⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-04 更新
Fine-grained Image-to-LiDAR Contrastive Distillation with Visual Foundation Models
Authors:Yifan Zhang, Junhui Hou
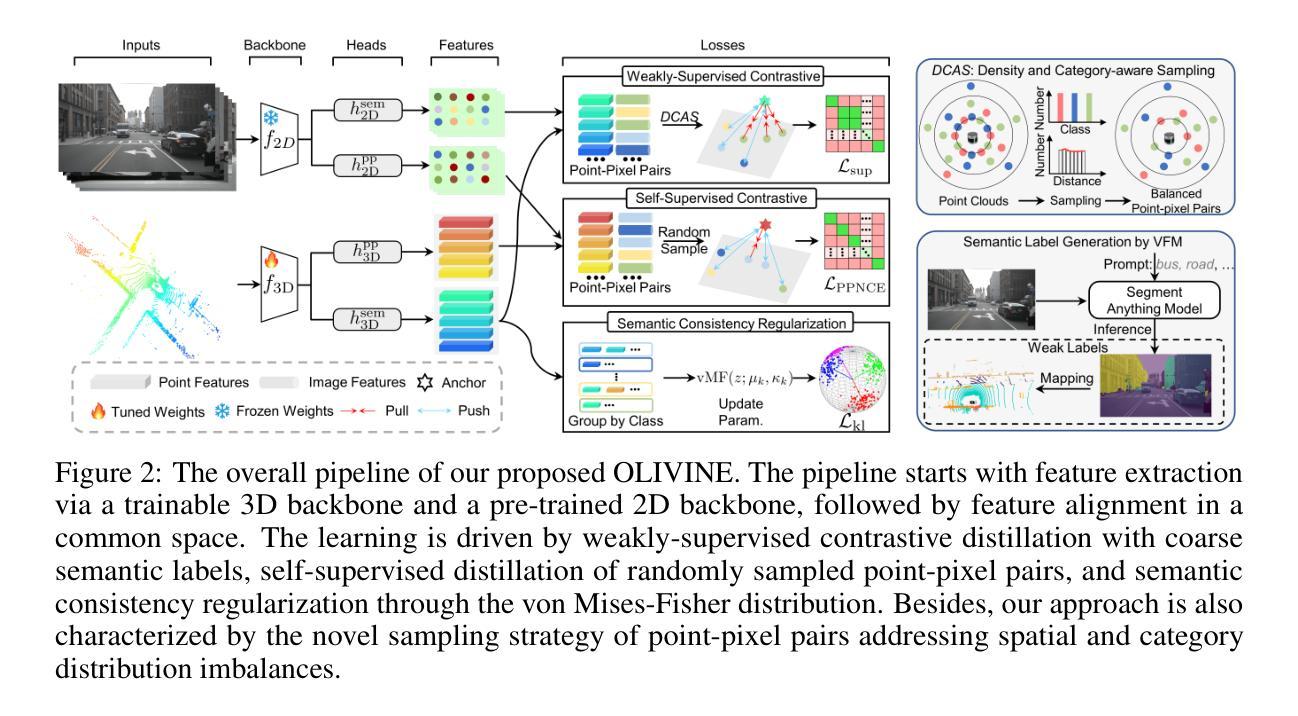
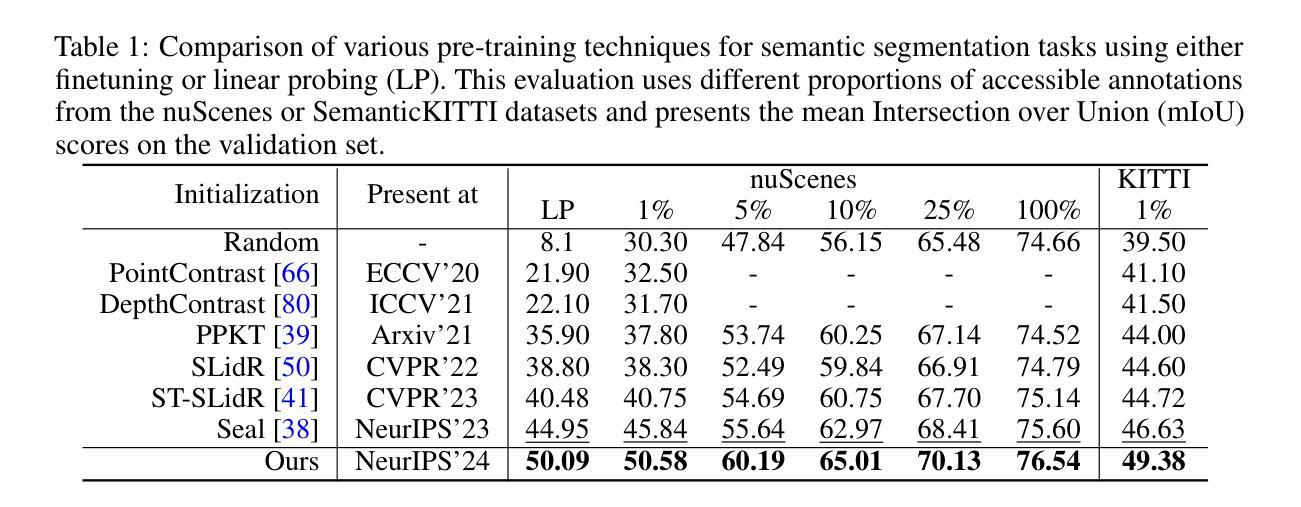
Contrastive image-to-LiDAR knowledge transfer, commonly used for learning 3D representations with synchronized images and point clouds, often faces a self-conflict dilemma. This issue arises as contrastive losses unintentionally dissociate features of unmatched points and pixels that share semantic labels, compromising the integrity of learned representations. To overcome this, we harness Visual Foundation Models (VFMs), which have revolutionized the acquisition of pixel-level semantics, to enhance 3D representation learning. Specifically, we utilize off-the-shelf VFMs to generate semantic labels for weakly-supervised pixel-to-point contrastive distillation. Additionally, we employ von Mises-Fisher distributions to structure the feature space, ensuring semantic embeddings within the same class remain consistent across varying inputs. Furthermore, we adapt sampling probabilities of points to address imbalances in spatial distribution and category frequency, promoting comprehensive and balanced learning. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach mitigates the challenges posed by traditional methods and consistently surpasses existing image-to-LiDAR contrastive distillation methods in downstream tasks. The source code is available at https://github.com/Eaphan/OLIVINE.
对比图像到激光雷达的知识迁移常用于学习同步图像和点云的3D表示,但经常面临自相矛盾的困境。这个问题是由于对比损失无意中解开了具有相同语义标签的不匹配点和像素的特征,从而损害了学习到的表示的完整性。为了克服这一问题,我们利用视觉基础模型(VFMs),它们已经彻底改变了像素级语义的获取,以增强3D表示学习。具体来说,我们利用现成的VFMs进行弱监督像素到点的对比蒸馏来生成语义标签。此外,我们还采用冯米塞斯-费舍尔分布来构建特征空间,确保同一类中的语义嵌入在不同输入下保持一致。此外,我们适应了点的采样概率来解决空间分布和类别频率的不平衡问题,促进了全面而平衡的学习。大量实验表明,我们的方法缓解了传统方法带来的挑战,并且在下游任务中始终超越了现有的图像到激光雷达对比蒸馏方法。源代码可在https://github.com/Eaphan/OLIVINE找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Camera-ready version in NeurIPS 2024
Summary
本文解决了对比图像到激光雷达知识迁移中的自冲突问题,通过利用视觉基础模型(VFMs)增强3D表示学习,采用弱监督像素到点对比蒸馏生成语义标签,并使用冯·米塞斯-费舍尔分布来构建特征空间,同时适应点采样概率以处理空间分布和类别频率的不平衡问题。实验表明,该方法缓解了传统方法的挑战,并在下游任务中超越了现有的图像到激光雷达对比蒸馏方法。
Key Takeaways
- 对比图像到激光雷达知识迁移存在自冲突问题,特征不匹配和像素语义标签的分离导致学习表示完整性受损。
- 利用视觉基础模型(VFMs)增强3D表示学习,提高像素级别语义的获取。
- 采用弱监督像素到点对比蒸馏生成语义标签,简化监督信息需求。
- 使用冯·米塞斯-费舍尔分布构建特征空间,确保同类语义嵌入在不同输入下的一致性。
- 适应点采样概率以处理空间分布和类别频率的不平衡,实现更全面和平衡的学习。
- 提出的方法通过解决传统方法的挑战,在下游任务中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图