⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-05 更新
RLAIF-V: Open-Source AI Feedback Leads to Super GPT-4V Trustworthiness
Authors:Tianyu Yu, Haoye Zhang, Qiming Li, Qixin Xu, Yuan Yao, Da Chen, Xiaoman Lu, Ganqu Cui, Yunkai Dang, Taiwen He, Xiaocheng Feng, Jun Song, Bo Zheng, Zhiyuan Liu, Tat-Seng Chua, Maosong Sun
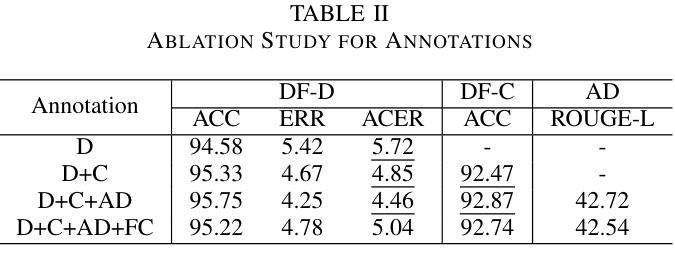
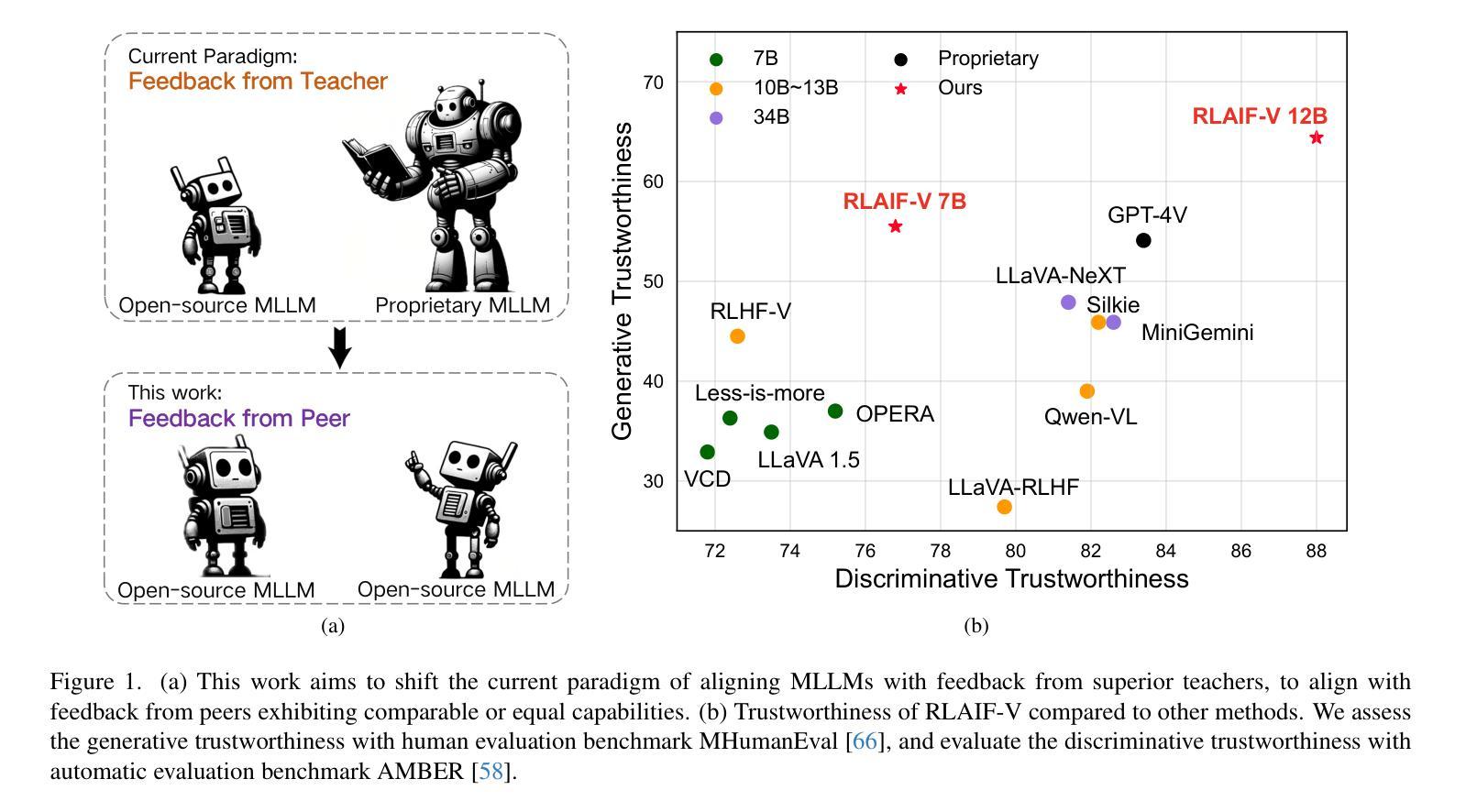
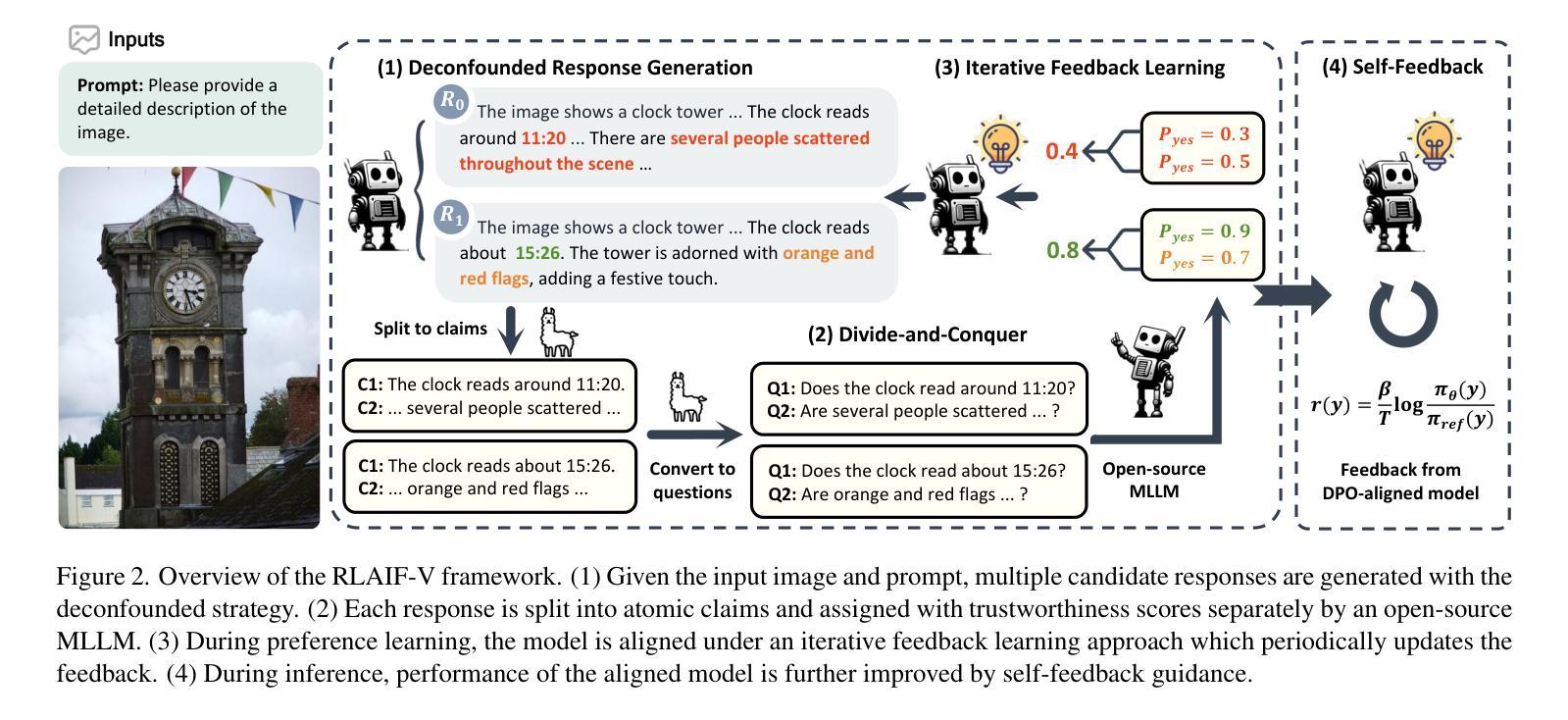
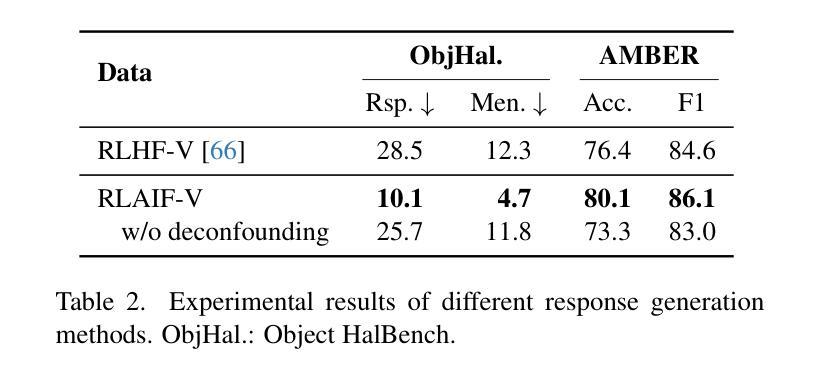
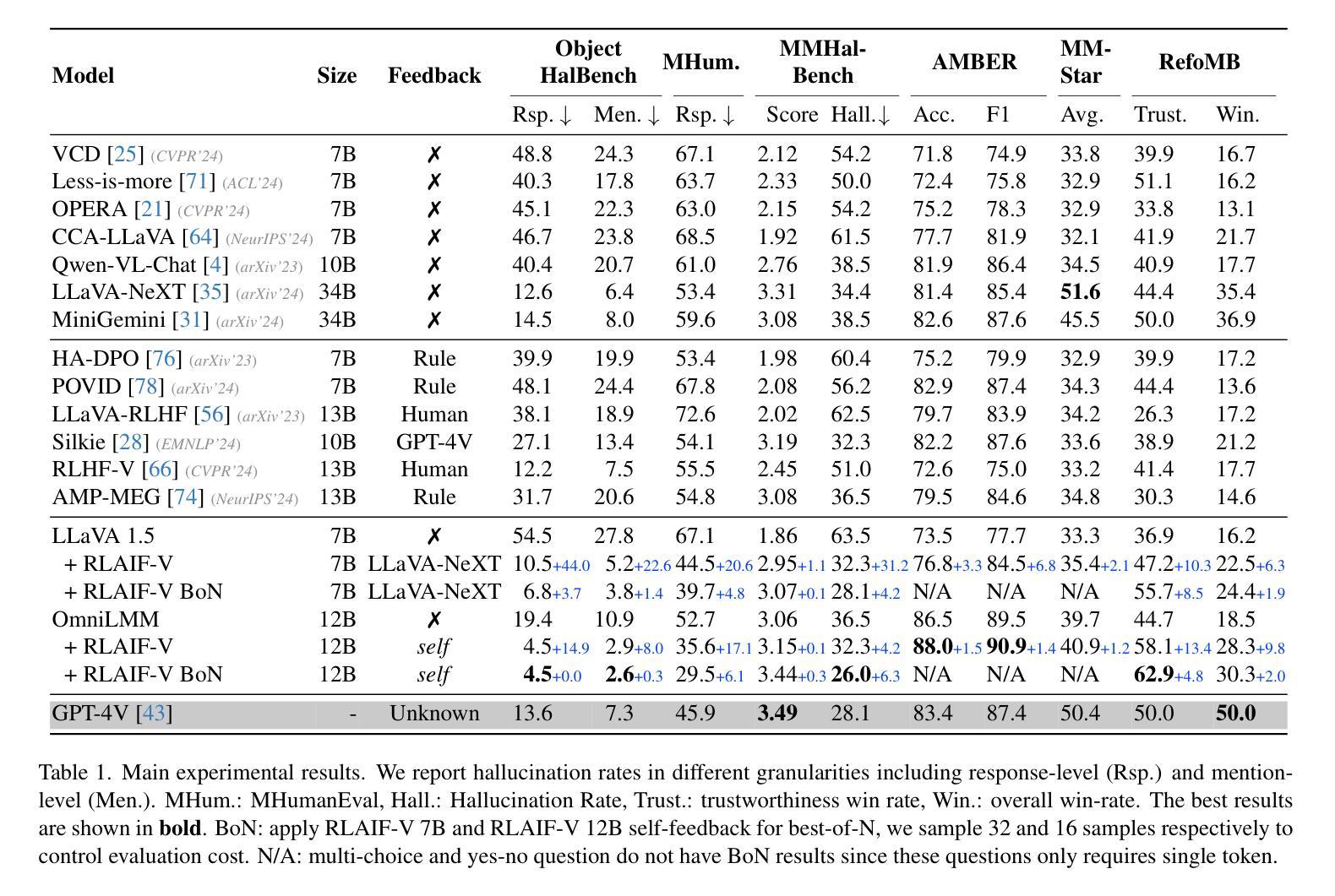
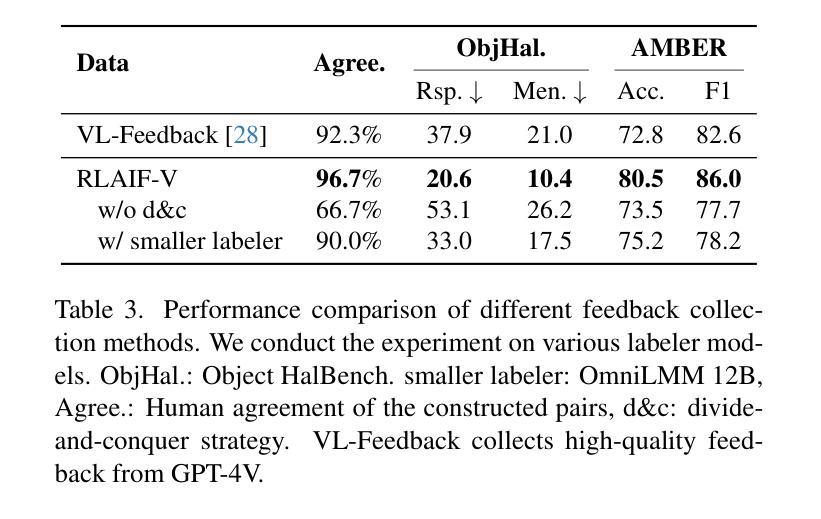
Traditional feedback learning for hallucination reduction relies on labor-intensive manual labeling or expensive proprietary models. This leaves the community without foundational knowledge about how to build high-quality feedback with open-source MLLMs. In this work, we introduce RLAIF-V, a novel framework that aligns MLLMs in a fully open-source paradigm. RLAIF-V maximally explores open-source MLLMs from two perspectives, including high-quality feedback data generation for preference learning and self-feedback guidance for inference-time scaling. Extensive experiments on six benchmarks in both automatic and human evaluation show that RLAIF-V substantially enhances the trustworthiness of models at both preference learning and inference time. RLAIF-V 7B reduces object hallucination by 80.7% and overall hallucination by 33.7%. Remarkably, RLAIF-V 12B further reveals the self-alignment potential of open-source MLLMs, where the model can learn from feedback of itself to achieve super GPT-4V trustworthiness.
传统的反馈学习在减少幻觉方面依赖于劳动密集的手动标注或昂贵的专有模型。这导致社区缺乏关于如何使用开源MLLM构建高质量反馈的基础知识。在这项工作中,我们介绍了RLAIF-V,这是一个全新的框架,它以完全开源的方式对齐MLLM。RLAIF-V从两个角度最大限度地挖掘开源MLLM的潜力,包括用于偏好学习的高质量反馈数据生成和用于推理时间缩放时的自我反馈指导。在六个基准测试上的自动和人类评估实验表明,RLAIF-V在偏好学习和推理时间两个方面都极大地提高了模型的可靠性。RLAIF-V 7B减少了物体幻觉达80.7%,总体幻觉减少了33.7%。值得注意的是,RLAIF-V 12B进一步揭示了开源MLLM的自我对齐潜力,模型可以从其自身的反馈中学习,达到超越GPT-4V的可信度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Website: https://github.com/RLHF-V/RLAIF-V
摘要
本研究介绍了RLAIF-V,一个全新的框架,以全开源的方式对齐大型语言模型(MLLMs)。RLAIF-V从高质量反馈数据生成和自反馈指导两个方面最大限度地探索了开源MLLMs。在自动和人类评估的六个基准测试上的实验表明,RLAIF-V在偏好学习和推理时间方面都大大提高了模型的可靠性。RLAIF-V 7B将物体幻觉减少了80.7%,总体幻觉减少了33.7%。值得注意的是,RLAIF-V 12B进一步揭示了开源MLLMs的自我对齐潜力,模型可以从自身的反馈中学习,以达到超越GPT-4V的可信程度。
关键见解
- RLAIF-V是一个全新的框架,用于在完全开源的情境下对齐大型语言模型(MLLMs)。
- RLAIF-V从高质量反馈数据生成和自反馈指导两个方面探索了开源MLLMs的潜力。
- 在多个基准测试上,RLAIF-V显著提高了模型在偏好学习和推理时间方面的可靠性。
- RLAIF-V 7B版本大幅减少了幻觉现象。
- RLAIF-V 12B版本展示了模型从自身反馈中学习的能力,达到超卓的可信程度。
- 该研究证明了开源MLLMs的巨大潜力,特别是在自我对齐和反馈学习方面。
- RLAIF-V框架为构建高质量反馈的开源MLLMs提供了新的方向。
点此查看论文截图

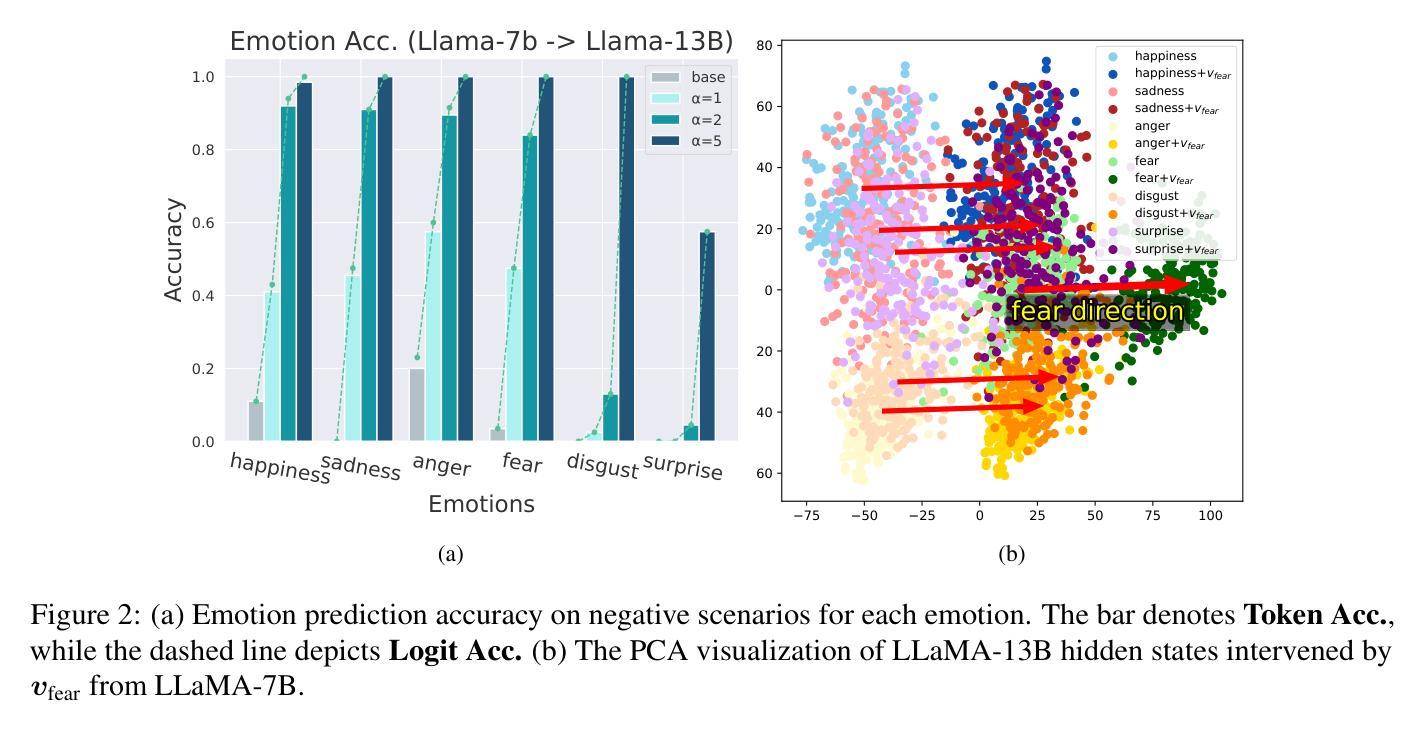
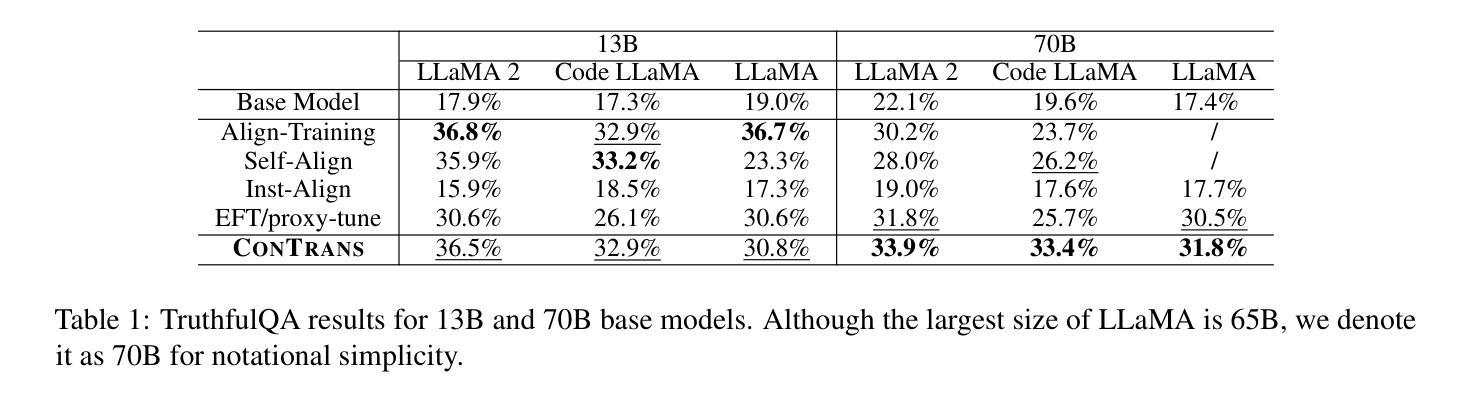
ConTrans: Weak-to-Strong Alignment Engineering via Concept Transplantation
Authors:Weilong Dong, Xinwei Wu, Renren Jin, Shaoyang Xu, Deyi Xiong
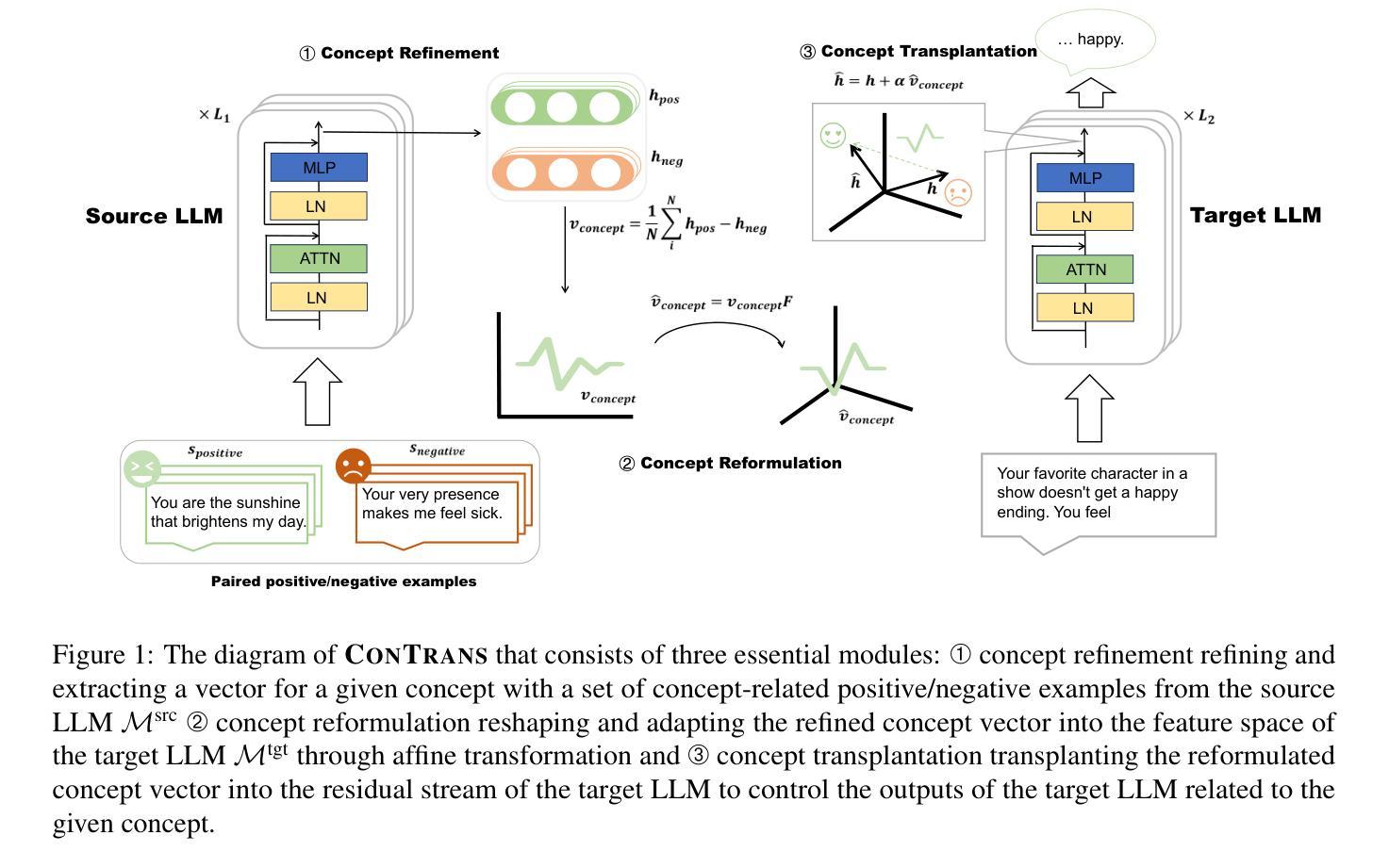
Ensuring large language models (LLM) behave consistently with human goals, values, and intentions is crucial for their safety but yet computationally expensive. To reduce the computational cost of alignment training of LLMs, especially for those with a huge number of parameters, and to reutilize learned value alignment, we propose ConTrans, a novel framework that enables weak-to-strong alignment transfer via concept transplantation. From the perspective of representation engineering, ConTrans refines concept vectors in value alignment from a source LLM (usually a weak yet aligned LLM). The refined concept vectors are then reformulated to adapt to the target LLM (usually a strong yet unaligned base LLM) via affine transformation. In the third step, ConTrans transplants the reformulated concept vectors into the residual stream of the target LLM. Experiments demonstrate the successful transplantation of a wide range of aligned concepts from 7B models to 13B and 70B models across multiple LLMs and LLM families. Remarkably, ConTrans even surpasses instruction-tuned models in terms of truthfulness. Experiment results validate the effectiveness of both inter-LLM-family and intra-LLM-family concept transplantation. Our work successfully demonstrates an alternative way to achieve weak-to-strong alignment generalization and control.
确保大型语言模型(LLM)与人类目标、价值观和意图保持一致至关重要,这对于其安全性至关重要,但计算上却很昂贵。为了降低LLM对齐训练的计算成本,特别是对于那些具有大量参数的LLM,并为了重新利用学习到的价值对齐,我们提出了ConTrans这一新型框架,它能够通过概念移植实现弱到强的对齐转移。从表示工程的角度来看,ConTrans通过细化价值对齐中的概念向量来改进源LLM(通常是一个弱小但对齐的LLM)。然后,经过细化的概念向量通过仿射变换被重新制定以适应目标LLM(通常是一个强大但未对齐的基础LLM)。第三步中,ConTrans将重新制定的概念向量移植到目标LLM的残差流中。实验表明,从多个LLM和LLM家族中的7B模型成功移植了多种对齐的概念到更大的模型(如使用与弱对齐LLM一致的道德价值观的概念)到更大的模型(如使用与弱对齐LLM一致的道德价值观的概念)到更大的模型(如13B和70B模型)。值得注意的是,ConTrans甚至超越了指令优化模型的真实性水平。实验结果验证了跨家族内跨家族内概念移植的有效性。我们的工作成功地证明了实现弱到强对齐泛化和控制的另一种可能途径。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)与人类目标、价值观和意图的一致性对其安全性至关重要,但计算成本高昂。为此,我们提出ConTrans框架,通过概念移植实现弱到强的对齐转移,降低LLM对齐训练的计算成本并复用已学习的价值对齐。ConTrans从表示工程的角度出发,精炼源LLM(通常是弱但对齐的LLM)中的概念向量,然后通过仿射变换适应目标LLM(通常是强但未对齐的基础LLM)。最后,将改革后的概念向量移植到目标LLM的残差流中。实验证明,从7B模型到13B和70B模型的广泛对齐概念移植成功,且在多个LLM和LLM家族中,ConTrans甚至超越了指令微调模型的真实性。
Key Takeaways
- ConTrans框架旨在降低LLM对齐训练的计算成本并复用已学习的价值对齐。
- 通过概念移植实现弱到强的对齐转移。
- ConTrans从表示工程的角度出发,精炼源LLM中的概念向量,并适应目标LLM。
- 改革后的概念向量被移植到目标LLM的残差流中。
- 实验证明概念移植的成功,并展示了ConTrans在多个LLM和LLM家族中的有效性。
- ConTrans甚至在某些方面超越了指令微调模型的真实性。
点此查看论文截图

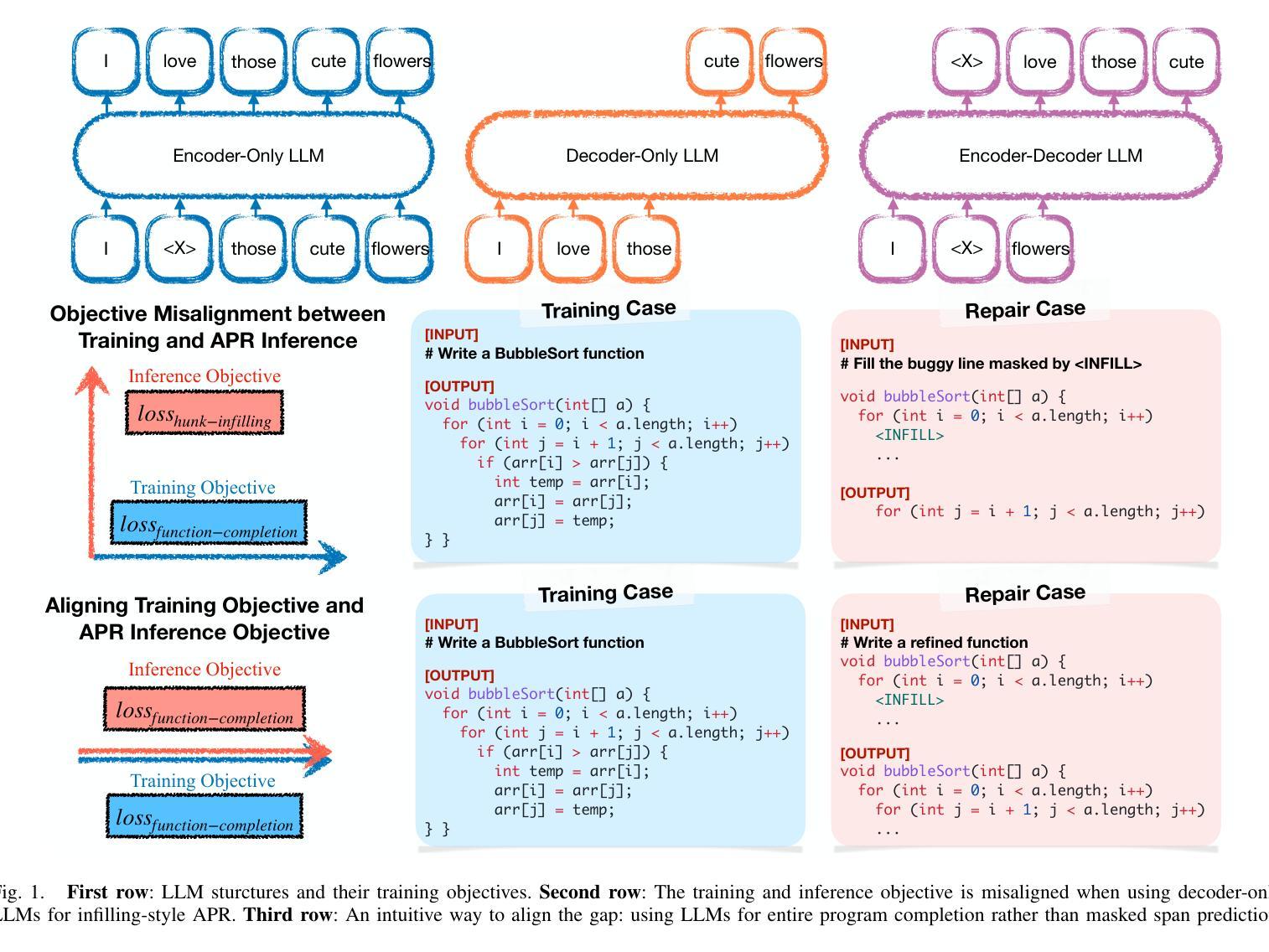
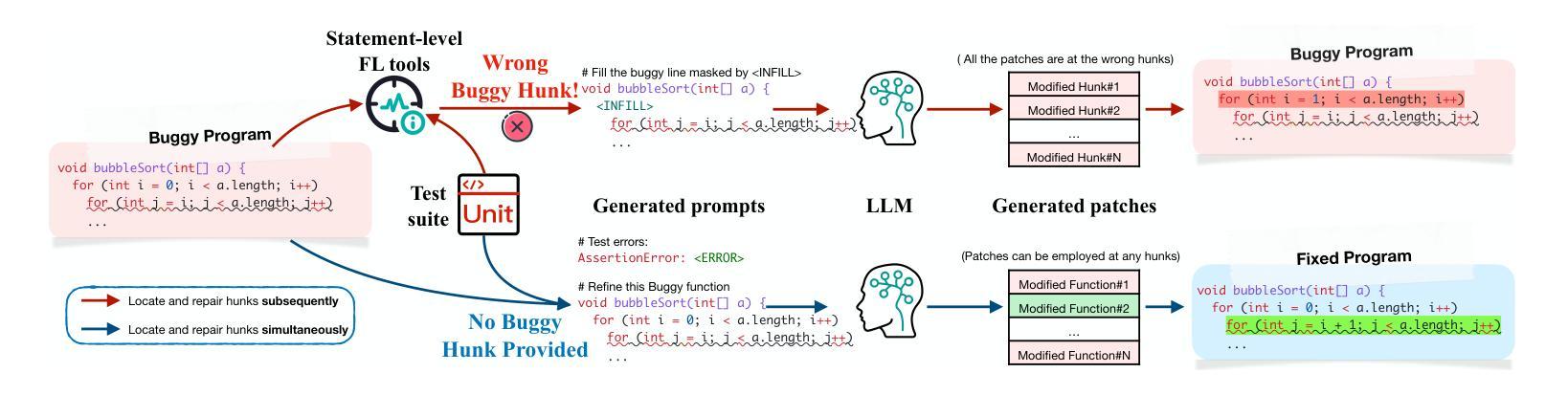
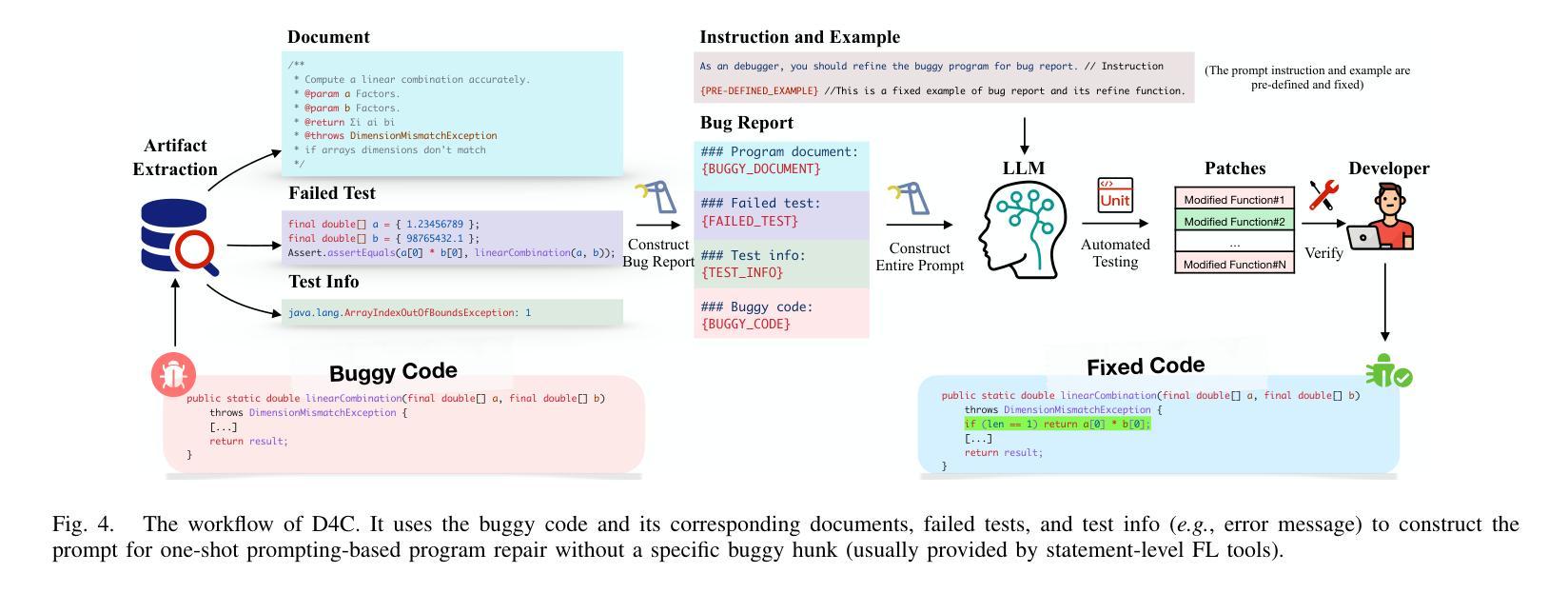
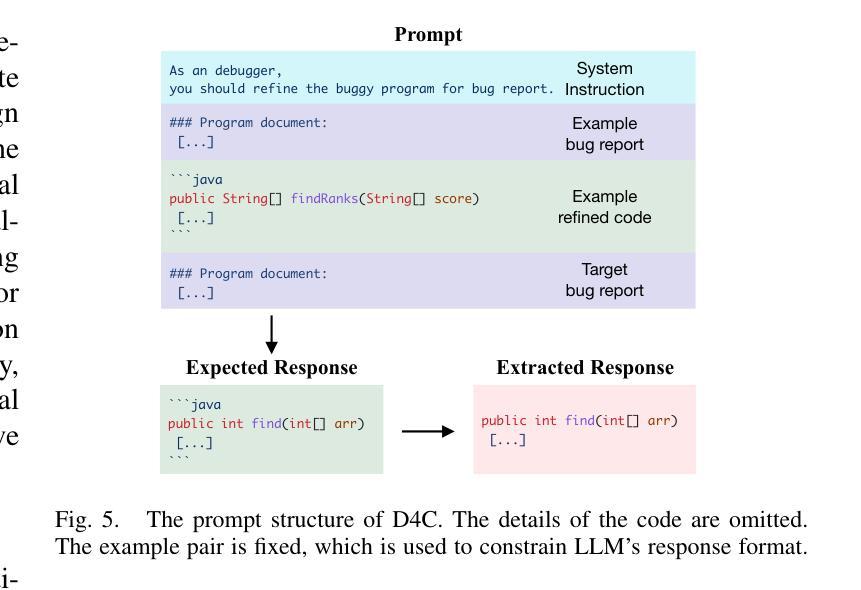
Aligning the Objective of LLM-based Program Repair
Authors:Junjielong Xu, Ying Fu, Shin Hwei Tan, Pinjia He
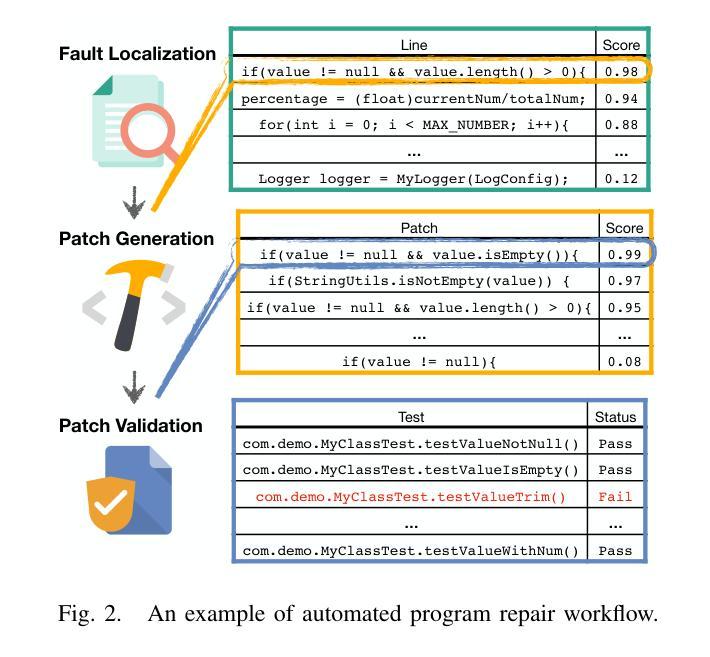
Large language models (LLMs) have achieved decent results on automated program repair (APR). However, the next token prediction training objective of decoder-only LLMs (e.g., GPT-4) is misaligned with the masked span prediction objective of current infilling-style methods, which impedes LLMs from fully leveraging pre-trained knowledge for program repair. In addition, while some LLMs can locate and repair bugs in certain functions using the related artifacts (e.g., test cases), existing methods still depend on statement-level fault localization methods to provide a list of buggy hunks for repair. This restriction hinders LLMs from exploring potential patches beyond the given locations. In this paper, we investigate a new approach to adapt LLMs to program repair. Our core insight is that LLM’s APR capability can be greatly improved by simply aligning the output to their training objective and allowing them to refine the whole program without first identifying faulty statements. Based on this insight, we designed D4C, a straightforward prompting framework for APR. D4C can repair 180 bugs correctly in Defects4J, with each patch being sampled only 10 times. This surpasses the SOTA APR methods with perfect fault localization by 10% and reduces the patch sampling number by 90%. Our findings reveal that (1) objective alignment is crucial for fully exploiting LLM’s pre-trained capability, and (2) replacing the traditional localize-buggy-hunks-then-repair workflow with direct debugging is more effective for LLM-based APR methods. Thus, we believe this paper introduces a new mindset for harnessing LLMs in APR.
大型语言模型(LLM)在自动化程序修复(APR)方面取得了不错的效果。然而,解码器仅针对下一个令牌预测的训练目标(例如GPT-4)与当前填充式方法的掩码跨度预测目标之间存在不匹配,这阻碍了LLM充分利用预训练知识进行程序修复。另外,虽然一些LLM能够利用相关工件(如测试用例)定位和修复某些函数中的错误,但现有方法仍然依赖于语句级故障定位方法来提供修复错误代码块列表。这种限制阻碍了LLM探索给定位置以外的潜在补丁。在本文中,我们研究了一种适应LLM进行程序修复的新方法。我们的核心见解是,通过简单对齐输出并允许它们在没有首先确定错误语句的情况下完善整个程序,可以大大提高LLM的APR能力。基于此见解,我们设计了D4C,一个用于APR的直接提示框架。D4C能够在Defects4J中正确修复180个错误,每个补丁只需采样10次。这超越了具有完美故障定位的SOTA APR方法,提高了10%,并将补丁采样数量减少了90%。我们的研究结果表明:(1)目标对齐对于充分利用LLM的预训练能力至关重要;(2)用直接调试替换传统的定位错误代码块然后进行修复的工作流程对于基于LLM的APR方法更为有效。因此,我们相信本文为在APR中利用LLM引入了一种新的思维方式。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICSE’25
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在自动化程序修复(APR)方面表现良好,但其在训练目标和修复流程上仍有待改进。本研究通过调整输出以符合训练目标并允许直接修复整个程序,提出了一种新的LLM适应APR的方法。设计了一种名为D4C的简洁提示框架,能在Defects4J中修复180个错误,减少了补丁采样次数。这表明目标对齐对充分利用LLM的预训练能力至关重要,并且直接在无需定位错误语句的情况下进行调试更为有效。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在APR方面已展现良好性能,但在训练目标和修复流程上存在潜在改进空间。
- 训练目标对齐对于提升LLM在APR中的表现至关重要。
- 传统先定位错误再修复的工作流程对于LLM-based的APR方法可能不够有效。
- 直接修复整个程序的策略相较于传统的局部修复方法更为高效。
- 新提出的D4C框架能成功修复更多错误,并减少补丁采样次数。
- LLM的潜力在于其能够利用预训练知识,通过调整输出和目标对齐进一步提升性能。
点此查看论文截图

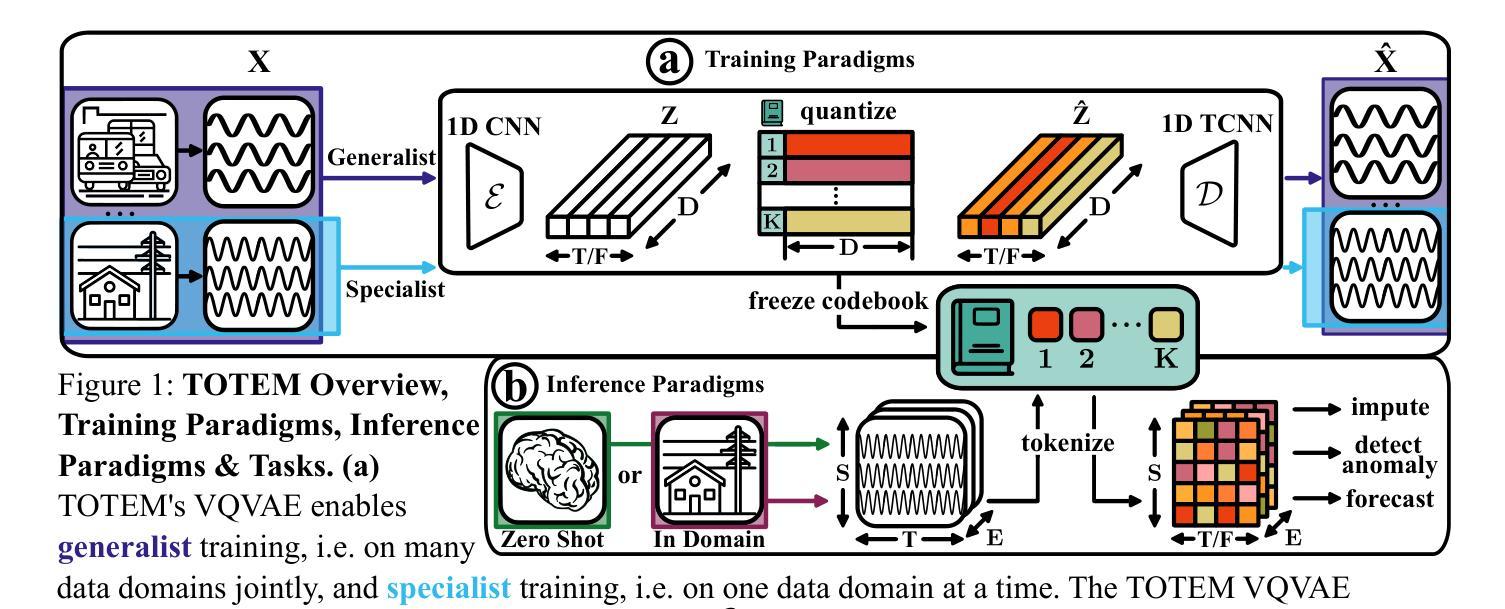
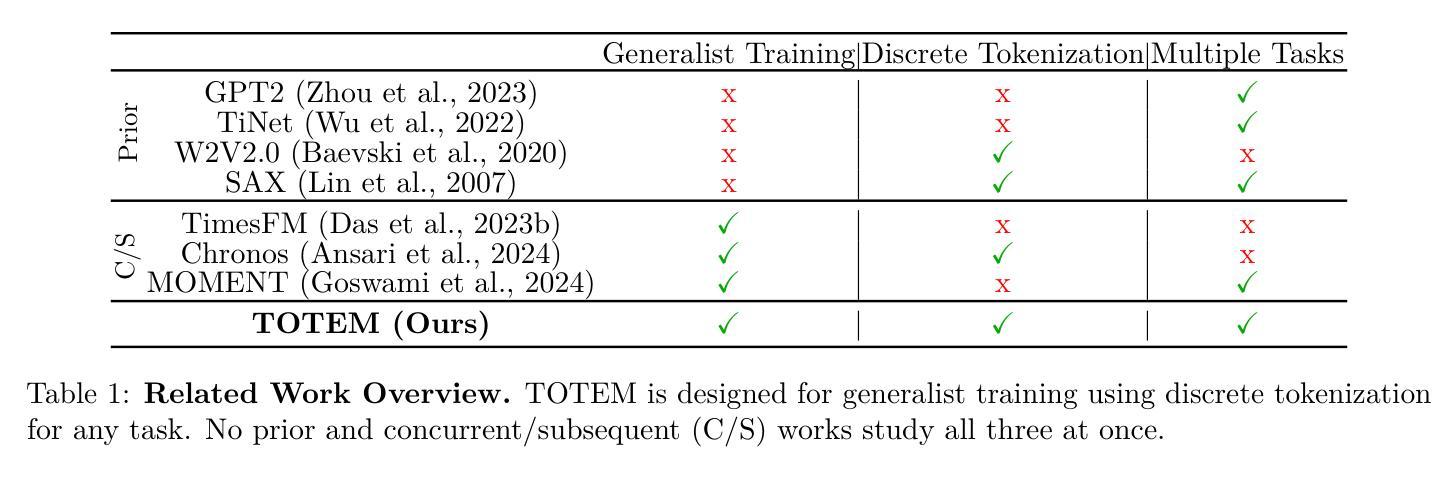
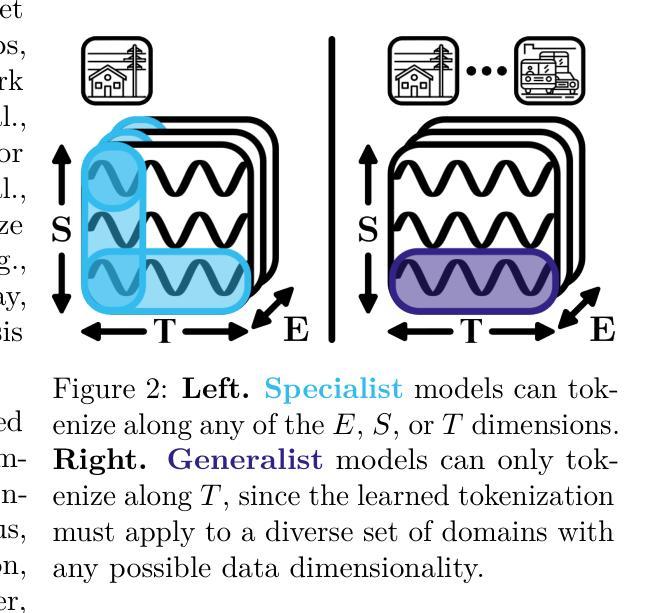
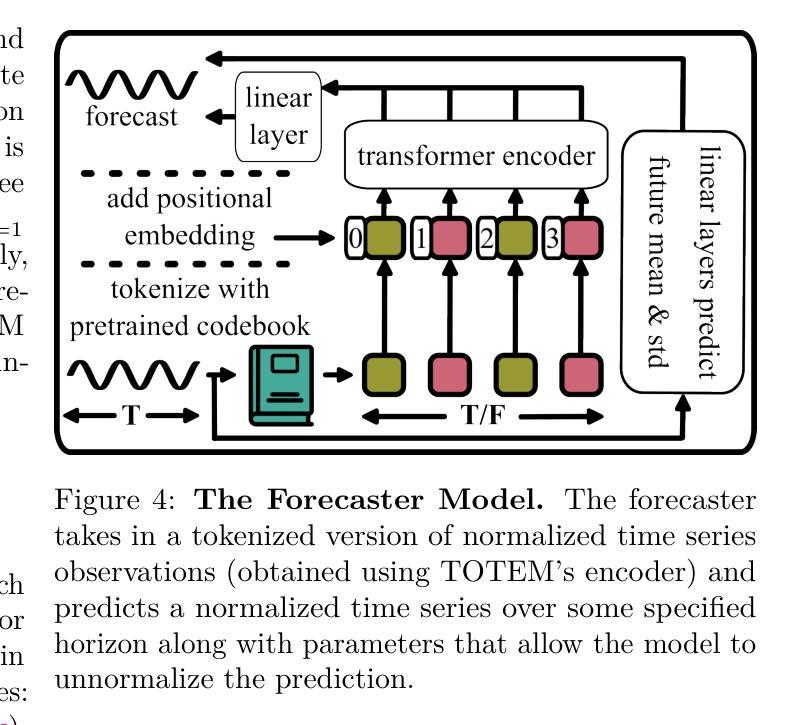
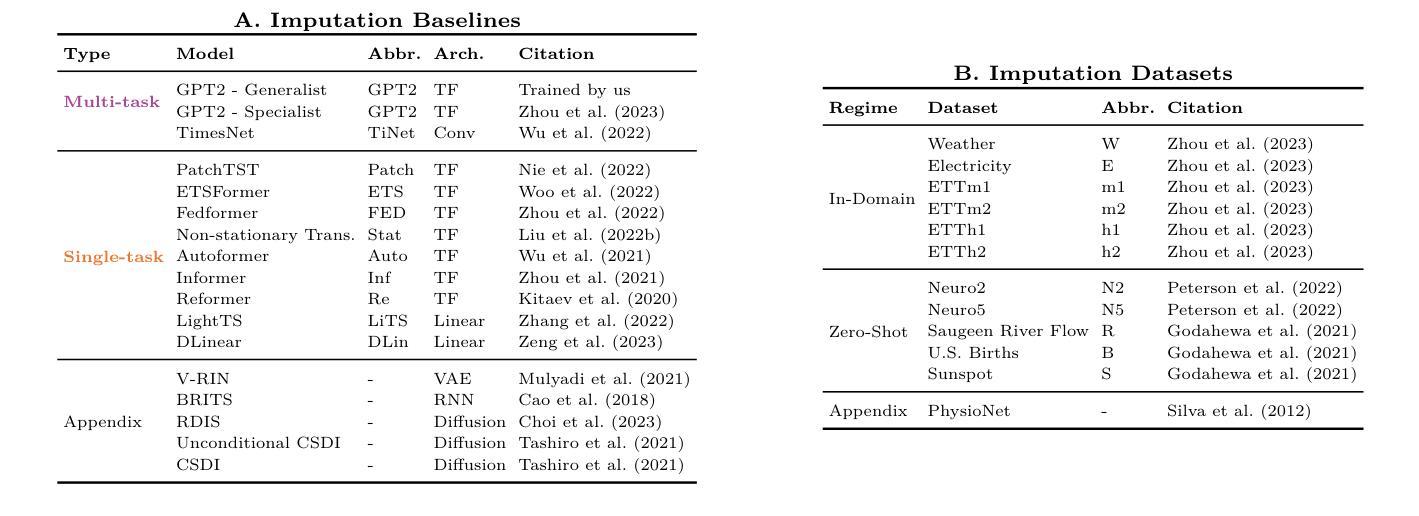
TOTEM: TOkenized Time Series EMbeddings for General Time Series Analysis
Authors:Sabera Talukder, Yisong Yue, Georgia Gkioxari
This work studies the problem of time series analysis with generalist (or foundation) models, which are models trained across many data domains. Drawing inspiration from the widespread success of large language models, we consider the simple strategy of discretely tokenizing time series data drawn from a myriad of datasets via self-supervision, then using the fixed tokenization to solve a variety of tasks across many data domains. Canonically, time series models are either trained on a single dataset or built in a task-specific manner (e.g., a forecasting-only model), where many use patches of time as inputs to the model. As such, performant generalist, discrete representation time series models explored across many tasks are of value. Our method, TOkenized Time Series EMbeddings (TOTEM), produces such generalist time series models with minimal or no fine-tuning while exhibiting strong zero-shot performance. We evaluate TOTEM extensively over nearly 500 experiments on three commonly-studied time series tasks with real-world data: imputation (17 baselines, 12 datasets), anomaly detection (19 baselines, 25 datasets), and forecasting (14 baselines, 12 datasets). We conclude that TOTEM matches or outperforms existing state-of-the-art models in both the canonical specialist setting (i.e., training one model on one domain) as well as the generalist setting (i.e., training a single model on many domains), which demonstrates the efficacy of tokenization for general time series analysis. The open-source implementation is available here: https://github.com/SaberaTalukder/TOTEM; a video summary is available here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OqrCpdb6MJk.
本文研究了使用时间序列分析通才(或基础)模型的问题,这些模型是在多个数据领域进行训练的。从大型语言模型的广泛成功中汲取灵感,我们考虑了一种简单策略,即通过自监督,从众多数据集中离散地标记时间序列数据,然后使用固定的标记法解决多个数据领域的各种任务。通常情况下,时间序列模型是在单个数据集上进行训练或以特定任务的方式构建(例如,仅用于预测的模型),其中许多人使用时间段作为模型的输入。因此,能够在多个任务上探索高性能的通才、离散表示时间序列模型是非常有价值的。我们的方法,即令牌化时间序列嵌入(TOTEM),能够产生这种通才时间序列模型,在几乎不需要微调的情况下表现出强大的零样本性能。我们在三个常见的时间序列任务上进行了近500次实验,对TOTEM进行了广泛评估,这些任务使用真实世界数据:填补(17个基准测试,12个数据集)、异常检测(19个基准测试,25个数据集)和预测(14个基准测试,12个数据集)。我们得出结论,无论是在专业设定(即在一个领域上训练一个模型)还是在通才设定(即在多个领域上训练一个模型)中,TOTEM都能与现有的最先进的模型相匹配或超越,这证明了令牌化对于一般时间序列分析的有效性。开源实现可在此处找到:https://github.com/SaberaTalukder/TOTEM;视频摘要可在此处观看:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OqrCpdb6MJk。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to TMLR (12/24), 33 pages. TMLR link: https://openreview.net/pdf?id=QlTLkH6xRC
Summary
本文研究了基于通用模型(或基础模型)的时间序列分析,这些模型在多个数据域上进行训练。文章受到大型语言模型广泛成功的启发,提出了一种简单策略,即离散地将来自多个数据集的时间序列数据进行自监督处理,然后使用固定的离散化数据解决多个数据域的各种任务。文章指出,典型的时间序列模型是在单一数据集上训练或在特定任务上构建(例如仅用于预测的模型),使用时间片段作为模型的输入。因此,研究能够跨多个任务表现优异的一般性离散表示时间序列模型具有重要意义。文章提出的TOTEM方法(Tokenized Time Series EMbeddings)即生成这样的通用时间序列模型,无需精细调整,并具有出色的零样本性能。在接近500个实验的大规模评估中,TOTEM在三个常见时间序列任务上的真实世界数据集中表现出色,匹配或超越了现有最先进的模型。无论是在特定领域的训练环境还是在多个域的通用环境设置下均展现良好性能,这证明了令牌化对于通用时间序列分析的有效性。论文还提供了开源实现和视频摘要链接。
Key Takeaways
- 文章研究了基于通用模型的时间序列分析策略,通过离散化的自监督处理解决多个数据域的任务。
- TOTEM方法是一种生成通用时间序列模型的方法,无需精细调整,并具有出色的零样本性能。
- TOTEM在三个常见时间序列任务(填补空缺、异常检测、预测)的广泛实验评估中表现出色。
- TOTEM在多个数据集上的表现匹配或超越了现有的先进模型。
- 文章强调了离散化的时间序列分析策略对于跨多个任务的通用性表现的重要性。
- 文章提供了开源实现和视频摘要链接供读者参考和进一步了解。
点此查看论文截图

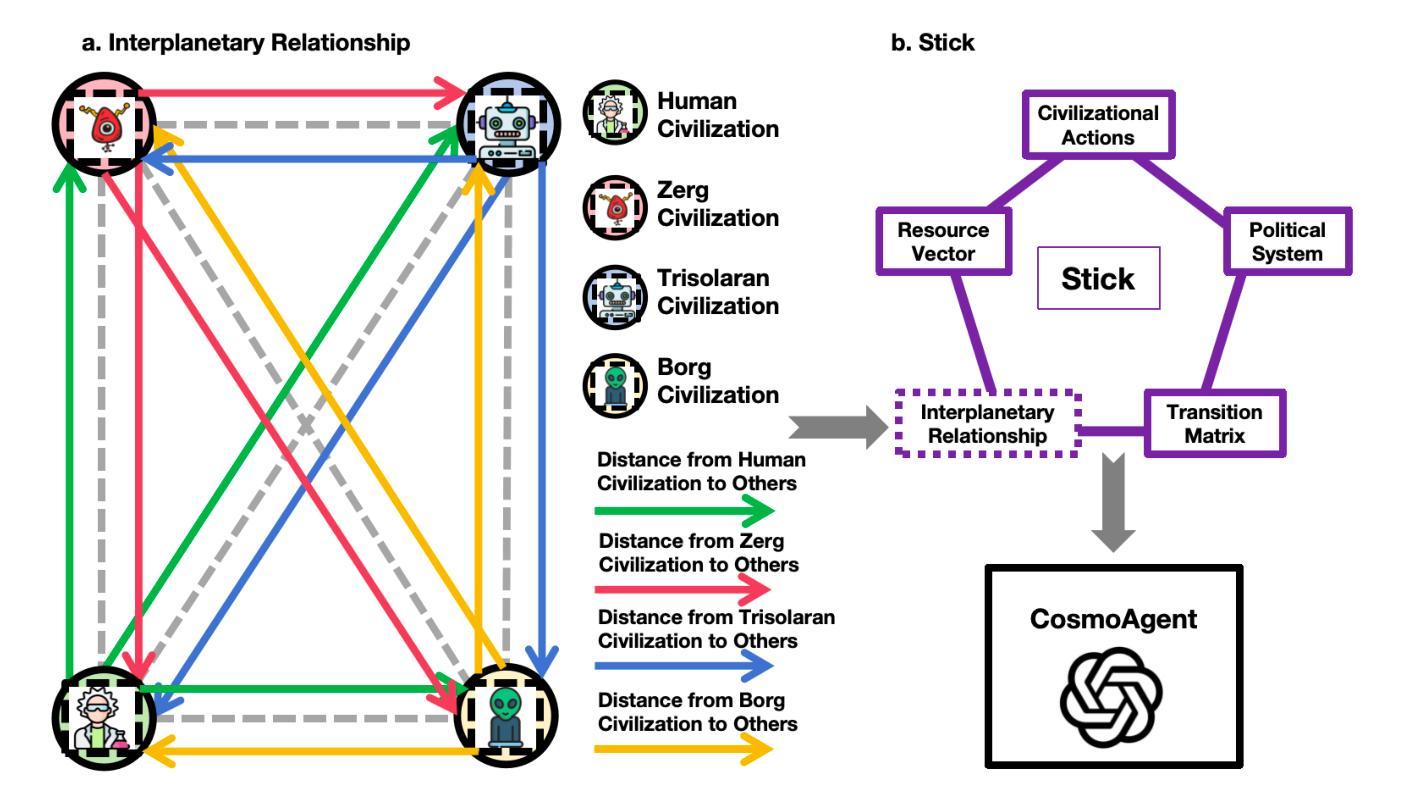
What if LLMs Have Different World Views: Simulating Alien Civilizations with LLM-based Agents
Authors:Zhaoqian Xue, Mingyu Jin, Beichen Wang, Suiyuan Zhu, Kai Mei, Hua Tang, Wenyue Hua, Mengnan Du, Yongfeng Zhang
This study introduces “CosmoAgent,” an innovative artificial intelligence system that utilizes Large Language Models (LLMs) to simulate complex interactions between human and extraterrestrial civilizations. This paper introduces a mathematical model for quantifying the levels of civilization development and further employs a state transition matrix approach to evaluate their trajectories. Through this methodology, our study quantitatively analyzes the growth trajectories of civilizations, providing insights into future decision-making at critical points of growth and saturation. Furthermore, this paper acknowledges the vast diversity of potential living conditions across the universe, which could foster unique cosmologies, ethical codes, and worldviews among different civilizations. Recognizing the Earth-centric bias inherent in current LLM designs, we propose the novel concept of using LLM agents with diverse ethical paradigms and simulating interactions between entities with distinct moral principles. This innovative research not only introduces a novel method for comprehending potential inter-civilizational dynamics but also holds practical value in enabling entities with divergent value systems to strategize, prevent conflicts, and engage in games under conditions of asymmetric information. The accompanying code is available at https://github.com/MingyuJ666/Simulating-Alien-Civilizations-with-LLM-based-Agents.
本研究介绍了“CosmoAgent”,这是一个创新的人工智能系统,利用大型语言模型(LLM)模拟人类与外星文明之间的复杂交互。本文介绍了一个量化文明发展水平数学模型,并进一步采用状态转移矩阵方法评估其轨迹。通过这种方法,我们的研究定量分析了文明的成长轨迹,为未来在增长和饱和的关键点上提供决策依据。此外,本文承认宇宙中潜在生存条件的巨大多样性,这可能会催生独特的宇宙观、道德准则和世界观在不同的文明之间。鉴于当前LLM设计所固有的以地球为中心的偏见,我们提出了使用具有不同道德规范的LLM代理人的新概念,并模拟不同道德原则实体之间的交互。这项创新的研究不仅引入了一种理解潜在文明间动态的新方法,而且在实体中实现了不同价值体系下的策略制定、冲突预防以及在不对称信息条件下的游戏等实际应用价值。相应的代码可通过访问链接获得:https://github.com/MingyuJ66HSSimulating-Alien-Civilizations-with-LLM-based-Agents。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:本研究介绍了一种名为“CosmoAgent”的创新人工智能系统,该系统利用大型语言模型(LLM)模拟人类与外星文明之间的复杂交互。研究提出了一种量化文明发展水平的方法论,并采用状态转移矩阵方法评估文明的发展轨迹。此外,该研究还考虑了宇宙中可能存在的多种多样的生存条件,可能促进形成不同的宇宙观、道德规范和世界观。因此,在利用LLM代理进行模拟时,考虑到了具有不同道德原则实体的交互情况。本研究不仅为理解潜在的文明间动态提供了新的方法,还具有实用价值,使得具有不同价值体系的实体能够在信息不对称的条件下进行策略制定、冲突预防和游戏互动。
Key Takeaways:
- “CosmoAgent”是一个利用大型语言模型模拟人类与外星文明交互的人工智能系统。
- 研究提出了量化文明发展水平的数学模型,并评估其发展轨迹。
- 宇宙中存在多样的生存条件,可能催生不同的宇宙观和道德规范。
- LLM代理在模拟中考虑了具有不同道德原则实体的交互情况。
- 该研究为理解潜在文明间动态提供了新的方法。
- 研究成果具有实用价值,有助于实体在信息不对称条件下进行策略制定和冲突预防。
点此查看论文截图


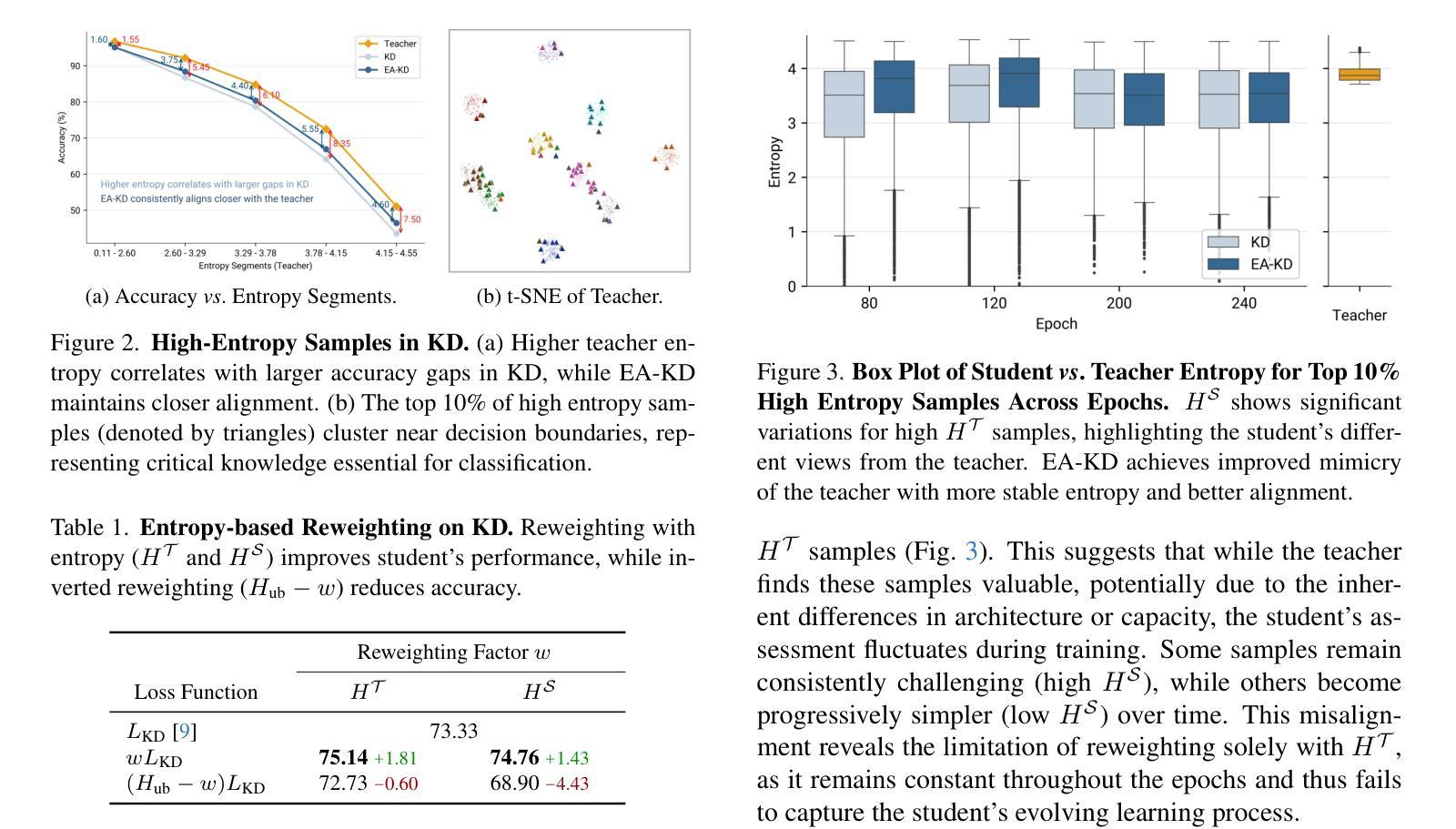
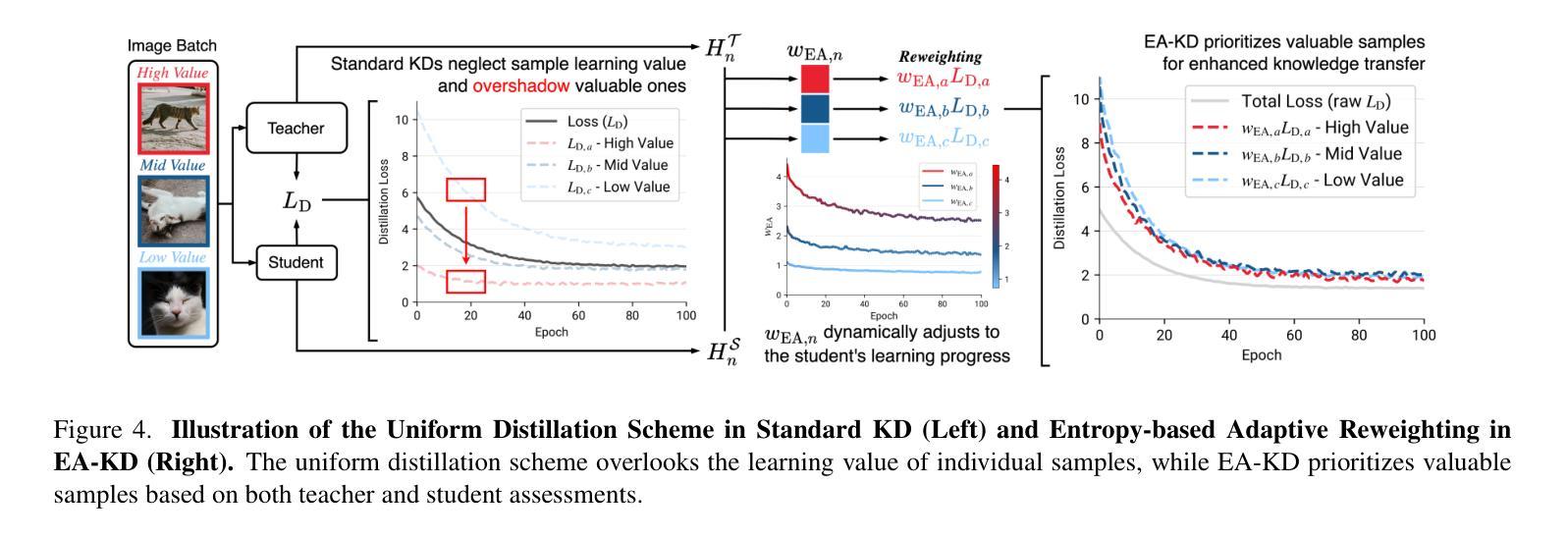
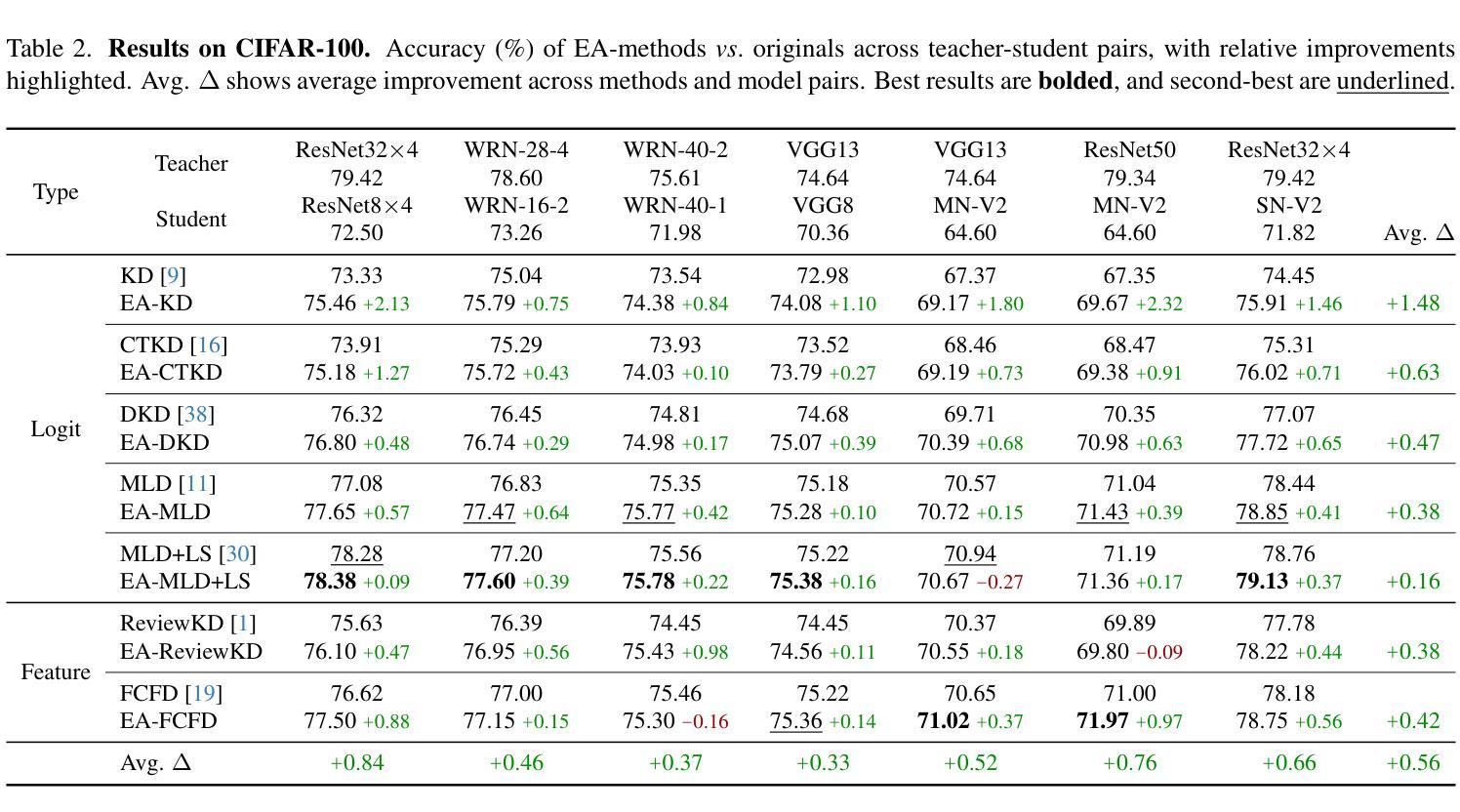
EA-KD: Entropy-based Adaptive Knowledge Distillation
Authors:Chi-Ping Su, Ching-Hsun Tseng, Bin Pu, Lei Zhao, Zhuangzhuang Chen, Shin-Jye Lee
Knowledge distillation (KD) enables a smaller “student” model to mimic a larger “teacher” model by transferring knowledge from the teacher’s output or features. However, most KD methods treat all samples uniformly, overlooking the varying learning value of each sample and thereby limiting effectiveness. In this paper, we propose Entropy-based Adaptive Knowledge Distillation (EA-KD), a simple yet effective plug-and-play KD method that prioritizes learning from valuable samples. EA-KD quantifies each sample’s learning value by strategically combining the entropy of the teacher and student output, then dynamically reweights the distillation loss to place greater emphasis on high-value samples. Extensive experiments across diverse KD frameworks and tasks$\unicode{x2014}$including image classification, object detection, and large language model (LLM) distillation$\unicode{x2014}$demonstrate that EA-KD consistently enhances performance, achieving state-of-the-art results with negligible computational cost. Our code will be publicly available.
知识蒸馏(KD)能够通过从教师模型的输出或特征转移知识,使较小的“学生”模型模仿较大的“教师”模型。然而,大多数KD方法都均匀处理所有样本,忽略了每个样本的不同学习价值,从而限制了有效性。在本文中,我们提出了基于熵的自适应知识蒸馏(EA-KD),这是一种简单而有效的即插即用KD方法,它优先从有价值的样本中学习。EA-KD通过战略性地结合教师和学生的输出熵来量化每个样本的学习价值,然后动态调整蒸馏损失,以更侧重于高价值样本。在包括图像分类、目标检测和大型语言模型(LLM)蒸馏等多种KD框架和任务上的大量实验表明,EA-KD始终提高了性能,实现了最先进的成果,且计算成本微乎其微。我们的代码将公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于熵的自适应知识蒸馏(EA-KD)是一种简单而有效的知识蒸馏方法,它结合了教师模型的输出和输出值的熵来计算样本的学习价值,并通过动态调整蒸馏损失权重,重点关注价值较高的样本进行学习。此方法在各种知识蒸馏框架和任务中都取得了最佳结果,提高了模型的性能且计算成本较低。公开可用的代码将有助于广泛采用此技术。
Key Takeaways
点此查看论文截图

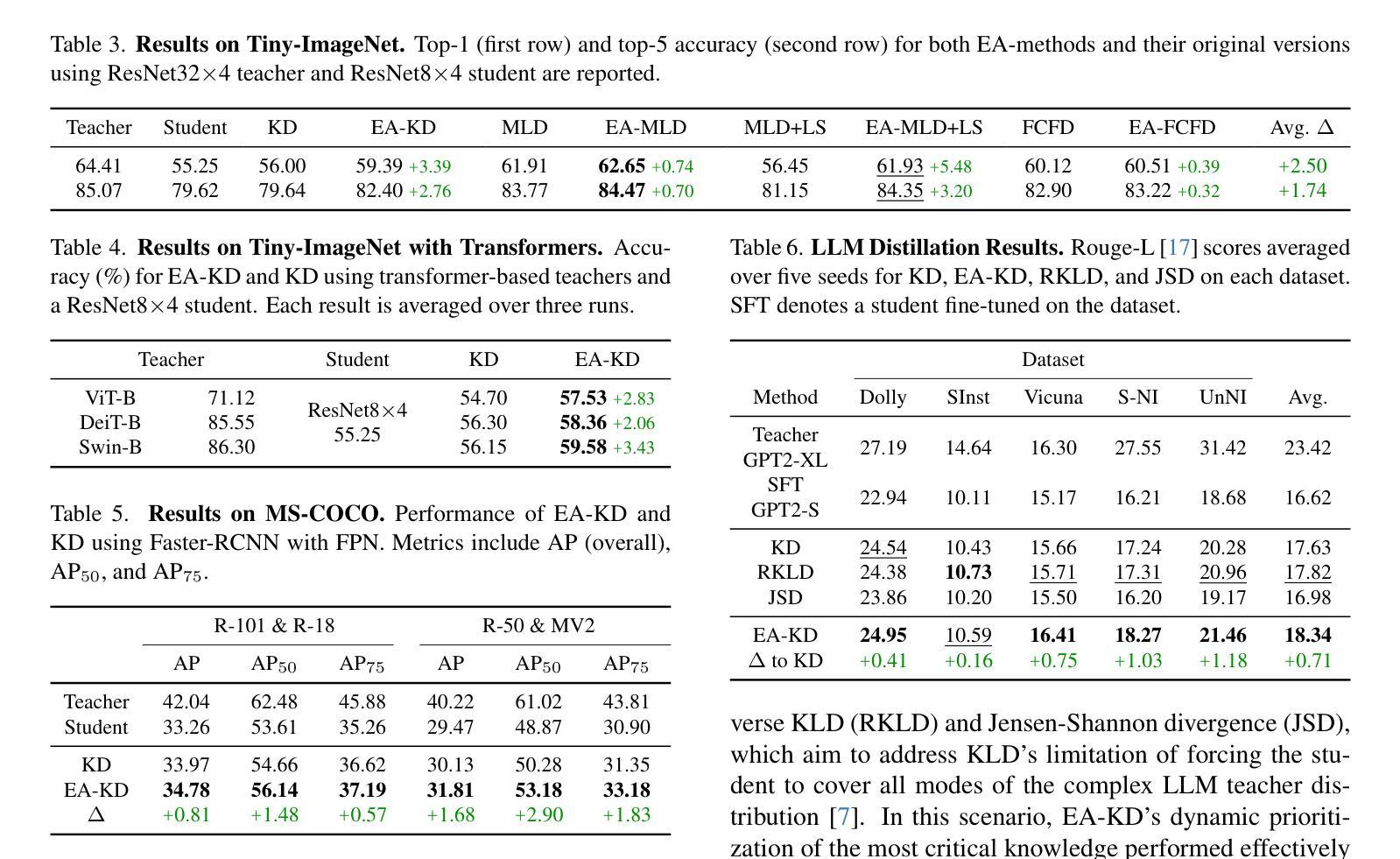
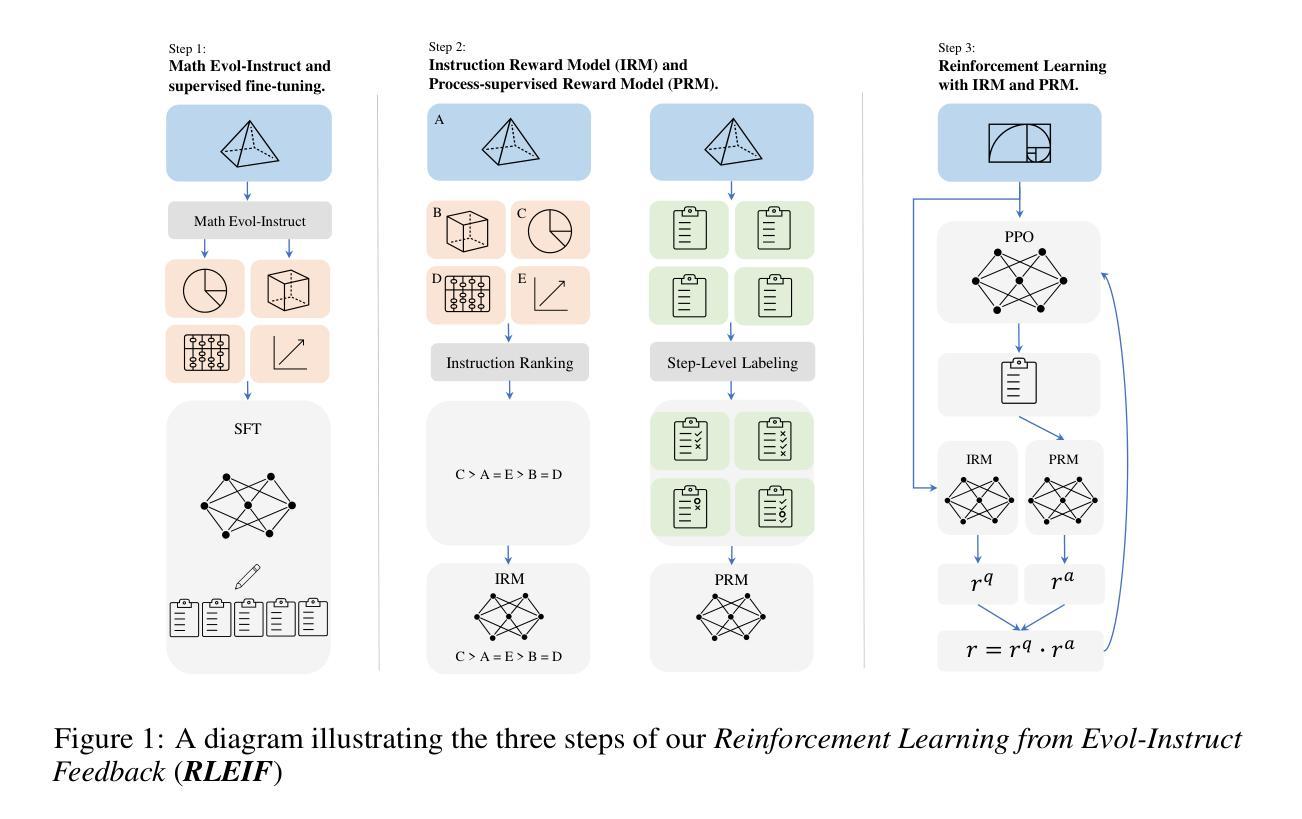
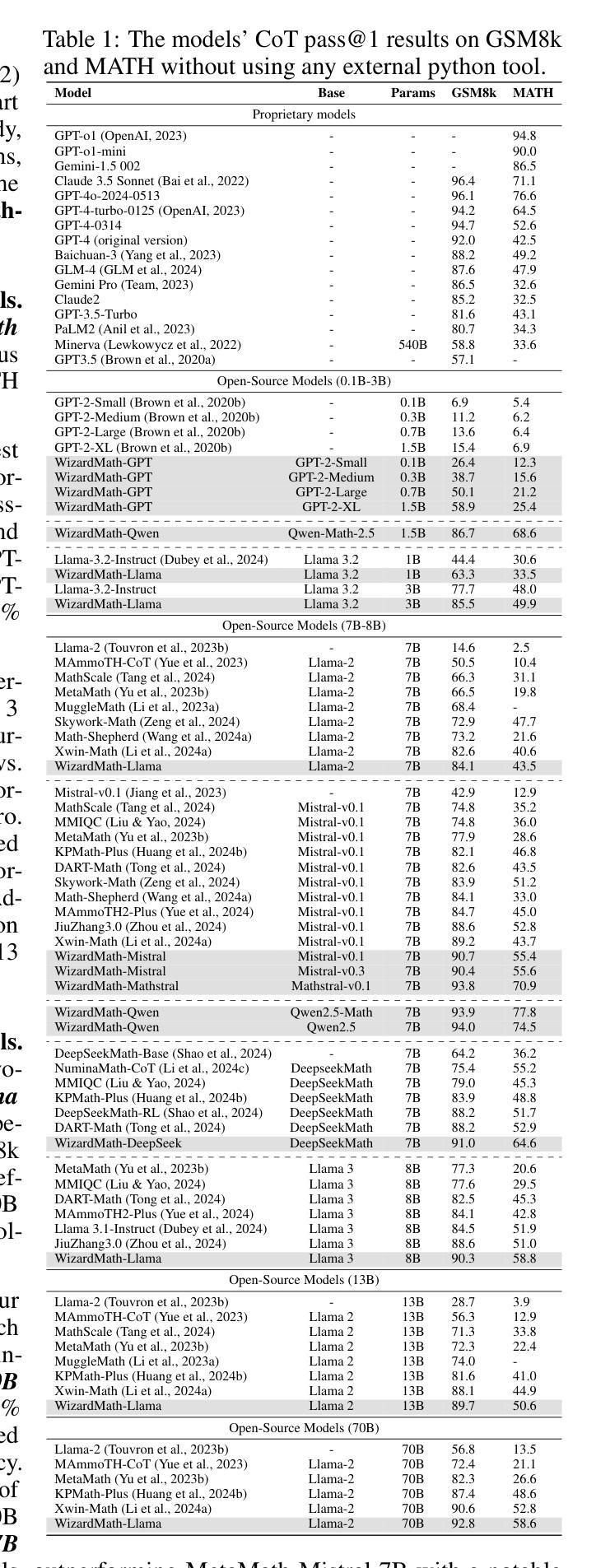
WizardMath: Empowering Mathematical Reasoning for Large Language Models via Reinforced Evol-Instruct
Authors:Haipeng Luo, Qingfeng Sun, Can Xu, Pu Zhao, Jianguang Lou, Chongyang Tao, Xiubo Geng, Qingwei Lin, Shifeng Chen, Yansong Tang, Dongmei Zhang
Large language models (LLMs), such as GPT-4, have shown remarkable performance in natural language processing (NLP) tasks, including challenging mathematical reasoning. However, most existing open-source models are only pre-trained on large-scale internet data and without math-related optimization. In this paper, we present WizardMath, which enhances the mathematical CoT reasoning abilities of LLMs without using external python tools, by applying our proposed Reinforcement Learning from Evol-Instruct Feedback (RLEIF) method to the domain of math. Through extensive experiments on two mathematical reasoning benchmarks, namely GSM8k and MATH, we reveal the extraordinary capabilities of our model. Remarkably, WizardMath-Mistral 7B surpasses top-tier open-source LLMs by a substantial margin with higher data efficiency. Furthermore, WizardMath 70B even outperforms GPT-3.5-Turbo, Claude 2, Gemini Pro and GPT-4-early-version. Additionally, our preliminary exploration highlights the pivotal role of instruction evolution and process supervision in achieving exceptional math performance. For more details refer to https://github.com/nlpxucan/WizardLM
大型语言模型(LLM),如GPT-4,在自然语言处理(NLP)任务中表现出卓越的性能,包括具有挑战性的数学推理。然而,大多数现有的开源模型仅在大规模互联网数据上进行预训练,并没有进行数学相关的优化。在本文中,我们介绍了WizardMath,它通过应用我们提出的强化学习从进化指令反馈(RLEIF)方法到数学领域,提高了LLM的数学CoT推理能力,且不使用外部python工具。我们在两个数学推理基准测试GSM8k和MATH上进行了大量实验,揭示了模型的卓越能力。值得注意的是,WizardMath-Mistral 7B以更高的数据效率大幅超越了顶级开源LLM。此外,WizardMath 70B甚至超越了GPT-3.5-Turbo、Claude 2、Gemini Pro和GPT-4的早期版本。我们的初步探索突显了指令演进和过程监督在实现卓越数学性能中的关键作用。想了解更多详情,请访问 https://github.com/nlpxucan/WizardLM
论文及项目相关链接
PDF LLM, Mathematical Reasoning
Summary
本论文介绍了WizardMath,一种增强大型语言模型(LLM)数学推理能力的方法,无需使用外部Python工具。通过应用强化学习从演化指令反馈(RLEIF)方法,WizardMath在数学领域表现出卓越性能。实验结果显示,WizardMath-Mistral 7B在GSM8k和MATH两个数学推理基准测试上大幅超越顶尖开源LLM,且数据效率更高。此外,WizardMath 70B甚至超越了GPT-3.5-Turbo、Claude 2、Gemini Pro和GPT-4早期版本。初步探索表明,指令演化和过程监督在实现卓越数学性能中起着关键作用。
Key Takeaways
- WizardMath方法增强了LLM的数学推理能力,且无需外部Python工具。
- 通过应用强化学习从演化指令反馈(RLEIF)方法,WizardMath在数学领域表现出卓越性能。
- WizardMath-Mistral 7B在GSM8k和MATH数学推理基准测试上超越顶尖开源LLM。
- WizardMath 70B的性能超越了GPT-3.5-Turbo、Claude 2、Gemini Pro和GPT-4早期版本。
- 该方法提高了数据效率。
- 初步探索表明指令演化和过程监督对实现卓越数学性能至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

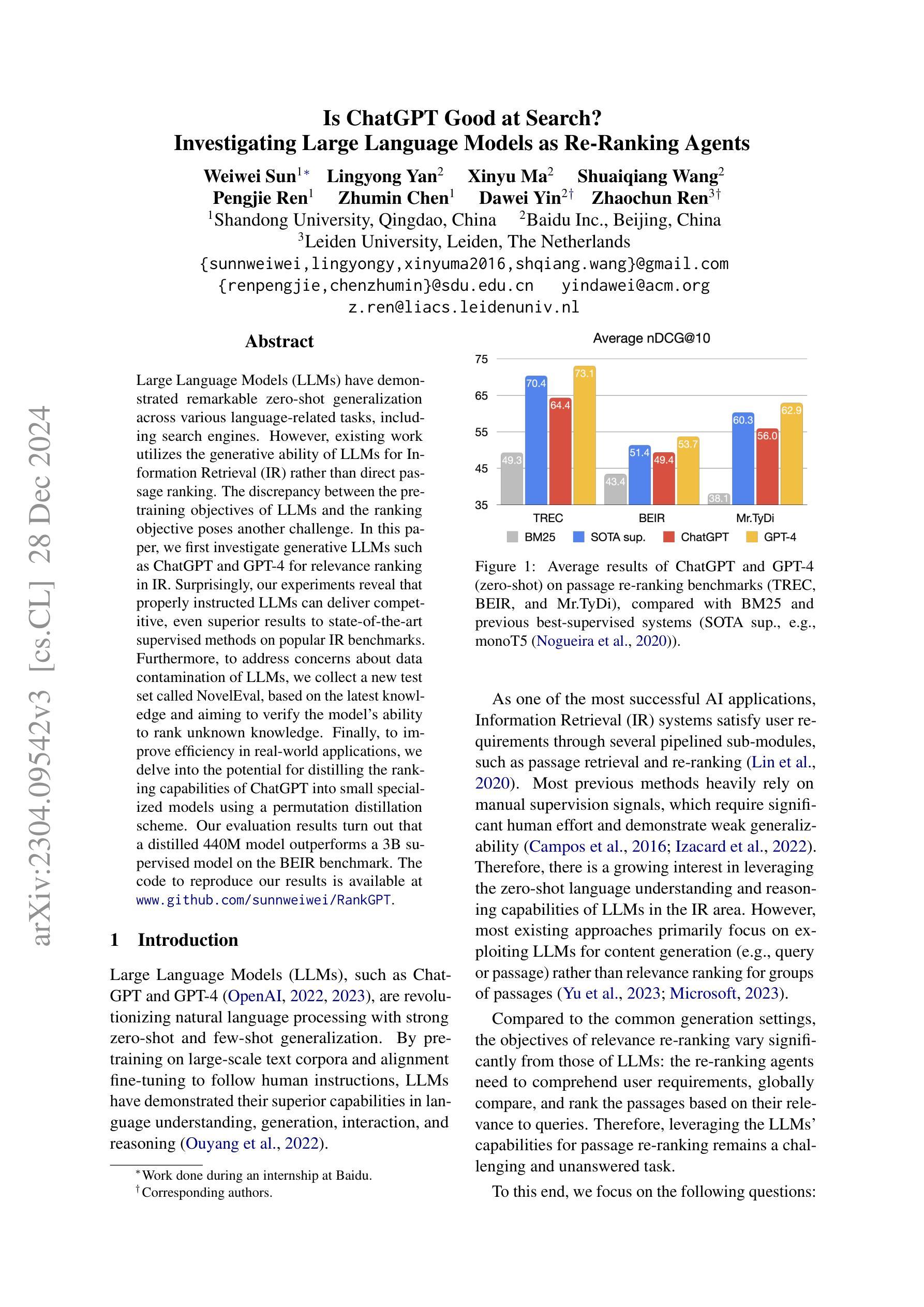
Is ChatGPT Good at Search? Investigating Large Language Models as Re-Ranking Agents
Authors:Weiwei Sun, Lingyong Yan, Xinyu Ma, Shuaiqiang Wang, Pengjie Ren, Zhumin Chen, Dawei Yin, Zhaochun Ren
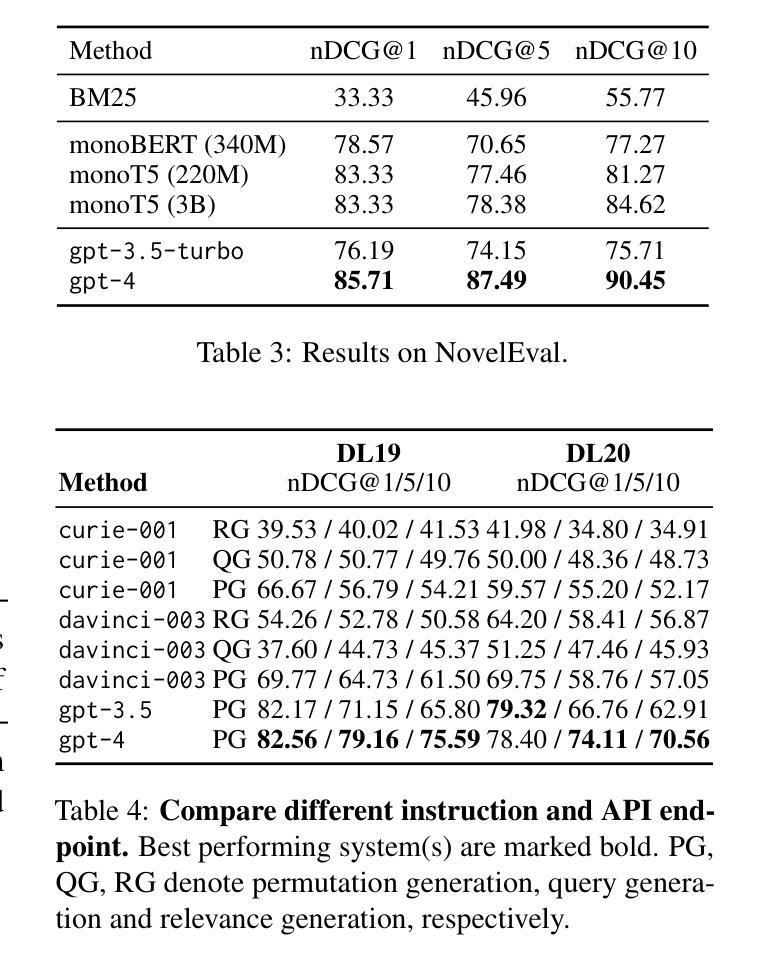
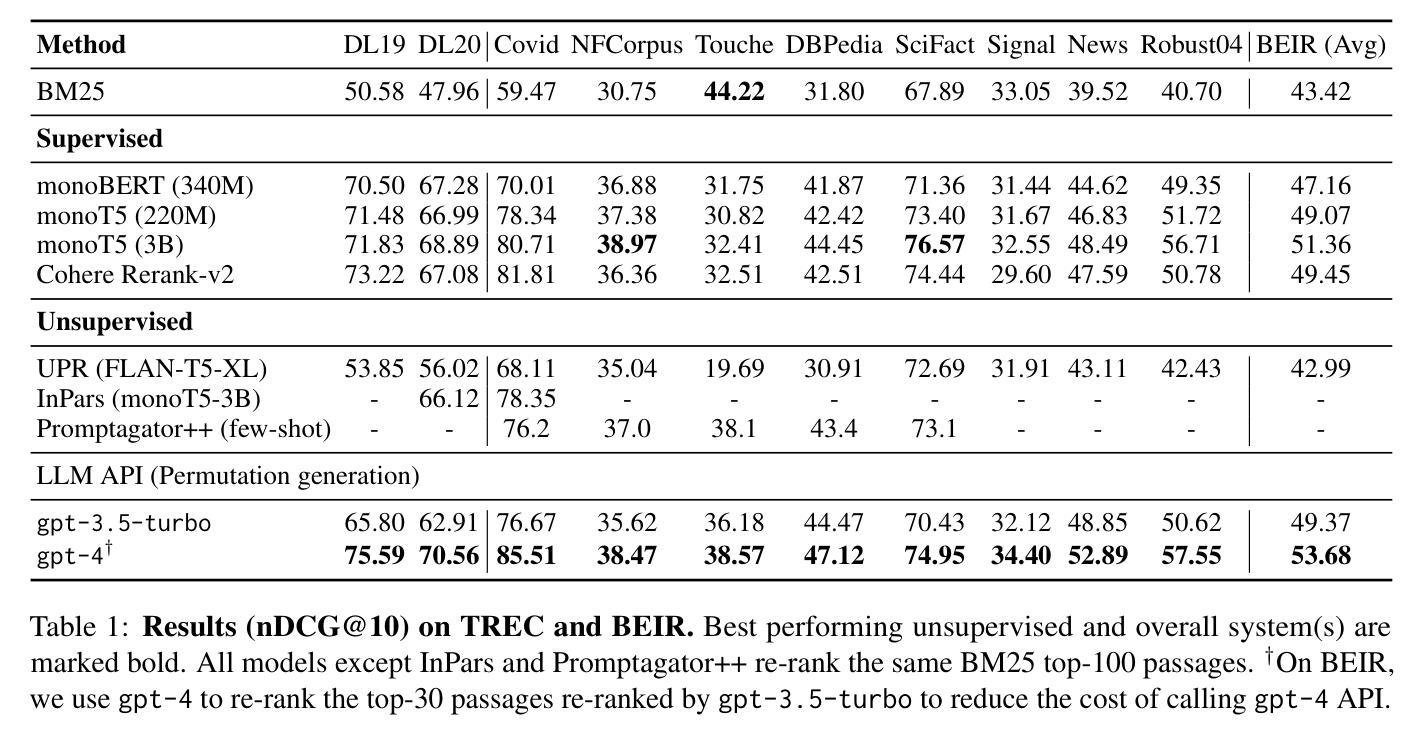
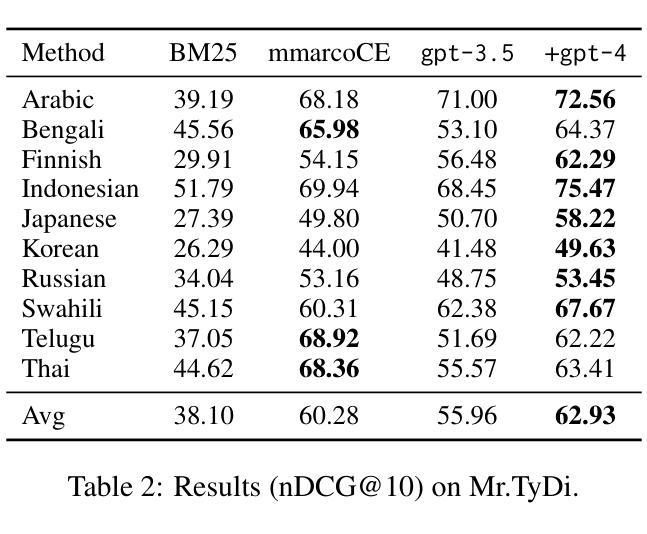
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable zero-shot generalization across various language-related tasks, including search engines. However, existing work utilizes the generative ability of LLMs for Information Retrieval (IR) rather than direct passage ranking. The discrepancy between the pre-training objectives of LLMs and the ranking objective poses another challenge. In this paper, we first investigate generative LLMs such as ChatGPT and GPT-4 for relevance ranking in IR. Surprisingly, our experiments reveal that properly instructed LLMs can deliver competitive, even superior results to state-of-the-art supervised methods on popular IR benchmarks. Furthermore, to address concerns about data contamination of LLMs, we collect a new test set called NovelEval, based on the latest knowledge and aiming to verify the model’s ability to rank unknown knowledge. Finally, to improve efficiency in real-world applications, we delve into the potential for distilling the ranking capabilities of ChatGPT into small specialized models using a permutation distillation scheme. Our evaluation results turn out that a distilled 440M model outperforms a 3B supervised model on the BEIR benchmark. The code to reproduce our results is available at www.github.com/sunnweiwei/RankGPT.
大型语言模型(LLM)在各种语言相关任务中表现出了显著的零样本泛化能力,包括搜索引擎。然而,现有工作主要利用LLM的生成能力进行信息检索(IR),而非直接进行段落排名。LLM的预训练目标与排名目标之间的差异构成了另一项挑战。在本文中,我们首先调查了用于信息检索中的相关性排名的生成式LLM,如ChatGPT和GPT-4。令人惊讶的是,我们的实验结果表明,在流行的IR基准测试中,经过适当指示的LLM可以产生具有竞争力的结果,甚至优于最先进的监督方法。此外,为了解决对LLM数据污染的担忧,我们收集了一个新的测试集,称为NovelEval,它基于最新知识,旨在验证模型对未知知识的排名能力。最后,为了提高在现实世界应用中的效率,我们深入探讨了使用置换蒸馏方案将ChatGPT的排名能力蒸馏到小型专用模型中的潜力。我们的评估结果表明,一个蒸馏后的4.4亿参数模型在BEIR基准测试中表现优于一个30亿参数监督模型。您可以在www.github.com/sunnweiwei/RankGPT上获取复制我们结果的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF EMNLP 2023
Summary
本文探讨了大型语言模型(LLMs)在搜索引擎信息检索(IR)中的零样本泛化能力。研究指出,通过适当指导,LLMs在IR排名任务上的表现可与最先进的监督方法相竞争,甚至更优。为验证模型对未知知识的排名能力,研究团队推出了新型测试集NovelEval。此外,研究还探索了利用permutation distillation方案将ChatGPT的排名能力蒸馏到小型专用模型中的可能性,结果显示蒸馏后的440M模型在BEIR基准测试中表现优于3B监督模型。相关代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs展现出强大的零样本泛化能力,可在各种语言任务中表现优异,包括搜索引擎。
- LLMs在信息检索(IR)的排名任务中表现良好,通过适当指导,其性能可与最先进的监督方法相竞争。
- 推出新型测试集NovelEval,用于验证模型对未知知识的排名能力。
- 利用permutation distillation方案,成功将ChatGPT的排名能力蒸馏到小型专用模型中。
- 蒸馏后的440M模型在BEIR基准测试中表现优于3B监督模型。
- 公开了相关代码以供研究使用。
点此查看论文截图