⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-04 更新
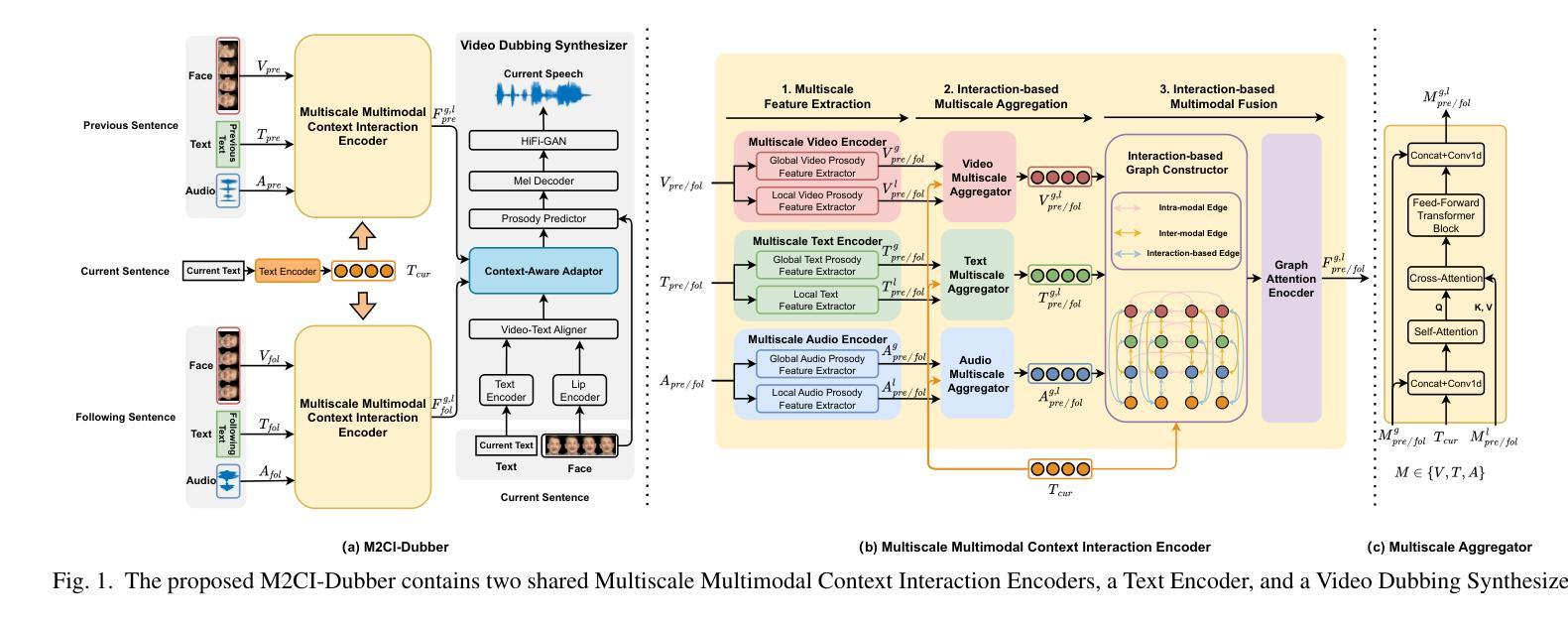
Towards Expressive Video Dubbing with Multiscale Multimodal Context Interaction
Authors:Yuan Zhao, Rui Liu, Gaoxiang Cong
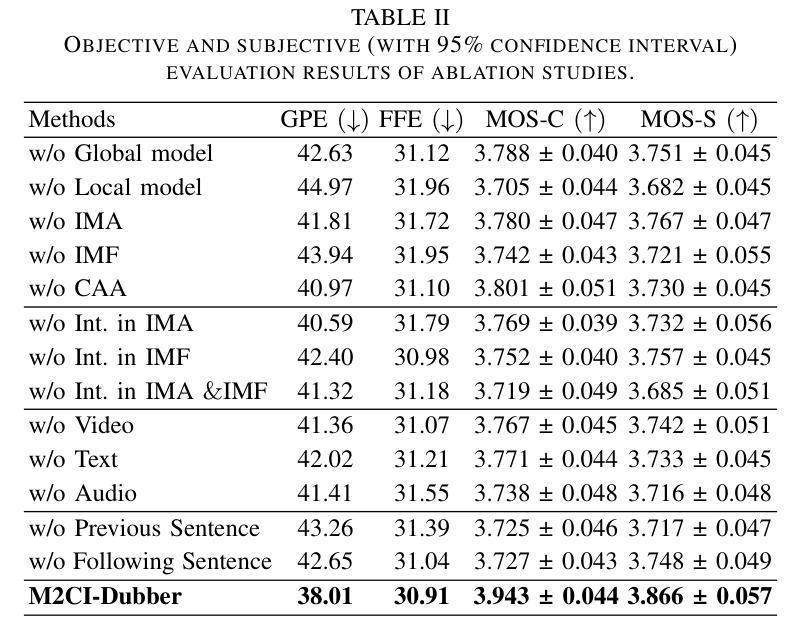
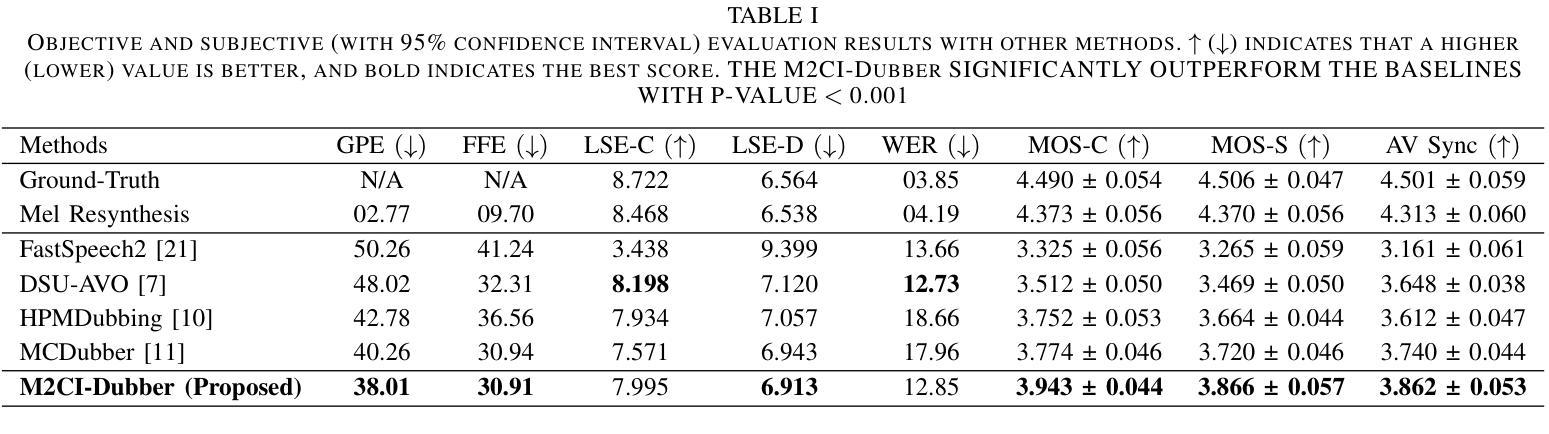
Automatic Video Dubbing (AVD) generates speech aligned with lip motion and facial emotion from scripts. Recent research focuses on modeling multimodal context to enhance prosody expressiveness but overlooks two key issues: 1) Multiscale prosody expression attributes in the context influence the current sentence’s prosody. 2) Prosody cues in context interact with the current sentence, impacting the final prosody expressiveness. To tackle these challenges, we propose M2CI-Dubber, a Multiscale Multimodal Context Interaction scheme for AVD. This scheme includes two shared M2CI encoders to model the multiscale multimodal context and facilitate its deep interaction with the current sentence. By extracting global and local features for each modality in the context, utilizing attention-based mechanisms for aggregation and interaction, and employing an interaction-based graph attention network for fusion, the proposed approach enhances the prosody expressiveness of synthesized speech for the current sentence. Experiments on the Chem dataset show our model outperforms baselines in dubbing expressiveness. The code and demos are available at \textcolor[rgb]{0.93,0.0,0.47}{https://github.com/AI-S2-Lab/M2CI-Dubber}.
自动视频配音(AVD)根据剧本生成与嘴唇动作和面部情绪相匹配的语音。最近的研究主要集中在构建多模态上下文以提高语音的表达能力,但忽略了两个关键问题:1)上下文中的多尺度语音表达属性会影响当前句子的语音。2)上下文中的语音线索与当前句子相互作用,影响最终的语音表达。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了M2CI-Dubber,这是一种用于AVD的多尺度多模态上下文交互方案。该方案包括两个共享的M2CI编码器,用于构建多尺度多模态上下文,并促进其与当前句子的深度交互。通过提取上下文中每种模态的全局和局部特征,利用基于注意力的机制进行聚合和交互,并采用基于交互的图注意力网络进行融合,所提出的方法提高了当前句子合成语音的表达能力。在Chem数据集上的实验表明,我们的模型在配音表现力方面优于基准模型。代码和演示可在https://github.com/AI-S2-Lab/M2CI-Dubber上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICASSP 2025
Summary
自动视频配音(AVD)技术能够根据脚本生成与唇部动作和面部表情对齐的语音。针对当前研究中存在的两个关键问题——多尺度语境表达属性对句子语调的影响以及语境中的语调线索与当前句子的交互作用,提出了M2CI-Dubber方案。该方案包括两个共享M2CI编码器,用于建模多尺度多模态语境,并与当前句子进行深度交互。通过提取语境中每个模态的全局和局部特征,利用基于注意力的机制进行聚合和交互,并采用基于交互的图注意力网络进行融合,提高了合成语音的语调表达力。在Chem数据集上的实验表明,我们的模型在配音表现力方面优于基准模型。
Key Takeaways
- AVD技术能够生成与唇部动作和面部表情对齐的语音。
- 当前AVD研究存在两个关键挑战:多尺度语境表达属性和语境中的语调线索与当前句子的交互影响。
- M2CI-Dubber方案旨在解决这两个挑战,包括建模多尺度多模态语境和与当前句子的深度交互。
- M2CI编码器用于提取语境中的全局和局部特征,每个模态都有涉及。
- 利用基于注意力的机制进行特征聚合和交互。
- 采用基于交互的图注意力网络进行融合,提高合成语音的语调表达力。
点此查看论文截图

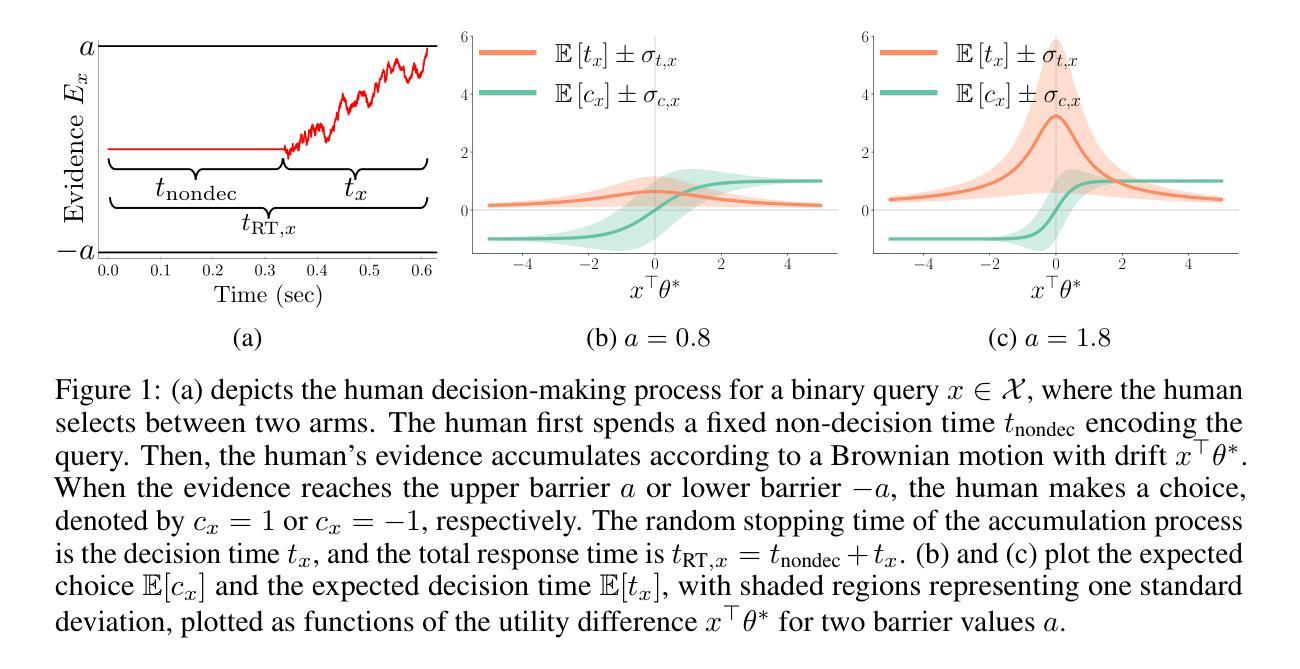
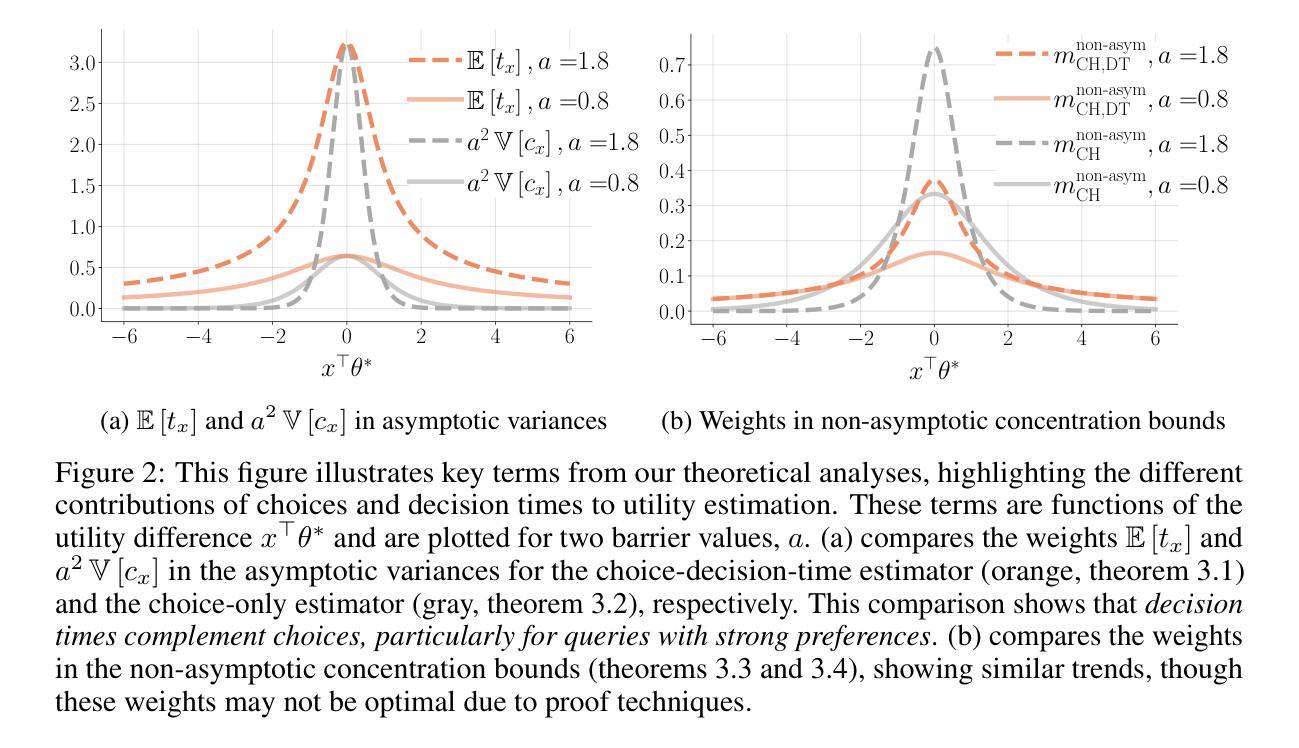
Enhancing Preference-based Linear Bandits via Human Response Time
Authors:Shen Li, Yuyang Zhang, Zhaolin Ren, Claire Liang, Na Li, Julie A. Shah
Interactive preference learning systems infer human preferences by presenting queries as pairs of options and collecting binary choices. Although binary choices are simple and widely used, they provide limited information about preference strength. To address this, we leverage human response times, which are inversely related to preference strength, as an additional signal. We propose a computationally efficient method that combines choices and response times to estimate human utility functions, grounded in the EZ diffusion model from psychology. Theoretical and empirical analyses show that for queries with strong preferences, response times complement choices by providing extra information about preference strength, leading to significantly improved utility estimation. We incorporate this estimator into preference-based linear bandits for fixed-budget best-arm identification. Simulations on three real-world datasets demonstrate that using response times significantly accelerates preference learning compared to choice-only approaches. Additional materials, such as code, slides, and talk video, are available at https://shenlirobot.github.io/pages/NeurIPS24.html
交互式偏好学习系统通过呈现选项对来询问问题并收集二元选择来推断人类偏好。虽然二元选择简单且广泛使用,但它们提供的关于偏好强度的信息有限。为了解决这个问题,我们利用与偏好强度成反比的人类反应时间作为额外的信号。我们提出了一种计算效率高的方法,该方法结合了选择和反应时间来估计人类效用函数,以心理学中的EZ扩散模型为基础。理论和实证分析表明,对于具有强烈偏好的查询,反应时间为选择提供了关于偏好强度的额外信息,从而显著提高了效用估计。我们将此估算器纳入基于偏好的线性bandits中进行固定预算的最佳手臂识别。在三个真实数据集上的模拟表明,与使用反应时间相比,仅使用选择的方法可以大大加速偏好学习。其他材料(如代码、幻灯片、视频等)可在https://shenlirobot.github.io/pages/NeurIPS24.html找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2024 (Oral) camera ready
Summary
基于人类偏好学习系统的研究,本文提出了一个结合选择反应时间和二元选择的方法,用于估计人类效用函数。通过利用人类反应时间与偏好强度之间的逆向关系作为额外的信号,对于偏好强烈的查询,反应时间能够提供更丰富的偏好强度信息,从而显著提高效用估计的准确性。此外,该研究还将此估计器应用于基于偏好的线性强盗模型中进行固定预算的最佳手臂识别任务。模拟实验表明,使用反应时间相较于仅依赖选择的方法能显著加速偏好学习。具体研究内容详见相关网站链接。
Key Takeaways
一、本文提出了一个结合选择反应时间和二元选择的方法,用于提高对人类偏好强度的估计准确性。
二、基于心理学中的EZ扩散模型,构建了人类反应时间与偏好强度之间的关联模型。
三、对于偏好强烈的查询,反应时间能够提供更丰富的偏好强度信息,以弥补二元选择的局限性。
四、该研究将估计器应用于固定预算的最佳手臂识别任务中,属于偏好学习领域的研究。
五、模拟实验显示,利用反应时间的方法在偏好学习上显著优于仅依赖选择的方法。
六、本研究内容还包含实践应用及辅助材料链接等额外信息。
点此查看论文截图