⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-04 更新
GAI: Generative Agents for Innovation
Authors:Masahiro Sato
This study examines whether collective reasoning among generative agents can facilitate novel and coherent thinking that leads to innovation. To achieve this, it proposes GAI, a new LLM-empowered framework designed for reflection and interaction among multiple generative agents to replicate the process of innovation. The core of the GAI framework lies in an architecture that dynamically processes the internal states of agents and a dialogue scheme specifically tailored to facilitate analogy-driven innovation. The framework’s functionality is evaluated using Dyson’s invention of the bladeless fan as a case study, assessing the extent to which the core ideas of the innovation can be replicated through a set of fictional technical documents. The experimental results demonstrate that models with internal states significantly outperformed those without, achieving higher average scores and lower variance. Notably, the model with five heterogeneous agents equipped with internal states successfully replicated the key ideas underlying the Dyson’s invention. This indicates that the internal state enables agents to refine their ideas, resulting in the construction and sharing of more coherent and comprehensive concepts.
本研究旨在探讨生成代理之间的集体推理是否能促进创新和连贯性的思考。为此,它提出了GAI,这是一个新的、由大型语言模型赋能的框架,旨在实现多个生成代理之间的反思和交互,从而复制创新过程。GAI框架的核心在于一种动态处理代理内部状态的架构,以及一种专门设计以促进类比驱动创新的对话方案。本研究以戴森的无叶风扇的发明作为案例研究来评估该框架的功能,评估创新的核心思想通过一系列虚构的技术文献能否得以复制。实验结果表明,具有内部状态的模型显著优于没有内部状态的模型,平均得分更高,方差更低。值得注意的是,具有内部状态的五个不同代理的模型成功复制了戴森发明的核心理念。这表明内部状态使代理能够完善其思想,导致构建和分享更连贯和全面的概念。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Added an Appendix section
Summary
该研究探讨了生成性代理之间的集体推理是否能够促进创新和产生连贯性思维。为此,它提出了GAI这一新型框架,利用大型语言模型赋能反思和代理间的交互,以模拟创新过程。其核心在于一种动态处理代理内部状态和专门设计的对话方案,以促进类比驱动的创新。该研究以戴森的无叶片风扇的发明作为案例研究,评估通过一系列虚构的技术文档能否复制创新的核心思想。实验结果表明,具有内部状态的模型表现优于没有内部状态的模型,平均得分更高且方差更低。特别是配备内部状态的五个不同代理的模型成功复制了戴森发明的核心思想。这表明内部状态使代理能够完善其想法,进而构建和分享更加连贯和综合的概念。
Key Takeaways
- 研究探讨了生成性代理间的集体推理对创新和连贯性思维的影响。
- 提出GAI框架,利用大型语言模型赋能反思和代理间的交互以模拟创新过程。
- GAI框架的核心在于处理代理内部状态和专门的对话方案以促进类比驱动的创新。
- 以戴森无叶片风扇的发明作为案例研究,评估创新核心思想的复制性。
- 实验结果显示具有内部状态的模型表现更佳,平均得分高且方差低。
- 配备内部状态的多个代理成功复制了戴森发明的核心思想。
点此查看论文截图


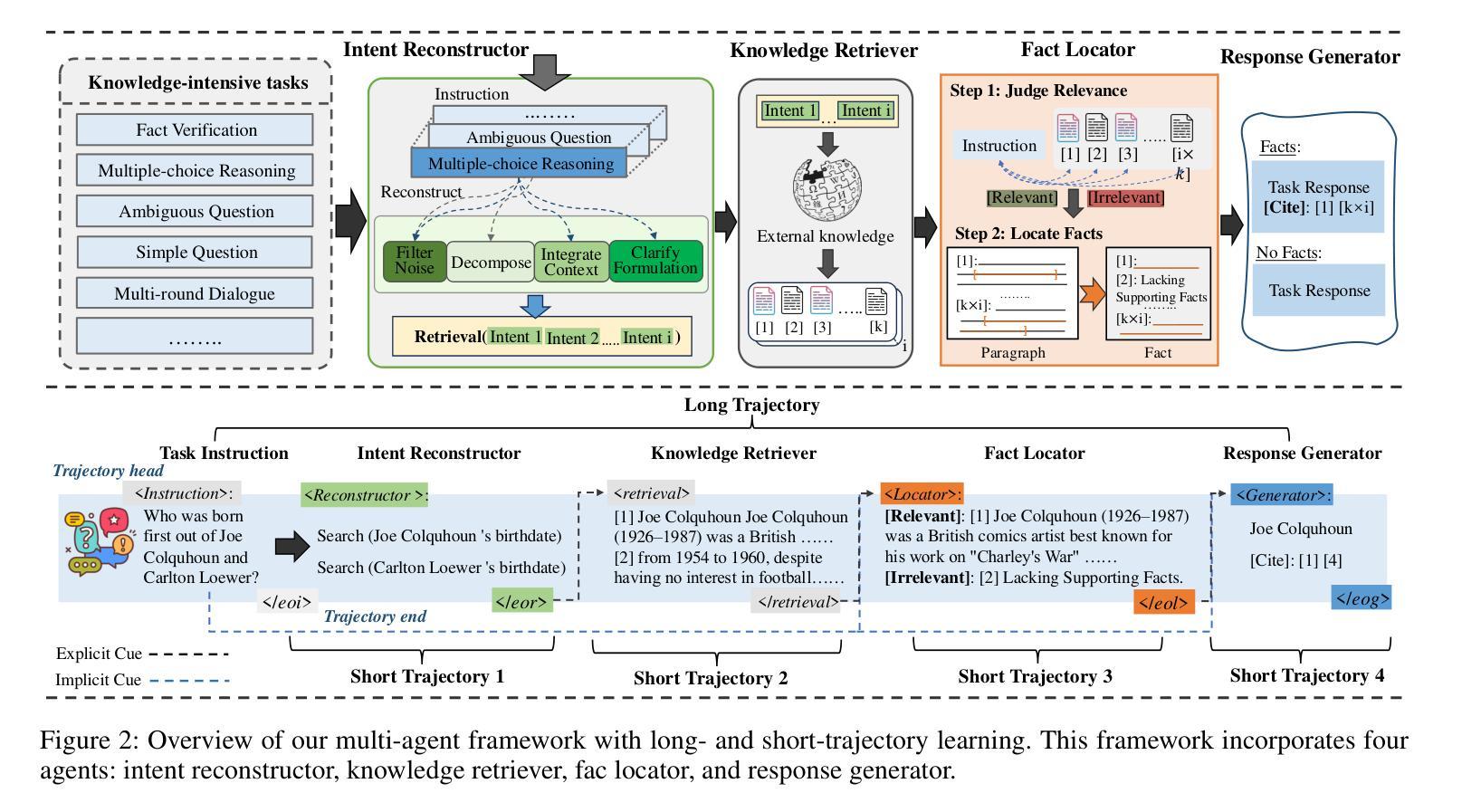
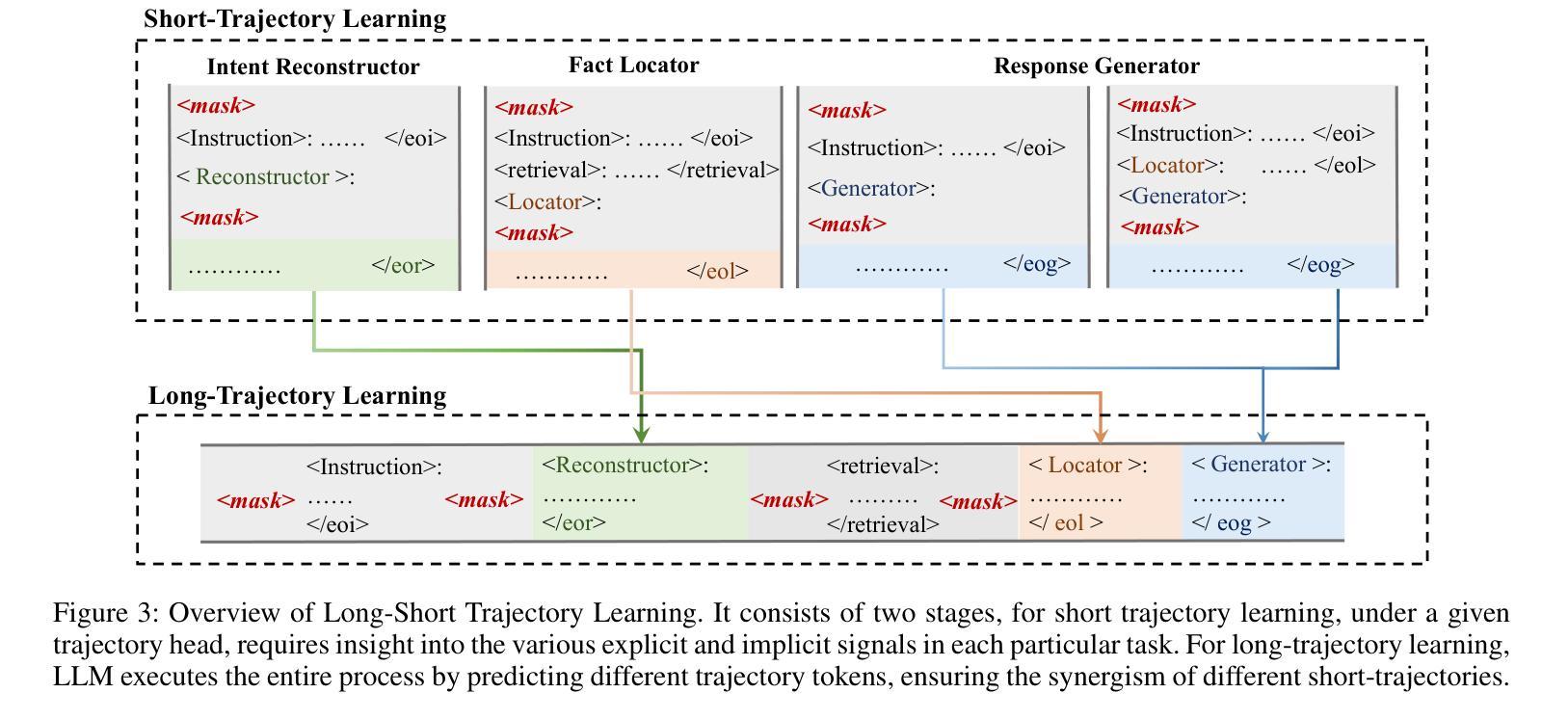
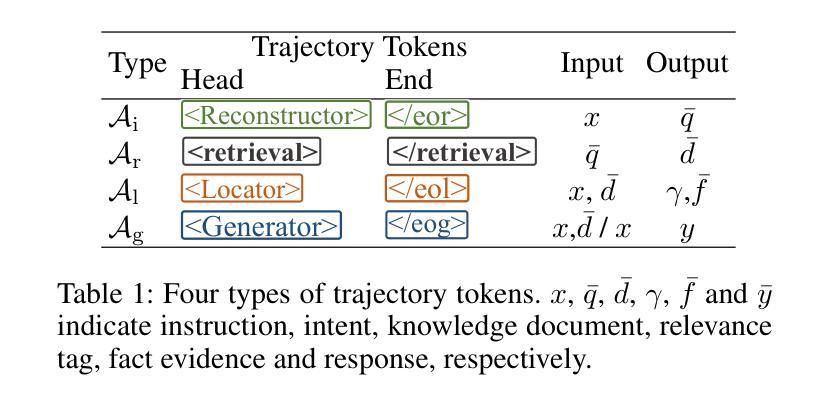
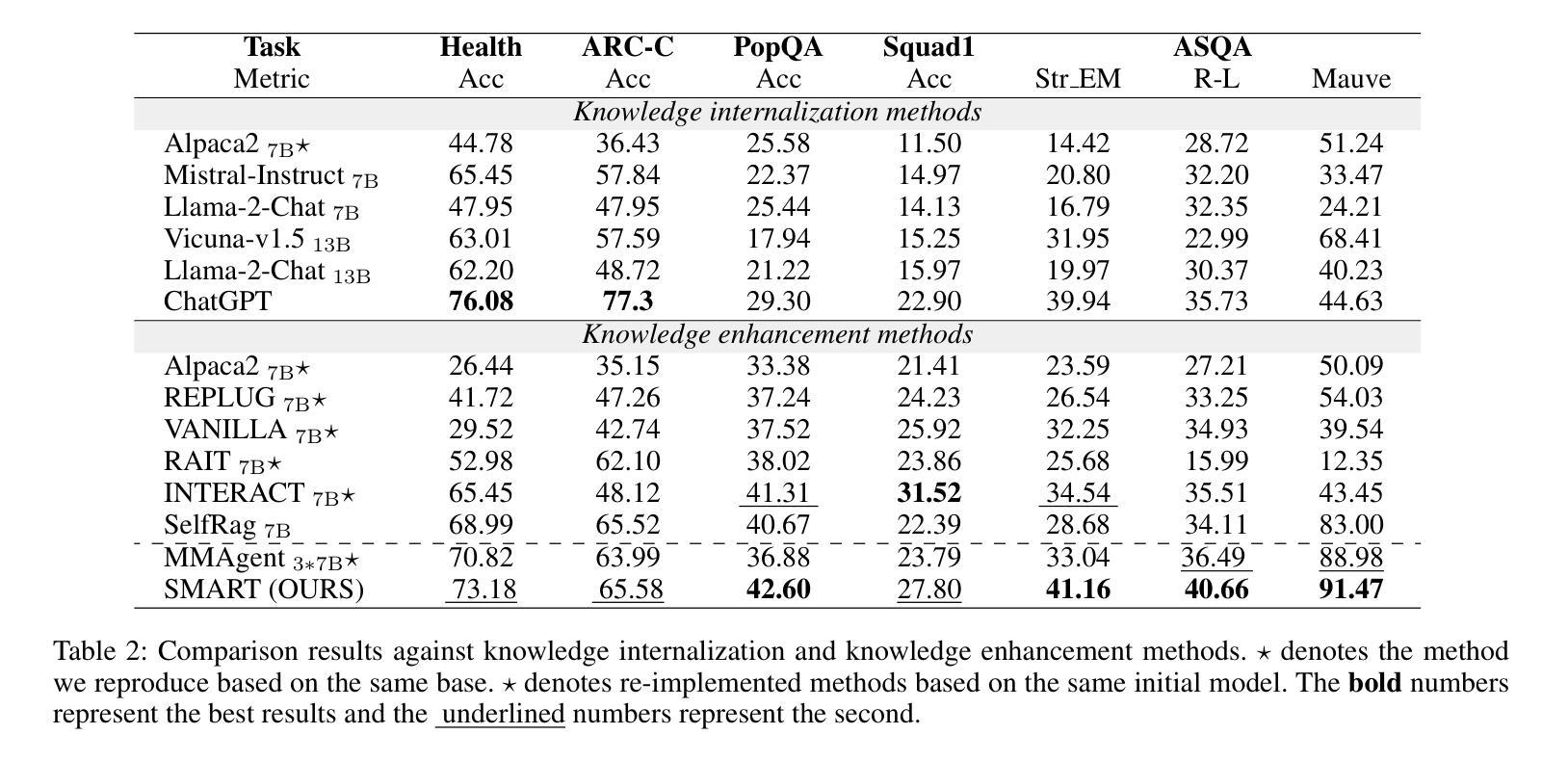
Synergistic Multi-Agent Framework with Trajectory Learning for Knowledge-Intensive Tasks
Authors:Shengbin Yue, Siyuan Wang, Wei Chen, Xuanjing Huang, Zhongyu Wei
Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have led to significant breakthroughs in various natural language processing tasks. However, generating factually consistent responses in knowledge-intensive scenarios remains a challenge due to issues such as hallucination, difficulty in acquiring long-tailed knowledge, and limited memory expansion. This paper introduces SMART, a novel multi-agent framework that leverages external knowledge to enhance the interpretability and factual consistency of LLM-generated responses. SMART comprises four specialized agents, each performing a specific sub-trajectory action to navigate complex knowledge-intensive tasks. We propose a multi-agent co-training paradigm, Long-Short Trajectory Learning, which ensures synergistic collaboration among agents while maintaining fine-grained execution by each agent. Extensive experiments on five knowledge-intensive tasks demonstrate SMART’s superior performance compared to widely adopted knowledge internalization and knowledge enhancement methods. Our framework can extend beyond knowledge-intensive tasks to more complex scenarios. Our code is available at https://github.com/yueshengbin/SMART.
最近大型语言模型(LLM)的进展已经在各种自然语言处理任务中取得了重大突破。然而,在知识密集型场景中生成事实一致的回复仍然是一个挑战,因为存在幻觉、获取长尾知识困难以及内存扩展有限等问题。本文介绍了SMART,一个利用外部知识提高LLM生成响应的可解释性和事实一致性的新型多智能体框架。SMART包含四个专业智能体,每个智能体执行特定的子轨迹动作,以完成复杂的知识密集型任务。我们提出了一种多智能体协同训练范式——长短轨迹学习,它确保了智能体之间的协同合作,同时保持了每个智能体的精细执行。在五个知识密集型任务上的大量实验表明,SMART的性能优于广泛采用的知识内化和知识增强方法。我们的框架可以扩展到知识密集型任务以外的更复杂的场景。我们的代码可在https://github.com/yueshengbin/SMART找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI2025
Summary
LLM在自然语言处理任务上的突破仍面临知识密集型场景中的事实一致性响应生成挑战。本文提出SMART多智能体框架,利用外部知识提高LLM生成响应的可解释性和事实一致性。SMART包括四个专业智能体,通过长期短期轨迹学习等协作训练方法确保协同合作并维持精细执行。在五个知识密集型任务上的实验显示SMART优于主流知识内化和增强方法。该框架可扩展至更复杂场景,代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在知识密集型场景中的事实一致性响应生成存在挑战。
- SMART框架利用外部知识提高LLM生成响应的可解释性和事实一致性。
- SMART包括四个专业智能体,分别执行特定子轨迹动作以完成复杂知识密集型任务。
- 提出长期短期轨迹学习协作训练方法,确保智能体之间的协同合作和精细执行。
- 在五个知识密集型任务上的实验显示SMART性能优于现有方法。
- SMART框架具有可扩展性,可应用于更复杂的场景。
点此查看论文截图

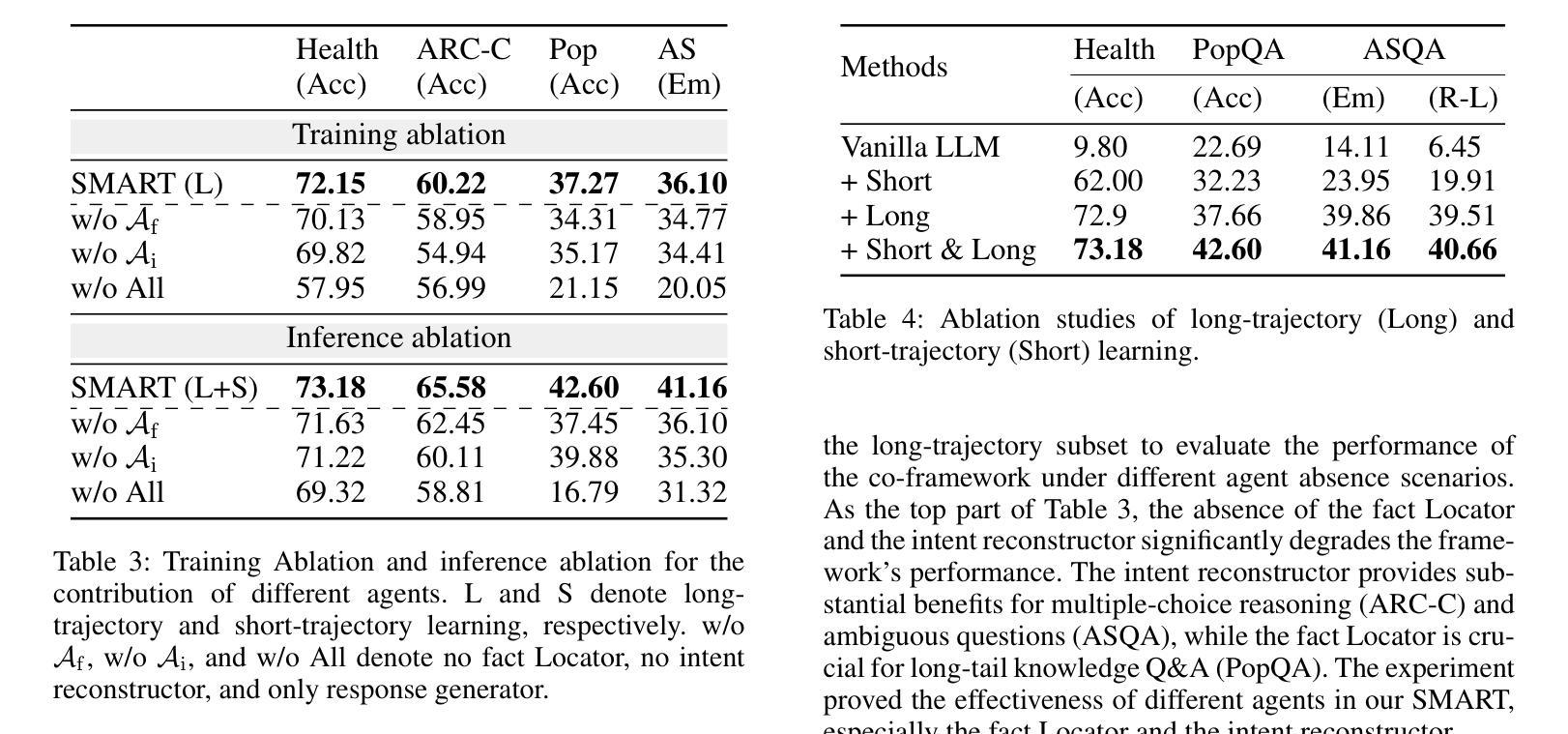
Beyond Numeric Awards: In-Context Dueling Bandits with LLM Agents
Authors:Fanzeng Xia, Hao Liu, Yisong Yue, Tongxin Li
In-context reinforcement learning (ICRL) is a frontier paradigm for solving reinforcement learning problems in the foundation model era. While ICRL capabilities have been demonstrated in transformers through task-specific training, the potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) out-of-the-box remains largely unexplored. Recent findings highlight that LLMs often face challenges when dealing with numerical contexts, and limited attention has been paid to evaluating their performance through preference feedback generated by the environment. This paper is the first to investigate LLMs as in-context decision-makers under the problem of Dueling Bandits (DB), a stateless preference-based reinforcement learning setting that extends the classic Multi-Armed Bandit (MAB) model by querying for preference feedback. We compare GPT-3.5 Turbo, GPT-4, GPT-4 Turbo, Llama 3.1, and o1-Preview against nine well-established DB algorithms. Our results reveal that our top-performing LLM, GPT-4 Turbo, has the zero-shot relative decision-making ability to achieve surprisingly low weak regret across all the DB environment instances by quickly including the best arm in duels. However, an optimality gap exists between LLMs and classic DB algorithms in terms of strong regret. LLMs struggle to converge and consistently exploit even when explicitly prompted to do so, and are sensitive to prompt variations. To bridge this gap, we propose an agentic flow framework: LLM with Enhanced Algorithmic Dueling (LEAD), which integrates off-the-shelf DB algorithms with LLM agents through fine-grained adaptive interplay. We show that LEAD has theoretical guarantees inherited from classic DB algorithms on both weak and strong regret. We validate its efficacy and robustness even with noisy and adversarial prompts. The design of our framework sheds light on how to enhance the trustworthiness of LLMs used for in-context decision-making.
基于上下文的强化学习(ICRL)是基础的模型时代解决强化学习问题的前沿范式。虽然通过特定任务的训练已经在Transformer中证明了ICRL的能力,但大型语言模型(LLM)的潜力尚未完全探索。最近的研究发现,LLM在处理数值上下文时常常面临挑战,而通过对环境生成的偏好反馈来评估其性能的注意力有限。本文首次调查了DB问题下的LLM作为上下文决策者的表现,DB是一种无状态的基于偏好的强化学习环境设置,它通过查询偏好反馈扩展了经典的多臂赌博机(MAB)模型。我们将GPT-3.5 Turbo、GPT-4、GPT-4 Turbo、Llama 3.1和o1-Preview与九种成熟的DB算法进行了比较。我们的结果表明,表现最佳的LLM GPT-4 Turbo具有零射击决策能力,在所有DB环境实例中实现了令人惊讶的低弱遗憾,通过快速将最佳手臂纳入决斗中。然而,在强遗憾方面,LLM与经典的DB算法之间仍然存在最优性差距。即使在明确要求这样做的情况下,LLM也难以收敛并始终进行剥削尝试且对提示的变化很敏感。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了一个代理流框架:带有增强算法决斗的LLM(LEAD),它通过精细的适应性交互将现成的DB算法与LLM代理集成在一起。我们证明了LEAD在弱遗憾和强遗憾方面都继承了经典DB算法的理论保证。即使在充满噪声和对抗性的提示下,我们也验证了其有效性和稳健性。我们的框架设计揭示了如何增强用于上下文决策LLM的可信度的启示。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
ICRL(基于情境强化学习)是处理基础模型时代强化学习问题的前沿范式。尽管已有研究证明其在Transformer中的任务特定训练能力,但大型语言模型(LLM)的原生潜力仍被忽略。本文主要探讨将LLM作为无状态偏好强化学习设置Dueling Bandits(DB)中的上下文决策者。对比了GPT-3.5 Turbo、GPT-4等多款大语言模型和一些经典的DB算法后发现LLM有一定的决策能力,但仍存在与经典算法之间的优劣差距。为缩短这一差距,提出了一种LLM强化算法融合框架LEAD,该框架具有理论保证,并在实际验证中展现出有效性和稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- ICRL是解决基础模型时代强化学习问题的重要前沿范式。
- LLM在解决数值上下文时面临挑战,尤其是在处理基于偏好的环境反馈方面。
- 在Dueling Bandits问题中,LLM展现出一定的决策能力,但在弱后悔和强后悔方面与经典算法存在差距。
- LLM对环境提示敏感,且存在收敛困难的问题。
- LEAD框架整合了DB算法与LLM代理,通过精细的自适应交互来提高LLM在情境决策中的可靠性。
- LEAD框架具有理论保证,且在模拟实验中表现出有效性和稳健性。
点此查看论文截图


What if LLMs Have Different World Views: Simulating Alien Civilizations with LLM-based Agents
Authors:Zhaoqian Xue, Mingyu Jin, Beichen Wang, Suiyuan Zhu, Kai Mei, Hua Tang, Wenyue Hua, Mengnan Du, Yongfeng Zhang
This study introduces “CosmoAgent,” an innovative artificial intelligence system that utilizes Large Language Models (LLMs) to simulate complex interactions between human and extraterrestrial civilizations. This paper introduces a mathematical model for quantifying the levels of civilization development and further employs a state transition matrix approach to evaluate their trajectories. Through this methodology, our study quantitatively analyzes the growth trajectories of civilizations, providing insights into future decision-making at critical points of growth and saturation. Furthermore, this paper acknowledges the vast diversity of potential living conditions across the universe, which could foster unique cosmologies, ethical codes, and worldviews among different civilizations. Recognizing the Earth-centric bias inherent in current LLM designs, we propose the novel concept of using LLM agents with diverse ethical paradigms and simulating interactions between entities with distinct moral principles. This innovative research not only introduces a novel method for comprehending potential inter-civilizational dynamics but also holds practical value in enabling entities with divergent value systems to strategize, prevent conflicts, and engage in games under conditions of asymmetric information. The accompanying code is available at https://github.com/MingyuJ666/Simulating-Alien-Civilizations-with-LLM-based-Agents.
本研究介绍了“CosmoAgent”,这是一个创新的人工智能系统,利用大型语言模型(LLM)模拟人类与外星文明之间的复杂交互。本文介绍了一个量化文明发展水平的数学模型,并进一步采用状态转移矩阵方法评估其轨迹。通过这种方法,我们的研究定量分析了文明的增长轨迹,为在增长和饱和的关键点提供未来决策的见解。此外,本文承认宇宙中潜在生活条件的巨大多样性,这可能会在不同的文明之间形成独特的宇宙观、道德准则和世界观。认识到当前LLM设计所固有的以地球为中心偏见,我们提出了使用具有不同道德范式LLM代理人的新概念,并模拟具有不同道德原则实体之间的交互。这项创新研究不仅介绍了一种理解潜在文明间动态的新型方法,而且在实际价值上使具有不同价值体系的实体能够在不对称信息条件下进行策略制定、避免冲突和参与游戏。相应的代码可在https://github.com/MingyuJ66QG-Simulation-Alien-Civilizations-with-LLM-based-Agents访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了“CosmoAgent”这一创新性人工智能系统,该系统运用大型语言模型(LLMs)模拟人类与外星文明之间的复杂交互。文章提出了一个数学模型来量化文明发展水平,并采用状态转移矩阵方法评估文明发展轨迹。此外,该研究还认识到宇宙中潜在生存条件的巨大多样性,可能会孕育出独特的宇宙观、道德准则和世界视角。针对当前LLM设计所固有的地球中心偏见,文章提出了使用具有不同道德范式的大型语言模型代理的概念,并模拟不同道德原则实体之间的交互。这项创新研究不仅为理解潜在的文明间动态提供了新的方法,而且具有实用价值,有助于不同价值体系的实体在信息不对称的条件下进行策略制定、冲突预防以及游戏互动。
Key Takeaways
- “CosmoAgent”是一个利用大型语言模型模拟人类与外星文明交互的人工智能系统。
- 通过数学模型量化文明发展水平,并采用状态转移矩阵方法评估其发展轨迹。
- 宇宙中潜在生存条件的多样性可能孕育出独特的宇宙观、道德准则和世界视角。
- 当前LLM设计存在地球中心偏见,需要采用具有不同道德范式的大型语言模型代理来克服。
- 通过模拟不同道德原则实体之间的交互,为理解潜在文明间动态提供了新的方法。
- 该研究具有实用价值,有助于不同价值体系的实体进行策略制定、冲突预防以及游戏互动。
点此查看论文截图


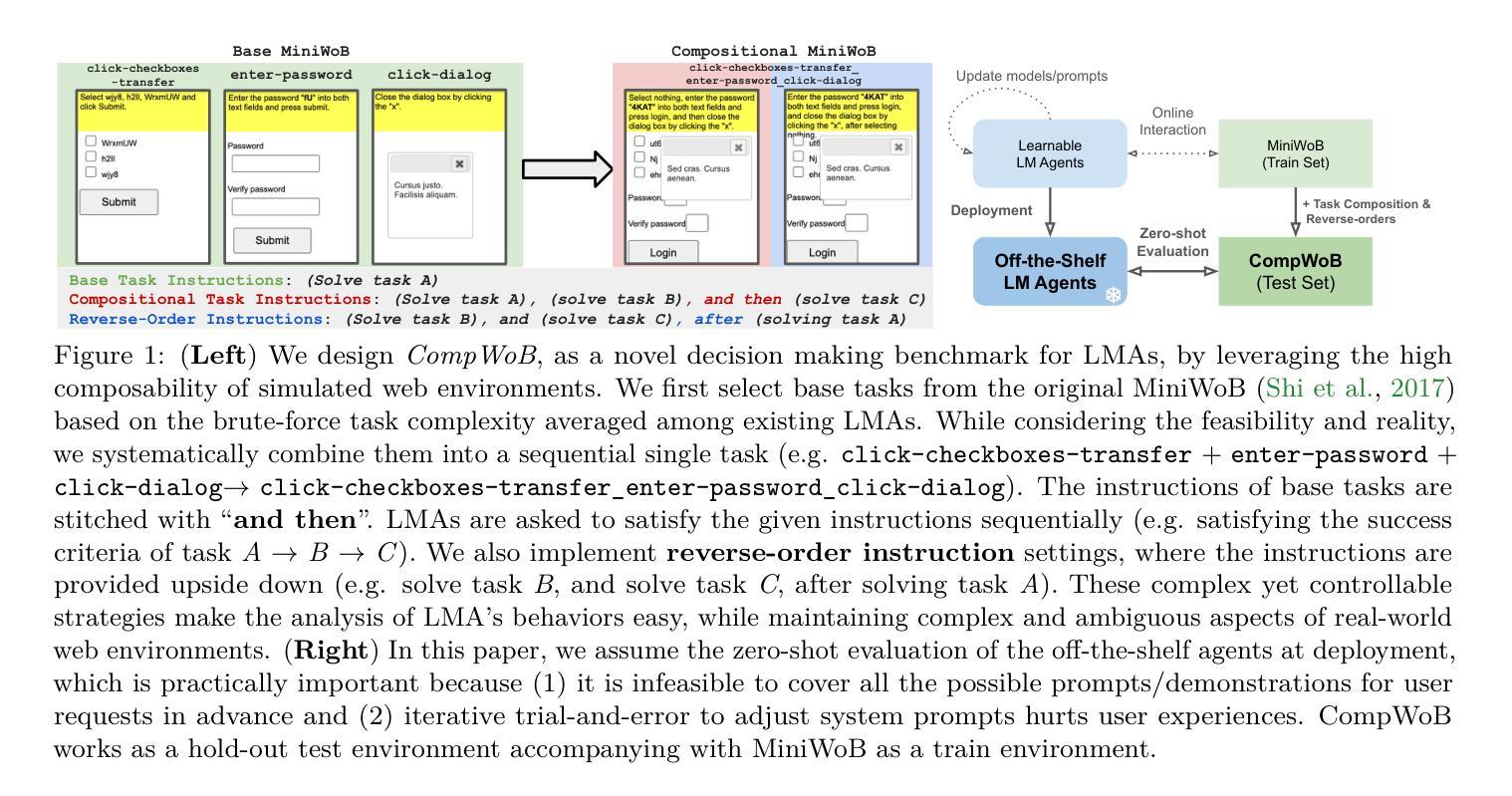
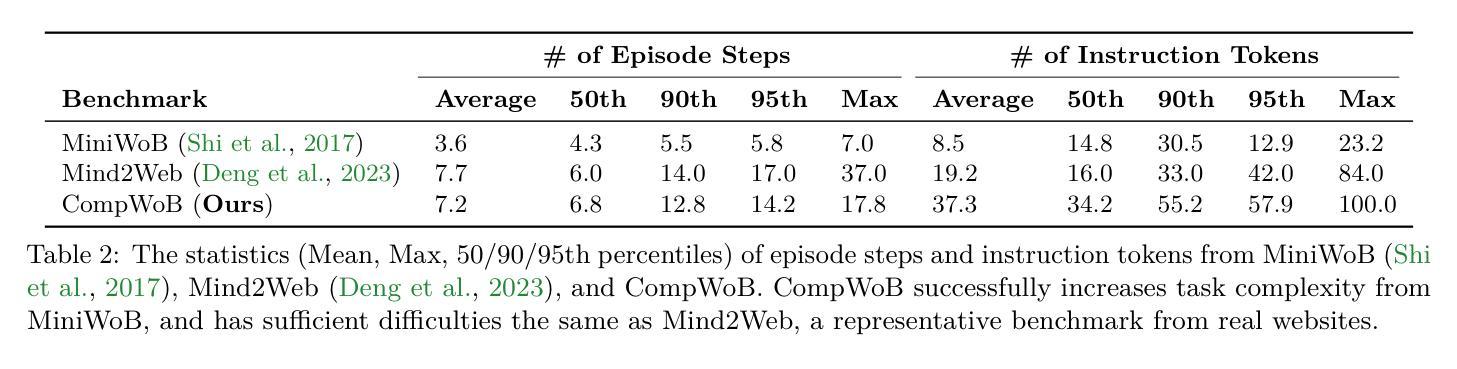
Exposing Limitations of Language Model Agents in Sequential-Task Compositions on the Web
Authors:Hiroki Furuta, Yutaka Matsuo, Aleksandra Faust, Izzeddin Gur
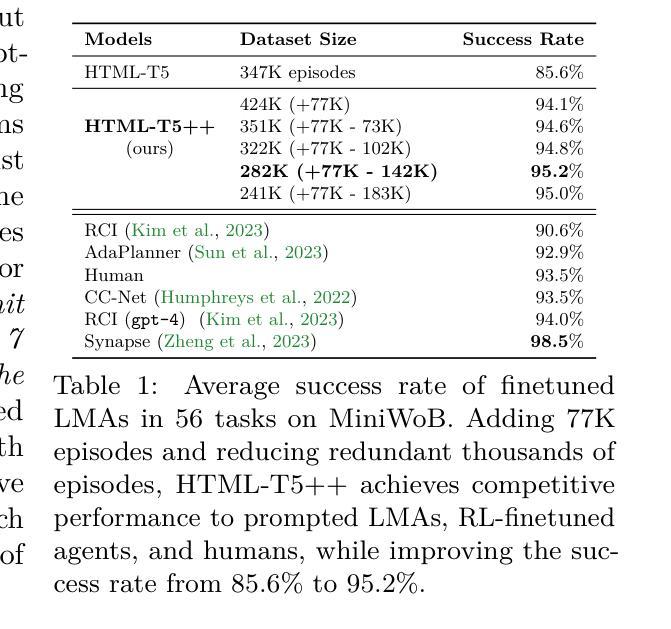
Language model agents (LMA) recently emerged as a promising paradigm on muti-step decision making tasks, often outperforming humans and other reinforcement learning agents. Despite the promise, their performance on real-world applications that often involve combinations of tasks is still underexplored. In this work, we introduce a new benchmark, called CompWoB – 50 new compositional web automation tasks reflecting more realistic assumptions. We show that while existing prompted LMAs (gpt-3.5-turbo or gpt-4) achieve 94.0% average success rate on base tasks, their performance degrades to 24.9% success rate on compositional tasks. On the other hand, transferred LMAs (finetuned only on base tasks) show less generalization gap, dropping from 85.4% to 54.8%. By balancing data distribution across tasks, we train a new model, HTML-T5++, that surpasses human-level performance (95.2%) on MiniWoB, and achieves the best zero-shot performance on CompWoB (61.5%). While these highlight the promise of small-scale finetuned and transferred models for task compositionality, their performance further degrades under different instruction compositions changing combinational order. In contrast to the recent remarkable success of LMA, our benchmark and detailed analysis emphasize the necessity of building LMAs that are robust and generalizable to task compositionality for real-world deployment.
语言模型代理(LMA)最近作为多步骤决策制定任务上的一种有前途的范式出现,通常胜过人类和其他强化学习代理。尽管很有前景,但它们在涉及组合任务的现实应用中的表现仍然鲜有研究。在这项工作中,我们引入了一个新的基准测试,称为CompWoB——包含50个新的组合式网络自动化任务,反映了更现实的假设。我们展示了现有的提示型LMA(如GPT-3.5 Turbo或GPT-4)在基础任务上达到了平均94.0%的成功率,但在组合任务上的性能下降到仅24.9%。另一方面,仅在基础任务上进行了微调的任务型LMA显示出了较小的泛化差距,从85.4%降至54.8%。通过平衡任务之间的数据分布,我们训练了一种新型模型HTML-T5++,它在MiniWoB上的性能超过了人类水平(95.2%),并在CompWoB上实现了最佳零样本性能(61.5%)。这些亮点突出了小型微调模型和迁移模型在任务组合方面的潜力,但它们在不同的指令组合和更改组合顺序时的性能会有所下降。与最近LMA的显著成功相比,我们的基准测试和详细分析强调了构建能够稳健且适用于任务组合性的LMA进行现实部署的必要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at Transactions on Machine Learning Research (TMLR), Code: https://github.com/google-research/google-research/tree/master/compositional_rl/compwob
Summary:语言模型代理(LMA)在多步决策任务上展现出巨大潜力,但在组合任务上的现实应用性能仍需探索。本文引入了一个新的基准测试CompWoB,包含50个新的组合网页自动化任务,更贴近现实假设。现有提示LMA在基础任务上表现良好,但在组合任务上性能下降到仅24.9%。经过微调的数据分布平衡的新模型HTML-T5++在小型基准测试上超越人类水平性能,并在CompWoB上实现最佳零样本性能(61.5%)。这凸显了构建具有任务组合性的稳健和通用性LMA的必要性。
Key Takeaways:
- LMA在多步决策任务上具有巨大潜力,但在涉及多个任务的现实应用中的性能尚未得到充分探索。
- 新基准测试CompWoB包含更多贴近现实的组合任务,用于评估LMA的性能。
- 现有提示LMA在基础任务上表现良好,但在复杂组合任务上的性能明显下降。
- 经过微调并平衡数据分布的新模型HTML-T5++在特定基准测试上表现优异,但仍需改进其在不同指令组合下的性能。
- LMA需要进一步提高在任务组合方面的稳健性和通用性,以适应现实世界的部署需求。
- 目前LMA在面临指令组合顺序变化时的性能下降问题亟待解决。
点此查看论文截图

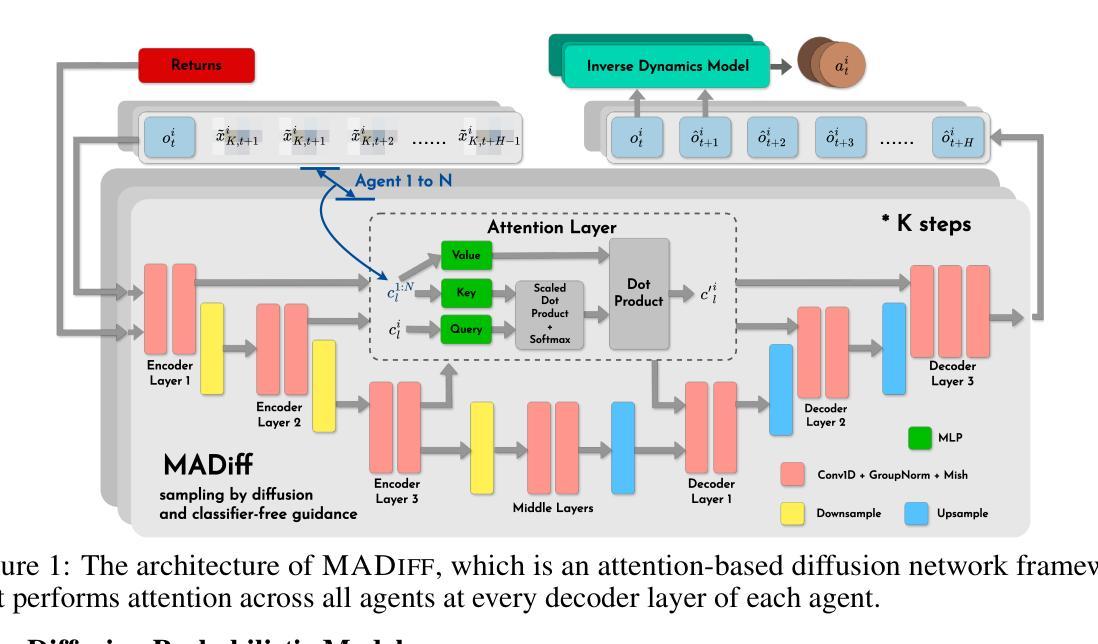
MADiff: Offline Multi-agent Learning with Diffusion Models
Authors:Zhengbang Zhu, Minghuan Liu, Liyuan Mao, Bingyi Kang, Minkai Xu, Yong Yu, Stefano Ermon, Weinan Zhang
Offline reinforcement learning (RL) aims to learn policies from pre-existing datasets without further interactions, making it a challenging task. Q-learning algorithms struggle with extrapolation errors in offline settings, while supervised learning methods are constrained by model expressiveness. Recently, diffusion models (DMs) have shown promise in overcoming these limitations in single-agent learning, but their application in multi-agent scenarios remains unclear. Generating trajectories for each agent with independent DMs may impede coordination, while concatenating all agents’ information can lead to low sample efficiency. Accordingly, we propose MADiff, which is realized with an attention-based diffusion model to model the complex coordination among behaviors of multiple agents. To our knowledge, MADiff is the first diffusion-based multi-agent learning framework, functioning as both a decentralized policy and a centralized controller. During decentralized executions, MADiff simultaneously performs teammate modeling, and the centralized controller can also be applied in multi-agent trajectory predictions. Our experiments demonstrate that MADiff outperforms baseline algorithms across various multi-agent learning tasks, highlighting its effectiveness in modeling complex multi-agent interactions. Our code is available at https://github.com/zbzhu99/madiff.
离线强化学习(RL)旨在从预存的数据集中学习策略,而无需进一步的交互,这使其成为一项具有挑战性的任务。Q学习算法在离线设置中存在外推误差问题,而监督学习方法受到模型表达能力的限制。最近,扩散模型(DMs)在单智能体学习中克服这些限制方面显示出潜力,但它们在多智能体场景中的应用仍不明确。为每个智能体生成轨迹的独立扩散模型可能会阻碍协调,而合并所有智能体的信息可能会导致样本效率低下。因此,我们提出了MADiff,它通过一个基于注意力的扩散模型来实现对多个智能体行为之间复杂协调的建模。据我们所知,MADiff是第一个基于扩散的多智能体学习框架,既可作为分散策略,也可作为集中控制器。在分散执行期间,MADiff同时进行队友建模,集中控制器也可用于多智能体轨迹预测。我们的实验表明,MADiff在各种多智能体学习任务上优于基线算法,突显其在模拟复杂多智能体交互方面的有效性。我们的代码可在https://github.com/zbzhu99/madiff找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 30 pages, 10 figures, 9 tables. Published at NeurIPS 2024
Summary
强化学习在离线环境下学习政策是一项挑战。Q-learning算法在离线设置中存在外推误差问题,而监督学习方法受限于模型表现力。扩散模型在单智能体学习中显示出克服这些限制的潜力,但在多智能体场景中的应用尚不清楚。MADiff是一个基于注意力机制的扩散模型,旨在模拟多个智能体行为之间的复杂协调,既是分散式政策又是集中式控制器。它在各种多智能体学习任务上表现出优于基线算法的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 离线强化学习面临挑战,Q-learning算法和监督学习方法各有局限。
- 扩散模型在多智能体学习中的应用具有潜力,但挑战在于如何处理多智能体之间的协调。
- MADiff是首个基于扩散的多智能体学习框架,兼具分散式政策和集中式控制功能。
- MADiff能同时进行队友建模,并在多智能体轨迹预测中发挥作用。
- 实验表明,MADiff在各种多智能体学习任务上的性能优于基线算法。
- MADiff能有效建模多智能体之间的复杂交互。
点此查看论文截图

(Almost Full) EFX for Three (and More) Types of Agents
Authors:Pratik Ghosal, Vishwa Prakash HV, Prajakta Nimbhorkar, Nithin Varma
We study the problem of determining an envy-free allocation of indivisible goods among multiple agents with additive valuations. EFX, which stands for envy-freeness up to any good, is a well-studied relaxation of the envy-free allocation problem and has been shown to exist for specific scenarios. EFX is known to exist for three agents, and for any number of agents when there are only two types of valuations. EFX allocations are also known to exist for four agents with at most one good unallocated. In this paper, we show that EFX exists with at most k-2 goods unallocated for any number of agents having k distinct valuations. Additionally, we show that complete EFX allocations exist when all but two agents have identical valuations.
我们研究了在多个代理中分配不可分物品的问题,这些代理具有可加性估价,目标是实现无嫉妒分配。EFX(代表任意物品的嫉妒无关性)是众所周知的嫉妒分配问题的松弛解法,并且针对某些特定场景已经被证明是存在的。已知对于三个代理存在EFX分配方案,对于仅有两种估价类型的情况,无论代理数量多少都存在EFX分配方案。对于拥有最多一个未分配物品的四个代理,也已知存在EFX分配方案。在本文中,我们证明了当代理拥有k个不同估价时,最多存在k-2个未分配的物品。此外,我们还证明了当除了两个代理之外的所有代理具有相同估价时,存在完全的EFX分配方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To appear at the 39th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2025)
Summary
本研究探讨了不可分物品在多个具有可加估值的代理之间实现无嫉妒分配的问题。针对特定场景,研究了名为EFX的分配方案的存在性,该方案是嫉妒分配问题的良好放宽条件。已知在三个代理或当存在两种类型的估值时,存在EFX分配。本研究进一步证明,在最多有k-2个物品未分配时,对于任何数量的代理存在EFX分配方案,当除两个代理外的所有代理具有相同估值时,存在完全EFX分配方案。
Key Takeaways
- 研究了不可分物品在多个代理之间的无嫉妒分配问题。
- EFX作为一种无嫉妒分配方案的放宽条件,在特定场景下已被研究并证实存在。
- 对于三个代理或存在两种类型的估值时,存在EFX分配方案。
- 本研究证明了对于任何数量的代理和具有k种不同估值的情况,存在最多有k-2个物品未分配的EFX分配方案。
- 当除两个代理外的所有代理具有相同估值时,存在完全EFX分配方案。
- 此研究进一步丰富了关于EFX分配方案的理论知识。
点此查看论文截图