⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-02 更新
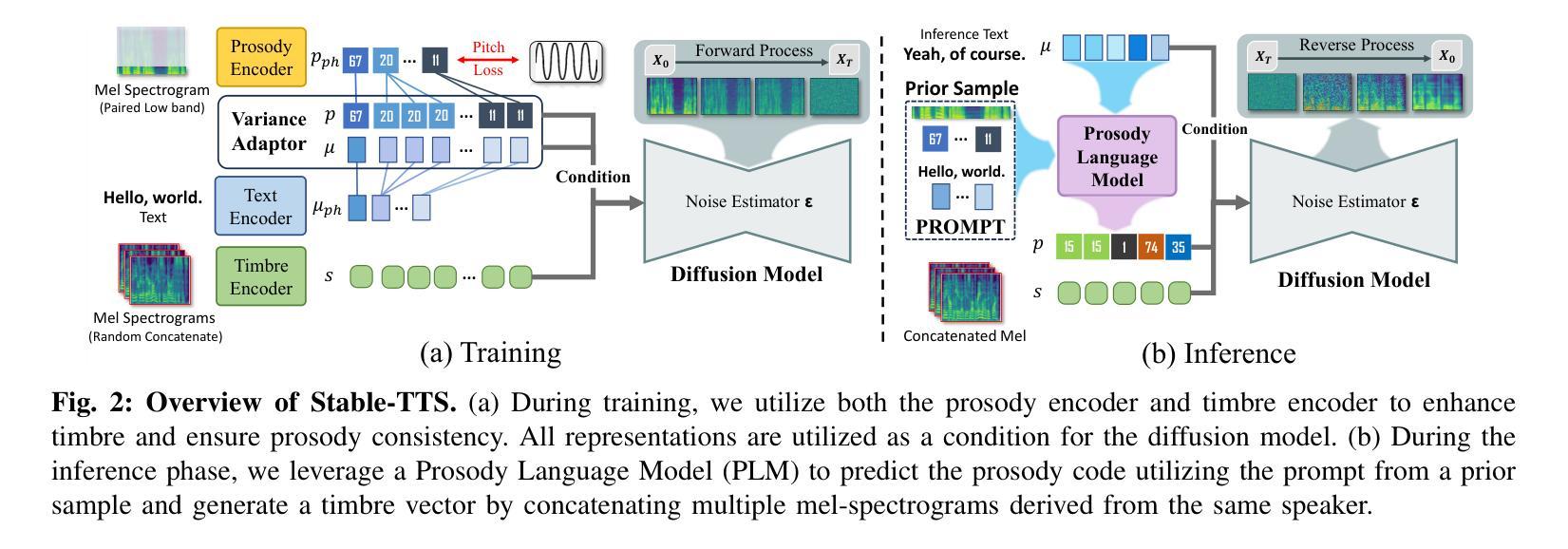
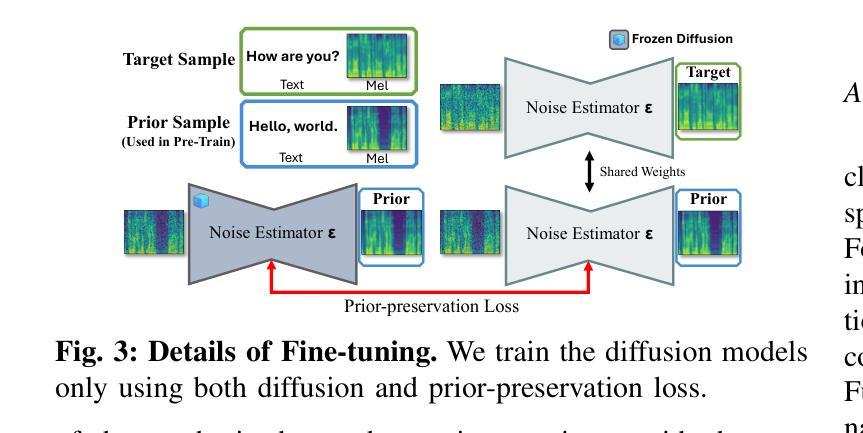
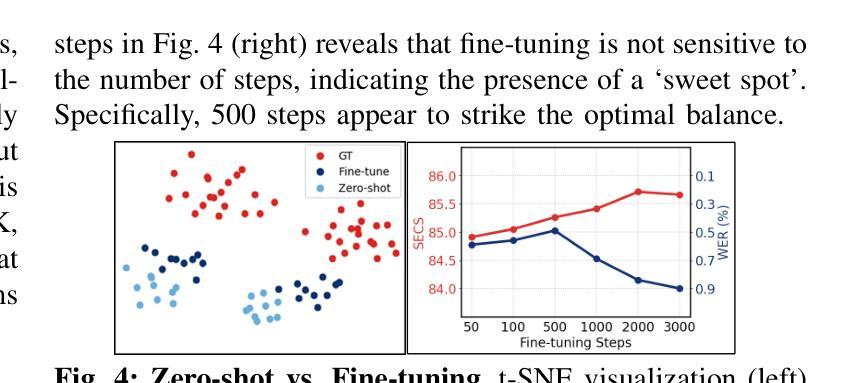
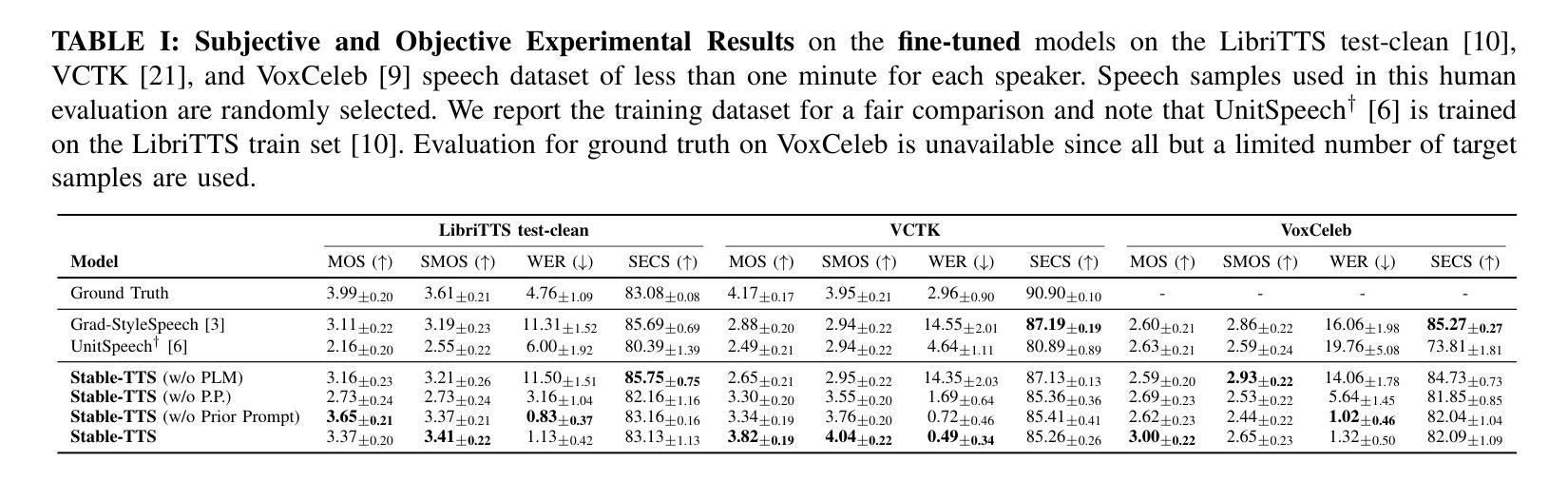
Stable-TTS: Stable Speaker-Adaptive Text-to-Speech Synthesis via Prosody Prompting
Authors:Wooseok Han, Minki Kang, Changhun Kim, Eunho Yang
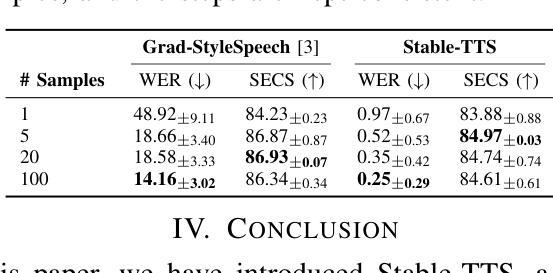
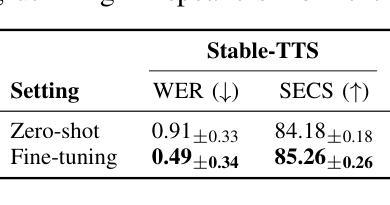
Speaker-adaptive Text-to-Speech (TTS) synthesis has attracted considerable attention due to its broad range of applications, such as personalized voice assistant services. While several approaches have been proposed, they often exhibit high sensitivity to either the quantity or the quality of target speech samples. To address these limitations, we introduce Stable-TTS, a novel speaker-adaptive TTS framework that leverages a small subset of a high-quality pre-training dataset, referred to as prior samples. Specifically, Stable-TTS achieves prosody consistency by leveraging the high-quality prosody of prior samples, while effectively capturing the timbre of the target speaker. Additionally, it employs a prior-preservation loss during fine-tuning to maintain the synthesis ability for prior samples to prevent overfitting on target samples. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of Stable-TTS even under limited amounts of and noisy target speech samples.
语音自适应文本转语音(TTS)合成因其广泛的应用领域,如个性化语音助手服务,而备受关注。尽管已经提出了多种方法,但它们对目标语音样本的数量或质量往往表现出较高的敏感性。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了Stable-TTS,这是一种新型的语音自适应TTS框架,它利用高质量预训练数据集的一个小子集,称为先验样本。具体来说,Stable-TTS通过利用先验样本的高质量韵律来实现韵律一致性,同时有效地捕捉目标说话者的音色。此外,它在微调过程中采用先验保持损失,以保持对先验样本的合成能力,防止对目标样本的过拟合。大量实验表明,即使在有限的和嘈杂的目标语音样本下,Stable-TTS也是有效的。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型的面向演讲者的自适应文本转语音(TTS)合成框架——Stable-TTS。它通过利用高质量预训练数据集中的一小部分先验样本,实现了对目标演讲者语调的一致性和音质的捕捉。此外,Stable-TTS在微调过程中采用先验保留损失,以保持对先验样本的合成能力,防止对目标样本的过拟合。即使在目标语音样本有限且噪声较大的情况下,Stable-TTS也表现出良好的效果。
Key Takeaways
- Stable-TTS是一种面向演讲者的自适应TTS合成框架,旨在解决现有方法对于目标语音样本数量或质量的敏感性。
- 该框架利用预训练数据集中的先验样本,实现语调一致性和音质的捕捉。
- 通过在微调过程中采用先验保留损失,Stable-TTS能够保持对先验样本的合成能力。
- Stable-TTS在目标语音样本有限和噪声较大的情况下也表现出良好的性能。
- 该框架能够实现个性化的语音助手服务等多种广泛应用。
- Stable-TTS对于提高TTS合成的稳定性和性能具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图

CrossSpeech++: Cross-lingual Speech Synthesis with Decoupled Language and Speaker Generation
Authors:Ji-Hoon Kim, Hong-Sun Yang, Yoon-Cheol Ju, Il-Hwan Kim, Byeong-Yeol Kim, Joon Son Chung
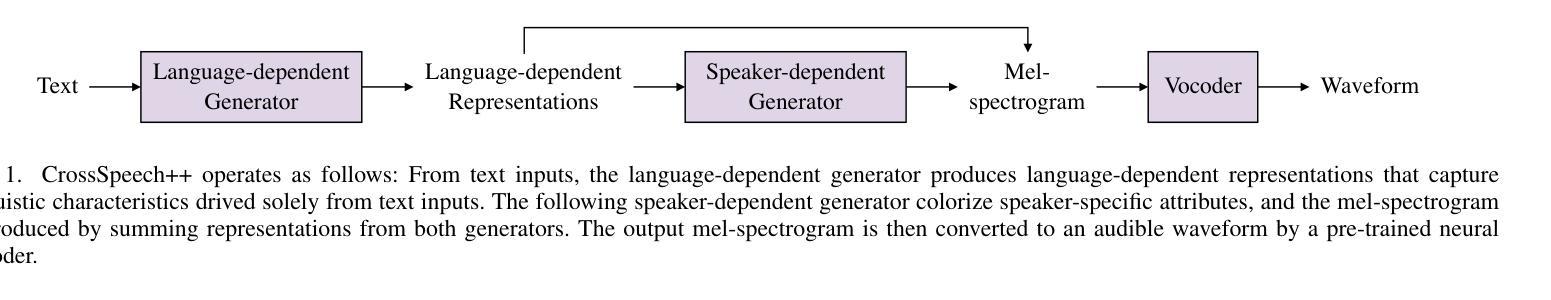
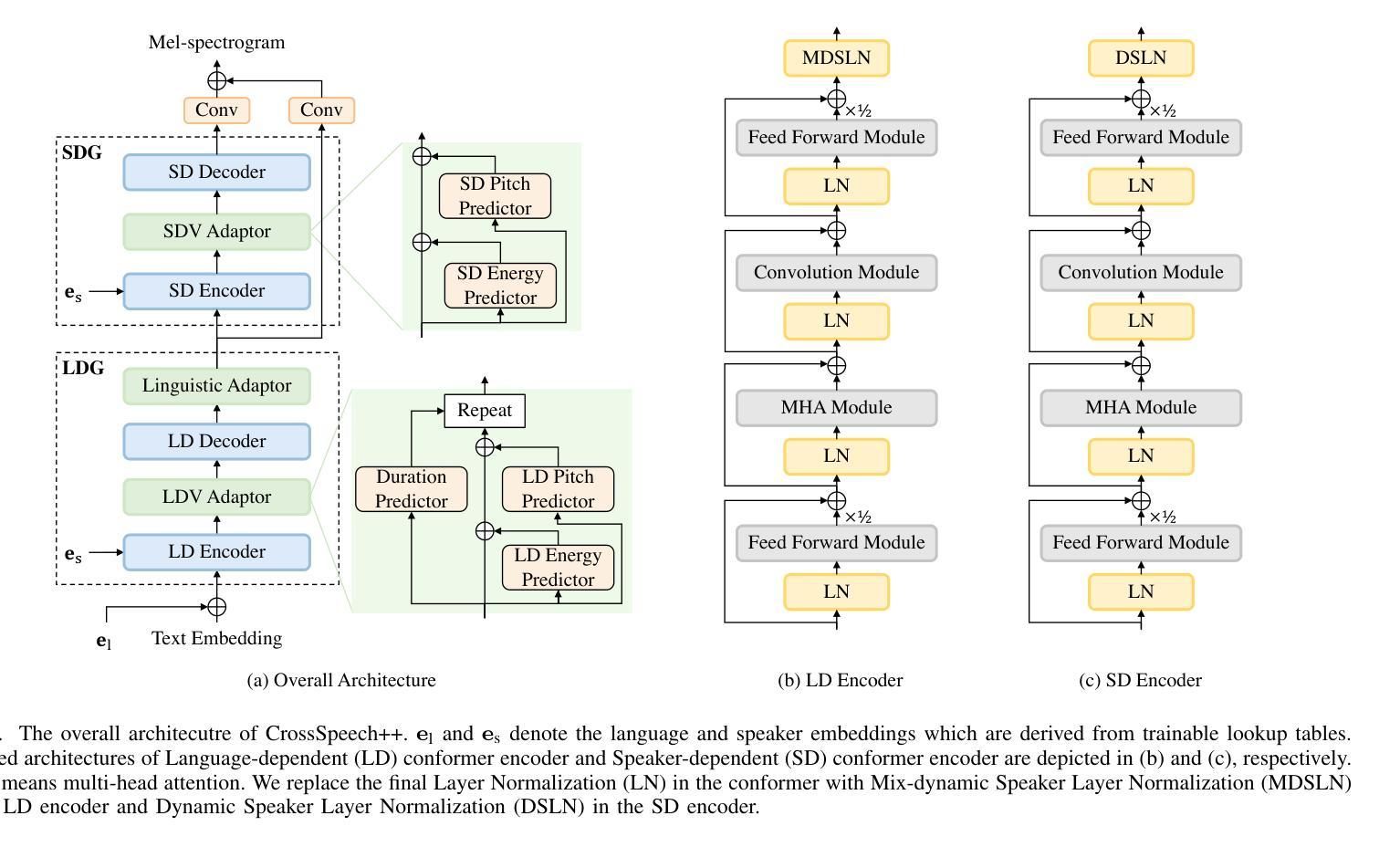
The goal of this work is to generate natural speech in multiple languages while maintaining the same speaker identity, a task known as cross-lingual speech synthesis. A key challenge of cross-lingual speech synthesis is the language-speaker entanglement problem, which causes the quality of cross-lingual systems to lag behind that of intra-lingual systems. In this paper, we propose CrossSpeech++, which effectively disentangles language and speaker information and significantly improves the quality of cross-lingual speech synthesis. To this end, we break the complex speech generation pipeline into two simple components: language-dependent and speaker-dependent generators. The language-dependent generator produces linguistic variations that are not biased by specific speaker attributes. The speaker-dependent generator models acoustic variations that characterize speaker identity. By handling each type of information in separate modules, our method can effectively disentangle language and speaker representation. We conduct extensive experiments using various metrics, and demonstrate that CrossSpeech++ achieves significant improvements in cross-lingual speech synthesis, outperforming existing methods by a large margin.
本文的目标是在保持相同说话人身份的同时生成多种语言的自然语音,这一任务被称为跨语言语音合成。跨语言语音合成的一个关键挑战是语言与说话人的纠缠问题,导致跨语言系统的质量落后于单语言系统。针对这一问题,我们提出了CrossSpeech++,它能够有效地解开语言和说话人信息,显著提高跨语言语音合成的质量。为此,我们将复杂的语音生成管道分解为两个简单的组件:语言相关生成器和说话人相关生成器。语言相关生成器产生不受特定说话人属性影响的语言变化。说话人相关生成器则模拟能够体现说话人身份的声学变化。通过在不同的模块中处理每种类型的信息,我们的方法可以有效地解开语言和说话人的表示。我们通过使用各种度量标准进行了大量实验,证明了CrossSpeech++在跨语言语音合成方面取得了显著改进,大大优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本提出了CrossSpeech++方案,旨在解决跨语言语音合成中的语言与说话人纠缠问题,从而提高跨语言语音合成的质量。该方案将复杂的语音生成管道简化为两个组件:语言相关生成器和说话人相关生成器。前者产生不受特定说话人属性影响的语言变化,后者模拟表征说话人身份的声学变化。通过单独处理每种类型的信息,该方法可以有效地解开语言和说话人的表示。
Key Takeaways
- CrossSpeech++旨在解决跨语言语音合成中的语言与说话人纠缠问题。
- 该方案通过分离语言相关和说话人相关信息来提高跨语言语音合成的质量。
- CrossSpeech++将复杂的语音生成管道简化为两个组件:语言相关生成器和说话人相关生成器。
- 语言相关生成器产生的语言变化不受特定说话人属性的影响。
- 说话人相关生成器模拟表征说话人身份的声学变化。
- 通过单独处理每种类型的信息,CrossSpeech++能够更有效地处理语言和说话人的表示。
点此查看论文截图

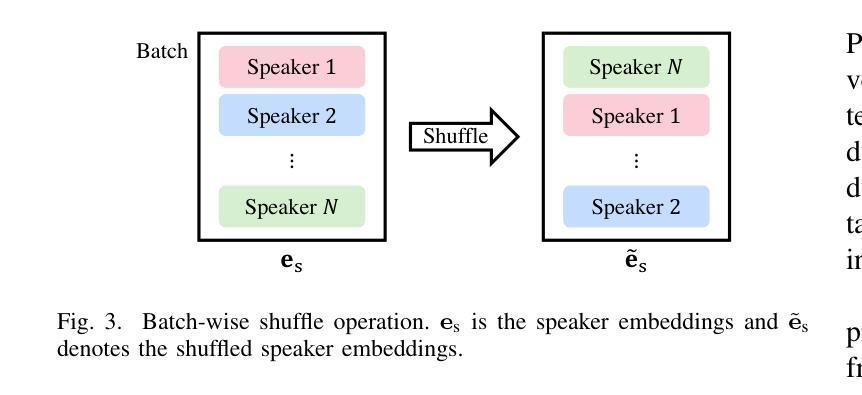
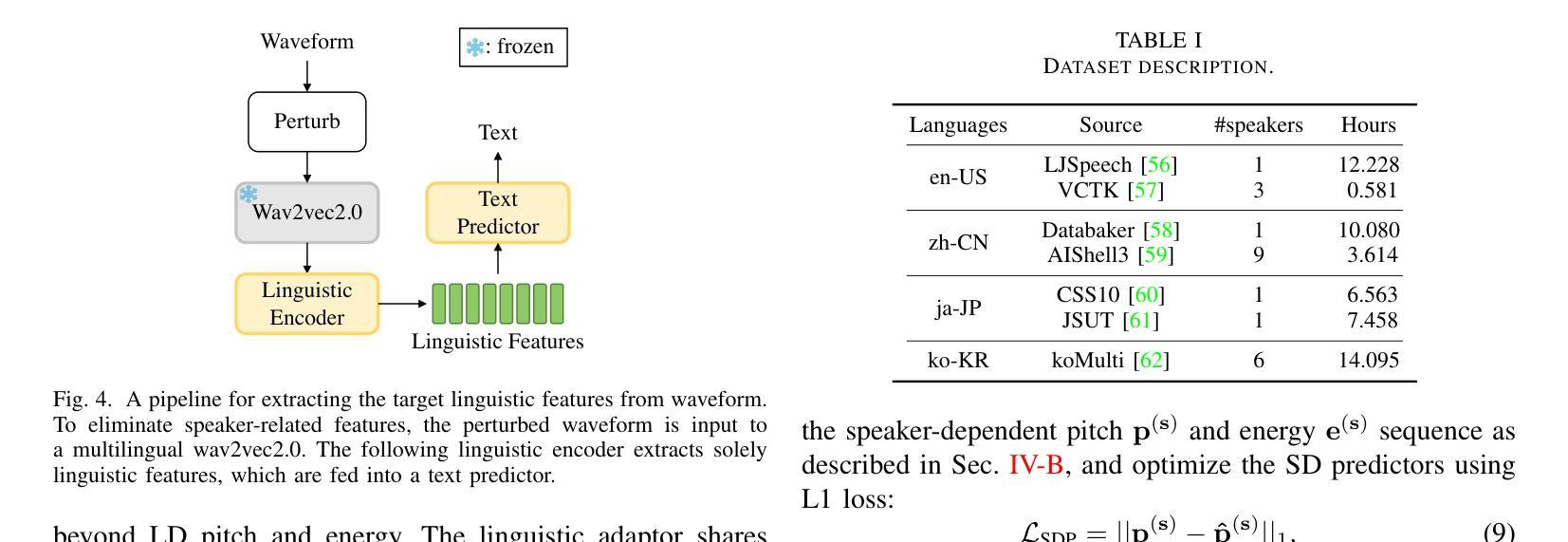
VoiceDiT: Dual-Condition Diffusion Transformer for Environment-Aware Speech Synthesis
Authors:Jaemin Jung, Junseok Ahn, Chaeyoung Jung, Tan Dat Nguyen, Youngjoon Jang, Joon Son Chung
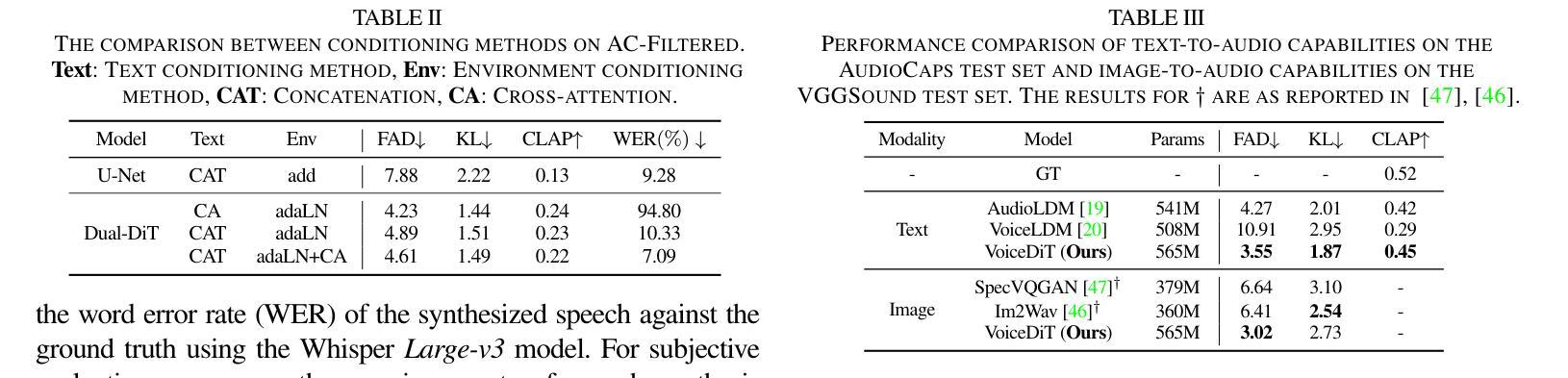
We present VoiceDiT, a multi-modal generative model for producing environment-aware speech and audio from text and visual prompts. While aligning speech with text is crucial for intelligible speech, achieving this alignment in noisy conditions remains a significant and underexplored challenge in the field. To address this, we present a novel audio generation pipeline named VoiceDiT. This pipeline includes three key components: (1) the creation of a large-scale synthetic speech dataset for pre-training and a refined real-world speech dataset for fine-tuning, (2) the Dual-DiT, a model designed to efficiently preserve aligned speech information while accurately reflecting environmental conditions, and (3) a diffusion-based Image-to-Audio Translator that allows the model to bridge the gap between audio and image, facilitating the generation of environmental sound that aligns with the multi-modal prompts. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that VoiceDiT outperforms previous models on real-world datasets, showcasing significant improvements in both audio quality and modality integration.
我们提出了VoiceDiT,这是一种多模态生成模型,能够根据文本和视觉提示生成对环境感知的语音和音频。虽然将语音与文本对齐对于可理解的语音至关重要,但在嘈杂的条件下实现这种对齐仍然是该领域一个重大且未被充分研究的挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种名为VoiceDiT的新型音频生成管道。该管道包括三个关键组件:(1)创建用于预训练的大规模合成语音数据集和用于精细调整的真实世界语音数据集;(2)Dual-DiT模型,该模型旨在高效保留对齐的语音信息,同时准确反映环境条件;(3)基于扩散的Image-to-Audio Translator,使模型能够弥合音频和图像之间的差距,促进与环境声音的生成,这与多模态提示相吻合。大量的实验结果表明,VoiceDiT在真实世界数据集上的表现优于以前的模型,在音频质量和模态集成方面都显示出显着改进。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICASSP 2025
Summary
文本介绍了一项名为VoiceDiT的多模态生成模型,该模型可以从文本和视觉提示中生成环境感知语音和音频。为解决噪声条件下语音与文本对齐的难题,该模型采用新型音频生成流程,包括大规模合成语音数据集用于预训练和优化现实世界语音数据集进行微调、设计的双DiT模型能够高效保留对齐语音信息并准确反映环境条件,以及基于扩散的图像到音频翻译器,可缩小音频与图像之间的差距,便于生成与环境提示相符的音频。实验结果表明,VoiceDiT在现实世界数据集上的表现优于先前模型,在音频质量和模态集成方面取得了显著改进。
Key Takeaways
- VoiceDiT是一个多模态生成模型,可以从文本和视觉提示生成环境感知的语音和音频。
- 噪声条件下语音与文本对齐是语音合成领域的重要挑战。
- VoiceDiT采用新型音频生成流程,包括预训练和微调阶段使用的大规模数据集。
- 双DiT模型能够高效保留对齐语音信息并反映环境条件。
- 扩散图像到音频翻译器有助于生成与环境提示相符的音频。
- VoiceDiT在现实世界数据集上的表现优于先前模型。
点此查看论文截图

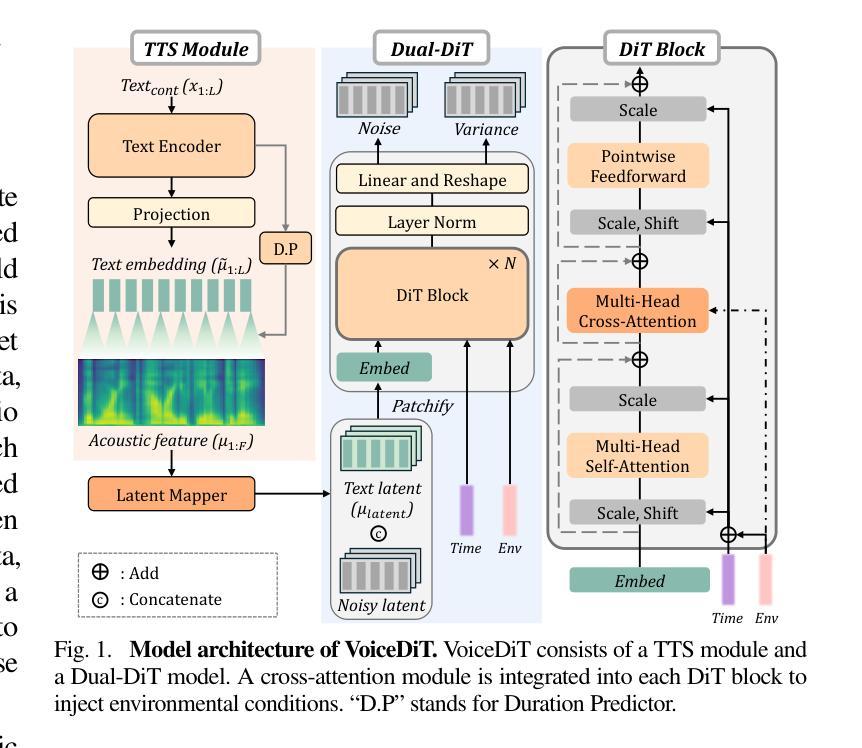
“I’ve Heard of You!”: Generate Spoken Named Entity Recognition Data for Unseen Entities
Authors:Jiawei Yu, Xiang Geng, Yuang Li, Mengxin Ren, Wei Tang, Jiahuan Li, Zhibin Lan, Min Zhang, Hao Yang, Shujian Huang, Jinsong Su
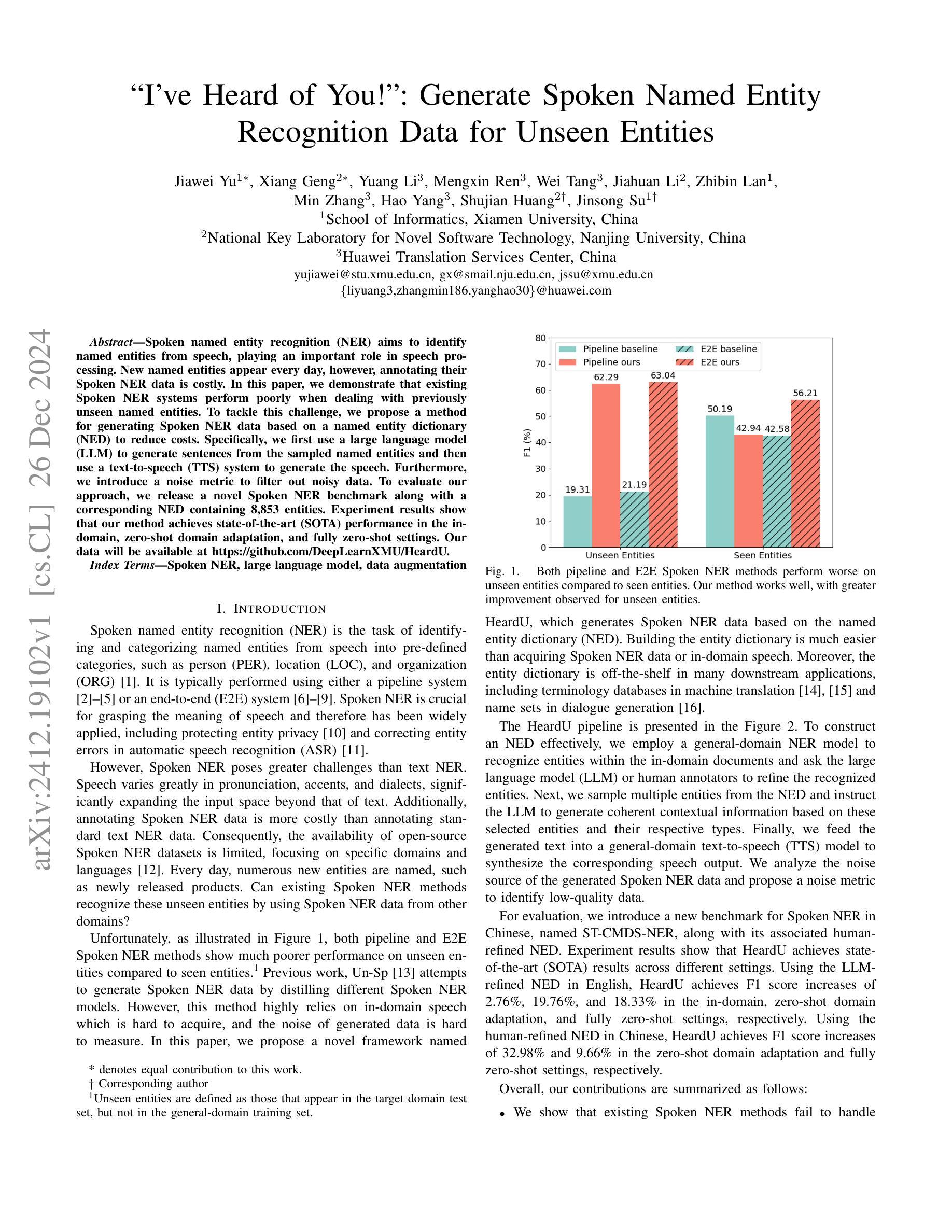
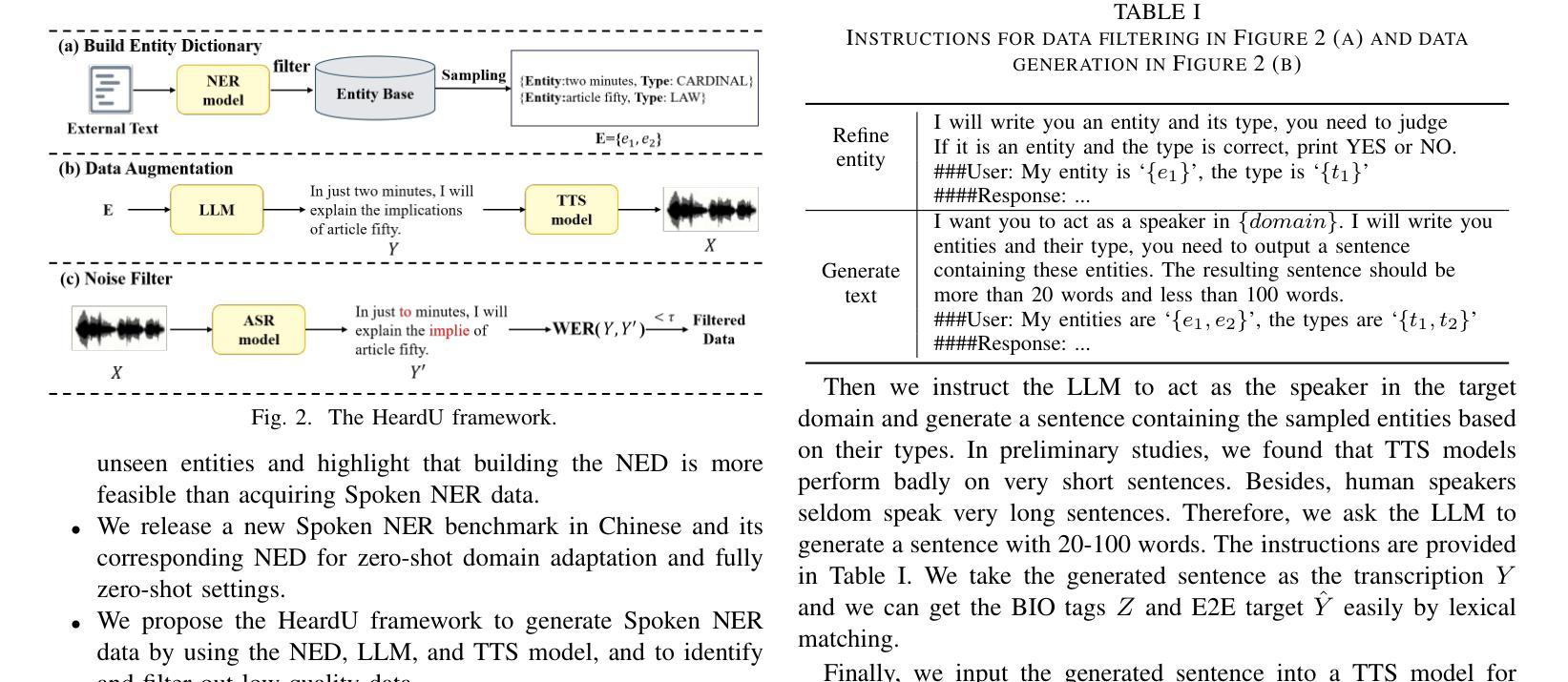
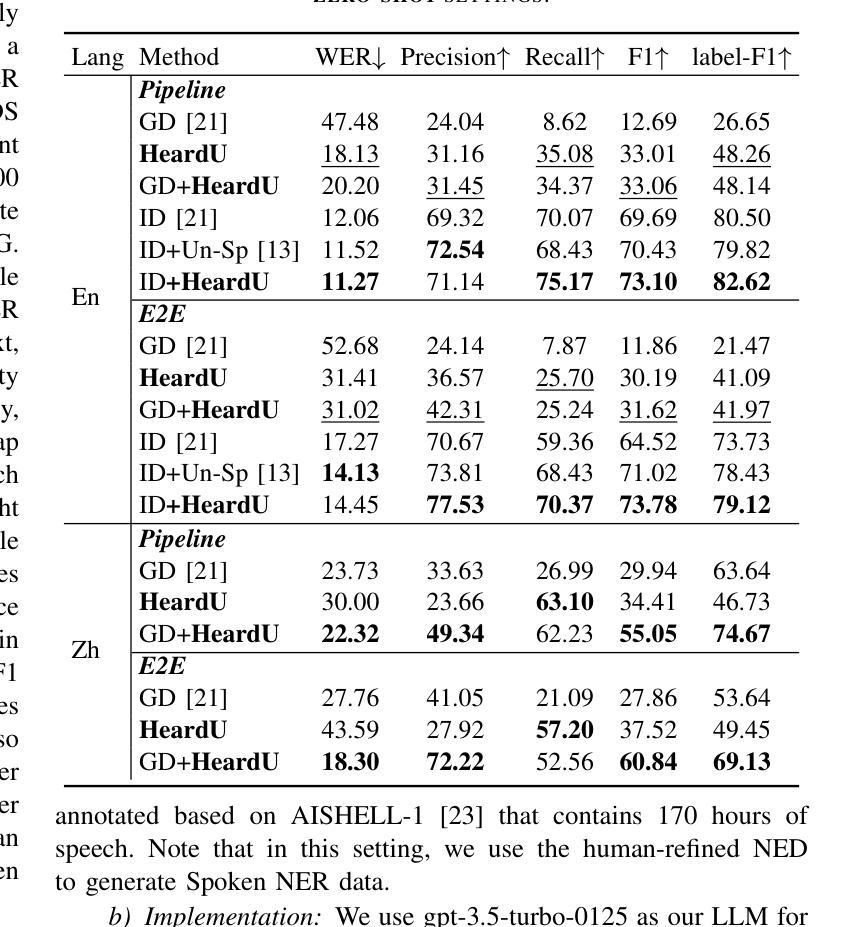
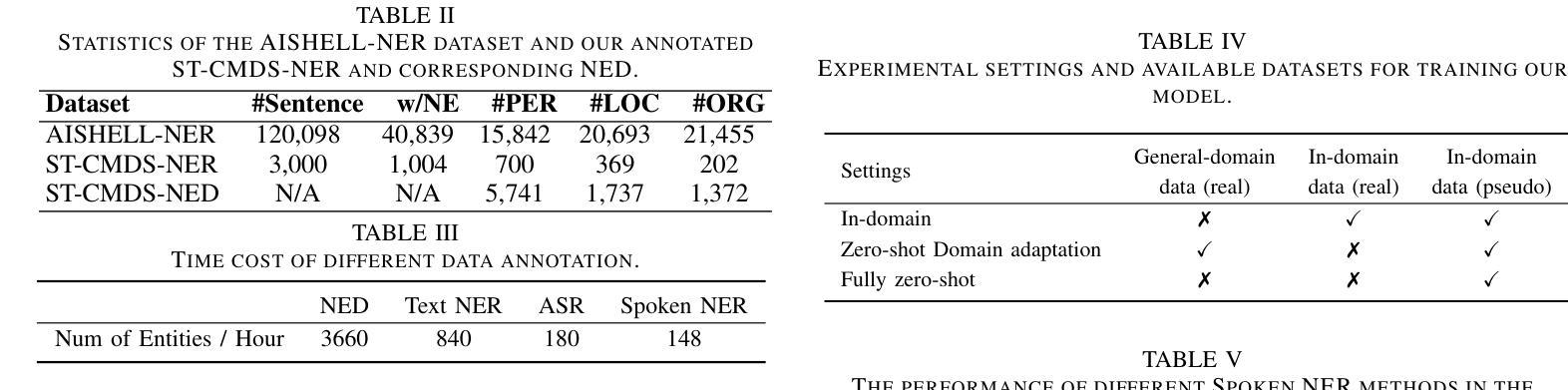
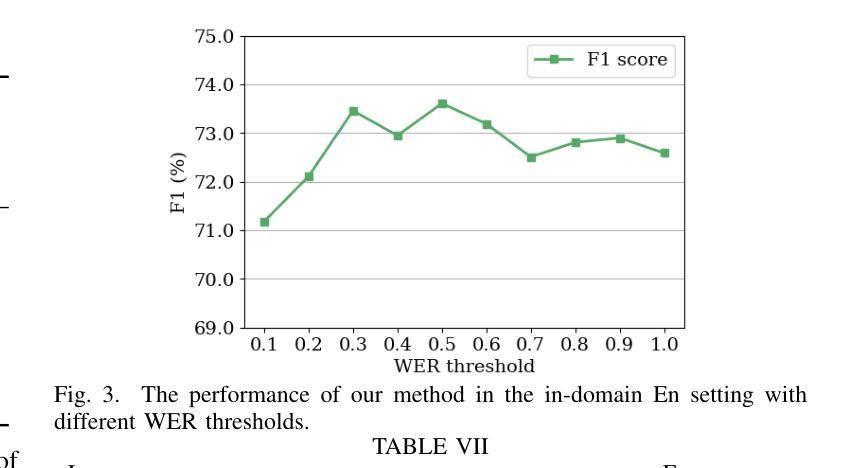
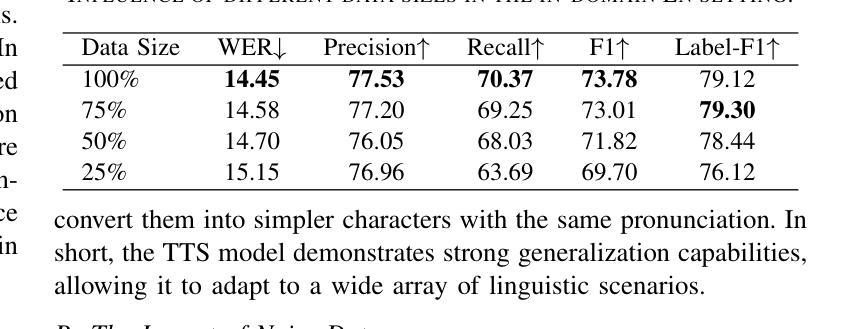
Spoken named entity recognition (NER) aims to identify named entities from speech, playing an important role in speech processing. New named entities appear every day, however, annotating their Spoken NER data is costly. In this paper, we demonstrate that existing Spoken NER systems perform poorly when dealing with previously unseen named entities. To tackle this challenge, we propose a method for generating Spoken NER data based on a named entity dictionary (NED) to reduce costs. Specifically, we first use a large language model (LLM) to generate sentences from the sampled named entities and then use a text-to-speech (TTS) system to generate the speech. Furthermore, we introduce a noise metric to filter out noisy data. To evaluate our approach, we release a novel Spoken NER benchmark along with a corresponding NED containing 8,853 entities. Experiment results show that our method achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in the in-domain, zero-shot domain adaptation, and fully zero-shot settings. Our data will be available at https://github.com/DeepLearnXMU/HeardU.
语音命名实体识别(NER)旨在从语音中识别命名实体,在语音识别处理中扮演着重要角色。每天都有新的命名实体出现,然而,对语音NER数据进行标注的成本很高。在本文中,我们展示了现有的语音NER系统在处理之前未见过的命名实体时表现不佳。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种基于命名实体词典(NED)生成语音NER数据的方法以降低成本。具体来说,我们首先使用大型语言模型(LLM)从采样的命名实体生成句子,然后使用文本到语音(TTS)系统生成语音。此外,我们还引入了一个噪声度量来过滤掉噪声数据。为了评估我们的方法,我们发布了一个新的语音NER基准测试,以及一个包含8853个实体的相应NED。实验结果表明,我们的方法在域内、零镜头域适应和完全零镜头设置中都达到了最先进的性能。我们的数据将在https://github.com/DeepLearnXMU/HeardU上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICASSP 2025
Summary
语音命名实体识别(Spoken NER)旨在从语音中识别命名实体,在语音识别处理中占据重要地位。现有系统在面对未见过的命名实体时表现不佳,标注语音NER数据成本高昂。本研究提出一种基于命名实体词典(NED)生成语音NER数据的方法降低成本。利用大型语言模型(LLM)从采样命名实体生成句子,再通过文本到语音(TTS)系统生成语音。此外,引入噪声度量以过滤噪声数据。研究发布新的语音NER基准与包含8,853个实体的对应NED。实验结果证明该方法在领域内、跨领域适应以及全零样本设置下均达到最新水平。相关数据将公开于https://github.com/DeepLearnXMU/HeardU。
Key Takeaways
- 语音命名实体识别(Spoken NER)在语音识别处理中很重要,面临标注成本高昂和面对未见实体识别性能下降的挑战。
- 提出一种基于命名实体词典(NED)生成语音NER数据的方法,降低成本并提高性能。
- 利用大型语言模型(LLM)从采样命名实体生成句子,再通过文本到语音(TTS)系统转化。
- 引入噪声度量机制以过滤生成的噪声数据。
- 发布新的语音NER基准与对应NED,包含大量实体数据。
- 实验结果显示该方法在多种设置下达到最新水平。
点此查看论文截图
Advancing NAM-to-Speech Conversion with Novel Methods and the MultiNAM Dataset
Authors:Neil Shah, Shirish Karande, Vineet Gandhi
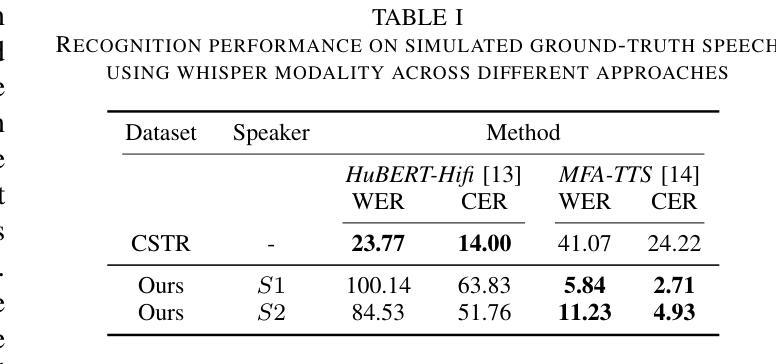
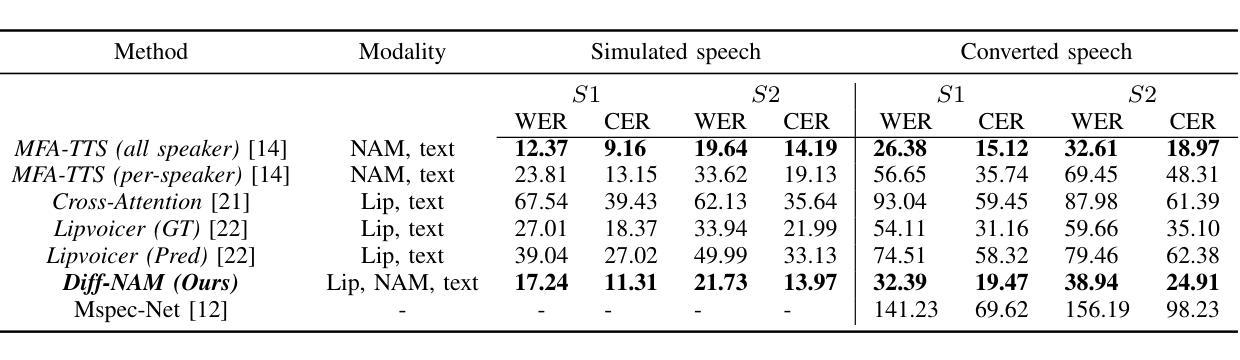
Current Non-Audible Murmur (NAM)-to-speech techniques rely on voice cloning to simulate ground-truth speech from paired whispers. However, the simulated speech often lacks intelligibility and fails to generalize well across different speakers. To address this issue, we focus on learning phoneme-level alignments from paired whispers and text and employ a Text-to-Speech (TTS) system to simulate the ground-truth. To reduce dependence on whispers, we learn phoneme alignments directly from NAMs, though the quality is constrained by the available training data. To further mitigate reliance on NAM/whisper data for ground-truth simulation, we propose incorporating the lip modality to infer speech and introduce a novel diffusion-based method that leverages recent advancements in lip-to-speech technology. Additionally, we release the MultiNAM dataset with over $7.96$ hours of paired NAM, whisper, video, and text data from two speakers and benchmark all methods on this dataset. Speech samples and the dataset are available at \url{https://diff-nam.github.io/DiffNAM/}
当前的非声低语(NAM)到语音技术依赖于语音克隆,通过模拟配对低语的原始语音来实现。然而,模拟的语音往往缺乏清晰度,在不同发音者之间的泛化效果较差。为了解决这个问题,我们专注于从配对的低语和文本中学习音素级别的对齐,并采用文本到语音(TTS)系统来模拟原始语音。为了减少对低语的依赖,我们直接从NAM学习音素对齐,尽管质量受到可用训练数据的限制。为了进一步减少对NAM/低语数据在模拟原始语音方面的依赖,我们提出利用唇型模式进行语音推断,并引入一种新型的基于扩散的方法,该方法利用最新的唇型到语音技术。此外,我们发布了MultiNAM数据集,其中包含来自两个发音者的超过7.96小时的配对NAM、低语、视频和文本数据,并在该数据集上对所有方法进行了基准测试。语音样本和数据集可通过https://diff-nam.github.io/DiffNAM/获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IEEE ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文主要介绍了针对现有非语音嘟囔(NAM)到语音转换技术的问题,提出了一种新的方法。通过从配对嘟囔和文本中学习音素级别的对齐,并使用文本到语音(TTS)系统模拟真实语音。为了减少对嘟囔的依赖,直接从NAM中学习音素对齐,但质量受限于可用训练数据。为了进一步提高对真实语音模拟的可靠性,文章结合了唇部特征并引入了一种基于扩散的方法,利用最新的唇部到语音技术。此外,文章还发布了包含超过7.96小时配对NAM、嘟囔、视频和文本数据的MultiNAM数据集,并在该数据集上对所有方法进行了基准测试。
Key Takeaways
- 当前非语音嘟囔(NAM)到语音转换技术主要依赖于声音克隆来模拟真实语音。
- 现有的模拟语音常常缺乏清晰度和在不同发言人之间的泛化能力。
- 新的方法专注于从配对嘟囔和文本中学习音素级别的对齐,并使用TTS系统模拟真实语音以提高清晰度。
- 直接从NAM中学习音素对齐是一种减少对嘟囔依赖的方法,但受限于训练数据的可用性。
- 为了更可靠地模拟真实语音,结合了唇部特征并引入了一种基于扩散的方法。
- 发布了一个名为MultiNAM的数据集,包含NAM、嘟囔、视频和文本数据,为基准测试提供了资源。
- 基准测试显示各种方法在MultiNAM数据集上的性能表现。
点此查看论文截图


MRI2Speech: Speech Synthesis from Articulatory Movements Recorded by Real-time MRI
Authors:Neil Shah, Ayan Kashyap, Shirish Karande, Vineet Gandhi
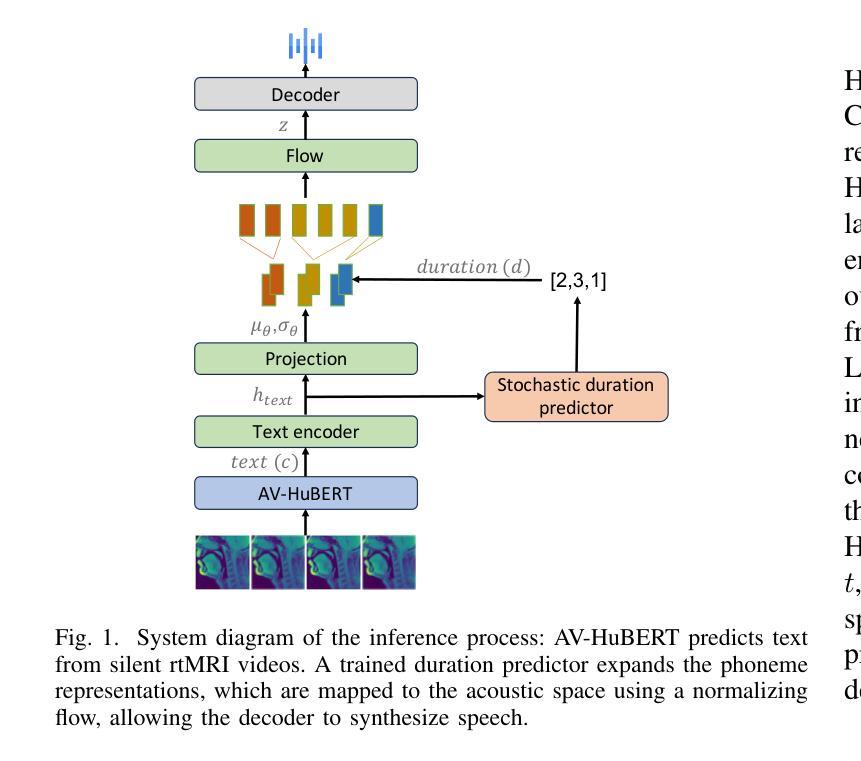
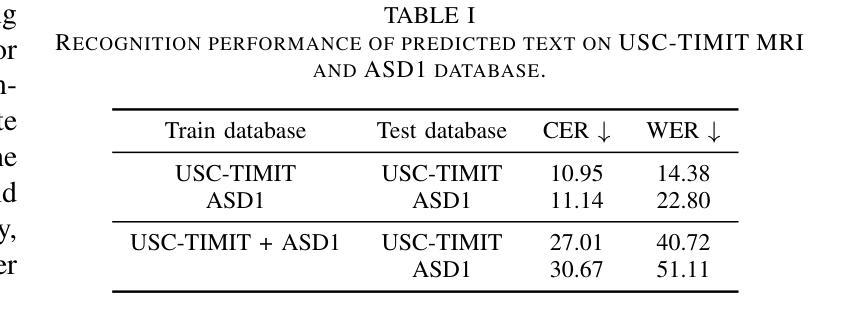
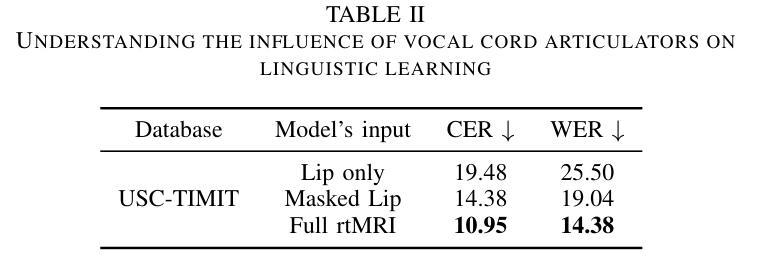
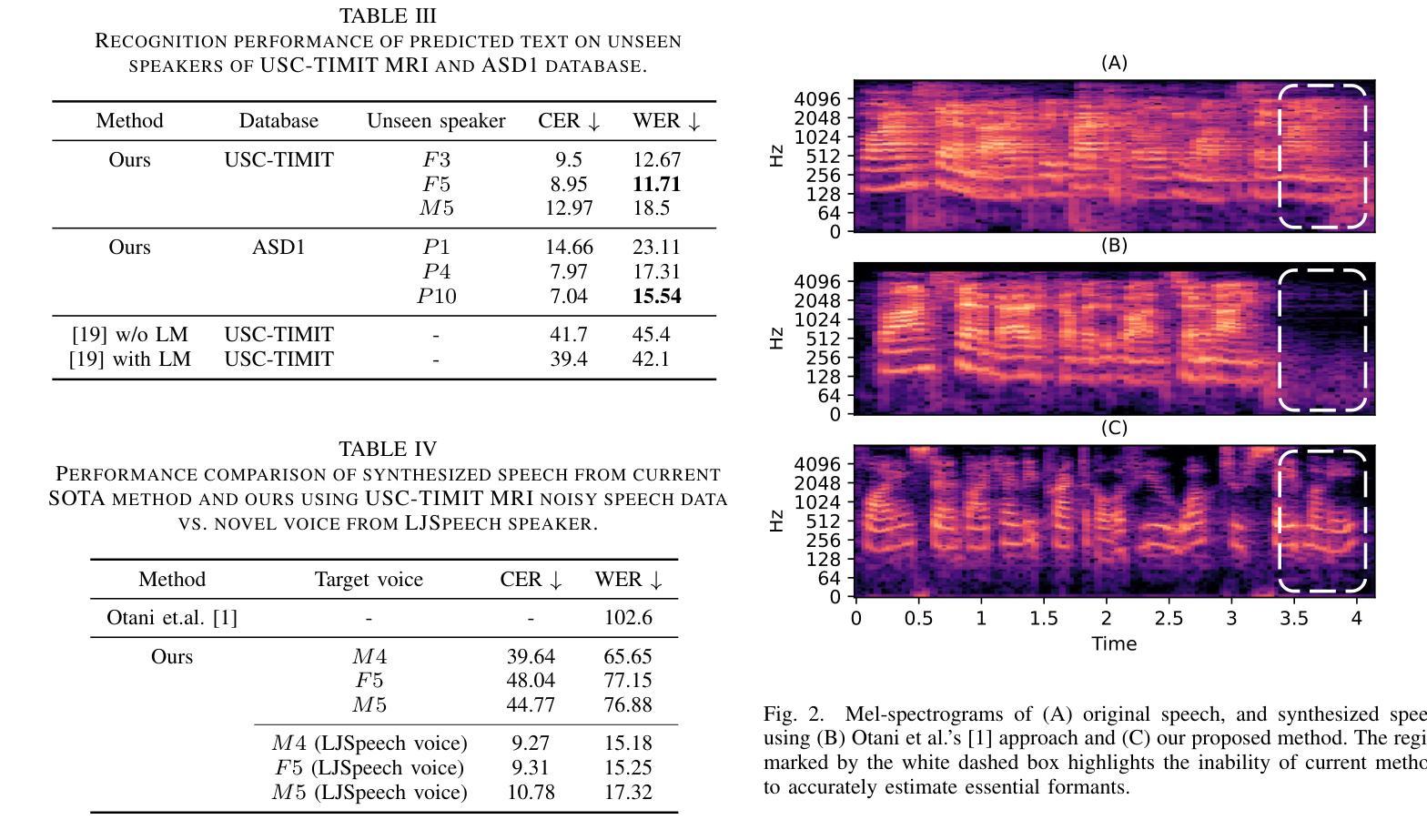
Previous real-time MRI (rtMRI)-based speech synthesis models depend heavily on noisy ground-truth speech. Applying loss directly over ground truth mel-spectrograms entangles speech content with MRI noise, resulting in poor intelligibility. We introduce a novel approach that adapts the multi-modal self-supervised AV-HuBERT model for text prediction from rtMRI and incorporates a new flow-based duration predictor for speaker-specific alignment. The predicted text and durations are then used by a speech decoder to synthesize aligned speech in any novel voice. We conduct thorough experiments on two datasets and demonstrate our method’s generalization ability to unseen speakers. We assess our framework’s performance by masking parts of the rtMRI video to evaluate the impact of different articulators on text prediction. Our method achieves a $15.18%$ Word Error Rate (WER) on the USC-TIMIT MRI corpus, marking a huge improvement over the current state-of-the-art. Speech samples are available at \url{https://mri2speech.github.io/MRI2Speech/}
之前基于实时磁共振成像(rtMRI)的语音合成模型很大程度上依赖于嘈杂的真实语音。直接在真实mel频谱图上应用损失会使语音内容与磁共振成像噪声混淆,导致语音清晰度降低。我们引入了一种新方法,该方法自适应多模态自监督AV-HuBERT模型,用于从rtMRI预测文本,并融入新的基于流技术的持续时间预测器,以实现针对特定说话人的对齐。预测的文本和持续时间随后被语音解码器用于合成任何新颖声音的语音。我们在两个数据集上进行了全面的实验,证明了我们的方法对于未见过的说话人的泛化能力。我们通过遮挡rtMRI视频的部分内容来评估我们的框架性能,以评估不同发音器对文本预测的影响。我们的方法在USC-TIMIT MRI语料库上实现了15.18%的单词错误率(WER),相较于当前最新技术,这是一个巨大的改进。语音样本可在[https://mri2speech.github.io/MRI2Speech/]上获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IEEE ICASSP 2025
Summary
基于实时磁共振成像(rtMRI)的语音合成模型过去依赖于噪声较大的真实语音。直接在真实mel频谱图上应用损失会导致语音内容与磁共振成像噪声混淆,降低语音清晰度。本研究引入了一种新型多模态自监督AV-HuBERT模型,用于从rtMRI预测文本,并融入新的基于流的时长预测器进行特定于说话者的对齐。预测的文本和时长随后被语音解码器用于合成任何新颖语音。在两项数据集上的实验证明,该方法能够推广到未见过的说话者。本研究通过遮挡rtMRI视频的部分内容来评估文本预测的影响,该方法在USC-TIMIT MRI语料库上实现了15.18%的词错误率(WER),较当前先进技术有很大改进。
Key Takeaways
- 实时MRI语音合成依赖噪声真实语音的问题。
- 直接在真实mel频谱图上应用损失会导致语音内容和MRI噪声混淆,影响语音清晰度。
- 引入新型多模态自监督AV-HuBERT模型,用于从rtMRI预测文本。
- 结合基于流的时长预测器进行特定说话者的对齐。
- 使用预测的文本和时长通过语音解码器合成语音。
- 方法可推广到未见过的说话者。
- 通过遮挡rtMRI视频部分内容进行文本预测评估,在USC-TIMIT MRI语料库上实现较低词错误率。
点此查看论文截图

Intra- and Inter-modal Context Interaction Modeling for Conversational Speech Synthesis
Authors:Zhenqi Jia, Rui Liu
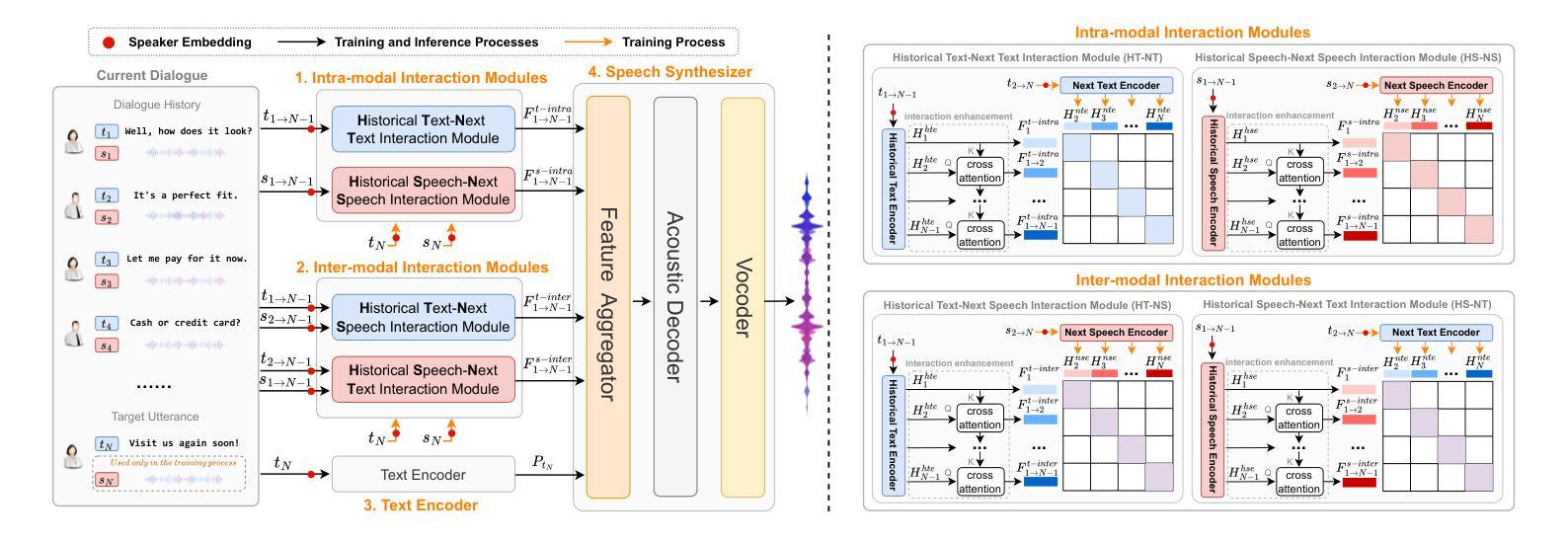
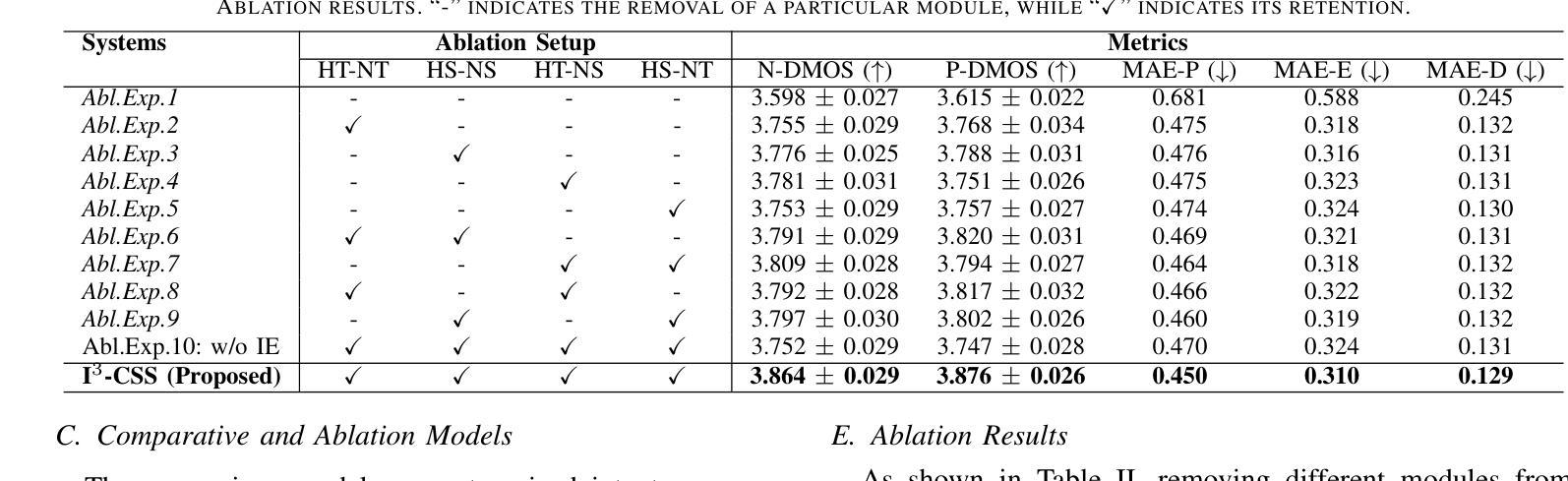
Conversational Speech Synthesis (CSS) aims to effectively take the multimodal dialogue history (MDH) to generate speech with appropriate conversational prosody for target utterance. The key challenge of CSS is to model the interaction between the MDH and the target utterance. Note that text and speech modalities in MDH have their own unique influences, and they complement each other to produce a comprehensive impact on the target utterance. Previous works did not explicitly model such intra-modal and inter-modal interactions. To address this issue, we propose a new intra-modal and inter-modal context interaction scheme-based CSS system, termed III-CSS. Specifically, in the training phase, we combine the MDH with the text and speech modalities in the target utterance to obtain four modal combinations, including Historical Text-Next Text, Historical Speech-Next Speech, Historical Text-Next Speech, and Historical Speech-Next Text. Then, we design two contrastive learning-based intra-modal and two inter-modal interaction modules to deeply learn the intra-modal and inter-modal context interaction. In the inference phase, we take MDH and adopt trained interaction modules to fully infer the speech prosody of the target utterance’s text content. Subjective and objective experiments on the DailyTalk dataset show that III-CSS outperforms the advanced baselines in terms of prosody expressiveness. Code and speech samples are available at https://github.com/AI-S2-Lab/I3CSS.
对话式语音合成(CSS)旨在有效利用多模式对话历史(MDH)来生成具有适当对话韵律的目标语句。CSS的关键挑战在于对MDH与目标语句之间交互的建模。需要注意的是,MDH中的文本和语音模式各自具有独特的影响,它们相互补充,对目标语句产生全面的影响。之前的工作并没有显式地建模这种内部模式和跨模式之间的交互。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于新模式的内部模式和跨模式交互方案的CSS系统,称为III-CSS。具体来说,在训练阶段,我们将MDH与目标语句中的文本和语音模式相结合,获得四种模态组合,包括历史文本-下一个文本、历史语音-下一个语音、历史文本-下一个语音,以及历史语音-下一个文本。然后,我们设计了两个基于对比学习的内部模式和两个跨模式交互模块,以深入学习内部和跨模式的上下文交互。在推理阶段,我们采用MDH和训练好的交互模块来完全推断目标语句文本内容的语音韵律。在DailyTalk数据集上的主观和客观实验表明,III-CSS在表达韵律方面超过了先进的基线方法。代码和语音样本可在https://github.com/AI-S2-Lab/I3CSS找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICASSP 2025
Summary
基于会话历史的多模态信息生成具有适当会话韵律的目标语句的会话语音合成(CSS)的主要挑战在于建模多模态对话历史(MDH)与目标语句之间的交互。针对这一问题,提出了基于对比学习的多模态交互方案的新型CSS系统——III-CSS。通过结合MDH与目标语句中的文本和语音模态,设计两种基于对比学习的模态内和模态间交互模块,以深度学习模态内和模态间的上下文交互。在推理阶段,采用MDH和训练好的交互模块来完全推断目标语句文本内容的语音韵律。实验表明,III-CSS在语音韵律表达方面优于先进基线。
Key Takeaways
- 会话语音合成(CSS)旨在利用多模态对话历史(MDH)生成具有适当会话韵律的目标语句。
- CSS的主要挑战在于建模MDH与目标语句之间的交互。
- 提出了基于对比学习的新型CSS系统——III-CSS,包含模态内和模态间的交互模块。
- 在训练阶段,结合MDH和目标语句的四种模态组合,包括历史文本-下一条文本、历史语音-下一条语音等。
- III-CSS通过深度学习模态内和模态间的上下文交互,提高语音韵律表达的准确性。
- 在推理阶段,采用MDH和训练好的交互模块来推断目标语句的语音韵律。
点此查看论文截图

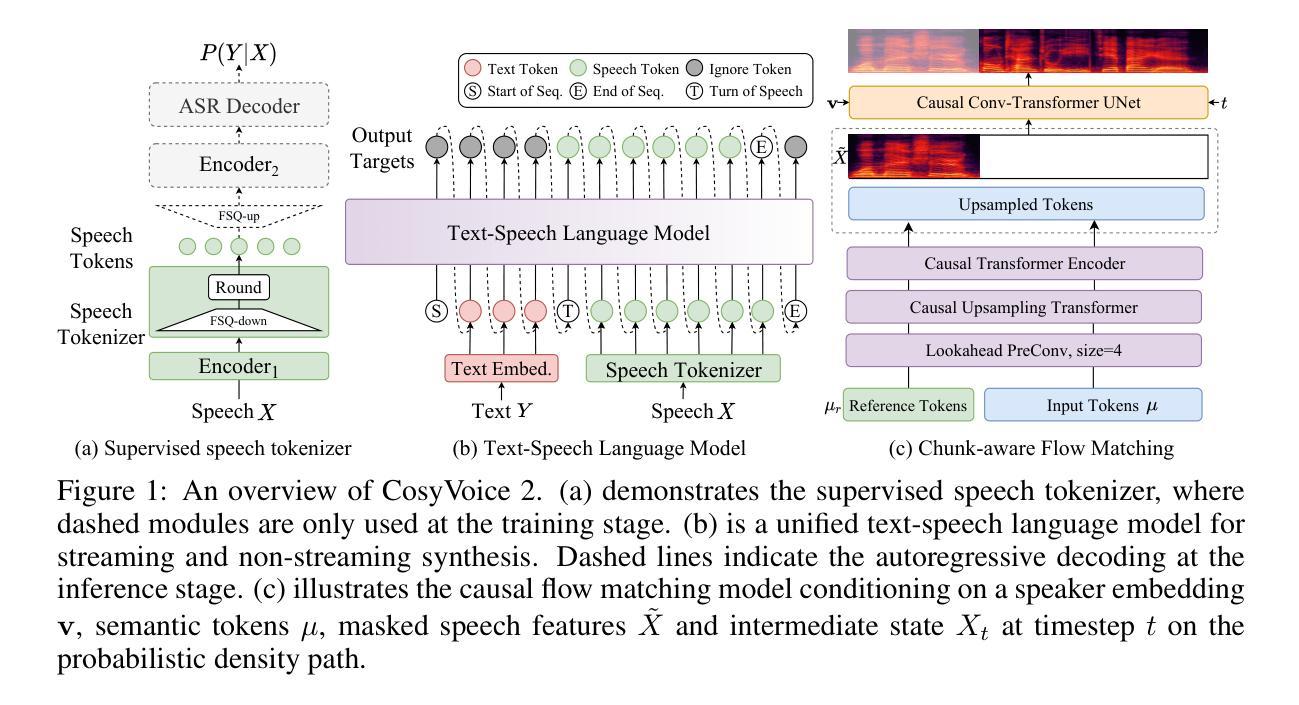
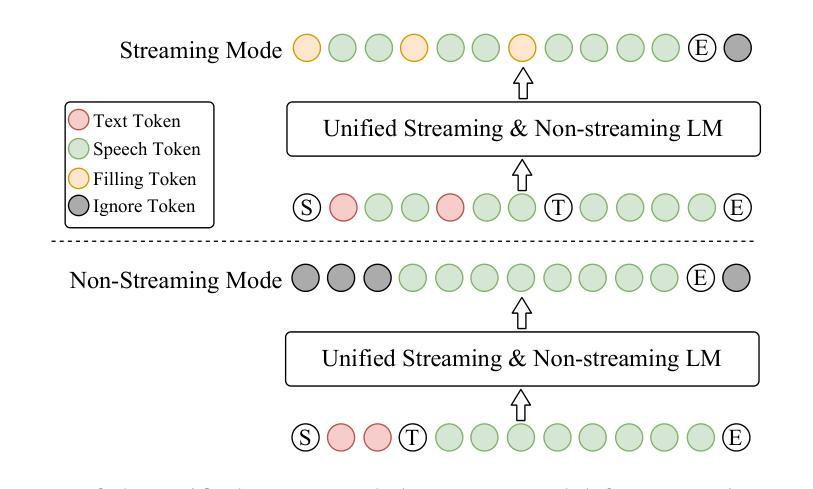
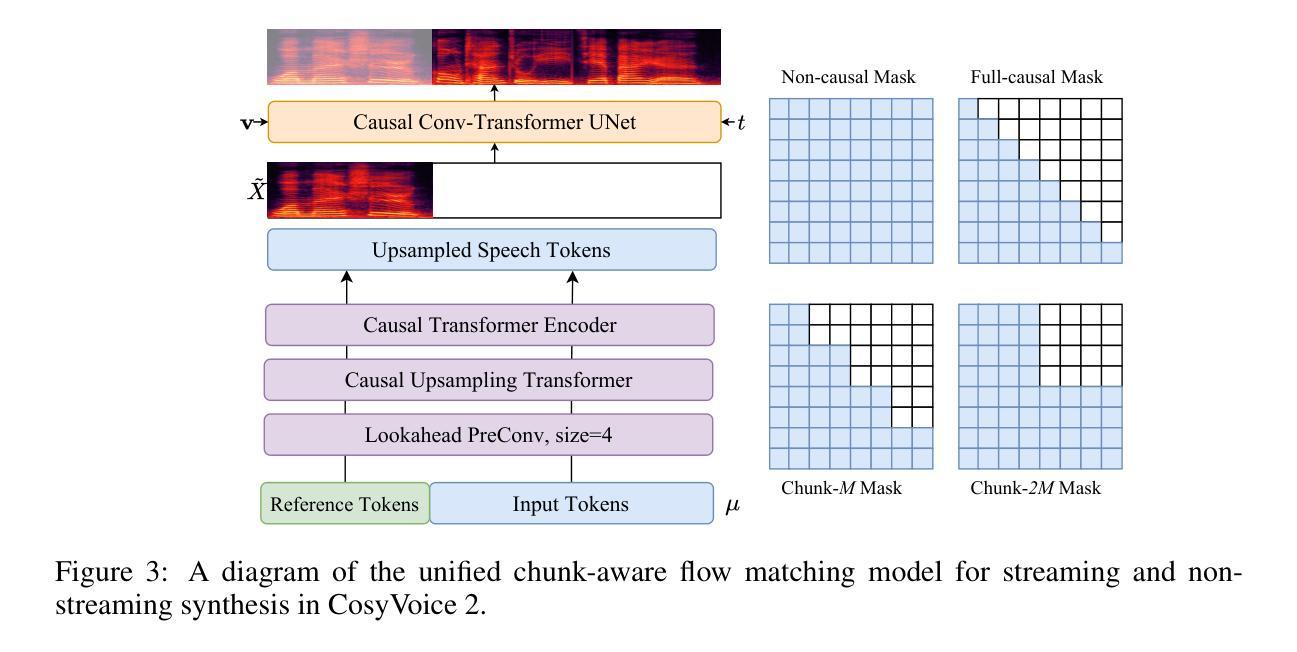
CosyVoice 2: Scalable Streaming Speech Synthesis with Large Language Models
Authors:Zhihao Du, Yuxuan Wang, Qian Chen, Xian Shi, Xiang Lv, Tianyu Zhao, Zhifu Gao, Yexin Yang, Changfeng Gao, Hui Wang, Fan Yu, Huadai Liu, Zhengyan Sheng, Yue Gu, Chong Deng, Wen Wang, Shiliang Zhang, Zhijie Yan, Jingren Zhou
In our previous work, we introduced CosyVoice, a multilingual speech synthesis model based on supervised discrete speech tokens. By employing progressive semantic decoding with two popular generative models, language models (LMs) and Flow Matching, CosyVoice demonstrated high prosody naturalness, content consistency, and speaker similarity in speech in-context learning. Recently, significant progress has been made in multi-modal large language models (LLMs), where the response latency and real-time factor of speech synthesis play a crucial role in the interactive experience. Therefore, in this report, we present an improved streaming speech synthesis model, CosyVoice 2, which incorporates comprehensive and systematic optimizations. Specifically, we introduce finite-scalar quantization to improve the codebook utilization of speech tokens. For the text-speech LM, we streamline the model architecture to allow direct use of a pre-trained LLM as the backbone. In addition, we develop a chunk-aware causal flow matching model to support various synthesis scenarios, enabling both streaming and non-streaming synthesis within a single model. By training on a large-scale multilingual dataset, CosyVoice 2 achieves human-parity naturalness, minimal response latency, and virtually lossless synthesis quality in the streaming mode. We invite readers to listen to the demos at https://funaudiollm.github.io/cosyvoice2.
在之前的工作中,我们介绍了CosyVoice,这是一个基于监督离散语音标记的多语种语音合成模型。通过采用两种流行的生成模型——语言模型和流匹配,进行渐进式语义解码,CosyVoice在语境中学习语音时表现出了高度的语调自然性、内容一致性和说话人相似性。最近,多模态大型语言模型(LLMs)取得了重大进展,其中语音合成的响应延迟和实时因子在交互体验中发挥了关键作用。因此,在本报告中,我们提出了一种改进的流式语音合成模型CosyVoice 2,它包含了全面系统的优化。具体来说,我们引入了有限标量量化法以提高语音标记的代码本利用率。对于文本-语音语言模型,我们简化了模型架构,允许直接使用预训练的大型语言模型作为骨干。此外,我们开发了一种块感知因果流匹配模型,以支持各种合成场景,能在单个模型内实现流式和非流式合成。通过在大规模多语种数据集上进行训练,CosyVoice 2达到了与人类相当的自然度、极短的响应延迟、以及几乎无损的合成质量。欢迎听众在https://funaudiollm.github.io/cosyvoice2上试听演示。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Tech report, work in progress
摘要
基于先前的工作,我们推出了CosyVoice 2,一个优化的流式语音合成模型。该模型采用有限标量量化改进语音令牌的码本利用率,优化文本语音的语言模型架构以直接使用预训练的大型语言模型作为骨干网。此外,我们开发了块感知因果流匹配模型,支持各种合成场景,能够在单个模型内实现流式和非流式合成。通过大规模多语种数据集的训练,CosyVoice 2达到了与人类自然度相当的水平,响应延迟最小化,流式合成质量几乎无损失。
关键见解
- CosyVoice 2是CosyVoice的改进版本,是一个优化的流式语音合成模型。
- 采用有限标量量化改进语音令牌的码本利用率,以提高语音合成的质量和效率。
- 优化文本语音的语言模型架构,允许直接使用预训练的大型语言模型作为骨干网。
- 开发块感知因果流匹配模型,支持各种合成场景。
- 模型能够支持流式和非流式合成两种模式,扩大了其应用场景范围。
- 通过大规模多语种数据集的训练,CosyVoice 2达到了高水平的自然度,与人类表现相当。
- 模型具有低响应延迟和几乎无损失的合成质量。可通过访问网站体验模型的演示效果:https://funaudiollm.github.io/cosyvoice2 。
点此查看论文截图

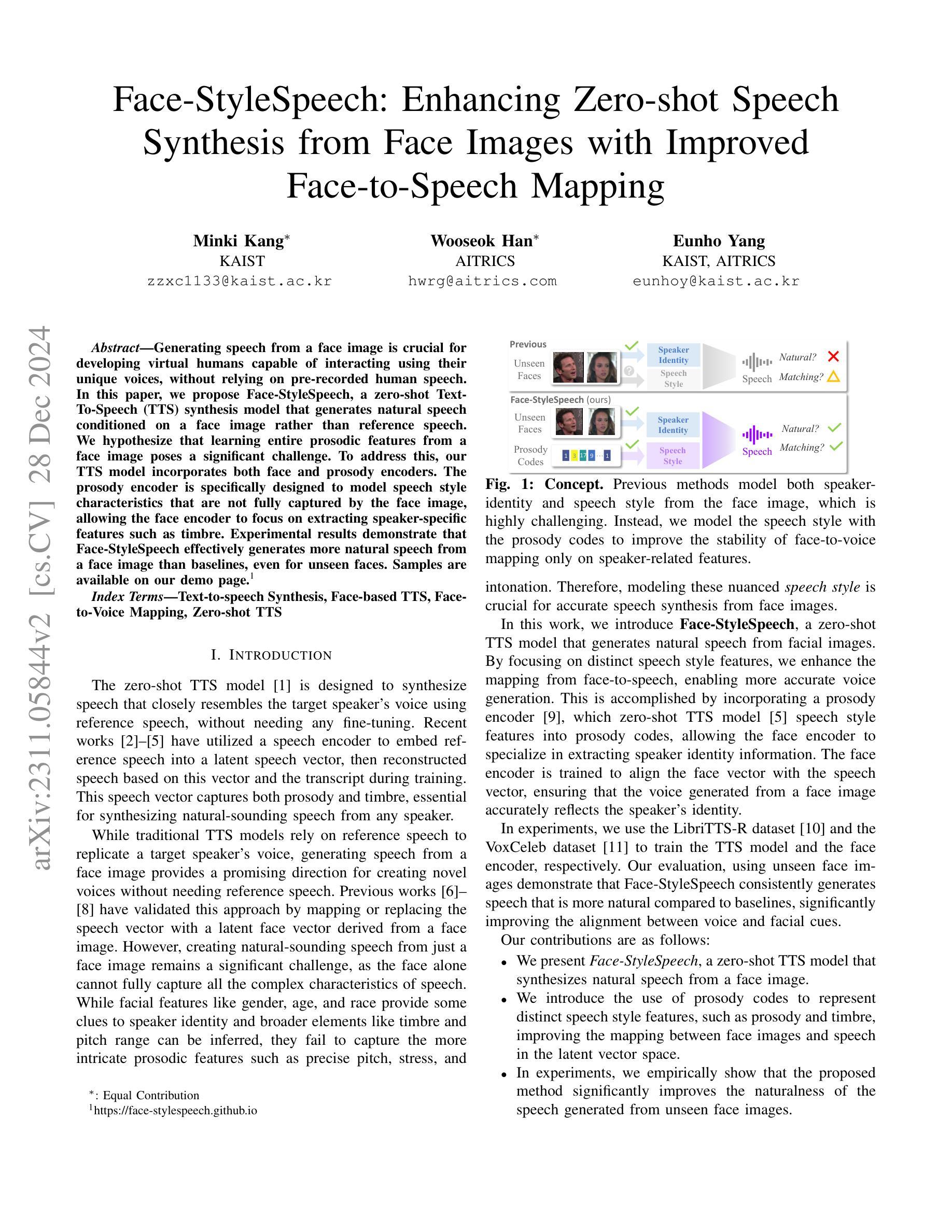
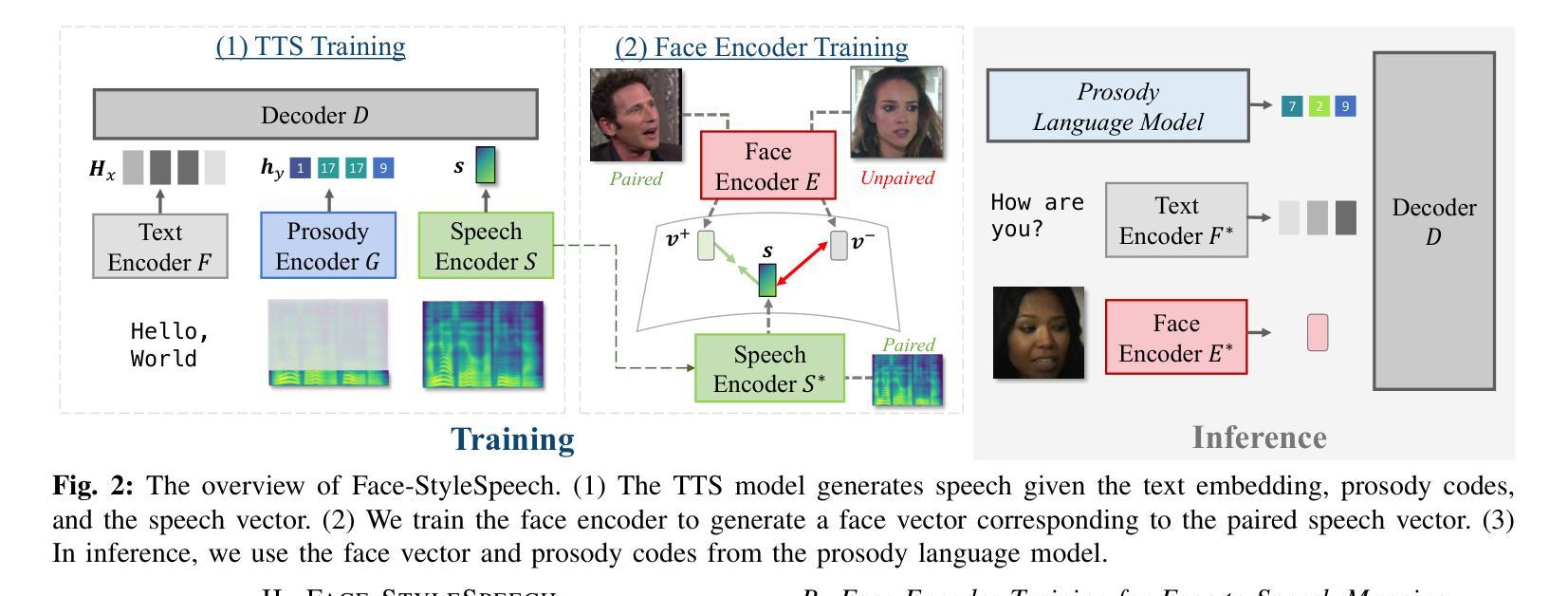
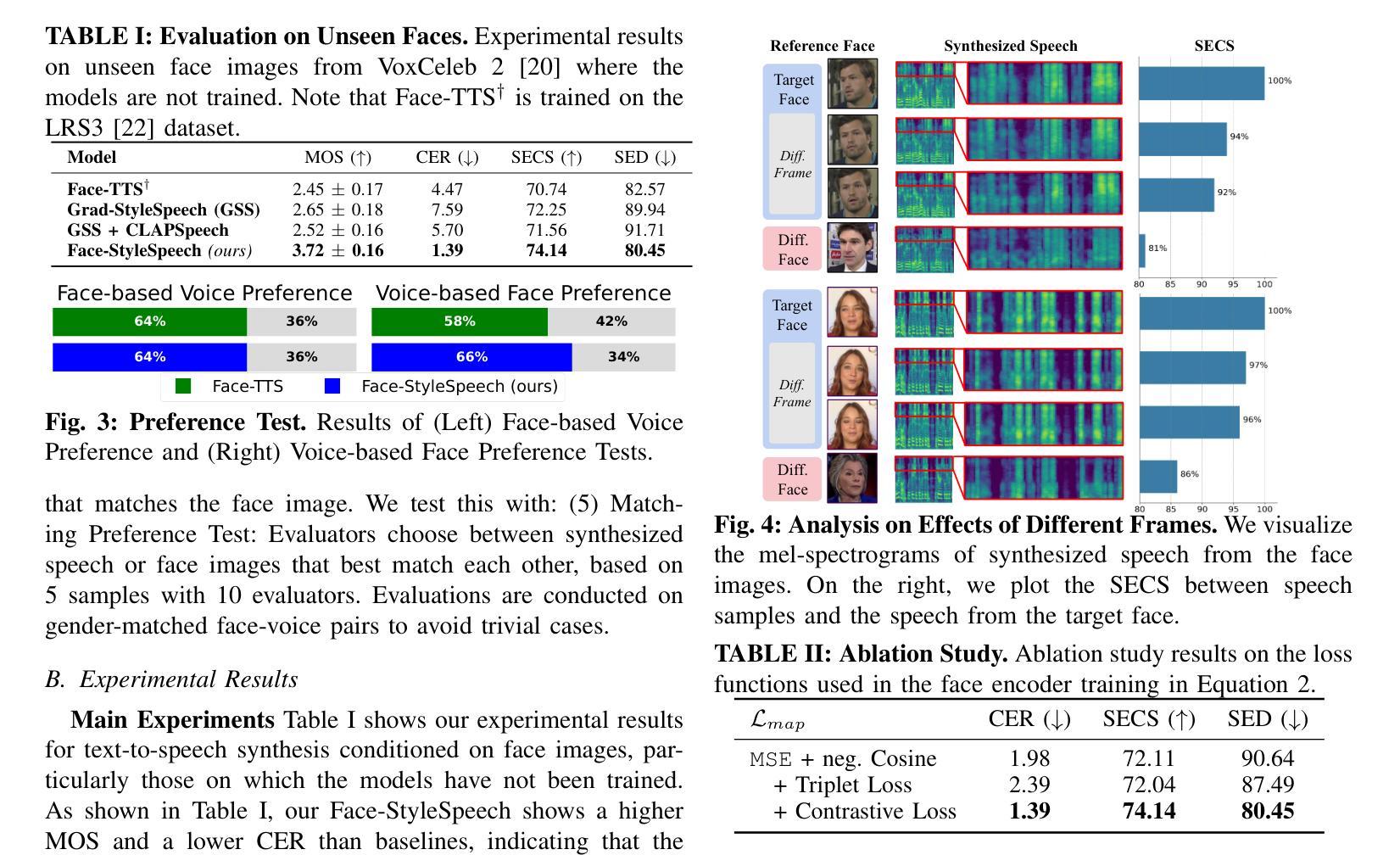
Face-StyleSpeech: Enhancing Zero-shot Speech Synthesis from Face Images with Improved Face-to-Speech Mapping
Authors:Minki Kang, Wooseok Han, Eunho Yang
Generating speech from a face image is crucial for developing virtual humans capable of interacting using their unique voices, without relying on pre-recorded human speech. In this paper, we propose Face-StyleSpeech, a zero-shot Text-To-Speech (TTS) synthesis model that generates natural speech conditioned on a face image rather than reference speech. We hypothesize that learning entire prosodic features from a face image poses a significant challenge. To address this, our TTS model incorporates both face and prosody encoders. The prosody encoder is specifically designed to model speech style characteristics that are not fully captured by the face image, allowing the face encoder to focus on extracting speaker-specific features such as timbre. Experimental results demonstrate that Face-StyleSpeech effectively generates more natural speech from a face image than baselines, even for unseen faces. Samples are available on our demo page.
从人脸图像生成语音对于开发能够使用其独特声音进行交互的虚拟人类至关重要,而无需依赖预先录制的人类语音。在本文中,我们提出了Face-StyleSpeech,这是一种零样本文本到语音(TTS)合成模型,它根据人脸图像而不是参考语音生成自然语音。我们假设从人脸图像中学习所有的韵律特征是一个巨大的挑战。为解决这一问题,我们的TTS模型结合了人脸和韵律编码器。韵律编码器专门用于建模语音风格特征,这些特征无法完全由人脸图像捕获,使得人脸编码器能够专注于提取说话人特定的特征,如音质。实验结果表明,Face-StyleSpeech能有效地从人脸图像生成比基线更自然的语音,即使对于未见过的面孔也是如此。样本可在我们的演示页面上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种零样本文本到语音(TTS)合成模型——Face-StyleSpeech,该模型能够根据人脸图像生成自然语音,而无需参考预录的语音。通过融入人脸和语调编码器,模型解决了从人脸图像学习全部韵律特征带来的挑战,使得生成语音更加自然。实验结果表明,Face-StyleSpeech在生成人脸图像对应的语音方面比基线方法更有效,即使对于未见过的面孔也能生成自然的语音。
Key Takeaways
- Face-StyleSpeech是一种零样本TTS合成模型,能根据人脸图像生成自然语音。
- 模型采用人脸和语调编码器融合,解决从人脸图像学习韵律特征的挑战。
- 人脸编码器专注于提取发音者特定特征,如音色。
- 模型在生成自然语音方面比基线方法更有效,尤其对于未见过的面孔。
- 模型生成的语音样本可在演示页面查看。
- 该技术对于开发能够使用独特声音进行交互的虚拟人具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图