⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-04 更新
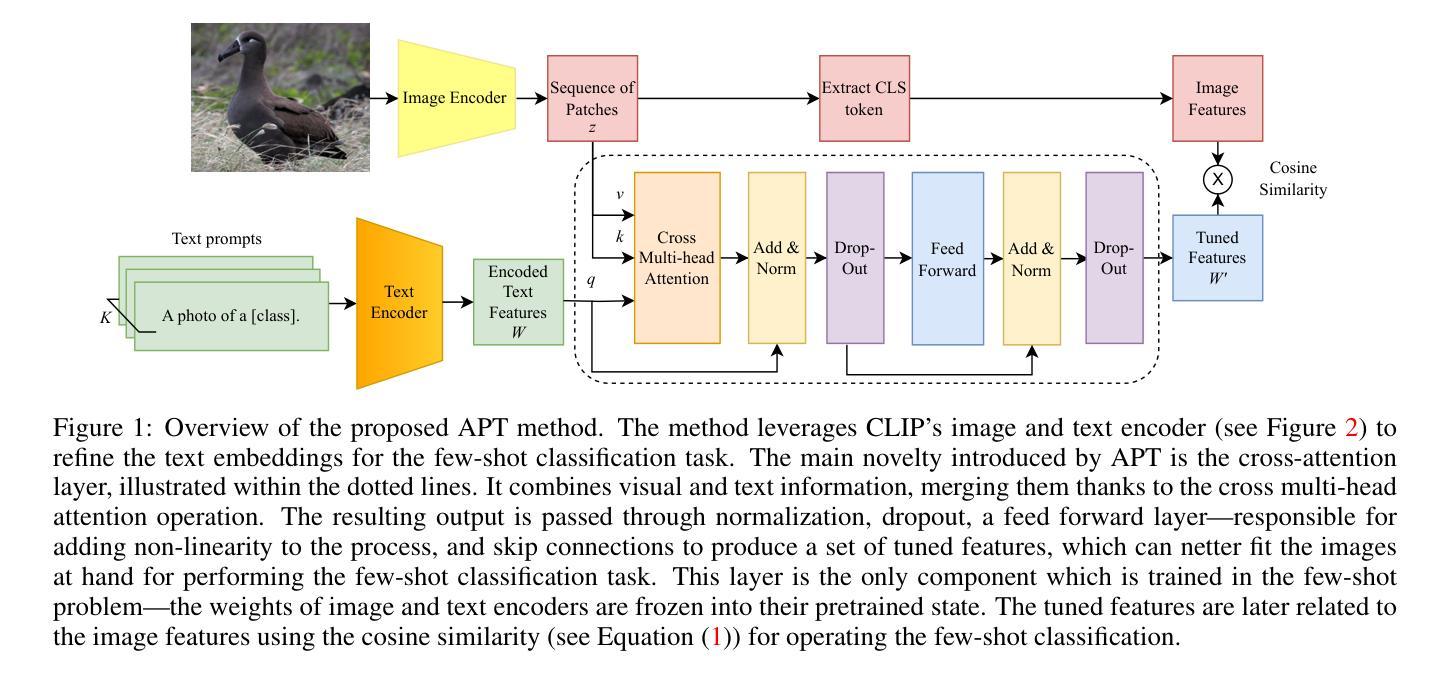
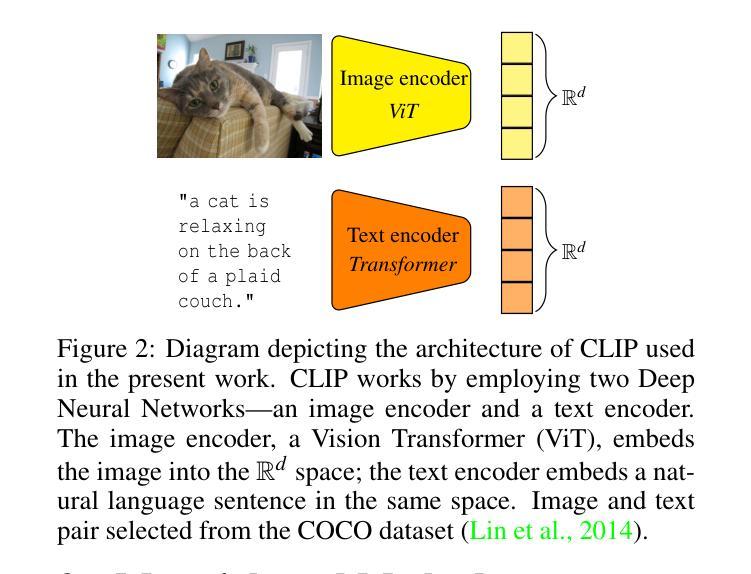
Adaptive Prompt Tuning: Vision Guided Prompt Tuning with Cross-Attention for Fine-Grained Few-Shot Learning
Authors:Eric Brouwer, Jan Erik van Woerden, Gertjan Burghouts, Matias Valdenegro-Toro, Marco Zullich
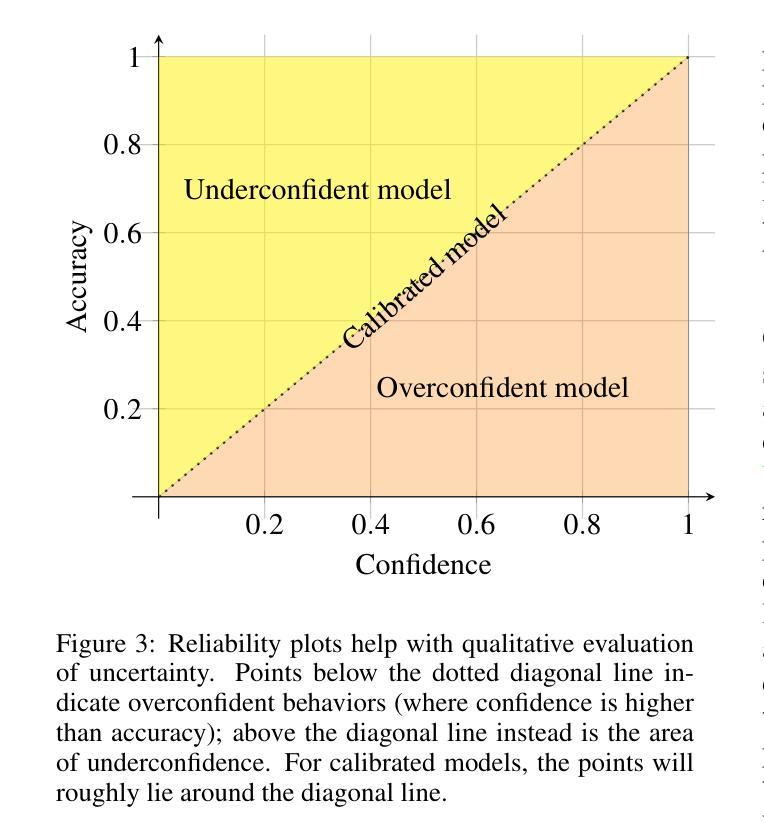
Few-shot, fine-grained classification in computer vision poses significant challenges due to the need to differentiate subtle class distinctions with limited data. This paper presents a novel method that enhances the Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training (CLIP) model through adaptive prompt tuning, guided by real-time visual inputs. Unlike existing techniques such as Context Optimization (CoOp) and Visual Prompt Tuning (VPT), which are constrained by static prompts or visual token reliance, the proposed approach leverages a cross-attention mechanism to dynamically refine text prompts for the image at hand. This enables an image-specific alignment of textual features with image patches extracted from the Vision Transformer, making the model more effective for datasets with high intra-class variance and low inter-class differences. The method is evaluated on several datasets, including CUBirds, Oxford Flowers, and FGVC Aircraft, showing significant performance gains over static prompt tuning approaches. To ensure these performance gains translate into trustworthy predictions, we integrate Monte-Carlo Dropout in our approach to improve the reliability of the model predictions and uncertainty estimates. This integration provides valuable insights into the model’s predictive confidence, helping to identify when predictions can be trusted and when additional verification is necessary. This dynamic approach offers a robust solution, advancing the state-of-the-art for few-shot fine-grained classification.
计算机视觉中的小样本精细分类面临着重大挑战,因为需要在有限的数据下区分微妙的类别差异。本文针对这一问题提出了一种通过自适应提示调整增强对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)模型的新方法,该方法由实时视觉输入引导。与现有的上下文优化(CoOp)和视觉提示调整(VPT)等技术不同,这些方法受到静态提示或视觉标记依赖的限制,本文提出的方法利用跨注意力机制动态完善针对当前图像的文本提示。这能够实现基于图像的文本特征对齐,与从视觉转换器中提取的图像块相匹配,使得该模型对于具有高强度类内差异和较低类间差异的数据集更为有效。该方法在多个数据集上进行了评估,包括CUBirds、牛津花卉和FGVC飞机,相对于静态提示调整方法,显示出显著的性能提升。为确保这些性能提升转化为可靠的预测,我们将蒙特卡洛Dropout集成到我们的方法中,以提高模型预测的可靠性和不确定性估计。这一集成提供了关于模型预测置信度的宝贵见解,有助于确定何时可以信任预测结果以及何时需要进行额外验证。这一动态方法为精细分类的小样本问题提供了稳健的解决方案,推动了最新技术的进展。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在有限数据下,计算机视觉中的小样本精细分类面临挑战。本文提出了一种通过自适应提示调整增强Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training(CLIP)模型的新方法,该方法由实时视觉输入引导。与现有的Context Optimization(CoOp)和Visual Prompt Tuning(VPT)等技术不同,所提出的方法利用跨注意力机制动态调整针对当前图像的文本提示。这使文本特征能够与从视觉转换器中提取的图像块进行图像特定对齐,对于具有高的类内变化和低的类间差异的数据集更有效。该方法在多个数据集上进行了评估,包括CUBirds、Oxford Flowers和FGVC Aircraft等,与静态提示调整方法相比取得了显著的性能提升。为确保性能提升转化为可靠的预测,我们整合了蒙特卡洛Dropout,以提高模型预测和不确定性估计的可靠性。这一动态方法提供了稳健的解决方案,推动了小样本精细分类的最新技术。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文提出了一种新的方法,通过自适应提示调整增强CLIP模型,以提高小样本精细分类的性能。
- 与现有的CoOp和VPT技术不同,该方法利用跨注意力机制动态调整文本提示,以更好地匹配当前图像的特征。
- 该方法能够在具有高的类内变化和低的类间差异的数据集上实现显著的性能提升。
- 在多个数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法优于静态提示调整方法。
- 为了确保模型预测的可靠性,整合了蒙特卡洛Dropout,提高模型预测和不确定性估计的可靠性。
- 该方法的动态性质使它对于处理复杂的视觉任务特别有效,尤其是在数据有限的情况下。
点此查看论文截图

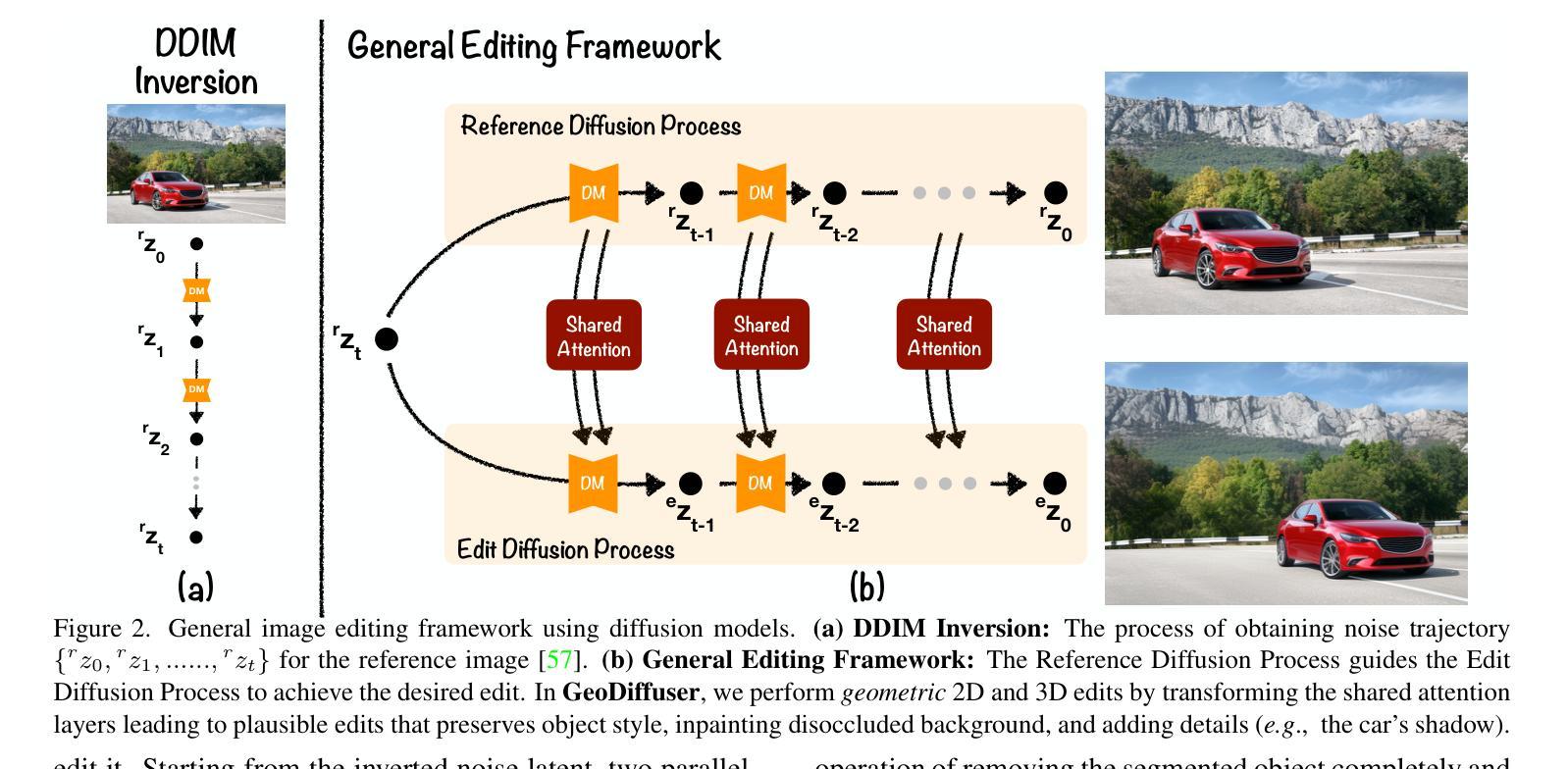
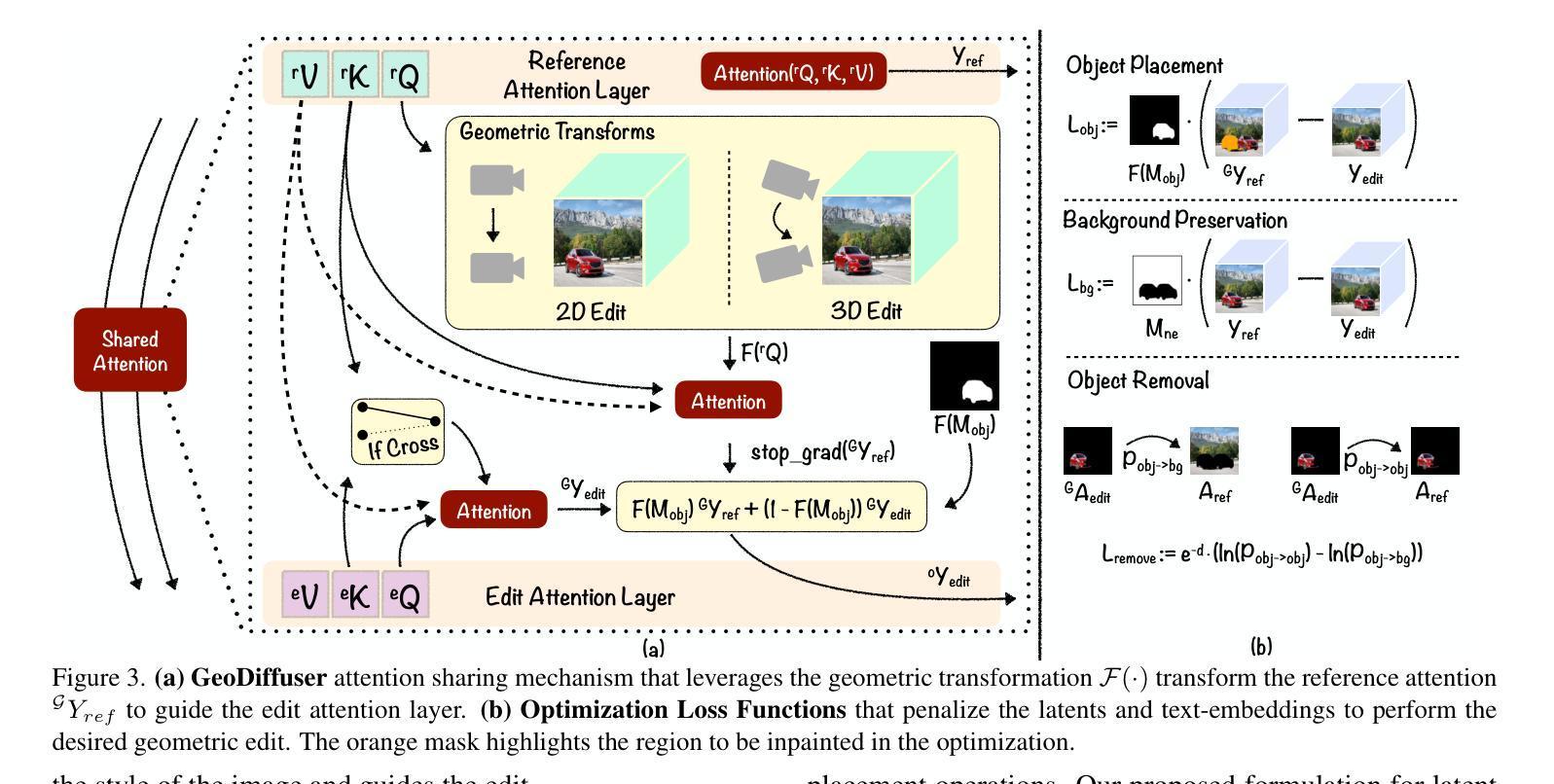
GeoDiffuser: Geometry-Based Image Editing with Diffusion Models
Authors:Rahul Sajnani, Jeroen Vanbaar, Jie Min, Kapil Katyal, Srinath Sridhar
The success of image generative models has enabled us to build methods that can edit images based on text or other user input. However, these methods are bespoke, imprecise, require additional information, or are limited to only 2D image edits. We present GeoDiffuser, a zero-shot optimization-based method that unifies common 2D and 3D image-based object editing capabilities into a single method. Our key insight is to view image editing operations as geometric transformations. We show that these transformations can be directly incorporated into the attention layers in diffusion models to implicitly perform editing operations. Our training-free optimization method uses an objective function that seeks to preserve object style but generate plausible images, for instance with accurate lighting and shadows. It also inpaints disoccluded parts of the image where the object was originally located. Given a natural image and user input, we segment the foreground object using SAM and estimate a corresponding transform which is used by our optimization approach for editing. GeoDiffuser can perform common 2D and 3D edits like object translation, 3D rotation, and removal. We present quantitative results, including a perceptual study, that shows how our approach is better than existing methods. Visit https://ivl.cs.brown.edu/research/geodiffuser.html for more information.
图像生成模型的巨大成功让我们能够构建可以根据文本或其他用户输入编辑图像的方法。然而,这些方法都是专用的,不够精确,需要额外的信息,或者仅限于2D图像编辑。我们提出了GeoDiffuser,这是一种基于零样本优化的方法,它将常见的2D和3D图像基于对象的编辑功能集成到一种方法中。我们的关键见解是将图像编辑操作视为几何变换。我们证明这些变换可以直接融入到扩散模型的注意力层中,以隐式执行编辑操作。我们的无训练优化方法使用目标函数,旨在保持对象风格但生成合理的图像,例如具有准确的照明和阴影。它还会对原始对象所在的图像中被遮挡的部分进行补全。给定自然图像和用户输入,我们使用SAM对前景对象进行分割,并估算相应的变换,然后我们的优化方法使用该变换进行编辑。GeoDiffuser可以执行常见的2D和3D编辑,如对象平移、3D旋转和移除。我们提供了定量结果,包括一项感知研究,展示我们的方法比现有方法更好。有关更多信息,请访问https://ivl.cs.brown.edu/research/geodiffuser.html。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to WACV 2025, Tucson, Arizona, USA. For project page, see https://ivl.cs.brown.edu/research/geodiffuser.html
Summary
图像生成模型的成功使我们能够建立基于文本或其他用户输入编辑图像的方法。然而,这些方法往往是专用的、不精确的,需要额外的信息,或仅限于2D图像编辑。我们推出GeoDiffuser,一种基于零样本优化的方法,将常见的2D和3D图像对象编辑功能统一到一种方法中。我们的关键见解是将图像编辑操作视为几何变换。我们表明,这些变换可以直接融入扩散模型的注意力层,以隐式执行编辑操作。我们的无训练优化方法使用目标函数,旨在保持对象风格但生成可信图像,例如具有准确光照和阴影。它还能修复图像中对象原本所在位置的遮挡部分。给定自然图像和用户输入,我们使用SAM分割前景对象,估计相应的变换,由我们的优化方法进行编辑。GeoDiffuser可以进行常见的2D和3D编辑,如对象平移、3D旋转和移除。
Key Takeaways
- 图像生成模型的成功推动了基于文本或用户输入的图像编辑方法的发展。
- 现有图像编辑方法存在局限性,如专用性、不精确性、需要额外信息等。
- GeoDiffuser是一种统一2D和3D图像编辑的方法,将图像编辑操作视为几何变换。
- GeoDiffuser隐式执行编辑操作,通过直接融入扩散模型的注意力层。
- GeoDiffuser的无训练优化方法旨在保持对象风格并生成具有准确光照和阴影的可信图像。
- GeoDiffuser能修复图像中对象原本所在位置的遮挡部分。
点此查看论文截图