⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-02 更新
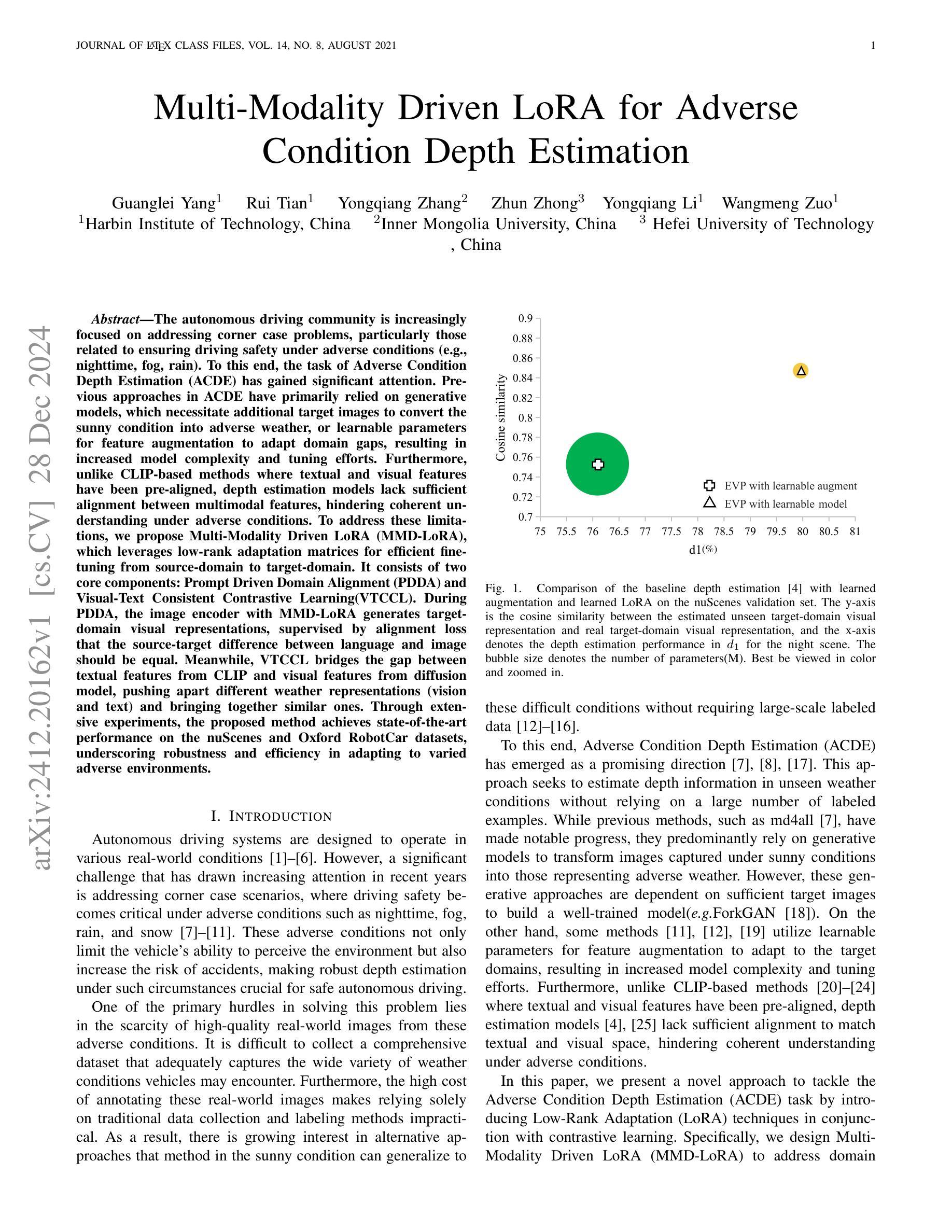
Multi-Modality Driven LoRA for Adverse Condition Depth Estimation
Authors:Guanglei Yang, Rui Tian, Yongqiang Zhang, Zhun Zhong, Yongqiang Li, Wangmeng Zuo
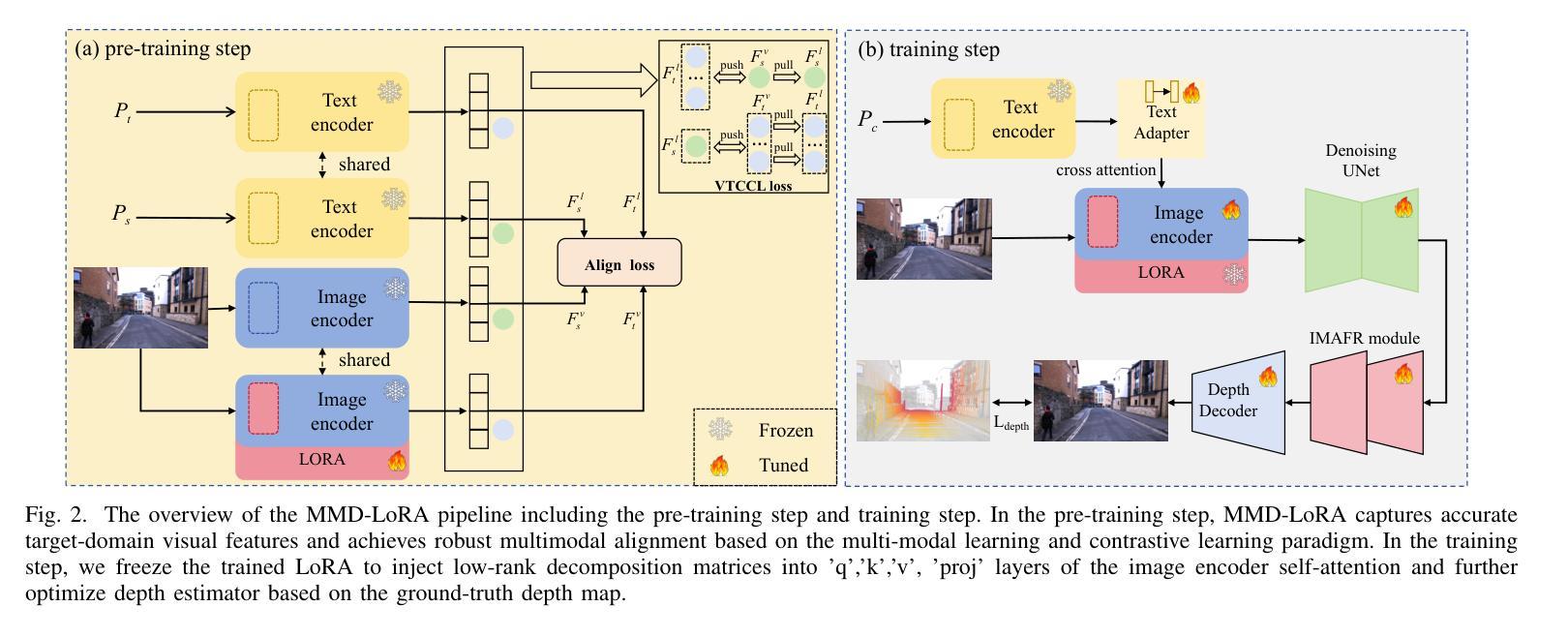
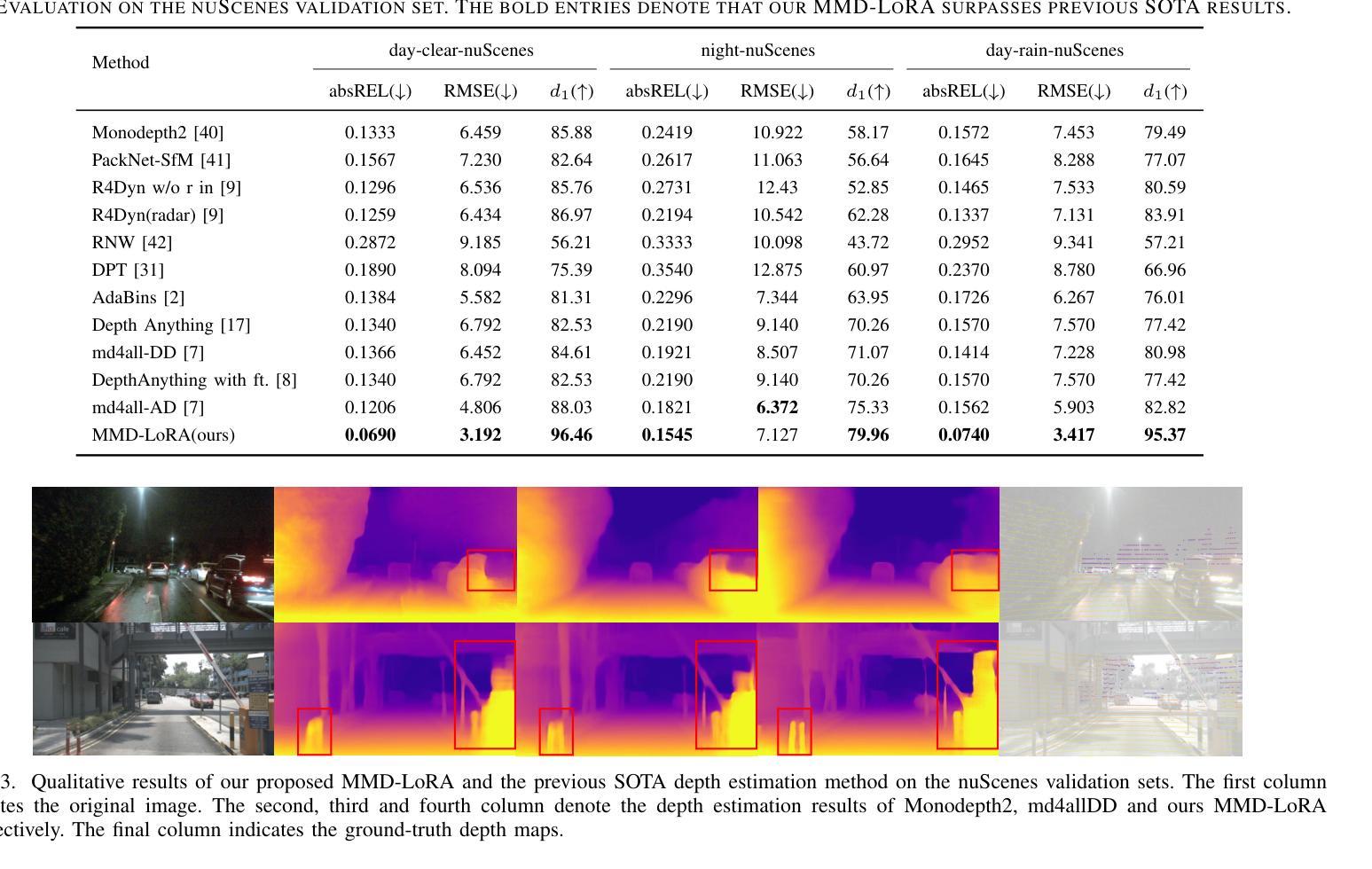
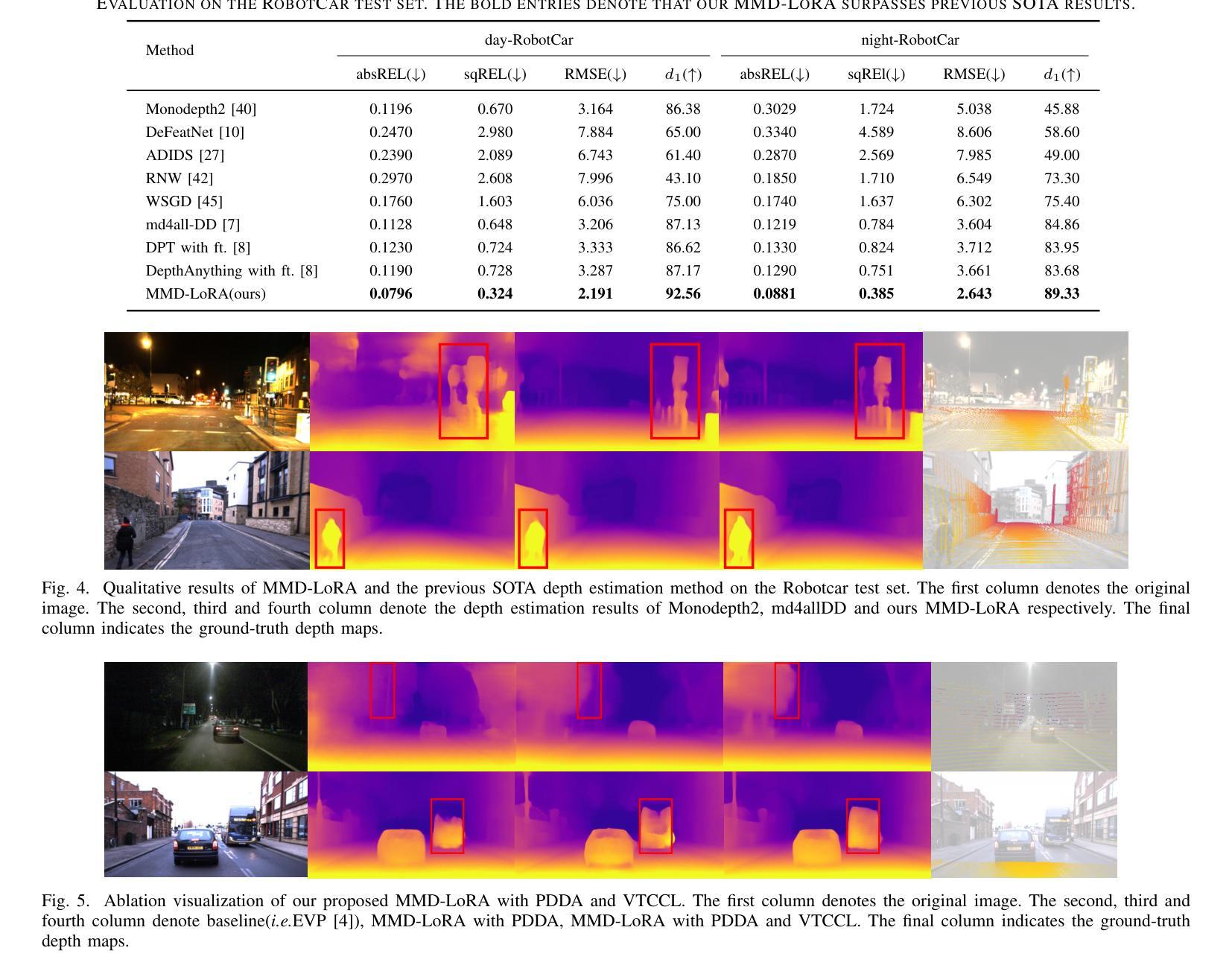
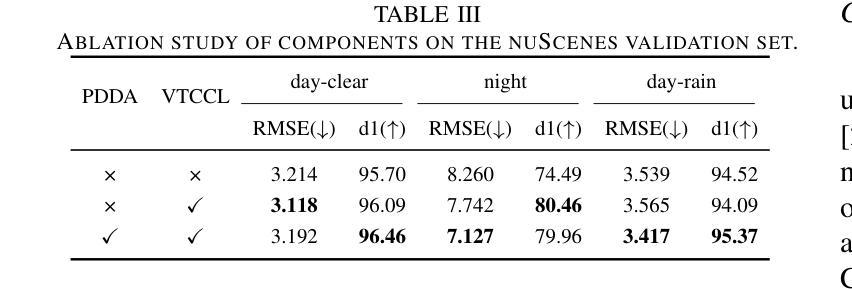
The autonomous driving community is increasingly focused on addressing corner case problems, particularly those related to ensuring driving safety under adverse conditions (e.g., nighttime, fog, rain). To this end, the task of Adverse Condition Depth Estimation (ACDE) has gained significant attention. Previous approaches in ACDE have primarily relied on generative models, which necessitate additional target images to convert the sunny condition into adverse weather, or learnable parameters for feature augmentation to adapt domain gaps, resulting in increased model complexity and tuning efforts. Furthermore, unlike CLIP-based methods where textual and visual features have been pre-aligned, depth estimation models lack sufficient alignment between multimodal features, hindering coherent understanding under adverse conditions. To address these limitations, we propose Multi-Modality Driven LoRA (MMD-LoRA), which leverages low-rank adaptation matrices for efficient fine-tuning from source-domain to target-domain. It consists of two core components: Prompt Driven Domain Alignment (PDDA) and Visual-Text Consistent Contrastive Learning(VTCCL). During PDDA, the image encoder with MMD-LoRA generates target-domain visual representations, supervised by alignment loss that the source-target difference between language and image should be equal. Meanwhile, VTCCL bridges the gap between textual features from CLIP and visual features from diffusion model, pushing apart different weather representations (vision and text) and bringing together similar ones. Through extensive experiments, the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance on the nuScenes and Oxford RobotCar datasets, underscoring robustness and efficiency in adapting to varied adverse environments.
自动驾驶领域越来越关注极端情况问题的解决方案,特别是与恶劣条件下的驾驶安全相关的问题(例如夜间、雾霾、雨天)。为此,恶劣条件深度估计(ACDE)任务引起了广泛关注。ACDE的先前方法主要依赖于生成模型,这些模型需要将晴朗条件下的图像转换为恶劣天气,或学习参数以增强特征以适应域差异,这增加了模型复杂性和调整工作。此外,与基于CLIP的方法不同,其中文本和视觉特征已经预先对齐,深度估计模型的多模态特征缺乏足够的对齐,阻碍了恶劣条件下的连贯理解。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了多模态驱动LoRA(MMD-LoRA),它利用低秩适应矩阵从源域到目标域进行高效的微调。它包括两个核心组件:提示驱动域对齐(PDDA)和视觉文本一致对比学习(VTCCL)。在PDDA期间,带有MMD-LoRA的图像编码器生成目标域的视觉表示,由对齐损失监督,该损失使语言和图像之间的源目标差异应相等。同时,VTCCL弥合了来自CLIP的文本特征和来自扩散模型的视觉特征之间的差距,将不同的天气表示(视觉和文本)分开并将相似的表示聚集在一起。通过广泛的实验,所提出的方法在nuScenes和Oxford RobotCar数据集上实现了卓越的性能,突显了在适应各种恶劣环境中的稳健性和效率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注自动驾驶领域中的极端情况问题处理,特别是在恶劣条件下的驾驶安全。为解决这一问题,研究者提出了名为Adverse Condition Depth Estimation(ACDE)的任务。之前的ACDE方法主要依赖生成模型,需要大量目标图像来转换天气条件或使用可学习参数进行特征增强来适应不同领域差异,增加了模型的复杂性和调优工作。为此,研究者提出了Multi-Modality Driven LoRA(MMD-LoRA)方法,通过低秩适应矩阵实现高效微调从源域到目标域的过程。它包括两个核心组件:Prompt Driven Domain Alignment(PDDA)和Visual-Text Consistent Contrastive Learning(VTCCL)。PDDA使图像编码器生成目标域视觉表示,通过对齐损失实现源域和目标域之间的语言与图像差异平衡。而VTCCL则缩小了CLIP文本特征和扩散模型视觉特征之间的差距,将不同的天气表示(视觉和文本)区分开并拉近相似的表示。实验证明,该方法在nuScenes和Oxford RobotCar数据集上取得了最佳性能,展现了在不同恶劣环境下的稳健性和适应性。
Key Takeaways
- 自动驾驶领域关注极端情况问题处理,尤其是恶劣条件下的驾驶安全。
- Adverse Condition Depth Estimation (ACDE)任务旨在解决这一问题。
- 以往的ACDE方法主要依赖生成模型,存在模型复杂度高和调优工作量大的问题。
- Multi-Modality Driven LoRA (MMD-LoRA)方法通过低秩适应矩阵实现高效微调源域到目标域的过程。
- PDDA组件通过图像编码器生成目标域视觉表示,并通过对齐损失实现源域和目标域之间的语言与图像平衡。
- VTCCL组件缩小了文本和视觉特征之间的差距,提高了不同天气条件下模型的稳健性。
点此查看论文截图
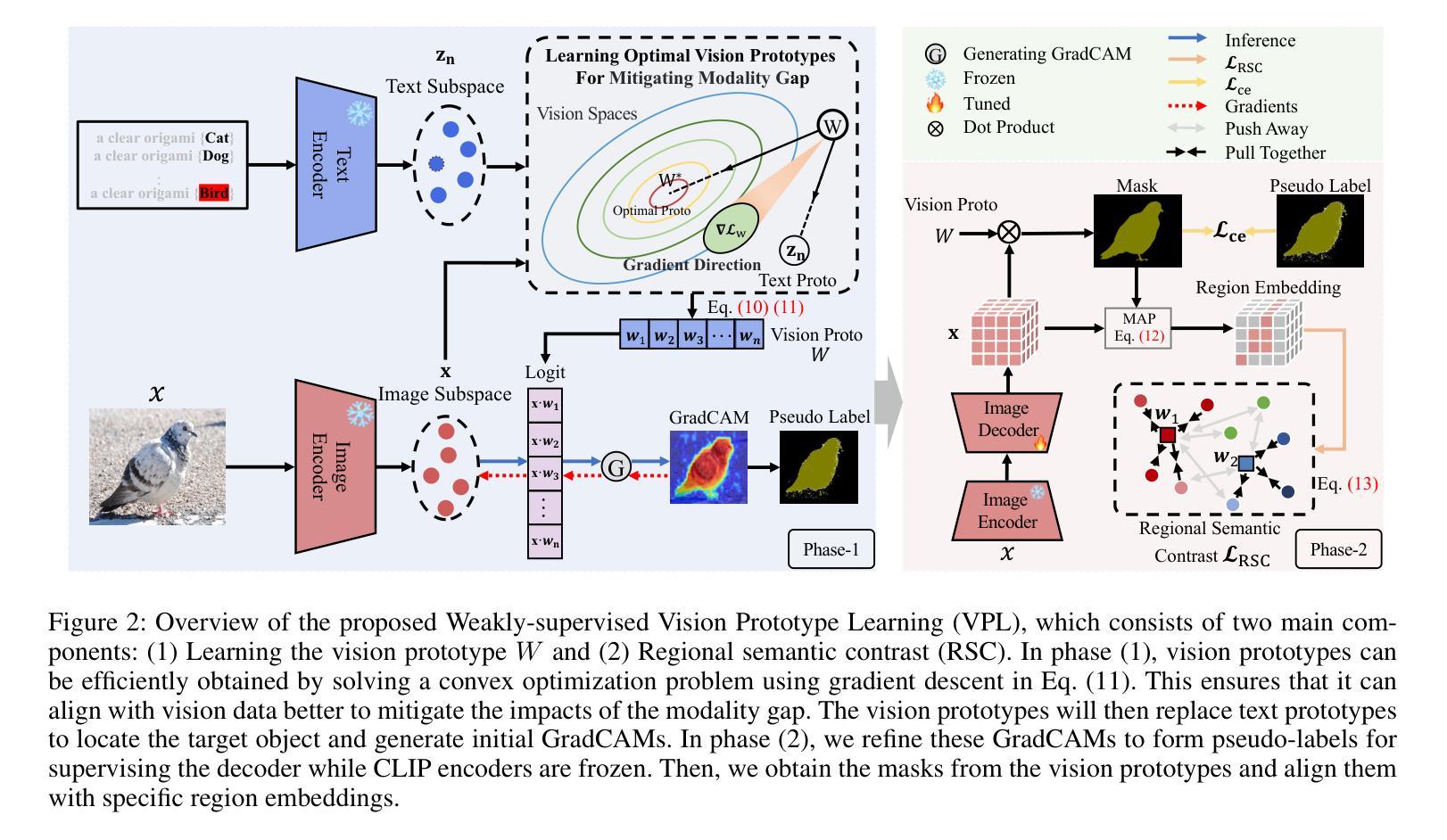
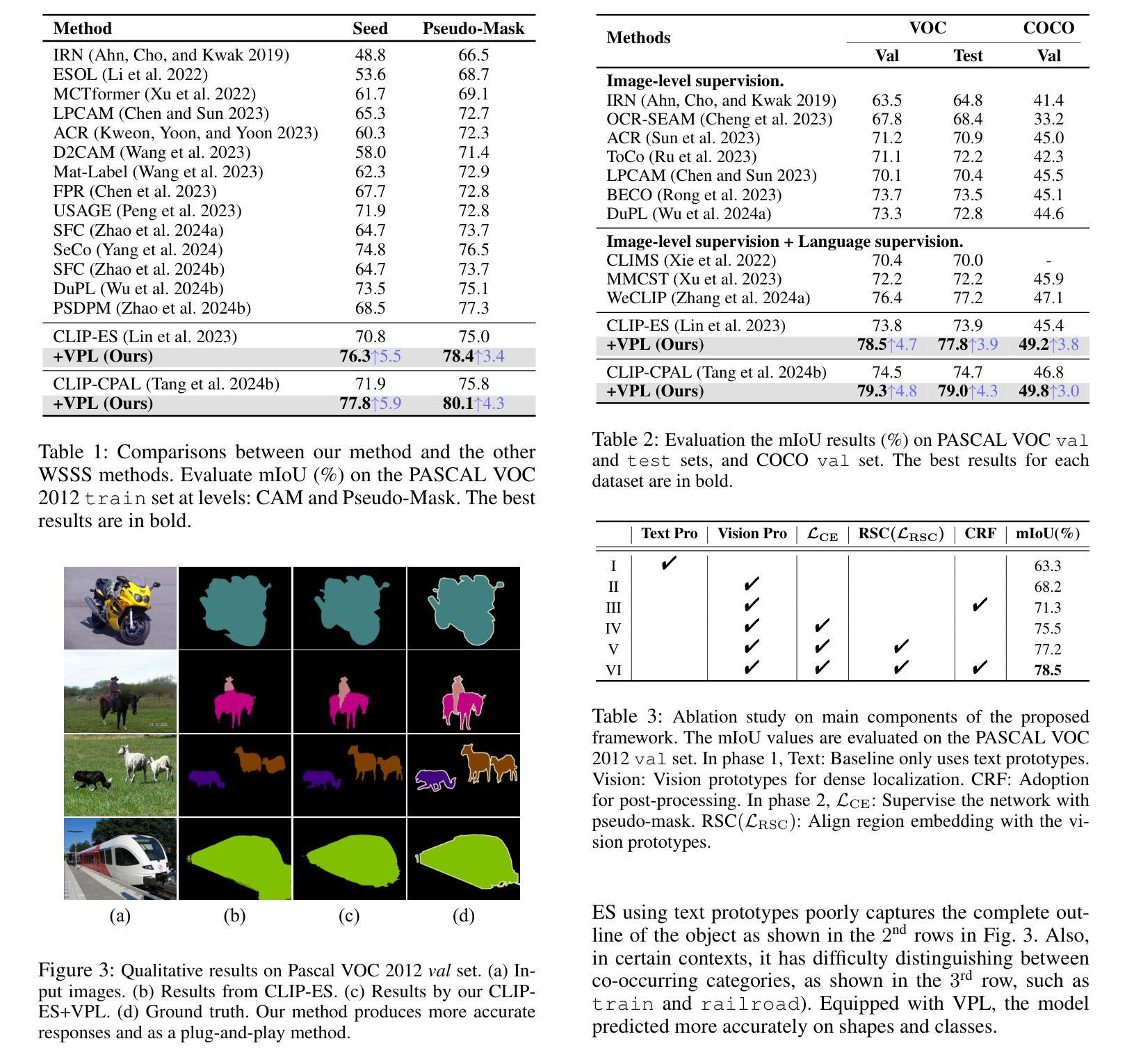
Toward Modality Gap: Vision Prototype Learning for Weakly-supervised Semantic Segmentation with CLIP
Authors:Zhongxing Xu, Feilong Tang, Zhe Chen, Yingxue Su, Zhiyi Zhao, Ge Zhang, Jionglong Su, Zongyuan Ge
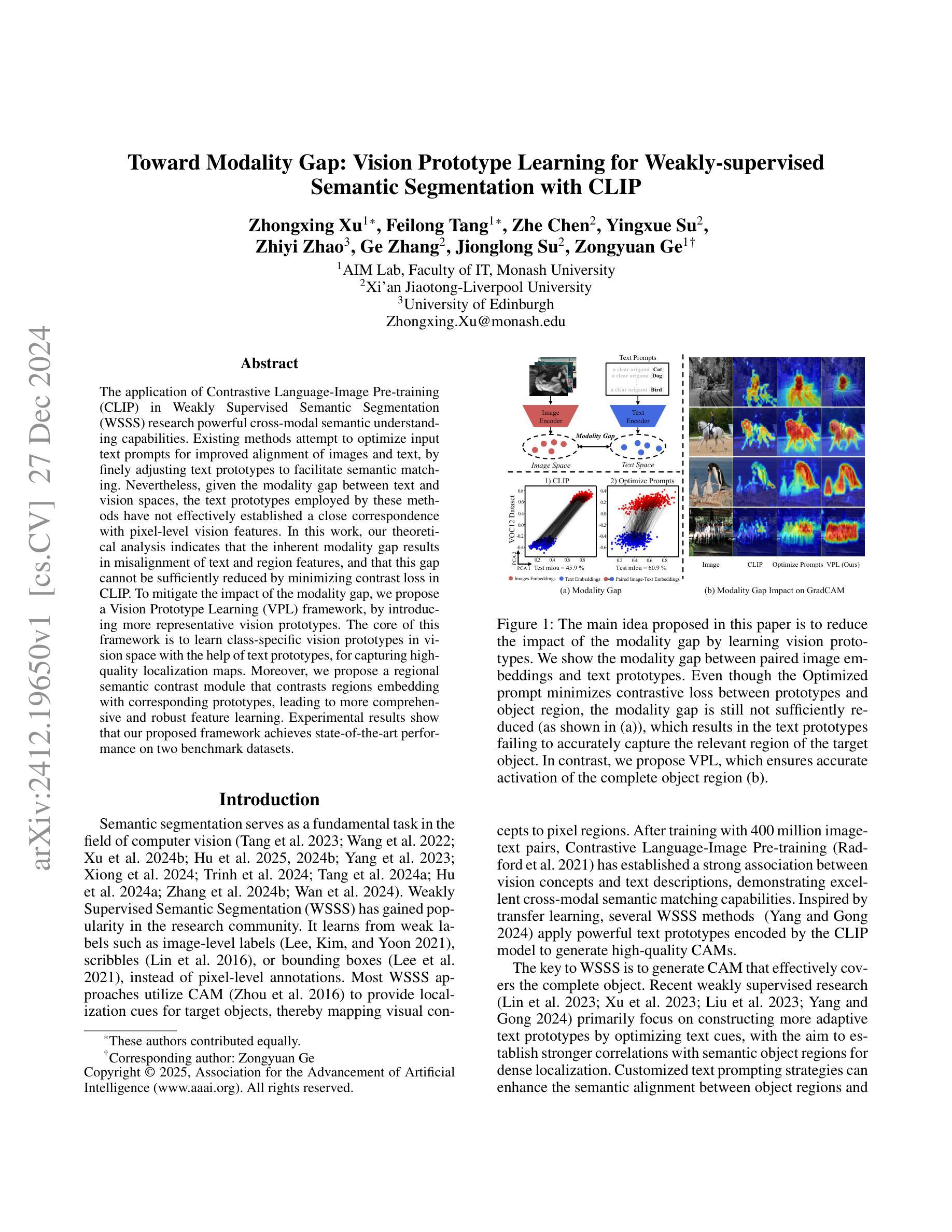
The application of Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) in Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation (WSSS) research powerful cross-modal semantic understanding capabilities. Existing methods attempt to optimize input text prompts for improved alignment of images and text, by finely adjusting text prototypes to facilitate semantic matching. Nevertheless, given the modality gap between text and vision spaces, the text prototypes employed by these methods have not effectively established a close correspondence with pixel-level vision features. In this work, our theoretical analysis indicates that the inherent modality gap results in misalignment of text and region features, and that this gap cannot be sufficiently reduced by minimizing contrast loss in CLIP. To mitigate the impact of the modality gap, we propose a Vision Prototype Learning (VPL) framework, by introducing more representative vision prototypes. The core of this framework is to learn class-specific vision prototypes in vision space with the help of text prototypes, for capturing high-quality localization maps. Moreover, we propose a regional semantic contrast module that contrasts regions embedding with corresponding prototypes, leading to more comprehensive and robust feature learning. Experimental results show that our proposed framework achieves state-of-the-art performance on two benchmark datasets.
在弱监督语义分割(WSSS)研究中,应用对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)具有强大的跨模态语义理解能力。现有方法试图通过微调文本提示来优化图像和文本的对齐方式,通过精细调整文本原型来促进语义匹配。然而,鉴于文本和视觉空间之间的模态差距,这些方法所采用的文本原型并未有效地与像素级视觉特征建立紧密对应关系。在我们的理论分析中,指出固有的模态差距会导致文本和区域特征的错位,并且仅仅通过减小CLIP中的对比损失不足以充分缩小这一差距。为了缓解模态差距的影响,我们提出了视觉原型学习(VPL)框架,通过引入更具代表性的视觉原型。该框架的核心是在视觉空间的帮助下,学习特定类别的视觉原型,以捕获高质量的定位图。此外,我们提出了区域语义对比模块,该模块将区域嵌入与相应的原型进行对比,从而实现更全面和稳健的特征学习。实验结果表明,我们提出的框架在两个基准数据集上达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training(CLIP)在Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation(WSSS)研究中的应用。文章指出当前方法通过优化文本提示来改进图像和文本的匹配度,但文本原型并未有效地与像素级视觉特征建立紧密对应关系。本文分析了文本和视觉空间之间的固有模态差距导致的文本和区域特征不匹配问题,并提出通过引入更具代表性的视觉原型来解决这一问题。同时,本文提出了Vision Prototype Learning(VPL)框架和区域语义对比模块,实现了高质量定位图的捕获和更全面、稳健的特征学习。实验结果表明,该框架在两个基准数据集上取得了最新性能。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP在WSSS研究中的应用展现了其强大的跨模态语义理解能力。
- 当前方法通过微调文本原型来优化图像和文本的匹配度,但仍存在模态差距问题。
- 模态差距导致文本和区域特征的不匹配,仅通过减小CLIP中的对比损失无法充分减少这种差距。
- 提出了Vision Prototype Learning(VPL)框架,通过引入更具代表性的视觉原型来解决模态差距问题。
- VPL框架的核心是在视觉空间的帮助下学习特定类别的视觉原型,以捕获高质量定位图。
- 提出了区域语义对比模块,通过区域嵌入与相应原型的对比,实现更全面和稳健的特征学习。
点此查看论文截图
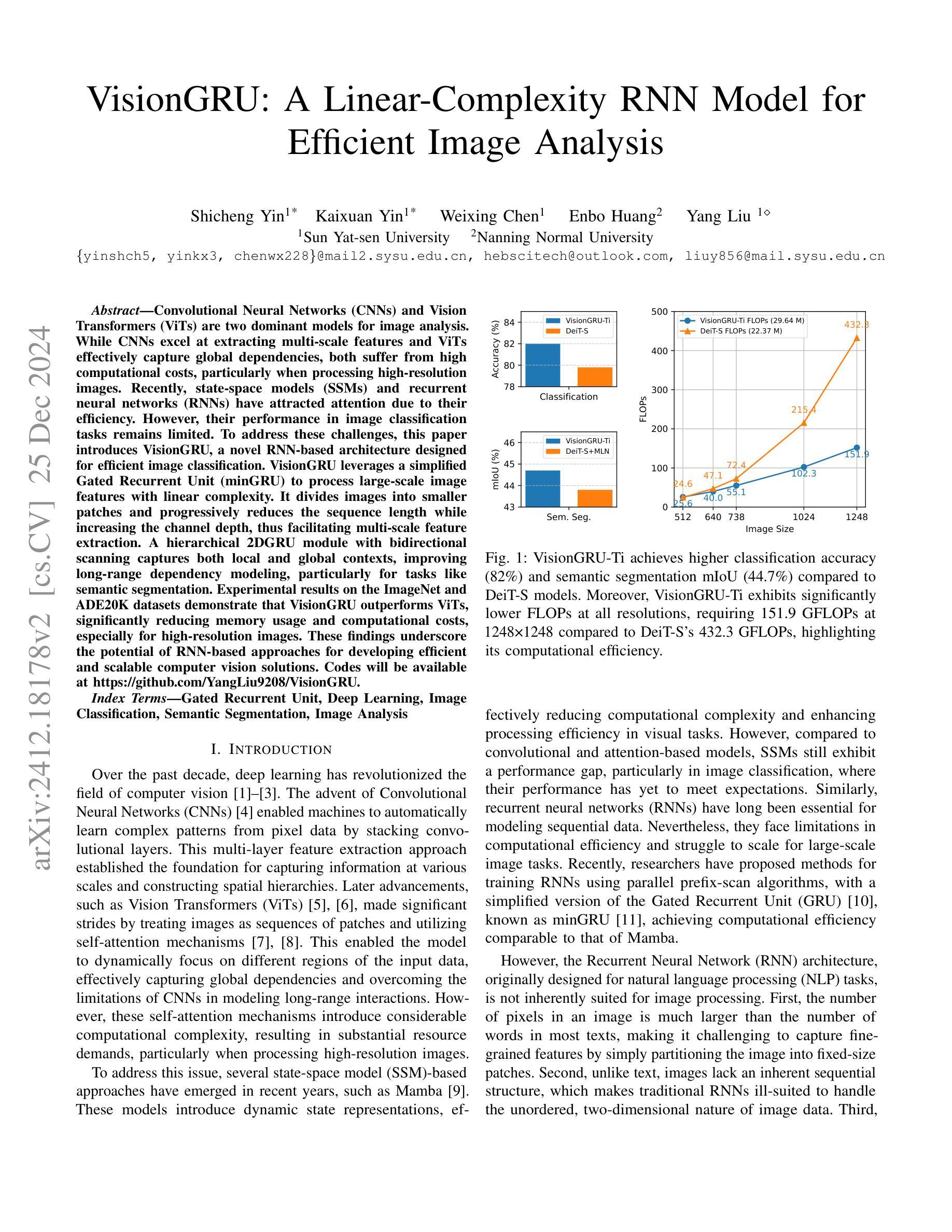
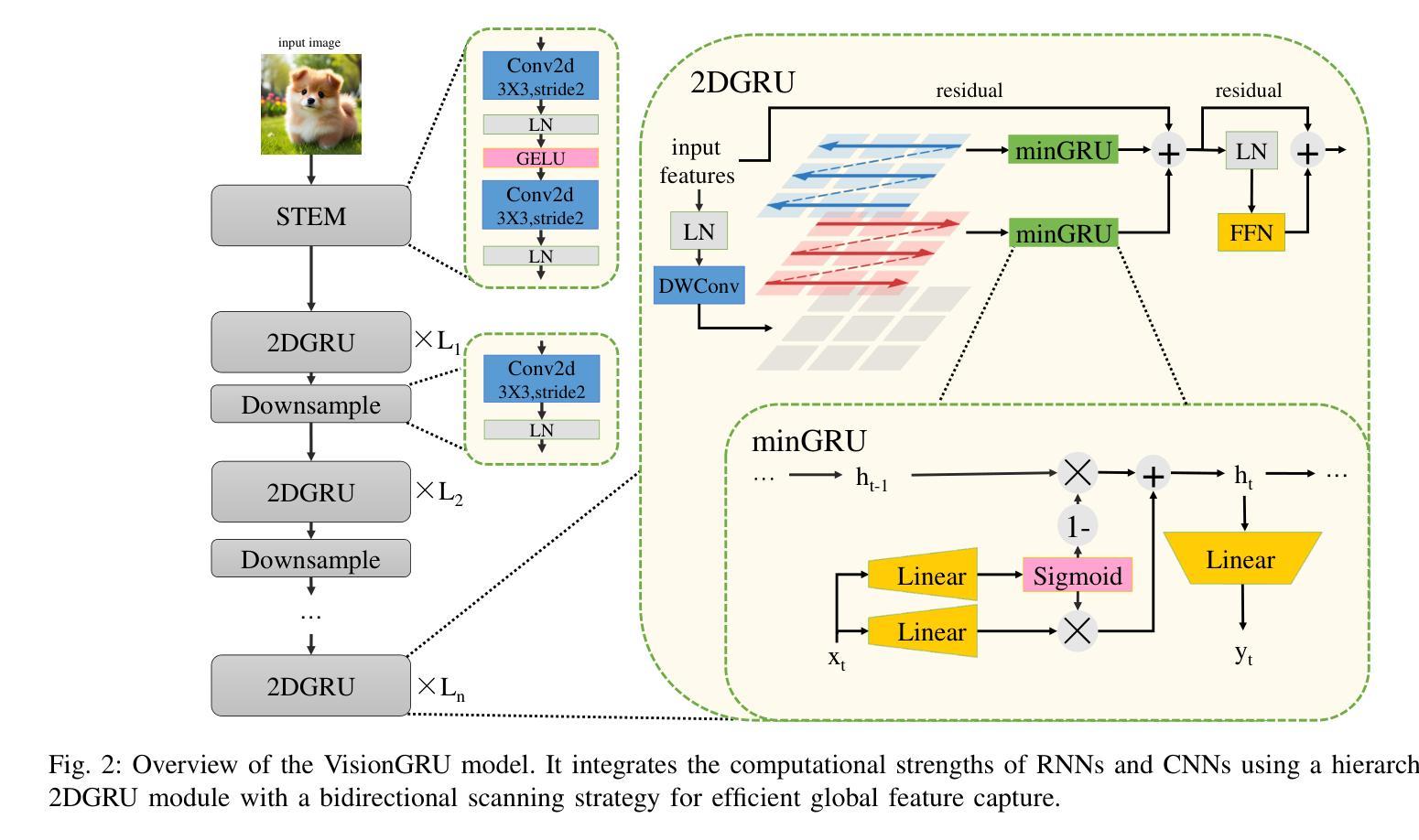
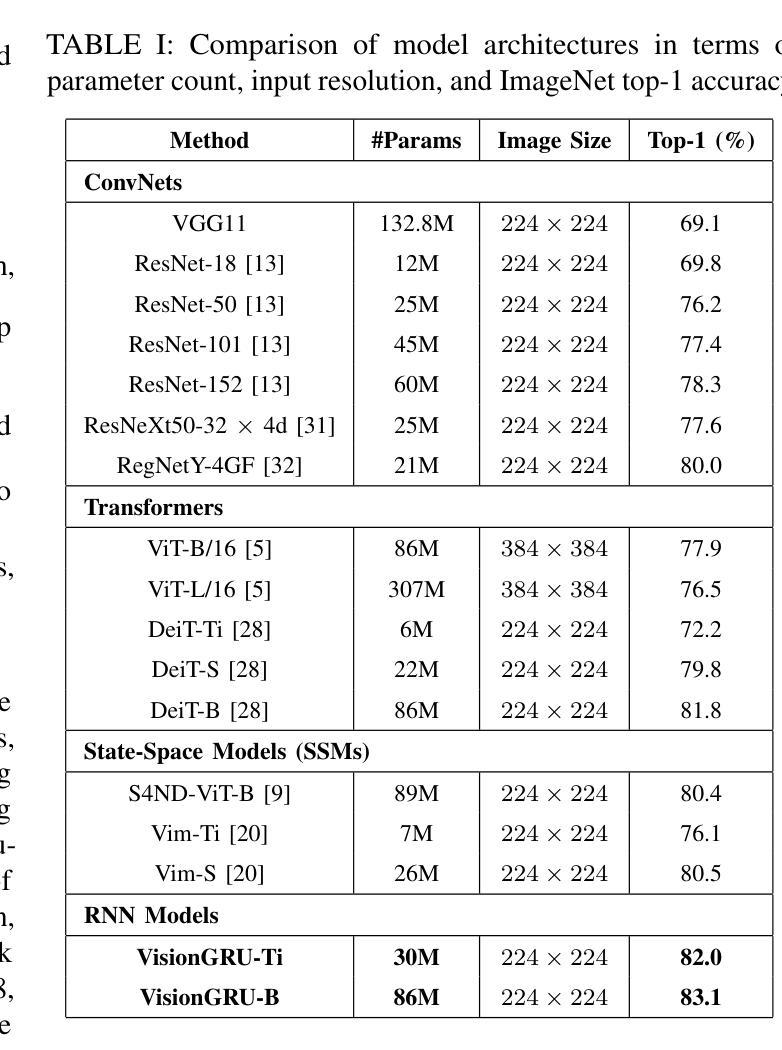
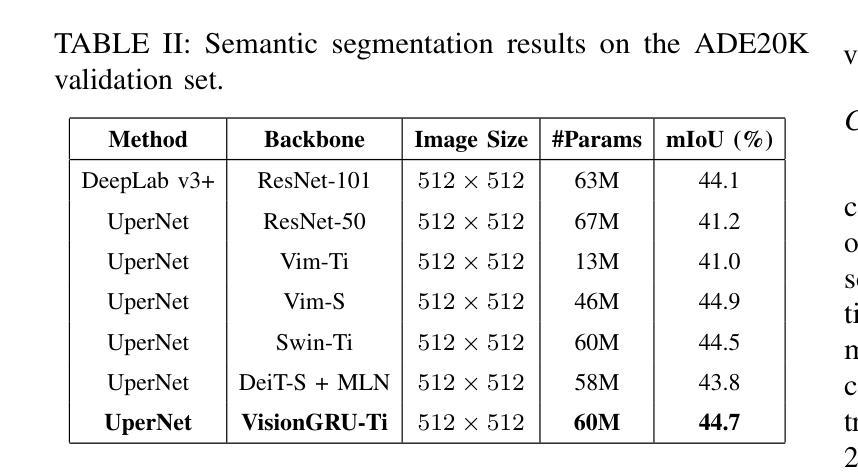
VisionGRU: A Linear-Complexity RNN Model for Efficient Image Analysis
Authors:Shicheng Yin, Kaixuan Yin, Weixing Chen, Enbo Huang, Yang Liu
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Vision Transformers (ViTs) are two dominant models for image analysis. While CNNs excel at extracting multi-scale features and ViTs effectively capture global dependencies, both suffer from high computational costs, particularly when processing high-resolution images. Recently, state-space models (SSMs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) have attracted attention due to their efficiency. However, their performance in image classification tasks remains limited. To address these challenges, this paper introduces VisionGRU, a novel RNN-based architecture designed for efficient image classification. VisionGRU leverages a simplified Gated Recurrent Unit (minGRU) to process large-scale image features with linear complexity. It divides images into smaller patches and progressively reduces the sequence length while increasing the channel depth, thus facilitating multi-scale feature extraction. A hierarchical 2DGRU module with bidirectional scanning captures both local and global contexts, improving long-range dependency modeling, particularly for tasks like semantic segmentation. Experimental results on the ImageNet and ADE20K datasets demonstrate that VisionGRU outperforms ViTs, significantly reducing memory usage and computational costs, especially for high-resolution images. These findings underscore the potential of RNN-based approaches for developing efficient and scalable computer vision solutions. Codes will be available at https://github.com/YangLiu9208/VisionGRU.
卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT)是图像分析的两种主导模型。虽然CNN擅长提取多尺度特征,而ViT能有效地捕捉全局依赖性,但两者都存在着较高的计算成本,特别是在处理高分辨率图像时。最近,由于状态空间模型(SSM)和循环神经网络(RNN)的效率,它们受到了人们的关注。然而,它们在图像分类任务中的表现仍然有限。为了解决这些挑战,本文提出了一种用于高效图像分类的新型RNN架构——VisionGRU。VisionGRU利用简化的门控循环单元(minGRU)以线性复杂度处理大规模图像特征。它将图像分成较小的斑块,逐步减少序列长度,同时增加通道深度,从而便于多尺度特征提取。具有双向扫描的分层2DGRU模块可以捕获局部和全局上下文,改进了长距离依赖建模,特别是对于语义分割等任务。在ImageNet和ADE20K数据集上的实验结果表明,VisionGRU优于ViT,大大降低了内存使用和计算成本,特别是在处理高分辨率图像时。这些发现强调了基于RNN的方法在开发高效且可扩展的计算机视觉解决方案方面的潜力。代码将在https://github.com/YangLiu9208/VisionGRU上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Codes will be available at https://github.com/YangLiu9208/VisionGRU
Summary
本文提出一种基于RNN的新型图像分类架构VisionGRU,利用简化的门控循环单元(minGRU)以线性复杂度处理大规模图像特征。VisionGRU通过分割图像成小块并渐进减少序列长度同时增加通道深度,实现多尺度特征提取。其层次化的2DGRU模块结合双向扫描,捕捉局部和全局上下文,改进了长距离依赖建模,特别是在语义分割等任务上表现优秀。在ImageNet和ADE20K数据集上的实验结果表明,VisionGRU优于ViTs,大幅降低了内存使用和计算成本,尤其适用于高分辨率图像。
Key Takeaways
- VisionGRU是一种新型的RNN架构,用于图像分类,结合了CNN和ViT的优点。
- VisionGRU使用简化的门控循环单元(minGRU)处理大规模图像特征,具有线性复杂度。
- VisionGRU通过分割图像成小块实现多尺度特征提取,渐进减少序列长度同时增加通道深度。
- 层次化的2DGRU模块结合双向扫描,能有效捕捉局部和全局上下文,改进长距离依赖建模。
- VisionGRU在语义分割等任务上表现优秀,实验结果表明其性能优于ViTs。
- VisionGRU降低了内存使用和计算成本,尤其适用于处理高分辨率图像。
点此查看论文截图

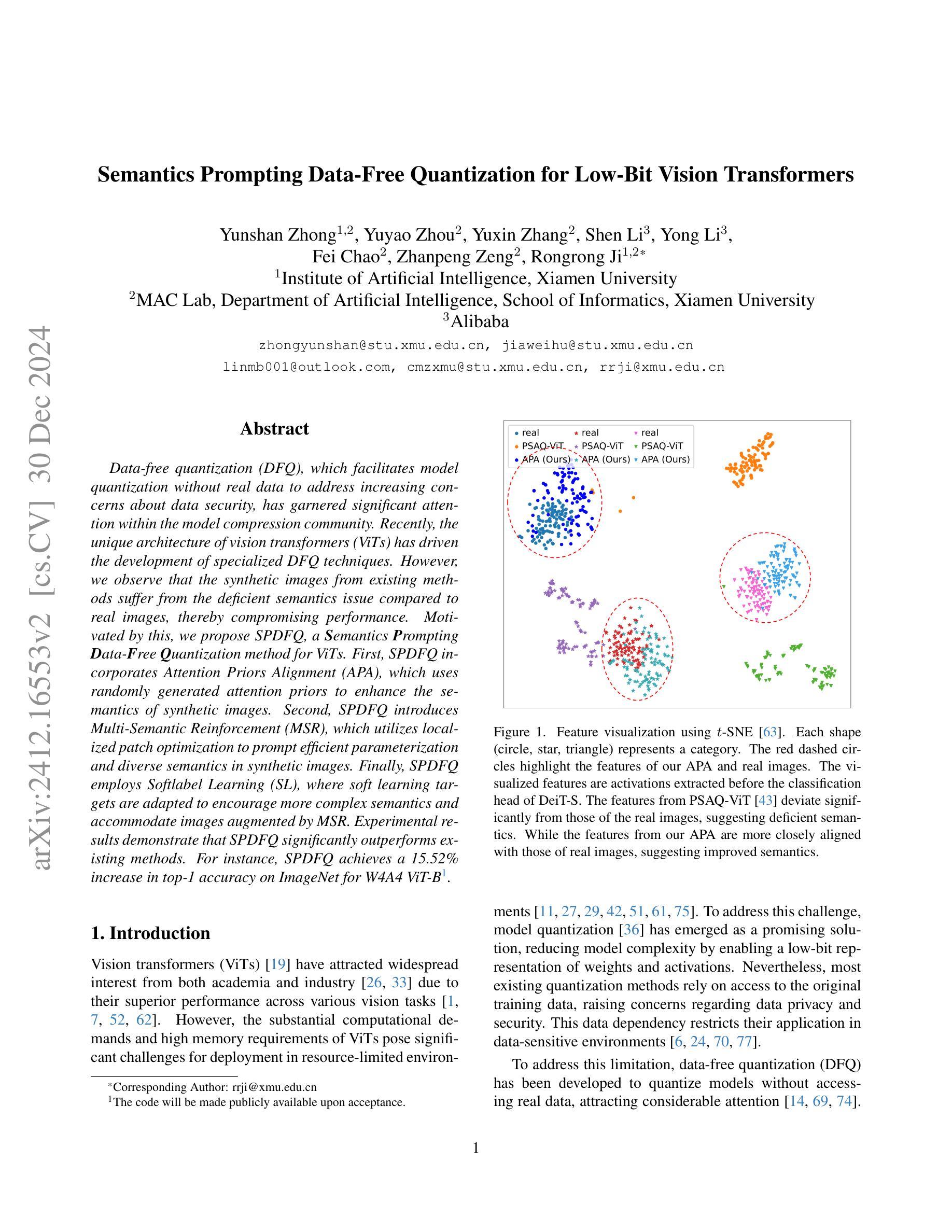
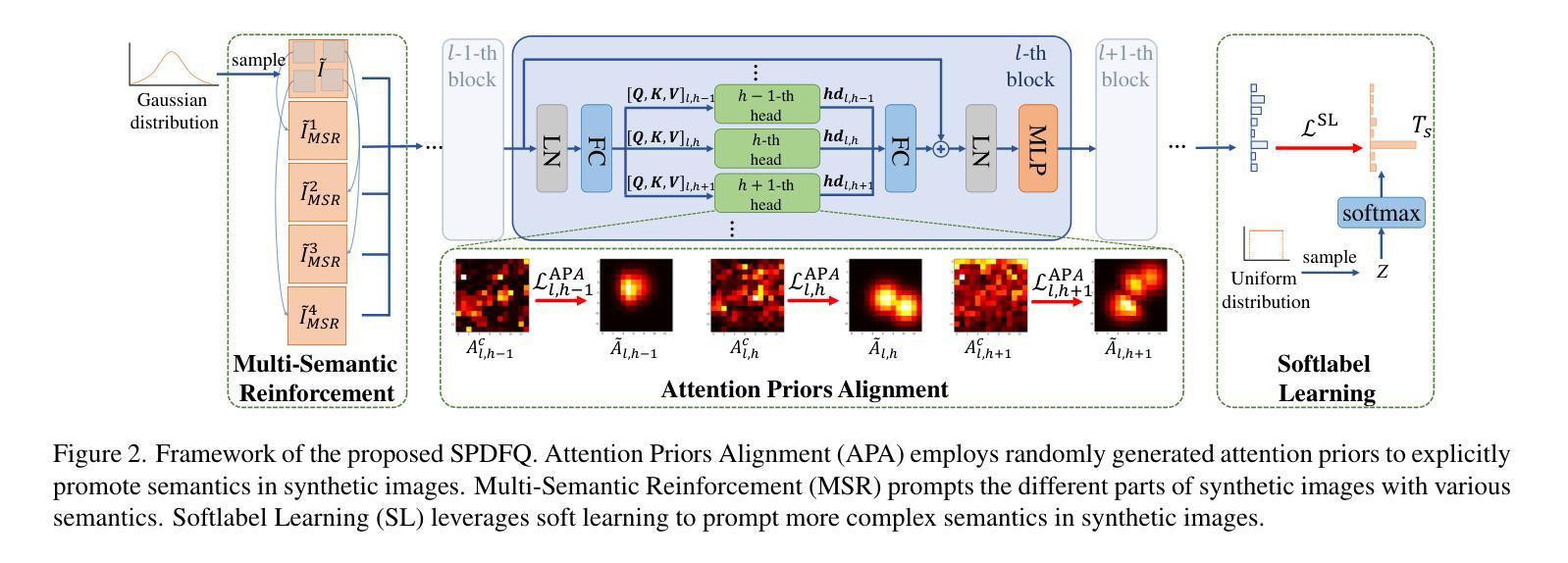
Semantics Prompting Data-Free Quantization for Low-Bit Vision Transformers
Authors:Yunshan Zhong, Yuyao Zhou, Yuxin Zhang, Shen Li, Yong Li, Fei Chao, Zhanpeng Zeng, Rongrong Ji
Data-free quantization (DFQ), which facilitates model quantization without real data to address increasing concerns about data security, has garnered significant attention within the model compression community. Recently, the unique architecture of vision transformers (ViTs) has driven the development of specialized DFQ techniques. However, we observe that the synthetic images from existing methods suffer from the deficient semantics issue compared to real images, thereby compromising performance. Motivated by this, we propose SPDFQ, a Semantics Prompting Data-Free Quantization method for ViTs. First, SPDFQ incorporates Attention Priors Alignment (APA), which uses randomly generated attention priors to enhance the semantics of synthetic images. Second, SPDFQ introduces Multi-Semantic Reinforcement (MSR), which utilizes localized patch optimization to prompt efficient parameterization and diverse semantics in synthetic images. Finally, SPDFQ employs Softlabel Learning (SL), where soft learning targets are adapted to encourage more complex semantics and accommodate images augmented by MSR. Experimental results demonstrate that SPDFQ significantly outperforms existing methods. For instance, SPDFQ achieves a 15.52% increase in top-1 accuracy on ImageNet for W4A4 ViT-B
无数据量化(DFQ)技术因其能够在无需真实数据的情况下实现模型量化,缓解了数据安全方面的担忧,在模型压缩领域引起了广泛关注。最近,视觉变压器(ViT)的独特架构推动了专门的DFQ技术的发展。然而,我们观察到现有方法生成的合成图像与真实图像相比存在语义缺陷问题,从而影响了性能。受此启发,我们提出了针对ViT的语义提示无数据量化方法SPDFQ。首先,SPDFQ结合了注意力先验对齐(APA),使用随机生成的注意力先验来增强合成图像的语义。其次,SPDFQ引入了多语义增强(MSR),利用局部斑块优化来提示合成图像中的高效参数化和多样语义。最后,SPDFQ采用软标签学习(SL),其中软学习目标是适应和鼓励更复杂的语义,并适应由MSR增强的图像。实验结果表明,SPDFQ显著优于现有方法。例如,在ImageNet上,SPDFQ在W4A4 ViT-B的top-1准确率上提高了15.52%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
数据无关的量化方法(DFQ)在模型压缩领域受到广泛关注,解决了对数据安全性的担忧。针对现有方法生成的合成图像语义不足的问题,本文提出了一种针对视觉变压器(ViTs)的语义提示数据无关量化方法(SPDFQ)。SPDFQ包括注意力先验对齐(APA)、多语义增强(MSR)和软标签学习(SL),以提高合成图像的语义性能。实验结果表明,SPDFQ显著优于现有方法,在ImageNet上的top-1准确率提高了15.52%。
Key Takeaways
- 数据无关的量化(DFQ)方法无需真实数据即可实现模型量化,解决数据安全性问题。
- 现有DFQ方法生成的合成图像存在语义不足的问题。
- 针对视觉变压器(ViTs)的SPDFQ方法旨在解决上述问题,包括APA、MSR和SL三大组成部分。
- APA利用随机生成的注意力先验增强合成图像的语义。
- MSR通过局部补丁优化实现高效参数化和合成图像中丰富的语义提示。
- SL采用软学习目标来鼓励更复杂的语义并适应由MSR增强的图像。
点此查看论文截图
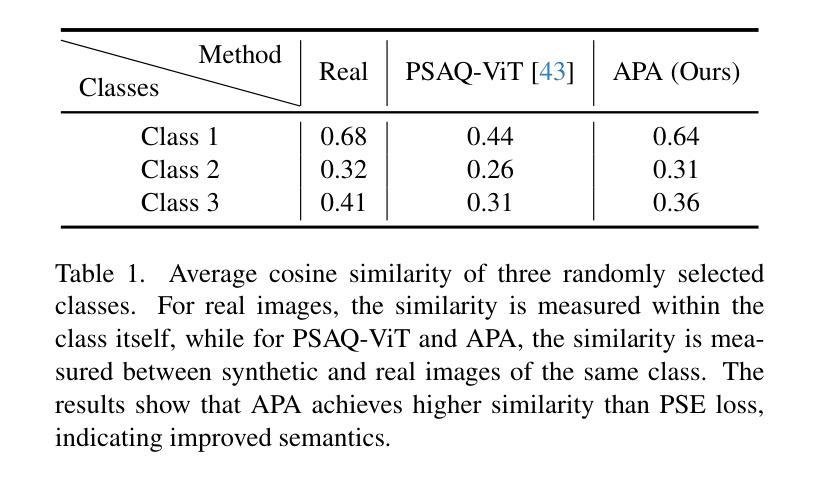
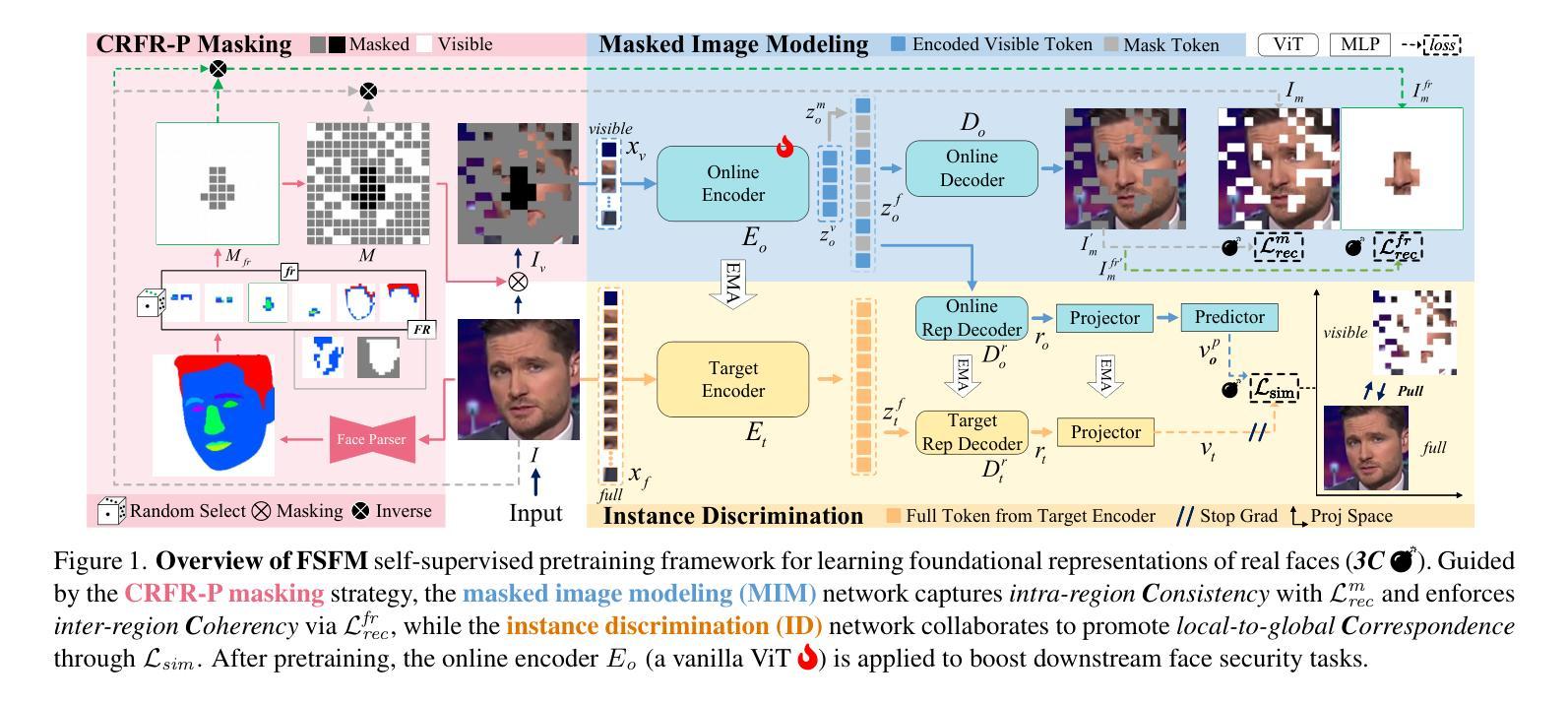
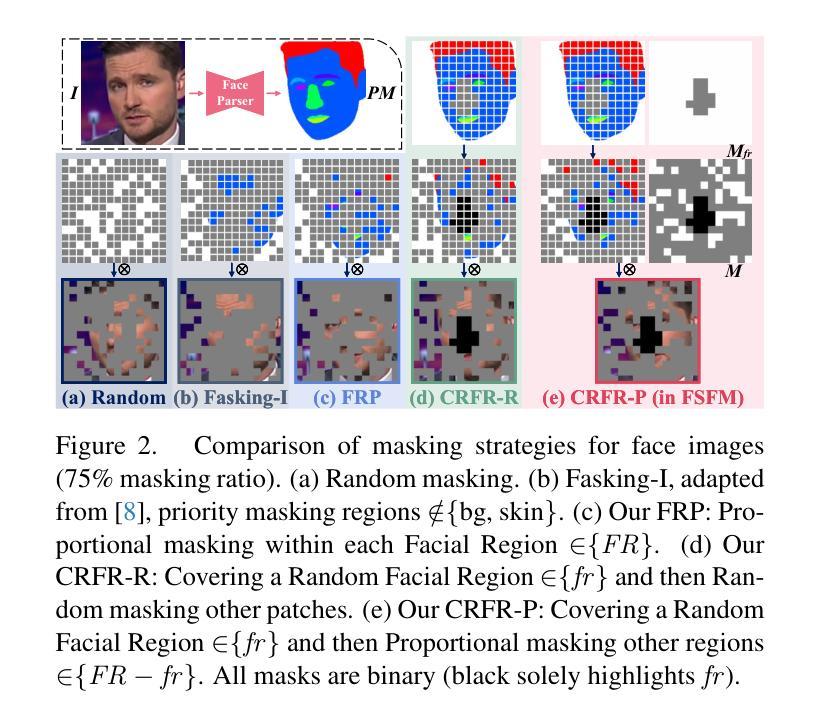
FSFM: A Generalizable Face Security Foundation Model via Self-Supervised Facial Representation Learning
Authors:Gaojian Wang, Feng Lin, Tong Wu, Zhenguang Liu, Zhongjie Ba, Kui Ren
This work asks: with abundant, unlabeled real faces, how to learn a robust and transferable facial representation that boosts various face security tasks with respect to generalization performance? We make the first attempt and propose a self-supervised pretraining framework to learn fundamental representations of real face images, FSFM, that leverages the synergy between masked image modeling (MIM) and instance discrimination (ID). We explore various facial masking strategies for MIM and present a simple yet powerful CRFR-P masking, which explicitly forces the model to capture meaningful intra-region consistency and challenging inter-region coherency. Furthermore, we devise the ID network that naturally couples with MIM to establish underlying local-to-global correspondence via tailored self-distillation. These three learning objectives, namely 3C, empower encoding both local features and global semantics of real faces. After pretraining, a vanilla ViT serves as a universal vision foundation model for downstream face security tasks: cross-dataset deepfake detection, cross-domain face anti-spoofing, and unseen diffusion facial forgery detection. Extensive experiments on 10 public datasets demonstrate that our model transfers better than supervised pretraining, visual and facial self-supervised learning arts, and even outperforms task-specialized SOTA methods.
本文提出了一个问题:在大量无标签的真实人脸情况下,如何学习一种稳健且可迁移的人脸表示,以提高各种人脸安全任务的泛化性能?我们首次尝试并提出一种自监督预训练框架,用于学习真实人脸图像的基本表示,FSFM,该框架利用掩膜图像建模(MIM)和实例判别(ID)之间的协同作用。我们探索了MIM的各种面部掩膜策略,并提出了一种简单而强大的CRFR-P掩膜,它明确地迫使模型捕捉区域内有意义的一致性以及区域间的连贯性。此外,我们还设计了一个与MIM自然结合的ID网络,通过定制的自蒸馏建立基本的局部到全局对应关系。这三个学习目标,即3C,使编码真实人脸的局部特征和全局语义成为可能。预训练后,一个普通的ViT作为通用视觉基础模型,用于下游人脸安全任务:跨数据集深度伪造检测、跨域面部防伪、未见扩散面部伪造检测。在10个公开数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的模型迁移效果优于监督预训练、视觉和面部自监督学习技术,甚至超越了任务专业化的最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 11 figures, project page: https://fsfm-3c.github.io
Summary
该工作通过自监督预训练学习真实人脸图像的基本表示,采用掩模图像建模(MIM)和实例判别(ID)的结合。提出多种面部掩模策略,其中CRFR-P掩模能促使模型捕捉区域内一致性及区域间连贯性。同时设计ID网络,与MIM结合建立局部到全局的对应关系。通过三个学习目标(3C)实现本地特征和全局语义的编码。预训练后,可作为下游人脸安全任务的通用视觉基础模型,如跨数据集深度伪造检测、跨域面部防伪和未见扩散面部伪造检测。在10个公开数据集上的实验表明,该模型的迁移效果优于监督预训练和其他面部自监督学习方法,甚至超越了任务专业化的SOTA方法。
Key Takeaways
- 该工作提出了一个自监督预训练框架来学习真实人脸图像的基本表示。
- 结合了掩模图像建模(MIM)和实例判别(ID)以增强模型的表示能力。
- 引入了一种新的面部掩模策略——CRFR-P,强调区域内和区域间的连贯性。
- 设计了与MIM结合的ID网络,建立局部到全局的对应关系。
- 通过三个学习目标实现本地特征和全局语义的编码,提高模型的通用性和迁移能力。
- 实验证明,该预训练模型在多种人脸安全任务上表现出优越性能,包括跨数据集深度伪造检测、面部防伪等。
点此查看论文截图


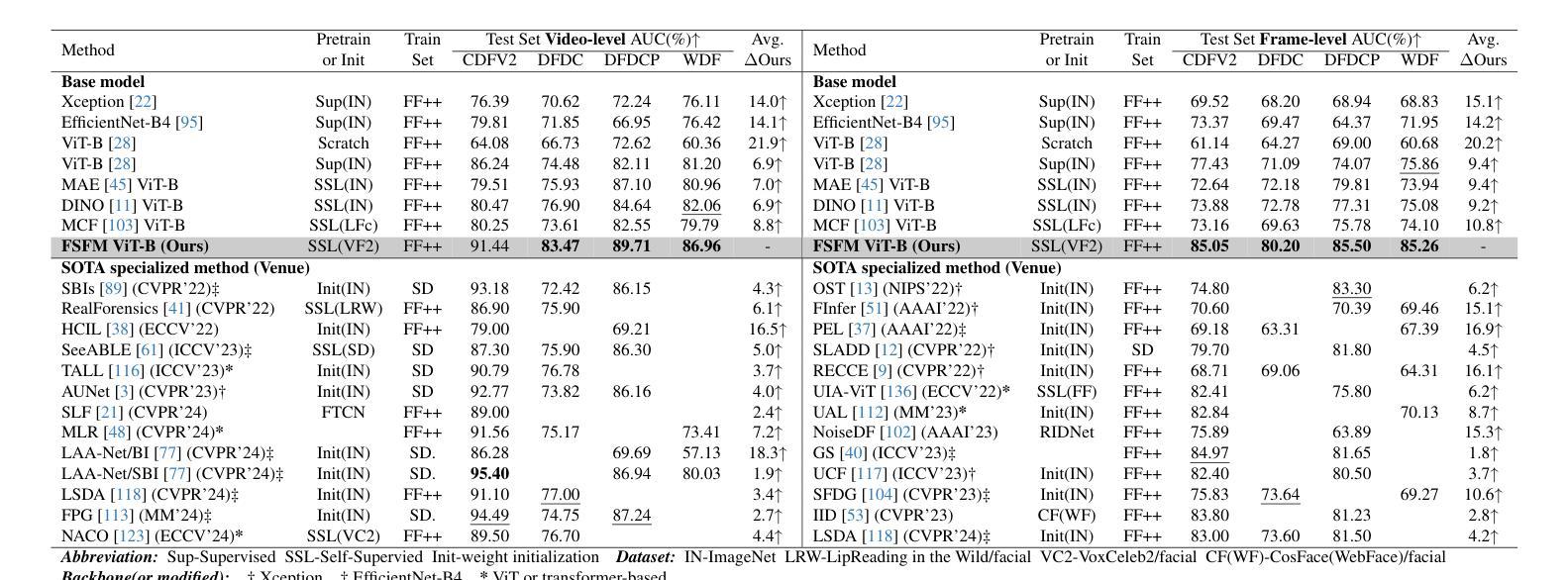
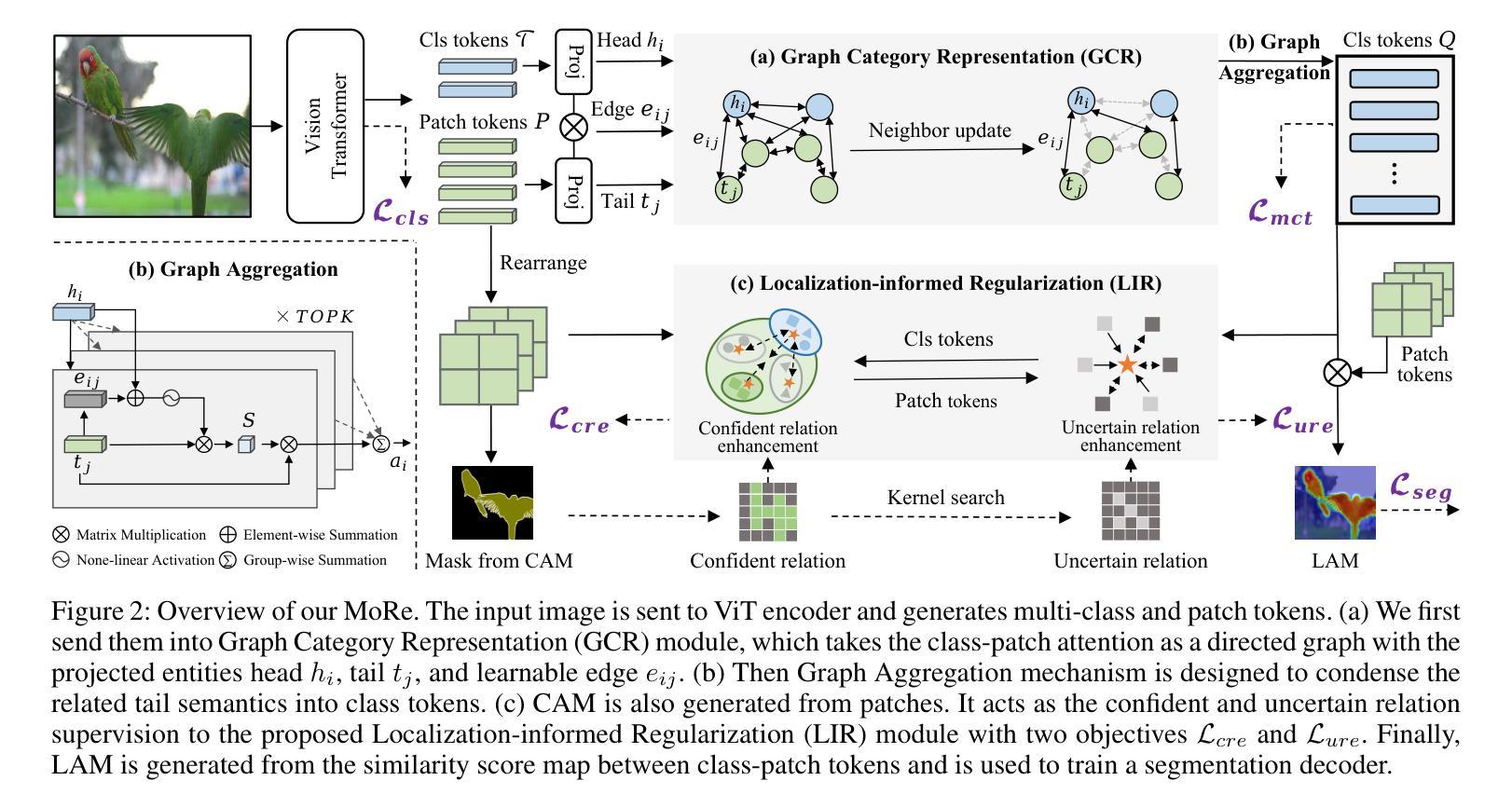
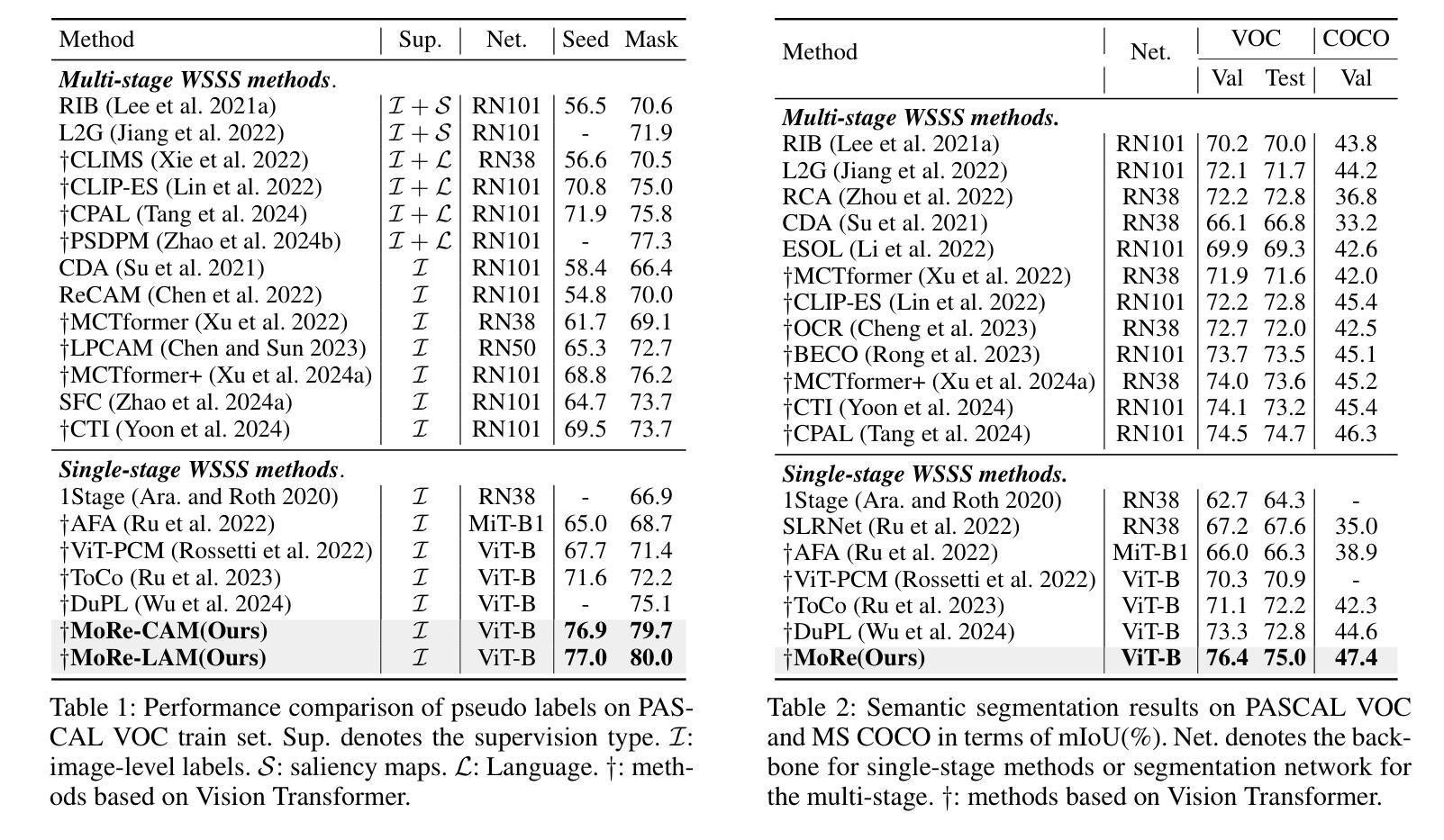
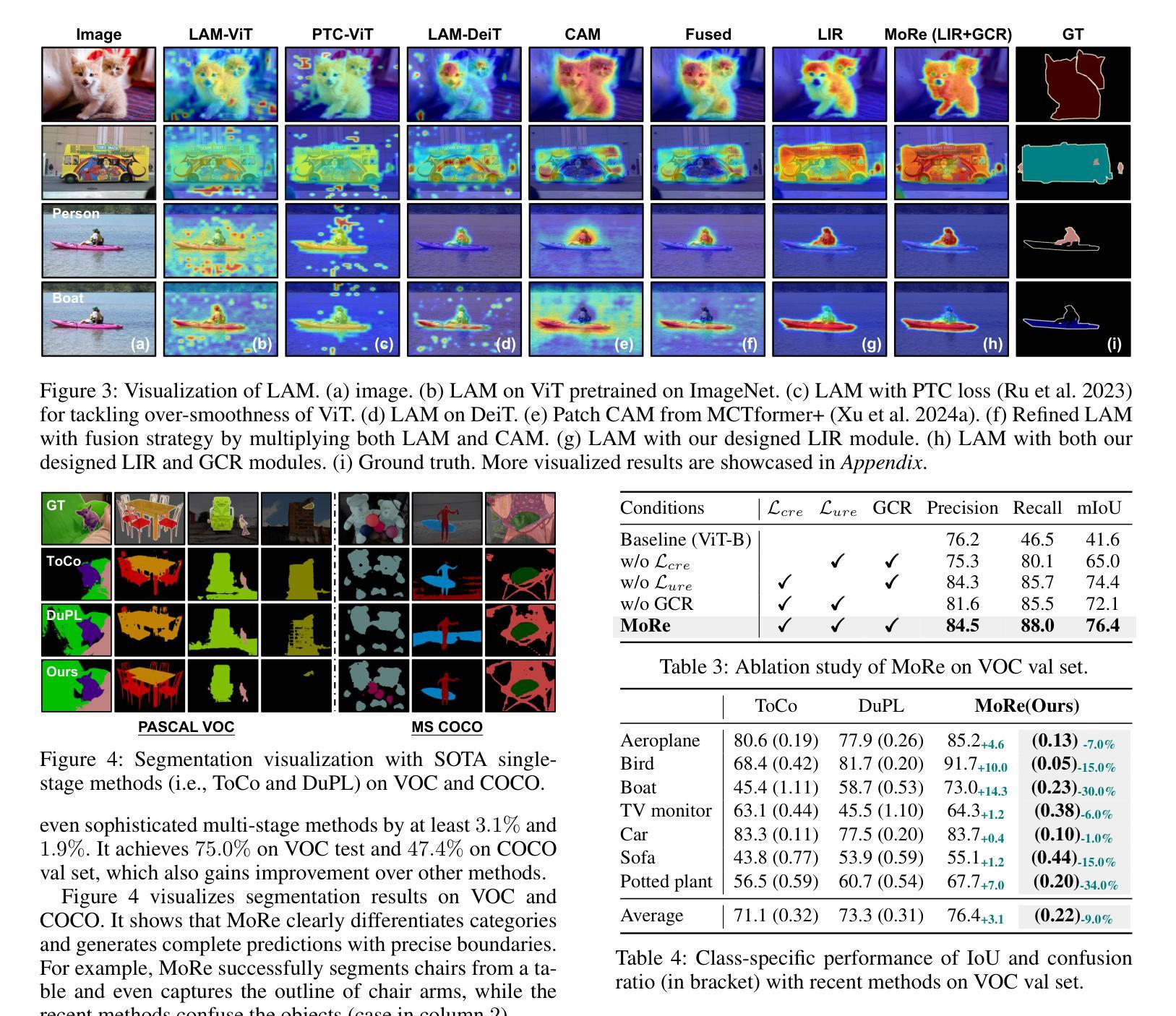
MoRe: Class Patch Attention Needs Regularization for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Zhiwei Yang, Yucong Meng, Kexue Fu, Shuo Wang, Zhijian Song
Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation (WSSS) with image-level labels typically uses Class Activation Maps (CAM) to achieve dense predictions. Recently, Vision Transformer (ViT) has provided an alternative to generate localization maps from class-patch attention. However, due to insufficient constraints on modeling such attention, we observe that the Localization Attention Maps (LAM) often struggle with the artifact issue, i.e., patch regions with minimal semantic relevance are falsely activated by class tokens. In this work, we propose MoRe to address this issue and further explore the potential of LAM. Our findings suggest that imposing additional regularization on class-patch attention is necessary. To this end, we first view the attention as a novel directed graph and propose the Graph Category Representation module to implicitly regularize the interaction among class-patch entities. It ensures that class tokens dynamically condense the related patch information and suppress unrelated artifacts at a graph level. Second, motivated by the observation that CAM from classification weights maintains smooth localization of objects, we devise the Localization-informed Regularization module to explicitly regularize the class-patch attention. It directly mines the token relations from CAM and further supervises the consistency between class and patch tokens in a learnable manner. Extensive experiments are conducted on PASCAL VOC and MS COCO, validating that MoRe effectively addresses the artifact issue and achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing recent single-stage and even multi-stage methods. Code is available at https://github.com/zwyang6/MoRe.
弱监督语义分割(WSSS)通常使用图像级别的标签和类别激活图(CAM)来实现密集预测。最近,视觉转换器(ViT)提供了一种生成定位图(Localization Attention Maps,LAM)的替代方案,该方案通过类别补丁注意力生成定位图。然而,由于对这类注意力的建模约束不足,我们观察到定位注意力图(LAM)经常面临伪影问题,即语义相关性极小的补丁区域会被类别标记错误激活。在这项工作中,我们提出MoRe来解决这个问题,并进一步研究LAM的潜力。我们的研究结果表明,对类别补丁注意力施加额外的正则化是必要的。为此,我们首先将注意力视为一种新型的有向图,并提出图类别表示模块来隐含地正则化类别补丁实体之间的交互。它确保类别标记动态地凝聚相关补丁信息,并在图形级别抑制不相关的伪影。其次,受分类权重CAM能维持对象定位平滑的启发,我们设计了定位信息正则化模块来显式地正则化类别补丁注意力。它从CAM中提取标记关系,并以可学习的方式监督类别标记和补丁标记之间的一致性。在PASCAL VOC和MS COCO上进行了大量实验,验证了MoRe有效地解决了伪影问题,达到了最先进的性能水平,超越了最新的单阶段甚至多阶段方法。代码可在https://github.com/zwyang6/MoRe上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI 2025
Summary
本文探讨了使用图像级标签进行弱监督语义分割(WSSS)的问题。虽然Vision Transformer(ViT)可以通过类补丁注意力生成定位注意力图(LAM),但由于缺乏对这类注意力的充分约束,LAM容易出现伪激活现象,即无关补丁区域被类标记错误激活。为解决这一问题,本文提出了MoRe方法,并探索了LAM的潜力。研究发现,对类补丁注意力施加额外的正则化是必要的。为此,本文首先关注注意力作为一种新型有向图,并提出图类别表示模块来隐含地规范类补丁实体间的交互。同时,受分类权重CAM保持对象定位平滑的启发,本文设计了定位信息正则化模块来显式地规范类补丁注意力。实验证明,MoRe有效地解决了伪激活问题,实现了PASCAL VOC和MS COCO数据集上的最新性能,超越了近期单阶段甚至多阶段方法。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformer (ViT) 可通过类补丁注意力生成定位注意力图(LAM)。
- LAM存在伪激活问题,即无关补丁区域被类标记错误激活。
- 对类补丁注意力施加额外的正则化是解决LAM伪激活问题的关键。
- 提出了图类别表示模块,隐含地规范类补丁实体间的交互。
- 设计了定位信息正则化模块,显式地规范类补丁注意力,利用分类权重CAM的平滑定位特性。
- MoRe方法在PASCAL VOC和MS COCO数据集上实现了最新性能。
点此查看论文截图

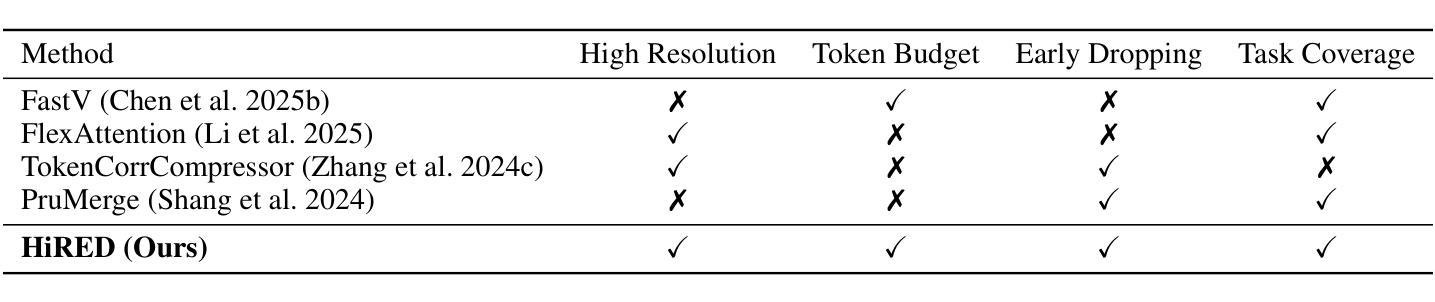
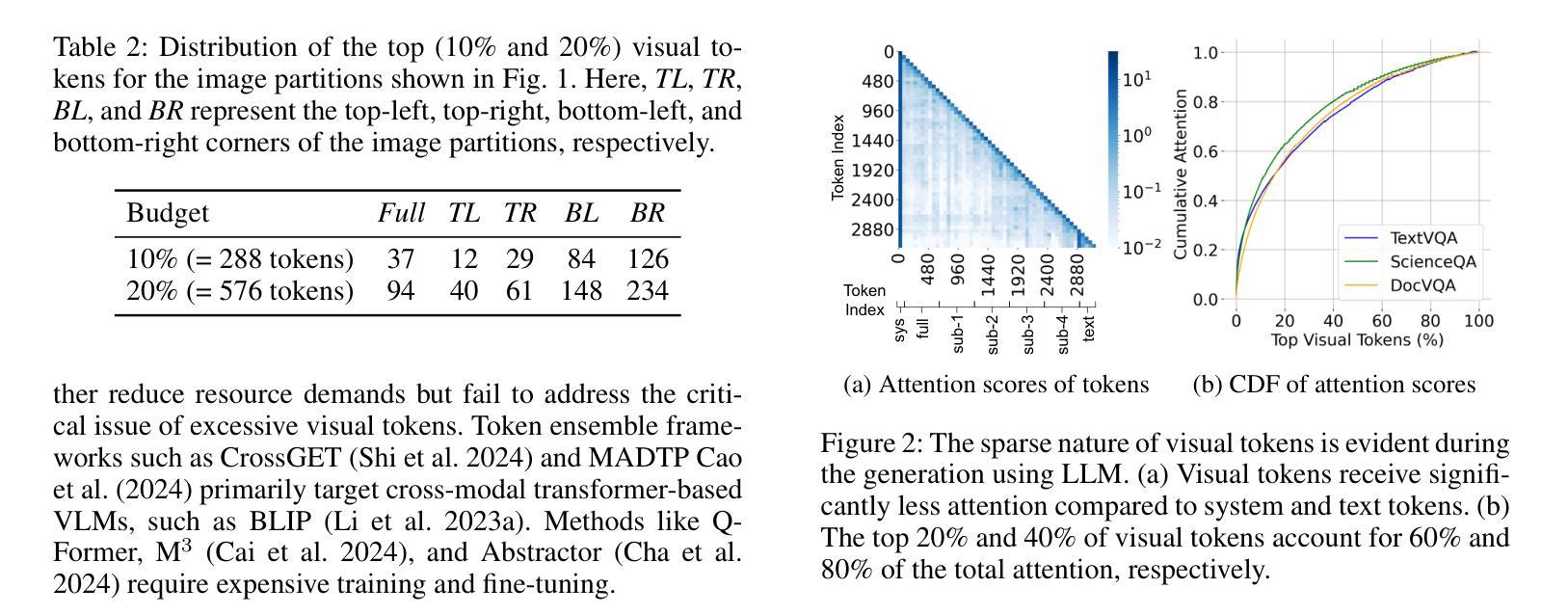
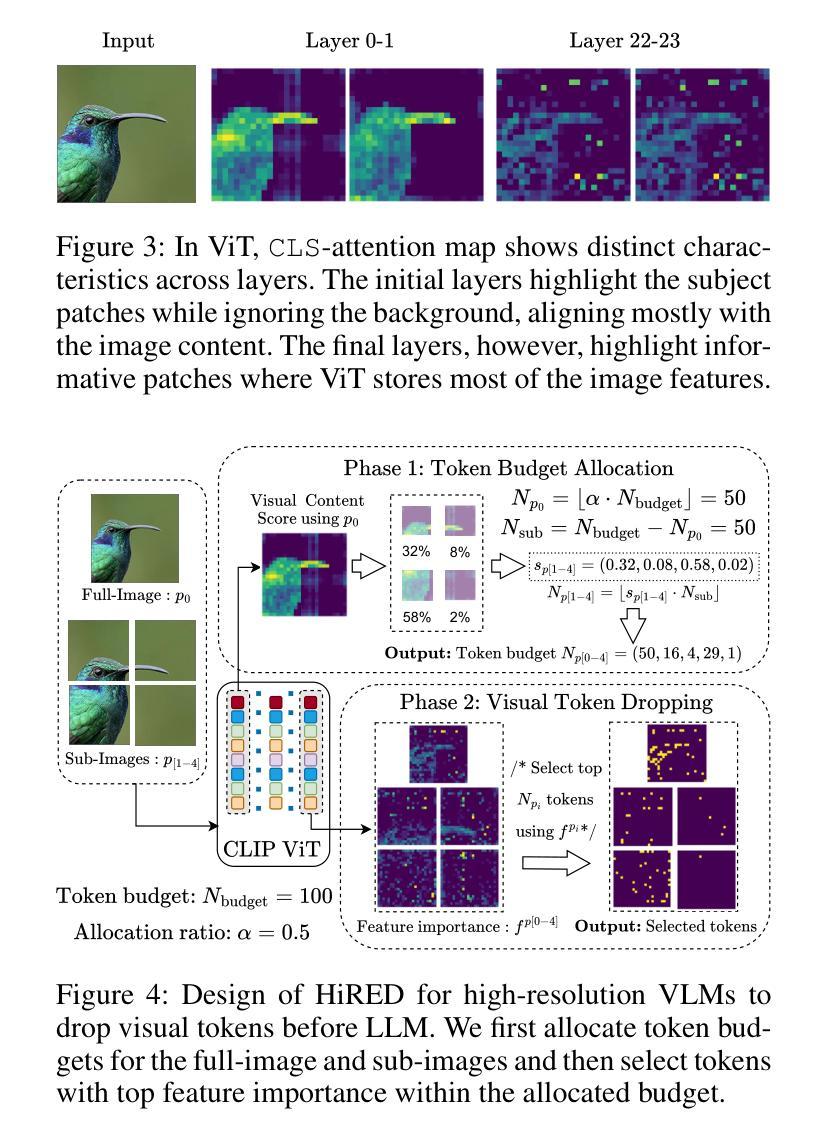
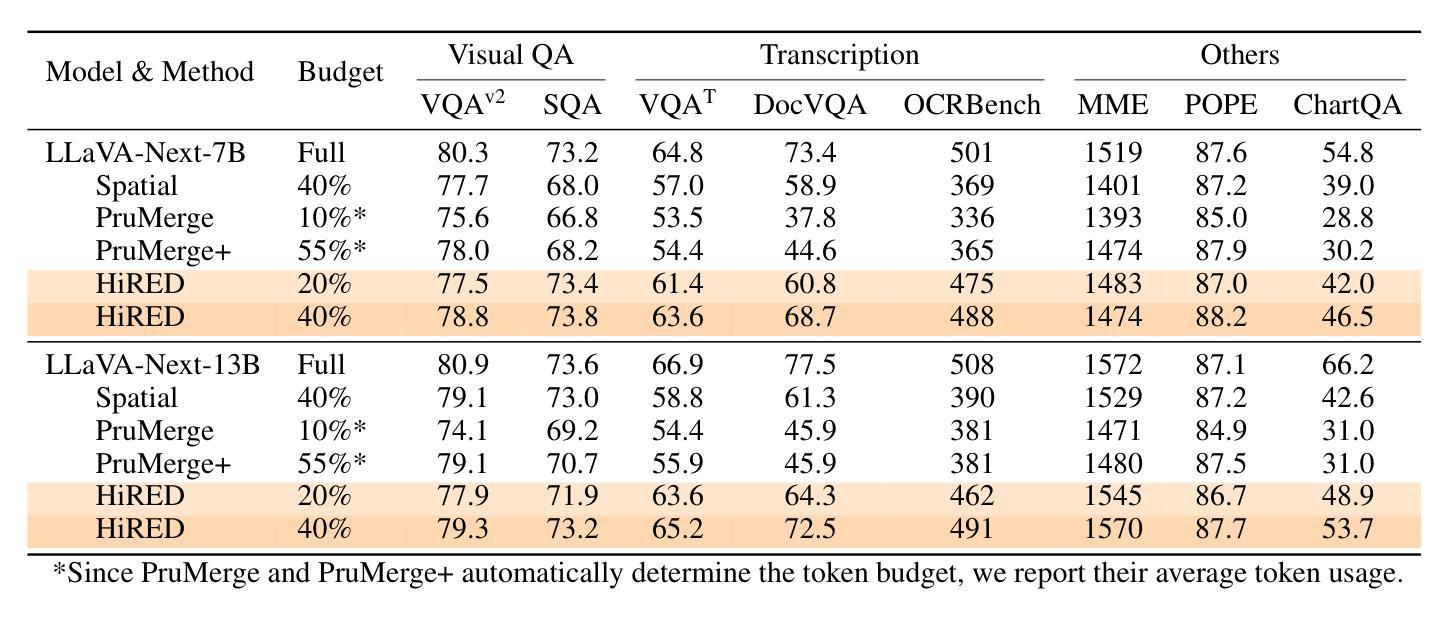
HiRED: Attention-Guided Token Dropping for Efficient Inference of High-Resolution Vision-Language Models
Authors:Kazi Hasan Ibn Arif, JinYi Yoon, Dimitrios S. Nikolopoulos, Hans Vandierendonck, Deepu John, Bo Ji
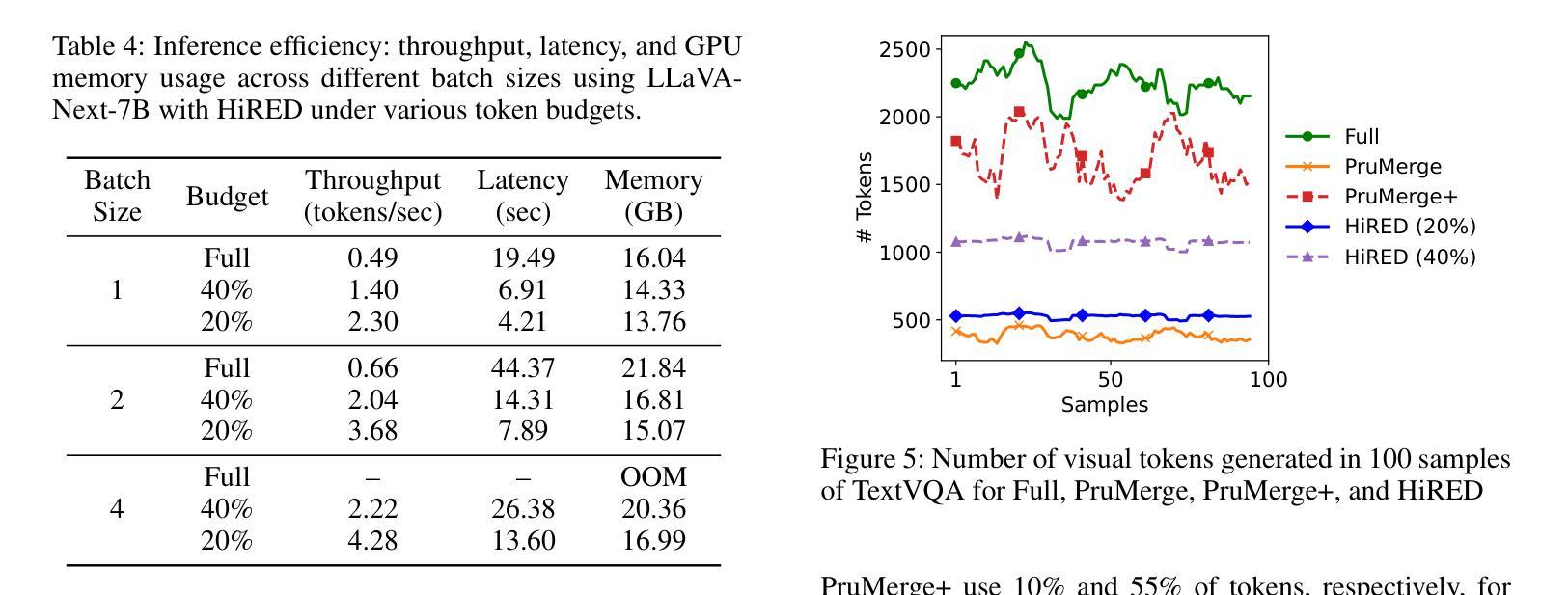
High-resolution Vision-Language Models (VLMs) are widely used in multimodal tasks to enhance accuracy by preserving detailed image information. However, these models often generate an excessive number of visual tokens due to the need to encode multiple partitions of a high-resolution image input. Processing such a large number of visual tokens through multiple transformer networks poses significant computational challenges, particularly for resource-constrained commodity GPUs. To address this challenge, we propose High-Resolution Early Dropping (HiRED), a plug-and-play token-dropping method designed to operate within a fixed token budget. HiRED leverages the attention of CLS token in the vision transformer (ViT) to assess the visual content of the image partitions and allocate an optimal token budget for each partition accordingly. The most informative visual tokens from each partition within the allocated budget are then selected and passed to the subsequent Large Language Model (LLM). We showed that HiRED achieves superior accuracy and performance, compared to existing token-dropping methods. Empirically, HiRED-20% (i.e., a 20% token budget) on LLaVA-Next-7B achieves a 4.7x increase in token generation throughput, reduces response latency by 78%, and saves 14% of GPU memory for single inference on an NVIDIA TESLA P40 (24 GB). For larger batch sizes (e.g., 4), HiRED-20% prevents out-of-memory errors by cutting memory usage by 30%, while preserving throughput and latency benefits. Code - https://github.com/hasanar1f/HiRED
高分辨率视觉语言模型(VLMs)在多模态任务中广泛应用,通过保留详细的图像信息来提高准确性。然而,由于需要对高分辨率图像输入的多个分区进行编码,这些模型通常会产生过多的视觉令牌。通过多个transformer网络处理如此大量的视觉令牌,带来了巨大的计算挑战,特别是对于资源受限的商品GPU。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了高分辨率早期丢弃(HiRED)策略,这是一种即插即用的令牌丢弃方法,旨在在一个固定的令牌预算内运行。HiRED利用视觉transformer(ViT)中CLS令牌的注意力来评估图像分区的视觉内容,并相应地分配每个分区的最佳令牌预算。然后,从每个分区中选择最具信息量的视觉令牌,并将其传递给随后的大型语言模型(LLM)。我们证明,与现有的令牌丢弃方法相比,HiRED在准确性和性能上均达到了优越水平。在实践中,HiRED-20%(即20%的令牌预算)在LLaVA-Next-7B上实现了令牌生成吞吐量4.7倍的提升,响应延迟减少了78%,并在NVIDIA TESLA P40(24GB)上单次推理节省了14%的GPU内存。对于较大的批次大小(例如4),HiRED-20%通过减少内存使用30%来防止内存溢出错误,同时保持吞吐量和延迟优势。代码-https://github.com/hasanar1f/HiRED
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in AAAI 2025
Summary
高解析度视觉语言模型(VLMs)在多模态任务中广泛应用,旨在保留图像详细信息以提高准确性。然而,由于需要编码高解析度图像的多个分区,这些模型会产生过多的视觉令牌。在资源受限的商品GPU上处理大量视觉令牌会带来重大计算挑战。为解决此问题,我们提出High-Resolution Early Dropping(HiRED)方法,这是一种旨在固定令牌预算内运行的即插即用令牌丢弃方法。HiRED利用视觉变压器(ViT)中的CLS令牌的注意力来评估图像分区的视觉内容,并为每个分区分配最佳令牌预算。随后,从每个分区中选择最具信息量的视觉令牌,并将其传递给随后的大型语言模型(LLM)。相比现有的令牌丢弃方法,HiRED在准确性和性能方面表现出卓越性能。具体而言,在LLaVA-Next-7B上,HiRED-20%(即20%令牌预算)使令牌生成吞吐量增加了4.7倍,响应延迟减少了78%,并节省了单个推理的GPU内存达14%。对于较大的批次大小(例如4),HiRED-20%能够在保持吞吐量和延迟优势的同时,通过减少内存使用30%来防止内存溢出错误。
Key Takeaways
- 高解析度视觉语言模型在处理多模态任务时,需要处理大量视觉令牌带来的计算挑战问题亟待解决。
- HiRED是一种旨在固定令牌预算内运行的令牌丢弃方法,可以有效应对这一挑战。
- HiRED利用视觉变压器中的CLS令牌的注意力机制来评估图像分区的视觉内容。
- HiRED为每个图像分区分配最优令牌预算并选择最具信息量的视觉令牌传递给大型语言模型。
- HiRED相比现有方法在准确性、性能和内存使用方面表现出卓越性能。
- 在特定实验中,HiRED显著提高了令牌生成吞吐量、降低了响应延迟并节省了GPU内存使用。
点此查看论文截图

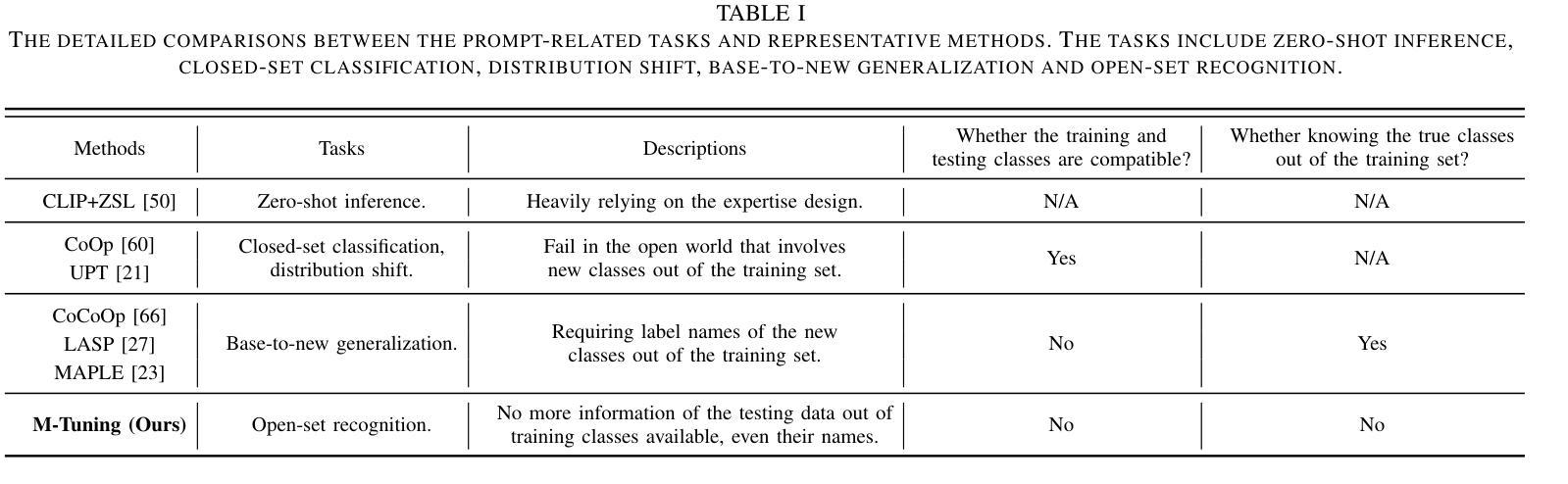
M-Tuning: Prompt Tuning with Mitigated Label Bias in Open-Set Scenarios
Authors:Ning Liao, Xiaopeng Zhang, Min Cao, Junchi Yan
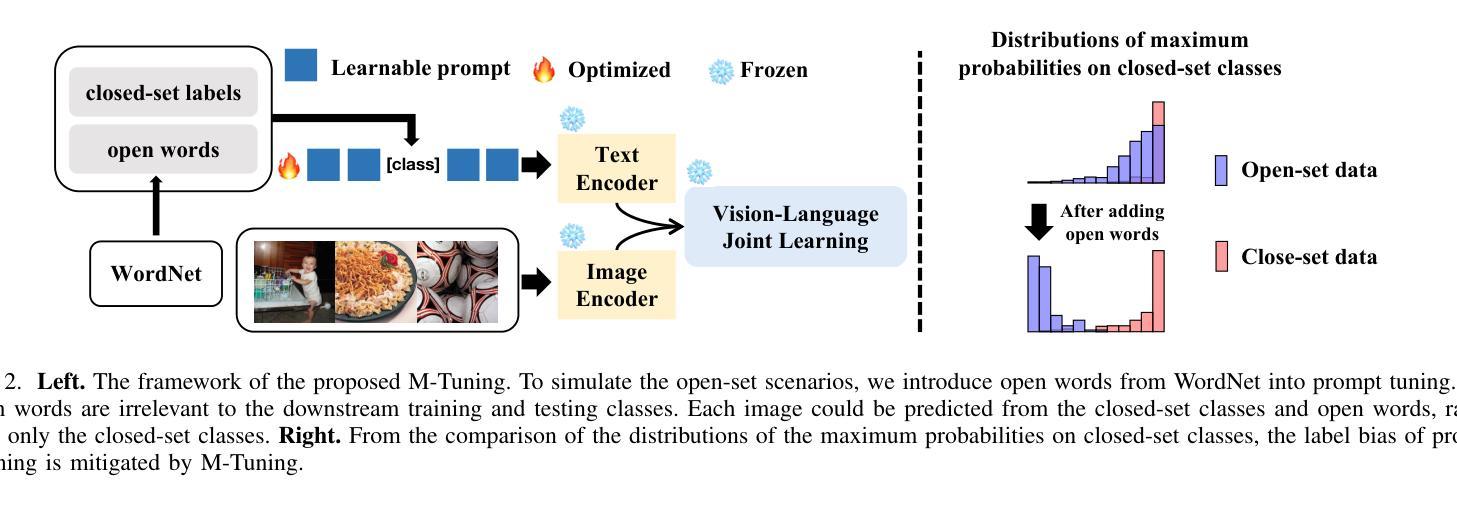
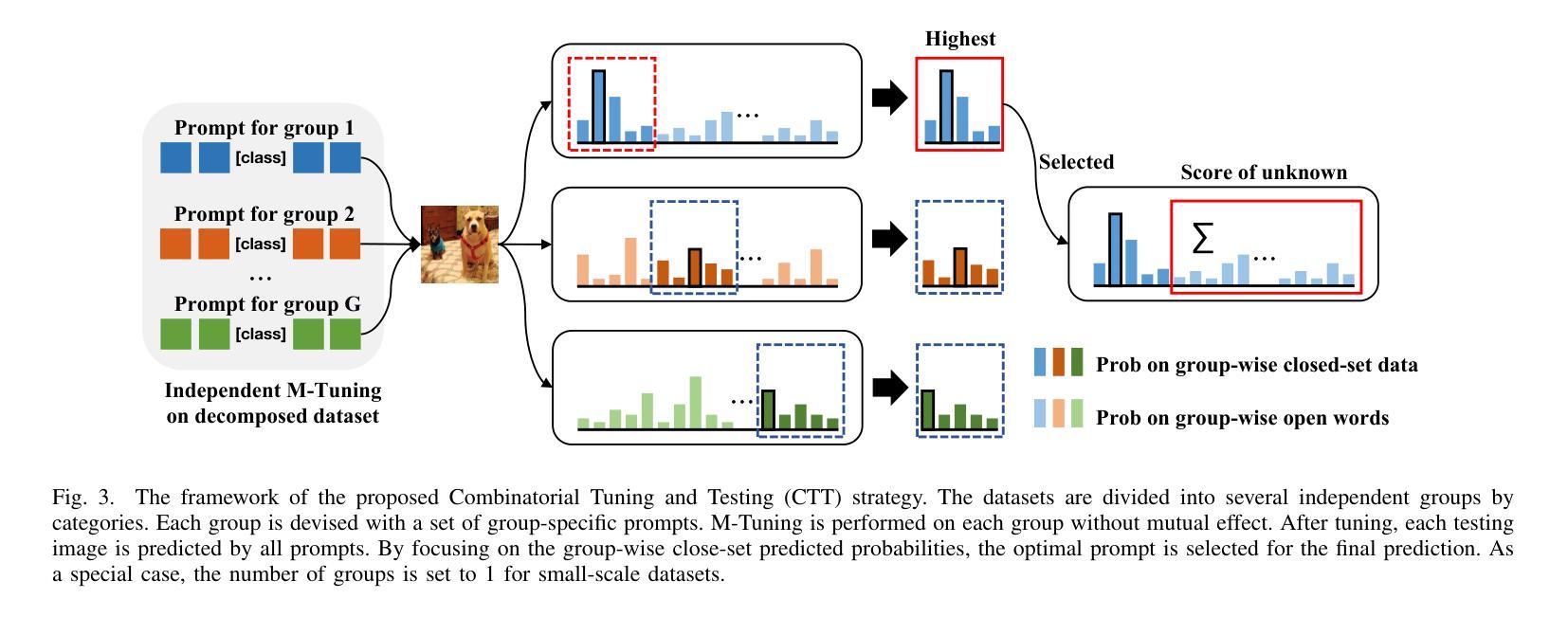
In realistic open-set scenarios where labels of a part of testing data are totally unknown, when vision-language (VL) prompt learning methods encounter inputs related to unknown classes (i.e., not seen during training), they always predict them as one of the training classes. The exhibited label bias causes difficulty in open set recognition (OSR), in which an image should be correctly predicted as one of the known classes or the unknown one. To achieve this goal, we propose a vision-language prompt tuning method with mitigated label bias (M-Tuning). It introduces open words from the WordNet to extend the range of words forming the prompt texts from only closed-set label words to more, and thus prompts are tuned in a simulated open-set scenario. Besides, inspired by the observation that classifying directly on large datasets causes a much higher false positive rate than on small datasets, we propose a Combinatorial Tuning and Testing (CTT) strategy for improving performance. CTT decomposes M-Tuning on large datasets as multiple independent group-wise tuning on fewer classes, then makes accurate and comprehensive predictions by selecting the optimal sub-prompt. Finally, given the lack of VL-based OSR baselines in the literature, especially for prompt methods, we contribute new baselines for fair comparisons. Our method achieves the best performance on datasets with various scales, and extensive ablation studies also validate its effectiveness.
在真实的开放集场景中,部分测试数据的标签是未知的,当视觉语言(VL)提示学习方法遇到与未知类别相关的输入时(即在训练期间未见过的),它们通常会预测为训练类别之一。这种表现出来的标签偏见给开放集识别(OSR)带来了困难,在OSR中,图像应该被正确预测为已知类别之一或未知类别。为了实现这一目标,我们提出了一种带有减轻标签偏见的视觉语言提示调整方法(M-Tuning)。它引入了WordNet中的开放词汇,扩大了构成提示文本的词的范围,从仅封闭集标签词到更多,从而对提示进行了模拟的开放集场景的调整。此外,受直接在大数据集上进行分类比在小数据集上导致更高的误报率的观察启发,我们提出了一种组合调整和测试(CTT)策略以提高性能。CTT将大型数据集上的M-Tuning分解为在较少类别上的多个独立组级调整,然后通过选择最佳子提示来进行准确和全面的预测。最后,鉴于文献中缺乏基于视觉语言的OSR基准线,尤其是提示方法,我们为公平比较提供了新的基准线。我们的方法在各种规模的数据集上取得了最佳性能,广泛的消融研究也验证了其有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE TCSVT
Summary:在真实开放场景中对未知标签数据的识别存在挑战,本文提出一种具有减轻标签偏见的视觉语言提示调整方法(M-Tuning)。通过引入WordNet中的开放词汇来扩展提示文本的词汇范围,并在模拟的开放场景中调整提示。此外,受小数据集上直接分类的假阳性率较低启发,我们提出了一种组合调整测试(CTT)策略来提高性能。最后,我们为公平比较提供了基于视觉语言(VL)的OSR基准线,并在不同规模的数据集上实现最佳性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 在现实开放场景识别中,存在将未知标签数据预测为训练类别的问题,这引发了标签偏见的问题。
- 本文提出了一种具有减轻标签偏见的视觉语言提示调整方法(M-Tuning),通过引入WordNet中的开放词汇来扩展提示文本的词汇范围。
- 组合调整测试(CTT)策略被提出以提高性能,通过将大型数据集的分类分解为多个独立的小组调整,然后在更少类别上进行准确和全面的预测。
- 缺少基于视觉语言(VL)的OSR基准线,特别是在提示方法方面,因此本文提供了公平比较的基准线。
- 本文的方法在不同规模的数据集上都取得了最佳性能。
- 广泛的消融研究验证了M-Tuning和CTT策略的有效性。
- 通过引入开放词汇和组合调整测试策略,本文为解决开放集识别问题提供了新的思路和方法。
点此查看论文截图