切相关。给出了五体$\alpha$+$4n$的四中子模型和四体超球模型的理论计算。$^{8}$He波函数显示出强烈的特定相关性,可能在极端周边反应情况下导致四中子连续谱的极低能结构。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 9 figures
Summary
对$^{8}$He束在氘靶上的反应进行了四中子连续统低能区的搜索研究。基于以往对$^{7}$H和$^{6}$H的研究数据,观察到$^4$n连续统中存在$3.5 \pm 0.7$和$3.2 \pm 0.8$MeV的凸起。对应事件数量较少,对应的截面较小,背景条件良好。理论计算展示了$^{8}$He的五体$\alpha$+$4n$和$^{4}$n的四体超球模型。$^{8}$He波函数含有强烈的特定关联,可能在极端外围反应场景中导致四中子连续统的极低能结构。
Key Takeaways
- 对$^{8}$He束在氘靶上的反应进行了搜索研究,目的是寻找四中子连续统的低能区域。
- 基于之前对$^{7}$H和$^{6}$H的研究数据进行分析。
- 在$^4$n连续统中观察到凸起结构,能量约为$3.5 \pm 0.7$和$3.2 \pm 0.8$MeV。
- 事件数量较少,对应的截面较小,背景条件良好,增强了观察到的这些事件的物理真实性。
- 存在一个转换过程:$^2$H($^8$He,$^3$He)$^7$H$\rightarrow ^3$H+$^4$n在最高$^7$H能量极限下变为$^2$H($^8$He,$^6$Li$^{\ast})^4n$反应。
- 低能区域的四中子谱与最低的第6个Li状态在第3个He和第3个H连续体中有着完美的相关性。
点此查看论文截图