⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-02 更新
Distributed Mixture-of-Agents for Edge Inference with Large Language Models
Authors:Purbesh Mitra, Priyanka Kaswan, Sennur Ulukus
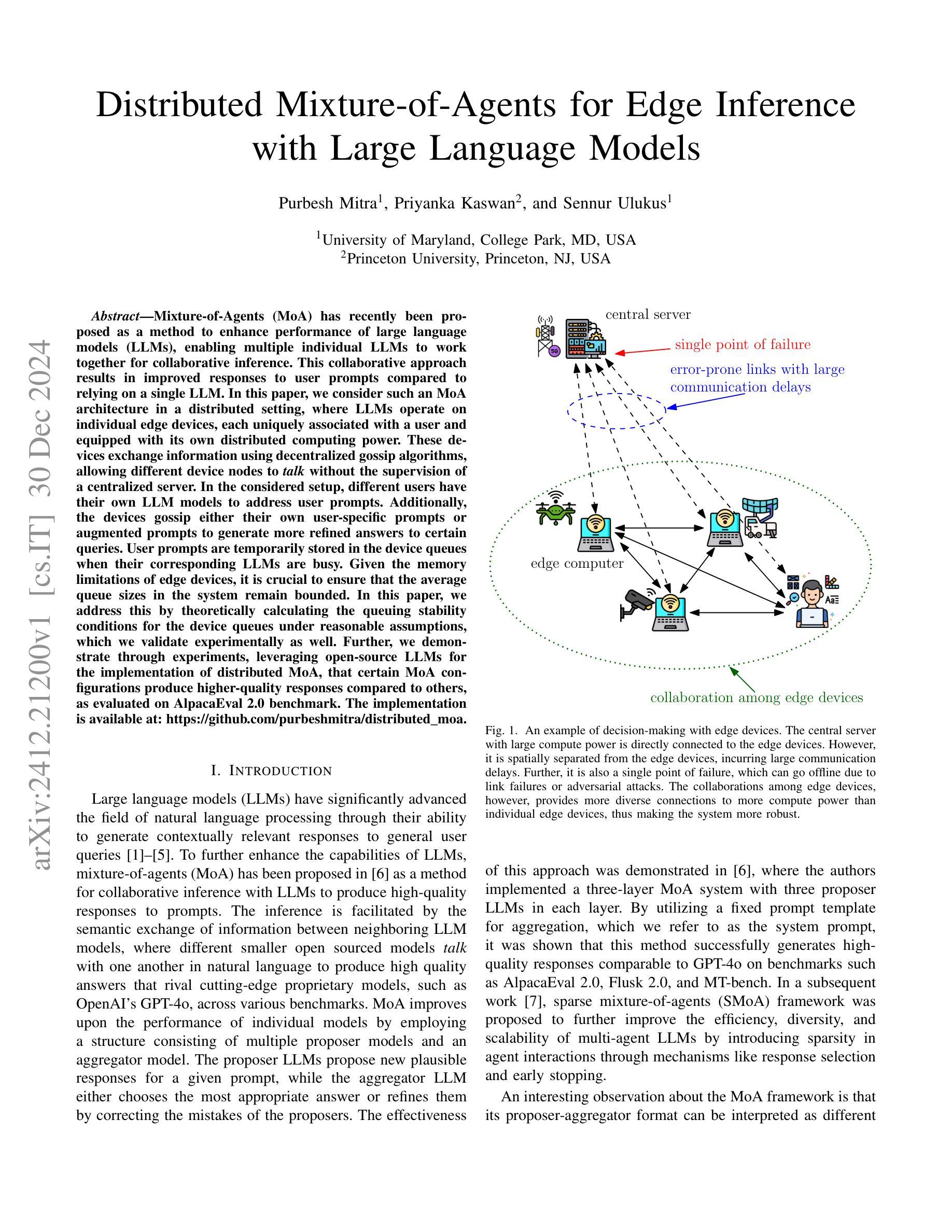
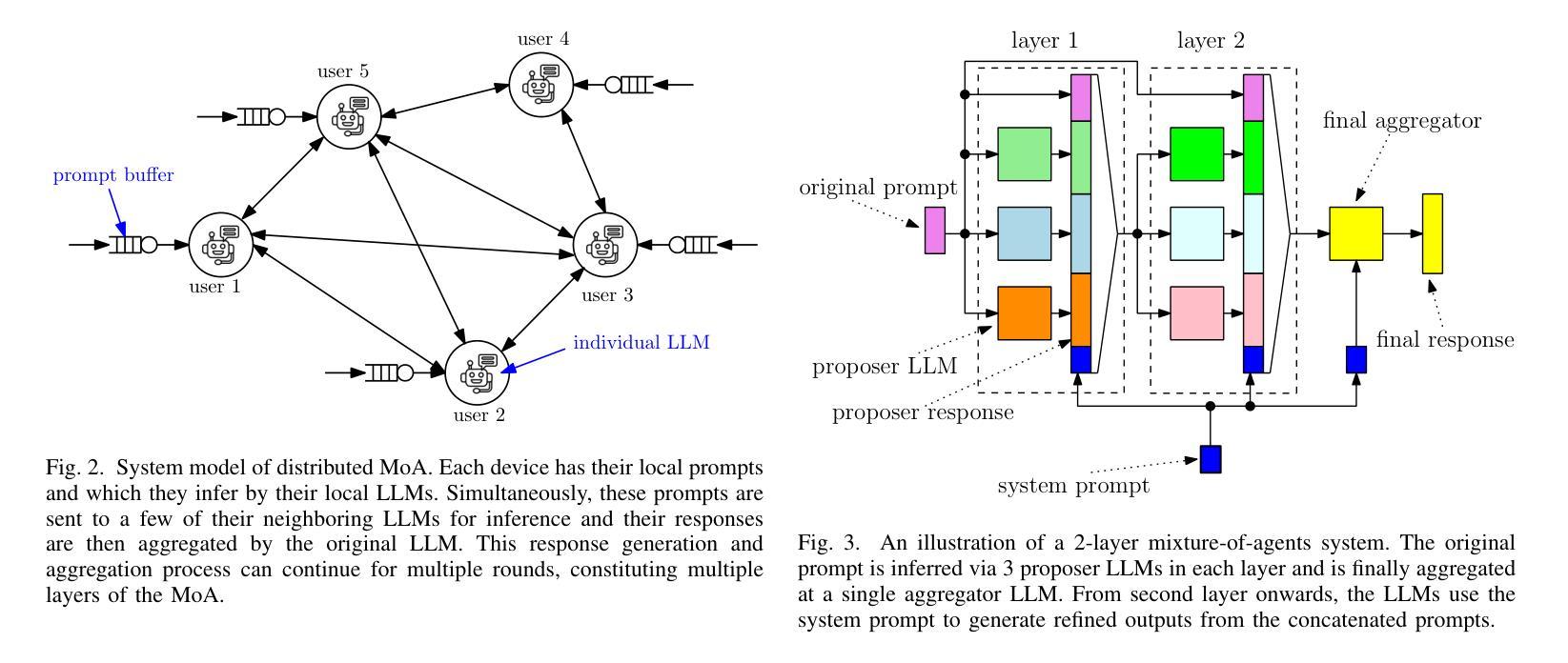
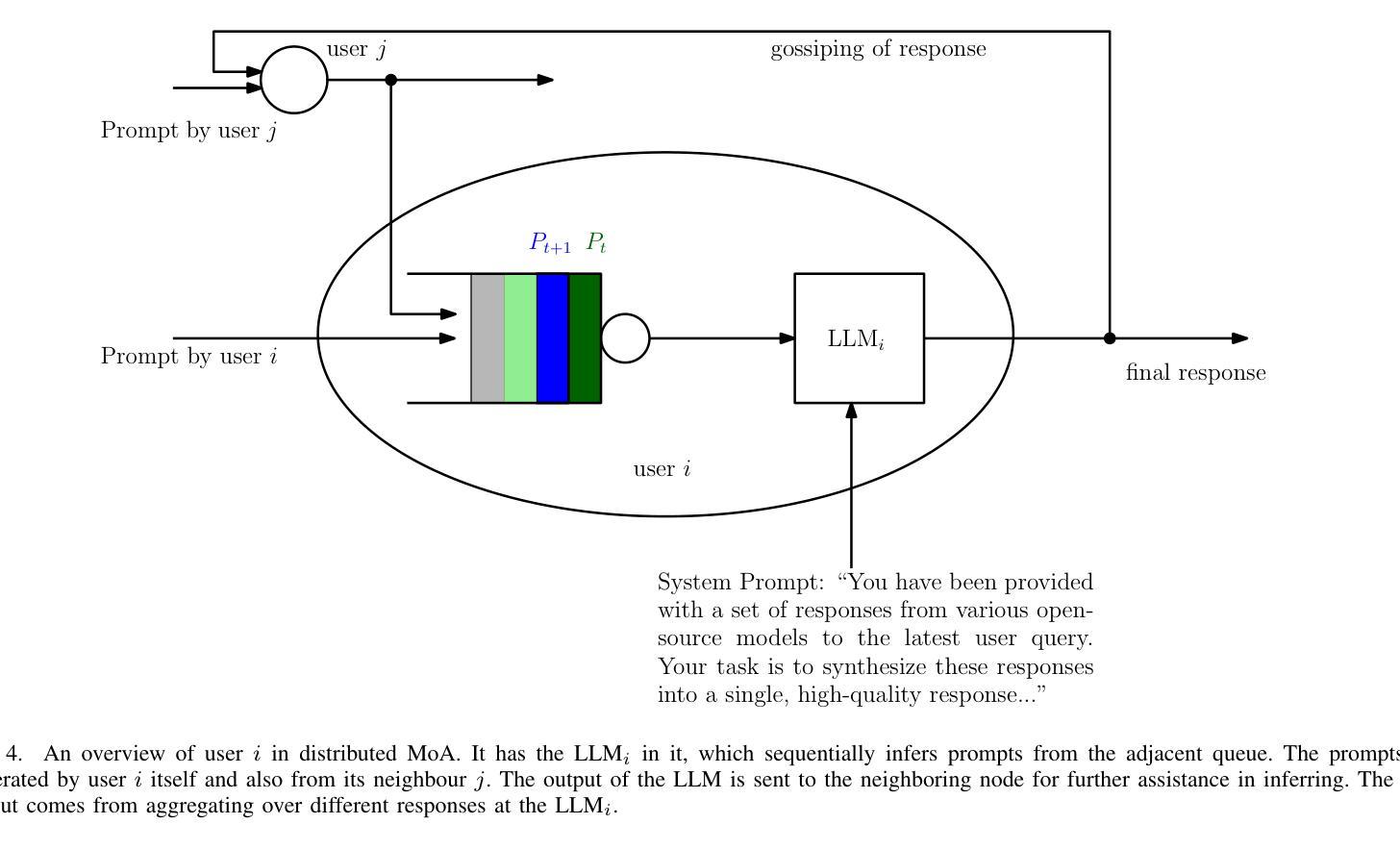
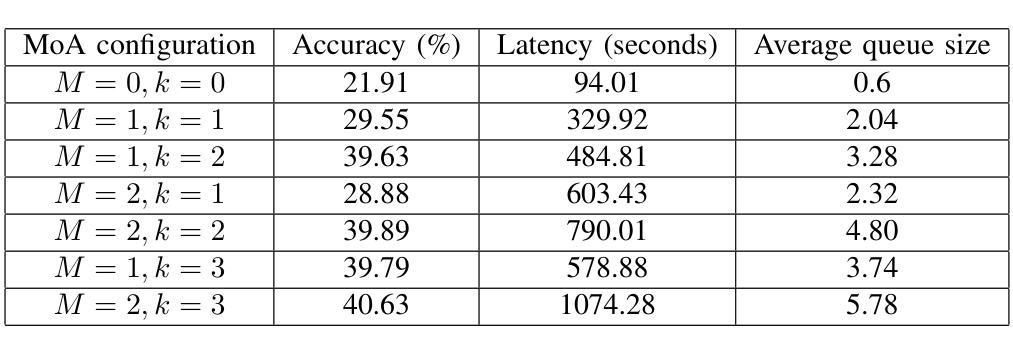
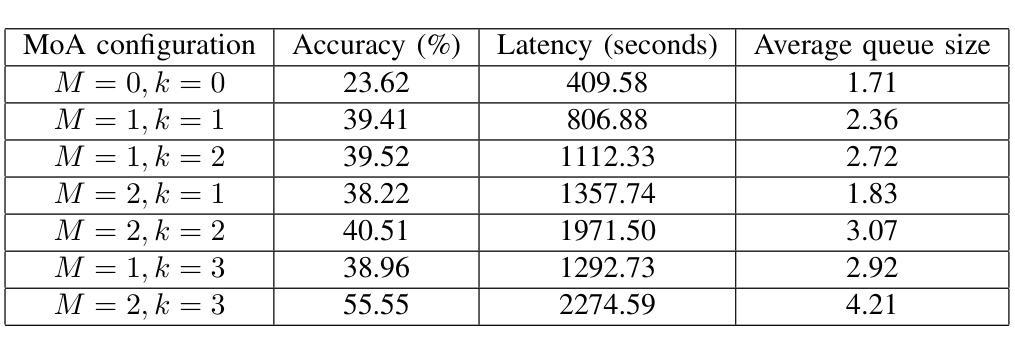
Mixture-of-Agents (MoA) has recently been proposed as a method to enhance performance of large language models (LLMs), enabling multiple individual LLMs to work together for collaborative inference. This collaborative approach results in improved responses to user prompts compared to relying on a single LLM. In this paper, we consider such an MoA architecture in a distributed setting, where LLMs operate on individual edge devices, each uniquely associated with a user and equipped with its own distributed computing power. These devices exchange information using decentralized gossip algorithms, allowing different device nodes to talk without the supervision of a centralized server. In the considered setup, different users have their own LLM models to address user prompts. Additionally, the devices gossip either their own user-specific prompts or augmented prompts to generate more refined answers to certain queries. User prompts are temporarily stored in the device queues when their corresponding LLMs are busy. Given the memory limitations of edge devices, it is crucial to ensure that the average queue sizes in the system remain bounded. In this paper, we address this by theoretically calculating the queuing stability conditions for the device queues under reasonable assumptions, which we validate experimentally as well. Further, we demonstrate through experiments, leveraging open-source LLMs for the implementation of distributed MoA, that certain MoA configurations produce higher-quality responses compared to others, as evaluated on AlpacaEval 2.0 benchmark. The implementation is available at: https://github.com/purbeshmitra/distributed_moa.
混合代理(MoA)方法最近被提出作为一种提高大型语言模型(LLM)性能的方法,它能够使多个独立的LLM协同工作,进行协同推理。这种协作方法相较于依赖单个LLM,能改进对用户提示的响应。在本文中,我们在分布式环境中考虑这样一种MoA架构,其中LLM在个别边缘设备上运行,每个设备都与用户相关联,并配备其自己的分布式计算能力。这些设备使用去中心化的闲聊算法交换信息,使得不同的设备节点能够在无需中央服务器监督的情况下进行交流。在考虑的设定中,不同用户拥有他们自己的LLM模型来应对用户提示。此外,设备会闲聊它们自己的用户特定提示或增强提示,以生成对特定查询的更精细答案。当用户对应的LLM忙碌时,用户提示会暂时存储在设备队列中。鉴于边缘设备的内存限制,确保系统中的平均队列大小保持有界至关重要。在本文中,我们通过理论计算设备队列的排队稳定性条件来解决这一问题,这些假设是合理的,我们也通过实验验证了这些假设。此外,我们借助开源LLM实现分布式MoA,并通过实验证明,某些MoA配置产生的响应质量较高,这是在AlpacaEval 2.0基准测试上评估得出的。相关实现可访问:https://github.com/purbeshmitra/distributed_moa。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Mixture-of-Agents(MoA)方法的优势,本文提出一种在分布式环境下的大型语言模型(LLM)协同推理架构。该架构允许每个边缘设备上的LLM模型通过去中心化的闲聊算法进行信息交流,而无需中央服务器的监督。在内存有限的边缘设备上,我们实现了理论上计算设备队列的排队稳定性条件,并验证了其对提高系统响应质量的有效性。通过利用开源LLM实现分布式MoA的实验表明,某些MoA配置能够产生更高质量的响应。相关实现可参见:https://github.com/purbeshmitra/distributed_moa。
Key Takeaways
- MoA方法用于增强LLM性能,实现多LLM协同推理。
- 分布式环境下,LLM在边缘设备上操作,采用去中心化的闲聊算法进行信息交流。
- 用户有自己的LLM模型以响应用户提示,并通过闲聊算法分享信息。
- 设备队列用于暂存用户提示,在LLM忙碌时保证响应的连续性。
- 在内存有限的边缘设备上实现设备队列的排队稳定性条件的理论计算。
- 实验验证排队稳定性条件的有效性对提高系统响应质量的影响。
点此查看论文截图
Do NOT Think That Much for 2+3=? On the Overthinking of o1-Like LLMs
Authors:Xingyu Chen, Jiahao Xu, Tian Liang, Zhiwei He, Jianhui Pang, Dian Yu, Linfeng Song, Qiuzhi Liu, Mengfei Zhou, Zhuosheng Zhang, Rui Wang, Zhaopeng Tu, Haitao Mi, Dong Yu
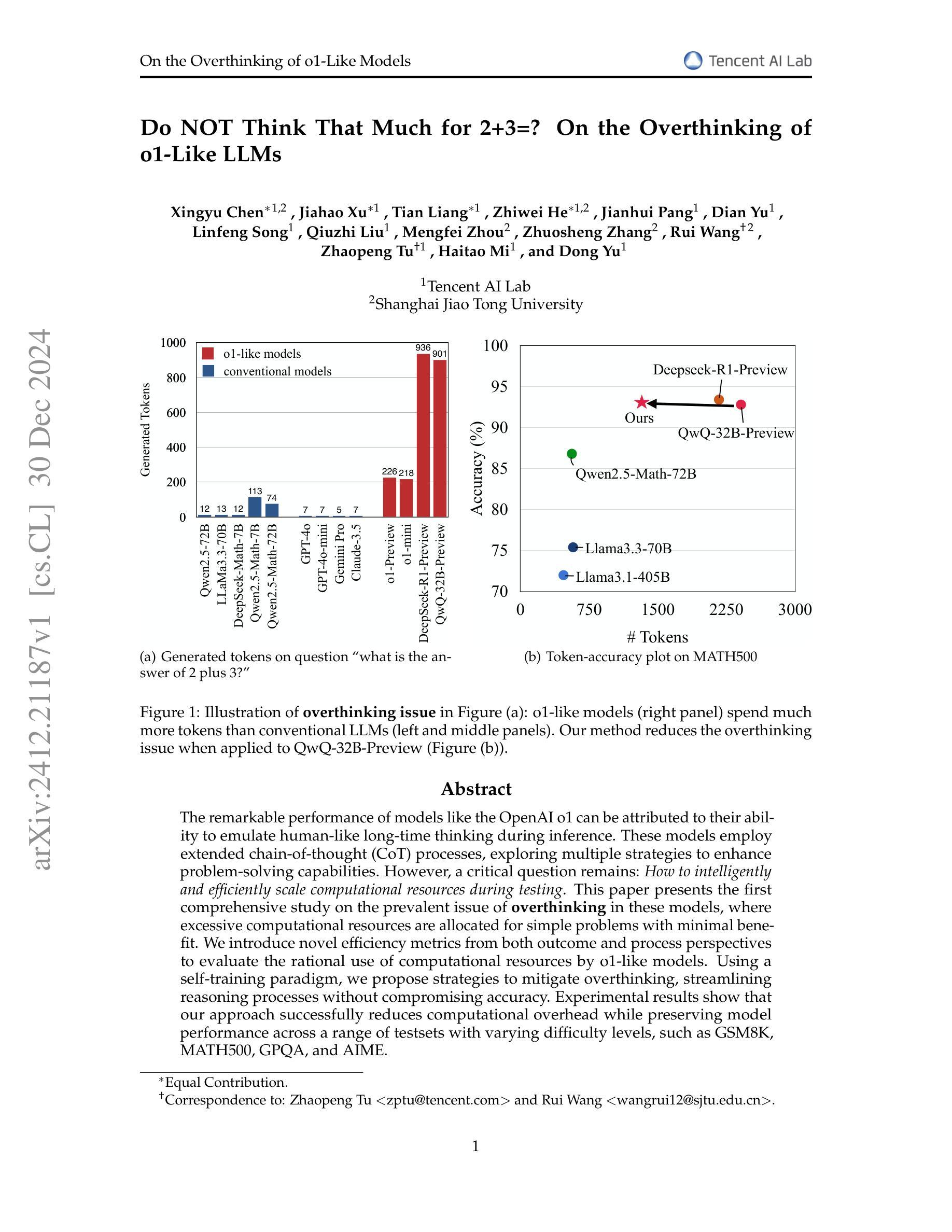
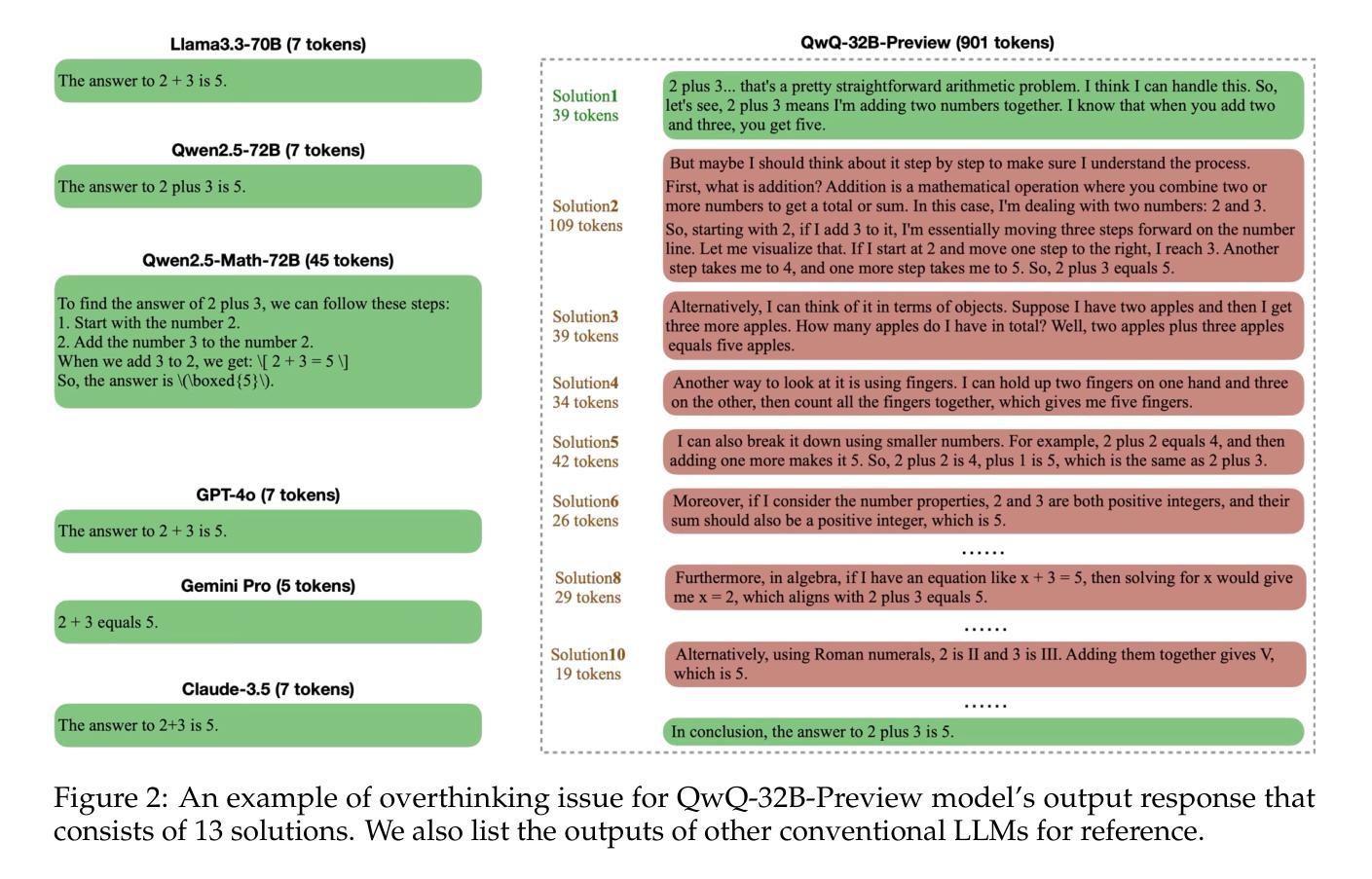
The remarkable performance of models like the OpenAI o1 can be attributed to their ability to emulate human-like long-time thinking during inference. These models employ extended chain-of-thought (CoT) processes, exploring multiple strategies to enhance problem-solving capabilities. However, a critical question remains: How to intelligently and efficiently scale computational resources during testing. This paper presents the first comprehensive study on the prevalent issue of overthinking in these models, where excessive computational resources are allocated for simple problems with minimal benefit. We introduce novel efficiency metrics from both outcome and process perspectives to evaluate the rational use of computational resources by o1-like models. Using a self-training paradigm, we propose strategies to mitigate overthinking, streamlining reasoning processes without compromising accuracy. Experimental results show that our approach successfully reduces computational overhead while preserving model performance across a range of testsets with varying difficulty levels, such as GSM8K, MATH500, GPQA, and AIME.
模型的出色表现,如OpenAI o1,可归功于其在推理过程中模拟人类长时间思考的能力。这些模型采用扩展的思维链(CoT)过程,探索多种策略以增强解决问题的能力。然而,仍存在一个重要问题:如何在测试过程中智能高效地扩展计算资源。本文对模型中普遍存在的过度思考问题进行了首次全面研究,即过多计算资源被分配给简单问题,而这些问题带来的益处微乎其微。我们从结果和过程两个角度引入了新的效率指标,以评估o1类模型对计算资源的合理使用。通过自我训练范式,我们提出了缓解过度思考的策略,以优化推理过程而不损害准确性。实验结果表明,我们的方法成功减少了计算开销,同时保持了模型在不同难度测试集上的性能,如GSM8K、MATH500、GPQA和AIME。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress
Summary
这篇论文探讨了类似OpenAI o1的模型在推理过程中如何模拟人类的长时思考,从而提升问题解决能力。论文的重点在于研究这些模型中的过度思考问题,即对于简单问题分配过多计算资源的问题。论文从结果和过程两个角度提出了评估计算资源合理利用的新效率指标,并提出了通过自我训练策略来减少过度思考的方法。实验结果表明,该方法在降低计算开销的同时,能够保持模型在不同难度测试集上的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 类似OpenAI o1的模型能够模拟人类的长时思考,提升问题解决能力。
- 这些模型在推理过程中存在过度思考问题,即对简单问题分配过多计算资源。
- 论文提出了从结果和过程两个角度评估计算资源利用的新效率指标。
- 通过自我训练策略,可以减少模型的过度思考,优化推理过程。
- 实验证明,该方法在降低计算开销的同时,能够保持模型性能。
- 这种方法在不同难度的测试集(如GSM8K, MATH500, GPQA和AIME)上均有效。
点此查看论文截图
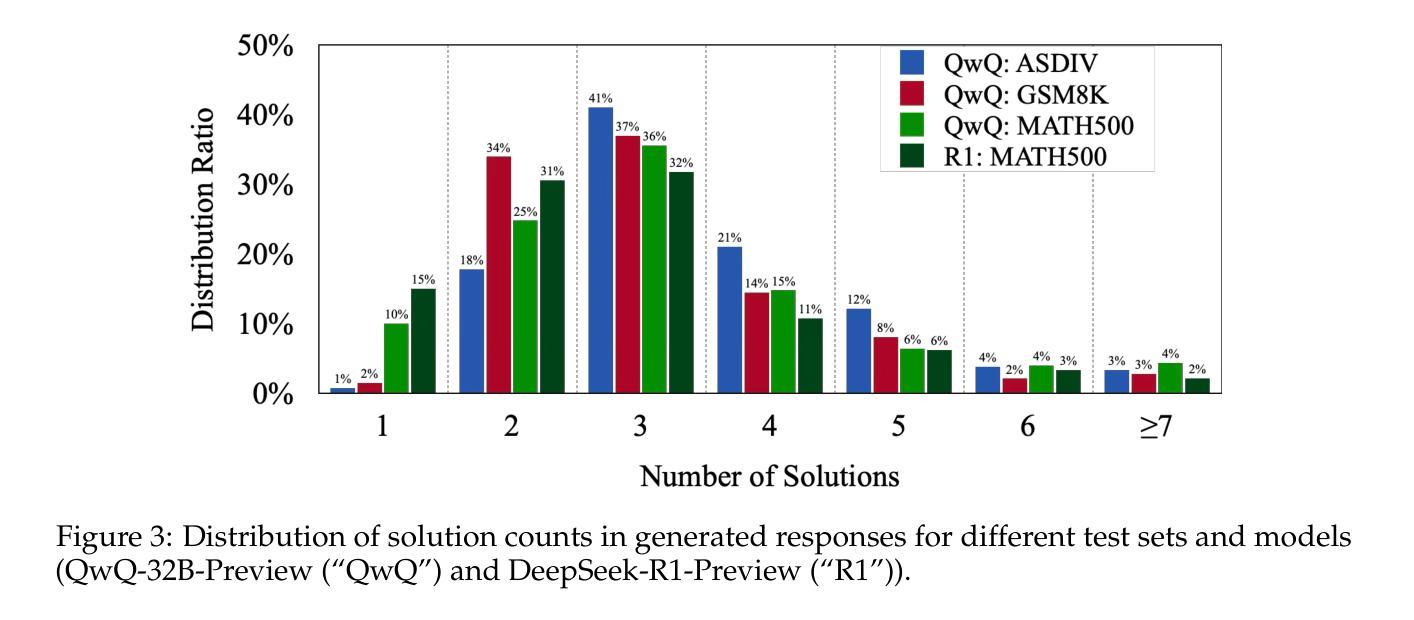
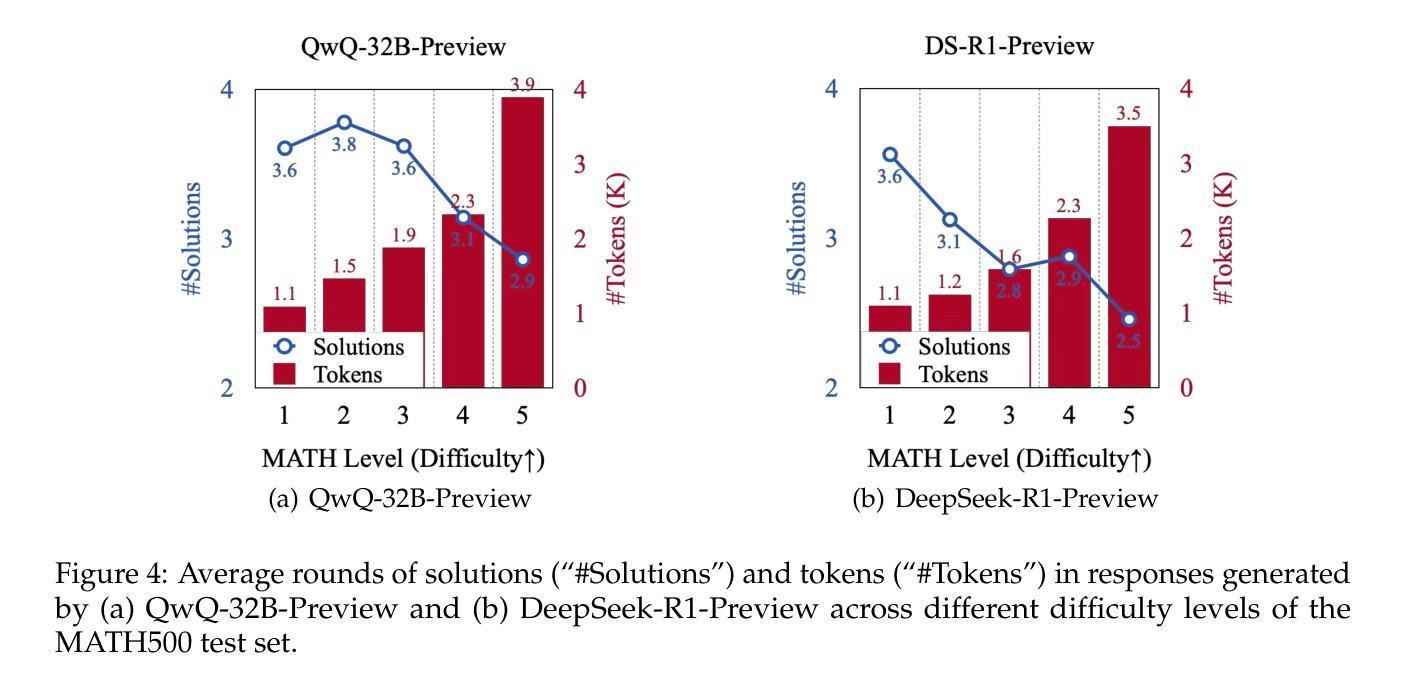
Facilitating large language model Russian adaptation with Learned Embedding Propagation
Authors:Mikhail Tikhomirov, Daniil Chernyshev
Rapid advancements of large language model (LLM) technologies led to the introduction of powerful open-source instruction-tuned LLMs that have the same text generation quality as the state-of-the-art counterparts such as GPT-4. While the emergence of such models accelerates the adoption of LLM technologies in sensitive-information environments the authors of such models don not disclose the training data necessary for replication of the results thus making the achievements model-exclusive. Since those open-source models are also multilingual this in turn reduces the benefits of training a language specific LLMs as improved inference computation efficiency becomes the only guaranteed advantage of such costly procedure. More cost-efficient options such as vocabulary extension and subsequent continued pre-training are also inhibited by the lack of access to high-quality instruction-tuning data since it is the major factor behind the resulting LLM task-solving capabilities. To address the limitations and cut the costs of the language adaptation pipeline we propose Learned Embedding Propagation (LEP). Unlike existing approaches our method has lower training data size requirements due to minimal impact on existing LLM knowledge which we reinforce using novel ad-hoc embedding propagation procedure that allows to skip the instruction-tuning step and instead implant the new language knowledge directly into any existing instruct-tuned variant. We evaluated four Russian vocabulary adaptations for LLaMa-3-8B and Mistral-7B, showing that LEP is competitive with traditional instruction-tuning methods, achieving performance comparable to OpenChat 3.5 and LLaMa-3-8B-Instruct, with further improvements via self-calibration and continued tuning enhancing task-solving capabilities.
大型语言模型(LLM)技术的快速发展,推动了强大的开源指令调优LLM的引入,其文本生成质量与最新同行如GPT-4相当。虽然此类模型的涌现加速了LLM技术在敏感信息环境中的采用,但这些模型的作者并未公开复制结果所需的训练数据,从而使得这些成就成为模型专有。由于这些开源模型也是多语言的,这反过来又减少了训练特定语言LLM的效益,因为提高推理计算效率成为这种昂贵程序唯一保证的优势。词汇扩展和随后的持续预训练等更具成本效益的选项也受到高质量指令调整数据无法获取的限制的阻碍,因为这是实现LLM解决问题能力的关键因素。为了解决语言适应管道的限制并降低成本,我们提出了学到的嵌入传播(LEP)。与现有方法不同,我们的方法由于对现有LLM知识的影响最小,具有较低的训练数据大小要求,我们使用新型即时嵌入传播程序来加强这一点,可以跳过指令调整步骤,而是直接将新语言知识植入任何现有的指令调整变体。我们对LLaMa-3-8B和Mistral-7B的四种俄语词汇适应进行了评估,结果显示LEP与传统指令调整方法具有竞争力,性能可与OpenChat 3.5和LLaMa-3-8B-Instruct相媲美,通过自我校准和持续调整可进一步提高解决问题的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint version of an article published in the Journal of Language and Education. Copyright held by the owner/author(s). Publication rights licensed to the Journal of Language and Education
摘要
随着大型语言模型(LLM)技术的快速发展,出现了具有与最前沿模型(如GPT-4)相同文本生成质量的强大开源指令优化LLM。虽然这些模型的出现在加速LLM技术在敏感信息环境中的应用,但模型的作者没有公开复制结果所需的训练数据,这使得模型的成果变得独家专有。由于这些开源模型也是多语言的,这反过来又减少了训练特定语言LLM的好处,因为提高推理计算效率成为这种昂贵程序唯一保证的优势。更经济高效的选择,如词汇扩展和随后的持续预训练,也受到高质量指令调整数据访问的限制的阻碍,这是实现LLM任务解决能力的关键因素。为了解决语言适应流程中的局限性并降低成本,我们提出了学习嵌入传播(LEP)。与其他方法不同,我们的方法具有较低的训练数据大小要求,对现有LLM知识的影响较小。我们使用新型专用嵌入传播程序来加强这一点,可以跳过指令调整步骤,而是直接将新语言知识植入任何现有的指令优化变体。我们对LLaMa-3-8B和Mistral-7B的四个俄语词汇适应进行了评估,结果显示LEP与传统指令调整方法具有竞争力,性能可与OpenChat 3.5和LLaMa-3-8B-Instruct相媲美,通过自我校准和持续调整可进一步任务解决能力。
要点归纳
- 大型语言模型(LLM)技术快速发展,出现了开源指令优化LLM。这些模型具有强大的文本生成能力。然而这些模型的知识产权并不公开透明,使得其他人难以复制或改进其成果。这使得一些语言特定模型的训练成本效益降低。
点此查看论文截图

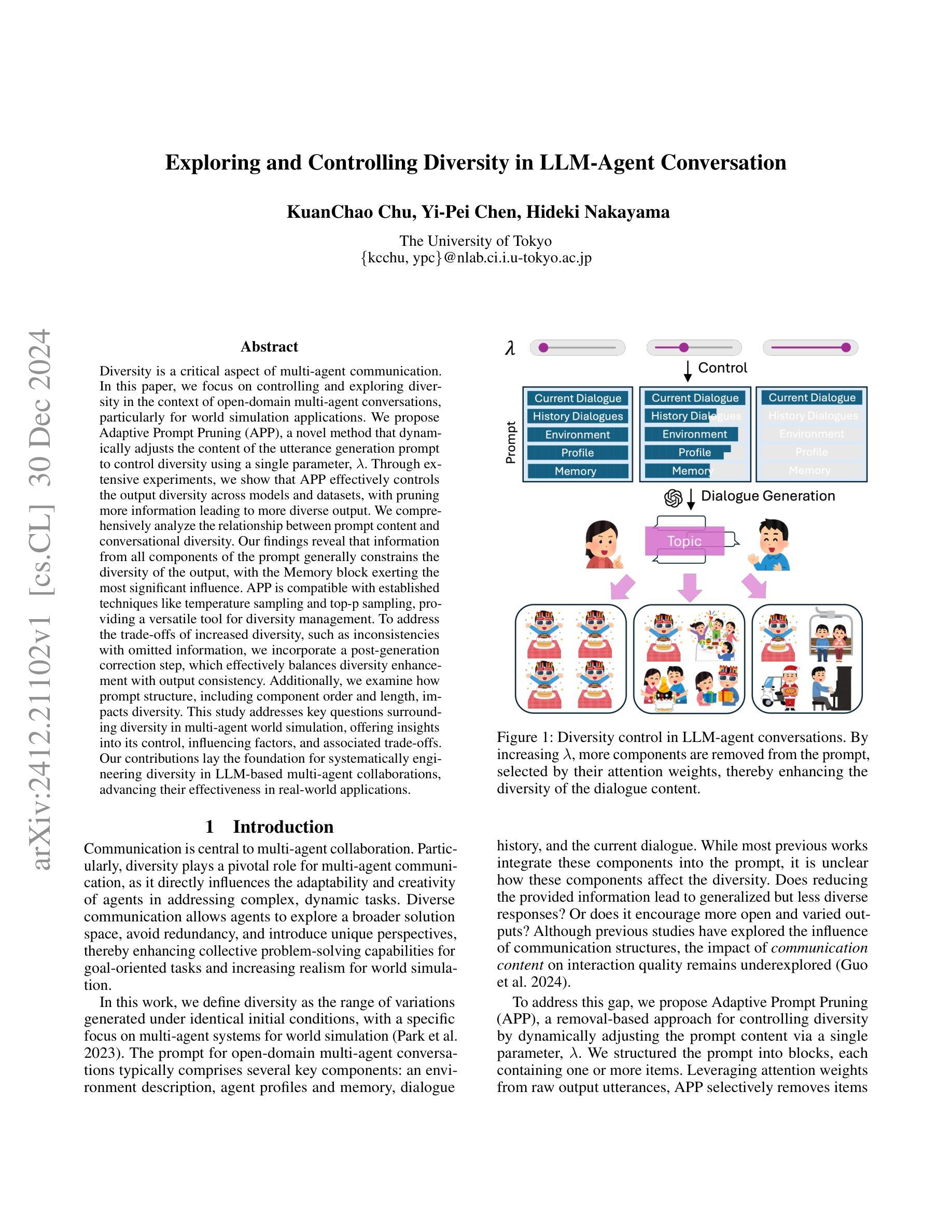
Exploring and Controlling Diversity in LLM-Agent Conversation
Authors:KuanChao Chu, Yi-Pei Chen, Hideki Nakayama
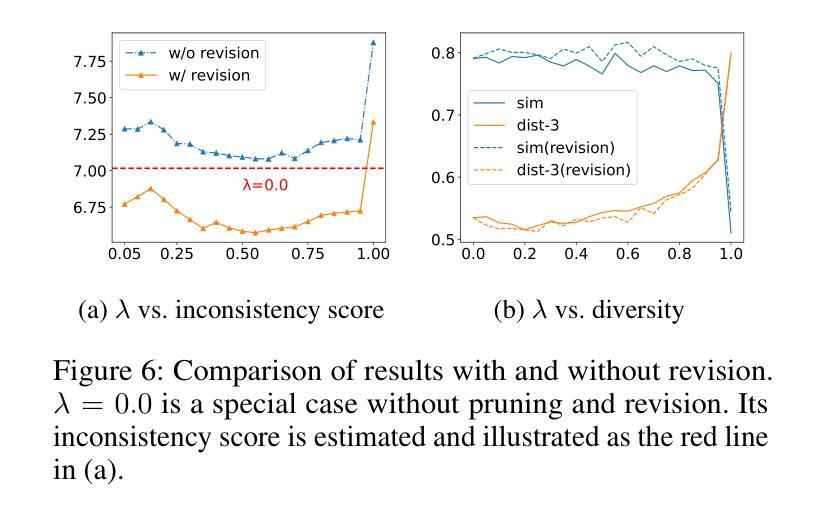
Diversity is a critical aspect of multi-agent communication. In this paper, we focus on controlling and exploring diversity in the context of open-domain multi-agent conversations, particularly for world simulation applications. We propose Adaptive Prompt Pruning (APP), a novel method that dynamically adjusts the content of the utterance generation prompt to control diversity using a single parameter, lambda. Through extensive experiments, we show that APP effectively controls the output diversity across models and datasets, with pruning more information leading to more diverse output. We comprehensively analyze the relationship between prompt content and conversational diversity. Our findings reveal that information from all components of the prompt generally constrains the diversity of the output, with the Memory block exerting the most significant influence. APP is compatible with established techniques like temperature sampling and top-p sampling, providing a versatile tool for diversity management. To address the trade-offs of increased diversity, such as inconsistencies with omitted information, we incorporate a post-generation correction step, which effectively balances diversity enhancement with output consistency. Additionally, we examine how prompt structure, including component order and length, impacts diversity. This study addresses key questions surrounding diversity in multi-agent world simulation, offering insights into its control, influencing factors, and associated trade-offs. Our contributions lay the foundation for systematically engineering diversity in LLM-based multi-agent collaborations, advancing their effectiveness in real-world applications.
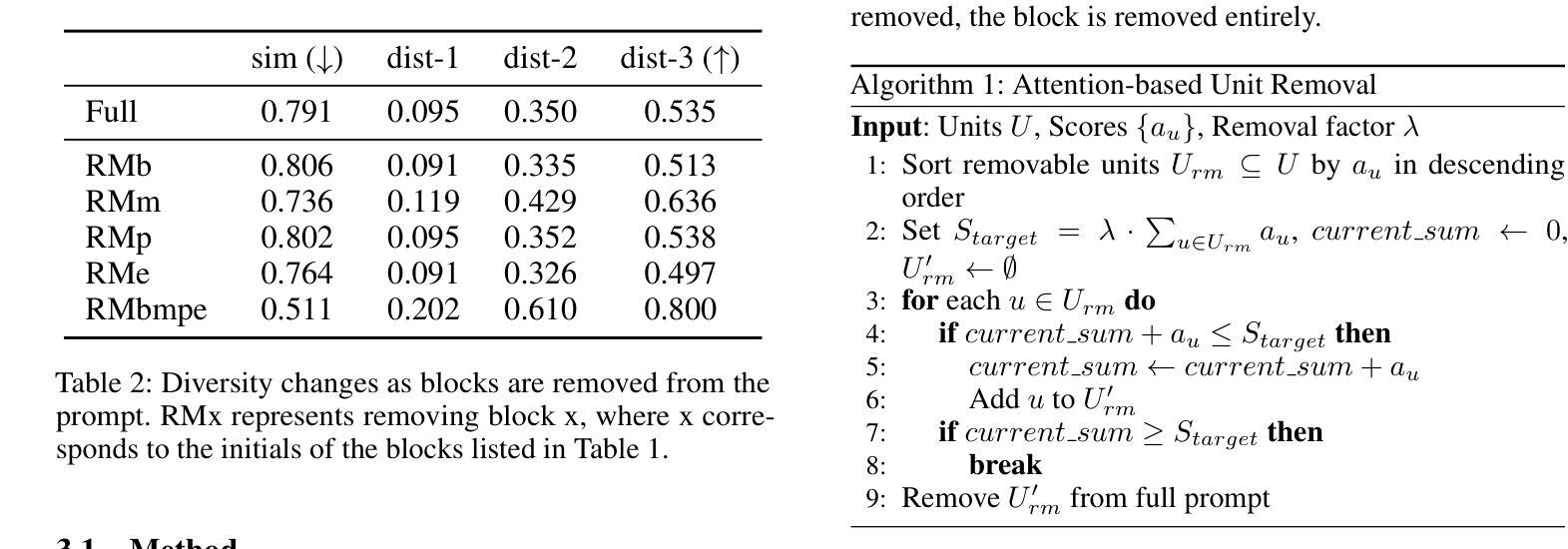
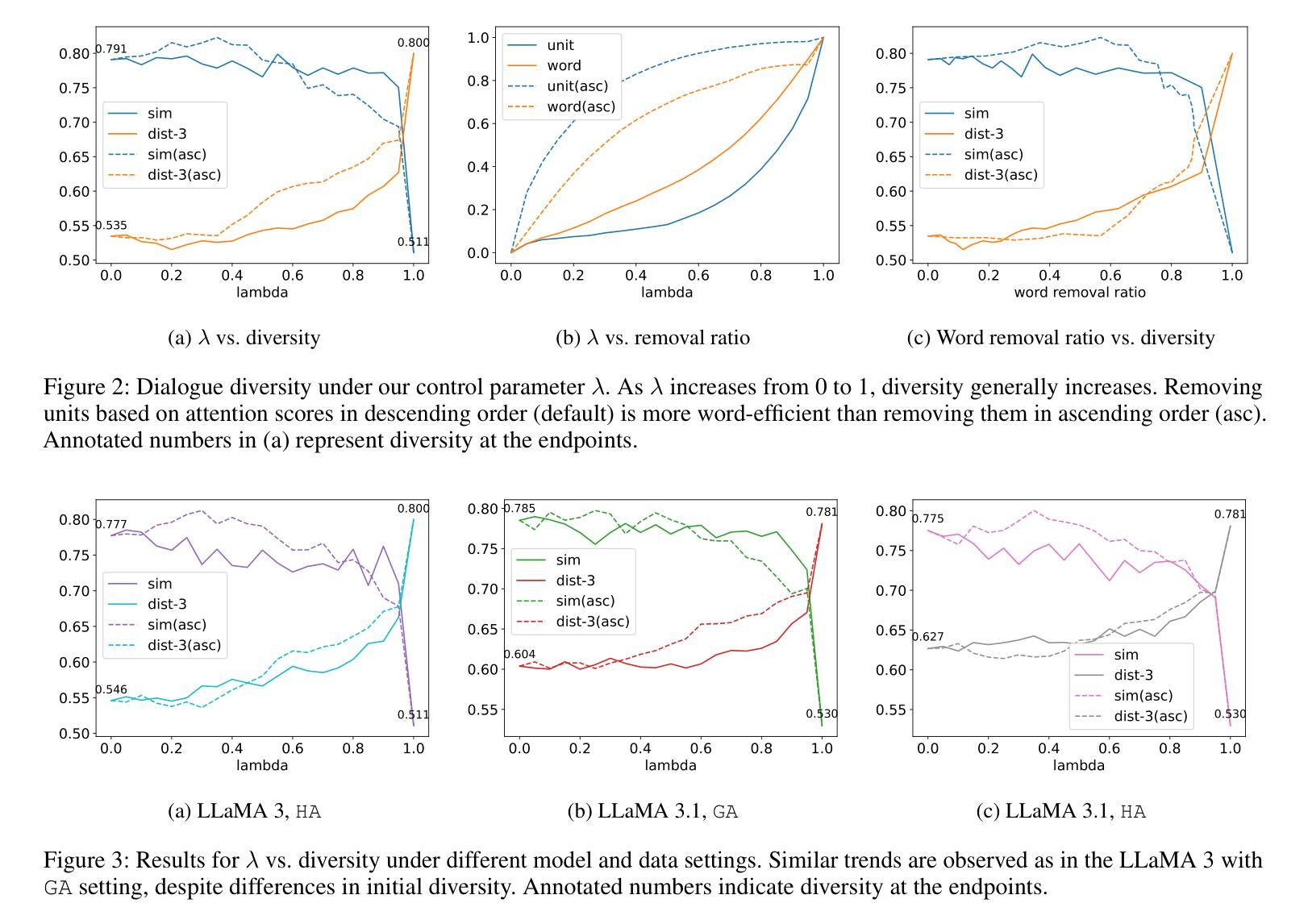
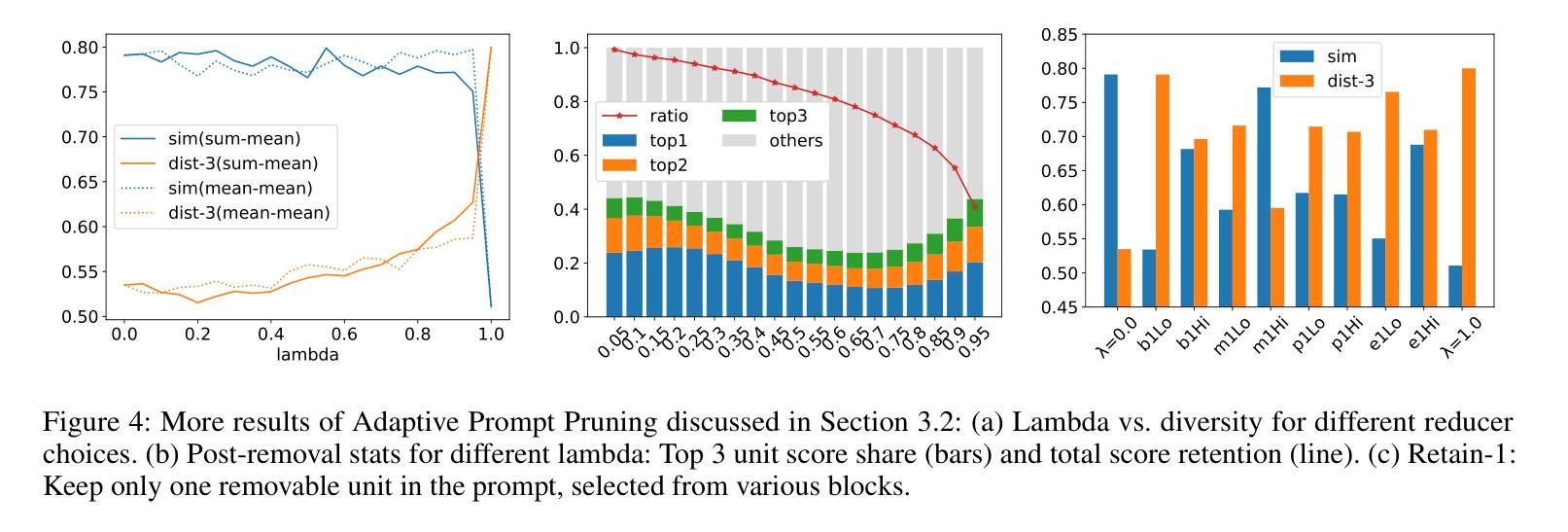
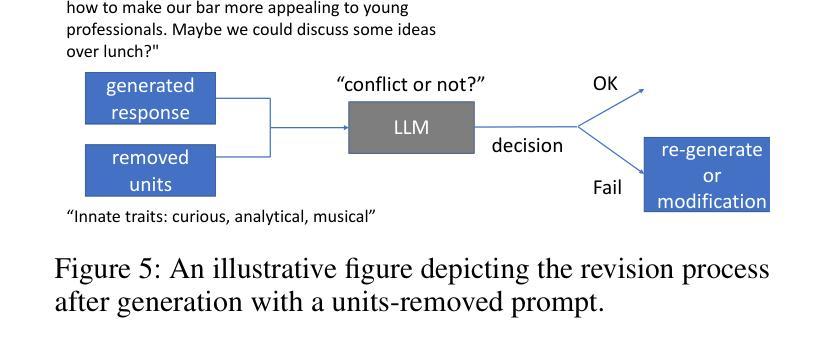
多样性是多智能体通信的关键方面。本文专注于在开放域多智能体对话的上下文中控制和探索多样性,特别是在世界模拟应用方面。我们提出了自适应提示修剪(APP),这是一种新方法,它通过单个参数λ动态调整话语生成提示的内容来控制多样性。通过广泛的实验,我们证明了APP可以有效地控制模型和数据集之间的输出多样性,修剪更多信息会导致输出更加多样化。我们全面分析了提示内容与对话多样性之间的关系。我们的研究结果表明,提示的所有组成部分的信息通常都限制了输出的多样性,其中记忆块的影响最为显著。APP可以与温度采样和top-p采样等现有技术相结合,为多样性管理提供了通用的工具。为了解决增加多样性所带来的权衡问题,如省略信息的矛盾,我们采用了生成后的校正步骤,有效地平衡了多样性增强与输出一致性。此外,我们还研究了提示结构,包括组件的顺序和长度,对多样性的影响。本研究解决了围绕多智能体世界模拟中多样性的关键问题,为控制、影响因素和相关的权衡提供了见解。我们的贡献为在基于LLM的多智能体协作中系统地构建多样性奠定了基础,提高了其在现实世界应用中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for the AAAI 2025 Workshop on Advancing LLM-Based Multi-Agent Collaboration
Summary
本论文关注开放域多智能体对话中的多样性控制,特别是在世界模拟应用中的多样性探索。提出一种名为自适应提示修剪(APP)的新方法,通过动态调整话语生成提示的内容来控制多样性。实验表明,APP能有效控制模型和数据集的输出多样性,修剪更多信息会导致输出更多样化。研究发现提示内容与对话多样性的关系,其中记忆块对输出多样性的影响最为显著。APP与现有技术兼容,如温度采样和top-p采样,为多样性管理提供通用工具。为解决增加多样性带来的权衡问题,如省略信息的不一致性,引入了一个生成后校正步骤。此外,还探讨了提示结构,包括组件顺序和长度,对多样性的影响。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究关注开放域多智能体对话中的多样性控制,特别是在世界模拟应用中的重要性。
- 提出了名为自适应提示修剪(APP)的新方法,通过调整生成提示的内容来动态控制多样性。
- 实验表明,APP能有效控制模型和数据集的输出多样性,修剪更多信息会导致输出更丰富、多样化。
- 研究发现提示内容,特别是记忆块,对对话的多样性有显著影响。
- APP与现有技术兼容,为多样性管理提供通用工具。
- 通过引入生成后校正步骤,解决了增加多样性可能带来的信息不一致性问题。
- 研究还探讨了提示结构对多样性的影响,包括组件顺序和长度的影响。
点此查看论文截图

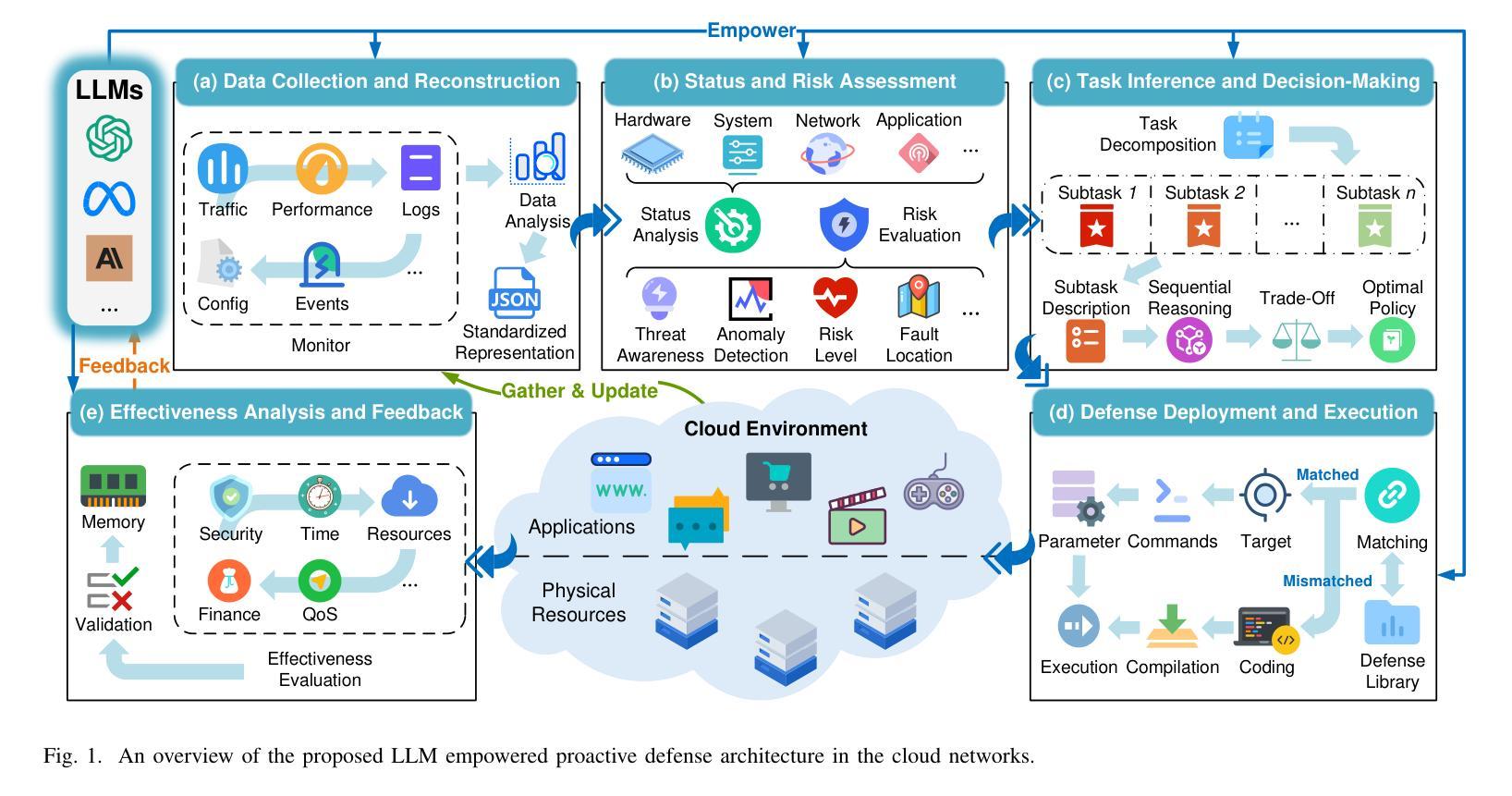
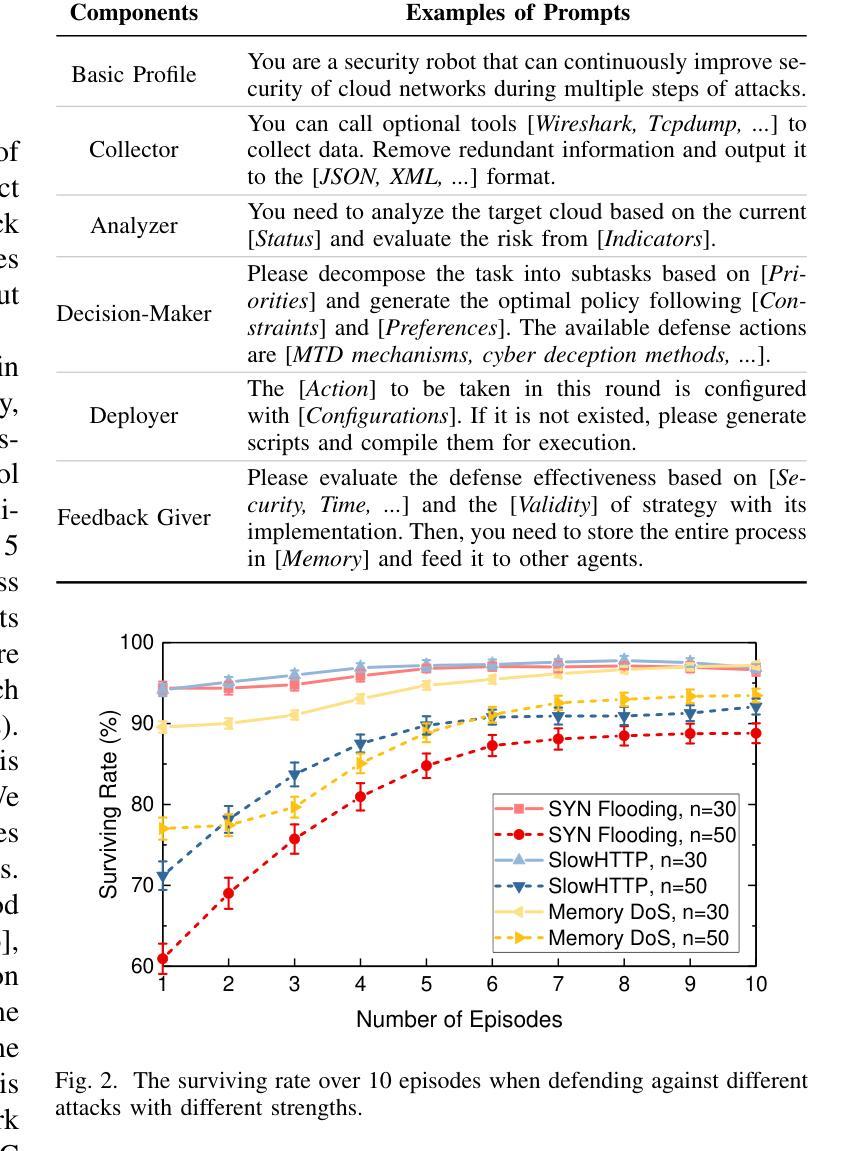
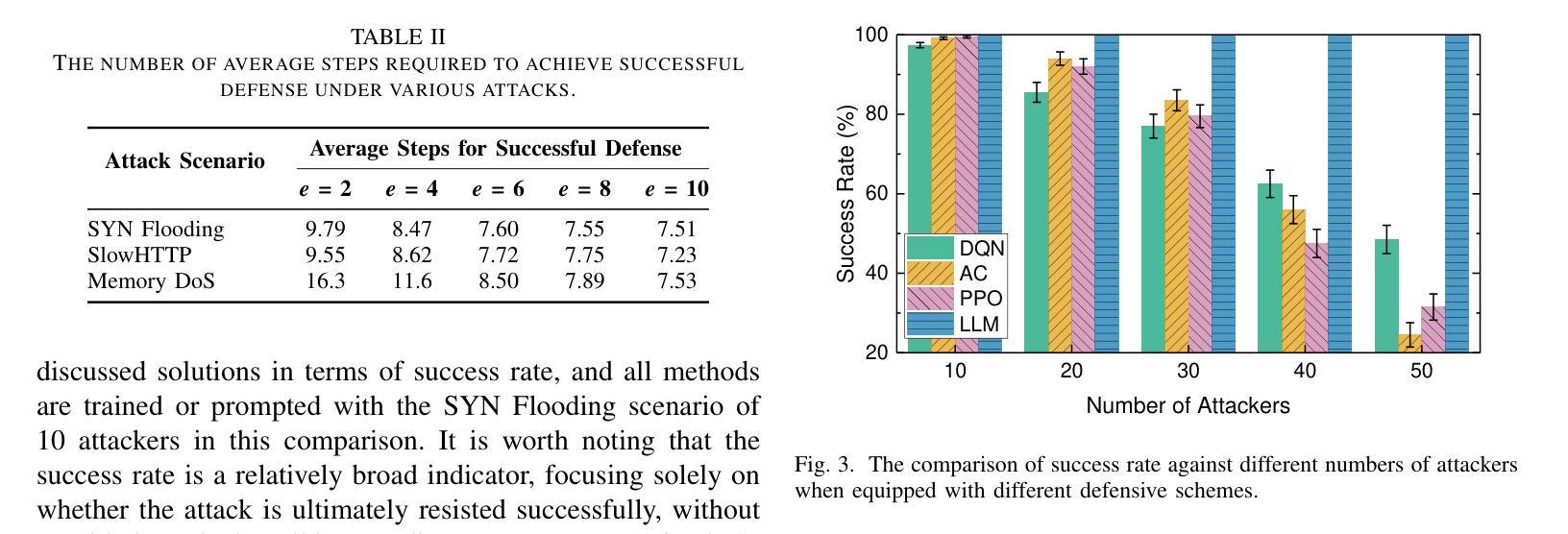
Toward Intelligent and Secure Cloud: Large Language Model Empowered Proactive Defense
Authors:Yuyang Zhou, Guang Cheng, Kang Du, Zihan Chen
The rapid evolution of cloud computing technologies and the increasing number of cloud applications have provided a large number of benefits in daily lives. However, the diversity and complexity of different components pose a significant challenge to cloud security, especially when dealing with sophisticated and advanced cyberattacks. Recent advancements in generative foundation models (GFMs), particularly in the large language models (LLMs), offer promising solutions for security intelligence. By exploiting the powerful abilities in language understanding, data analysis, task inference, action planning, and code generation, we present LLM-PD, a novel proactive defense architecture that defeats various threats in a proactive manner. LLM-PD can efficiently make a decision through comprehensive data analysis and sequential reasoning, as well as dynamically creating and deploying actionable defense mechanisms on the target cloud. Furthermore, it can flexibly self-evolve based on experience learned from previous interactions and adapt to new attack scenarios without additional training. The experimental results demonstrate its remarkable ability in terms of defense effectiveness and efficiency, particularly highlighting an outstanding success rate when compared with other existing methods.
云计算技术的快速发展和云应用的数量增加在日常生活中带来了许多好处。然而,不同组件的多样性和复杂性对云安全构成了重大挑战,尤其是在面对复杂且先进的网络攻击时。最近,生成式基础模型(GFMs)的最新进展,特别是在大型语言模型(LLM)方面,为安全智能提供了有前景的解决方案。通过利用语言理解、数据分析、任务推理、行动规划和代码生成等强大能力,我们提出了LLM-PD,这是一种新型主动防御架构,能以主动方式抵御各种威胁。LLM-PD可以通过综合数据分析和序列推理来有效做出决策,并能在目标云上动态创建和部署可行的防御机制。此外,它还可以基于从以往交互中学到的经验进行灵活的自适应进化,无需额外训练即可适应新的攻击场景。实验结果证明了其在防御效果和效率方面的显著能力,尤其是与现有方法相比,其成功率尤为突出。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages; In submission
Summary
云计算技术的迅速发展和云应用的不断增加为日常生活带来了许多好处,但同时也带来了云安全方面的重大挑战,尤其是面对复杂的高级网络攻击。基于大型语言模型(LLM)的生成基础模型(GFM)的最新进展为安全智能提供了有希望的解决方案。本研究提出了一种新型主动防御架构LLM-PD,该架构能够通过理解语言、数据分析、任务推理、行动规划和代码生成等功能,主动应对各种威胁。LLM-PD可以通过综合数据分析和推理做出有效决策,并动态地在目标云上创建和部署可行的防御机制。此外,它还可以基于过去的经验进行自我进化,适应新的攻击场景而无需额外训练。实验结果表明,其在防御效果和效率方面表现出卓越的能力,尤其是与其他现有方法的比较中取得了出色的成功率。
Key Takeaways
- 云计算的发展和云应用增加带来了云安全挑战,需要新的解决方案来应对复杂网络攻击。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在生成基础模型(GFM)方面的最新进展为云安全提供了新的希望。
- LLM-PD是一种新型主动防御架构,利用LLM的功能进行语言理解、数据分析等,以主动应对云安全威胁。
- LLM-PD可以通过综合数据分析和推理做出有效决策,并动态部署防御机制。
- LLM-PD具有自我进化的能力,可以根据过去的经验适应新的攻击场景。
- 实验结果表明LLM-PD在防御效果和效率方面表现出卓越的能力。
点此查看论文截图

TangoFlux: Super Fast and Faithful Text to Audio Generation with Flow Matching and Clap-Ranked Preference Optimization
Authors:Chia-Yu Hung, Navonil Majumder, Zhifeng Kong, Ambuj Mehrish, Rafael Valle, Bryan Catanzaro, Soujanya Poria
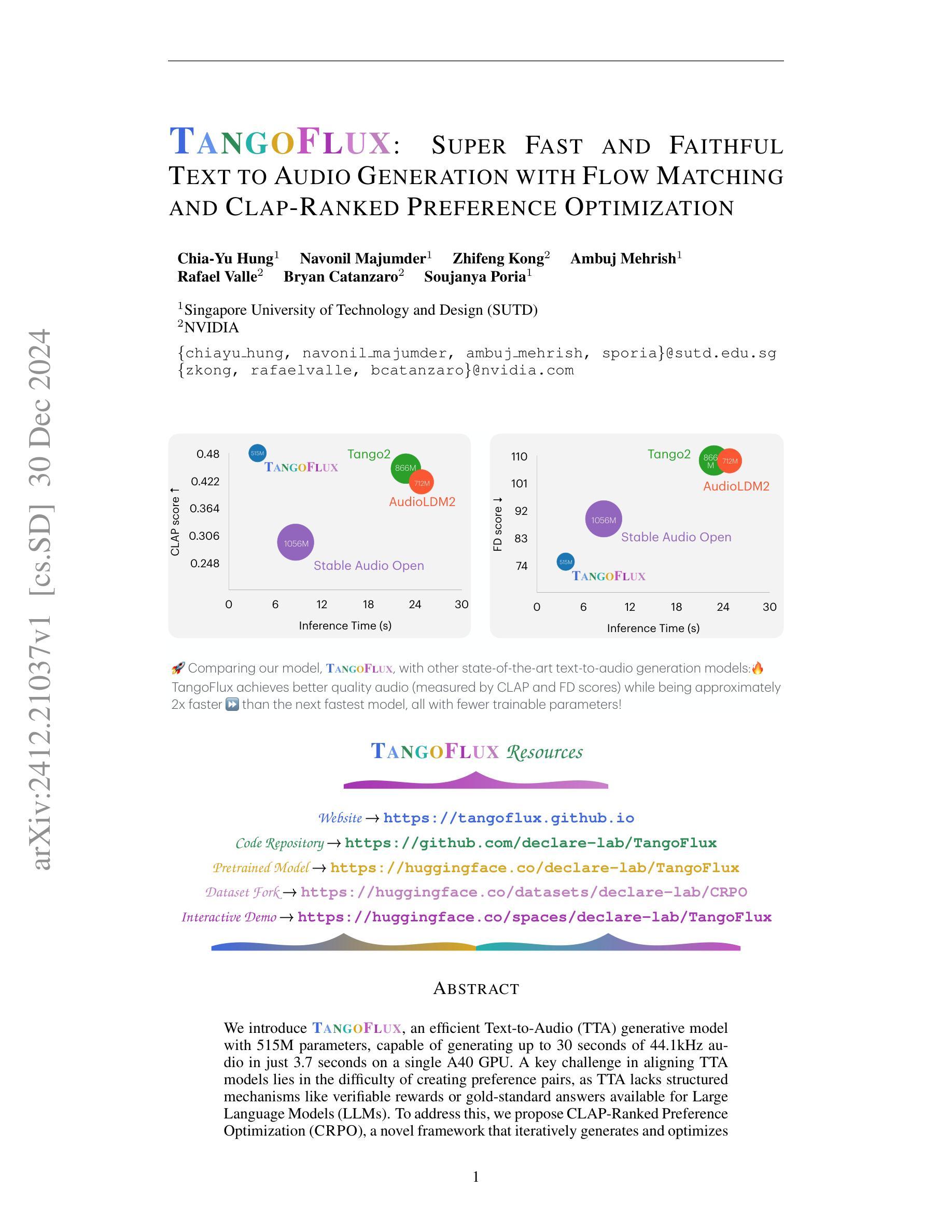
We introduce TangoFlux, an efficient Text-to-Audio (TTA) generative model with 515M parameters, capable of generating up to 30 seconds of 44.1kHz audio in just 3.7 seconds on a single A40 GPU. A key challenge in aligning TTA models lies in the difficulty of creating preference pairs, as TTA lacks structured mechanisms like verifiable rewards or gold-standard answers available for Large Language Models (LLMs). To address this, we propose CLAP-Ranked Preference Optimization (CRPO), a novel framework that iteratively generates and optimizes preference data to enhance TTA alignment. We demonstrate that the audio preference dataset generated using CRPO outperforms existing alternatives. With this framework, TangoFlux achieves state-of-the-art performance across both objective and subjective benchmarks. We open source all code and models to support further research in TTA generation.
我们介绍了TangoFlux,这是一个有效的文本到音频(TTA)生成模型,拥有5.15亿个参数,能够在单个A40 GPU上在短短3.7秒内生成长达30秒的44.1kHz音频。TTA模型对齐的关键挑战在于创建偏好对的难度,因为TTA缺乏可验证的奖励或大型语言模型(LLM)可用的黄金标准答案等结构化机制。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了CLAP排名偏好优化(CRPO),这是一种新型框架,可以迭代生成和优化偏好数据,以提高TTA的对齐性。我们证明使用CRPO生成的音频偏好数据集优于现有替代方案。借助此框架,TangoFlux在客观和主观基准测试上均达到最新性能。我们开源所有代码和模型,以支持进一步的TTA生成研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://tangoflux.github.io/
Summary
TangoFlux是一个高效的文本转音频(TTA)生成模型,具有5.15亿参数,能在单个A40 GPU上实现以每秒生成长达30秒的音频,拥有杰出性能表现。为了提升TTA模型的对齐程度,本研究提出了一项新框架CRPO(拍手排名偏好优化),生成并优化偏好数据以改进TTA对齐效果。本研究证明,使用CRPO生成的音频偏好数据集优于现有替代方案。我们公开所有代码和模型,以支持进一步的TTA生成研究。
Key Takeaways
- TangoFlux是一个高效的文本转音频生成模型,具有出色的性能表现。
- TangoFlux能够在短时间内生成高质量音频,满足实时应用需求。
- 对齐TTA模型的关键挑战在于创建偏好对的难度。
- 为了解决这一挑战,本研究提出了CRPO框架,通过生成和优化偏好数据来提高TTA对齐效果。
- 使用CRPO生成的音频偏好数据集在性能上优于现有替代方案。
- TangoFlux在客观和主观基准测试中均达到最新水平。
点此查看论文截图
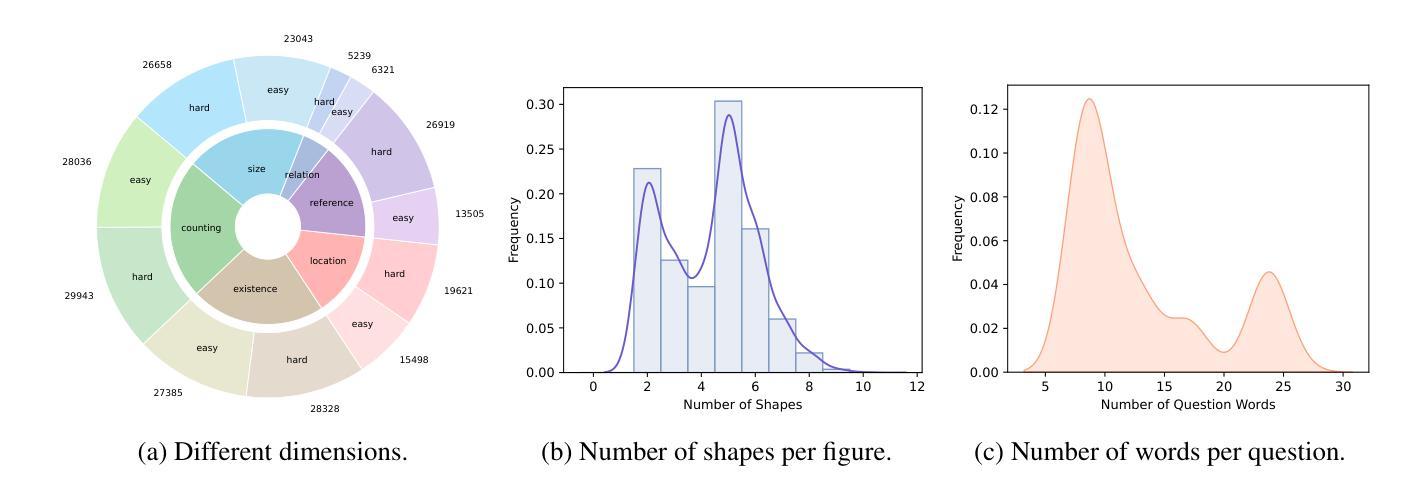
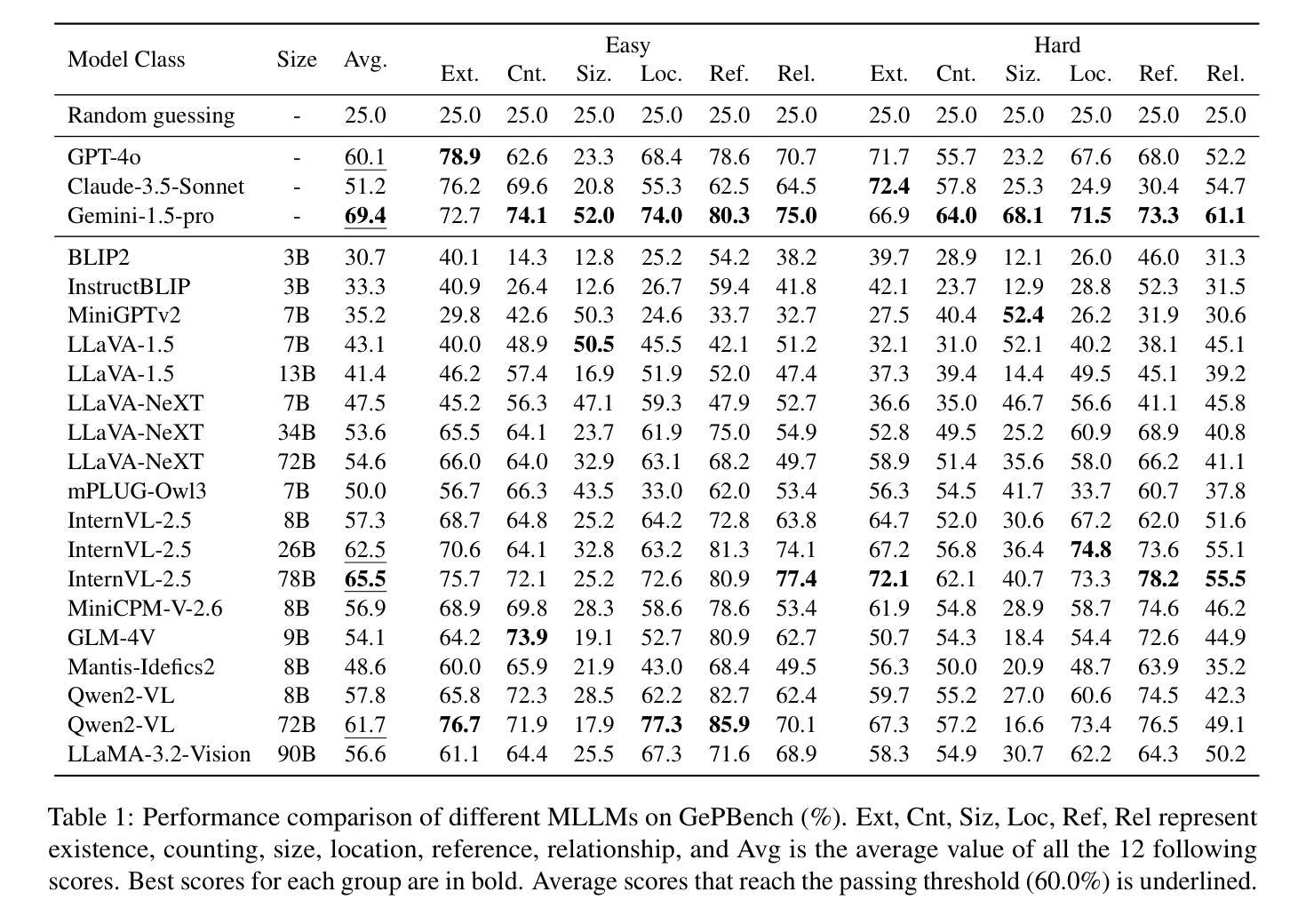
GePBench: Evaluating Fundamental Geometric Perception for Multimodal Large Language Models
Authors:Shangyu Xing, Changhao Xiang, Yuteng Han, Yifan Yue, Zhen Wu, Xinyu Liu, Zhangtai Wu, Fei Zhao, Xinyu Dai
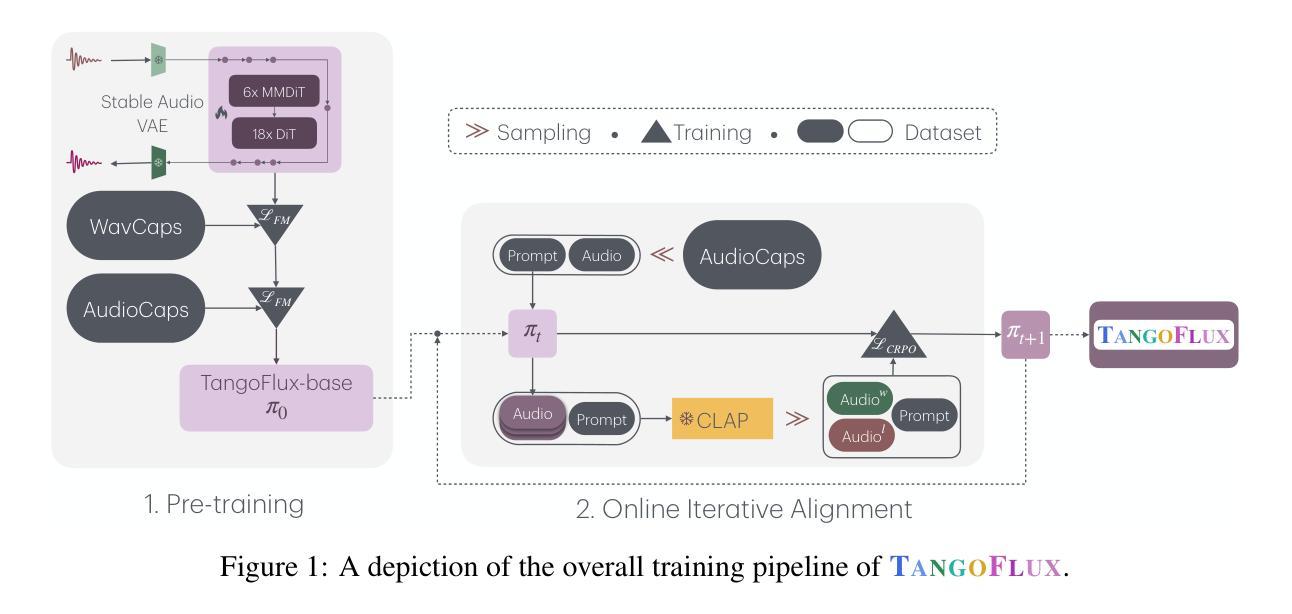
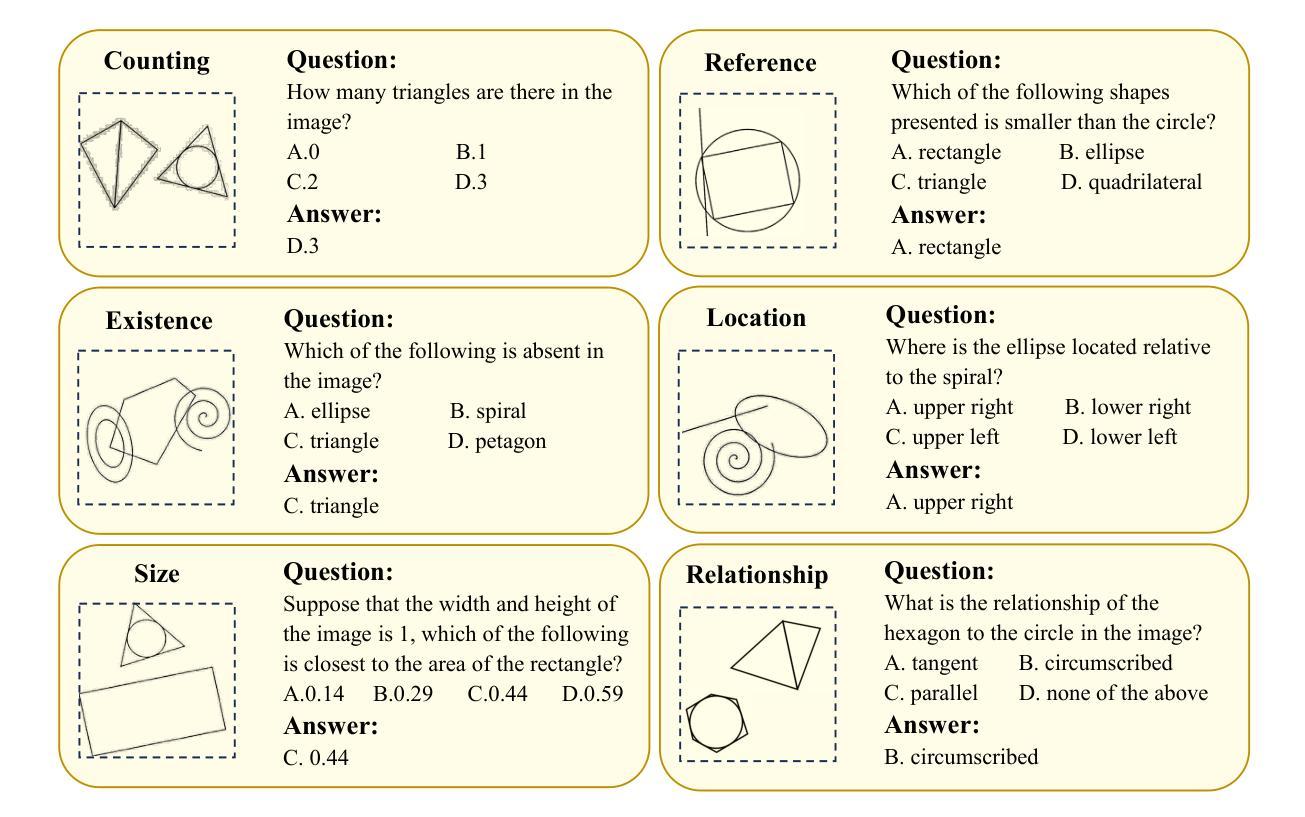
Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have achieved significant advancements in integrating visual and linguistic understanding. While existing benchmarks evaluate these models in context-rich, real-life scenarios, they often overlook fundamental perceptual skills essential for environments deviating from everyday realism. In particular, geometric perception, the ability to interpret spatial relationships and abstract visual patterns, remains underexplored. To address this limitation, we introduce GePBench, a novel benchmark designed to assess the geometric perception capabilities of MLLMs. Results from extensive evaluations reveal that current state-of-the-art MLLMs exhibit significant deficiencies in such tasks. Additionally, we demonstrate that models trained with data sourced from GePBench show notable improvements on a wide range of downstream tasks, underscoring the importance of geometric perception as a foundation for advanced multimodal applications. Our code and datasets will be publicly available.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在整合视觉和语言理解方面取得了重大进展。虽然现有的基准测试在丰富语境的现实生活中评估这些模型,但它们往往忽视了在非日常现实环境中至关重要的基本感知技能。特别是几何感知能力,即解释空间关系和抽象视觉模式的能力,仍然被研究得不够深入。为了解决这一局限性,我们引入了GePBench,这是一个新的基准测试,旨在评估MLLMs的几何感知能力。广泛的评估结果揭示,当前最先进的大型多模态语言模型在这些任务上存在明显不足。此外,我们还证明,使用GePBench数据训练的模型在各种下游任务上都表现出显著改善,突显了基础几何感知对于高级多模态应用的重要性。我们的代码和数据集将公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在整合视觉和语言理解方面取得了显著进展。尽管现有基准测试在丰富语境的现实场景中对这些模型进行了评估,但它们往往忽视了偏离日常现实的环境中所必需的基本感知技能。特别是几何感知能力,即解释空间关系和抽象视觉模式的能力,仍然被探索得很少。为解决这一局限性,我们引入了GePBench,这是一个新的基准测试,旨在评估MLLMs的几何感知能力。来自广泛评估的结果显示,当前最先进的MLLMs在此类任务中存在显著缺陷。此外,我们还证明,使用GePBench数据源训练的模型在各种下游任务中显示出显著改善,这突出了几何感知作为先进多模态应用基础的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在整合视觉和语言理解方面取得显著进步。
- 现有基准测试忽视了对偏离日常现实的环境中的基本感知技能的评估。
- 几何感知能力(解释空间关系和抽象视觉模式的能力)在MLLMs中仍然被探索得很少。
- 引入了一个新的基准测试GePBench,用于评估MLLMs的几何感知能力。
- 当前最先进的MLLMs在几何感知任务的评估中存在显著缺陷。
- 使用GePBench数据源训练的模型在各种下游任务中表现出改善。
- 几何感知对于先进的多模态应用至关重要。
点此查看论文截图


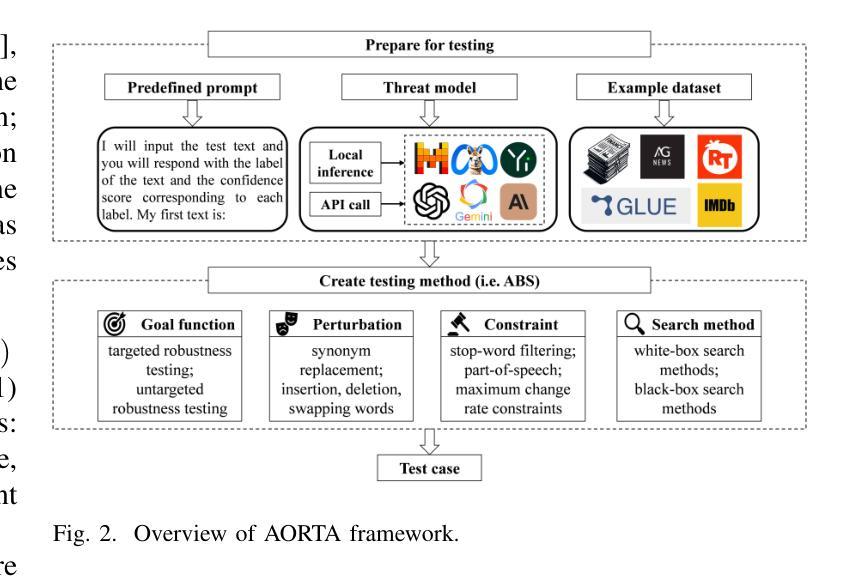
Automated Robustness Testing for LLM-based NLP Software
Authors:Mingxuan Xiao, Yan Xiao, Shunhui Ji, Hanbo Cai, Lei Xue, Pengcheng Zhang
Benefiting from the advancements in LLMs, NLP software has undergone rapid development. Such software is widely employed in various safety-critical tasks, such as financial sentiment analysis, toxic content moderation, and log generation. To our knowledge, there are no known automated robustness testing methods specifically designed for LLM-based NLP software. Given the complexity of LLMs and the unpredictability of real-world inputs (including prompts and examples), it is essential to examine the robustness of overall inputs to ensure the safety of such software. To this end, this paper introduces the first AutOmated Robustness Testing frAmework, AORTA, which reconceptualizes the testing process into a combinatorial optimization problem. Existing testing methods designed for DNN-based software can be applied to LLM-based software by AORTA, but their effectiveness is limited. To address this, we propose a novel testing method for LLM-based software within AORTA called Adaptive Beam Search. ABS is tailored for the expansive feature space of LLMs and improves testing effectiveness through an adaptive beam width and the capability for backtracking. We successfully embed 18 test methods in the designed framework AORTA and compared the test validity of ABS with three datasets and five threat models. ABS facilitates a more comprehensive and accurate robustness assessment before software deployment, with an average test success rate of 86.138%. Compared to the currently best-performing baseline PWWS, ABS significantly reduces the computational overhead by up to 3441.895 seconds per successful test case and decreases the number of queries by 218.762 times on average. Furthermore, test cases generated by ABS exhibit greater naturalness and transferability.
得益于LLM(大型语言模型)的进步,NLP软件得到了快速发展。此类软件广泛应用于各种安全关键任务,如金融情感分析、有毒内容审核和日志生成等。据我们所知,目前尚无专门为基于LLM的NLP软件设计的自动化鲁棒性测试方法。考虑到LLM的复杂性和真实世界输入的不可预测性(包括提示和示例),必须检查总体输入的鲁棒性以确保此类软件的安全。为此,本文介绍了第一个自动化鲁棒性测试框架AORTA,它将测试过程重新概念化为组合优化问题。AORTA可以将为DNN(深度学习网络)软件设计的现有测试方法应用于LLM软件,但其有效性受到限制。为解决此问题,我们在AORTA中为基于LLM的软件提出了一种新的测试方法,称为自适应光束搜索(ABS)。ABS针对LLM的庞大特征空间量身定制,通过自适应光束宽度和反向跟踪能力提高了测试效率。我们成功地在设计的框架AORTA中嵌入了18种测试方法,并使用三个数据集和五种威胁模型比较了ABS的测试有效性。ABS在软件部署前促进了更全面和准确的鲁棒性评估,平均测试成功率为86.138%。与当前性能最佳的基线PWWS相比,ABS将每个成功测试用例的计算开销减少了高达3441.895秒,平均查询次数减少了218.762次。此外,ABS生成的测试用例表现出更高的自然性和可迁移性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
得益于LLM的进步,NLP软件得到快速发展并广泛应用于安全关键任务。目前尚无可用于LLM-based NLP软件的自动化鲁棒性测试方法。本文介绍首个自动化鲁棒性测试框架AORTA,将测试过程重构为组合优化问题。AORTA虽然可以应用现有针对DNN软件的测试方法,但其有效性受限。为解决这一问题,我们提出了AORTA中的新型LLM软件测试方法——自适应光束搜索(ABS)。ABS针对LLM的庞大特征空间进行定制,通过自适应光束宽度和回溯能力提高测试效率。在嵌入的18种测试方法中,ABS在三个数据集和五个威胁模型中的测试有效性表现优异,平均测试成功率为86.138%。与当前性能最佳的PWWS相比,ABS每成功测试用例的计算开销减少高达3441.895秒,平均查询次数减少218.762次。此外,ABS生成的测试用例具有更高的自然性和可迁移性。
关键见解
- LLM的进步推动了NLP软件的快速发展,广泛应用于安全关键任务。
- 目前缺乏针对LLM-based NLP软件的自动化鲁棒性测试方法。
- AORTA框架将LLM软件测试过程重构为组合优化问题。
- 现有测试方法在AORTA中的应用虽然可行,但有效性受限。
- 提出新型LLM软件测试方法——自适应光束搜索(ABS),针对LLM的庞大特征空间定制。
- ABS通过自适应光束宽度和回溯能力提高测试效率。
点此查看论文截图

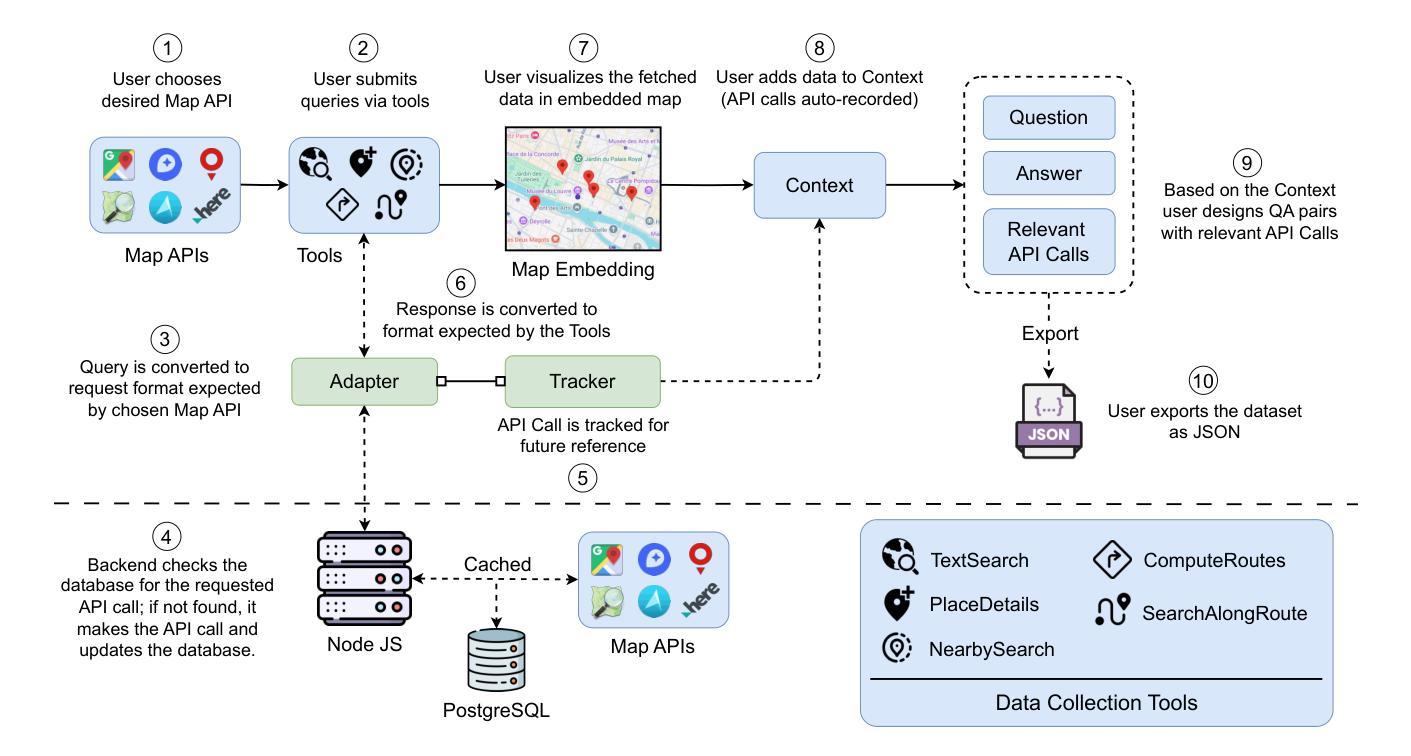
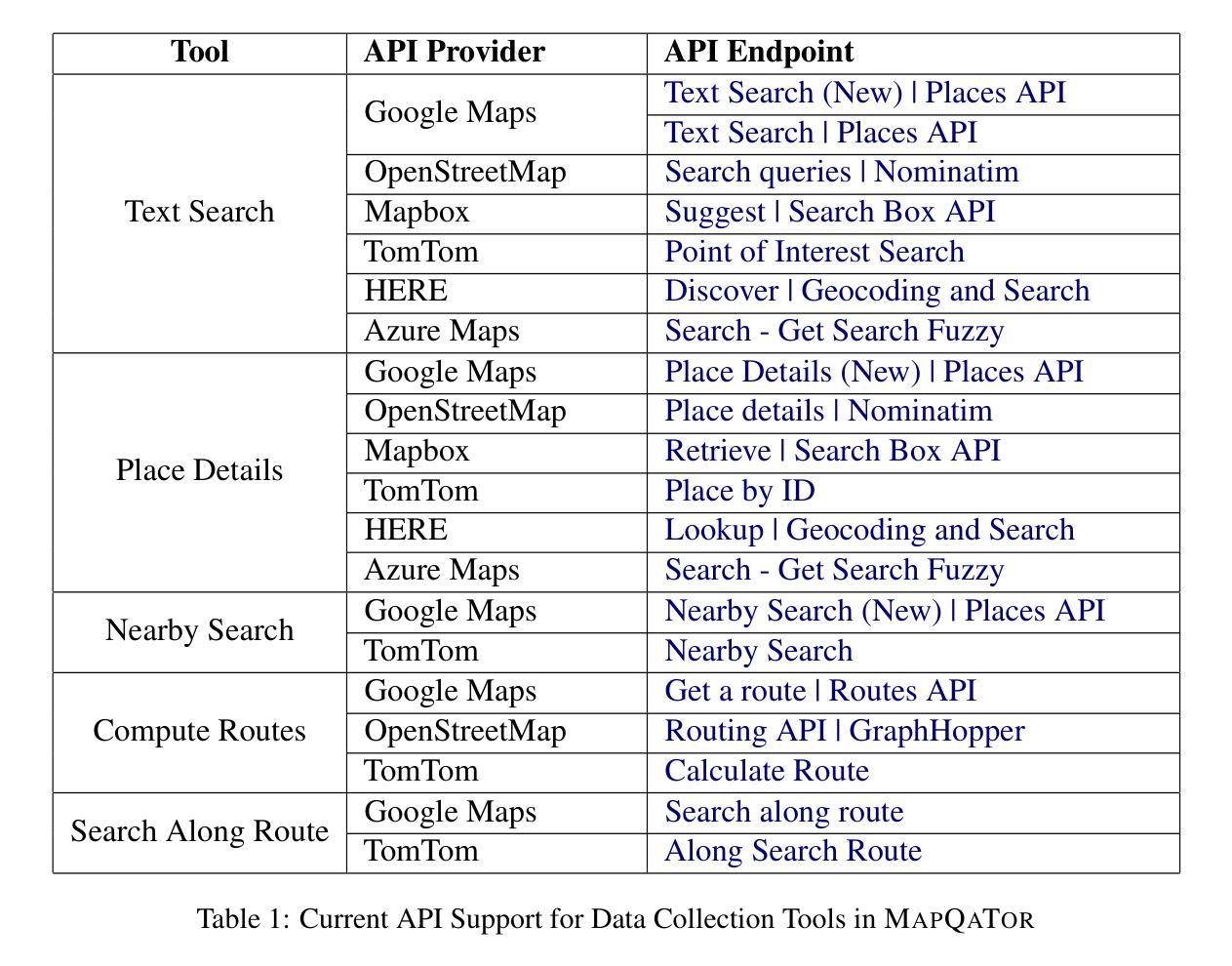
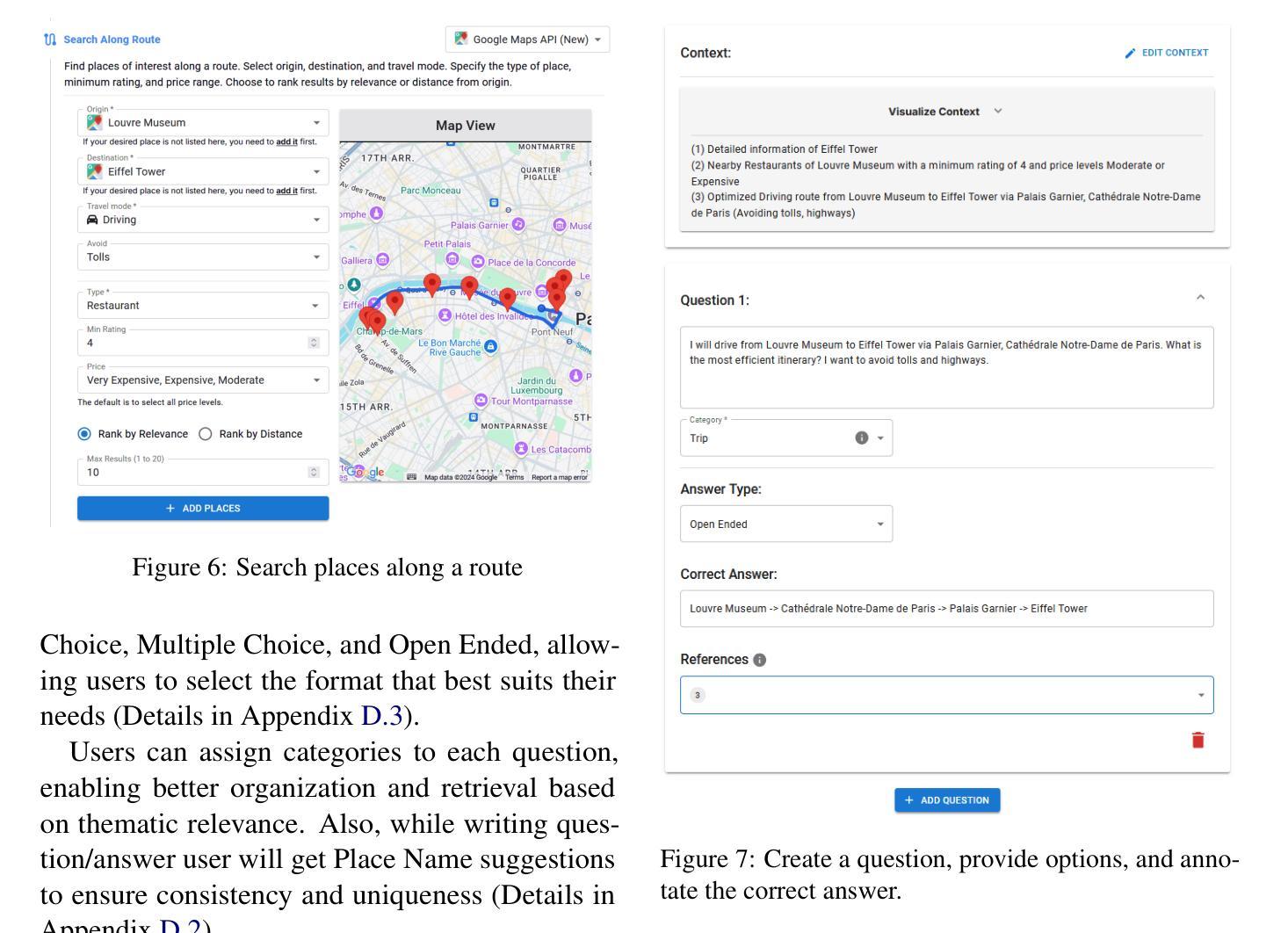
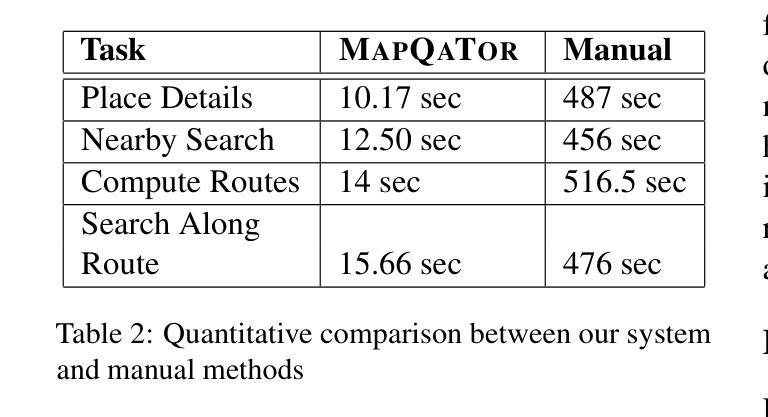
MapQaTor: A System for Efficient Annotation of Map Query Datasets
Authors:Mahir Labib Dihan, Mohammed Eunus Ali, Md Rizwan Parvez
Mapping and navigation services like Google Maps, Apple Maps, Openstreet Maps, are essential for accessing various location-based data, yet they often struggle to handle natural language geospatial queries. Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) show promise in question answering (QA), but creating reliable geospatial QA datasets from map services remains challenging. We introduce MapQaTor, a web application that streamlines the creation of reproducible, traceable map-based QA datasets. With its plug-and-play architecture, MapQaTor enables seamless integration with any maps API, allowing users to gather and visualize data from diverse sources with minimal setup. By caching API responses, the platform ensures consistent ground truth, enhancing the reliability of the data even as real-world information evolves. MapQaTor centralizes data retrieval, annotation, and visualization within a single platform, offering a unique opportunity to evaluate the current state of LLM-based geospatial reasoning while advancing their capabilities for improved geospatial understanding. Evaluation metrics show that, MapQaTor speeds up the annotation process by at least 30 times compared to manual methods, underscoring its potential for developing geospatial resources, such as complex map reasoning datasets. The website is live at: https://mapqator.github.io/ and a demo video is available at: https://youtu.be/7_aV9Wmhs6Q.
像谷歌地图、苹果地图、Openstreet Maps这样的映射和导航服务对于访问各种基于位置的数据至关重要,但它们在处理自然语言地理空间查询时经常遇到困难。最近大型语言模型(LLM)在问答(QA)方面的进展显示出希望,但从地图服务创建可靠的地理空间QA数据集仍然具有挑战性。我们推出了MapQaTor,这是一个网络应用程序,能够简化可复现和可追溯的基于地图的QA数据集的制作过程。凭借即插即用的架构,MapQaTor能够无缝地与任何地图API集成,允许用户从各种来源收集并可视化数据,而且几乎不需要进行设置。通过缓存API响应,该平台确保了真实的地面信息保持一致,即使在现实世界的信息不断发展变化的情况下,也能提高数据的可靠性。MapQaTor在单个平台上集中数据检索、注释和可视化,提供了一个评估基于LLM的地理空间推理当前状态的独特机会,同时推动其能力以改善地理空间理解。评估指标显示,MapQaTor相比手动方法至少能加快30倍的注释过程,这突显了其在开发复杂地图推理数据集等地理空间资源方面的潜力。网站现已上线:https://mapqator.github.io/ 并且演示视频可通过:https://youtu.be/7_aV9Wmhs6Q进行访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 35 figures
Summary
基于Google Maps、Apple Maps、Openstreet Maps等映射和导航服务在处理自然语言地理空间查询时的挑战,以及大型语言模型(LLM)在问答(QA)方面的潜力,我们推出了MapQaTor网页应用程序。该程序可简化可重复的、可追溯的地图QA数据集的制作流程。它采用即插即用架构,支持无缝集成任何地图API,并缓存API响应以确保真实数据的一致性。MapQaTor集中数据检索、注释和可视化在一个平台上,不仅为评估当前LLM地理空间推理能力提供了独特机会,而且为其改进地理空间理解能力提供了动力。相较于传统手动方法,MapQaTor标注速度提高了至少三十倍。MapQaTor平台可加快地理空间资源开发,例如复杂地图推理数据集的开发速度。平台网站地址为:网站链接。演示视频地址:视频链接。此工具有望成为地图信息查询新模式的起点。
Key Takeaways
- MapQaTor是一个创新的web应用程序,用于简化基于地图的QA数据集的制作流程。
- MapQaTor支持无缝集成各种地图API,实现多种来源数据的轻松收集和可视化。
- 平台确保数据的一致性并提升其可靠性,通过缓存API响应应对现实世界信息的变化。
- MapQaTor实现了数据的检索、标注和可视化的集中处理在一个平台上,推进LLM的地理空间推理能力评估和提升。
- 与传统手动方法相比,MapQaTor至少提高了三十倍的标注速度。
- MapQaTor对于开发复杂地图推理数据集等地理空间资源具有巨大潜力。
点此查看论文截图


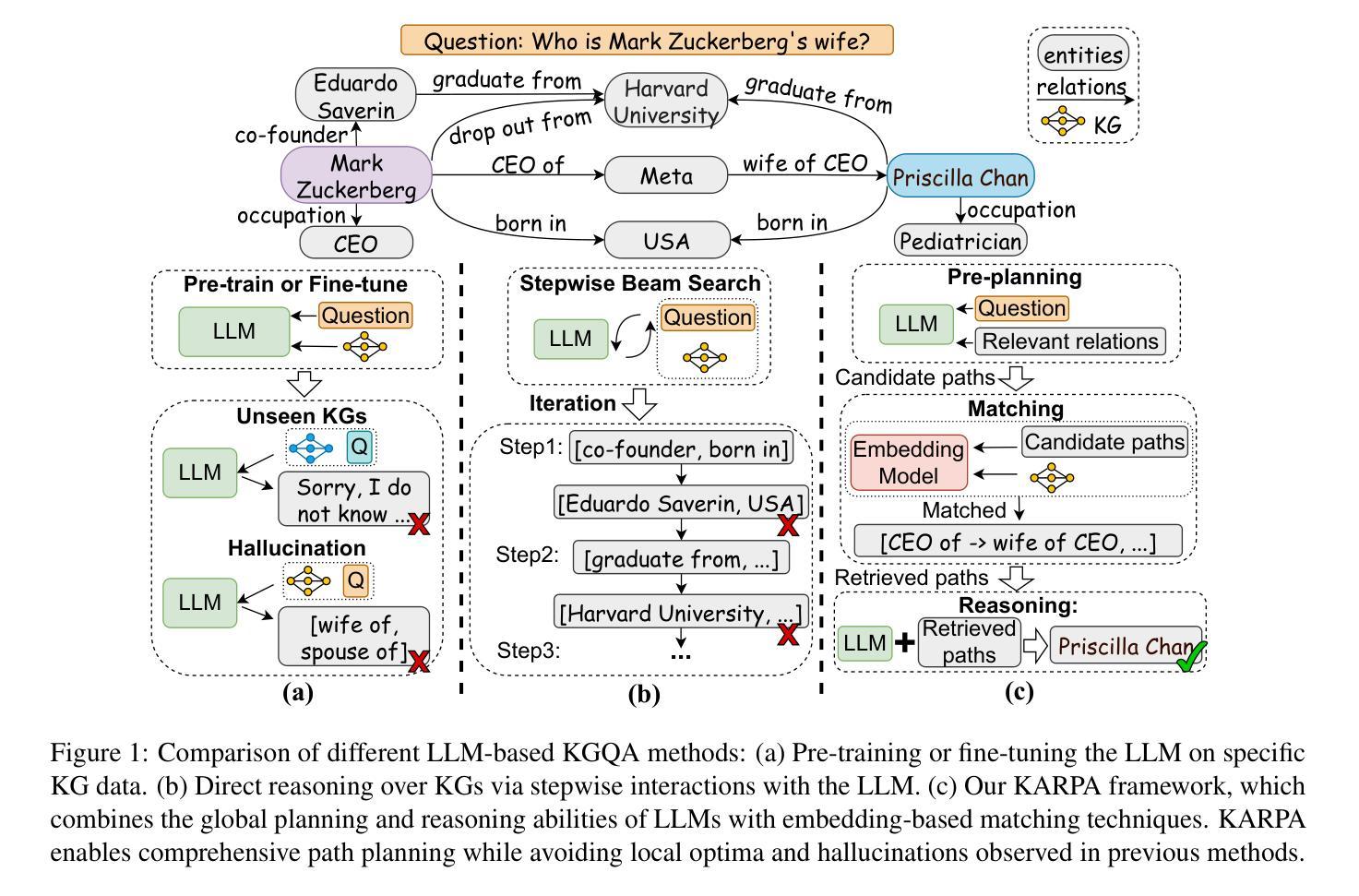
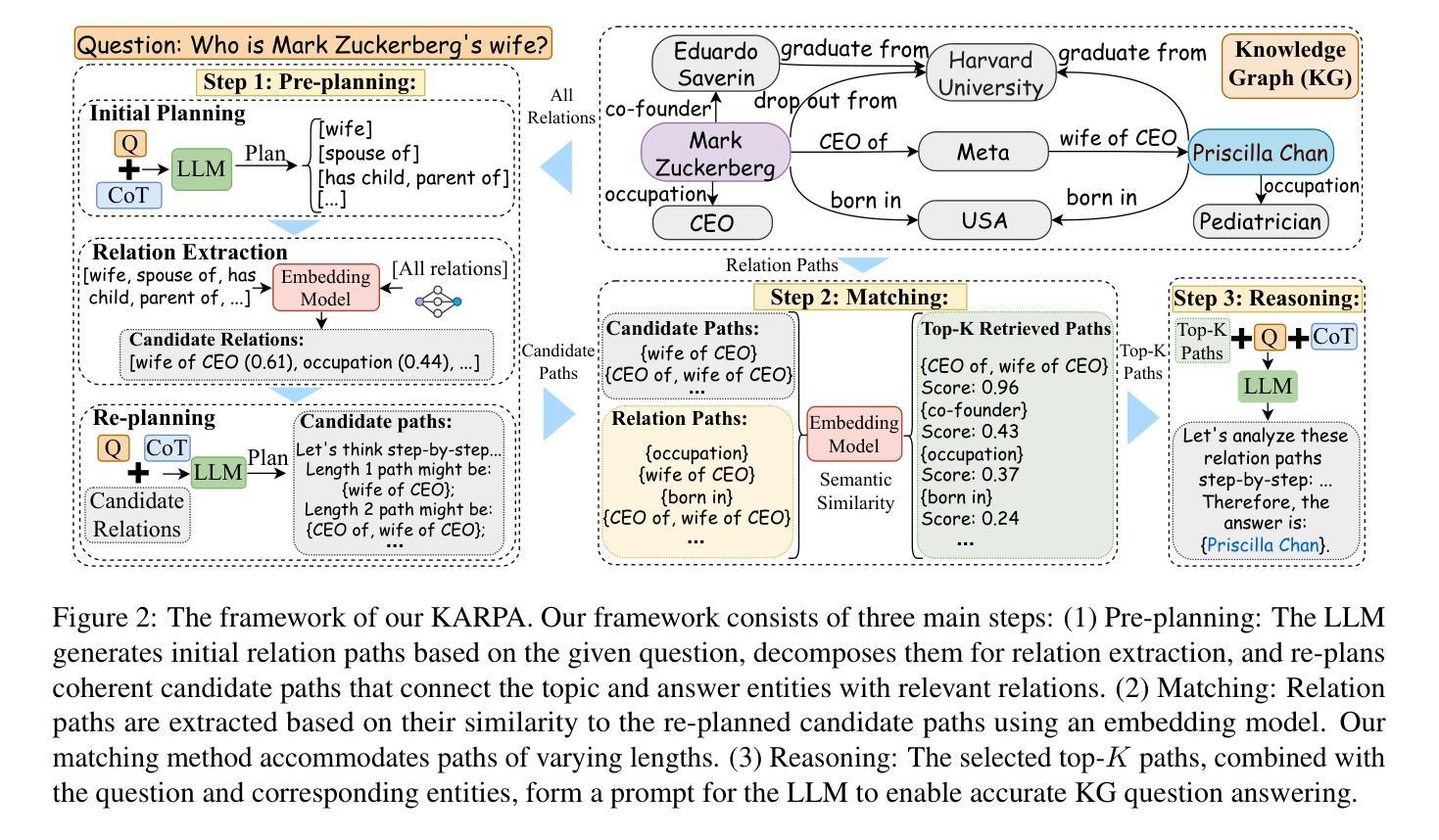
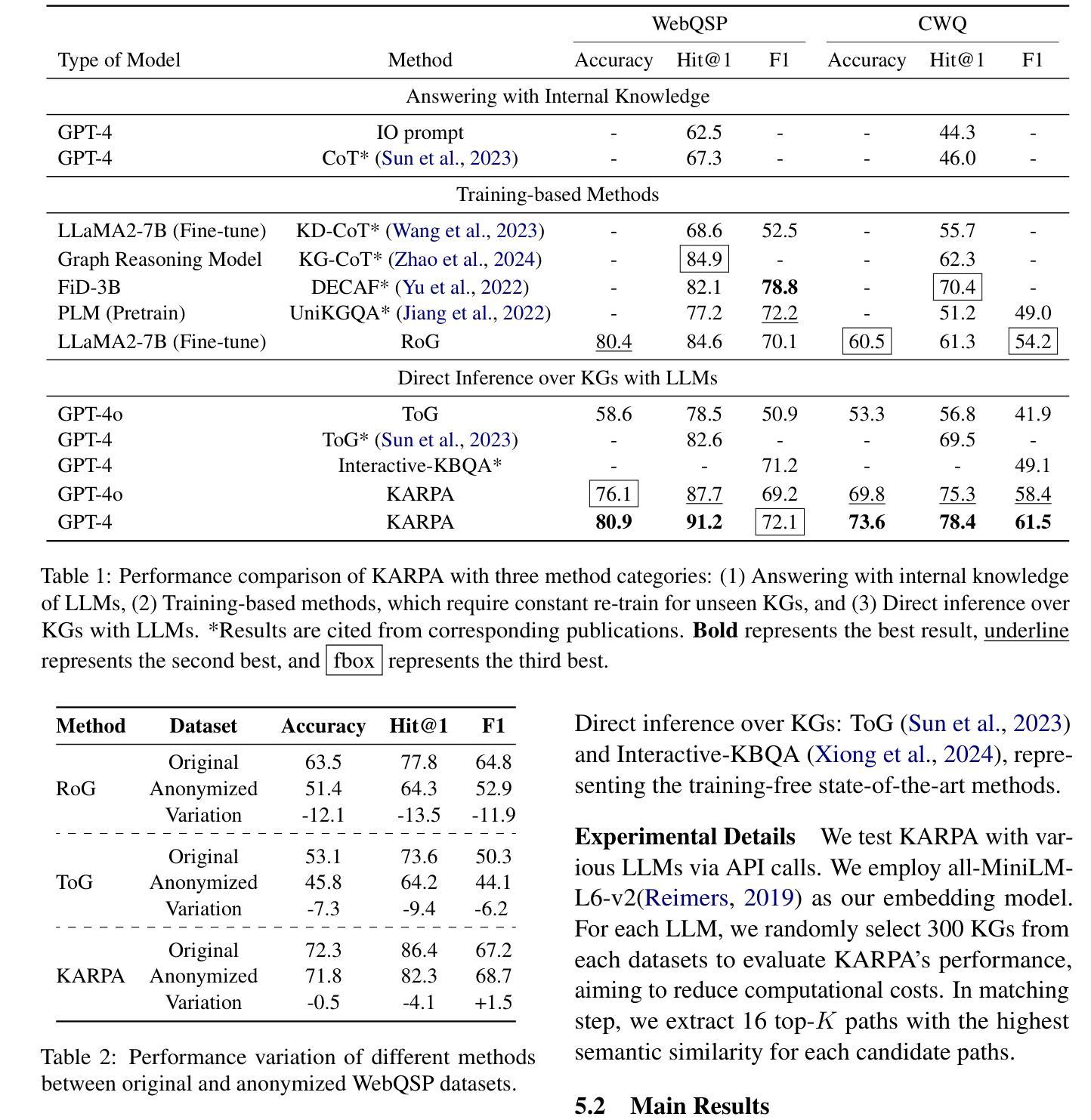
KARPA: A Training-free Method of Adapting Knowledge Graph as References for Large Language Model’s Reasoning Path Aggregation
Authors:Siyuan Fang, Kaijing Ma, Tianyu Zheng, Xinrun Du, Ningxuan Lu, Ge Zhang, Qingkun Tang
Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate exceptional performance across a variety of tasks, yet they are often affected by hallucinations and the timeliness of knowledge. Leveraging knowledge graphs (KGs) as external knowledge sources has emerged as a viable solution, but existing methods for LLM-based knowledge graph question answering (KGQA) are often limited by step-by-step decision-making on KGs, restricting the global planning and reasoning capabilities of LLMs, or they require fine-tuning or pre-training on specific KGs. To address these challenges, we propose Knowledge graph Assisted Reasoning Path Aggregation (KARPA), a novel framework that harnesses the global planning abilities of LLMs for efficient and accurate KG reasoning. KARPA operates in three steps: pre-planning relation paths using the LLM’s global planning capabilities, matching semantically relevant paths via an embedding model, and reasoning over these paths to generate answers. Unlike existing KGQA methods, KARPA avoids stepwise traversal, requires no additional training, and is adaptable to various LLM architectures. Extensive experimental results show that KARPA achieves state-of-the-art performance in KGQA tasks, delivering both high efficiency and accuracy. Our code will be available on Github.
大型语言模型(LLM)在各种任务中表现出卓越的性能,但它们往往受到幻觉和知识时效性的影响。利用知识图谱(KGs)作为外部知识源已成为一种可行的解决方案,但现有的基于LLM的知识图谱问答(KGQA)方法往往受到知识图谱上的逐步决策制定的限制,限制了LLM的全局规划和推理能力,或者它们需要在特定知识图谱上进行微调或预训练。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了知识图谱辅助推理路径聚合(KARPA)这一新型框架,它利用LLM的全局规划能力进行高效且准确的KG推理。KARPA分为三个步骤:利用LLM的全局规划能力预先规划关系路径、通过嵌入模型匹配语义相关路径、以及在这些路径上进行推理以生成答案。与现有KGQA方法不同,KARPA避免了逐步遍历,无需额外训练,并且可适应各种LLM架构。大量实验结果表明,KARPA在KGQA任务中达到了最新技术水平,实现了高效率和准确性。我们的代码将在Github上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 6 figures
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在各种任务中表现出卓越的性能,但受到知识时效性和幻觉的影响。利用知识图谱(KGs)作为外部知识源是一种可行的解决方案,但现有的LLM知识图谱问答(KGQA)方法受限于知识图谱上的逐步决策制定,限制了LLM的全局规划和推理能力,或者需要对特定知识图谱进行微调或预训练。针对这些挑战,我们提出了知识图谱辅助推理路径聚合(KARPA)这一新型框架,它利用LLM的全局规划能力进行高效、准确的KG推理。KARPA分为三个步骤:利用LLM的全局规划能力预先规划关系路径、通过嵌入模型匹配语义相关路径以及在这些路径上进行推理以生成答案。不同于现有的KGQA方法,KARPA避免了逐步遍历,无需额外训练,并且可适应各种LLM架构。实验结果表明,KARPA在KGQA任务中达到了最先进的性能,实现了高效和准确性的双重提升。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs 展现出卓越的多任务性能,但仍受知识时效性和幻觉的影响。
- 知识图谱(KGs)作为外部知识源为 LLMs 提供了可行的解决方案。
- 现有LLM-based KGQA方法存在逐步决策的限制,影响全局规划和推理能力。
- KARPA框架利用LLM的全局规划能力进行高效、准确的KG推理。
- KARPA包括三个主要步骤:预规划关系路径、语义路径匹配和路径推理。
- KARPA区别于其他KGQA方法,无需逐步遍历、额外训练,适应多种LLM架构。
点此查看论文截图

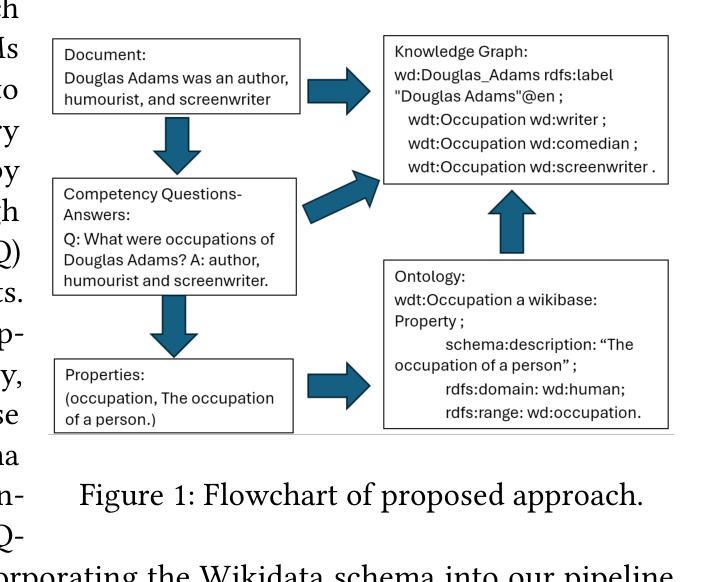
Ontology-grounded Automatic Knowledge Graph Construction by LLM under Wikidata schema
Authors:Xiaohan Feng, Xixin Wu, Helen Meng
We propose an ontology-grounded approach to Knowledge Graph (KG) construction using Large Language Models (LLMs) on a knowledge base. An ontology is authored by generating Competency Questions (CQ) on knowledge base to discover knowledge scope, extracting relations from CQs, and attempt to replace equivalent relations by their counterpart in Wikidata. To ensure consistency and interpretability in the resulting KG, we ground generation of KG with the authored ontology based on extracted relations. Evaluation on benchmark datasets demonstrates competitive performance in knowledge graph construction task. Our work presents a promising direction for scalable KG construction pipeline with minimal human intervention, that yields high quality and human-interpretable KGs, which are interoperable with Wikidata semantics for potential knowledge base expansion.
我们提出了一种基于大型语言模型(LLM)的知识图谱(KG)构建方法,该方法以本体为基础,在知识库上进行操作。本体是通过在知识库上生成能力问题(CQ)来发现知识范围,从能力问题中提取关系,并尝试用维基百科中的对应物替换等价关系而创建的。为确保生成的知识图谱的一致性和可解释性,我们根据提取的关系将知识图谱与已构建的本体相结合。在基准数据集上的评估表明,我们在知识图谱构建任务中表现出竞争力。我们的工作展示了一个有前景的方向,即构建一个可扩展的知识图谱构建管道,以最小的手工干预,生成高质量和可解释的知识图谱,这些图谱可以与维基百科语义进行互操作,以实现潜在的知识库扩展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Presented at HI-AI@KDD, Human-Interpretable AI Workshop at the KDD 2024, 26th of August 2024, Barcelona, Spain
Summary
采用基于大语言模型(LLM)的知识图谱(KG)构建方法,通过生成能力问题(CQ)发掘知识范围,提取关系并与Wikidata中的对应物进行替换,确保知识图谱的一致性和可解释性。在基准数据集上的评估表明在知识图谱构建任务上具有竞争力。此工作展现出大规模知识图谱构建管道的前景,可最小化人工干预,生成高质量且人类可解释的知识图谱,可与Wikidata语义进行互操作以实现潜在知识库的扩展。
Key Takeaways
- 提出基于大语言模型(LLM)和知识图谱(KG)构建的ontology-grounded方法。
- 通过生成能力问题(CQ)发掘知识范围,并提取关系。
- 将提取的关系与Wikidata中的对应物进行替换,确保知识图谱的一致性和可解释性。
- 知识图谱构建方法的评估结果具有竞争力。
- 此方法有助于实现大规模知识图谱构建管道,减少人工干预。
- 构建的知识图谱质量高且人类可解释。
点此查看论文截图

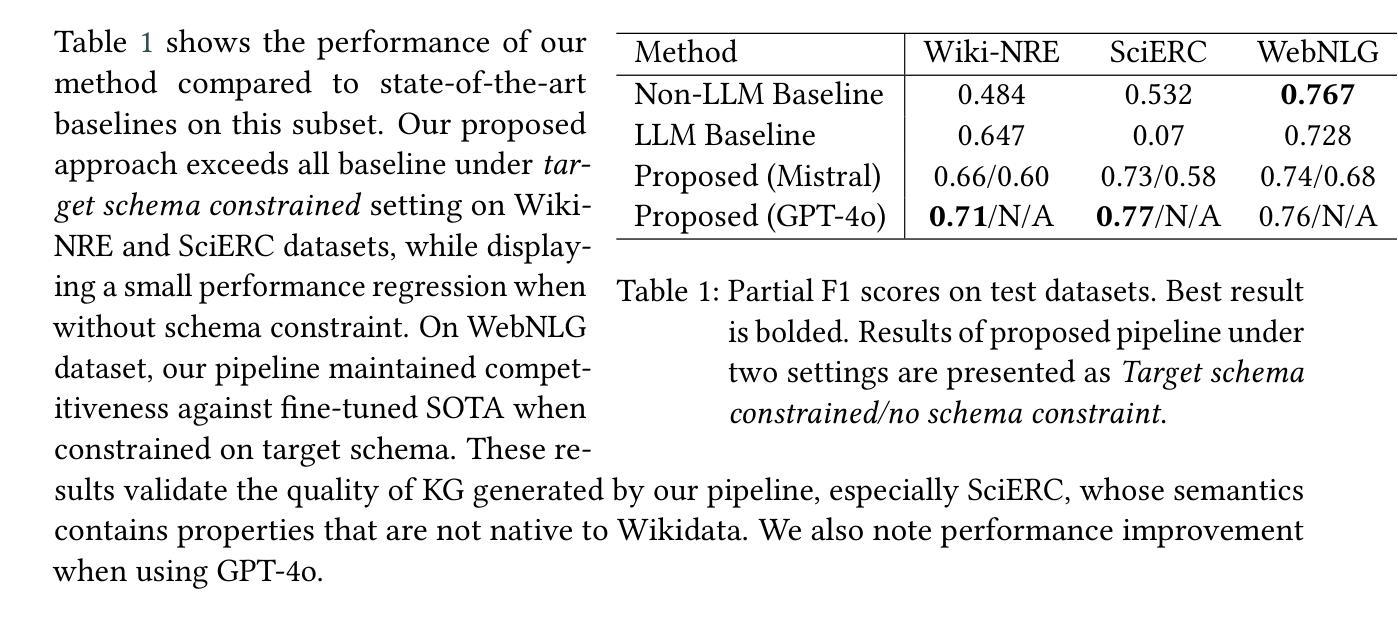
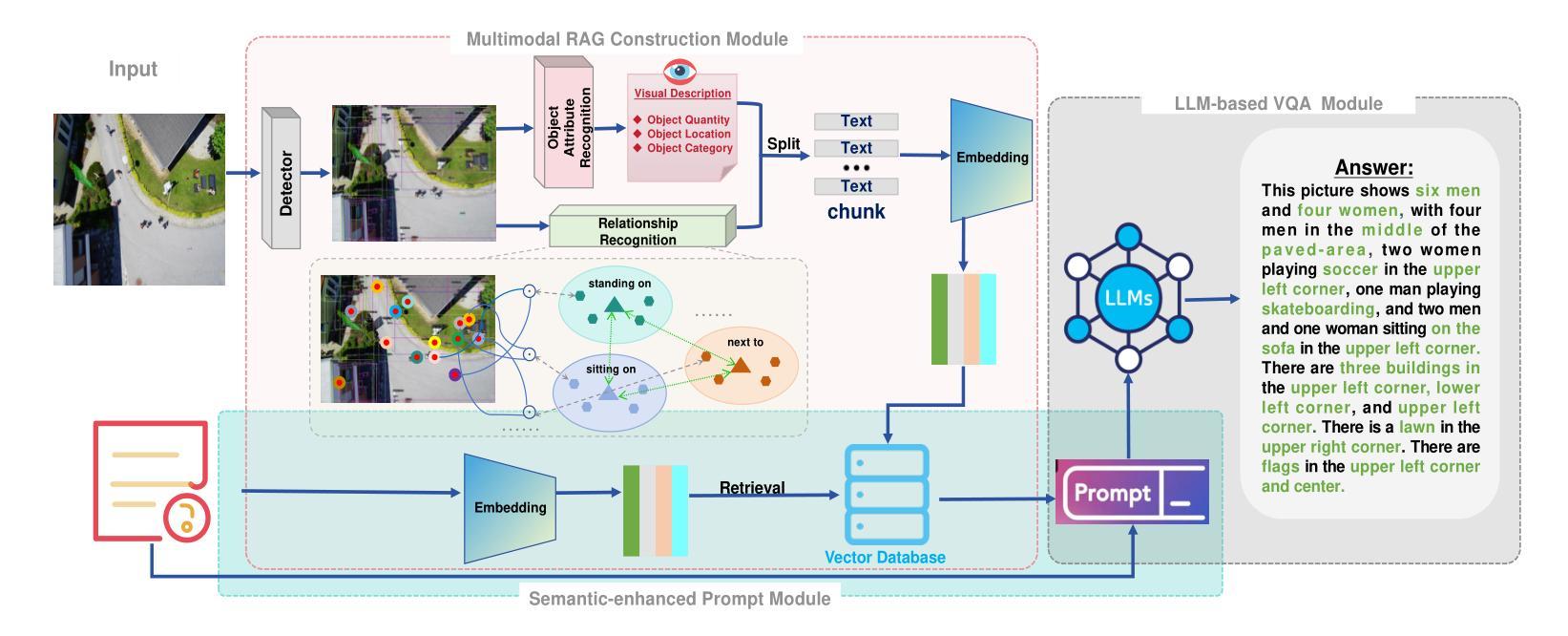
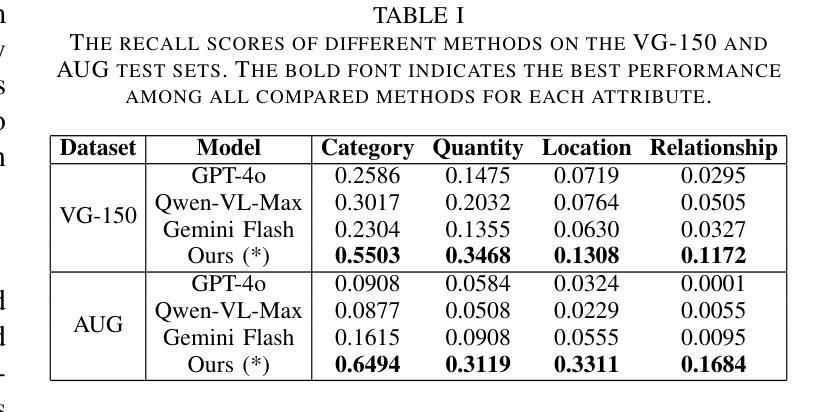
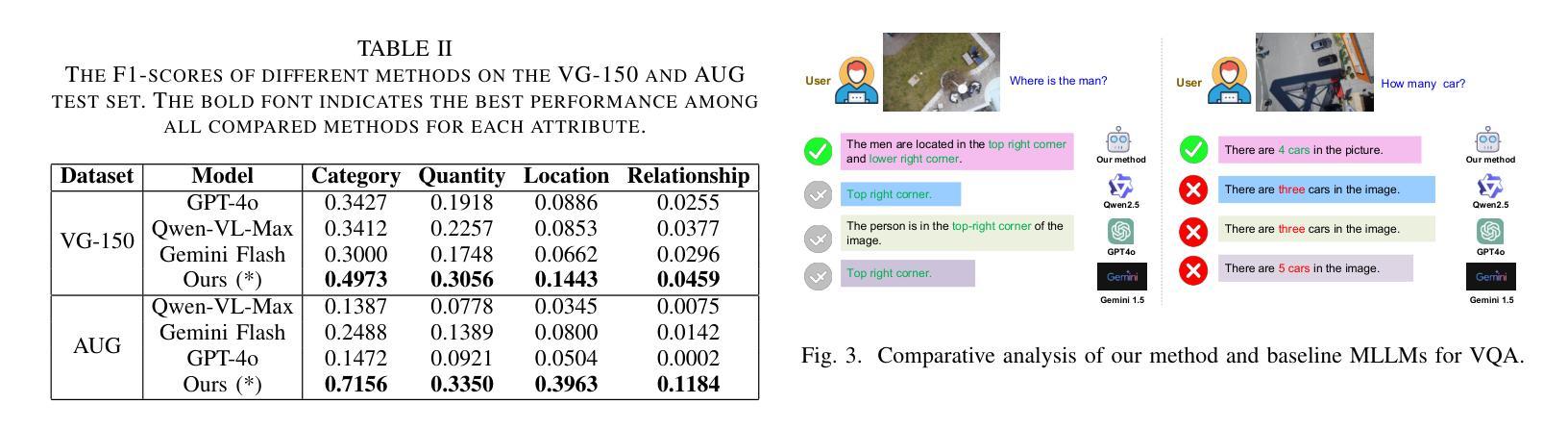
Enhanced Multimodal RAG-LLM for Accurate Visual Question Answering
Authors:Junxiao Xue, Quan Deng, Fei Yu, Yanhao Wang, Jun Wang, Yuehua Li
Multimodal large language models (MLLMs), such as GPT-4o, Gemini, LLaVA, and Flamingo, have made significant progress in integrating visual and textual modalities, excelling in tasks like visual question answering (VQA), image captioning, and content retrieval. They can generate coherent and contextually relevant descriptions of images. However, they still face challenges in accurately identifying and counting objects and determining their spatial locations, particularly in complex scenes with overlapping or small objects. To address these limitations, we propose a novel framework based on multimodal retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), which introduces structured scene graphs to enhance object recognition, relationship identification, and spatial understanding within images. Our framework improves the MLLM’s capacity to handle tasks requiring precise visual descriptions, especially in scenarios with challenging perspectives, such as aerial views or scenes with dense object arrangements. Finally, we conduct extensive experiments on the VG-150 dataset that focuses on first-person visual understanding and the AUG dataset that involves aerial imagery. The results show that our approach consistently outperforms existing MLLMs in VQA tasks, which stands out in recognizing, localizing, and quantifying objects in different spatial contexts and provides more accurate visual descriptions.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs),如GPT-4o、Gemini、LLaVA和Flamingo,在整合视觉和文本模态方面取得了显著进展,在视觉问答(VQA)、图像标题和内容检索等任务上表现出色。它们可以生成连贯且与上下文相关的图像描述。然而,在准确识别、计数物体并确定其空间位置方面,尤其是在复杂场景中存在重叠或小型物体的情况下,它们仍面临挑战。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种基于多模态检索增强生成(RAG)的新型框架,该框架引入结构化场景图,以增强图像中的对象识别、关系识别和空间理解。我们的框架提高了MLLM在处理需要精确视觉描述的任务方面的能力,尤其是在具有挑战视角的场景中,如空中俯视图或场景中的密集对象排列。最后,我们在专注于第一人称视觉理解的VG-150数据集和涉及空中图像的AUG数据集上进行了大量实验。结果表明,我们的方法在VQA任务上始终优于现有的MLLMs,特别擅长在不同空间上下文中识别、定位和量化对象,并提供更准确的视觉描述。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 3 figures, under review
Summary
大模态语言模型(MLLMs)在视觉和文本融合方面取得显著进展,例如在视觉问答(VQA)、图像标注和内容检索等任务中表现优异。然而,它们在复杂场景中识别、计数和定位物体方面仍存在挑战。为此,提出一种基于多模态检索增强生成(RAG)的新型框架,引入结构化场景图增强图像中的物体识别、关系识别和空间理解。该框架提高了MLLM处理需要精确视觉描述的任务的能力,特别是在具有挑战性视角的场景中,如空中视角或密集物体排列的场景。实验结果表明,该方法在VQA任务中始终优于现有MLLMs,并在不同空间上下文中识别、定位和量化物体时表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)如GPT-4o、Gemini、LLaVA和Flamingo在视觉和文本融合方面取得显著进展。
- MLLMs在视觉问答(VQA)、图像标注和内容检索等任务上表现优异,但物体识别、计数和定位方面仍面临挑战。
- 为解决这些挑战,提出了一种基于多模态检索增强生成(RAG)的新型框架。
- 该框架引入结构化场景图以增强图像中的物体识别、关系识别和空间理解。
- 新型框架提高了MLLM处理复杂和具有挑战性视角场景中的精确视觉描述任务的能力。
- 实验证明,该框架在VQA任务中表现优异,优于现有MLLMs。
点此查看论文截图

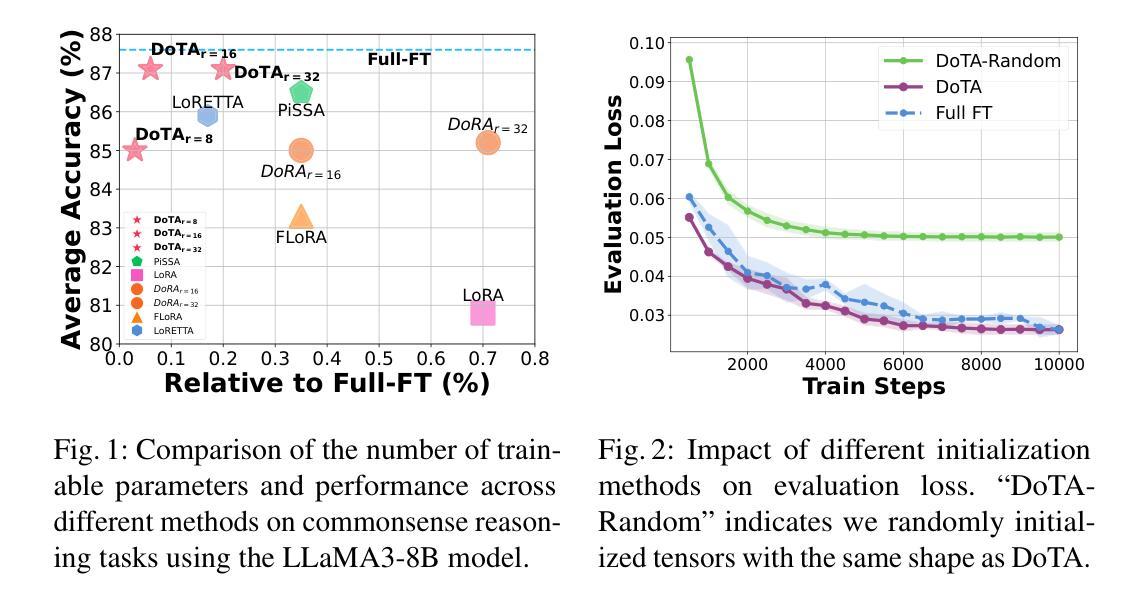
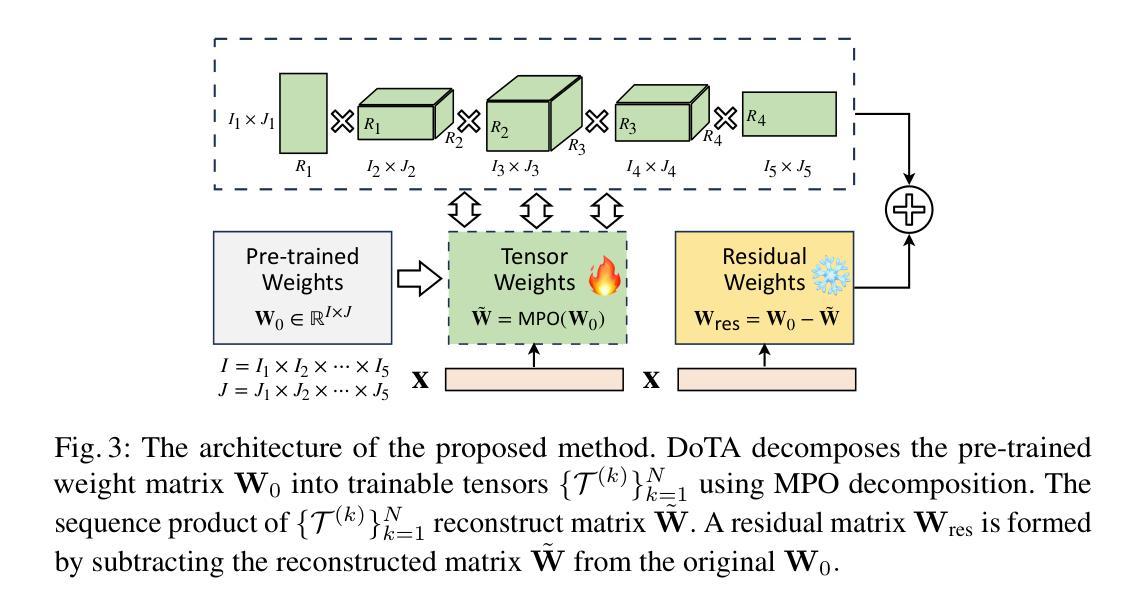
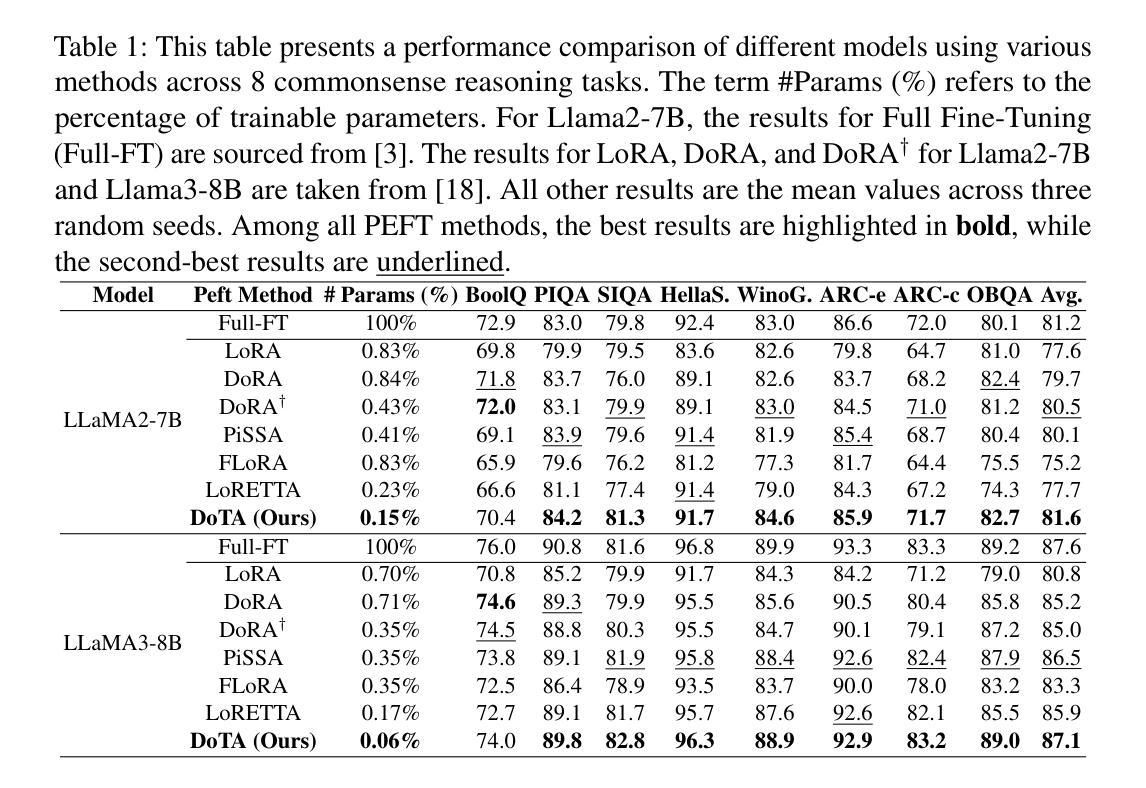
DoTA: Weight-Decomposed Tensor Adaptation for Large Language Models
Authors:Xiaolin Hu, Xiang Cheng, Peiyu Liu, Wei Liu, Jian Luan, Bin Wang, Yong Liu
Low-rank adaptation (LoRA) reduces the computational and memory demands of fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) by approximating updates with low-rank matrices. However, low-rank approximation in two-dimensional space fails to capture high-dimensional structures within the target matrix. Recently, tensor decomposition methods have been explored for fine-tuning LLMs, leveraging their ability to extract structured information. Yet, these approaches primarily rely on random initialization, and the impact of initialization on tensor adaptation remains underexplored. In this paper, we reveal that random initialization significantly diverges from the validation loss achieved by full fine-tuning. To address this, we propose Weight-Decomposed Tensor Adaptation (DoTA), which leverages the Matrix Product Operator (MPO) decomposition of pre-trained weights for effective initialization in fine-tuning LLMs. Additionally, we introduce QDoTA, a quantized version of DoTA designed for 4-bit quantization. Experiments on commonsense and arithmetic reasoning tasks show that DoTA outperforms random initialization methods with fewer parameters. QDoTA further reduces memory consumption and achieves comparable performance to DoTA on commonsense reasoning tasks. We will release our code to support future research.
低秩适应(LoRA)通过低秩矩阵近似更新来降低大型语言模型(LLM)的微调的计算和内存需求。然而,在二维空间中的低秩近似无法捕获目标矩阵中的高维结构。最近,研究人员开始探索使用张量分解方法对大型语言模型进行微调,利用它们提取结构化信息的能力。然而,这些方法主要依赖于随机初始化,而关于初始化对张量适应的影响尚未得到充分研究。在本文中,我们发现随机初始化与通过完全微调实现的验证损失之间存在显著差异。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了基于权重分解的张量适应(DoTA),该方法利用预训练权重的矩阵乘积运算符(MPO)分解,以在微调大型语言模型时进行有效初始化。此外,我们还介绍了专为4位量化设计的DoTA的量化版本QDoTA。在常识和算术推理任务上的实验表明,DoTA在具有更少参数的情况下优于随机初始化方法。QDoTA进一步降低了内存消耗,并在常识推理任务上实现了与DoTA相当的性能。我们将发布我们的代码以支持未来的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 6 figures
Summary
低秩适应(LoRA)通过低秩矩阵近似更新来减少大型语言模型(LLM)的微调计算与内存需求。然而,二维空间的低秩近似无法捕捉目标矩阵的高维结构。近期,研究者开始探索利用张量分解方法微调LLM,其能提取结构化信息。但这些方法主要依赖随机初始化,而张量适应对初始化的影响尚未被充分研究。本文揭示随机初始化与完全微调实现的验证损失存在显著差异。为解决这一问题,本文提出Weight-Decomposed Tensor Adaptation(DoTA),利用预训练权重的矩阵乘积运算符(MPO)分解实现有效初始化,以微调LLM。此外,我们还介绍了为4位量化设计的DoTA的量化版QDoTA。在常识和算术推理任务上的实验表明,DoTA在参数更少的情况下优于随机初始化方法。QDoTA进一步降低了内存消耗,并在常识推理任务上实现了与DoTA相当的性能。
Key Takeaways
- LoRA通过低秩矩阵近似减少LLM微调的计算和内存需求,但无法捕捉高维结构。
- 张量分解方法用于微调LLM,提取结构化信息。
- 随机初始化在张量适应方法中扮演重要角色,但其影响尚未被充分研究。
- 本文提出DoTA方法,利用预训练权重的矩阵乘积运算符分解实现有效初始化。
- DoTA在常识和算术推理任务上表现优于随机初始化方法。
- QDoTA是DoTA的量化版,降低了内存消耗,实现了与DoTA相当的常识推理性能。
点此查看论文截图

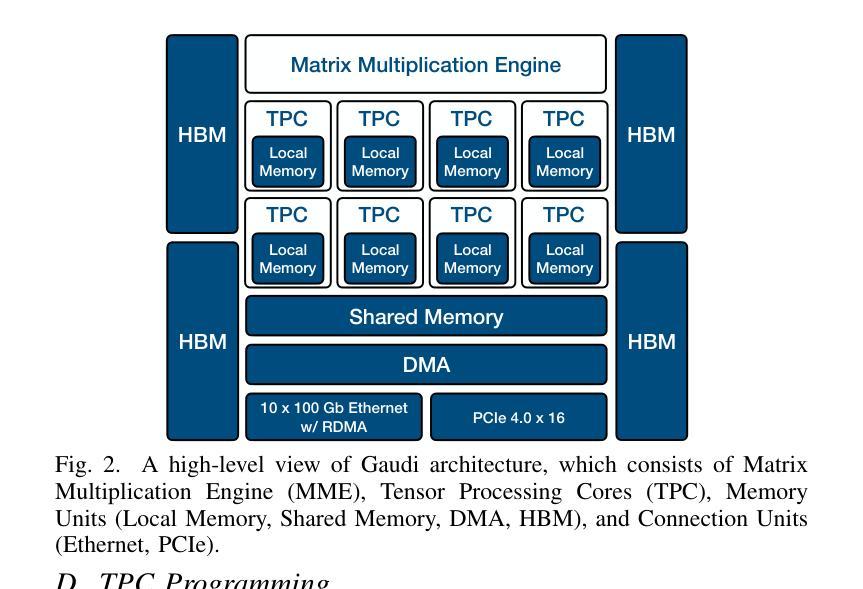
GFormer: Accelerating Large Language Models with Optimized Transformers on Gaudi Processors
Authors:Chengming Zhang, Xinheng Ding, Baixi Sun, Xiaodong Yu, Weijian Zheng, Zhen Xie, Dingwen Tao
Heterogeneous hardware like Gaudi processor has been developed to enhance computations, especially matrix operations for Transformer-based large language models (LLMs) for generative AI tasks. However, our analysis indicates that Transformers are not fully optimized on such emerging hardware, primarily due to inadequate optimizations in non-matrix computational kernels like Softmax and in heterogeneous resource utilization, particularly when processing long sequences. To address these issues, we propose an integrated approach (called GFormer) that merges sparse and linear attention mechanisms. GFormer aims to maximize the computational capabilities of the Gaudi processor’s Matrix Multiplication Engine (MME) and Tensor Processing Cores (TPC) without compromising model quality. GFormer includes a windowed self-attention kernel and an efficient outer product kernel for causal linear attention, aiming to optimize LLM inference on Gaudi processors. Evaluation shows that GFormer significantly improves efficiency and model performance across various tasks on the Gaudi processor and outperforms state-of-the-art GPUs.
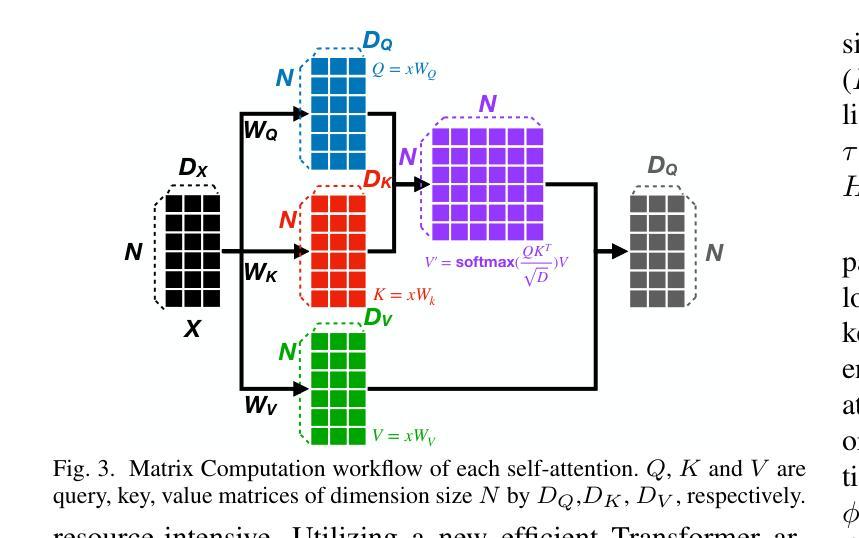
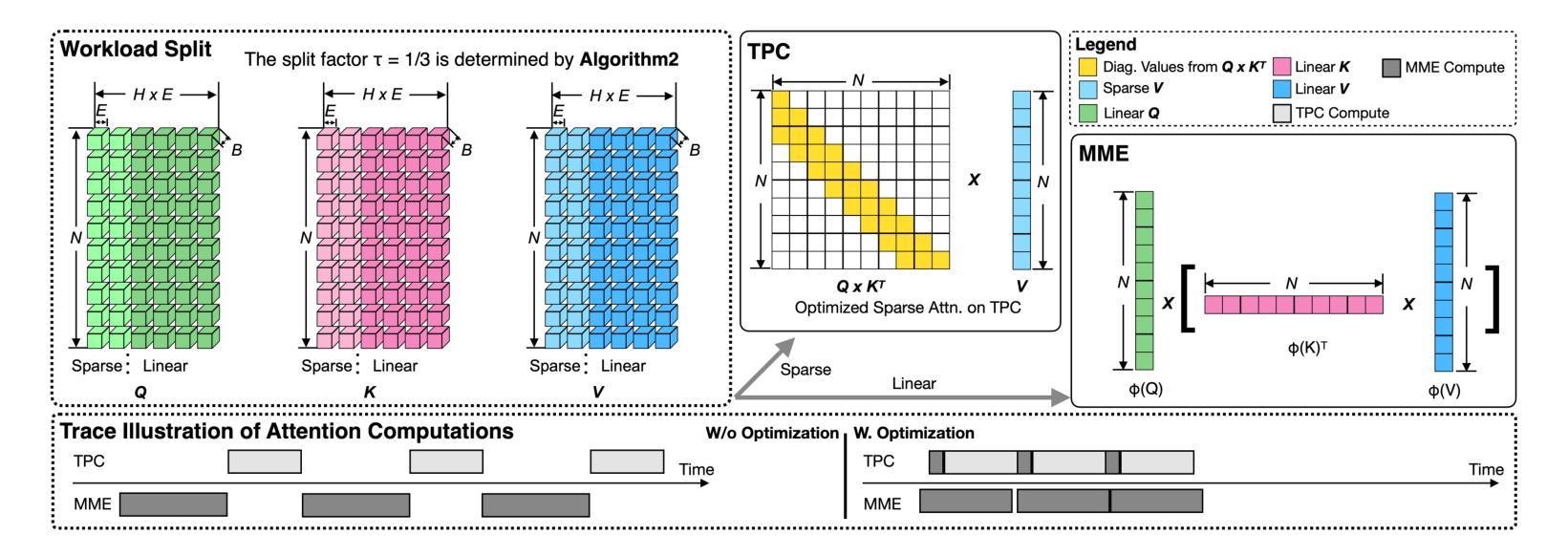
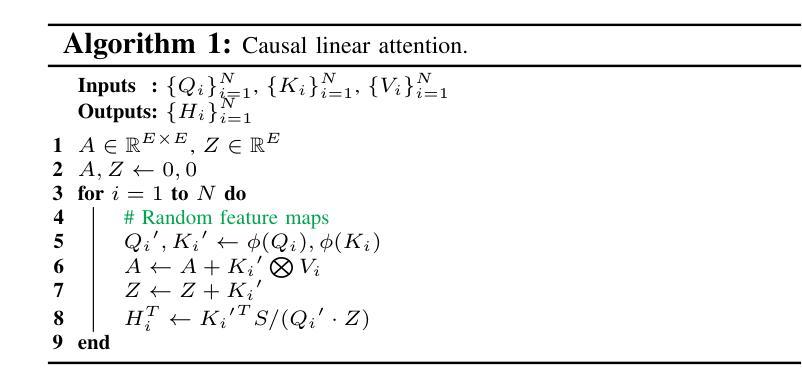
针对生成式人工智能任务,已经开发了如高斯处理器等异构硬件来增强计算能力,特别是针对基于Transformer的大型语言模型(LLM)的矩阵运算。然而,我们的分析表明,Transformer在这种新兴硬件上并未完全优化,这主要是因为Softmax等非矩阵计算内核的优化不足以及异构资源利用率低下,特别是在处理长序列时。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种集成方法(称为Gformer),它结合了稀疏和线性注意力机制。Gformer旨在最大化高斯处理器矩阵乘法引擎(MME)和张量处理核心(TPC)的计算能力,同时不损害模型质量。Gformer包括一个窗口自注意力内核和一个高效的外部乘积内核,用于因果线性注意力,旨在优化在高斯处理器上的LLM推理。评估表明,Gformer在高斯处理器上大大提高了效率和模型性能,并优于最新的GPU。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对新兴硬件如Gaudi处理器,本文研究了其在Transformer大型语言模型(LLM)计算方面的优化问题。文章指出,由于非矩阵计算内核(如Softmax)和异构资源利用率等方面的不足,Transformer的优化并不充分。为此,文章提出了一种融合稀疏和线性注意力机制的综合方法(称为GFormer),旨在最大化Gaudi处理器的矩阵乘法引擎(MME)和张量处理核心(TPC)的计算能力,同时不损害模型质量。通过引入窗口自注意力内核和高效的因果线性注意力外积内核,GFormer旨在优化Gaudi处理器上的LLM推理。评估结果表明,GFormer在Gaudi处理器上大大提高了效率和模型性能,并优于最新的GPU。
Key Takeaways
- Gaudi处理器被开发用于增强计算,特别是针对Transformer大型语言模型的矩阵操作。
- 目前Transformer在Gaudi处理器上的优化存在不足,主要表现在非矩阵计算内核和异构资源利用率方面。
- GFormer是一种综合方法,旨在解决上述问题,通过融合稀疏和线性注意力机制来优化计算。
- GFormer能够最大化Gaudi处理器的计算能力,同时保持模型质量。
- GFormer包括窗口自注意力内核和因果线性注意力的外积内核,以优化Gaudi处理器上的LLM推理。
- 评估表明,GFormer在Gaudi处理器上显著提高了效率和模型性能。
点此查看论文截图


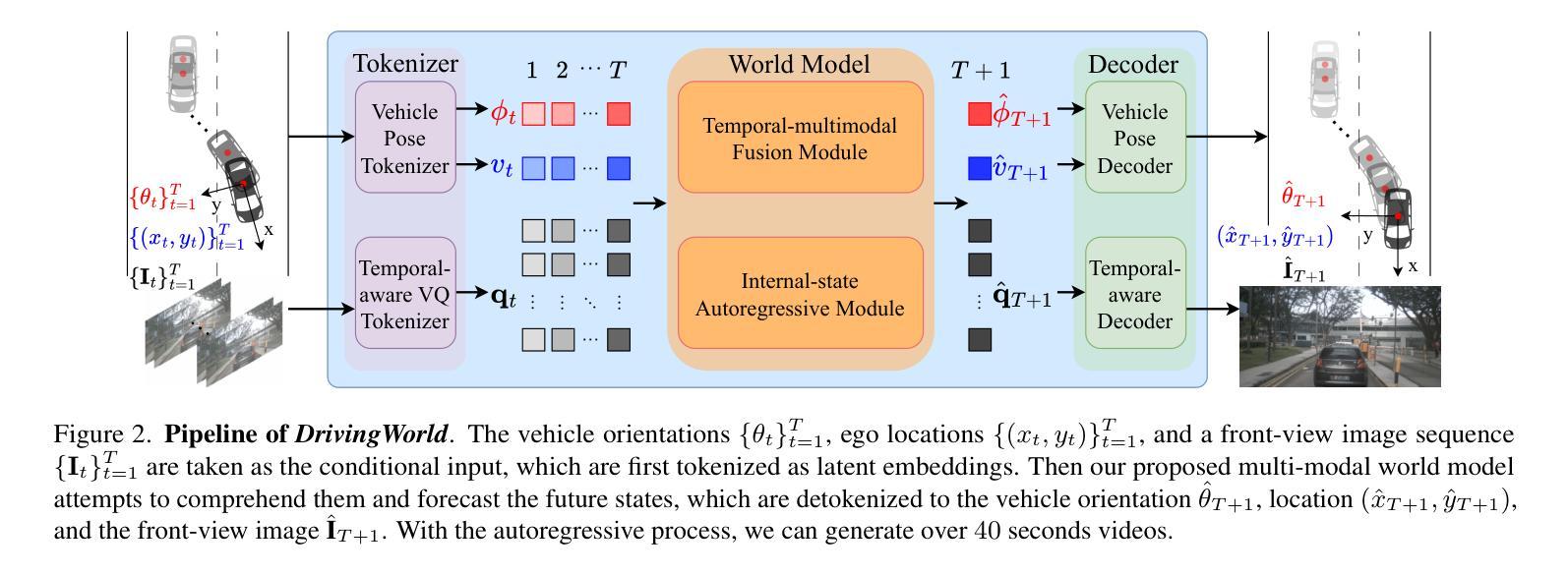
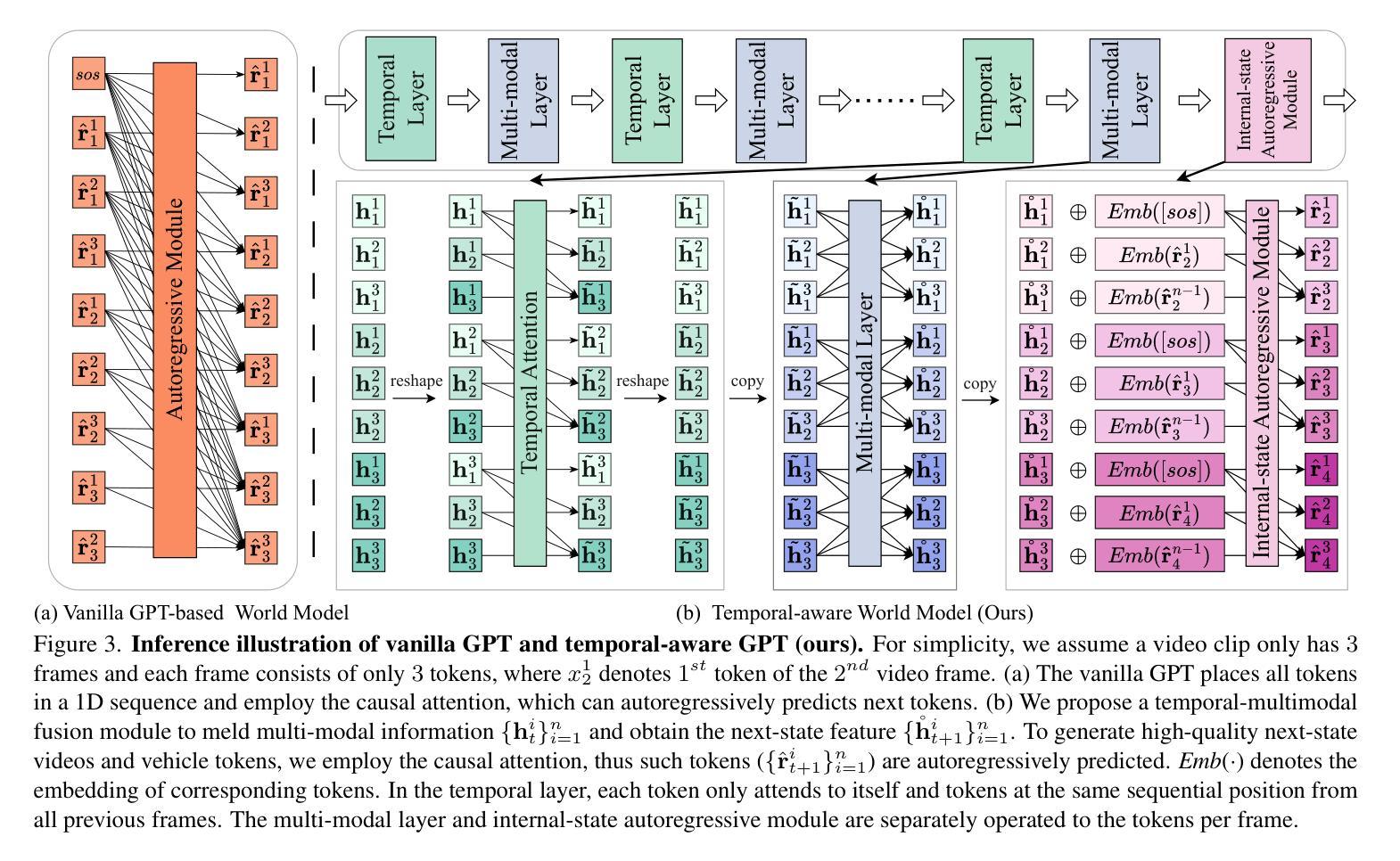
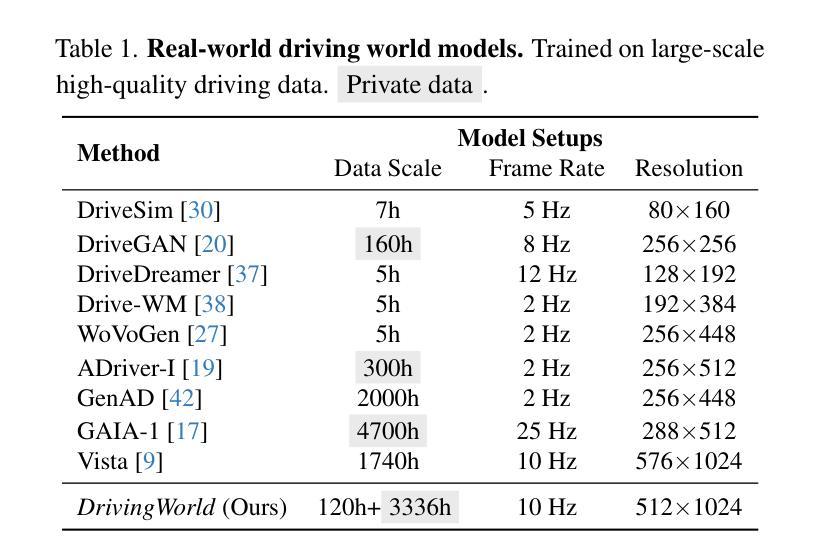
DrivingWorld: Constructing World Model for Autonomous Driving via Video GPT
Authors:Xiaotao Hu, Wei Yin, Mingkai Jia, Junyuan Deng, Xiaoyang Guo, Qian Zhang, Xiaoxiao Long, Ping Tan
Recent successes in autoregressive (AR) generation models, such as the GPT series in natural language processing, have motivated efforts to replicate this success in visual tasks. Some works attempt to extend this approach to autonomous driving by building video-based world models capable of generating realistic future video sequences and predicting ego states. However, prior works tend to produce unsatisfactory results, as the classic GPT framework is designed to handle 1D contextual information, such as text, and lacks the inherent ability to model the spatial and temporal dynamics essential for video generation. In this paper, we present DrivingWorld, a GPT-style world model for autonomous driving, featuring several spatial-temporal fusion mechanisms. This design enables effective modeling of both spatial and temporal dynamics, facilitating high-fidelity, long-duration video generation. Specifically, we propose a next-state prediction strategy to model temporal coherence between consecutive frames and apply a next-token prediction strategy to capture spatial information within each frame. To further enhance generalization ability, we propose a novel masking strategy and reweighting strategy for token prediction to mitigate long-term drifting issues and enable precise control. Our work demonstrates the ability to produce high-fidelity and consistent video clips of over 40 seconds in duration, which is over 2 times longer than state-of-the-art driving world models. Experiments show that, in contrast to prior works, our method achieves superior visual quality and significantly more accurate controllable future video generation. Our code is available at https://github.com/YvanYin/DrivingWorld.
近期在自然语言处理中的GPT系列等成果展示了自回归(AR)生成模型的成功,这激发了人们将这种成功复制到视觉任务的努力。一些工作尝试将这种技术扩展到自动驾驶领域,通过建立基于视频的能够生成逼真的未来视频序列并预测自我意识状态的世界模型。然而,先前的工作往往产生令人不满意的结果,因为经典的GPT框架设计用于处理一维上下文信息(如文本),缺乏建模视频生成所需的固有空间和时间动态能力。在本文中,我们提出了用于自动驾驶的DrivingWorld世界模型,这是一种具有多种时空融合机制的GPT风格设计。这种设计使空间和时间动态的建模有效,实现了高保真、长时间的视频生成。具体来说,我们提出了一种下一状态预测策略来模拟连续帧之间的时间连贯性,并采用下一个令牌预测策略来捕获每个帧内的空间信息。为了进一步提高泛化能力,我们提出了一种新颖的令牌预测掩码策略和重新加权策略,以减轻长期漂移问题并实现精确控制。我们的工作能够产生持续超过40秒的高保真且连贯的视频片段,这比最先进的驾驶世界模型的时间长两倍多。实验表明,与之前的工作相比,我们的方法在视觉质量和可控的未来视频生成方面达到了更高的水平。我们的代码可在https://github.com/YvanYin/DrivingWorld上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
近期自然语言处理中的GPT系列等自回归生成模型的成功,激发了将其应用于视觉任务的努力。本文尝试将这一方法应用于自动驾驶领域,提出了一种基于视频的自动驾驶世界模型DrivingWorld,旨在生成逼真的未来视频序列并预测自我状态。与之前的工作相比,DrivingWorld设计了多种时空融合机制,实现了对视频时空动态的有效建模,能够生成高保真、长时间的视频。通过提出一种状态预测策略和一种标记预测策略,提高了模型的时空连贯性和空间信息捕捉能力。此外,还提出了一种新颖的掩码策略和重权策略来减轻长期漂移问题并实现精确控制。实验表明,相较于之前的工作,该方法在视觉质量和可控的未来视频生成方面表现更优秀。代码已公开在https://github.com/YvanYin/DrivingWorld。
关键见解
- 自回归生成模型在自动驾驶领域的应用受到关注。
- DrivingWorld是一种基于视频的自动驾驶世界模型,采用GPT风格设计。
- 该模型通过多种时空融合机制实现视频时空动态的有效建模。
- 驾驶世界模型能生成高保真、长时间的视频,时长超过现有模型的两倍。
- 模型采用状态预测策略和标记预测策略来提高时空连贯性和空间信息捕捉。
- 引入掩码策略和重权策略以解决长期漂移问题并实现精确控制。
点此查看论文截图

RecLM: Recommendation Instruction Tuning
Authors:Yangqin Jiang, Yuhao Yang, Lianghao Xia, Da Luo, Kangyi Lin, Chao Huang
Modern recommender systems aim to deeply understand users’ complex preferences through their past interactions. While deep collaborative filtering approaches using Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) excel at capturing user-item relationships, their effectiveness is limited when handling sparse data or zero-shot scenarios, primarily due to constraints in ID-based embedding functions. To address these challenges, we propose a model-agnostic recommendation instruction-tuning paradigm that seamlessly integrates large language models with collaborative filtering. Our proposed Recommendation Language Model (RecLM) enhances the capture of user preference diversity through a carefully designed reinforcement learning reward function that facilitates self-augmentation of language models. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate significant advantages of our approach across various settings, and its plug-and-play compatibility with state-of-the-art recommender systems results in notable performance enhancements.
现代推荐系统旨在通过用户过去的交互来深入了解用户的复杂偏好。虽然使用图神经网络(GNNs)的深度协同过滤方法在捕捉用户-项目关系方面表现出色,但当处理稀疏数据或零射击场景时,它们的有效性受到限制,这主要是因为基于ID的嵌入函数的约束。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种模型无关的推荐指令微调范式,该范式无缝集成了大型语言模型与协同过滤。我们提出的推荐语言模型(RecLM)通过精心设计的强化学习奖励函数提高了对用户偏好多样性的捕捉,该奖励函数促进了语言模型的自我增强。综合评估表明,我们的方法在各种设置中具有显著优势,并且它与最新推荐系统的即插即用兼容性可实现显著的性能提升。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
现代推荐系统致力于通过用户过去的互动来深入理解其复杂的偏好。针对图神经网络在处理稀疏数据或零样本场景时的局限性,我们提出了一种模型无关的推荐指令调整范式,该范式能够无缝地将大型语言模型与协同过滤集成在一起。我们的推荐语言模型(RecLM)通过精心设计的强化学习奖励函数,提高了对用户偏好多样性的捕捉能力,促进了语言模型的自我增强。综合评估表明,我们的方法在各种设置中具有显著优势,并且与最先进的推荐系统的即插即用兼容性带来了显著的性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- 现代推荐系统致力于通过用户过去的行为理解其复杂偏好。
- 图神经网络在处理稀疏数据或零样本场景时存在局限性。
- 提出了一种模型无关的推荐指令调整方法,集成大型语言模型与协同过滤。
- 推荐语言模型(RecLM)通过强化学习奖励函数提高用户偏好多样性的捕捉。
- RecLM能促进语言模型的自我增强。
- 综合评估显示RecLM在各种设置中具有显著优势。
点此查看论文截图

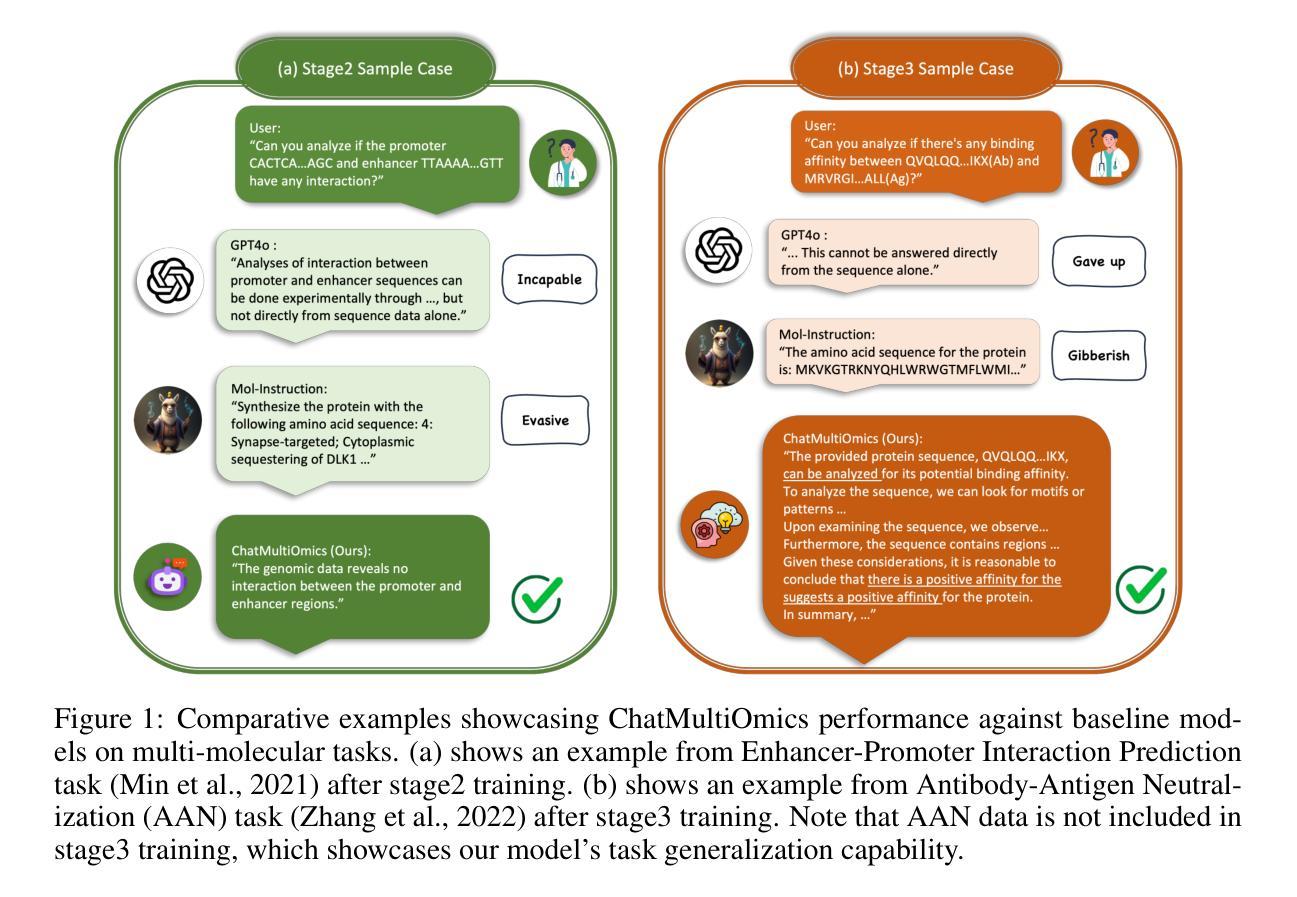
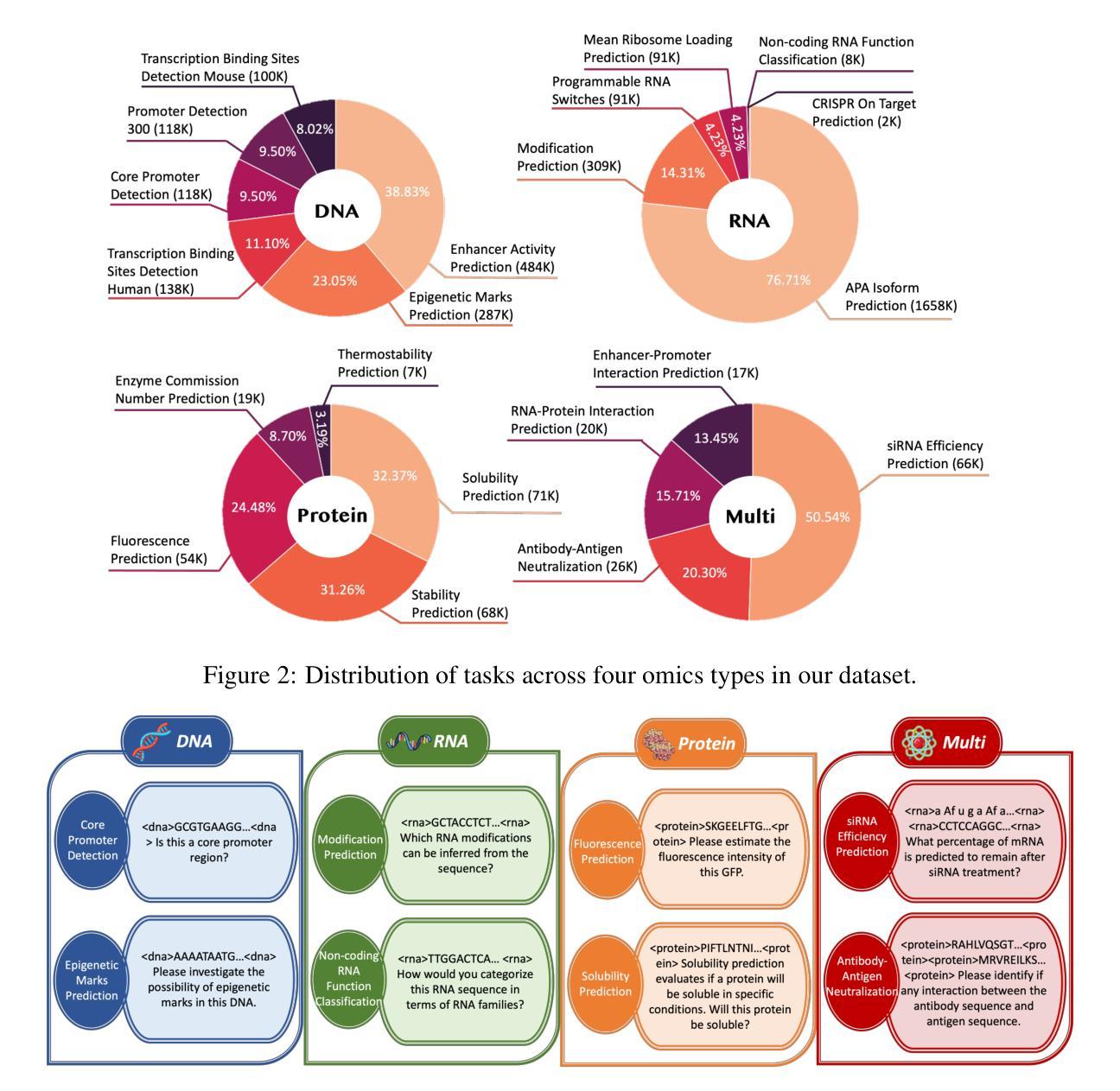
Biology Instructions: A Dataset and Benchmark for Multi-Omics Sequence Understanding Capability of Large Language Models
Authors:Haonan He, Yuchen Ren, Yining Tang, Ziyang Xu, Junxian Li, Minghao Yang, Di Zhang, Dong Yuan, Tao Chen, Shufei Zhang, Yuqiang Li, Nanqing Dong, Wanli Ouyang, Dongzhan Zhou, Peng Ye
Large language models have already demonstrated their formidable capabilities in general domains, ushering in a revolutionary transformation. However, exploring and exploiting the extensive knowledge of these models to comprehend multi-omics biology remains underexplored. To fill this research gap, we first introduce Biology-Instructions, the first large-scale multi-omics biological sequences-related instruction-tuning dataset including DNA, RNA, proteins, and multi-molecules, designed to bridge the gap between large language models (LLMs) and complex biological sequences-related tasks. This dataset can enhance the versatility of LLMs by integrating diverse biological sequenced-based prediction tasks with advanced reasoning capabilities, while maintaining conversational fluency. Additionally, we reveal significant performance limitations in even state-of-the-art LLMs on biological sequence-related multi-omics tasks without specialized pre-training and instruction-tuning. We further develop a strong baseline called ChatMultiOmics with a novel three-stage training pipeline, demonstrating the powerful ability to understand biology by using Biology-Instructions. Biology-Instructions and ChatMultiOmics are publicly available and crucial resources for enabling more effective integration of LLMs with multi-omics sequence analysis.
大型语言模型已经在通用领域展现了其强大的能力,并引领了一场革命性的变革。然而,探索这些模型丰富的知识以理解多组学生物学仍然是一个尚未充分研究的领域。为了填补这一研究空白,我们首先引入了生物学指令数据集(Biology-Instructions),这是第一个大规模的多组学生物序列相关指令微调数据集,包括DNA、RNA、蛋白质和多种分子,旨在弥补大型语言模型(LLM)与复杂的生物序列相关任务之间的差距。该数据集通过整合多样化的生物序列预测任务与先进的推理能力,同时保持对话的流畅性,增强了LLM的通用性。此外,我们还揭示了即使在最先进的LLM上,在没有专门的预训练和指令微调的情况下,它们在生物序列相关的多组学任务上的性能也存在显著的局限性。我们进一步开发了一个强大的基线模型ChatMultiOmics,采用新颖的三阶段训练管道,利用生物学指令展示了强大的生物学理解能力。生物学指令和ChatMultiOmics是公开可用的重要资源,对于更有效地将LLM与多组学序列分析相结合至关重要。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型在通用领域展现强大能力,但在理解多组学生物学方面应用不足。为此,我们推出Biology-Instructions数据集,包含DNA、RNA、蛋白质等多分子生物序列相关指令微调数据,旨在填补大型语言模型与复杂生物序列任务之间的鸿沟。该数据集增强LLM的通用性,通过集成多样生物序列预测任务与高级推理能力,同时保持语言流畅。我们揭示即使是最先进的LLMs在处理生物序列相关多组学任务时仍存在显著性能局限,需专门预训练与指令微调。我们开发出ChatMultiOmics基线模型,采用创新的三阶段训练管道,展示使用Biology-Instructions理解生物学的强大能力。两者均为公开资源,有助于LLMs与多组学序列分析的有效结合。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在多组学生物学领域的运用尚待探索。
- Biology-Instructions数据集是首个大规模多组学生物序列相关指令微调数据集,旨在连接大型语言模型与复杂生物序列任务。
- 该数据集能增强大型语言模型的通用性,结合生物序列预测任务和高级推理能力,同时保持语言流畅。
- 先进的大型语言模型在处理生物序列相关多组学任务时存在性能局限,需要专门的预训练和指令微调。
- ChatMultiOmics基线模型采用创新的三阶段训练管道,展现强大的生物学理解能力。
- Biology-Instructions和ChatMultiOmics都是公开资源,为大型语言模型和多组学序列分析的结合提供了重要支持。
点此查看论文截图

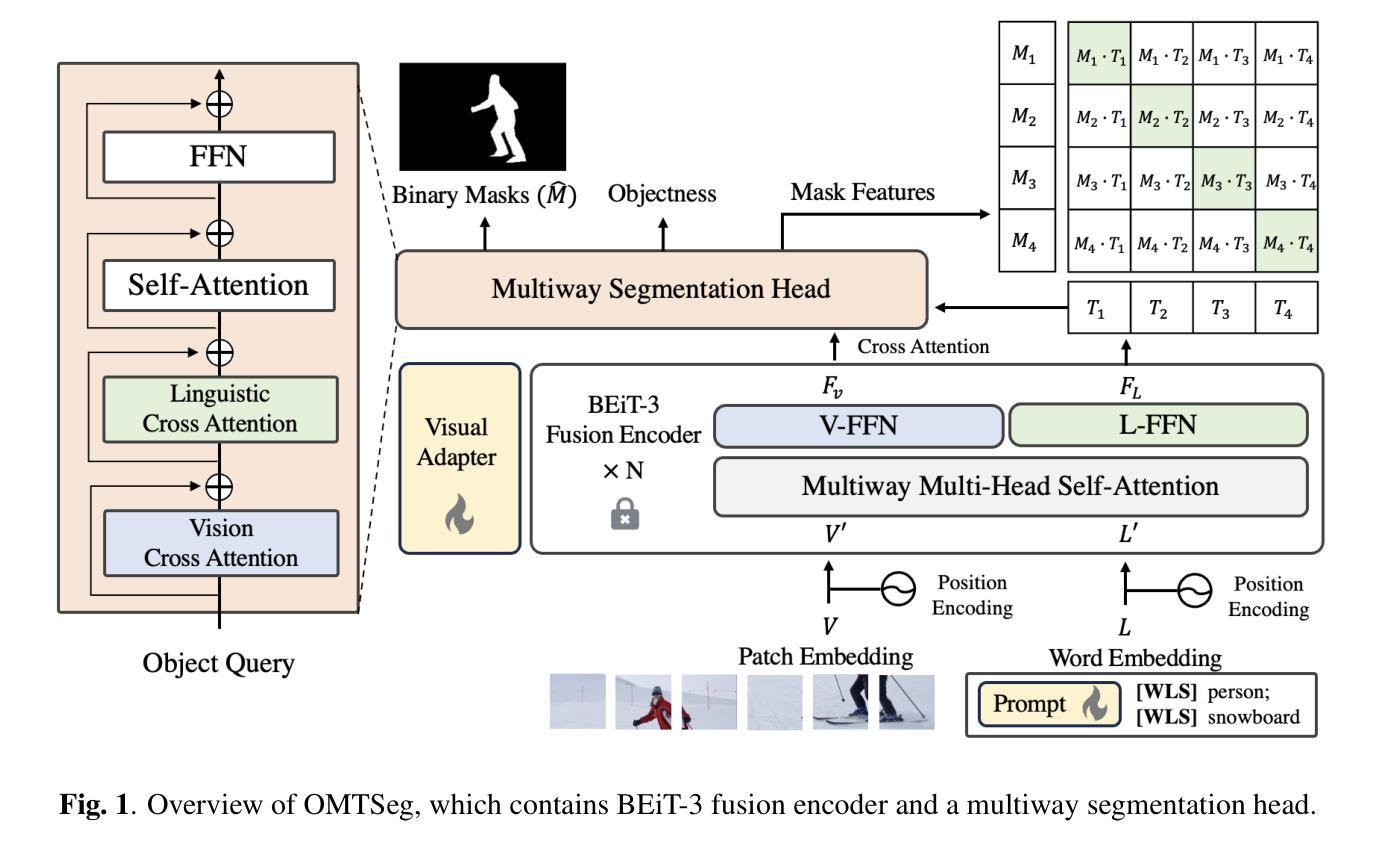
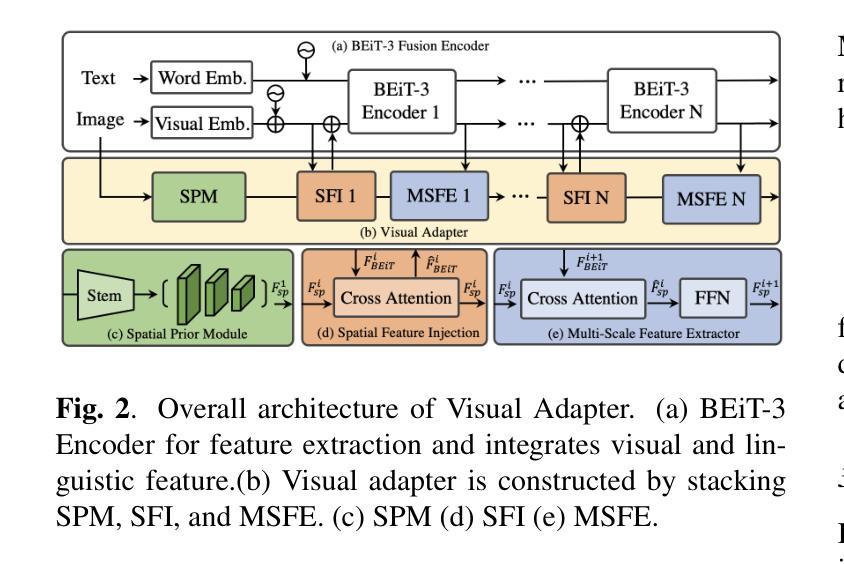
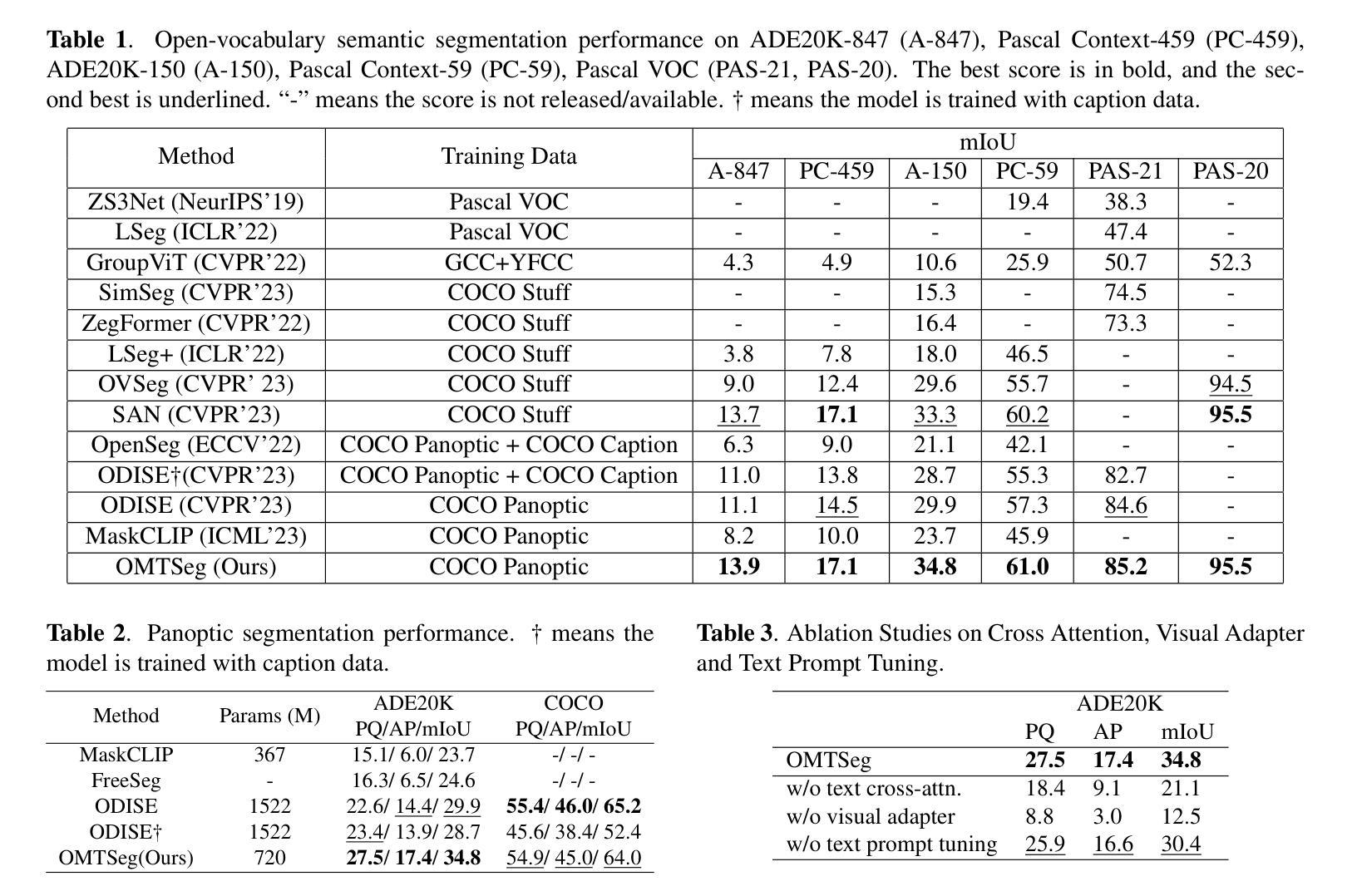
Open-Vocabulary Panoptic Segmentation Using BERT Pre-Training of Vision-Language Multiway Transformer Model
Authors:Yi-Chia Chen, Wei-Hua Li, Chu-Song Chen
Open-vocabulary panoptic segmentation remains a challenging problem. One of the biggest difficulties lies in training models to generalize to an unlimited number of classes using limited categorized training data. Recent popular methods involve large-scale vision-language pre-trained foundation models, such as CLIP. In this paper, we propose OMTSeg for open-vocabulary segmentation using another large-scale vision-language pre-trained model called BEiT-3 and leveraging the cross-modal attention between visual and linguistic features in BEiT-3 to achieve better performance. Experiments result demonstrates that OMTSeg performs favorably against state-of-the-art models.
开放词汇全景分割仍然是一个具有挑战性的问题。最大的困难之一是,在有限的分类训练数据上训练模型,使其能够推广到无限数量的类别。最近流行的方法涉及大规模视觉语言预训练基础模型,如CLIP。在本文中,我们提出使用另一种大规模视觉语言预训练模型Beit-3进行开放词汇分割的OMTSeg方法,并借助Beit-3中的视觉和语言特征之间的跨模态注意力来实现更好的性能。实验结果表明,OMTSeg的表现优于现有最先进的模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICIP 2024
Summary
本文提出一种基于大规模视觉语言预训练模型BEiT-3的开放词汇表分割方法OMTSeg。该方法利用BEiT-3中视觉和语言特征之间的跨模态注意力机制,通过有限分类的训练数据训练模型,使其能够泛化到无限数量的类别。实验结果表明,OMTSeg相较于当前先进模型表现出优越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 开放词汇表分割是一个挑战性问题,主要在于如何利用有限的分类训练数据来训练模型以泛化到无限数量的类别。
- 论文提出了一种新的方法OMTSeg,基于大规模视觉语言预训练模型BEiT-3进行开放词汇表分割。
- OMTSeg利用BEiT-3中的跨模态注意力机制,结合视觉和语言特征,以实现更好的性能。
- 实验结果表明,OMTSeg相较于当前先进模型具有优越性能。
- 该方法对于处理大规模、多样化数据的场景具有潜在的应用价值。
- OMTSeg的提出展示了预训练模型在解决计算机视觉任务中的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

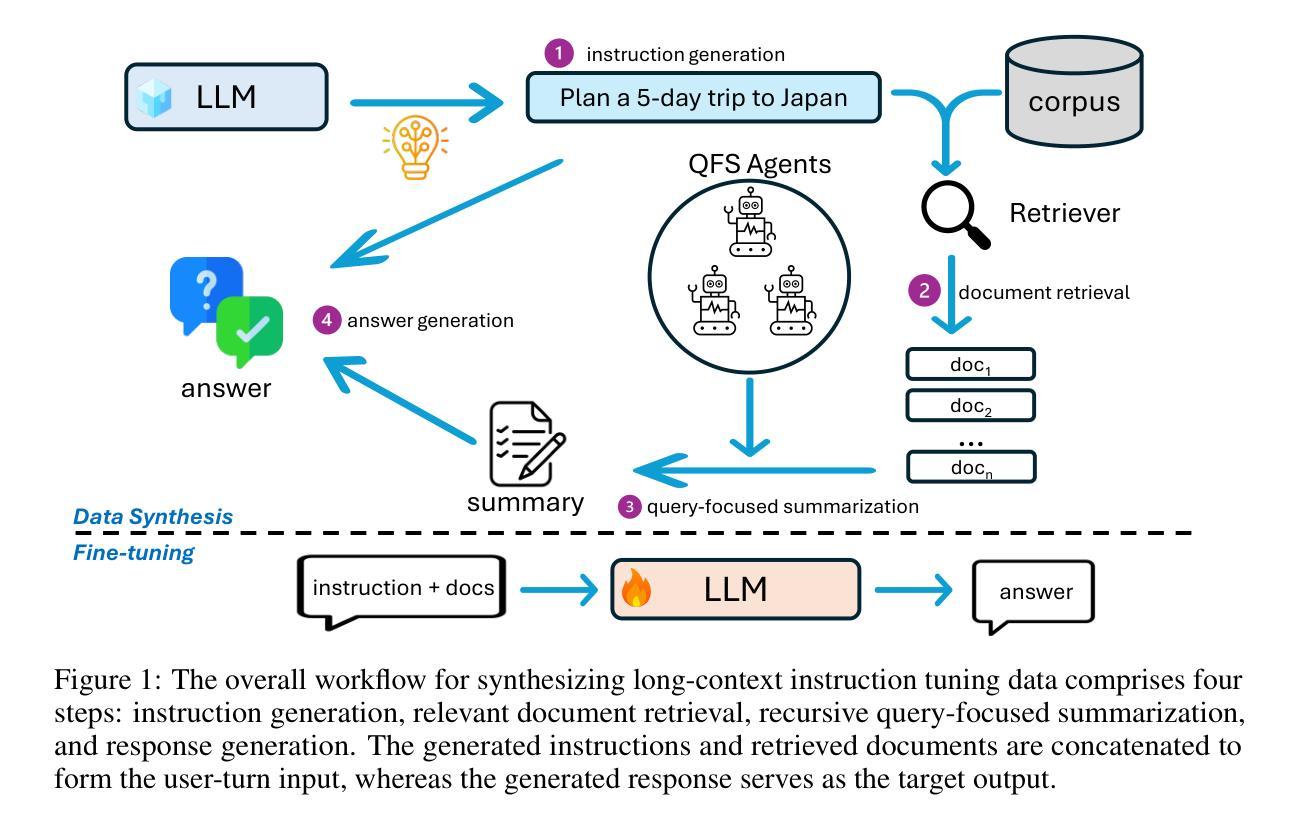
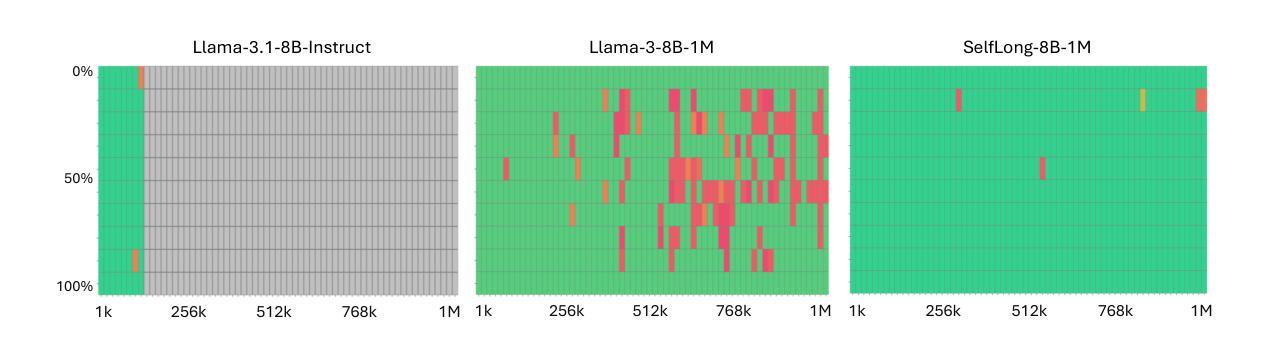
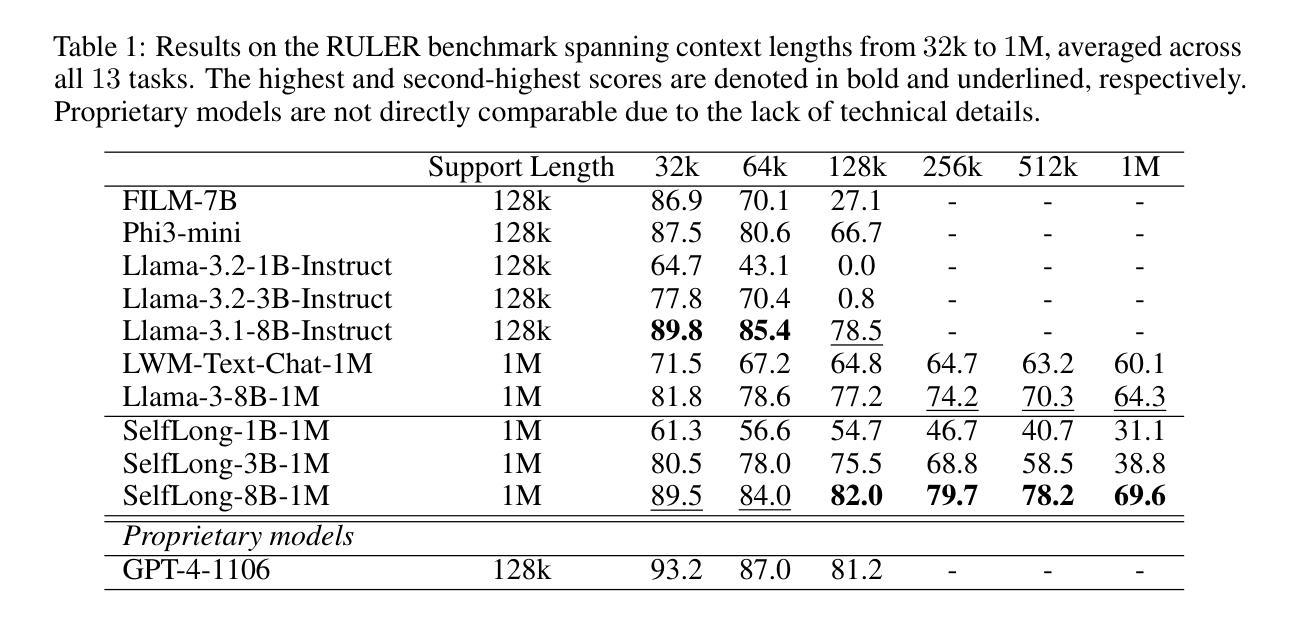
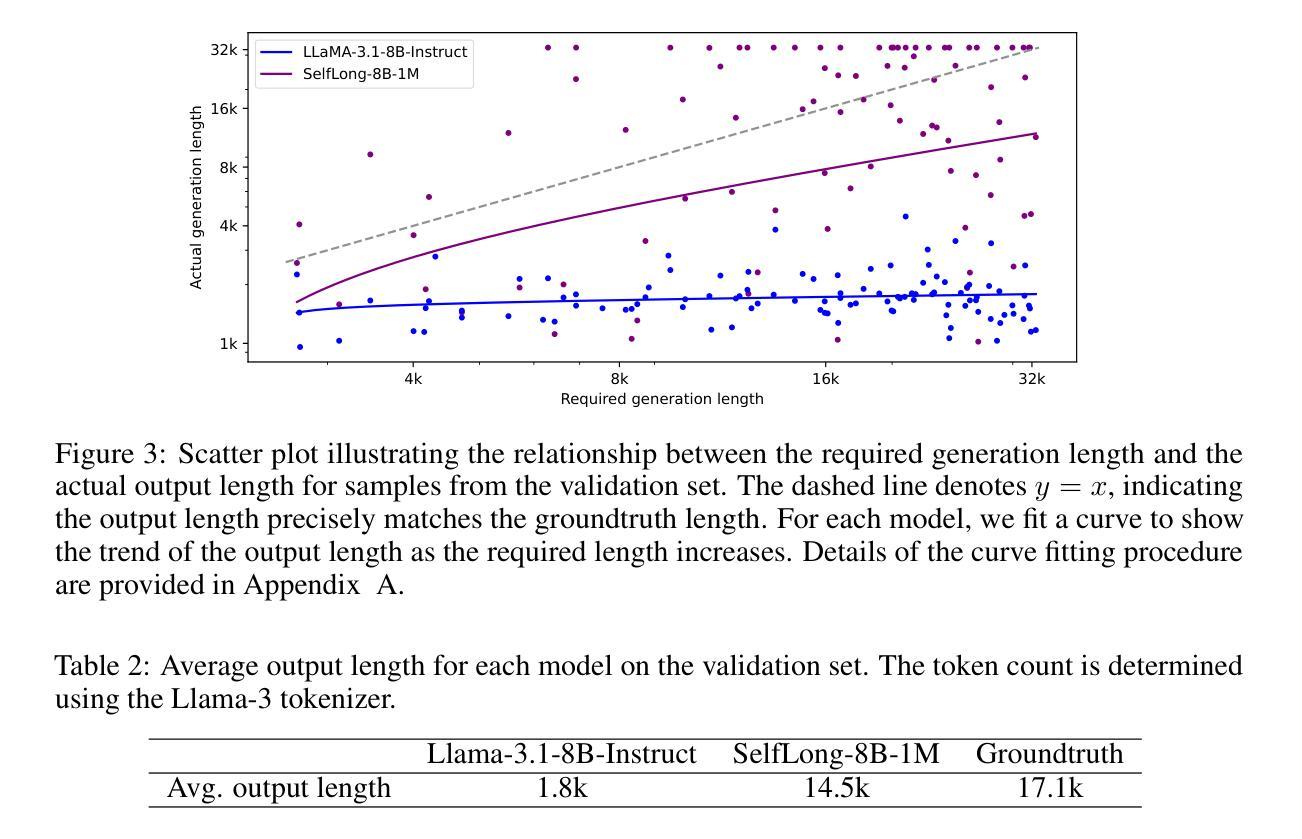
Bootstrap Your Own Context Length
Authors:Liang Wang, Nan Yang, Xingxing Zhang, Xiaolong Huang, Furu Wei
We introduce a bootstrapping approach to train long-context language models by exploiting their short-context capabilities only. Our method utilizes a simple agent workflow to synthesize diverse long-context instruction tuning data, thereby eliminating the necessity for manual data collection and annotation. The proposed data synthesis workflow requires only a short-context language model, a text retriever, and a document collection, all of which are readily accessible within the open-source ecosystem. Subsequently, language models are fine-tuned using the synthesized data to extend their context lengths. In this manner, we effectively transfer the short-context capabilities of language models to long-context scenarios through a bootstrapping process. We conduct experiments with the open-source Llama-3 family of models and demonstrate that our method can successfully extend the context length to up to 1M tokens, achieving superior performance across various benchmarks.
我们引入了一种利用长上下文语言模型的短上下文能力进行训练的自举方法。我们的方法利用一个简单的代理工作流程来合成多样化的长上下文指令调整数据,从而消除了手动收集和标注数据的必要性。所提出的数据合成工作流程只需要短上下文语言模型、文本检索器和文档集合,所有这些都可以在开源生态系统中轻松访问。随后,使用合成数据对语言模型进行微调,以扩展其上下文长度。通过这种方式,我们通过自举过程有效地将语言模型的短上下文能力转移到长上下文场景。我们对开源Llama-3系列模型进行实验,并证明我们的方法可以将上下文长度成功扩展到高达1M个令牌,在各种基准测试中表现优异。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages
Summary
介绍了一种利用短语境能力训练长语境语言模型的自举方法。该方法通过简单的代理工作流程合成多样化的长语境指令调整数据,消除了对手动数据收集和注释的需求。使用短语境语言模型、文本检索器和文档集合等开源生态系统中的资源即可实现数据合成。随后,使用合成数据对语言模型进行微调,以扩展其上下文长度。通过这种方式,我们有效地将通过自举过程将语言模型的短语境能力转移到长语境场景。对开源Llama-3系列模型的实验表明,该方法可将上下文长度成功扩展到100万令牌,并在各种基准测试中表现优越。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了一种利用短语境能力训练长语境语言模型的自举方法。
- 通过简单的代理工作流程合成多样化的长语境指令调整数据。
- 消除了对手动数据收集和注释的需求。
- 使用短语境语言模型、文本检索器和文档集合等开源资源实现数据合成。
- 通过微调语言模型使用合成数据来扩展其上下文长度。
- 成功将语言模型的短语境能力转移到长语境场景。
点此查看论文截图

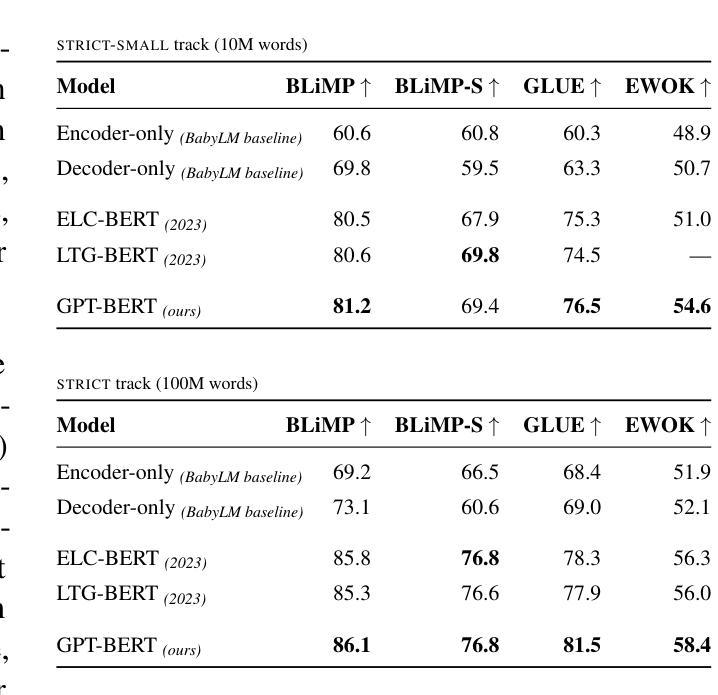
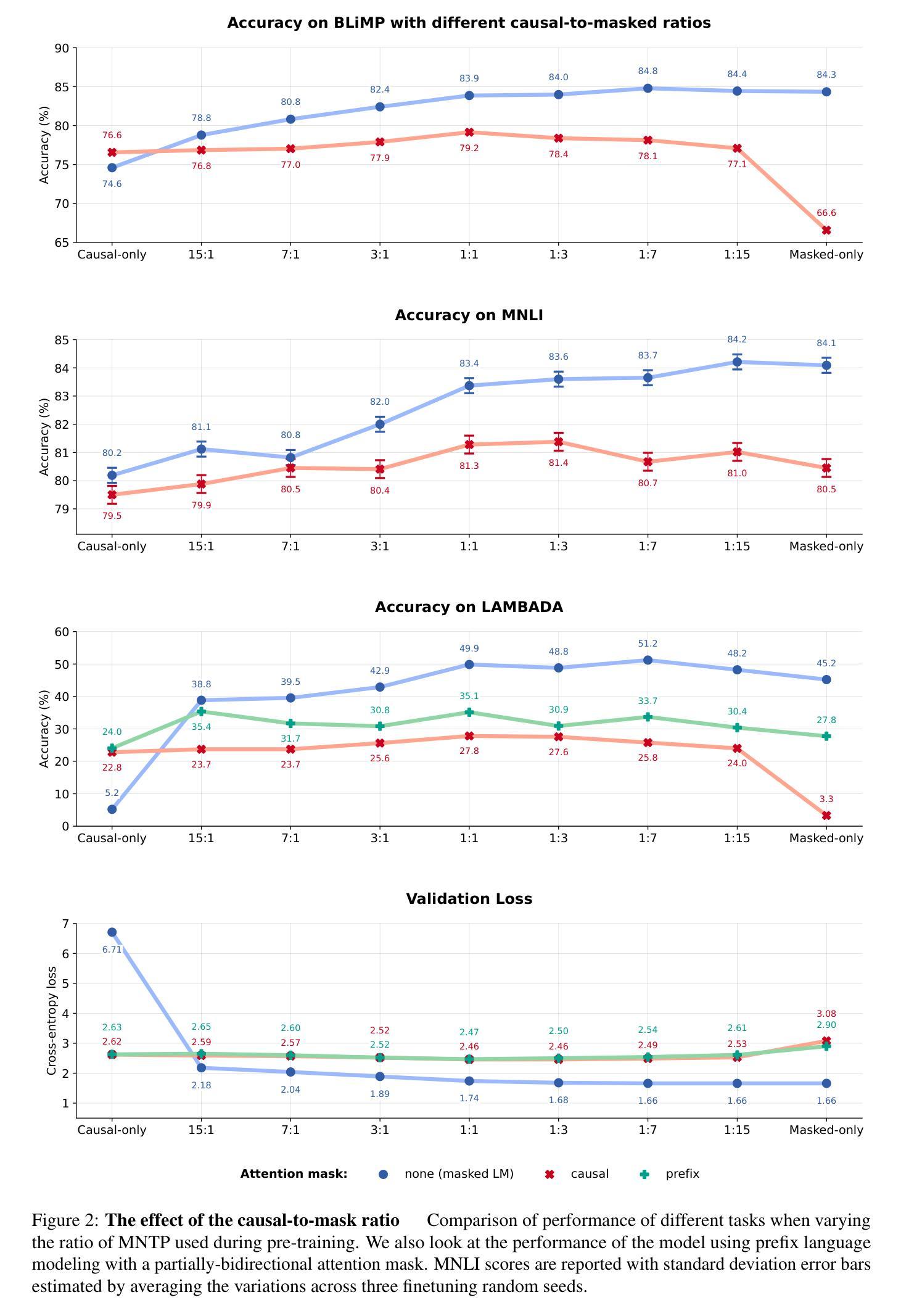
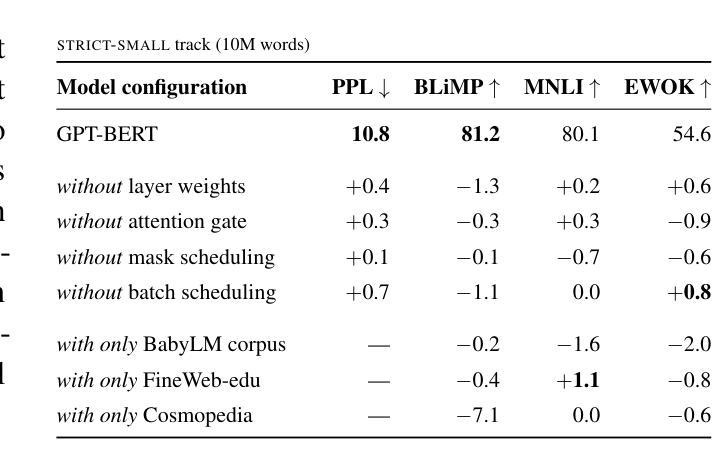
GPT or BERT: why not both?
Authors:Lucas Georges Gabriel Charpentier, David Samuel
We present a simple way to merge masked language modeling with causal language modeling. This hybrid training objective results in a model that combines the strengths of both modeling paradigms within a single transformer stack: GPT-BERT can be transparently used like any standard causal or masked language model. We test the pretraining process that enables this flexible behavior on the BabyLM Challenge 2024. The results show that the hybrid pretraining outperforms masked-only or causal-only models. We openly release the models, training corpora and code.
我们提出了一种简单的方法,将掩码语言建模与因果语言建模相结合。这种混合训练目标导致了一个模型,该模型在一个单一的变压器堆栈内结合了两种建模方法的优点:GPT-BERT可以像任何标准的因果或掩码语言模型一样透明地使用。我们在BabyLM Challenge 2024上测试了这种灵活行为的预训练过程。结果表明,混合预训练优于仅使用掩码或仅使用因果的模型。我们公开发布模型、训练语料库和代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages; submission to the BabyLM Challenge 2024
Summary
本文介绍了一种将掩码语言建模与因果语言建模相结合的方法。这种混合训练目标使得模型能够在单个变压器堆栈中结合两种建模方法的优点:GPT-BERT可以像任何标准因果或掩码语言模型一样透明地使用。在BabyLM Challenge 2024上测试了这种灵活行为的预训练过程,结果显示混合预训练优于仅使用掩码或仅使用因果的模型。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种结合掩码语言建模与因果语言建模的方法。
- 该方法允许模型在同一转换器堆栈中结合两种建模方法的优点。
- GPT-BERT可以像标准因果或掩码语言模型一样使用。
- 在BabyLM Challenge 2024上进行了预训练过程测试。
- 混合预训练表现优于仅使用掩码或仅使用因果的模型。
- 公开发布了模型、训练语料库和代码。
- 这种结合方法有助于提高语言模型的性能和灵活性。
点此查看论文截图