⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-03 更新
When SAM2 Meets Video Shadow and Mirror Detection
Authors:Leiping Jie
As the successor to the Segment Anything Model (SAM), the Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2) not only improves performance in image segmentation but also extends its capabilities to video segmentation. However, its effectiveness in segmenting rare objects that seldom appear in videos remains underexplored. In this study, we evaluate SAM2 on three distinct video segmentation tasks: Video Shadow Detection (VSD) and Video Mirror Detection (VMD). Specifically, we use ground truth point or mask prompts to initialize the first frame and then predict corresponding masks for subsequent frames. Experimental results show that SAM2’s performance on these tasks is suboptimal, especially when point prompts are used, both quantitatively and qualitatively. Code is available at \url{https://github.com/LeipingJie/SAM2Video}
作为Segment Anything Model(SAM)的继任者,Segment Anything Model 2(SAM2)不仅在图像分割性能上有所提升,还能将能力扩展至视频分割。然而,它在分割视频中极少出现的罕见物体方面的效果尚未得到充分探索。本研究中,我们在三个不同的视频分割任务上评估了SAM2的表现:视频阴影检测(VSD)和视频镜像检测(VMD)。具体来说,我们使用真实点或遮罩提示来初始化第一帧,然后预测后续帧的相应遮罩。实验结果表明,SAM2在这些任务上的表现并不理想,尤其是使用点提示时,无论在数量上和质量上都是如此。相关代码可访问:\url{https://github.com/LeipingJie/SAM2Video}
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report
Summary
医学图像领域的Segment Anything Model 2(SAM2)模型在视频分割方面有所突破,但在罕见物体的视频分割上表现有待提高。本研究对SAM2在视频阴影检测和视频镜像检测等三个不同视频分割任务上的性能进行了评估。使用真实标记点或遮罩提示初始化第一帧,然后预测后续帧的相应遮罩。代码可通过链接https://github.com/LeipingJie/SAM2Video获取。
Key Takeaways
- SAM2作为Segment Anything Model(SAM)的继任者,不仅在图像分割方面提升了性能,还扩展了视频分割的能力。
- 本研究对SAM2在视频阴影检测(VSD)和视频镜像检测(VMD)等视频分割任务上的性能进行了评估。
- 使用真实标记点或遮罩提示来初始化第一帧,并预测后续帧的相应遮罩,是SAM2在处理视频分割任务时的一种重要方法。
- 实验结果显示,SAM2在这些任务上的表现并不理想,特别是在使用点提示时,定量和定性表现均不佳。
- SAM2在罕见物体的视频分割上的性能还需进一步探索和提升。
点此查看论文截图




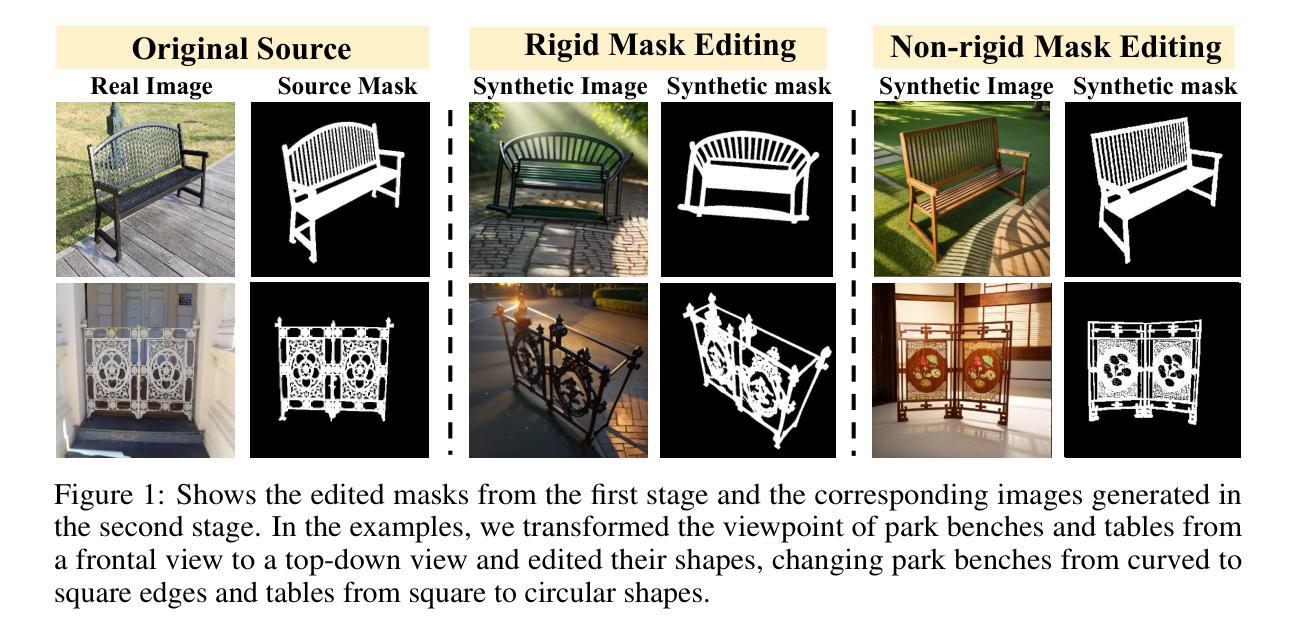
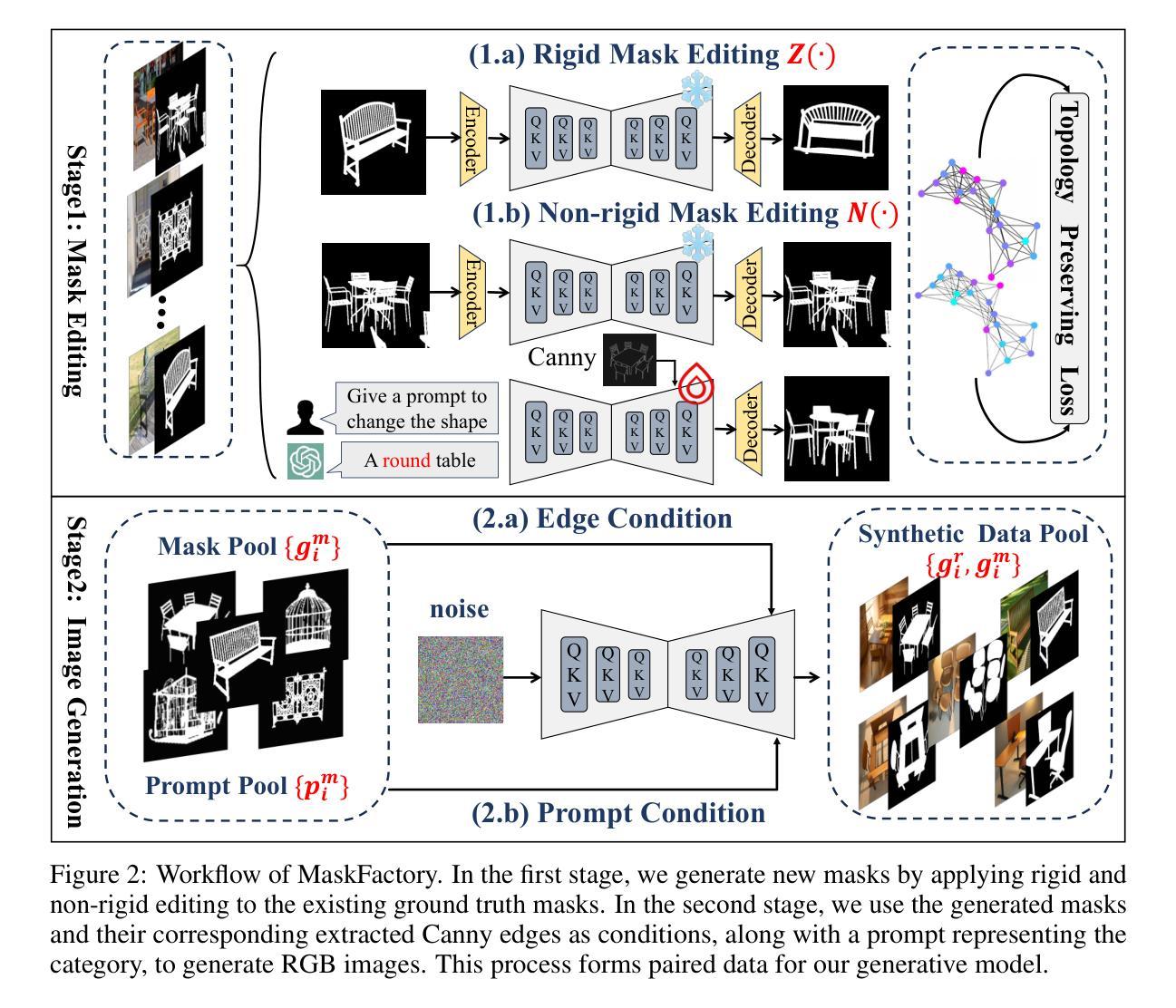
Mask Factory: Towards High-quality Synthetic Data Generation for Dichotomous Image Segmentation
Authors:Haotian Qian, YD Chen, Shengtao Lou, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Xiaogang Jin, Deng-Ping Fan
Dichotomous Image Segmentation (DIS) tasks require highly precise annotations, and traditional dataset creation methods are labor intensive, costly, and require extensive domain expertise. Although using synthetic data for DIS is a promising solution to these challenges, current generative models and techniques struggle with the issues of scene deviations, noise-induced errors, and limited training sample variability. To address these issues, we introduce a novel approach, \textbf{\ourmodel{}}, which provides a scalable solution for generating diverse and precise datasets, markedly reducing preparation time and costs. We first introduce a general mask editing method that combines rigid and non-rigid editing techniques to generate high-quality synthetic masks. Specially, rigid editing leverages geometric priors from diffusion models to achieve precise viewpoint transformations under zero-shot conditions, while non-rigid editing employs adversarial training and self-attention mechanisms for complex, topologically consistent modifications. Then, we generate pairs of high-resolution image and accurate segmentation mask using a multi-conditional control generation method. Finally, our experiments on the widely-used DIS5K dataset benchmark demonstrate superior performance in quality and efficiency compared to existing methods. The code is available at \url{https://qian-hao-tian.github.io/MaskFactory/}.
二值图像分割(DIS)任务需要高度精确的标注,而传统的数据集创建方法劳动强度大、成本高,并需要广泛的领域专业知识。虽然使用合成数据对于DIS是一个解决这些挑战的很有前景的解决方案,但当前的生成模型和技术仍然面临场景偏差、噪声引起的错误以及训练样本变化有限等问题。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了一种新方法——ourmodel,它为生成多样且精确的数据集提供了可扩展的解决方案,显著减少了准备时间和成本。我们首先引入了一种通用的掩膜编辑方法,该方法结合了刚性和非刚性编辑技术来生成高质量合成掩膜。具体来说,刚性编辑利用扩散模型的几何先验知识,在无样本条件下实现精确的视点转换,而非刚性编辑则采用对抗性训练和自注意力机制进行复杂且拓扑一致的修改。然后,我们使用多条件控制生成方法生成高分辨率图像和精确分割掩膜对。最后,我们在广泛使用的DIS5K数据集基准测试上进行的实验表明,与现有方法相比,我们的方法在质量和效率方面表现出卓越的性能。代码可在[https://qian-hao-tian.github.io/MaskFactory/]访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型图像分割数据集生成方法——我们的模型(ourmodel),解决了传统创建数据集方式所面临的劳动强度大、成本高昂和领域专业知识需求强等问题。通过结合刚性和非刚性编辑技术,生成高质量合成掩膜,并利用多条件控制生成方法生成高分辨率图像和精确分割掩膜。在广泛使用的DIS5K数据集上进行的实验证明了该方法在质量和效率上的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 图像分割任务需要大量精确标注的数据集,传统创建方法成本高且需要大量领域专业知识。
- 当前生成模型面临场景偏差、噪声引起的错误和训练样本变化有限等问题。
- 提出了一种新型图像分割数据集生成方法——我们的模型(ourmodel),旨在解决上述问题。
- 结合刚性和非刚性编辑技术,生成高质量合成掩膜。
- 利用多条件控制生成方法生成高分辨率图像和精确分割掩膜。
- 在广泛使用的DIS5K数据集上进行了实验验证,证明该方法的优越性。
点此查看论文截图


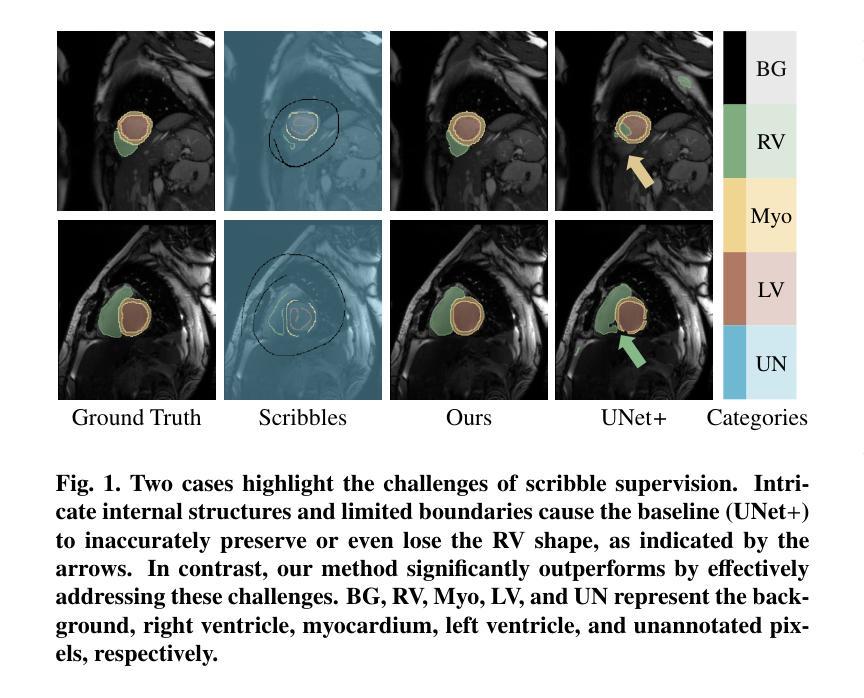
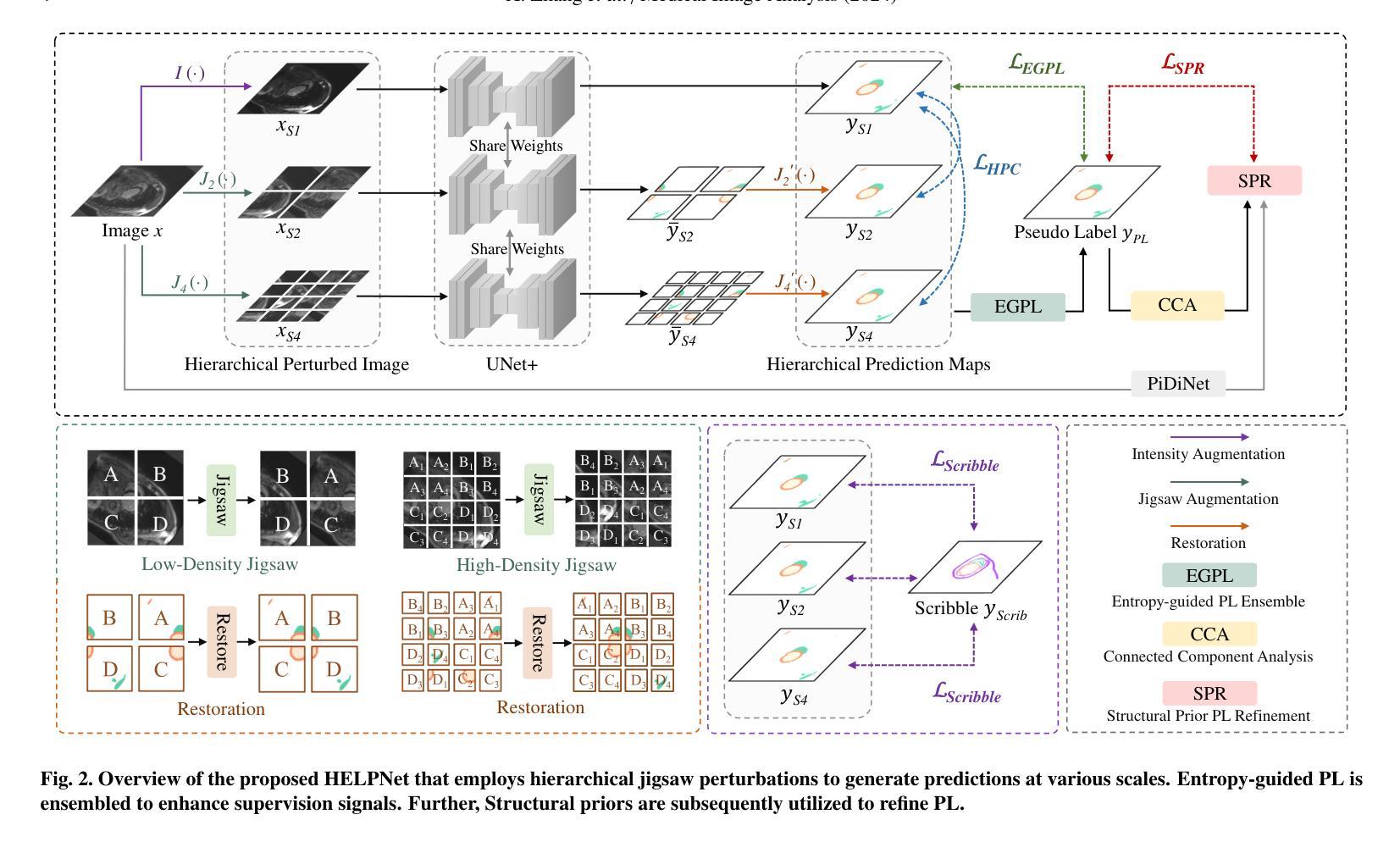
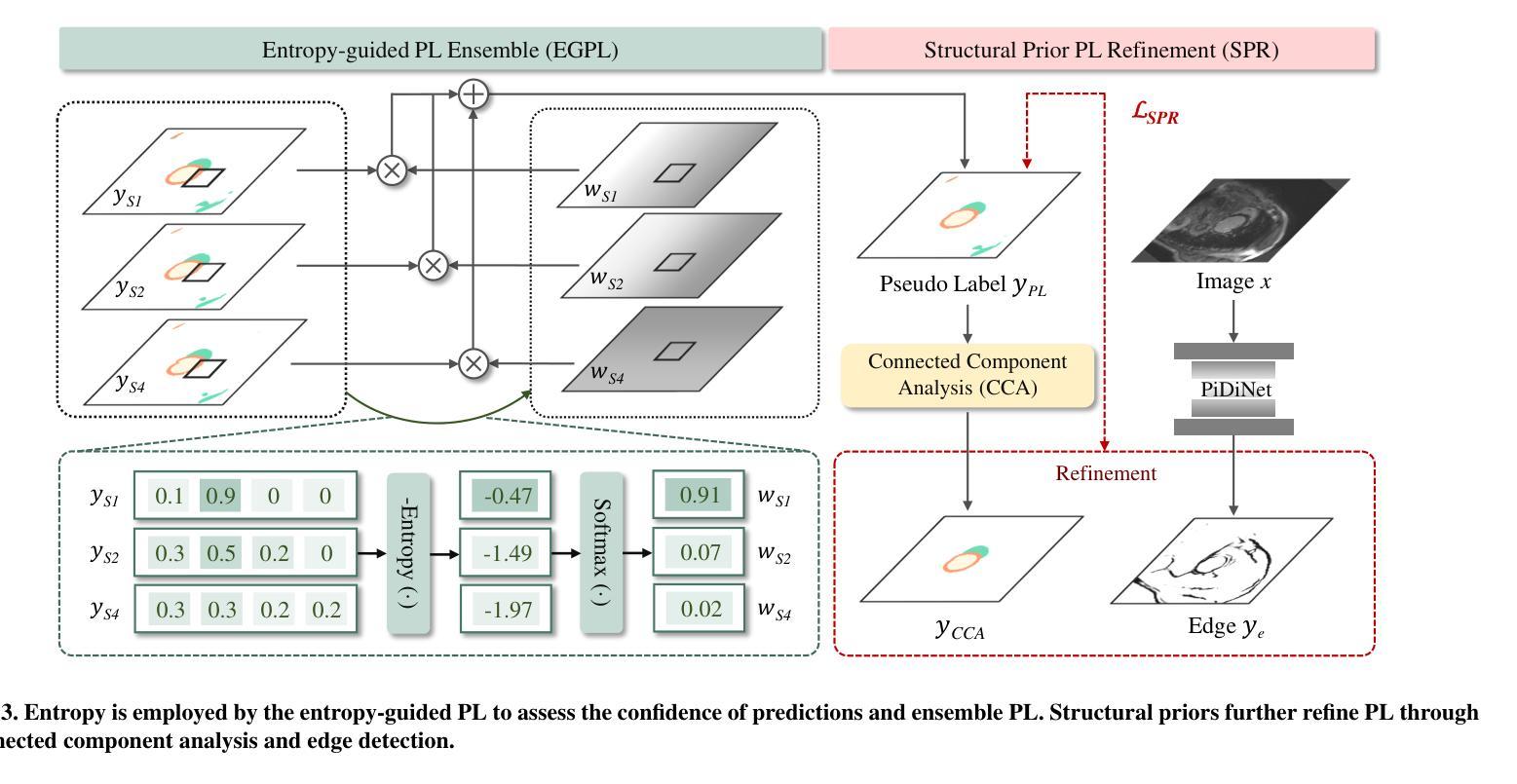
HELPNet: Hierarchical Perturbations Consistency and Entropy-guided Ensemble for Scribble Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Xiao Zhang, Shaoxuan Wu, Peilin Zhang, Zhuo Jin, Xiaosong Xiong, Qirong Bu, Jingkun Chen, Jun Feng
Creating fully annotated labels for medical image segmentation is prohibitively time-intensive and costly, emphasizing the necessity for innovative approaches that minimize reliance on detailed annotations. Scribble annotations offer a more cost-effective alternative, significantly reducing the expenses associated with full annotations. However, scribble annotations offer limited and imprecise information, failing to capture the detailed structural and boundary characteristics necessary for accurate organ delineation. To address these challenges, we propose HELPNet, a novel scribble-based weakly supervised segmentation framework, designed to bridge the gap between annotation efficiency and segmentation performance. HELPNet integrates three modules. The Hierarchical perturbations consistency (HPC) module enhances feature learning by employing density-controlled jigsaw perturbations across global, local, and focal views, enabling robust modeling of multi-scale structural representations. Building on this, the Entropy-guided pseudo-label (EGPL) module evaluates the confidence of segmentation predictions using entropy, generating high-quality pseudo-labels. Finally, the structural prior refinement (SPR) module incorporates connectivity and bounded priors to enhance the precision and reliability and pseudo-labels. Experimental results on three public datasets ACDC, MSCMRseg, and CHAOS show that HELPNet significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods for scribble-based weakly supervised segmentation and achieves performance comparable to fully supervised methods. The code is available at https://github.com/IPMI-NWU/HELPNet.
为医学图像分割创建完全注释的标签是非常耗时和昂贵的,这强调了对创新方法的必要性,这些方法需要尽量减少对详细注释的依赖。涂鸦注释提供了一种更具成本效益的替代方案,显著降低了与完整注释相关的费用。然而,涂鸦注释提供的信息有限且不准确,无法捕捉到用于准确器官描绘所需的详细结构和边界特征。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了HELPNet,这是一个基于涂鸦的弱监督分割框架,旨在弥补注释效率和分割性能之间的差距。HELPNet集成了三个模块。分层扰动一致性(HPC)模块通过采用全局、局部和焦点视图上的密度控制拼图扰动来增强特征学习,从而实现对多尺度结构表示的稳健建模。在此基础上,熵引导伪标签(EGPL)模块使用熵评估分割预测的信心,生成高质量的伪标签。最后,结构先验细化(SPR)模块结合了连接和边界先验知识,提高了伪标签的精确性和可靠性。在ACDC、MSCMRseg和CHAOS三个公共数据集上的实验结果表明,HELPNet在基于涂鸦的弱监督分割方面显著优于最新方法,并且在性能上可与全监督方法相媲美。代码可在https://github.com/IPMI-NWU/HELPNet获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
一种创新的医学图像分割标注方法HELPNet被提出,旨在通过层次化扰动一致性模块、熵引导伪标签模块和结构先验细化模块,缩小涂鸦注释与分割性能之间的差距,提高标注效率并兼顾分割性能。该方法在三个公共数据集上的实验结果表明,HELPNet在涂鸦注释的弱监督分割方面显著优于现有技术,并与全监督方法相当。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割的完全注释标签创建是耗时且成本高昂的,需要创新方法来减少依赖详细的注释。
- 涂鸦注释作为一种更经济的方法,显著降低了全注释的费用,但提供的信息有限且不精确。
- HELPNet是一个基于涂鸦的弱监督分割框架,旨在解决注释效率和分割性能之间的平衡问题。
- HELPNet包含三个模块:层次化扰动一致性模块、熵引导伪标签模块和结构先验细化模块。
- 层次化扰动一致性模块通过密度控制的拼图扰动增强特征学习,并建模多尺度结构表示。
- 熵引导伪标签模块利用熵评估分割预测的置信度,生成高质量伪标签。
- 结构先验细化模块结合连通性和边界先验提高伪标签的精度和可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

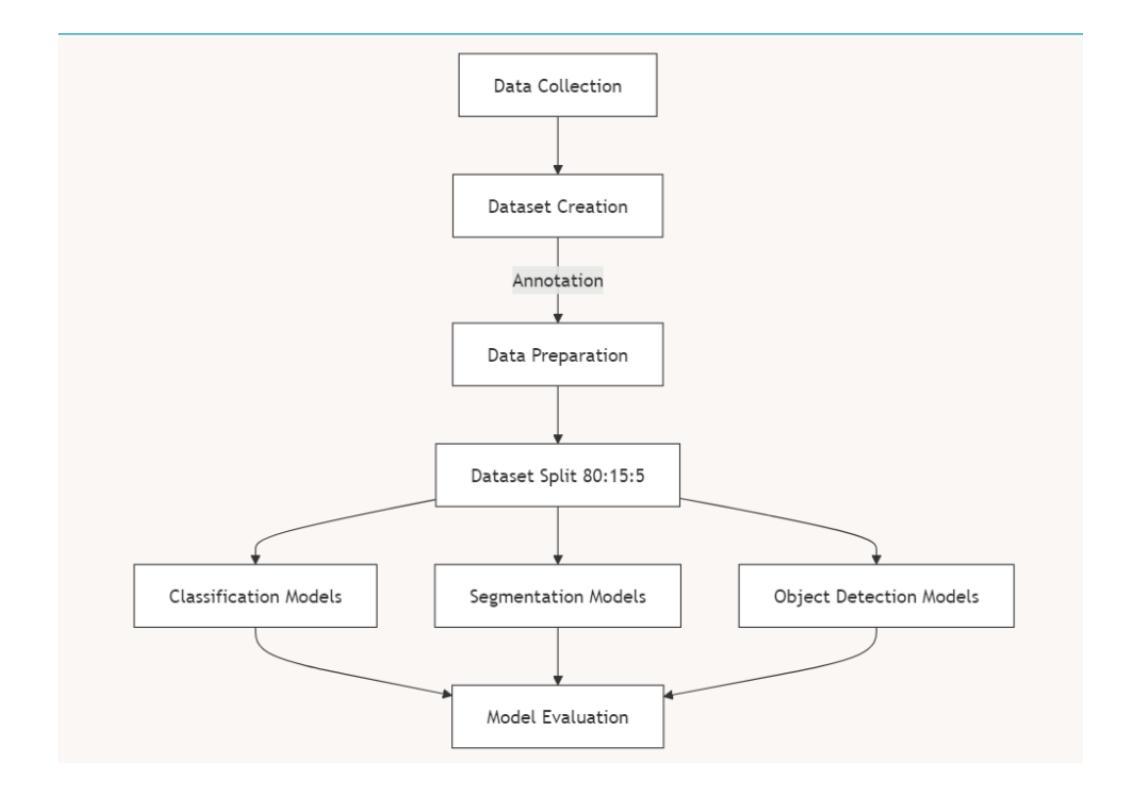
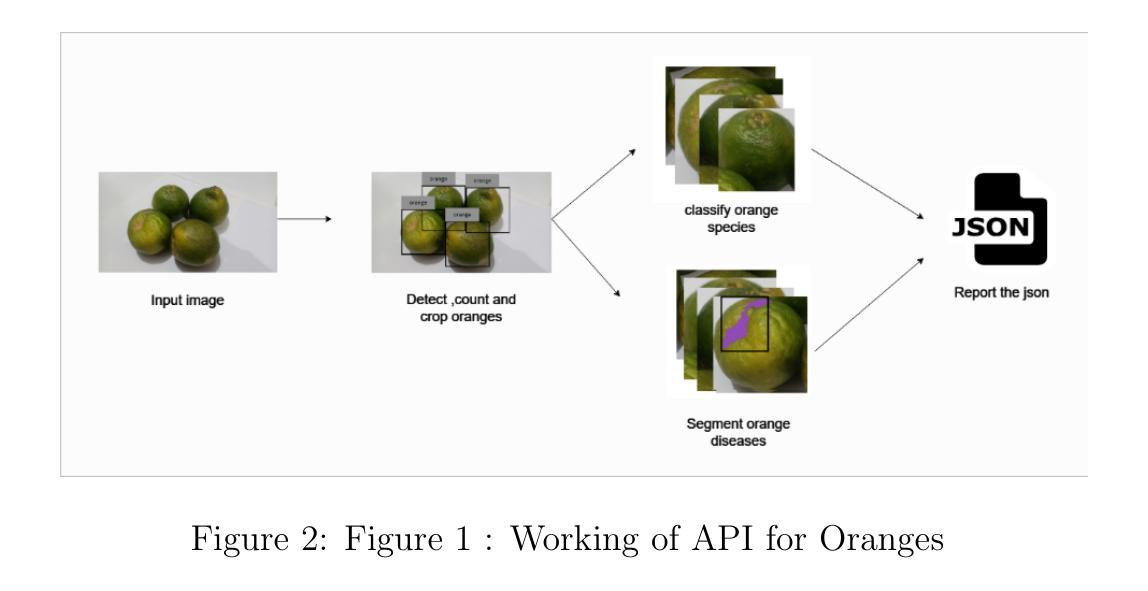
Edge-AI for Agriculture: Lightweight Vision Models for Disease Detection in Resource-Limited Settings
Authors:Harsh Joshi
This research paper presents the development of a lightweight and efficient computer vision pipeline aimed at assisting farmers in detecting orange diseases using minimal resources. The proposed system integrates advanced object detection, classification, and segmentation models, optimized for deployment on edge devices, ensuring functionality in resource-limited environments. The study evaluates the performance of various state-of-the-art models, focusing on their accuracy, computational efficiency, and generalization capabilities. Notable findings include the Vision Transformer achieving 96 accuracy in orange species classification and the lightweight YOLOv8-S model demonstrating exceptional object detection performance with minimal computational overhead. The research highlights the potential of modern deep learning architectures to address critical agricultural challenges, emphasizing the importance of model complexity versus practical utility. Future work will explore expanding datasets, model compression techniques, and federated learning to enhance the applicability of these systems in diverse agricultural contexts, ultimately contributing to more sustainable farming practices.
这篇研究论文介绍了一个轻量级、高效率的计算机视觉流程的开发情况,该流程旨在利用最少的资源帮助农民检测柑橘疾病。所提出的系统集成了先进的对象检测、分类和分割模型,针对边缘设备进行部署优化,确保在资源有限的环境中也能正常运行。该研究评估了各种最新模型的表现,主要关注其准确性、计算效率和泛化能力。值得注意的是,Vision Transformer在柑橘品种分类方面达到了96%的准确率,而轻量级的YOLOv8-S模型在对象检测方面表现出卓越的性能,计算开销极小。该研究突出了现代深度学习架构解决重要农业挑战的潜力,强调模型复杂度与实际效用之间的平衡。未来的工作将探索扩大数据集、模型压缩技术和联邦学习,以提高这些系统在各种农业环境中的适用性,最终为更可持续的农业实践做出贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究开发了一种轻量级、高效率的计算机视觉管道,旨在利用有限的资源协助农民检测柑橘疾病。该系统整合了先进的物体检测、分类和分割模型,优化后可在边缘设备上部署,确保在资源受限的环境中也能正常运行。研究评估了多种最新模型的性能,重点关注其准确性、计算效率和泛化能力。研究表明,Vision Transformer在柑橘品种分类方面的准确率达到了96%,而轻量级的YOLOv8-S模型在物体检测方面表现出卓越的性能,计算开销极小。该研究强调了现代深度学习架构在解决农业挑战中的潜力,并强调了模型复杂度与实际效用之间的平衡。未来的工作将探索扩大数据集、模型压缩技术和联邦学习,以提高这些系统在多种农业环境中的适用性,为更可持续的农业实践做出贡献。
Key Takeaways
- 研究开发了一种轻量级、高效率的计算机视觉管道,用于协助农民检测柑橘疾病。
- 系统整合了先进的物体检测、分类和分割模型,适用于边缘设备部署。
- 研究评估了多种最新模型的性能,包括准确性、计算效率和泛化能力。
- Vision Transformer在柑橘品种分类上的准确率达到了96%。
- YOLOv8-S模型在物体检测方面表现出卓越的性能,且计算开销小。
- 研究强调了现代深度学习架构在农业挑战中的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

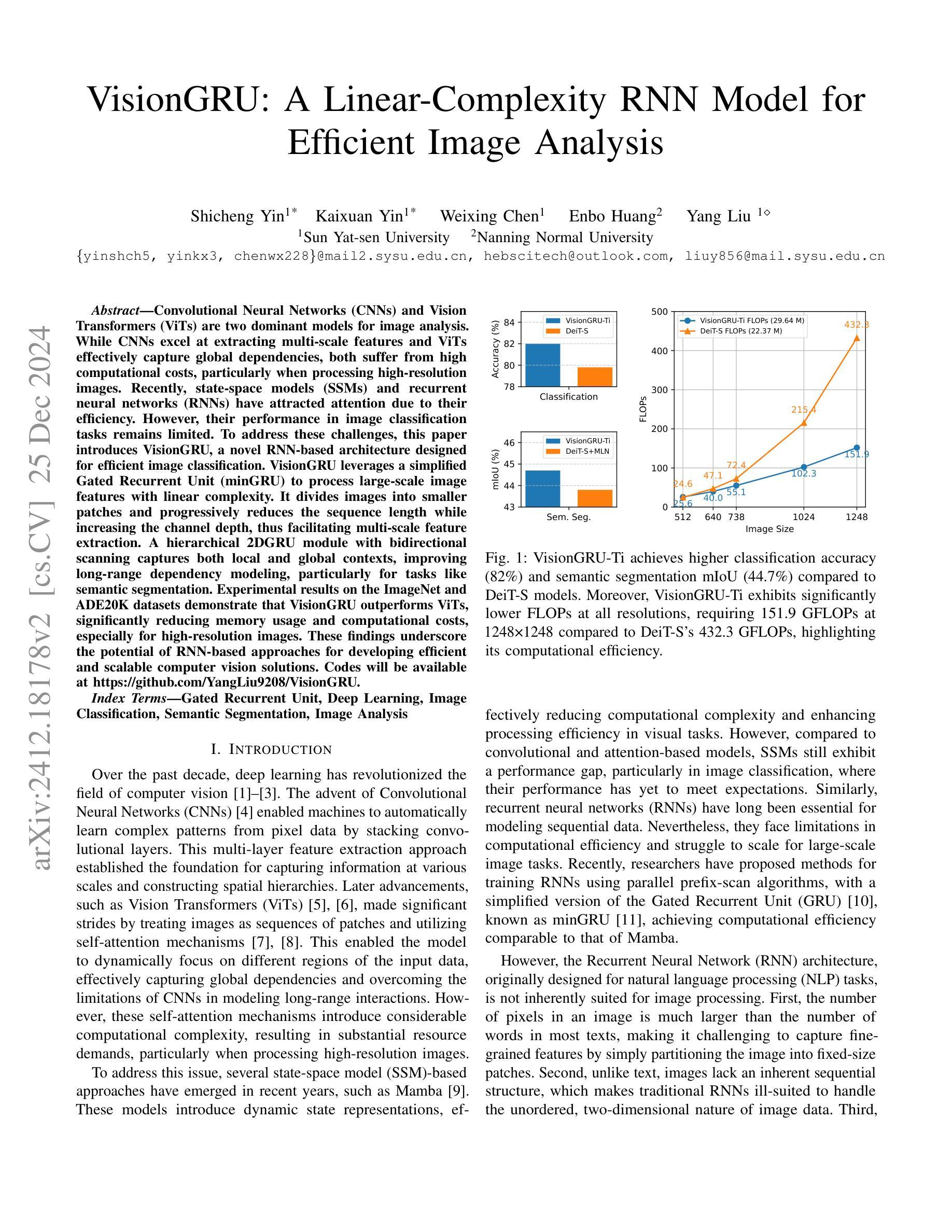
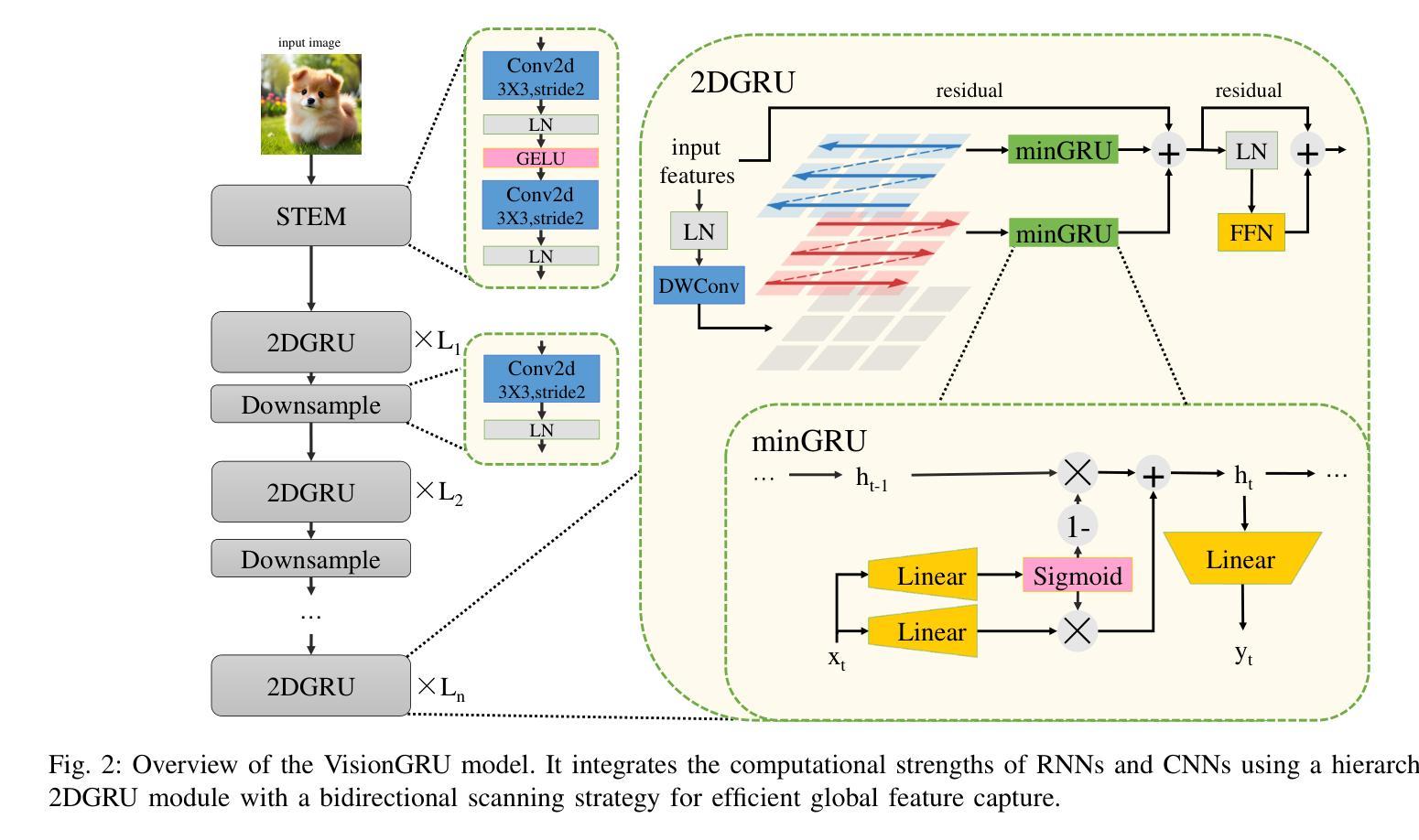
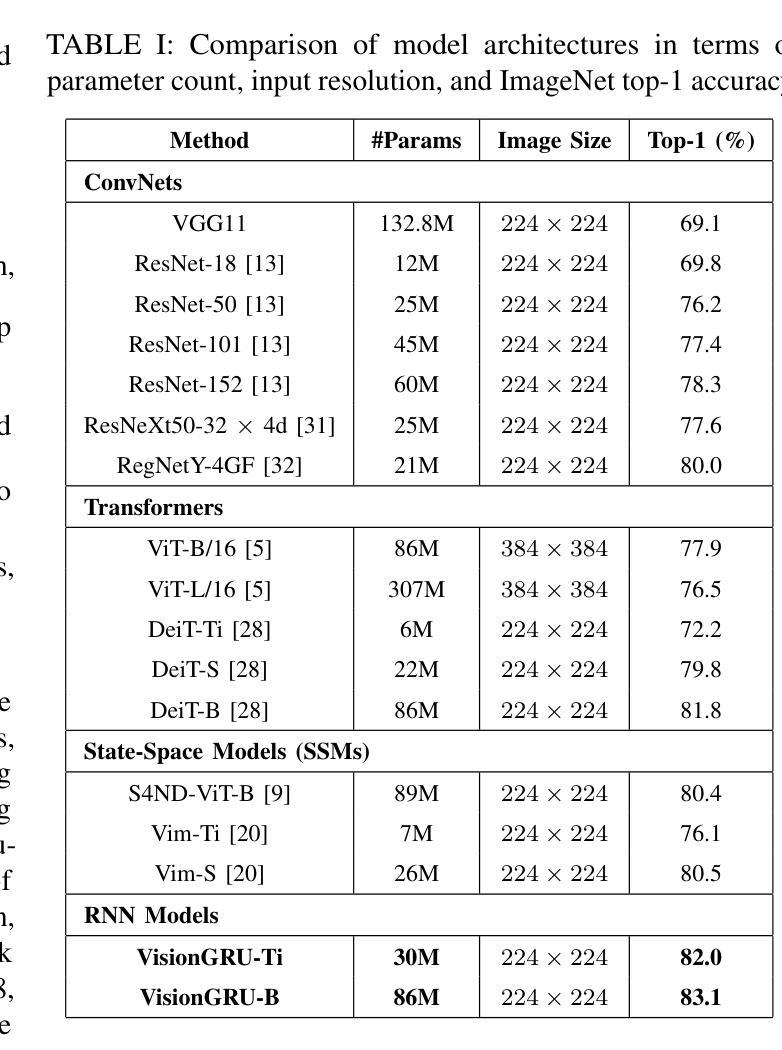
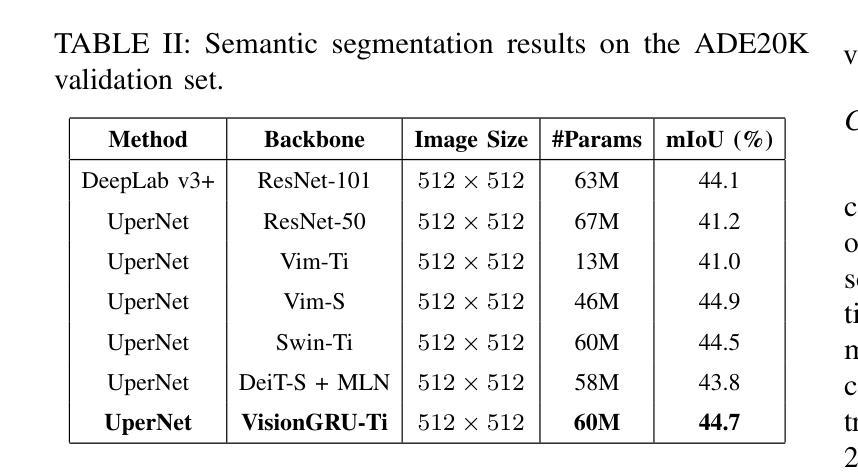
VisionGRU: A Linear-Complexity RNN Model for Efficient Image Analysis
Authors:Shicheng Yin, Kaixuan Yin, Weixing Chen, Enbo Huang, Yang Liu
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Vision Transformers (ViTs) are two dominant models for image analysis. While CNNs excel at extracting multi-scale features and ViTs effectively capture global dependencies, both suffer from high computational costs, particularly when processing high-resolution images. Recently, state-space models (SSMs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) have attracted attention due to their efficiency. However, their performance in image classification tasks remains limited. To address these challenges, this paper introduces VisionGRU, a novel RNN-based architecture designed for efficient image classification. VisionGRU leverages a simplified Gated Recurrent Unit (minGRU) to process large-scale image features with linear complexity. It divides images into smaller patches and progressively reduces the sequence length while increasing the channel depth, thus facilitating multi-scale feature extraction. A hierarchical 2DGRU module with bidirectional scanning captures both local and global contexts, improving long-range dependency modeling, particularly for tasks like semantic segmentation. Experimental results on the ImageNet and ADE20K datasets demonstrate that VisionGRU outperforms ViTs, significantly reducing memory usage and computational costs, especially for high-resolution images. These findings underscore the potential of RNN-based approaches for developing efficient and scalable computer vision solutions. Codes will be available at https://github.com/YangLiu9208/VisionGRU.
卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT)是图像分析中的两种主导模型。虽然CNN擅长提取多尺度特征,而ViT能有效捕捉全局依赖性,但两者都存在计算成本高的问题,特别是在处理高分辨率图像时。近年来,由于效率较高,状态空间模型(SSM)和循环神经网络(RNN)引起了人们的关注。然而,它们在图像分类任务中的表现仍然有限。为了解决这些挑战,本文提出了一种用于高效图像分类的新型RNN架构——VisionGRU。VisionGRU利用简化的门控循环单元(minGRU)以线性复杂度处理大规模图像特征。它将图像分成较小的斑块,逐步减少序列长度,同时增加通道深度,从而便于多尺度特征提取。具有双向扫描的分层2DGRU模块可以捕获局部和全局上下文,改进了长距离依赖建模,尤其适用于语义分割等任务。在ImageNet和ADE20K数据集上的实验结果表明,VisionGRU优于ViTs,极大地减少了内存使用和计算成本,尤其对于高分辨率图像。这些发现强调了基于RNN的方法在开发高效且可扩展的计算机视觉解决方案方面的潜力。代码将在https://github.com/YangLiu9208/VisionGRU上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Codes will be available at https://github.com/YangLiu9208/VisionGRU
Summary
该论文提出了一种基于RNN的新型图像分类架构——VisionGRU,用于解决CNN和ViT在处理高分辨率图像时的高计算成本问题。VisionGRU利用简化的门控循环单元(minGRU)以线性复杂度处理大规模图像特征,通过分割图像成小块并渐进式减少序列长度同时增加通道深度,实现多尺度特征提取。其层次化的2DGRU模块结合双向扫描,能捕捉局部和全局上下文,尤其对于语义分割等任务,在长期依赖建模方面表现出色。在ImageNet和ADE20K数据集上的实验结果表明,VisionGRU在降低内存使用和计算成本的同时,性能优于ViT,尤其是处理高分辨率图像时。
Key Takeaways
- VisionGRU是一种新型的RNN架构,旨在解决图像分类中的高计算成本问题。
- VisionGRU利用简化的Gated Recurrent Unit(minGRU)处理大规模图像特征,具有线性复杂度。
- 通过将图像分割成小块,VisionGRU实现了多尺度特征提取。
- VisionGRU采用层次化的2DGRU模块,结合双向扫描,以捕捉局部和全局上下文。
- VisionGRU在图像分类任务中表现出良好的性能,特别是在处理高分辨率图像时。
- 与ViT相比,VisionGRU在降低内存使用和计算成本的同时,实现了更高的性能。
点此查看论文截图

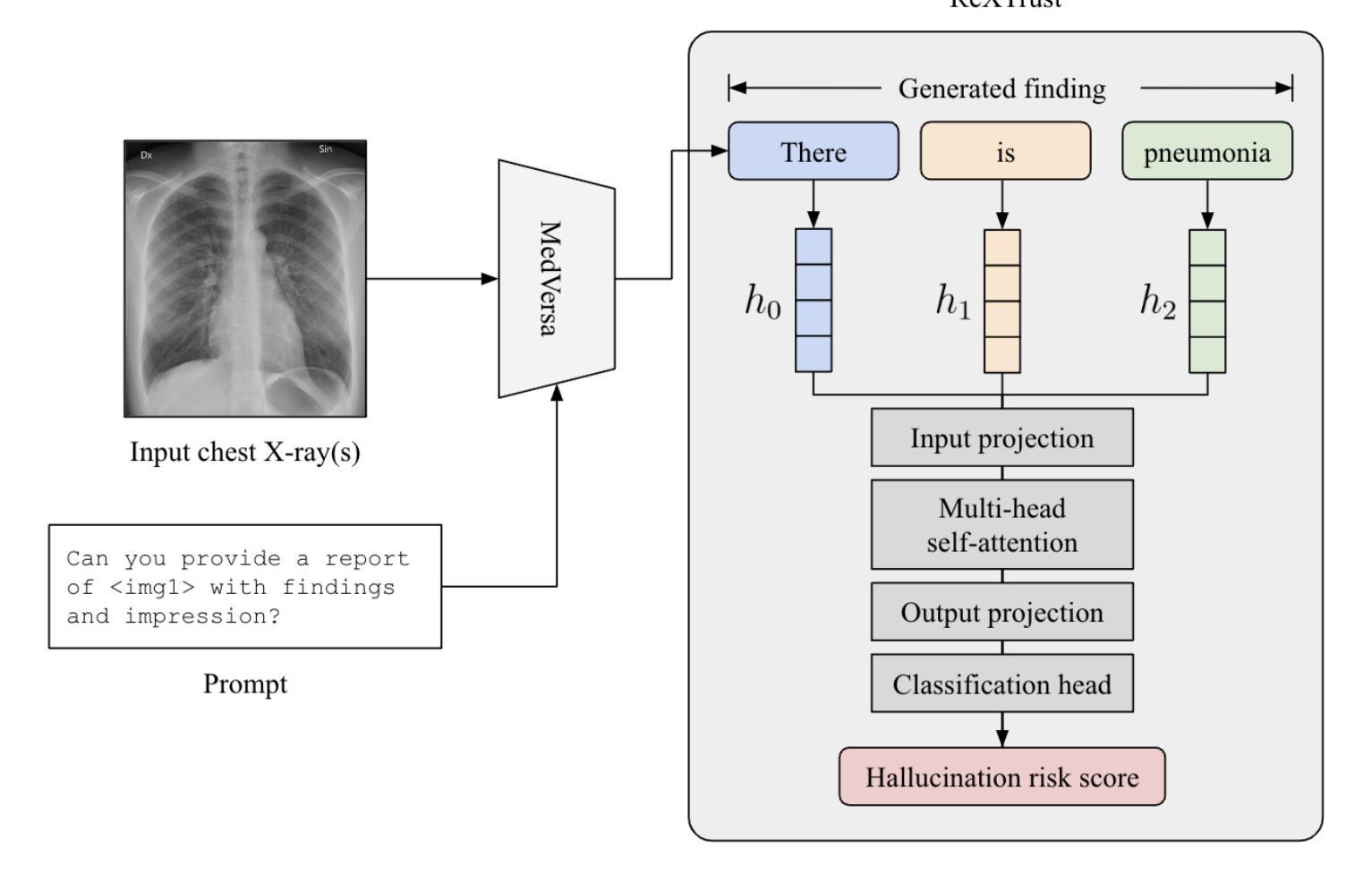
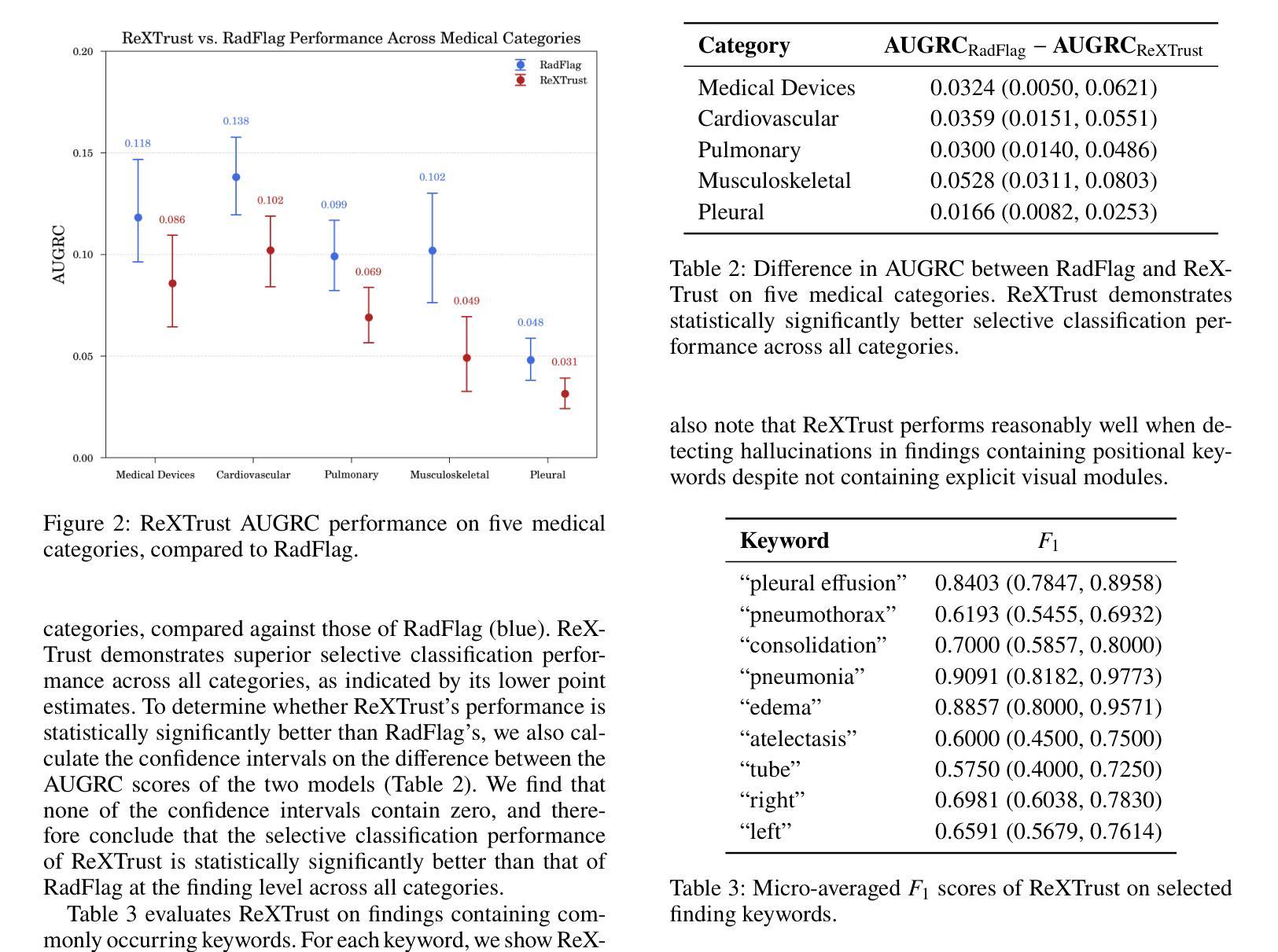
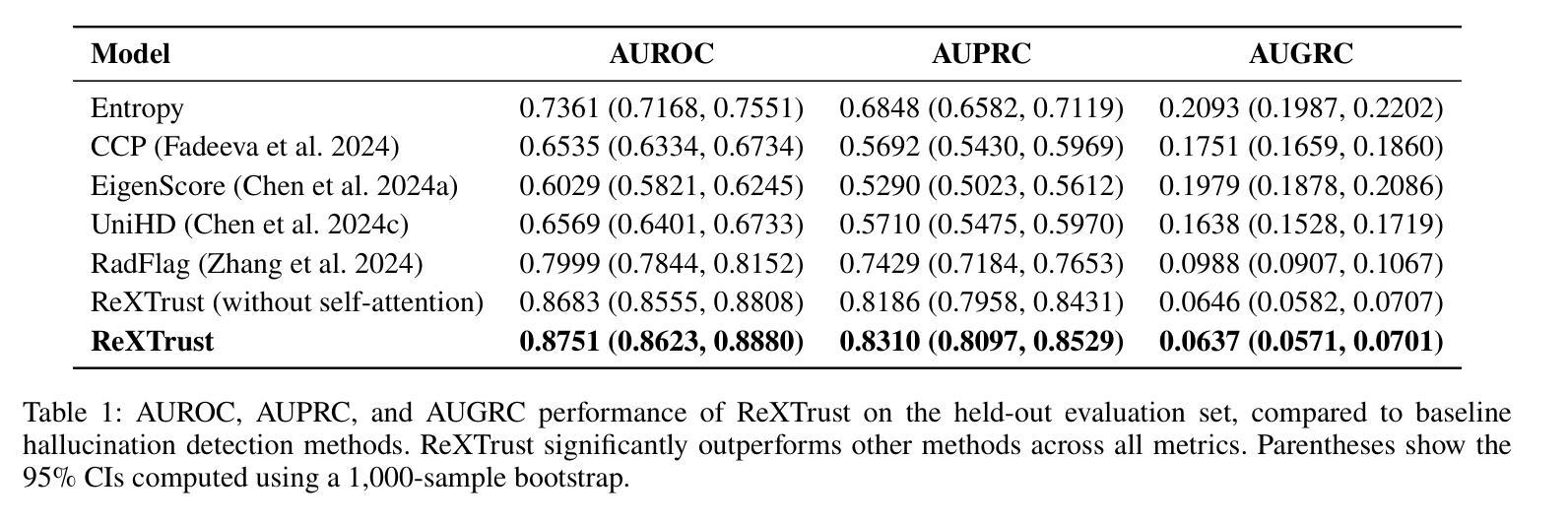
ReXTrust: A Model for Fine-Grained Hallucination Detection in AI-Generated Radiology Reports
Authors:Romain Hardy, Sung Eun Kim, Pranav Rajpurkar
The increasing adoption of AI-generated radiology reports necessitates robust methods for detecting hallucinations–false or unfounded statements that could impact patient care. We present ReXTrust, a novel framework for fine-grained hallucination detection in AI-generated radiology reports. Our approach leverages sequences of hidden states from large vision-language models to produce finding-level hallucination risk scores. We evaluate ReXTrust on a subset of the MIMIC-CXR dataset and demonstrate superior performance compared to existing approaches, achieving an AUROC of 0.8751 across all findings and 0.8963 on clinically significant findings. Our results show that white-box approaches leveraging model hidden states can provide reliable hallucination detection for medical AI systems, potentially improving the safety and reliability of automated radiology reporting.
随着AI生成的放射学报告越来越多地被采纳,需要可靠的检测幻象(可能对患者护理产生影响的不真实或没有根据的陈述)的方法。我们提出了ReXTrust,这是一个用于精细粒度幻象检测的新型框架,适用于AI生成的放射学报告。我们的方法利用大型视觉语言模型的隐藏状态序列来生成发现级别的幻象风险分数。我们在MIMIC-CXR数据集的一个子集上评估了ReXTrust,并展示了相较于现有方法的卓越性能,在所有发现中的AUROC达到0.8751,在具有临床意义上的发现中达到0.8963。我们的结果表明,利用模型隐藏状态的white-box方法可以为医疗AI系统提供可靠的幻象检测,从而提高自动放射报告的可靠性和安全性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to AIMedHealth 10 pages, 5 figures
Summary
基于人工智能生成的医学影像报告中的假或未经证实陈述对患者护理可能产生的影响,需要强大的方法来检测这些陈述的可靠性。本文介绍了ReXTrust,这是一种用于精细粒度幻觉检测的新颖框架。我们的方法利用大型视觉语言模型的隐藏状态序列来生成发现级别的幻觉风险分数。在MIMIC-CXR数据集的一个子集上评估ReXTrust,显示出比现有方法更高的性能,所有发现达到AUROC的0.8751,临床重要发现达到AUROC的0.8963。我们的结果表明,利用模型隐藏状态的白色盒子方法可为医疗人工智能系统提供可靠的幻觉检测,从而可能提高自动化医学影像报告的可靠性和安全性。
Key Takeaways
- AI生成的医学影像报告中存在假或未经证实陈述的风险。
- ReXTrust是一种用于精细粒度幻觉检测的框架。
- ReXTrust利用大型视觉语言模型的隐藏状态序列来生成发现级别的幻觉风险分数。
- 在MIMIC-CXR数据集上评估ReXTrust,显示出优越的性能。
- ReXTrust在所有发现上的AUROC为0.8751,在具有临床意义发现上为0.8963。
- 利用模型隐藏状态的白色盒子方法可以可靠地检测医学人工智能系统中的幻觉。
点此查看论文截图

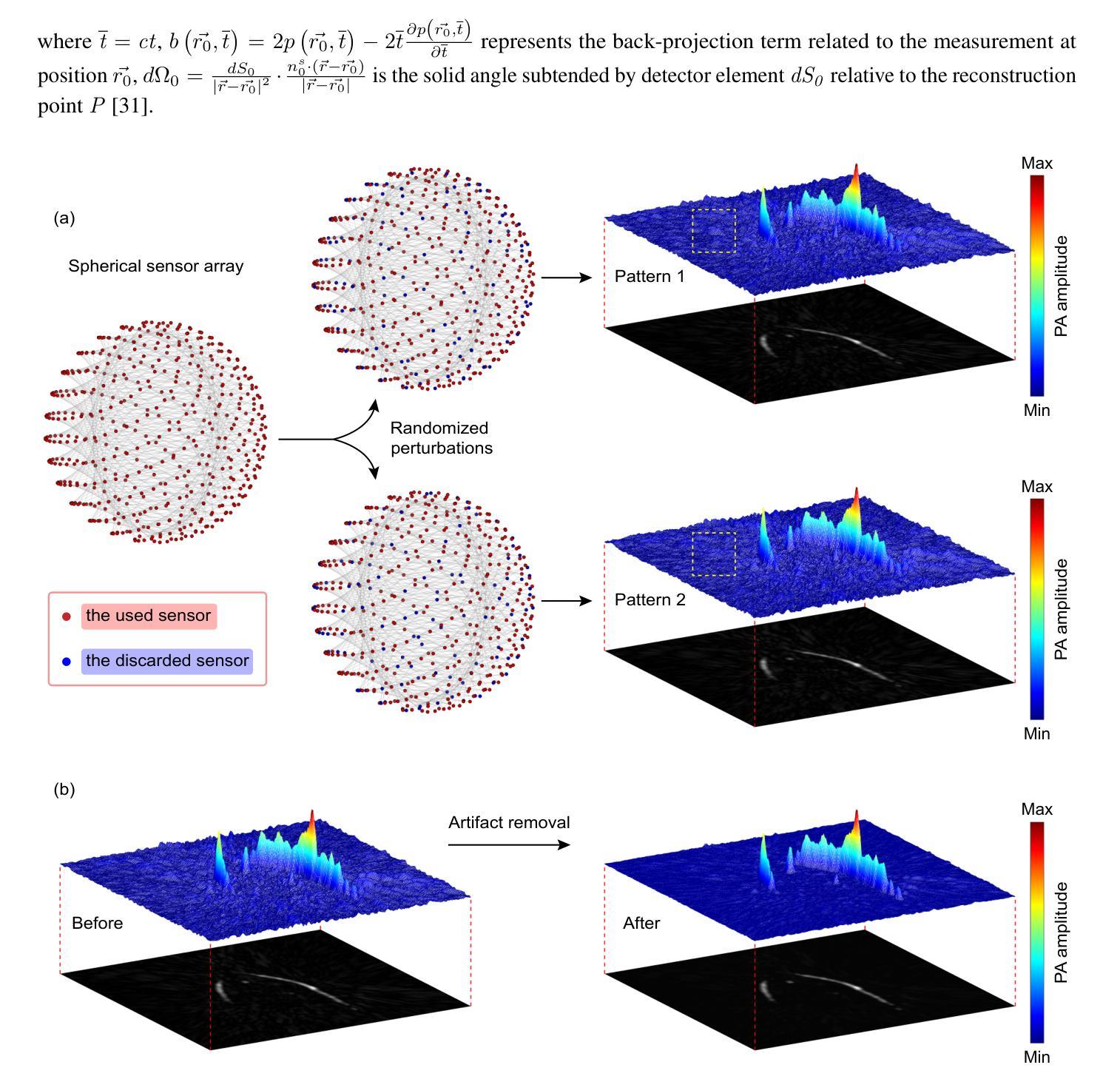
Zero-Shot Artifact2Artifact: Self-incentive artifact removal for photoacoustic imaging without any data
Authors:Shuang Li, Qian Chen, Chulhong Kim, Seongwook Choi, Yibing Wang, Yu Zhang, Changhui Li
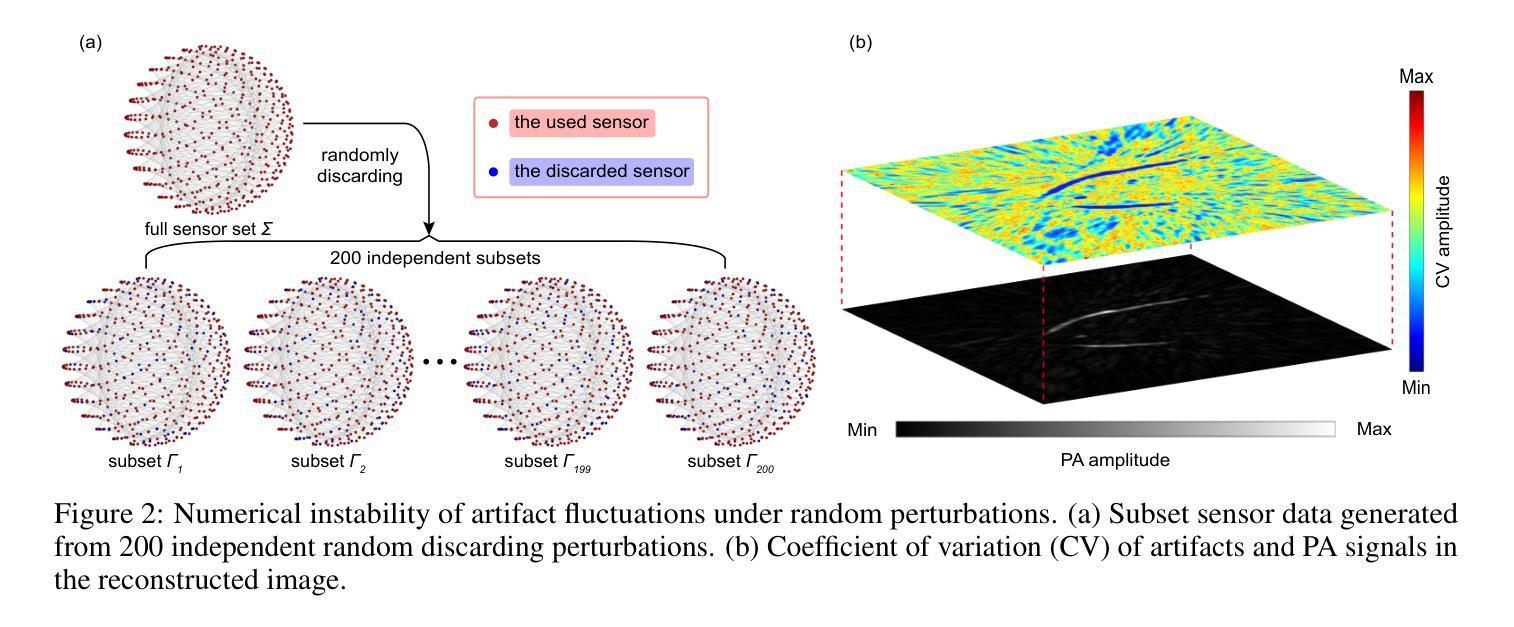
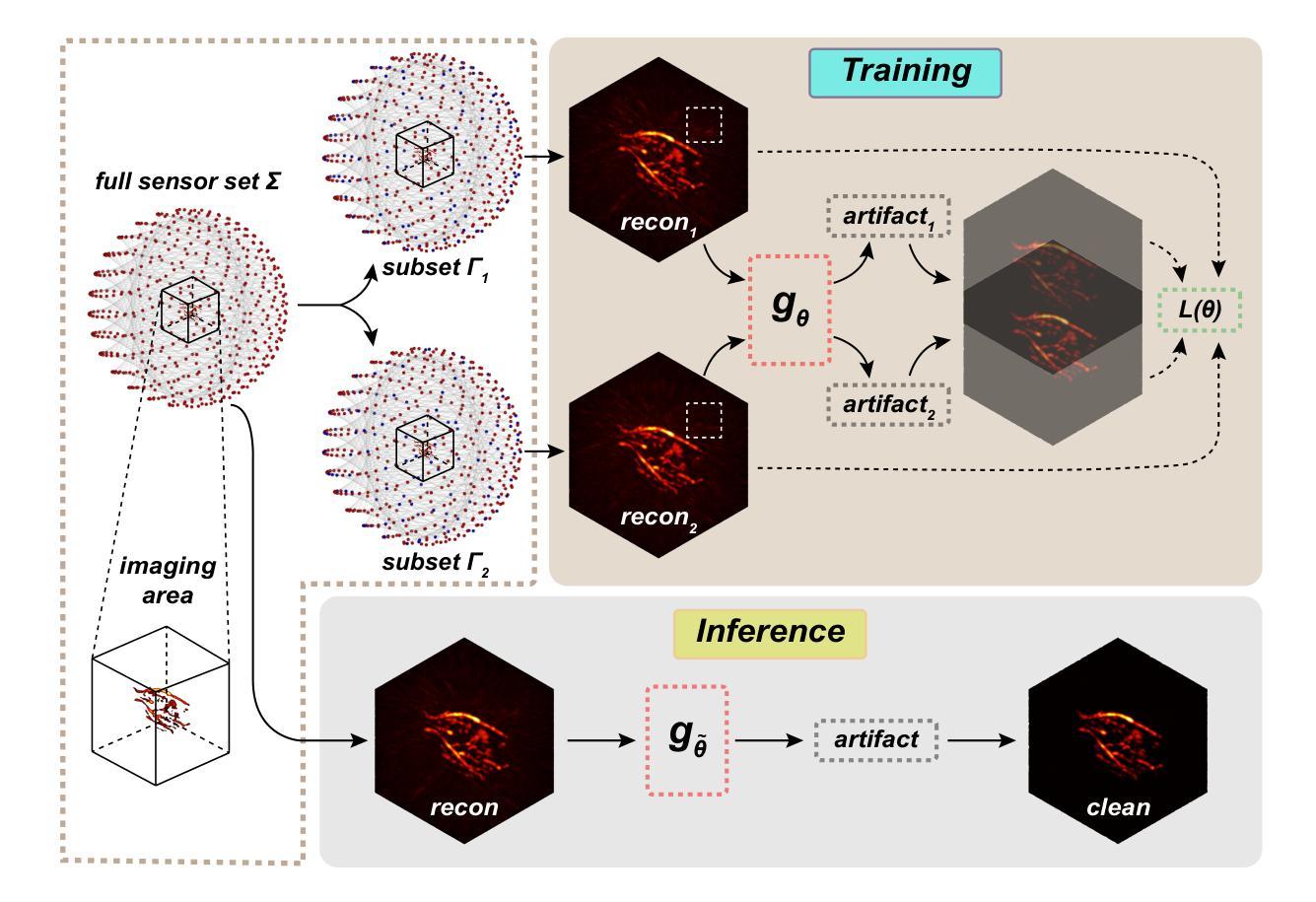
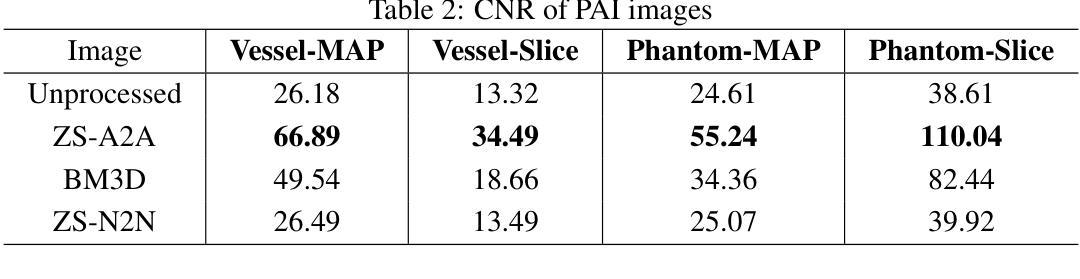
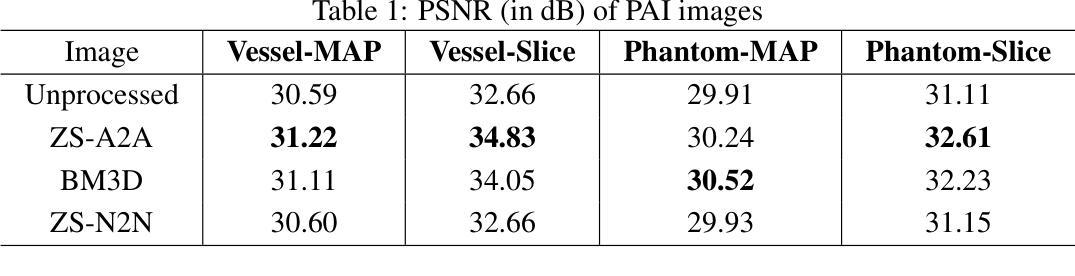
Photoacoustic imaging (PAI) uniquely combines optical contrast with the penetration depth of ultrasound, making it critical for clinical applications. However, the quality of 3D PAI is often degraded due to reconstruction artifacts caused by the sparse and angle-limited configuration of detector arrays. Existing iterative or deep learning-based methods are either time-consuming or require large training datasets, significantly limiting their practical application. Here, we propose Zero-Shot Artifact2Artifact (ZS-A2A), a zero-shot self-supervised artifact removal method based on a super-lightweight network, which leverages the fact that reconstruction artifacts are sensitive to irregularities caused by data loss. By introducing random perturbations to the acquired PA data, it spontaneously generates subset data, which in turn stimulates the network to learn the artifact patterns in the reconstruction results, thus enabling zero-shot artifact removal. This approach requires neither training data nor prior knowledge of the artifacts, and is capable of artifact removal for 3D PAI. For maximum amplitude projection (MAP) images or slice images in 3D PAI acquired with arbitrarily sparse or angle-limited detector arrays, ZS-A2A employs a self-incentive strategy to complete artifact removal and improves the Contrast-to-Noise Ratio (CNR). We validated ZS-A2A in both simulation study and $ in\ vivo $ animal experiments. Results demonstrate that ZS-A2A achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance compared to existing zero-shot methods, and for the $ in\ vivo $ rat liver, ZS-A2A improves CNR from 17.48 to 43.46 in just 8 seconds. The project for ZS-A2A will be available in the following GitHub repository: https://github.com/JaegerCQ/ZS-A2A.
光声成像(PAI)独特地结合了光学对比度和超声的穿透深度,使其成为临床应用的关键技术。然而,由于探测器阵列配置稀疏且角度受限导致的重建伪影,三维PAI的质量往往会下降。现有的迭代或基于深度学习的方法要么耗时过长,要么需要大量训练数据集,从而极大地限制了其实际应用。在这里,我们提出了基于超轻量级网络的零样本自监督伪影去除方法——Zero-Shot Artifact2Artifact(ZS-A2A)。该方法利用重建伪影对数据丢失引起的不规则性敏感的机制。通过对采集的PA数据进行随机扰动,它自发地生成子集数据,从而刺激网络学习重建结果中的伪影模式,从而实现零样本伪影去除。这种方法既不需要训练数据,也不需要事先了解伪影信息,并且能够对三维PAI进行伪影去除。对于使用任意稀疏或角度受限的探测器阵列获得的三维PAI的最大振幅投影图像或切片图像,ZS-A2A采用自我激励策略完成伪影去除,提高了信噪比(CNR)。我们通过仿真研究和体内动物实验验证了ZS-A2A的有效性。结果表明,与现有的零样本方法相比,ZS-A2A达到了最先进的性能;对于体内大鼠肝脏实验,ZS-A2A在短短8秒内将CNR从17.48提高到43.46。ZS-A2A的项目将在以下GitHub仓库中提供:https://github.com/JaegerCQ/ZS-A2A。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于零样本自监督的去除光声成像(PAI)重建伪影的方法——Zero-Shot Artifact2Artifact(ZS-A2A)。该方法利用超轻量级网络,通过引入随机扰动到获取的PA数据,自发地生成子集数据,从而学习重建结果中的伪影模式,实现零样本伪影去除。该方法既不需要训练数据,也不需要事先了解伪影信息,并能有效去除3D PAI中的伪影。实验验证显示,ZS-A2A在模拟研究和体内动物实验中均实现了卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 光声成像(PAI)结合了光学对比度和超声波的穿透深度,对于临床应用至关重要。
- 3D PAI的质量通常由于探测器阵列的稀疏和角度限制配置而受到影响,导致重建伪影。
- 现有方法,如迭代或深度学习,存在耗时长或需要大量训练数据的问题,限制了实际应用。
- ZS-A2A方法基于零样本自监督学习,利用超轻量级网络去除重建伪影。
- ZS-A2A通过引入随机扰动到获取的PA数据,自发生成子集数据,刺激网络学习伪影模式。
- ZS-A2A既不需要训练数据,也不需要关于伪影的先验知识,能有效去除3D PAI中的伪影。
- 实验验证显示,ZS-A2A在模拟研究和体内动物实验中均表现出卓越性能,显著提高对比噪声比(CNR)。
点此查看论文截图

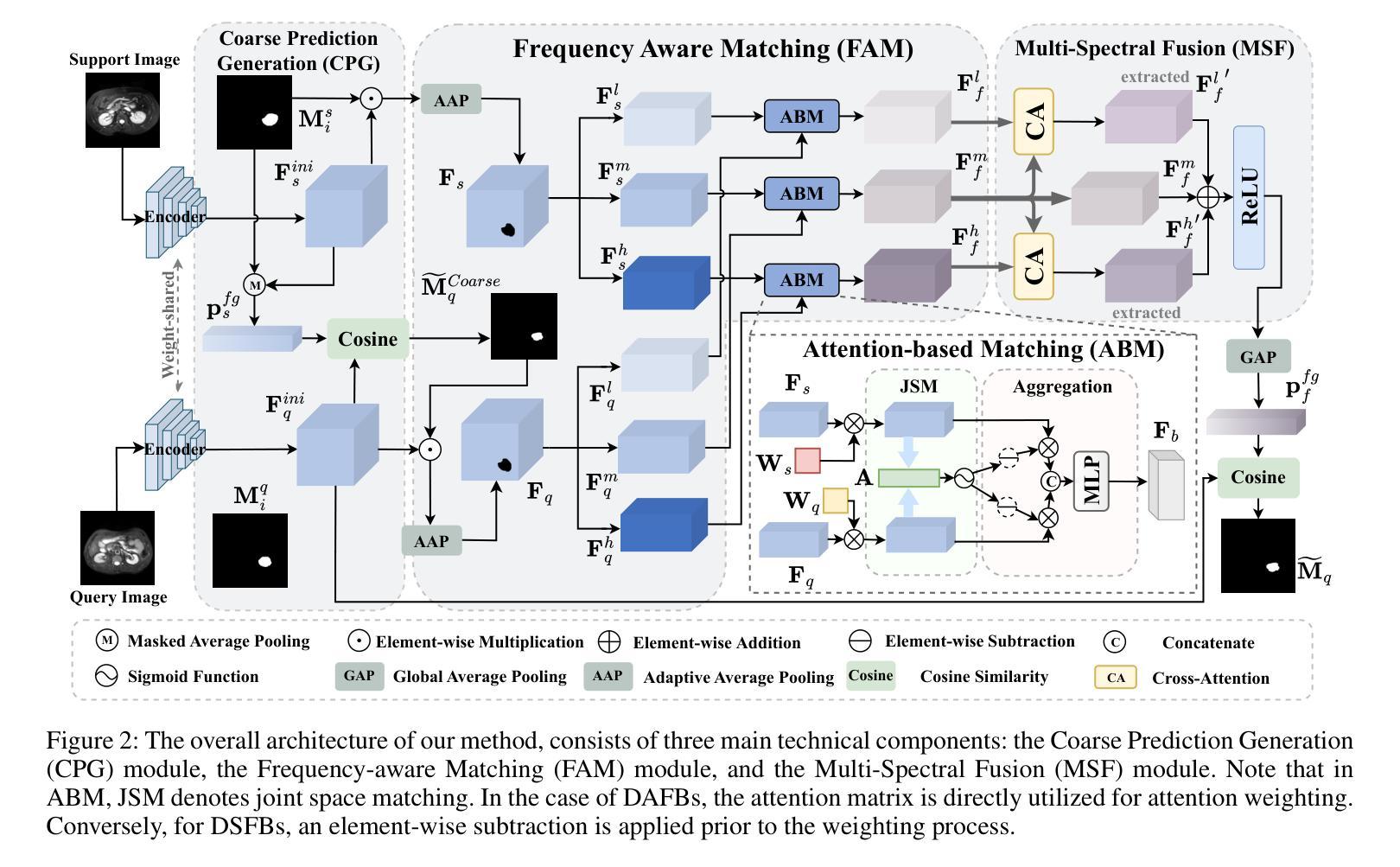
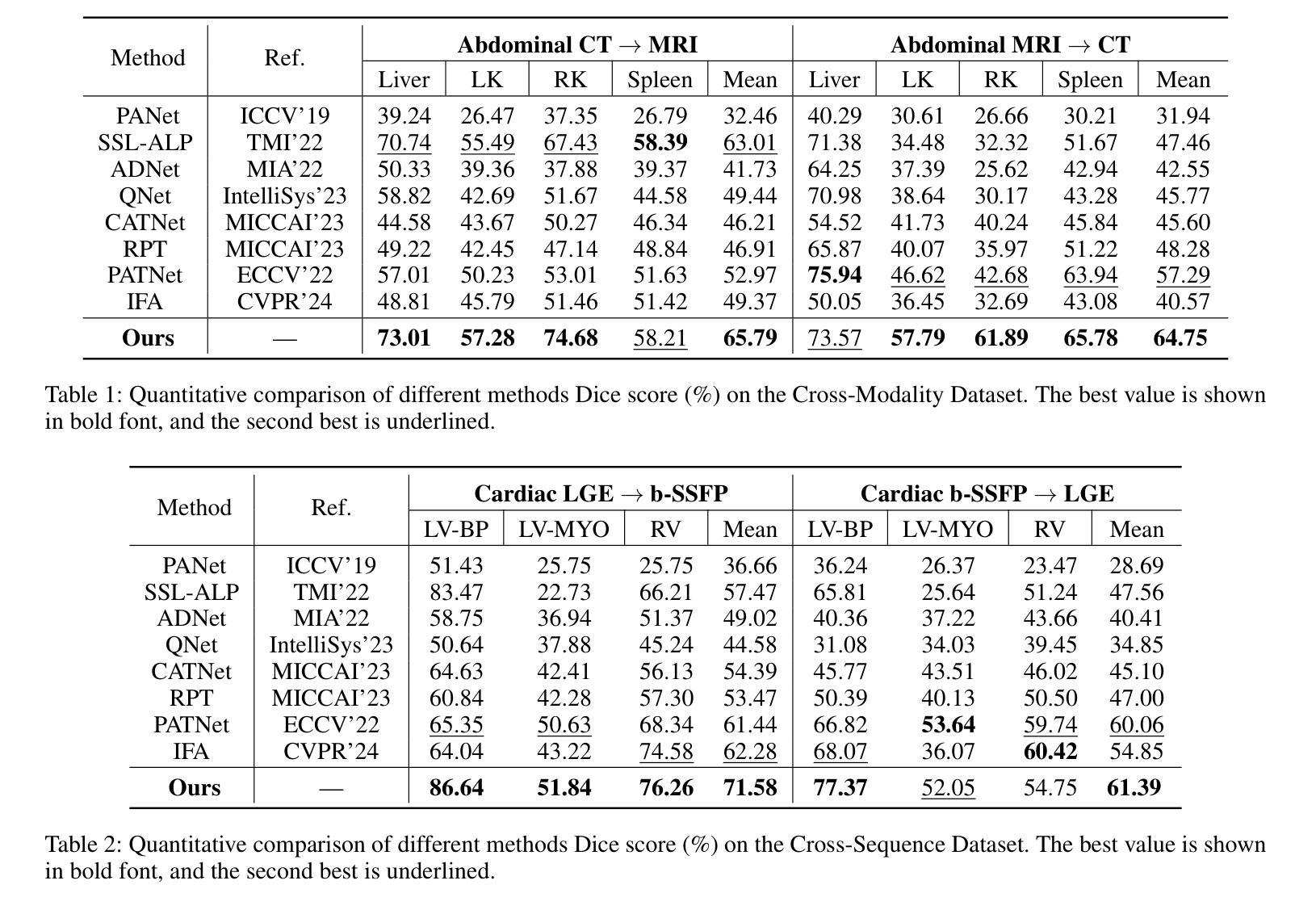
FAMNet: Frequency-aware Matching Network for Cross-domain Few-shot Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Yuntian Bo, Yazhou Zhu, Lunbo Li, Haofeng Zhang
Existing few-shot medical image segmentation (FSMIS) models fail to address a practical issue in medical imaging: the domain shift caused by different imaging techniques, which limits the applicability to current FSMIS tasks. To overcome this limitation, we focus on the cross-domain few-shot medical image segmentation (CD-FSMIS) task, aiming to develop a generalized model capable of adapting to a broader range of medical image segmentation scenarios with limited labeled data from the novel target domain. Inspired by the characteristics of frequency domain similarity across different domains, we propose a Frequency-aware Matching Network (FAMNet), which includes two key components: a Frequency-aware Matching (FAM) module and a Multi-Spectral Fusion (MSF) module. The FAM module tackles two problems during the meta-learning phase: 1) intra-domain variance caused by the inherent support-query bias, due to the different appearances of organs and lesions, and 2) inter-domain variance caused by different medical imaging techniques. Additionally, we design an MSF module to integrate the different frequency features decoupled by the FAM module, and further mitigate the impact of inter-domain variance on the model’s segmentation performance. Combining these two modules, our FAMNet surpasses existing FSMIS models and Cross-domain Few-shot Semantic Segmentation models on three cross-domain datasets, achieving state-of-the-art performance in the CD-FSMIS task.
现有的小样医疗图像分割模型(FSMIS)无法解决医学成像中的一个实际问题:由于不同成像技术导致的领域偏移,限制了其在当前FSMIS任务中的应用。为了克服这一局限性,我们专注于跨领域小样医疗图像分割(CD-FSMIS)任务,旨在开发一种通用模型,能够在有限的新目标领域标记数据的情况下,适应更广泛的医疗图像分割场景。我们受到不同领域间频率域相似性特征的启发,提出了一种频率感知匹配网络(FAMNet),它包括两个关键组件:频率感知匹配(FAM)模块和多光谱融合(MSF)模块。FAM模块解决了元学习阶段的两个问题:1)由于器官和病变的不同外观导致的域内方差(intra-domain variance)和由不同医学成像技术导致的域间方差(inter-domain variance)。此外,我们设计了一个MSF模块,以整合由FAM模块分离的不同的频率特征,并进一步减轻跨域方差对模型分割性能的影响。结合这两个模块,我们的FAMNet在三个跨域数据集上的表现超越了现有的FSMIS模型和跨域小样语义分割模型,在CD-FSMIS任务中达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by the 39th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-25)
Summary
针对现有医学图像分割模型的局限性,提出了一个基于频率感知匹配网络(FAMNet)的跨域小样医学图像分割(CD-FSMIS)任务解决方案。通过FAM模块和MSF模块的协同作用,有效解决了由于不同成像技术引起的域漂移问题,提高了模型在有限标签数据下的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 现有医学图像分割模型面临跨域问题,即不同成像技术导致的域偏移限制了其适用性。
- 提出了一种新的跨域小样医学图像分割(CD-FSMIS)任务,旨在开发一个能够在有限标签数据下适应更广泛医学图像分割场景的通用模型。
- FAMNet模型由频率感知匹配(FAM)模块和多光谱融合(MSF)模块两个关键组件组成。
- FAM模块解决了元学习阶段的两个主要问题:由于器官和病变的不同外观引起的域内方差以及由于不同医学成像技术引起的域间方差。
- MSF模块旨在整合由FAM模块分离的不同的频率特征,进一步减轻域间方差对模型分割性能的影响。
- FAMNet在三个跨域数据集上的表现超过了现有的FSMIS模型和跨域小样语义分割模型,在CD-FSMIS任务中达到了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

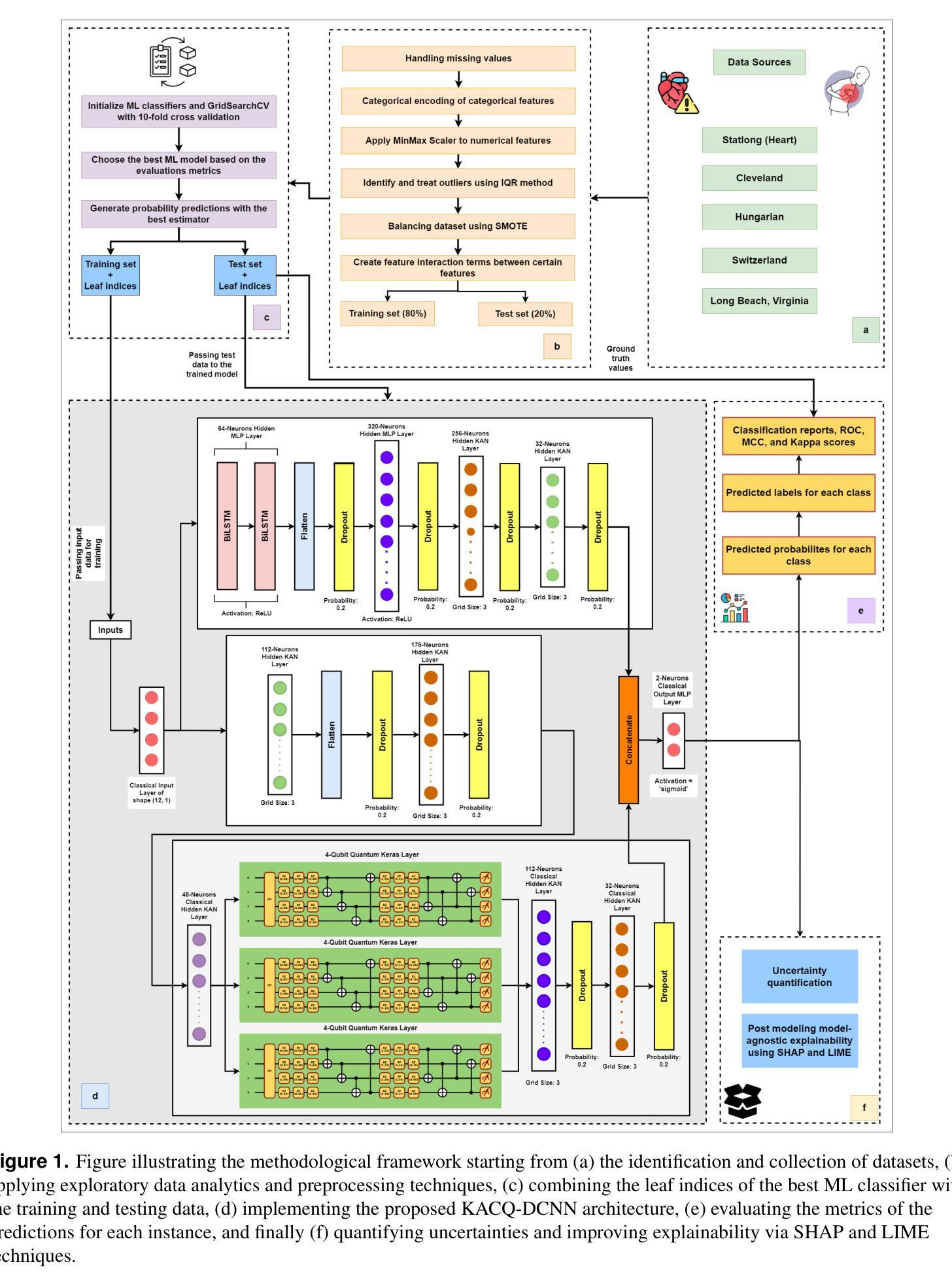
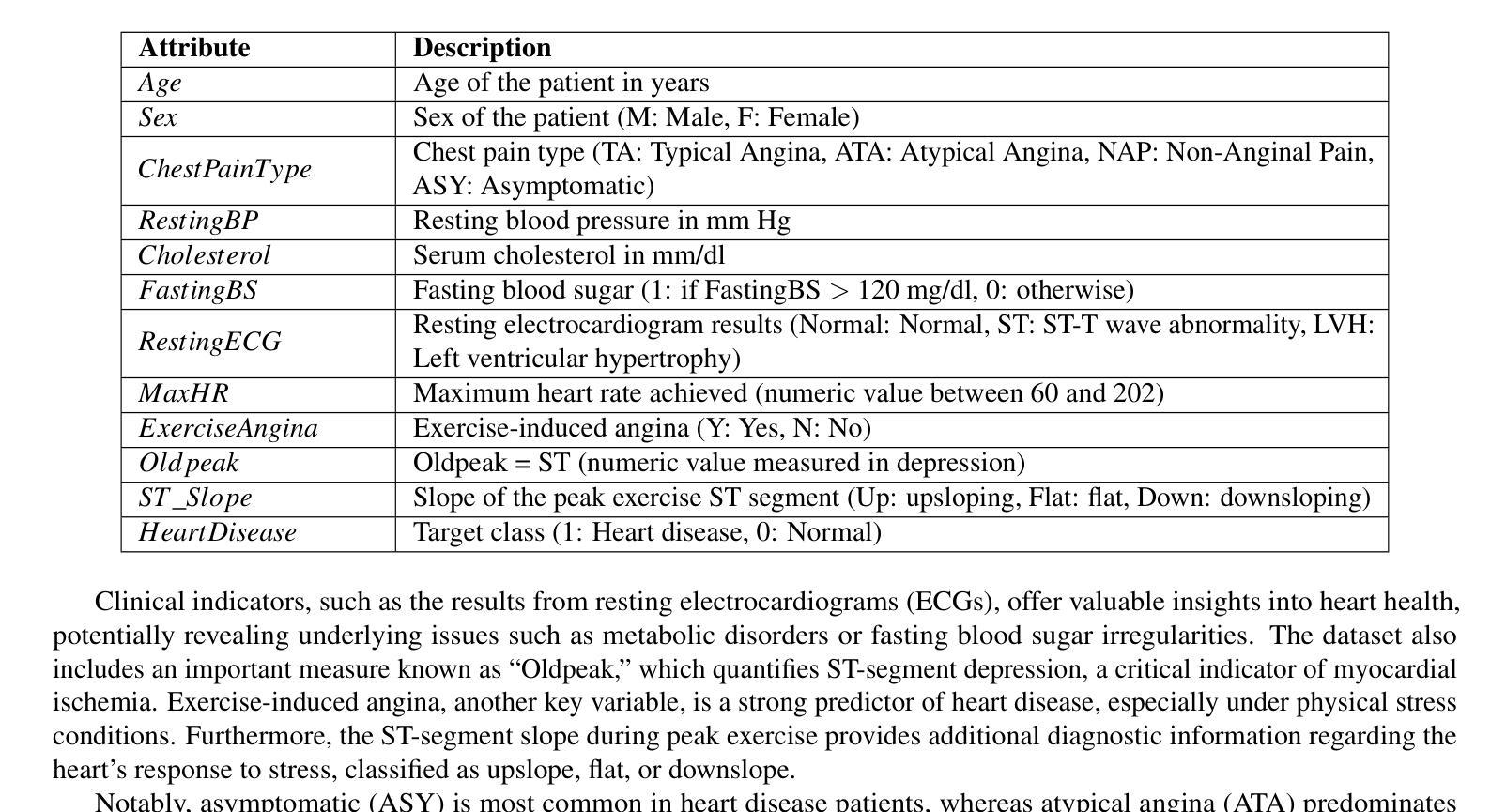
KACQ-DCNN: Uncertainty-Aware Interpretable Kolmogorov-Arnold Classical-Quantum Dual-Channel Neural Network for Heart Disease Detection
Authors:Md Abrar Jahin, Md. Akmol Masud, M. F. Mridha, Zeyar Aung, Nilanjan Dey
Heart failure is a leading cause of global mortality, necessitating improved diagnostic strategies. Classical machine learning models struggle with challenges such as high-dimensional data, class imbalances, poor feature representations, and lack of interpretability. While quantum machine learning holds promise, current hybrid models have not fully exploited quantum advantages. In this paper, we propose the Kolmogorov-Arnold Classical-Quantum Dual-Channel Neural Network (KACQ-DCNN), a novel hybrid architecture that replaces traditional multilayer perceptrons with Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs), enabling learnable univariate activation functions. Our KACQ-DCNN 4-qubit, 1-layer model outperforms 37 benchmark models, including 16 classical and 12 quantum neural networks, achieving an accuracy of 92.03%, with macro-average precision, recall, and F1 scores of 92.00%. It also achieved a ROC-AUC of 94.77%, surpassing other models by significant margins, as validated by paired t-tests with a significance threshold of 0.0056 (after Bonferroni correction). Ablation studies highlight the synergistic effect of classical-quantum integration, improving performance by about 2% over MLP variants. Additionally, LIME and SHAP explainability techniques enhance feature interpretability, while conformal prediction provides robust uncertainty quantification. Our results demonstrate that KACQ-DCNN improves cardiovascular diagnostics by combining high accuracy with interpretability and uncertainty quantification.
心力衰竭是全球主要的死亡原因之一,需要改进诊断策略。经典机器学习模型面临高维数据、类别不平衡、特征表示不佳和缺乏可解释性等方面的挑战。虽然量子机器学习很有前景,但当前的混合模型还没有完全发挥量子优势。在本文中,我们提出了Kolmogorov-Arnold经典-量子双通道神经网络(KACQ-DCNN),这是一种新型混合架构,用Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KANs)替代了传统的多层感知器,使学习单变量激活函数成为可能。我们的KACQ-DCNN是一个4量子位、1层的模型,表现优于37种基准模型,包括16种经典模型和12种量子神经网络,准确率达到了92.03%,宏观平均精度、召回率和F1分数均为92.00%。其ROC-AUC达到了94.77%,超越其他模型一大截,这一结果通过配对t检验得到验证,显著性阈值为0.0056(经Bonferroni校正后)。消融研究突出了经典与量子集成的协同作用,与多层感知机变种相比,性能提高了约2%。此外,LIME和SHAP的可解释性技术提高了特征的可解释性,而顺应性预测提供了稳健的不确定性量化。我们的结果证明,KACQ-DCNN通过结合高准确性、可解释性和不确定性量化,改进了心血管疾病的诊断。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出一种新型混合神经网络架构——Kolmogorov-Arnold经典量子双通道神经网络(KACQ-DCNN),用于心脏衰竭的诊断。该架构采用Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KAN)替代传统多层感知器,实现可学习的单变量激活函数。KACQ-DCNN模型在心脏衰竭诊断上表现出优异的性能,相较于37种基准模型,其准确率高达92.03%,同时具有较高的宏平均精确度、召回率和F1得分。此外,该模型还具有良好的可解释性和不确定性量化能力。
关键见解
- KACQ-DCNN是一种新型的混合神经网络架构,结合了经典机器学习和量子机器学习的优势。
- 该架构采用Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KAN),使模型能够处理高维数据、类不平衡和特征表示不良等问题。
- KACQ-DCNN在心脏衰竭诊断方面表现出较高的准确率,达到92.03%,并具有较高的宏平均精确度、召回率和F1得分。
- 模型通过LIME和SHAP解释性技术提高了特征的可解释性,使得诊断结果更易于理解。
- 通过配对t检验验证了模型的性能优势,并证明了其在显著性水平下的稳定性。
- 消融研究显示了经典与量子整合的协同作用,相较于多层感知器变体,性能提高了约2%。
点此查看论文截图

Feasibility Study of a Diffusion-Based Model for Cross-Modal Generation of Knee MRI from X-ray: Integrating Radiographic Feature Information
Authors:Zhe Wang, Yung Hsin Chen, Aladine Chetouani, Fabian Bauer, Yuhua Ru, Fang Chen, Liping Zhang, Rachid Jennane, Mohamed Jarraya
Knee osteoarthritis (KOA) is a prevalent musculoskeletal disorder, often diagnosed using X-rays due to its cost-effectiveness. While Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) provides superior soft tissue visualization and serves as a valuable supplementary diagnostic tool, its high cost and limited accessibility significantly restrict its widespread use. To explore the feasibility of bridging this imaging gap, we conducted a feasibility study leveraging a diffusion-based model that uses an X-ray image as conditional input, alongside target depth and additional patient-specific feature information, to generate corresponding MRI sequences. Our findings demonstrate that the MRI volumes generated by our approach is visually closer to real MRI scans. Moreover, increasing inference steps enhances the continuity and smoothness of the synthesized MRI sequences. Through ablation studies, we further validate that integrating supplementary patient-specific information, beyond what X-rays alone can provide, enhances the accuracy and clinical relevance of the generated MRI, which underscores the potential of leveraging external patient-specific information to improve the MRI generation. This study is available at https://zwang78.github.io/.
膝关节骨关节炎(KOA)是一种常见的骨骼肌肉疾病,由于其成本效益高,通常通过X射线进行诊断。虽然磁共振成像(MRI)提供了出色的软组织可视化效果,并作为有价值的辅助诊断工具,但其高昂的成本和有限的可及性极大地限制了其广泛应用。为了探索缩小这一成像差距的可行性,我们进行了一项可行性研究,利用基于扩散的模型,以X射线图像作为条件输入,同时以目标深度和额外的患者特定特征信息,生成相应的MRI序列。我们的研究结果表明,通过我们的方法生成的MRI体积在视觉上更接近真实的MRI扫描结果。而且,增加推理步骤可以提高合成MRI序列的连续性和平滑度。通过消融研究,我们进一步验证了除了X射线所提供的之外,整合额外的患者特定信息可以提高生成的MRI的准确性和临床相关性,这突显了利用外部患者特定信息改善MRI生成的潜力。该研究可通过以下网址获取:https://zwang78.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了膝关节骨关节炎(KOA)的影像诊断问题。研究利用扩散模型,以X光图像为条件输入,结合目标深度和患者特定特征信息,生成相应的MRI序列。研究结果表明,该方法生成的MRI体积在视觉上更接近真实MRI扫描结果,增加推理步骤可提高合成MRI序列的连续性和平滑度。通过消融研究验证了结合患者特定信息能提高生成的MRI准确性和临床相关性。
Key Takeaways
- 膝关节骨关节炎(KOA)是常见的肌肉骨骼疾病,通常使用X光进行成本效益诊断。
- 核磁共振成像(MRI)能提供优质的软组织可视化效果,是宝贵的辅助诊断工具,但其高昂成本和有限的可访问性限制了广泛使用。
- 研究采用扩散模型,以X光图像为条件输入,生成相应的MRI序列,以缩小影像诊断的差距。
- 生成MRI体积在视觉上更接近真实MRI扫描结果。
- 增加推理步骤可提高合成MRI序列的连续性和平滑度。
- 消融研究证明结合患者特定信息能提高生成的MRI准确性和临床相关性。
点此查看论文截图

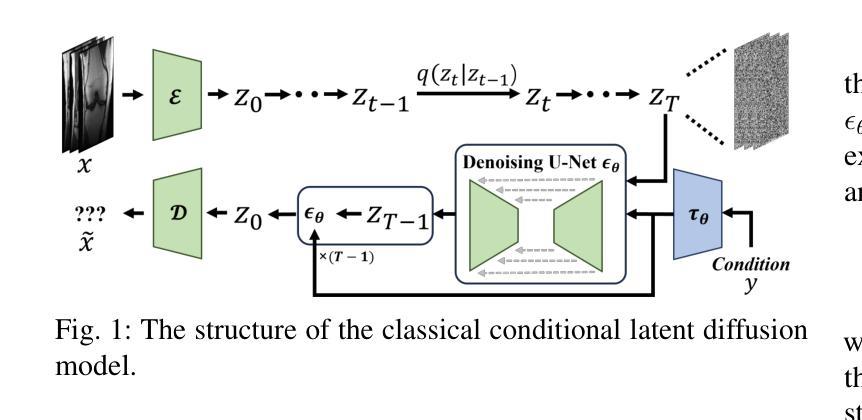
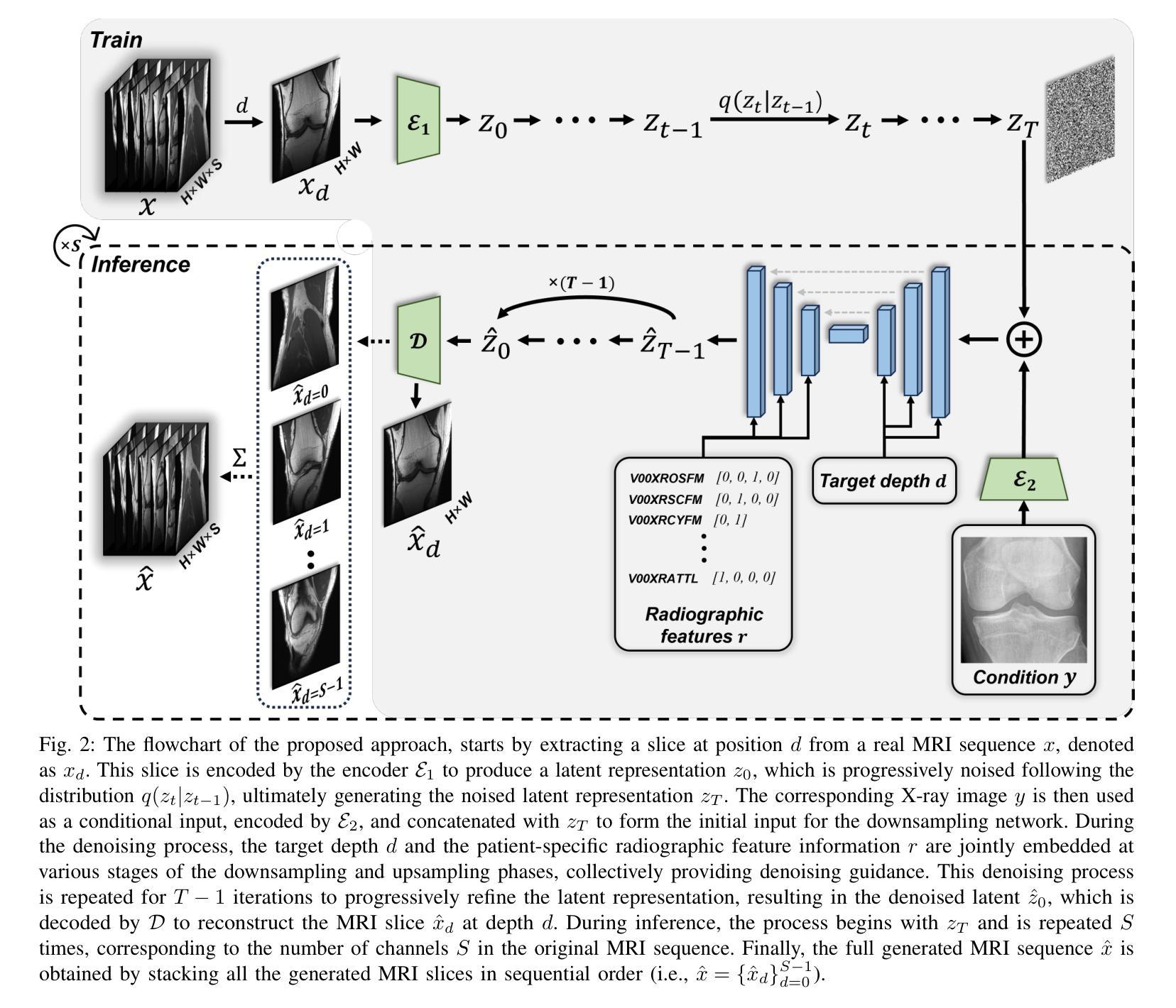

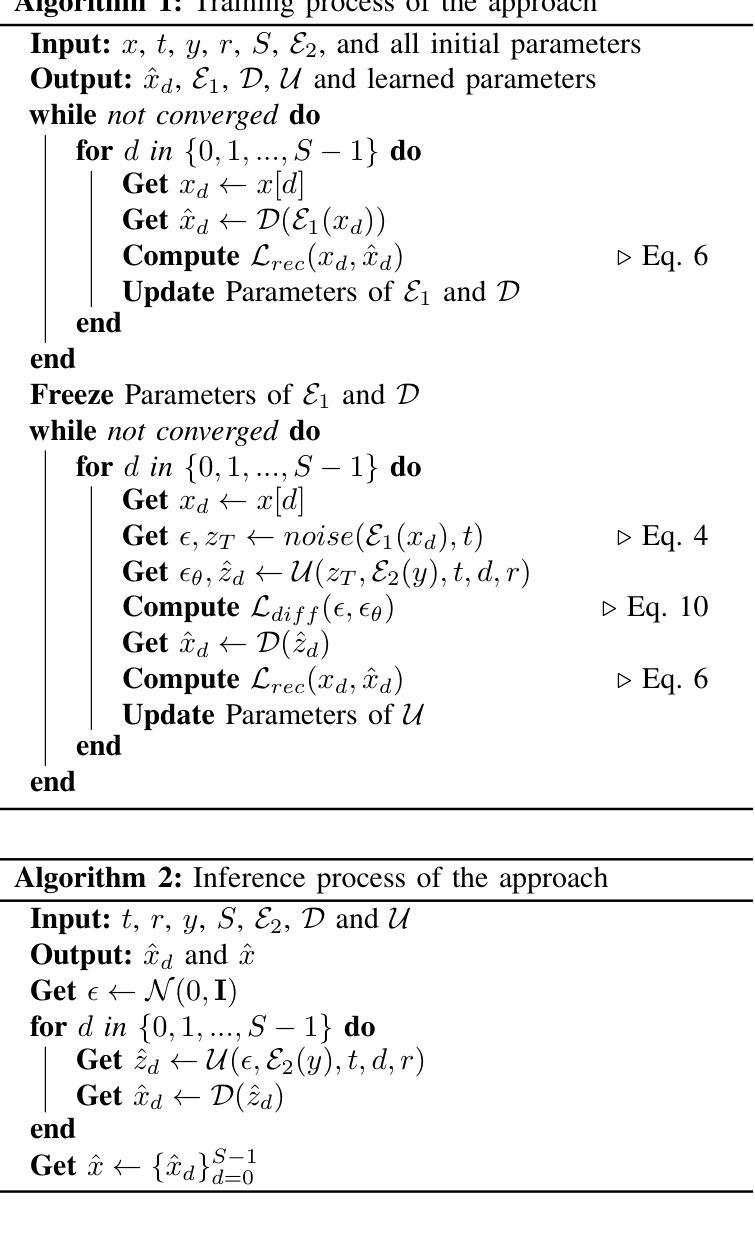
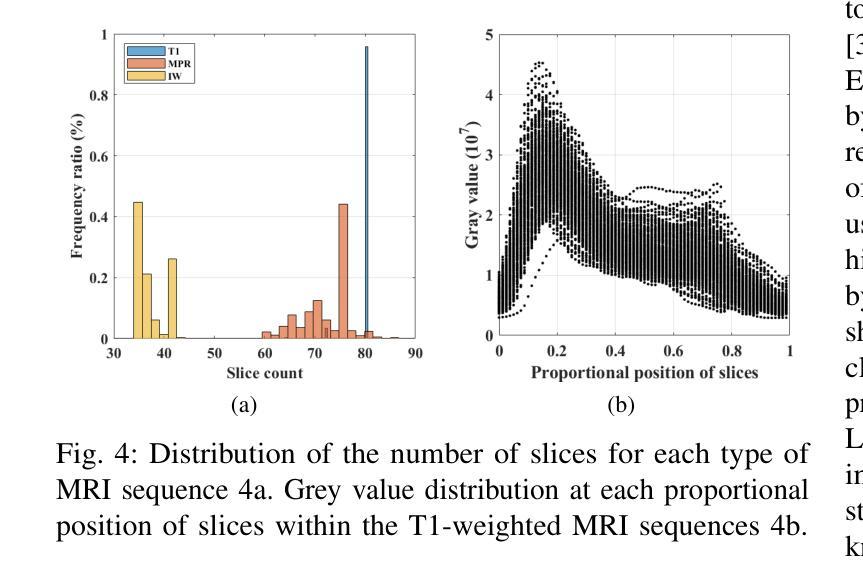
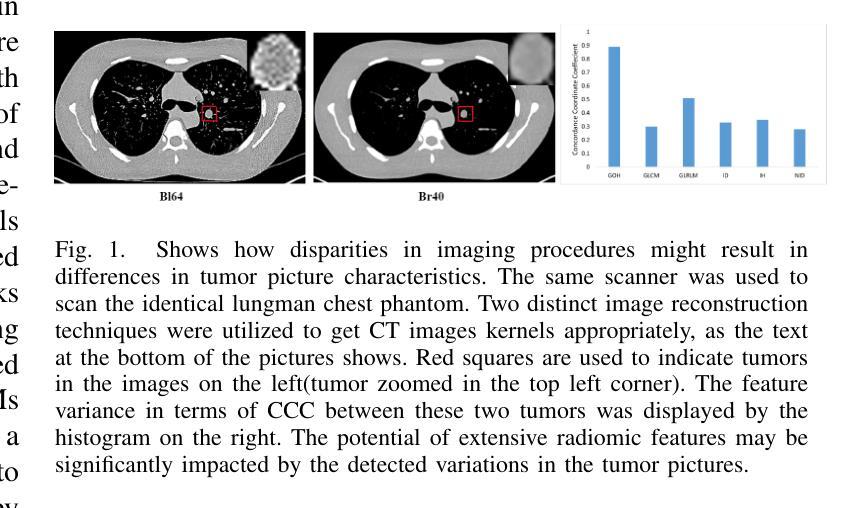
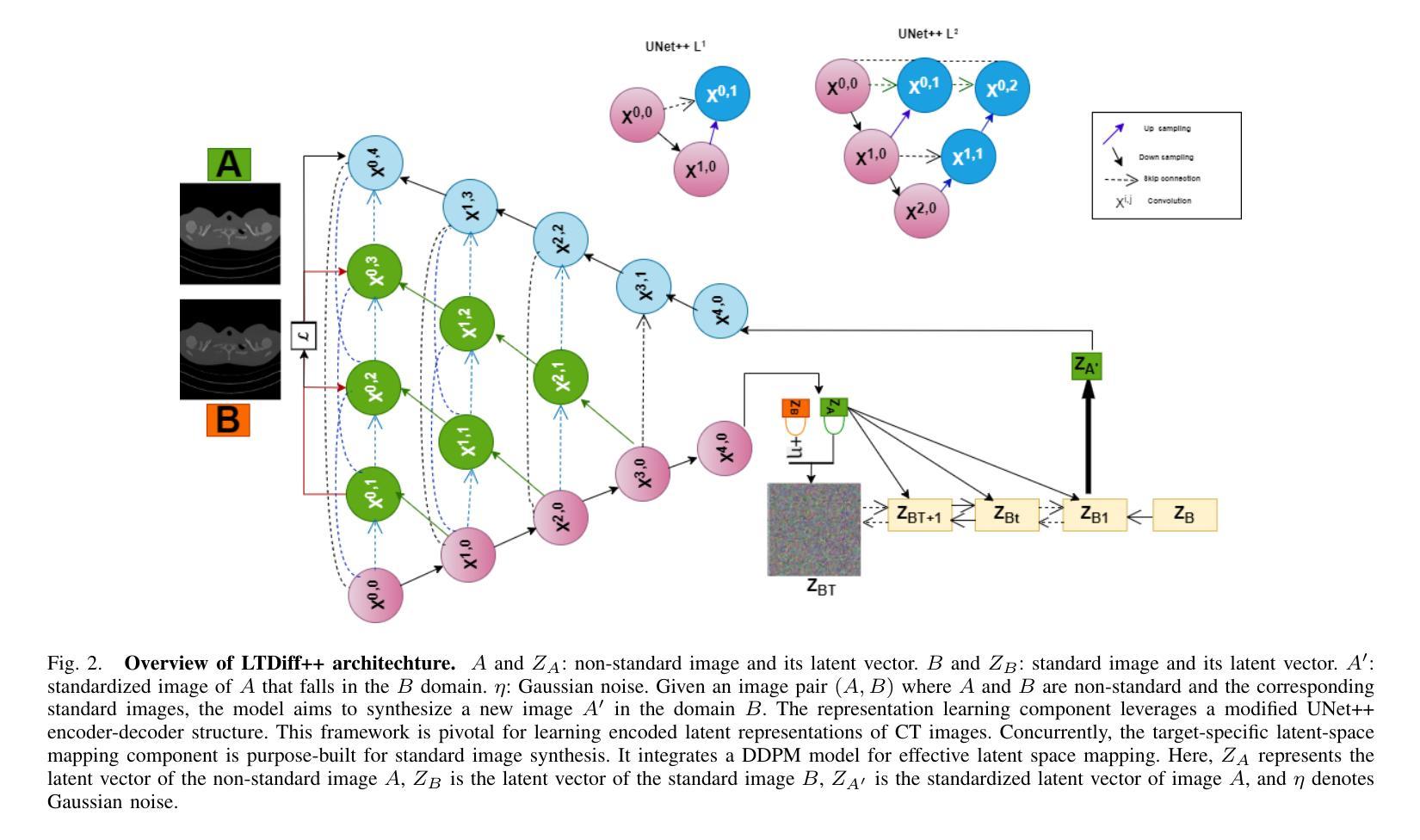
Multiscale Latent Diffusion Model for Enhanced Feature Extraction from Medical Images
Authors:Rabeya Tus Sadia, Jie Zhang, Jin Chen
Various imaging modalities are used in patient diagnosis, each offering unique advantages and valuable insights into anatomy and pathology. Computed Tomography (CT) is crucial in diagnostics, providing high-resolution images for precise internal organ visualization. CT’s ability to detect subtle tissue variations is vital for diagnosing diseases like lung cancer, enabling early detection and accurate tumor assessment. However, variations in CT scanner models and acquisition protocols introduce significant variability in the extracted radiomic features, even when imaging the same patient. This variability poses considerable challenges for downstream research and clinical analysis, which depend on consistent and reliable feature extraction. Current methods for medical image feature extraction, often based on supervised learning approaches, including GAN-based models, face limitations in generalizing across different imaging environments. In response to these challenges, we propose LTDiff++, a multiscale latent diffusion model designed to enhance feature extraction in medical imaging. The model addresses variability by standardizing non-uniform distributions in the latent space, improving feature consistency. LTDiff++ utilizes a UNet++ encoder-decoder architecture coupled with a conditional Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model (DDPM) at the latent bottleneck to achieve robust feature extraction and standardization. Extensive empirical evaluations on both patient and phantom CT datasets demonstrate significant improvements in image standardization, with higher Concordance Correlation Coefficients (CCC) across multiple radiomic feature categories. Through these advancements, LTDiff++ represents a promising solution for overcoming the inherent variability in medical imaging data, offering improved reliability and accuracy in feature extraction processes.
在患者诊断中,各种成像模式被广泛应用,每种模式都有其独特的优势和对于解剖学和病理学有价值的见解。计算机断层扫描(CT)在诊断中至关重要,它提供高分辨率图像,用于精确的内部器官可视化。CT检测细微组织变化的能力对于诊断肺癌等疾病至关重要,能够实现早期检测和准确的肿瘤评估。然而,CT扫描仪型号和采集协议的差异会在提取放射学特征时引入重大变化,即使在为同一患者成像时也是如此。这种变化给下游研究和临床分析带来了巨大挑战,这些分析依赖于一致和可靠的特征提取。当前基于医学图像特征提取的方法,通常基于有监督学习方法,包括基于GAN的模型,在推广至不同成像环境时面临局限。为应对这些挑战,我们提出了LTDiff++,这是一种多尺度潜在扩散模型,旨在增强医学成像中的特征提取。该模型通过标准化潜在空间中的非均匀分布来解决变异性问题,提高特征的一致性。LTDiff++采用UNet++编码器-解码器架构,结合潜在瓶颈处的条件去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM),实现稳健的特征提取和标准化。在患者和幻影CT数据集上的大量实证评估表明,图像标准化的改进非常显著,多个放射学特征类别的符合度相关系数(CCC)有所提高。通过这些进步,LTDiff++是克服医学成像数据固有可变性的一个有前途的解决方案,为特征提取过程提供了改进的可信度和准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF version_3
Summary:
医学成像中多种模态的应用对于患者诊断至关重要,各有独特优势。计算机断层扫描(CT)在诊断中尤为重要,能生成高解析度图像,精确展示内部器官,对于如肺癌等疾病的诊断具有重要意义。然而,不同CT扫描仪型号和采集协议导致的放射组学特征提取差异,为下游研究和临床分析带来挑战。为应对这一问题,提出LTDiff++这一多尺度潜在扩散模型,通过标准化潜在空间的非均匀分布来提升医学成像的特征提取。模型利用UNet++编码器-解码器架构,结合潜在瓶颈处的条件去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM),实现稳健的特征提取和标准化。在患者和幻影CT数据集上的大量实证评估显示,图像标准化有明显改善,各类放射组学特征的符合度关联系数(CCC)更高。因此,LTDiff++是解决医学成像数据固有变异性的有前途的解决方案,可提升特征提取的可靠性和准确性。
Key Takeaways:
- 医学成像中多种成像模态的应用为患者诊断提供了独特的优势。
- CT扫描在诊断中起关键作用,能够早期检测并准确评估肿瘤。
- 不同CT扫描仪和采集协议导致特征提取的显著变化,为下游研究和临床分析带来挑战。
- LTDiff++模型被提出以解决这一问题,通过标准化潜在空间的非均匀分布来提升医学成像的特征提取。
- LTDiff++利用UNet++和条件DDPM来实现稳健的特征提取和标准化。
- 在多个数据集上的实证评估显示,LTDiff++在图像标准化方面有明显改善。
点此查看论文截图

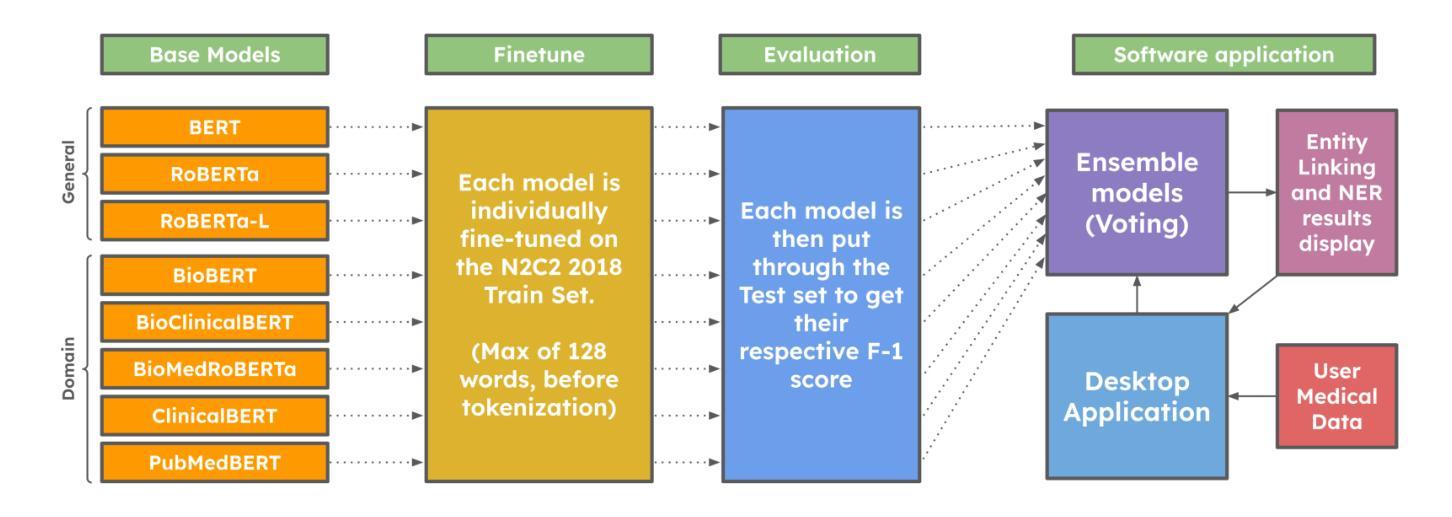
INSIGHTBUDDY-AI: Medication Extraction and Entity Linking using Large Language Models and Ensemble Learning
Authors:Pablo Romero, Lifeng Han, Goran Nenadic
Medication Extraction and Mining play an important role in healthcare NLP research due to its practical applications in hospital settings, such as their mapping into standard clinical knowledge bases (SNOMED-CT, BNF, etc.). In this work, we investigate state-of-the-art LLMs in text mining tasks on medications and their related attributes such as dosage, route, strength, and adverse effects. In addition, we explore different ensemble learning methods (\textsc{Stack-Ensemble} and \textsc{Voting-Ensemble}) to augment the model performances from individual LLMs. Our ensemble learning result demonstrated better performances than individually fine-tuned base models BERT, RoBERTa, RoBERTa-L, BioBERT, BioClinicalBERT, BioMedRoBERTa, ClinicalBERT, and PubMedBERT across general and specific domains. Finally, we build up an entity linking function to map extracted medical terminologies into the SNOMED-CT codes and the British National Formulary (BNF) codes, which are further mapped to the Dictionary of Medicines and Devices (dm+d), and ICD. Our model’s toolkit and desktop applications are publicly available (at \url{https://github.com/HECTA-UoM/ensemble-NER}).
药物提取和挖掘在医疗保健NLP研究中发挥着重要作用,因为它在医院环境中的实际应用,例如将其映射到标准临床知识库(如SNOMED-CT、BNF等)。在这项工作中,我们调查了最先进的文本挖掘任务中的大型语言模型(LLMs),针对药物及其相关属性(如剂量、给药途径、强度和不良反应)进行研究。此外,我们还探索了不同的集成学习方法(Stack-Ensemble和Voting-Ensemble),以提高单个大型语言模型的性能。我们的集成学习结果显示,在一般和特定领域上,其性能均优于经过单独微调的基础模型,如BERT、RoBERTa、RoBERTa-L、BioBERT、BioClinicalBERT、BioMedRoBERTa、ClinicalBERT和PubMedBERT。最后,我们建立了一个实体链接功能,将提取的医疗术语映射到SNOMED-CT代码和英国国家配方集(BNF)代码,并进一步映射到药品和设备词典(dm+d)和ICD。我们的模型工具包和桌面应用程序已公开可用(网址:https://github.com/HECTA-UoM/ensemble-NER)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ongoing work, 24 pages
Summary
本文主要探讨了医药提取和挖掘在医疗自然语言处理研究中的重要性,特别是在医院环境中的实际应用。研究内容包括使用最先进的大型语言模型(LLMs)进行药物文本挖掘任务,探索不同的集成学习方法来提高模型性能,并构建一个实体链接功能,将提取的医疗术语映射到SNOMED-CT代码和英国国家处方集(BNF)代码等标准临床知识库中。模型的工具包和桌面应用程序已公开发布。
Key Takeaways
- 医药提取和挖掘在医疗自然语言处理研究中具有重要性,尤其在医院环境中的实际应用。
- 使用最先进的大型语言模型(LLMs)进行药物文本挖掘任务。
- 探索了不同的集成学习方法(如Stack-Ensemble和Voting-Ensemble)来提高模型性能。
- 集成学习模型在一般和特定领域上的表现均优于单个精细调整的基准模型。
- 构建了一个实体链接功能,将提取的医疗术语映射到SNOMED-CT代码等标准临床知识库中。
- 模型公开可用,并提供了桌面应用程序。
点此查看论文截图

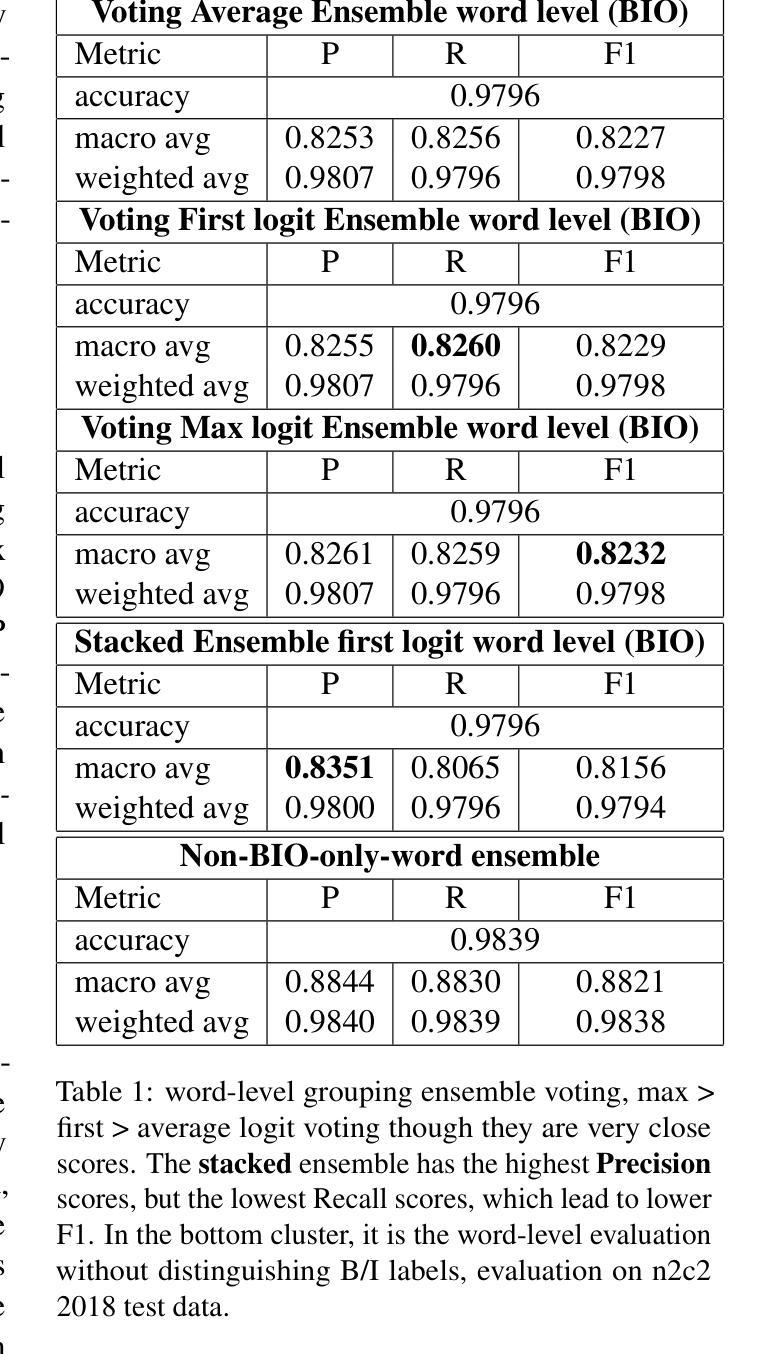
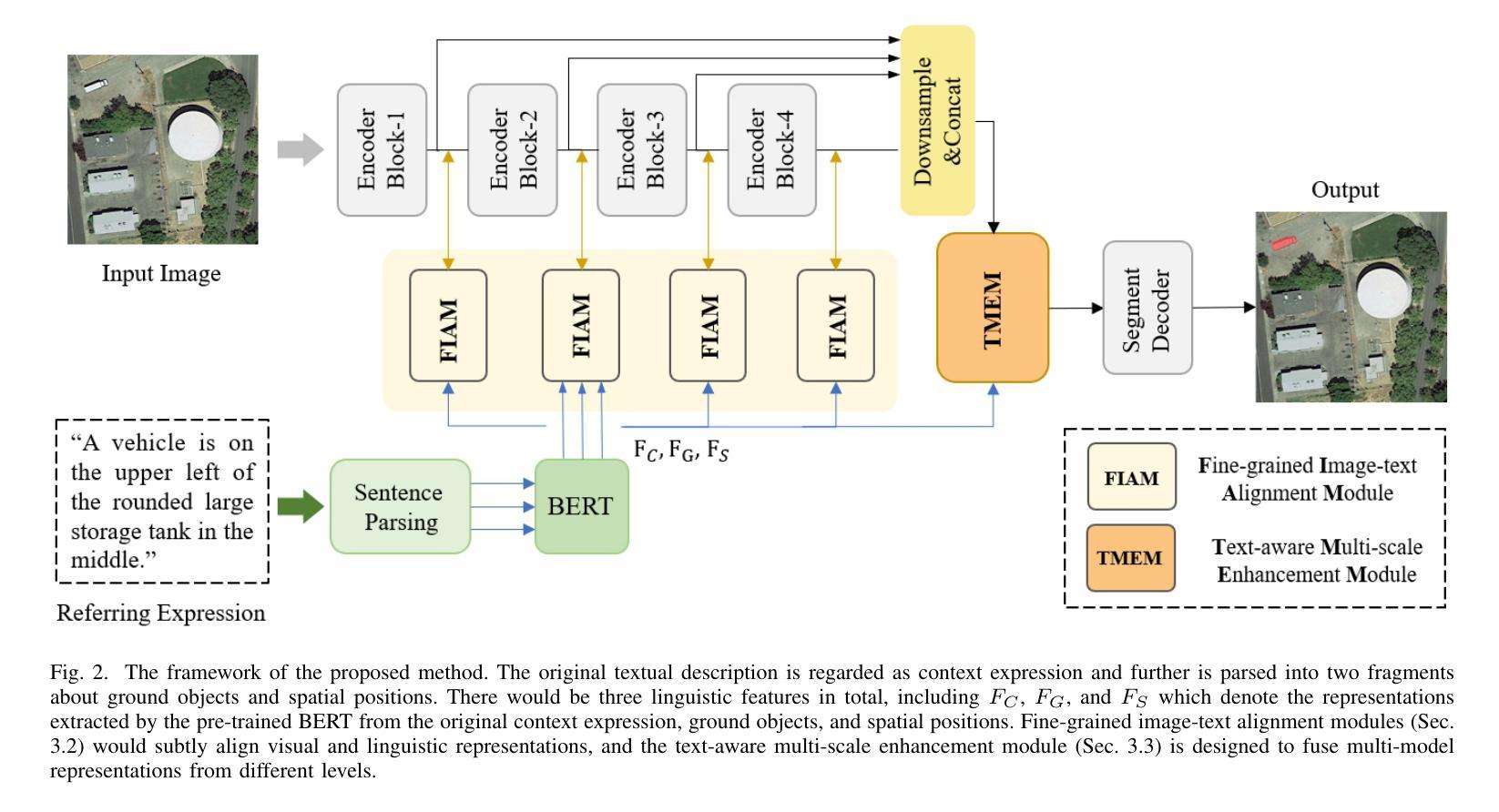
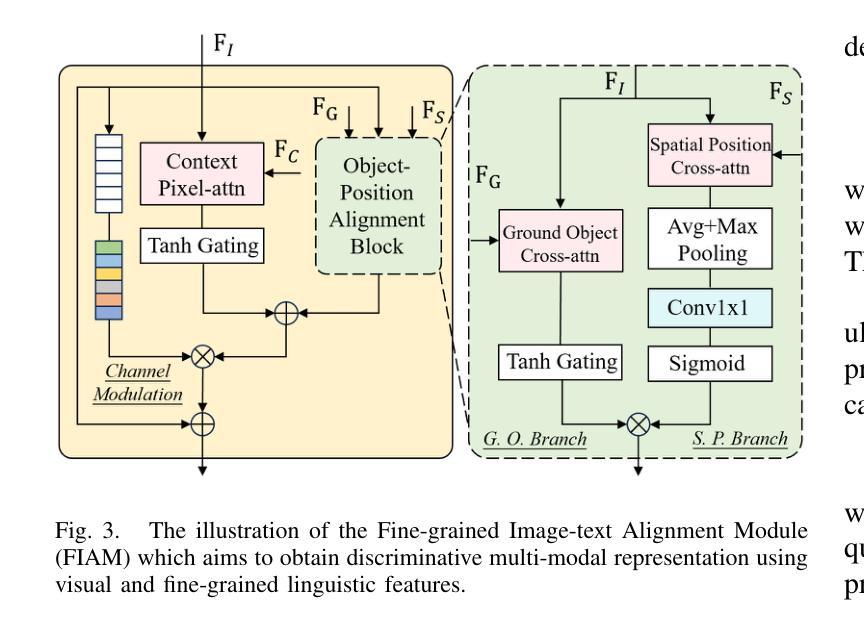
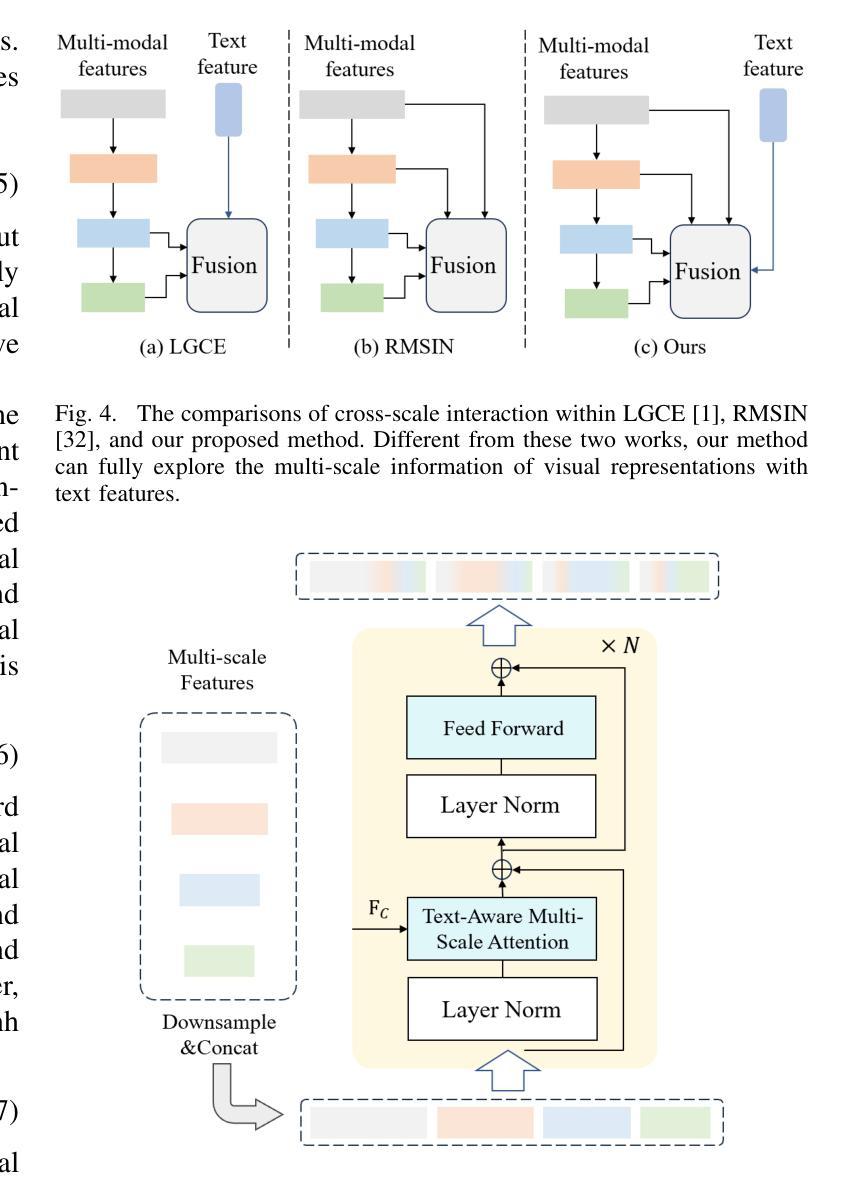
Exploring Fine-Grained Image-Text Alignment for Referring Remote Sensing Image Segmentation
Authors:Sen Lei, Xinyu Xiao, Tianlin Zhang, Heng-Chao Li, Zhenwei Shi, Qing Zhu
Given a language expression, referring remote sensing image segmentation (RRSIS) aims to identify ground objects and assign pixel-wise labels within the imagery. The one of key challenges for this task is to capture discriminative multi-modal features via text-image alignment. However, the existing RRSIS methods use one vanilla and coarse alignment, where the language expression is directly extracted to be fused with the visual features. In this paper, we argue that a ``fine-grained image-text alignment’’ can improve the extraction of multi-modal information. To this point, we propose a new referring remote sensing image segmentation method to fully exploit the visual and linguistic representations. Specifically, the original referring expression is regarded as context text, which is further decoupled into the ground object and spatial position texts. The proposed fine-grained image-text alignment module (FIAM) would simultaneously leverage the features of the input image and the corresponding texts, obtaining better discriminative multi-modal representation. Meanwhile, to handle the various scales of ground objects in remote sensing, we introduce a Text-aware Multi-scale Enhancement Module (TMEM) to adaptively perform cross-scale fusion and intersections. We evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed method on two public referring remote sensing datasets including RefSegRS and RRSIS-D, and our method obtains superior performance over several state-of-the-art methods. The code will be publicly available at https://github.com/Shaosifan/FIANet.
对于给定的语言表达式,遥感图像分割引用(RRSIS)旨在识别地面目标并为图像中的每个像素分配标签。此任务的关键挑战之一是通过文本图像对齐来捕获判别式多模态特征。然而,现有的RRSIS方法使用一种普通的粗对齐方式,其中直接提取语言表达式与视觉特征进行融合。在本文中,我们认为“精细的图像文本对齐”可以改善多模态信息的提取。针对这一点,我们提出了一种新的遥感图像分割引用方法,以充分利用视觉和语言学表示。具体来说,原始引用表达式被视为上下文文本,并进一步解耦为地面目标和空间位置文本。所提出的精细图像文本对齐模块(FIAM)将同时利用输入图像和相应文本的特征,以获得更好的判别式多模态表示。同时,为了处理遥感中地面目标的各种尺度,我们引入了文本感知多尺度增强模块(TMEM)来执行自适应跨尺度融合和交叉。我们在两个公开的遥感引用数据集RefSegRS和RRSIS-D上评估了所提出方法的有效性,与几种最新方法相比,我们的方法获得了优越的性能。代码将公开在https://github.com/Shaosifan/FIANet。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE TGRS
Summary
针对遥感图像分割中的指代分割任务,现有方法通常使用较为粗糙的文本-图像对齐方式,难以有效提取多模态特征。本文提出了一种新的精细粒度图像-文本对齐方法,通过同时利用图像和对应文本的特征,获得更好的多模态表示。此外,为了处理遥感中地面目标的各种尺度,引入了文本感知多尺度增强模块,实现跨尺度融合和交集。在公开数据集上的实验表明,该方法性能优于其他先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感图像分割中的指代分割任务旨在通过语言表达式识别地面目标并为图像中的每个像素分配标签。
- 现有方法使用较粗的文本-图像对齐方式,难以提取多模态特征。
- 本文提出了一种新的精细粒度图像-文本对齐方法,改进了多模态信息的提取。
- 引入了文本感知多尺度增强模块,处理遥感中地面目标的各种尺度。
- 方法在公开数据集上的性能优于其他先进方法。
- 提出的代码将公开可用。
点此查看论文截图


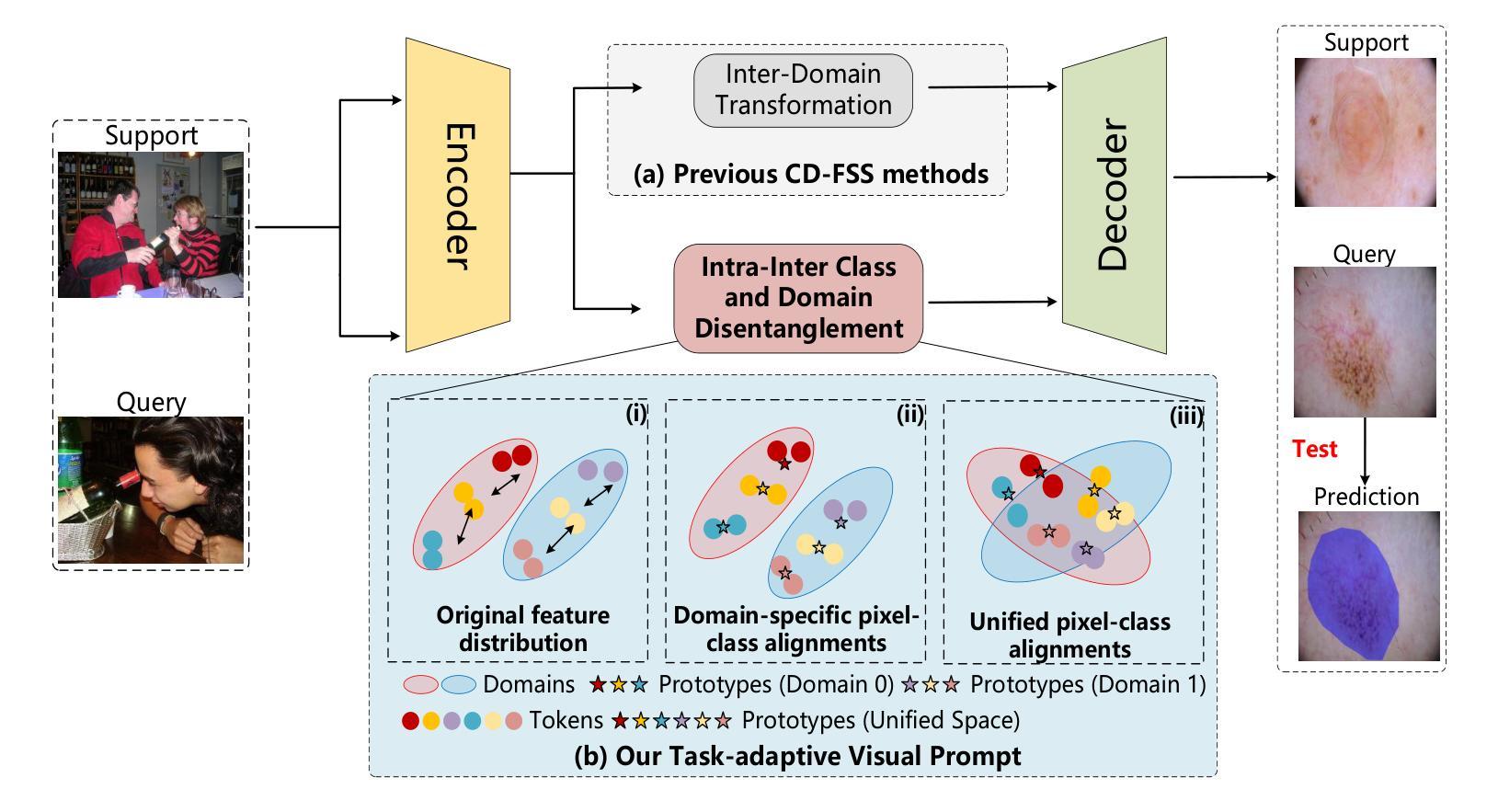
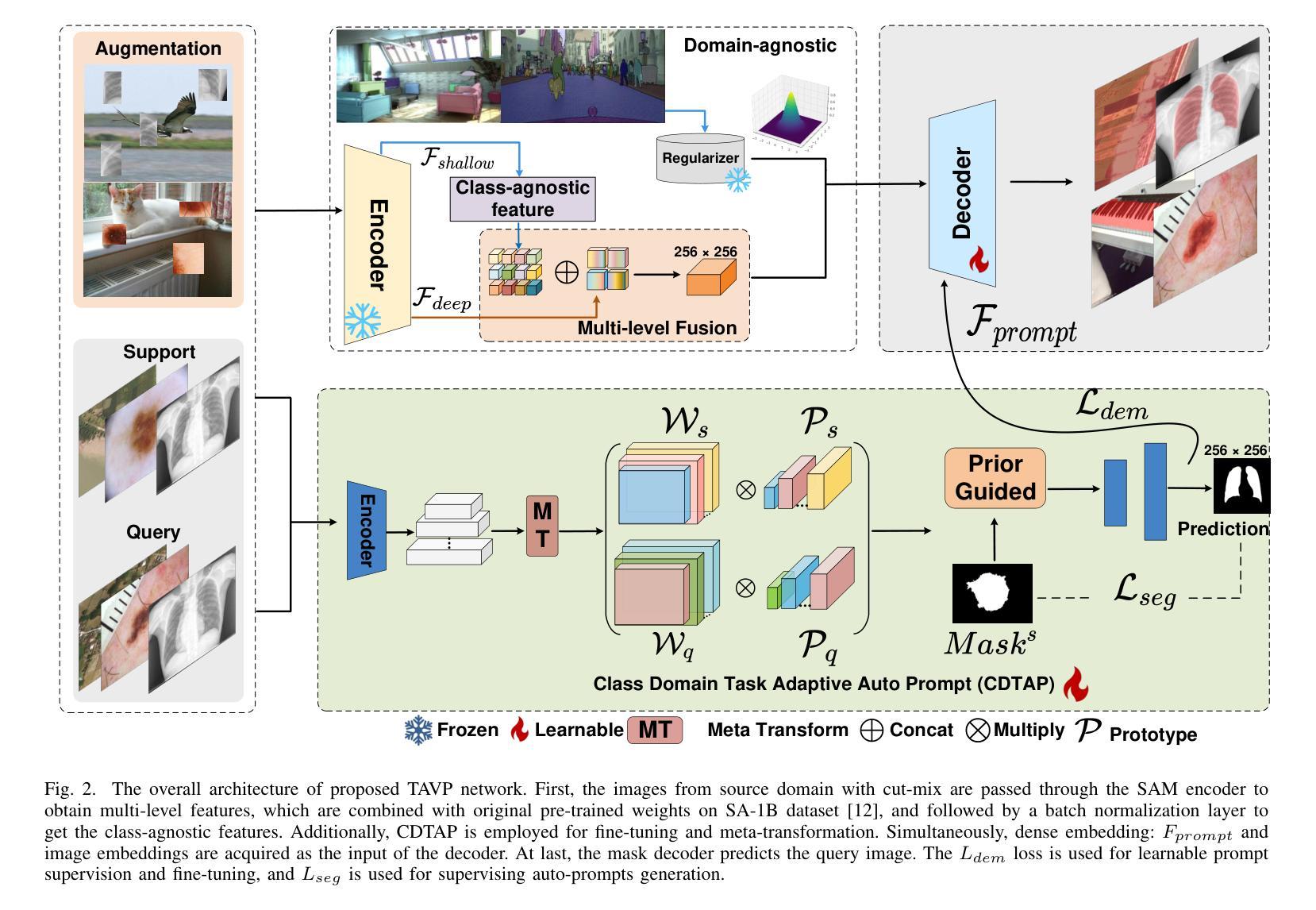
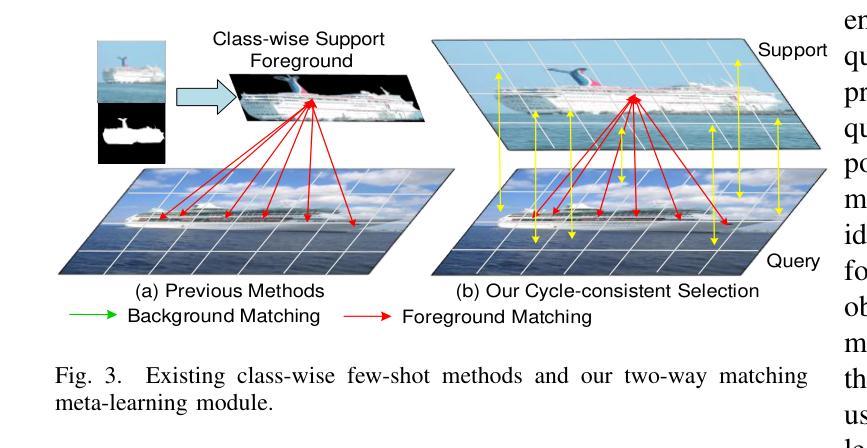
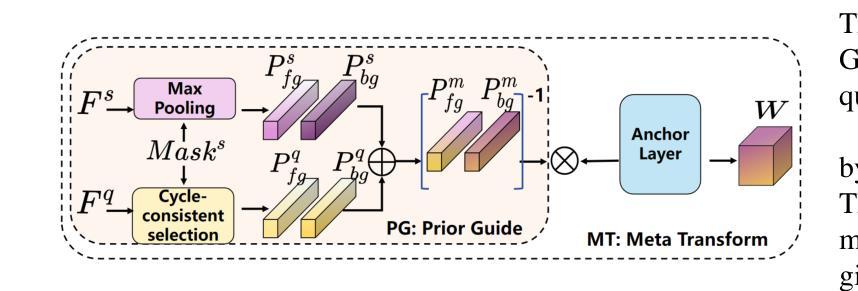
TAVP: Task-Adaptive Visual Prompt for Cross-domain Few-shot Segmentation
Authors:Jiaqi Yang, Yaning Zhang, Jingxi Hu, Xiangjian He, Linlin Shen, Guoping Qiu
While large visual models (LVM) demonstrated significant potential in image understanding, due to the application of large-scale pre-training, the Segment Anything Model (SAM) has also achieved great success in the field of image segmentation, supporting flexible interactive cues and strong learning capabilities. However, SAM’s performance often falls short in cross-domain and few-shot applications. Previous work has performed poorly in transferring prior knowledge from base models to new applications. To tackle this issue, we propose a task-adaptive auto-visual prompt framework, a new paradigm for Cross-dominan Few-shot segmentation (CD-FSS). First, a Multi-level Feature Fusion (MFF) was used for integrated feature extraction as prior knowledge. Besides, we incorporate a Class Domain Task-Adaptive Auto-Prompt (CDTAP) module to enable class-domain agnostic feature extraction and generate high-quality, learnable visual prompts. This significant advancement uses a unique generative approach to prompts alongside a comprehensive model structure and specialized prototype computation. While ensuring that the prior knowledge of SAM is not discarded, the new branch disentangles category and domain information through prototypes, guiding it in adapting the CD-FSS. Comprehensive experiments across four cross-domain datasets demonstrate that our model outperforms the state-of-the-art CD-FSS approach, achieving an average accuracy improvement of 1.3% in the 1-shot setting and 11.76% in the 5-shot setting.
虽然大型视觉模型(LVM)在图像理解方面表现出了巨大的潜力,这是由于大规模预训练的应用,但Segment Anything Model(SAM)也在图像分割领域取得了巨大的成功,支持灵活的交互式线索和强大的学习能力。然而,SAM在跨域和少量应用中的表现往往不尽如人意。先前的工作在将基础模型的先验知识转移到新应用上的表现不佳。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种任务自适应自动视觉提示框架,这是一种新的Cross-dominan Few-shot segmentation(CD-FSS)范式。首先,我们使用多层次特征融合(MFF)进行集成特征提取作为先验知识。此外,我们融入了Class Domain Task-Adaptive Auto-Prompt(CDTAP)模块,以实现类域无关的特征提取,并生成高质量、可学习的视觉提示。这一重大进展采用了一种独特的生成提示方法,辅以全面的模型结构和专门的原型计算。在确保SAM的先验知识不被丢弃的同时,新分支通过原型解开类别和域信息,从而引导其适应CD-FSS。在四个跨域数据集上的综合实验表明,我们的模型超越了最先进的CD-FSS方法,在1次拍摄的情况下平均准确率提高了1.3%,在5次拍摄的情况下平均准确率提高了11.76%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型视觉模型在图像理解方面显示出巨大潜力,Segment Anything Model (SAM) 在图像分割领域也取得了很大成功,具有灵活的交互式提示和强大的学习能力。但在跨域和少量样本应用中,SAM的表现往往不尽如人意。为解决这一问题,我们提出了任务自适应自动视觉提示框架,这是一种新的跨域少量分割(CD-FSS)范式。我们通过多级别特征融合(MFF)进行先验知识融合,并结合类域任务自适应自动提示(CDTAP)模块,实现类域无关的特征提取,生成高质量、可学习的视觉提示。该模型结构全面,使用独特的生成式提示方法,并通过原型计算进行引导。实验证明,我们的模型在四个跨域数据集上的表现优于最新的CD-FSS方法,在1-shot和5-shot设置下平均准确率分别提高了1.3%和11.76%。
Key Takeaways
- 大型视觉模型(LVM)在图像理解方面表现出显著潜力。
- Segment Anything Model (SAM) 在图像分割领域取得很大成功,但存在跨域和少量样本应用中的性能短板。
- 提出了任务自适应自动视觉提示框架,一种针对跨域少量分割(CD-FSS)的新范式。
- 使用多级别特征融合(MFF)进行先验知识融合。
- 结合类域任务自适应自动提示(CDTAP)模块,实现类域无关的特征提取和高质量视觉提示生成。
- 模型采用独特的生成式提示方法和全面的模型结构。
点此查看论文截图

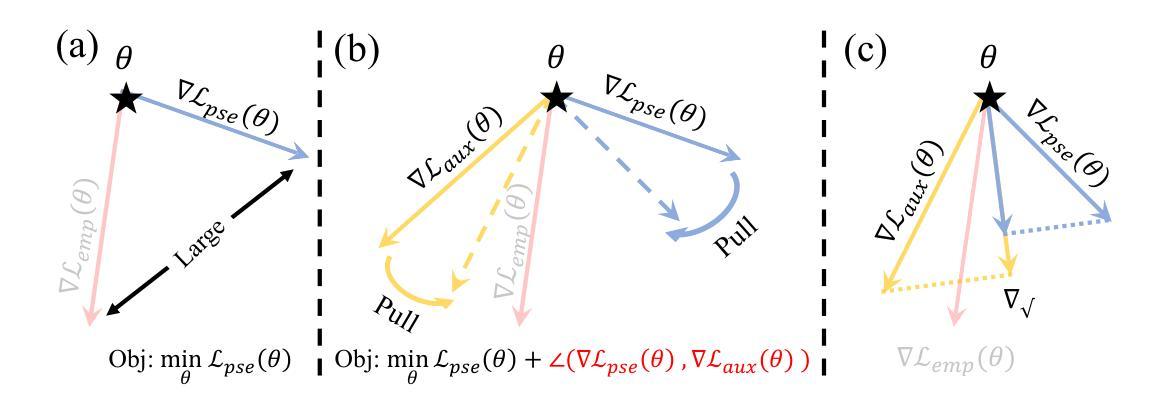
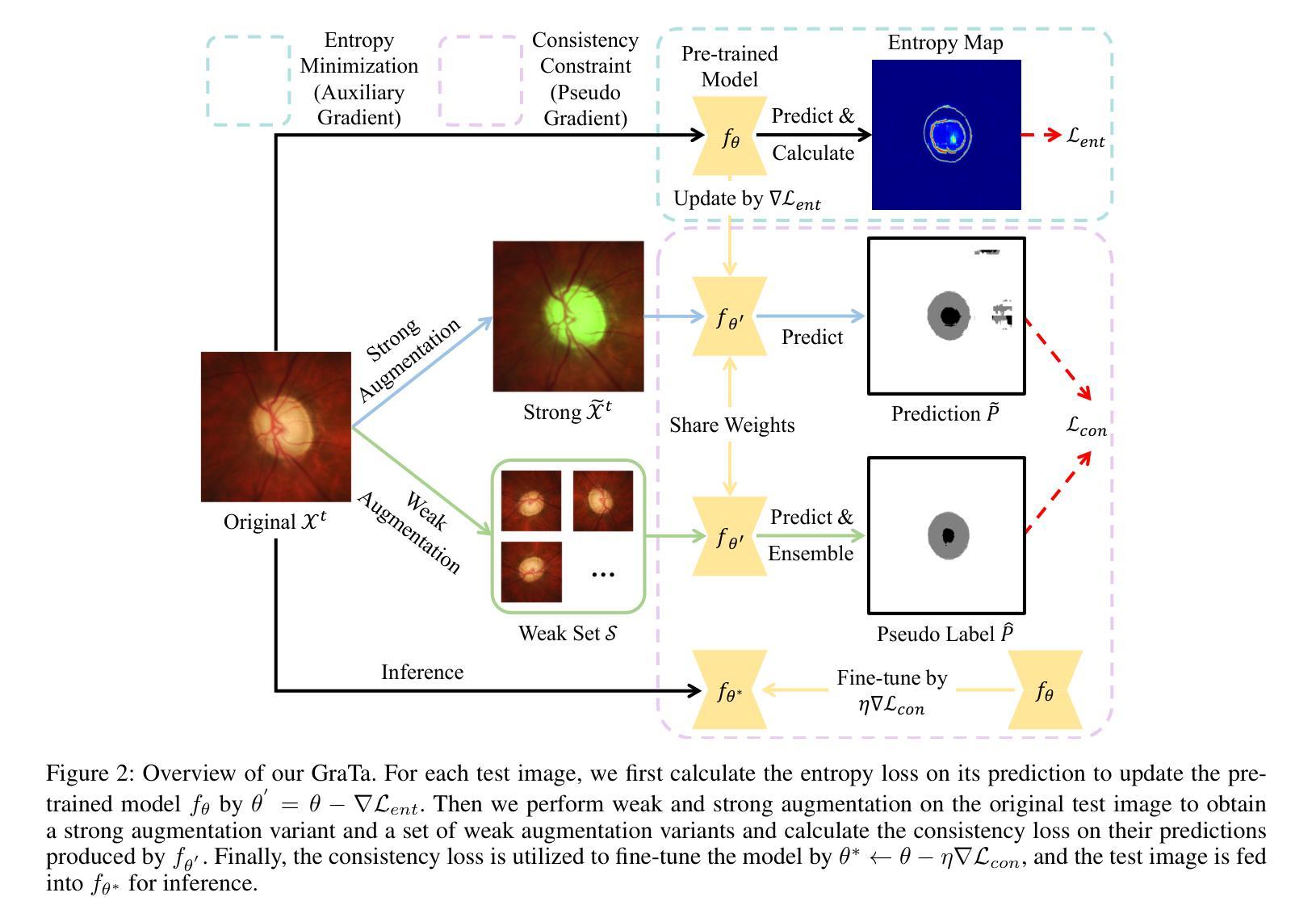
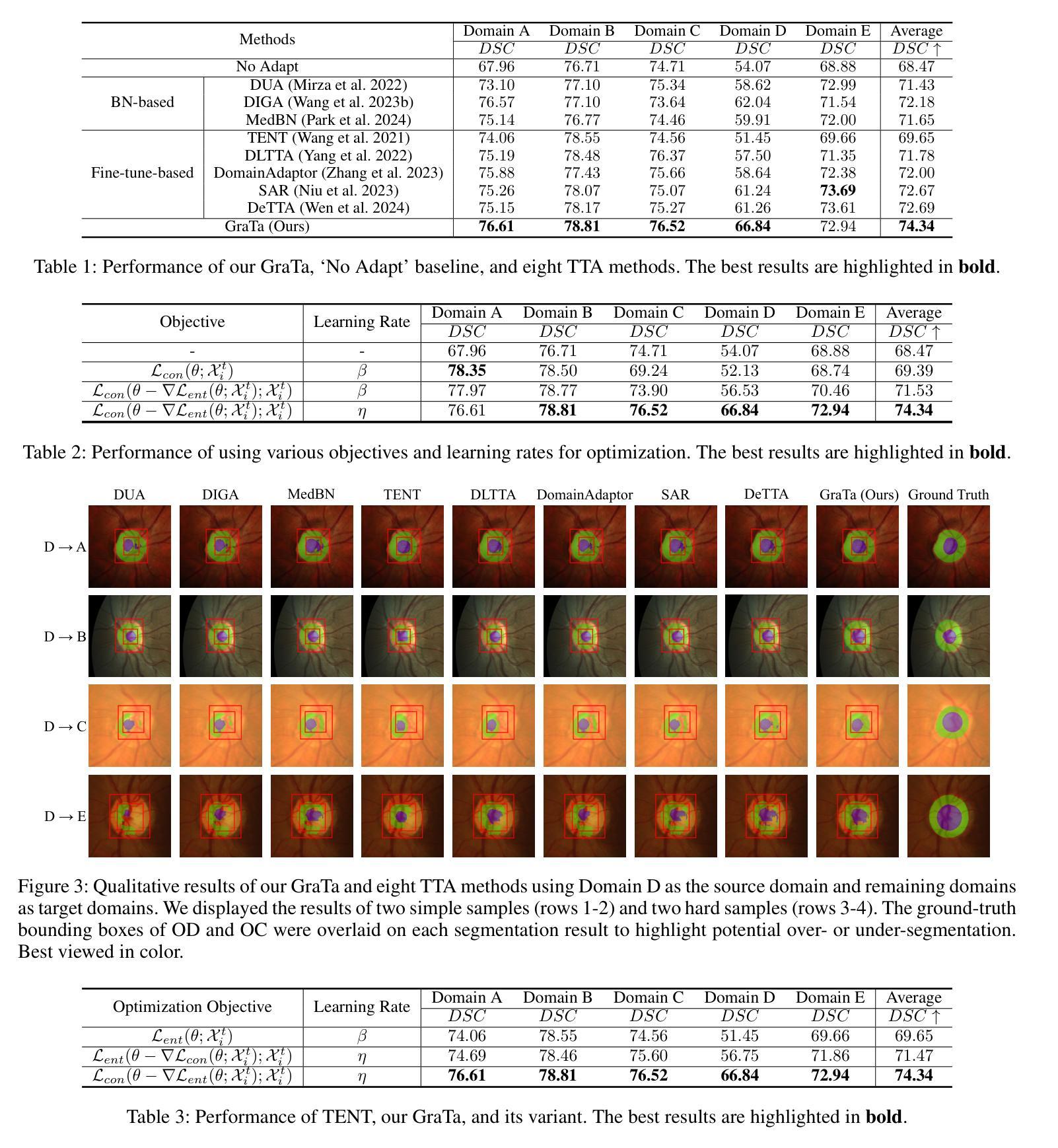
Gradient Alignment Improves Test-Time Adaptation for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Ziyang Chen, Yiwen Ye, Yongsheng Pan, Yong Xia
Although recent years have witnessed significant advancements in medical image segmentation, the pervasive issue of domain shift among medical images from diverse centres hinders the effective deployment of pre-trained models. Many Test-time Adaptation (TTA) methods have been proposed to address this issue by fine-tuning pre-trained models with test data during inference. These methods, however, often suffer from less-satisfactory optimization due to suboptimal optimization direction (dictated by the gradient) and fixed step-size (predicated on the learning rate). In this paper, we propose the Gradient alignment-based Test-time adaptation (GraTa) method to improve both the gradient direction and learning rate in the optimization procedure. Unlike conventional TTA methods, which primarily optimize the pseudo gradient derived from a self-supervised objective, our method incorporates an auxiliary gradient with the pseudo one to facilitate gradient alignment. Such gradient alignment enables the model to excavate the similarities between different gradients and correct the gradient direction to approximate the empirical gradient related to the current segmentation task. Additionally, we design a dynamic learning rate based on the cosine similarity between the pseudo and auxiliary gradients, thereby empowering the adaptive fine-tuning of pre-trained models on diverse test data. Extensive experiments establish the effectiveness of the proposed gradient alignment and dynamic learning rate and substantiate the superiority of our GraTa method over other state-of-the-art TTA methods on a benchmark medical image segmentation task. The code and weights of pre-trained source models are available at https://github.com/Chen-Ziyang/GraTa.
尽管近年来医学图像分割领域取得了显著进展,但来自不同中心的医学图像存在的领域偏移问题仍然阻碍着预训练模型的有效部署。许多测试时适应(TTA)方法已被提出,通过推理过程中的测试数据对预训练模型进行微调来解决这个问题。然而,这些方法通常由于优化方向不佳(由梯度决定)和固定步长(以学习率预测)而导致优化效果不尽人意。在本文中,我们提出了基于梯度对齐的测试时适应(GraTa)方法,以改进优化过程中的梯度方向和学习率。不同于主要优化自监督目标派生出的伪梯度的传统TTA方法,我们的方法结合了辅助梯度和伪梯度,以实现梯度对齐。这种梯度对齐使模型能够挖掘不同梯度之间的相似性,并纠正梯度方向以近似当前分割任务的实证梯度。此外,我们基于伪梯度和辅助梯度之间的余弦相似性设计了一种动态学习率,从而实现在多样测试数据上对预训练模型的自适应微调。大量实验验证了所提出的梯度对齐和动态学习率的有效性,并证实我们的GraTa方法在基准医学图像分割任务上优于其他最先进的TTA方法。预训练模型的代码和权重可在https://github.com/Chen-Ziyang/GraTa上获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
本文提出一种基于梯度对齐的测试时自适应(GraTa)方法,改进了优化过程中的梯度方向和学习率。该方法通过结合伪梯度和辅助梯度实现梯度对齐,能挖掘不同梯度间的相似性并校正梯度方向以逼近当前分割任务的实证梯度。同时,基于余弦相似度设计动态学习率,使预训练模型在多样测试数据上实现自适应微调。实验证明该方法在基准医疗图像分割任务上表现优越。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗图像分割中,不同来源的图像存在的领域偏移问题影响了预训练模型的有效部署。
- 测试时自适应(TTA)方法通过测试数据在推理时对预训练模型进行微调。
- 现有TTA方法由于梯度方向和学习率的不足,优化效果常不理想。
- GraTa方法结合伪梯度和辅助梯度实现梯度对齐,优化梯度方向。
- 动态学习率设计基于伪梯度和辅助梯度的余弦相似度,实现自适应微调。
- GraTa方法在基准医疗图像分割任务上表现优越,优于其他先进TTA方法。
点此查看论文截图

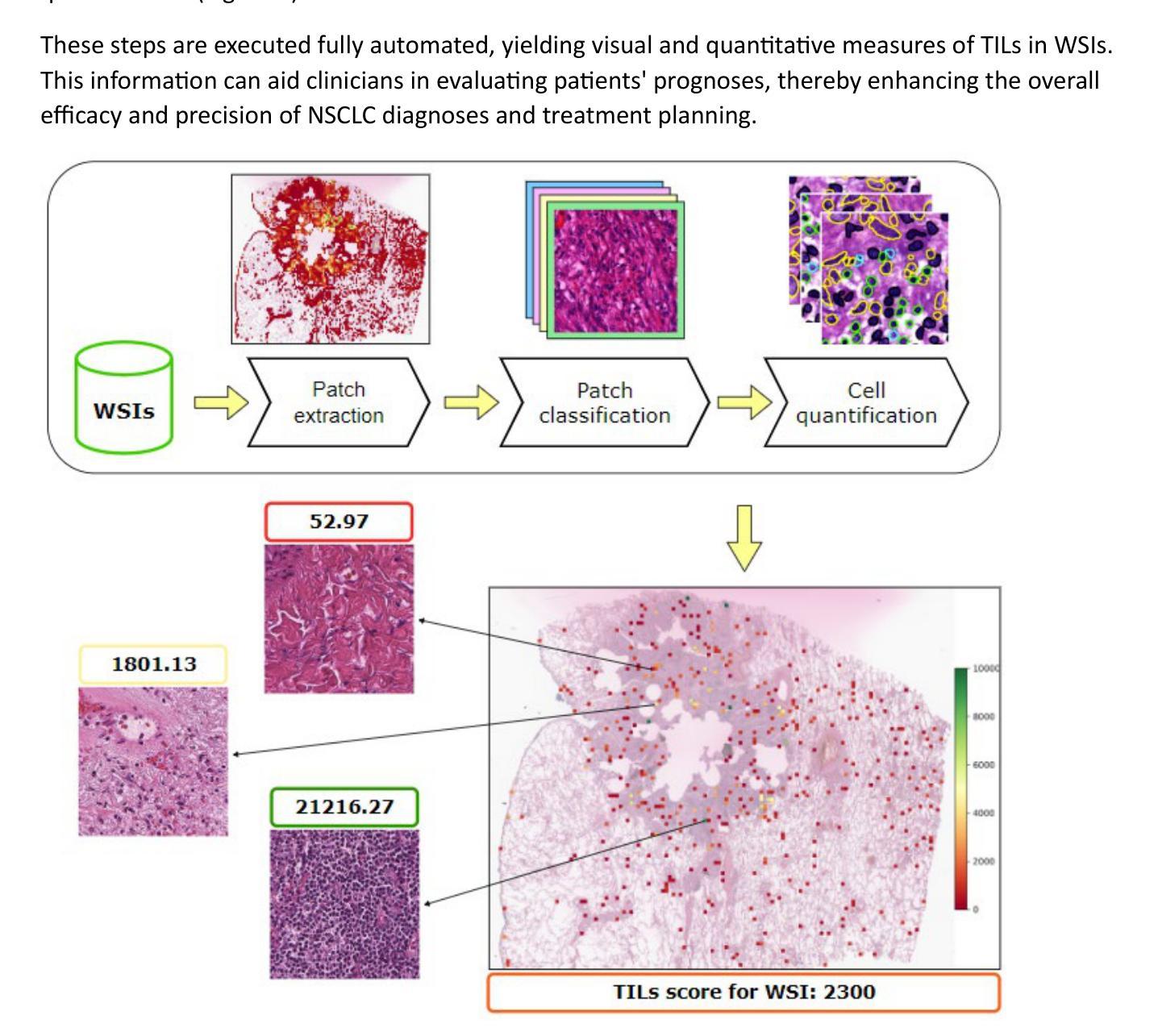
Fast TILs – A Pipeline for Efficient TILs Estimation in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Authors:Nikita Shvetsov, Anders Sildnes, Masoud Tafavvoghi, Lill-Tove Rasmussen Busund, Stig Dalen, Kajsa Møllersen, Lars Ailo Bongo, Thomas K. Kilvaer
Addressing the critical need for accurate prognostic biomarkers in cancer treatment, quantifying tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) presents considerable challenges. Manual TIL quantification in whole slide images (WSIs) is laborious and subject to variability, potentially undermining patient outcomes. Our study introduces an automated pipeline that utilizes semi-stochastic patch sampling, patch classification to retain prognostically relevant patches, and cell quantification using the HoVer-Net model to streamline the TIL evaluation process. This pipeline efficiently excludes approximately 70% of areas not relevant for prognosis and requires only 5% of the remaining patches to maintain prognostic accuracy (c-index = 0.65). The computational efficiency achieved does not sacrifice prognostic accuracy, as demonstrated by the TILs score’s strong association with patient survival, which outperforms traditional CD8 IHC scoring methods. While the pipeline demonstrates potential for enhancing NSCLC prognostication and personalization of treatment, comprehensive clinical validation is still required. Future research should focus on verifying its broader clinical utility and investigating additional biomarkers to improve NSCLC prognosis.
针对癌症治疗中准确预后生物标志物的迫切需求,非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)中肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞(TILs)的量化面临相当大的挑战。在全幻灯片图像(WSI)中进行手动TIL量化既费时又存在可变因素,可能会对患者预后结果产生潜在影响。我们的研究引入了一个自动化流程,该流程采用半随机补丁采样,通过补丁分类保留与预后相关的补丁,并使用HoVer-Net模型进行细胞量化,以简化TIL评估过程。该流程有效地排除了大约70%与预后无关的区域,并仅保留约剩余区域的5%,以保持预后准确性(c指数= 0.65)。所实现的计算效率并没有牺牲预后准确性,如TIL评分与患者生存的强烈相关性所示,其优于传统的CD8免疫组织化学评分方法。虽然该流程在增强NSCLC预后和治疗个性化方面显示出潜力,但仍需要进行全面的临床验证。未来的研究应侧重于验证其在临床上的更广泛应用,并研究其他生物标志物以提高NSCLC的预后效果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 25 pages, 10 figures, 7 appendix pages
Summary
本文介绍了一种针对非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)中肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞(TILs)的自动化评估流程。该流程采用半随机补丁采样、补丁分类保留预后相关补丁以及使用HoVer-Net模型进行细胞计数,提高了TIL评估的效率,在保证预后准确性的同时大大减少了评估的工作量。此流程展示的TILs评分与患者生存有强关联,并优于传统的CD8免疫组织化学评分方法。尽管该流程在非小细胞肺癌预后和个性化治疗方面显示出潜力,但仍需全面的临床验证。
Key Takeaways
- 肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞(TILs)在非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)中的量化是一个挑战,手动量化劳动强度大且结果不稳定。
- 引入的自动化流程利用半随机补丁采样和HoVer-Net模型提高了效率,仅需要很少一部分区域就能维持准确的预后评估。
- 该流程在保证计算效率的同时,并未牺牲预后准确性,展示了强大的患者生存关联。
- 与传统CD8 IHC评分方法相比,此流程展现出更好的性能。
- 此流程在NSCLC的预后和个性化治疗方面显示出潜力,但仍需全面的临床验证。
- 未来研究应侧重于验证该流程在临床上的广泛应用。
点此查看论文截图

Nanoscale cuticle mass density variations influenced by pigmentation in butterfly wing scales
Authors:Deepan Balakrishnan, Anupama Prakash, Benedikt J. Daurer, Cédric Finet, Ying Chen Lim, Zhou Shen, Pierre Thibault, Antónia Monteiro, N. Duane Loh
How pigment distribution influences the cuticle density within a microscopic butterfly wing scale, and how both impact final reflected color remains unknown. We used ptychographic X-ray computed tomography to quantitatively determine, at nanoscale resolutions, the three-dimensional mass density of scales with pigmentation differences. By comparing cuticle densities between pairs of scales with pigmentation differences, we determine that the density of the lower lamina is inversely correlated with pigmentation. In the upper lamina structure, low pigment levels also correlate with sheet-like chitin structures as opposed to rod-like structures. Within each scale, we determine that the lower lamina in all scales has the highest density and distinct layers within the lower lamina help explain reflected color. We hypothesize that pigments, in addition to absorbing specific wavelengths, can affect cuticle polymerization, density, and refractive index, thereby impacting reflected wavelengths that produce colors.
色素分布如何影响微观蝴蝶翅膀鳞片内的角质层密度,以及两者如何共同影响最终反射的颜色仍是未知的。我们使用X射线计算机断层扫描术定量测定具有不同色素沉着的鳞片的三维质量密度,达到纳米级分辨率。通过比较具有不同色素沉着的鳞片之间的角质层密度,我们发现下层鳞片的密度与色素沉着呈负相关。在上层结构中,低色素水平与片状几丁质结构相关,而不是杆状结构。在每个鳞片内部,我们确定所有鳞片的下层都具有最高的密度,下层内的不同层有助于解释反射颜色。我们假设除了吸收特定波长外,色素还可以影响角质层的聚合、密度和折射率,从而影响反射波长并产生颜色。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文利用X射线计算机断层扫描技术,定量研究了具有不同色素分布的蝴蝶翅膀鳞片的三维质量密度。研究发现,鳞片下层的密度与色素含量呈负相关,而在上层结构中,低色素水平与片状几丁质结构相关。此外,每个鳞片中下层具有最高的密度,并且不同层之间的结构有助于解释反射的颜色。因此,本文假设色素除了吸收特定波长外,还可能影响角质层聚合、密度和折射率,从而影响反射波长产生的颜色。
Key Takeaways
- 利用X射线计算机断层扫描技术定量研究蝴蝶翅膀鳞片的三维质量密度。
- 发现鳞片下层的密度与色素含量呈负相关。
- 在上层结构中,低色素水平与片状几丁质结构有关。
- 每个鳞片中下层具有最高的密度。
- 不同层之间的结构有助于解释反射的颜色。
- 色素可能影响角质层的聚合、密度和折射率。
点此查看论文截图