⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-04 更新
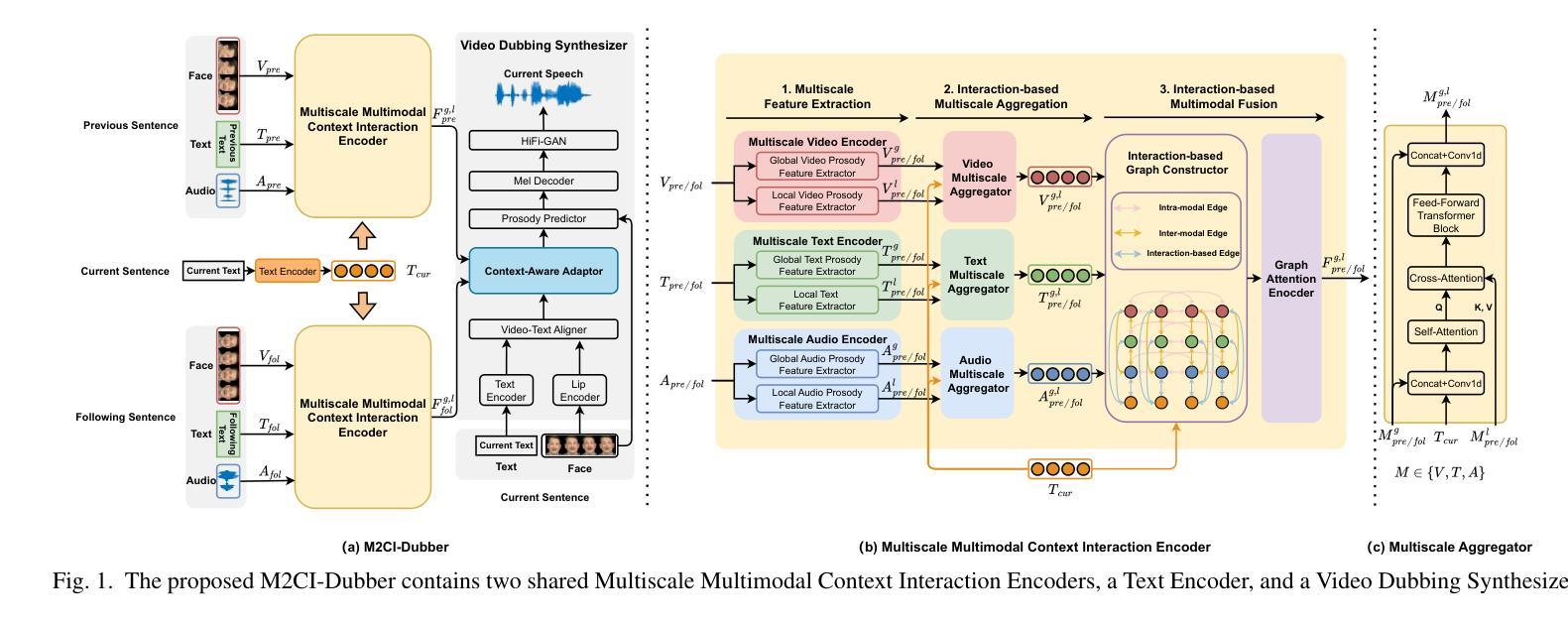
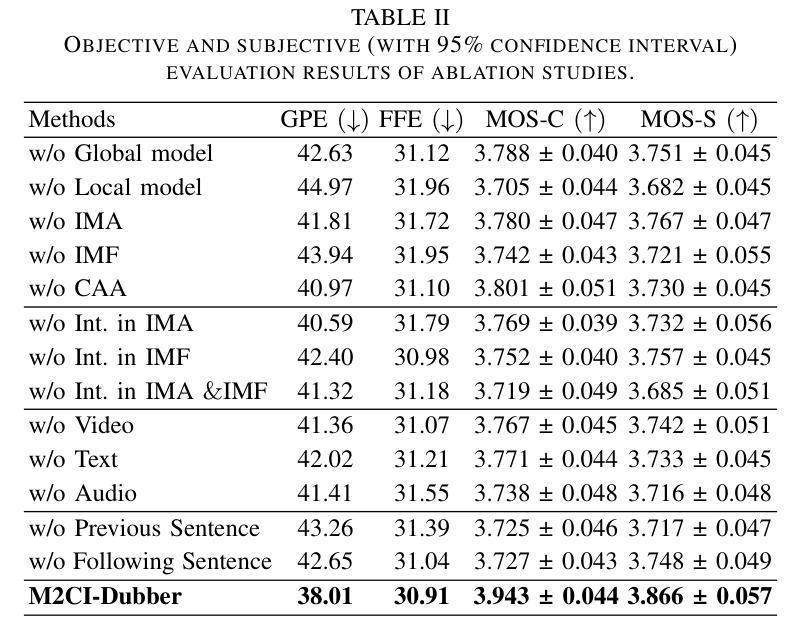
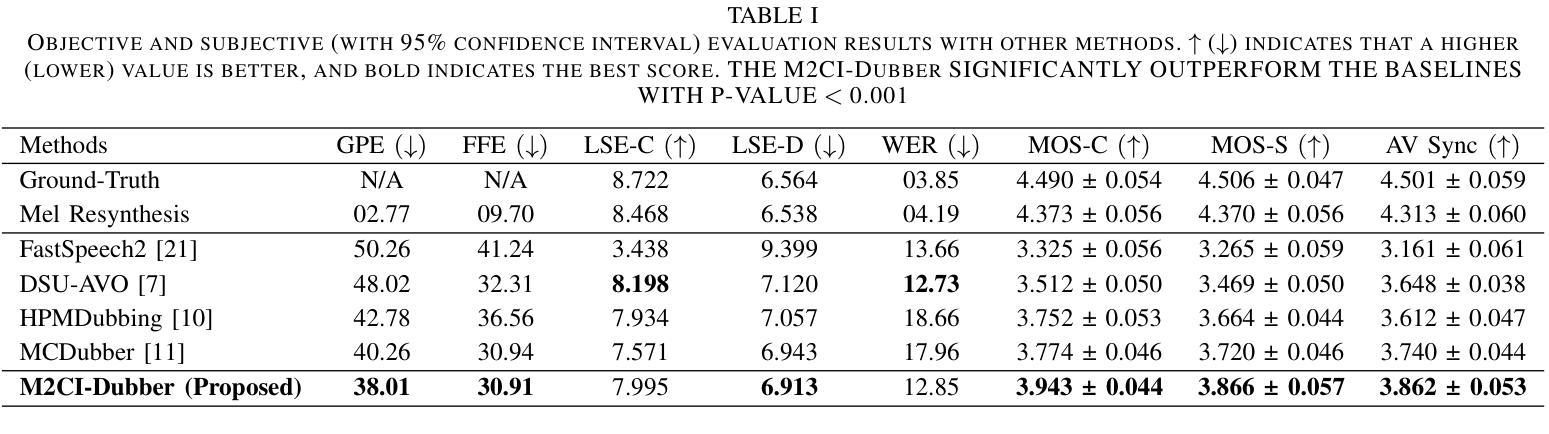
Towards Expressive Video Dubbing with Multiscale Multimodal Context Interaction
Authors:Yuan Zhao, Rui Liu, Gaoxiang Cong
Automatic Video Dubbing (AVD) generates speech aligned with lip motion and facial emotion from scripts. Recent research focuses on modeling multimodal context to enhance prosody expressiveness but overlooks two key issues: 1) Multiscale prosody expression attributes in the context influence the current sentence’s prosody. 2) Prosody cues in context interact with the current sentence, impacting the final prosody expressiveness. To tackle these challenges, we propose M2CI-Dubber, a Multiscale Multimodal Context Interaction scheme for AVD. This scheme includes two shared M2CI encoders to model the multiscale multimodal context and facilitate its deep interaction with the current sentence. By extracting global and local features for each modality in the context, utilizing attention-based mechanisms for aggregation and interaction, and employing an interaction-based graph attention network for fusion, the proposed approach enhances the prosody expressiveness of synthesized speech for the current sentence. Experiments on the Chem dataset show our model outperforms baselines in dubbing expressiveness. The code and demos are available at \textcolor[rgb]{0.93,0.0,0.47}{https://github.com/AI-S2-Lab/M2CI-Dubber}.
自动视频配音(AVD)根据脚本生成与唇部动作和面部情绪相匹配的语音。最近的研究集中在建立多模态上下文以提高韵律表达性,但忽略了两个关键问题:1)上下文中的多尺度韵律表达属性会影响当前句子的韵律。2)上下文中的韵律线索与当前句子相互作用,影响最终的韵律表达性。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了M2CI-Dubber,这是一种用于AVD的多尺度多模态上下文交互方案。该方案包括两个共享的M2CI编码器,用于建立多尺度多模态上下文,并促进其与当前句子的深度交互。通过提取上下文中每种模态的全局和局部特征,利用基于注意力的机制进行聚合和交互,并采用基于交互的图注意力网络进行融合,所提出的方法提高了当前句子合成语音的韵律表达性。在Chem数据集上的实验表明,我们的模型在配音表达性方面优于基准模型。代码和演示可在https://github.com/AI-S2-Lab/M2CI-Dubber上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICASSP 2025
Summary
视频自动配音(AVD)技术通过脚本生成与唇动和面部表情相匹配的语音。最近的研究主要集中在建立多模态语境模型以提高语调的表达能力,但忽视了两个关键问题:1)多尺度语境表达属性对当前句子语调的影响;2)语境中的语调线索与当前句子的互动。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了M2CI-Dubber方案,这是一种多尺度多模态语境交互的AVD方案。该方案包括两个共享M2CI编码器,以建立多尺度多模态语境模型并促进其与当前句子的深度交互。通过提取上下文中每个模态的全局和局部特征,利用基于注意力的机制进行聚合和交互,并使用基于交互的图注意力网络进行融合,提高了合成语音的语调表达能力。在Chem数据集上的实验表明,我们的模型在配音表现力方面优于基准模型。
Key Takeaways
- AVD技术能生成与视频内容匹配的语音。
- 最近研究集中在建立多模态语境模型以提升语调表达力。
- 现有研究忽视了多尺度语境表达属性及语境中的语调线索与当前句子的互动。
- 提出M2CI-Dubber方案,包含多尺度多模态语境交互模型。
- M2CI编码器用于建模多尺度多模态语境并与当前句子进行深度交互。
- 通过提取全局和局部特征、利用注意力机制及图注意力网络融合信息来提高语调表达力。
点此查看论文截图

Zero-resource Speech Translation and Recognition with LLMs
Authors:Karel Mundnich, Xing Niu, Prashant Mathur, Srikanth Ronanki, Brady Houston, Veera Raghavendra Elluru, Nilaksh Das, Zejiang Hou, Goeric Huybrechts, Anshu Bhatia, Daniel Garcia-Romero, Kyu J. Han, Katrin Kirchhoff
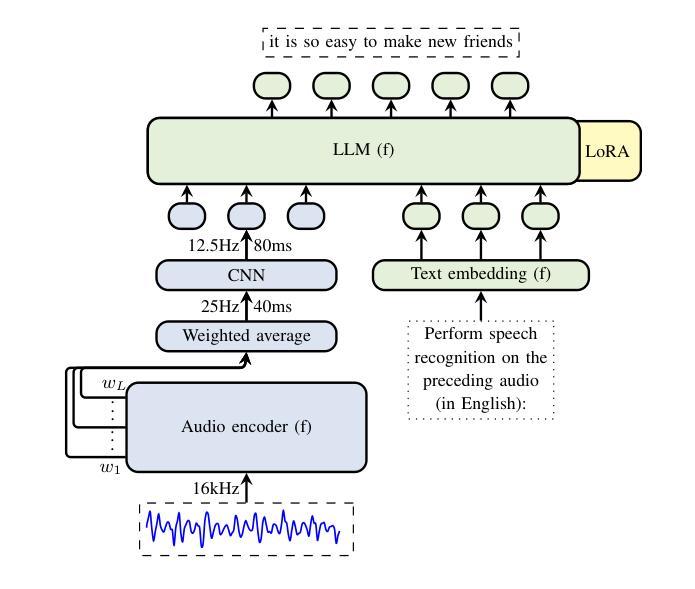
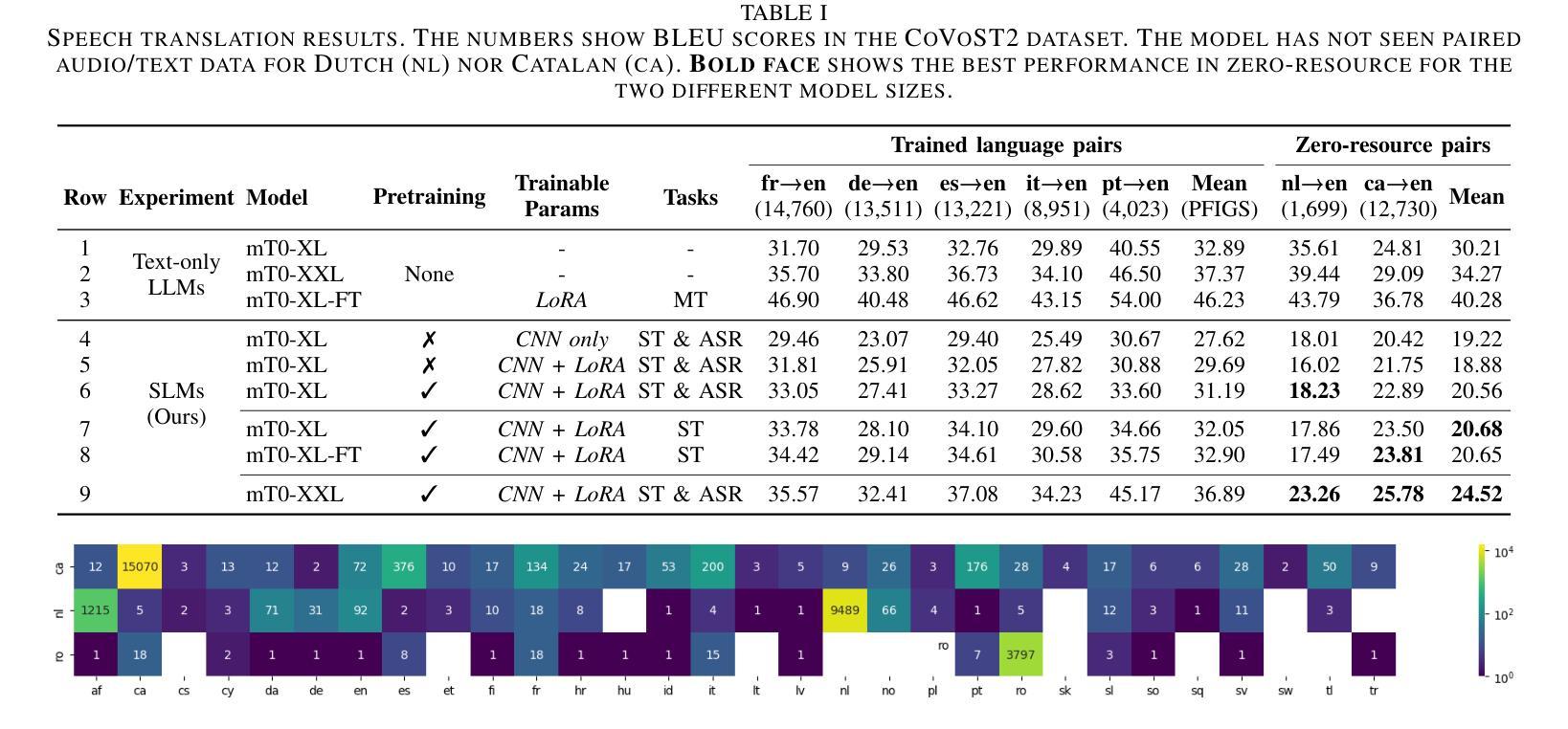
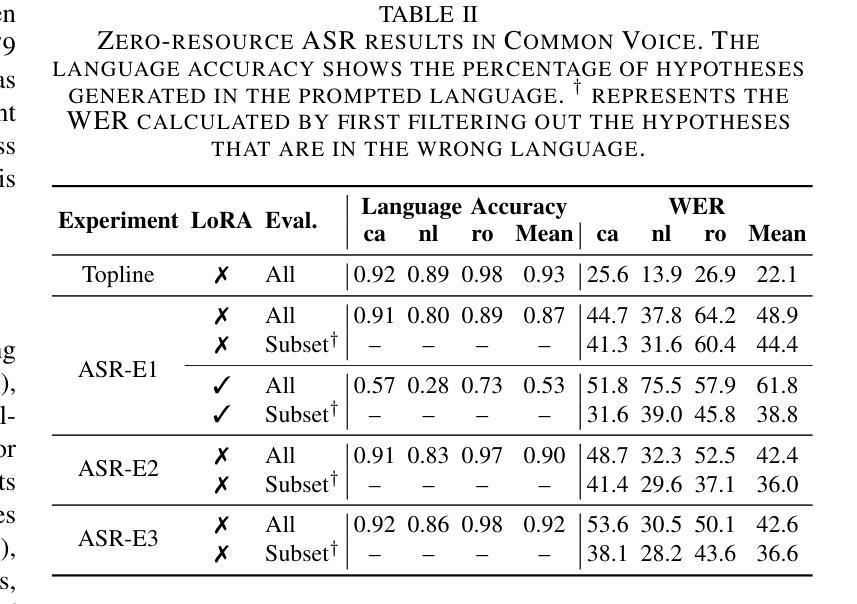
Despite recent advancements in speech processing, zero-resource speech translation (ST) and automatic speech recognition (ASR) remain challenging problems. In this work, we propose to leverage a multilingual Large Language Model (LLM) to perform ST and ASR in languages for which the model has never seen paired audio-text data. We achieve this by using a pre-trained multilingual speech encoder, a multilingual LLM, and a lightweight adaptation module that maps the audio representations to the token embedding space of the LLM. We perform several experiments both in ST and ASR to understand how to best train the model and what data has the most impact on performance in previously unseen languages. In ST, our best model is capable to achieve BLEU scores over 23 in CoVoST2 for two previously unseen languages, while in ASR, we achieve WERs of up to 28.2%. We finally show that the performance of our system is bounded by the ability of the LLM to output text in the desired language.
尽管最近语音处理领域有所进展,但零资源语音翻译(ST)和自动语音识别(ASR)仍是具有挑战性的问题。在这项工作中,我们提出利用多语言大型语言模型(LLM)来执行ST和ASR,针对模型从未接触过的配对语音文本数据的语言。我们通过使用预训练的多语言语音编码器、多语言LLM和一个轻量级适配模块(该模块将语音表示映射到LLM的令牌嵌入空间)来实现这一点。我们在ST和ASR中进行了多次实验,以了解如何最好地训练模型,以及哪些数据对以前未见过的语言的性能影响最大。在ST中,我们最好的模型能够在CoVoST2中达到超过23的BLEU分数,用于两种以前未见过的语言;而在ASR中,我们达到高达28.2%的WER。最后,我们表明,我们系统的性能受限于LLM输出所需语言文本的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICASSP 2025, 5 pages, 2 figures, 2 tables
Summary
本研究探讨了零资源语音翻译(ST)和自动语音识别(ASR)的难题,并提出利用多语言大型语言模型(LLM)在从未接触过配对音频文本数据的语言中进行ST和ASR。通过预训练的多语言语音编码器、多语言LLM和轻量级适配模块,将语音表示映射到LLM的令牌嵌入空间。在ST和ASR方面进行了多次实验,以了解如何最佳地训练模型和哪些数据对未见语言的性能影响最大。在ST方面,最佳模型在CoVoST2中的BLEU得分超过23,而在ASR方面,我们达到了高达28.2%的WER。最终结果表明,系统的性能受限于LLM输出所需语言文本的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 零资源语音翻译(ST)和自动语音识别(ASR)仍是具有挑战性的难题。
- 研究提出利用多语言大型语言模型(LLM)在未见过的语言中进行ST和ASR。
- 通过预训练的多语言语音编码器、多语言LLM和轻量级适配模块实现语音到文本的转换。
- 在ST和ASR方面进行了多次实验,以优化模型训练并了解数据对性能的影响。
- 在ST方面,最佳模型的BLEU得分在CoVoST2测试中超过23。
- 在ASR方面,达到了高达28.2%的字错误率(WER)。
点此查看论文截图

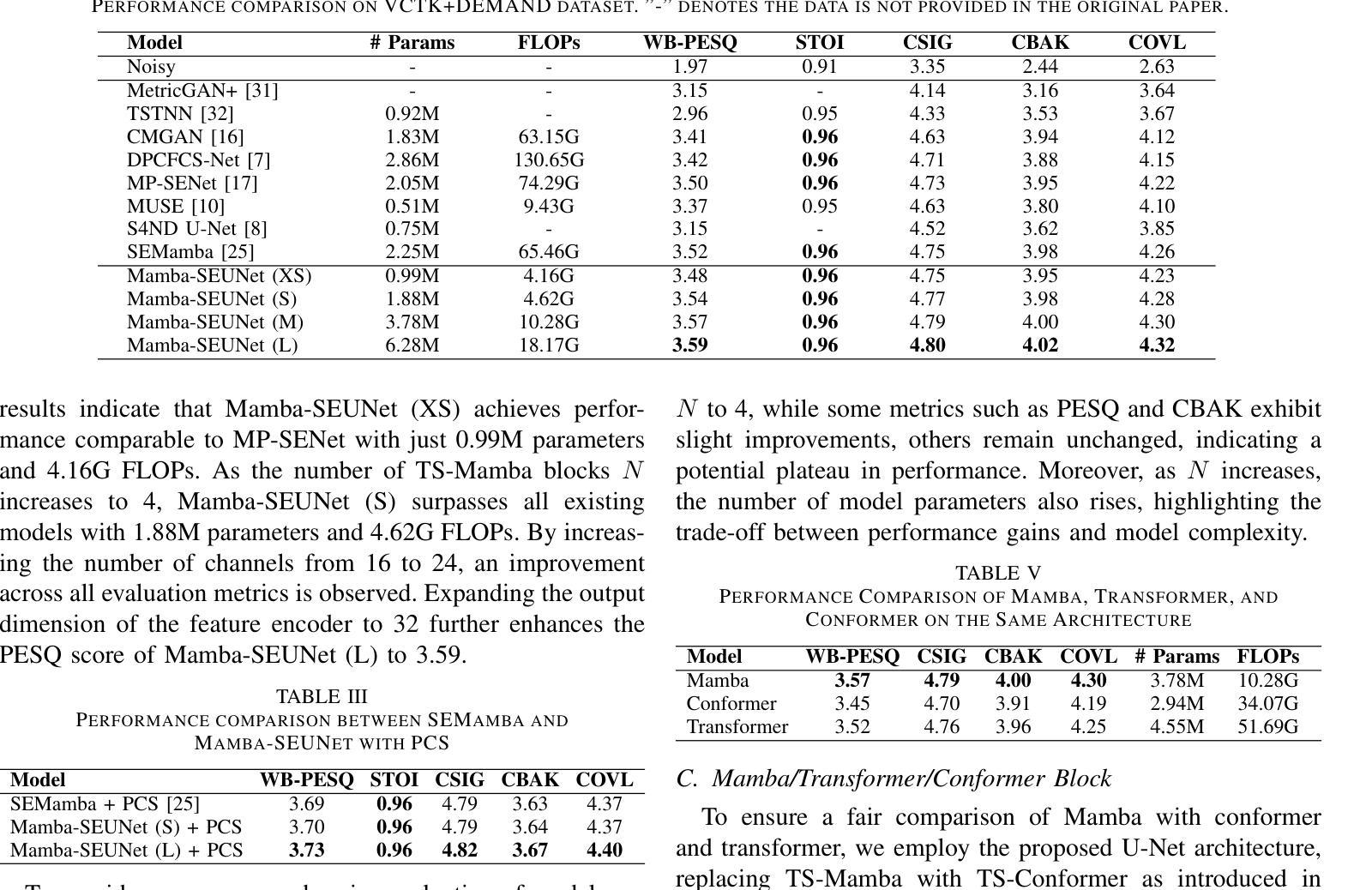
Mamba-SEUNet: Mamba UNet for Monaural Speech Enhancement
Authors:Junyu Wang, Zizhen Lin, Tianrui Wang, Meng Ge, Longbiao Wang, Jianwu Dang
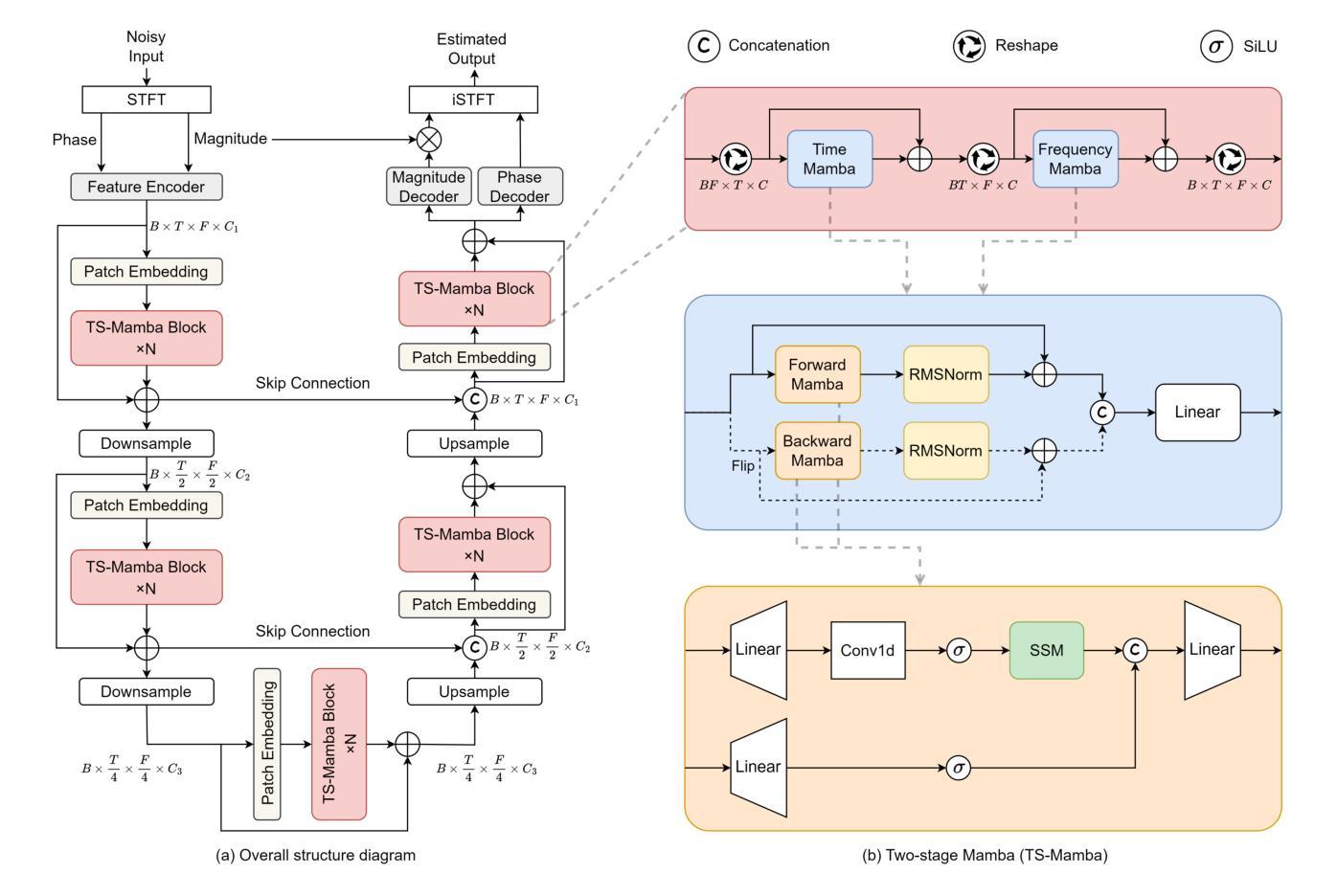
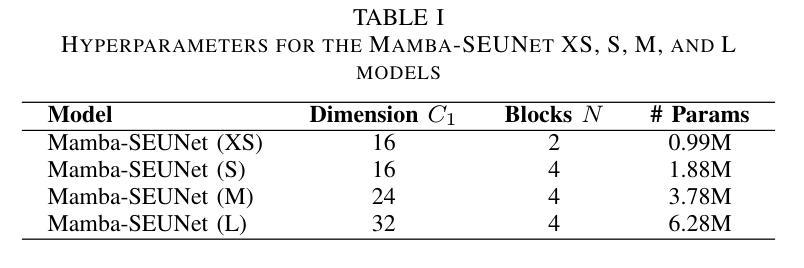
In recent speech enhancement (SE) research, transformer and its variants have emerged as the predominant methodologies. However, the quadratic complexity of the self-attention mechanism imposes certain limitations on practical deployment. Mamba, as a novel state-space model (SSM), has gained widespread application in natural language processing and computer vision due to its strong capabilities in modeling long sequences and relatively low computational complexity. In this work, we introduce Mamba-SEUNet, an innovative architecture that integrates Mamba with U-Net for SE tasks. By leveraging bidirectional Mamba to model forward and backward dependencies of speech signals at different resolutions, and incorporating skip connections to capture multi-scale information, our approach achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance. Experimental results on the VCTK+DEMAND dataset indicate that Mamba-SEUNet attains a PESQ score of 3.59, while maintaining low computational complexity. When combined with the Perceptual Contrast Stretching technique, Mamba-SEUNet further improves the PESQ score to 3.73.
在最近的语音增强(SE)研究中,Transformer及其变体已经成为主要的方法论。然而,自注意力机制的二次复杂性对实际部署施加了一定的限制。Mamba作为一种新型的状态空间模型(SSM),由于其建模长序列的强大能力和相对较低的计算复杂性,在自然语言处理和计算机视觉中得到了广泛应用。在这项工作中,我们介绍了Mamba-SEUNet,这是一种将Mamba与U-Net相结合用于SE任务的创新架构。通过利用双向Mamba来建模语音信号在不同分辨率上的前后依赖性,并加入跳过连接来捕获多尺度信息,我们的方法达到了最新(SOTA)的性能。在VCTK+DEMAND数据集上的实验结果表明,Mamba-SEUNet的PESQ得分为3.59,同时保持较低的计算复杂性。当与感知对比度拉伸技术相结合时,Mamba-SEUNet进一步将PESQ得分提高到3.73。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICASSP 2025, 5 pages, 1 figures, 5 tables
总结
本文介绍了在语音增强领域的一种新型融合架构Mamba-SEUNet。该架构结合了Mamba和U-Net的优势,通过利用双向Mamba建模语音信号的前向和后向依赖关系,并结合跳跃连接捕获多尺度信息,实现了先进的性能。在VCTK+DEMAND数据集上的实验结果表明,Mamba-SEUNet在保持较低计算复杂度的情况下取得了PESQ得分为3.59的成绩。当与感知对比度拉伸技术相结合时,Mamba-SEUNet的PESQ得分进一步提高至3.73。
要点
- 近期语音增强研究中,transformer及其变体是主要的方法论。但自注意力机制的二次复杂性对实际应用部署造成了一定限制。
- Mamba作为一种新型的状态空间模型(SSM),在自然语言处理和计算机视觉领域有广泛应用,其擅长于建模长序列且计算复杂度相对较低。
- Mamba-SEUNet是一个创新架构,结合了Mamba和U-Net的优势用于语音增强任务。
- Mamba-SEUNet利用双向Mamba建模语音信号的不同分辨率的前向和后向依赖关系,并结合跳跃连接捕获多尺度信息。
- 实验结果表明,Mamba-SEUNet在VCTK+DEMAND数据集上取得了较高的PESQ得分,显示出其优秀的性能。
- Mamba-SEUNet在保持较低计算复杂度的同时取得了先进的效果。
点此查看论文截图

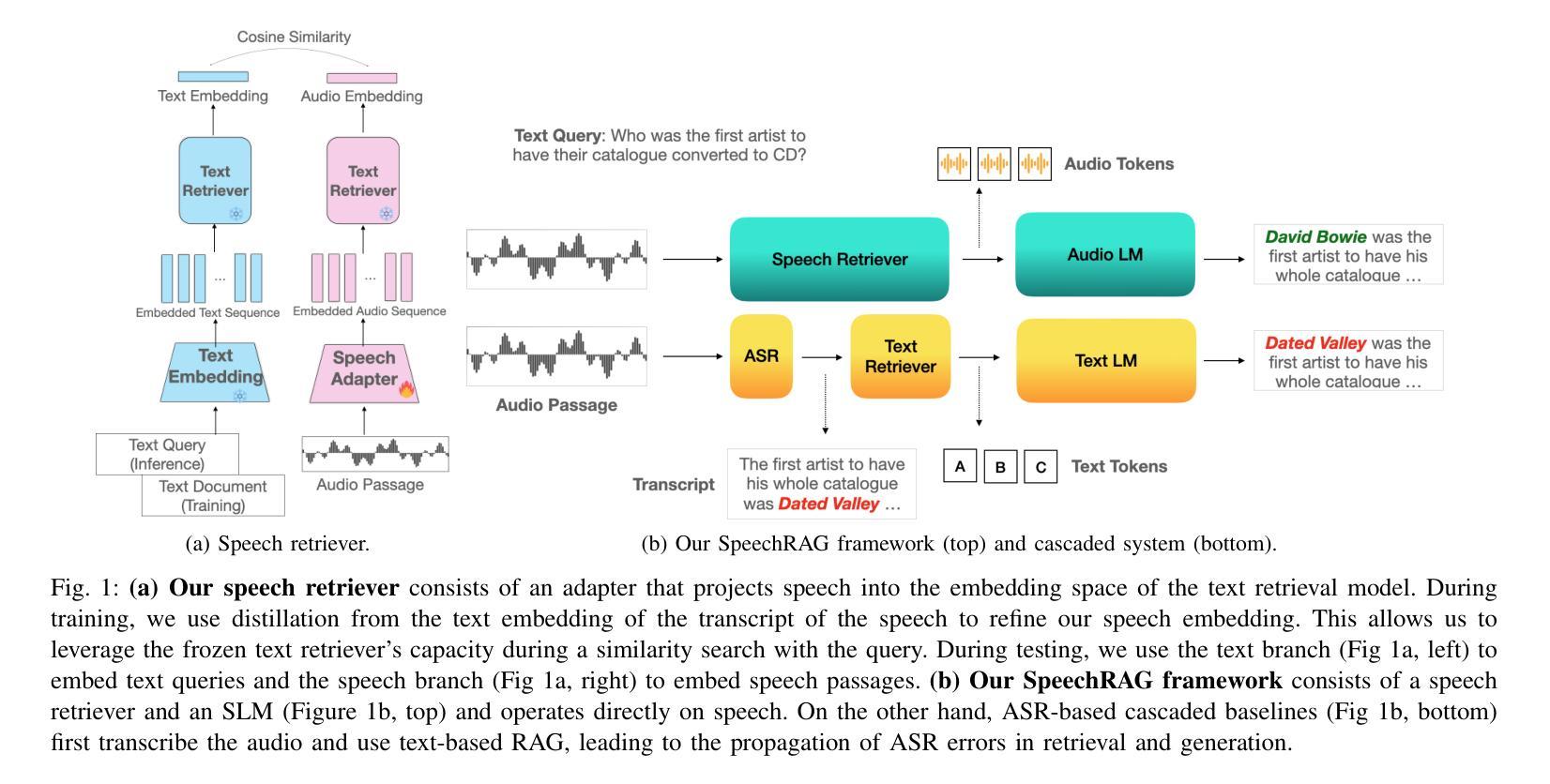
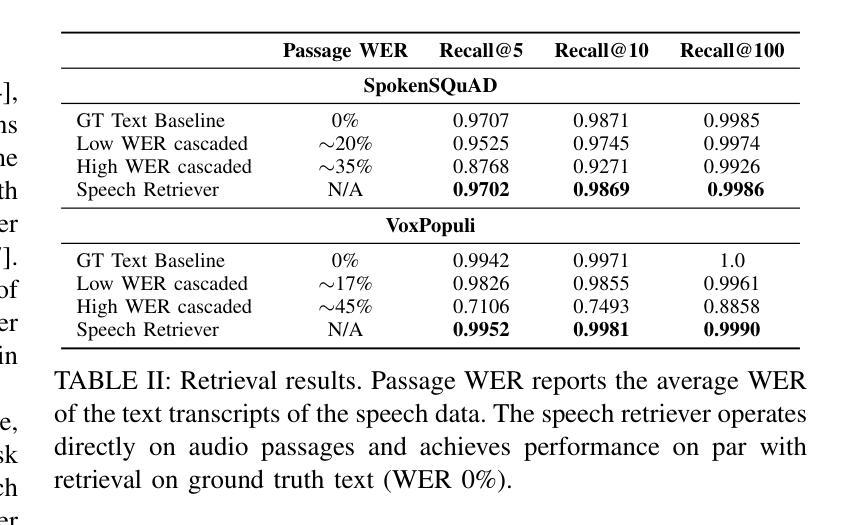
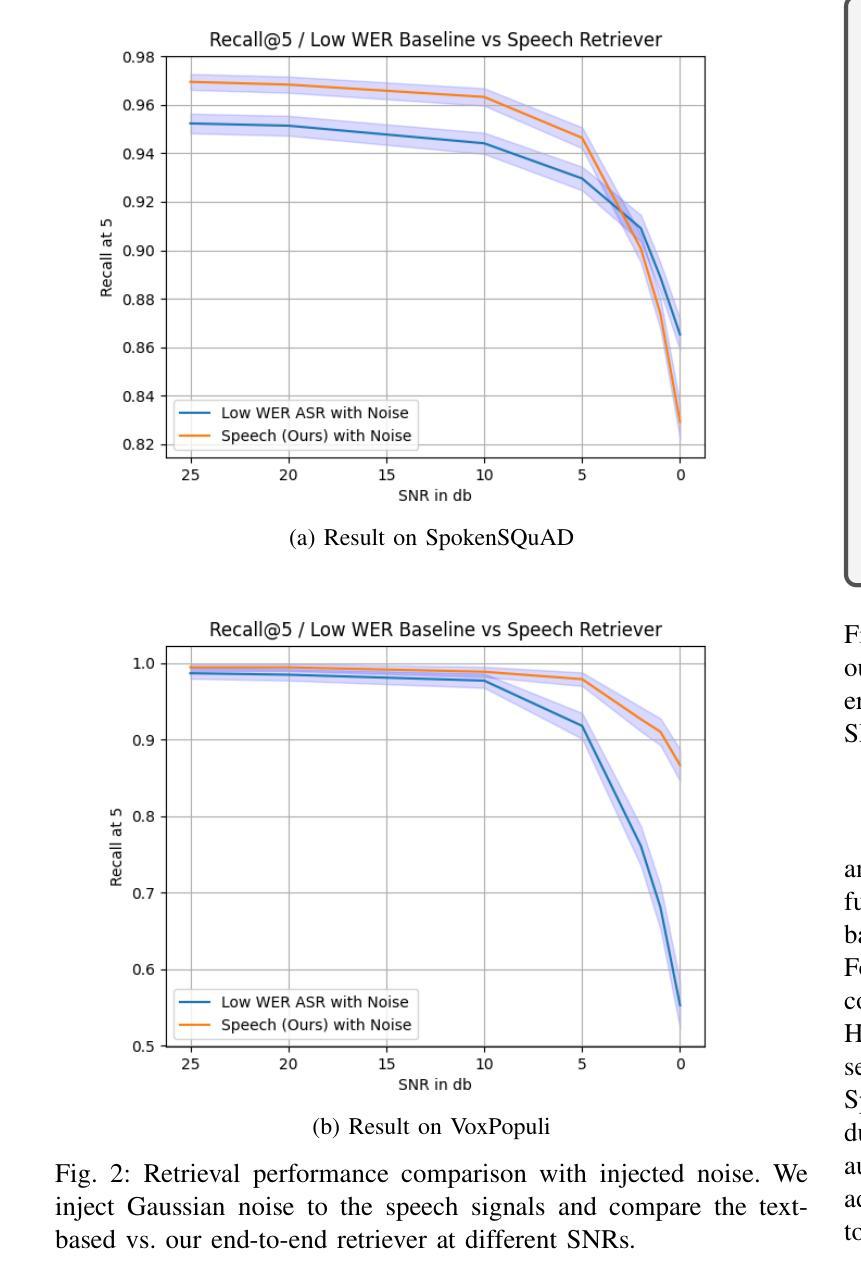
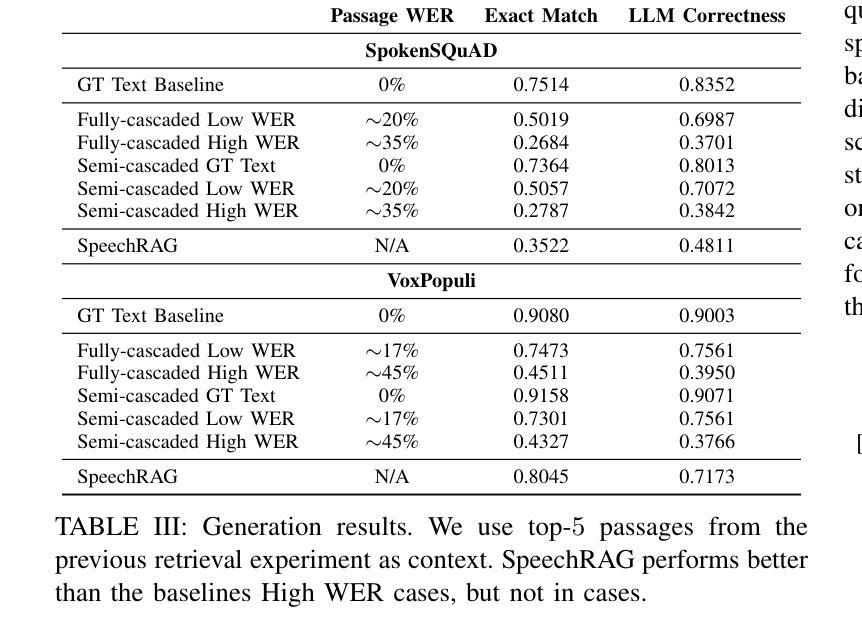
Speech Retrieval-Augmented Generation without Automatic Speech Recognition
Authors:Do June Min, Karel Mundnich, Andy Lapastora, Erfan Soltanmohammadi, Srikanth Ronanki, Kyu Han
One common approach for question answering over speech data is to first transcribe speech using automatic speech recognition (ASR) and then employ text-based retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) on the transcriptions. While this cascaded pipeline has proven effective in many practical settings, ASR errors can propagate to the retrieval and generation steps. To overcome this limitation, we introduce SpeechRAG, a novel framework designed for open-question answering over spoken data. Our proposed approach fine-tunes a pre-trained speech encoder into a speech adapter fed into a frozen large language model (LLM)–based retrieval model. By aligning the embedding spaces of text and speech, our speech retriever directly retrieves audio passages from text-based queries, leveraging the retrieval capacity of the frozen text retriever. Our retrieval experiments on spoken question answering datasets show that direct speech retrieval does not degrade over the text-based baseline, and outperforms the cascaded systems using ASR. For generation, we use a speech language model (SLM) as a generator, conditioned on audio passages rather than transcripts. Without fine-tuning of the SLM, this approach outperforms cascaded text-based models when there is high WER in the transcripts.
针对语音数据的问答的一种常见方法首先是使用自动语音识别(ASR)进行语音转录,然后在转录上应用基于文本的检索增强生成(RAG)。虽然这种级联管道已在许多实际场景中证明是有效的,但ASR错误可能会传播到检索和生成步骤。为了克服这一局限性,我们引入了SpeechRAG,这是一个专为开放式问题回答口语数据设计的新框架。我们提出的方法对预训练的语音编码器进行微调,将其调整为适应冻结的大型语言模型(LLM)的语音适配器检索模型。通过对文本和语音的嵌入空间进行对齐,我们的语音检索器直接从基于文本的查询中检索音频片段,利用冻结的文本检索器的检索能力。我们在口语问答数据集上的检索实验表明,直接语音检索并不亚于基于文本的基线,并且表现优于使用ASR的级联系统。对于生成,我们使用语音语言模型(SLM)作为生成器,以音频片段为条件,而不是文本。在不微调SLM的情况下,当转录中的字词错误率(WER)较高时,这种方法的表现优于级联的基于文本模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICASSP 2025
Summary:为提高语音识别(ASR)在问答系统中的性能,避免ASR错误对检索和生成步骤的影响,提出SpeechRAG框架。该框架通过微调预训练的语音编码器,将语音适配器输入到基于大型语言模型(LLM)的检索模型中,实现文本和语音嵌入空间的对齐。此语音检索器可直接从基于文本的查询中检索音频片段,利用冻结文本检索器的检索能力。实验表明,直接语音检索在口语问答数据集上的表现不亚于基于文本的基线方法,且在ASR使用级错误率较高时表现优于级联系统。对于生成部分,使用基于音频片段而非转录本的语音语言模型(SLM)作为生成器,无需对SLM进行微调即可超越级联的文本模型。
Key Takeaways:
- SpeechRAG框架旨在提高在口语问答系统中的性能,解决ASR错误传播的问题。
- 通过微调预训练的语音编码器并输入到基于LLM的检索模型中,实现SpeechRAG框架。
- SpeechRAG实现了文本和语音嵌入空间的直接对齐,允许直接检索音频片段。
- 实验表明,直接语音检索在口语问答数据集上的表现与基于文本的基线方法相当或更好。
- 在ASR存在高错误率的情况下,SpeechRAG在性能上超越了级联系统。
- 使用基于音频片段的SLM作为生成器,无需微调即可提高生成性能。
点此查看论文截图


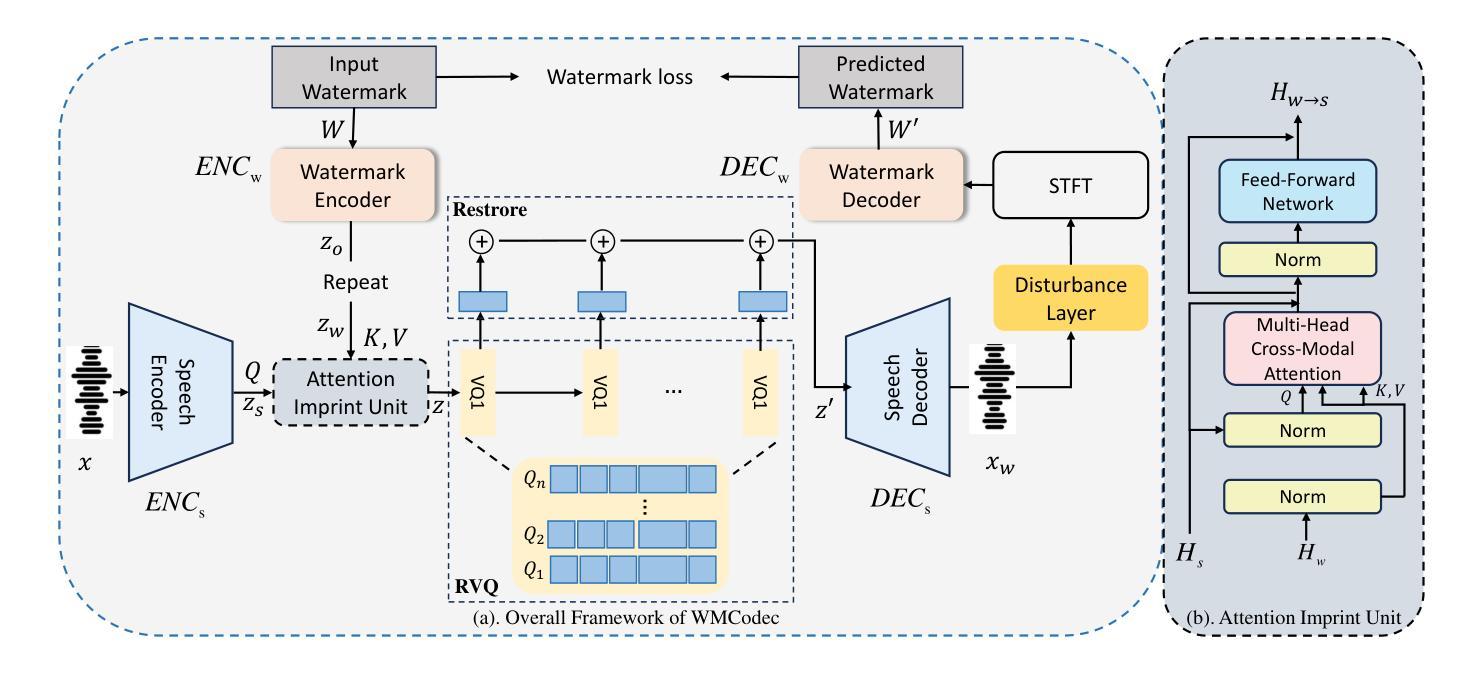
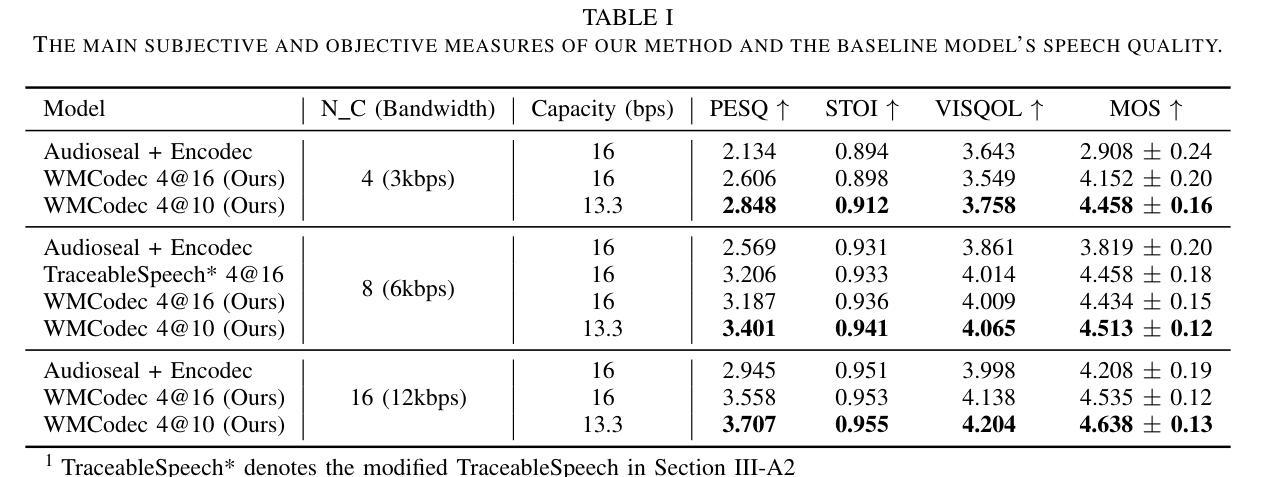
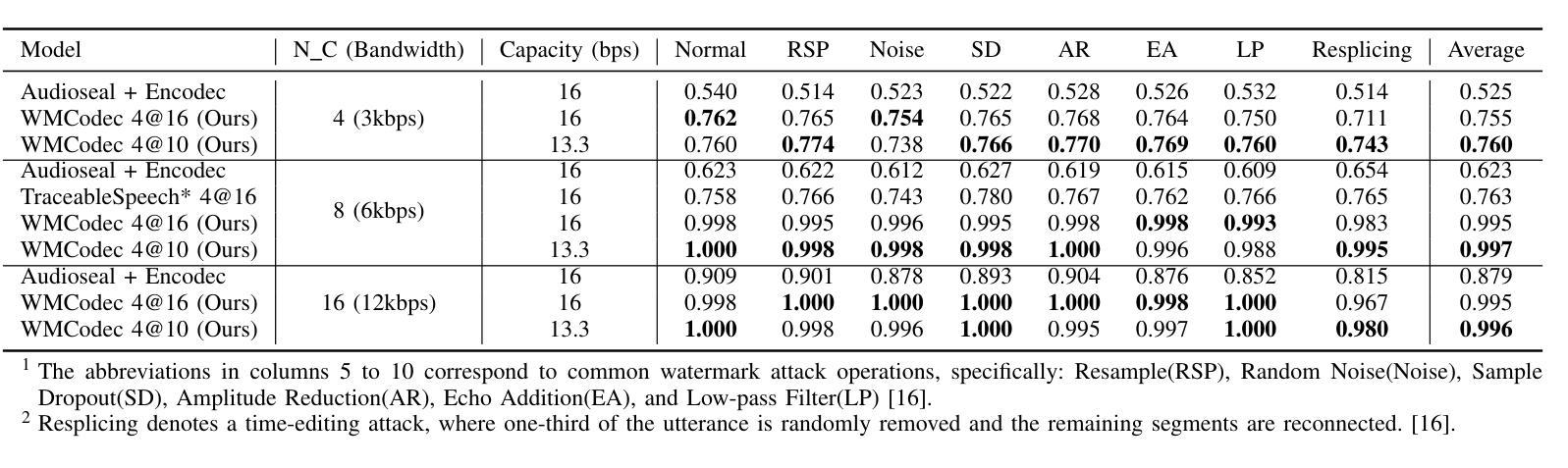
WMCodec: End-to-End Neural Speech Codec with Deep Watermarking for Authenticity Verification
Authors:Junzuo Zhou, Jiangyan Yi, Yong Ren, Jianhua Tao, Tao Wang, Chu Yuan Zhang
Recent advances in speech spoofing necessitate stronger verification mechanisms in neural speech codecs to ensure authenticity. Current methods embed numerical watermarks before compression and extract them from reconstructed speech for verification, but face limitations such as separate training processes for the watermark and codec, and insufficient cross-modal information integration, leading to reduced watermark imperceptibility, extraction accuracy, and capacity. To address these issues, we propose WMCodec, the first neural speech codec to jointly train compression-reconstruction and watermark embedding-extraction in an end-to-end manner, optimizing both imperceptibility and extractability of the watermark. Furthermore, We design an iterative Attention Imprint Unit (AIU) for deeper feature integration of watermark and speech, reducing the impact of quantization noise on the watermark. Experimental results show WMCodec outperforms AudioSeal with Encodec in most quality metrics for watermark imperceptibility and consistently exceeds both AudioSeal with Encodec and reinforced TraceableSpeech in extraction accuracy of watermark. At bandwidth of 6 kbps with a watermark capacity of 16 bps, WMCodec maintains over 99% extraction accuracy under common attacks, demonstrating strong robustness.
近年来语音欺骗技术的进展要求在神经语音编解码器中采用更强大的验证机制,以确保语音的真实性。当前的方法在压缩之前嵌入数字水印,然后从重建的语音中提取水印进行验证,但面临水印和编解码器需要单独训练、跨模态信息融合不足等局限性,导致水印的不可感知性、提取准确性和容量降低。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了WMCodec,这是第一个联合训练压缩-重建和嵌入水印的端到端神经语音编解码器,以优化水印的不可感知性和可提取性。此外,我们设计了一个迭代式的注意力印记单元(AIU),用于更深层地整合水印和语音特征,减少量化噪声对水印的影响。实验结果表明,WMCodec在大多数质量指标上优于带有Encodec的AudioSeal的水印不可感知性,并且在提取水印的准确性方面始终超过带有Encodec的AudioSeal和增强的TraceableSpeech。在带宽为6kbps、水印容量为16bps的情况下,WMCodec在常见攻击下保持超过99%的提取准确率,显示出强大的稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期语音伪装技术的进步对神经网络语音编解码器的身份验证机制提出了更高要求。为此提出了一种名为WMCodec的神经网络语音编解码器,首次将压缩重建和水印嵌入提取以端到端的方式进行联合训练,优化水印的不感知性和提取能力。设计了一种迭代注意力印记单元(AIU),用于更深层地整合水印和语音特征,减少量化噪声对水印的影响。实验结果表明,WMCodec在水印的不感知性和提取准确性方面优于AudioSeal和Encodec,并且在带宽为6kbps、水印容量为16bps的条件下,面对常见攻击仍能保持超过99%的提取准确性,展现出强大的稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 语音伪装技术的进步要求神经网络语音编解码器加强身份验证机制。
- WMCodec是首个将压缩重建和水印嵌入提取联合训练的神经网络语音编解码器。
- WMCodec优化了水印的不感知性和提取能力。
- 迭代注意力印记单元(AIU)用于更深层地整合水印和语音特征。
- AIU设计减少了量化噪声对水印的影响。
- 实验表明WMCodec在水印不感知性和提取准确性方面优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

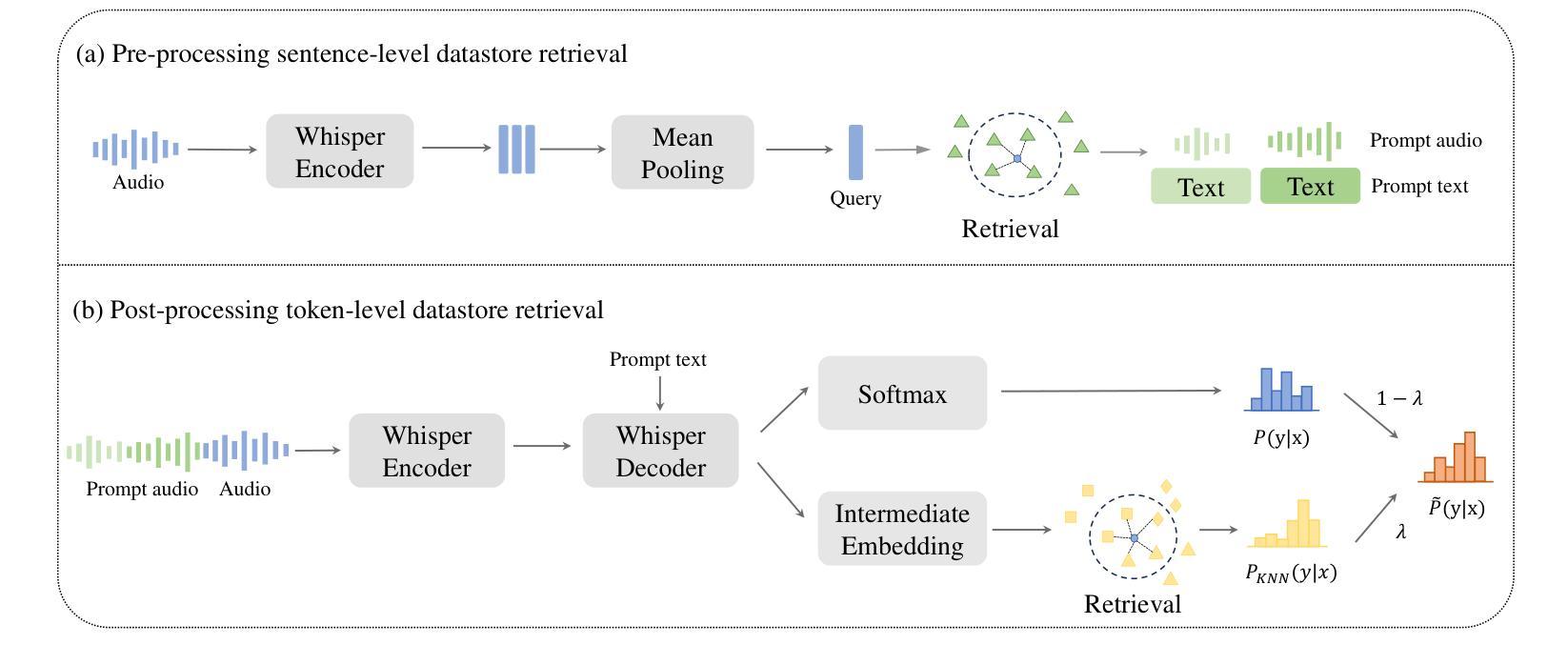
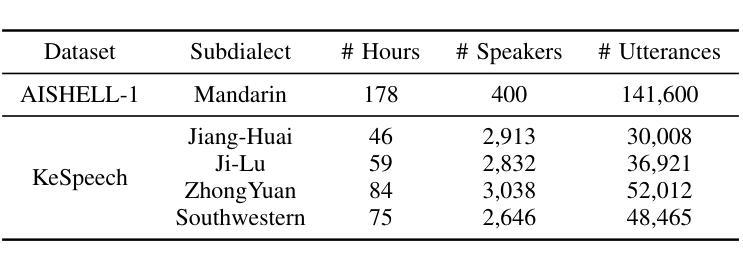
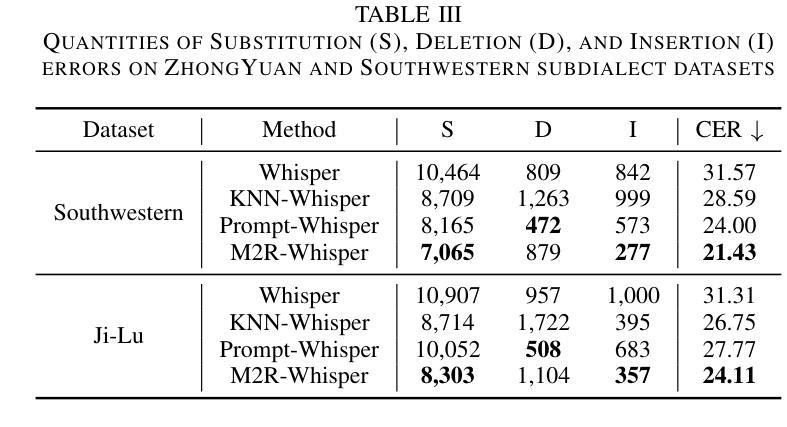
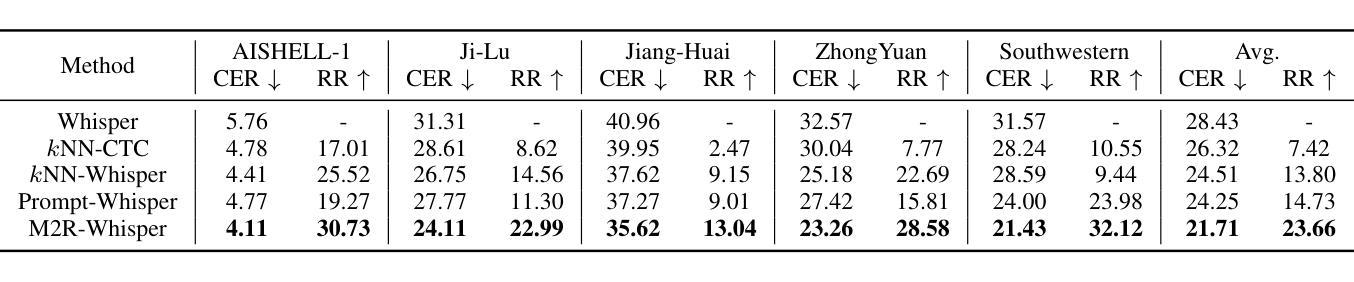
M2R-Whisper: Multi-stage and Multi-scale Retrieval Augmentation for Enhancing Whisper
Authors:Jiaming Zhou, Shiwan Zhao, Jiabei He, Hui Wang, Wenjia Zeng, Yong Chen, Haoqin Sun, Aobo Kong, Yong Qin
State-of-the-art models like OpenAI’s Whisper exhibit strong performance in multilingual automatic speech recognition (ASR), but they still face challenges in accurately recognizing diverse subdialects. In this paper, we propose M2R-whisper, a novel multi-stage and multi-scale retrieval augmentation approach designed to enhance ASR performance in low-resource settings. Building on the principles of in-context learning (ICL) and retrieval-augmented techniques, our method employs sentence-level ICL in the pre-processing stage to harness contextual information, while integrating token-level k-Nearest Neighbors (kNN) retrieval as a post-processing step to further refine the final output distribution. By synergistically combining sentence-level and token-level retrieval strategies, M2R-whisper effectively mitigates various types of recognition errors. Experiments conducted on Mandarin and subdialect datasets, including AISHELL-1 and KeSpeech, demonstrate substantial improvements in ASR accuracy, all achieved without any parameter updates.
当前最先进的模型,如OpenAI的Whisper,在多语种自动语音识别(ASR)方面表现出强大的性能,但它们在识别多样的次方言方面仍面临挑战。在本文中,我们提出了M2R-whisper,这是一种新型的多阶段多尺度检索增强方法,旨在提高低资源环境下的ASR性能。我们的方法基于上下文学习(ICL)和检索增强技术,在预处理阶段采用句子级ICL来利用上下文信息,同时集成基于标记级的k最近邻(kNN)检索作为后处理步骤,以进一步优化最终输出分布。通过协同结合句子级和标记级检索策略,M2R-whisper有效地减轻了各种类型的识别错误。在包括AISHELL-1和KeSpeech在内的普通话和次方言数据集上进行的实验表明,ASR准确率有了显著提高,所有这些改进都没有涉及任何参数更新。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
M2R-whisper是一种针对低资源环境下语音识别性能提升的多阶段多尺度检索增强方法。该方法结合上下文学习(ICL)和检索增强技术,通过预处理阶段的句子级ICL利用上下文信息,以及后处理阶段的基于k近邻(kNN)的token级检索来进一步优化最终输出分布。该方法有效缓解了各种识别错误,在普通话和方言数据集上的实验显示语音识别准确率显著提升。
Key Takeaways
- M2R-whisper是一种针对多语种自动语音识别(ASR)的新颖方法,旨在提升低资源环境下的性能。
- 方法结合了上下文学习和检索增强技术。
- 通过预处理阶段的句子级上下文学习,有效利用上下文信息。
- 采用后处理阶段的基于k近邻(kNN)的token级检索,进一步优化最终输出分布。
- M2R-whisper能有效缓解各种识别错误。
- 在普通话和方言数据集上的实验显示,ASR准确率显著提升。
点此查看论文截图

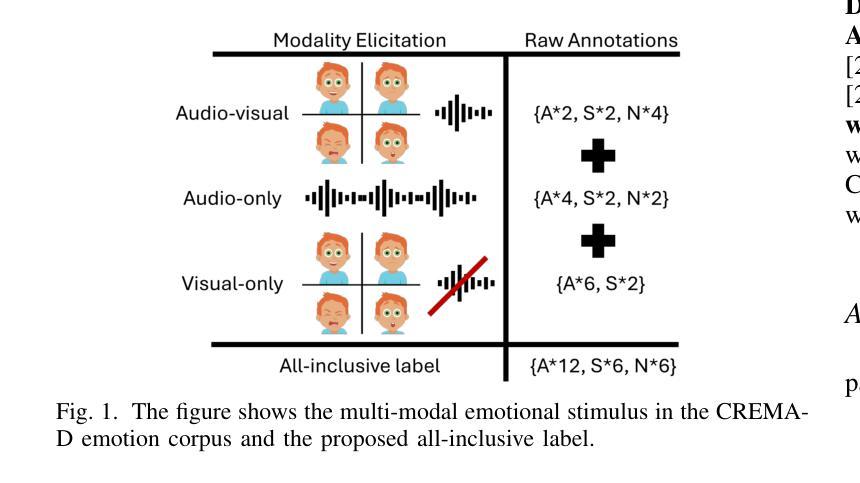
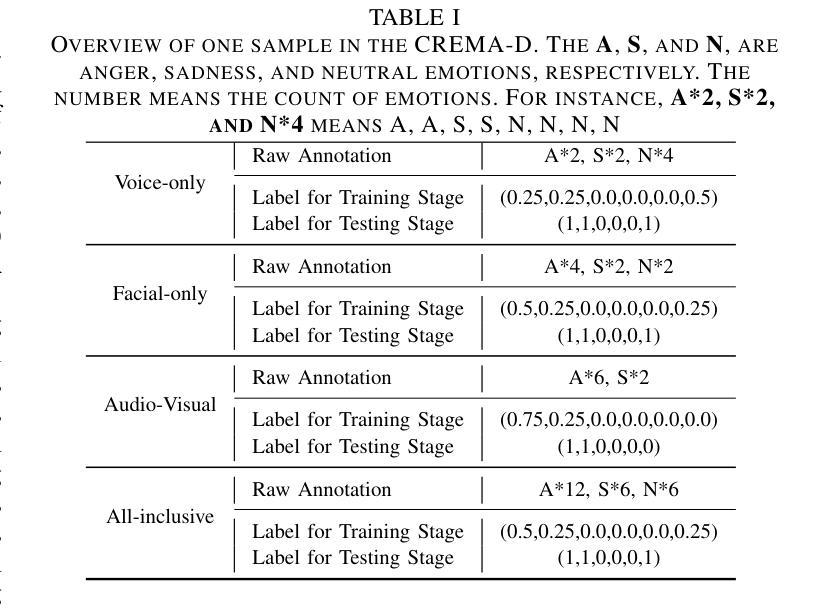
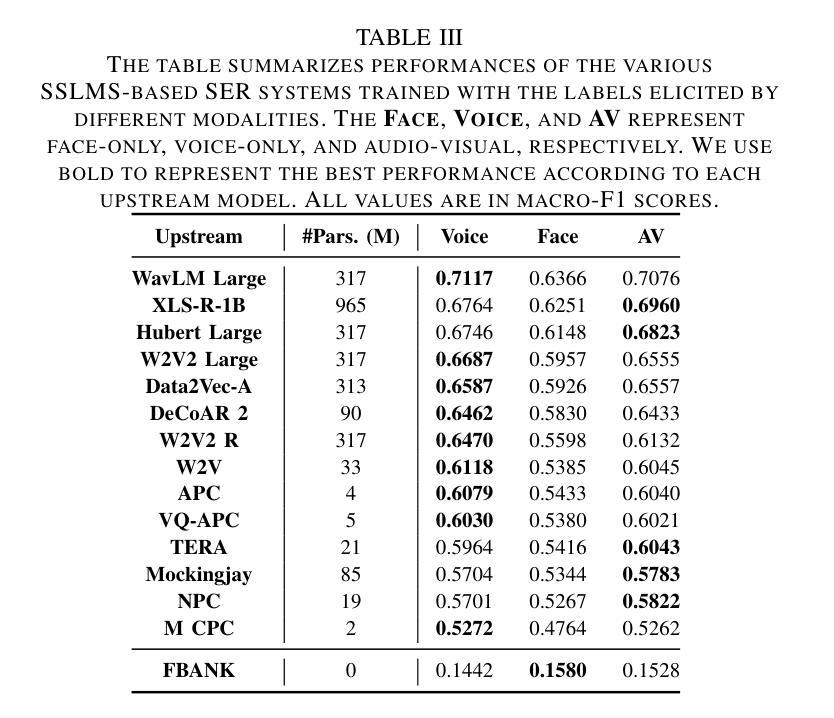
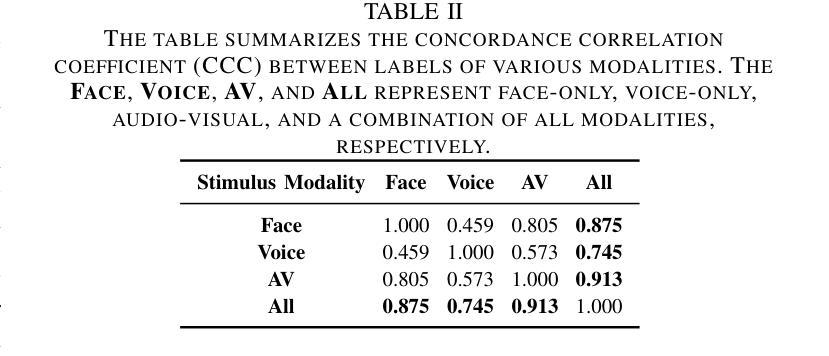
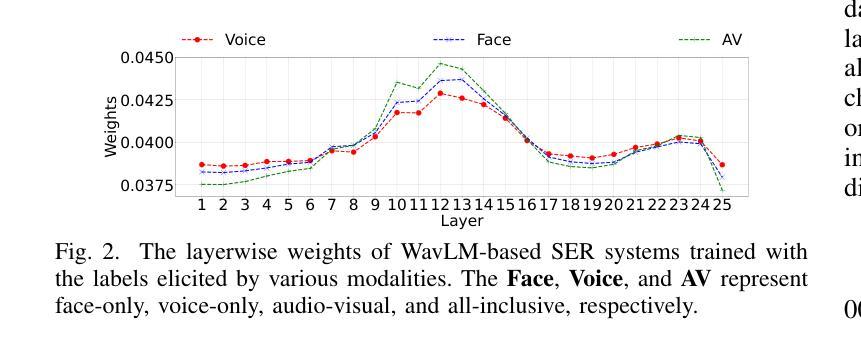
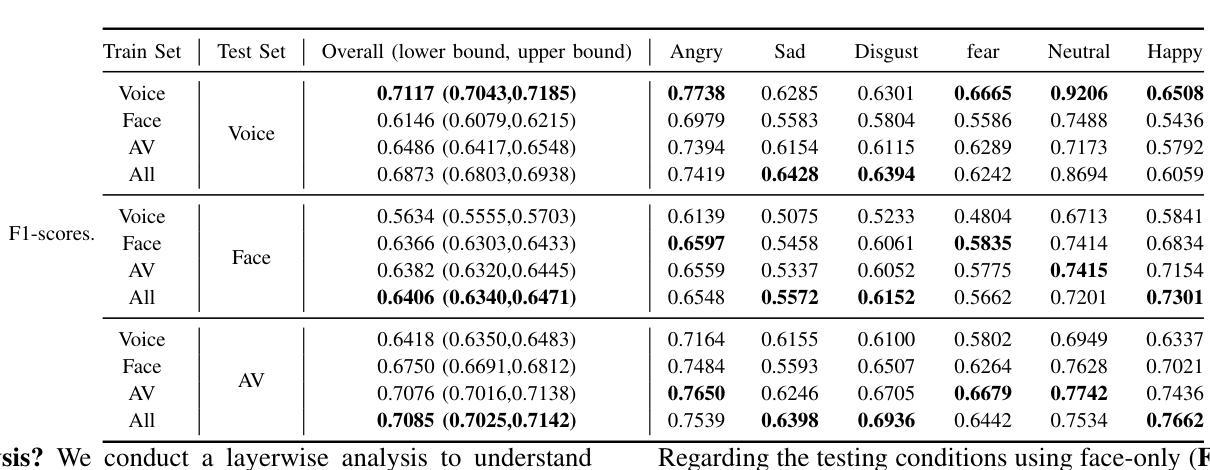
Stimulus Modality Matters: Impact of Perceptual Evaluations from Different Modalities on Speech Emotion Recognition System Performance
Authors:Huang-Cheng Chou, Haibin Wu, Chi-Chun Lee
Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) systems rely on speech input and emotional labels annotated by humans. However, various emotion databases collect perceptional evaluations in different ways. For instance, the IEMOCAP dataset uses video clips with sounds for annotators to provide their emotional perceptions. However, the most significant English emotion dataset, the MSP-PODCAST, only provides speech for raters to choose the emotional ratings. Nevertheless, using speech as input is the standard approach to training SER systems. Therefore, the open question is the emotional labels elicited by which scenarios are the most effective for training SER systems. We comprehensively compare the effectiveness of SER systems trained with labels elicited by different modality stimuli and evaluate the SER systems on various testing conditions. Also, we introduce an all-inclusive label that combines all labels elicited by various modalities. We show that using labels elicited by voice-only stimuli for training yields better performance on the test set, whereas labels elicited by voice-only stimuli.
语音情感识别(SER)系统依赖于语音输入和人工标注的情感标签。然而,不同的情感数据库采用各种方式收集感知评估。例如,IEMOCAP数据集使用带有声音的视频剪辑供注释者提供他们的情感感知。然而,最大的英语情感数据集MSP-PODCAST只提供语音供评估者选择情感评分。尽管如此,使用语音作为输入是训练SER系统的标准方法。因此,公开的问题是哪种场景引发的情感标签对于训练SER系统最有效。我们全面比较了使用不同模式刺激引发的标签训练的SER系统的有效性,并在各种测试条件下对其进行了评估。此外,我们还引入了一个包容性标签,该标签结合了由各种模式引发的所有标签。我们的研究表明,使用仅由声音刺激引发的标签进行训练在测试集上取得了更好的性能,而由多种模态结合产生的标签性能并未达到最佳。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 2 figures, 4 tables, acceptance for ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文主要探讨了语音情感识别(SER)系统的训练数据标注方式及其有效性。文章指出不同情感数据库通过不同的方式收集感知评价,如IEMOCAP数据集使用视频剪辑和声音供注释者提供情感感知,而最大的英语情感数据库MSP-PODCAST仅提供语音供评估者选择情感评分。文章全面比较了使用不同模态刺激产生的标签训练的SER系统的有效性,并在各种测试条件下对系统进行了评估。研究结果表明,使用仅由语音刺激产生的标签进行训练在测试集上表现更好。
Key Takeaways
- 语音情感识别(SER)系统依赖于人类标注的语音输入和情感标签。
- 不同情感数据库采用不同方式收集感知评价,如IEMOCAP和MSP-PODCAST数据集。
- 使用不同模态刺激产生的标签训练的SER系统的有效性存在疑问。
- 全面比较了使用不同方式产生的标签训练的SER系统的性能。
- 引入了一个包含所有标签的全面标签,这些标签是由各种模态引发的。
- 研究表明,使用仅由语音刺激产生的标签进行训练在测试集上的表现更佳。
点此查看论文截图

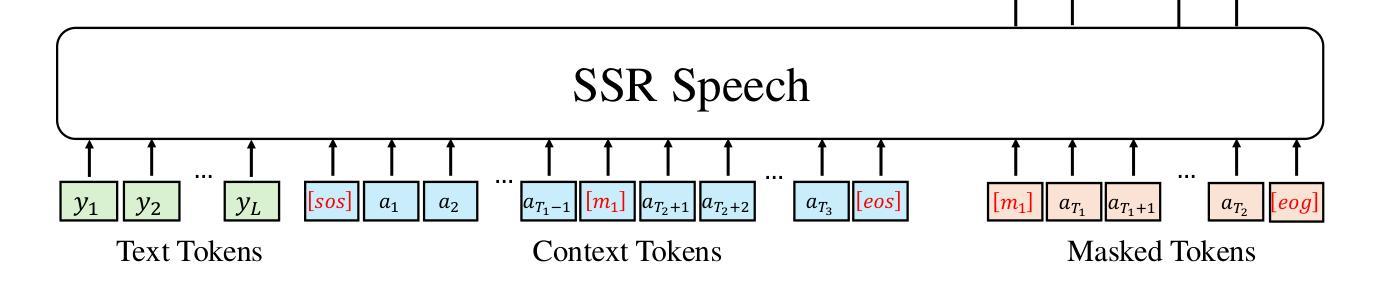
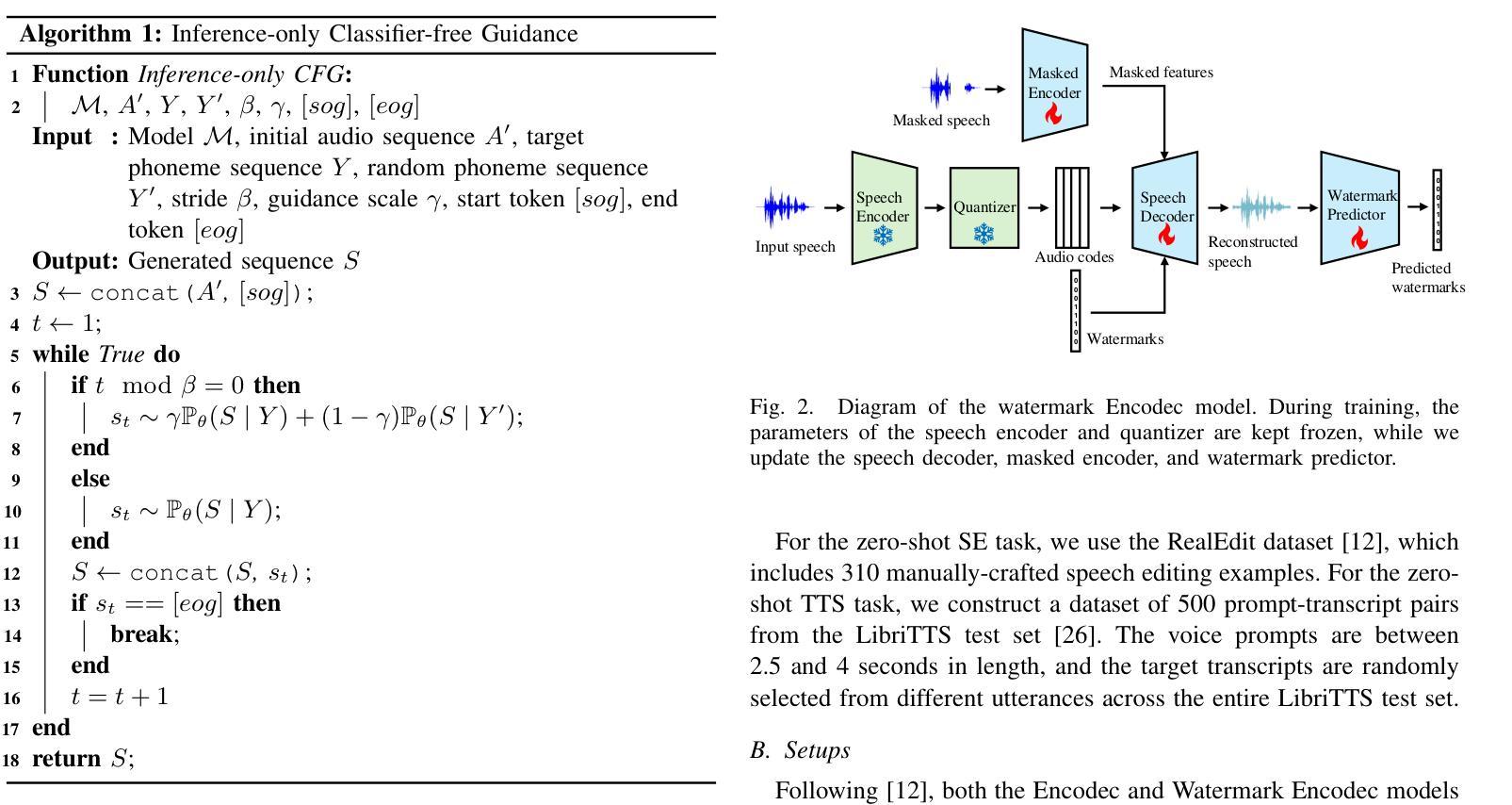
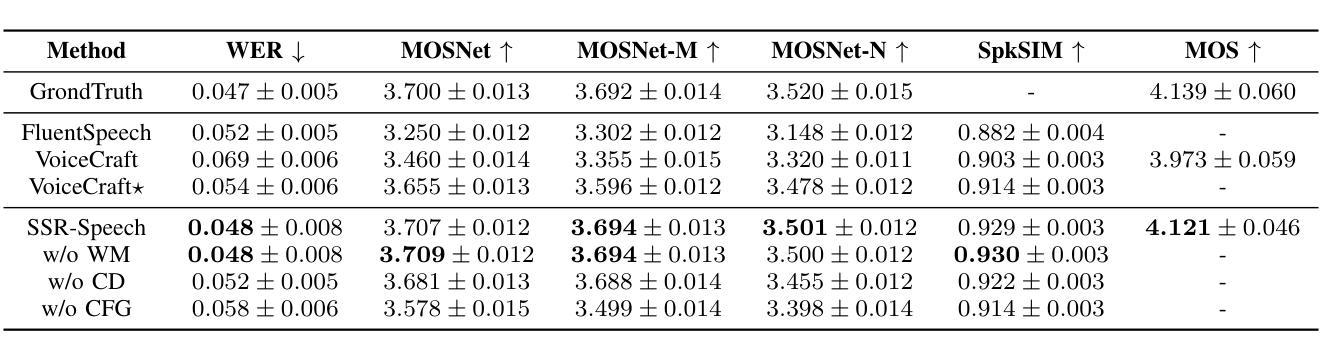
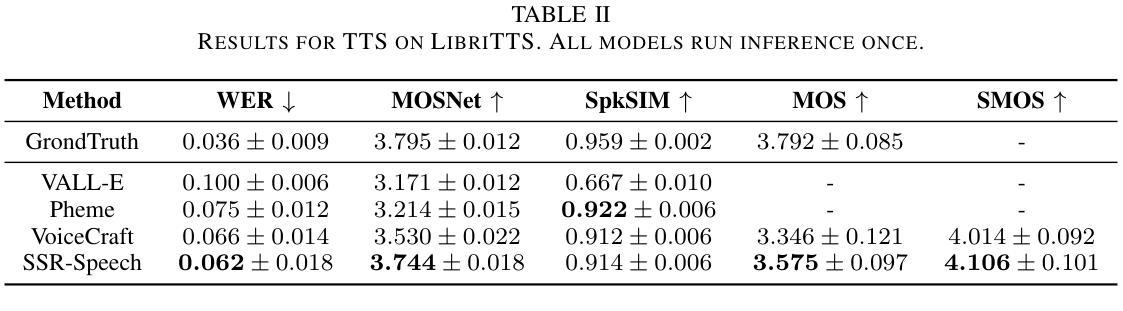
SSR-Speech: Towards Stable, Safe and Robust Zero-shot Text-based Speech Editing and Synthesis
Authors:Helin Wang, Meng Yu, Jiarui Hai, Chen Chen, Yuchen Hu, Rilin Chen, Najim Dehak, Dong Yu
In this paper, we introduce SSR-Speech, a neural codec autoregressive model designed for stable, safe, and robust zero-shot textbased speech editing and text-to-speech synthesis. SSR-Speech is built on a Transformer decoder and incorporates classifier-free guidance to enhance the stability of the generation process. A watermark Encodec is proposed to embed frame-level watermarks into the edited regions of the speech so that which parts were edited can be detected. In addition, the waveform reconstruction leverages the original unedited speech segments, providing superior recovery compared to the Encodec model. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in the RealEdit speech editing task and the LibriTTS text-to-speech task, surpassing previous methods. Furthermore, SSR-Speech excels in multi-span speech editing and also demonstrates remarkable robustness to background sounds. The source code and demos are released.
在这篇论文中,我们介绍了SSR-Speech,这是一款为稳定、安全和稳健的零起点文本基础语音编辑和文本到语音合成而设计的神经编码自回归模型。SSR-Speech基于Transformer解码器构建,并采用了无分类器引导技术以增强生成过程的稳定性。我们提出了一种水印Encodec,可以将帧级水印嵌入语音的编辑区域,以便检测哪些部分被编辑过。此外,波形重建利用了原始未编辑的语音片段,与Encodec模型相比,提供了更出色的恢复效果。我们的方法在现实编辑语音任务(RealEdit)和LibriTTS文本到语音任务中取得了最先进的性能表现,超越了以前的方法。此外,SSR-Speech在多跨度语音编辑方面表现出色,并且对背景声音表现出惊人的稳健性。源代码和演示已经发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文介绍了SSR-Speech,一种用于稳定、安全和稳健的零样本文本语音编辑和文本到语音合成的神经编码自回归模型。SSR-Speech基于Transformer解码器构建,采用无分类器引导提高生成过程的稳定性。提出了水印Encodec,可将帧级水印嵌入语音的编辑区域,以检测哪些部分被编辑过。此外,波形重建利用原始未编辑的语音片段,提供了比Encodec模型更出色的恢复效果。SSR-Speech在RealEdit语音编辑任务和LibriTTS文本到语音任务上达到了最新技术性能水平,超越了以前的方法。此外,SSR-Speech在多跨度语音编辑方面表现出色,并且对背景声音具有惊人的稳健性。已发布源代码和演示。
Key Takeaways
- SSR-Speech是一种神经编码自回归模型,用于稳定、安全和稳健的零样本文本语音编辑和文本到语音合成。
- SSR-Speech采用Transformer解码器和无分类器引导增强生成稳定性。
- SSR-Speech提出了水印Encodec技术,能够检测语音中哪些部分被编辑过。
- 波形重建利用原始未编辑的语音片段,实现优质恢复。
- SSR-Speech在RealEdit语音编辑任务和LibriTTS文本到语音任务上表现优异,超越先前方法。
- SSR-Speech擅长多跨度语音编辑。
点此查看论文截图

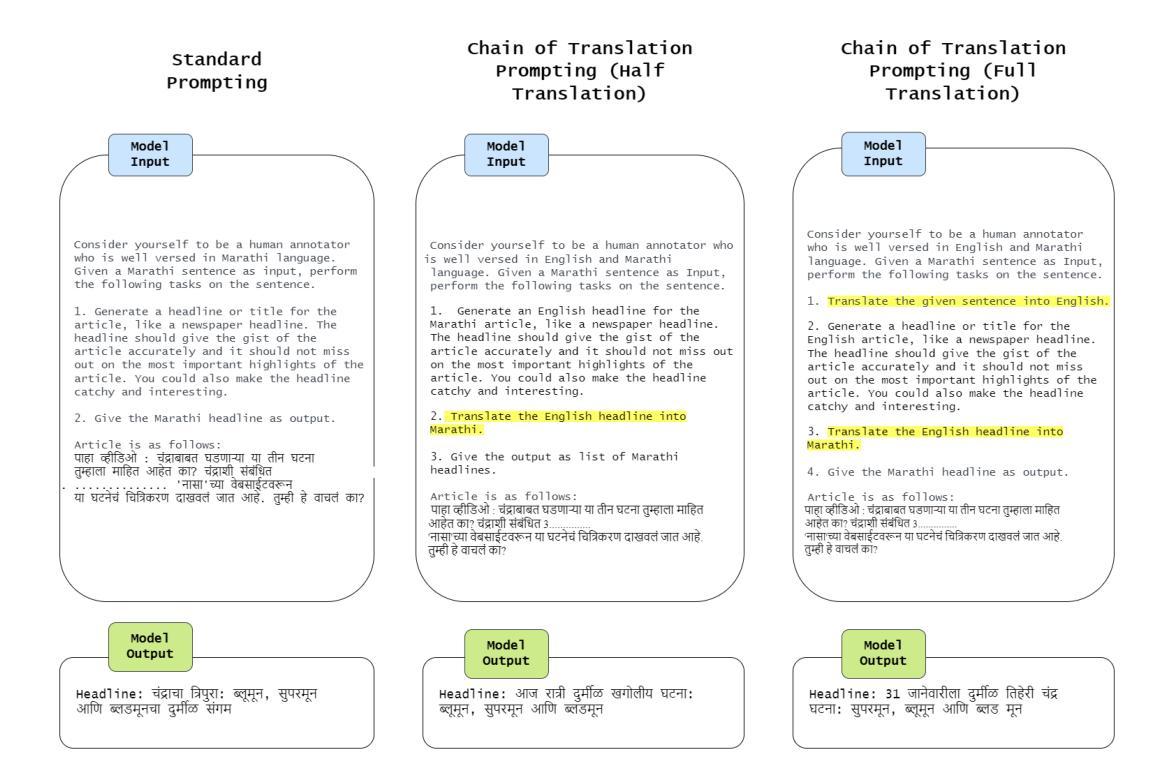
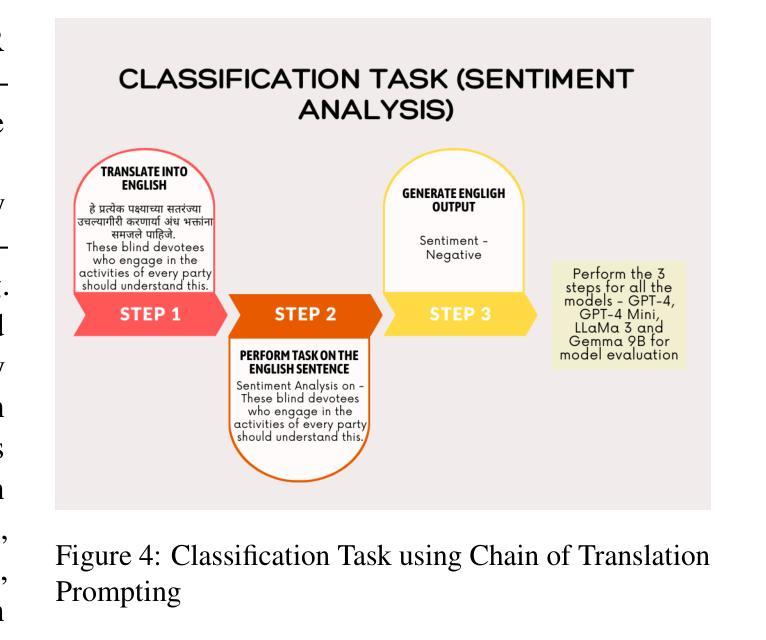
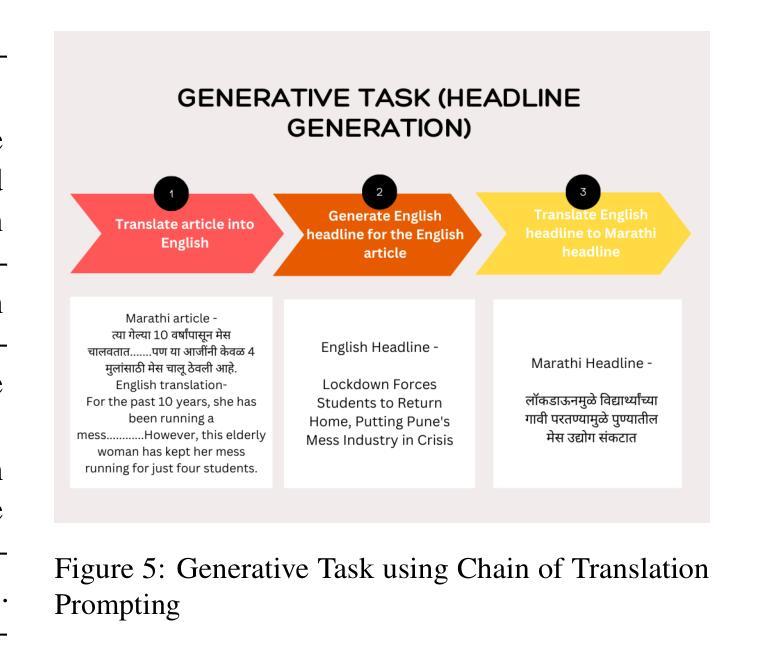
Chain-of-Translation Prompting (CoTR): A Novel Prompting Technique for Low Resource Languages
Authors:Tejas Deshpande, Nidhi Kowtal, Raviraj Joshi
This paper introduces Chain of Translation Prompting (CoTR), a novel strategy designed to enhance the performance of language models in low-resource languages. CoTR restructures prompts to first translate the input context from a low-resource language into a higher-resource language, such as English. The specified task like generation, classification, or any other NLP function is then performed on the translated text, with the option to translate the output back to the original language if needed. All these steps are specified in a single prompt. We demonstrate the effectiveness of this method through a case study on the low-resource Indic language Marathi. The CoTR strategy is applied to various tasks, including sentiment analysis, hate speech classification, subject classification and text generation, and its efficacy is showcased by comparing it with regular prompting methods. Our results underscore the potential of translation-based prompting strategies to significantly improve multilingual LLM performance in low-resource languages, offering valuable insights for future research and applications. We specifically see the highest accuracy improvements with the hate speech detection task. The technique also has the potential to enhance the quality of synthetic data generation for underrepresented languages using LLMs.
本文介绍了翻译链提示(CoTR)这一新型策略,旨在提高低资源语言的语言模型性能。CoTR重新构建提示,首先将输入上下文从低资源语言翻译到资源更丰富的语言,如英语。然后在翻译后的文本上执行指定任务,如生成、分类或其他任何NLP功能,如果需要将输出翻译回原始语言。所有这些步骤都在一个提示中指定。我们通过针对低资源印度语言马拉地语进行案例研究,展示了该方法的有效性。CoTR策略应用于各种任务,包括情感分析、仇恨言论分类、主题分类和文本生成,通过与常规提示方法的比较,展示了其有效性。我们的结果强调基于翻译的提示策略在提高低资源语言的多语种大型语言模型性能方面的潜力,为未来研究和应用提供了宝贵的见解。我们特别看到仇恨言论检测任务获得了最高的精度提升。该技术还具有提高使用大型语言模型对代表性不足的语言合成数据生成质量的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at PACLIC 38 (2024)
Summary
此论文提出一种名为“翻译链提示”(CoTR)的新策略,旨在提升低资源语言的语言模型的性能。CoTR通过重新构建提示,先将输入内容从低资源语言翻译到资源丰富、如英语这样的语言,然后在翻译后的文本上执行指定任务,如生成、分类或其他NLP功能。如果需要,还可以将输出翻译回原始语言。所有这些步骤都在一个提示中指定。我们通过在马拉地语这一低资源印度语言上进行的案例研究,证明了该方法的实用性。此策略适用于各种任务,包括情感分析、仇恨言论分类、主题分类和文本生成等。我们的研究结果显示翻译提示策略具有显著改善低资源语言的多语种大型语言模型性能的潜力,为未来的研究和应用提供了有价值的见解。特别地,仇恨言论检测任务的效果提升最为显著。此技术还有助于提高使用大型语言模型对代表性不足的语种合成数据生成的品质。
Key Takeaways
- CoTR是一种新型策略,旨在增强低资源语言的语言模型性能。
- CoTR通过翻译输入内容从低资源语言到资源丰富语言来提升语言模型的性能。
- 此策略适用于各种NLP任务,包括情感分析、仇恨言论分类、主题分类和文本生成等。
- CoTR在马拉地语这一低资源印度语言上的案例研究证明了其有效性。
- 与常规提示方法相比,CoTR策略显著提高仇恨言论检测任务的准确性。
- CoTR具有改善代表性不足的语种合成数据生成的品质潜力。
点此查看论文截图


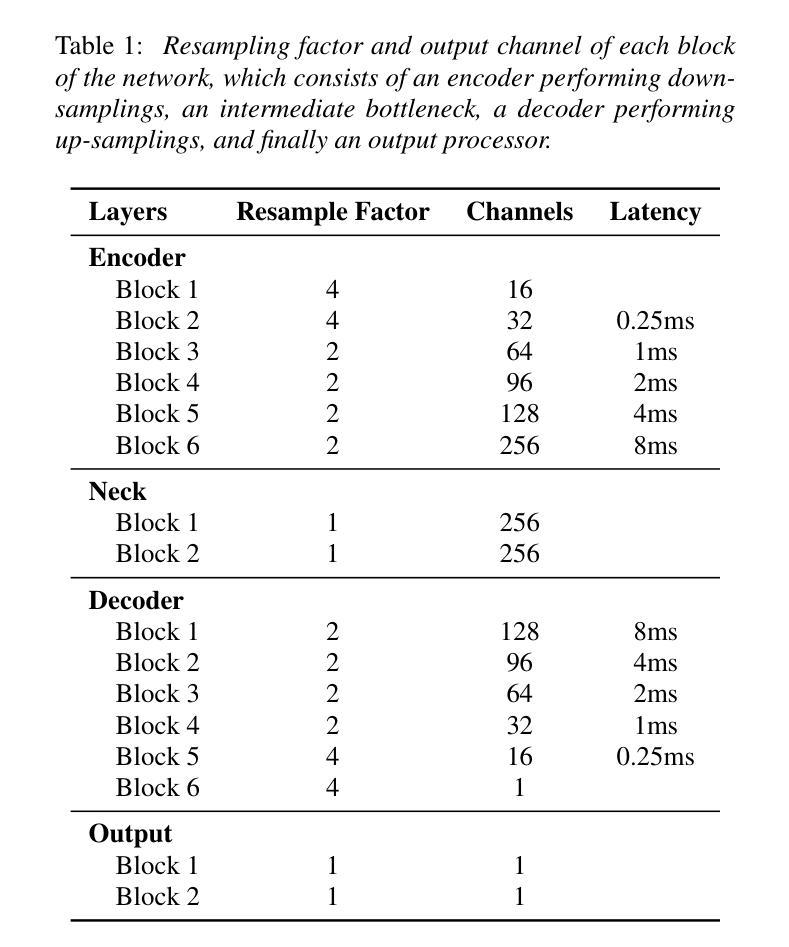
Real-time Speech Enhancement on Raw Signals with Deep State-space Modeling
Authors:Yan Ru Pei, Ritik Shrivastava, FNU Sidharth
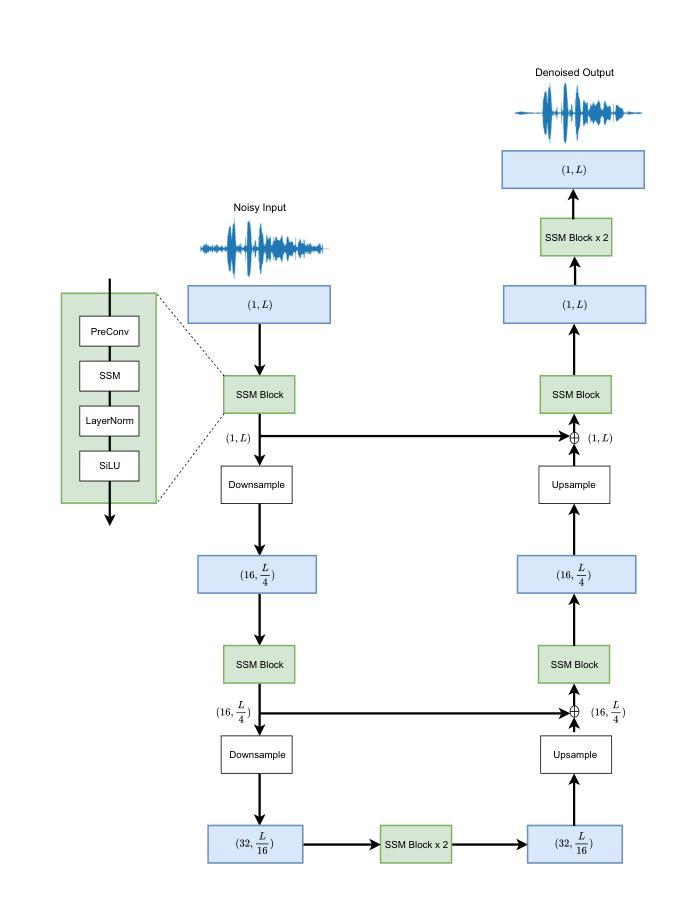
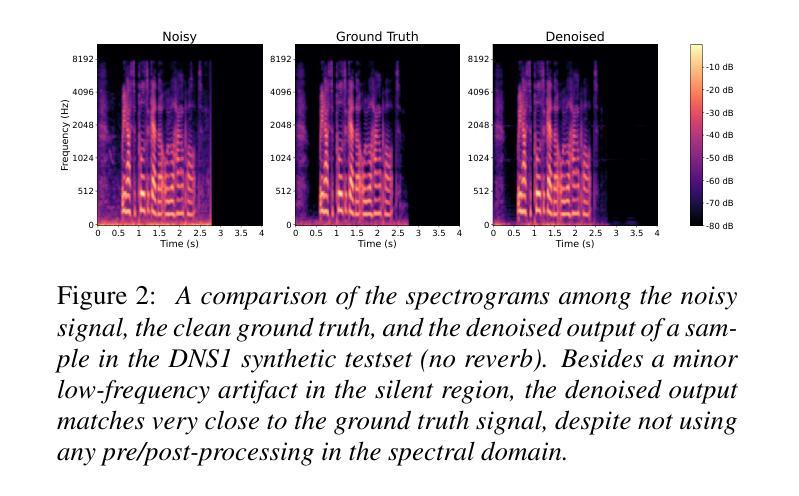
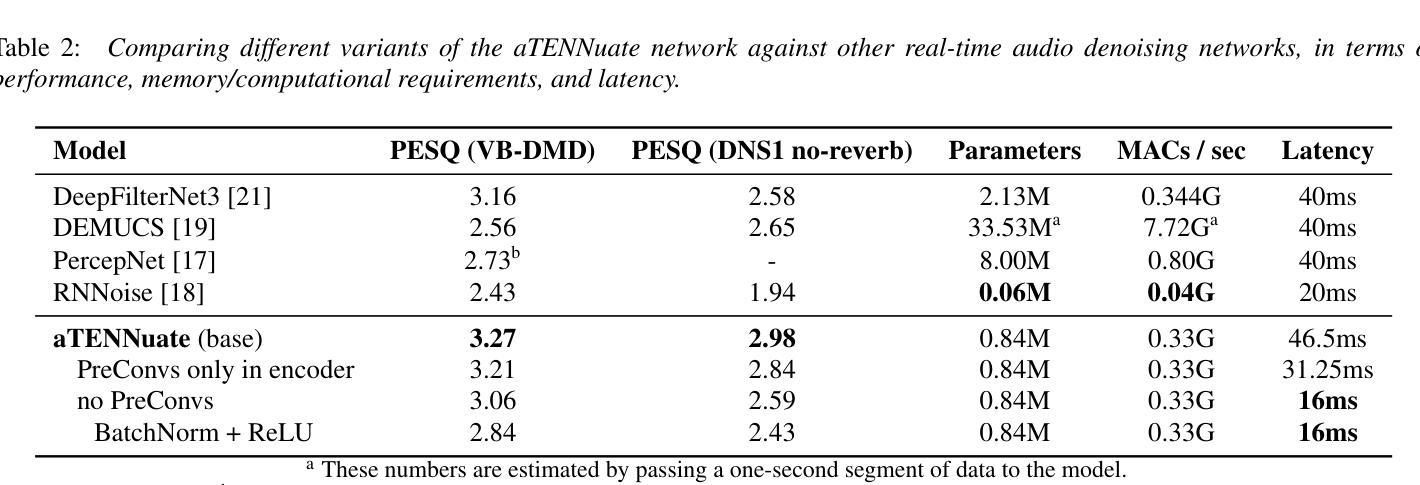
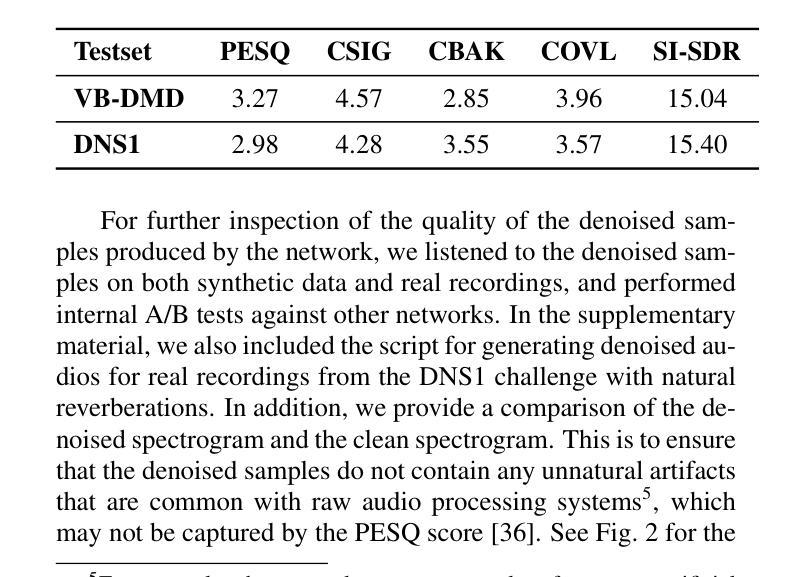
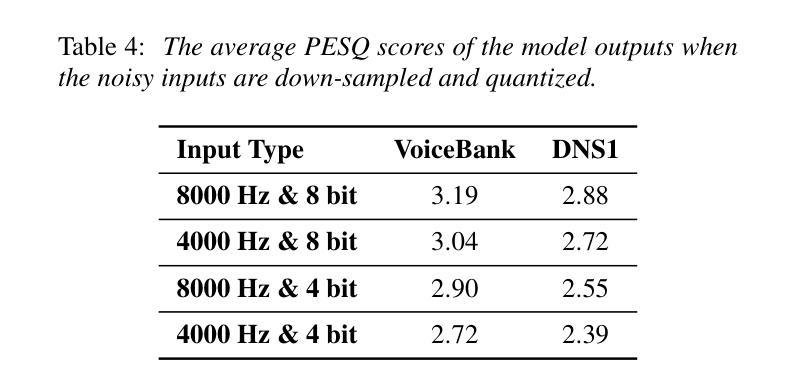
We present aTENNuate, a simple deep state-space autoencoder configured for efficient online raw speech enhancement in an end-to-end fashion. The network’s performance is primarily evaluated on raw speech denoising, with additional assessments on tasks such as super-resolution and de-quantization. We benchmark aTENNuate on the VoiceBank + DEMAND and the Microsoft DNS1 synthetic test sets. The network outperforms previous real-time denoising models in terms of PESQ score, parameter count, MACs, and latency. Even as a raw waveform processing model, the model maintains high fidelity to the clean signal with minimal audible artifacts. In addition, the model remains performant even when the noisy input is compressed down to 4000Hz and 4 bits, suggesting general speech enhancement capabilities in low-resource environments. Code is available at github.com/Brainchip-Inc/aTENNuate
我们提出了aTENNuate,这是一个简单的深度状态空间自编码器,以端到端的方式配置,用于高效的在线原始语音增强。该网络的主要评估是基于原始语音去噪,还包括超分辨率和去量化等任务的评估。我们在VoiceBank + DEMAND和Microsoft DNS1合成测试集上对aTENNuate进行了基准测试。该网络在PESQ得分、参数计数、MACs和延迟方面优于以前的实时去噪模型。即使作为原始波形处理模型,该模型对清洁信号的保真度也很高,几乎听不到杂音。此外,即使嘈杂的输入压缩到4000Hz和4位时,该模型仍然性能卓越,表明其在低资源环境中具有一般的语音增强能力。代码可在github.com/Brainchip-Inc/aTENNuate找到。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
本文介绍了aTENNuate,一个简洁的深度状态空间自编码器,用于在线原始语音增强,以端到端的方式进行配置。该网络在原始语音降噪方面进行了主要评估,并对超分辨率和去量化等任务进行了额外评估。在VoiceBank + DEMAND和Microsoft DNS1合成测试集上,aTENNuate的基准测试表明其在PESQ得分、参数计数、乘积累操作和延迟等方面优于现有的实时降噪模型。即使作为原始波形处理模型,该模型对清洁信号的保真度依然很高,几乎无听觉失真。此外,即使在嘈杂输入被压缩至4000Hz和4比特的情况下,该模型依然表现优异,显示其在低资源环境中具有一般的语音增强能力。代码可在github.com/Brainchip-Inc/aTENNuate找到。
关键见解
- aTENNuate是一个深度状态空间自编码器,用于在线原始语音增强。
- 该网络在原始语音降噪方面有出色的表现。
- aTENNuate在VoiceBank + DEMAND和Microsoft DNS1合成测试集上的基准测试优于其他实时降噪模型。
- aTENNuate在保持高保真清洁信号的同时,几乎无听觉失真。
- aTENNuate能够在低资源环境中表现出良好的语音增强能力。
- aTENNuate具备处理压缩语音的能力,即使输入被压缩至4000Hz和4比特,依然能够保持优良性能。
点此查看论文截图

Multimodal Human-Autonomous Agents Interaction Using Pre-Trained Language and Visual Foundation Models
Authors:Linus Nwankwo, Elmar Rueckert
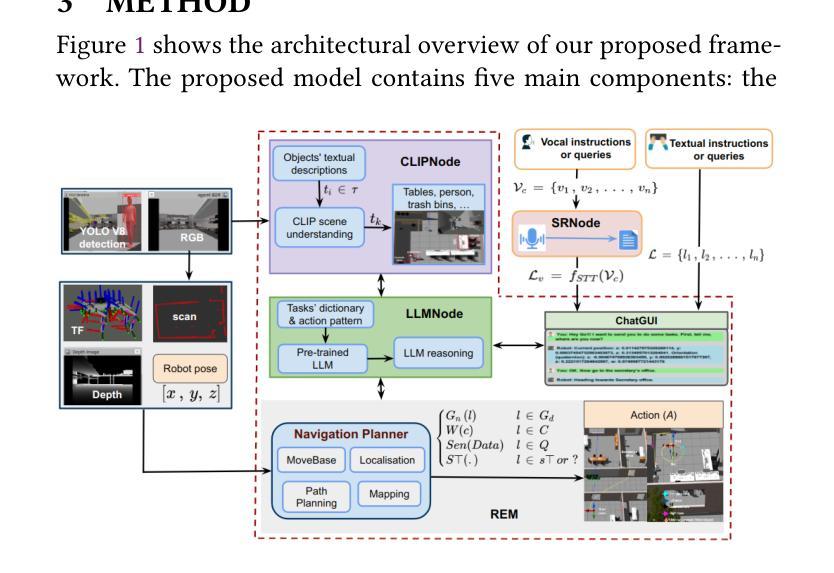
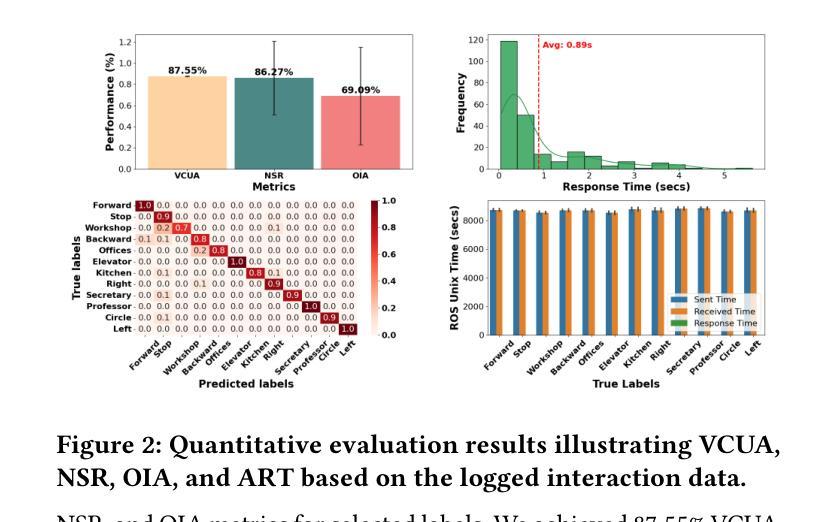
In this paper, we extended the method proposed in [21] to enable humans to interact naturally with autonomous agents through vocal and textual conversations. Our extended method exploits the inherent capabilities of pre-trained large language models (LLMs), multimodal visual language models (VLMs), and speech recognition (SR) models to decode the high-level natural language conversations and semantic understanding of the robot’s task environment, and abstract them to the robot’s actionable commands or queries. We performed a quantitative evaluation of our framework’s natural vocal conversation understanding with participants from different racial backgrounds and English language accents. The participants interacted with the robot using both spoken and textual instructional commands. Based on the logged interaction data, our framework achieved 87.55% vocal commands decoding accuracy, 86.27% commands execution success, and an average latency of 0.89 seconds from receiving the participants’ vocal chat commands to initiating the robot’s actual physical action. The video demonstrations of this paper can be found at https://linusnep.github.io/MTCC-IRoNL/.
在这篇论文中,我们将[21]中提出的方法进行扩展,使人类能够通过语音和文本对话与自主代理进行自然交互。我们的扩展方法利用预训练的大型语言模型(LLM)、多模态视觉语言模型(VLM)和语音识别(SR)模型的固有功能,解码高级自然语言对话和机器人任务环境的语义理解,并将其抽象化为机器人的可操作命令或查询。我们对框架的自然语音对话理解进行了定量评估,参与者来自不同的种族背景和英语口音。参与者使用口语和文本指令命令与机器人进行交互。根据记录的交互数据,我们的框架实现了87.55%的语音命令解码准确率、86.27%的命令执行成功率,从接收参与者的语音聊天命令到启动机器人的实际物理动作的平均延迟时间为0.89秒。本论文的视频演示可在https://linusnep.github.io/MTCC-IRoNL/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本论文扩展了方法[21],使人类能够通过语音和文本与自主智能体进行自然交互。该研究利用预训练的大型语言模型、多模态视觉语言模型和语音识别模型的固有功能,解码高级自然语言对话,理解机器人的任务环境语义,并将其抽象为机器人的可执行命令或查询。研究人员对不同种族背景和英语口音的参与者进行了定量分析评估。结果显示,参与者在以口语和文本形式与机器人互动时,我们的框架实现了高达87.55%的语音命令解码准确率、86.27%的命令执行成功率,以及从接收参与者语音聊天命令到启动机器人实际物理动作的平均延迟仅为0.89秒。视频演示内容可通过链接观看:[https://linusnep.github.io/MTCC-IRoNL/]进行查看。
Key Takeaways
- 研究扩展了方法[21],将人类自然交流能力赋予了与自主智能体的互动中。
- 框架采用了预训练的大型语言模型、多模态视觉语言模型和语音识别模型等技术。
- 通过定量分析评估,证明了该框架在处理口语指令时的高效性,达到了87.55%的语音命令解码准确率以及命令执行成功率达到了86.27%。
- 平均延迟时间仅为0.89秒,响应迅速。
- 该框架成功将复杂的人类交流信息转化为机器人的实际动作指令。
- 实验覆盖了不同种族背景和英语口音的参与者,展现了系统的广泛适应性。
点此查看论文截图
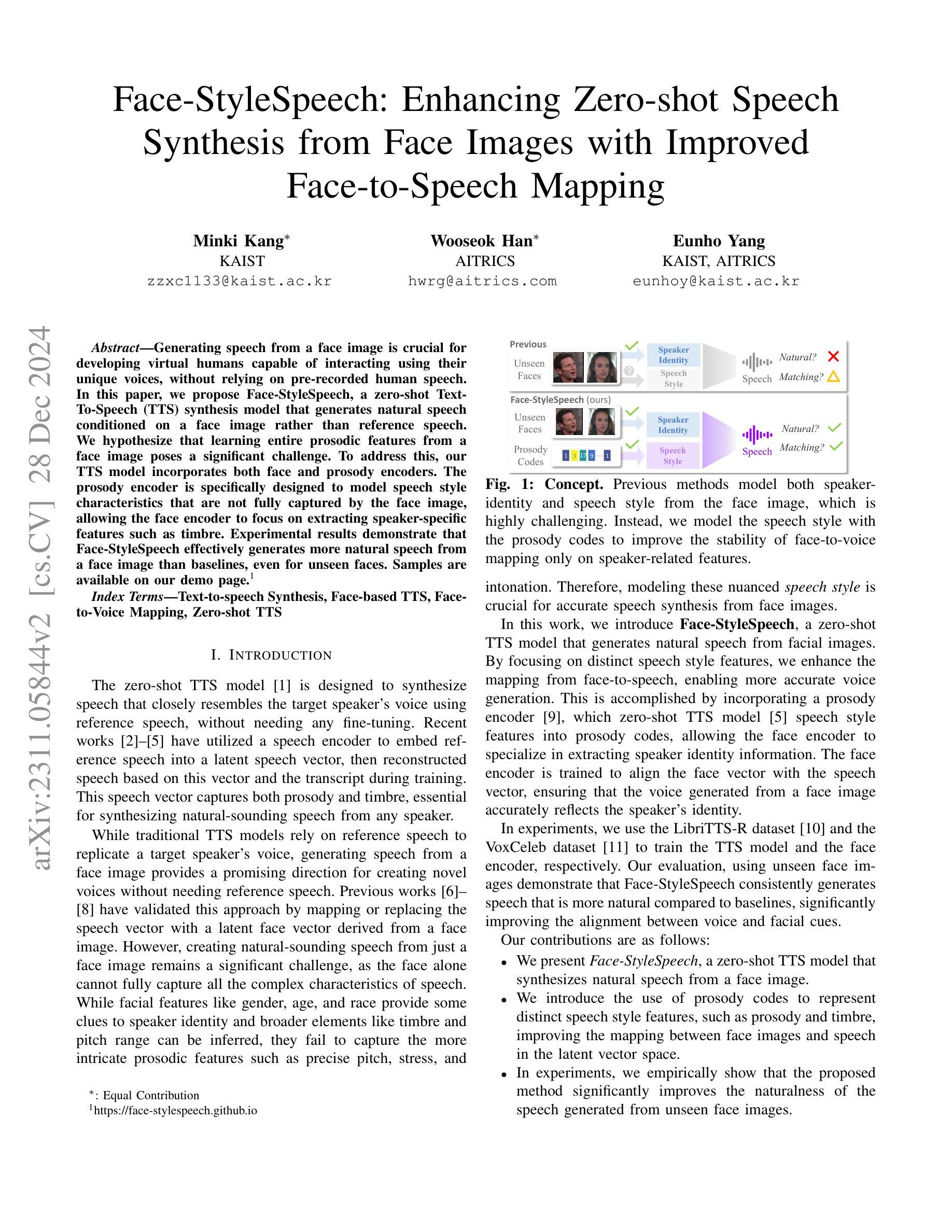
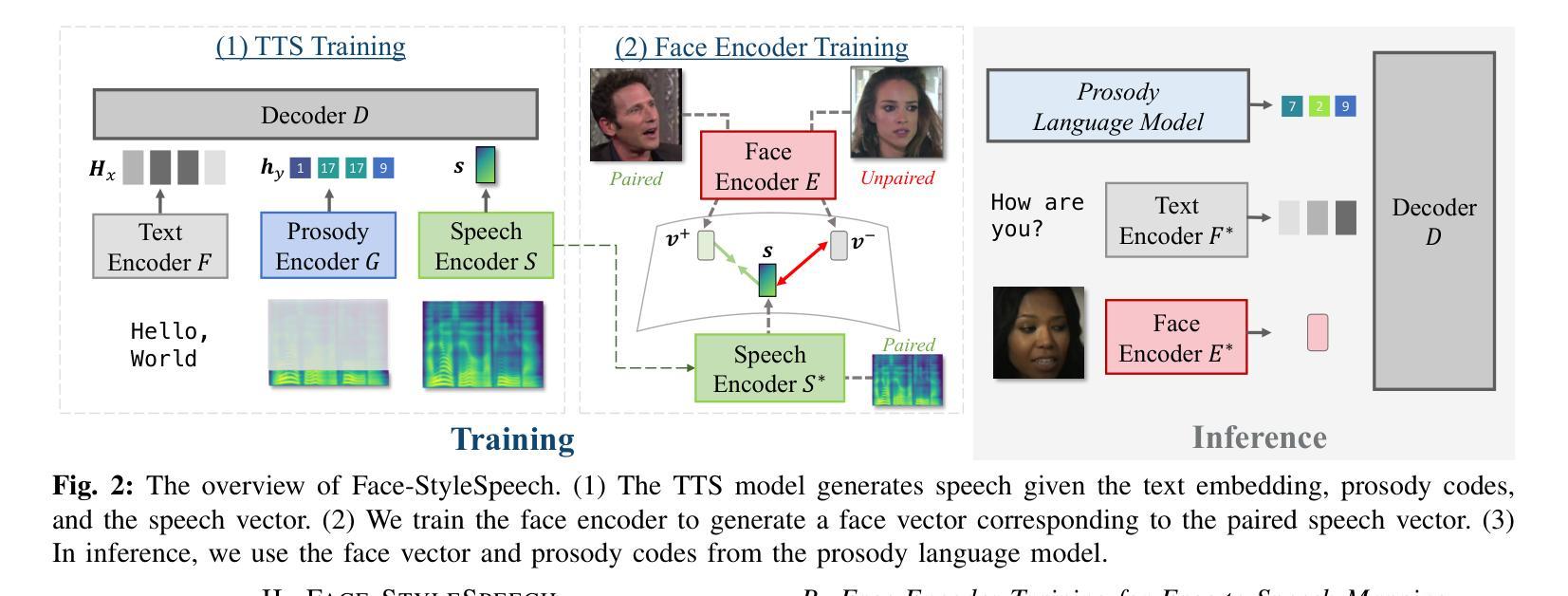
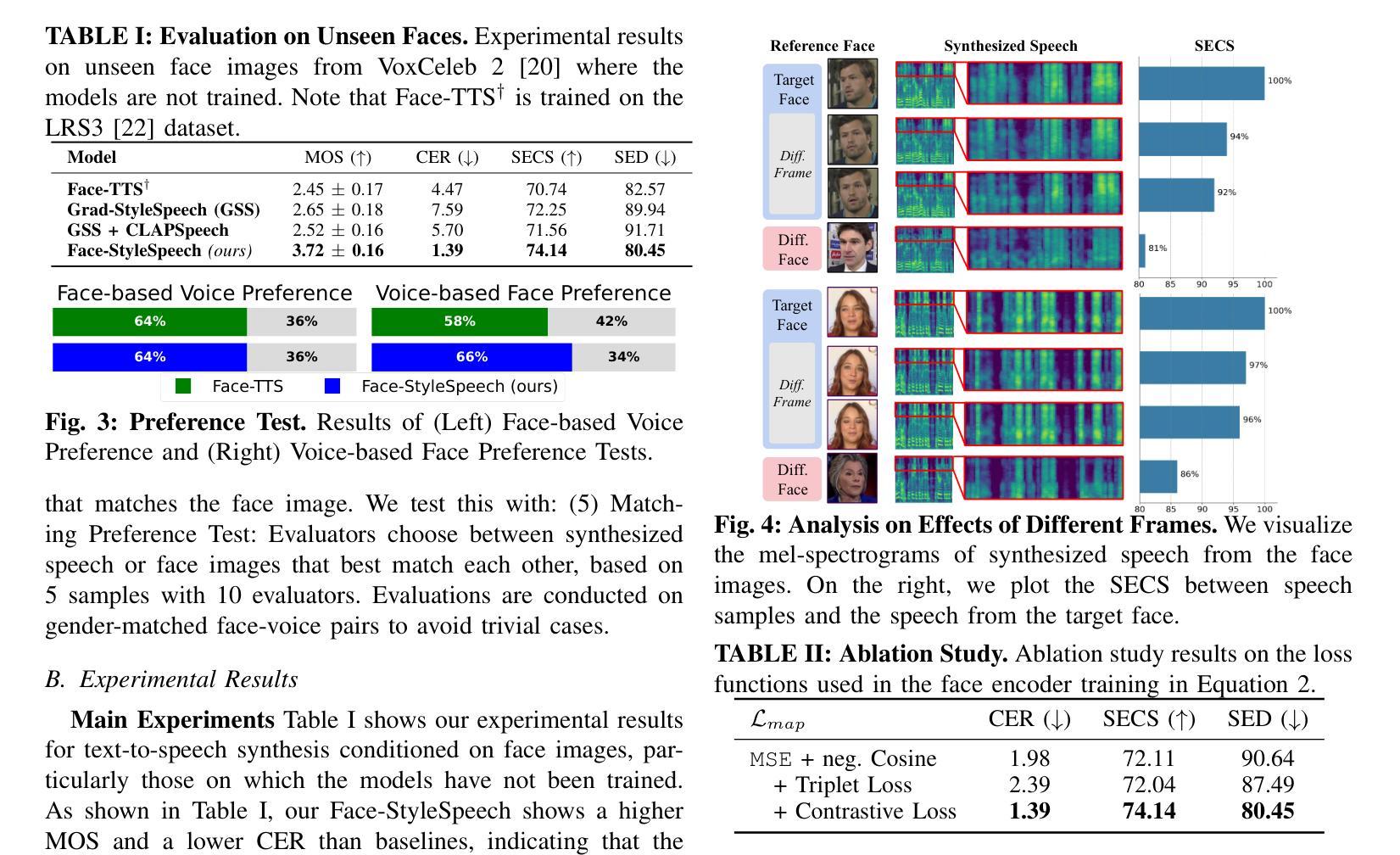
Face-StyleSpeech: Enhancing Zero-shot Speech Synthesis from Face Images with Improved Face-to-Speech Mapping
Authors:Minki Kang, Wooseok Han, Eunho Yang
Generating speech from a face image is crucial for developing virtual humans capable of interacting using their unique voices, without relying on pre-recorded human speech. In this paper, we propose Face-StyleSpeech, a zero-shot Text-To-Speech (TTS) synthesis model that generates natural speech conditioned on a face image rather than reference speech. We hypothesize that learning entire prosodic features from a face image poses a significant challenge. To address this, our TTS model incorporates both face and prosody encoders. The prosody encoder is specifically designed to model speech style characteristics that are not fully captured by the face image, allowing the face encoder to focus on extracting speaker-specific features such as timbre. Experimental results demonstrate that Face-StyleSpeech effectively generates more natural speech from a face image than baselines, even for unseen faces. Samples are available on our demo page.
从面部图像生成语音对于开发能够使用其独特声音进行交互的虚拟人类至关重要,而无需依赖预先录制的人类语音。在本文中,我们提出了Face-StyleSpeech,这是一种零样本文本到语音(TTS)合成模型,它根据面部图像而不是参考语音生成自然语音。我们假设从面部图像学习整个韵律特征是一个巨大的挑战。为解决这一问题,我们的TTS模型结合了面部和韵律编码器。韵律编码器专门用于建模语音风格特征,这些特征不能完全从面部图像中获取,从而允许面部编码器专注于提取发音人特定特征,如音色。实验结果表明,Face-StyleSpeech能够从面部图像生成比基线更自然的语音,即使对于未见过的面孔也是如此。样本可在我们的演示页面上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICASSP 2025
Summary
基于面部图像生成语音对于开发能够使用其独特声音进行交互的虚拟人类至关重要。本文提出Face-StyleSpeech,一种零样本文本到语音(TTS)合成模型,该模型根据面部图像生成自然语音,而非依赖预录制的语音。为应对从面部图像学习整体韵律特征的挑战,我们的TTS模型结合了面部和韵律编码器。韵律编码器专门设计用于模拟面部图像无法完全捕捉的语音风格特征,使得面部编码器能够专注于提取说话人的特征,如音质。实验结果表明,Face-StyleSpeech能够更有效地根据面部图像生成更自然的语音,超越基线模型,甚至对于未见过的面孔也是如此。
Key Takeaways
- Face-StyleSpeech是一种零样本TTS合成模型,能够根据面部图像生成自然语音。
- 模型结合面部和韵律编码器,以应对从面部图像学习韵律特征的挑战。
- 韵律编码器用于模拟面部图像无法完全捕捉的语音风格特征。
- 面部编码器专注于提取说话人的特征,如音质。
- 实验结果显示,Face-StyleSpeech在生成基于面部图像的语音方面表现优越,超越基线模型。
- 该模型生成的语音对于未见过的面孔同样有效。
点此查看论文截图