⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-04 更新
Prometheus: 3D-Aware Latent Diffusion Models for Feed-Forward Text-to-3D Scene Generation
Authors:Yuanbo Yang, Jiahao Shao, Xinyang Li, Yujun Shen, Andreas Geiger, Yiyi Liao
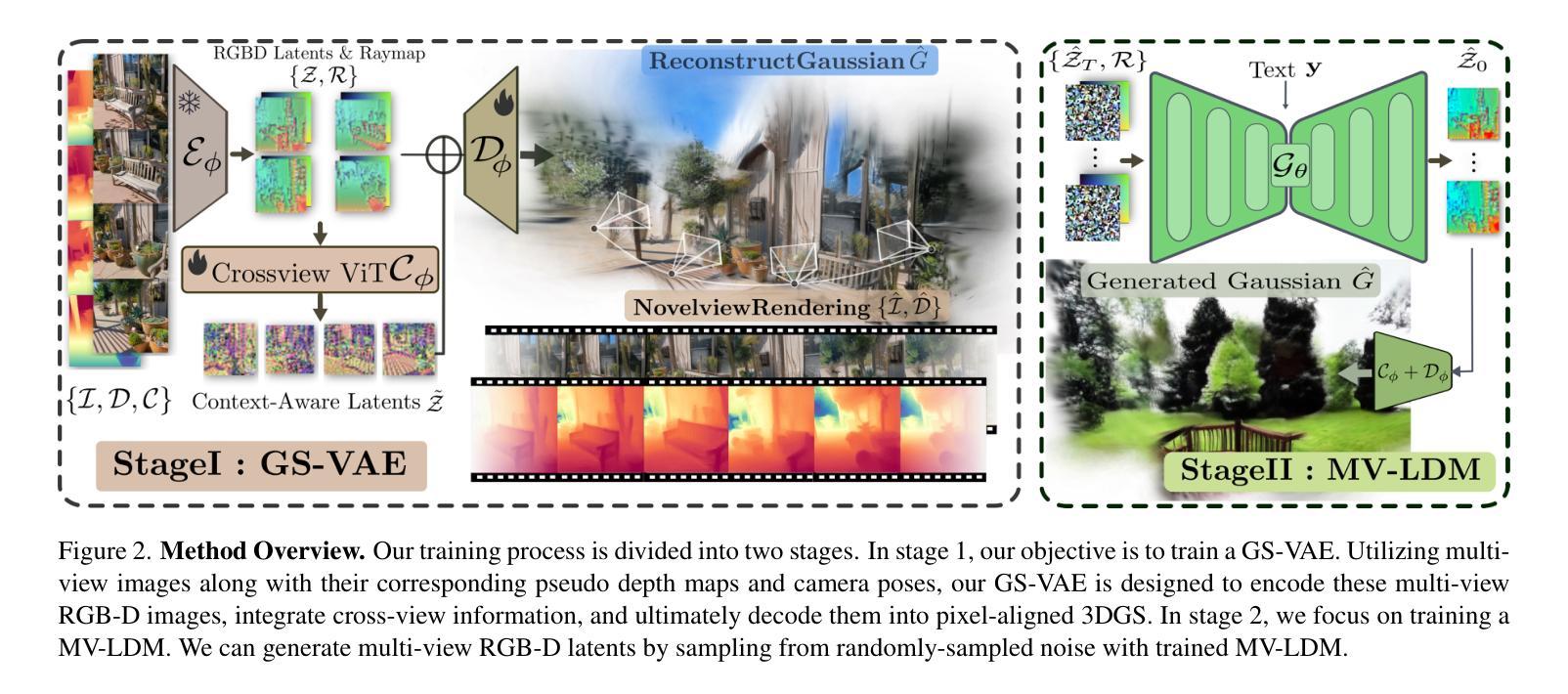
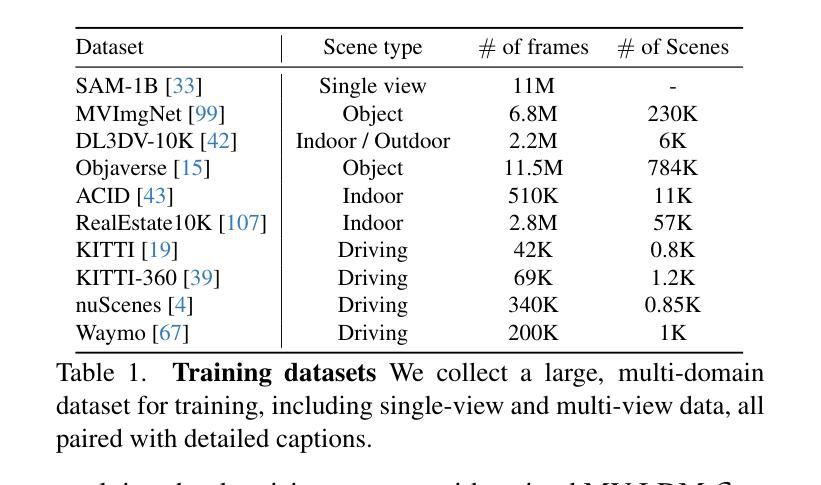
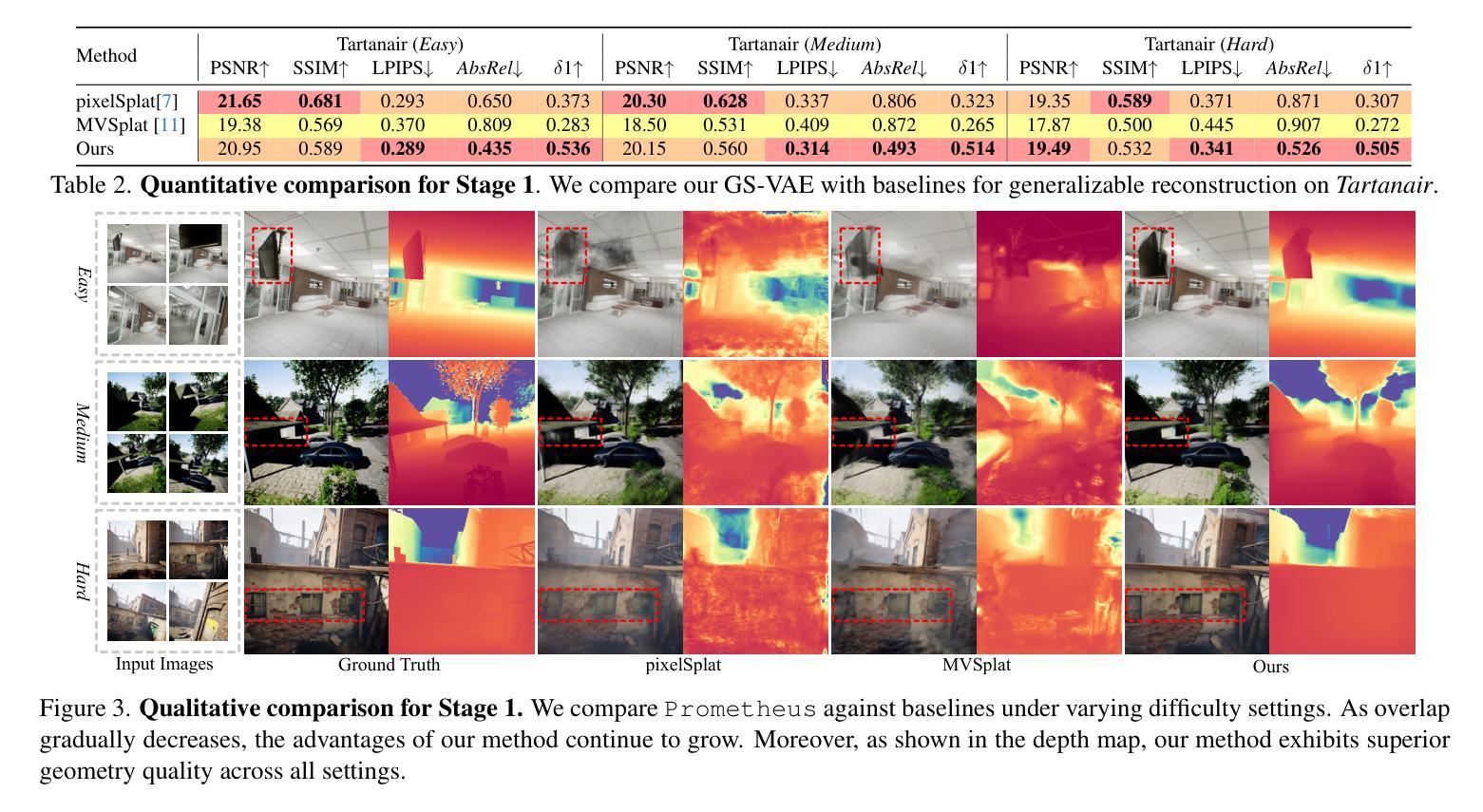
In this work, we introduce Prometheus, a 3D-aware latent diffusion model for text-to-3D generation at both object and scene levels in seconds. We formulate 3D scene generation as multi-view, feed-forward, pixel-aligned 3D Gaussian generation within the latent diffusion paradigm. To ensure generalizability, we build our model upon pre-trained text-to-image generation model with only minimal adjustments, and further train it using a large number of images from both single-view and multi-view datasets. Furthermore, we introduce an RGB-D latent space into 3D Gaussian generation to disentangle appearance and geometry information, enabling efficient feed-forward generation of 3D Gaussians with better fidelity and geometry. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in both feed-forward 3D Gaussian reconstruction and text-to-3D generation. Project page: https://freemty.github.io/project-prometheus/
在这项工作中,我们引入了Prometheus,这是一个用于文本到三维场景生成的3D感知潜在扩散模型,可以在对象和场景级别快速实现。我们将三维场景的生成作为潜在扩散框架中的多视图前馈像素对齐的3D高斯生成问题。为了确保模型的通用性,我们在预训练的文本到图像生成模型的基础上构建模型,只需进行微调即可进一步训练,并使用大量的单视图和多视图数据集进行训练。此外,我们在三维高斯生成中引入了RGB-D潜在空间,以分离外观和几何信息,从而实现高效的前馈三维高斯生成,提高保真度和几何精度。大量的实验结果证明了我们的方法在三维高斯重建和文本到三维场景生成方面的有效性。更多内容请参考我们的项目主页:https://freemty.github.io/project-prometheus/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本工作引入Prometheus,这是一款基于文本至场景级别的三维扩散模型,可实现物体与场景的即时三维生成。我们利用预训练文本至图像生成模型作为基础,通过最小调整构建模型,并使用大量单视角和多视角图像数据集进行训练,确保模型具有通用性。引入RGB-D潜在空间到三维高斯生成中,解耦外观和几何信息,实现高效的三维高斯生成。实验结果证明该方法在三维高斯重建和文本至三维生成中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- Prometheus是一个文本至场景级别的三维扩散模型。
- 该模型能够实现物体和场景的即时三维生成。
- 模型基于预训练的文本至图像生成模型构建,只需进行最小调整。
- 使用大量单视角和多视角图像数据集进行训练,确保模型的通用性。
- 模型引入了RGB-D潜在空间以解耦外观和几何信息。
- 该方法实现了高效的三维高斯生成。
点此查看论文截图

EraseAnything: Enabling Concept Erasure in Rectified Flow Transformers
Authors:Daiheng Gao, Shilin Lu, Shaw Walters, Wenbo Zhou, Jiaming Chu, Jie Zhang, Bang Zhang, Mengxi Jia, Jian Zhao, Zhaoxin Fan, Weiming Zhang
Removing unwanted concepts from large-scale text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models while maintaining their overall generative quality remains an open challenge. This difficulty is especially pronounced in emerging paradigms, such as Stable Diffusion (SD) v3 and Flux, which incorporate flow matching and transformer-based architectures. These advancements limit the transferability of existing concept-erasure techniques that were originally designed for the previous T2I paradigm (e.g., SD v1.4). In this work, we introduce EraseAnything, the first method specifically developed to address concept erasure within the latest flow-based T2I framework. We formulate concept erasure as a bi-level optimization problem, employing LoRA-based parameter tuning and an attention map regularizer to selectively suppress undesirable activations. Furthermore, we propose a self-contrastive learning strategy to ensure that removing unwanted concepts does not inadvertently harm performance on unrelated ones. Experimental results demonstrate that EraseAnything successfully fills the research gap left by earlier methods in this new T2I paradigm, achieving state-of-the-art performance across a wide range of concept erasure tasks.
从大规模文本到图像(T2I)的扩散模型中移除不需要的概念并保持其整体的生成质量仍然是一个待解决的难题。这种难度在稳定扩散(SD)v3和Flux等新兴范式中尤为突出,这些新兴范式融入了流匹配和基于变压器的架构。这些进步限制了原本为早期T2I范式(例如SD v1.4)设计的概念删除技术的可转移性。在这项工作中,我们介绍了EraseAnything,这是首个专门开发以解决最新流式T2I框架中概念删除问题的方法。我们将概念删除表述为两级优化问题,采用基于LoRA的参数调整和注意力图正则化来有选择性地抑制不需要的激活。此外,我们提出了一种自我对比学习策略,以确保移除不需要的概念不会无意中损害对无关概念的性能。实验结果表明,EraseAnything成功填补了早期方法在这一新T2I范式中的研究空白,在广泛的概念删除任务中实现了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 18 figures
Summary
本文介绍了针对最新基于流的文本到图像(T2I)框架中的概念擦除问题,提出了一种新方法EraseAnything。该方法将概念擦除公式化为一个两级优化问题,并采用LoRA参数调整和注意力图正则化来选择性抑制不需要的激活。此外,还提出了一种自我对比学习策略,以确保在去除不需要的概念时不会意外地损害其他相关概念的性能。实验结果表明,EraseAnything在新的T2I范式中填补了早期方法的空白,并在各种概念擦除任务上实现了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- EraseAnything是专门为最新基于流的文本到图像(T2I)框架中的概念擦除问题开发的方法。
- 该方法将概念擦除公式化为一个两级优化问题。
- LoRA参数调整和注意力图正则化被用来选择性抑制不需要的激活。
- EraseAnything采用自我对比学习策略,确保在去除不需要的概念时不会损害其他概念的性能。
- 现有的概念擦除技术在新的T2I范式(如Stable Diffusion v3和Flux)中的转移性受到限制。
- EraseAnything填补了早期方法在T2I范式中的空白,实现了广泛的概念擦除任务的最先进性能。
点此查看论文截图


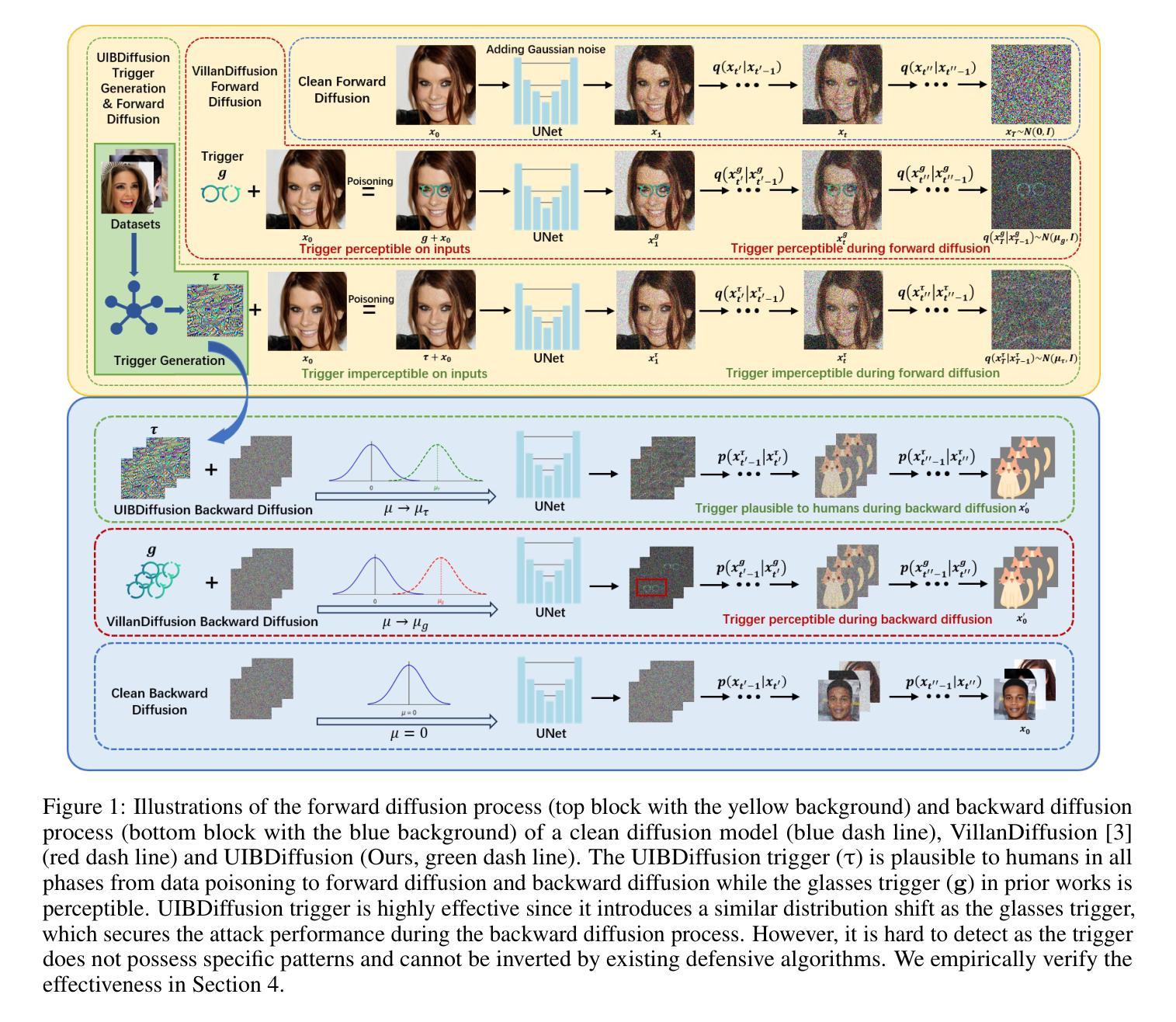
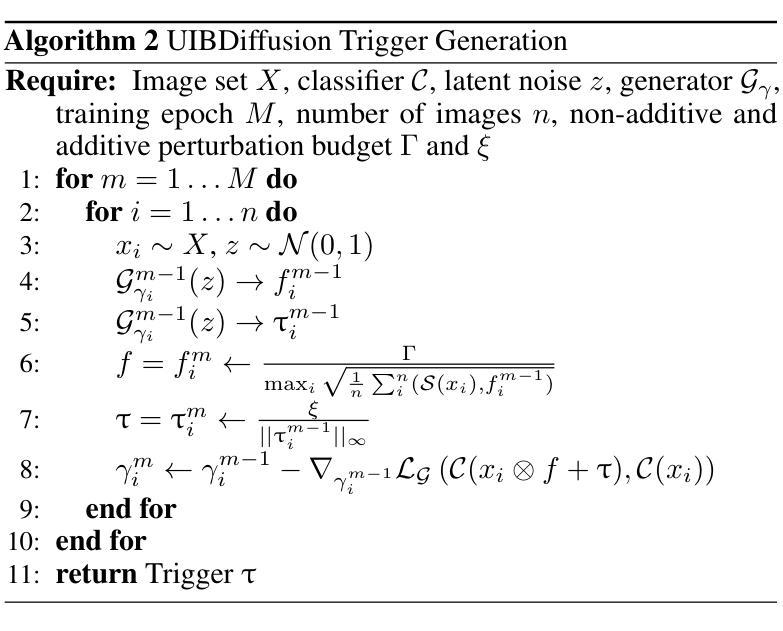
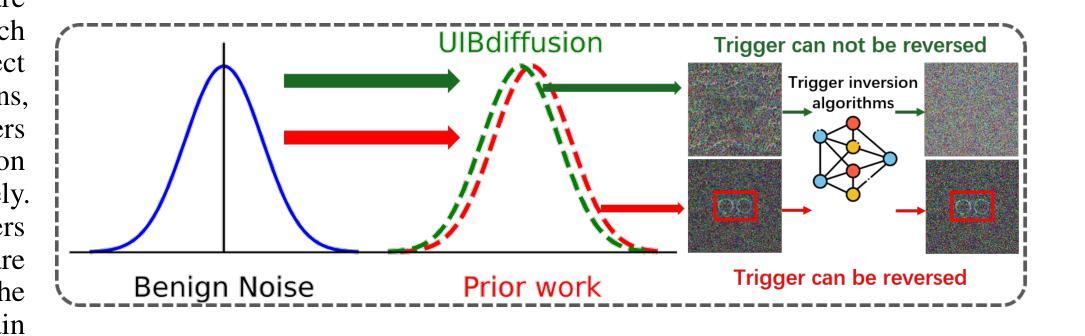
UIBDiffusion: Universal Imperceptible Backdoor Attack for Diffusion Models
Authors:Yuning Han, Bingyin Zhao, Rui Chu, Feng Luo, Biplab Sikdar, Yingjie Lao
Recent studies show that diffusion models (DMs) are vulnerable to backdoor attacks. Existing backdoor attacks impose unconcealed triggers (e.g., a gray box and eyeglasses) that contain evident patterns, rendering remarkable attack effects yet easy detection upon human inspection and defensive algorithms. While it is possible to improve stealthiness by reducing the strength of the backdoor, doing so can significantly compromise its generality and effectiveness. In this paper, we propose UIBDiffusion, the universal imperceptible backdoor attack for diffusion models, which allows us to achieve superior attack and generation performance while evading state-of-the-art defenses. We propose a novel trigger generation approach based on universal adversarial perturbations (UAPs) and reveal that such perturbations, which are initially devised for fooling pre-trained discriminative models, can be adapted as potent imperceptible backdoor triggers for DMs. We evaluate UIBDiffusion on multiple types of DMs with different kinds of samplers across various datasets and targets. Experimental results demonstrate that UIBDiffusion brings three advantages: 1) Universality, the imperceptible trigger is universal (i.e., image and model agnostic) where a single trigger is effective to any images and all diffusion models with different samplers; 2) Utility, it achieves comparable generation quality (e.g., FID) and even better attack success rate (i.e., ASR) at low poison rates compared to the prior works; and 3) Undetectability, UIBDiffusion is plausible to human perception and can bypass Elijah and TERD, the SOTA defenses against backdoors for DMs. We will release our backdoor triggers and code.
近期研究表明,扩散模型(DMs)容易受到后门攻击。现有的后门攻击采用未隐蔽的触发器(例如,灰盒和眼镜),这些触发器包含明显的模式,虽然攻击效果显著,但很容易通过人工检查和防御算法进行检测。虽然通过减弱后门强度可以提高隐蔽性,但这样做可能会显著损害其通用性和有效性。在本文中,我们提出了针对扩散模型的通用隐蔽后门攻击方法UIBDiffusion,使我们能够在躲避最新防御措施的同时实现卓越的攻击和生成性能。我们提出了一种基于通用对抗性扰动(UAPs)的新型触发器生成方法,并揭示这种最初被设计用于欺骗预训练判别模型的扰动,可以适应成为针对DMs的强大隐蔽后门触发器。我们在多种类型的DMs、多种采样器以及不同数据集和目标上评估了UIBDiffusion。实验结果表明,UIBDiffusion具有三个优势:1)通用性,隐蔽触发器是通用的(即图像和模型无关),单个触发器对所有图像和不同采样器的所有扩散模型都有效;2)实用性,它在低毒率下的生成质量(例如FID)与先前作品相当,甚至攻击成功率(即ASR)更高;3)不可检测性,UIBDiffusion对人类感知是合理的,并且能够绕过针对DM后门的最新防御手段Elijah和TERD。我们将发布我们的后门触发器和代码。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
扩散模型(DMs)存在后门攻击的风险。现有的后门攻击方法会使用明显的触发物(如灰盒和眼镜),这些触发物含有明显的模式,易于人类检查和防御算法的检测。在提高隐蔽性的同时降低后门强度可能会导致其通用性和效果大打折扣。本文提出了针对扩散模型的通用隐蔽后门攻击方法UIBDiffusion,它可以在躲避现有最先进的防御手段的同时实现出色的攻击和生成性能。我们提出了一种基于通用对抗性扰动(UAPs)的新型触发物生成方法,并发现这种扰动,最初被设计用来欺骗预训练的判别模型,可以适应成为针对DMs的强大隐蔽后门触发物。我们在多种类型的扩散模型、不同采样器以及多个数据集和目标上评估了UIBDiffusion。实验结果表明,UIBDiffusion具有三个优势:1)通用性,隐蔽触发物是通用的(即图像和模型无关),单个触发物对所有图像和所有扩散模型及不同采样器均有效;2)实用性,它在低毒率下的生成质量(例如FID)与先前的工作相当,甚至攻击成功率(即ASR)更高;3)隐蔽性,UIBDiffusion对人类感知是合理的,可以绕过Elijah和TERD等针对DMs后门的最先进防御手段。我们将发布我们的后门触发器和代码。
要点提炼
- 扩散模型(DMs)面临后门攻击风险,现有方法使用明显触发物,易检测。
- 提出UIBDiffusion方法,实现针对DMs的隐蔽后门攻击。
- 基于通用对抗性扰动(UAPs)的触发物生成,适用于多种扩散模型和采样器。
- UIBDiffusion具有三大优势:通用性、实用性和隐蔽性。
- UIBDiffusion可实现高水平的攻击性能同时躲避现有防御手段。
- 将发布后门触发器和代码以供研究使用。
- 为扩散模型的安全性问题提供了新的思考和解决方案。
点此查看论文截图



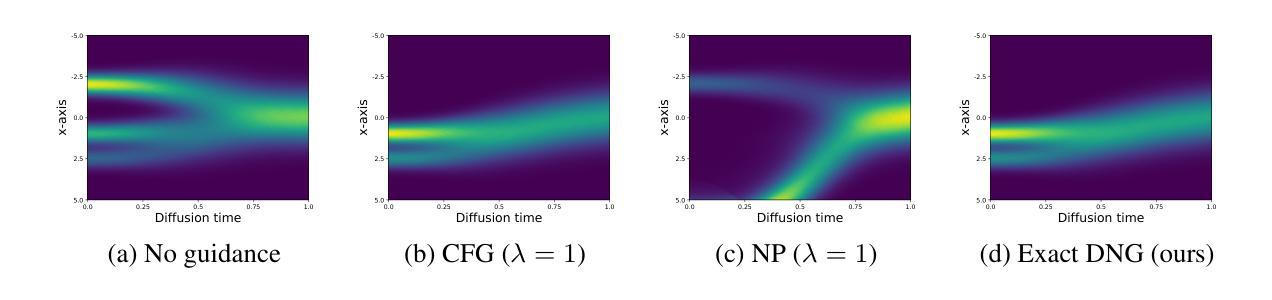
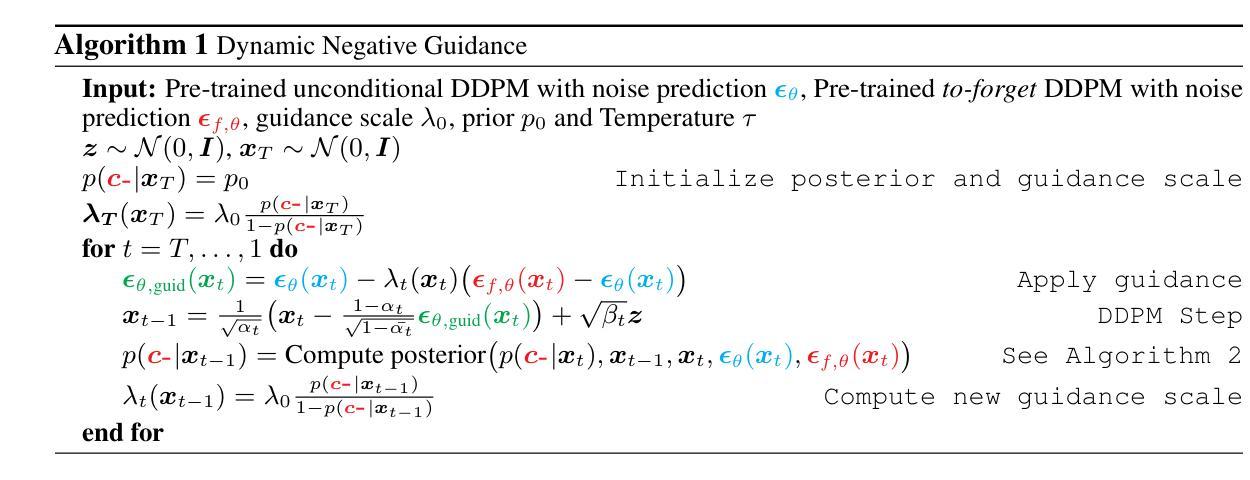
Dynamic Negative Guidance of Diffusion Models
Authors:Felix Koulischer, Johannes Deleu, Gabriel Raya, Thomas Demeester, Luca Ambrogioni
Negative Prompting (NP) is widely utilized in diffusion models, particularly in text-to-image applications, to prevent the generation of undesired features. In this paper, we show that conventional NP is limited by the assumption of a constant guidance scale, which may lead to highly suboptimal results, or even complete failure, due to the non-stationarity and state-dependence of the reverse process. Based on this analysis, we derive a principled technique called Dynamic Negative Guidance, which relies on a near-optimal time and state dependent modulation of the guidance without requiring additional training. Unlike NP, negative guidance requires estimating the posterior class probability during the denoising process, which is achieved with limited additional computational overhead by tracking the discrete Markov Chain during the generative process. We evaluate the performance of DNG class-removal on MNIST and CIFAR10, where we show that DNG leads to higher safety, preservation of class balance and image quality when compared with baseline methods. Furthermore, we show that it is possible to use DNG with Stable Diffusion to obtain more accurate and less invasive guidance than NP.
负向提示(NP)在扩散模型中得到了广泛应用,特别是在文本到图像的应用中,用于防止生成不需要的特征。在本文中,我们展示了传统的NP受到恒定指导尺度的假设的限制,这可能导致结果高度不理想,甚至完全失败,原因是反向过程具有非平稳性和状态依赖性。基于这一分析,我们推导出了一种基于原理的技术,称为动态负向指导(DNG),它依赖于近最优的时间和状态依赖的指导调制,而无需额外的训练。与NP不同,负向指导需要在去噪过程中估计后验类别概率,这可以通过在生成过程中跟踪离散马尔可夫链来实现,并且只需要有限的额外计算开销。我们在MNIST和CIFAR10上评估了DNG类消除的性能,结果显示,与基准方法相比,DNG提高了安全性,保持了类别平衡和图像质量。此外,我们还展示了将DNG与Stable Diffusion结合使用,可以获得比NP更准确、侵入性较小的指导。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper currently under review. Submitted to ICLR 2025. Our implementation is available at https://github.com/FelixKoulischer/Dynamic-Negative-Guidance.git
Summary
本文探讨了扩散模型中的负提示(NP)技术的局限性,特别是在文本转图像应用中的使用。文章提出了一种新的技术——动态负指导(DNG),该技术能够在不需要额外训练的情况下,对指导和调制进行近优的时间和状态依赖性的调整。在MNIST和CIFAR10上的评估表明,与基准方法相比,DNG在安全性、保持类平衡和图像质量方面表现出更高的性能。此外,将DNG与Stable Diffusion结合使用,可以获得比NP更准确、侵入性较小的指导。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型中广泛使用的负提示(NP)技术存在局限性,尤其是在文本转图像应用中。
- 动态负指导(DNG)是一种新的技术,能够近优地调整指导和调制的时间和状态依赖性。
- DNG不需要额外的训练。
- 在MNIST和CIFAR10上的评估显示,DNG在安全性、保持类平衡和图像质量方面优于基准方法。
- DNG技术可以有效地防止生成不需要的特征。
- DNG可用于提高Stable Diffusion的准确性并减少侵入性。
点此查看论文截图

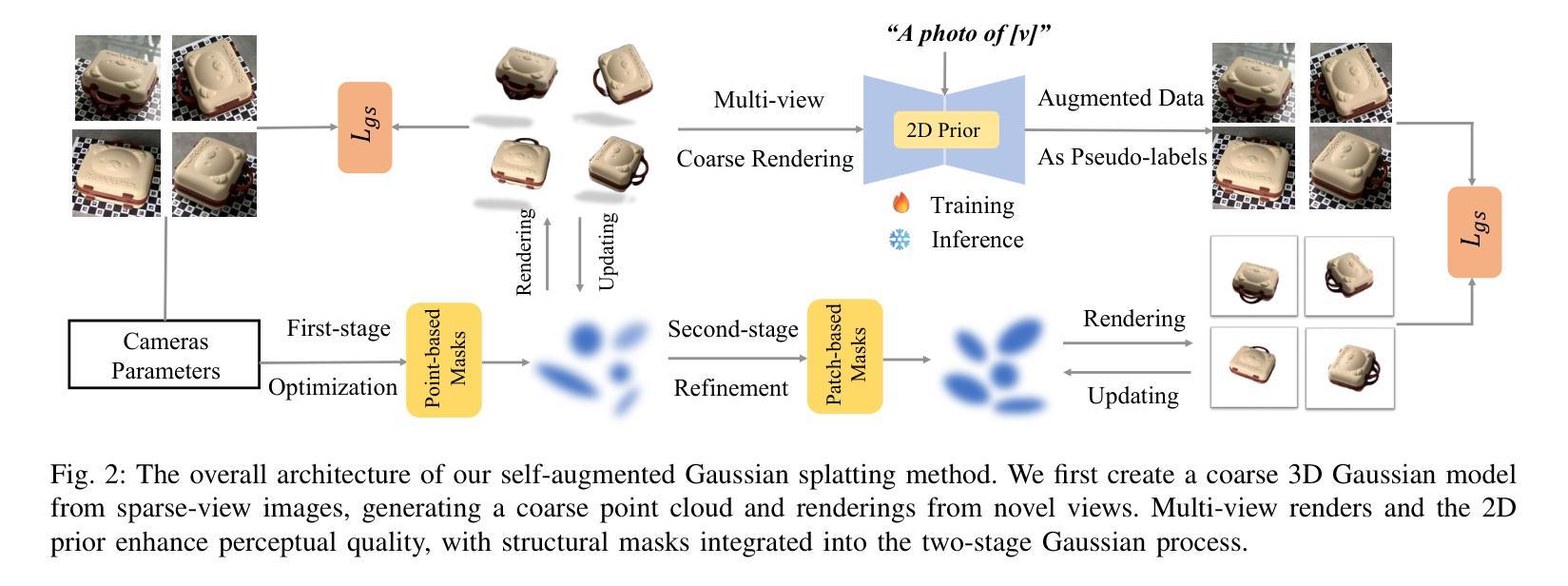
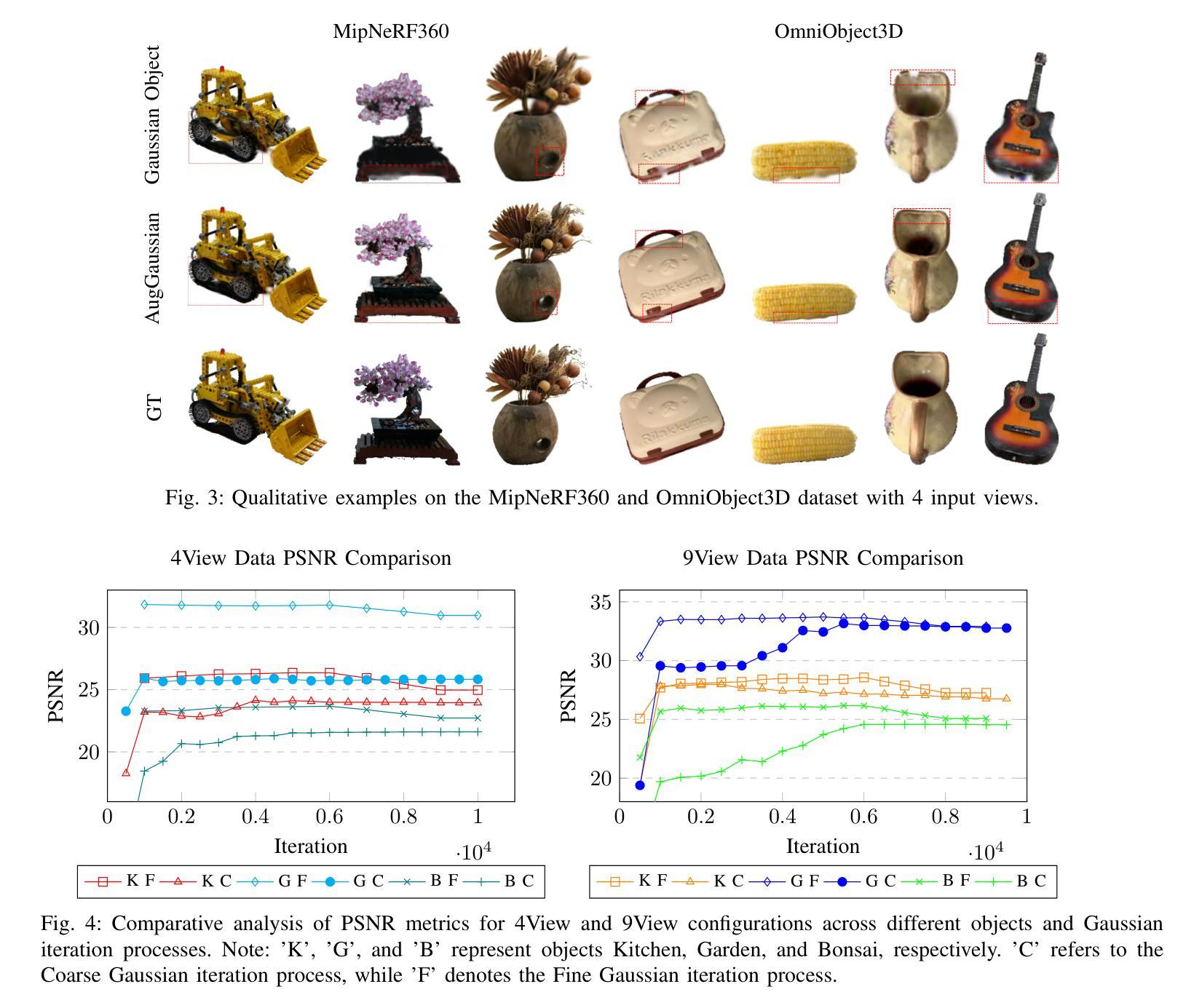
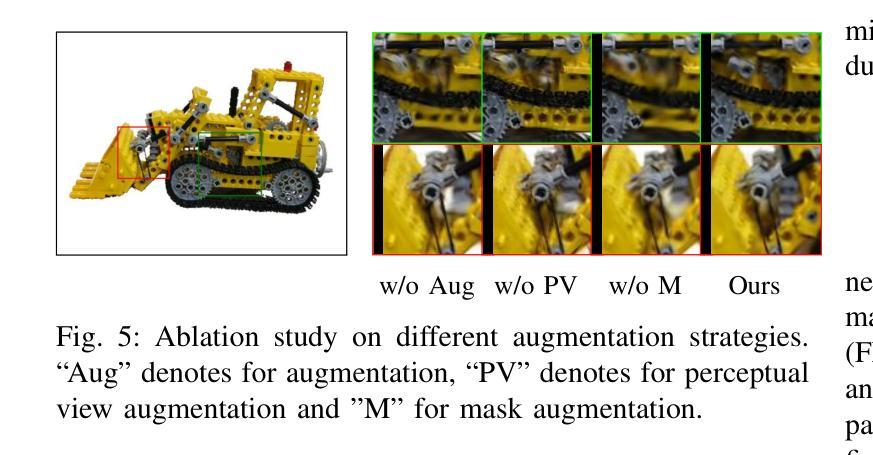
AugGS: Self-augmented Gaussians with Structural Masks for Sparse-view 3D Reconstruction
Authors:Bi’an Du, Lingbei Meng, Wei Hu
Sparse-view 3D reconstruction is a major challenge in computer vision, aiming to create complete three-dimensional models from limited viewing angles. Key obstacles include: 1) a small number of input images with inconsistent information; 2) dependence on input image quality; and 3) large model parameter sizes. To tackle these issues, we propose a self-augmented two-stage Gaussian splatting framework enhanced with structural masks for sparse-view 3D reconstruction. Initially, our method generates a basic 3D Gaussian representation from sparse inputs and renders multi-view images. We then fine-tune a pre-trained 2D diffusion model to enhance these images, using them as augmented data to further optimize the 3D Gaussians. Additionally, a structural masking strategy during training enhances the model’s robustness to sparse inputs and noise. Experiments on benchmarks like MipNeRF360, OmniObject3D, and OpenIllumination demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in perceptual quality and multi-view consistency with sparse inputs.
稀疏视角下的三维重建是计算机视觉领域的一大挑战,旨在从有限的视角创建完整的三维模型。主要障碍包括:1)输入图像数量少且信息不一致;2)依赖于输入图像的质量;以及3)模型参数规模大。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种基于结构掩膜的自增强两阶段高斯喷射框架,用于稀疏视角下的三维重建。首先,我们的方法从稀疏输入生成基本的三维高斯表示,并呈现多视角图像。然后,我们使用预训练的二维扩散模型对这些图像进行微调以增强其质量,将其作为增强数据进一步优化三维高斯表示。此外,在训练过程中采用结构掩膜策略增强了模型对稀疏输入和噪声的鲁棒性。在MipNeRF360、OmniObject3D和OpenIllumination等基准测试上的实验表明,我们的方法在感知质量和多视角一致性方面达到了先进性能,且在稀疏输入情况下表现尤为出色。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文介绍了针对稀疏视角3D重建的主要挑战及其解决方案。通过提出一种基于自增强和两阶段高斯涂抹框架的方法,结合结构掩码技术,实现了从有限视角信息构建完整三维模型的目标。首先生成基本的三维高斯表示,并利用预训练的二维扩散模型进行图像增强,作为扩充数据进一步优化三维高斯模型。实验证明,该方法在感知质量和多视角一致性方面达到了领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 稀疏视角3D重建面临的主要挑战包括输入图像数量少且信息不一致、依赖输入图像质量和模型参数规模过大。
- 提出了一种自增强两阶段高斯涂抹框架,用于解决稀疏视角3D重建问题。
- 通过生成基本的三维高斯表示并从稀疏输入渲染多视角图像,为3D重建提供基础。
- 利用预训练的二维扩散模型增强图像,作为扩充数据进一步优化三维高斯模型。
- 结合结构掩码技术在训练过程中增强模型对稀疏输入和噪声的鲁棒性。
- 在MipNeRF360、OmniObject3D和OpenIllumination等基准测试上进行了实验验证,表明该方法在感知质量和多视角一致性方面达到领先水平。
点此查看论文截图

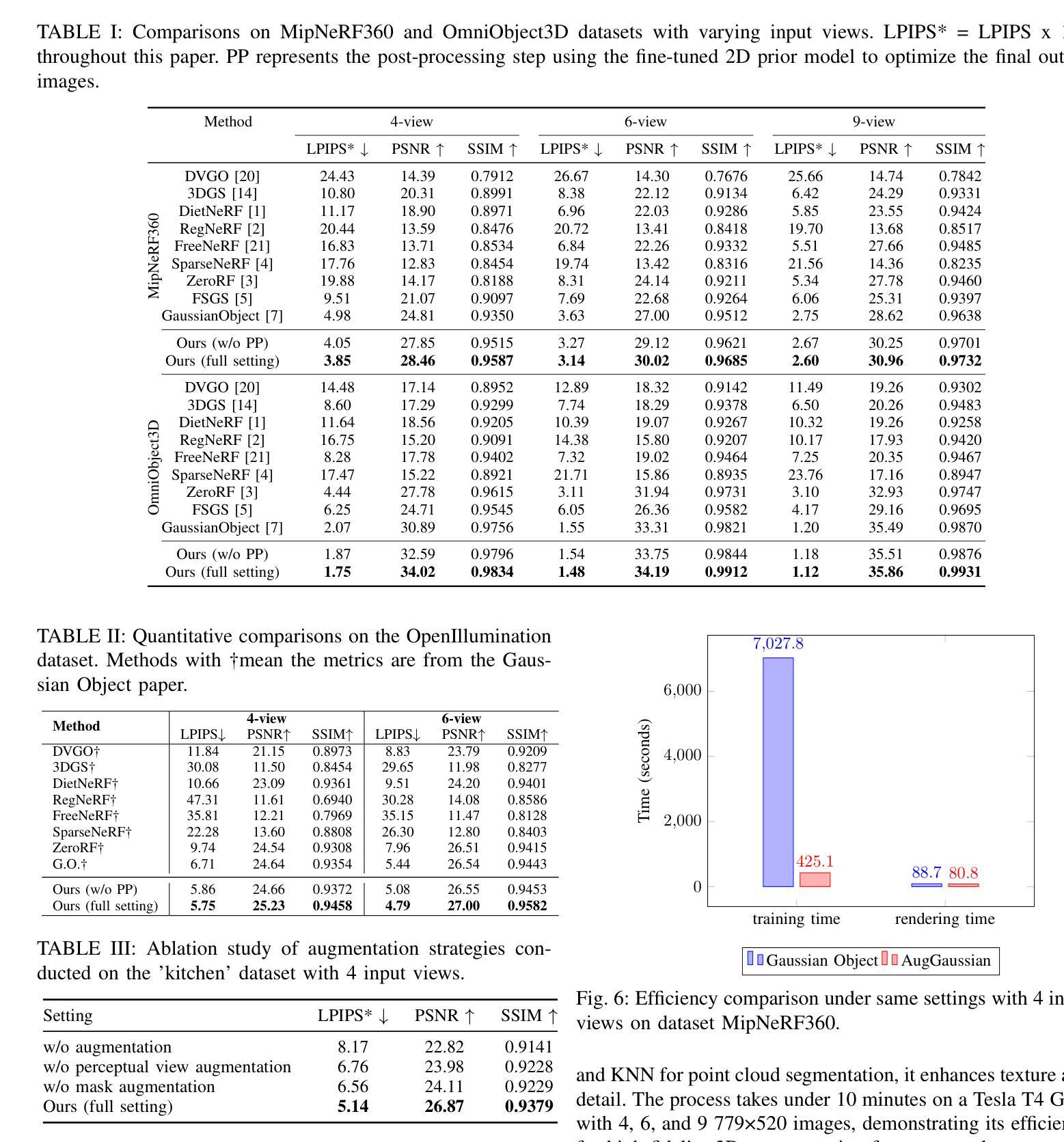
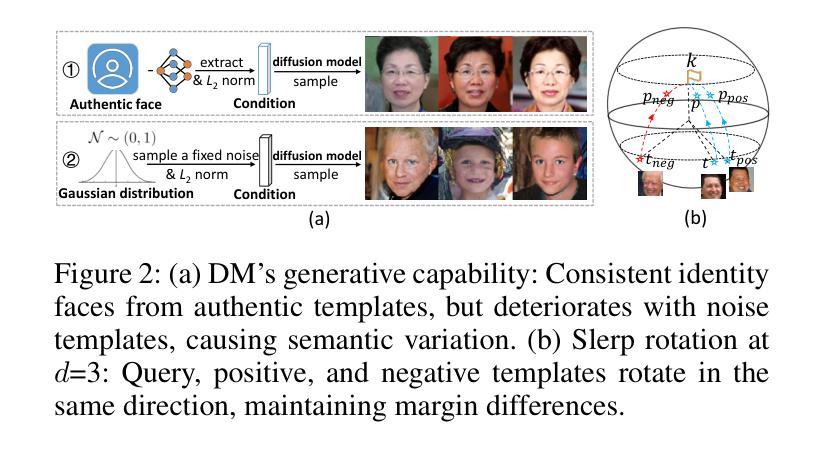
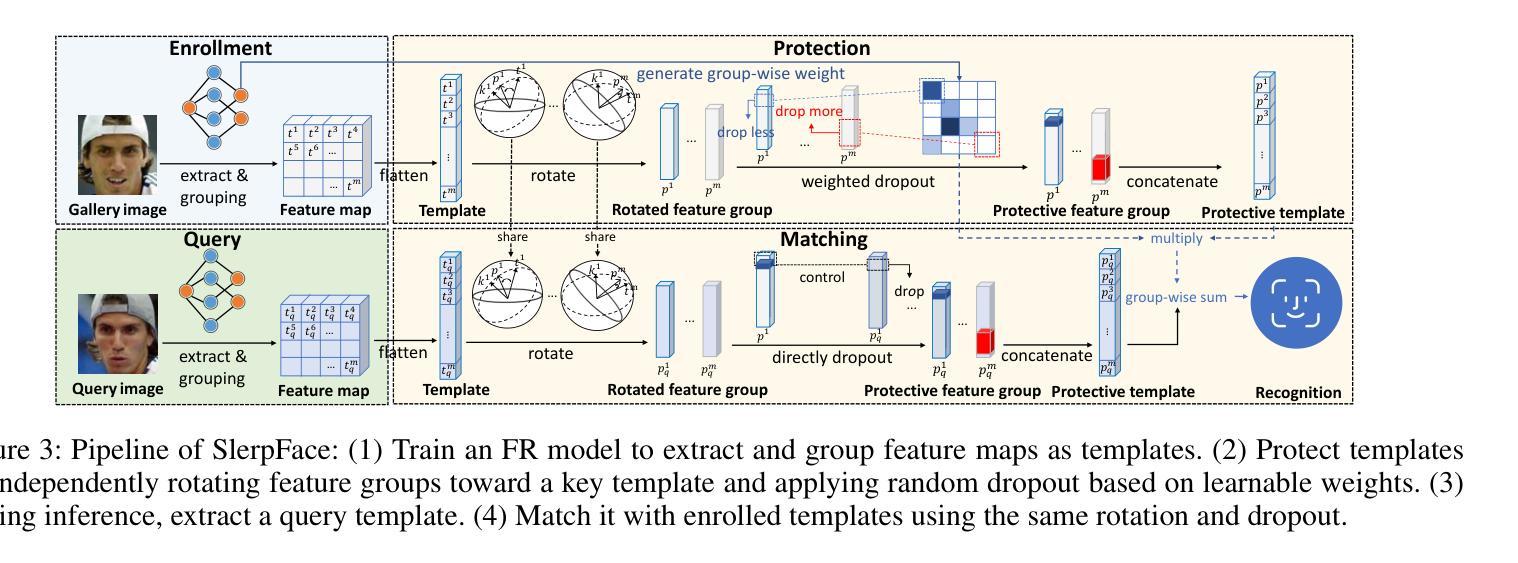
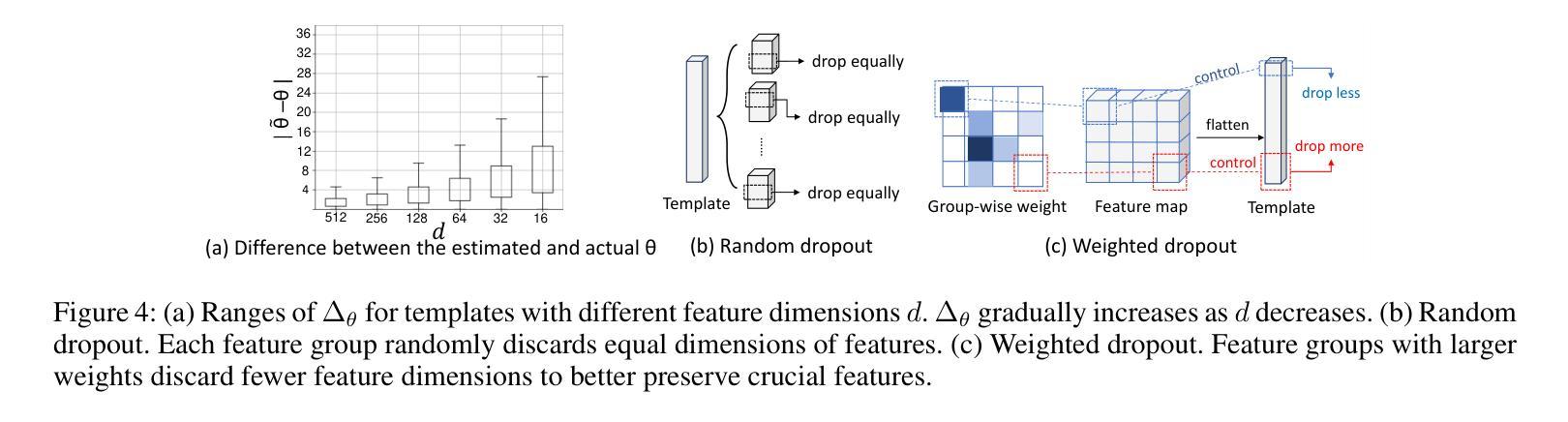
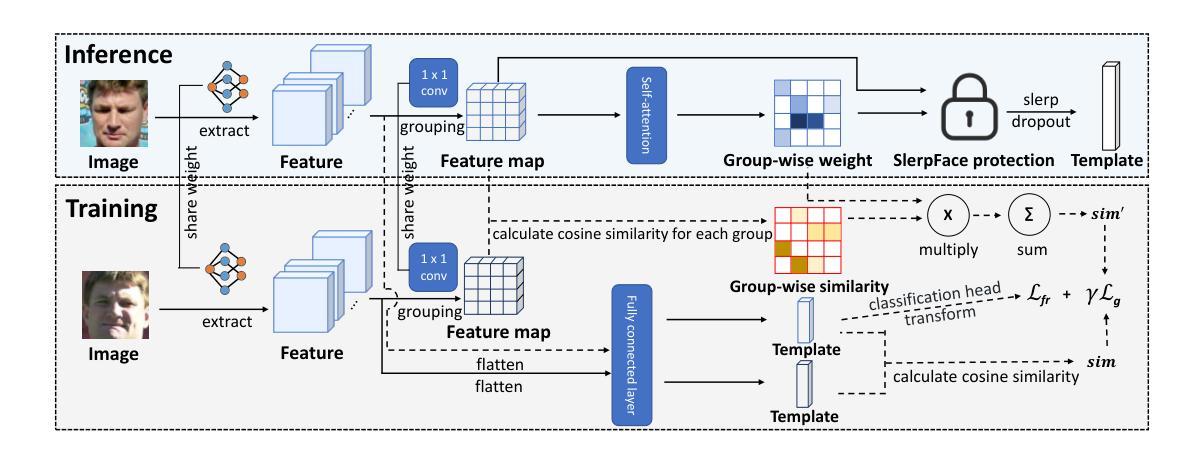
SlerpFace: Face Template Protection via Spherical Linear Interpolation
Authors:Zhizhou Zhong, Yuxi Mi, Yuge Huang, Jianqing Xu, Guodong Mu, Shouhong Ding, Jingyun Zhang, Rizen Guo, Yunsheng Wu, Shuigeng Zhou
Contemporary face recognition systems use feature templates extracted from face images to identify persons. To enhance privacy, face template protection techniques are widely employed to conceal sensitive identity and appearance information stored in the template. This paper identifies an emerging privacy attack form utilizing diffusion models that could nullify prior protection. The attack can synthesize high-quality, identity-preserving face images from templates, revealing persons’ appearance. Based on studies of the diffusion model’s generative capability, this paper proposes a defense by rotating templates to a noise-like distribution. This is achieved efficiently by spherically and linearly interpolating templates on their located hypersphere. This paper further proposes to group-wisely divide and drop out templates’ feature dimensions, to enhance the irreversibility of rotated templates. The proposed techniques are concretized as a novel face template protection technique, SlerpFace. Extensive experiments show that SlerpFace provides satisfactory recognition accuracy and comprehensive protection against inversion and other attack forms, superior to prior arts.
当代人脸识别系统使用从人脸图像中提取的特征模板来识别个人。为了增强隐私保护,广泛采用人脸模板保护技术来隐藏存储在模板中的敏感身份和外观信息。本文发现了一种利用扩散模型的新兴隐私攻击形式,可能会使先前的保护失效。这种攻击可以从模板中合成高质量、保留身份的人脸图像,从而揭示个人的外观。基于扩散模型的生成能力研究,本文提出了一种通过旋转模板到类似噪声的分布来进行防御的方法。这是通过在超球体上球面和线性插值模板来实现的。本文还提出将模板的特征维度分组并删除,以增强旋转模板的不可逆性。所提出的技术被具体化为一种新型的人脸模板保护技术——SlerpFace。大量实验表明,SlerpFace提供令人满意的识别精度和全面的保护,对抗解密和其他攻击形式,优于先前技术。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了当代人脸识别系统使用特征模板进行身份识别的情况,并指出为了保护隐私,采取了保护面部模板的技术来掩盖存储在模板中的敏感身份和外观信息。然而,本文发现了一种利用扩散模型的新型隐私攻击方式,该攻击可以从模板中合成高质量、保留身份的人脸图像,从而揭示个人的外观信息。针对扩散模型的生成能力,本文提出了一种通过旋转模板到噪声状分布的防御策略,并在超球体上实现球面线性插值。此外,本文还提出了分组智能的模板特征维度删减策略,以提高旋转模板的不可逆性。这些技术被具体化为一种新型面部模板保护技术——SlerpFace。实验表明,SlerpFace在提供识别准确性的同时,对逆转变种及其他攻击形式提供了出色的保护,超越了先前技术。
Key Takeaways
- 当代人脸识别系统使用特征模板进行身份识别。
- 面部模板保护技术用于掩盖存储在模板中的敏感身份和外观信息。
- 出现了一种新型隐私攻击方式,利用扩散模型从模板中合成高质量人脸图像。
- 提出了通过旋转模板到噪声状分布的防御策略。
- 实现了球面线性插值技术以提高旋转模板的安全性。
- 提出了分组智能的模板特征维度删减策略以增强模板的不可逆性。
点此查看论文截图

Adapting to Unknown Low-Dimensional Structures in Score-Based Diffusion Models
Authors:Gen Li, Yuling Yan
This paper investigates score-based diffusion models when the underlying target distribution is concentrated on or near low-dimensional manifolds within the higher-dimensional space in which they formally reside, a common characteristic of natural image distributions. Despite previous efforts to understand the data generation process of diffusion models, existing theoretical support remains highly suboptimal in the presence of low-dimensional structure, which we strengthen in this paper. For the popular Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model (DDPM), we find that the dependency of the error incurred within each denoising step on the ambient dimension $d$ is in general unavoidable. We further identify a unique design of coefficients that yields a converges rate at the order of $O(k^{2}/\sqrt{T})$ (up to log factors), where $k$ is the intrinsic dimension of the target distribution and $T$ is the number of steps. This represents the first theoretical demonstration that the DDPM sampler can adapt to unknown low-dimensional structures in the target distribution, highlighting the critical importance of coefficient design. All of this is achieved by a novel set of analysis tools that characterize the algorithmic dynamics in a more deterministic manner.
本文研究了基于分数的扩散模型,当底层目标分布集中在它们正式存在的高维空间中的低维流形上或附近时,这是自然图像分布的一个常见特征。尽管之前已经有人努力理解扩散模型的数据生成过程,但在存在低维结构的情况下,现有的理论支持仍然远远不够,我们在本文中加强了这一点。对于流行的去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM),我们发现每个去噪步骤中产生的错误对环境维度$d$的依赖通常是不可避免的。我们进一步识别出了一种独特的系数设计,其收敛速率为$O(k^{2}/\sqrt{T})$(包含对数因子),其中$k$是目标分布的内在维度,$T$是步骤数。这首次从理论上证明了DDPM采样器可以适应目标分布中未知的低维结构,突出了系数设计的关键重要性。所有这些都是通过一套新型的分析工具实现的,这些工具以更确定的方式描述了算法的动力学特征。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted to NeurIPS 2024
Summary
本文研究了基于分数扩散模型在目标分布集中于或接近低维流形时的表现,这常见于自然图像分布。对于流行的去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM),本文分析了在每个去噪步骤中误差对周围维度的依赖是不可避免的,并设计了一种独特的系数,使得收敛速度达到O(k^2/√T),其中k为目标分布的内在维度,T为步骤数。这证明了DDPM采样器能够适应目标分布中的未知低维结构,强调系数设计的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 分数扩散模型在低维流形上的表现是研究重点,自然图像分布常具有此特性。
- 对于DDPM模型,在去噪过程中误差对周围维度的依赖是普遍存在的。
- 设计了一种独特的系数,提高了模型的收敛速度,达到O(k^2/√T)。
- 该设计使得DDPM能够适应目标分布中的未知低维结构。
- 系数设计在扩散模型中起到关键作用。
- 本文提供了新型分析工具,以更确定的方式描述了算法动态。
点此查看论文截图

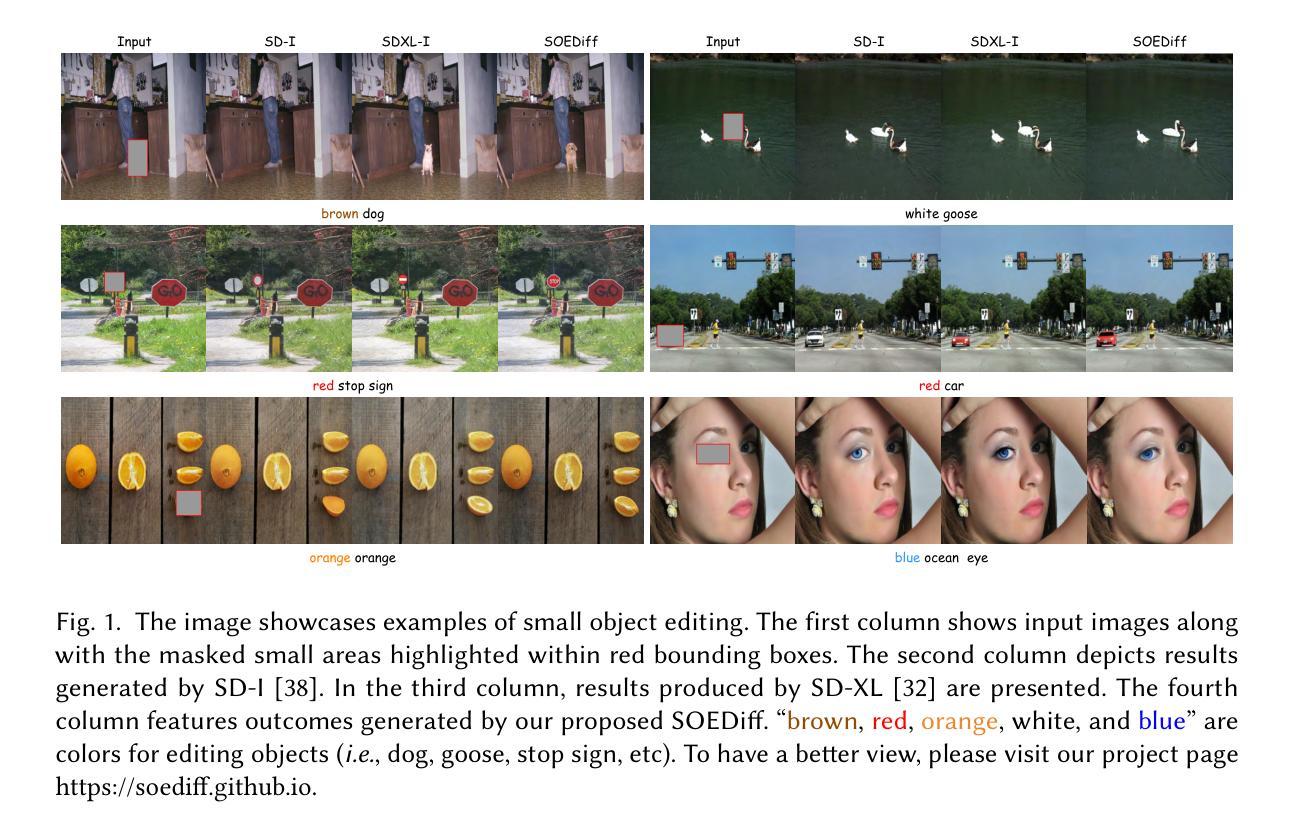
SOEDiff: Efficient Distillation for Small Object Editing
Authors:Yiming Wu, Qihe Pan, Zhen Zhao, Zicheng Wang, Sifan Long, Ronghua Liang
In this paper, we delve into a new task known as small object editing (SOE), which focuses on text-based image inpainting within a constrained, small-sized area. Despite the remarkable success have been achieved by current image inpainting approaches, their application to the SOE task generally results in failure cases such as Object Missing, Text-Image Mismatch, and Distortion. These failures stem from the limited use of small-sized objects in training datasets and the downsampling operations employed by U-Net models, which hinders accurate generation. To overcome these challenges, we introduce a novel training-based approach, SOEDiff, aimed at enhancing the capability of baseline models like StableDiffusion in editing small-sized objects while minimizing training costs. Specifically, our method involves two key components: SO-LoRA, which efficiently fine-tunes low-rank matrices, and Cross-Scale Score Distillation loss, which leverages high-resolution predictions from the pre-trained teacher diffusion model. Our method presents significant improvements on the test dataset collected from MSCOCO and OpenImage, validating the effectiveness of our proposed method in small object editing. In particular, when comparing SOEDiff with SD-I model on the OpenImage-f dataset, we observe a 0.99 improvement in CLIP-Score and a reduction of 2.87 in FID.
本文中,我们深入探讨了名为小对象编辑(SOE)的新任务,该任务专注于在受限的小区域内进行基于文本的图像填充。尽管当前的图像填充方法在技术上取得了显著的进步,但它们应用于SOE任务通常会导致对象缺失、文本与图像不匹配以及失真等失败案例。这些失败源于训练数据集中小对象的有限使用以及U-Net模型的下采样操作,这阻碍了准确的生成。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了一种新型的基于训练的方法SOEDiff,旨在增强基线模型(如StableDiffusion)编辑小对象的能力,同时降低训练成本。具体来说,我们的方法包括两个关键组件:SO-LoRA,它可以有效地微调低阶矩阵;以及跨尺度得分蒸馏损失,它利用预训练教师扩散模型的高分辨率预测。我们的方法在MSCOCO和OpenImage收集的测试数据集上取得了显著的改进,验证了我们在小对象编辑方法中的有效性。特别是当将SOEDiff与SD-I模型在OpenImage-f数据集上进行比较时,我们观察到CLIP得分提高了0.99,FID降低了2.87。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF preprint
Summary:
本文介绍了一项新任务——小目标编辑(SOE),专注于在限定的小区域内进行文本基础的图像补全。当前图像补全方法在小目标编辑任务中的应用常出现失败情况,如目标缺失、文本与图像不匹配和失真。为解决这些问题,提出了一种基于训练的方法SOEDiff,旨在提高基线模型如StableDiffusion编辑小目标的能力,同时降低训练成本。该方法包括两个关键组件:SO-LoRA,用于有效微调低秩矩阵;Cross-Scale Score Distillation损失,利用预训练教师扩散模型的高分辨率预测。在MSCOCO和OpenImage收集的测试数据集上,该方法在小目标编辑任务上取得了显著改进。
Key Takeaways:
- 文中介绍了一种新的任务——小目标编辑(SOE),专注于小区域的文本图像补全。
- 当前图像补全方法在小目标编辑任务中易出现目标缺失、文本与图像不匹配和失真等问题。
- 为解决上述问题,提出了基于训练的方法SOEDiff,旨在提高模型对小目标编辑的能力并降低训练成本。
- SOEDiff包含两个关键组件:SO-LoRA和Cross-Scale Score Distillation损失。
- SO-LoRA用于有效微调低秩矩阵。
- Cross-Scale Score Distillation损失利用预训练教师扩散模型的高分辨率预测。
点此查看论文截图



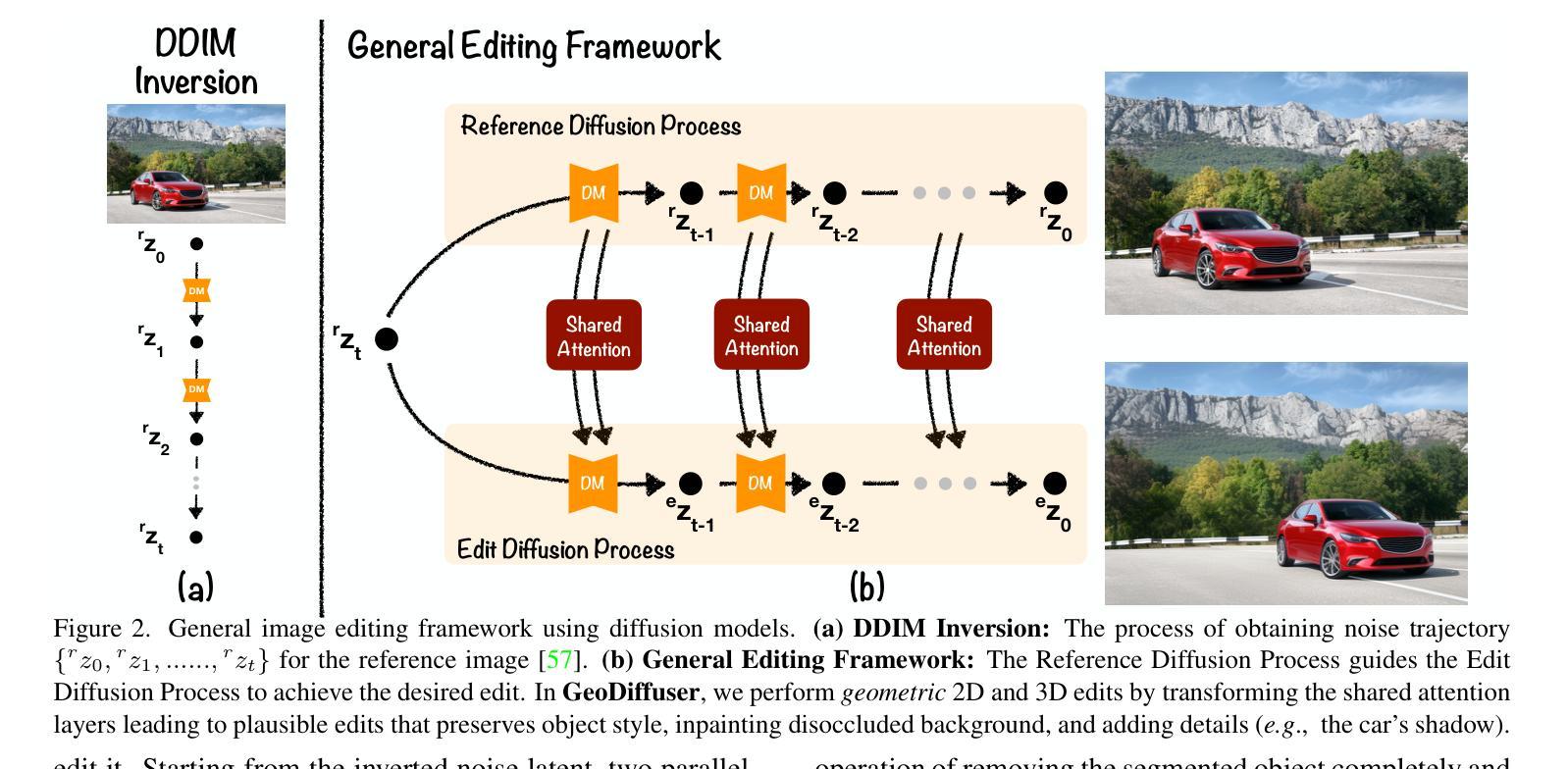
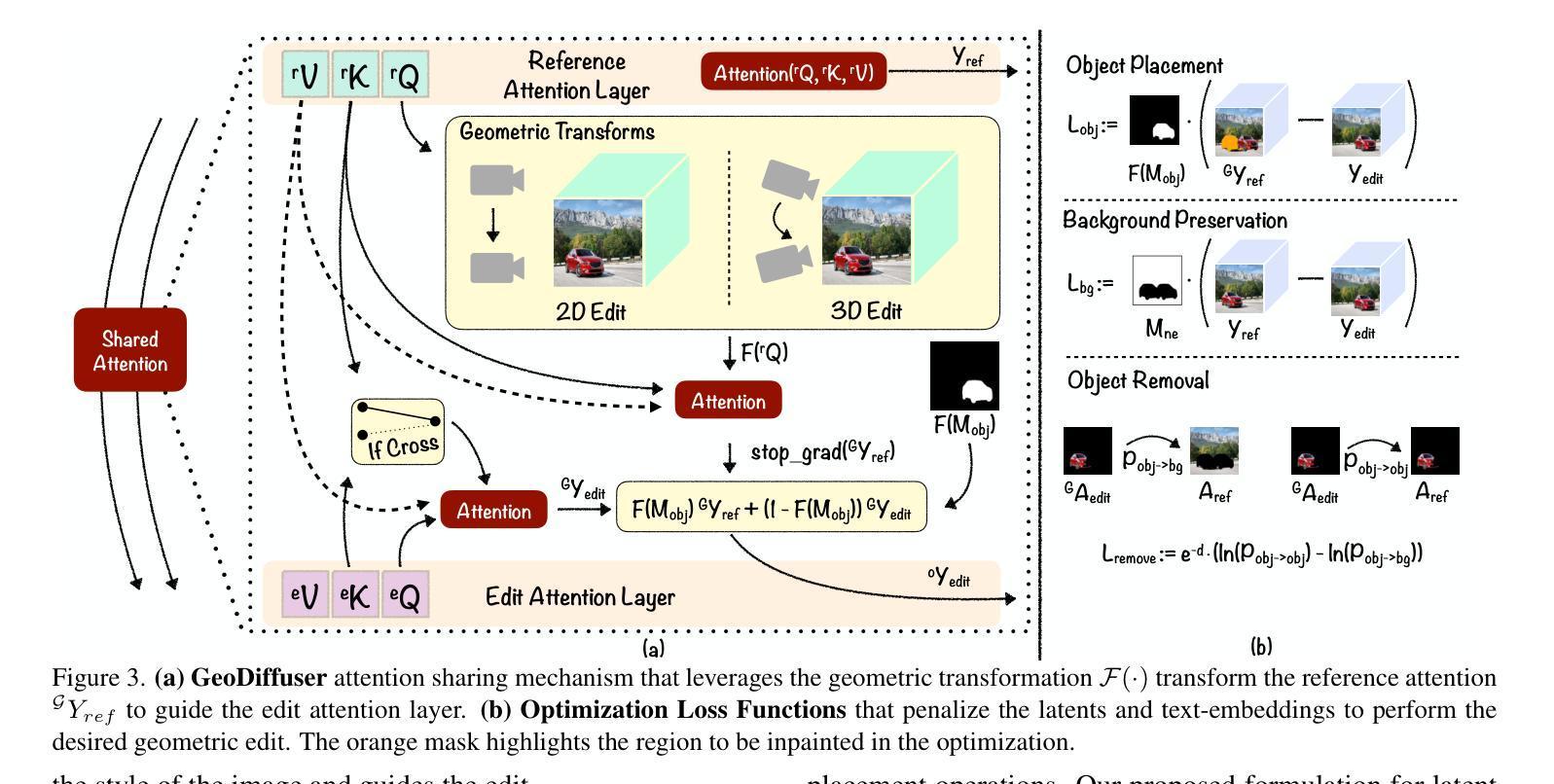
GeoDiffuser: Geometry-Based Image Editing with Diffusion Models
Authors:Rahul Sajnani, Jeroen Vanbaar, Jie Min, Kapil Katyal, Srinath Sridhar
The success of image generative models has enabled us to build methods that can edit images based on text or other user input. However, these methods are bespoke, imprecise, require additional information, or are limited to only 2D image edits. We present GeoDiffuser, a zero-shot optimization-based method that unifies common 2D and 3D image-based object editing capabilities into a single method. Our key insight is to view image editing operations as geometric transformations. We show that these transformations can be directly incorporated into the attention layers in diffusion models to implicitly perform editing operations. Our training-free optimization method uses an objective function that seeks to preserve object style but generate plausible images, for instance with accurate lighting and shadows. It also inpaints disoccluded parts of the image where the object was originally located. Given a natural image and user input, we segment the foreground object using SAM and estimate a corresponding transform which is used by our optimization approach for editing. GeoDiffuser can perform common 2D and 3D edits like object translation, 3D rotation, and removal. We present quantitative results, including a perceptual study, that shows how our approach is better than existing methods. Visit https://ivl.cs.brown.edu/research/geodiffuser.html for more information.
图像生成模型的成功使我们能够建立能够根据文本或其他用户输入编辑图像的方法。然而,这些方法都是定制的,不精确,需要额外信息,或者仅限于2D图像编辑。我们提出了GeoDiffuser,这是一种基于零样本优化的方法,它将常见的2D和3D图像基于对象的编辑功能集成到一种方法中。我们的关键见解是将图像编辑操作视为几何变换。我们表明,这些变换可以直接集成到扩散模型的注意力层中,以隐式执行编辑操作。我们的无训练优化方法使用目标函数,该函数旨在保持对象风格,但生成逼真的图像,例如具有准确的照明和阴影。它还会对原始对象所在位置被遮挡的图像部分进行填充。给定自然图像和用户输入,我们使用SAM对前景对象进行分割,并估算相应的变换,然后我们的优化方法使用该变换进行编辑。GeoDiffuser可以执行常见的2D和3D编辑,如对象平移、3D旋转和移除。我们提供了定量结果,包括一项感知研究,该研究展示了我们的方法比现有方法更好。有关更多信息,请访问https://ivl.cs.brown.edu/research/geodiffuser.html。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to WACV 2025, Tucson, Arizona, USA. For project page, see https://ivl.cs.brown.edu/research/geodiffuser.html
Summary
基于扩散模型的图像编辑方法GeoDiffuser融合了常见的二维和三维图像编辑功能,将图像编辑操作视为几何变换并直接融入扩散模型的注意力层。该方法无需训练,通过优化目标函数保留物体风格同时生成可信图像,可完成物体移动、三维旋转和移除等常见二维和三维编辑任务。详情访问链接。
Key Takeaways
- GeoDiffuser是一个零样本优化方法,实现了统一的二维和三维图像编辑能力。
- 它将图像编辑操作视为几何变换并融入扩散模型的注意力层。
- 该方法无需训练,使用目标函数优化来保留物体风格并生成可信图像。
- GeoDiffuser可以执行常见的二维和三维编辑任务,如物体移动、三维旋转和移除。
- 该方法通过分段前景物体和用户输入来进行编辑操作。
- 定量结果和感知研究表明,GeoDiffuser优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

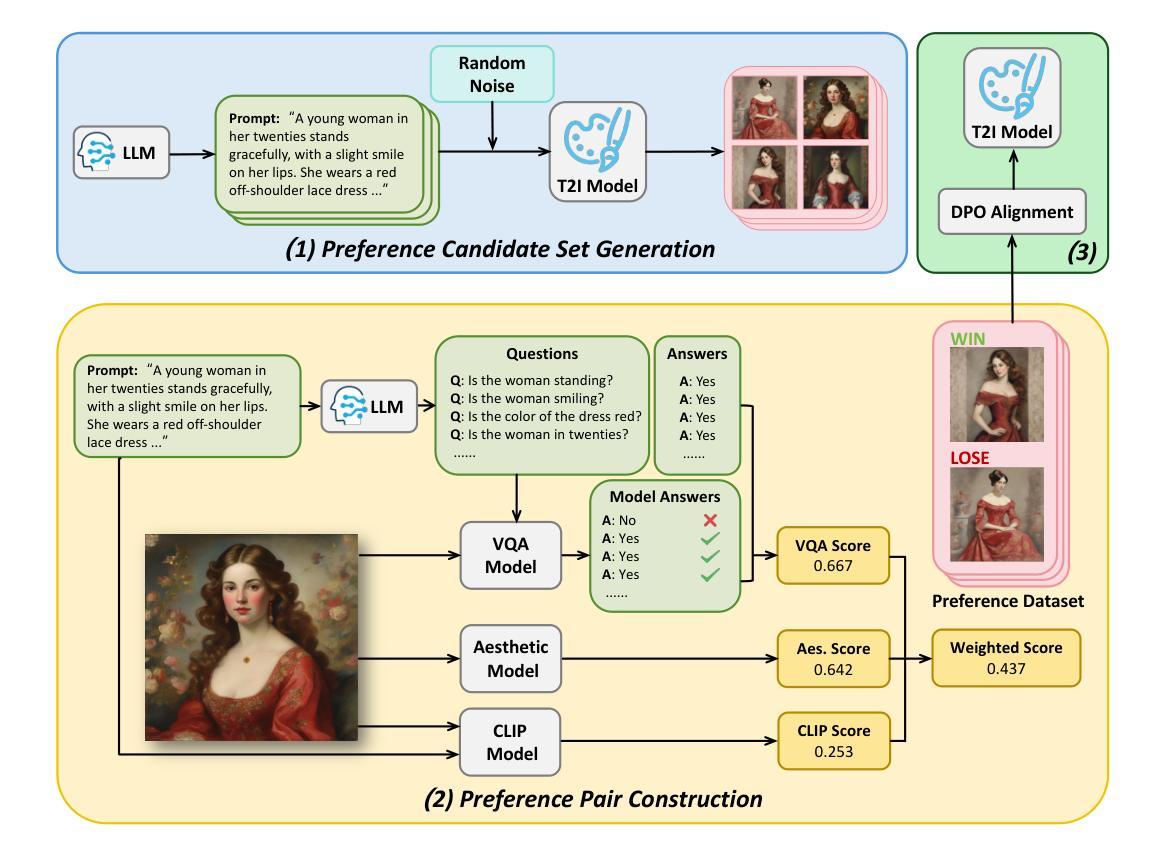
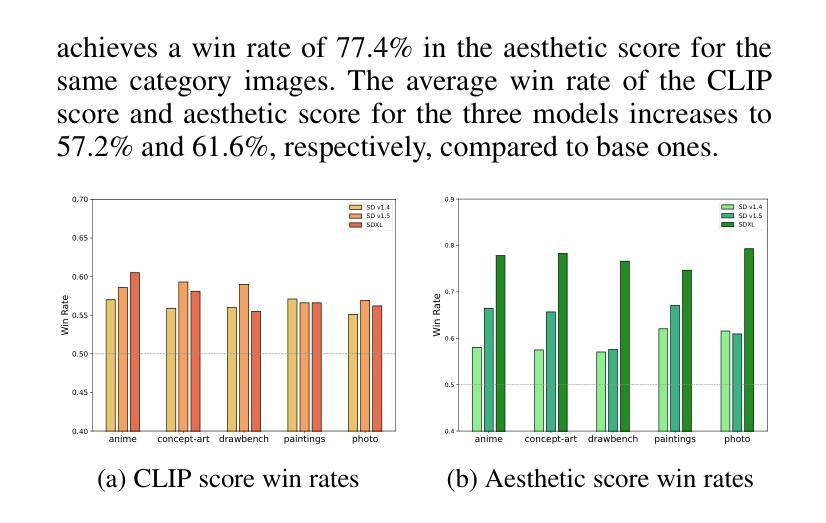
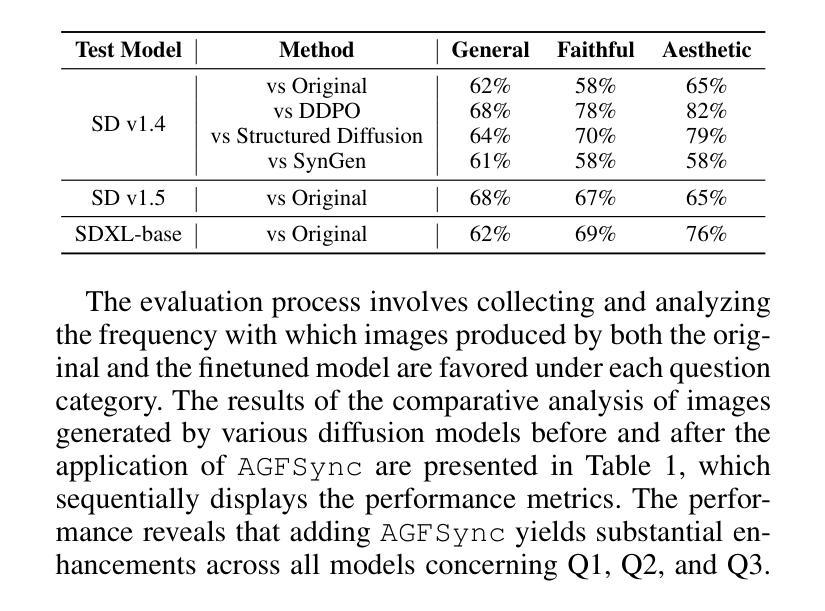
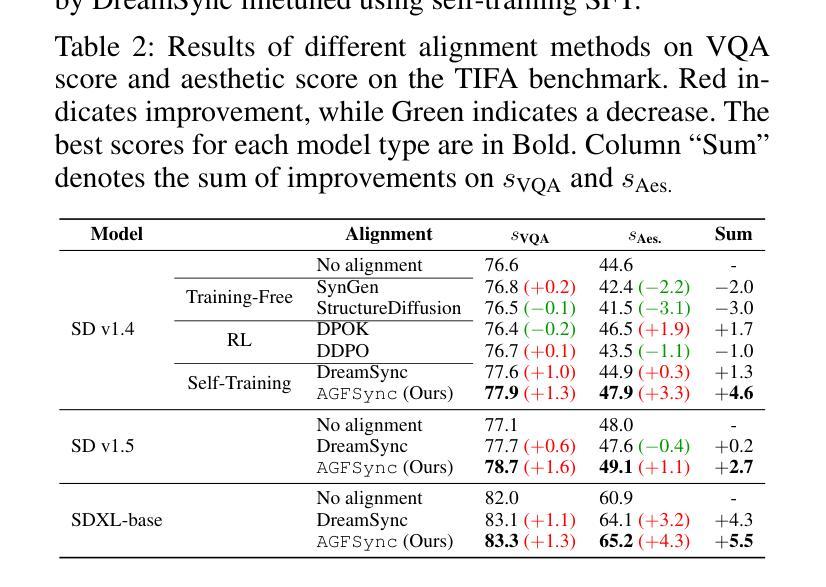
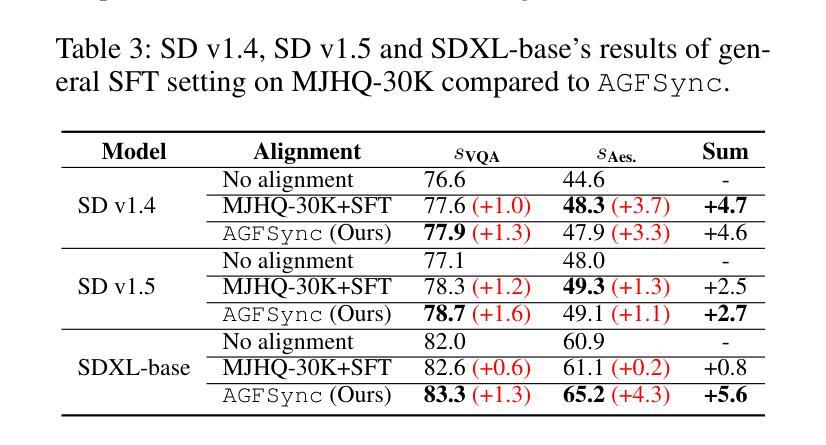
AGFSync: Leveraging AI-Generated Feedback for Preference Optimization in Text-to-Image Generation
Authors:Jingkun An, Yinghao Zhu, Zongjian Li, Enshen Zhou, Haoran Feng, Xijie Huang, Bohua Chen, Yemin Shi, Chengwei Pan
Text-to-Image (T2I) diffusion models have achieved remarkable success in image generation. Despite their progress, challenges remain in both prompt-following ability, image quality and lack of high-quality datasets, which are essential for refining these models. As acquiring labeled data is costly, we introduce AGFSync, a framework that enhances T2I diffusion models through Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) in a fully AI-driven approach. AGFSync utilizes Vision-Language Models (VLM) to assess image quality across style, coherence, and aesthetics, generating feedback data within an AI-driven loop. By applying AGFSync to leading T2I models such as SD v1.4, v1.5, and SDXL-base, our extensive experiments on the TIFA dataset demonstrate notable improvements in VQA scores, aesthetic evaluations, and performance on the HPSv2 benchmark, consistently outperforming the base models. AGFSync’s method of refining T2I diffusion models paves the way for scalable alignment techniques. Our code and dataset are publicly available at https://anjingkun.github.io/AGFSync.
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在图像生成方面取得了显著的成功。尽管有所进展,但在指令遵循能力、图像质量和缺乏高质量数据集等方面仍存在挑战,这些对于完善这些模型至关重要。由于获取标记数据成本高昂,我们引入了AGFSync框架,通过全AI驱动的方法直接优化偏好(DPO)增强T2I扩散模型。AGFSync利用视觉语言模型(VLM)从风格、连贯性和美学三个方面评估图像质量,在AI驱动的循环中生成反馈数据。通过将AGFSync应用于领先的T2I模型,如SD v1.4、v1.5和SDXL-base,我们在TIFA数据集上的大量实验表明,VQA分数、美学评价和HPSv2基准测试性能均有显著提高,始终优于基础模型。AGFSync对T2I扩散模型的精炼方法为可扩展的对齐技术铺平了道路。我们的代码和数据集可在https://anjingkun.github.io/AGFSync公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI-2025
Summary
文本介绍了T2I扩散模型在图像生成方面的显著成果,但也指出了存在的挑战,如提示遵循能力、图像质量和缺乏高质量数据集等。为解决这些问题,提出了一种名为AGFSync的框架,通过直接偏好优化(DPO)以全AI驱动的方式增强T2I扩散模型。AGFSync利用视觉语言模型(VLM)评估图像质量,包括风格、连贯性和美学方面,并在AI驱动的循环中生成反馈数据。在TIFA数据集上的实验表明,AGFSync在VQA分数、美学评估以及HPSv2基准测试上的表现均有显著提高,且始终优于基础模型。AGFSync的方法为T2I扩散模型的精炼提供了可扩展的对齐技术途径。
Key Takeaways
- T2I扩散模型在图像生成方面取得显著成功,但仍面临提示遵循能力、图像质量和数据集质量方面的挑战。
- AGFSync框架通过全AI驱动的方式增强T2I扩散模型,引入直接偏好优化(DPO)。
- AGFSync利用视觉语言模型(VLM)评估图像质量,包括风格、连贯性和美学。
- AGFSync在TIFA数据集上的实验表现优异,提高了VQA分数、美学评估以及HPSv2基准测试成绩。
- AGFSync显著优于基础模型,为T2I扩散模型的精炼提供了可扩展的对齐技术途径。
- AGFSync方法和数据集已公开可用,网址为https://anjingkun.github.io/AGFSync。
- 引入AGFSync框架为解决扩散模型面临的挑战提供了新的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

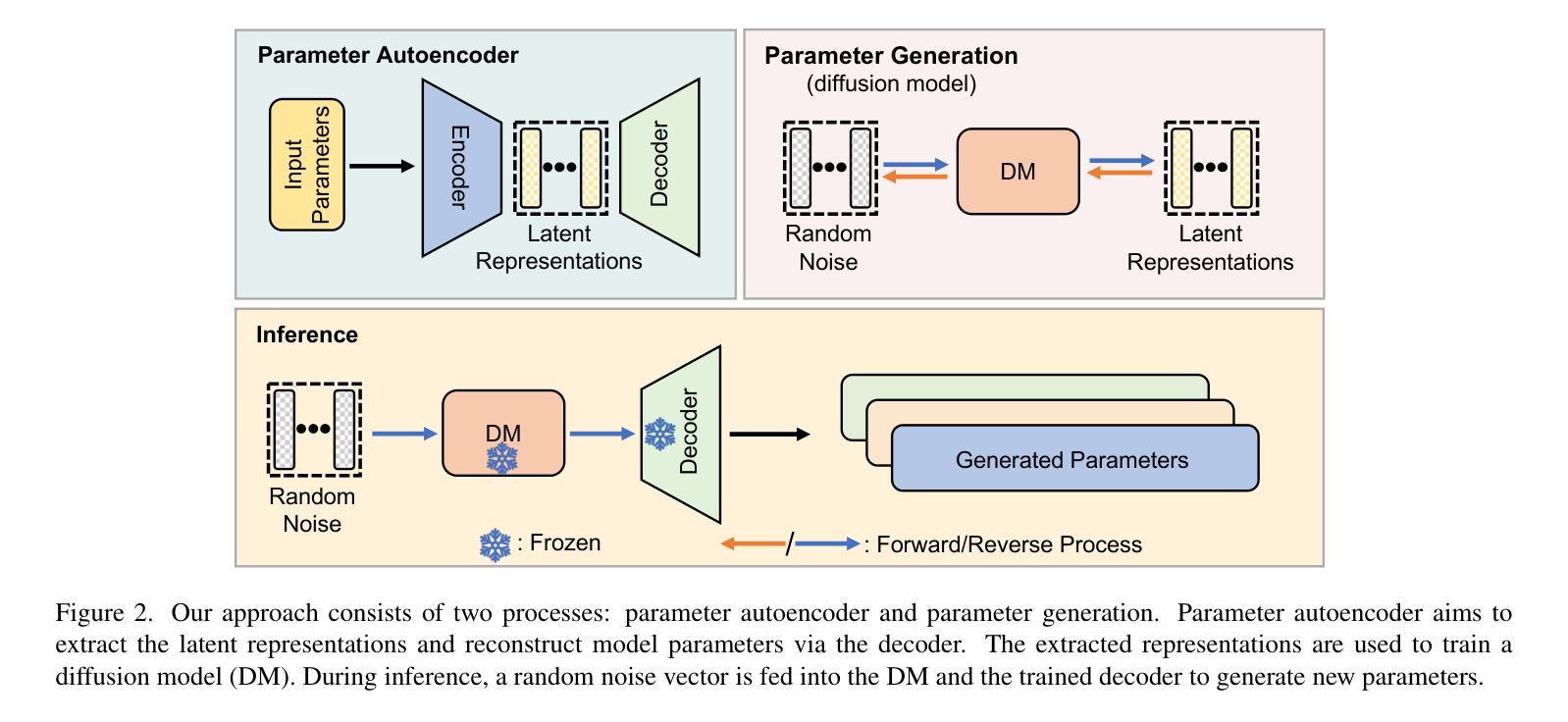
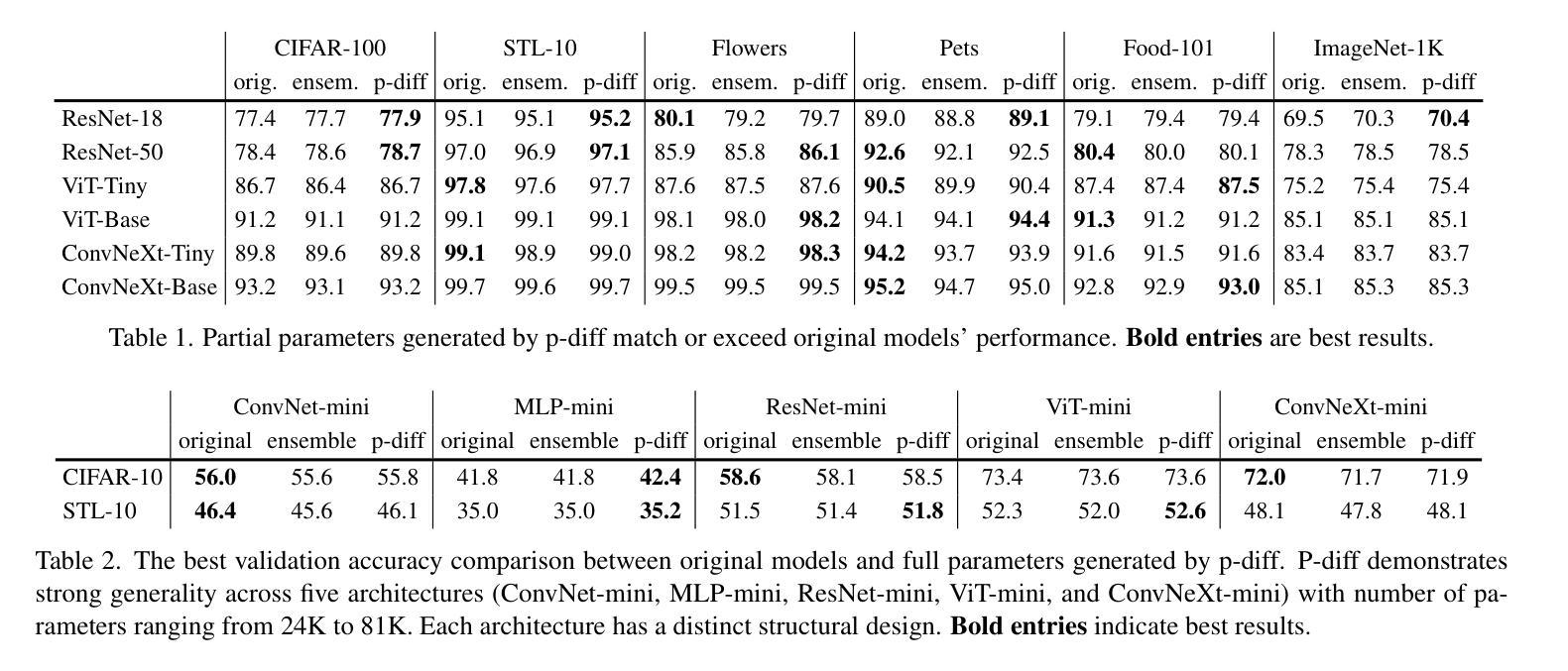
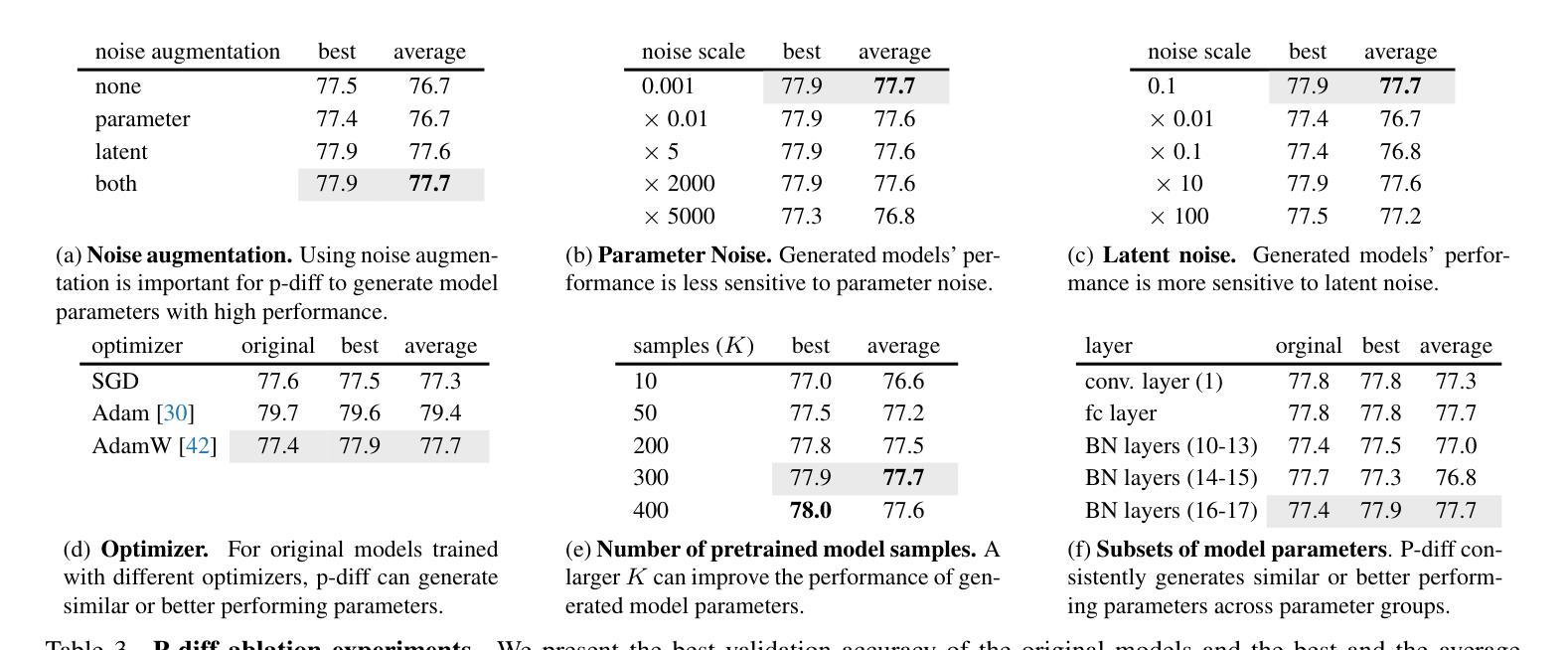
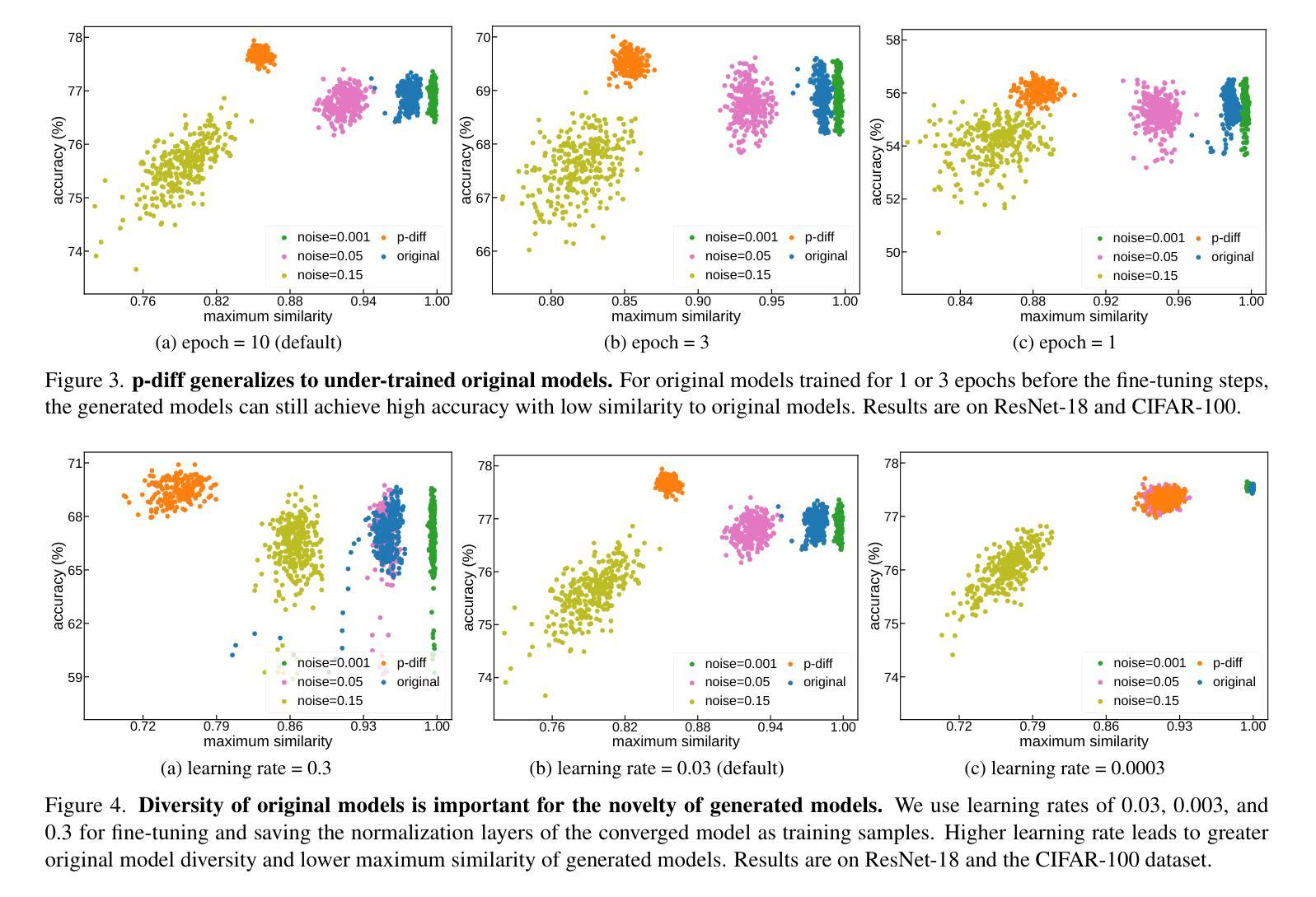
Neural Network Diffusion
Authors:Kai Wang, Dongwen Tang, Boya Zeng, Yida Yin, Zhaopan Xu, Yukun Zhou, Zelin Zang, Trevor Darrell, Zhuang Liu, Yang You
Diffusion models have achieved remarkable success in image and video generation. In this work, we demonstrate that diffusion models can also \textit{generate high-performing neural network parameters}. Our approach is simple, utilizing an autoencoder and a diffusion model. The autoencoder extracts latent representations of a subset of the trained neural network parameters. Next, a diffusion model is trained to synthesize these latent representations from random noise. This model then generates new representations, which are passed through the autoencoder’s decoder to produce new subsets of high-performing network parameters. Across various architectures and datasets, our approach consistently generates models with comparable or improved performance over trained networks, with minimal additional cost. Notably, we empirically find that the generated models are not memorizing the trained ones. Our results encourage more exploration into the versatile use of diffusion models. Our code is available \href{https://github.com/NUS-HPC-AI-Lab/Neural-Network-Diffusion}{here}.
扩散模型在图像和视频生成方面取得了显著的成功。在这项工作中,我们证明扩散模型也能生成高性能的神经网络参数。我们的方法很简单,利用自编码器和扩散模型。自编码器提取训练神经网络参数子集中的潜在表示。接下来,训练扩散模型从随机噪声中合成这些潜在表示。该模型然后生成新的表示,通过自编码器的解码器产生新的高性能网络参数子集。在各种架构和数据集上,我们的方法始终能生成与训练网络性能相当或更好的模型,且只需极少的额外成本。值得注意的是,我们从实验中发现,生成的模型并没有记忆训练模型。我们的结果鼓励更多探索扩散模型的通用用途。我们的代码可在[https://github.com/NUS-HPC-AI-Lab/Neural-Network-Diffusion](此处)找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF We introduce a novel approach for parameter generation, named neural network parameter diffusion (\textbf{p-diff}), which employs a standard latent diffusion model to synthesize a new set of parameters
Summary
本文展示了扩散模型在生成高性能神经网络参数方面的潜力。通过结合自编码器与扩散模型,该研究首先提取训练神经网络参数的潜在表示,然后用扩散模型从这些潜在表示中合成新的网络参数。这种方法生成的新模型性能与训练网络相当或更优,且额外成本较低。研究还表明生成的模型不会记忆训练模型。该研究的代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型可用于生成高性能神经网络参数。
- 结合自编码器和扩散模型,提取并合成神经网络参数的潜在表示。
- 生成模型的性能与训练网络相当或更优。
- 扩散模型的额外成本较低。
- 生成的模型不会记忆训练模型。
- 该研究为扩散模型的多元应用提供了启示。
点此查看论文截图

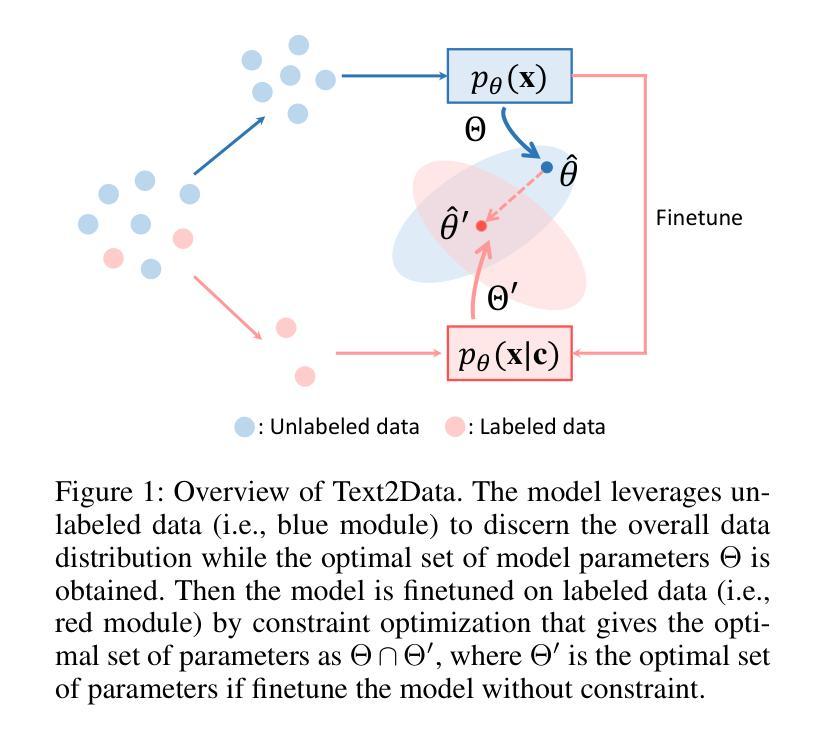
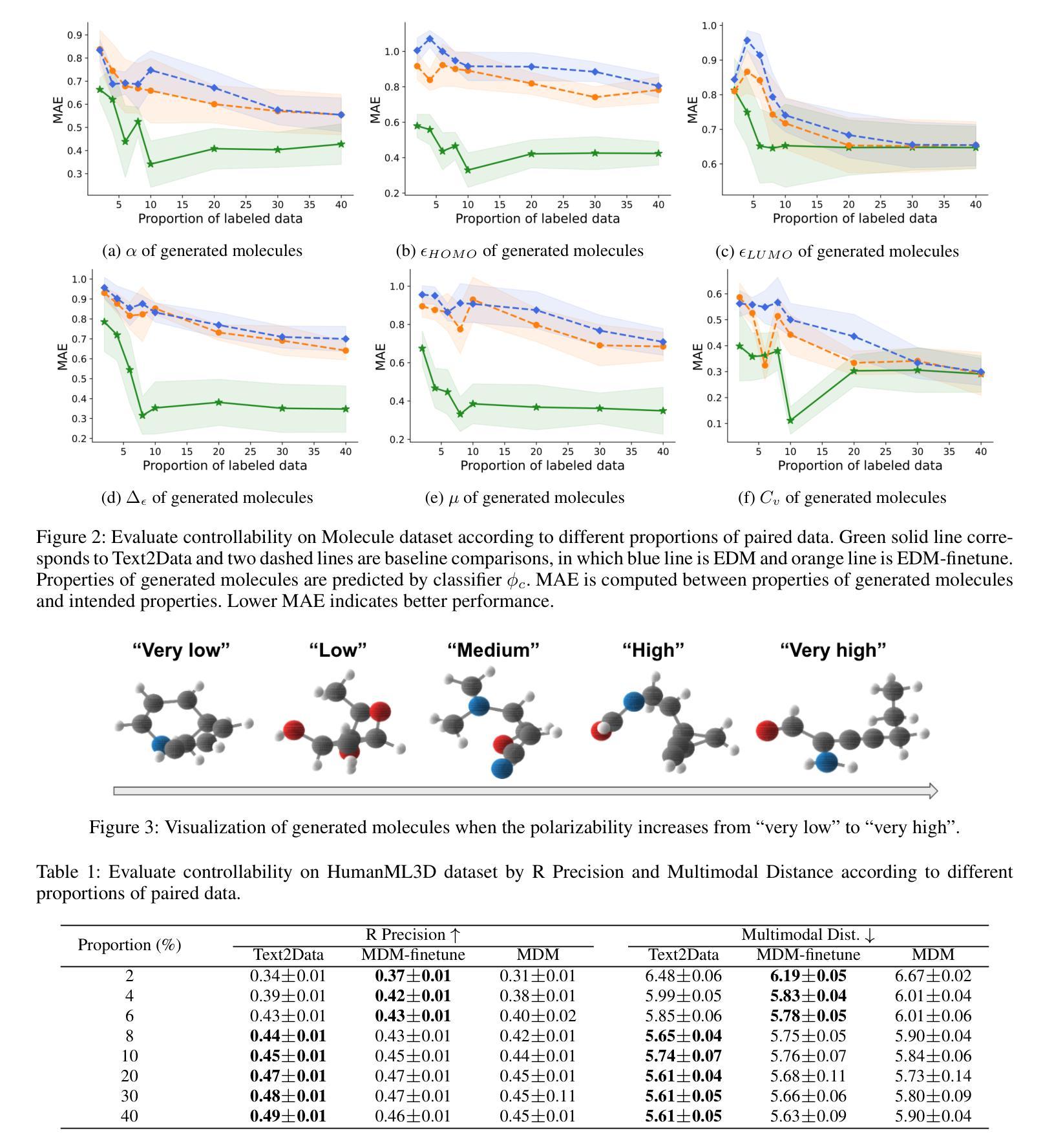
Text2Data: Low-Resource Data Generation with Textual Control
Authors:Shiyu Wang, Yihao Feng, Tian Lan, Ning Yu, Yu Bai, Ran Xu, Huan Wang, Caiming Xiong, Silvio Savarese
Natural language serves as a common and straightforward signal for humans to interact seamlessly with machines. Recognizing the importance of this interface, the machine learning community is investing considerable effort in generating data that is semantically coherent with textual instructions. While strides have been made in text-to-data generation spanning image editing, audio synthesis, video creation, and beyond, low-resource areas characterized by expensive annotations or complex data structures, such as molecules, motion dynamics, and time series, often lack textual labels. This deficiency impedes supervised learning, thereby constraining the application of advanced generative models for text-to-data tasks. In response to these challenges in the low-resource scenario, we propose Text2Data, a novel approach that utilizes unlabeled data to understand the underlying data distribution through an unsupervised diffusion model. Subsequently, it undergoes controllable finetuning via a novel constraint optimization-based learning objective that ensures controllability and effectively counteracts catastrophic forgetting. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that Text2Data is able to achieve enhanced performance regarding controllability across various modalities, including molecules, motions and time series, when compared to existing baselines.
自然语言是人类与机器无缝交互的常见且直观信号。认识到这一接口的重要性,机器学习社区正在投入大量精力生成与文本指令语义连贯的数据。虽然在图像编辑、音频合成、视频创建等文本到数据生成方面取得了进展,但标注昂贵或数据结构复杂的低资源领域,如分子、运动动力学和时序数据等,通常缺乏文本标签。这种缺乏阻碍了监督学习,从而限制了高级生成模型在文本到数据任务中的应用。针对低资源场景中的这些挑战,我们提出了Text2Data这一新方法,它利用无标签数据通过无监督扩散模型理解底层数据分布。随后,它通过基于新型约束优化的学习目标进行可控微调,确保可控性并有效对抗灾难性遗忘。综合实验表明,与现有基线相比,Text2Data在各种模式(包括分子、运动和时序数据)下在可控性方面取得了提高的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Thirty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-25)
Summary
文本指出自然语言是人类与机器交互的通用和直观信号。机器学习领域正在致力于生成与文本指令语义上一致的数据。尽管文本在图像编辑、音频合成、视频创建等方面的文本到数据生成有所进展,但在低资源领域,如分子、运动动力学和时序等,由于缺乏文本标签,阻碍了监督学习,限制了高级生成模型在文本到数据任务中的应用。为此,提出Text2Data方法,利用无标签数据通过无监督扩散模型理解底层数据分布,并通过新型约束优化学习目标实现可控微调。实验证明,Text2Data在分子、运动和时序等跨模态领域实现良好可控性表现优于现有基线。
Key Takeaways
- 自然语言是人类与机器交互的重要接口,机器学习领域正努力生成与文本指令语义一致的数据。
- 文本到数据生成已在多个领域取得进展,但低资源领域由于缺乏文本标签而面临挑战。
- Text2Data方法利用无标签数据通过无监督扩散模型理解底层数据分布。
- Text2Data通过可控微调实现模型的可控性,有效对抗灾难性遗忘。
- Text2Data在分子、运动和时序等跨模态领域的表现优于现有基线。
- 约束优化学习目标是实现Text2Data可控性的关键。
点此查看论文截图

Realistic Noise Synthesis with Diffusion Models
Authors:Qi Wu, Mingyan Han, Ting Jiang, Chengzhi Jiang, Jinting Luo, Man Jiang, Haoqiang Fan, Shuaicheng Liu
Deep denoising models require extensive real-world training data, which is challenging to acquire. Current noise synthesis techniques struggle to accurately model complex noise distributions. We propose a novel Realistic Noise Synthesis Diffusor (RNSD) method using diffusion models to address these challenges. By encoding camera settings into a time-aware camera-conditioned affine modulation (TCCAM), RNSD generates more realistic noise distributions under various camera conditions. Additionally, RNSD integrates a multi-scale content-aware module (MCAM), enabling the generation of structured noise with spatial correlations across multiple frequencies. We also introduce Deep Image Prior Sampling (DIPS), a learnable sampling sequence based on depth image prior, which significantly accelerates the sampling process while maintaining the high quality of synthesized noise. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our RNSD method significantly outperforms existing techniques in synthesizing realistic noise under multiple metrics and improving image denoising performance.
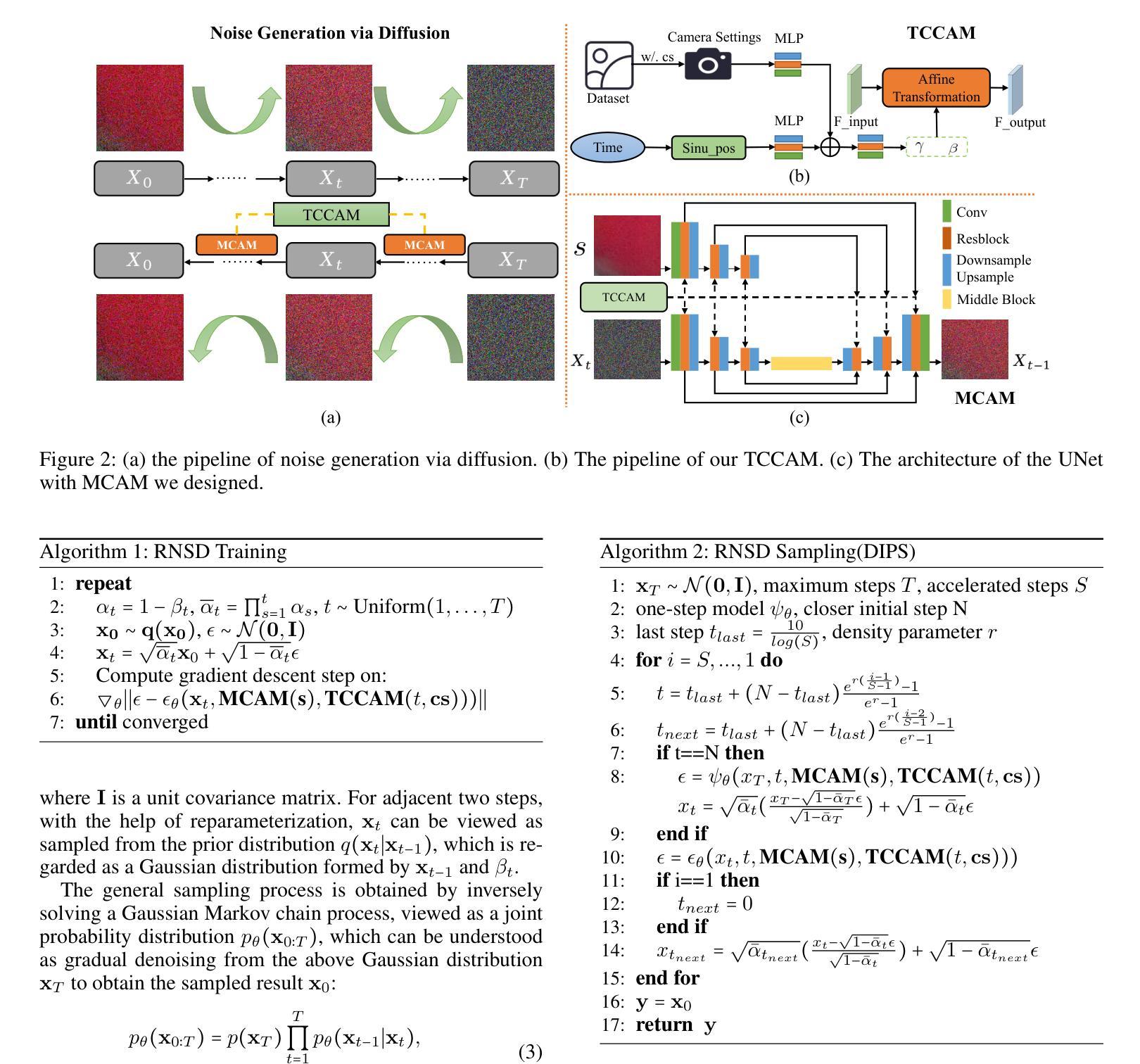
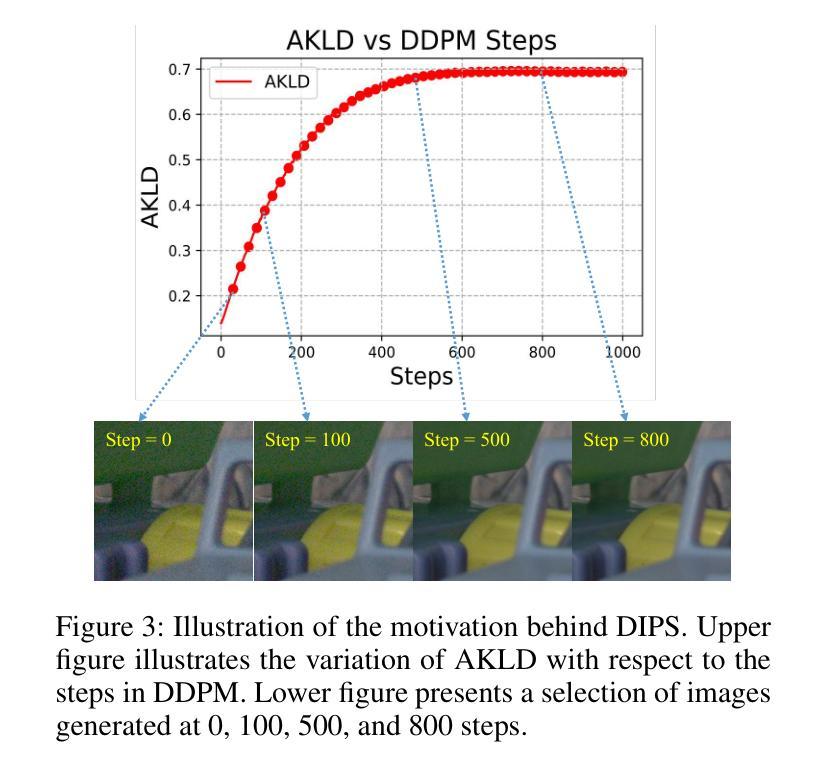
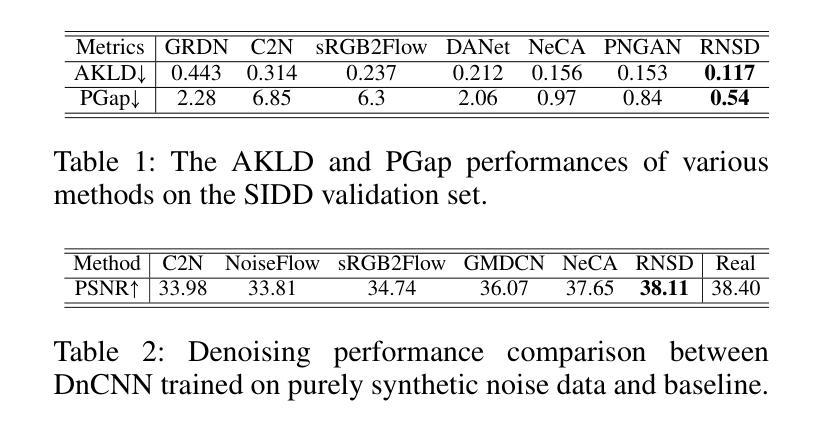
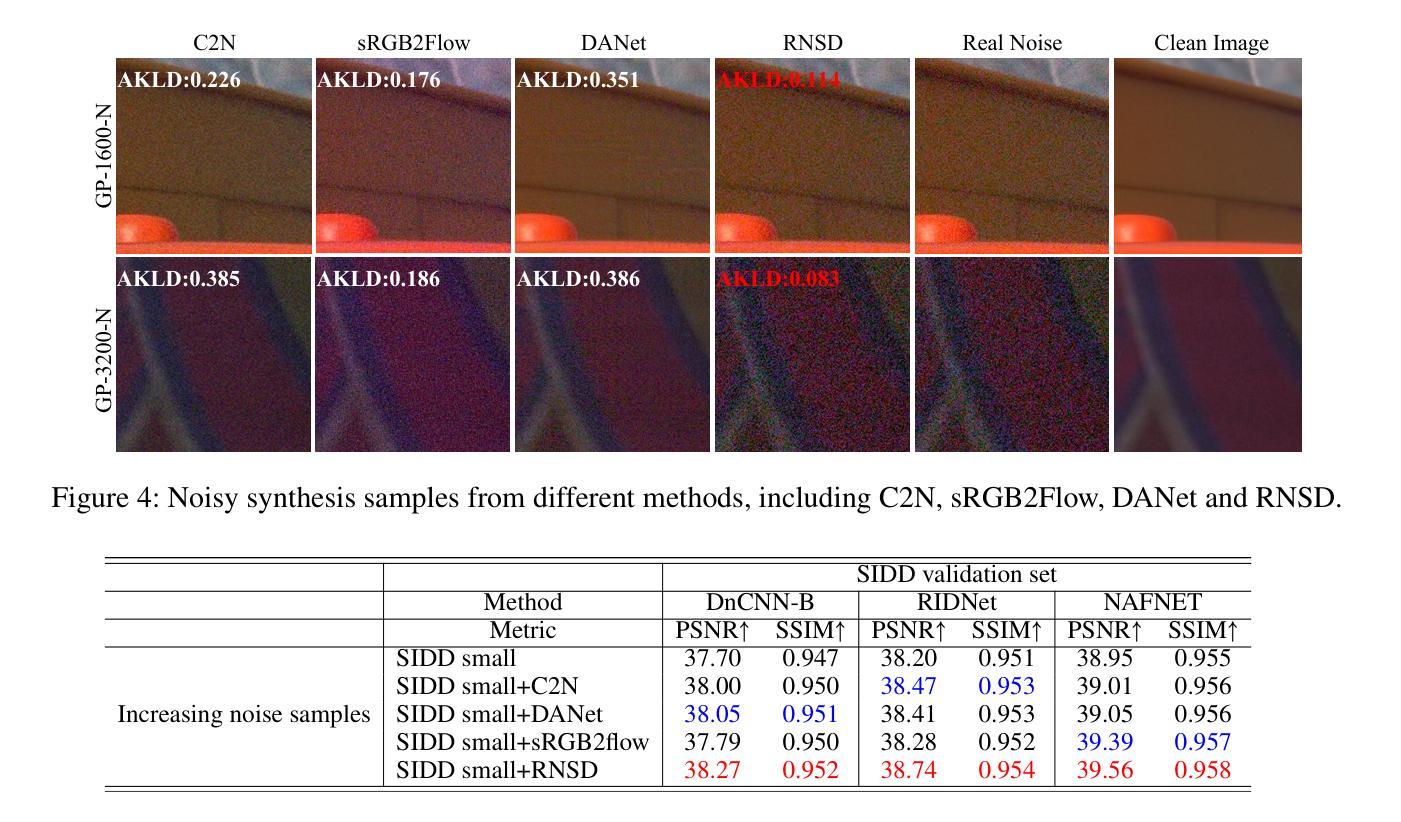
深度去噪模型需要大量的真实世界训练数据,这很难获取。当前的噪声合成技术在准确模拟复杂的噪声分布方面存在困难。我们提出了一种使用扩散模型的新型Realistic Noise Synthesis Diffusor(RNSD)方法,以解决这些挑战。RNSD通过将相机设置编码为时间感知相机条件仿射调制(TCCAM),在各种相机条件下生成更真实的噪声分布。此外,RNSD还集成了一个多尺度内容感知模块(MCAM),能够生成具有多个频率之间空间相关性的结构化噪声。我们还引入了基于深度图像先验的Deep Image Prior Sampling(DIPS)可学习采样序列,它在保持合成噪声高质量的同时,显著加速了采样过程。大量实验表明,我们的RNSD方法在多个指标下合成现实噪声的性能显著优于现有技术,并提高了图像去噪性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI25
Summary
利用扩散模型提出一种新的真实噪声合成扩散器(RNSD)方法,解决深度降噪模型面临的实际挑战。RNSD结合时间感知相机条件仿射调制(TCCAM)和多尺度内容感知模块(MCAM),生成更符合各种相机条件下的真实噪声分布。此外,引入深度图像先验采样(DIPS)可加速采样过程并保持合成噪声的高质量。实验证明,RNSD方法在多个指标上显著优于现有技术,提高了图像去噪性能。
Key Takeaways
- 提出的Realistic Noise Synthesis Diffusor (RNSD)方法使用扩散模型解决深度降噪模型的挑战。
- RNSD结合时间感知相机条件仿射调制(TCCAM),生成更符合相机条件下的真实噪声分布。
- 多尺度内容感知模块(MCAM)使RNSD能够生成具有空间相关性的结构噪声。
- 引入Deep Image Prior Sampling (DIPS)以提高采样速度并保持噪声合成的高质量。
- RNSD在多个指标上显著优于现有噪声合成技术。
- RNSD方法能提高图像去噪性能。
点此查看论文截图