⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-01-06 更新
FGAseg: Fine-Grained Pixel-Text Alignment for Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Bingyu Li, Da Zhang, Zhiyuan Zhao, Junyu Gao, Xuelong Li
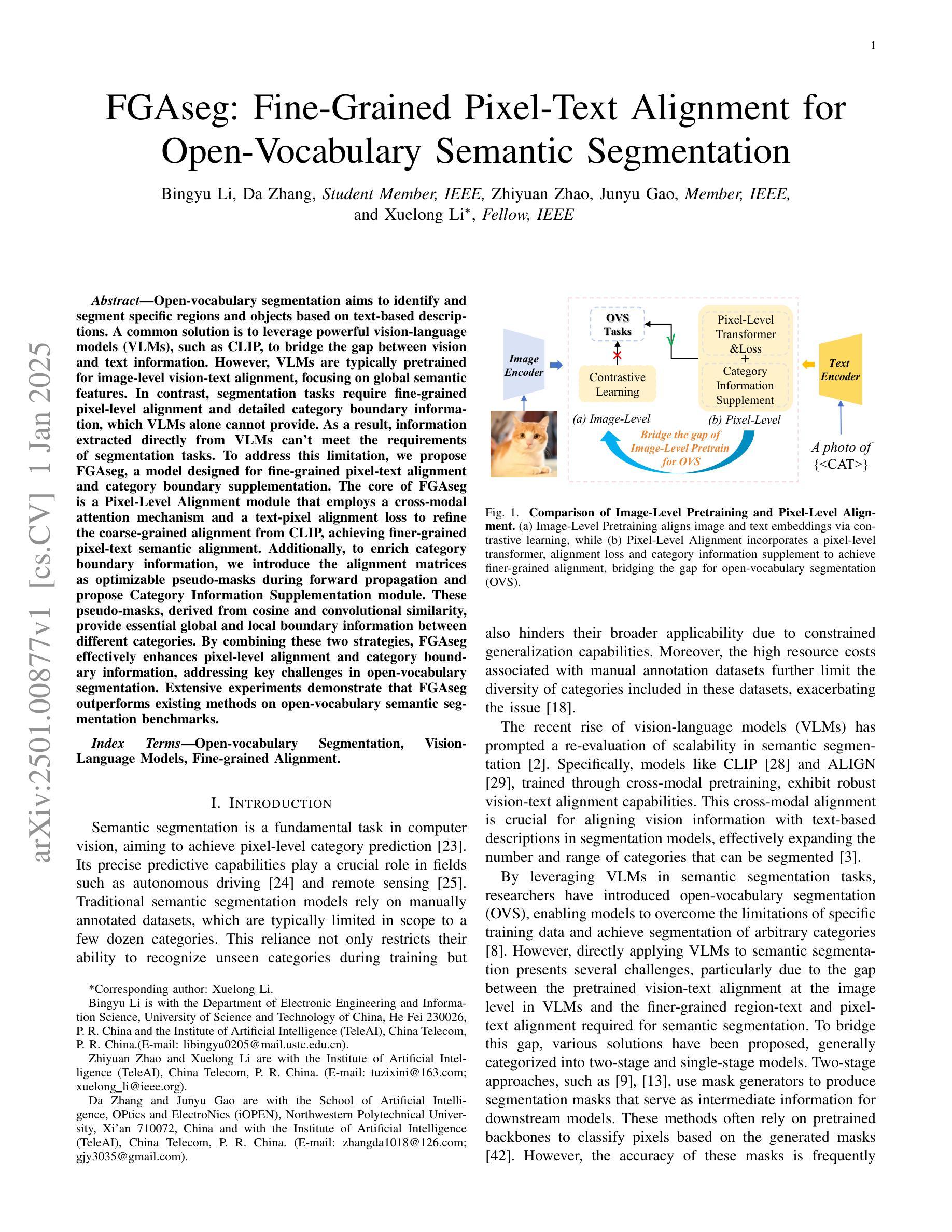
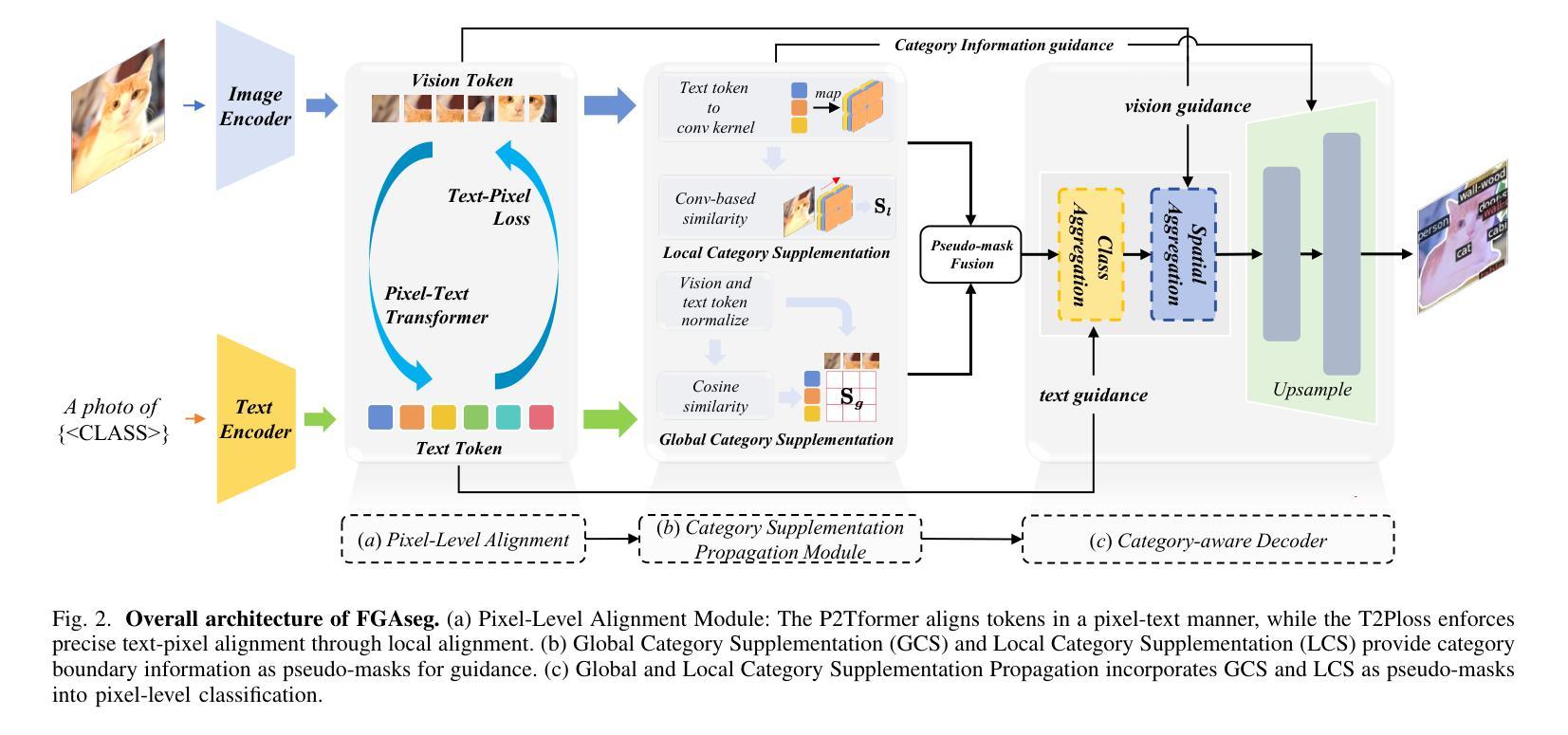
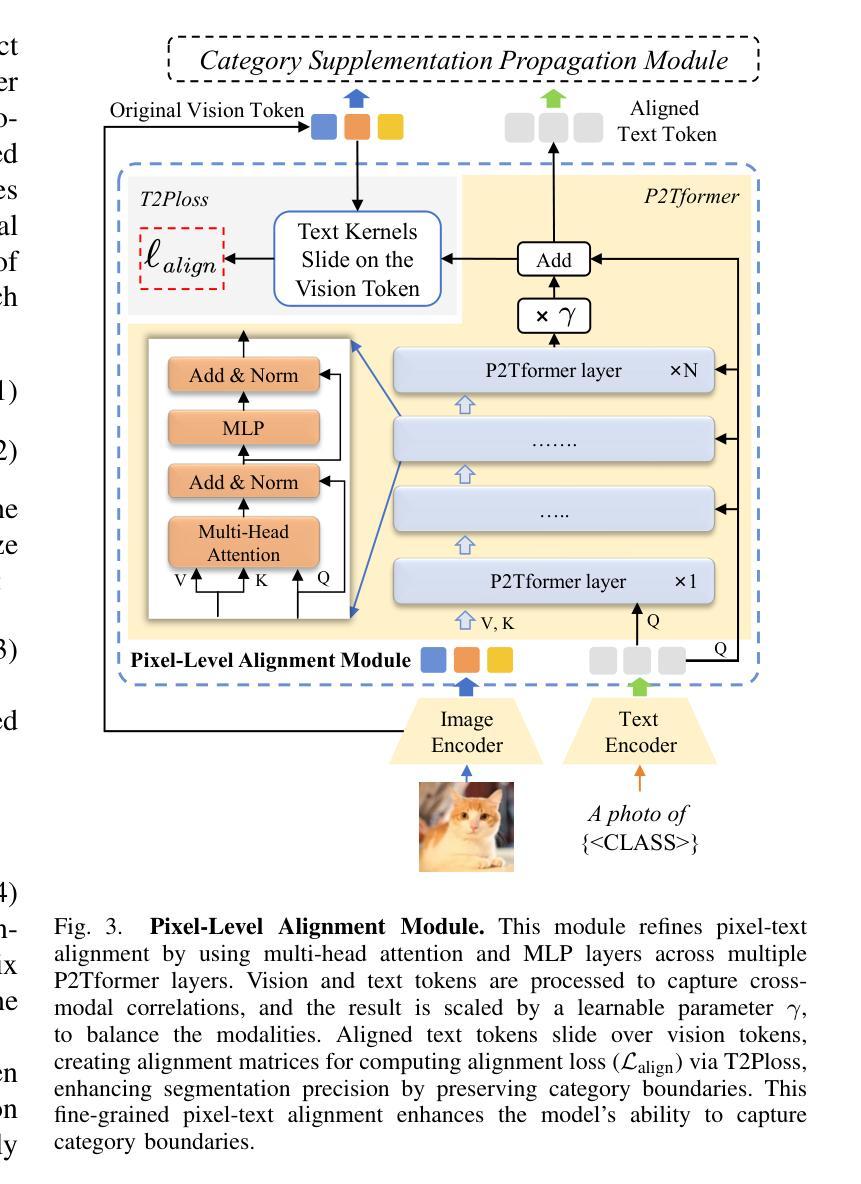
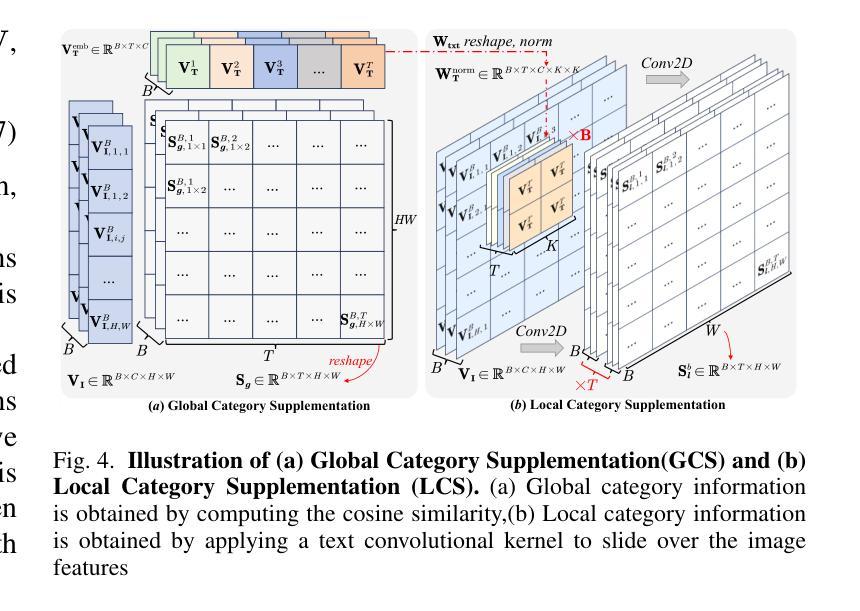
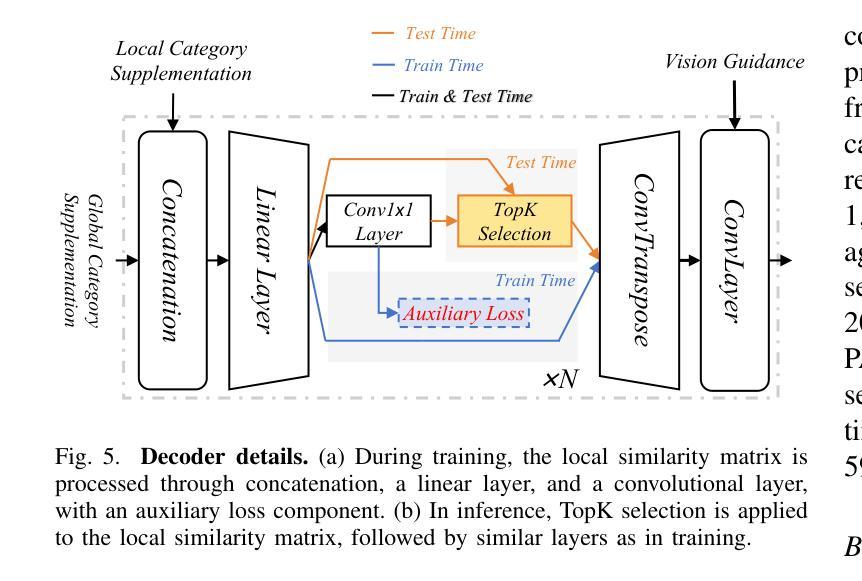
Open-vocabulary segmentation aims to identify and segment specific regions and objects based on text-based descriptions. A common solution is to leverage powerful vision-language models (VLMs), such as CLIP, to bridge the gap between vision and text information. However, VLMs are typically pretrained for image-level vision-text alignment, focusing on global semantic features. In contrast, segmentation tasks require fine-grained pixel-level alignment and detailed category boundary information, which VLMs alone cannot provide. As a result, information extracted directly from VLMs can’t meet the requirements of segmentation tasks. To address this limitation, we propose FGAseg, a model designed for fine-grained pixel-text alignment and category boundary supplementation. The core of FGAseg is a Pixel-Level Alignment module that employs a cross-modal attention mechanism and a text-pixel alignment loss to refine the coarse-grained alignment from CLIP, achieving finer-grained pixel-text semantic alignment. Additionally, to enrich category boundary information, we introduce the alignment matrices as optimizable pseudo-masks during forward propagation and propose Category Information Supplementation module. These pseudo-masks, derived from cosine and convolutional similarity, provide essential global and local boundary information between different categories. By combining these two strategies, FGAseg effectively enhances pixel-level alignment and category boundary information, addressing key challenges in open-vocabulary segmentation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FGAseg outperforms existing methods on open-vocabulary semantic segmentation benchmarks.
开放词汇分割旨在基于文本描述来识别和分割特定区域和对象。一种常见解决方案是利用强大的视觉语言模型(VLMs),如CLIP,来弥合视觉和文本信息之间的差距。然而,VLMs通常进行图像级别的视觉文本对齐预训练,侧重于全局语义特征。相比之下,分割任务需要精细的像素级对齐和详细的类别边界信息,这是仅凭VLMs无法提供的。因此,直接从VLMs中提取的信息不能满足分割任务的要求。为了弥补这一限制,我们提出了FGAseg模型,该模型旨在实现精细像素文本对齐和类别边界补充。FGAseg的核心是像素级对齐模块,该模块采用跨模态注意力机制和文本像素对齐损失来优化CLIP的粗略对齐,实现更精细的像素文本语义对齐。此外,为了丰富类别边界信息,我们在前向传播过程中引入了优化后的伪掩码作为对齐矩阵,并提出了类别信息补充模块。这些伪掩码来源于余弦和卷积相似性,提供了不同类别之间至关重要的全局和局部边界信息。通过结合这两种策略,FGAseg有效地提高了像素级对齐和类别边界信息,解决了开放词汇分割中的关键挑战。大量实验表明,在开放词汇语义分割基准测试中,FGAseg的性能优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于文本描述的开放词汇分割旨在识别和分割特定区域和对象。为解决现有视觉语言模型(VLMs)在像素级对齐和类别边界信息提供方面的不足,提出FGAseg模型,实现精细像素文本对齐和类别边界补充。通过像素级对齐模块和类别信息补充模块,FGAseg提高了开放词汇分割的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 开放词汇分割基于文本描述进行特定区域和对象的识别与分割。
- 现有视觉语言模型(VLMs)如CLIP在像素级对齐和类别边界信息提供上存在局限。
- FGAseg模型包括像素级对齐模块,通过跨模态注意机制和文本像素对齐损失实现精细像素文本语义对齐。
- FGAseg引入可优化的伪掩膜作为对齐矩阵,提供全局和局部边界信息。
- 伪掩膜是通过余弦和卷积相似性得到的。
点此查看论文截图
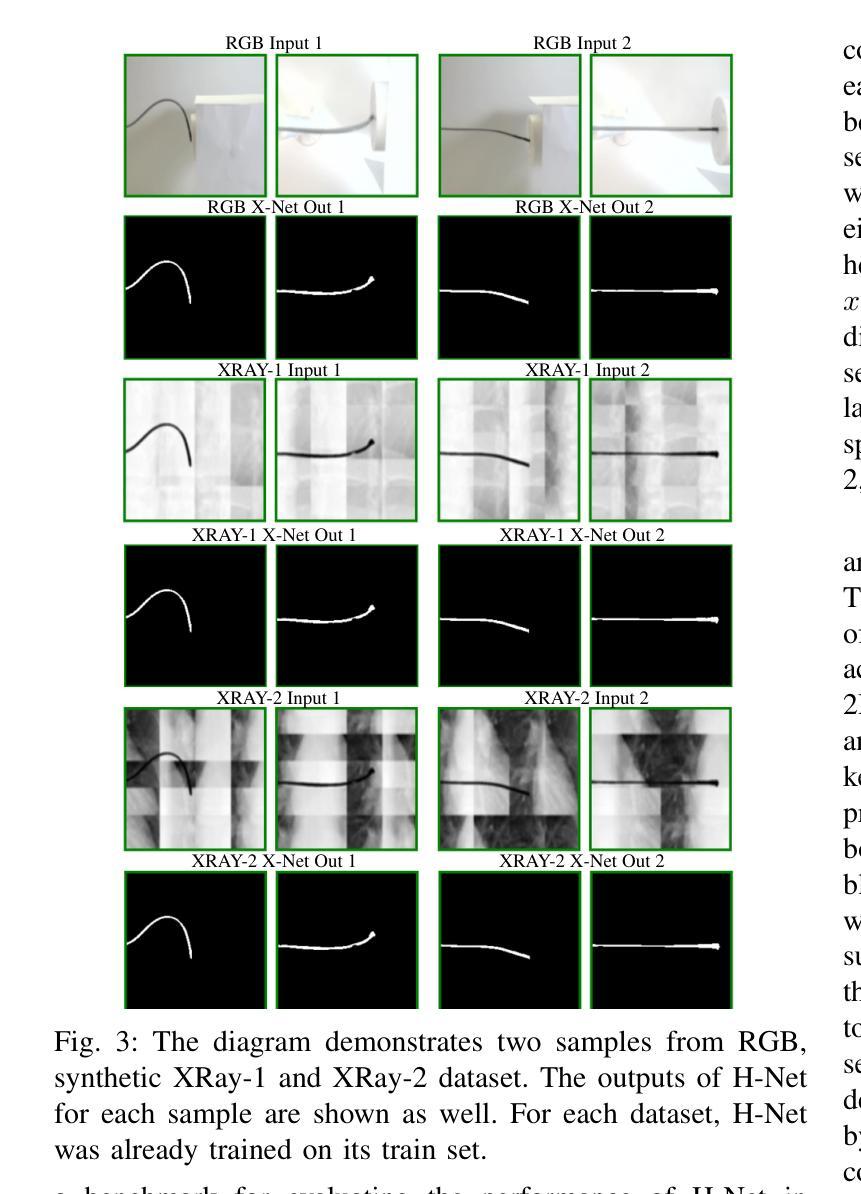
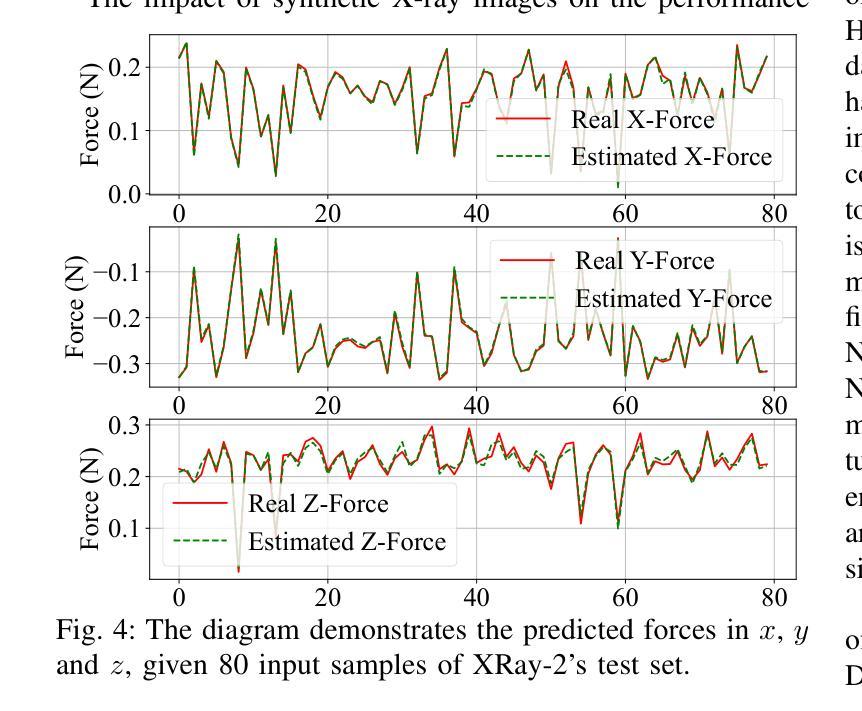
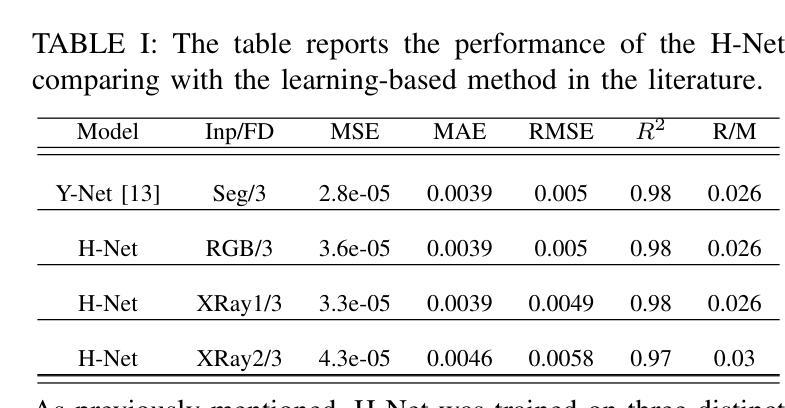
H-Net: A Multitask Architecture for Simultaneous 3D Force Estimation and Stereo Semantic Segmentation in Intracardiac Catheters
Authors:Pedram Fekri, Mehrdad Zadeh, Javad Dargahi
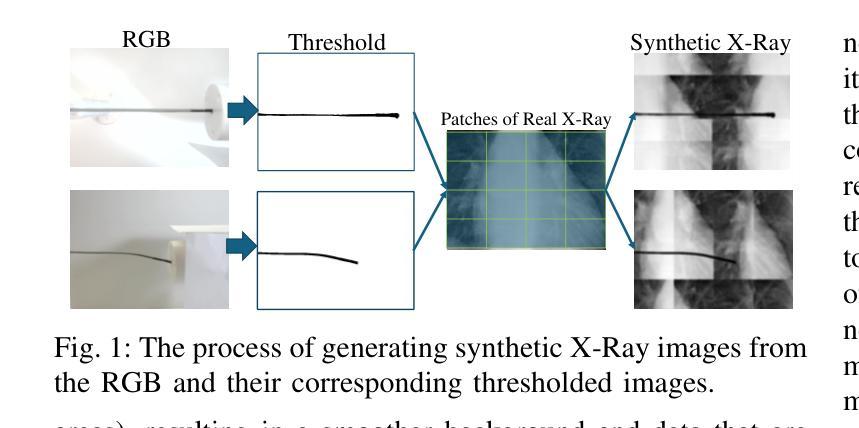
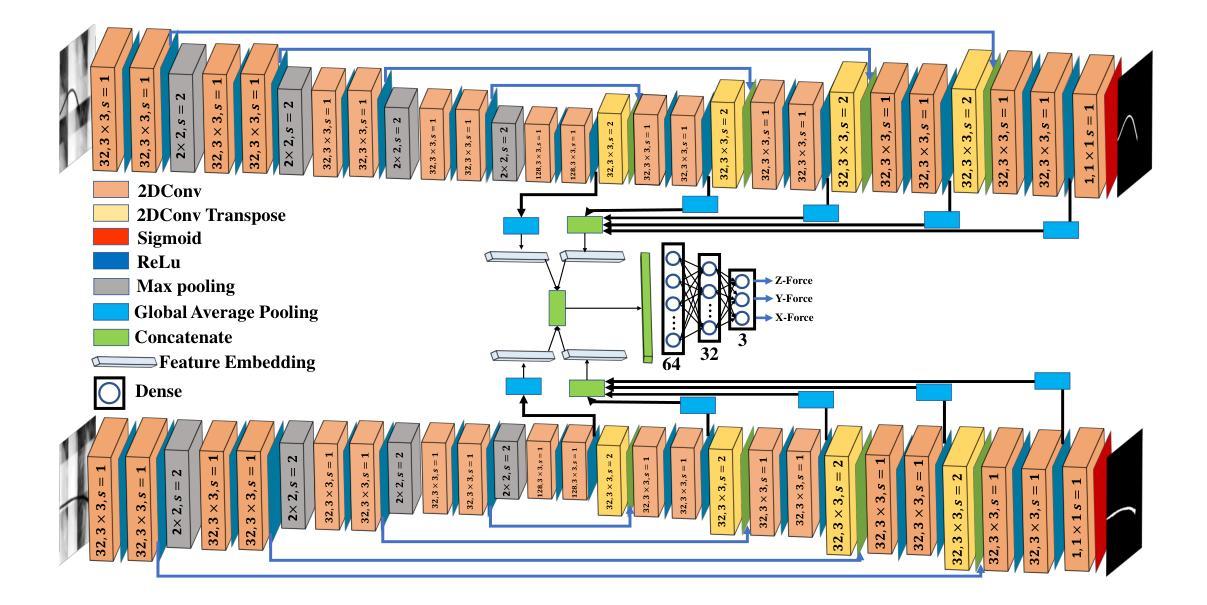
The success rate of catheterization procedures is closely linked to the sensory data provided to the surgeon. Vision-based deep learning models can deliver both tactile and visual information in a sensor-free manner, while also being cost-effective to produce. Given the complexity of these models for devices with limited computational resources, research has focused on force estimation and catheter segmentation separately. However, there is a lack of a comprehensive architecture capable of simultaneously segmenting the catheter from two different angles and estimating the applied forces in 3D. To bridge this gap, this work proposes a novel, lightweight, multi-input, multi-output encoder-decoder-based architecture. It is designed to segment the catheter from two points of view and concurrently measure the applied forces in the x, y, and z directions. This network processes two simultaneous X-Ray images, intended to be fed by a biplane fluoroscopy system, showing a catheter’s deflection from different angles. It uses two parallel sub-networks with shared parameters to output two segmentation maps corresponding to the inputs. Additionally, it leverages stereo vision to estimate the applied forces at the catheter’s tip in 3D. The architecture features two input channels, two classification heads for segmentation, and a regression head for force estimation through a single end-to-end architecture. The output of all heads was assessed and compared with the literature, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance in both segmentation and force estimation. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, this is the first time such a model has been proposed
导管插入手术的成功率与为外科医生提供的感官数据密切相关。基于视觉的深度学习模型能够以无传感器的方式提供触觉和视觉信息,同时生产成本效益高。考虑到这些模型对于有限计算资源的设备的复杂性,研究主要集中于力估计和导管分割两个方面。然而,缺乏一种能够同时从两个不同角度分割导管并在3D空间中估计施加力的综合架构。为了弥补这一空白,这项工作提出了一种新型轻量级的多输入多输出编码器-解码器架构。它旨在从两个视角分割导管,并同时测量x、y、z方向上的施加力。该网络处理两个实时的X光图像,意图通过双平面荧光镜检查系统输入,展示从不同角度看到的导管偏转。它使用两个具有共享参数的并行子网络来输出与输入相对应的两个分割图。此外,它利用立体视觉来估计导管尖端的施加力在三维空间中的情况。该架构具有两个输入通道、两个用于分割的分类头和一个用于力估计的回归头,采用单一端到端的架构。所有头的输出都经过了评估和比较,与文献相比,在分割和力估计方面都显示出卓越的性能。据作者所知,这是首次提出此类模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究利用基于视觉的深度学习模型实现了触觉与视觉信息的融合感知,应用于医疗领域中的导管插入手术。针对现有模型在有限计算资源下的局限性,提出一种新型轻量级的多输入多输出编码解码器架构,同时从不同角度分割导管并估计三维作用力。架构具备两输入通道、两个分割分类头和用于估计作用力的回归头。输出结果展示领先性能,并有望推动相关领域的发展。这一创新性模型的提出具有重要的实际意义。
Key Takeaways
- 深测模型融合触觉和视觉信息为导管插入手术提供感知数据。
- 针对现有模型的局限性,提出了新型轻量级的多输入多输出编码解码器架构。
- 同时从不同角度分割导管并估计三维作用力。
- 架构包含两输入通道、两个用于分割的分类头和用于估计作用力的回归头。
- 输出结果在分割和力估计方面表现出卓越性能。
- 该模型为相关领域的发展开辟了新的道路。
点此查看论文截图

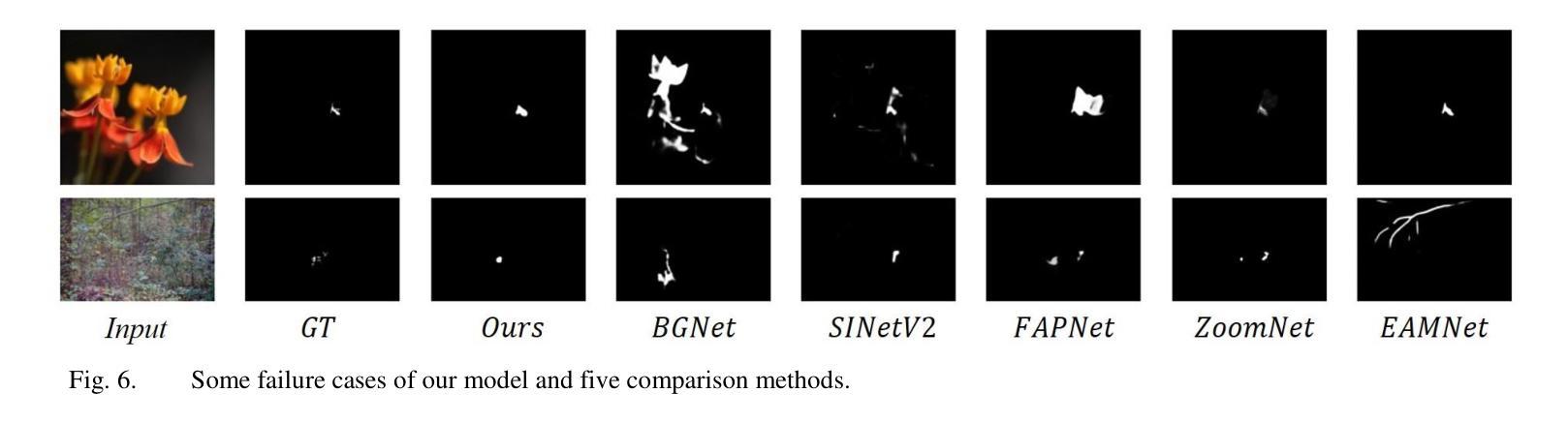
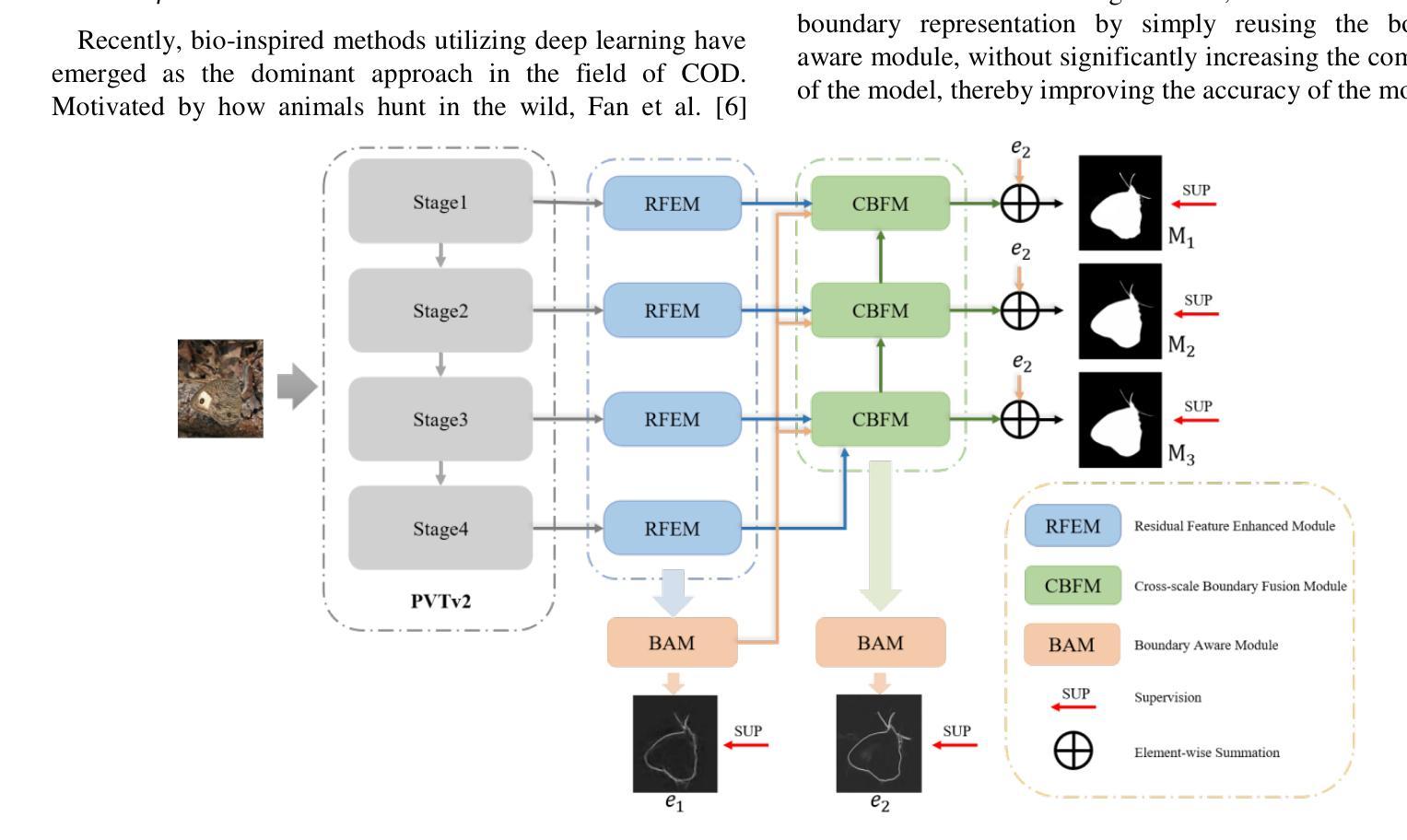
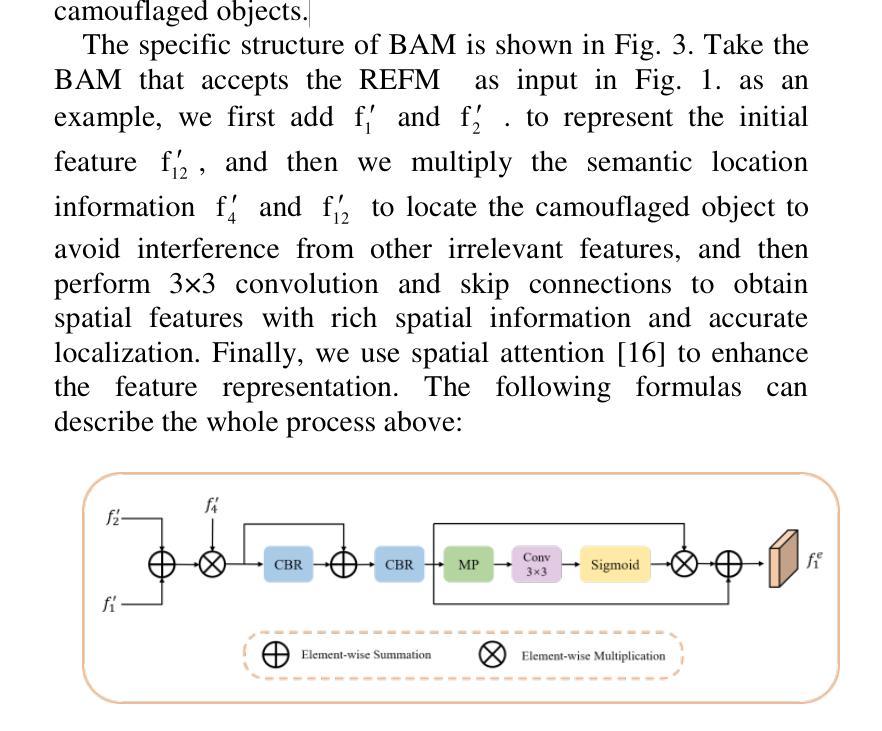
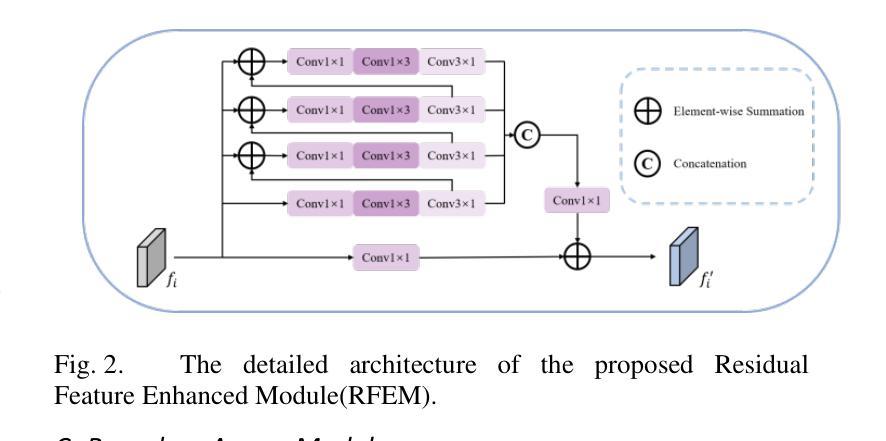
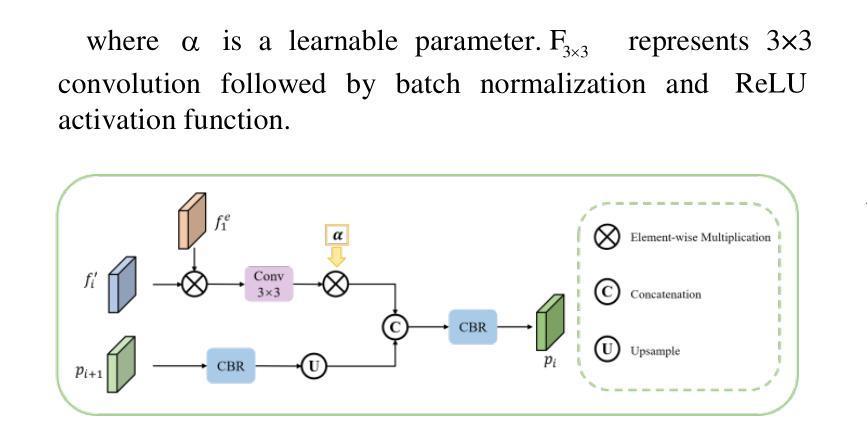
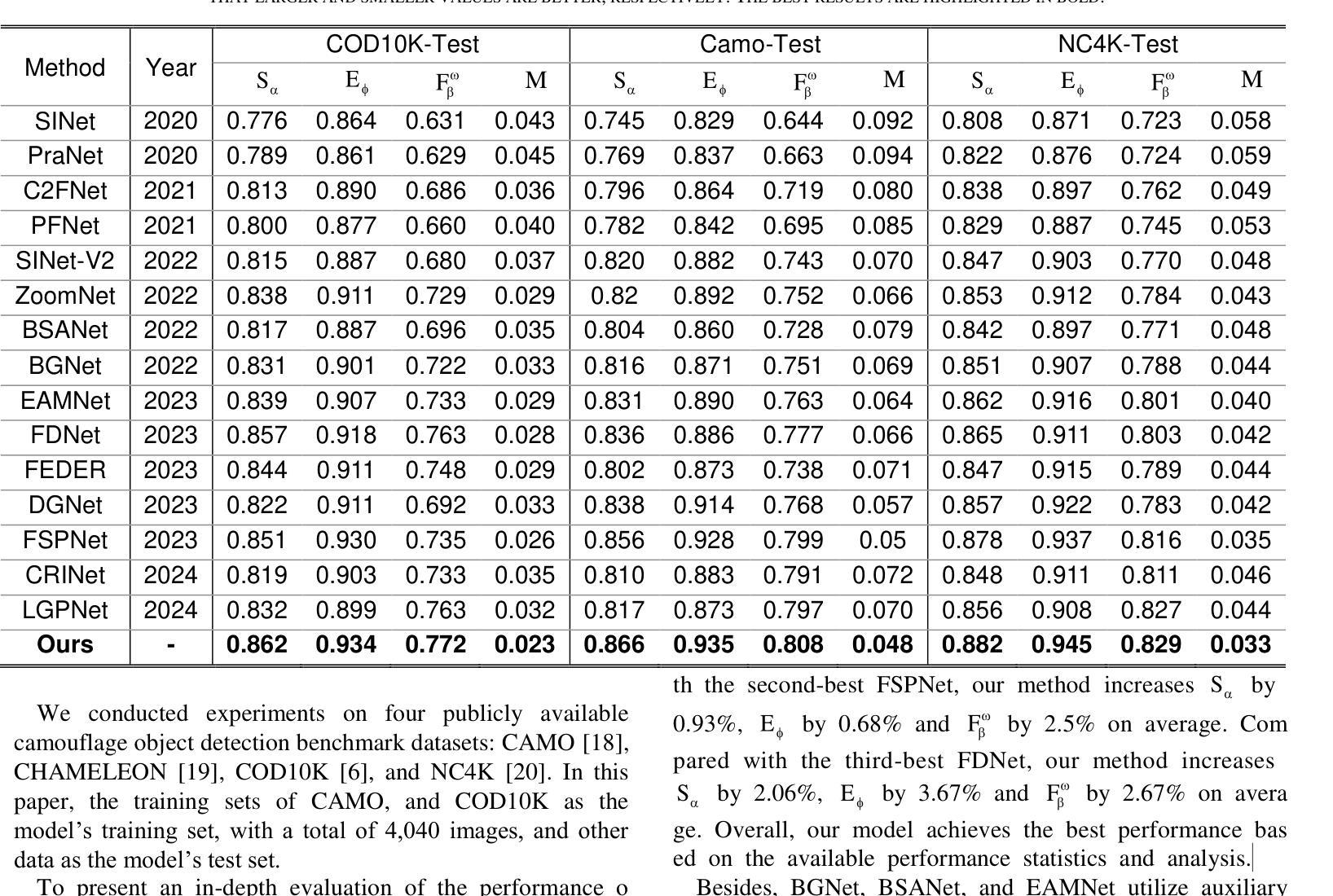
B2Net: Camouflaged Object Detection via Boundary Aware and Boundary Fusion
Authors:Junmin Cai, Han Sun, Ningzhong Liu
Camouflaged object detection (COD) aims to identify objects in images that are well hidden in the environment due to their high similarity to the background in terms of texture and color. However, existing most boundary-guided camouflage object detection algorithms tend to generate object boundaries early in the network, and inaccurate edge priors often introduce noises in object detection. Address on this issue, we propose a novel network named B2Net aiming to enhance the accuracy of obtained boundaries by reusing boundary-aware modules at different stages of the network. Specifically, we present a Residual Feature Enhanced Module (RFEM) with the goal of integrating more discriminative feature representations to enhance detection accuracy and reliability. After that, the Boundary Aware Module (BAM) is introduced to explore edge cues twice by integrating spatial information from low-level features and semantic information from high-level features. Finally, we design the Cross-scale Boundary Fusion Module(CBFM) that integrate information across different scales in a top-down manner, merging boundary features with object features to obtain a comprehensive feature representation incorporating boundary information. Extensive experimental results on three challenging benchmark datasets demonstrate that our proposed method B2Net outperforms 15 state-of-art methods under widely used evaluation metrics. Code will be made publicly available.
隐蔽目标检测(COD)旨在识别图像中与周围环境高度相似的目标,这些目标在纹理和颜色方面与背景极为相似而难以被发现。然而,大多数现有的边界引导隐蔽目标检测算法倾向于在网络中早期生成目标边界,而不准确的边缘先验通常会在目标检测中引入噪声。针对这一问题,我们提出了一种名为B2Net的新型网络,旨在通过在网络的不同阶段重复使用边界感知模块来提高所获得的边界的准确性。具体来说,我们提出了残差特征增强模块(RFEM),旨在集成更具区分性的特征表示,以提高检测准确性和可靠性。之后,引入了边界感知模块(BAM),通过整合低级特征的空间信息和高级特征的语义信息,两次探索边缘线索。最后,我们设计了跨尺度边界融合模块(CBFM),以自上而下地整合不同尺度的信息,将边界特征与对象特征合并,以获得包含边界信息的综合特征表示。在三个具有挑战性的基准数据集上的大量实验结果表明,我们提出的B2Net方法在常用的评估指标上超越了15种最新方法。代码将公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了一种针对伪装对象检测(COD)的新网络模型B2Net。针对现有边界引导伪装对象检测算法易产生对象边界早期化的问题,B2Net通过在不同网络阶段重用边界感知模块来提高获得边界的准确性。同时,引入了残差特征增强模块(RFEM)和边界感知模块(BAM),分别用于集成更具判别性的特征表示和提高检测准确性和可靠性,以及通过整合低层次特征的空间信息和高层次特征的语义信息来探索边缘线索。最后,设计了跨尺度边界融合模块(CBFM),以自上而下地整合不同尺度的信息,将边界特征与对象特征合并,获得包含边界信息的全面特征表示。在三个具有挑战性的基准数据集上的广泛实验结果表明,所提出的B2Net方法在常用的评估指标上优于其他15种最新方法。
Key Takeaways
- 伪装对象检测(COD)的目标是识别图像中由于纹理和颜色与背景高度相似而隐藏的对象。
- 现有大多数边界引导伪装对象检测算法倾向于在网络早期生成对象边界,这可能导致不准确的边缘先验信息引入对象检测中的噪声。
- B2Net网络通过重用边界感知模块来提高获得边界的准确性,并设计了三个关键模块:Residual Feature Enhanced Module (RFEM)、Boundary Aware Module (BAM)、Cross-scale Boundary Fusion Module (CBFM)。
- RFEM模块旨在集成更具判别性的特征表示,以提高检测准确性和可靠性。
- BAM模块通过整合低层次特征的空间信息和高层次特征的语义信息,探索边缘线索。
- CBFM模块以自上而下地方式整合不同尺度的信息,将边界特征和对象特征合并,形成包含边界信息的全面特征表示。
- 在三个具有挑战性的基准数据集上的实验结果表明,B2Net方法优于其他15种最新方法。
点此查看论文截图



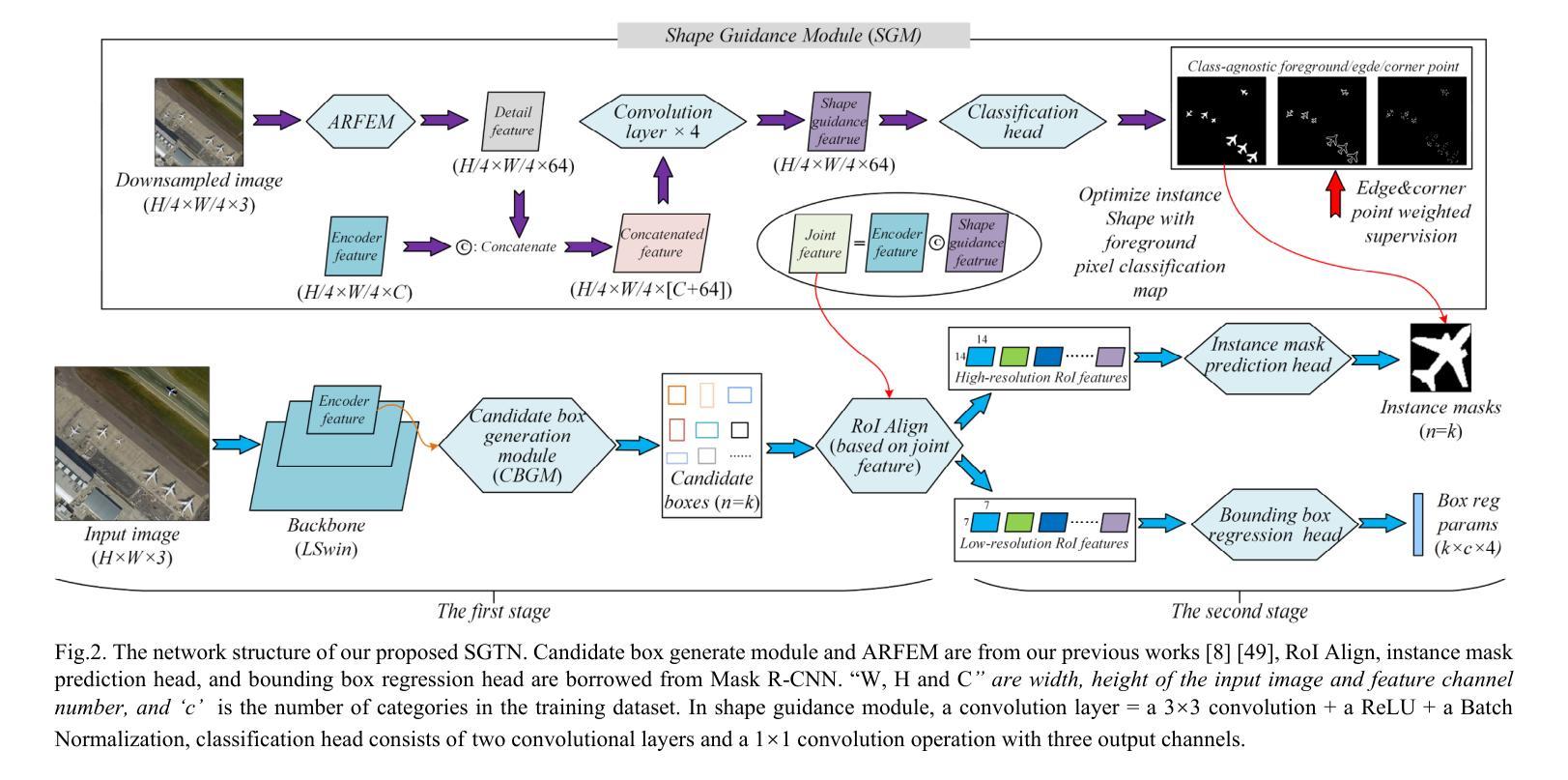
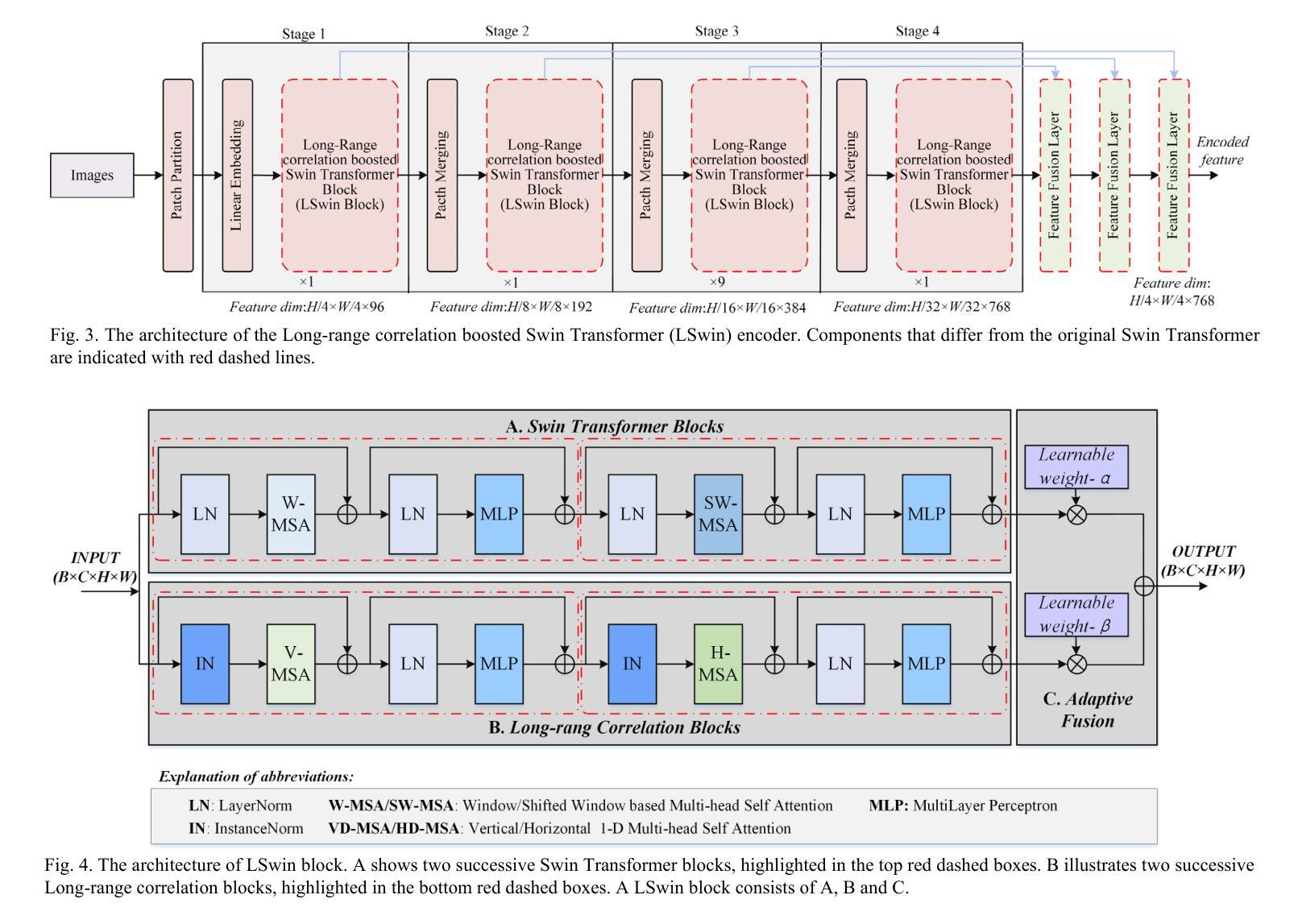
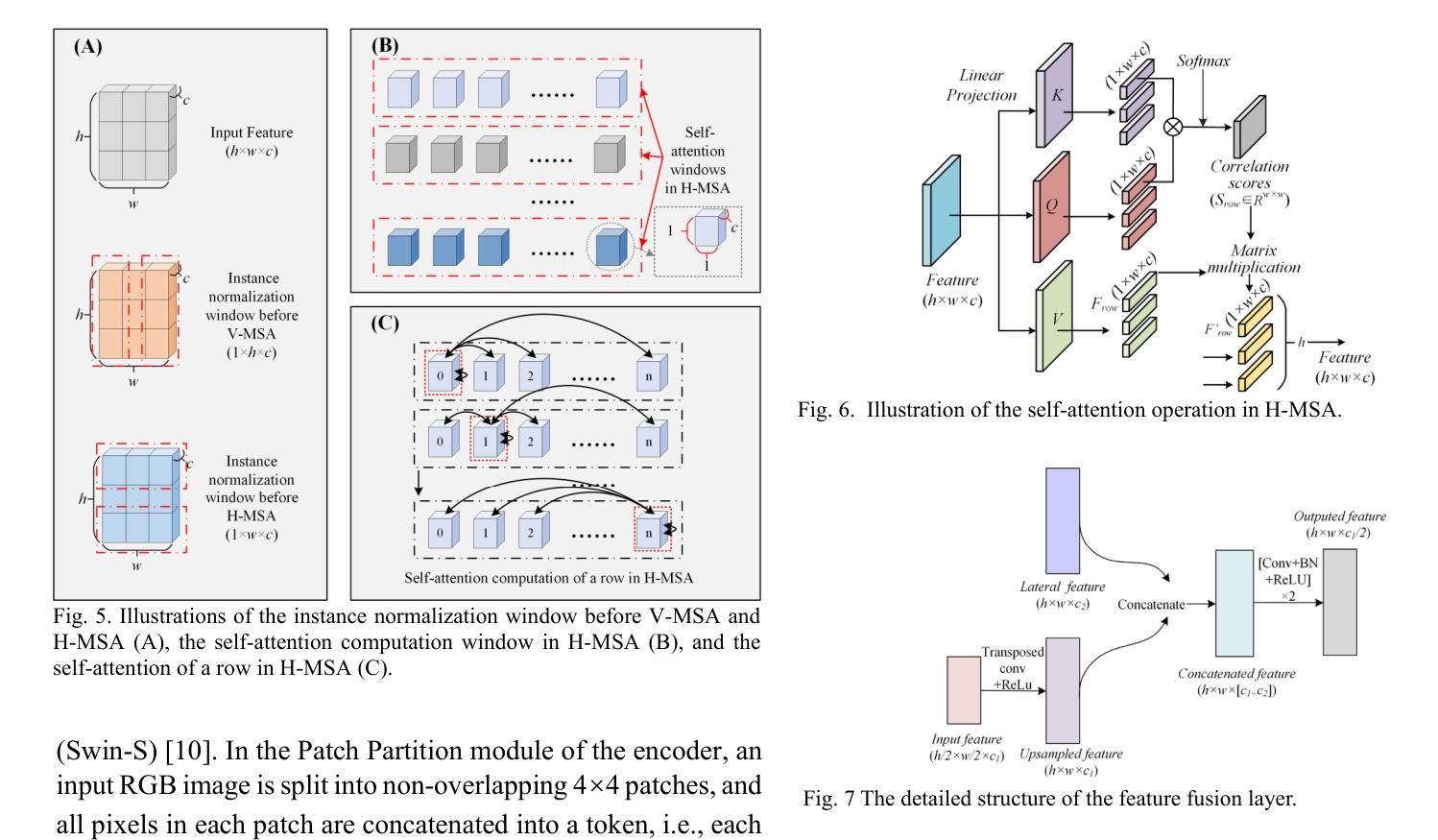
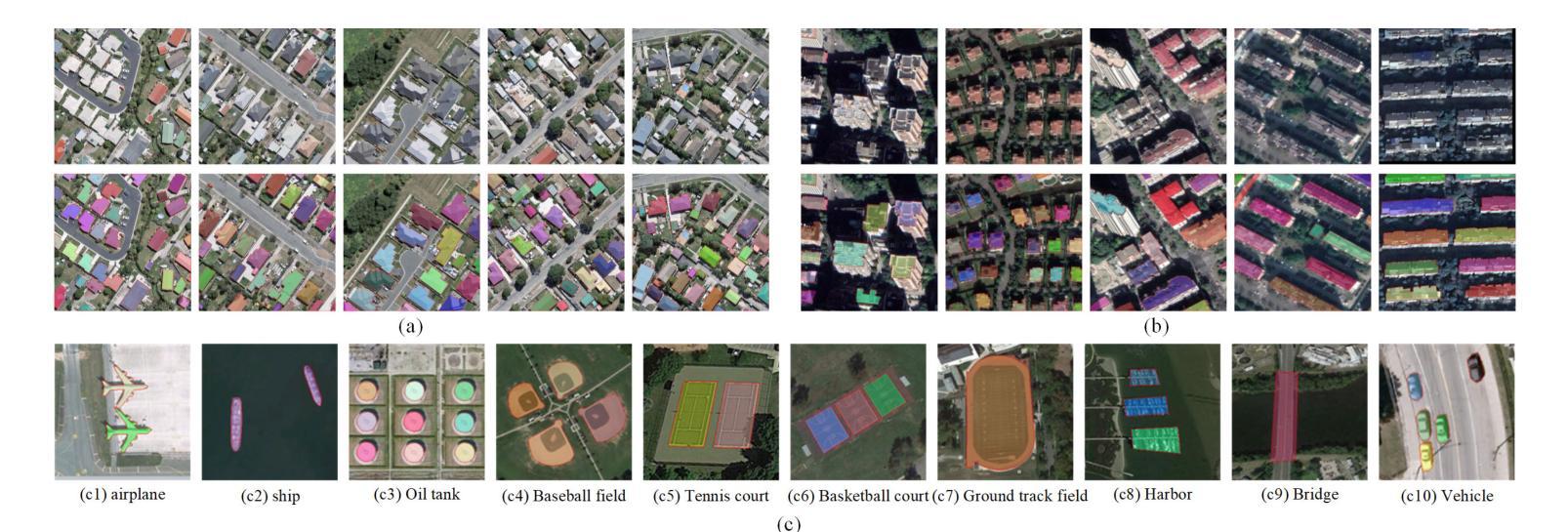
A Novel Shape Guided Transformer Network for Instance Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images
Authors:Dawen Yu, Shunping Ji
Instance segmentation performance in remote sensing images (RSIs) is significantly affected by two issues: how to extract accurate boundaries of objects from remote imaging through the dynamic atmosphere, and how to integrate the mutual information of related object instances scattered over a vast spatial region. In this study, we propose a novel Shape Guided Transformer Network (SGTN) to accurately extract objects at the instance level. Inspired by the global contextual modeling capacity of the self-attention mechanism, we propose an effective transformer encoder termed LSwin, which incorporates vertical and horizontal 1D global self-attention mechanisms to obtain better global-perception capacity for RSIs than the popular local-shifted-window based Swin Transformer. To achieve accurate instance mask segmentation, we introduce a shape guidance module (SGM) to emphasize the object boundary and shape information. The combination of SGM, which emphasizes the local detail information, and LSwin, which focuses on the global context relationships, achieve excellent RSI instance segmentation. Their effectiveness was validated through comprehensive ablation experiments. Especially, LSwin is proved better than the popular ResNet and Swin transformer encoder at the same level of efficiency. Compared to other instance segmentation methods, our SGTN achieves the highest average precision (AP) scores on two single-class public datasets (WHU dataset and BITCC dataset) and a multi-class public dataset (NWPU VHR-10 dataset). Code will be available at http://gpcv.whu.edu.cn/data/.
遥感图像(RSIs)中的实例分割性能受到两个问题的显著影响:一是如何通过动态大气从遥感图像中提取对象的精确边界,二是如何整合广泛空间区域内相关对象实例的相互信息。本研究提出了一种新型的Shape Guided Transformer Network(SGTN),以准确地在实例级别提取对象。受到自注意力机制全局上下文建模能力的启发,我们提出了一种有效的变压器编码器LSwin。它结合了垂直和水平1D全局自注意力机制,获得了比基于局部移位窗口的流行Swin Transformer更好的RSIs全局感知能力。为了实现精确的实例掩膜分割,我们引入了一个形状指导模块(SGM)来强调对象边界和形状信息。SGM强调局部细节信息,而LSwin侧重于全局上下文关系,二者结合实现了出色的RSI实例分割。其有效性通过全面的消融实验得到了验证。特别地,在相同的效率下,LSwin被证明优于流行的ResNet和Swin transformer编码器。与其他实例分割方法相比,我们的SGTN在两个单公开数据集(WHU数据集和BITCC数据集)和一个多类公开数据集(NWPU VHR-10数据集)上获得了最高的平均精度(AP)分数。代码将在http://gpcv.whu.edu.cn/data/上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 15 figures
Summary
本文提出一种新型Shape Guided Transformer Network(SGTN),用于解决遥感图像实例分割中的两大问题:准确提取动态大气环境下的遥感成像目标边界以及整合广泛空间区域分散的相关目标实例的相互信息。采用全局上下文建模能力的自注意力机制,提出了有效的LSwin变压器编码器,结合形状引导模块(SGM)进行准确的目标实例级分割。在三个公开数据集上的实验表明,该网络实现了高效且准确的实例分割。
Key Takeaways
- SGTN被提出以解决遥感图像实例分割中的两大核心问题:边界提取和相互信息整合。
- 引入LSwin变压器编码器,结合垂直和水平1D全局自注意力机制,提高全局感知能力。
- 形状引导模块(SGM)用于强调目标边界和形状信息,结合LSwin实现准确实例分割。
- 通过综合消融实验验证了方法的有效性,LSwin在效率上与流行的ResNet和Swin变压器编码器相比表现更佳。
- SGTN在三个公开数据集上实现了最高的平均精度(AP)得分。
点此查看论文截图