⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-04 更新
SpecDETR: A Transformer-based Hyperspectral Point Object Detection Network
Authors:Zhaoxu Li, Wei An, Gaowei Guo, Longguang Wang, Yingqian Wang, Zaiping Lin
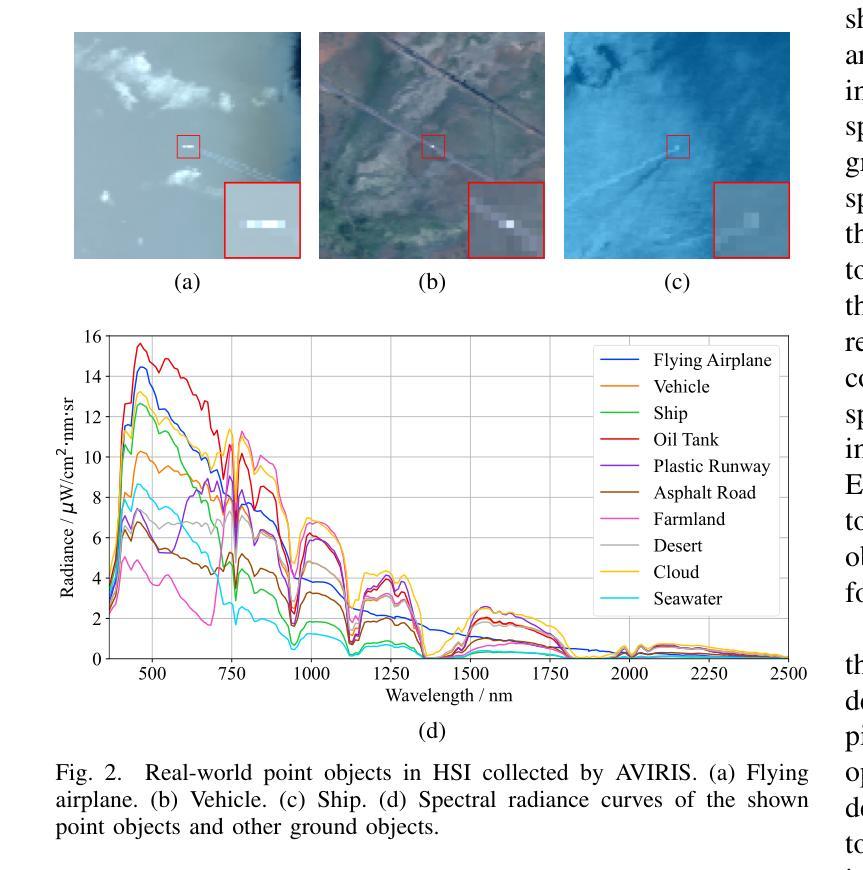
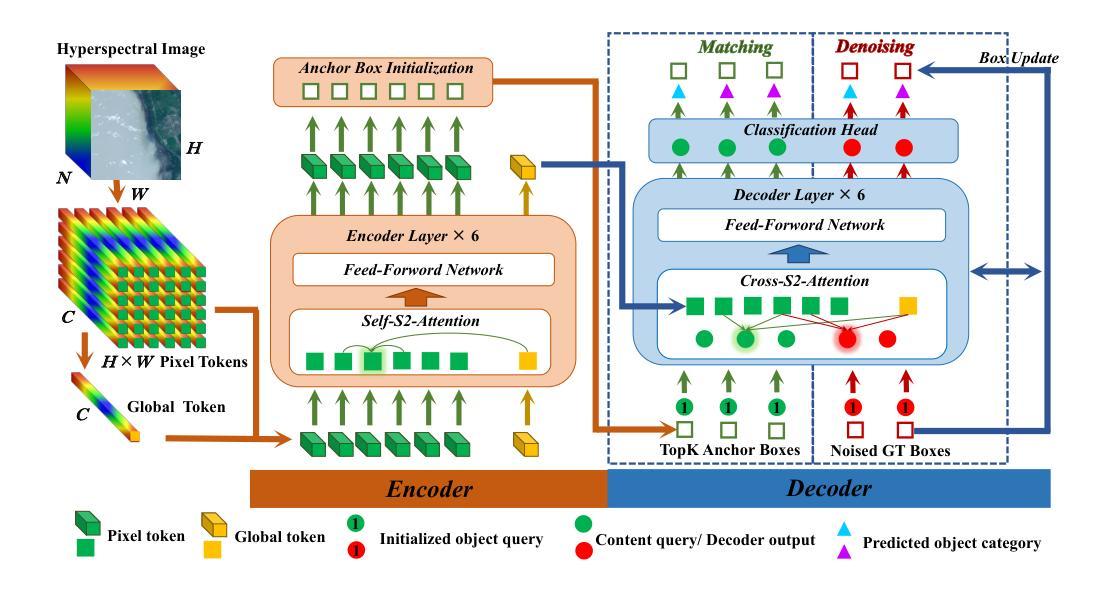
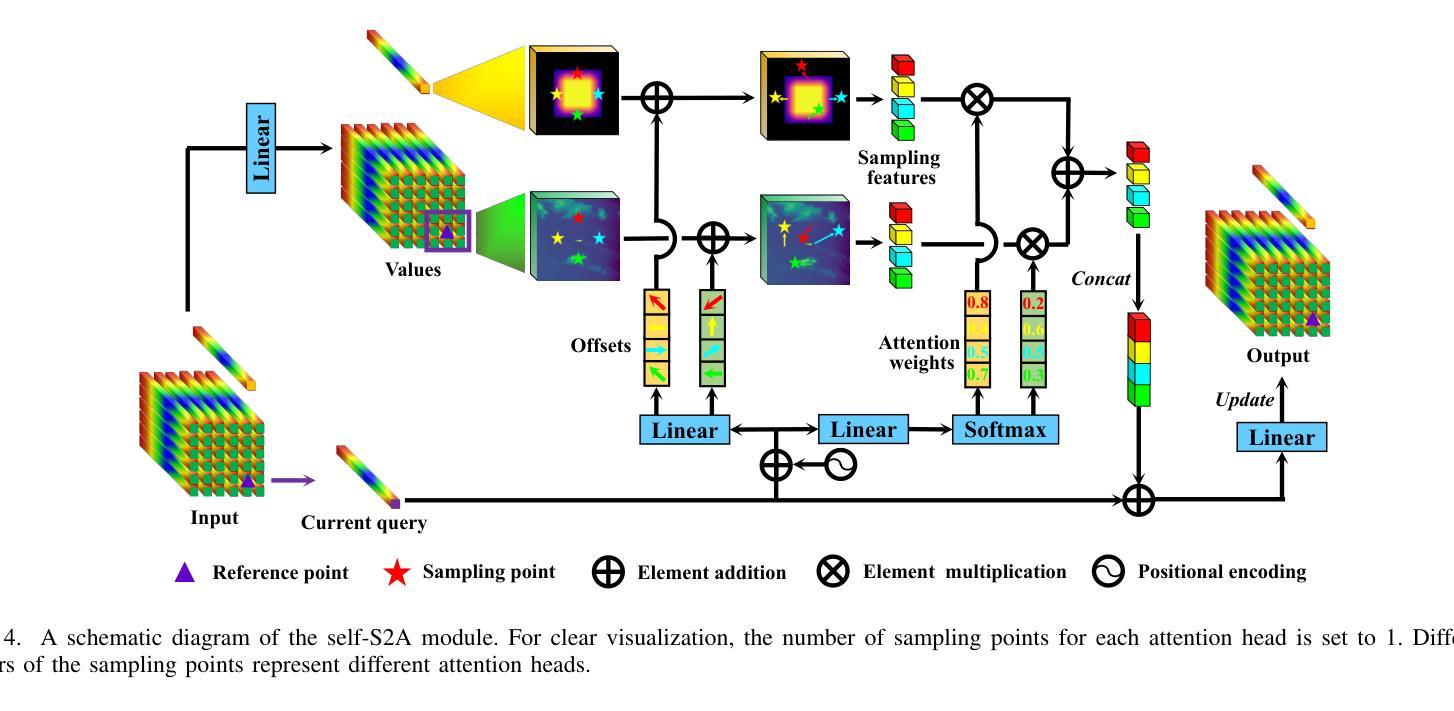
Hyperspectral target detection (HTD) aims to identify specific materials based on spectral information in hyperspectral imagery and can detect extremely small objects, some of which occupy a smaller than one-pixel area. However, existing HTD methods are developed based on per-pixel binary classification, which limits the feature representation capability for instance-level objects. In this paper, we rethink the hyperspectral target detection from the point object detection perspective, and propose the first specialized network for hyperspectral multi-class point object detection, SpecDETR. Without the visual foundation model of the current object detection framework, SpecDETR treats each pixel in input images as a token and uses a multi-layer Transformer encoder with self-excited subpixel-scale attention modules to directly extract joint spatial-spectral features from images. During feature extraction, we introduce a self-excited mechanism to enhance object features through self-excited amplification, thereby accelerating network convergence. Additionally, SpecDETR regards point object detection as a one-to-many set prediction problem, thereby achieving a concise and efficient DETR decoder that surpasses the state-of-the-art (SOTA) DETR decoder. We develop a simulated hyperSpectral Point Object Detection benchmark termed SPOD, and for the first time, evaluate and compare the performance of current object detection networks and HTD methods on hyperspectral point object detection. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed SpecDETR outperforms SOTA object detection networks and HTD methods. Our code and dataset are available at https://github.com/ZhaoxuLi123/SpecDETR.
超光谱目标检测(HTD)旨在基于超光谱图像中的光谱信息识别特定材料,并能够检测极小物体,其中一些物体的面积小于一个像素。然而,现有的HTD方法主要是基于像素级二元分类开发的,这限制了其在实例级物体的特征表示能力。在本文中,我们重新思考了超光谱目标检测的点对象检测角度,并首次提出了针对超光谱多类点对象检测的专用网络SpecDETR。SpecDETR摒弃了当前对象检测框架的视觉基础模型,将输入图像中的每个像素视为令牌,并使用带有自激发子像素尺度注意力模块的多层Transformer编码器直接从图像中提取联合空间-光谱特征。在特征提取过程中,我们引入了一种自激发机制,通过自激发放大增强目标特征,从而加速网络收敛。此外,SpecDETR将点对象检测视为一个一对多的集合预测问题,从而实现了一个简洁高效且超越最新(SOTA)DETR解码器的DETR解码器。我们开发了一个名为SPOD的超光谱点对象检测模拟基准测试集,首次对当前的对象检测网络和高光谱目标检测方法进行超光谱点对象检测的性能评估和比较。大量实验表明,我们提出的SpecDETR在对象检测网络和HTD方法上均表现出超越最新技术的性能。我们的代码和数据集可在https://github.com/ZhaoxuLi123/SpecDETR上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种专门用于超光谱多类点目标检测的网络SpecDETR,采用基于点目标检测的角度重新思考超光谱目标检测问题。该网络采用多层Transformer编码器,具有自激发子像素尺度注意力模块,可直接从图像中提取联合空间-光谱特征。通过自激发机制增强目标特征,并简化了DETR解码器。在超光谱点目标检测基准测试SPOD上进行评估,显示SpecDETR优于当前的目标检测网络和HTD方法。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种针对超光谱多类点目标检测的专用网络SpecDETR。
- 采用基于点目标检测的角度重新思考超光谱目标检测问题。
- 使用多层Transformer编码器和自激发子像素尺度注意力模块提取联合空间-光谱特征。
- 通过自激发机制增强目标特征,加速网络收敛。
- 将点目标检测视为一个一对一集预测问题,实现简洁高效的DETR解码器。
- 建立了超光谱点目标检测基准测试SPOD。
点此查看论文截图

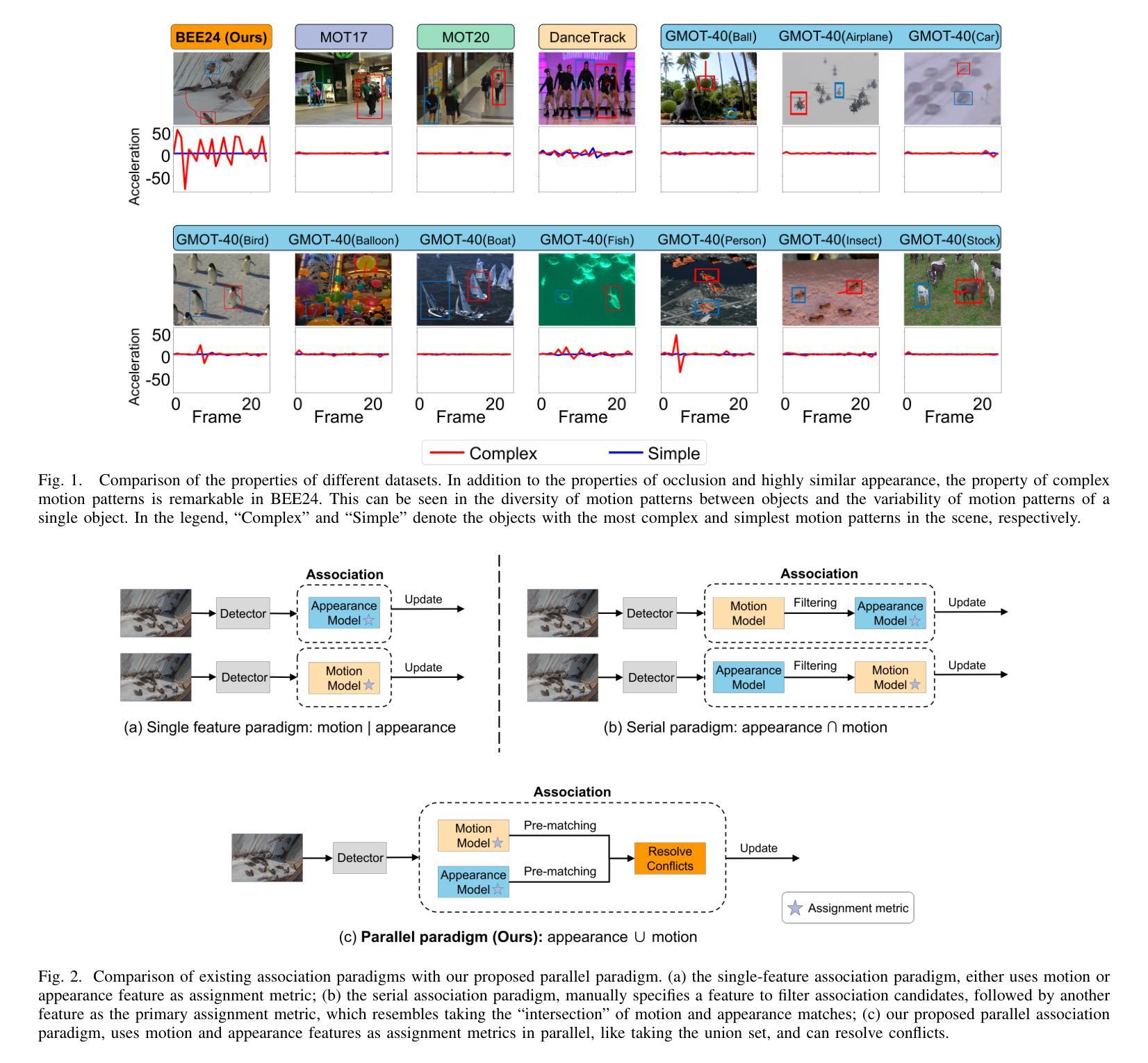
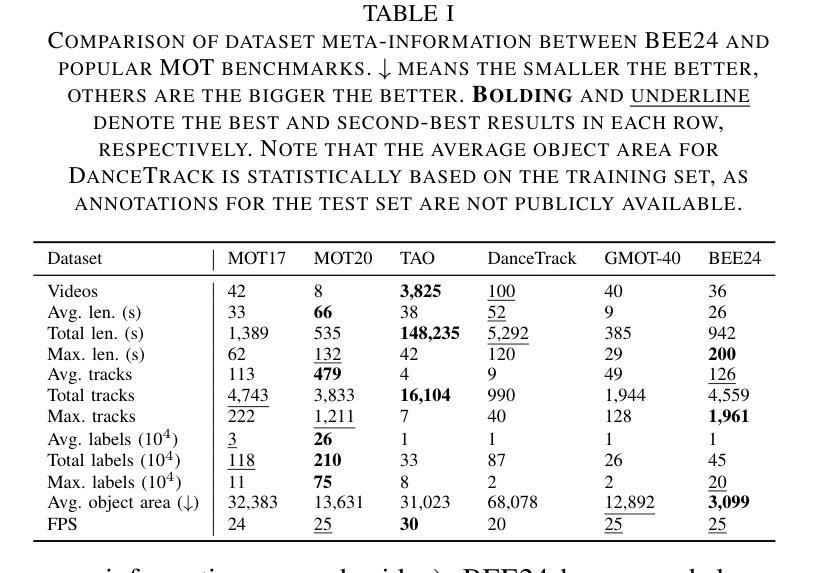
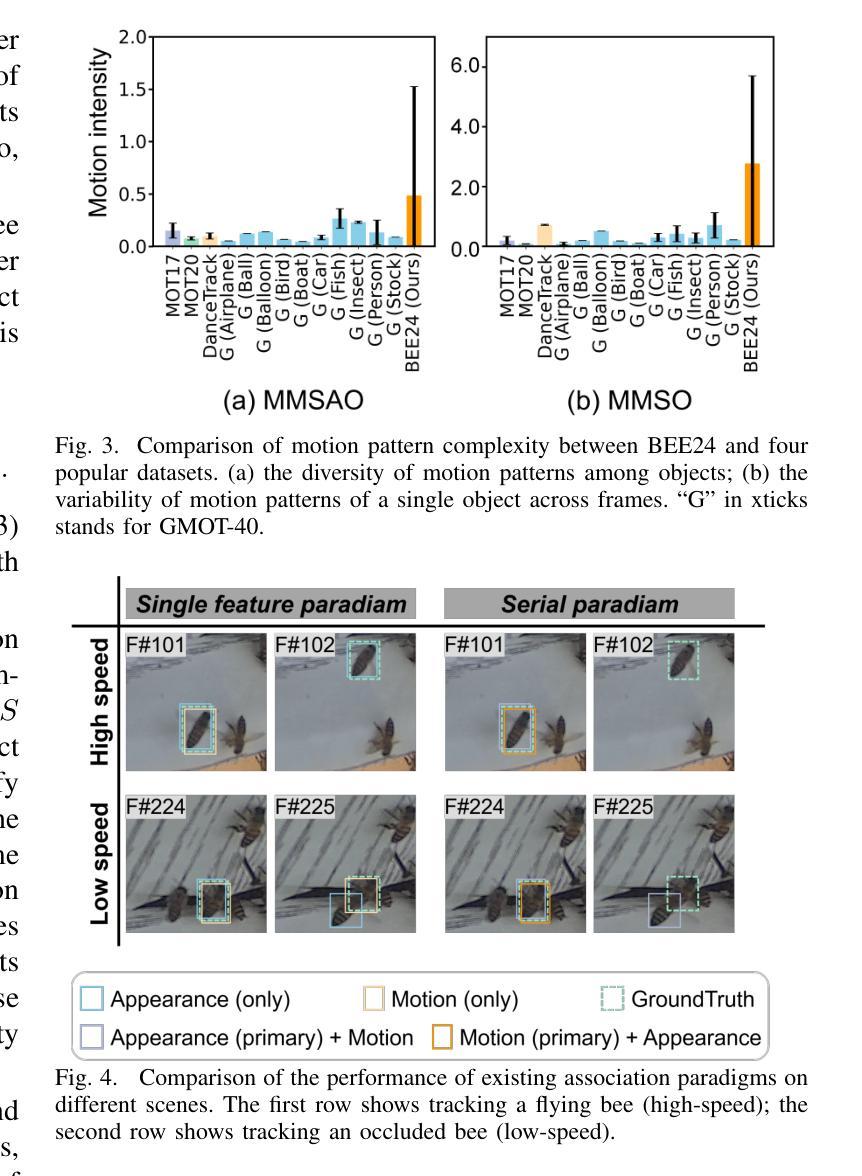
TOPIC: A Parallel Association Paradigm for Multi-Object Tracking under Complex Motions and Diverse Scenes
Authors:Xiaoyan Cao, Yiyao Zheng, Yao Yao, Huapeng Qin, Xiaoyu Cao, Shihui Guo
Video data and algorithms have been driving advances in multi-object tracking (MOT). While existing MOT datasets focus on occlusion and appearance similarity, complex motion patterns are widespread yet overlooked. To address this issue, we introduce a new dataset called BEE24 to highlight complex motions. Identity association algorithms have long been the focus of MOT research. Existing trackers can be categorized into two association paradigms: single-feature paradigm (based on either motion or appearance feature) and serial paradigm (one feature serves as secondary while the other is primary). However, these paradigms are incapable of fully utilizing different features. In this paper, we propose a parallel paradigm and present the Two rOund Parallel matchIng meChanism (TOPIC) to implement it. The TOPIC leverages both motion and appearance features and can adaptively select the preferable one as the assignment metric based on motion level. Moreover, we provide an Attention-based Appearance Reconstruction Module (AARM) to reconstruct appearance feature embeddings, thus enhancing the representation of appearance features. Comprehensive experiments show that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on four public datasets and BEE24. Moreover, BEE24 challenges existing trackers to track multiple similar-appearing small objects with complex motions over long periods, which is critical in real-world applications such as beekeeping and drone swarm surveillance. Notably, our proposed parallel paradigm surpasses the performance of existing association paradigms by a large margin, e.g., reducing false negatives by 6% to 81% compared to the single-feature association paradigm. The introduced dataset and association paradigm in this work offer a fresh perspective for advancing the MOT field. The source code and dataset are available at https://github.com/holmescao/TOPICTrack.
视频数据和算法在多目标跟踪(MOT)方面取得了进展。虽然现有的MOT数据集侧重于遮挡和外观相似性,但复杂的运动模式普遍存在却被忽视。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了一个新的数据集BEE24来突出复杂的运动。身份关联算法一直是MOT研究的重点。现有的跟踪器可以归纳为两种关联范式:单特征范式(基于运动或外观特征)和序列范式(一个特征作为次要特征,另一个作为主要特征)。然而,这些范式无法充分利用不同的特征。在本文中,我们提出了一种并行范式,并提出了两阶段并行匹配机制(TOPIC)来实现它。TOPIC利用运动特征和外观特征,并能根据运动水平自适应地选择更合适的特征作为分配指标。此外,我们提供了一个基于注意力的外观重建模块(AARM)来重建外观特征嵌入,从而增强外观特征的表示。综合实验表明,我们的方法在四个公共数据集和BEE24上达到了最先进的性能。而且,BEE24对现有的跟踪器提出了挑战,要求在长时间内跟踪多个外观相似的小对象的复杂运动,这在养蜂和无人机集群监控等实际应用中至关重要。值得注意的是,我们提出的并行范式在性能上大大超过了现有的关联范式,例如与单特征关联范式相比,减少了误报率为6%至81%。本文中引入的数据集和关联范式为推进MOT领域提供了新的视角。源代码和数据集可在https://github.com/holmescao/TOPICTrack找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Image Processing (TIP), 16 pages, 12 figures, 7 tables
Summary
本文介绍了针对多目标跟踪(MOT)领域的新数据集BEE24,用于突出复杂运动模式的重要性。文章提出了一种新的并行关联范式和基于两轮并行匹配机制(TOPIC)的算法来实现多目标跟踪。TOPIC算法能够利用运动与外观特征,根据运动级别自适应选择更合适的特征作为分配度量标准。此外,文章还提出了基于注意力的外观重建模块(AARM),以增强外观特征的表示。实验证明,该方法在四个公共数据集及BEE24上的表现达到领先水平,特别是在复杂运动下的多个相似小目标的跟踪上具有挑战性。这为推动MOT领域的发展提供了新的视角。
Key Takeaways
- 引入新数据集BEE24,重点突出了复杂运动模式在视频数据处理中的重要性。
- 提出了一种新的并行关联范式,克服了现有单一特征关联范式的局限性。
- 介绍了基于两轮并行匹配机制(TOPIC)的算法,该算法能自适应选择最佳特征进行目标分配。
- 提出了注意力机制下的外观重建模块(AARM),增强了外观特征的表示能力。
- 在多个公共数据集上的实验证明了该方法的有效性,尤其在处理复杂运动下相似小目标的跟踪问题上表现出显著优势。
- 文章提出的并行关联范式和BEE24数据集为推进多目标跟踪领域的发展提供了新的视角和机遇。
点此查看论文截图