⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-02 更新
Bringing Objects to Life: 4D generation from 3D objects
Authors:Ohad Rahamim, Ori Malca, Dvir Samuel, Gal Chechik
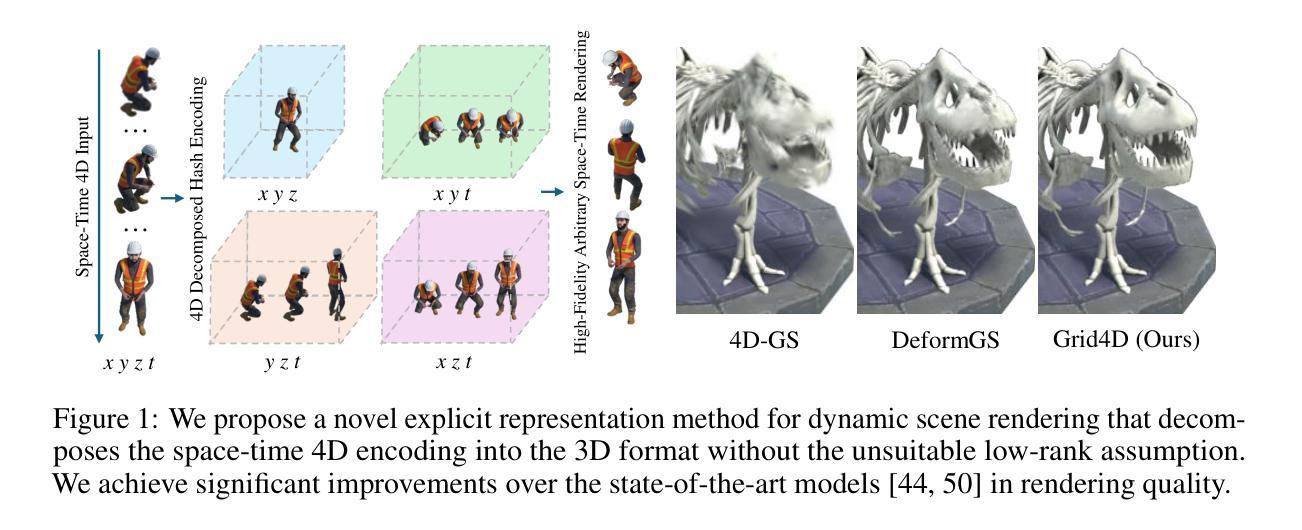
Recent advancements in generative modeling now enable the creation of 4D content (moving 3D objects) controlled with text prompts. 4D generation has large potential in applications like virtual worlds, media, and gaming, but existing methods provide limited control over the appearance and geometry of generated content. In this work, we introduce a method for animating user-provided 3D objects by conditioning on textual prompts to guide 4D generation, enabling custom animations while maintaining the identity of the original object. We first convert a 3D mesh into a ``static” 4D Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) that preserves the visual attributes of the input object. Then, we animate the object using an Image-to-Video diffusion model driven by text. To improve motion realism, we introduce an incremental viewpoint selection protocol for sampling perspectives to promote lifelike movement and a masked Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) loss, which leverages attention maps to focus optimization on relevant regions. We evaluate our model in terms of temporal coherence, prompt adherence, and visual fidelity and find that our method outperforms baselines that are based on other approaches, achieving up to threefold improvements in identity preservation measured using LPIPS scores, and effectively balancing visual quality with dynamic content.
最近生成模型领域的进展现在已能够实现使用文本提示创建4D内容(动态3D物体)。4D生成在虚拟世界、媒体和游戏等领域具有巨大潜力,但现有方法对于生成内容的外貌和几何结构的控制有限。在这项工作中,我们介绍了一种通过文本提示进行条件动画处理用户提供的3D物体的方法,以指导4D生成,实现在保持原始物体身份的同时进行自定义动画。我们首先将3D网格转换为“静态”的4D神经辐射场(NeRF),以保留输入物体的视觉属性。然后,我们使用文本驱动的图像到视频的扩散模型对物体进行动画处理。为了提高运动逼真度,我们引入了增量视角选择协议用于采样视角,以促进更逼真的运动,以及遮罩分数蒸馏采样(SDS)损失,该损失利用注意力图将优化重点放在相关区域。我们从时间连贯性、提示遵循程度和视觉保真度三个方面评估了我们的模型,发现我们的方法在其他方法的基础上表现更好,在通过LPIPS分数测量的身份保留方面实现了高达三倍的提升,并在视觉质量与动态内容之间实现了有效平衡。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种通过文本提示驱动用户提供的3D对象动画的方法,实现了4D内容的生成。该方法先将3D网格转换为静态的4D神经辐射场(NeRF),保留输入对象的视觉属性,然后使用图像到视频的扩散模型进行动画化。为提高运动真实感,引入了增量视角选择协议和带注意力图的掩膜得分蒸馏采样(SDS)损失。实验表明,该方法在保持身份连续性、遵循提示和视觉保真度方面优于其他方法,实现了三倍的身份保留改进。
Key Takeaways
- 该技术能够创建通过文本提示控制的4D内容(动态3D对象)。
- 将3D网格转换为静态的4D神经辐射场(NeRF),保留对象的视觉属性。
- 使用图像到视频的扩散模型对对象进行动画化。
- 引入增量视角选择协议,促进更逼真的运动。
- 使用掩膜得分蒸馏采样(SDS)损失提高运动真实感,利用注意力图优化相关区域。
- 在保持身份连续性、遵循提示和视觉保真度方面优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

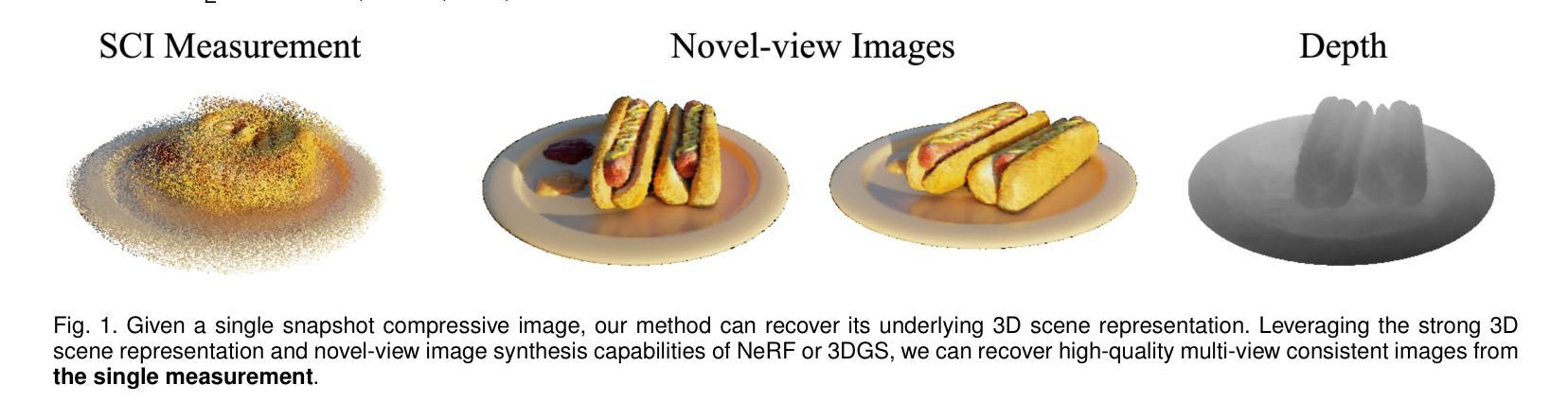
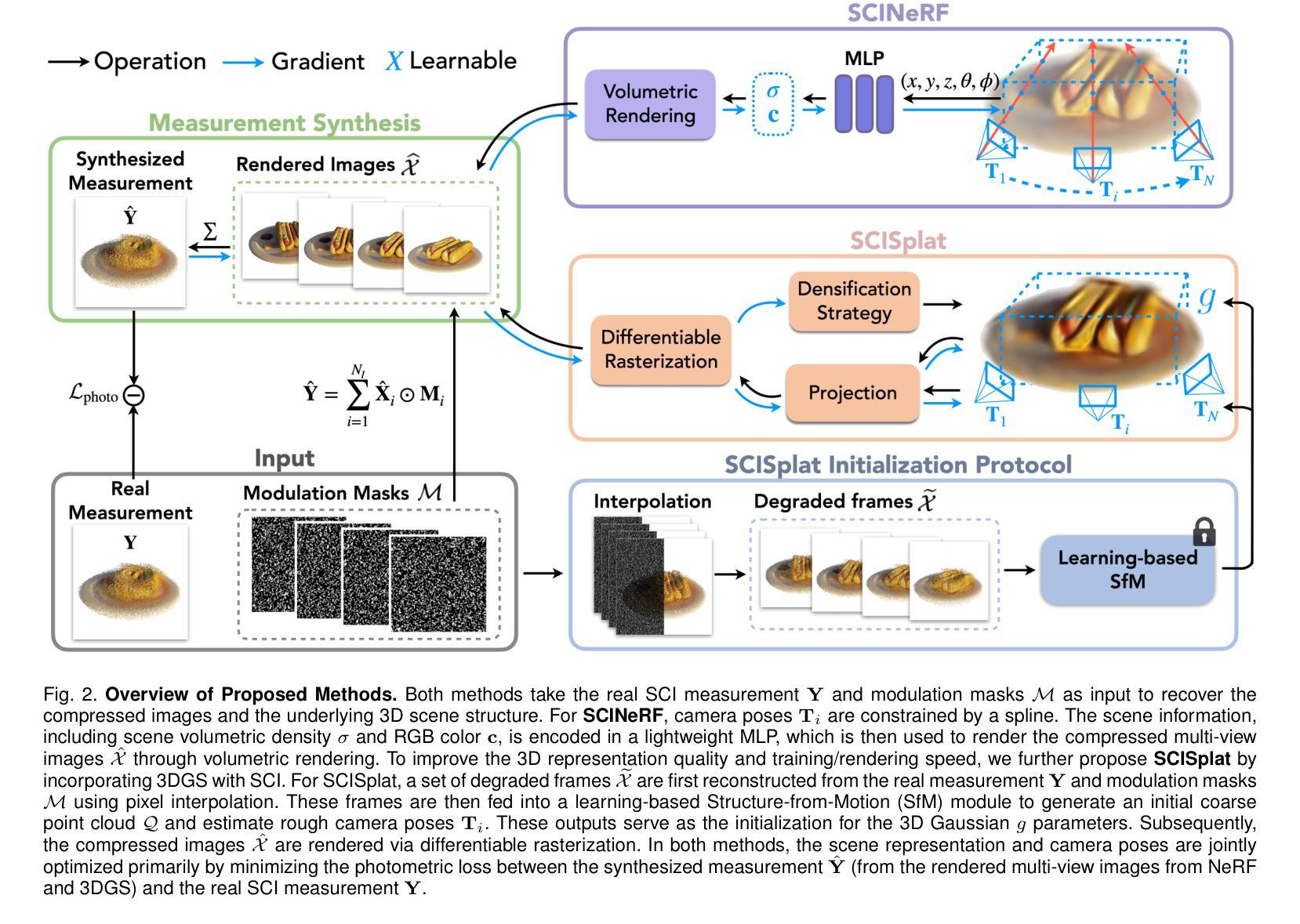
Learning Radiance Fields from a Single Snapshot Compressive Image
Authors:Yunhao Li, Xiang Liu, Xiaodong Wang, Xin Yuan, Peidong Liu
In this paper, we explore the potential of Snapshot Compressive Imaging (SCI) technique for recovering the underlying 3D scene structure from a single temporal compressed image. SCI is a cost-effective method that enables the recording of high-dimensional data, such as hyperspectral or temporal information, into a single image using low-cost 2D imaging sensors. To achieve this, a series of specially designed 2D masks are usually employed, reducing storage and transmission requirements and offering potential privacy protection. Inspired by this, we take one step further to recover the encoded 3D scene information leveraging powerful 3D scene representation capabilities of neural radiance fields (NeRF). Specifically, we propose SCINeRF, in which we formulate the physical imaging process of SCI as part of the training of NeRF, allowing us to exploit its impressive performance in capturing complex scene structures. In addition, we further integrate the popular 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) framework and propose SCISplat to improve 3D scene reconstruction quality and training/rendering speed by explicitly optimizing point clouds into 3D Gaussian representations. To assess the effectiveness of our method, we conduct extensive evaluations using both synthetic data and real data captured by our SCI system. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed approach surpasses the state-of-the-art methods in terms of image reconstruction and novel view synthesis. Moreover, our method also exhibits the ability to render high frame-rate multi-view consistent images in real time by leveraging SCI and the rendering capabilities of 3DGS. Codes will be available at: https://github.com/WU- CVGL/SCISplat.
本文探讨了快照压缩成像(SCI)技术在从单个时间压缩图像中恢复潜在的三维场景结构方面的潜力。SCI是一种经济高效的方法,它能够将高维数据(如光谱或时间信息)使用低成本的二维成像传感器记录为单个图像。为实现这一点,通常采用一系列专门设计的二维掩膜,以降低存储和传输要求并提供潜在的隐私保护。在此基础上,我们更进一步利用神经辐射场(NeRF)的强大三维场景表示能力,恢复编码的三维场景信息。具体来说,我们提出了SCINeRF,其中我们将SCI的物理成像过程作为NeRF训练的一部分,使我们能够利用其捕捉复杂场景结构的令人印象深刻的表现。此外,我们进一步集成了流行的三维高斯喷绘(3DGS)框架,并提出了SCISplat,通过显式优化点云到三维高斯表示来提高三维场景重建质量以及训练和渲染速度。为了评估我们方法的有效性,我们使用合成数据和由我们的SCI系统捕获的真实数据进行了广泛评估。实验结果表明,我们提出的方法在图像重建和新颖视图合成方面超过了最先进的方法。而且,我们的方法还展示了利用SCI和3DGS的渲染能力实时呈现高帧率多视角一致图像的能力。代码将在https://github.com/WU-CVGL/SCISplat上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文探讨了基于快照压缩成像(SCI)技术恢复潜在三维场景结构的方法,从单张时间压缩图像中恢复三维场景信息。SCI是一种经济高效的方法,能够使用低成本的二维成像传感器记录高维数据,如超光谱或时间信息。通过设计一系列二维掩膜实现编码过程,这种方法减少了存储和传输需求,并提供潜在隐私保护。本研究在此基础上进一步采用神经网络辐射场(NeRF)强大的三维场景表示能力恢复编码的三维场景信息。具体来说,我们提出了SCINeRF方法,将SCI的物理成像过程纳入NeRF的训练过程中,利用其在捕捉复杂场景结构方面的出色性能。此外,我们整合了流行的三维高斯喷涂(3DGS)框架,提出了SCISplat方法,通过优化点云到三维高斯表示形式提高三维场景重建质量并加速训练和渲染速度。通过合成数据和由我们的SCI系统捕获的真实数据进行了广泛评估,实验结果表明我们的方法超越最先进的图像重建和新型视图合成方法。此外,我们的方法还展现了借助SCI和3DGS的渲染能力实时渲染高帧率多视角一致图像的能力。相关代码将发布在:https://github.com/WU-CVGL/SCISplat。
要点摘要
- 研究利用快照压缩成像(SCI)技术从单张时间压缩图像中恢复三维场景结构。
- SCI方法利用低成本的二维成像传感器记录高维数据。
- 提出SCINeRF方法,结合NeRF的三维场景表示能力恢复编码的三维场景信息。
- 结合三维高斯喷涂(3DGS)框架的SCISplat方法提高了三维场景重建质量和训练/渲染速度。
- 实验结果表明,所提出的方法在图像重建和新型视图合成方面超越现有技术。
- 方法能够实时渲染高帧率多视角一致图像。
点此查看论文截图
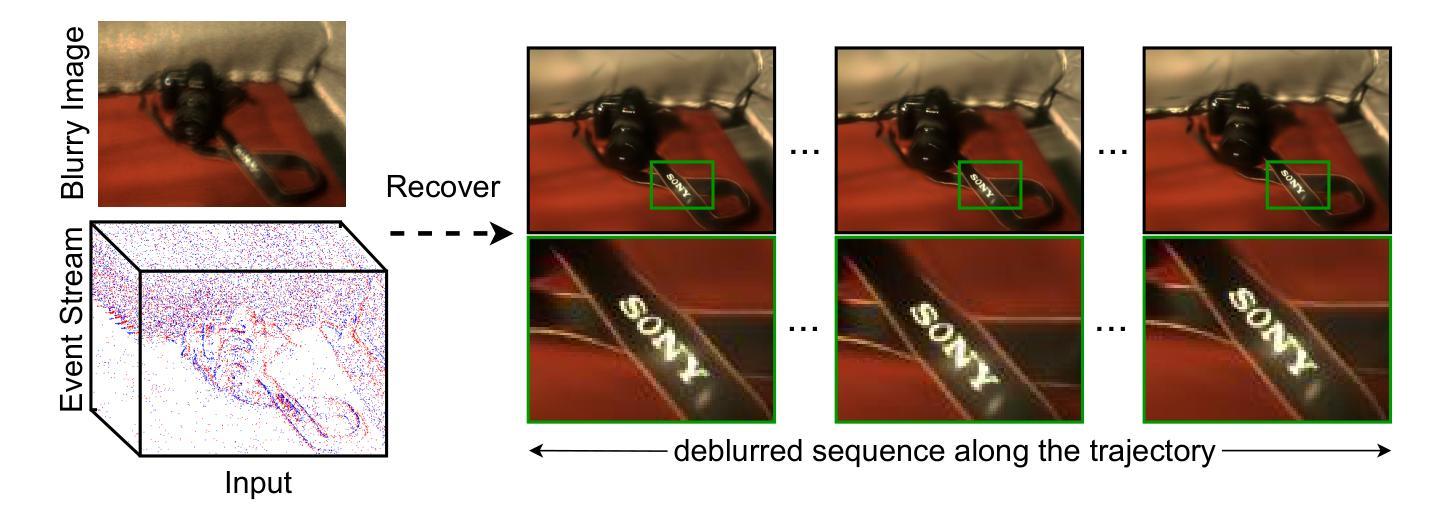
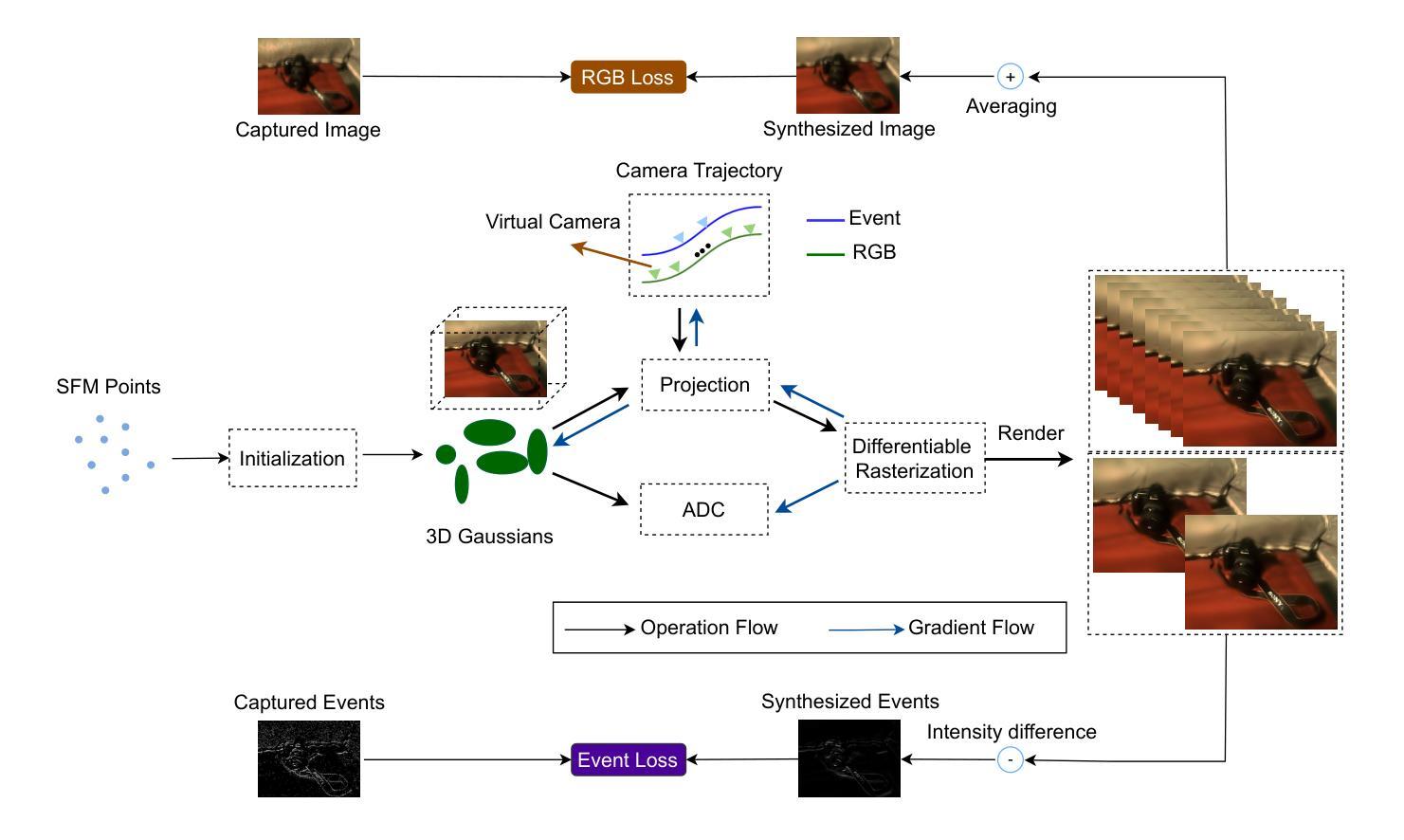
BeSplat – Gaussian Splatting from a Single Blurry Image and Event Stream
Authors:Gopi Raju Matta, Reddypalli Trisha, Kaushik Mitra
Novel view synthesis has been greatly enhanced by the development of radiance field methods. The introduction of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has effectively addressed key challenges, such as long training times and slow rendering speeds, typically associated with Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), while maintaining high-quality reconstructions. In this work (BeSplat), we demonstrate the recovery of sharp radiance field (Gaussian splats) from a single motion-blurred image and its corresponding event stream. Our method jointly learns the scene representation via Gaussian Splatting and recovers the camera motion through Bezier SE(3) formulation effectively, minimizing discrepancies between synthesized and real-world measurements of both blurry image and corresponding event stream. We evaluate our approach on both synthetic and real datasets, showcasing its ability to render view-consistent, sharp images from the learned radiance field and the estimated camera trajectory. To the best of our knowledge, ours is the first work to address this highly challenging ill-posed problem in a Gaussian Splatting framework with the effective incorporation of temporal information captured using the event stream.
随着辐射场方法的发展,新型视图合成技术得到了极大的增强。3D高斯喷涂技术(3DGS)的引入有效地解决了与神经辐射场(NeRF)通常相关的主要挑战,如训练时间长和渲染速度慢,同时保持了高质量的重建。在这项工作(BeSplat)中,我们展示了从单个运动模糊图像及其相应的事件流中恢复锐利的辐射场(高斯喷涂)的能力。我们的方法通过高斯喷涂联合学习场景表示,并通过贝塞尔SE(3)公式有效恢复相机运动,从而最小化合成和真实世界测量之间的模糊图像和相应事件流的差异。我们在合成数据集和真实数据集上评估了我们的方法,展示了从学习的辐射场和估计的相机轨迹渲染出一致、清晰图像的能力。据我们所知,我们的工作是在高斯喷涂框架下解决这一极具挑战性的不适定问题的首批工作之一,有效地结合了使用事件流捕获的时间信息。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at EVGEN2025, WACV-25 Workshop
Summary
本文介绍了如何通过引入3D高斯Splatting(3DGS)技术,解决神经辐射场(NeRF)长期存在的训练时间长和渲染速度慢的问题,同时保持了高质量的重构。该研究展示了从单张运动模糊图像及其对应的事件流中恢复出锐化的辐射场(高斯Splats)的能力。该方法通过高斯Splatting学习场景表示,并通过Bezier SE(3)公式有效地恢复相机运动,最小化合成图像和真实世界测量之间的模糊图像和对应事件流的差异。在合成和真实数据集上的评估证明了该方法能够从学习的辐射场和估计的相机轨迹中渲染出连贯、清晰的图像。这是首次在Gaussian Splatting框架下解决这一具有挑战性的不适定问题,并有效利用事件流捕获的暂时信息。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了3D高斯Splatting技术以解决NeRF存在的训练时间长和渲染速度慢的问题。
- 成功从单张运动模糊图像及其对应的事件流中恢复出锐化的辐射场。
- 通过高斯Splatting学习场景表示,并有效地恢复相机运动。
- 利用Bezier SE(3)公式最小化合成图像和真实测量之间的差异。
- 在合成和真实数据集上的评估证明了该方法的有效性。
- 该方法能够渲染出连贯、清晰的图像。
点此查看论文截图

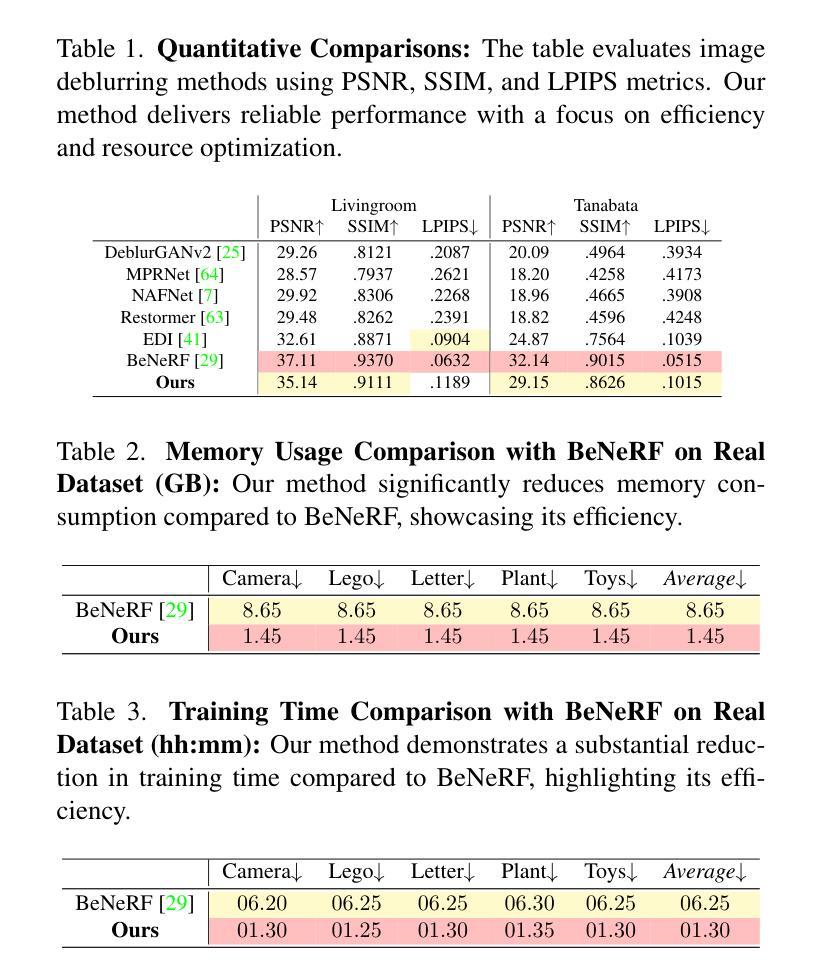
Generating Editable Head Avatars with 3D Gaussian GANs
Authors:Guohao Li, Hongyu Yang, Yifang Men, Di Huang, Weixin Li, Ruijie Yang, Yunhong Wang
Generating animatable and editable 3D head avatars is essential for various applications in computer vision and graphics. Traditional 3D-aware generative adversarial networks (GANs), often using implicit fields like Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), achieve photorealistic and view-consistent 3D head synthesis. However, these methods face limitations in deformation flexibility and editability, hindering the creation of lifelike and easily modifiable 3D heads. We propose a novel approach that enhances the editability and animation control of 3D head avatars by incorporating 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) as an explicit 3D representation. This method enables easier illumination control and improved editability. Central to our approach is the Editable Gaussian Head (EG-Head) model, which combines a 3D Morphable Model (3DMM) with texture maps, allowing precise expression control and flexible texture editing for accurate animation while preserving identity. To capture complex non-facial geometries like hair, we use an auxiliary set of 3DGS and tri-plane features. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach delivers high-quality 3D-aware synthesis with state-of-the-art controllability. Our code and models are available at https://github.com/liguohao96/EGG3D.
生成可动画化和可编辑的3D头像对于计算机视觉和图形学中的各种应用至关重要。传统的基于隐式场的3D感知生成对抗网络(GANs),常常使用如神经辐射场(NeRF)等技术,实现了逼真的、视角一致的3D头像合成。然而,这些方法在变形灵活性和可编辑性方面存在局限性,阻碍了生动且易于修改的3D头像的创建。我们提出了一种结合显式三维表示法——三维高斯喷射(3DGS)的新方法,以提高三维头像的可编辑性和动画控制力。这种方法使得光照控制更加容易,可编辑性也更强。我们的方法的核心是可编辑高斯头(EG-Head)模型,它将三维可变形模型(3DMM)与纹理映射相结合,允许精确的表情控制和灵活的纹理编辑,以实现准确的动画同时保留身份特征。为了捕捉头发等非面部复杂几何结构,我们使用一组辅助的3DGS和三平面特征。大量实验证明,我们的方法实现了高质量的具有先进可控性的三维感知合成。我们的代码和模型可在https://github.com/liguohao96/EGG3D获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了生成可动画和可编辑的3D头像的重要性及其在计算机视觉和图形学中的多种应用。传统的使用NeRF等隐式场的3D GANs虽然可以实现逼真的3D头像合成,但在变形灵活性和可编辑性方面存在局限。本文提出了一种新方法,通过引入3D高斯涂抹(3DGS)作为明确的3D表示,提高了3D头像的可编辑性和动画控制。该方法使用可编辑的高斯头像(EG-Head)模型,结合3D形态模型和纹理映射,实现精确的表情控制和灵活的纹理编辑,同时保持身份识别。为了捕捉非面部几何形状(如头发),使用了辅助的3DGS和三平面特征。实验证明,该方法实现了高质量的3D感知合成,并具有较高的可控性。
Key Takeaways
- 生成可动画和可编辑的3D头像对于计算机视觉和图形学应用至关重要。
- 传统使用NeRF的3D GANs在变形灵活性和可编辑性方面存在局限。
- 引入3D高斯涂抹(3DGS)作为明确的3D表示,提高了3D头像的可编辑性和动画控制。
- 可编辑的高斯头像(EG-Head)模型结合了3D形态模型和纹理映射,实现精确的表情控制和灵活的纹理编辑。
- 为了捕捉非面部几何形状(如头发),使用了辅助的3DGS和三平面特征。
- 该方法实现了高质量的3D感知合成,并具有高度的可控性。
点此查看论文截图

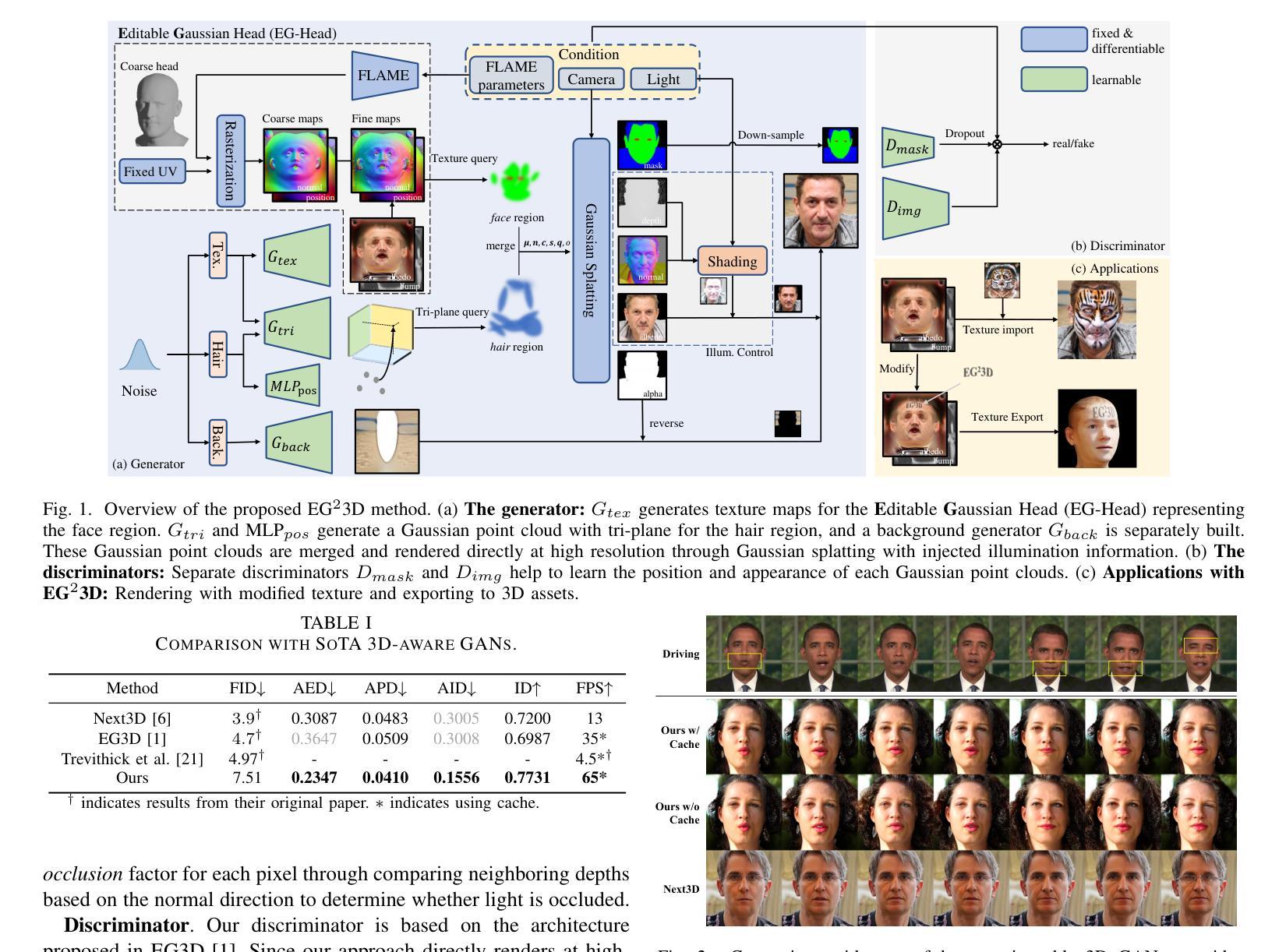

MVS-GS: High-Quality 3D Gaussian Splatting Mapping via Online Multi-View Stereo
Authors:Byeonggwon Lee, Junkyu Park, Khang Truong Giang, Sungho Jo, Soohwan Song
This study addresses the challenge of online 3D model generation for neural rendering using an RGB image stream. Previous research has tackled this issue by incorporating Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) or 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) as scene representations within dense SLAM methods. However, most studies focus primarily on estimating coarse 3D scenes rather than achieving detailed reconstructions. Moreover, depth estimation based solely on images is often ambiguous, resulting in low-quality 3D models that lead to inaccurate renderings. To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel framework for high-quality 3DGS modeling that leverages an online multi-view stereo (MVS) approach. Our method estimates MVS depth using sequential frames from a local time window and applies comprehensive depth refinement techniques to filter out outliers, enabling accurate initialization of Gaussians in 3DGS. Furthermore, we introduce a parallelized backend module that optimizes the 3DGS model efficiently, ensuring timely updates with each new keyframe. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art dense SLAM methods, particularly excelling in challenging outdoor environments.
本研究旨在应对使用RGB图像流进行神经渲染的在线3D模型生成挑战。之前的研究已经通过结合神经辐射场(NeRF)或3D高斯喷绘(3DGS)作为密集SLAM方法内的场景表示来解决这个问题。然而,大多数研究主要集中在估计粗糙的3D场景,而不是实现详细的重建。此外,仅基于图像的深度估计往往具有模糊性,导致质量较低的3D模型,从而导致渲染不准确。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了一种基于在线多视图立体(MVS)方法的高质量的3DGS建模新框架。我们的方法使用来自局部时间窗口的连续帧来估计MVS深度,并采用全面的深度细化技术来过滤异常值,从而实现3DGS中高斯值的准确初始化。此外,我们还引入了一个并行化的后端模块,该模块可以有效地优化3DGS模型,确保每个新关键帧都能及时得到更新。实验结果表明,我们的方法在挑战性户外环境中表现优异,超越了最先进的密集SLAM方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 6 figures, submitted to IEEE ICRA 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种基于在线多视角立体(MVS)方法的高质量三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)建模框架,用于解决在线三维模型生成中的神经渲染挑战。通过利用序列帧的局部时间窗口估计MVS深度,并应用全面的深度优化技术过滤异常值,实现了高精度的三维场景重建和渲染。此外,还引入了并行后端模块,优化3DGS模型的效率,确保及时更新每个新关键帧。实验结果表明,该方法优于现有密集SLAM方法,特别是在具有挑战性的室外环境中表现更优秀。
Key Takeaways
研究背景:在线三维模型生成对于神经渲染是一个挑战,尤其是基于RGB图像流进行估计。先前的研究主要聚焦于通过引入NeRF或3DGS技术来建立场景表示,但这些研究更多地关注粗略的三维场景估计而非详细重建。
局限性的解决:针对现有研究的不足,本研究提出了一种新颖的基于在线多视角立体(MVS)方法的框架进行高质量建模。该框架通过利用局部时间窗口内的序列帧估计MVS深度,解决了深度估计的模糊性问题。
深度优化技术:通过全面的深度优化技术过滤异常值,提高了深度估计的准确性,从而实现了高精度的三维场景重建和渲染。
并行后端模块:引入并行后端模块以优化3DGS模型的效率,确保每个新关键帧都能得到及时更新。
实验结果:实验结果表明,该研究提出的方法在性能上超越了现有的密集SLAM方法。特别是在挑战性的室外环境中,其表现尤为出色。这种方法的优势在于能够生成更准确、更精细的三维模型。
方法创新点:该研究的主要创新点在于结合了在线多视角立体方法和深度优化技术,实现了高质量的三维场景重建和渲染效果。同时,引入的并行后端模块进一步提高了效率。
点此查看论文截图



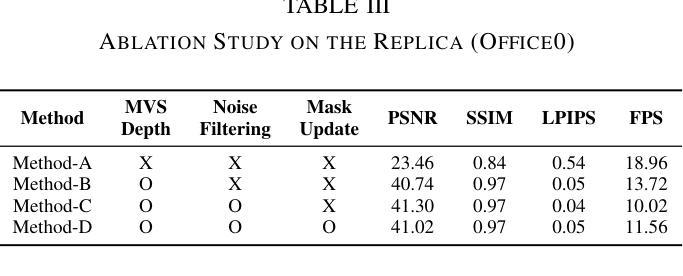
Humans as a Calibration Pattern: Dynamic 3D Scene Reconstruction from Unsynchronized and Uncalibrated Videos
Authors:Changwoon Choi, Jeongjun Kim, Geonho Cha, Minkwan Kim, Dongyoon Wee, Young Min Kim
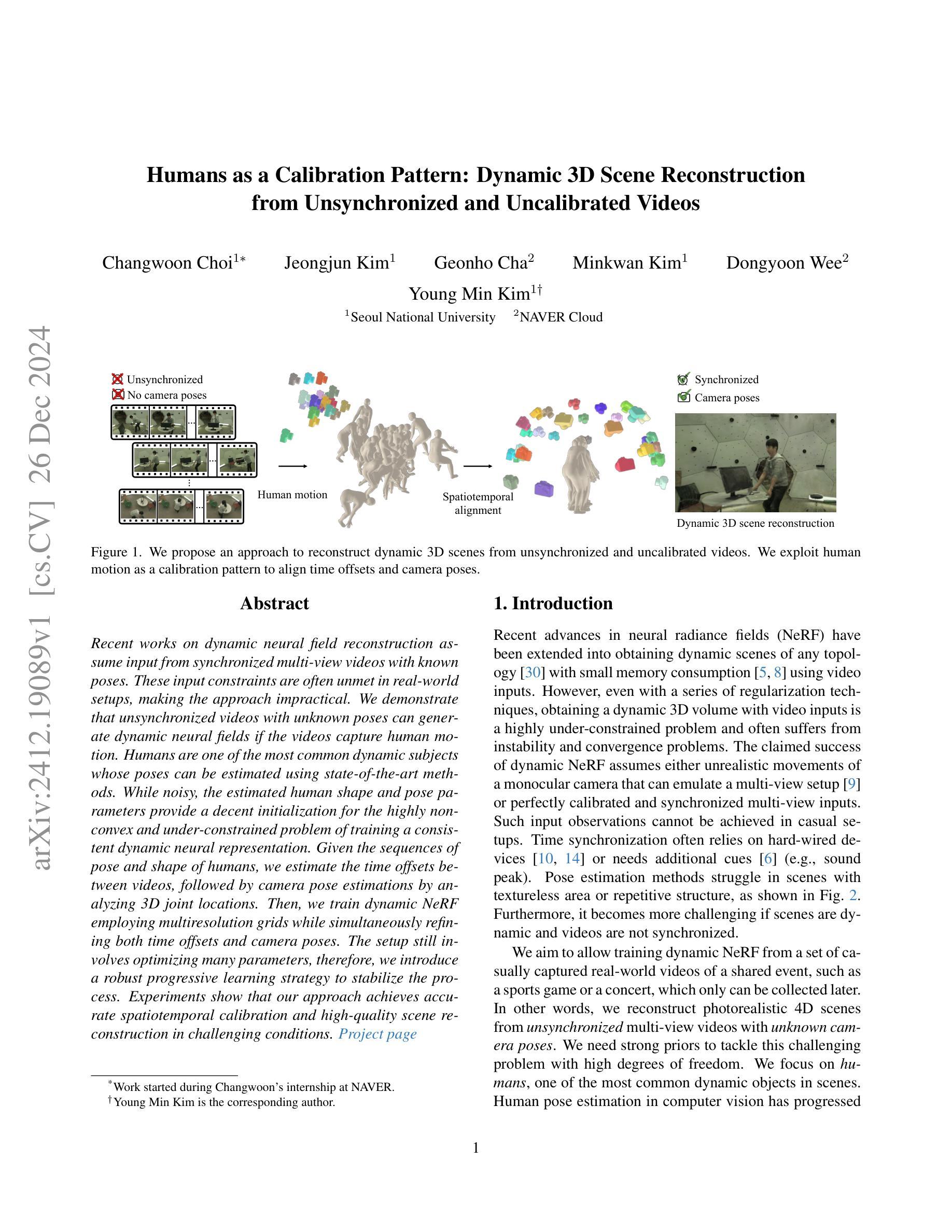
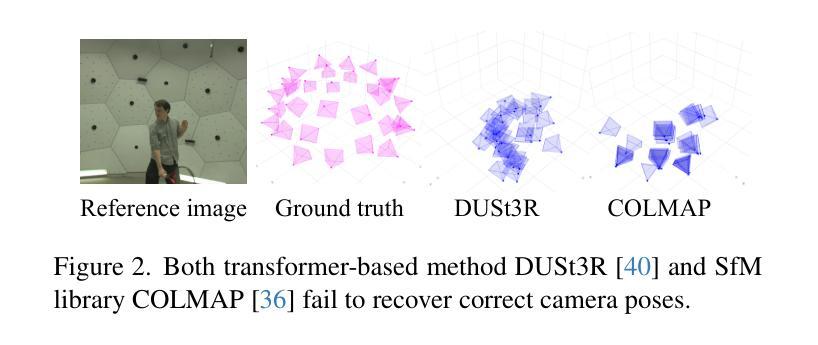
Recent works on dynamic neural field reconstruction assume input from synchronized multi-view videos with known poses. These input constraints are often unmet in real-world setups, making the approach impractical. We demonstrate that unsynchronized videos with unknown poses can generate dynamic neural fields if the videos capture human motion. Humans are one of the most common dynamic subjects whose poses can be estimated using state-of-the-art methods. While noisy, the estimated human shape and pose parameters provide a decent initialization for the highly non-convex and under-constrained problem of training a consistent dynamic neural representation. Given the sequences of pose and shape of humans, we estimate the time offsets between videos, followed by camera pose estimations by analyzing 3D joint locations. Then, we train dynamic NeRF employing multiresolution rids while simultaneously refining both time offsets and camera poses. The setup still involves optimizing many parameters, therefore, we introduce a robust progressive learning strategy to stabilize the process. Experiments show that our approach achieves accurate spatiotemporal calibration and high-quality scene reconstruction in challenging conditions.
关于动态神经网络重建的最新工作假设输入来自同步的多视角视频,并且已知姿态。然而在实际环境中,这些输入约束通常无法得到满足,使得这种方法不切实际。我们证明,对于捕捉人类动作的视频,即使视频不同步且姿态未知,也能生成动态神经网络。人类是最常见的动态主题之一,其姿态可以使用最新方法进行估计。虽然存在噪声,但估计出的人类形状和姿态参数对于训练一致的动态神经网络这一高度非凸和欠约束的问题提供了一个不错的初始值。给定人类姿势和形状的序列,我们估计视频之间的时间偏移,然后通过分析3D关节位置进行相机姿态估计。然后,我们采用多分辨率网格训练动态NeRF,同时调整时间偏移和相机姿态。该设置仍然需要优化许多参数,因此,我们引入了一种稳健的渐进学习策略来稳定这一过程。实验表明,我们的方法实现了准确的时空标定和高质量的场景重建,在具有挑战的环境中也能取得良好的效果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文解决动态神经场重建在真实世界场景中的实用性问题。通过对人体姿态的估计和时空校准的优化,实现动态神经场重建。使用多分辨率网格和渐进学习方法,提高了场景重建的质量和稳定性。即使面对不同步视频和未知姿态的挑战,本文方法仍然可以生成高质量的场景重建结果。
Key Takeaways
- 研究工作解决动态神经场重建在真实场景中的局限性,尤其是视频同步和姿态未知的问题。
- 提出使用人体姿态估计来解决训练动态神经表示中的高度非凸和欠约束问题。
- 通过对人体姿态和形状的序列进行时间偏移估计和摄像机姿态估计,实现了对摄像机角度的调整和优化。
- 利用多分辨率网格技术训练动态NeRF模型,提高模型性能。
- 提出一种稳健的渐进学习策略来稳定训练过程。
- 实验表明,即使在具有挑战性的条件下,该方法的时空校准准确性较高且场景重建质量较好。
点此查看论文截图
Developing Cryptocurrency Trading Strategy Based on Autoencoder-CNN-GANs Algorithms
Authors:Zhuohuan Hu, Richard Yu, Zizhou Zhang, Haoran Zheng, Qianying Liu, Yining Zhou
This paper leverages machine learning algorithms to forecast and analyze financial time series. The process begins with a denoising autoencoder to filter out random noise fluctuations from the main contract price data. Then, one-dimensional convolution reduces the dimensionality of the filtered data and extracts key information. The filtered and dimensionality-reduced price data is fed into a GANs network, and its output serve as input of a fully connected network. Through cross-validation, a model is trained to capture features that precede large price fluctuations. The model predicts the likelihood and direction of significant price changes in real-time price sequences, placing trades at moments of high prediction accuracy. Empirical results demonstrate that using autoencoders and convolution to filter and denoise financial data, combined with GANs, achieves a certain level of predictive performance, validating the capabilities of machine learning algorithms to discover underlying patterns in financial sequences. Keywords - CNN;GANs; Cryptocurrency; Prediction.
本文利用机器学习算法对金融时间序列进行预测和分析。流程始于使用降噪自编码器对主合约价格数据进行随机噪声波动的过滤。然后,一维卷积对过滤后的数据进行降维并提取关键信息。过滤和降维后的价格数据被输入到GANs网络中,其输出作为全连接网络的输入。通过交叉验证,训练模型以捕获先于大幅价格波动的特征。该模型预测实时价格序列中重大价格变动的可能性和方向,在高预测准确性的时刻进行交易。实证结果表明,结合使用自编码器和卷积对金融数据进行过滤和去噪,结合GANs,达到了一定的预测性能,验证了机器学习算法在发现金融序列中潜在模式方面的能力。关键词——卷积神经网络、生成对抗网络、加密货币、预测。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The paper was accepted by 2024 4th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Robotics, and Communication(ICAIRC 2024)
摘要
本文利用机器学习算法对金融时间序列进行预测与分析。通过降噪自编码器过滤主合同价格数据中的随机噪声波动,一维卷积降低数据维度并提取关键信息。经过过滤和降维的价格数据输入生成对抗网络,其输出作为全连接网络的输入。通过交叉验证,训练模型捕捉大价格波动前的特征。该模型预测实时价格序列中重大价格变化的可能性和方向,在高预测准确率时刻进行交易。实证结果表明,结合自编码器、卷积降噪和生成对抗网络,机器学习算法在发现金融序列中的潜在模式方面具有一定的预测性能。
要点
- 使用降噪自编码器过滤金融时间序列数据中的随机噪声。
- 一维卷积用于降低数据维度并提取关键信息。
- 结合生成对抗网络(GANs)和全连接网络进行模型训练。
- 通过交叉验证,模型能够捕捉大价格波动前的特征。
- 模型可预测实时价格序列中重大价格变化的可能性和方向。
- 实证结果表明,结合自编码器和卷积的金融数据预处理,以及GANs的使用,机器学习算法具有良好的预测性能。
点此查看论文截图

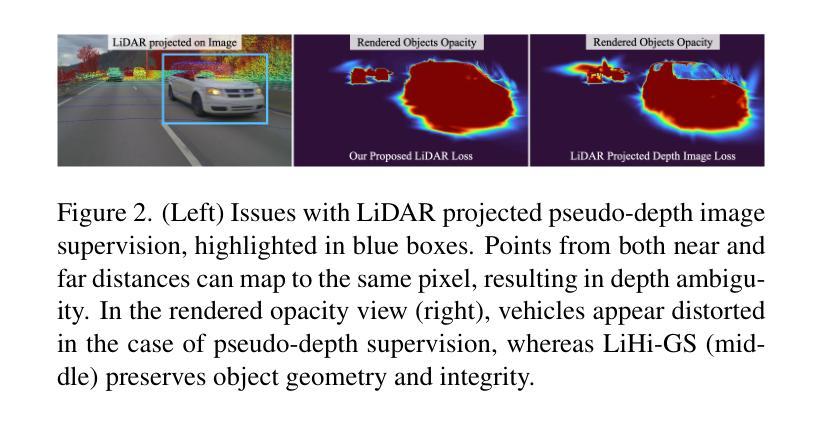
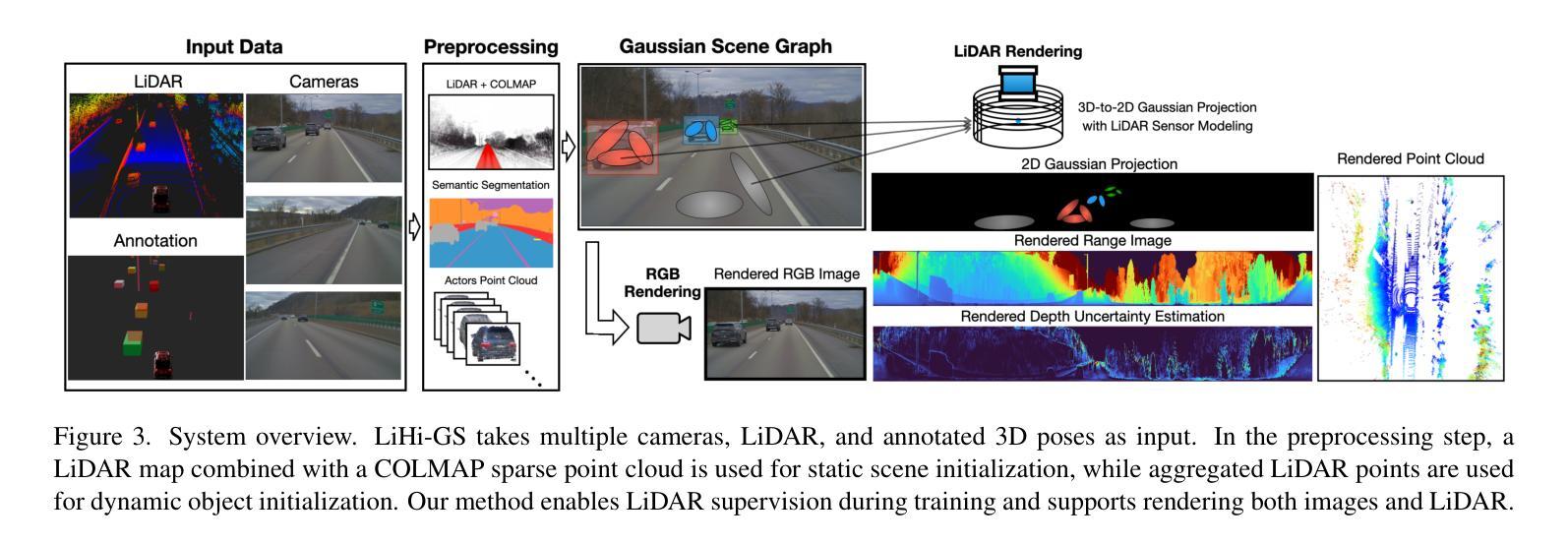
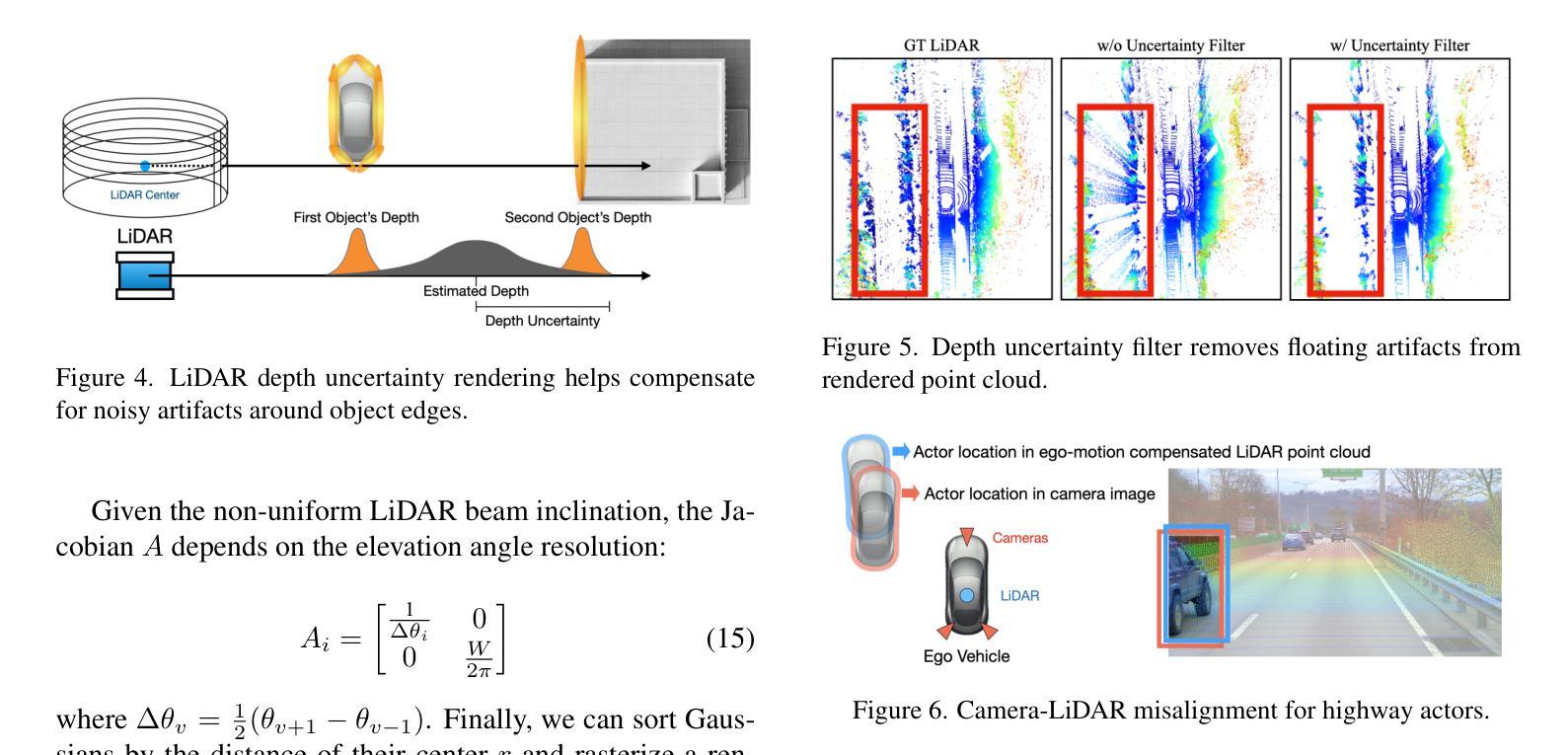
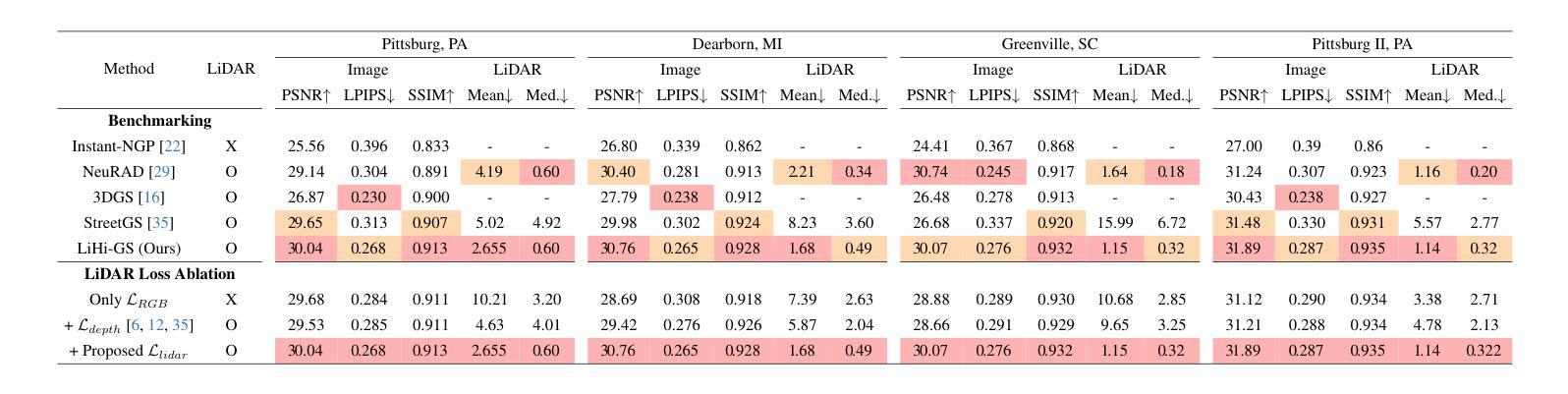
LiHi-GS: LiDAR-Supervised Gaussian Splatting for Highway Driving Scene Reconstruction
Authors:Pou-Chun Kung, Xianling Zhang, Katherine A. Skinner, Nikita Jaipuria
Photorealistic 3D scene reconstruction plays an important role in autonomous driving, enabling the generation of novel data from existing datasets to simulate safety-critical scenarios and expand training data without additional acquisition costs. Gaussian Splatting (GS) facilitates real-time, photorealistic rendering with an explicit 3D Gaussian representation of the scene, providing faster processing and more intuitive scene editing than the implicit Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs). While extensive GS research has yielded promising advancements in autonomous driving applications, they overlook two critical aspects: First, existing methods mainly focus on low-speed and feature-rich urban scenes and ignore the fact that highway scenarios play a significant role in autonomous driving. Second, while LiDARs are commonplace in autonomous driving platforms, existing methods learn primarily from images and use LiDAR only for initial estimates or without precise sensor modeling, thus missing out on leveraging the rich depth information LiDAR offers and limiting the ability to synthesize LiDAR data. In this paper, we propose a novel GS method for dynamic scene synthesis and editing with improved scene reconstruction through LiDAR supervision and support for LiDAR rendering. Unlike prior works that are tested mostly on urban datasets, to the best of our knowledge, we are the first to focus on the more challenging and highly relevant highway scenes for autonomous driving, with sparse sensor views and monotone backgrounds. Visit our project page at: https://umautobots.github.io/lihi_gs
真实感三维场景重建在自动驾驶中扮演着重要角色。它可以从现有数据集中生成新的数据,模拟关键安全场景,并在无需额外采集成本的情况下扩展训练数据。高斯拼贴(GS)技术通过场景的显式三维高斯表示,实现了实时真实感渲染,相较于隐式神经辐射场(NeRF)提供了更快的处理和更直观的场景编辑。尽管关于高斯拼贴的研究已经在自动驾驶应用方面取得了有前景的进展,但它们忽略了两个关键方面:首先,现有方法主要集中在低速且特征丰富的城市场景上,忽略了高速公路场景在自动驾驶中的重要地位。其次,虽然激光雷达在自动驾驶平台中很普遍,但现有方法主要依赖图像进行学习,仅将激光雷达用于初步估计或不精确的传感器建模,从而未能充分利用激光雷达提供的丰富深度信息,并限制了合成激光雷达数据的能力。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的高斯拼贴方法,用于动态场景合成和编辑。通过激光雷达监督和支持激光雷达渲染,改进了场景重建。据我们所知,与大多数仅在城市数据集上测试的先前工作不同,我们首次关注更具挑战性和高度相关的自动驾驶高速公路场景,具有稀疏的传感器视图和单调的背景。请访问我们的项目页面:https://umautobots.github.io/lihi_gs 。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在自动驾驶中,基于LiDAR的三维场景重建具有重要的研究价值。本文通过引入高斯渲染技术,结合LiDAR的丰富深度信息,提出了一种新型的动态场景合成与编辑方法。此方法不仅提高了场景重建的精度,还支持LiDAR渲染,适用于高速公路场景。此研究对自动驾驶的数据扩充及模拟安全关键场景具有重要意义。
Key Takeaways
- 光场渲染技术在自动驾驶中具有重要的应用价值,尤其是生成新的数据集以模拟安全关键场景和扩大训练数据方面。
- 高斯渲染(GS)方法提供了一种实时、逼真的渲染方式,通过明确的3D高斯场景表示,实现更快的处理和更直观的场景编辑。
- 目前GS方法主要关注低速度、特征丰富的城市场景,但在高速公路场景的自动驾驶应用中仍显不足。
- LiDAR在自动驾驶平台中普及,但现有方法主要依赖图像学习,未充分利用LiDAR提供的丰富深度信息。
- 本文提出了一种新型的GS方法,通过LiDAR监督和支持LiDAR渲染,改善了场景重建效果。
- 与大多数仅在城市数据集上测试的方法不同,本文首次专注于更具挑战性和高度相关的高速公路场景。
点此查看论文截图

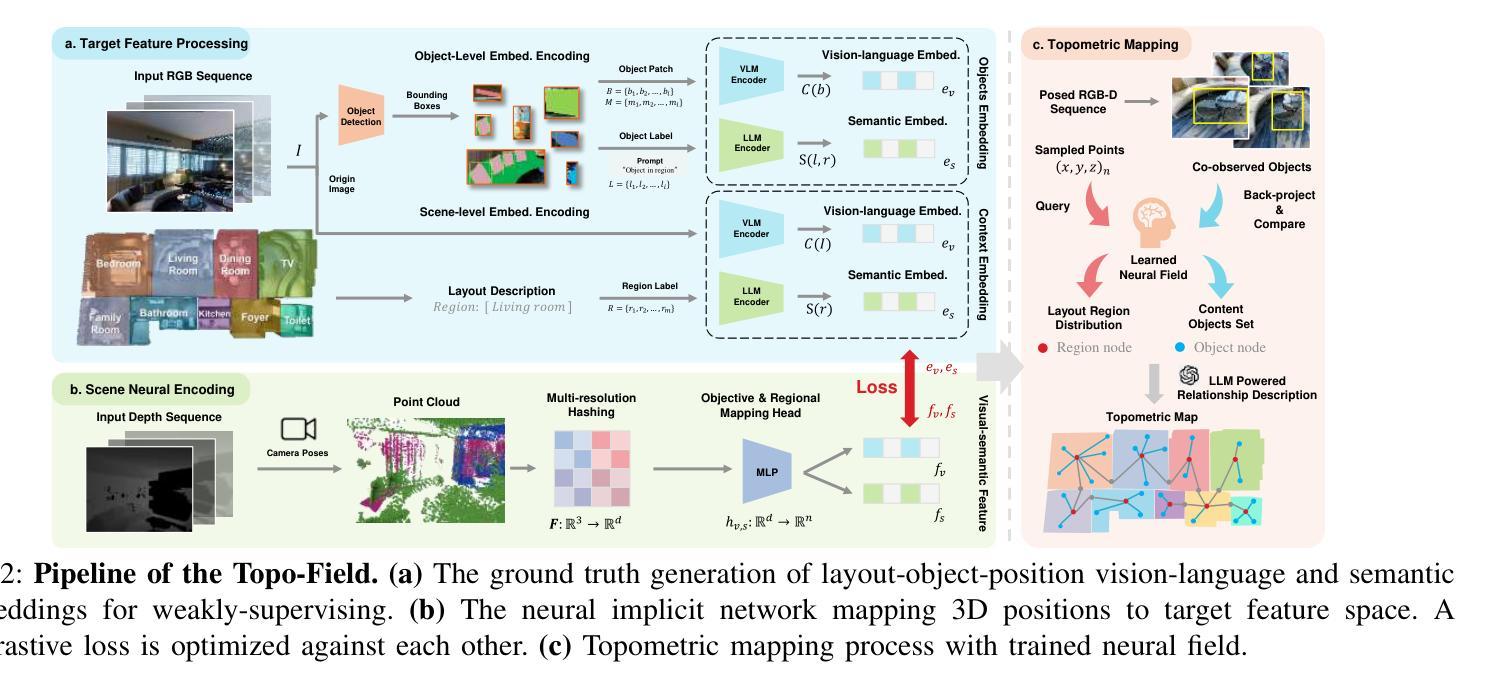
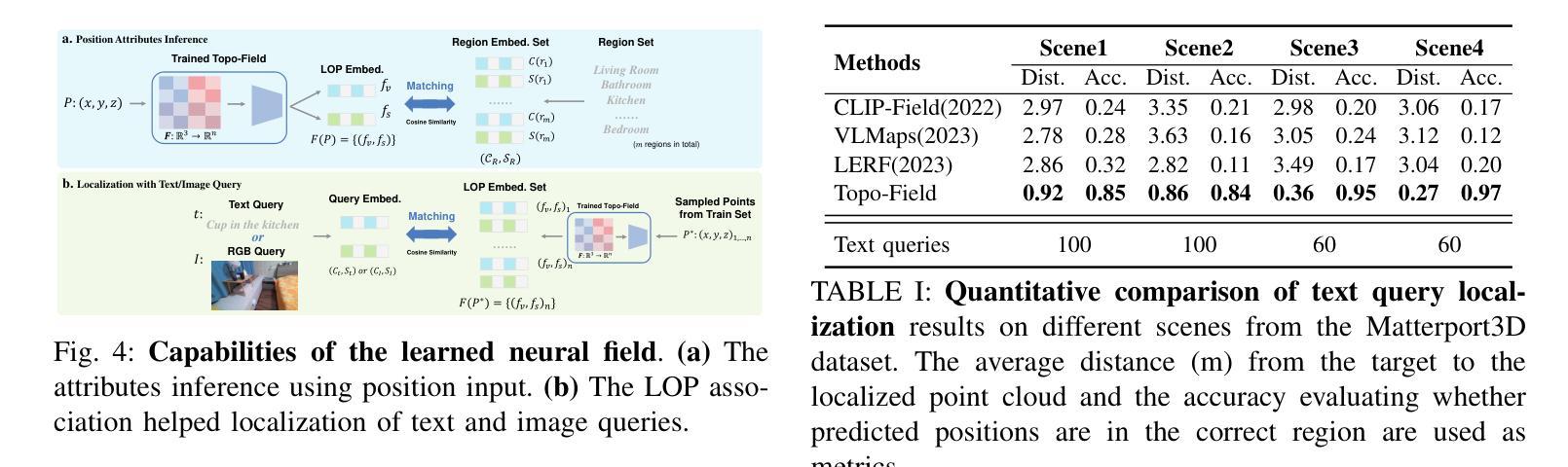
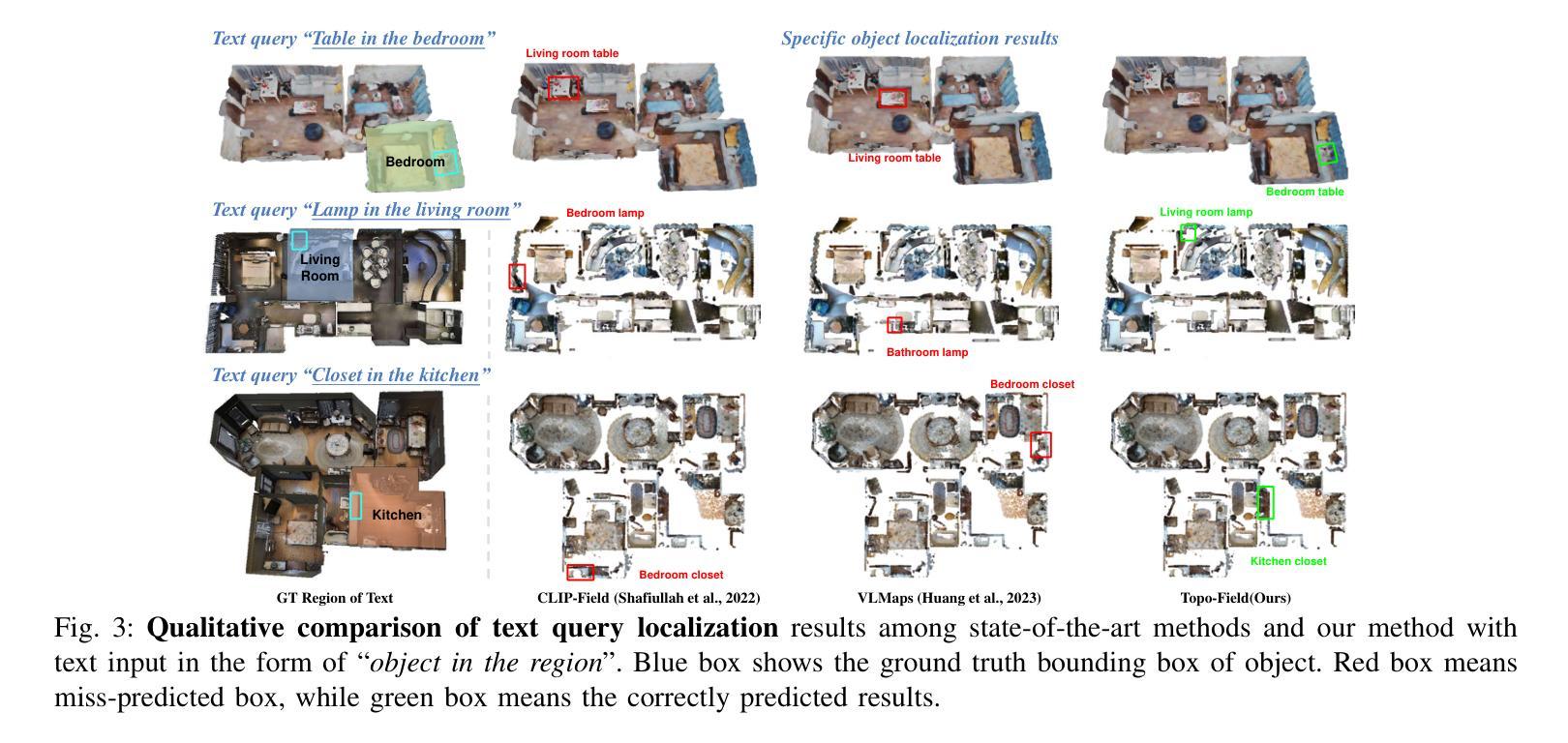
Topo-Field: Topometric mapping with Brain-inspired Hierarchical Layout-Object-Position Fields
Authors:Jiawei Hou, Wenhao Guan, Longfei Liang, Jianfeng Feng, Xiangyang Xue, Taiping Zeng
Mobile robots require comprehensive scene understanding to operate effectively in diverse environments, enriched with contextual information such as layouts, objects, and their relationships. Although advances like neural radiation fields (NeRFs) offer high-fidelity 3D reconstructions, they are computationally intensive and often lack efficient representations of traversable spaces essential for planning and navigation. In contrast, topological maps are computationally efficient but lack the semantic richness necessary for a more complete understanding of the environment. Inspired by a population code in the postrhinal cortex (POR) strongly tuned to spatial layouts over scene content rapidly forming a high-level cognitive map, this work introduces Topo-Field, a framework that integrates Layout-Object-Position (LOP) associations into a neural field and constructs a topometric map from this learned representation. LOP associations are modeled by explicitly encoding object and layout information, while a Large Foundation Model (LFM) technique allows for efficient training without extensive annotations. The topometric map is then constructed by querying the learned neural representation, offering both semantic richness and computational efficiency. Empirical evaluations in multi-room environments demonstrate the effectiveness of Topo-Field in tasks such as position attribute inference, query localization, and topometric planning, successfully bridging the gap between high-fidelity scene understanding and efficient robotic navigation.
移动机器人需要全面的场景理解,才能在各种环境中有效运行,这些环境富含布局、物体及其关系的上下文信息。尽管神经辐射场(NeRF)等先进技术提供了高保真度的3D重建,但它们计算量大,通常缺乏对可通行空间的有效表示,这对于规划和导航至关重要。相比之下,拓扑地图计算效率高,但缺乏必要的语义丰富性,无法更全面地理解环境。这项工作受到后梨状皮层(POR)中人群编码的启发,该编码对场景内容中的空间布局进行快速高级认知地图构建,介绍了一种名为Topo-Field的框架,该框架将布局-对象-位置(LOP)关联集成到神经场中,并从这种学习表示中构建拓扑地图。LOP关联通过显式编码对象和布局信息来建模,而大型基础模型(LFM)技术则可实现高效训练,无需广泛注释。然后,通过查询学习到的神经表示来构建拓扑地图,提供丰富的语义和计算效率。在多房间环境中的经验评估表明,Topo-Field在位置属性推断、查询定位和拓扑规划等任务中的有效性,成功弥合了高保真场景理解和高效机器人导航之间的差距。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为Topo-Field的框架,融合布局-物体-位置(LOP)关联到神经网络中,构建拓扑地图。利用种群编码和后颞叶皮层(POR)的空间布局敏感性,以及大型基础模型(LFM)技术,实现高效学习与训练。Topo-Field能在多房间环境中进行有效评估,成功应用于位置属性推断、查询定位和拓扑规划任务,实现了高保真场景理解与高效机器人导航之间的桥梁。
Key Takeaways
- Topo-Field框架结合了布局、物体和位置(LOP)的关联,构建了一个神经场模型用于机器人场景理解。
- 借鉴后颞叶皮层(POR)的种群编码思想,快速形成高级认知地图。
- 采用大型基础模型(LFM)技术,实现无需大量标注的高效训练。
- Topo-Field能构建拓扑地图,兼具语义丰富性和计算效率。
- 在多房间环境中进行实证评估,表现优异。
- 成功应用于位置属性推断、查询定位和拓扑规划任务。
点此查看论文截图


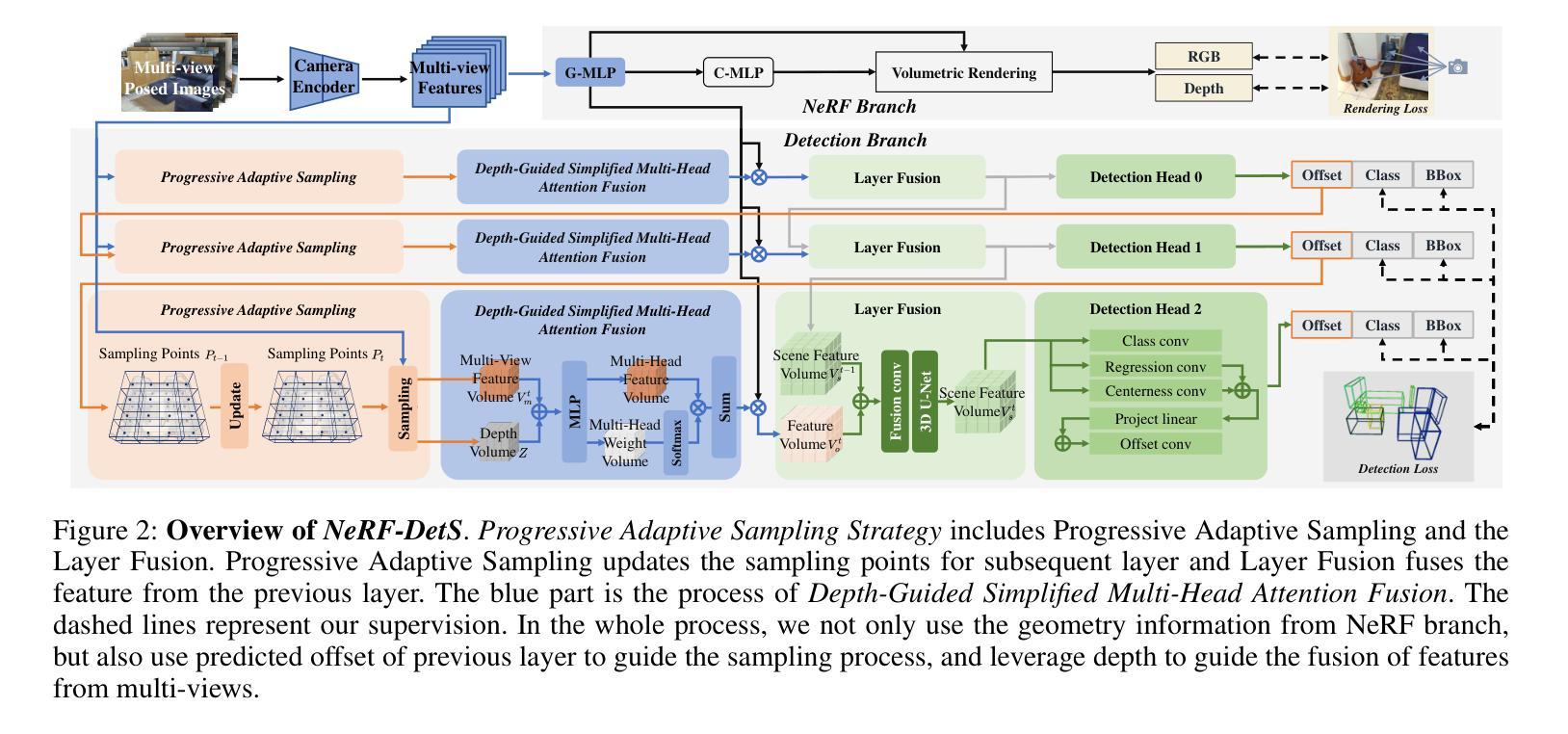
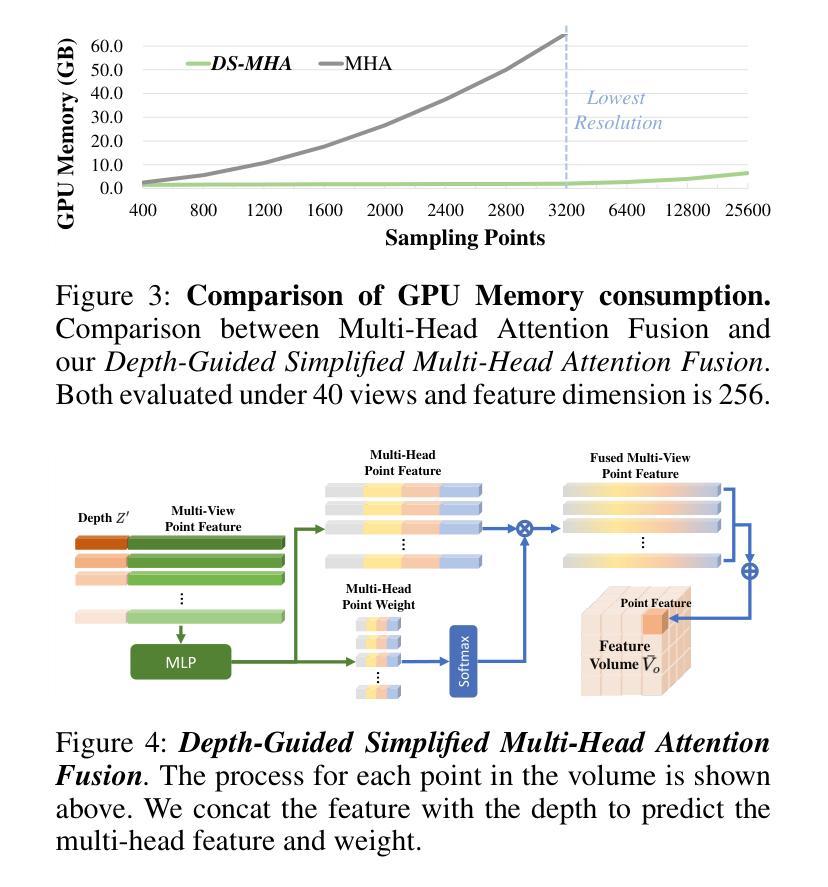
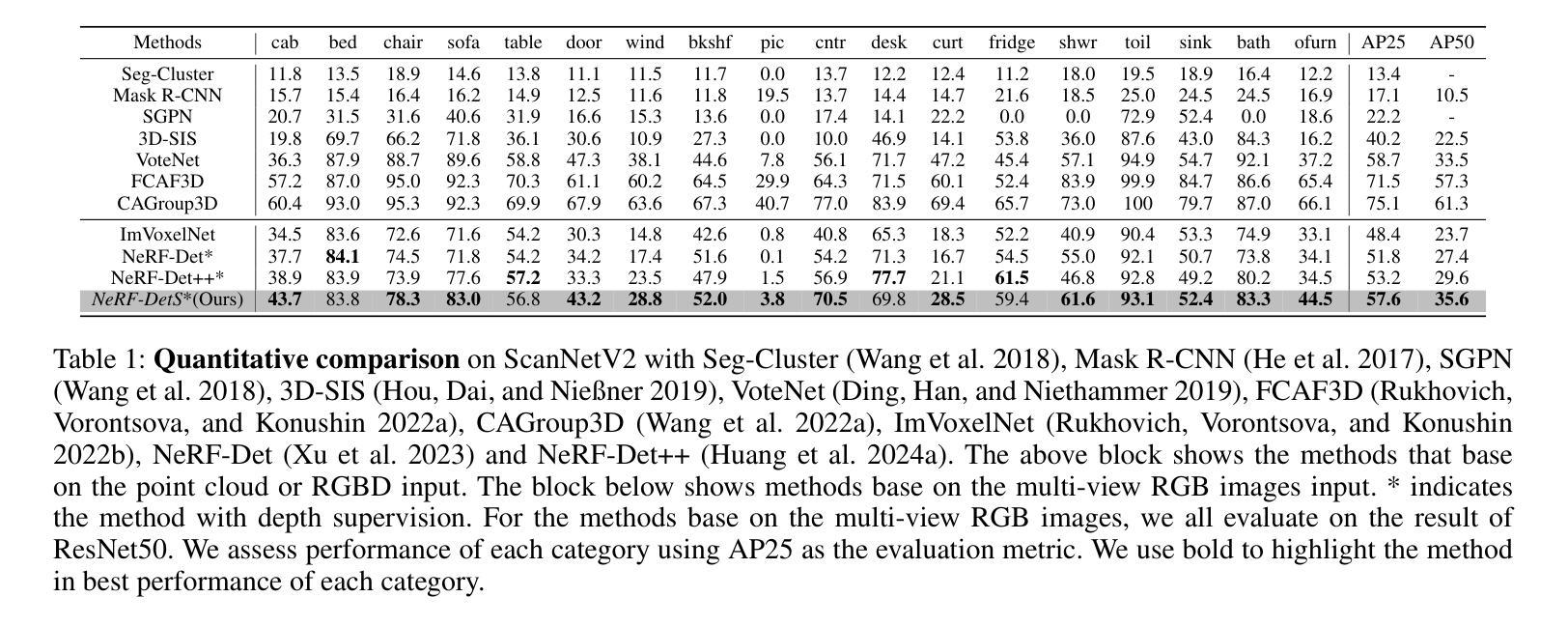
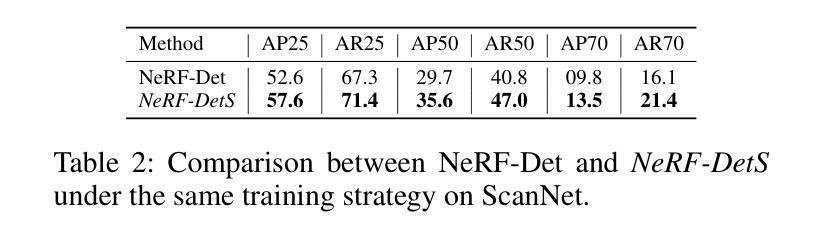
NeRF-DetS: Enhanced Adaptive Spatial-wise Sampling and View-wise Fusion Strategies for NeRF-based Indoor Multi-view 3D Object Detection
Authors:Chi Huang, Xinyang Li, Yansong Qu, Changli Wu, Xiaofan Li, Shengchuan Zhang, Liujuan Cao
In indoor scenes, the diverse distribution of object locations and scales makes the visual 3D perception task a big challenge. Previous works (e.g, NeRF-Det) have demonstrated that implicit representation has the capacity to benefit the visual 3D perception task in indoor scenes with high amount of overlap between input images. However, previous works cannot fully utilize the advancement of implicit representation because of fixed sampling and simple multi-view feature fusion. In this paper, inspired by sparse fashion method (e.g, DETR3D), we propose a simple yet effective method, NeRF-DetS, to address above issues. NeRF-DetS includes two modules: Progressive Adaptive Sampling Strategy (PASS) and Depth-Guided Simplified Multi-Head Attention Fusion (DS-MHA). Specifically, (1)PASS can automatically sample features of each layer within a dense 3D detector, using offsets predicted by the previous layer. (2)DS-MHA can not only efficiently fuse multi-view features with strong occlusion awareness but also reduce computational cost. Extensive experiments on ScanNetV2 dataset demonstrate our NeRF-DetS outperforms NeRF-Det, by achieving +5.02% and +5.92% improvement in mAP under IoU25 and IoU50, respectively. Also, NeRF-DetS shows consistent improvements on ARKITScenes.
在室内场景中,物体位置和尺度的多样分布使得视觉3D感知任务面临巨大挑战。先前的工作(例如NeRF-Det)已经证明,隐式表示有益于室内场景的视觉3D感知任务,尤其在输入图像之间存在大量重叠时。然而,由于固定的采样和简单的多视图特征融合,先前的工作不能完全利用隐式表示的进步。本文受稀疏方式方法的启发(例如DETR3D),提出了一种简单而有效的方法NeRF-DetS来解决上述问题。NeRF-DetS包括两个模块:渐进式自适应采样策略(PASS)和深度引导简化多头注意力融合(DS-MHA)。具体来说,(1)PASS可以自动在密集3D检测器内的每一层采样特征,使用前一层的预测偏移。(2)DS-MHA不仅可以有效地融合多视图特征,具有强烈的遮挡意识,而且可以降低计算成本。在ScanNetV2数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的NeRF-DetS优于NeRF-Det,在IoU25和IoU50的mAP上分别提高了+5.02%和+5.92%。此外,NeRF-DetS在ARKITScenes上也表现出了一致性的改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
室内场景中,物体位置和尺度的多样性使得视觉3D感知任务极具挑战。NeRF-DetS是一种简单有效的方法,解决了之前工作中固定采样和简单多视角特征融合的问题。NeRF-DetS包括两个模块:渐进自适应采样策略(PASS)和深度引导简化多头注意力融合(DS-MHA)。PASS可自动在密集3D检测器中每层采样特征,使用前一层的预测偏移。DS-MHA不仅能有效地融合具有强遮挡意识的多个视角特征,还能降低计算成本。在ScanNetV2数据集上的实验表明,NeRF-DetS优于NeRF-Det,在IoU25和IoU50下mAP分别提高了+5.02%和+5.92%。同时,NeRF-DetS在ARKITScenes上也表现出一致的提升。
Key Takeaways
- 室内场景中,物体位置和尺度的多样性使得视觉3D感知具有挑战性。
- 之前的作品如NeRF-Det虽展示了隐式表示在视觉3D感知任务中的潜力,但无法充分利用其优势。
- NeRF-DetS通过引入两个模块:PASS和DS-MHA,解决了固定采样和简单多视角特征融合的问题。
- PASS能自动在密集3D检测器的每一层进行特征采样。
- DS-MHA能高效融合多视角特征,增强遮挡意识并降低计算成本。
- 在ScanNetV2数据集上的实验显示,NeRF-DetS相比NeRF-Det有显著提升。
点此查看论文截图