⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-06 更新
nnY-Net: Swin-NeXt with Cross-Attention for 3D Medical Images Segmentation
Authors:Haixu Liu, Zerui Tao, Wenzhen Dong, Qiuzhuang Sun
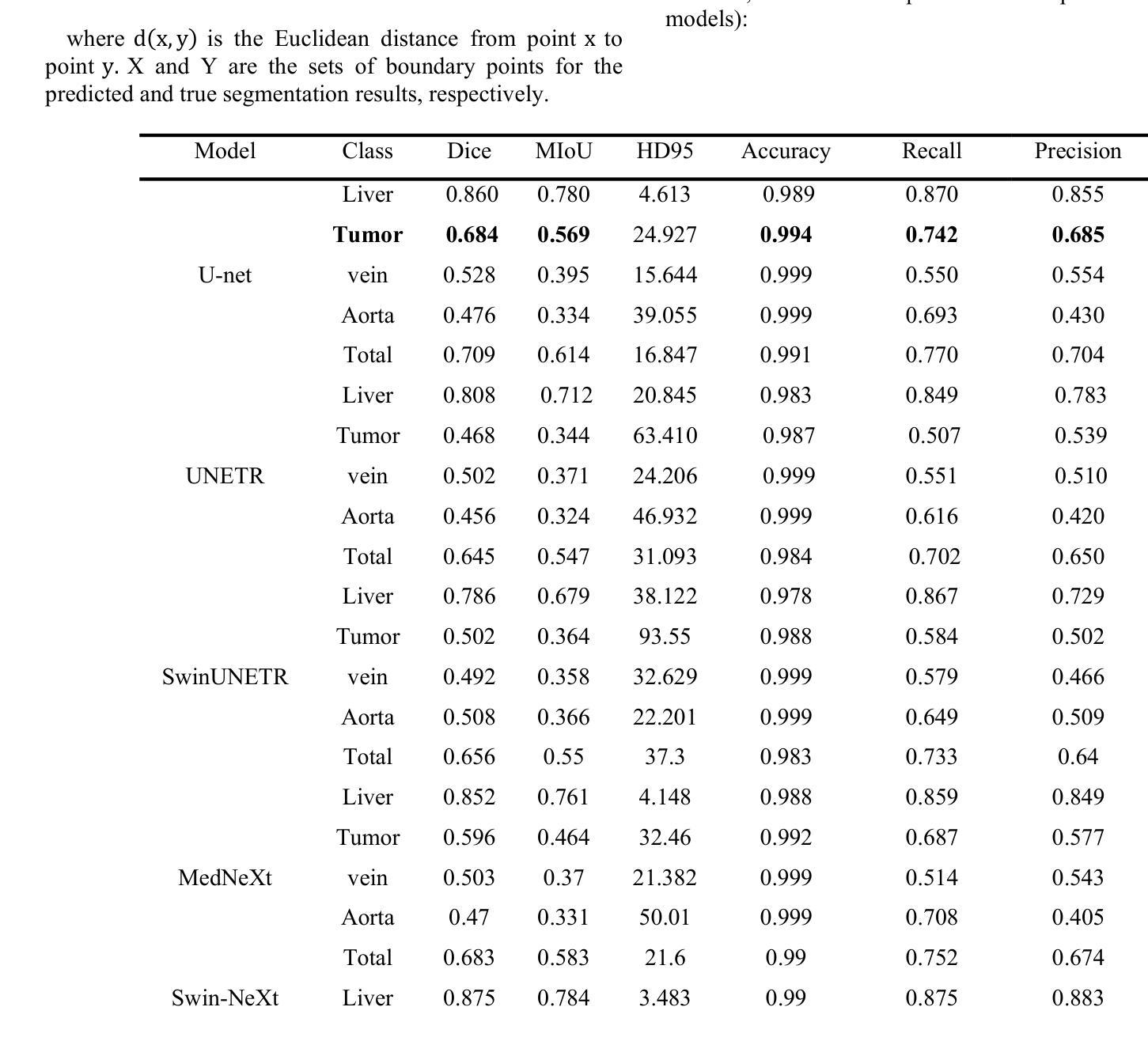
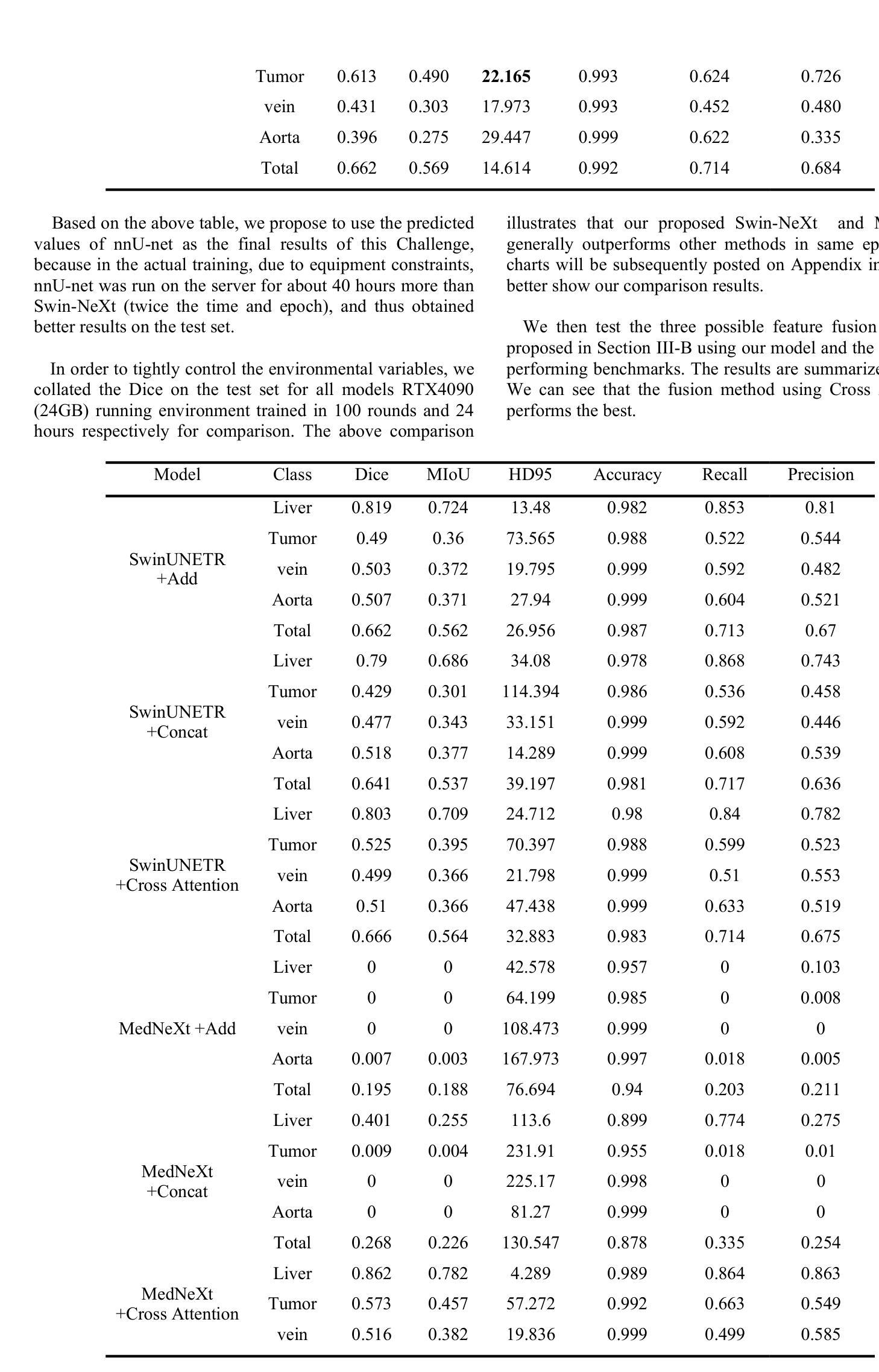
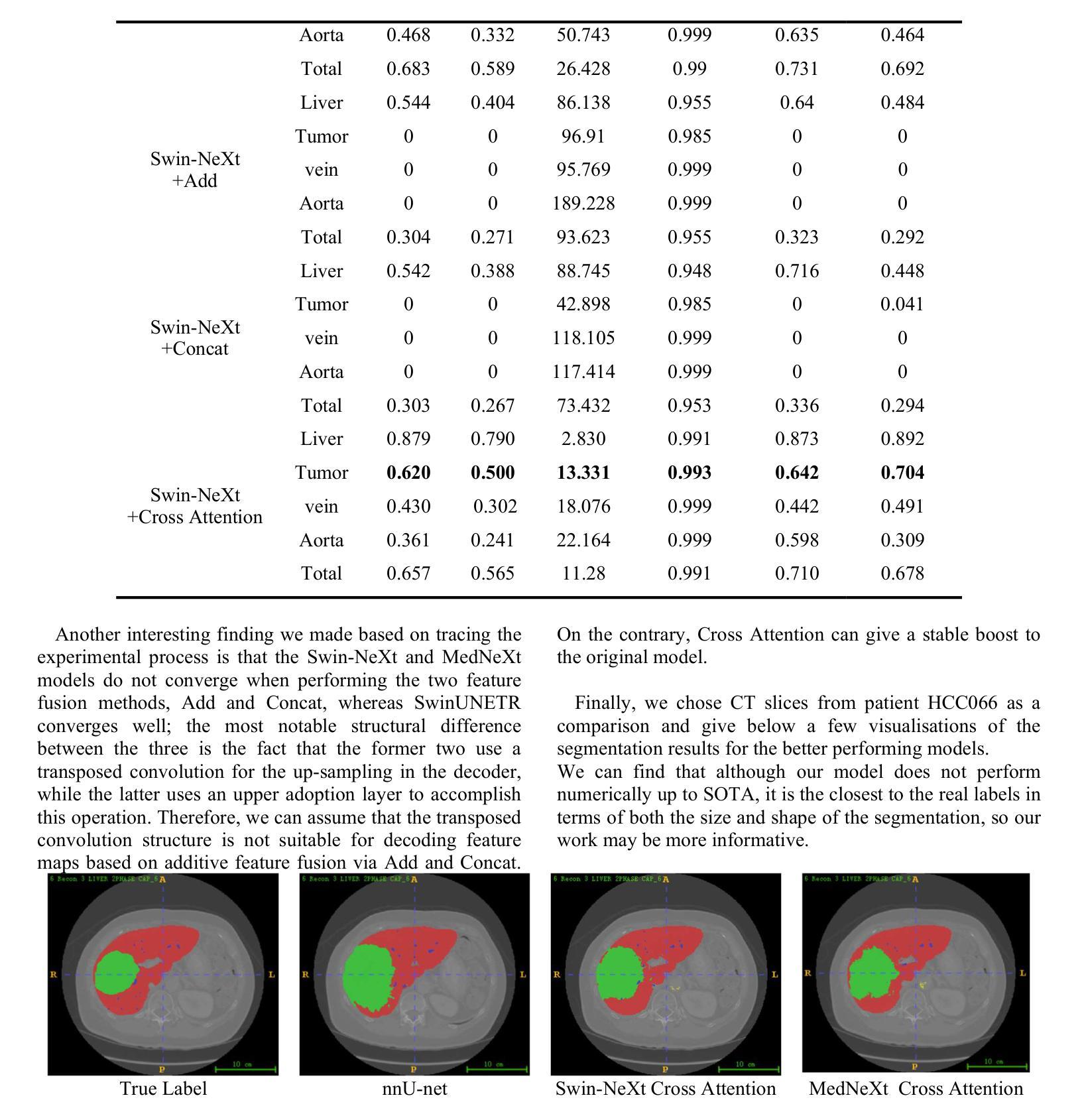
This paper provides a novel 3D medical image segmentation model structure called nnY-Net. This name comes from the fact that our model adds a cross-attention module at the bottom of the U-net structure to form a Y structure. We integrate the advantages of the two latest SOTA models, MedNeXt and SwinUNETR, and use Swin Transformer as the encoder and ConvNeXt as the decoder to innovatively design the Swin-NeXt structure. Our model uses the lowest-level feature map of the encoder as Key and Value and uses patient features such as pathology and treatment information as Query to calculate the attention weights in a Cross Attention module. Moreover, we simplify some pre- and post-processing as well as data enhancement methods in 3D image segmentation based on the dynUnet and nnU-net frameworks. We integrate our proposed Swin-NeXt with Cross-Attention framework into this framework. Last, we construct a DiceFocalCELoss to improve the training efficiency for the uneven data convergence of voxel classification.
本文提出了一种新型的3D医学图像分割模型结构,名为nnY-Net。这个名字的由来是因为我们的模型在U-net结构的底部添加了一个交叉注意模块,形成Y形结构。我们整合了最新两个顶尖模型MedNeXt和SwinUNETR的优点,创新地设计了Swin-NeXt结构,使用Swin Transformer作为编码器,ConvNeXt作为解码器。我们的模型以编码器的最低级特征图作为键和值,以患者特征(如病理和治疗信息)作为查询,在交叉注意模块中计算注意力权重。此外,我们简化了基于dynUnet和nnU-net框架的3D图像分割的预处理和后处理以及数据增强方法。我们将我们提出的带有交叉注意框架的Swin-NeXt集成到这一框架中。最后,我们构建了DiceFocalCELoss,以提高voxel分类数据不均匀时的训练效率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI
Summary
基于U-net结构的新型三维医学图像分割模型nnY-Net被提出。该模型结合了MedNeXt和SwinUNETR两种最新顶尖模型的优势,采用Swin Transformer作为编码器,ConvNeXt作为解码器,创新设计了Swin-NeXt结构。模型使用编码器最低级别的特征映射作为键和值,并利用患者特征(如病理和治疗信息)作为查询来计算交叉注意力模块中的注意力权重。此外,基于dynUnet和nnU-net框架简化了部分预处理和后处理以及数据增强方法。最后构建了DiceFocalCELoss以提高数据不均衡收敛时的训练效率。
Key Takeaways
- nnY-Net是一种新型的三维医学图像分割模型,基于U-net结构,结合了MedNeXt和SwinUNETR的优势。
- 模型创新性地结合了Swin Transformer编码器和ConvNeXt解码器,构成Swin-NeXt结构。
- 模型使用交叉注意力模块,利用患者特征(如病理和治疗信息)计算注意力权重。
- 该模型简化了预处理和后处理流程以及数据增强方法,基于dynUnet和nnU-net框架。
- nnY-Net框架中集成了Swin-NeXt与交叉注意力框架。
- 模型构建了DiceFocalCELoss,旨在提高数据不均衡收敛时的训练效率。
点此查看论文截图
ProjectedEx: Enhancing Generation in Explainable AI for Prostate Cancer
Authors:Xuyin Qi, Zeyu Zhang, Aaron Berliano Handoko, Huazhan Zheng, Mingxi Chen, Ta Duc Huy, Vu Minh Hieu Phan, Lei Zhang, Linqi Cheng, Shiyu Jiang, Zhiwei Zhang, Zhibin Liao, Yang Zhao, Minh-Son To
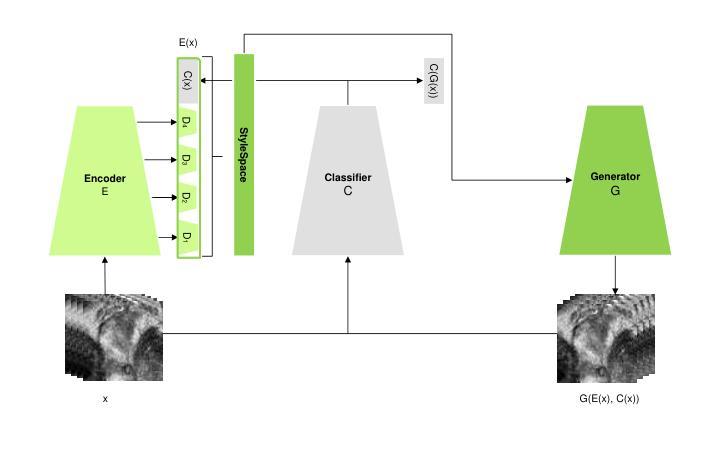
Prostate cancer, a growing global health concern, necessitates precise diagnostic tools, with Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) offering high-resolution soft tissue imaging that significantly enhances diagnostic accuracy. Recent advancements in explainable AI and representation learning have significantly improved prostate cancer diagnosis by enabling automated and precise lesion classification. However, existing explainable AI methods, particularly those based on frameworks like generative adversarial networks (GANs), are predominantly developed for natural image generation, and their application to medical imaging often leads to suboptimal performance due to the unique characteristics and complexity of medical image. To address these challenges, our paper introduces three key contributions. First, we propose ProjectedEx, a generative framework that provides interpretable, multi-attribute explanations, effectively linking medical image features to classifier decisions. Second, we enhance the encoder module by incorporating feature pyramids, which enables multiscale feedback to refine the latent space and improves the quality of generated explanations. Additionally, we conduct comprehensive experiments on both the generator and classifier, demonstrating the clinical relevance and effectiveness of ProjectedEx in enhancing interpretability and supporting the adoption of AI in medical settings. Code will be released at https://github.com/Richardqiyi/ProjectedEx
前列腺癌是一个日益严重的全球健康问题,需要精确的诊断工具。磁共振成像(MRI)提供了高分辨率的软组织成像,显著提高了诊断的准确性。最近,在可解释的人工智能和表示学习方面的进展已经通过实现自动化和精确的病变分类显著改善了前列腺癌的诊断。然而,现有的可解释人工智能方法,特别是基于生成对抗网络(GANs)等框架的方法,主要是为自然图像生成而开发的,由于其独特的特点和医学图像的复杂性,它们在医学成像中的应用往往导致性能不佳。为了应对这些挑战,我们的论文提出了三个主要贡献。首先,我们提出了ProjectedEx,一个生成框架,提供可解释的多属性解释,有效地将医学图像特征与分类器决策联系起来。其次,我们通过融入特征金字塔增强了编码器模块,这启用了多尺度反馈来优化潜在空间并提高了生成解释的质量。此外,我们对生成器和分类器都进行了全面的实验,证明了ProjectedEx在临床相关性和有效性方面的作用,提高了可解释性并支持在医疗环境中采用人工智能。代码将在https://github.com/Richardqiyi/ProjectedEx公布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本摘要提出了一种针对前列腺癌诊断的新型解释性人工智能框架——ProjectedEx。该框架结合了磁共振成像技术和解释性人工智能,能有效链接医学图像特征与分类器决策,提高诊断准确性。此外,该项目通过融入特征金字塔增强编码器模块,改善了潜在空间的质量,提高了生成的解释质量。实验证明,ProjectedEx在临床相关性和提高人工智能解释性方面效果显著。
Key Takeaways
- 前列腺癌成为全球健康难题,需要精确的诊断工具。
- 磁共振成像(MRI)技术为前列腺癌诊断提供了高分辨率软组织成像,提高了诊断准确性。
- 人工智能和表示学习的发展改善了前列腺癌的自动和精确病灶分类。
- 现有的人工智能解释方法,特别是基于生成对抗网络(GANs)的方法,在医学成像中的应用因医学图像的独特特征和复杂性而表现不佳。
- ProjectedEx是一个新的解释性人工智能框架,有效链接医学图像特征和分类器决策。
- 通过融入特征金字塔增强编码器模块,ProjectedEx改善了潜在空间的质量,提高了生成的解释质量。
点此查看论文截图

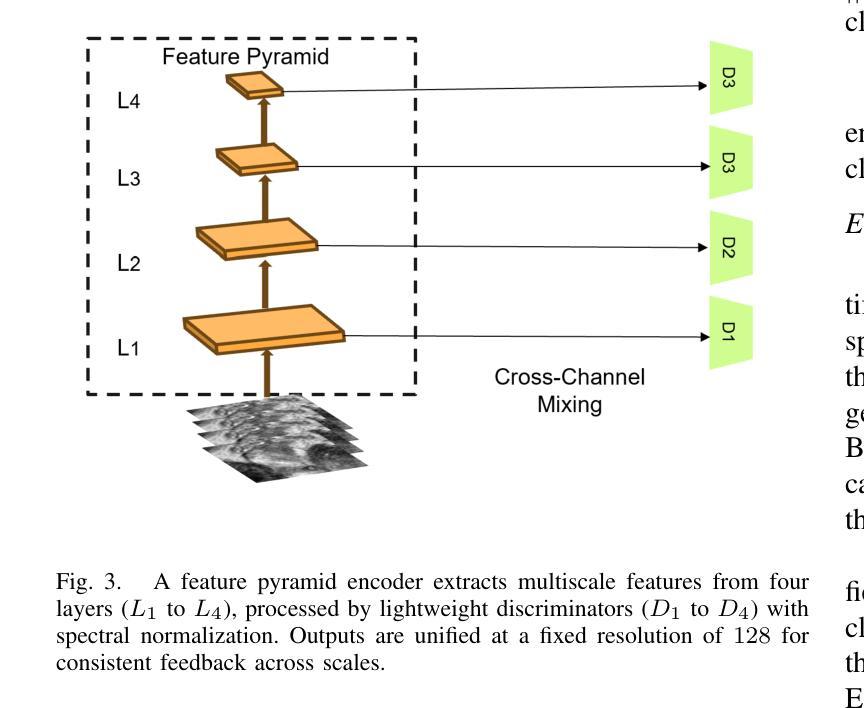
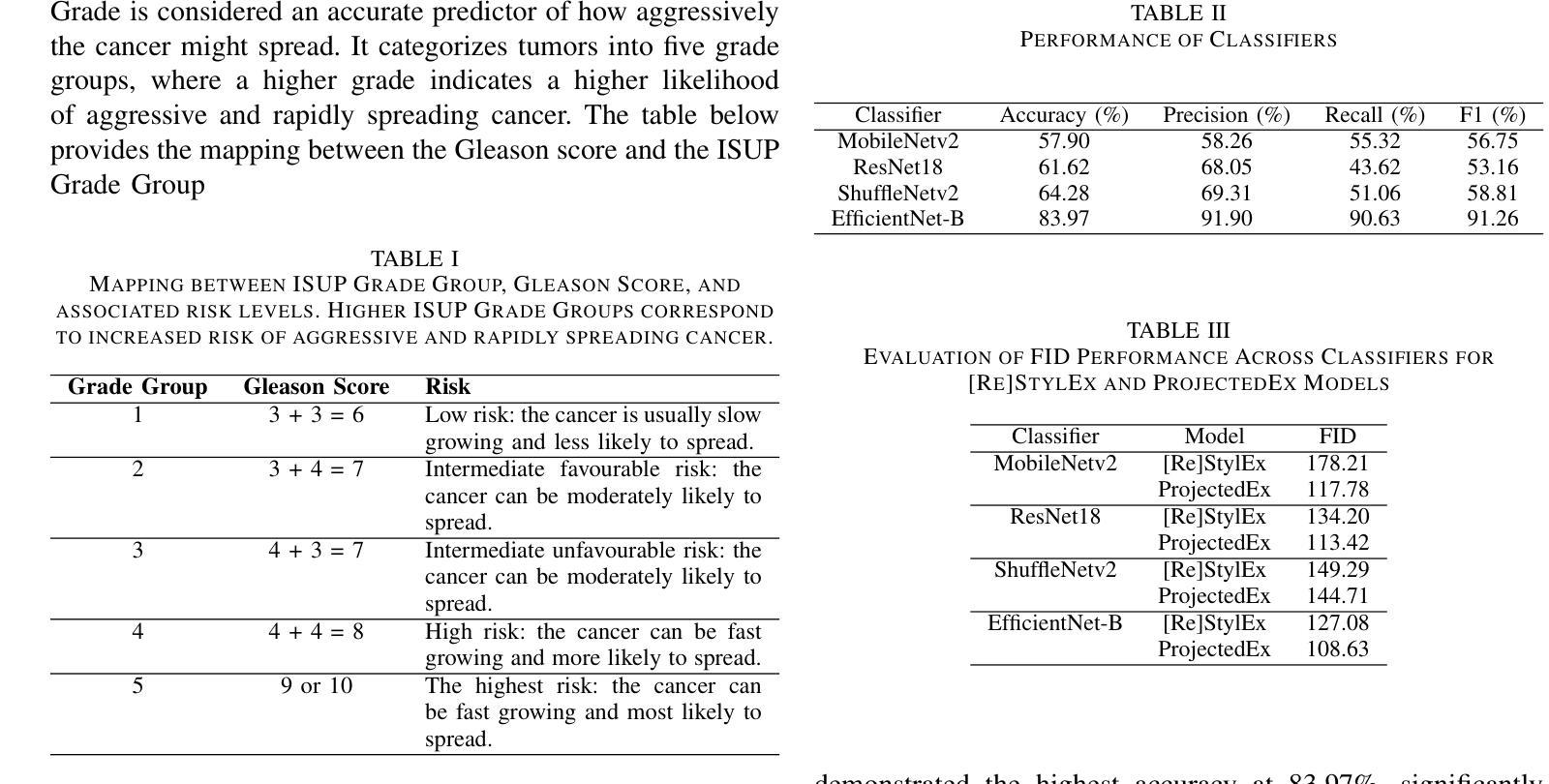
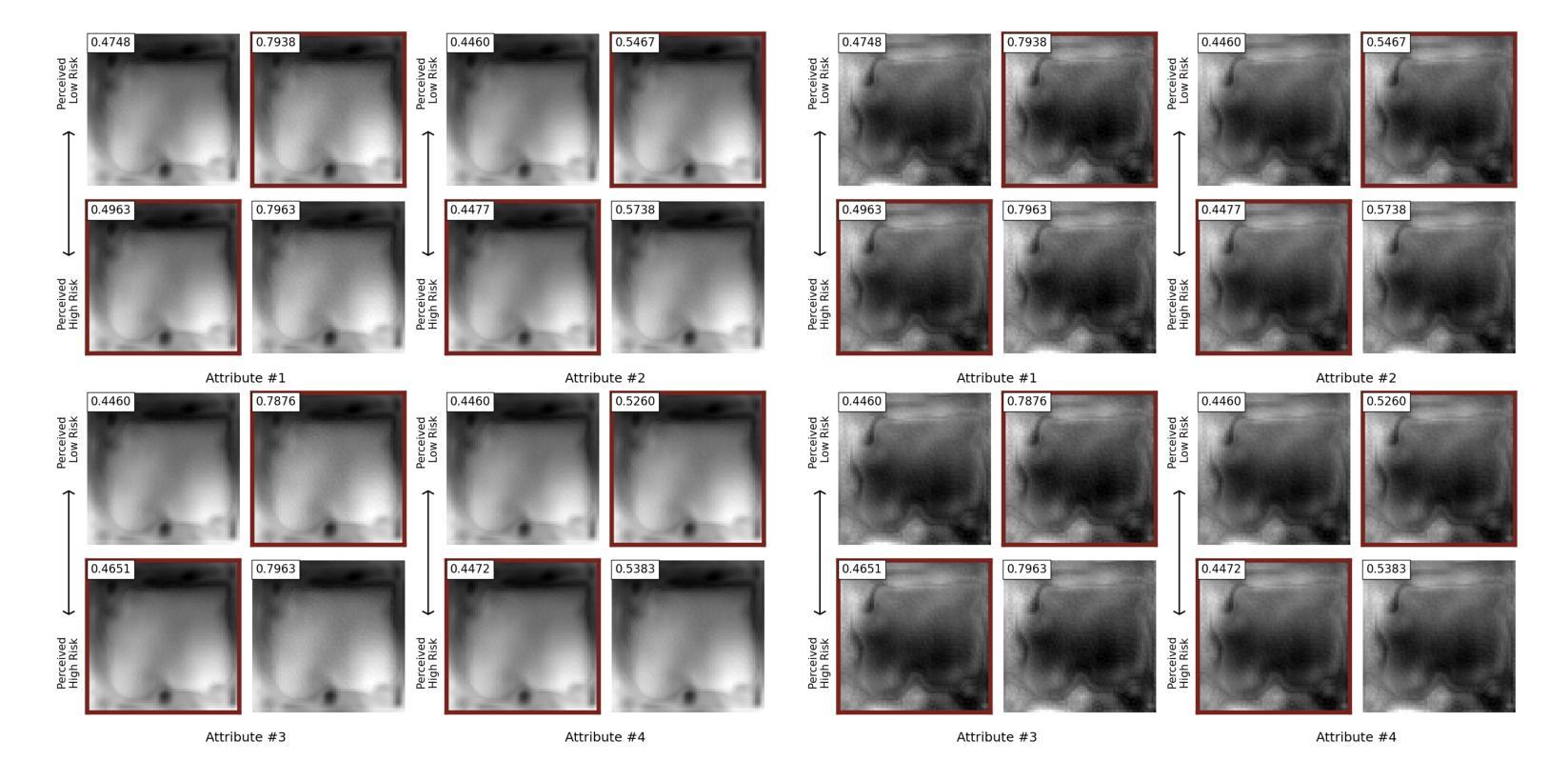
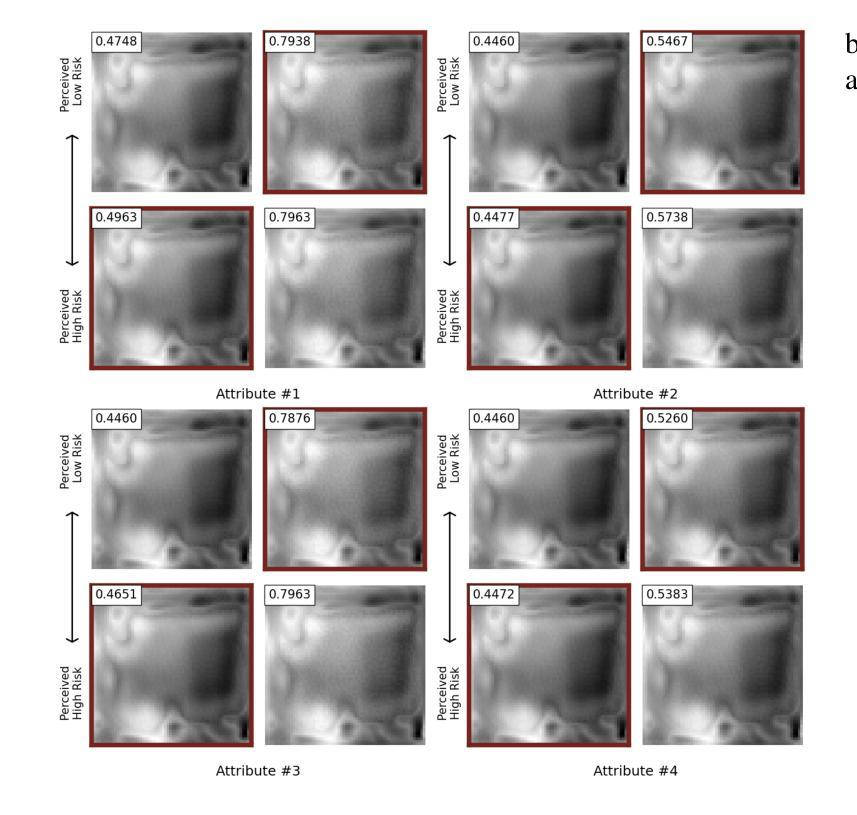
Generalized Task-Driven Medical Image Quality Enhancement with Gradient Promotion
Authors:Dong Zhang, Kwang-Ting Cheng
Thanks to the recent achievements in task-driven image quality enhancement (IQE) models like ESTR, the image enhancement model and the visual recognition model can mutually enhance each other’s quantitation while producing high-quality processed images that are perceivable by our human vision systems. However, existing task-driven IQE models tend to overlook an underlying fact – different levels of vision tasks have varying and sometimes conflicting requirements of image features. To address this problem, this paper proposes a generalized gradient promotion (GradProm) training strategy for task-driven IQE of medical images. Specifically, we partition a task-driven IQE system into two sub-models, i.e., a mainstream model for image enhancement and an auxiliary model for visual recognition. During training, GradProm updates only parameters of the image enhancement model using gradients of the visual recognition model and the image enhancement model, but only when gradients of these two sub-models are aligned in the same direction, which is measured by their cosine similarity. In case gradients of these two sub-models are not in the same direction, GradProm only uses the gradient of the image enhancement model to update its parameters. Theoretically, we have proved that the optimization direction of the image enhancement model will not be biased by the auxiliary visual recognition model under the implementation of GradProm. Empirically, extensive experimental results on four public yet challenging medical image datasets demonstrated the superior performance of GradProm over existing state-of-the-art methods.
得益于最近任务驱动图像质量增强(IQE)模型(如ESTR)的成就,图像增强模型和视觉识别模型可以相互促进彼此的量化,同时生成高质量的处理图像,这些图像可以被我们的视觉系统所感知。然而,现有的任务驱动IQE模型往往忽视了一个基本事实——不同层次的视觉任务对图像特征的要求各不相同,有时甚至存在冲突。为了解决这一问题,本文提出了一种用于医学图像任务驱动的IQE的广义梯度提升(GradProm)训练策略。具体来说,我们将任务驱动的IQE系统划分为两个子模型,即用于图像增强的主流模型和用于视觉识别的辅助模型。在训练过程中,GradProm仅使用视觉识别模型和图像增强模型的梯度来更新图像增强模型的参数,但仅在两个子模型的梯度方向相同时才进行更新,这通过它们的余弦相似性来衡量。如果这两个子模型的梯度方向不一致,GradProm只使用图像增强模型的梯度来更新其参数。理论上,我们已经证明,在GradProm的实现下,图像增强模型的优化方向不会受到辅助视觉识别模型的影响。在四个公开且具有挑战性的医学图像数据集上的大量实验结果表明,GradProm的性能优于现有的最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted by IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence
Summary
本文提出一种针对医学图像任务驱动图像质量增强(IQE)的广义梯度提升(GradProm)训练策略。该策略将IQE系统分为两个子模型:主流模型用于图像增强,辅助模型用于视觉识别。训练时,GradProm仅使用视觉识别模型和图像增强模型的梯度更新图像增强模型的参数,且仅在两者梯度方向相同时进行。当梯度方向不一致时,仅使用图像增强模型的梯度更新参数。理论证明,GradProm实施下,图像增强模型的优化方向不会受到辅助视觉识别模型的影响。在四个公共且具有挑战性的医学图像数据集上的实验结果表明,GradProm优于现有最先进的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 任务驱动图像质量增强(IQE)模型如ESTR能够互相提升图像增强模型和视觉识别模型的量化能力。
- 现有IQE模型忽略了不同视觉任务对图像特征的不同甚至冲突的需求。
- 本文提出的广义梯度提升(GradProm)训练策略针对医学图像的任务驱动IQE。
- GradProm将IQE系统分为两个子模型:用于图像增强的主流模型和用于视觉识别的辅助模型。
- GradProm在训练时仅使用两个子模型梯度一致时的梯度更新图像增强模型的参数。
- 理论证明,GradProm保证图像增强模型的优化方向不会受到辅助视觉识别模型的影响。
点此查看论文截图
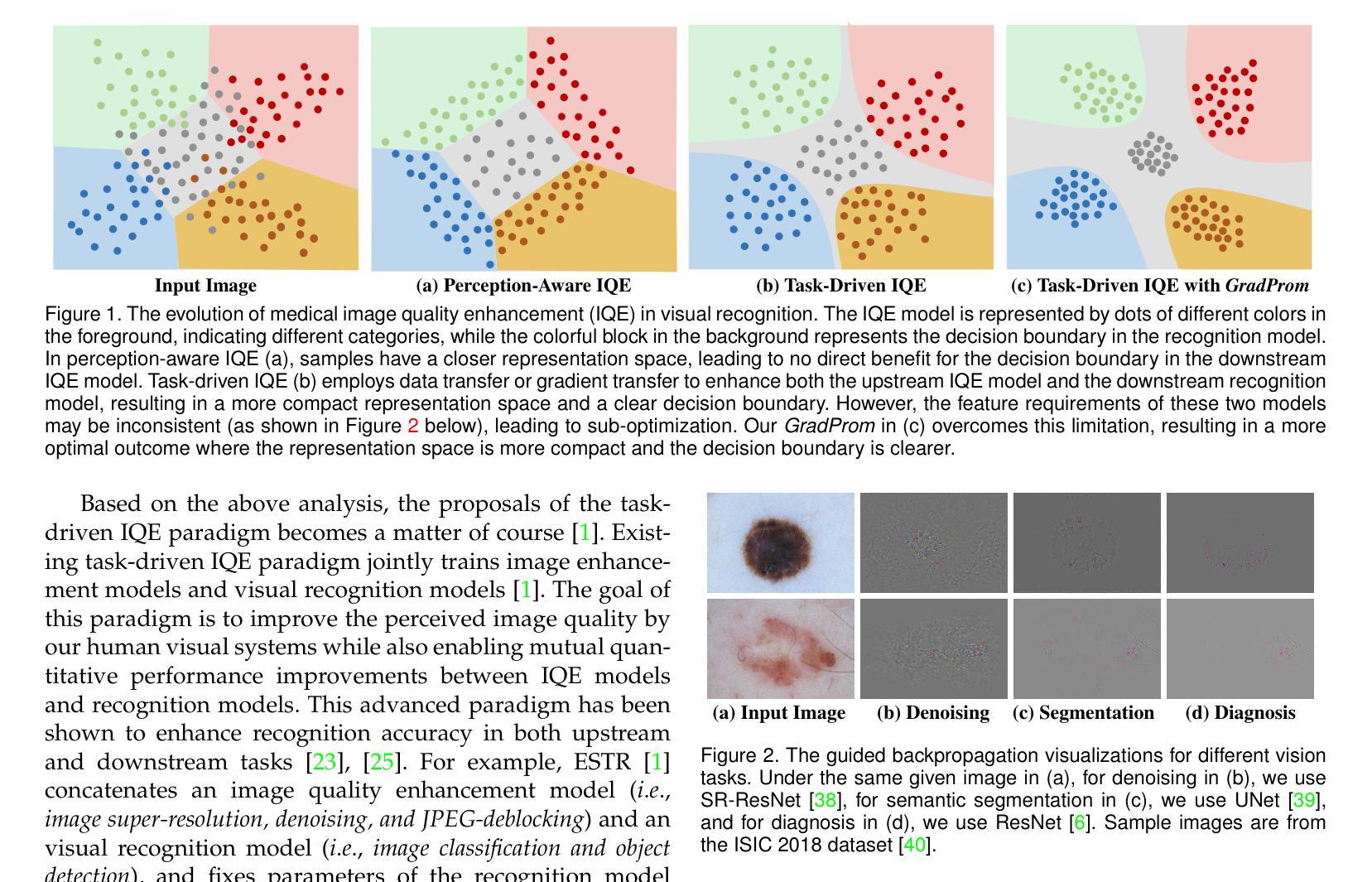
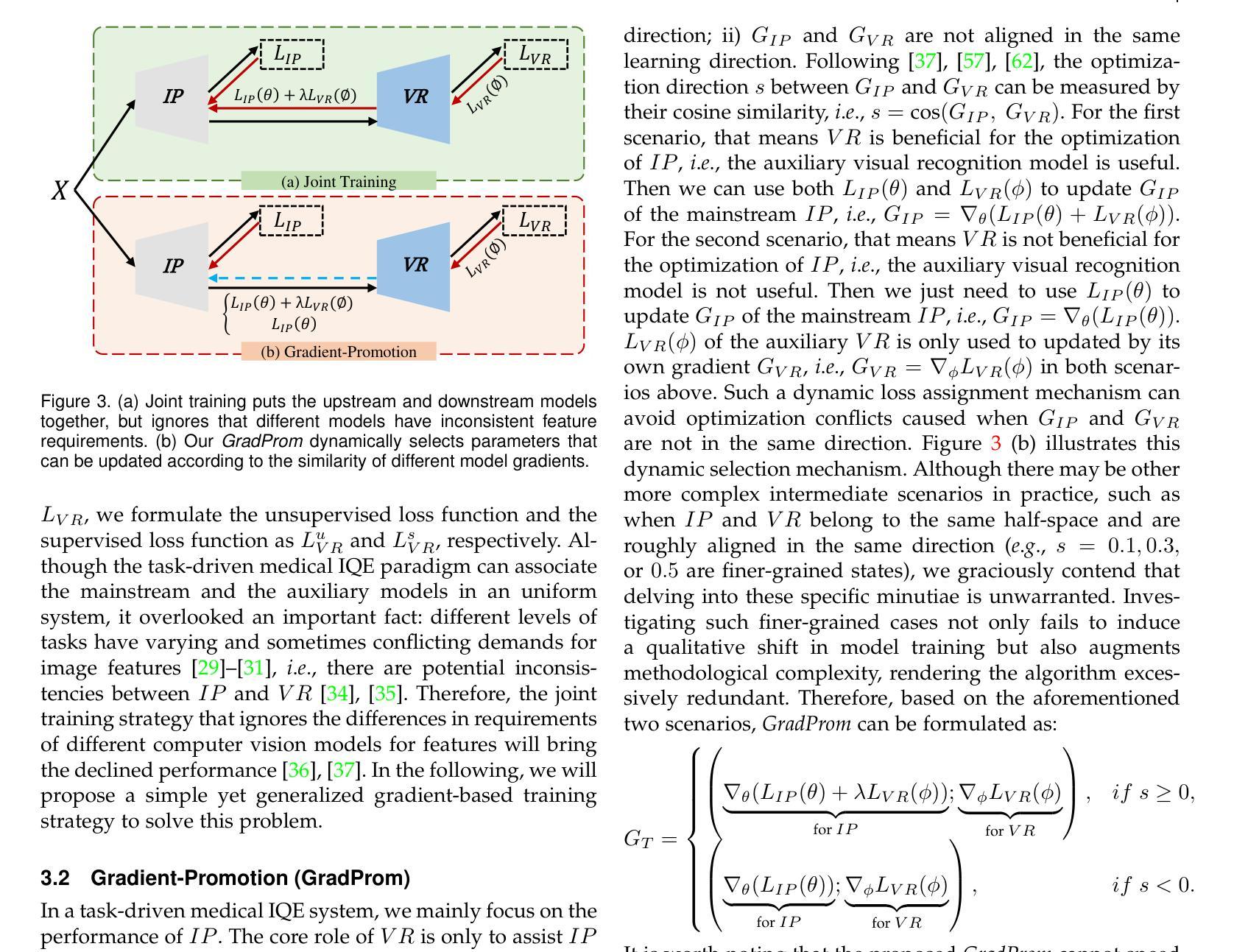
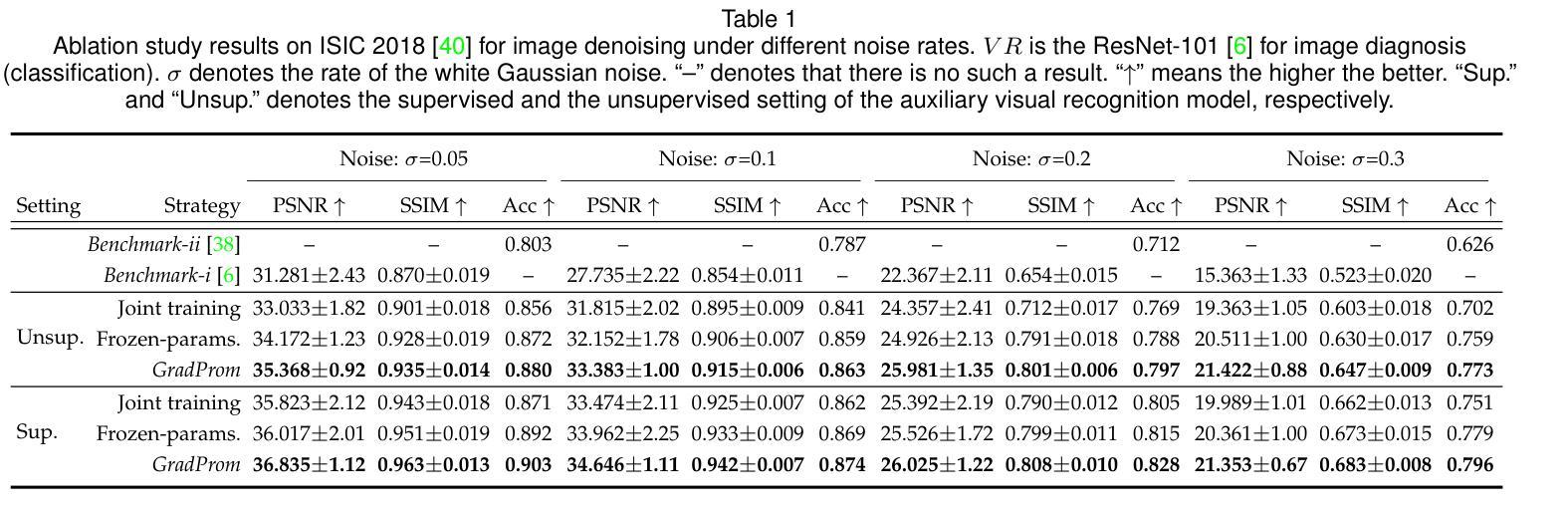
Scale-wise Bidirectional Alignment Network for Referring Remote Sensing Image Segmentation
Authors:Kun Li, George Vosselman, Michael Ying Yang
The goal of referring remote sensing image segmentation (RRSIS) is to extract specific pixel-level regions within an aerial image via a natural language expression. Recent advancements, particularly Transformer-based fusion designs, have demonstrated remarkable progress in this domain. However, existing methods primarily focus on refining visual features using language-aware guidance during the cross-modal fusion stage, neglecting the complementary vision-to-language flow. This limitation often leads to irrelevant or suboptimal representations. In addition, the diverse spatial scales of ground objects in aerial images pose significant challenges to the visual perception capabilities of existing models when conditioned on textual inputs. In this paper, we propose an innovative framework called Scale-wise Bidirectional Alignment Network (SBANet) to address these challenges for RRSIS. Specifically, we design a Bidirectional Alignment Module (BAM) with learnable query tokens to selectively and effectively represent visual and linguistic features, emphasizing regions associated with key tokens. BAM is further enhanced with a dynamic feature selection block, designed to provide both macro- and micro-level visual features, preserving global context and local details to facilitate more effective cross-modal interaction. Furthermore, SBANet incorporates a text-conditioned channel and spatial aggregator to bridge the gap between the encoder and decoder, enhancing cross-scale information exchange in complex aerial scenarios. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed method achieves superior performance in comparison to previous state-of-the-art methods on the RRSIS-D and RefSegRS datasets, both quantitatively and qualitatively. The code will be released after publication.
遥感图像分割(RRSIS)的目标是通过对自然语言表达式进行解析,提取航空图像中的特定像素级区域。最近的进展,特别是基于Transformer的融合设计,已经在这个领域取得了显著的进步。然而,现有的方法主要关注在跨模态融合阶段使用语言感知指导来优化视觉特征,忽视了从视觉到语言的互补流。这一局限性通常会导致表示不相关或次优。此外,航空图像中地面对象的各种空间尺度对模型的视觉感知能力构成了挑战,尤其是在接受文本输入的情况下。在本文中,我们提出了一种名为尺度双向对齐网络(SBANet)的创新框架来解决RRSIS的这些挑战。具体来说,我们设计了一个双向对齐模块(BAM),其中包含可学习的查询令牌,以选择性和有效地表示视觉和语言特征,强调与关键令牌相关的区域。BAM通过动态特征选择块进一步增强,旨在提供宏观和微观级别的视觉特征,保留全局上下文和局部细节,以促进更有效的跨模态交互。此外,SBANet结合了文本条件通道和空间聚合器,以缩小编码器和解码器之间的差距,增强复杂航空场景中跨尺度信息交换。大量实验表明,与RRSIS-D和RefSegRS数据集上的最新方法相比,我们的方法在定量和定性方面都实现了卓越的性能。代码将在发表后发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
摘要
遥感图像分割(RRSIS)的目标是通过自然语言表达式提取航空图像中的特定像素级区域。最近的进步,特别是基于Transformer的融合设计,已经在这个领域取得了显著的进步。然而,现有方法主要集中在利用语言感知指导来优化视觉特征,忽视了从视觉到语言的互补流动。这种局限性通常会导致表示不相关或次优。此外,航空图像中地面对象的空间尺度多样性给现有模型在文本输入条件下的视觉感知能力带来了挑战。本文提出了一种创新的框架,称为Scale-wise Bidirectional Alignment Network (SBANet),以解决RRSIS的这些挑战。我们设计了带有可学习查询标记的双向对齐模块(BAM),以选择和有效地表示视觉和语言特征,强调与关键标记相关的区域。BAM进一步通过动态特征选择块增强,旨在提供宏观和微观级别的视觉特征,保留全局上下文和局部细节,以促进更有效的跨模态交互。此外,SBANet结合了文本条件通道和空间聚合器,以缩小编码器和解码器之间的差距,增强复杂航空场景中的跨尺度信息交换。大量实验表明,与RRSIS-D和RefSegRS数据集上的最新方法相比,我们所提出的方法在定量和定性方面都实现了卓越的性能。
关键见解
- 遥感图像分割(RRSIS)的目标是通过自然语言表达式提取航空图像中的特定像素级区域。
- 现有方法主要关注于使用语言感知指导在跨模态融合阶段优化视觉特征,但忽视了从视觉到语言的互补流动。
- 航空图像中地面对象的空间尺度多样性给现有模型带来挑战。
- 本文提出了一种创新的框架SBANet,包括双向对齐模块(BAM)和动态特征选择块,以更有效地处理视觉和语言特征。
- SBANet通过文本条件通道和空间聚合器增强了跨尺度信息交换。
- 实验表明,SBANet在RRSIS-D和RefSegRS数据集上的性能优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图


Role of Chalcogen atoms in In Situ Exfoliation for Large-Area 2D Semiconducting Transition Metal Dichalcogenides
Authors:Zhiying Dan, Ronak Sarmasti Emami, Giovanna Feraco, Melina Vavali, Dominic Gerlach, Petra Rudolf, Antonija Grubišić-Čabo
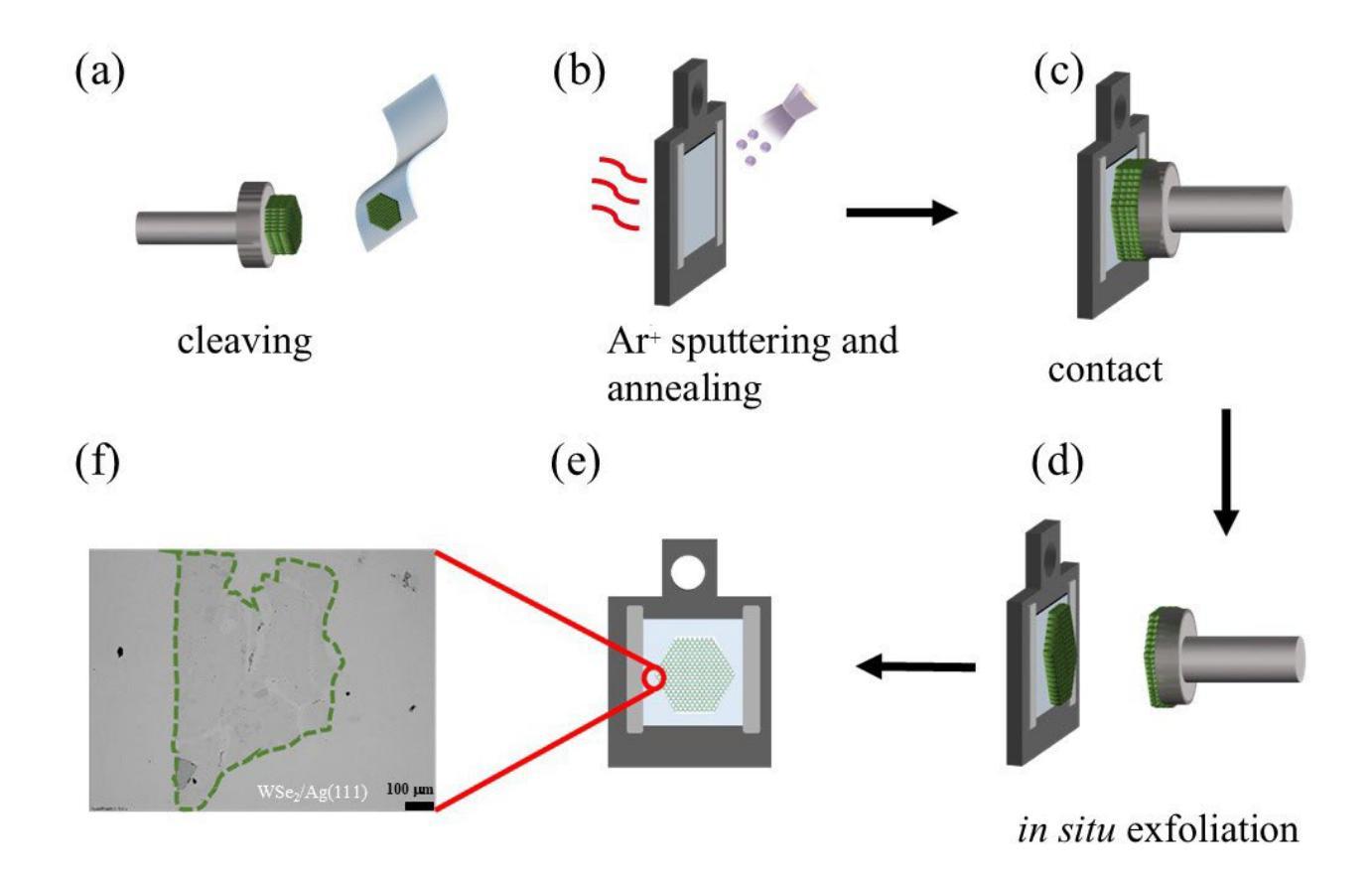
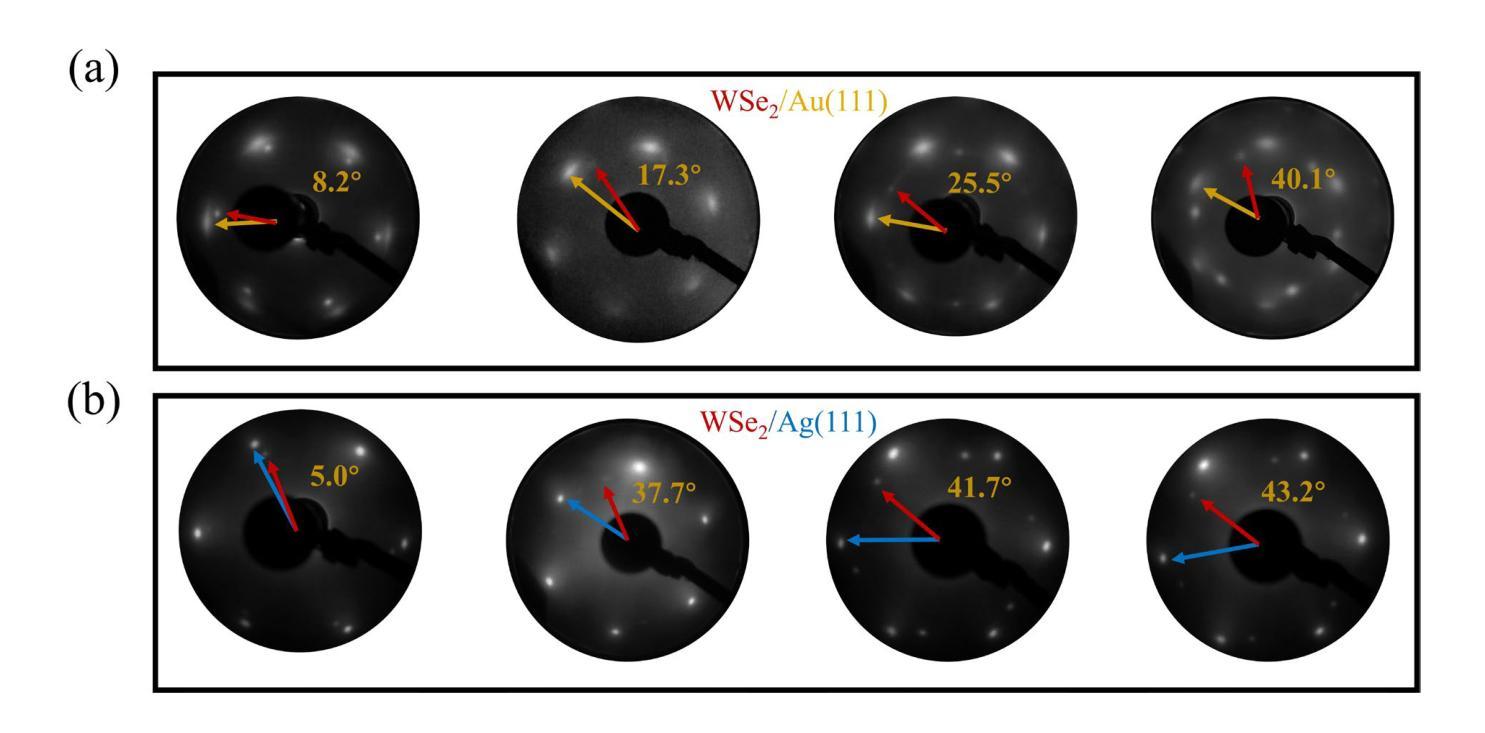
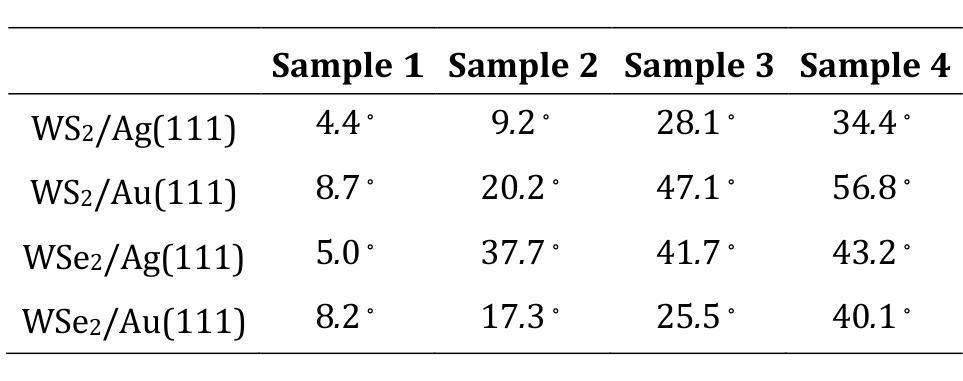
Two-dimensional (2D) transition metal dichalcogenides have emerged as a promising platform for next-generation optoelectronic and spintronic devices. Mechanical exfoliation using adhesive tape remains the dominant method for preparing 2D materials of highest quality, including transition metal dichalcogenides, but always results in small-sized flakes. This limitation poses a significant challenge for investigations and applications where large scale flakes are needed. To overcome these constraints, we explored the preparation of 2D WS2 and WSe2 using a recently developed kinetic in situ single-layer synthesis method (KISS). In particular, we focused on the influence of different substrates, Au and Ag, and chalcogen atoms, S and Se, on the yield and quality of the 2D films. The crystallinity and spatial morphology of the 2D films were characterized using optical microscopy and atomic force microscopy, providing a comprehensive assessment of exfoliation quality. Low-energy electron diffraction verified that there is no preferential orientation between the 2D film and the substrate, while optical microscopy revealed that WSe2 consistently outperformed WS2 in producing large monolayers, regardless of the substrate used. Finally, X-ray diffraction and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy demonstrate that no covalent bonds are formed between the 2D material and the underlying substrate. These results identify KISS method as a non-destructive approach for a more scalable approach of high-quality 2D transition metal dichalcogenides.
二维(2D)过渡金属二卤化物已成为下一代光电子和自旋电子器件的有前途的平台。使用胶带剥离法仍是制备包括过渡金属二卤化物在内的高质量二维材料的主要方法,但总是产生尺寸较小的薄片。这一局限性对于需要大规模薄片的研究和应用构成重大挑战。为了克服这些限制,我们探索了使用最近开发的动力学原位单层合成方法(KISS)制备二维WS2和WSe2。特别是,我们关注不同的基底(Au和Ag)以及硫族原子(S和Se)对二维薄膜的产量和质量的影响。二维薄膜的结晶度和空间形态通过光学显微镜和原子力显微镜表征,从而全面评估剥离质量。低能电子衍射证明二维薄膜与基底之间不存在择优取向,而光学显微镜显示,无论使用何种基底,WSe2在生成大型单层方面始终优于WS2。最后,X射线衍射和X射线光电子能谱证明二维材料与底层基底之间没有形成共价键。这些结果将KISS方法确定为一种非破坏性的方法,可以更大规模地应用高质量二维过渡金属二卤化物。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Article (13 pages, 5 figures) and supporting information (5 pages, 6 figures)
Summary
本文探索了使用新型的KISS方法合成二维WS2和WSe2材料,研究了不同基底(Au和Ag)和硫族元素(S和Se)对二维薄膜的产率和品质的影响。该方法被证实可以有效合成高质量大尺寸二维薄膜材料,并未对基底形成任何共价键,是一种可扩展的非破坏性方法。
Key Takeaways
- 过渡金属二卤化物在光电子学和自旋电子学器件领域具有潜力。
- 机械剥离法仍是制备高质量二维材料的常用方法,但难以获得大尺寸薄膜。
- KISS方法可用于合成二维WS2和WSe2材料。
- 基底类型和硫族元素对二维薄膜的产率和质量有影响。
- KISS方法合成的二维薄膜具有优良的单晶结构和空间形态。
- 非晶化验证显示基底与二维薄膜间没有优先取向性。
点此查看论文截图

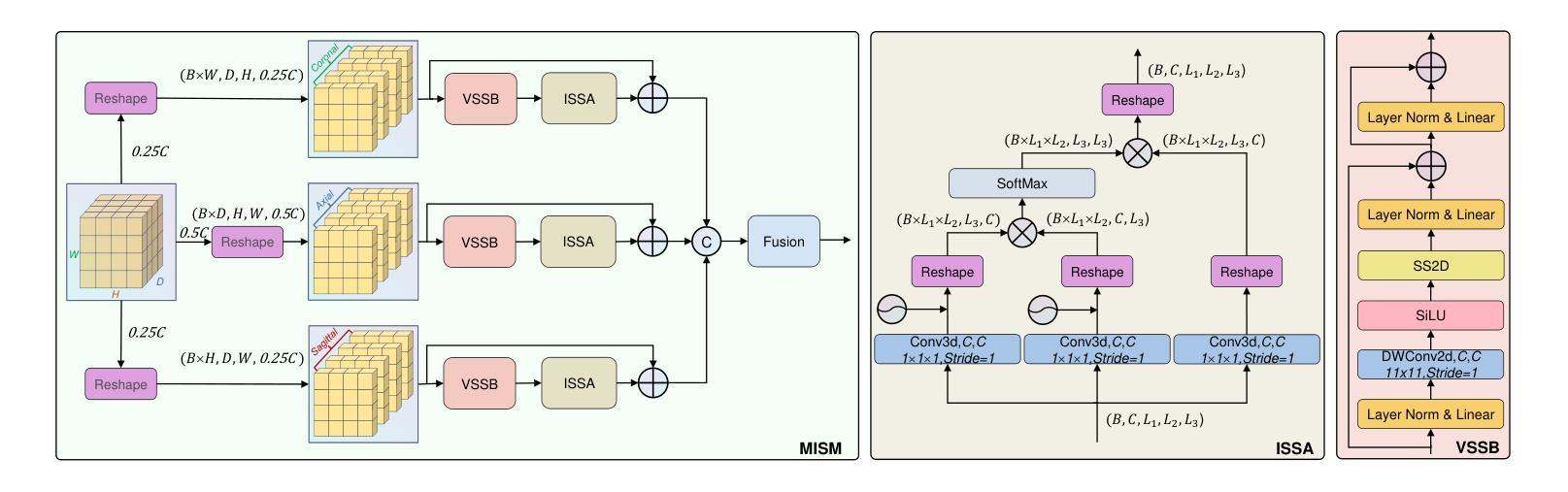
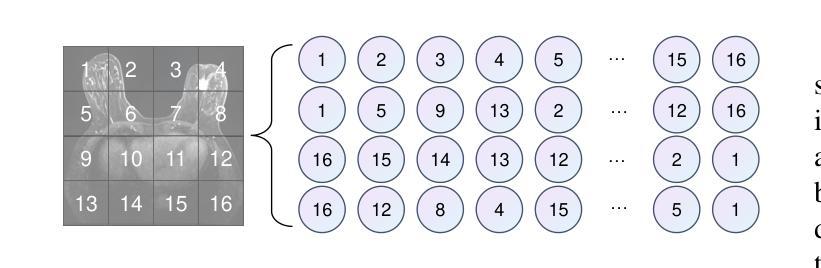
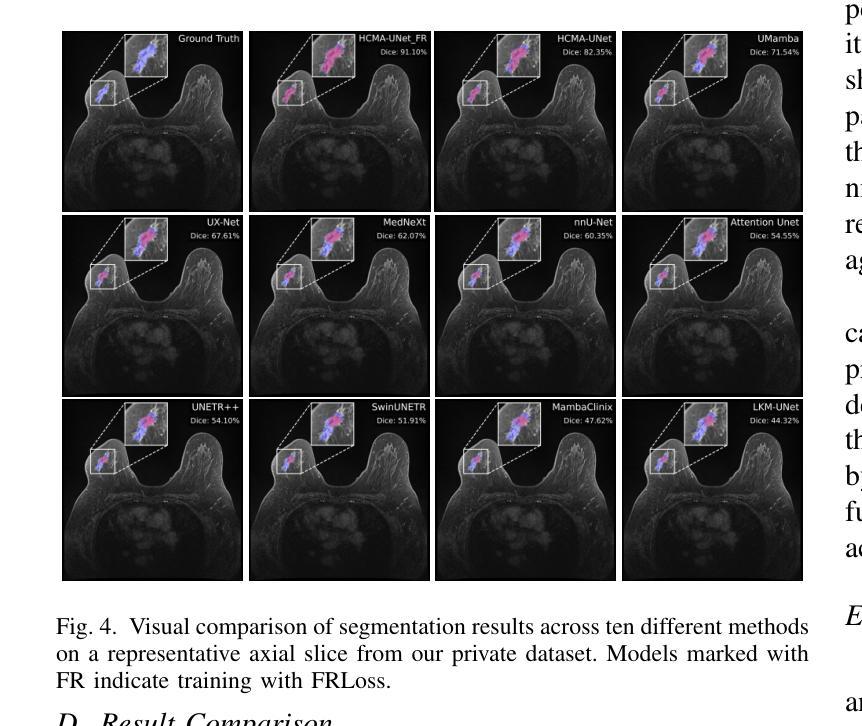
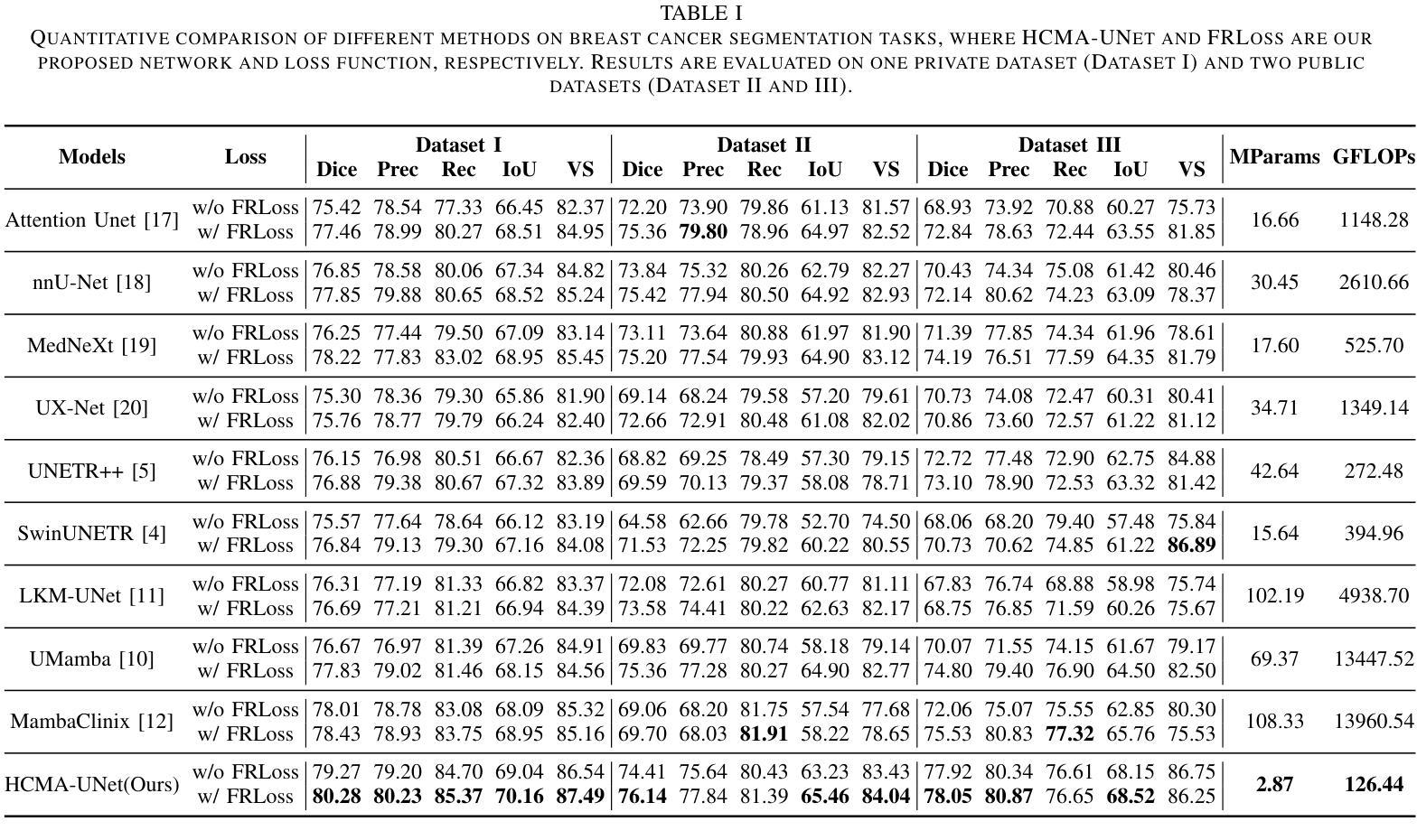
HCMA-UNet: A Hybrid CNN-Mamba UNet with Inter-Slice Self-Attention for Efficient Breast Cancer Segmentation
Authors:Haoxuan Li, Wei song, Peiwu Qin, Xi Yuan, Zhenglin Chen
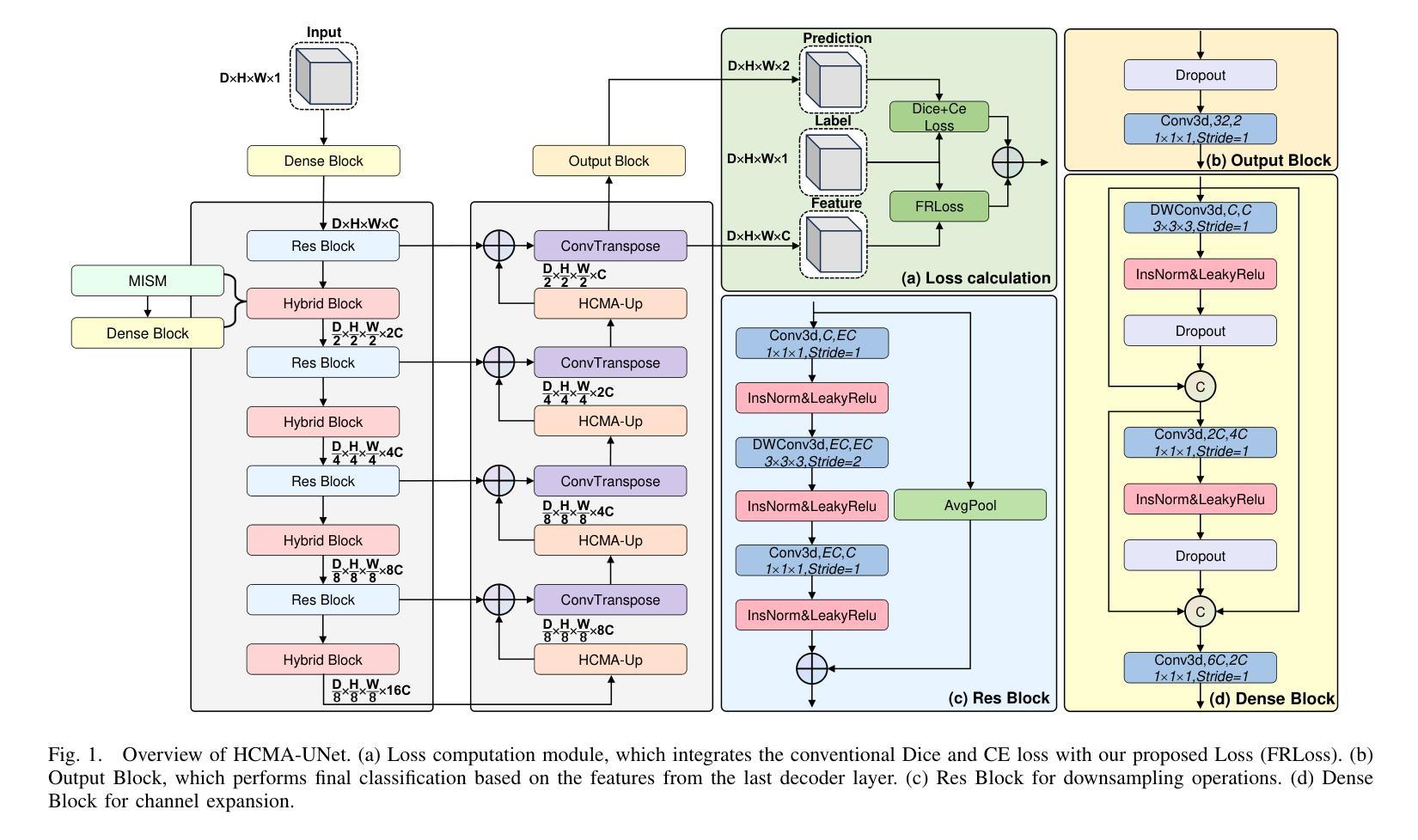
Breast cancer lesion segmentation in DCE-MRI remains challenging due to heterogeneous tumor morphology and indistinct boundaries. To address these challenges, this study proposes a novel hybrid segmentation network, HCMA-UNet, for lesion segmentation of breast cancer. Our network consists of a lightweight CNN backbone and a Multi-view Inter-Slice Self-Attention Mamba (MISM) module. The MISM module integrates Visual State Space Block (VSSB) and Inter-Slice Self-Attention (ISSA) mechanism, effectively reducing parameters through Asymmetric Split Channel (ASC) strategy to achieve efficient tri-directional feature extraction. Our lightweight model achieves superior performance with 2.87M parameters and 126.44 GFLOPs. A Feature-guided Region-aware loss function (FRLoss) is proposed to enhance segmentation accuracy. Extensive experiments on one private and two public DCE-MRI breast cancer datasets demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance while maintaining computational efficiency. FRLoss also exhibits good cross-architecture generalization capabilities. The source code and dataset is available on this link.
乳腺癌在动态对比增强磁共振成像(DCE-MRI)中的病灶分割仍然是一个挑战,这是由于肿瘤形态学异质性以及边界不清晰所导致的。为了解决这些挑战,本研究提出了一种新型的混合分割网络HCMA-UNet,用于乳腺癌病灶的分割。我们的网络由轻量级的CNN骨干网和多视图切片间自注意力Mamba(MISM)模块组成。MISM模块结合了视觉状态空间块(VSSB)和切片间自注意力(ISSA)机制,通过不对称分裂通道(ASC)策略有效地减少参数,实现高效的三向特征提取。我们的轻量级模型具有出色的性能,包含287万参数和每秒浮点运算次数为126.44次。为了提高分割精度,提出了基于特征的区域感知损失函数(FRLoss)。在一个私有和两个公开的动态对比增强磁共振成像乳腺癌数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在实现最新性能的同时保持了计算效率。此外,FRLoss还展现出良好的跨架构泛化能力。源代码和数据集可在链接中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新型的混合分割网络HCMA-UNet,用于乳腺癌病变的分割。该网络包含轻量级CNN骨干和Multi-view Inter-Slice Self-Attention Mamba(MISM)模块,实现了高效的三向特征提取。通过采用特征引导的Region感知损失函数(FRLoss),提高了分割精度。在多个数据集上的实验表明,该方法达到了最先进的性能,同时保持了计算效率。
Key Takeaways
- 乳腺癌DCE-MRI图像分割具有挑战性,主要由于肿瘤形态异质性和边界模糊。
- 提出了一种新型的混合分割网络HCMA-UNet,包含轻量级CNN骨干和MISM模块。
- MISM模块结合了VSSB和ISSA机制,通过ASC策略有效减少参数,实现三向特征提取。
- HCMA-UNet模型性能优越,参数为2.87M,计算量为126.44 GFLOPs。
- 引入FRLoss函数提高分割精度,并在多个数据集上实现最佳性能。
- FRLoss函数具有良好的跨架构泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

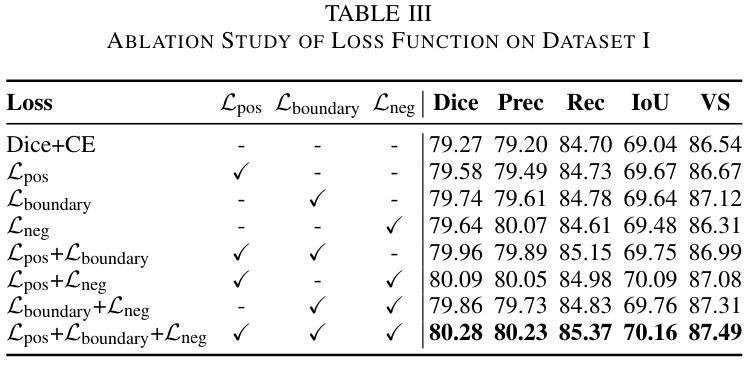
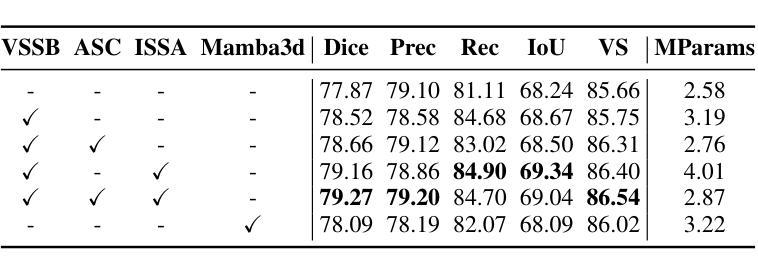
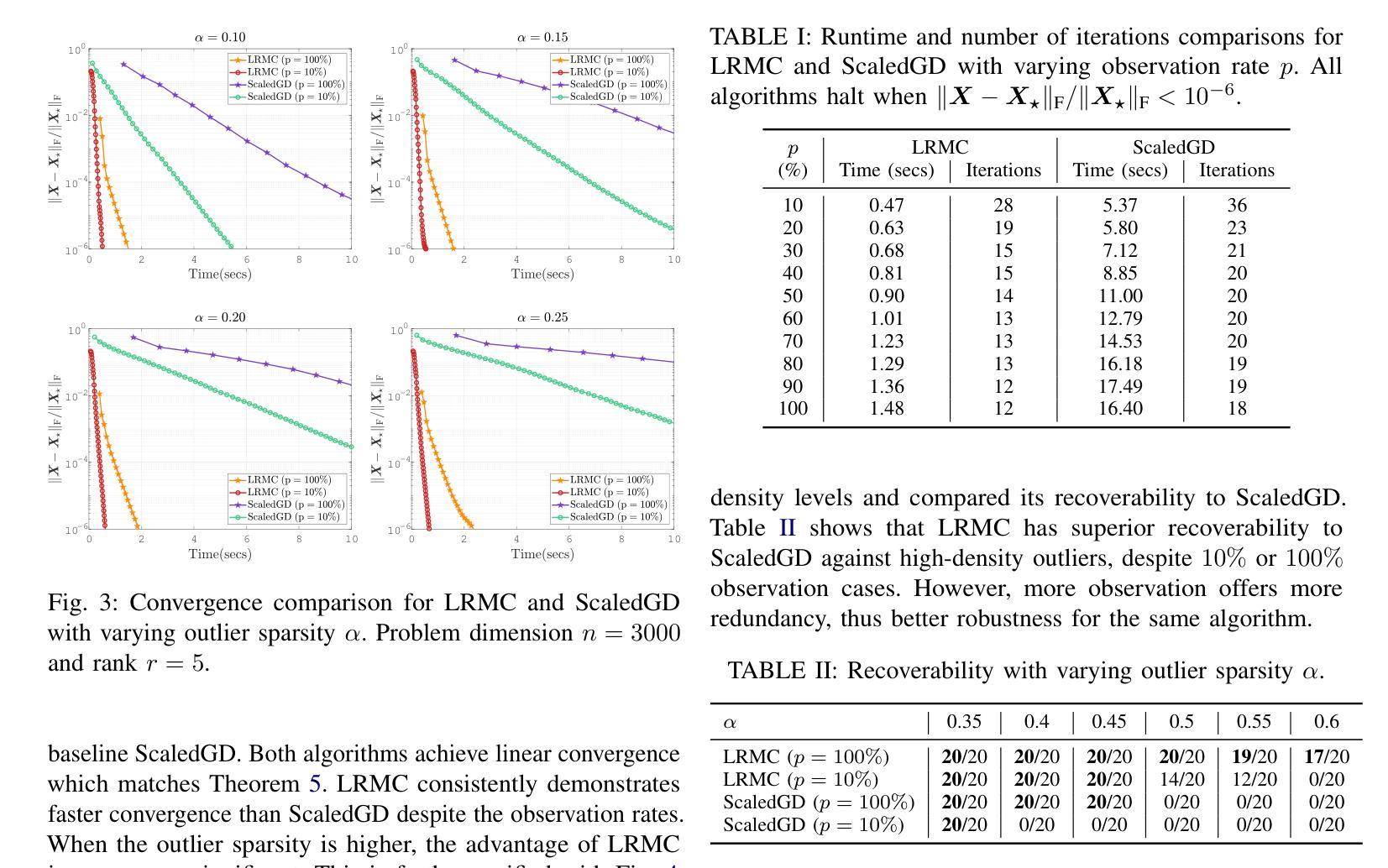
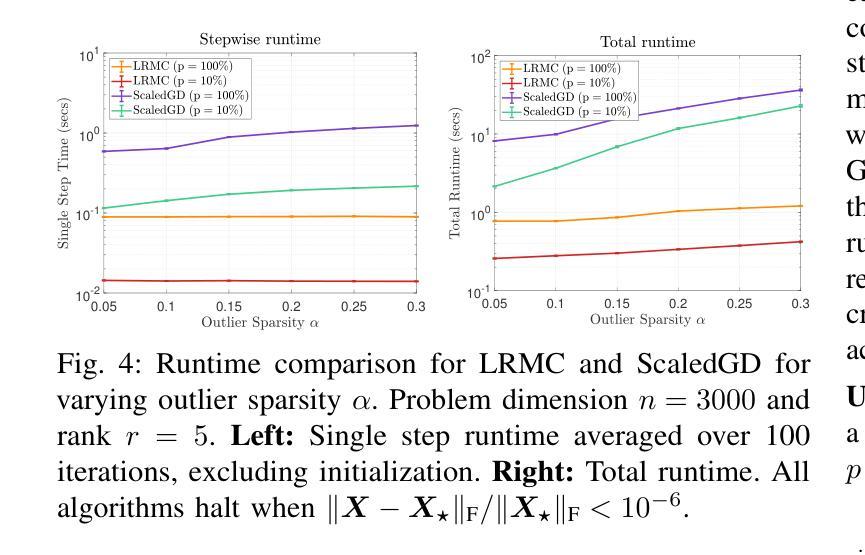
Deeply Learned Robust Matrix Completion for Large-scale Low-rank Data Recovery
Authors:HanQin Cai, Chandra Kundu, Jialin Liu, Wotao Yin
Robust matrix completion (RMC) is a widely used machine learning tool that simultaneously tackles two critical issues in low-rank data analysis: missing data entries and extreme outliers. This paper proposes a novel scalable and learnable non-convex approach, coined Learned Robust Matrix Completion (LRMC), for large-scale RMC problems. LRMC enjoys low computational complexity with linear convergence. Motivated by the proposed theorem, the free parameters of LRMC can be effectively learned via deep unfolding to achieve optimum performance. Furthermore, this paper proposes a flexible feedforward-recurrent-mixed neural network framework that extends deep unfolding from fix-number iterations to infinite iterations. The superior empirical performance of LRMC is verified with extensive experiments against state-of-the-art on synthetic datasets and real applications, including video background subtraction, ultrasound imaging, face modeling, and cloud removal from satellite imagery.
鲁棒矩阵补全(RMC)是一种广泛应用于机器学习领域的工具,它能同时解决低秩数据分析中的两个关键问题:数据缺失和极端异常值。本文针对大规模RMC问题,提出了一种新的可伸缩、可学习的非凸方法,称为学习鲁棒矩阵补全(LRMC)。LRMC具有较低的计算复杂度,并能实现线性收敛。受定理的启发,LRMC的自由参数可以通过深度展开进行有效地学习,以达到最佳性能。此外,本文提出了一种灵活的反馈递归混合神经网络框架,它将深度展开从固定迭代扩展到无限迭代。通过大量的实验验证了LRMC在合成数据集和实际应用中的卓越表现,包括视频背景去除、超声成像、面部建模以及卫星图像的云去除等。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2110.05649
Summary
新型可学习非凸方法(LRMC)应用于大规模鲁棒矩阵补全(RMC),该方法具备低计算复杂度及线性收敛性,并能通过深度展开有效地学习自由参数以获得最佳性能。此外,本文提出了一个灵活的混合神经网络框架,将深度展开从固定迭代次数扩展到无限迭代次数。LRMC在合成数据集和实际应用中的表现均优于其他最新技术,包括视频背景去除、超声成像、面部建模和卫星图像去云等。
Key Takeaways
- LRMC是一种新型的可学习非凸方法,用于解决大规模鲁棒矩阵补全(RMC)问题。
- LRMC具备低计算复杂度和线性收敛性。
- 通过深度展开,LRMC的自由参数可以有效地学习,以实现最佳性能。
- 提出了一个灵活的混合神经网络框架,将深度展开从固定迭代扩展到无限迭代。
- LRMC在合成数据集上的表现优于其他最新技术。
- LRMC在视频背景去除、超声成像、面部建模等实际应用中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

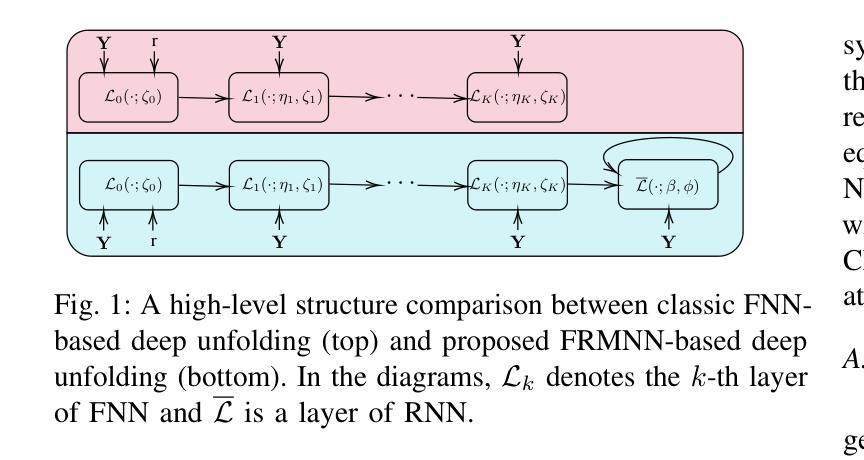
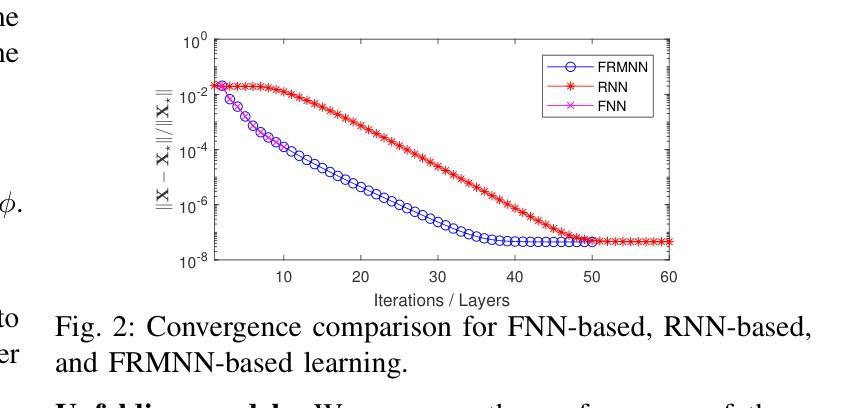
Leaf diseases detection using deep learning methods
Authors:El Houcine El Fatimi
This study, our main topic is to devlop a new deep-learning approachs for plant leaf disease identification and detection using leaf image datasets. We also discussed the challenges facing current methods of leaf disease detection and how deep learning may be used to overcome these challenges and enhance the accuracy of disease detection. Therefore, we have proposed a novel method for the detection of various leaf diseases in crops, along with the identification and description of an efficient network architecture that encompasses hyperparameters and optimization methods. The effectiveness of different architectures was compared and evaluated to see the best architecture configuration and to create an effective model that can quickly detect leaf disease. In addition to the work done on pre-trained models, we proposed a new model based on CNN, which provides an efficient method for identifying and detecting plant leaf disease. Furthermore, we evaluated the efficacy of our model and compared the results to those of some pre-trained state-of-the-art architectures.
本研究的主要课题是开发一种新的深度学习方法来识别农作物叶片疾病并检测叶片图像数据集。我们还讨论了当前叶片疾病检测方法面临的挑战,以及如何利用深度学习来克服这些挑战并增强疾病检测的准确性。因此,我们提出了一种检测农作物各种叶片疾病的新方法,并确定和描述了一个有效的网络架构,该架构涵盖了超参数和优化方法。我们比较并评估了不同架构的有效性,以找出最佳的架构配置并创建一个可以快速检测叶片疾病的有效模型。除了对预训练模型所做的工作外,我们还提出了一种基于CNN的新模型,该模型提供了一种有效识别与检测植物叶片疾病的方法。此外,我们还评估了我们模型的效力,并将结果与某些先进的预训练架构进行了比较。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 252 pages , 42 images
Summary
本研究提出了一种新的深度学习方法和网络架构,用于农作物叶片疾病的识别和检测。通过对比不同架构的效能,最终确定了最佳配置,提高了叶片疾病检测的准确性。同时,本研究也基于CNN提出了一个新模型,并与一些预训练的最先进架构进行了比较和评估。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究关注植物叶片疾病的识别和检测,提出新的深度学习方法和网络架构。
- 研究探讨了当前叶片疾病检测方法的挑战,并探讨了深度学习如何克服这些挑战。
- 通过对比不同架构的效能,确定了最佳网络配置,提高了叶片疾病检测的准确性。
- 研究提出了一种基于CNN的新模型,用于叶片疾病的识别和检测。
- 新模型展示了高效的叶片疾病识别与检测能力。
- 研究对提出的模型进行了评估,并与一些预训练的最先进架构进行了比较。
点此查看论文截图

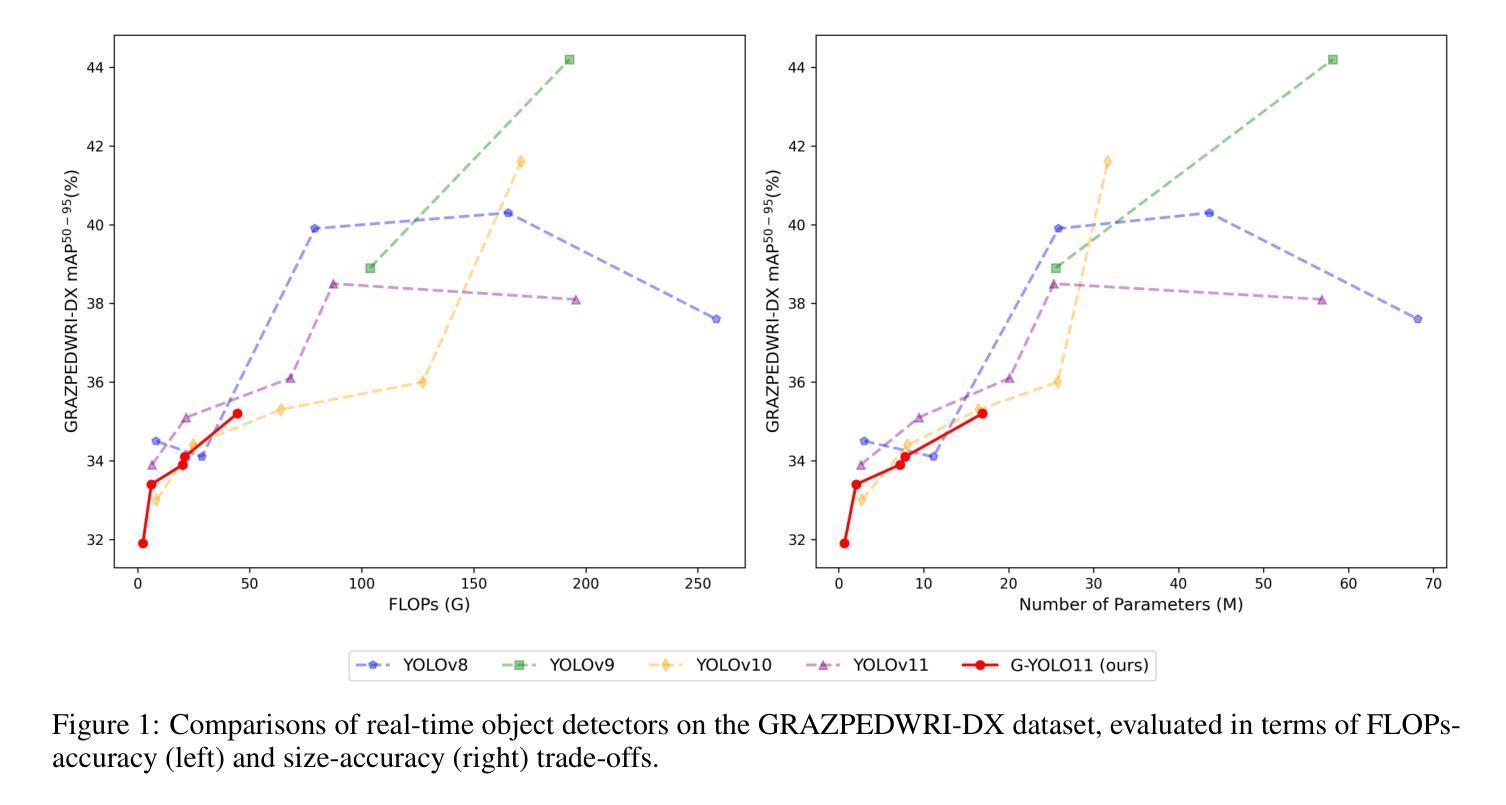
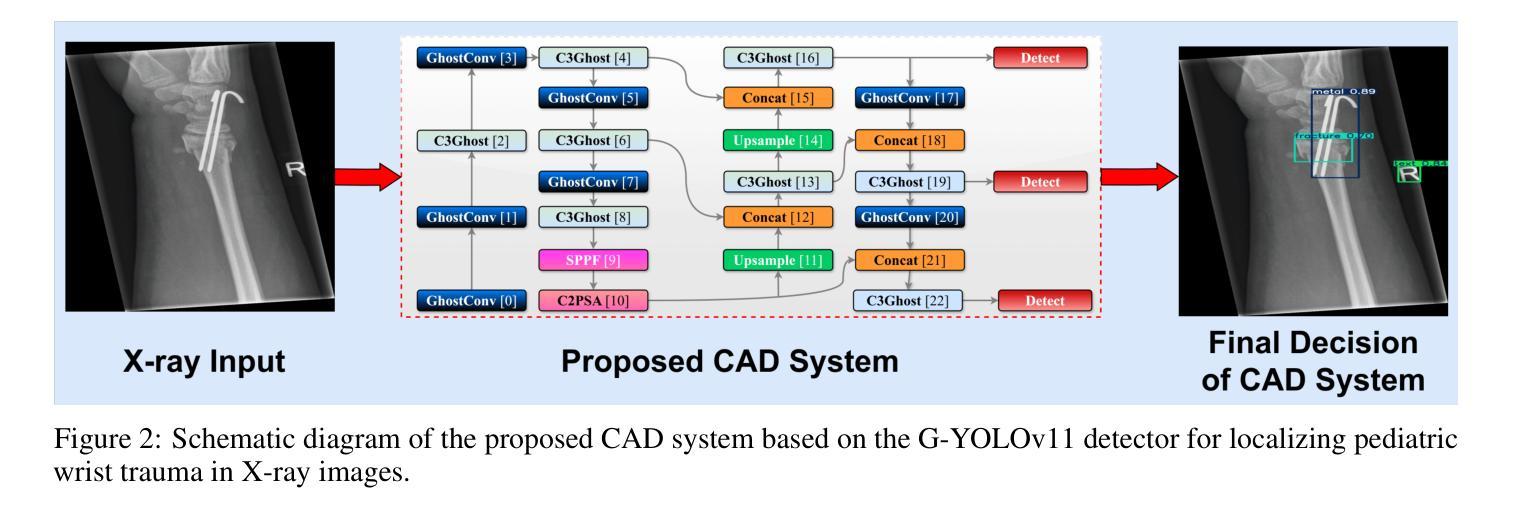
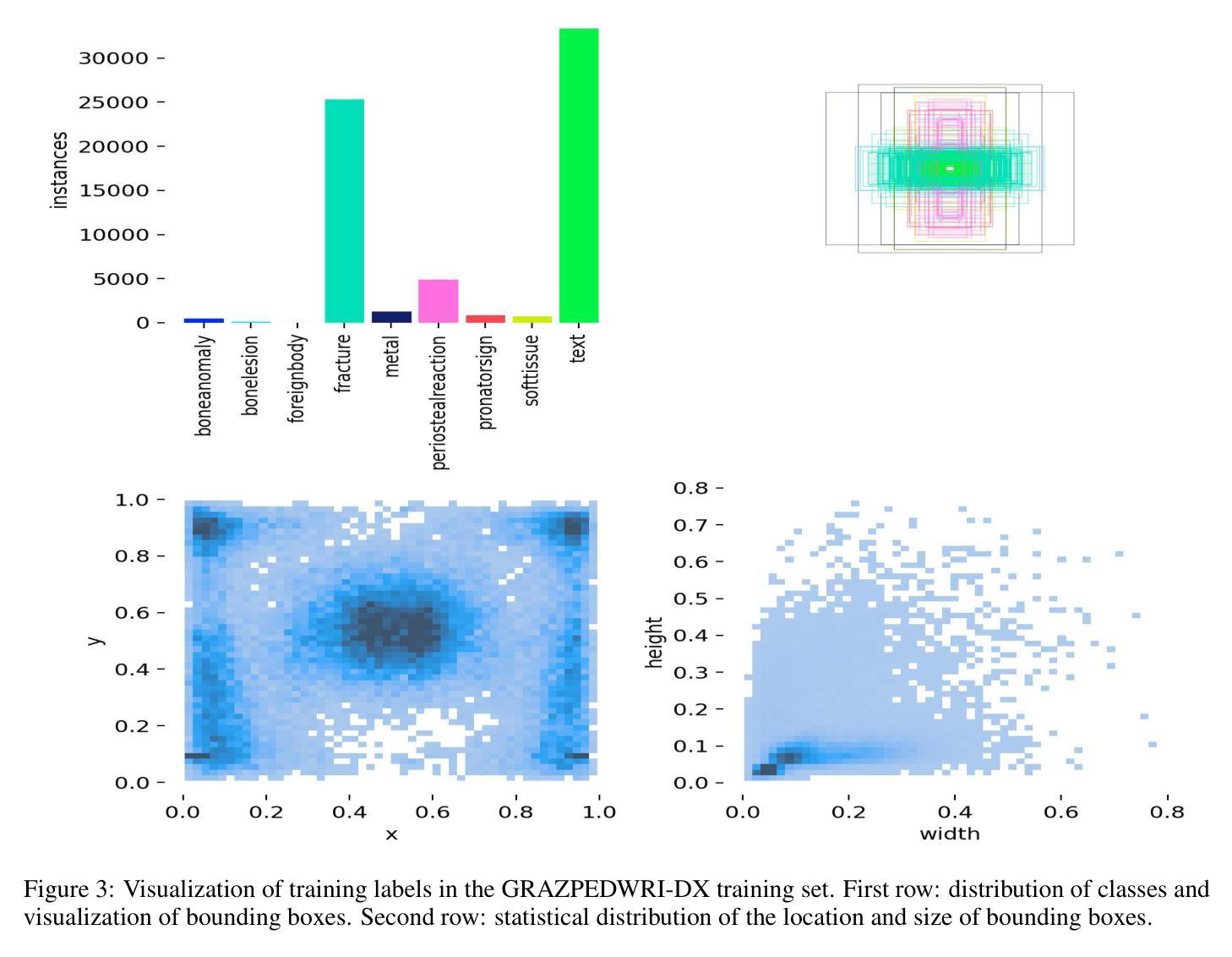
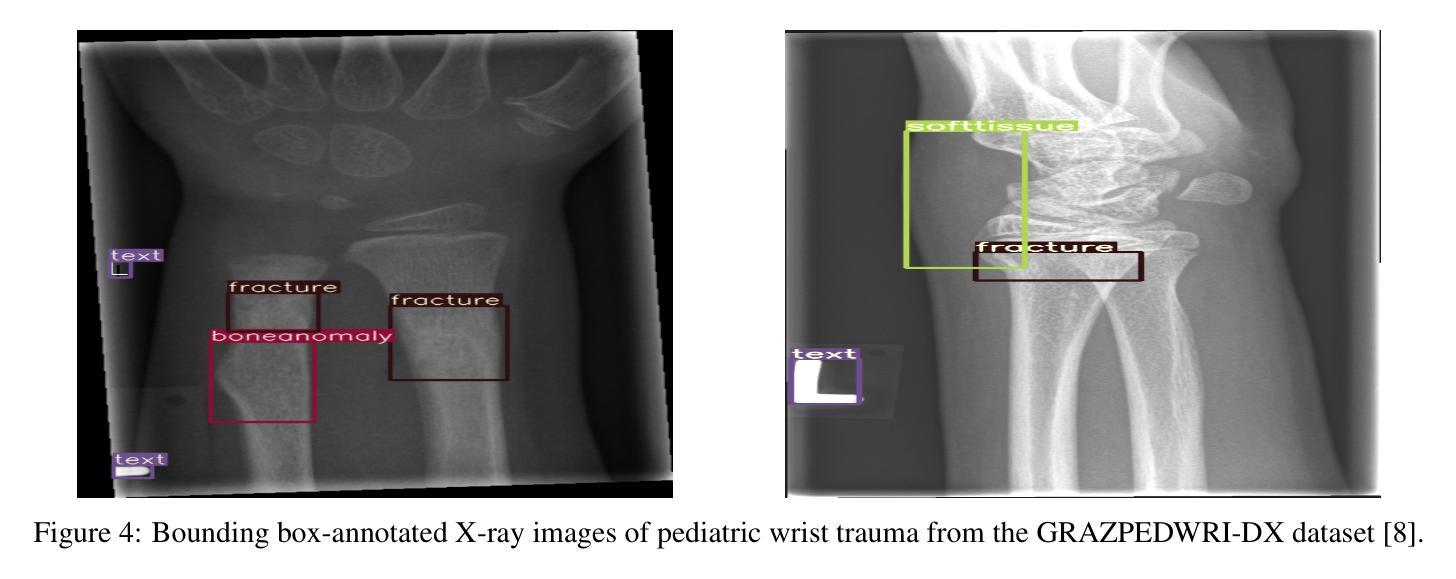
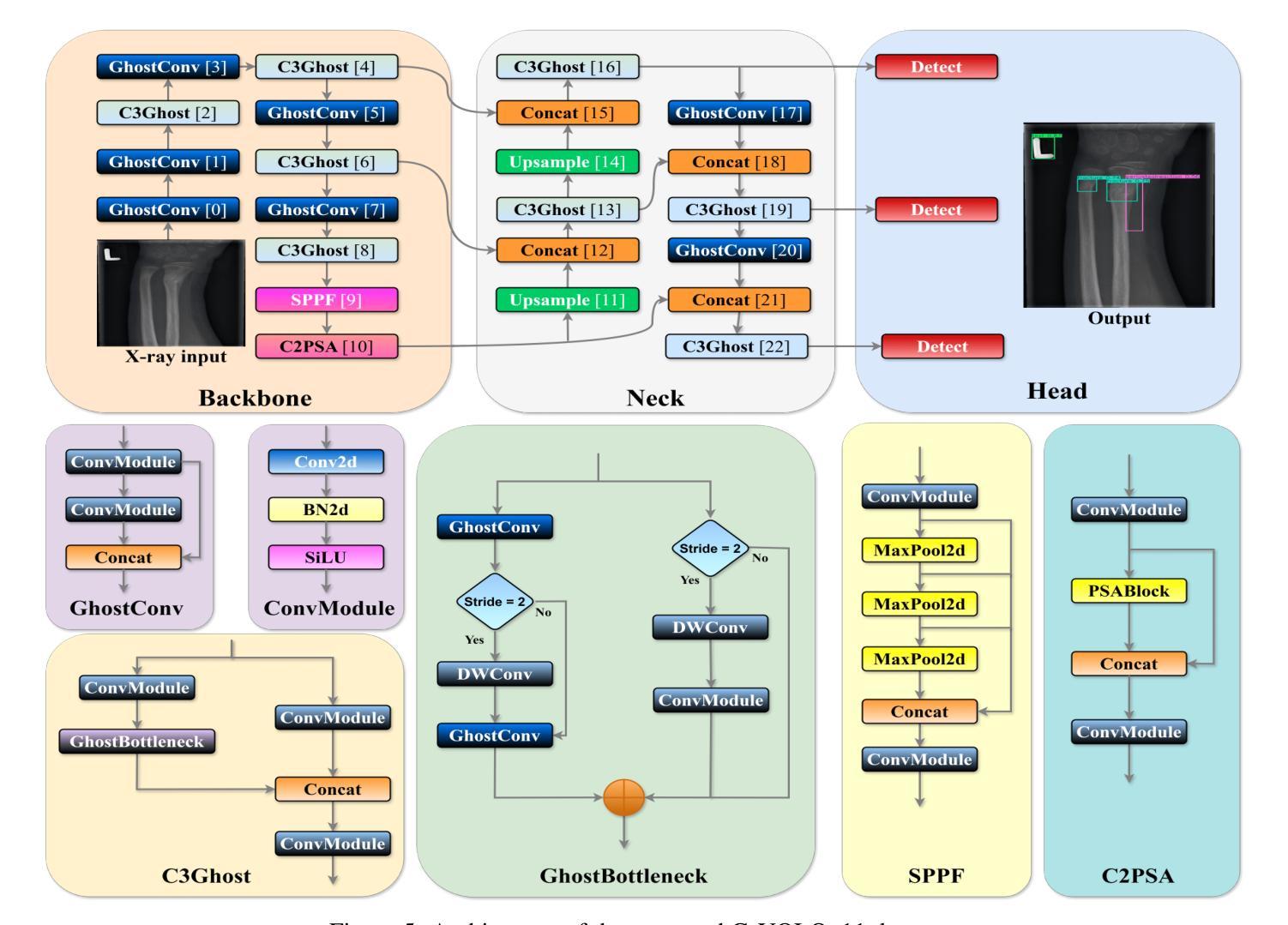
Lightweight G-YOLOv11: Advancing Efficient Fracture Detection in Pediatric Wrist X-rays
Authors:Abdesselam Ferdi
Computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems have greatly improved the interpretation of medical images by radiologists and surgeons. However, current CAD systems for fracture detection in X-ray images primarily rely on large, resource-intensive detectors, which limits their practicality in clinical settings. To address this limitation, we propose a novel lightweight CAD system based on the YOLO detector for fracture detection. This system, named ghost convolution-based YOLOv11 (G-YOLOv11), builds on the latest version of the YOLO detector family and incorporates the ghost convolution operation for feature extraction. The ghost convolution operation generates the same number of feature maps as traditional convolution but requires fewer linear operations, thereby reducing the detector’s computational resource requirements. We evaluated the performance of the proposed G-YOLOv11 detector on the GRAZPEDWRI-DX dataset, achieving an mAP@0.5 of 0.535 with an inference time of 2.4 ms on an NVIDIA A10 GPU. Compared to the standard YOLOv11l, G-YOLOv11l achieved reductions of 13.6% in mAP@0.5 and 68.7% in size. These results establish a new state-of-the-art benchmark in terms of efficiency, outperforming existing detectors. Code and models are available at https://github.com/AbdesselamFerdi/G-YOLOv11.
计算机辅助诊断(CAD)系统极大地提高了放射科医师和外科医师对医学图像的解释能力。然而,当前用于X射线图像骨折检测的CAD系统主要依赖于大型、资源密集型的检测器,这在临床上限制了它们的实用性。为了解决这一限制,我们提出了一种基于YOLO检测器的轻量级CAD系统,用于骨折检测。该系统名为基于Ghost卷积的YOLOv11(G-YOLOv11),它建立在YOLO检测器家族最新版本的基础上,并融入了Ghost卷积操作进行特征提取。Ghost卷积操作生成的特性图数量与传统卷积相同,但所需的线性操作更少,从而降低了检测器的计算资源需求。我们在GRAZPEDWRI-DX数据集上评估了所提出的G-YOLOv11检测器的性能,在NVIDIA A10 GPU上实现0.5的mAP@0.5为0.535,推理时间为2.4毫秒。与标准YOLOv11相比,G-YOLOv11在mAP@0.5上实现了13.6%的降低,体积减少了68.7%。这些结果达到了最新的效率基准点,超越了现有的检测器。代码和模型可在https://github.com/AbdesselamFerdi/G-YOLOv1实现这一目标的过程中我们的GitHub项目是一个完整的仓库,包含了所有相关的代码和模型文件。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于YOLO检测器的轻量化计算机辅助诊断(CAD)系统用于X光影像骨折检测,命名为G-YOLOv11。该系统采用最新YOLO探测器家族版本,并结合ghost卷积操作进行特征提取,以较少的计算资源生成相同数量的特征图。在GRAZPEDWRI-DX数据集上评估,G-YOLOv11探测器在NVIDIA A10 GPU上的推理时间为2.4毫秒,mAP@0.5达到0.535,相较于标准YOLOv11l,在mAP@0.5上降低了13.6%,体积减小了68.7%,展现出卓越的效率。
Key Takeaways
- CAD系统在医学图像解读中的应用:说明计算机辅助诊断(CAD)系统对提高放射科医师和外科医生对医学图像的解读能力具有重要作用。
- 当前X光影像骨折检测CAD系统的局限性:指出当前用于X光影像骨折检测的CAD系统主要依赖于大型、资源密集型的探测器,限制了其在临床环境中的实用性。
- G-YOLOv11系统的提出:介绍了一种新型的基于YOLO检测器的轻量化CAD系统,用于X光影像骨折检测。
- G-YOLOv11系统的特点:强调G-YOLOv11系统采用ghost卷积操作进行特征提取,能够减少计算资源需求。
- G-YOLOv11系统的性能评估:在GRAZPEDWRI-DX数据集上进行的评估表明,G-YOLOv11系统具有高效性能,相较于标准YOLOv11l有显著改善。
- G-YOLOv11系统的可用资源:提供G-YOLOv11系统的代码和模型可供下载。
点此查看论文截图

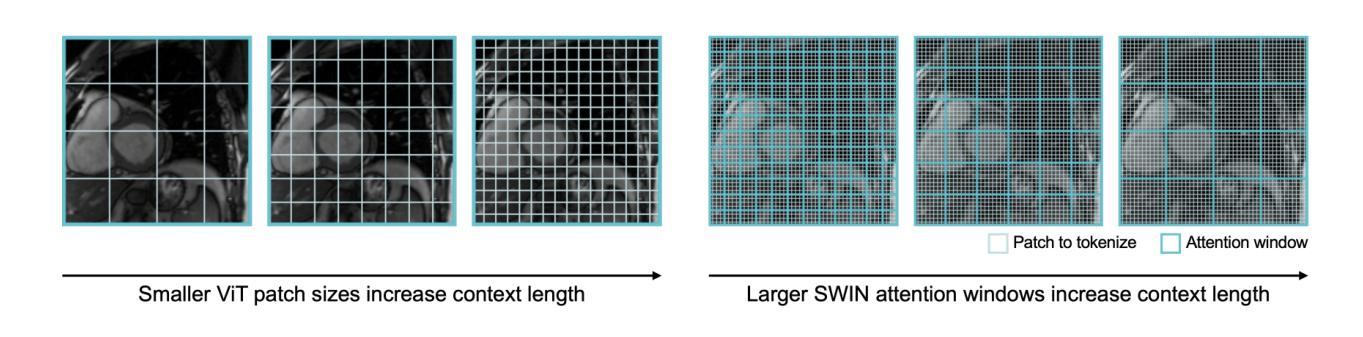
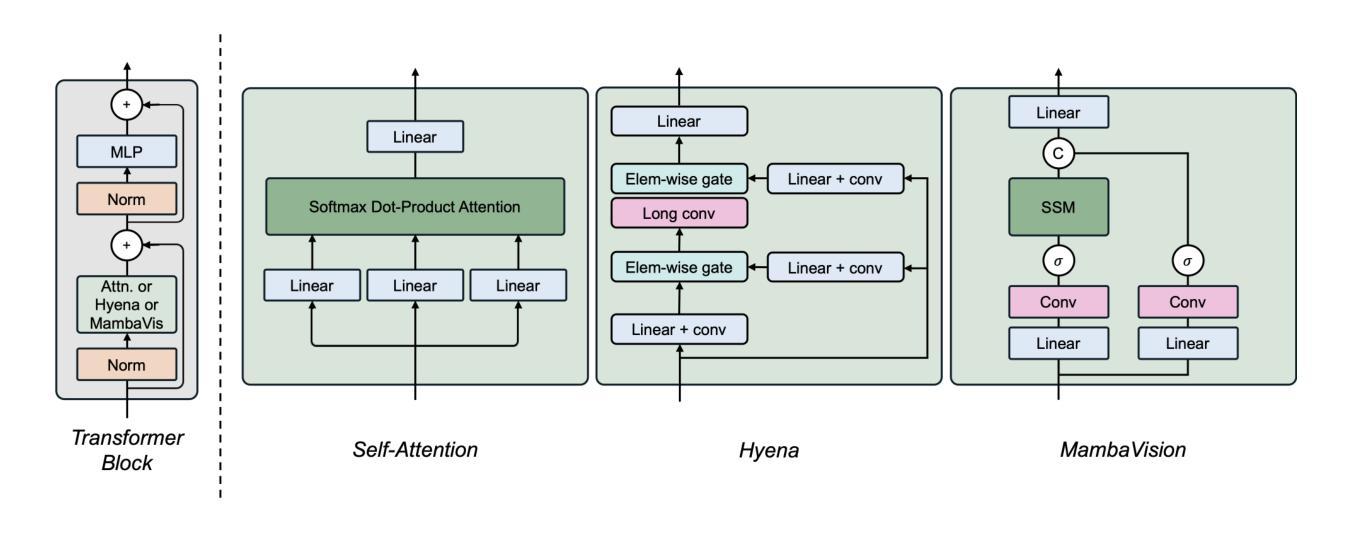
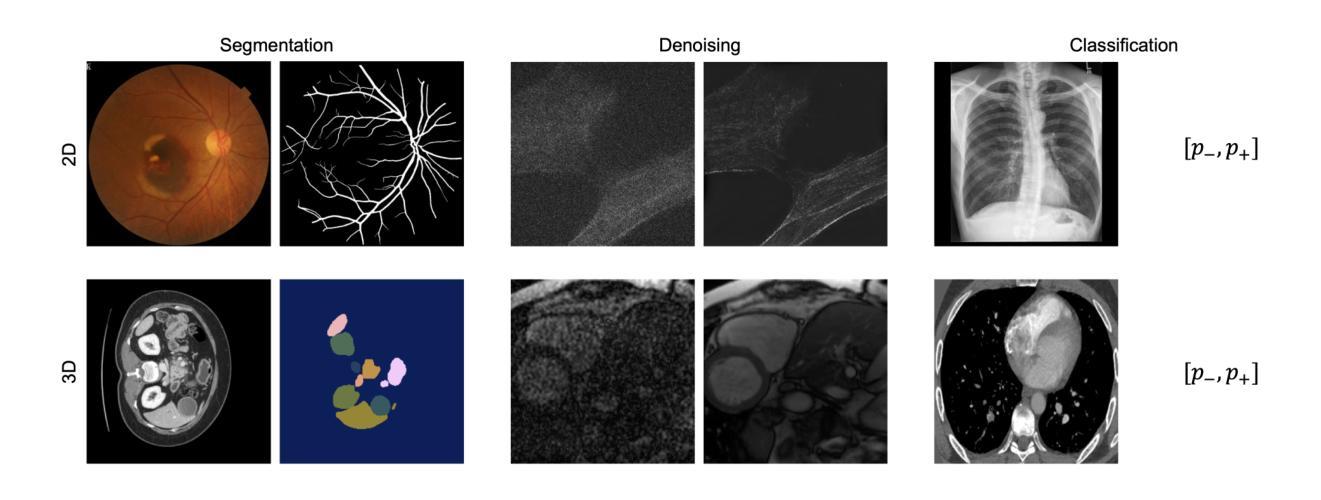
A Study on Context Length and Efficient Transformers for Biomedical Image Analysis
Authors:Sarah M. Hooper, Hui Xue
Biomedical imaging modalities often produce high-resolution, multi-dimensional images that pose computational challenges for deep neural networks. These computational challenges are compounded when training transformers due to the self-attention operator, which scales quadratically with context length. Recent developments in long-context models have potential to alleviate these difficulties and enable more efficient application of transformers to large biomedical images, although a systematic evaluation on this topic is lacking. In this study, we investigate the impact of context length on biomedical image analysis and we evaluate the performance of recently proposed long-context models. We first curate a suite of biomedical imaging datasets, including 2D and 3D data for segmentation, denoising, and classification tasks. We then analyze the impact of context length on network performance using the Vision Transformer and Swin Transformer by varying patch size and attention window size. Our findings reveal a strong relationship between context length and performance, particularly for pixel-level prediction tasks. Finally, we show that recent long-context models demonstrate significant improvements in efficiency while maintaining comparable performance, though we highlight where gaps remain. This work underscores the potential and challenges of using long-context models in biomedical imaging.
生物医学成像模式通常产生高分辨率、多维图像,为深度神经网络带来计算挑战。由于自注意力算子的影响,这些计算挑战在训练变压器时更加复杂,自注意力算子的计算量与上下文长度成二次方关系。虽然针对此主题的系统性评估仍有所欠缺,但最近的长上下文模型的发展具有缓解这些困难并促进变压器在大型生物医学图像上更有效率应用的潜力。在这项研究中,我们研究了上下文长度对生物医学图像分析的影响,并评估了最近提出的长上下文模型的性能。我们首先整理了一套生物医学成像数据集,包括用于分割、去噪和分类任务的二维和三维数据。然后我们通过改变补丁大小和注意力窗口大小,使用视觉变压器和Swin变压器分析上下文长度对网络性能的影响。我们的研究发现上下文长度与性能之间存在密切关系,特别是在像素级预测任务中。最后,我们证明了最近的长上下文模型在保持性能的同时显示出显著的效率提升,尽管我们也指出了仍存在差距的地方。这项工作突出了在长上下文模型在生物医学成像中的潜力和挑战。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at ML4H 2024
摘要
生物医学成像模态产生的高分辨率、多维图像对深度神经网络带来了计算挑战,尤其是在训练变压器时,自注意力算子会使计算量随上下文长度二次方增长。虽然已有研究提出长上下文模型有潜力缓解这些困难,使变压器在大型生物医学图像上的应用更加高效,但对此主题的系统性评估仍缺乏。本研究旨在探讨上下文长度对生物医学图像分析的影响,并评估最近提出的长上下文模型的性能。首先,我们整理了一套生物医学成像数据集,包括用于分割、去噪和分类任务的二维和三维数据。然后,通过改变补丁大小和注意力窗口大小,分析上下文长度对网络性能的影响,使用视觉变压器和Swin变压器进行试验。我们的研究发现上下文长度与性能之间存在密切关系,特别是在像素级预测任务中。最后,我们证明了最新的长上下文模型在保持性能的同时,显示出显著的效率提升,但也指出了仍存在的一些不足。这项工作突出了在长上下文模型在生物医学成像中的潜力和挑战。
关键见解
- 高分辨率、多维生物医学图像对深度神经网络的计算带来了挑战,特别是在处理长上下文信息时。
- 自注意力算子的计算复杂度随上下文长度的增长而增加,成为训练变压器时的瓶颈。
- 缺乏关于长上下文模型在生物医学图像分析中的系统性评估。
- 本研究通过试验验证了上下文长度对网络性能的重要影响,特别是在像素级预测任务中。
- 近期提出的长上下文模型在提高效率的同时保持了良好的性能。
- 尽管有这些改进,但在应用长上下文模型进行生物医学图像分析时仍存在一些不足和潜在挑战。
点此查看论文截图

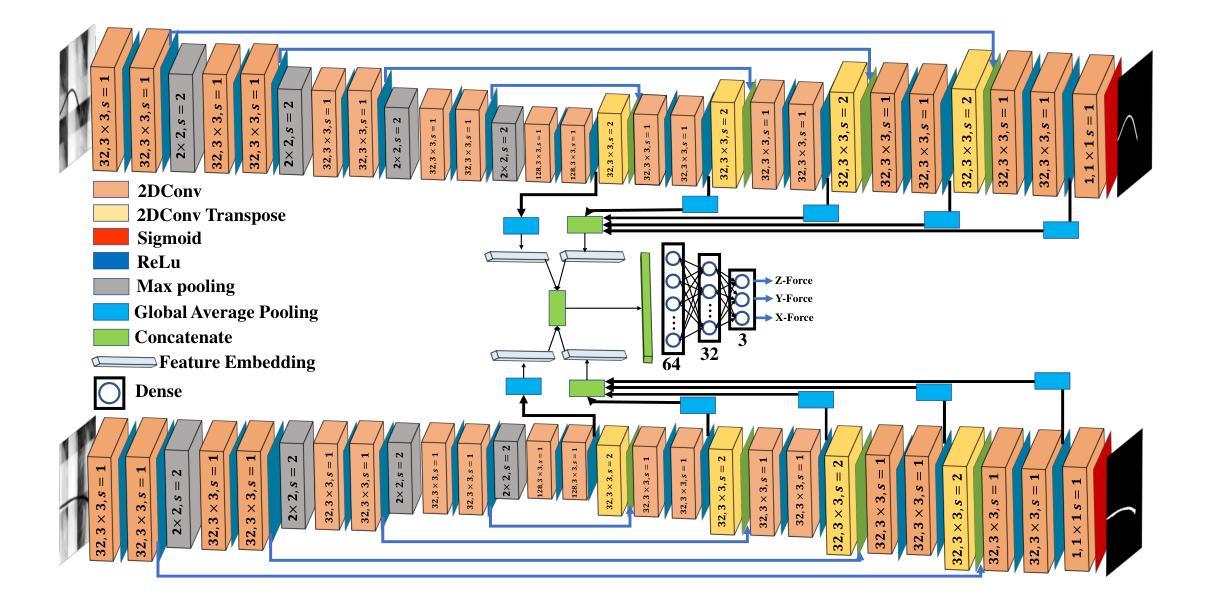
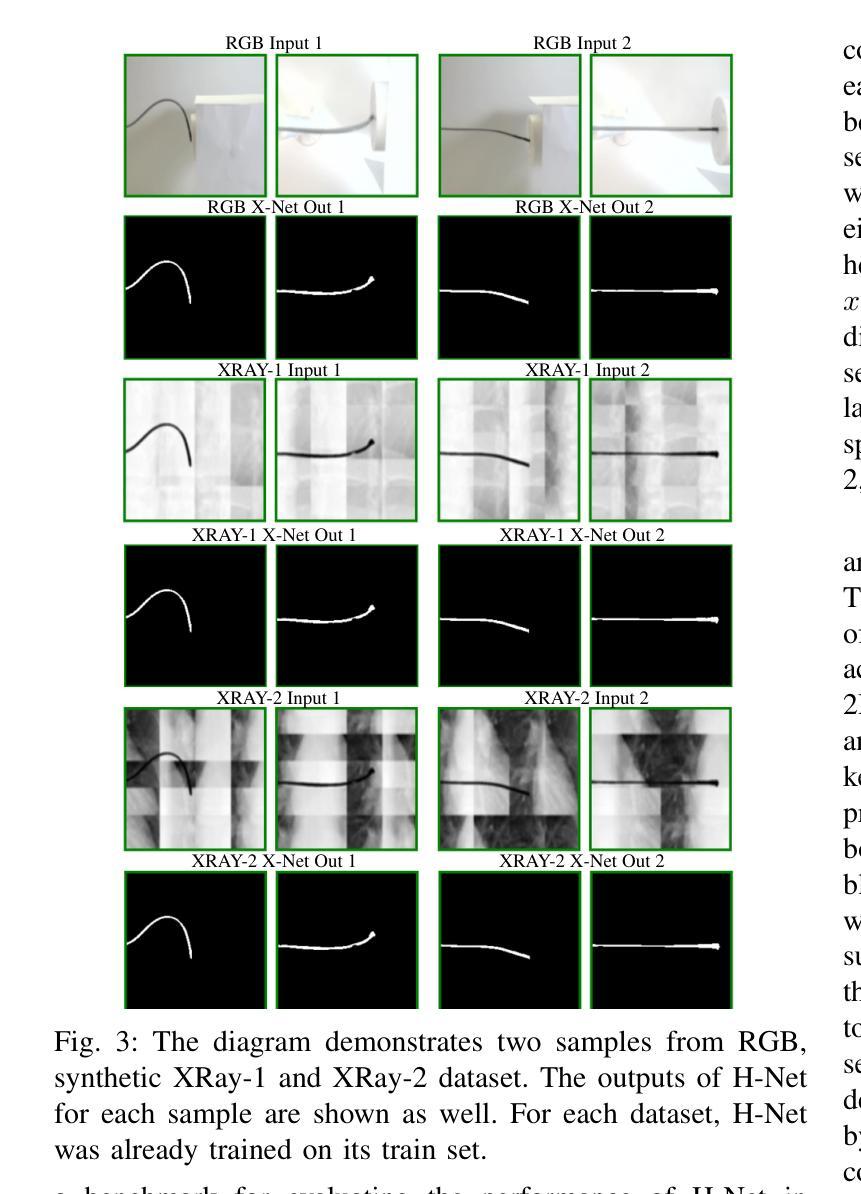
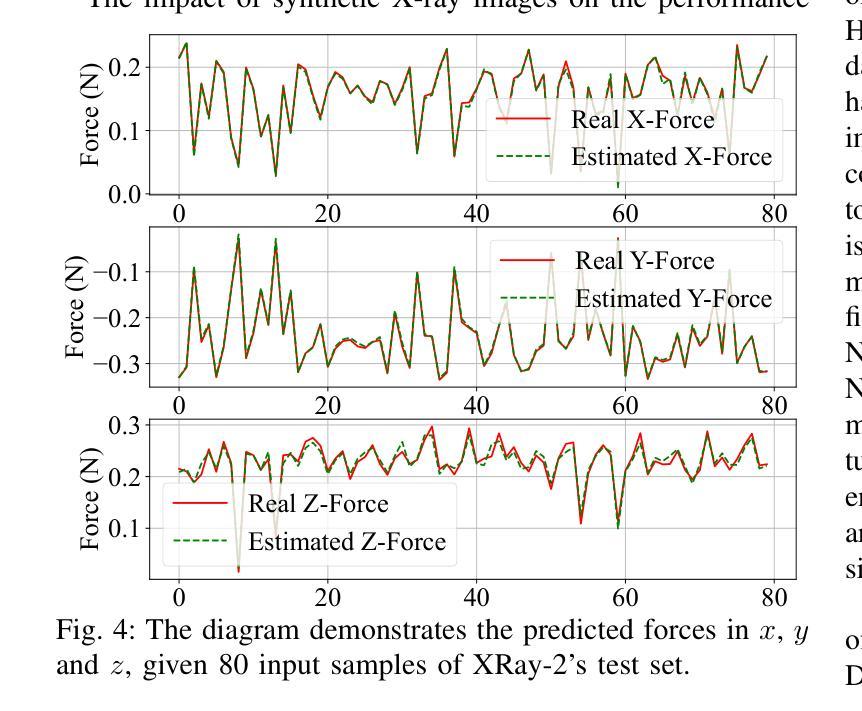
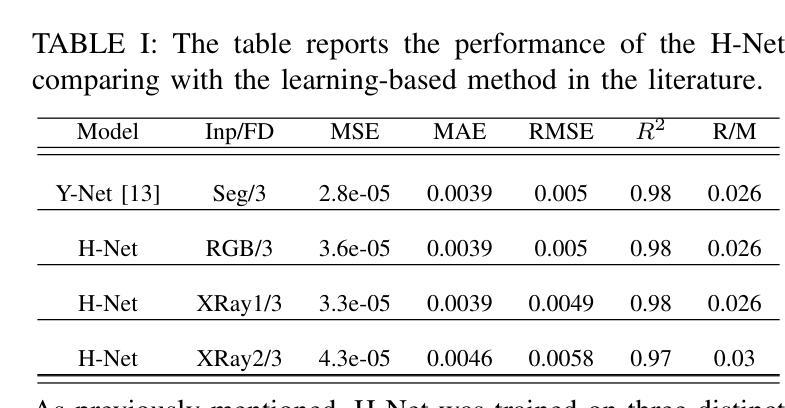
H-Net: A Multitask Architecture for Simultaneous 3D Force Estimation and Stereo Semantic Segmentation in Intracardiac Catheters
Authors:Pedram Fekri, Mehrdad Zadeh, Javad Dargahi
The success rate of catheterization procedures is closely linked to the sensory data provided to the surgeon. Vision-based deep learning models can deliver both tactile and visual information in a sensor-free manner, while also being cost-effective to produce. Given the complexity of these models for devices with limited computational resources, research has focused on force estimation and catheter segmentation separately. However, there is a lack of a comprehensive architecture capable of simultaneously segmenting the catheter from two different angles and estimating the applied forces in 3D. To bridge this gap, this work proposes a novel, lightweight, multi-input, multi-output encoder-decoder-based architecture. It is designed to segment the catheter from two points of view and concurrently measure the applied forces in the x, y, and z directions. This network processes two simultaneous X-Ray images, intended to be fed by a biplane fluoroscopy system, showing a catheter’s deflection from different angles. It uses two parallel sub-networks with shared parameters to output two segmentation maps corresponding to the inputs. Additionally, it leverages stereo vision to estimate the applied forces at the catheter’s tip in 3D. The architecture features two input channels, two classification heads for segmentation, and a regression head for force estimation through a single end-to-end architecture. The output of all heads was assessed and compared with the literature, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance in both segmentation and force estimation. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, this is the first time such a model has been proposed
导管插入手术的成功率与为外科医生提供的感官数据密切相关。基于视觉的深度学习模型能够以无传感器的方式提供触觉和视觉信息,同时制造成本效益高。考虑到这些模型对于有限计算资源的设备的复杂性,研究主要集中于单独的力估计和导管分段。然而,缺乏一种能够同时从两个不同角度分割导管并在3D中估计施加力的综合架构。为了弥补这一空白,这项工作提出了一种新型轻量级的多输入多输出编码器-解码器架构。它旨在从两个观点分割导管,并同时测量x、y和z方向上的施加力。该网络处理两个同时的X光图像,旨在由双平面荧光镜检查系统提供,显示从不同角度看到的导管的偏转。它使用两个具有共享参数的并行子网络来输出与输入相对应的两个分割图。此外,它利用立体视觉来估计导管尖端在3D中施加的力。该架构具有两个输入通道、两个用于分割的分类头和一个用于力估计的回归头,通过单个端到端架构实现。所有头部的输出均经过评估并与文献进行比较,在分割和力估计方面都显示出最先进的技术性能。据作者所知,这是首次提出此类模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要介绍了一种新型的轻量级多输入多输出编码器-解码器架构,该架构旨在从两个视角对导管进行分割,并同时测量在XYZ方向上的应用力。它处理来自双平面荧光镜检查系统的实时X光图像,使用两个并行子网络输出与输入相对应的两个分割图,并利用立体视觉估计导管的3D力。该架构在分割和力估计方面均表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉深度学习模型能以无传感器的方式为外科医生提供触觉和视觉信息,且生产成本较为低廉。
- 目前对于计算资源有限的设备,研究主要集中在力估计和导管分割两个方面。
- 缺乏一种能够同时从两个不同角度分割导管并估计3D应用力的综合架构。
- 本文提出了一种新型的轻量级多输入多输出编码器-解码器架构,能够同时处理两个视角的X光图像,并进行导管分割和力估计。
- 该架构使用两个并行子网络处理输入图像,生成两个分割图,并有一个回归头用于力估计。
- 该架构利用立体视觉技术估计导管的3D力。
点此查看论文截图

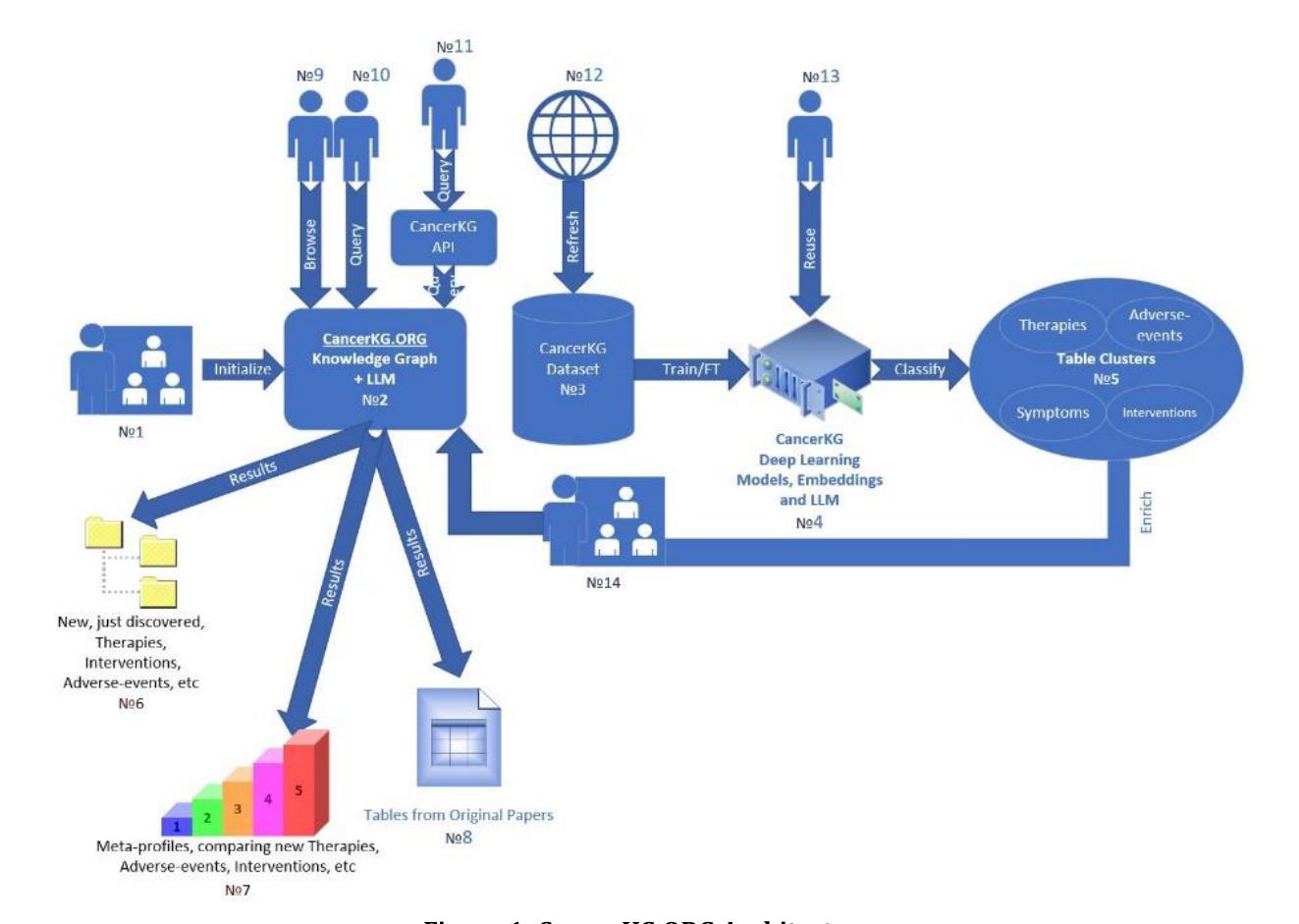
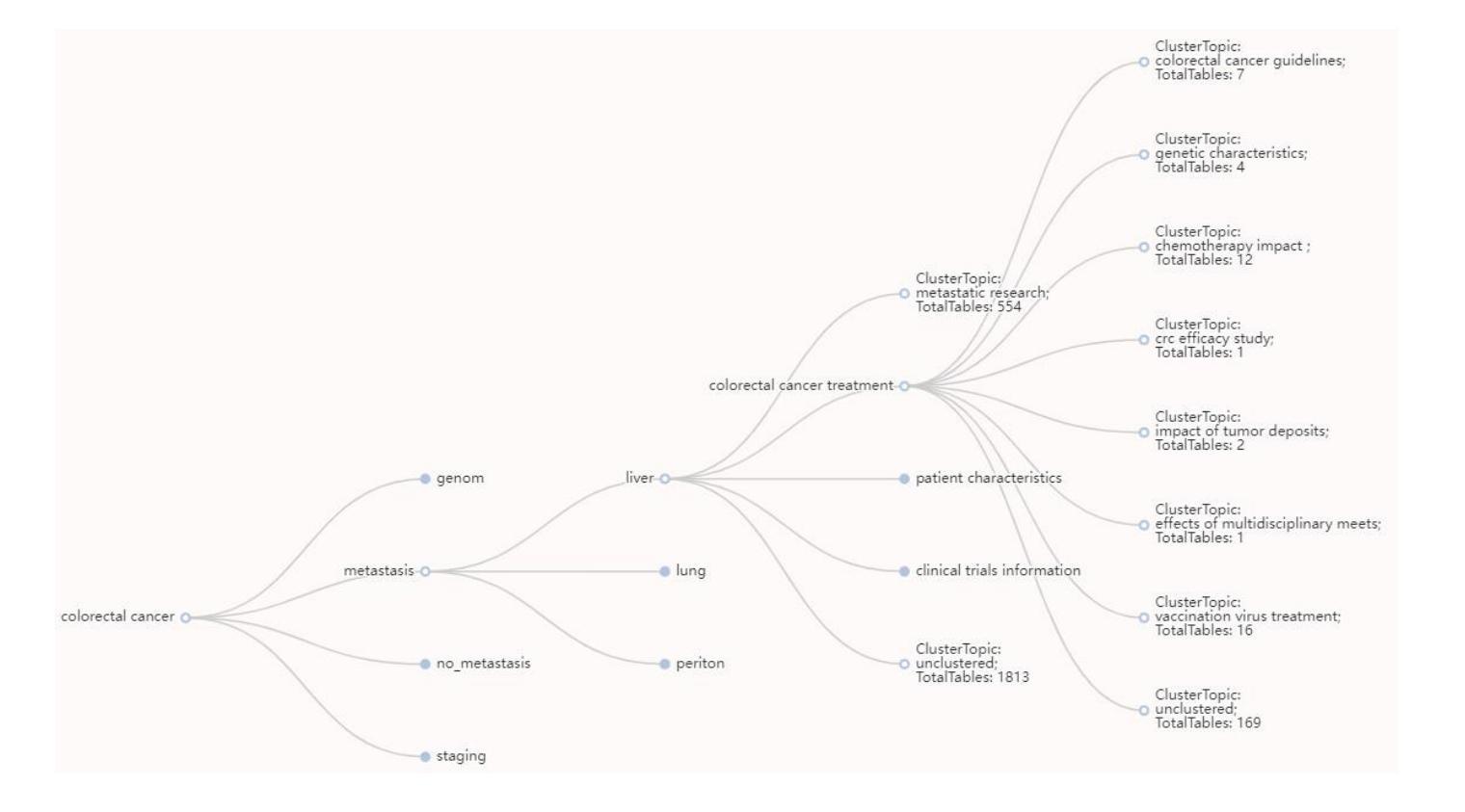
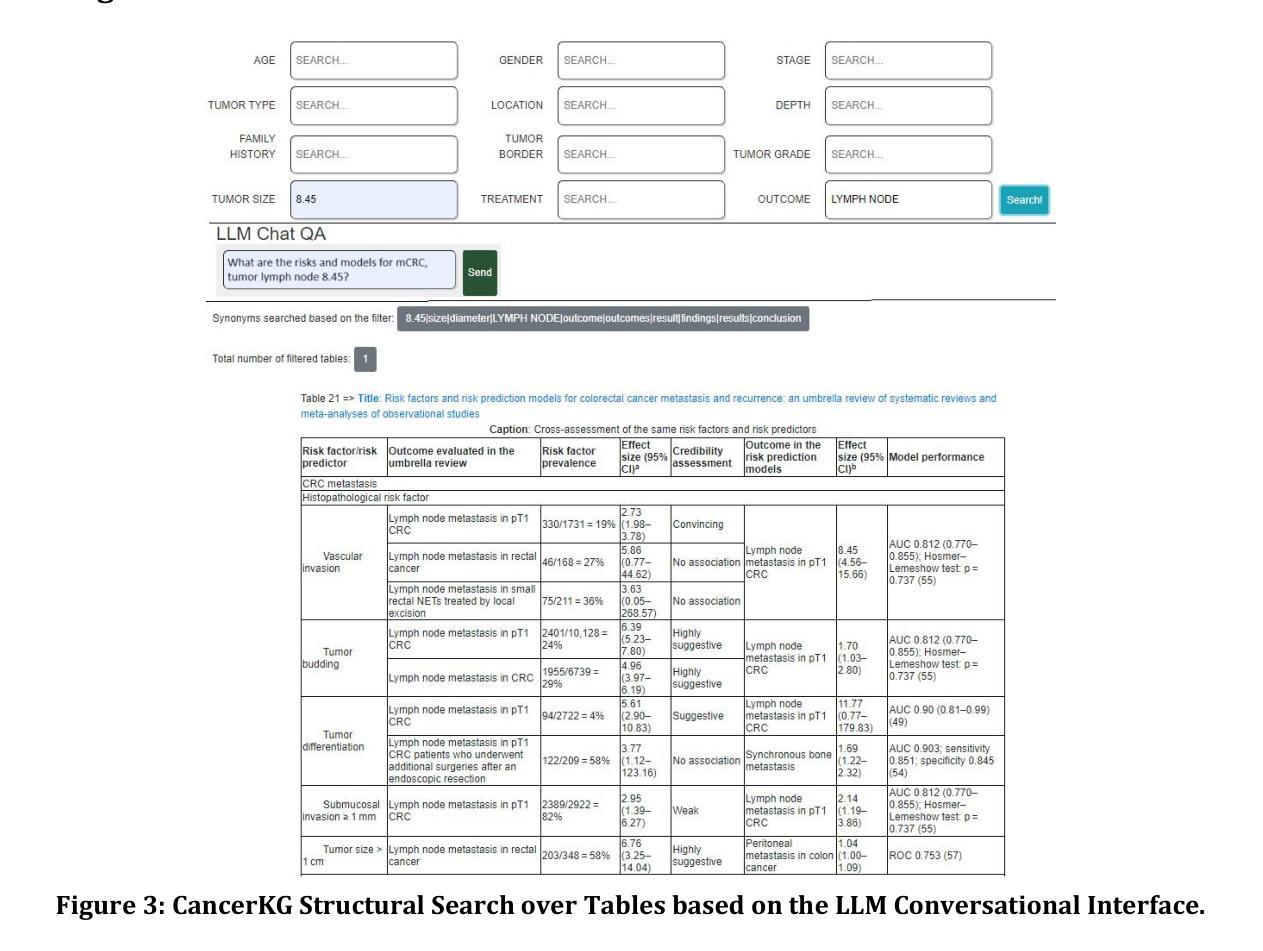
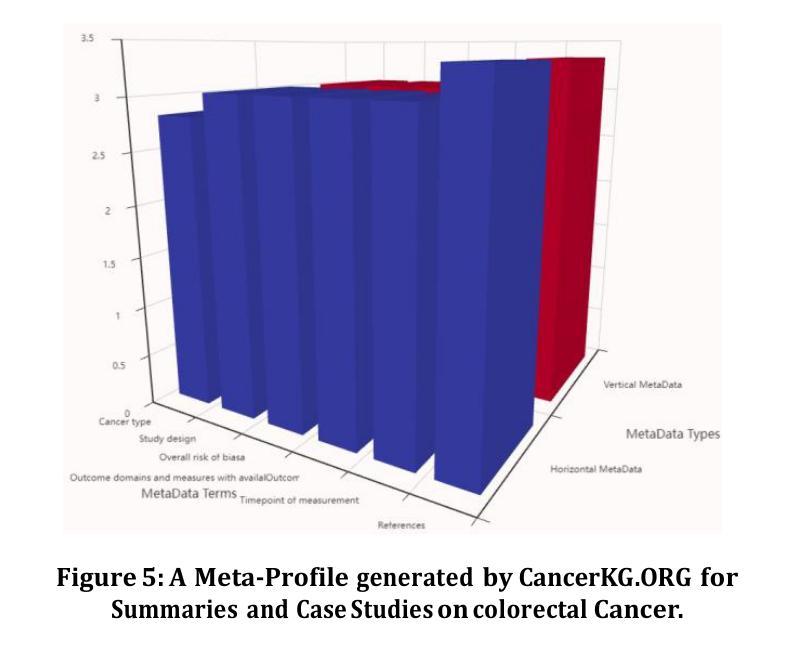
CancerKG.ORG A Web-scale, Interactive, Verifiable Knowledge Graph-LLM Hybrid for Assisting with Optimal Cancer Treatment and Care
Authors:Michael Gubanov, Anna Pyayt, Aleksandra Karolak
Here, we describe one of the first Web-scale hybrid Knowledge Graph (KG)-Large Language Model (LLM), populated with the latest peer-reviewed medical knowledge on colorectal Cancer. It is currently being evaluated to assist with both medical research and clinical information retrieval tasks at Moffitt Cancer Center, which is one of the top Cancer centers in the U.S. and in the world. Our hybrid is remarkable as it serves the user needs better than just an LLM, KG or a search-engine in isolation. LLMs as is are known to exhibit hallucinations and catastrophic forgetting as well as are trained on outdated corpora. The state of the art KGs, such as PrimeKG, cBioPortal, ChEMBL, NCBI, and other require manual curation, hence are quickly getting stale. CancerKG is unsupervised and is capable of automatically ingesting and organizing the latest medical findings. To alleviate the LLMs shortcomings, the verified KG serves as a Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) guardrail. CancerKG exhibits 5 different advanced user interfaces, each tailored to serve different data modalities better and more convenient for the user.
这里我们描述了一个首批基于Web的大型混合知识图谱(KG)大语言模型(LLM)之一,其中融入了最新的经过同行评审的关于结肠癌的医学知识。它目前正在莫菲特癌症中心进行评估,以辅助医学研究和临床信息检索任务。莫菲特癌症中心是美国乃至全球顶尖的癌症中心之一。我们的混合模型非常出色,因为它比单独使用LLM、KG或搜索引擎更能满足用户需求。众所周知,LLM会出现幻觉和灾难性遗忘,并且是在过时的语料库上进行训练的。最新最前沿的KGs,如PrimeKG、cBioPortal、ChEMBL和NCBI等,需要人工维护,因此很容易过时。CancerKG是无监督的,能够自动摄取并整理最新的医学发现。为了缓解LLM的不足,经过验证的KG作为检索增强生成(RAG)的界限。CancerKG展现了五种不同的高级用户界面,每个界面都针对不同的数据模式进行了优化,更好地为用户服务并带来便利。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文描述了一种结合最新同行评审医学知识、针对结肠癌的Web规模混合知识图谱(KG)大型语言模型(LLM)。该模型在Moffitt癌症中心进行医学研究和临床信息检索任务的评估,表现优异,能更好地满足用户需求。与传统的LLM、KG或搜索引擎相比,其优势明显。CancerKG具有自动摄取和组织最新医学发现的能力,并能缓解LLM的缺点。
Key Takeaways
- 描述了一种针对结肠癌的Web规模混合知识图谱(KG)大型语言模型(LLM)。
- 该模型在Moffitt癌症中心的医学研究和临床信息检索任务中表现优异。
- CancerKG结合了知识图谱(KG)和语言模型(LLM)的优势,可以更好地满足用户需求。
- LLM存在的缺陷如幻觉和灾难性遗忘在该模型中得到了缓解。
- CancerKG具有自动摄取和组织最新医学发现的能力。
- 该模型具有5种高级用户界面,方便用户使用并适应不同的数据模式。
点此查看论文截图

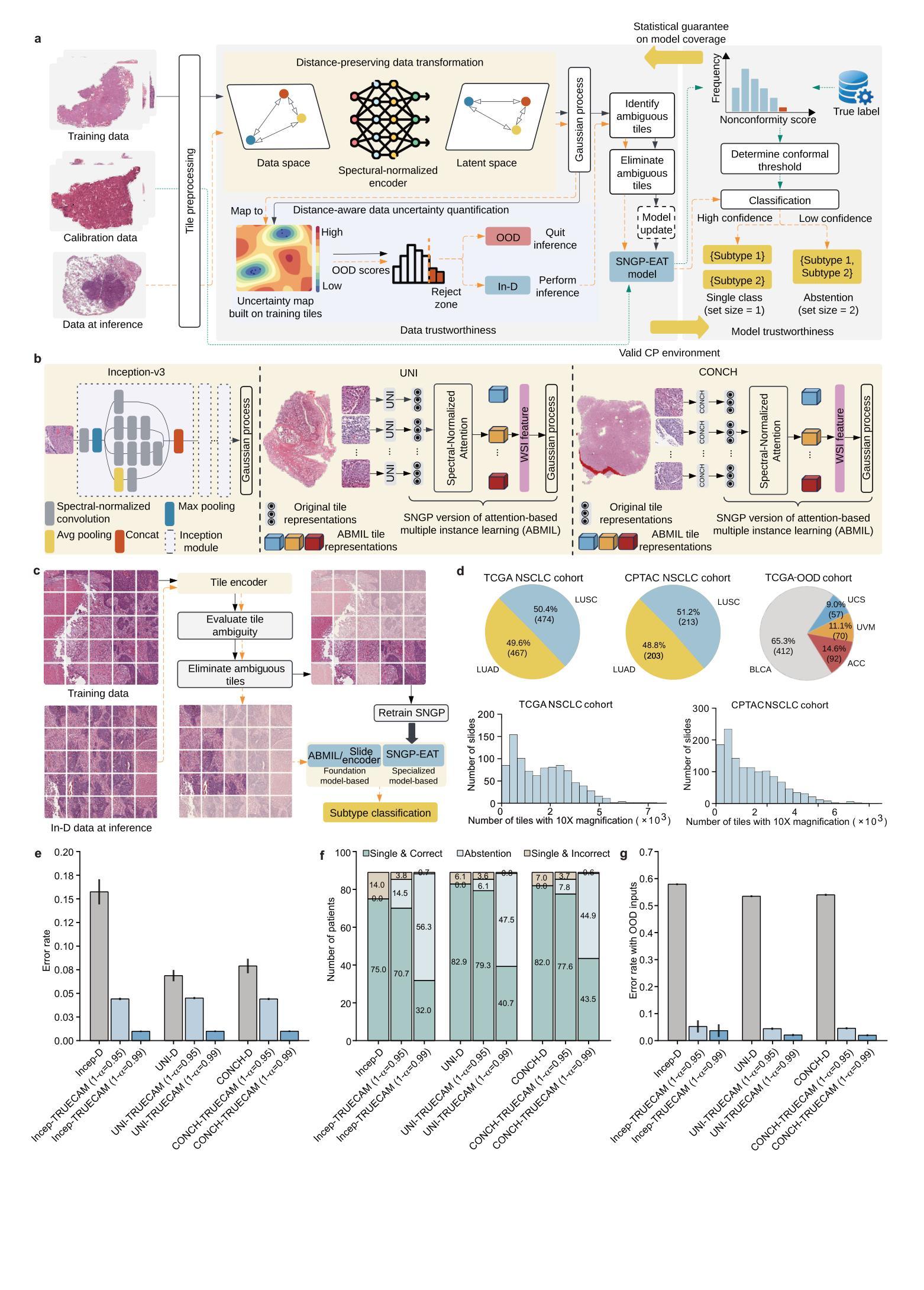
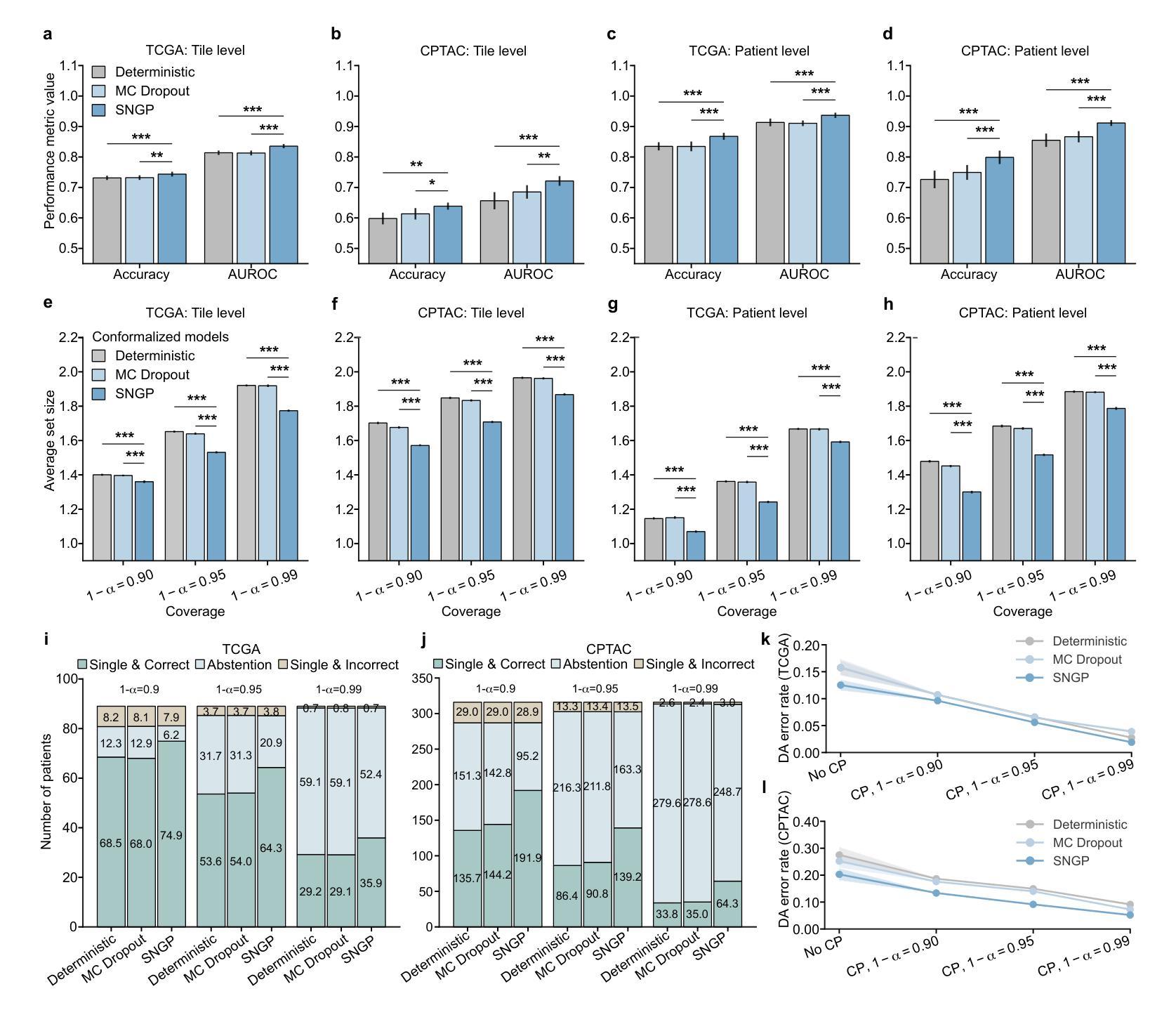
Implementing Trust in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosis with a Conformalized Uncertainty-Aware AI Framework in Whole-Slide Images
Authors:Xiaoge Zhang, Tao Wang, Chao Yan, Fedaa Najdawi, Kai Zhou, Yuan Ma, Yiu-ming Cheung, Bradley A. Malin
Ensuring trustworthiness is fundamental to the development of artificial intelligence (AI) that is considered societally responsible, particularly in cancer diagnostics, where a misdiagnosis can have dire consequences. Current digital pathology AI models lack systematic solutions to address trustworthiness concerns arising from model limitations and data discrepancies between model deployment and development environments. To address this issue, we developed TRUECAM, a framework designed to ensure both data and model trustworthiness in non-small cell lung cancer subtyping with whole-slide images. TRUECAM integrates 1) a spectral-normalized neural Gaussian process for identifying out-of-scope inputs and 2) an ambiguity-guided elimination of tiles to filter out highly ambiguous regions, addressing data trustworthiness, as well as 3) conformal prediction to ensure controlled error rates. We systematically evaluated the framework across multiple large-scale cancer datasets, leveraging both task-specific and foundation models, illustrate that an AI model wrapped with TRUECAM significantly outperforms models that lack such guidance, in terms of classification accuracy, robustness, interpretability, and data efficiency, while also achieving improvements in fairness. These findings highlight TRUECAM as a versatile wrapper framework for digital pathology AI models with diverse architectural designs, promoting their responsible and effective applications in real-world settings.
确保可信度是发展社会负责任的人工智能(AI)的基础,特别是在癌症诊断中,误诊可能会带来严重的后果。当前的数字病理AI模型缺乏系统解决方案,无法解决模型局限性和模型部署与开发环境之间数据差异所产生的可信度问题。为了解决这一问题,我们开发了TRUECAM框架,旨在确保在非小细胞肺癌亚型分类的全幻灯片图像中数据和模型的可信度。TRUECAM集成了1)光谱归一化神经高斯过程,用于识别超出范围输入;2)歧义引导瓦片消除,以过滤掉高度模糊区域,解决数据可信度问题;以及3)符合预测要求,以确保控制误差率。我们在多个大规模癌症数据集上系统地评估了该框架,利用特定任务和基础模型,表明用TRUECAM包装的AI模型在分类精度、稳健性、可解释性和数据效率方面显著优于缺乏此类指导的模型,同时在公平性方面也实现了改进。这些发现突出了TRUECAM作为一个通用包装框架,适用于具有不同架构设计的数字病理AI模型,促进其在实际环境中的负责任和有效应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注人工智能在癌症诊断中的信任度问题,特别是在非小细胞肺癌亚型诊断中。为此,研究团队提出了TRUECAM框架,该框架通过多项技术确保数据和模型的信任度,包括识别超出范围输入的神经高斯过程、过滤高度模糊区域的模糊引导瓷砖消除法以及确保控制错误率的预测一致性。经过大规模癌症数据集的系统评估,发现TRUECAM包装的AI模型在分类精度、稳健性、可解释性和数据效率方面显著优于缺乏此类指导的模型,并实现了公平性的改进。这表明TRUECAM框架适用于各种设计的数字病理学AI模型,促进了其在现实环境中的负责任和有效应用。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能在癌症诊断中的信任度至关重要,尤其是在非小细胞肺癌亚型诊断中。
- 当前数字病理学AI模型缺乏解决信任度问题的系统性解决方案。
- TRUECAM框架被开发出来解决数据和模型的信任度问题。
- TRUECAM通过多项技术确保信任度,包括神经高斯过程、模糊引导瓷砖消除法和预测一致性。
- TRUECAM包装的AI模型在分类精度、稳健性、可解释性和数据效率方面表现优越。
- TRUECAM实现了公平性的改进,适用于各种设计的数字病理学AI模型。
点此查看论文截图