⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-04 更新
Adaptive Prompt Tuning: Vision Guided Prompt Tuning with Cross-Attention for Fine-Grained Few-Shot Learning
Authors:Eric Brouwer, Jan Erik van Woerden, Gertjan Burghouts, Matias Valdenegro-Toro, Marco Zullich
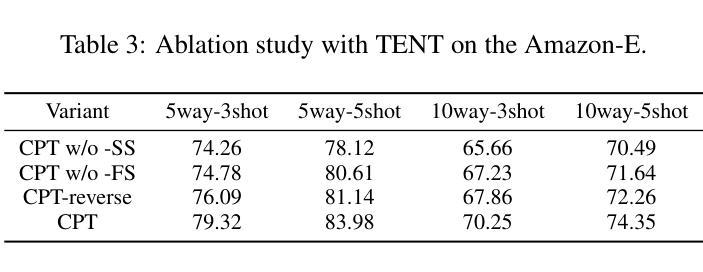
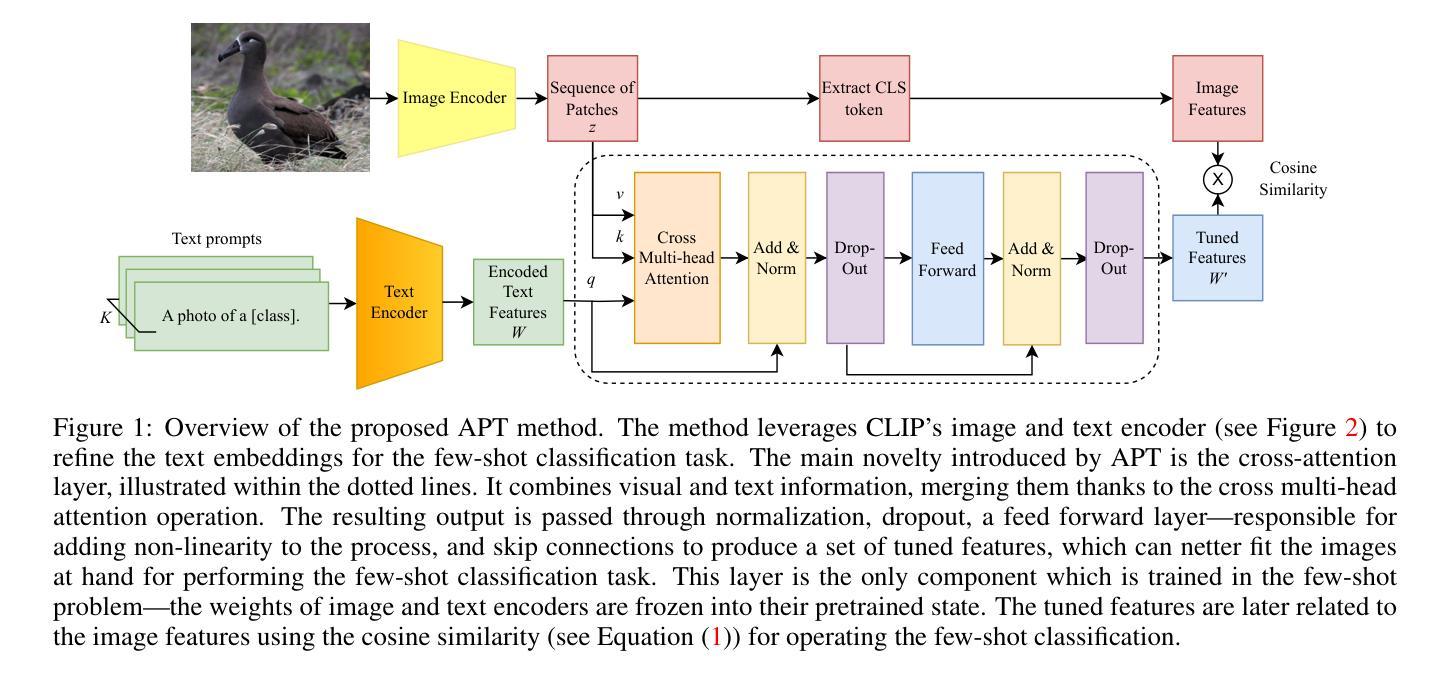
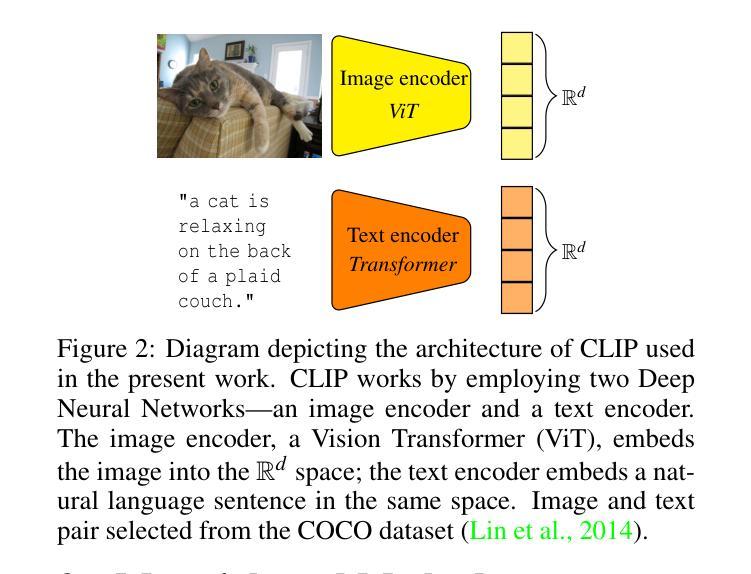
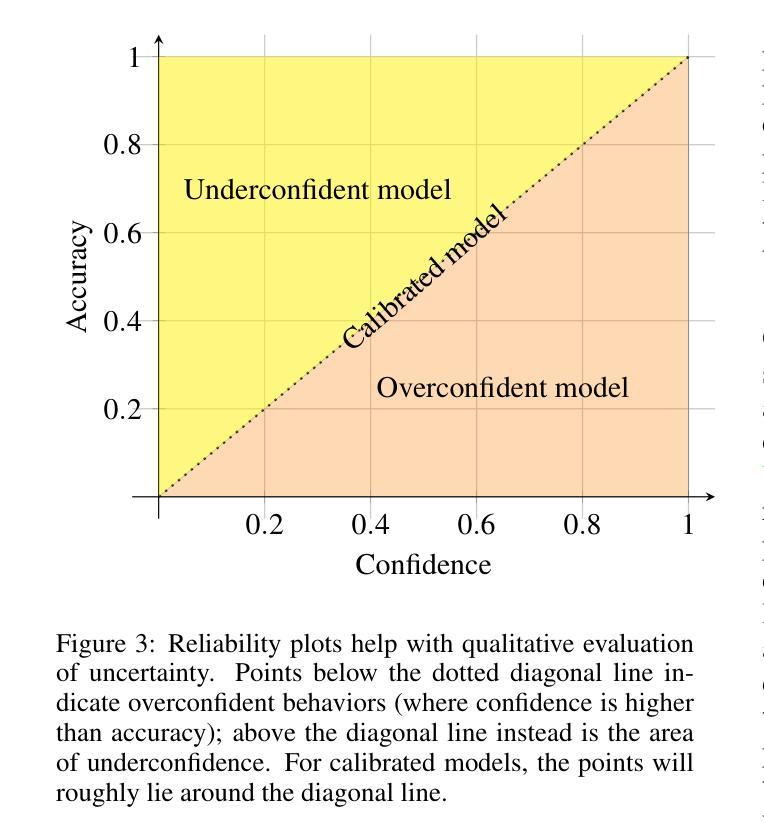
Few-shot, fine-grained classification in computer vision poses significant challenges due to the need to differentiate subtle class distinctions with limited data. This paper presents a novel method that enhances the Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training (CLIP) model through adaptive prompt tuning, guided by real-time visual inputs. Unlike existing techniques such as Context Optimization (CoOp) and Visual Prompt Tuning (VPT), which are constrained by static prompts or visual token reliance, the proposed approach leverages a cross-attention mechanism to dynamically refine text prompts for the image at hand. This enables an image-specific alignment of textual features with image patches extracted from the Vision Transformer, making the model more effective for datasets with high intra-class variance and low inter-class differences. The method is evaluated on several datasets, including CUBirds, Oxford Flowers, and FGVC Aircraft, showing significant performance gains over static prompt tuning approaches. To ensure these performance gains translate into trustworthy predictions, we integrate Monte-Carlo Dropout in our approach to improve the reliability of the model predictions and uncertainty estimates. This integration provides valuable insights into the model’s predictive confidence, helping to identify when predictions can be trusted and when additional verification is necessary. This dynamic approach offers a robust solution, advancing the state-of-the-art for few-shot fine-grained classification.
在计算机视觉领域,小样本精细分类面临重大挑战,因为需要在有限的数据下区分微妙的类别差异。本文提出了一种通过自适应提示调整增强对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)模型的新方法,该方法由实时视觉输入引导。与现有的上下文优化(CoOp)和视觉提示调整(VPT)等技术不同,这些技术受限于静态提示或视觉标记的依赖,所提出的方法利用跨注意力机制动态调整当前图像的文本提示。这使得文本特征与从视觉转换器提取的图像块实现特定图像对齐,使模型对于具有高的类内差异性和低的类间差异性的数据集更加有效。该方法在多个数据集上进行了评估,包括CUBirds、Oxford Flowers和FGVC Aircraft等数据集,与静态提示调整方法相比显示出显著的性能提升。为确保这些性能提升转化为可靠的预测,我们将蒙特卡洛Dropout集成到我们的方法中,以提高模型预测和不确定性估计的可靠性。这种集成提供了关于模型预测置信度的宝贵见解,有助于确定何时可以信任预测以及何时需要额外的验证。这种动态方法为精细分类提供了一个稳健的解决方案,推动了小样本精细分类的最新技术进展。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于自适应提示调整的新方法,增强Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training(CLIP)模型,通过实时视觉输入进行引导,以进行小样本、精细分类的任务。该方法利用跨注意力机制动态调整文本提示,与当前图像相匹配,从而提高模型在类内差异细微、类间差异较大的数据集上的性能。集成Monte-Carlo Dropout提高模型的预测可靠性和不确定性估计,为模型的预测置信度提供有价值的信息。这是一种动态的方法,为小样精细分类任务提供了稳健的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 该方法通过自适应提示调整增强CLIP模型,以进行小样本、精细分类的任务。
- 利用跨注意力机制动态调整文本提示,以匹配当前图像。
- 与现有的CoOp和VPT技术相比,该方法具有更高的灵活性,能够更好地处理类内差异细微、类间差异较大的数据集。
- 集成Monte-Carlo Dropout提高模型的预测可靠性和不确定性估计。
- 通过实时视觉输入进行引导,提高了模型的性能。
- 该方法在不同的数据集上进行了评估,包括CUBirds、Oxford Flowers和FGVC Aircraft,并实现了显著的性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

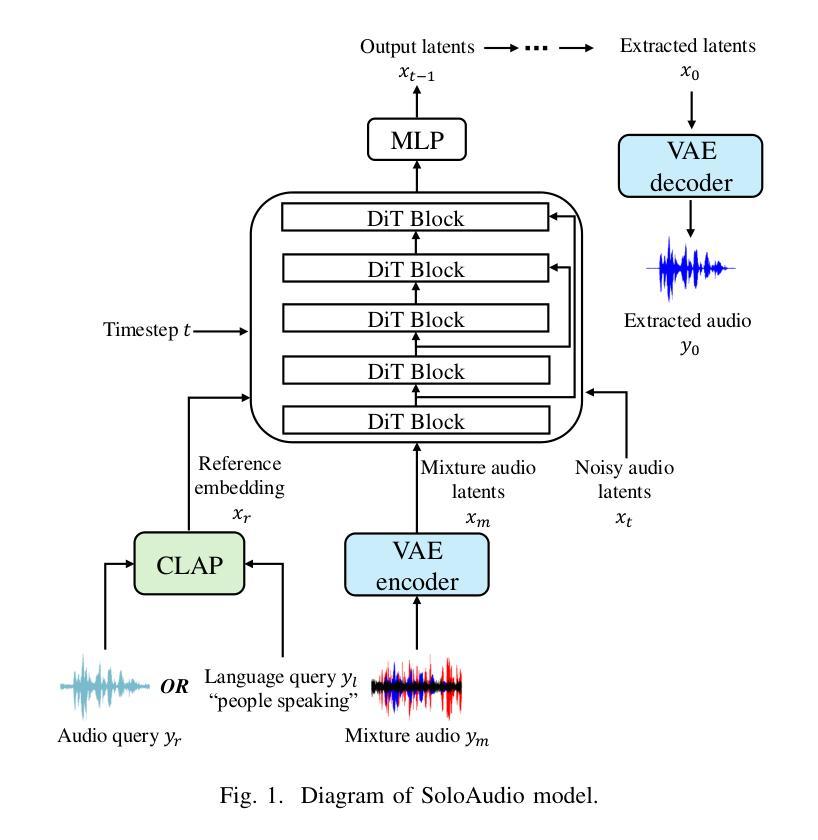
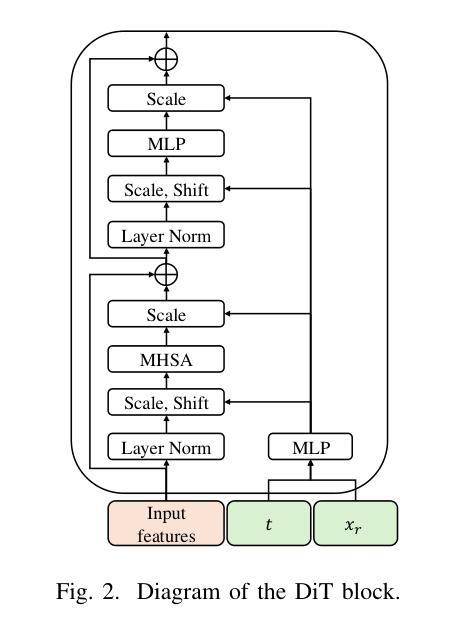
SoloAudio: Target Sound Extraction with Language-oriented Audio Diffusion Transformer
Authors:Helin Wang, Jiarui Hai, Yen-Ju Lu, Karan Thakkar, Mounya Elhilali, Najim Dehak
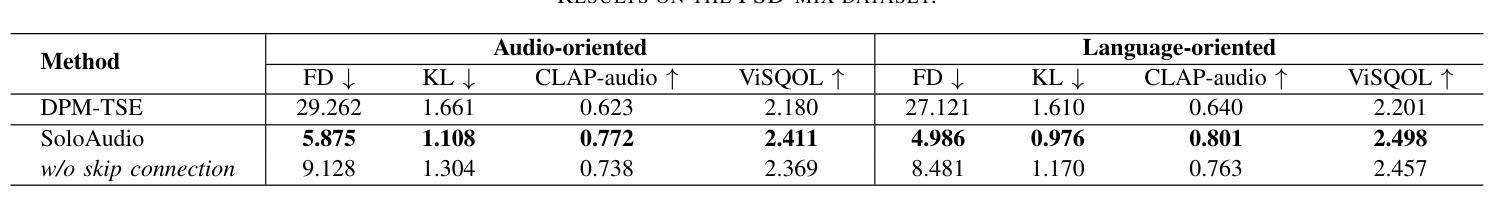
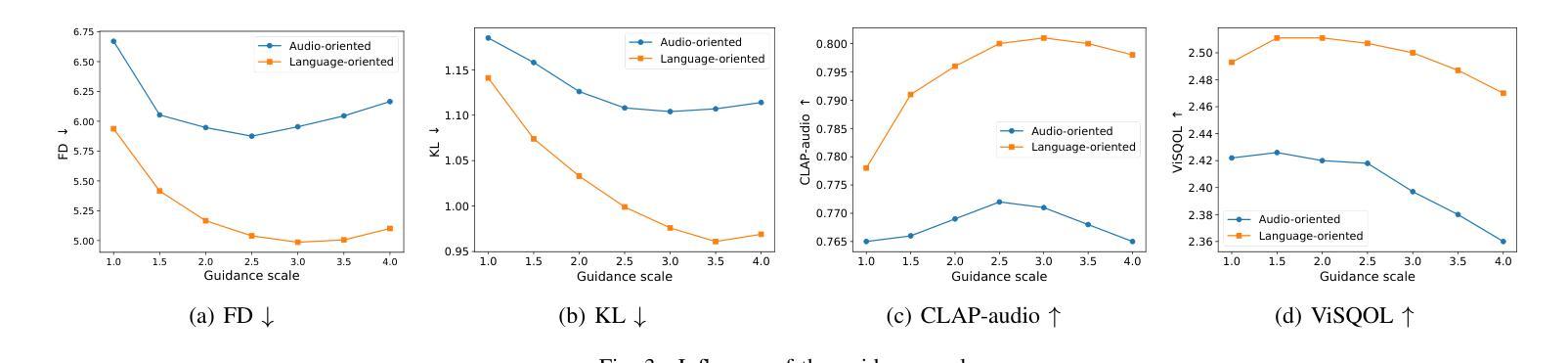
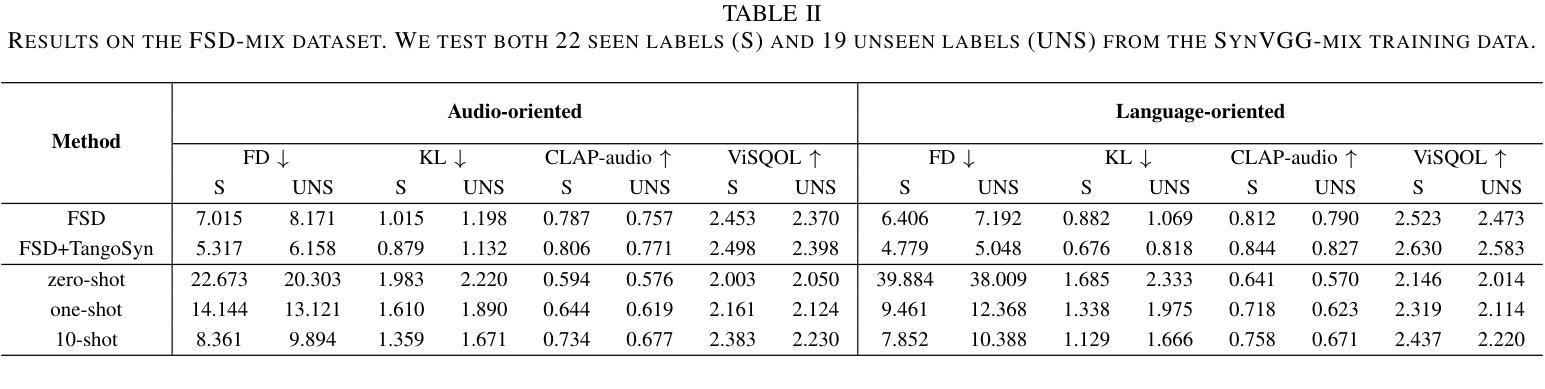
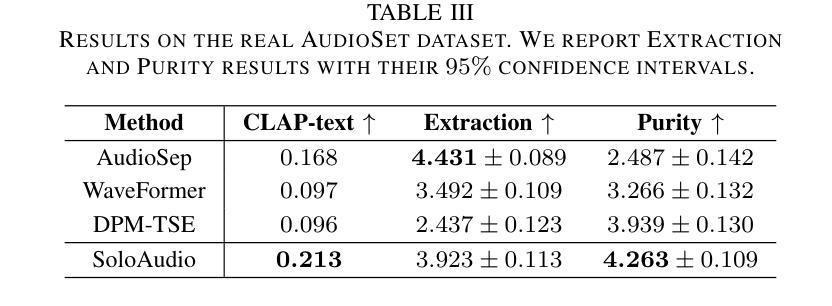
In this paper, we introduce SoloAudio, a novel diffusion-based generative model for target sound extraction (TSE). Our approach trains latent diffusion models on audio, replacing the previous U-Net backbone with a skip-connected Transformer that operates on latent features. SoloAudio supports both audio-oriented and language-oriented TSE by utilizing a CLAP model as the feature extractor for target sounds. Furthermore, SoloAudio leverages synthetic audio generated by state-of-the-art text-to-audio models for training, demonstrating strong generalization to out-of-domain data and unseen sound events. We evaluate this approach on the FSD Kaggle 2018 mixture dataset and real data from AudioSet, where SoloAudio achieves the state-of-the-art results on both in-domain and out-of-domain data, and exhibits impressive zero-shot and few-shot capabilities. Source code and demos are released.
本文介绍了SoloAudio,这是一种基于扩散的目标声音提取(TSE)新型生成模型。我们的方法训练音频上的潜在扩散模型,用操作潜在特征的跳跃连接Transformer替换之前的U-Net主干。SoloAudio通过利用CLAP模型作为目标声音的特征提取器,支持面向音频和面向语言的TSE。此外,SoloAudio还利用最先进的文本到音频模型生成的合成音频进行训练,在对域外数据和未见声音事件的泛化方面表现出色。我们在FSD Kaggle 2018混合数据集和AudioSet的真实数据上评估了这种方法,SoloAudio在域内和域外数据上都取得了最新结果,并展现出令人印象深刻的零样本和少样本能力。现已发布源代码和演示。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文介绍了SoloAudio,一种基于扩散的新型目标声音提取生成模型。该模型对音频进行训练,用带有跳跃连接的Transformer替换之前的U-Net主干,在潜在特征上运行。SoloAudio支持面向音频和面向语言的声音目标提取,利用CLAP模型作为目标声音的特征提取器。此外,SoloAudio利用最先进的文本到音频模型生成的合成音频进行训练,表现出对域外数据和未见声音事件的强大泛化能力。在FSD Kaggle 2018混合数据集和AudioSet真实数据上的评估显示,SoloAudio在域内和域外数据上都达到了最新技术成果,并展现了令人印象深刻的零样本和少样本能力。
Key Takeaways
- SoloAudio是一种基于扩散的生成模型,用于目标声音提取。
- 该模型使用跳跃连接的Transformer替代了传统的U-Net结构。
- SoloAudio支持音频和语言两种取向的目标声音提取。
- CLAP模型被用作特征提取器来提取目标声音。
- 利用合成音频进行训练,展现出对未见声音事件的强大泛化能力。
- 在多个数据集上的评估证明了SoloAudio的先进性能,特别是零样本和少样本场景下的性能表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

Benchmarking the Performance of Pre-trained LLMs across Urdu NLP Tasks
Authors:Munief Hassan Tahir, Sana Shams, Layba Fiaz, Farah Adeeba, Sarmad Hussain
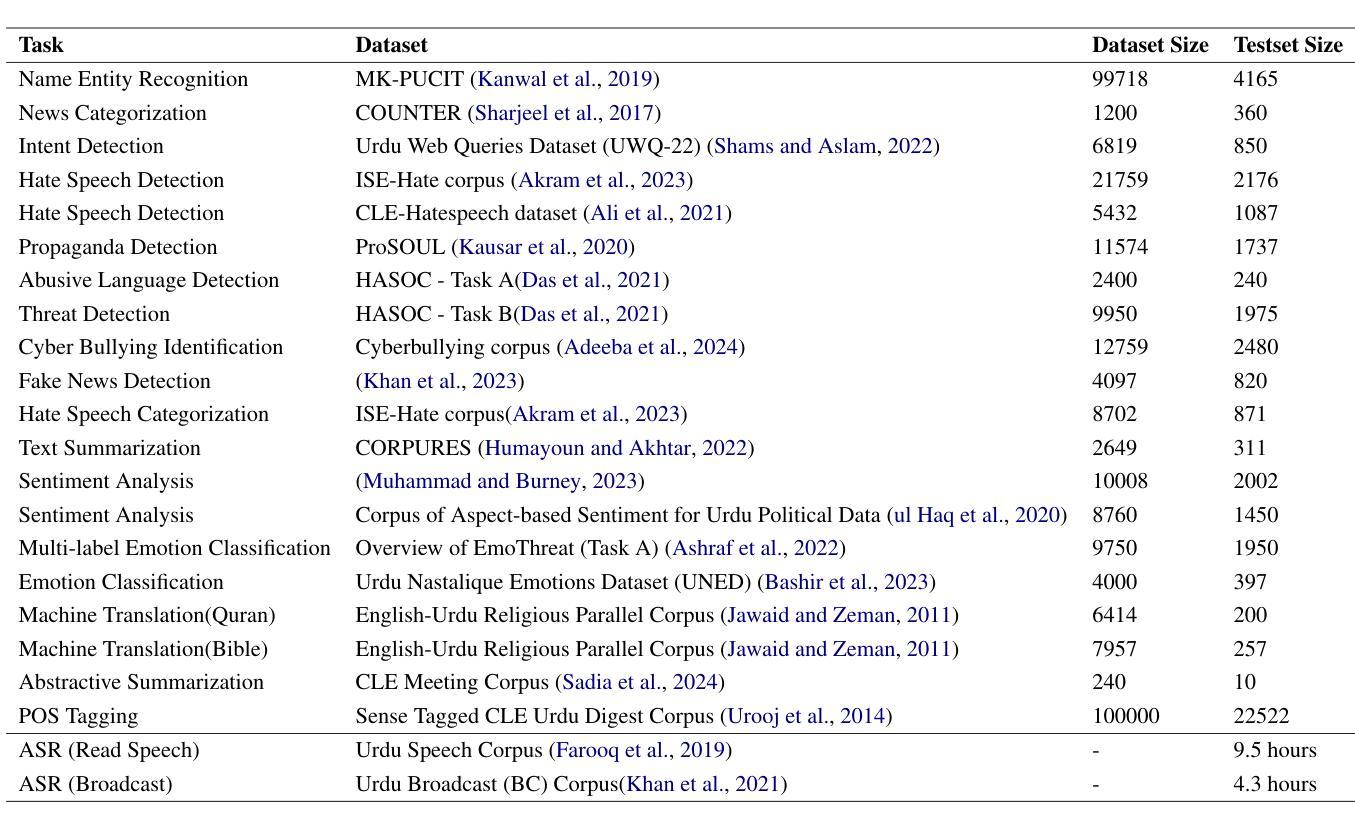
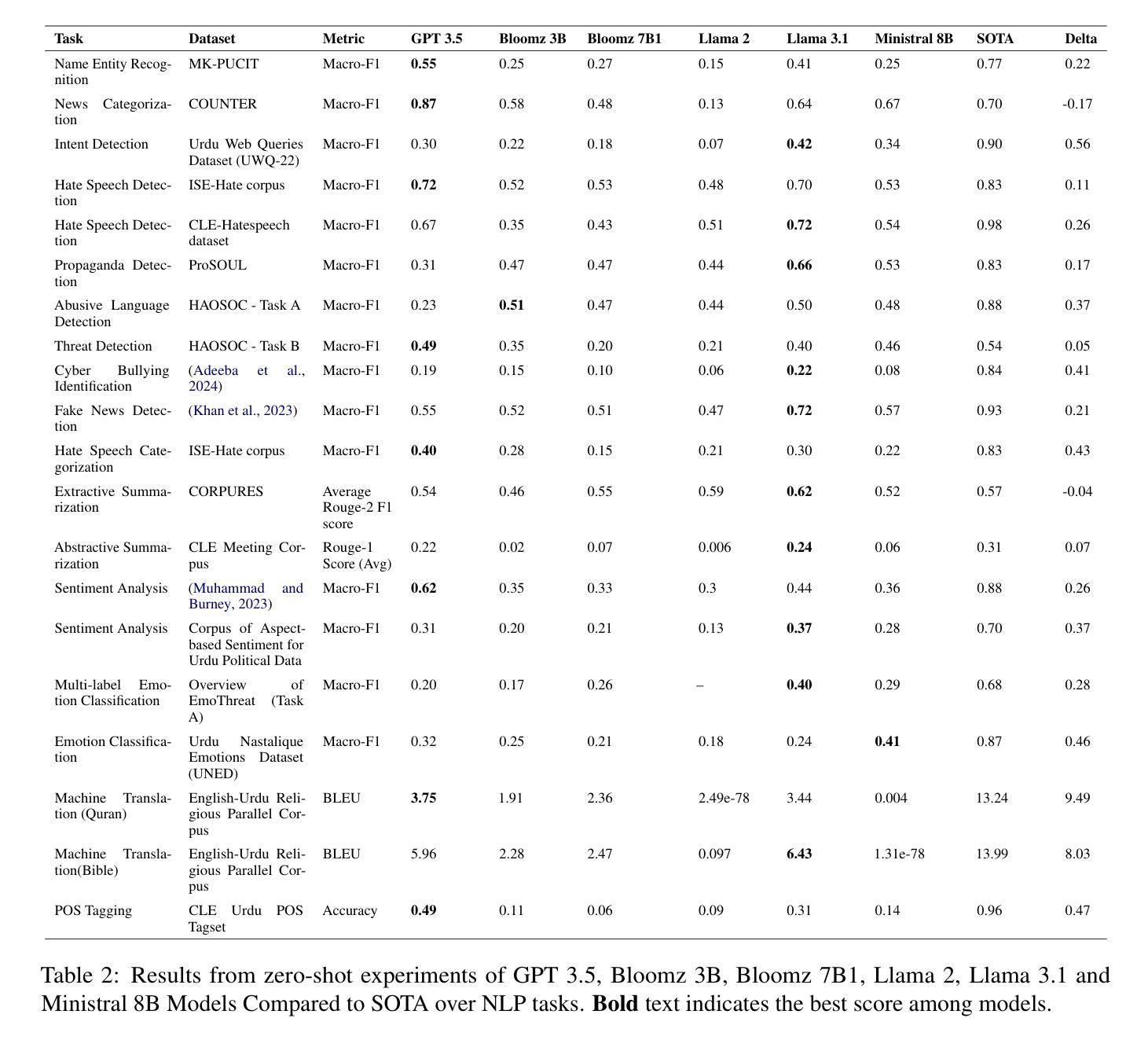
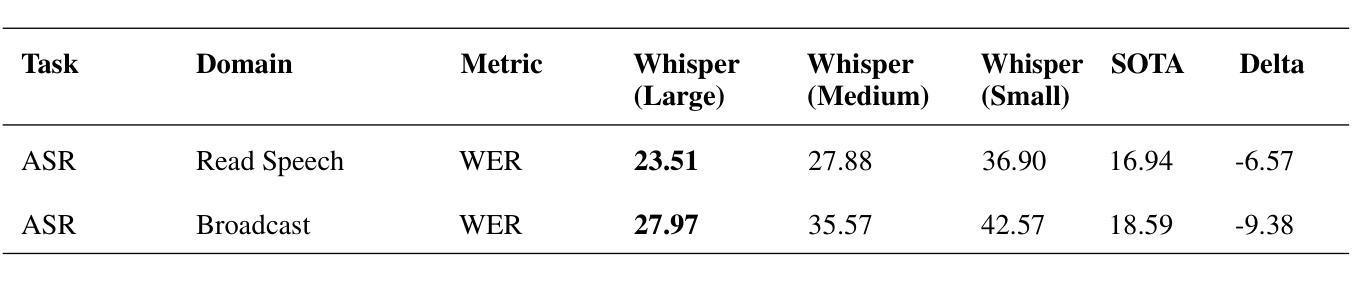
Large Language Models (LLMs) pre-trained on multilingual data have revolutionized natural language processing research, by transitioning from languages and task specific model pipelines to a single model adapted on a variety of tasks. However majority of existing multilingual NLP benchmarks for LLMs provide evaluation data in only few languages with little linguistic diversity. In addition these benchmarks lack quality assessment against the respective state-of the art models. This study presents an in-depth examination of 7 prominent LLMs: GPT-3.5-turbo, Llama 2-7B-Chat, Llama 3.1-8B, Bloomz 3B, Bloomz 7B1, Ministral-8B and Whisper (Large, medium and small variant) across 17 tasks using 22 datasets, 13.8 hours of speech, in a zero-shot setting, and their performance against state-of-the-art (SOTA) models, has been compared and analyzed. Our experiments show that SOTA models currently outperform encoder-decoder models in majority of Urdu NLP tasks under zero-shot settings. However, comparing Llama 3.1-8B over prior version Llama 2-7B-Chat, we can deduce that with improved language coverage, LLMs can surpass these SOTA models. Our results emphasize that models with fewer parameters but richer language-specific data, like Llama 3.1-8B, often outperform larger models with lower language diversity, such as GPT-3.5, in several tasks.
大型语言模型(LLM)通过在多种语言数据上进行预训练,实现了从特定语言和任务模型管道到适应多种任务的单一模型的转变,从而彻底改变了自然语言处理研究。然而,现有的大多数针对LLM的多语言NLP基准测试只提供几种语言的评估数据,语言多样性较低。此外,这些基准测试缺乏针对相应最新模型的质量评估。本研究对7种突出的LLM进行了深入研究:GPT-3.5-turbo、Llama 2-7B-Chat、Llama 3.1-8B、Bloomz 3B、Bloomz 7B1、Ministral-8B和Whisper(大、中、小型变体)。我们在22个数据集、13.8小时语音的17个任务中,进行了零样本设置下的实验,比较了它们与最新模型的表现。实验表明,在零样本设置下的大多数乌尔都语NLP任务中,最新模型目前的表现优于编码器-解码器模型。然而,通过比较Llama 3.1-8B与之前的版本Llama 2-7B-Chat,我们可以得出结论,随着语言覆盖率的提高,LLM可以超越这些最新模型。我们的结果强调,具有较少参数但语言特定数据更丰富的模型,如Llama 3.1-8B,往往在许多任务中表现优于具有较低语言多样性但规模更大的模型,如GPT-3.5。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了7种主流的大型语言模型(LLMs)在17项任务中的性能表现,涉及多语言数据集和零样本设置。实验表明,在大多数乌尔都语自然语言处理任务中,当前的最佳模型(SOTA)在零样本设置下表现出优于编码器-解码器模型的效果。同时,改进语言覆盖率的LLM(如Llama 3.1-8B相比其前身Llama 2-7B-Chat)在部分任务上表现优异,甚至超越SOTA模型。研究还发现,在某些任务中,拥有较少参数但语言特定数据更丰富的模型(如Llama 3.1-8B)往往优于拥有更多参数但语言多样性较低的模型(如GPT-3.5)。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在多语言NLP任务中的表现受到关注,但现有基准测试的语言多样性和质量评估存在不足。
- 在大多数乌尔都语NLP任务中,当前最佳模型(SOTA)在零样本设置下优于编码器-解码器模型。
- 改进语言覆盖率的LLM(如Llama 3.1-8B)在某些任务上表现优异,甚至超越SOTA模型。
- 拥有较少参数但语言特定数据丰富的模型在某些任务中表现更佳。
- LLMs的评估需要在多种任务和多种语言背景下进行,以全面评估其性能。
- 现有LLMs在语言覆盖率和任务适应性方面仍有改进空间。
点此查看论文截图

CPT: Competence-progressive Training Strategy for Few-shot Node Classification
Authors:Qilong Yan, Yufeng Zhang, Jinghao Zhang, Jingpu Duan, Jian Yin
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have made significant advancements in node classification, but their success relies on sufficient labeled nodes per class in the training data. Real-world graph data often exhibits a long-tail distribution with sparse labels, emphasizing the importance of GNNs’ ability in few-shot node classification, which entails categorizing nodes with limited data. Traditional episodic meta-learning approaches have shown promise in this domain, but they face an inherent limitation: it might lead the model to converge to suboptimal solutions because of random and uniform task assignment, ignoring task difficulty levels. This could lead the meta-learner to face complex tasks too soon, hindering proper learning. Ideally, the meta-learner should start with simple concepts and advance to more complex ones, like human learning. So, we introduce CPT, a novel two-stage curriculum learning method that aligns task difficulty with the meta-learner’s progressive competence, enhancing overall performance. Specifically, in CPT’s initial stage, the focus is on simpler tasks, fostering foundational skills for engaging with complex tasks later. Importantly, the second stage dynamically adjusts task difficulty based on the meta-learner’s growing competence, aiming for optimal knowledge acquisition. Extensive experiments on popular node classification datasets demonstrate significant improvements of our strategy over existing methods.
图神经网络(GNNs)在节点分类方面取得了重大进展,但其成功依赖于训练数据中每类的足够标签节点。现实世界的图数据经常表现出标签稀疏的长尾分布,这强调了图神经网络在少量节点分类中的能力的重要性,这涉及到在有限数据下对节点进行分类。传统的阶段性元学习方法在此领域显示出潜力,但它们面临一个内在的限制:由于随机和均匀的任务分配,可能会导致模型收敛到次优解决方案。这可能导致元学习者过早地面临复杂任务,阻碍适当的学习。理想情况下,元学习者应该从简单的概念开始,逐步学习更复杂的概念,就像人类学习一样。因此,我们引入了CPT,这是一种新型的两阶段课程学习方法,它根据元学习者的进步能力来调整任务难度,从而提高整体性能。具体来说,在CPT的初始阶段,重点是更简单的任务,为日后处理复杂任务培养基础技能。重要的是,第二阶段根据元学习者不断增长的能力动态调整任务难度,以实现最佳知识获取。在流行的节点分类数据集上进行的广泛实验证明,我们的策略在现有方法的基础上取得了显著改进。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF v2. arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2206.11972 by other authors
Summary
图神经网络(GNNs)在节点分类方面取得了显著进展,但其成功依赖于训练数据中每个类别的足够标签节点。现实世界的图数据通常呈现标签稀疏的长尾分布,这强调了在少量数据节点分类中GNNs能力的重要性。传统的情景性元学习方法在该领域显示出了一定的前景,但它们面临一个固有的局限性:由于随机和统一的分配任务,可能会导致模型收敛到次优解。这可能会使元学习者过早地面临复杂任务,阻碍适当的学习。因此,我们引入CPT,这是一种新颖的两阶段课程学习方法,将任务难度与元学习者的进步能力相匹配,从而提高整体性能。在CPT的初始阶段,重点放在较简单的任务上,为日后处理复杂任务培养基础技能。重要的是,第二阶段根据元学习者的不断增长的能力动态调整任务难度,以实现最佳知识获取。在流行的节点分类数据集上进行的大量实验表明,我们的策略在现有方法上取得了显著改进。
Key Takeaways
- GNNs在节点分类方面表现出色,但依赖充足的标签数据。
- 现实世界图数据通常具有标签稀疏的特点,强调少样本节点分类的重要性。
- 传统元学习方法可能因任务分配的随机性和统一性而收敛到次优解。
- 元学习者应先从简单任务开始学习,再逐渐面对复杂任务。
- 引入CPT,一种两阶段课程学习方法,根据元学习者的进步能力调整任务难度。
- CPT初始阶段强调基础技能的培养。
点此查看论文截图