⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-04 更新
SegKAN: High-Resolution Medical Image Segmentation with Long-Distance Dependencies
Authors:Shengbo Tan, Rundong Xue, Shipeng Luo, Zeyu Zhang, Xinran Wang, Lei Zhang, Daji Ergu, Zhang Yi, Yang Zhao, Ying Cai
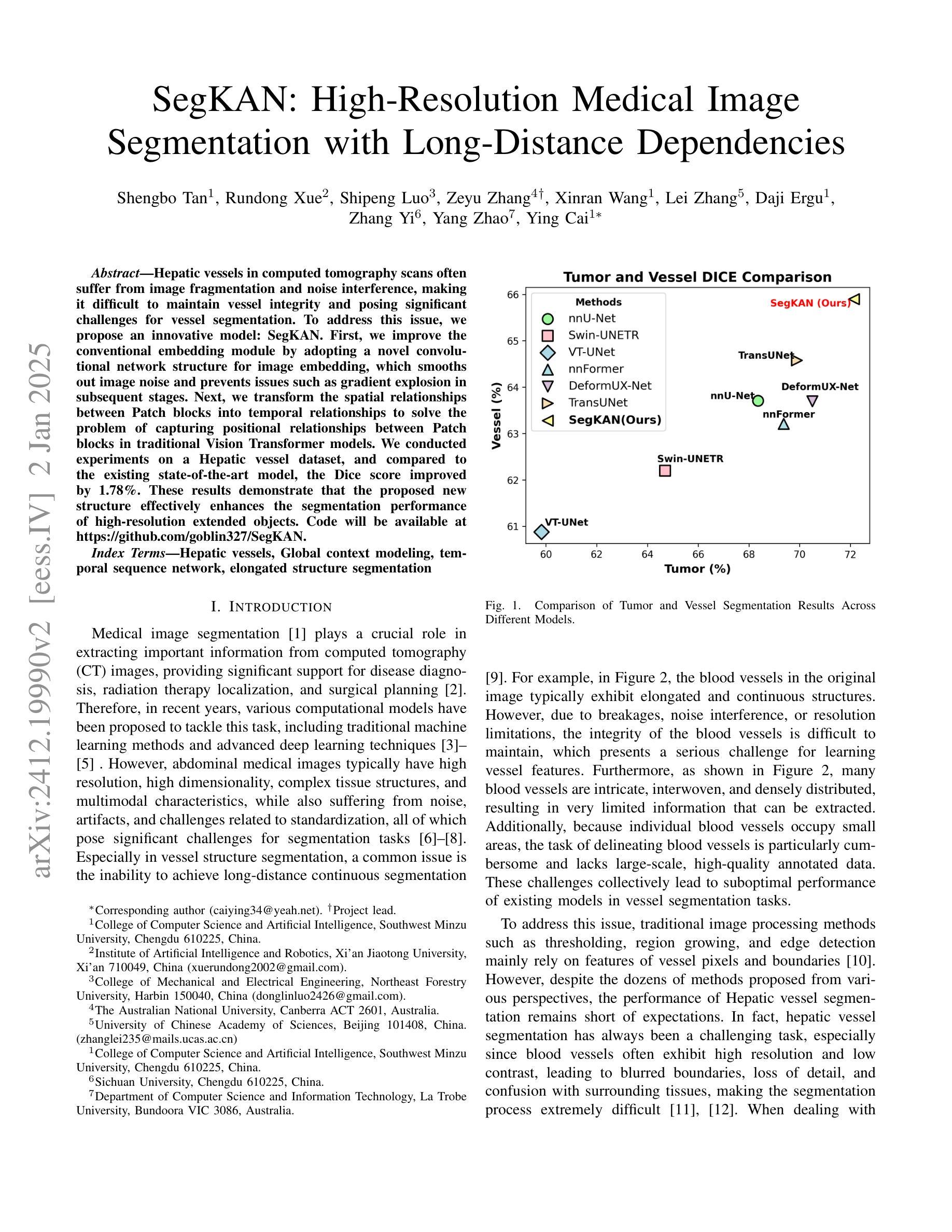
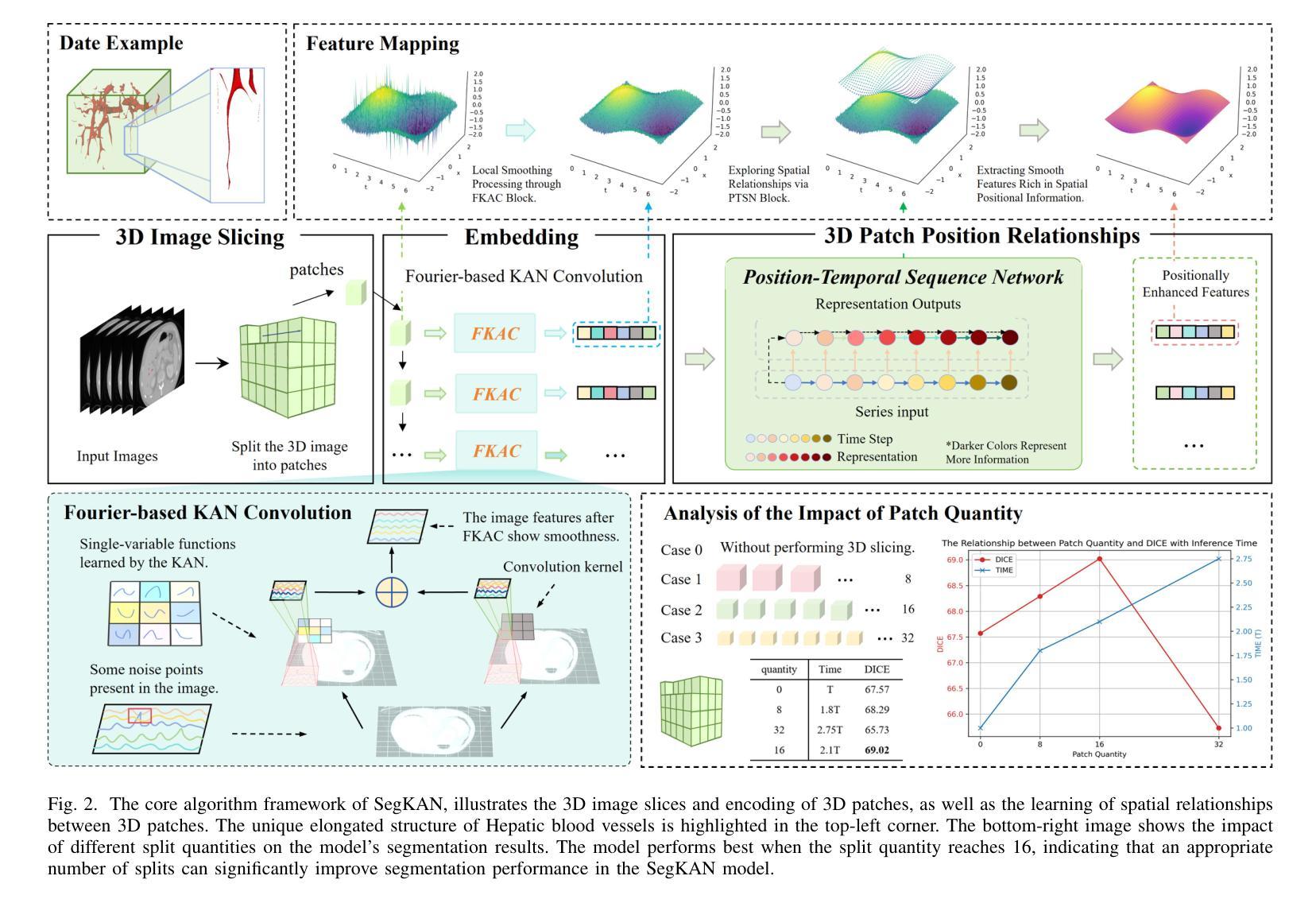
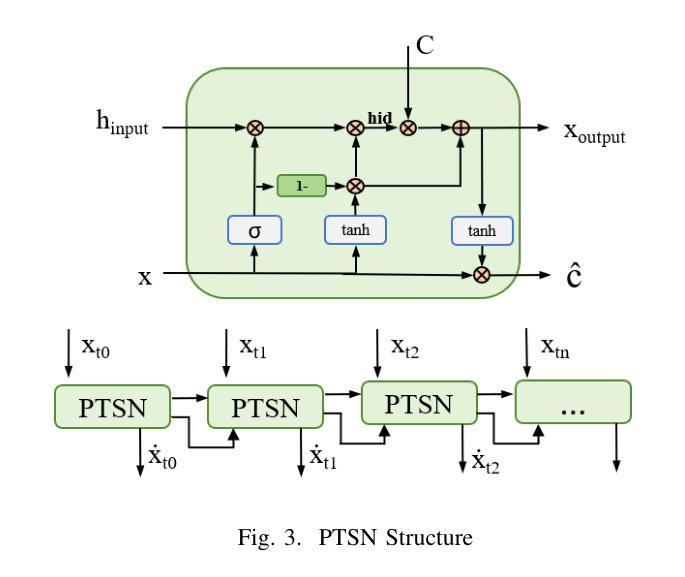
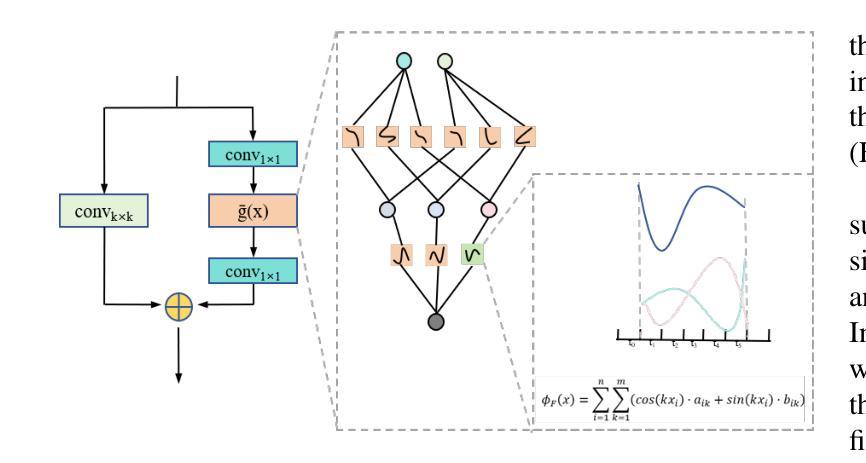
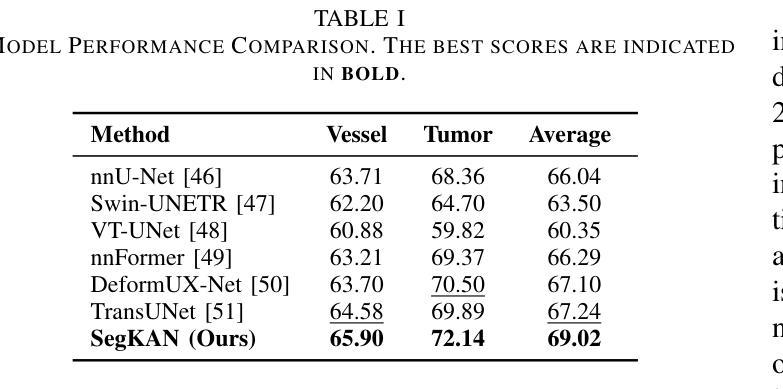
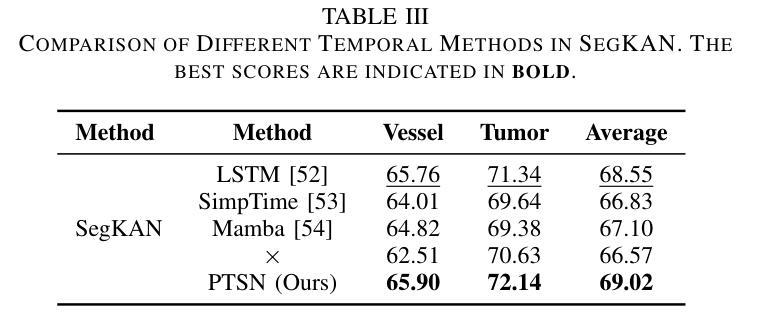
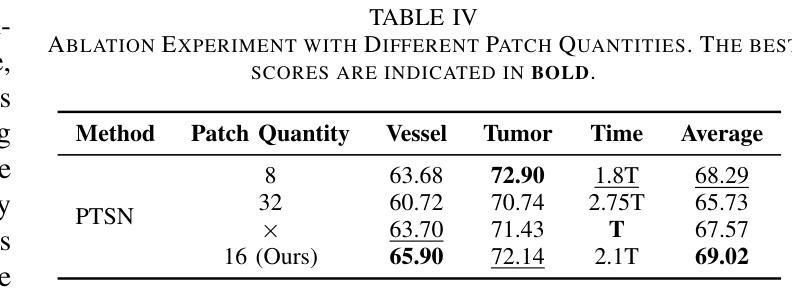
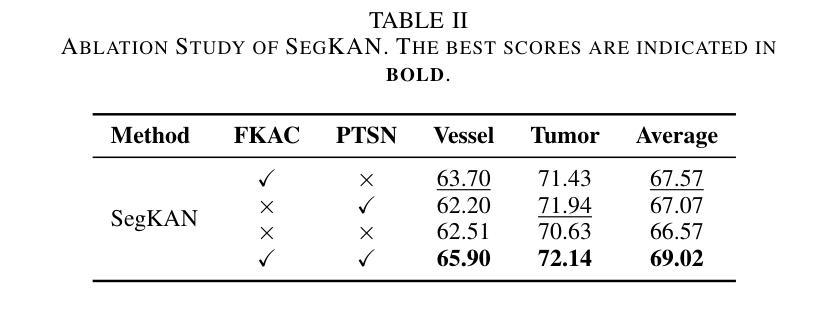
Hepatic vessels in computed tomography scans often suffer from image fragmentation and noise interference, making it difficult to maintain vessel integrity and posing significant challenges for vessel segmentation. To address this issue, we propose an innovative model: SegKAN. First, we improve the conventional embedding module by adopting a novel convolutional network structure for image embedding, which smooths out image noise and prevents issues such as gradient explosion in subsequent stages. Next, we transform the spatial relationships between Patch blocks into temporal relationships to solve the problem of capturing positional relationships between Patch blocks in traditional Vision Transformer models. We conducted experiments on a Hepatic vessel dataset, and compared to the existing state-of-the-art model, the Dice score improved by 1.78%. These results demonstrate that the proposed new structure effectively enhances the segmentation performance of high-resolution extended objects. Code will be available at https://github.com/goblin327/SegKAN
在计算机断层扫描中,肝脏血管经常受到图像碎片和噪声干扰的影响,这使得保持血管的完整性变得困难,并为血管分割带来了重大挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种创新模型:SegKAN。首先,我们改进了传统的嵌入模块,采用了一种新型的卷积网络结构进行图像嵌入,该结构可以平滑图像噪声,防止后续阶段的梯度爆炸等问题。其次,我们将Patch块之间的空间关系转换为时间关系,解决了传统视觉Transformer模型中捕获Patch块之间位置关系的问题。我们在肝脏血管数据集上进行了实验,与现有最先进的模型相比,Dice得分提高了1.78%。这些结果表明,所提出的新结构有效地提高了高分辨率扩展对象的分割性能。代码将在https://github.com/goblin327/SegKAN上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新的模型SegKAN,用于解决肝脏血管在CT扫描中的图像碎片化及噪声干扰问题,从而提高血管分割的准确性。SegKAN通过改进传统嵌入模块并采用新型卷积网络结构进行图像嵌入,平滑图像噪声,并在后续阶段防止梯度爆炸等问题。此外,SegKAN转换Patch块之间的空间关系为时间关系,解决了传统视觉转换器模型中捕获Patch块之间位置关系的问题。实验结果显示,与现有最先进的模型相比,SegKAN在肝脏血管数据集上的Dice得分提高了1.78%,表明该新结构有效提高了高分辨率扩展对象的分割性能。
Key Takeaways
- SegKAN模型被提出以解决肝脏血管在CT扫描中的图像碎片化及噪声干扰问题。
- SegKAN改进了传统嵌入模块,采用新型卷积网络结构进行图像嵌入,以平滑图像噪声并防止梯度爆炸。
- SegKAN转换Patch块之间的空间关系为时间关系,以改善传统视觉转换器模型在捕获Patch块位置关系方面的问题。
- 实验结果显SegKAN在肝脏血管数据集上的性能优于现有最先进的模型,Dice得分提高了1.78%。
- SegKAN能有效提高高分辨率扩展对象的分割性能。
- SegKAN的代码将公开在https://github.com/goblin327/SegKAN。
- 该模型的应用将有助于提高医学图像分析中血管分割的准确性和效率。
点此查看论文截图
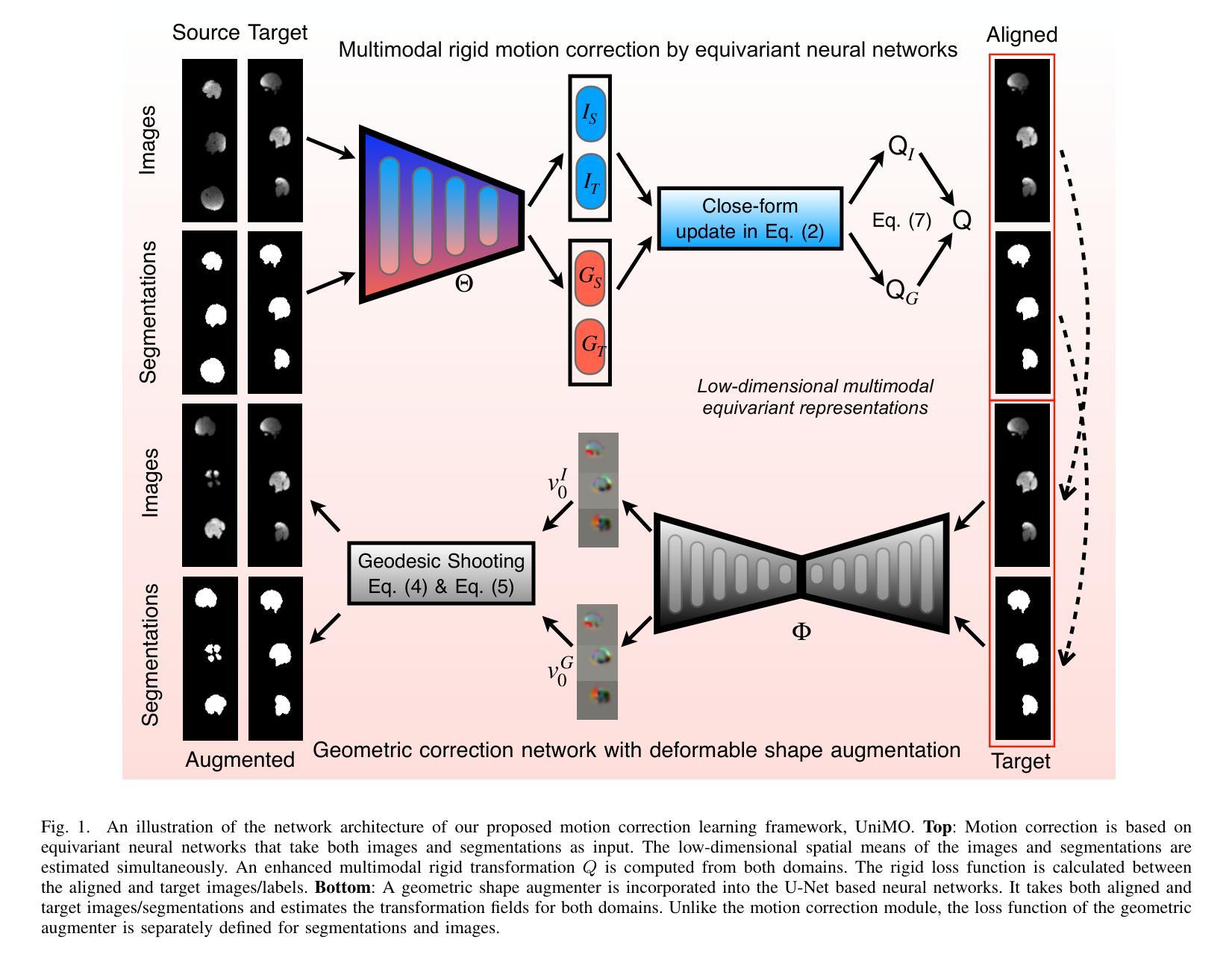
UniMo: Universal Motion Correction For Medical Images without Network Retraining
Authors:Jian Wang, Razieh Faghihpirayesh, Danny Joca, Polina Golland, Ali Gholipour
In this paper, we introduce a Universal Motion Correction (UniMo) framework, leveraging deep neural networks to tackle the challenges of motion correction across diverse imaging modalities. Our approach employs advanced neural network architectures with equivariant filters, overcoming the limitations of current models that require iterative inference or retraining for new image modalities. UniMo enables one-time training on a single modality while maintaining high stability and adaptability for inference across multiple unseen image modalities. We developed a joint learning framework that integrates multimodal knowledge from both shape and images that faithfully improve motion correction accuracy despite image appearance variations. UniMo features a geometric deformation augmenter that enhances the robustness of global motion correction by addressing any local deformations whether they are caused by object deformations or geometric distortions, and also generates augmented data to improve the training process. Our experimental results, conducted on various datasets with four different image modalities, demonstrate that UniMo surpasses existing motion correction methods in terms of accuracy. By offering a comprehensive solution to motion correction, UniMo marks a significant advancement in medical imaging, especially in challenging applications with wide ranges of motion, such as fetal imaging. The code for this work is available online, https://github.com/IntelligentImaging/UNIMO/.
本文介绍了一个通用运动校正(UniMo)框架,它利用深度神经网络来解决跨不同成像模式运动校正的挑战。我们的方法采用先进的神经网络架构和等价滤波器,克服了当前模型需要迭代推理或针对新图像模式进行再训练的局限性。UniMo实现了单一模态的一次性训练,同时保持了跨多个未见图像模式推理的高稳定性和适应性。我们开发了一个联合学习框架,该框架结合了形状和图像的跨模态知识,尽管图像外观发生变化,也能忠实地提高运动校正的准确性。UniMo具有几何变形增强器,它通过解决局部变形(无论是由于对象变形还是几何失真引起的)增强了全局运动校正的稳健性,并且还生成了增强数据以改进训练过程。我们的实验结果是在具有四种不同图像模式的各种数据集上进行的,证明了UniMo在准确性上超越了现有的运动校正方法。通过为运动校正提供全面解决方案,UniMo在医学成像领域取得了重大进展,特别是在具有大范围运动的挑战性应用中,如胎儿成像。该工作的代码可在网上找到:https://github.com/IntelligentImaging/UNIMO/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 6 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种利用深度神经网络解决多种成像模式运动校正问题的通用运动校正(UniMo)框架。该框架采用先进的神经网络架构和等价滤波器,克服了当前模型需要迭代推理或针对新图像模式进行再训练的局限性。UniMo框架能够在单一模态上进行一次性训练,同时保持对多种未见图像模式的高稳定性和适应性。通过整合形状和图像的跨模态知识,UniMo提高了运动校正的准确性,即使在图像外观变化的情况下也是如此。此外,UniMo还包含一个几何变形增强器,该增强器提高了全局运动校正的稳健性,解决了局部变形问题,并生成额外的数据以改进训练过程。在多种数据集和四种不同图像模式上的实验结果表明,UniMo在准确性上超越了现有的运动校正方法。它为运动校正提供了一个全面的解决方案,标志着医学影像技术的一大进步,特别是在大范围运动的挑战性应用中,如胎儿成像。
Key Takeaways
- UniMo框架利用深度神经网络解决了多种成像模式的运动校正问题。
- 该框架采用先进的神经网络架构和等价滤波器,具有高度的稳定性和适应性。
- UniMo实现了在单一模态上的一次性训练,并能够在多种未见图像模式上进行推理。
- 通过整合形状和图像的跨模态知识,UniMo提高了运动校正的准确性。
- UniMo包含一个几何变形增强器,可解决局部变形问题并增强全局运动校正的稳健性。
- UniMo生成额外的数据以改进训练过程。
点此查看论文截图

Boosting Memory Efficiency in Transfer Learning for High-Resolution Medical Image Classification
Authors:Yijin Huang, Pujin Cheng, Roger Tam, Xiaoying Tang
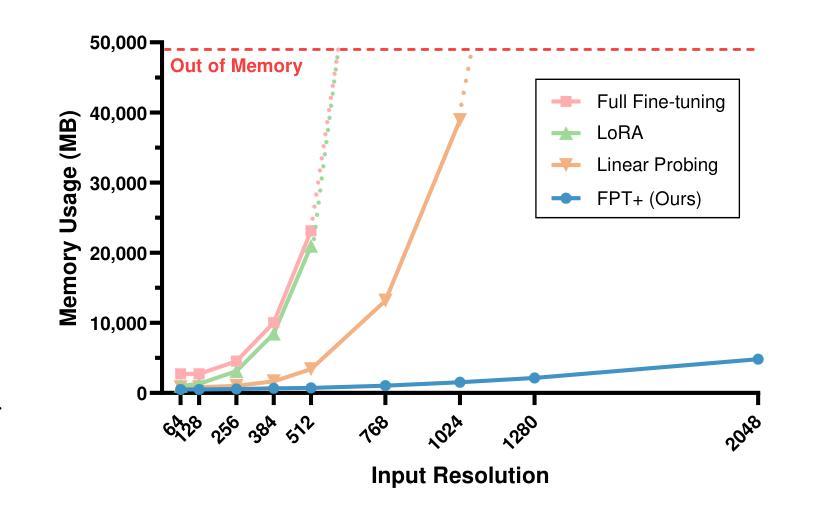
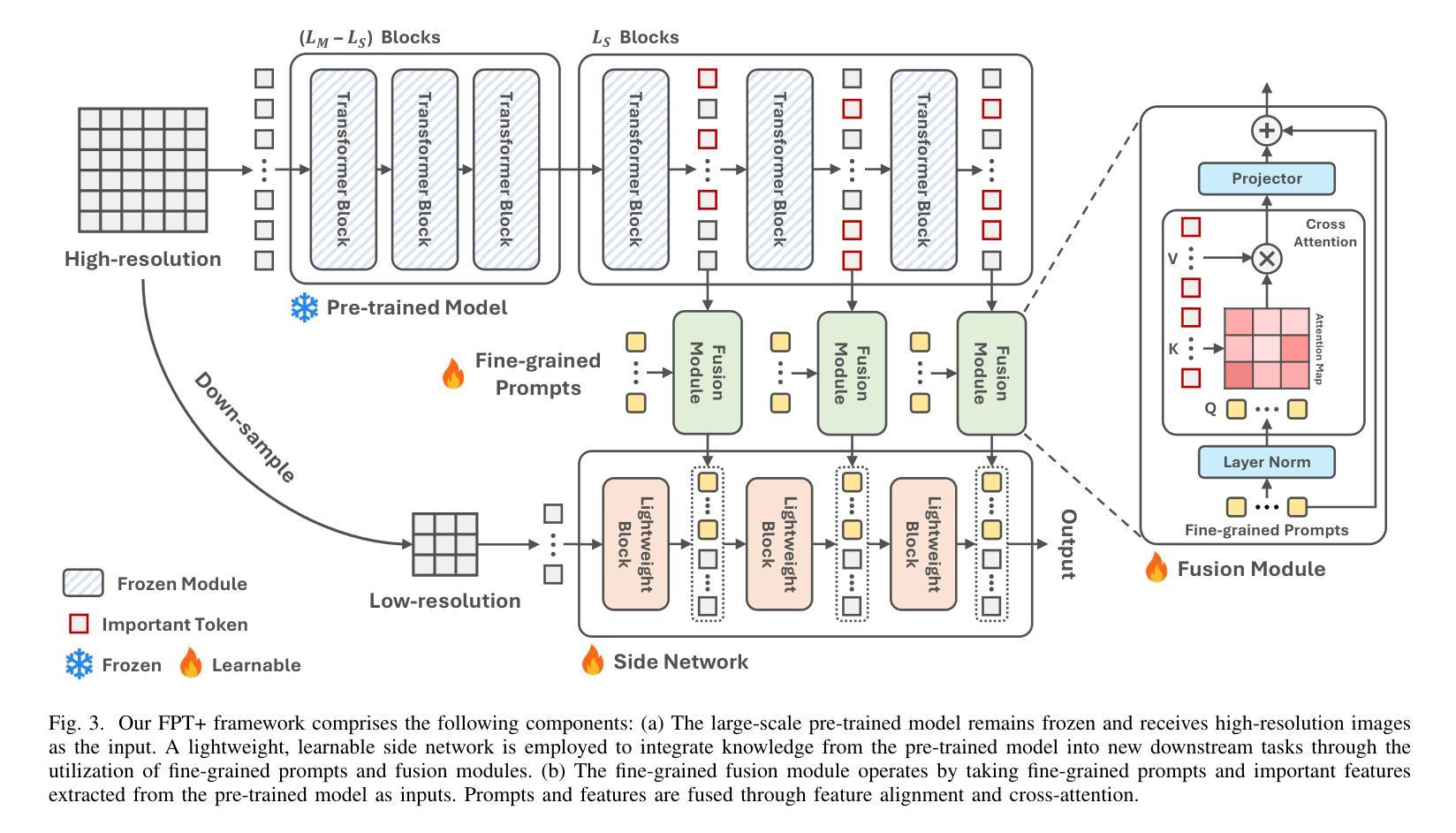
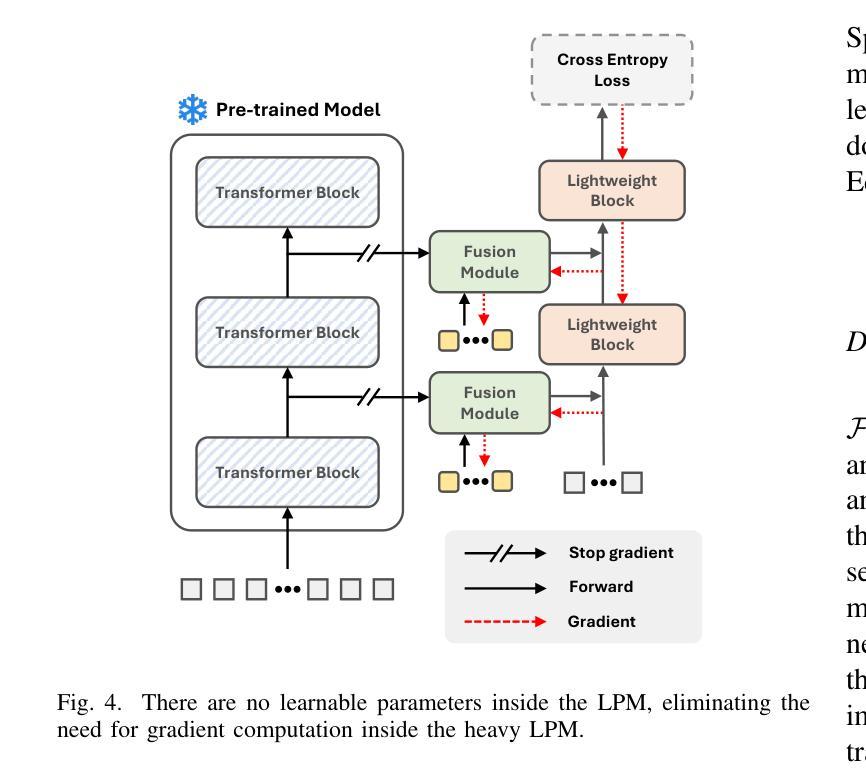
The success of large-scale pre-trained models has established fine-tuning as a standard method for achieving significant improvements in downstream tasks. However, fine-tuning the entire parameter set of a pre-trained model is costly. Parameter-efficient transfer learning (PETL) has recently emerged as a cost-effective alternative for adapting pre-trained models to downstream tasks. Despite its advantages, the increasing model size and input resolution present challenges for PETL, as the training memory consumption is not reduced as effectively as the parameter usage. In this paper, we introduce Fine-grained Prompt Tuning plus (FPT+), a PETL method designed for high-resolution medical image classification, which significantly reduces the training memory consumption compared to other PETL methods. FPT+ performs transfer learning by training a lightweight side network and accessing pre-trained knowledge from a large pre-trained model (LPM) through fine-grained prompts and fusion modules. Specifically, we freeze the LPM of interest and construct a learnable lightweight side network. The frozen LPM processes high-resolution images to extract fine-grained features, while the side network employs corresponding down-sampled low-resolution images to minimize the memory usage. To enable the side network to leverage pre-trained knowledge, we propose fine-grained prompts and fusion modules, which collaborate to summarize information through the LPM’s intermediate activations. We evaluate FPT+ on eight medical image datasets of varying sizes, modalities, and complexities. Experimental results demonstrate that FPT+ outperforms other PETL methods, using only 1.03% of the learnable parameters and 3.18% of the memory required for fine-tuning an entire ViT-B model. Our code is available https://github.com/YijinHuang/FPT.
大规模预训练模型的成功使得微调成为在下游任务中实现显著改进的标准方法。然而,对预训练模型进行整体参数微调的成本很高。近期,参数高效迁移学习(PETL)作为一种经济实惠的替代方案应运而生,用于将预训练模型适应到下游任务。尽管有其优势,但随着模型大小和输入分辨率的增加,PETL面临挑战,因为训练内存消耗并没有像参数使用那样有效地减少。在本文中,我们介绍了精细提示微调加(FPT+),这是一种针对高分辨率医学图像分类设计的PETL方法,与其他PETL方法相比,它显著减少了训练内存消耗。FPT+通过训练一个轻量级侧网络并通过精细提示和融合模块访问大型预训练模型(LPM)的预训练知识,从而进行迁移学习。具体来说,我们冻结感兴趣的LPM并构建一个可学习的轻量级侧网络。冻结的LPM处理高分辨率图像以提取精细特征,而侧网络则使用相应的下采样低分辨率图像来最小化内存使用。为了允许侧网络利用预训练知识,我们提出了精细提示和融合模块,它们通过LPM的中间激活来协作汇总信息。我们在八个不同大小、模态和复杂度的医学图像数据集上评估了FPT+。实验结果表明,FPT+在其他PETL方法上表现出色,仅使用1.03%的可学习参数和3.18%的记忆,用于微调整个ViT-B模型。我们的代码可在https://github.com/YijinHuang/FPT获取。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
大型预训练模型的巨大成功确立了微调作为实现下游任务显著改进的标准方法。然而,微调预训练模型的所有参数是成本高昂的。参数高效迁移学习(PETL)最近作为一种经济实惠的预训练模型适应下游任务的替代方法而兴起。尽管有其优点,但随着模型大小和输入分辨率的增加,PETL面临挑战,因为训练内存消耗并没有像参数使用那样有效地减少。本文介绍了用于高分辨率医学图像分类的精细提示微调加强版(FPT+),这是一种PETL方法,与其他PETL方法相比,它显著减少了训练内存消耗。FPT+通过训练轻量级侧网络并通过对齐预训练知识来实现迁移学习,对齐通过精细提示和融合模块进行。具体来说,我们冻结感兴趣的LPM并构建了一个可学习的轻量级侧网络。冻结的LPM处理高分辨率图像以提取精细特征,而侧网络则使用相应的降采样低分辨率图像来最小化内存使用。为了使侧网络能够利用预训练知识,我们提出了精细提示和融合模块,它们通过LPM的中间激活来协作总结信息。我们在八个医学图像数据集上评估了FPT+,这些数据集大小、模态和复杂性各不相同。实验结果表明,FPT+在只使用0.79%的参数和较小内存需求的情况下,即可超越其他PETL方法实现性能表现,对ViT-B模型的微调仅需要3.18%的内存。我们的代码可通过https://github.com/YijinHuang/FPT获取。
关键见解
- 大规模预训练模型的成功确立了微调作为改进下游任务的标准方法,但微调整个参数集成本高昂。
- 参数高效迁移学习(PETL)作为适应预训练模型到下游任务的替代方法具有优势。
- FPT+是一种针对高分辨医学图像分类的PETL方法,显著减少训练内存消耗。
- FPT+通过训练轻量级侧网络并利用预训练知识来实现迁移学习,这些知识通过精细提示和融合模块获取。
- 冻结的LPM处理高分辨率图像以提取精细特征,而侧网络使用低分辨率图像优化内存使用。
- 精细提示和融合模块使侧网络能够利用预训练知识。
点此查看论文截图

Real World Federated Learning with a Knowledge Distilled Transformer for Cardiac CT Imaging
Authors:Malte Tölle, Philipp Garthe, Clemens Scherer, Jan Moritz Seliger, Andreas Leha, Nina Krüger, Stefan Simm, Simon Martin, Sebastian Eble, Halvar Kelm, Moritz Bednorz, Florian André, Peter Bannas, Gerhard Diller, Norbert Frey, Stefan Groß, Anja Hennemuth, Lars Kaderali, Alexander Meyer, Eike Nagel, Stefan Orwat, Moritz Seiffert, Tim Friede, Tim Seidler, Sandy Engelhardt
Federated learning is a renowned technique for utilizing decentralized data while preserving privacy. However, real-world applications often face challenges like partially labeled datasets, where only a few locations have certain expert annotations, leaving large portions of unlabeled data unused. Leveraging these could enhance transformer architectures ability in regimes with small and diversely annotated sets. We conduct the largest federated cardiac CT analysis to date (n=8,104) in a real-world setting across eight hospitals. Our two-step semi-supervised strategy distills knowledge from task-specific CNNs into a transformer. First, CNNs predict on unlabeled data per label type and then the transformer learns from these predictions with label-specific heads. This improves predictive accuracy and enables simultaneous learning of all partial labels across the federation, and outperforms UNet-based models in generalizability on downstream tasks. Code and model weights are made openly available for leveraging future cardiac CT analysis.
联邦学习是利用分散数据同时保护隐私的知名技术。然而,现实世界的应用经常面临部分标注数据集的挑战,只有少数地点拥有某些专家标注,导致大量未标注数据无法使用。利用这些数据可以增强小且多样化标注集中的变换器架构的能力。我们在八个医院的真实世界环境中进行了迄今为止最大的联邦心脏CT分析(n=8,104)。我们的两步半监督策略将任务特定CNN的知识蒸馏到变换器中。首先,CNN按标签类型对未标记数据进行预测,然后变换器通过特定标签头从这些预测中学习。这提高了预测精度,能够在联邦中同时学习所有部分标签,并且在下游任务上的泛化性能优于基于UNet的模型。代码和模型权重已公开提供,可用于未来的心脏CT分析。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了联邦学习在利用分散数据的同时保护隐私的技术。针对现实世界中只有部分地点拥有特定专家标注、大量未标注数据未被使用的问题,文章通过利用这些未标注数据,增强了在小型和多样化标注集下的转换器架构能力。研究团队进行了迄今为止最大的联邦心脏CT分析(n=8,104),跨越八家医院。他们采用的两步半监督策略将任务特定CNN的知识蒸馏到转换器中。首先,CNN按标签类型对未标记数据进行预测,然后转换器从这些预测中学习,并配备有标签特定头。这种方法提高了预测精度,能够同时学习联邦中的所有部分标签,并且在下游任务上的通用性优于基于UNet的模型。代码和模型权重已公开提供,可用于将来的心脏CT分析。
Key Takeaways
- 联邦学习能够利用分散数据的同时保护隐私。
- 部分数据集只有部分标注,大量未标注数据未得到利用。
- 通过利用未标注数据,可增强在小型和多样化标注集下的转换器架构能力。
- 研究团队进行了大规模(n=8,104)的联邦心脏CT分析,涉及八家医院的数据。
- 采用的两步半监督策略将CNN的知识蒸馏到转换器中。
- 该方法提高了预测精度,并能同时学习所有部分标签。
点此查看论文截图

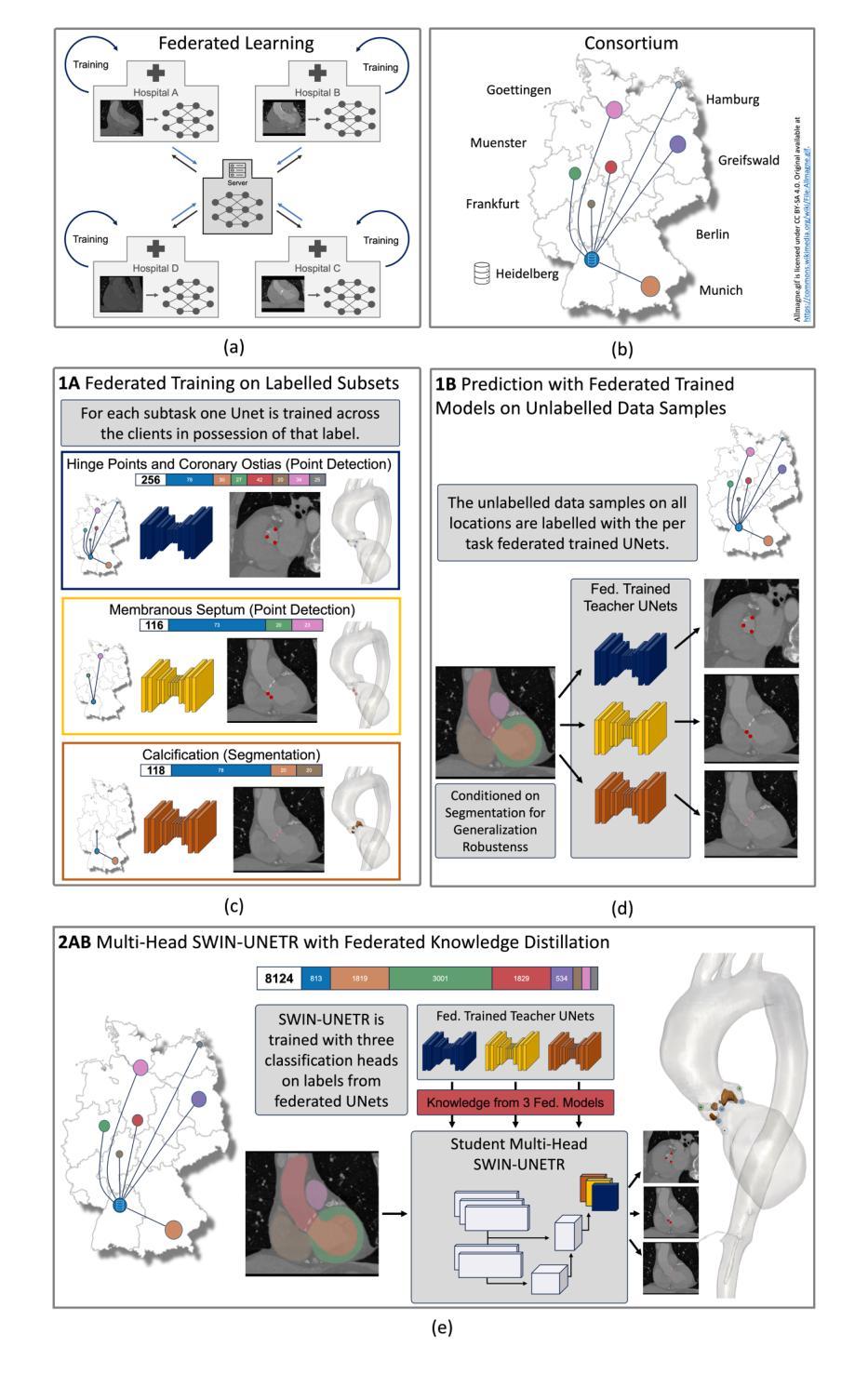
Multi-modal Evidential Fusion Network for Trustworthy PET/CT Tumor Segmentation
Authors:Yuxuan Qi, Li Lin, Jiajun Wang, Bin Zhang, Jingya Zhang
Accurate tumor segmentation in PET/CT images is crucial for computer-aided cancer diagnosis and treatment. The primary challenge lies in effectively integrating the complementary information from PET and CT images. In clinical settings, the quality of PET and CT images often varies significantly, leading to uncertainty in the modality information extracted by networks. To address this challenge, we propose a novel Multi-modal Evidential Fusion Network (MEFN), which consists of two core stages: Cross-Modal Feature Learning (CFL) and Multi-modal Trustworthy Fusion (MTF). The CFL stage aligns features across different modalities and learns more robust feature representations, thereby alleviating the negative effects of domain gap. The MTF stage utilizes mutual attention mechanisms and an uncertainty calibrator to fuse modality features based on modality uncertainty and then fuse the segmentation results under the guidance of Dempster-Shafer Theory. Besides, a new uncertainty perceptual loss is introduced to force the model focusing on uncertain features and hence improve its ability to extract trusted modality information. Extensive comparative experiments are conducted on two publicly available PET/CT datasets to evaluate the performance of our proposed method whose results demonstrate that our MEFN significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods with improvements of 3.10% and 3.23% in DSC scores on the AutoPET dataset and the Hecktor dataset, respectively. More importantly, our model can provide radiologists with credible uncertainty of the segmentation results for their decision in accepting or rejecting the automatic segmentation results, which is particularly important for clinical applications. Our code will be available at https://github.com/QPaws/MEFN.
在PET/CT图像中进行准确的肿瘤分割对于计算机辅助的癌症诊断和治疗至关重要。主要挑战在于有效地整合PET和CT图像中的互补信息。在临床环境中,PET和CT图像的质量经常有很大的差异,导致网络提取的模态信息存在不确定性。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了一种新的多模态证据融合网络(MEFN),它包含两个阶段:跨模态特征学习(CFL)和多模态可信融合(MTF)。CFL阶段对不同模态的特征进行对齐,学习更稳健的特征表示,从而减轻领域差距的负面影响。MTF阶段利用相互注意机制和不确定性校准器,基于模态不确定性融合模态特征,然后在Dempster-Shafer理论的指导下融合分割结果。此外,引入了一种新的不确定性感知损失,以迫使模型关注不确定的特征,从而提高其提取可信模态信息的能力。我们在两个公开的PET/CT数据集上进行了广泛的对比实验,以评估我们提出的方法的性能。结果表明,我们的MEFN在DSC得分上显著优于最先进的方法,在AutoPET数据集和Hecktor数据集上分别提高了3.10%和3.23%。更重要的是,我们的模型可以为放射科医生提供分割结果的可靠不确定性,以供他们决定是否接受或拒绝自动分割结果,这在临床应用中是特别重要的。我们的代码将在https://github.com/QPaws/MEFN上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
提出一种多模态证据融合网络(MEFN),用于PET/CT图像的肿瘤分割。网络包括两个阶段:跨模态特征学习(CFL)和跨模态可信融合(MTF)。CFL阶段实现对不同模态的特征对齐,学习更稳健的特征表示,缓解领域差距的负面影响。MTF阶段利用互注意机制和不确定性校准器,基于模态不确定性融合模态特征,并在Dempster-Shafer理论的指导下融合分割结果。引入新的不确定性感知损失,使模型关注不确定特征,提高提取可靠模态信息的能力。在公开PET/CT数据集上的实验表明,MEFN在DSC得分上较先进方法提高了3.10%和3.23%,并为放射科医生提供可信的分割结果不确定性,有助于他们决定是否接受自动分割结果,具有临床意义。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态图像分割的挑战在于整合PET和CT图像的互补信息。
- 提出的多模态证据融合网络(MEFN)包含跨模态特征学习(CFL)和跨模态可信融合(MTF)两个阶段。
- CFL阶段实现不同模态的特征对齐,增强稳健性特征学习,减少领域差距影响。
- MTF阶段利用互注意机制和不确定性校准器,结合模态不确定性进行特征融合和分割结果融合。
- 引入不确定性感知损失,使模型更注重不确定特征,提高提取可靠模态信息的准确度。
- 在公开数据集上的实验显示,MEFN显著优于其他方法,提高了分割精度。
- MEFN能为放射科医生提供分割结果的可信不确定性,有助于临床决策。
点此查看论文截图

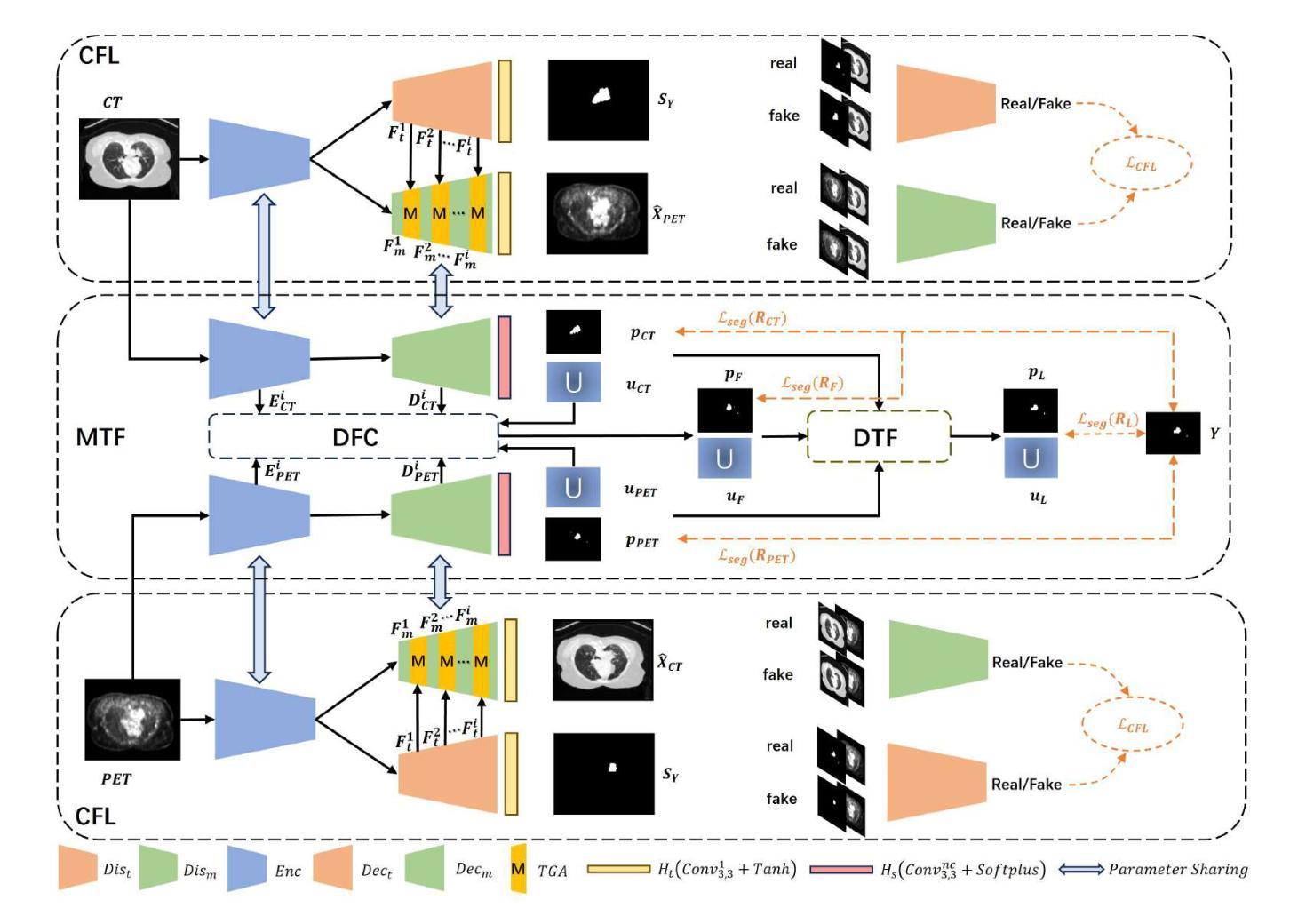
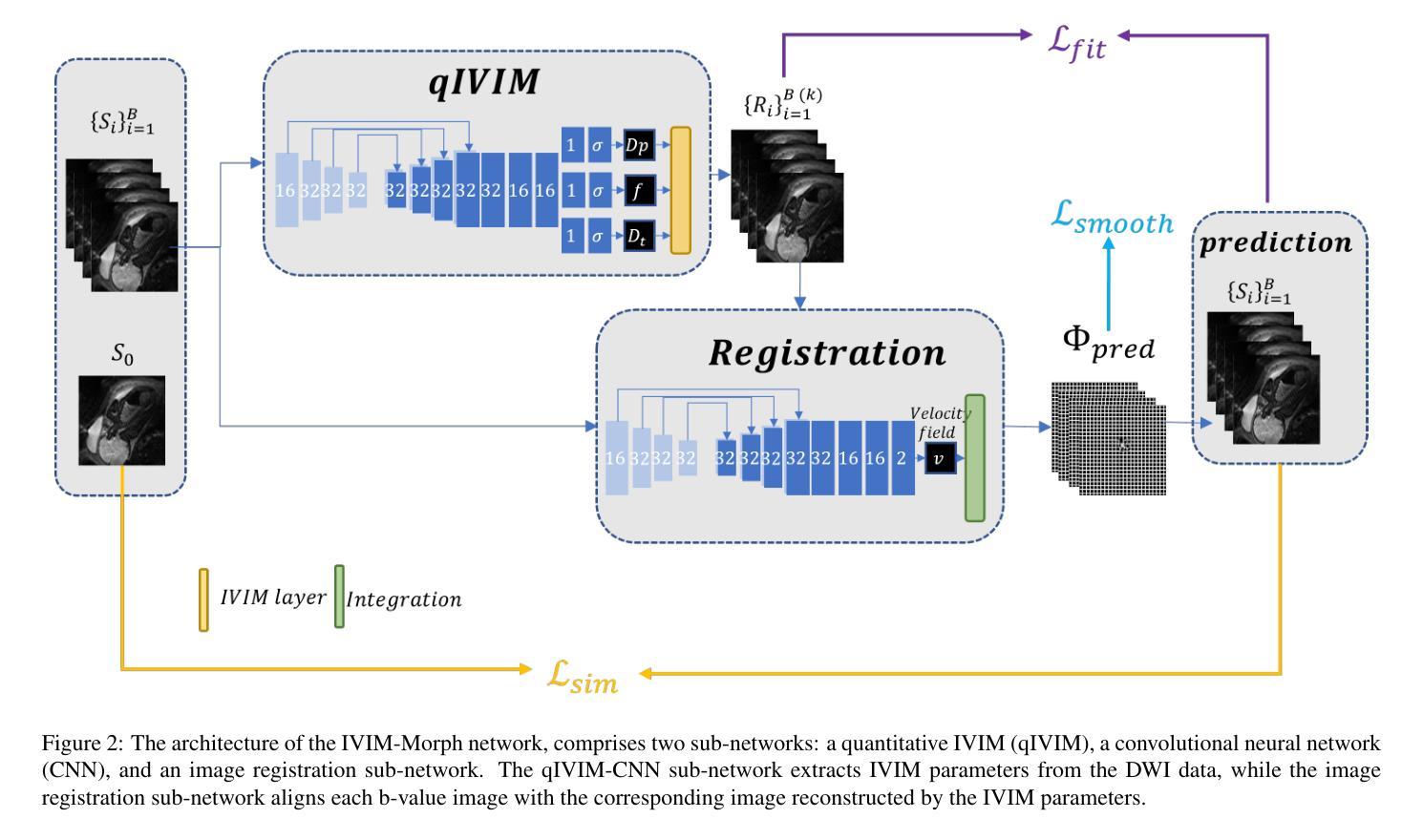
IVIM-Morph: Motion-compensated quantitative Intra-voxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) analysis for functional fetal lung maturity assessment from diffusion-weighted MRI data
Authors:Noga Kertes, Yael Zaffrani-Reznikov, Onur Afacan, Sila Kurugol, Simon K. Warfield, Moti Freiman
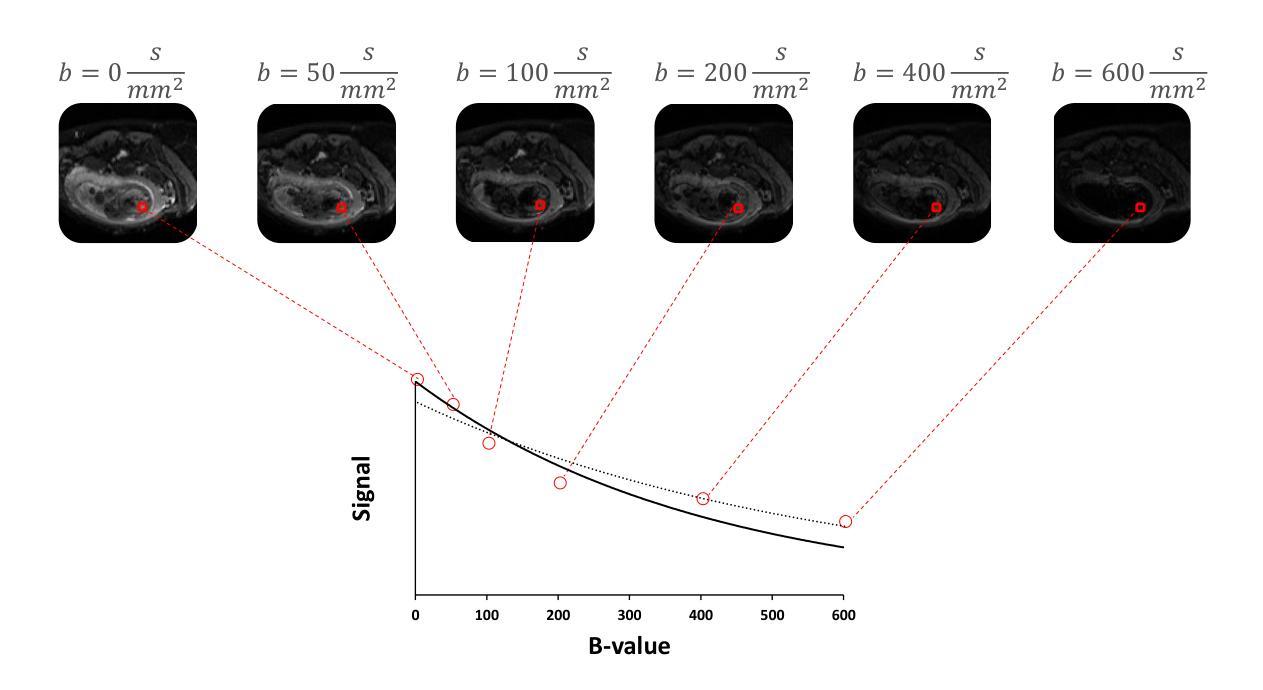
Quantitative analysis of pseudo-diffusion in diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DWI) data shows potential for assessing fetal lung maturation and generating valuable imaging biomarkers. Yet, the clinical utility of DWI data is hindered by unavoidable fetal motion during acquisition. We present IVIM-morph, a self-supervised deep neural network model for motion-corrected quantitative analysis of DWI data using the Intra-voxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) model. IVIM-morph combines two sub-networks, a registration sub-network, and an IVIM model fitting sub-network, enabling simultaneous estimation of IVIM model parameters and motion. To promote physically plausible image registration, we introduce a biophysically informed loss function that effectively balances registration and model-fitting quality. We validated the efficacy of IVIM-morph by establishing a correlation between the predicted IVIM model parameters of the lung and gestational age (GA) using fetal DWI data of 39 subjects. IVIM-morph exhibited a notably improved correlation with gestational age (GA) when performing in-vivo quantitative analysis of fetal lung DWI data during the canalicular phase. IVIM-morph shows potential in developing valuable biomarkers for non-invasive assessment of fetal lung maturity with DWI data. Moreover, its adaptability opens the door to potential applications in other clinical contexts where motion compensation is essential for quantitative DWI analysis. The IVIM-morph code is readily available at: https://github.com/TechnionComputationalMRILab/qDWI-Morph.
对扩散加权磁共振成像(DWI)数据中的伪扩散进行定量分析,在评估胎儿肺成熟度和产生有价值的成像生物标志物方面具有潜力。然而,DWI数据的临床应用受到采集过程中不可避免的胎儿运动的影响。我们提出了IVIM-morph,这是一种基于自监督深度神经网络模型的DWI数据运动校正定量分析系统,它采用体素内非相干运动(IVIM)模型。IVIM-morph结合了两个子网络,一个注册子网络和一个IVIM模型拟合子网络,可以同时估计IVIM模型参数和运动。为了促进物理上合理的图像配准,我们引入了一个基于生物物理信息的损失函数,该损失函数可以有效地平衡配准和模型拟合质量。我们通过建立肺预测的IVIM模型参数与胎龄(GA)之间的相关性,验证了IVIM-morph的有效性,使用的是来自39名胎儿的DWI数据。在胎儿肺DWI数据的峡部阶段的体内定量分析中,IVIM-morph与胎龄(GA)的相关性显著提高。IVIM-morph在利用DWI数据对胎儿肺成熟度进行无创评估方面具有发展有价值生物标志物的潜力。此外,其适应性为在其它需要定量DWI分析的运动补偿的临床环境中应用打开了大门。IVIM-morph的代码可轻松获取于:https://github.com/TechnionComputationalMRILab/qDWI-Morph。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in the journal: “Medical Image Analysis”
Summary
该文介绍了利用定量扩散加权磁共振成像(DWI)数据评估胎儿肺成熟度的方法。研究中提出了一种名为IVIM-morph的自监督深度神经网络模型,该模型使用Intra-voxel Incoherent Motion(IVIM)模型进行运动校正的定量DWI数据分析。IVIM-morph结合了配准子网络和IVIM模型拟合子网络,可以同时估计IVIM模型参数和运动。通过引入生物物理信息损失函数,促进物理上合理的图像配准,有效平衡配准和模型拟合质量。使用胎儿DWI数据对IVIM-morph进行验证,结果表明预测的IVIM模型参数与胎龄有良好相关性,特别是在肺导管期。IVIM-morph具有开发基于DWI数据的胎儿肺成熟度非侵入评估生物标志物的潜力,并且其适应性为其他需要定量DWI分析的运动补偿临床应用提供了可能性。
Key Takeaways
- 利用定量扩散加权磁共振成像(DWI)数据评估胎儿肺成熟度具有潜力。
- IVIM-morph是一个自监督深度神经网络模型,用于运动校正的定量DWI数据分析。
- IVIM-morph结合了配准和IVIM模型拟合,可以同时估计模型参数和运动。
- 通过引入生物物理信息损失函数,促进了物理上合理的图像配准。
- IVIM-morph在胎儿肺DWI数据的体内定量分析中表现出与胎龄的良好相关性。
- IVIM-morph具有开发基于DWI数据的非侵入性胎儿肺成熟度评估生物标志物的潜力。
- IVIM-morph的适应性为其在其他需要定量DWI分析的运动补偿临床应用中的使用提供了可能性。
点此查看论文截图

Improve Myocardial Strain Estimation based on Deformable Groupwise Registration with a Locally Low-Rank Dissimilarity Metric
Authors:Haiyang Chen, Juan Gao, Zhuo Chen, Chenhao Gao, Sirui Huo, Meng Jiang, Jun Pu, Chenxi Hu
Background: Current mainstream cardiovascular magnetic resonance-feature tracking (CMR-FT) methods, including optical flow and pairwise registration, often suffer from the drift effect caused by accumulative tracking errors. Here, we developed a CMR-FT method based on deformable groupwise registration with a locally low-rank (LLR) dissimilarity metric to improve myocardial tracking and strain estimation accuracy. Methods: The proposed method, Groupwise-LLR, performs feature tracking by iteratively updating the entire displacement field across all cardiac phases to minimize the sum of the patchwise signal ranks of the deformed movie. The method was compared with alternative CMR-FT methods including the Farneback optical flow, a sequentially pairwise registration method, and a global low rankness-based groupwise registration method via a simulated dataset (n = 20), a public cine data set (n = 100), and an in-house tagging-MRI patient dataset (n = 16). The proposed method was also compared with two general groupwise registration methods, nD+t B-Splines and pTVreg, in simulations and in vivo tracking. Results: On the simulated dataset, Groupwise-LLR achieved the lowest point tracking errors and voxelwise/global strain errors. On the public dataset, Groupwise-LLR achieved the lowest contour tracking errors, reduced the drift effect in late-diastole, and preserved similar inter-observer reproducibility as the alternative methods. On the patient dataset, Groupwise-LLR correlated better with tagging-MRI for radial strains than the other CMR-FT methods in multiple myocardial segments and levels. Conclusions: The proposed Groupwise-LLR reduces the drift effect and provides more accurate myocardial tracking and strain estimation than the alternative methods. The method may thus facilitate a more accurate estimation of myocardial strains for clinical assessments of cardiac function.
背景:当前主流的心血管磁共振特征跟踪(CMR-FT)方法,包括光学流和配对注册,经常受到由累积跟踪误差引起的漂移效应的影响。在这里,我们开发了一种基于可变形组注册和局部低秩(LLR)差异度量的CMR-FT方法,以提高心肌跟踪和应变估计的准确性。方法:所提出的方法(Groupwise-LLR)通过迭代更新所有心脏阶段的整个位移场,以最小化变形电影中的斑块信号等级和,来执行特征跟踪。该方法通过模拟数据集(n=20)、公共电影数据集(n=100)和院内标签MRI患者数据集(n=16)与替代的CMR-FT方法(包括Farneback光学流、顺序配对注册方法和基于全局低秩的组注册方法)进行比较。所提出的方法还在模拟和体内跟踪中与两种通用的组注册方法nD+t B-Splines和pTVreg进行了比较。结果:在模拟数据集上,Groupwise-LLR达到了最低的点跟踪误差和体素级/全局应变误差。在公共数据集上,Groupwise-LLR取得了最低的轮廓跟踪误差,减少了舒张后期的漂移效应,并保持了与其他方法的相似观察者间可重复性。在患者数据集上,相较于其他CMR-FT方法,Groupwise-LLR在多心肌节段和水平上与标签MRI在径向应变上具有更好的相关性。结论:所提出的Groupwise-LLR减少了漂移效应,并提供了比其他方法更准确的心肌跟踪和应变估计。因此,该方法可能有助于更准确估计心肌应变,用于临床心脏功能评估。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于可变形组注册和局部低秩(LLR)差异度量的心血管磁共振特征跟踪(CMR-FT)方法,旨在提高心肌跟踪和应变估计的准确性。新方法通过迭代更新所有心脏阶段的整个位移场,以最小化变形电影的斑块信号等级和,从而进行特征跟踪。在模拟数据集、公开电影数据集和院内标签MRI患者数据集上的比较结果表明,该方法在点跟踪误差、轮廓跟踪误差、整体应变误差等方面表现优异,并减少了舒张后期的漂移效应。因此,所提出的方法可能更准确地估计心肌应变,有助于临床心脏功能评估。
Key Takeaways
- 当前主流的心血管磁共振特征跟踪方法常受到由累积跟踪误差导致的漂移效应影响。
- 提出了基于可变形组注册和局部低秩差异度量的新方法(Groupwise-LLR)来改善心肌跟踪和应变估计。
- Groupwise-LLR方法通过迭代更新整个位移场来最小化变形电影的斑块信号等级和,实现特征跟踪。
- 在模拟、公开和患者数据集上的比较显示,Groupwise-LLR在跟踪准确性和应变估计方面优于其他CMR-FT方法。
- Groupwise-LLR在模拟数据集中实现了最低的点跟踪误差和全局应变误差。
- 在公共数据集中,Groupwise-LLR减少了舒张后期的漂移效应,并保持与其他方法的类似观察者间可重复性。
点此查看论文截图


